Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
338results about How to "Easy to erase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
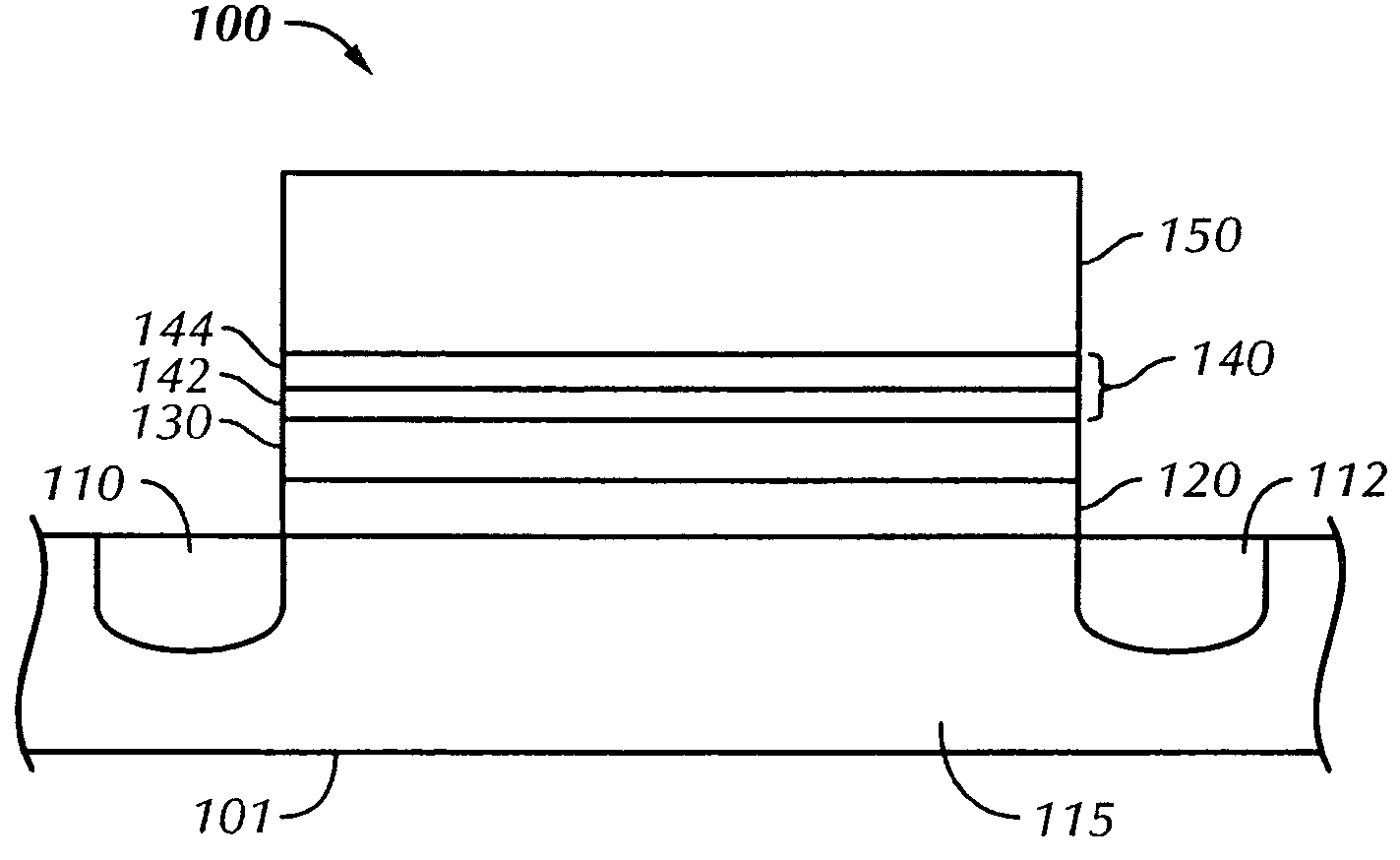
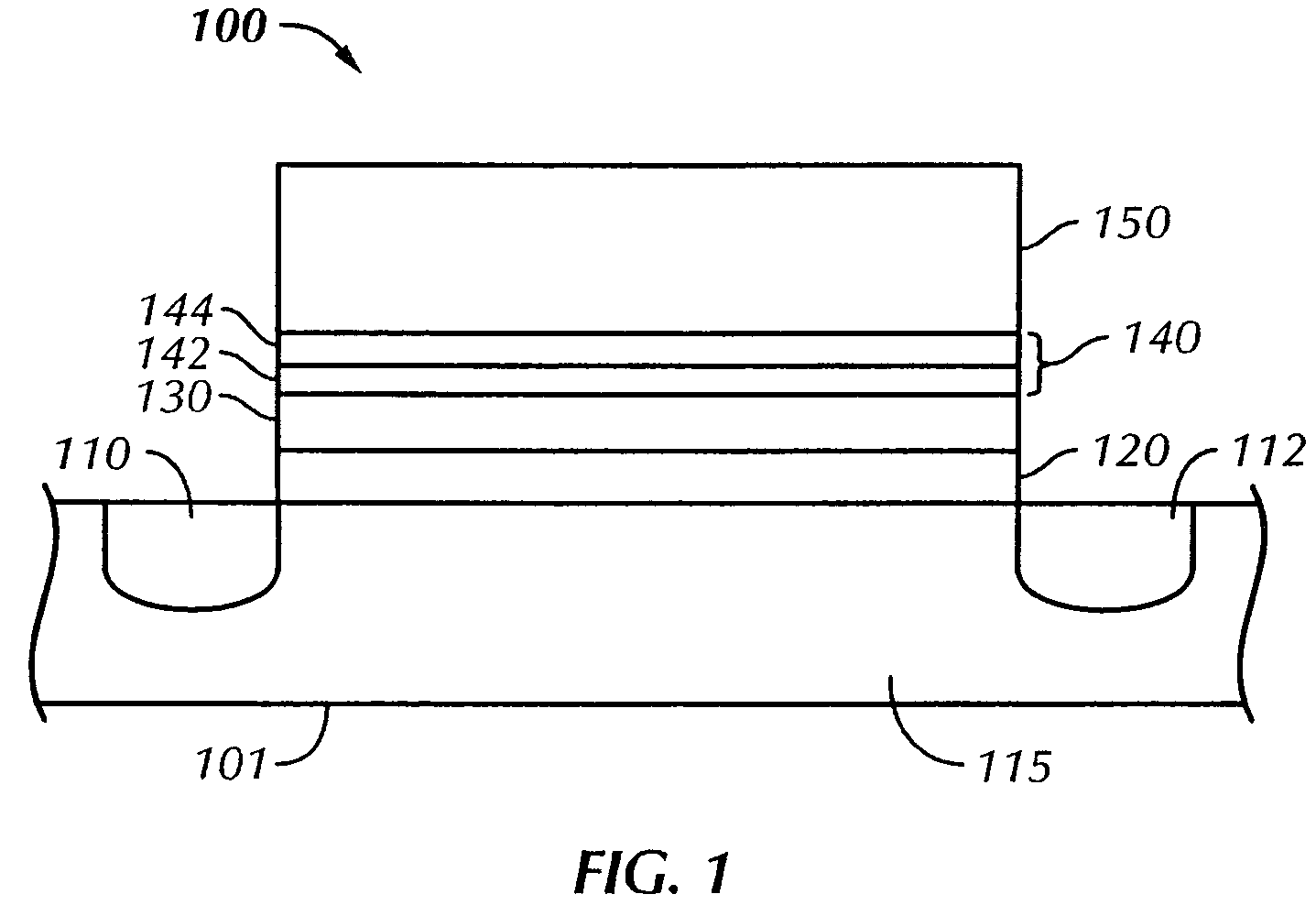
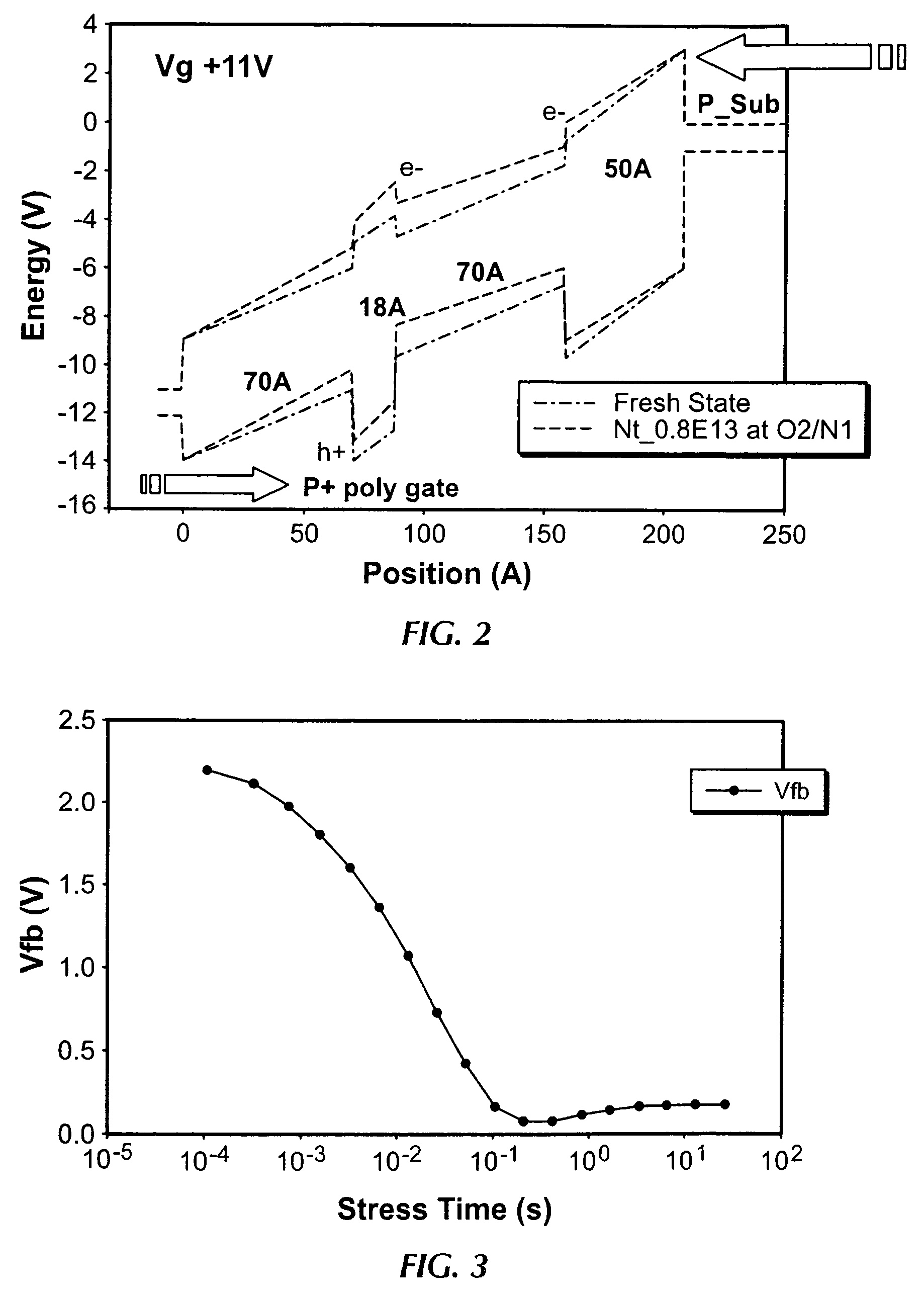
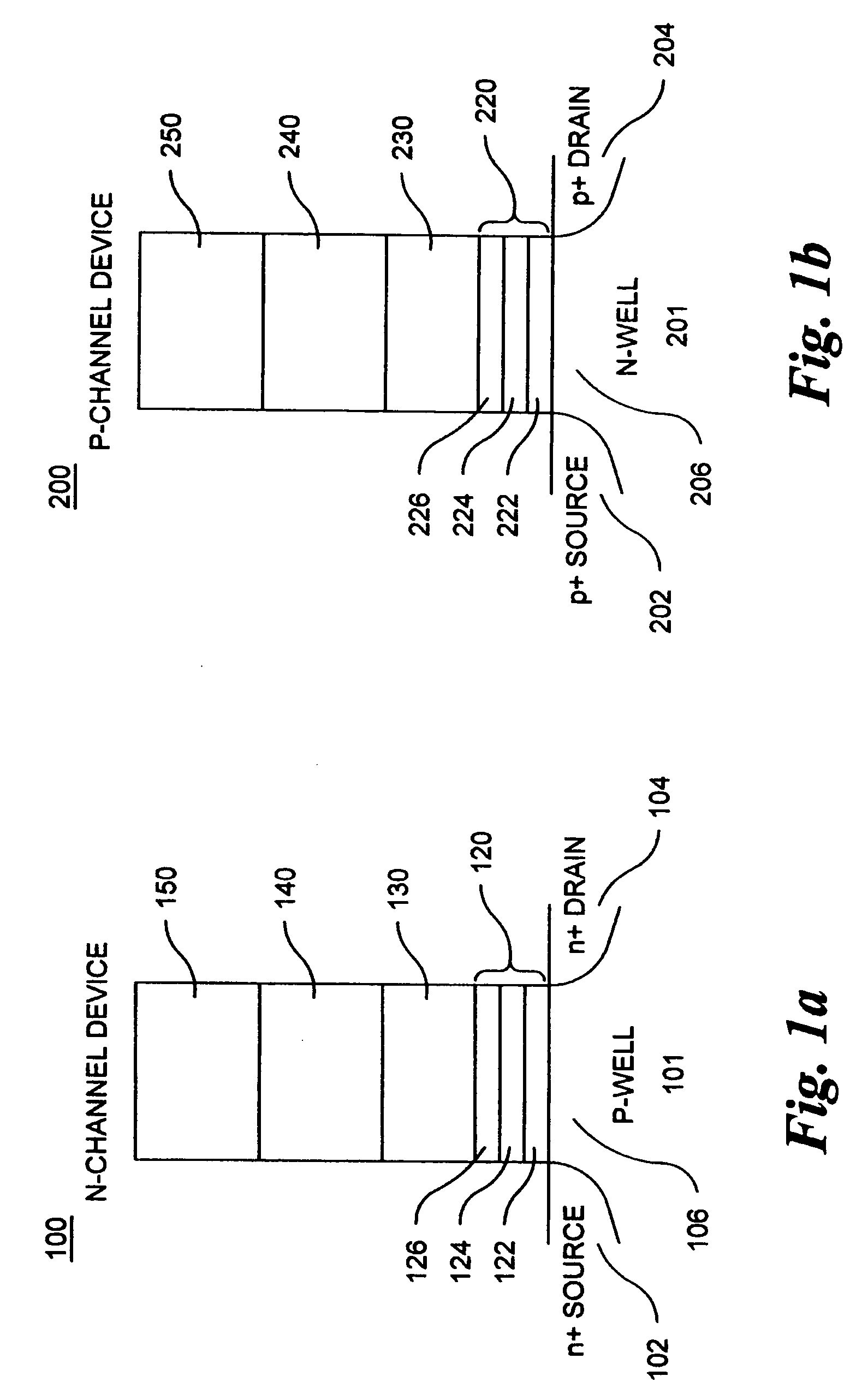
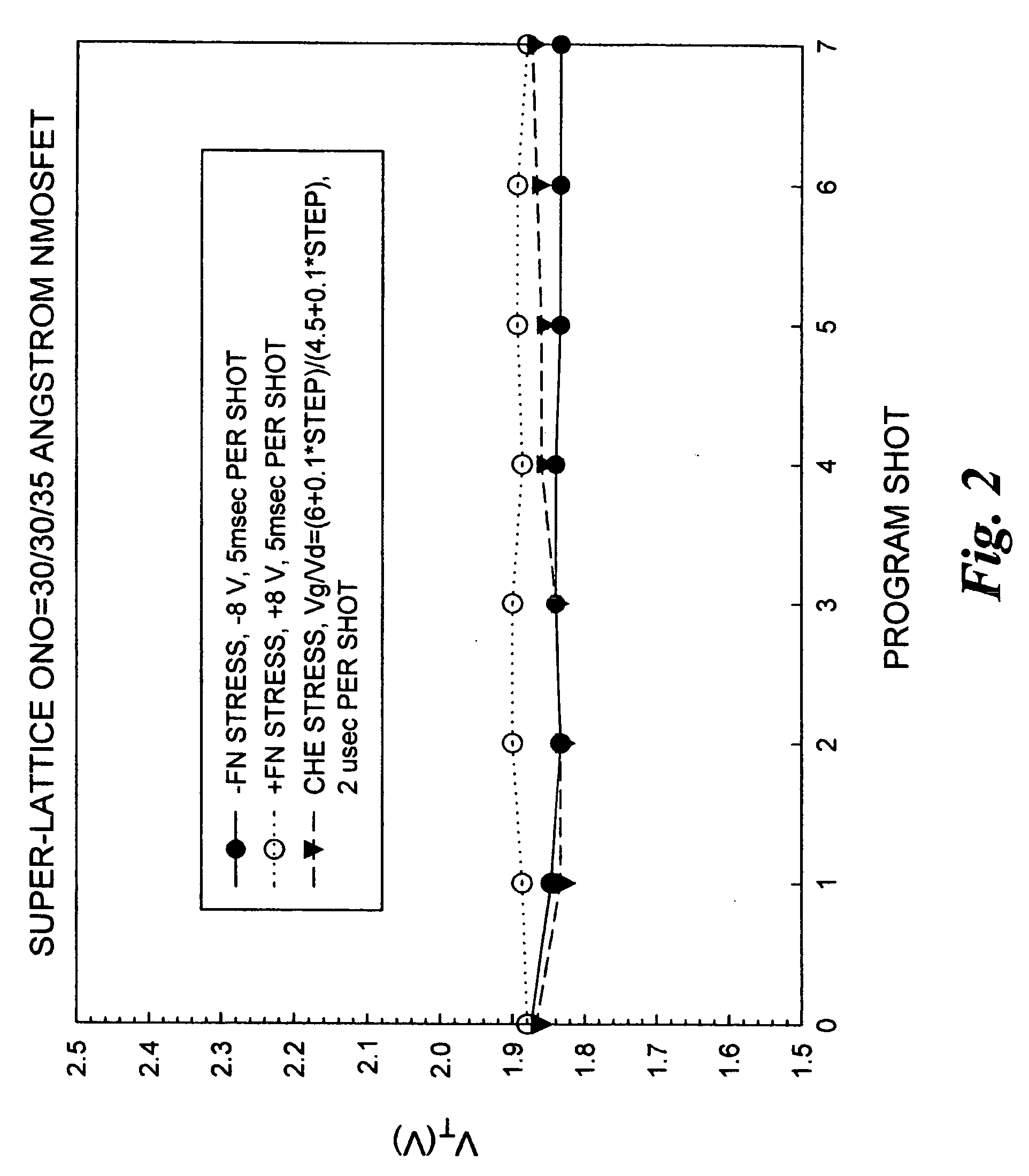
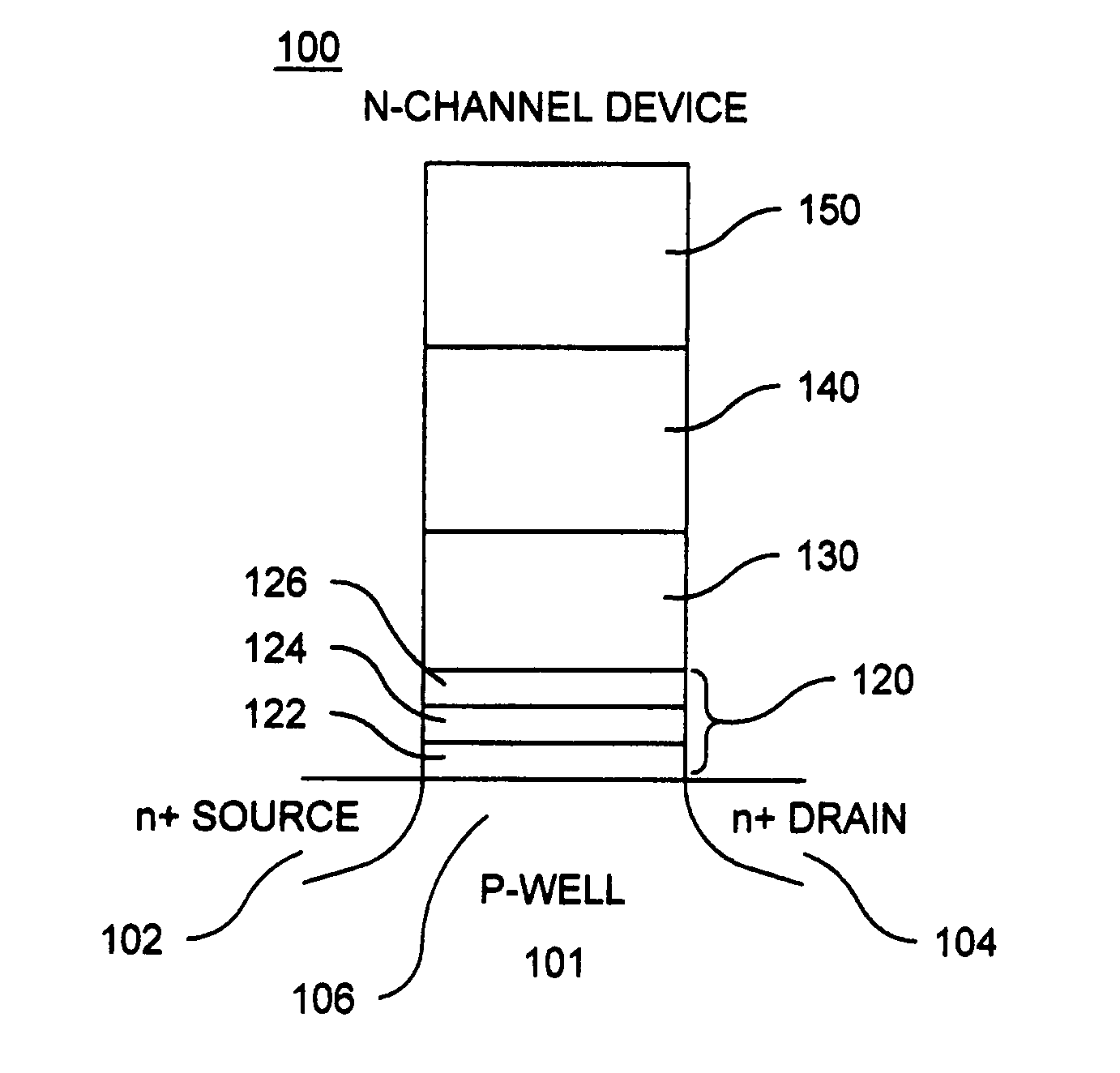
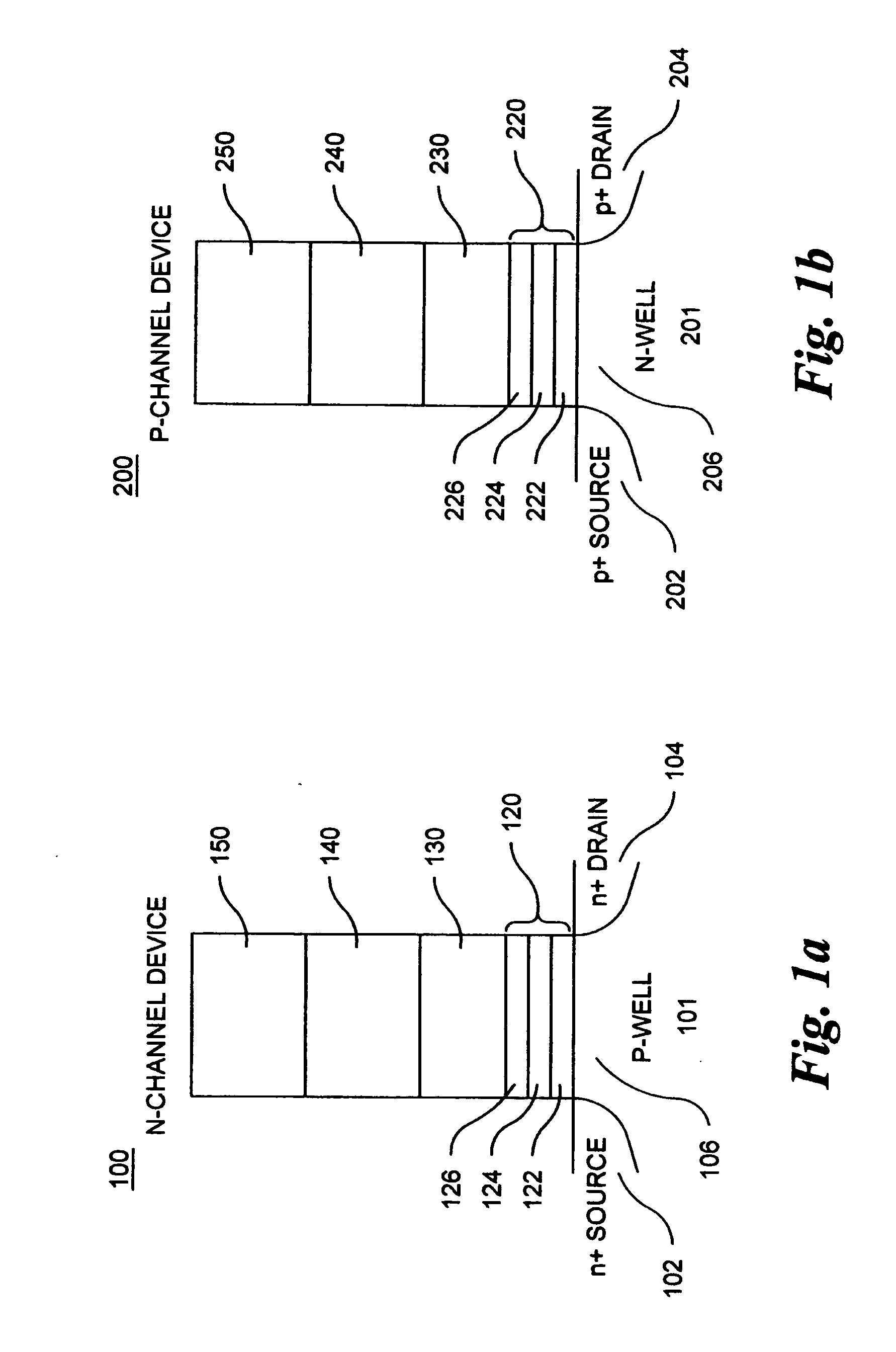
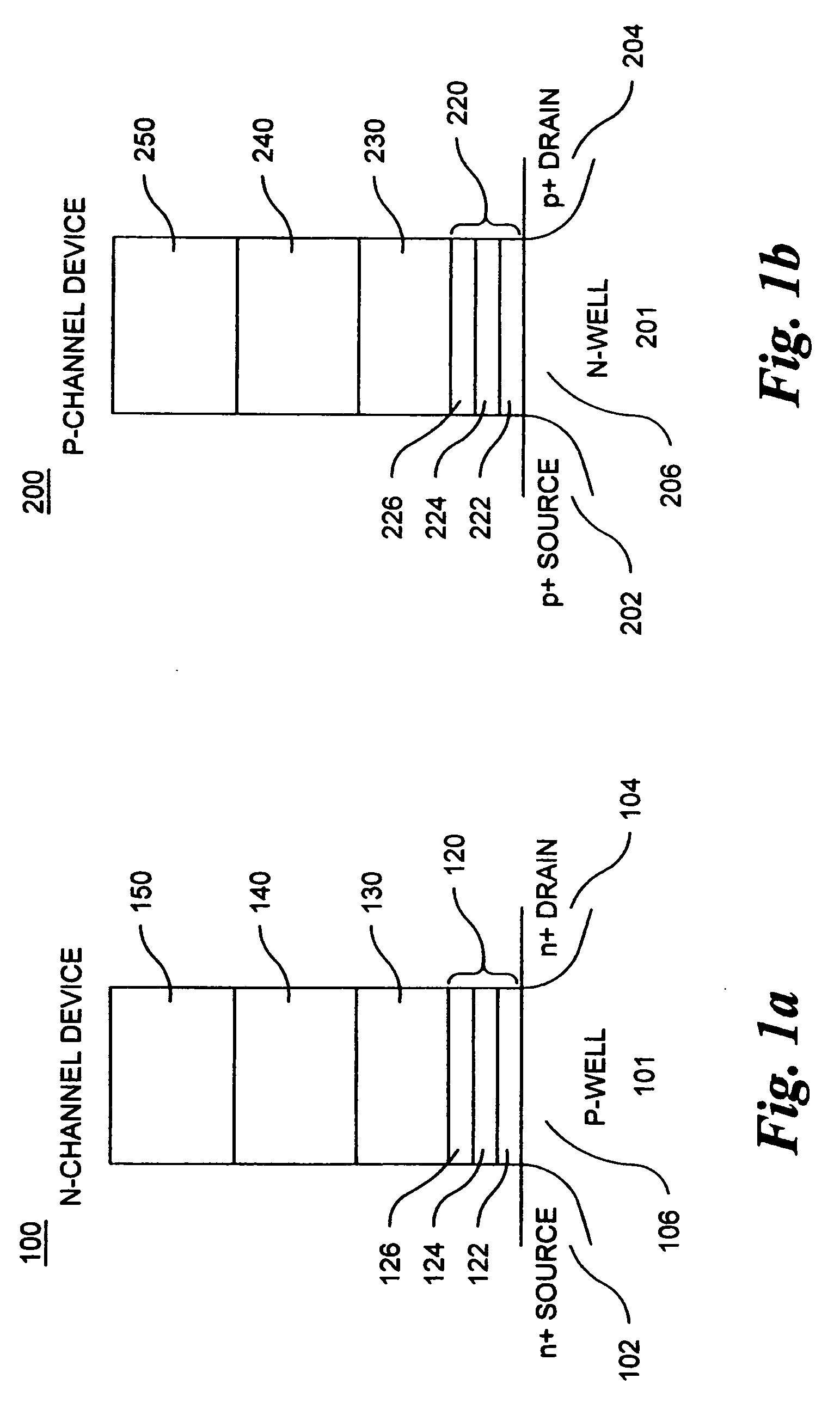
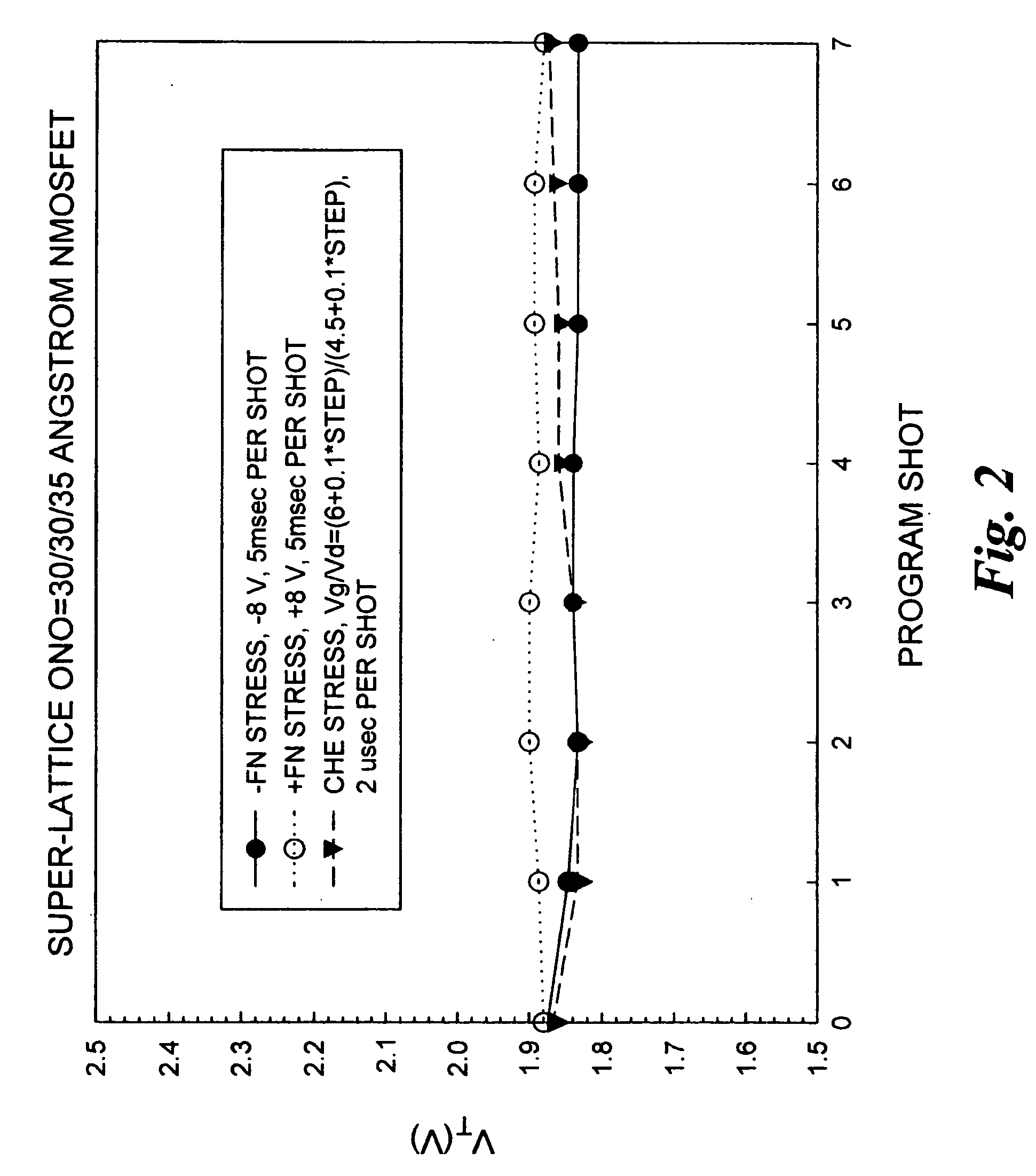
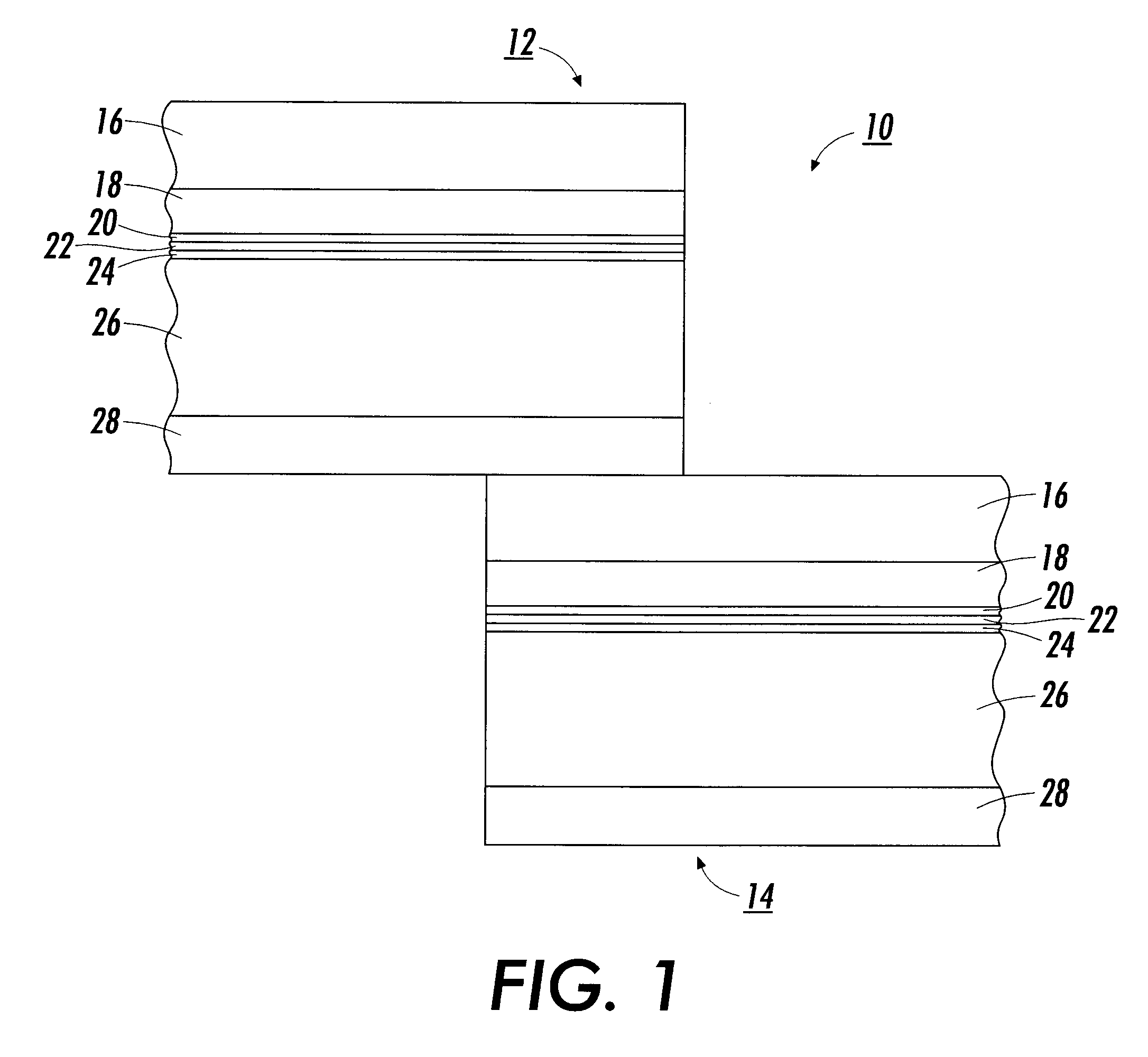
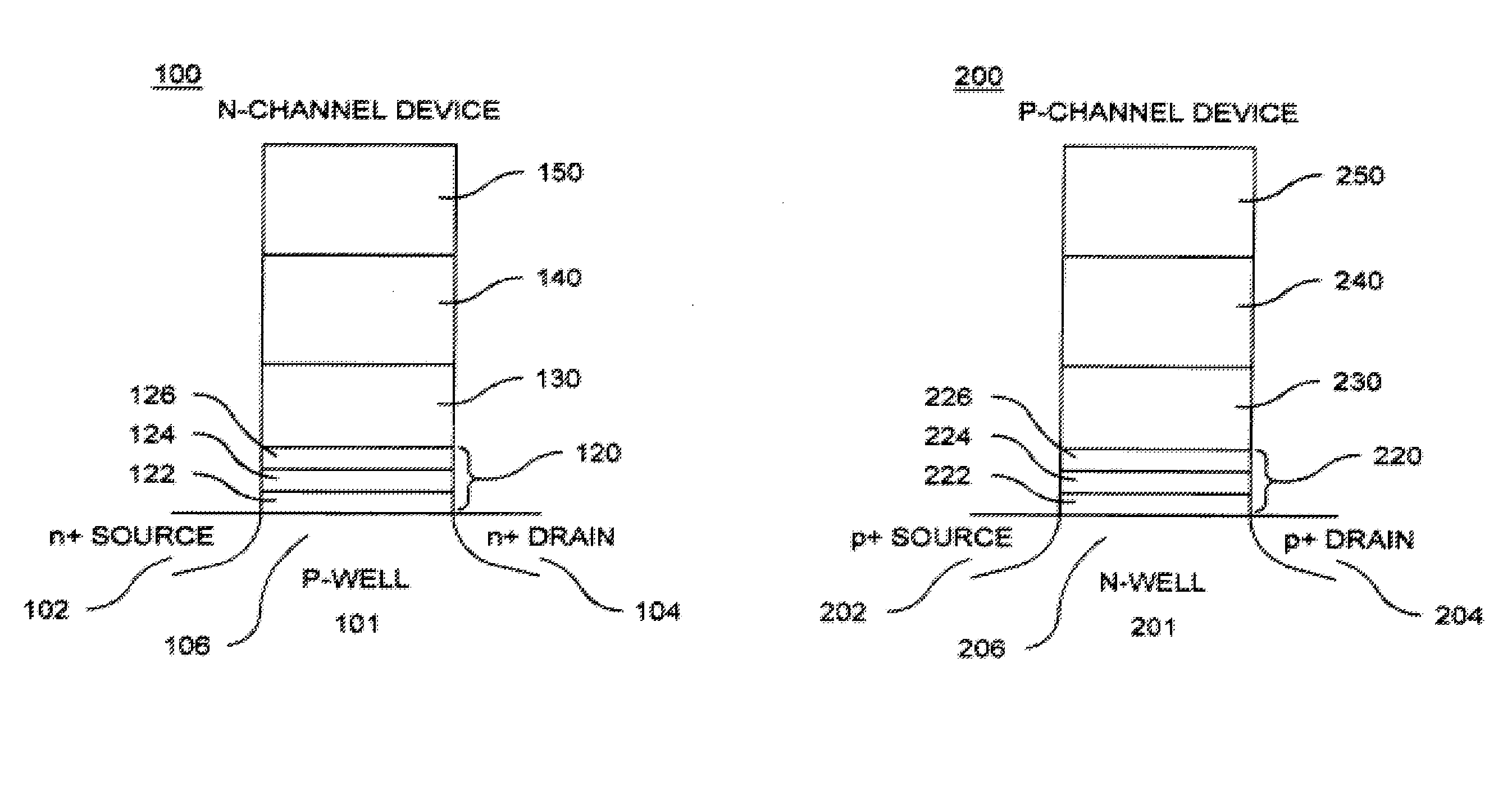
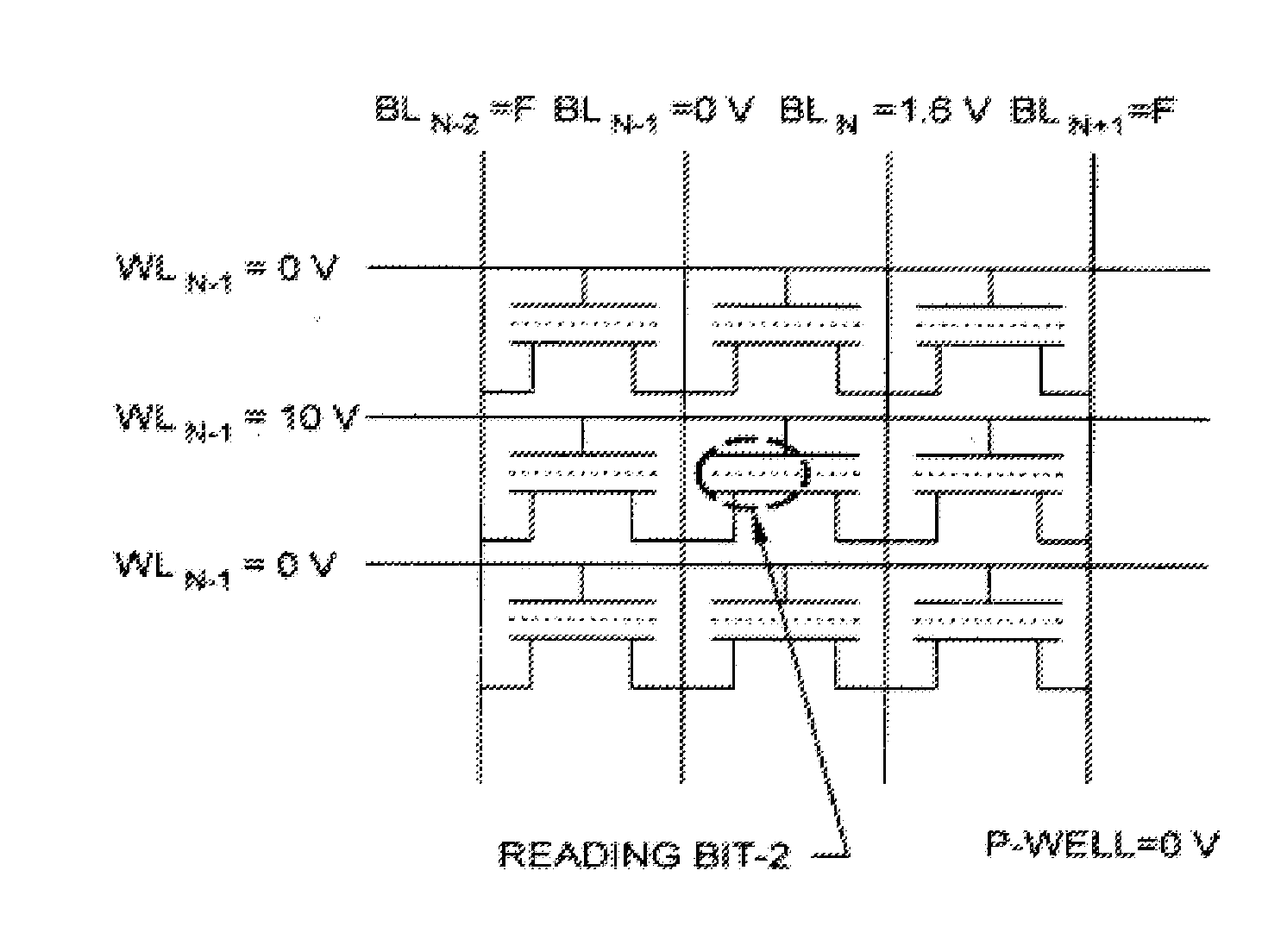
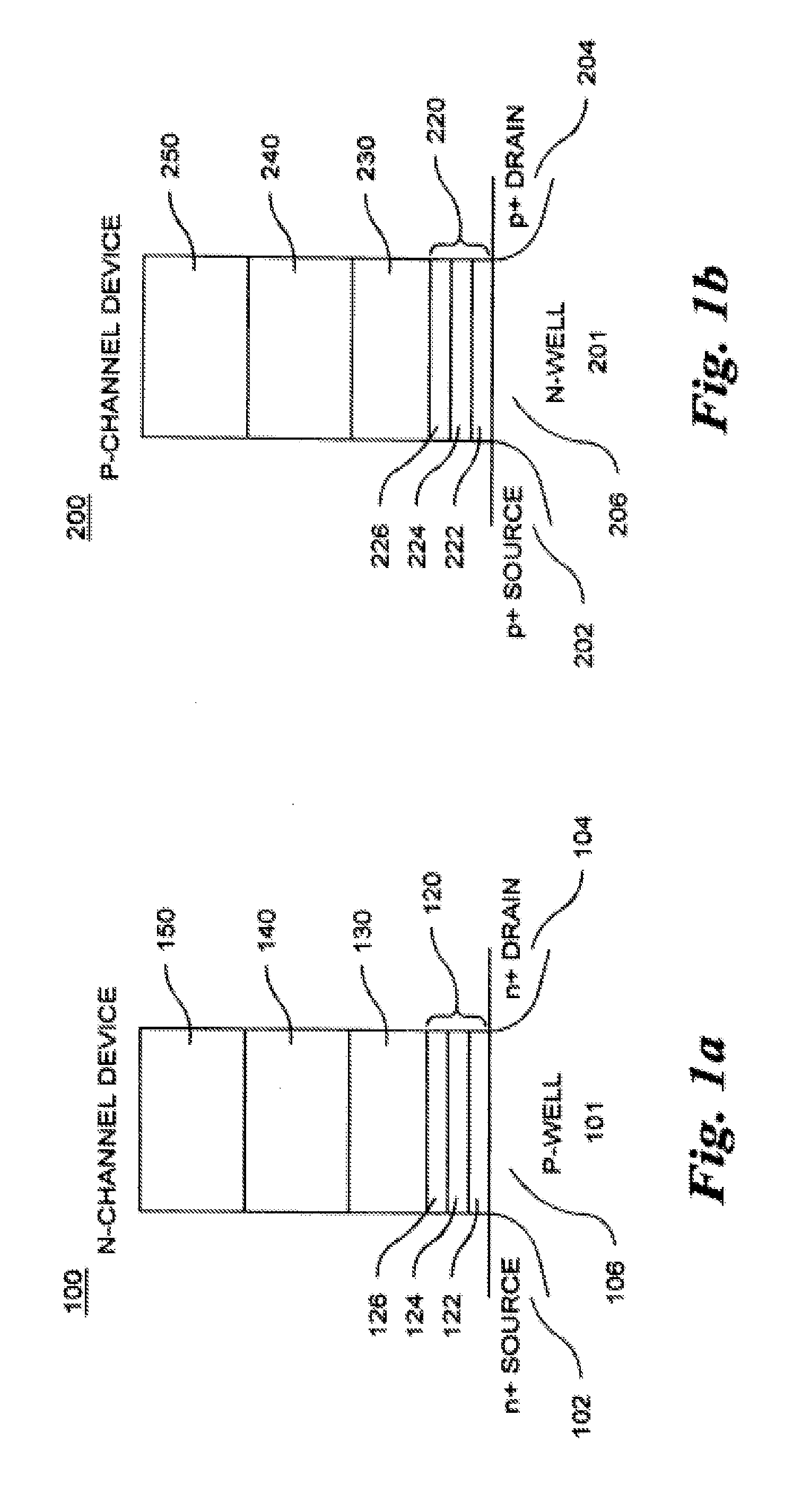
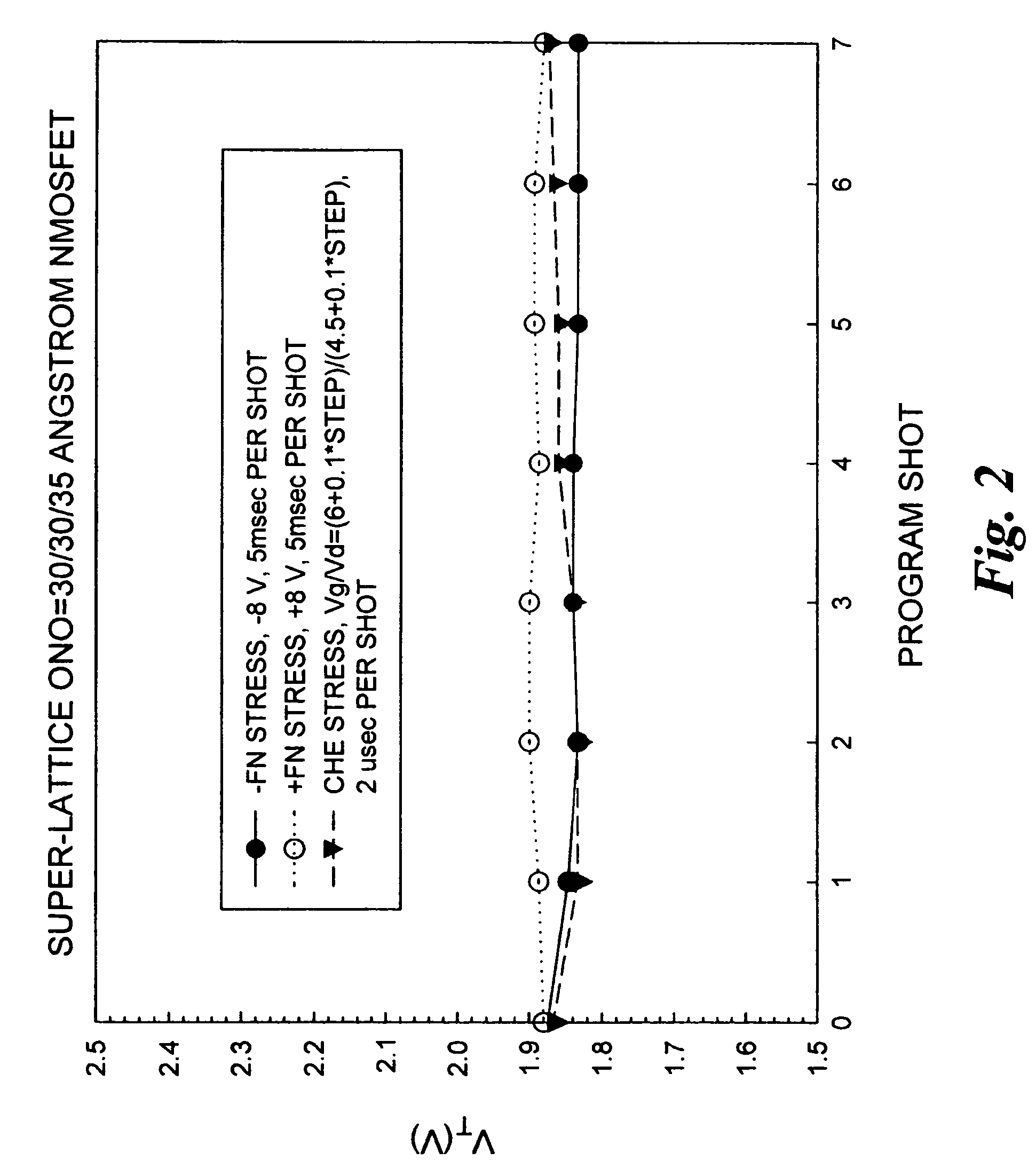
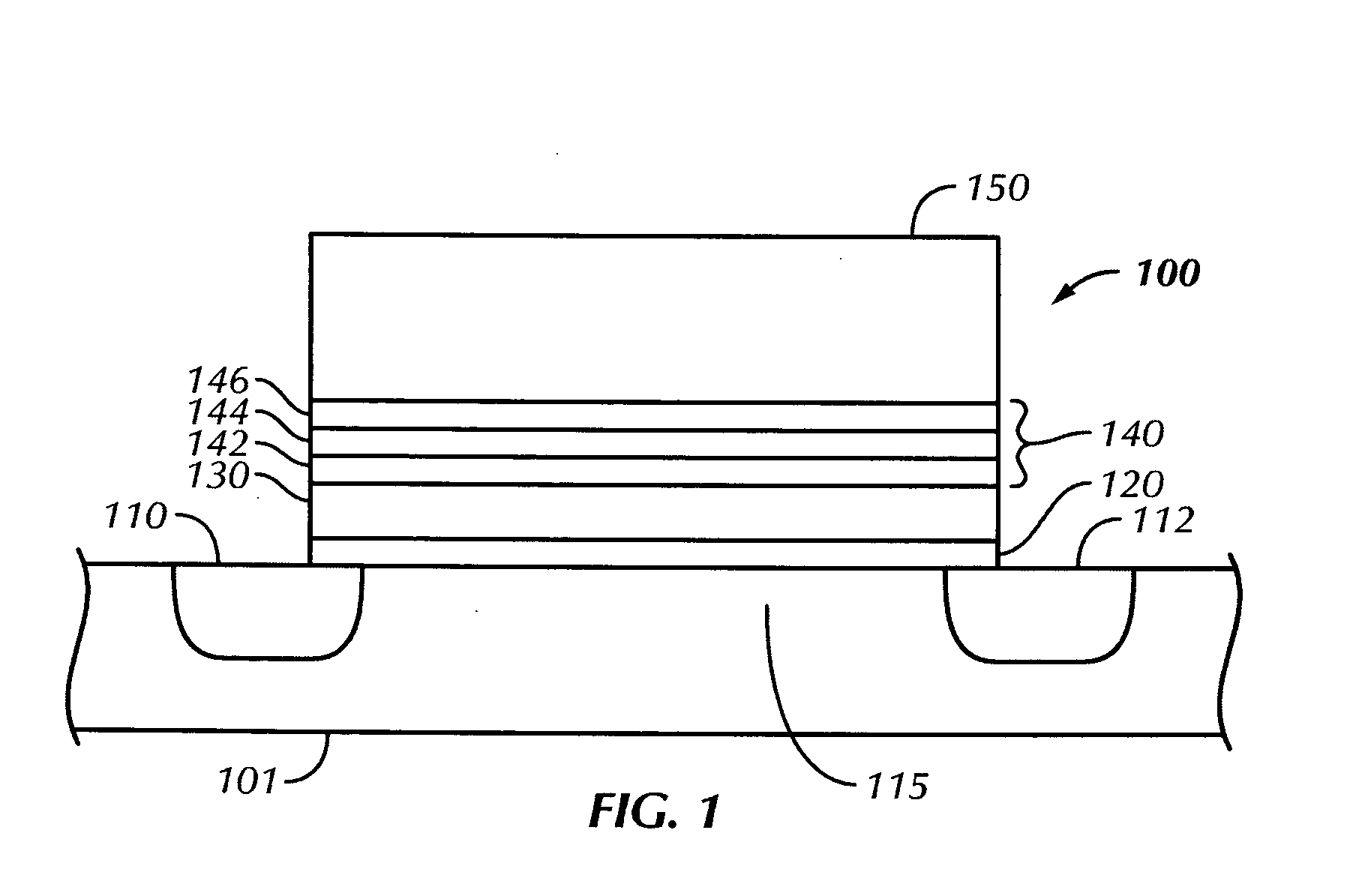
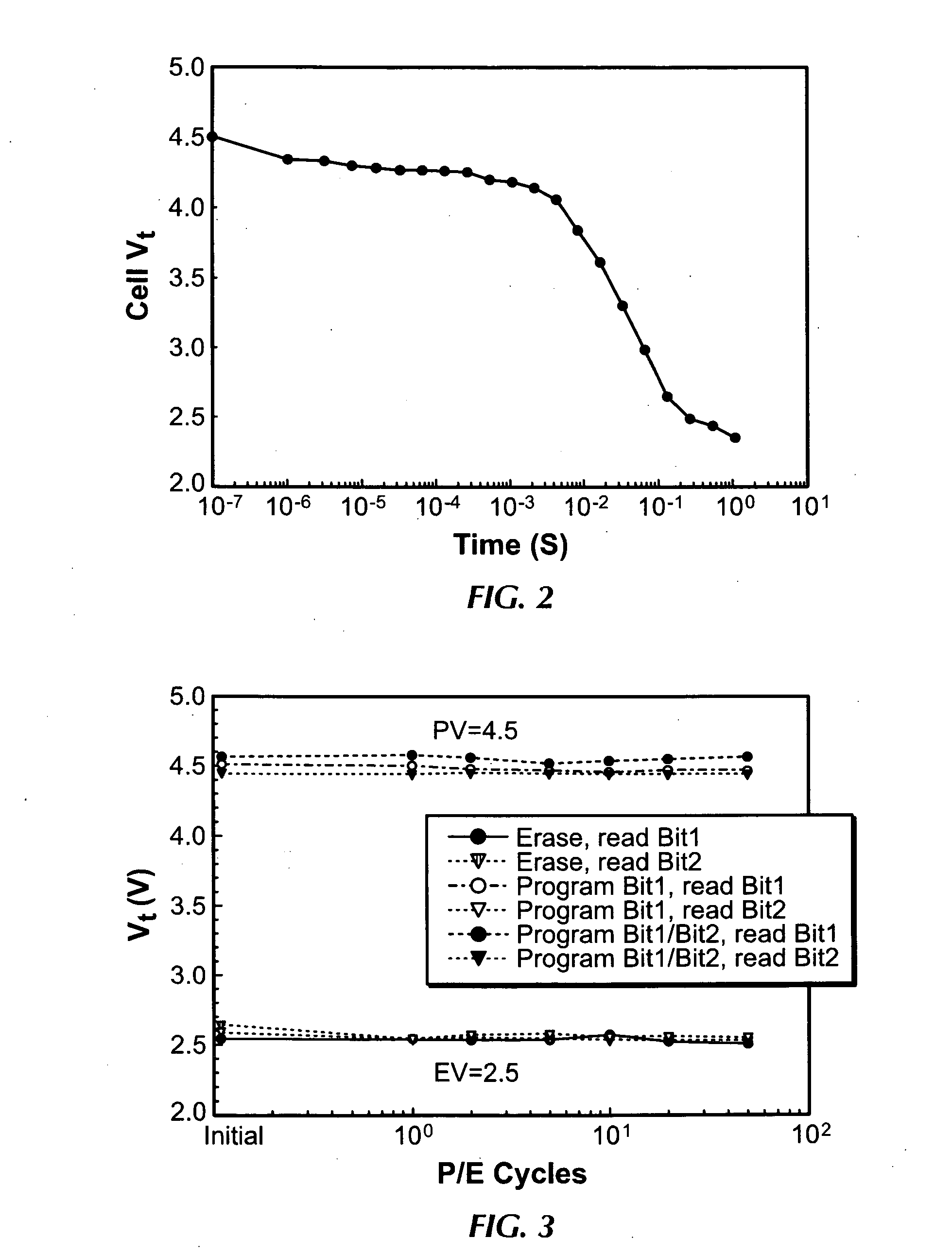
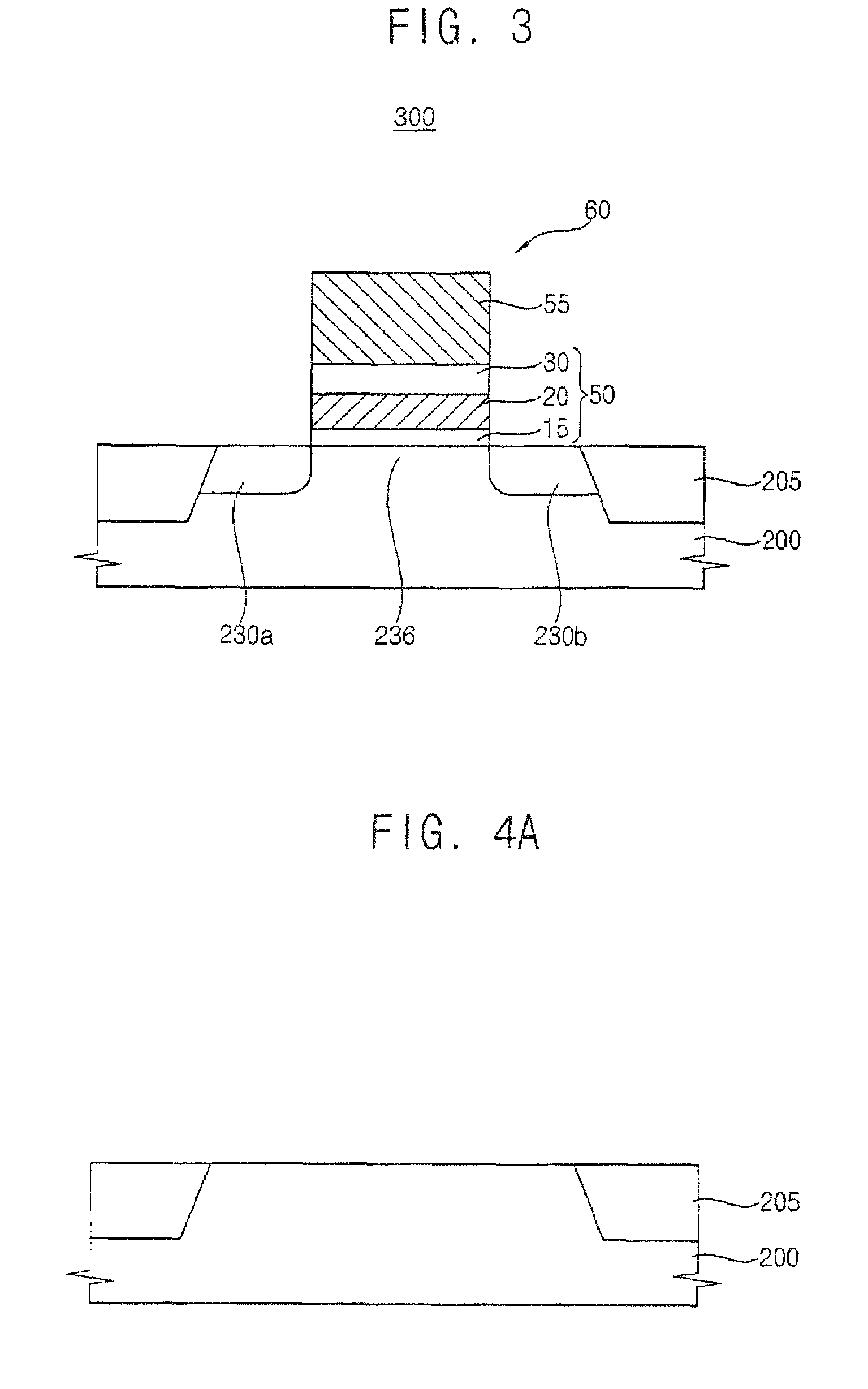
Methods of operating non-volatile memory cells having an oxide/nitride multilayer insulating structure
ActiveUS7450423B2Easy to eraseReduce interface damageTransistorRead-only memoriesNitrideDielectric layer
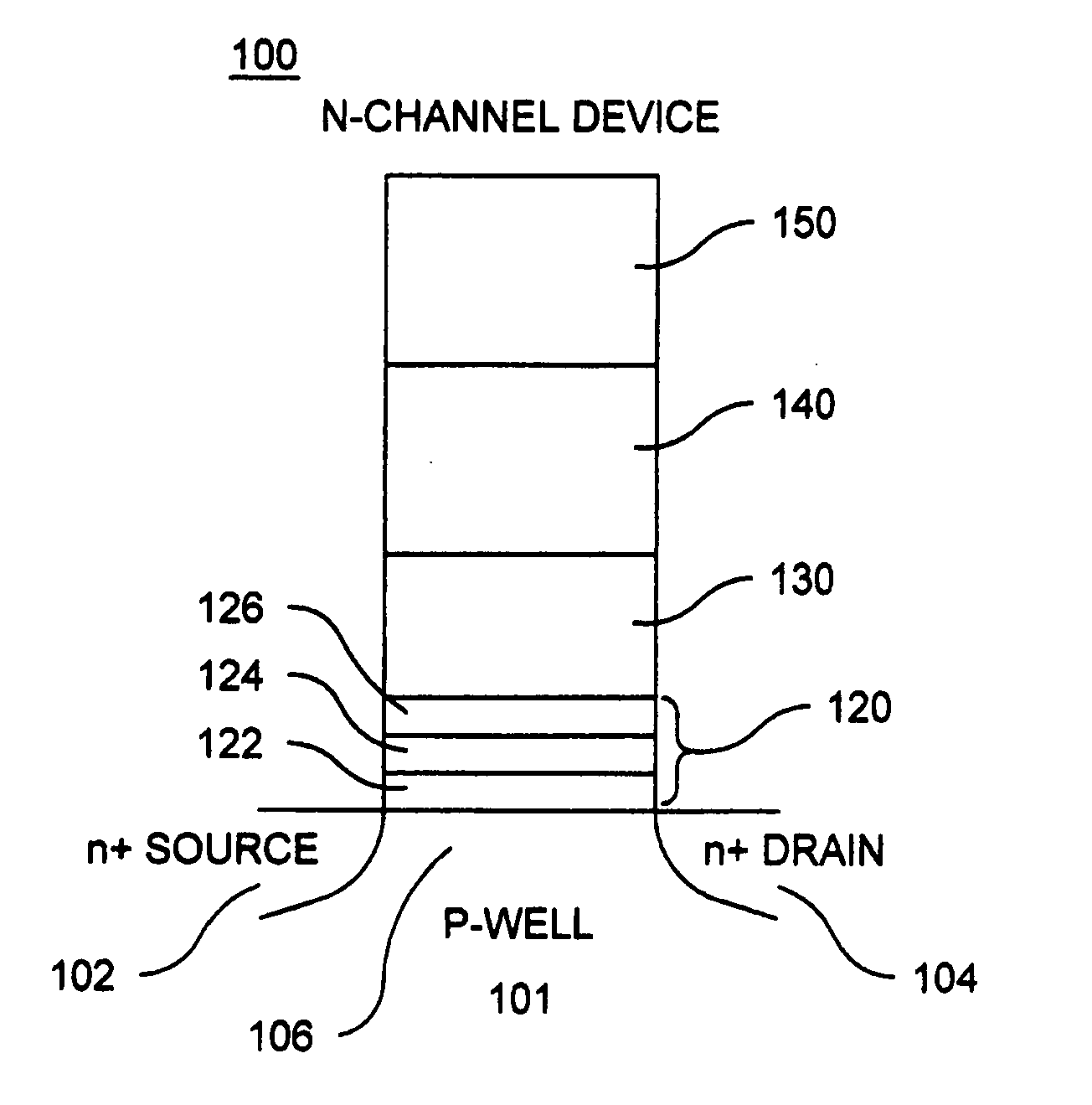
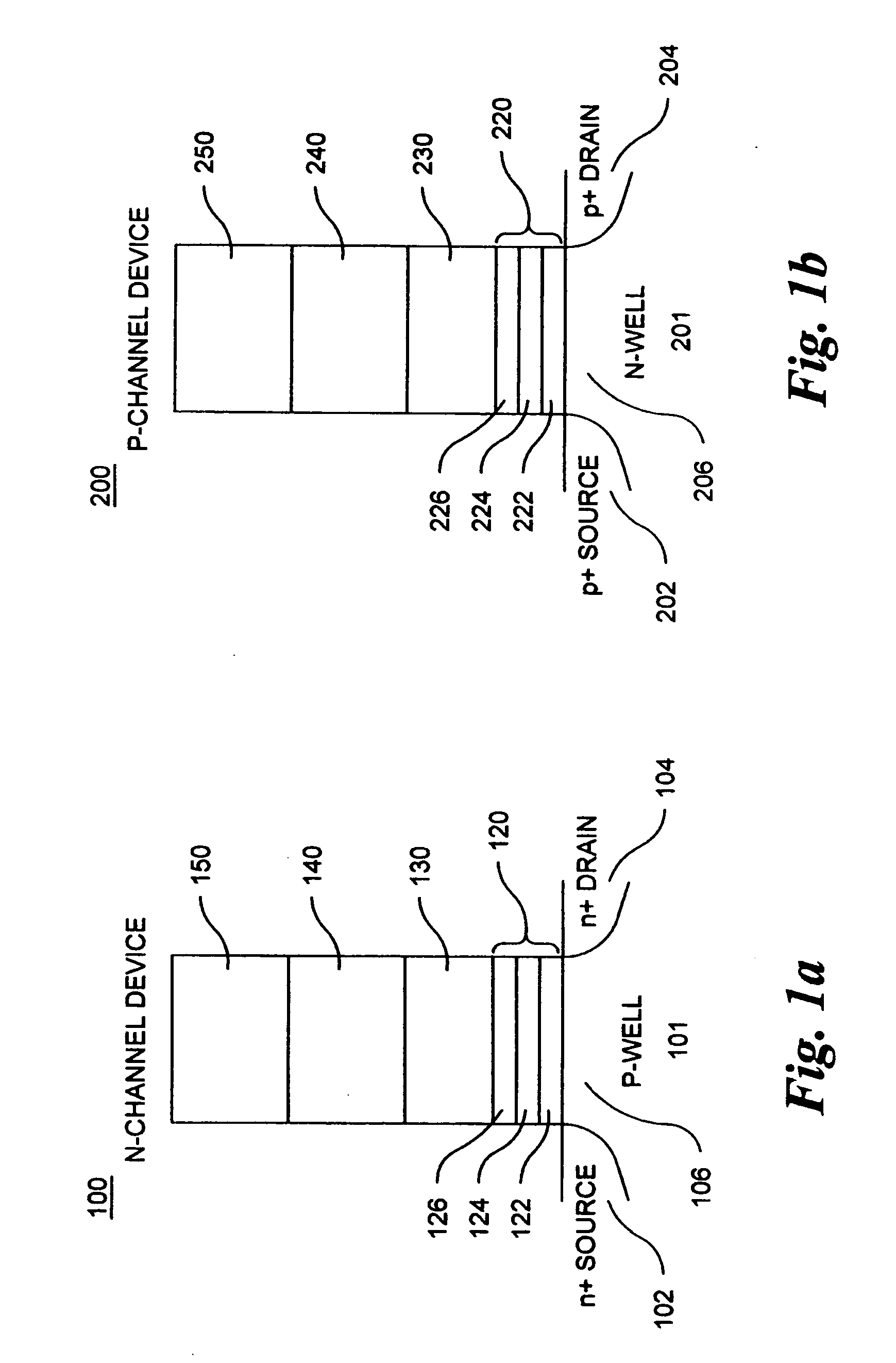
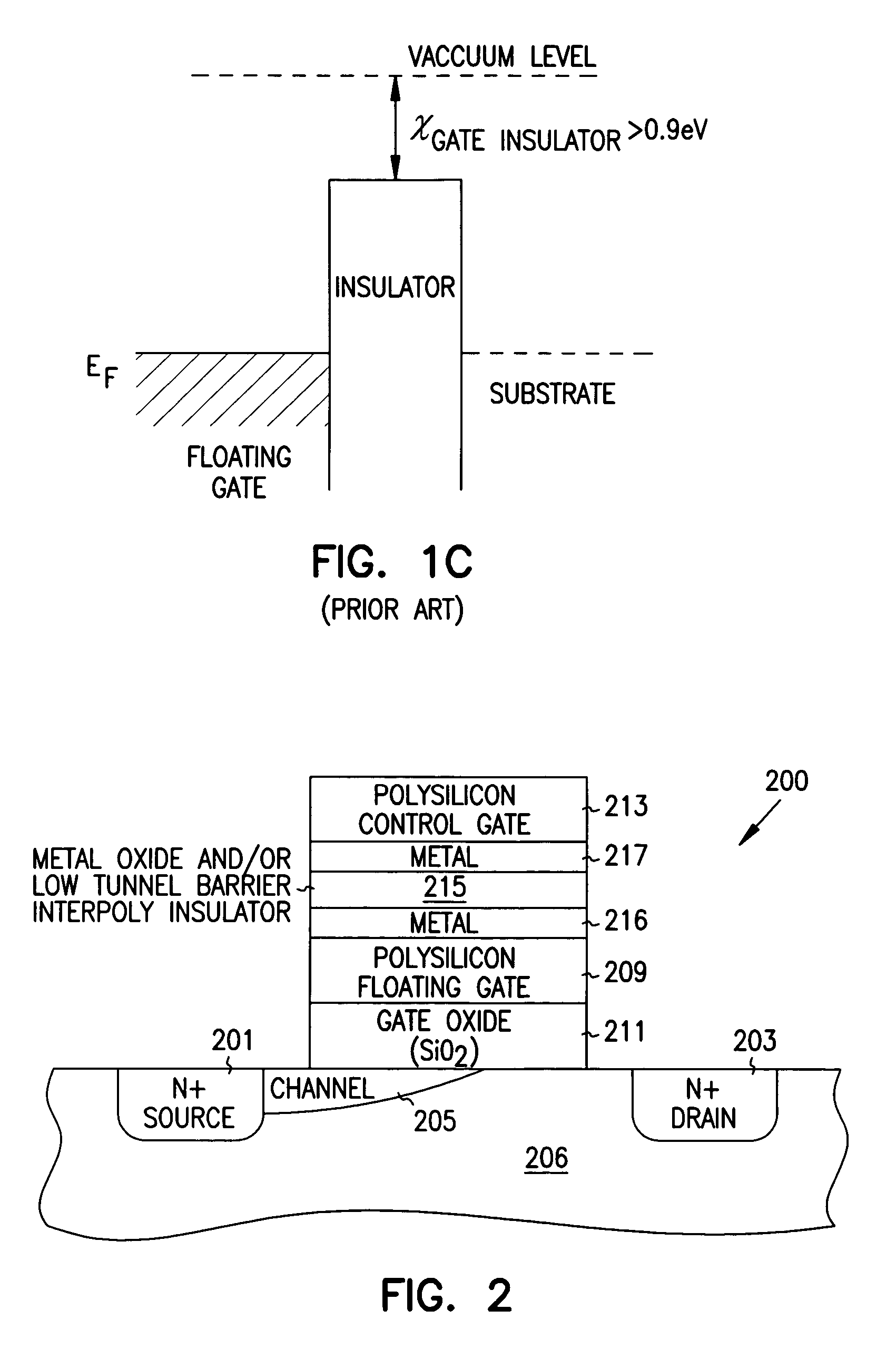
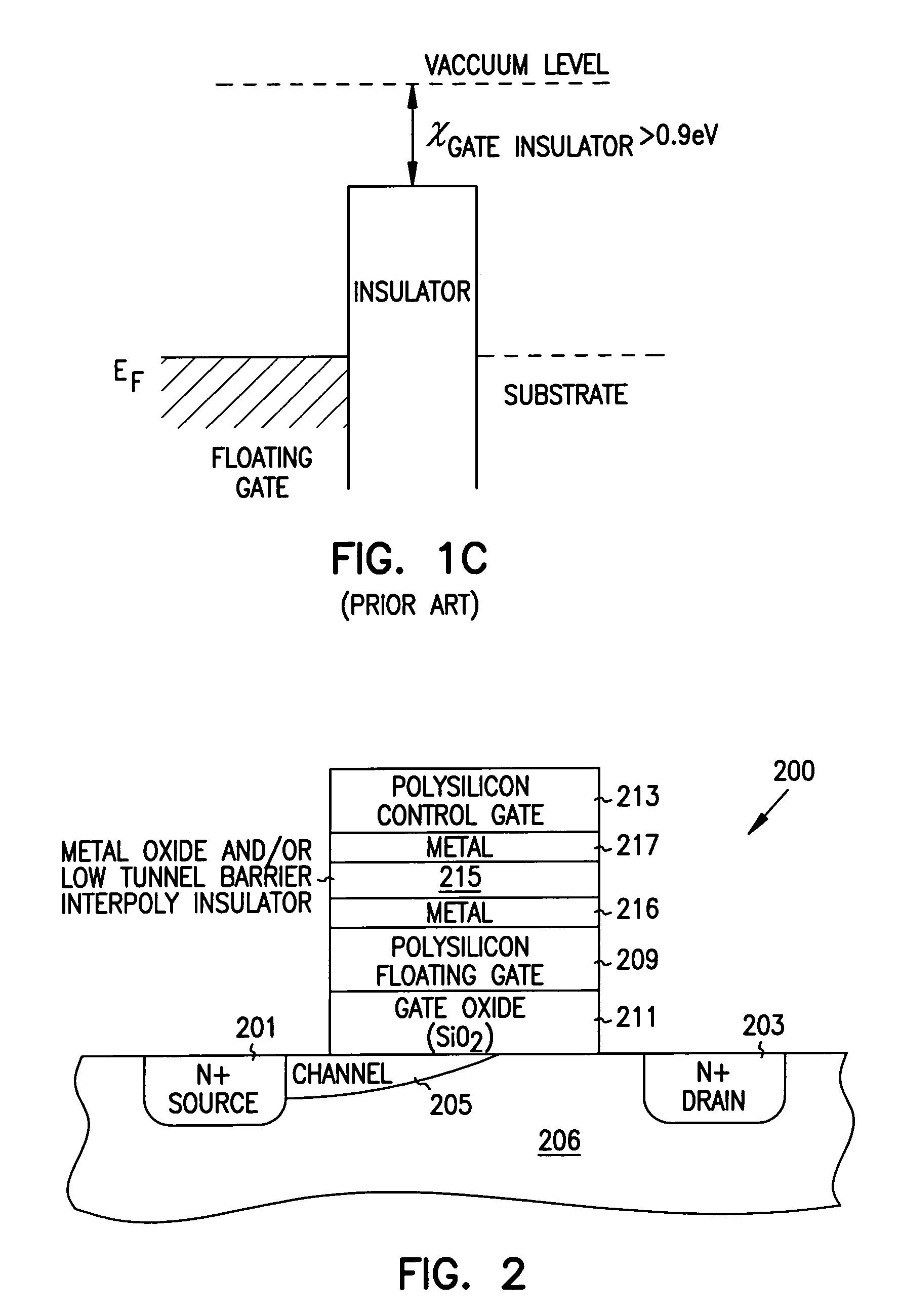
A method of operating a memory cell by applying a positive voltage to the gate sufficient to cause hole tunneling from the gate toward the charge storage layer is disclosed. The method is applied to a memory cell including a semiconductor layer having at least two source / drain regions disposed below a surface of the semiconductor layer and separated by a channel region. The memory cell also has a lower insulating layer disposed above the channel region; a charge storage layer disposed above the lower insulating layer; an upper insulating multi-layer structure disposed above the charge storage layer. The upper insulating multi-layer structure comprises a lower dielectric layer and an upper nitride layer disposed above the lower dielectric layer and the memory cell has a gate disposed above the upper insulating multi-layer structure.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Non-volatile memory cells, memory arrays including the same and methods of operating cells and arrays
ActiveUS20060202261A1Easy to eraseLarge operating windowSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesEngineeringDielectric structure
Memory cells comprising: a semiconductor substrate having a source region and a drain region disposed below a surface of the substrate and separated by a channel region; a tunnel dielectric structure disposed above the channel region, the tunnel dielectric structure comprising at least one layer having a small hole-tunneling-barrier height; a charge storage layer disposed above the tunnel dielectric structure; an insulating layer disposed above the charge storage layer; and a gate electrode disposed above the insulating layer are described along with arrays thereof and methods of operation.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Non-volatile memory cells, memory arrays including the same and methods of operating cells and arrays
ActiveUS20060198190A1Easy to optimizeEasy to eraseSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesDielectric structureCondensed matter physics
Memory cells comprising: a semiconductor substrate having a source region and a drain region disposed below a surface of the substrate and separated by a channel region; a tunnel dielectric structure disposed above the channel region, the tunnel dielectric structure comprising at least one layer having a small hole-tunneling-barrier height; a charge storage layer disposed above the tunnel dielectric structure; an insulating layer disposed above the charge storage layer; and a gate electrode disposed above the insulating layer are described along with arrays thereof and methods of operation.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Non-volatile memory cells, memory arrays including the same and methods of operating cells and arrays
InactiveUS20060198189A1Easy to eraseLarge operating windowRead-only memoriesDigital storageDielectric structureCondensed matter physics
Memory cells comprising: a semiconductor substrate having a source region and a drain region disposed below a surface of the substrate and separated by a channel region; a tunnel dielectric structure disposed above the channel region, the tunnel dielectric structure comprising at least one layer having a small hole-tunneling-barrier height; a charge storage layer disposed above the tunnel dielectric structure; an insulating layer disposed above the charge storage layer; and a gate electrode disposed above the insulating layer are described along with arrays thereof and methods of operation.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
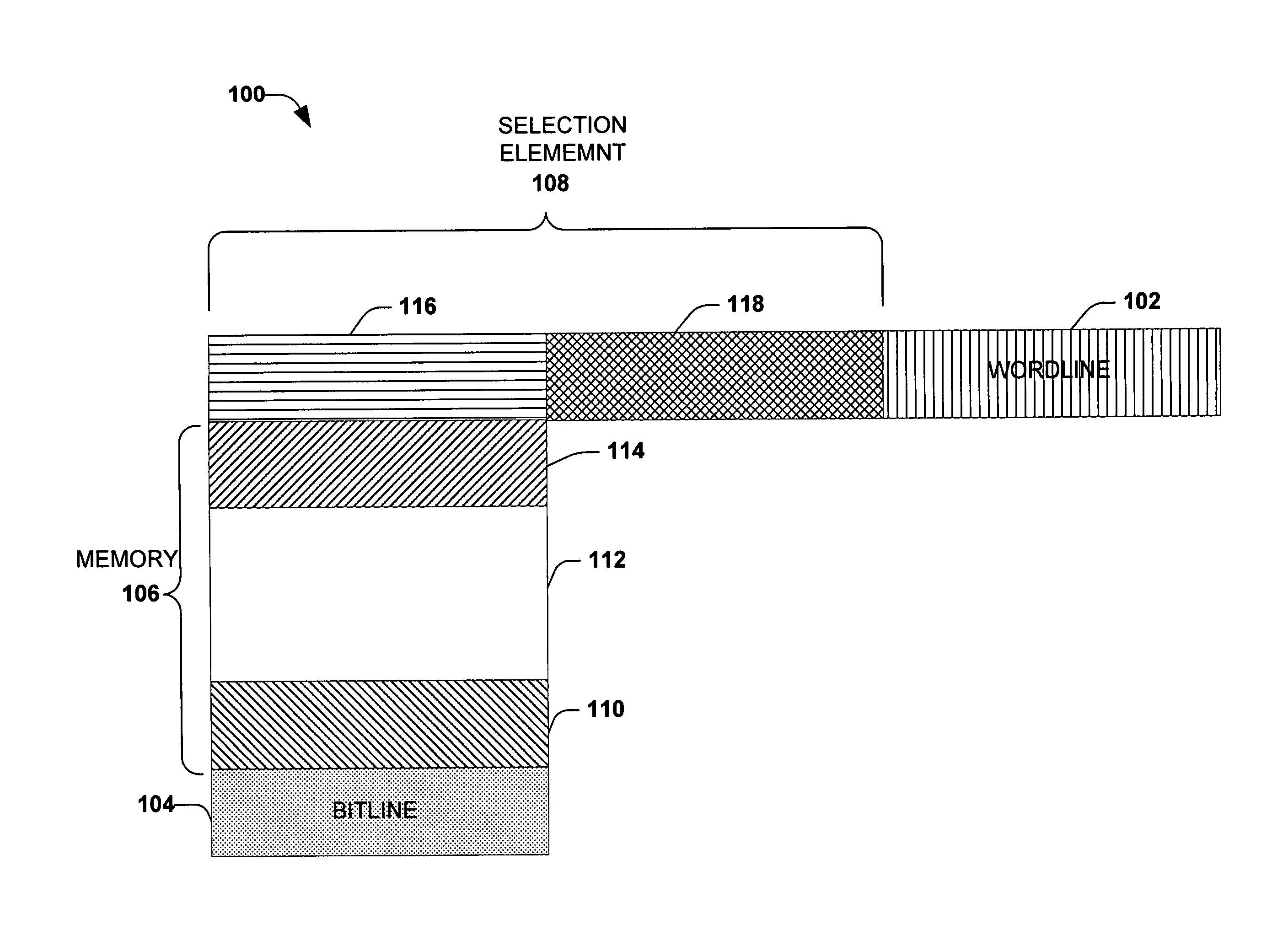
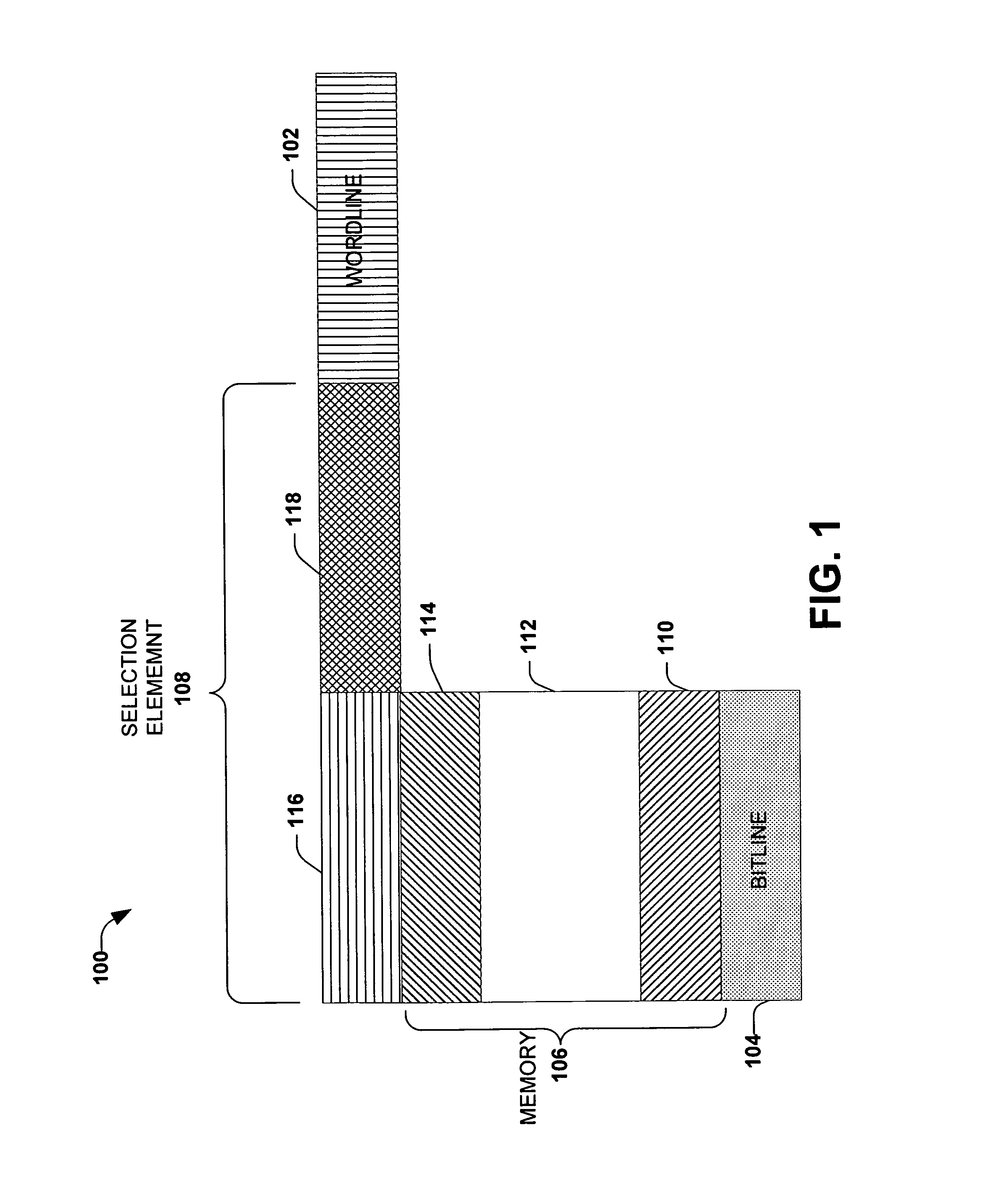
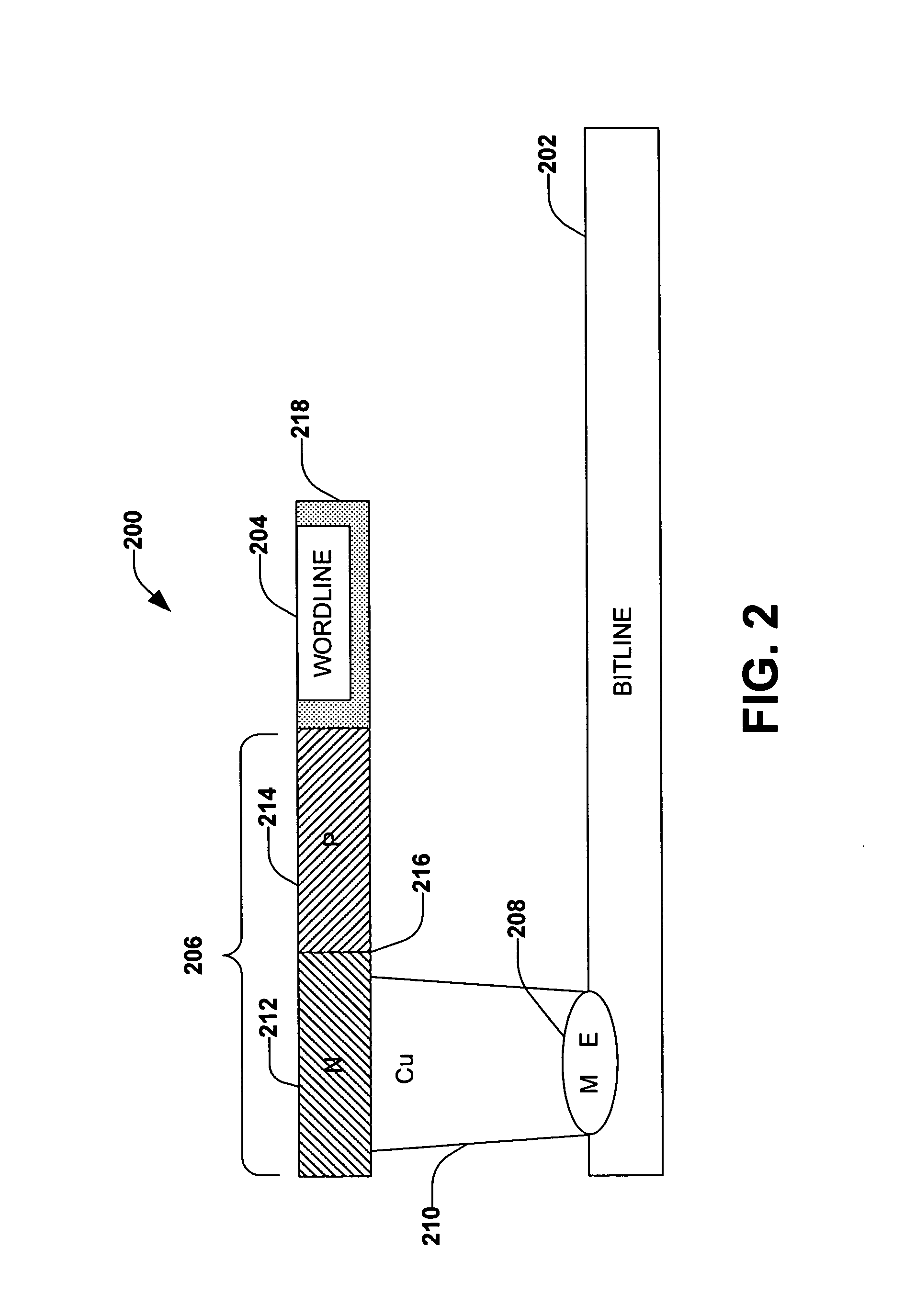
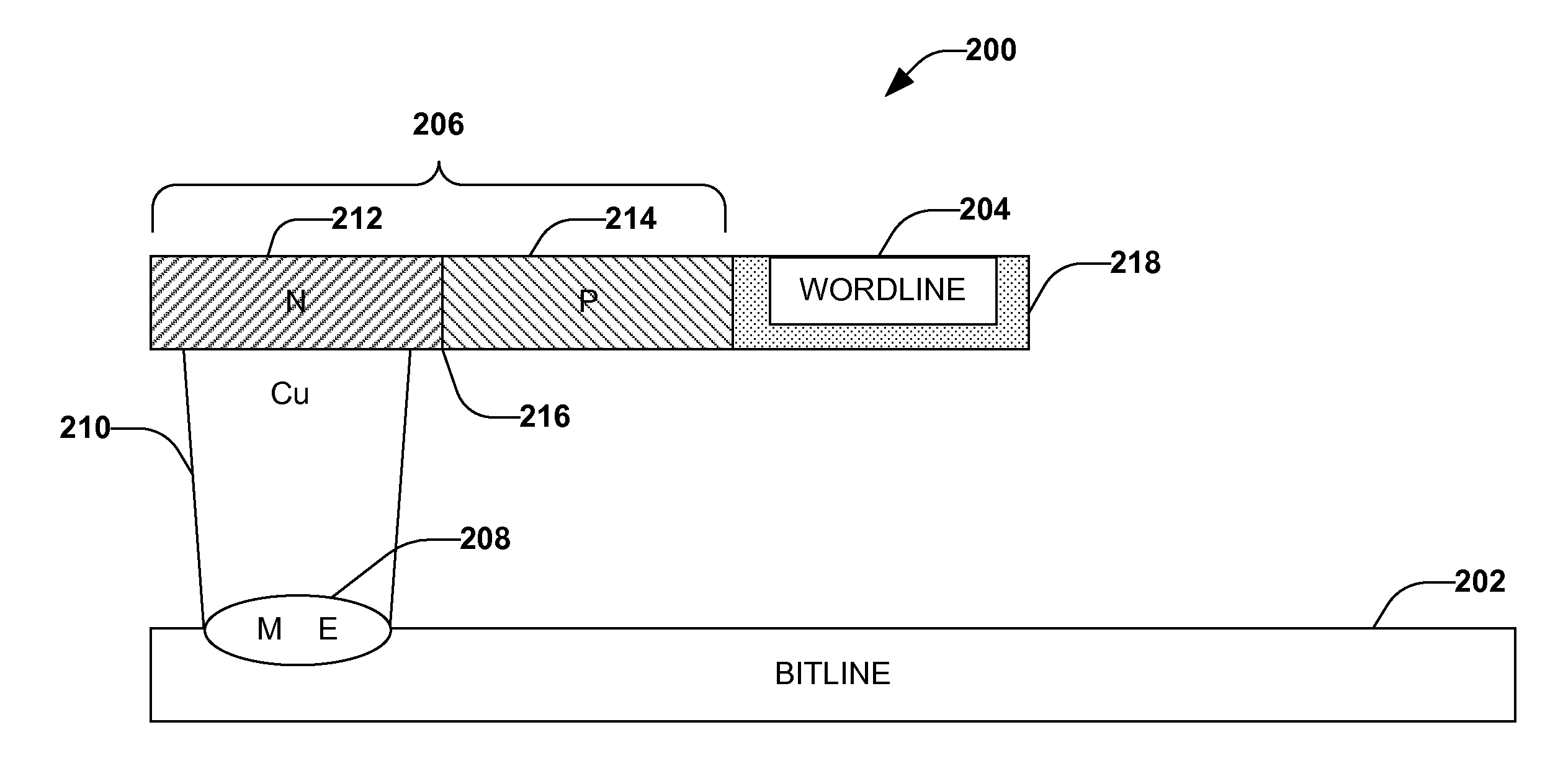
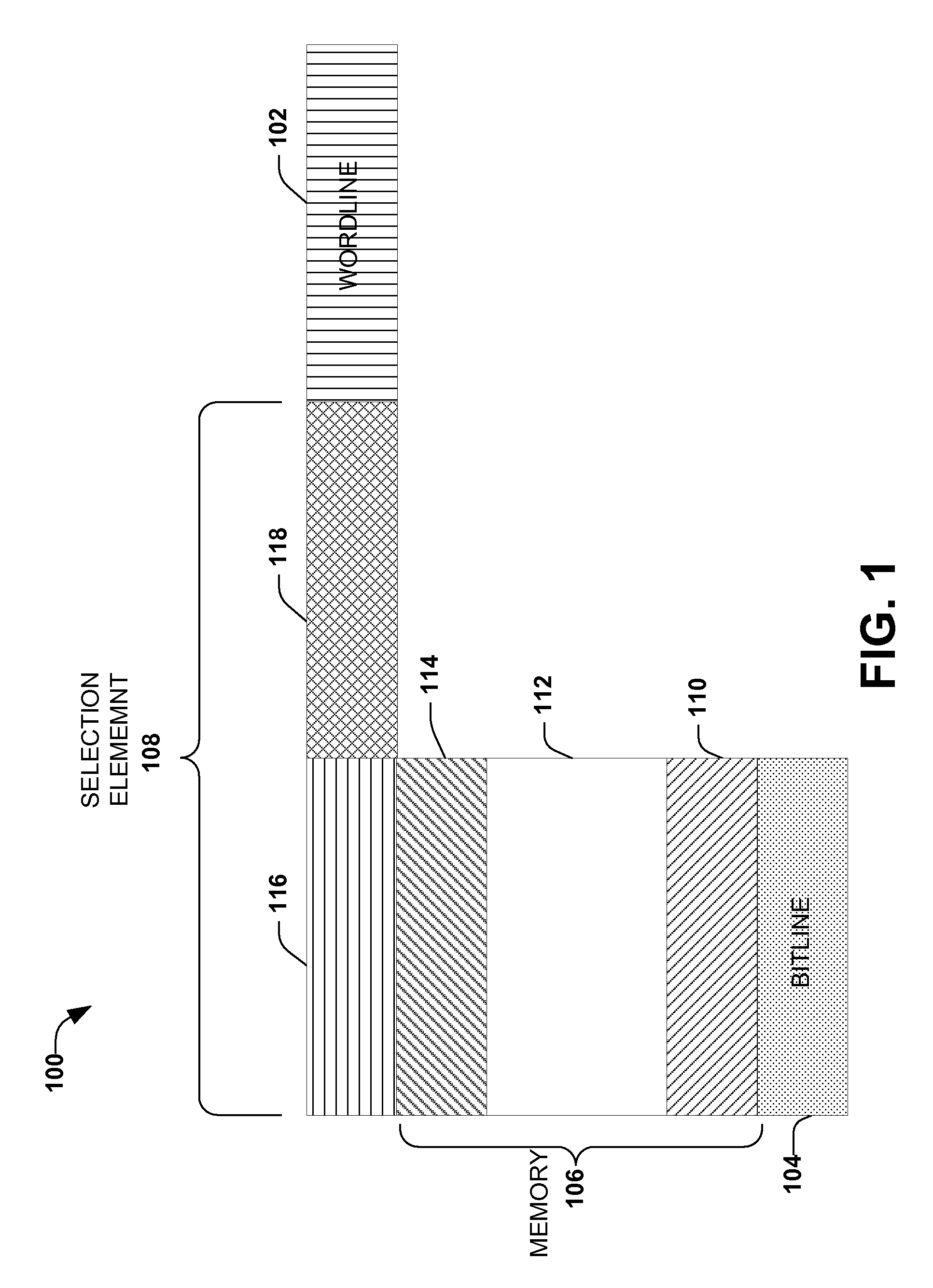
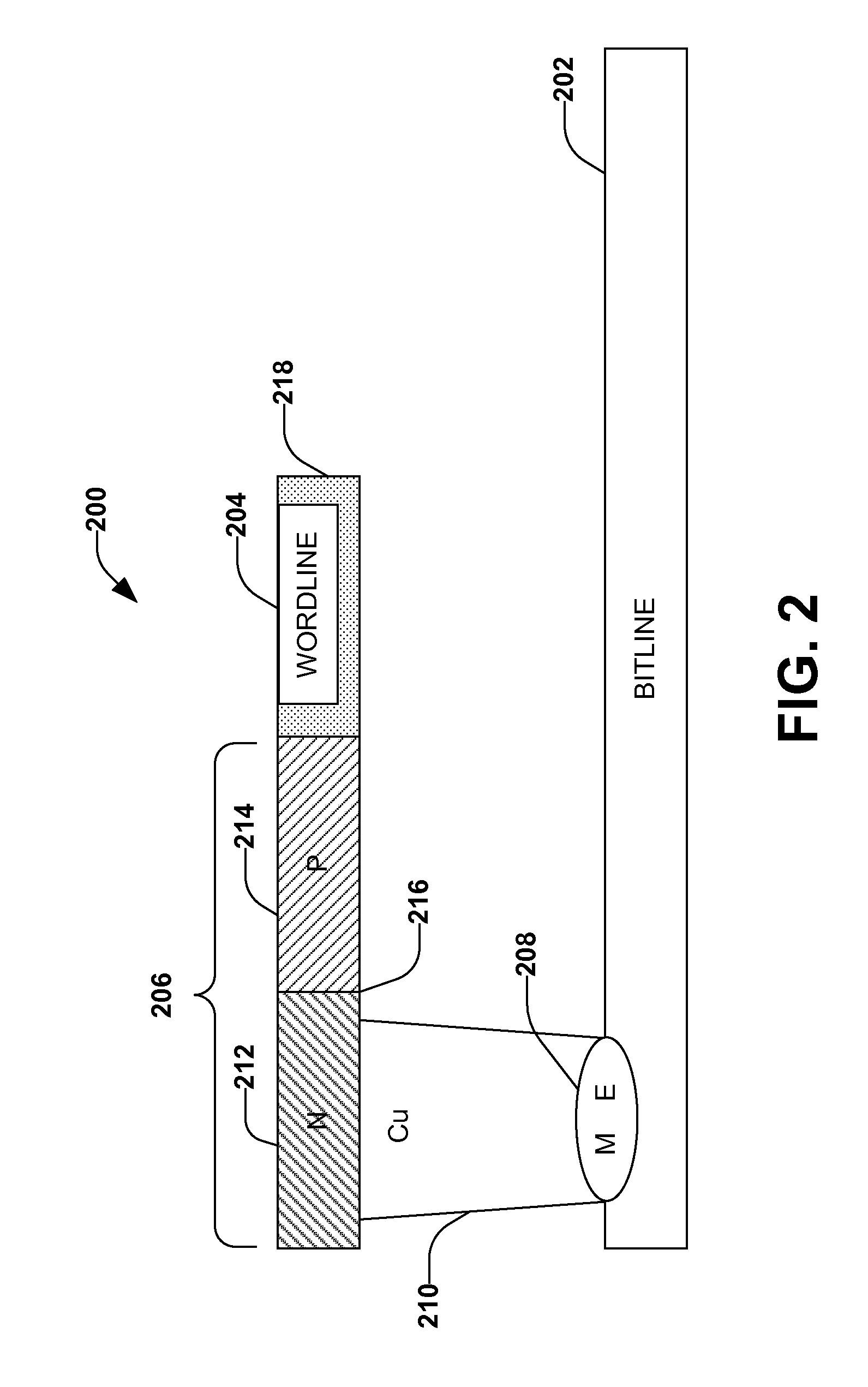
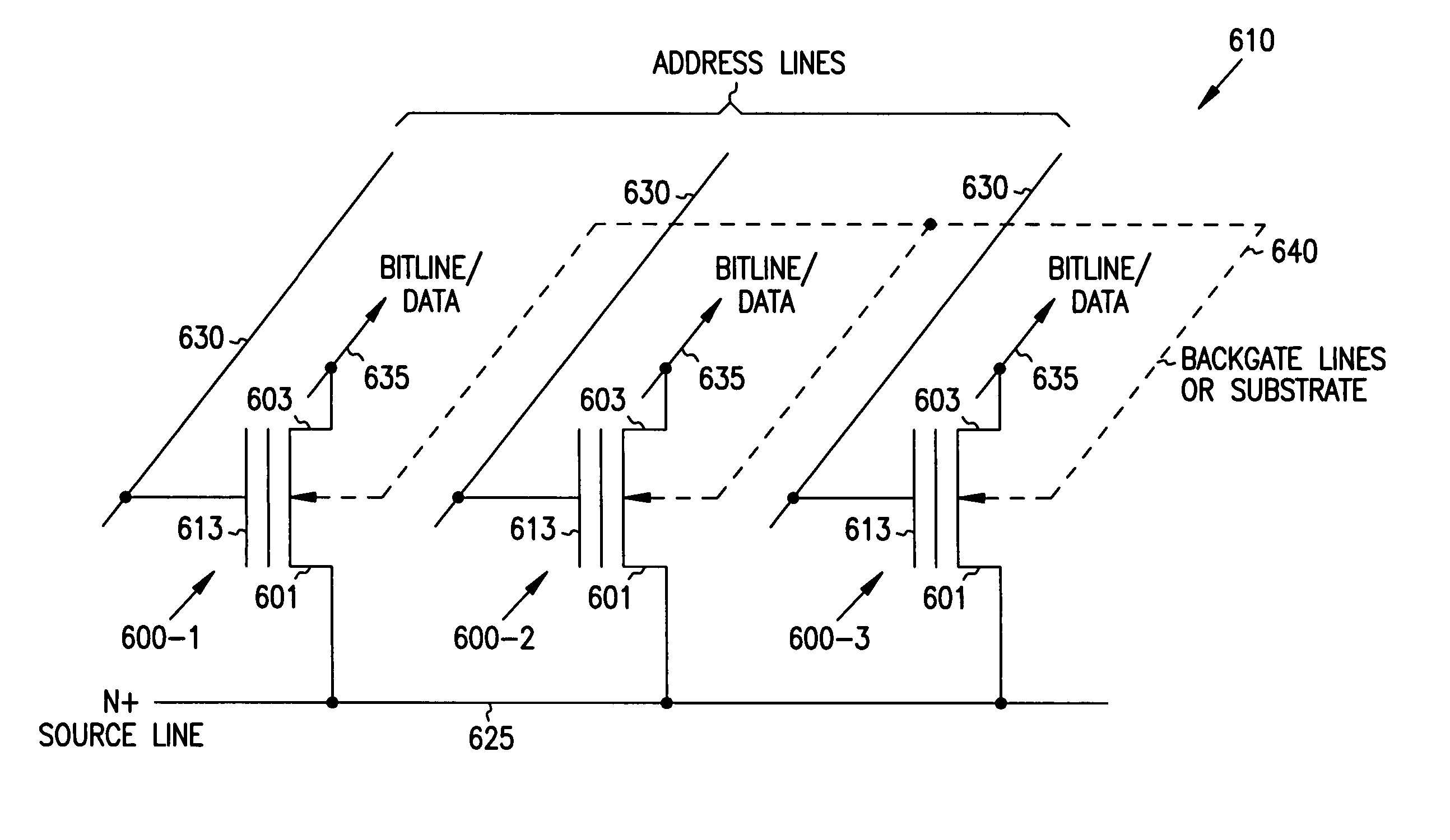
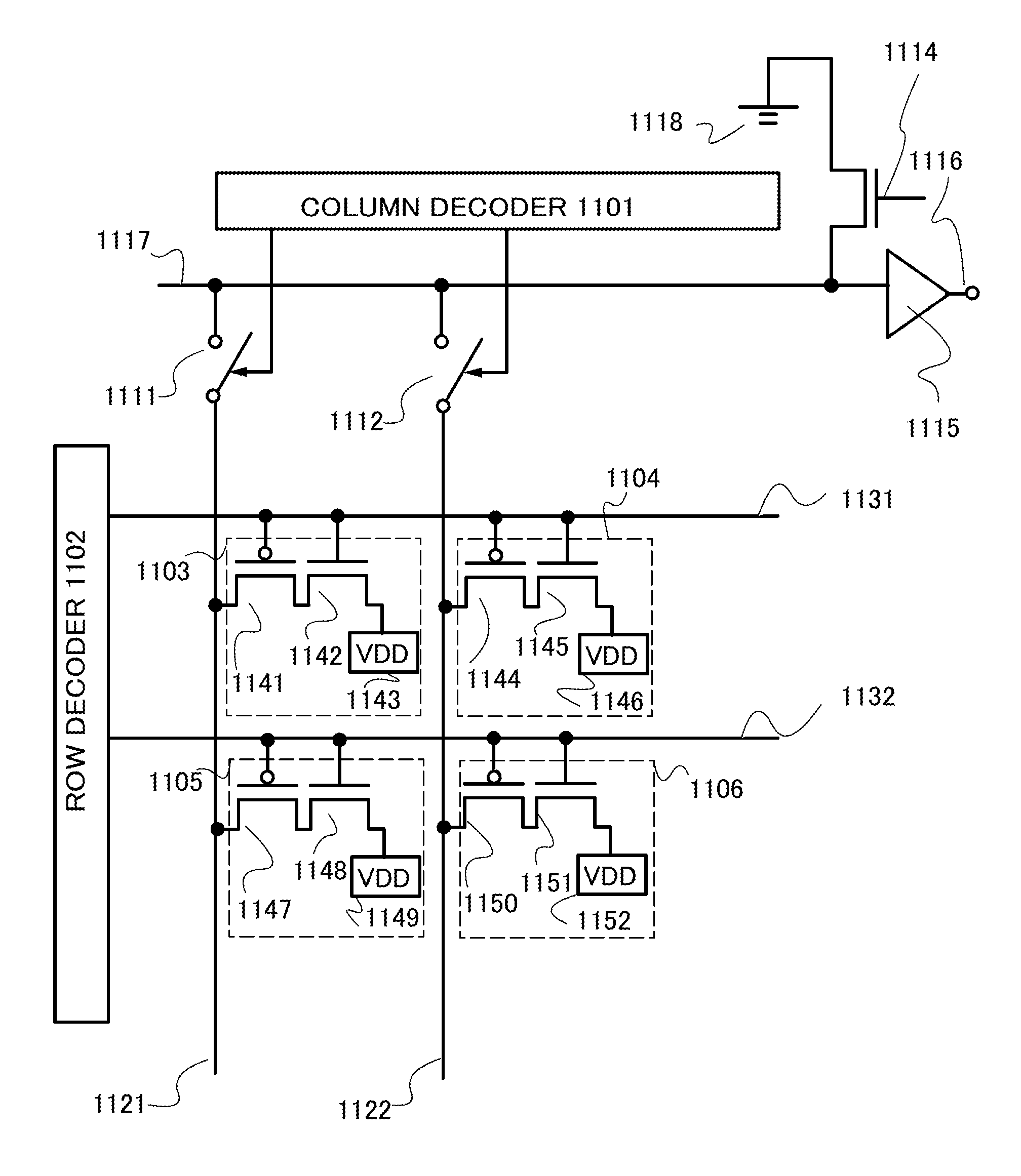
Memory device with a selection element and a control line in a substantially similar layer
ActiveUS7391064B1Reduce complexityMitigate vertical stacking issueTransistorSolid-state devicesControl lineSemiconductor
The invention facilitates manufacture of semiconductor memory components by reducing the number of layers required to implement a semiconductor memory device. The invention provides for a selection element to be formed in the same layer as one of the control lines (e.g. one of the wordline and bitline). In one embodiment of the invention, a diode is implemented as the selection element within the same layer as one of the control lines. Production of the selection element within the same layer as one of the wordline and bitline reduces problems associated with vertical stacking, increases device yield and reduces related production costs. The invention also provides an efficient method of producing memory devices with the selection element in the same layer as one of the control lines.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
Non-volatile memory cells, memory arrays including the same and methods of operating cells and arrays
ActiveUS20060202252A1Easy to optimizeEasy to eraseSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesTunnel barrierEngineering
Memory cells comprising: a semiconductor substrate having a source region and a drain region disposed below a surface of the substrate and separated by a channel region; a tunnel dielectric structure disposed above the channel region, the tunnel dielectric structure comprising at least one layer having a small hole-tunneling-barrier height; a charge storage layer disposed above the tunnel dielectric structure; an insulating layer disposed above the charge storage layer; and a gate electrode disposed above the insulating layer are described along with arrays thereof and methods of operation.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD +1
Memory device with a selection element and a control line in a substantially similar layer
ActiveUS7696017B1Reduce complexityMitigate vertical stacking issuesSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingControl lineEngineering
The invention facilitates manufacture of semiconductor memory components by reducing the number of layers required to implement a semiconductor memory device. The invention provides for a selection element to be formed in the same layer as one of the control lines (e.g. one of the wordline and bitline). In one embodiment of the invention, a diode is implemented as the selection element within the same layer as one of the control lines. Production of the selection element within the same layer as one of the wordline and bitline reduces problems associated with vertical stacking, increases device yield and reduces related production costs. The invention also provides an efficient method of producing memory devices with the selection element in the same layer as one of the control lines.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
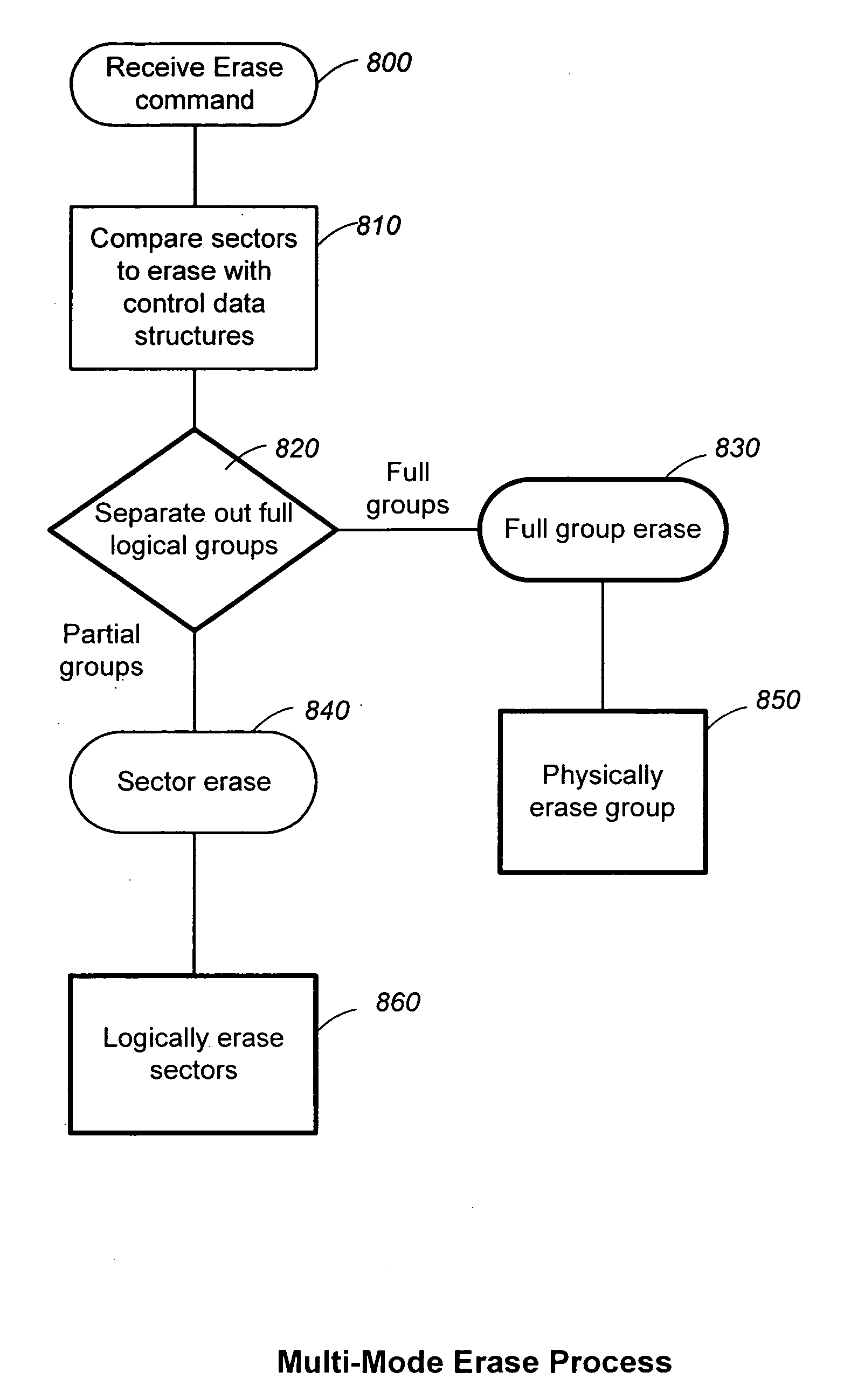
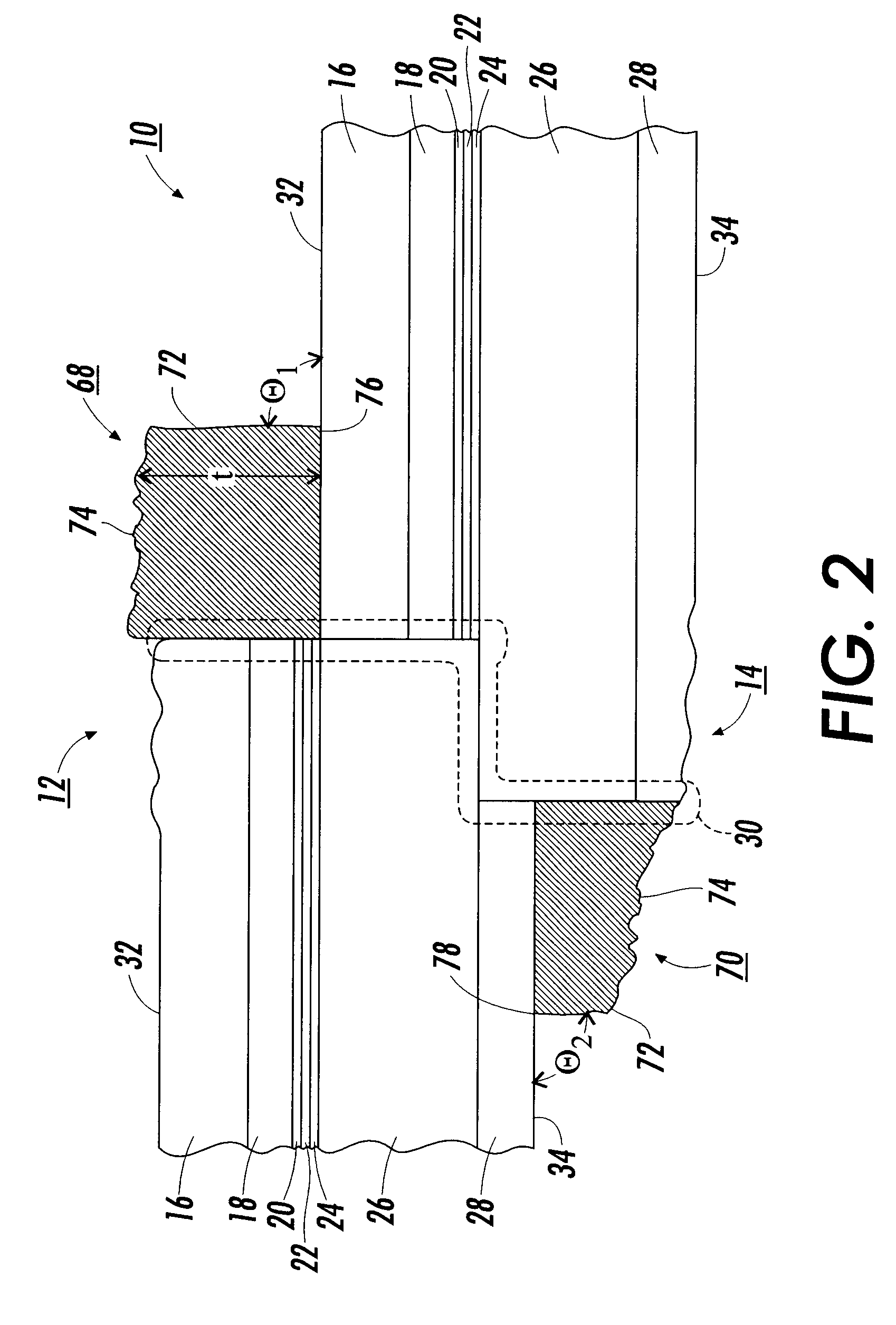
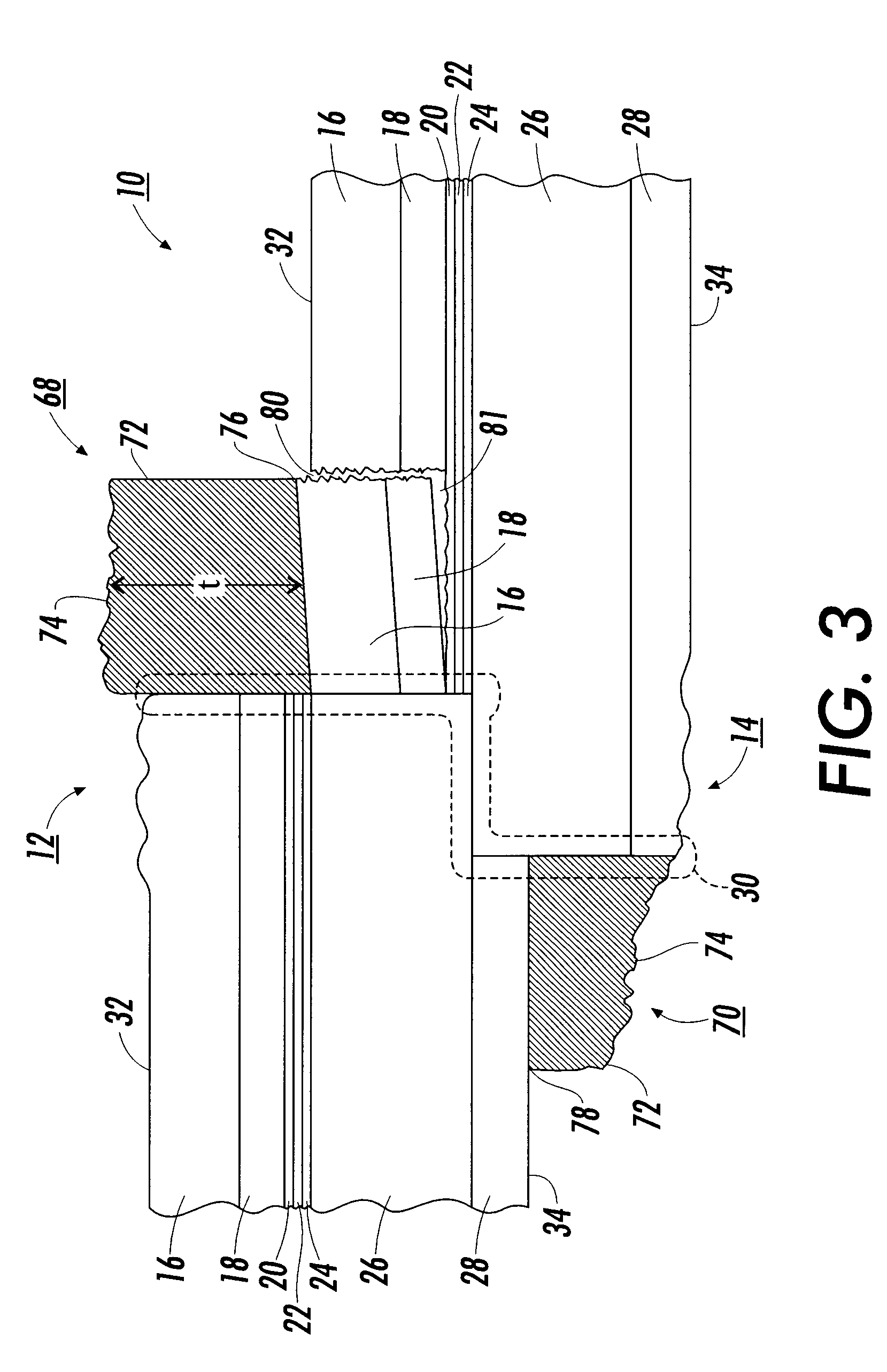
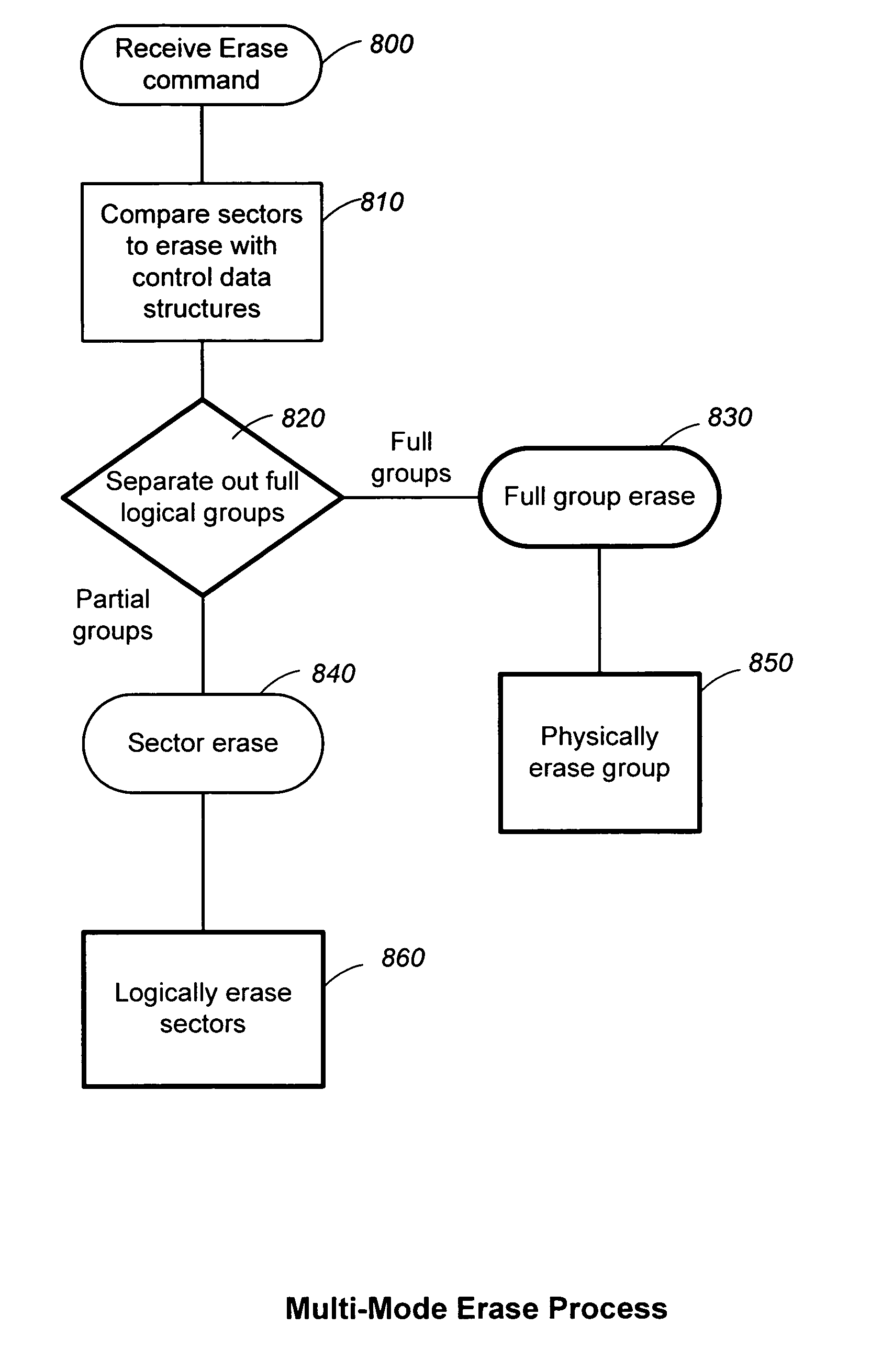
Structures for the management of erase operations in non-volatile memories
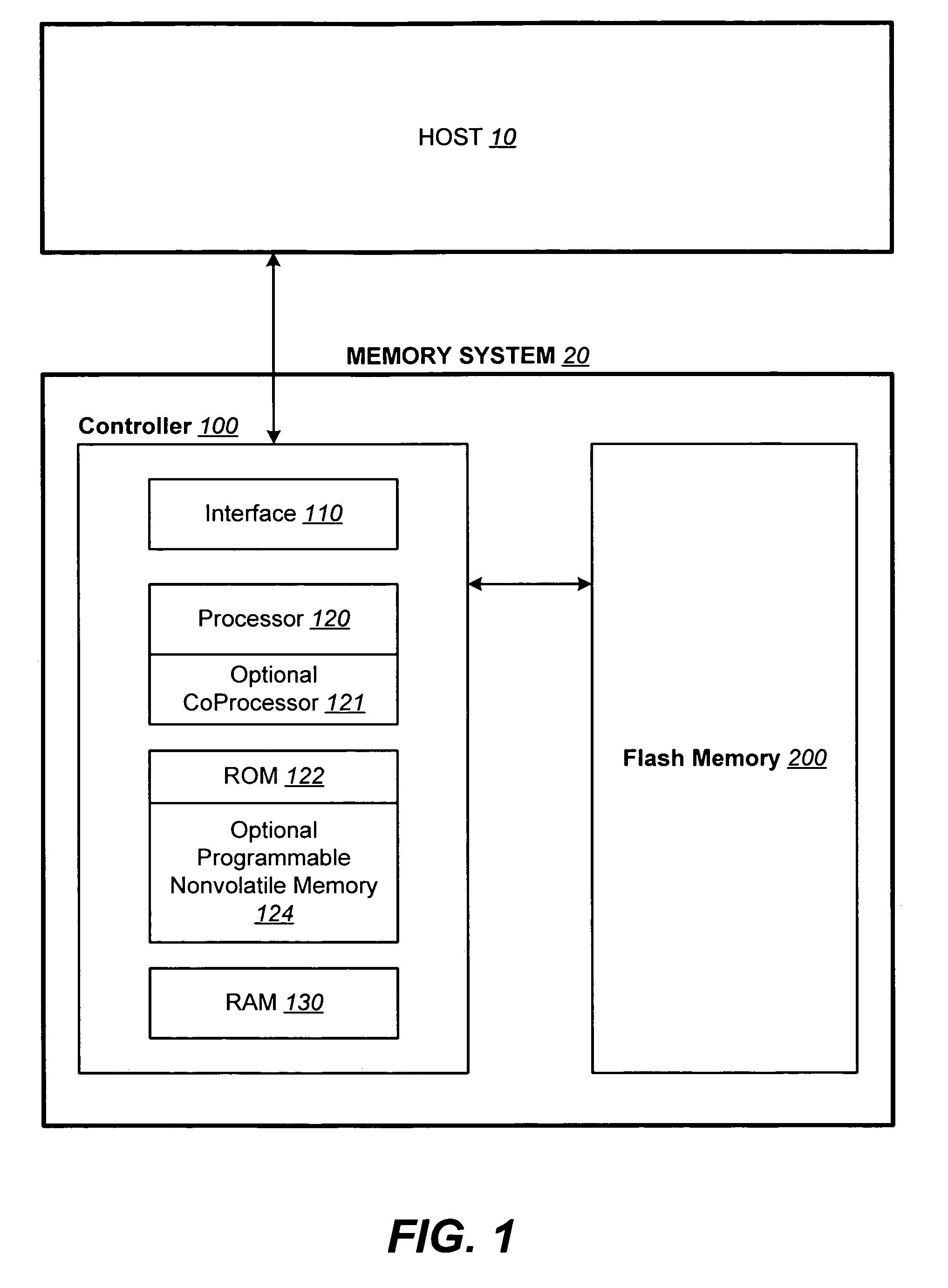
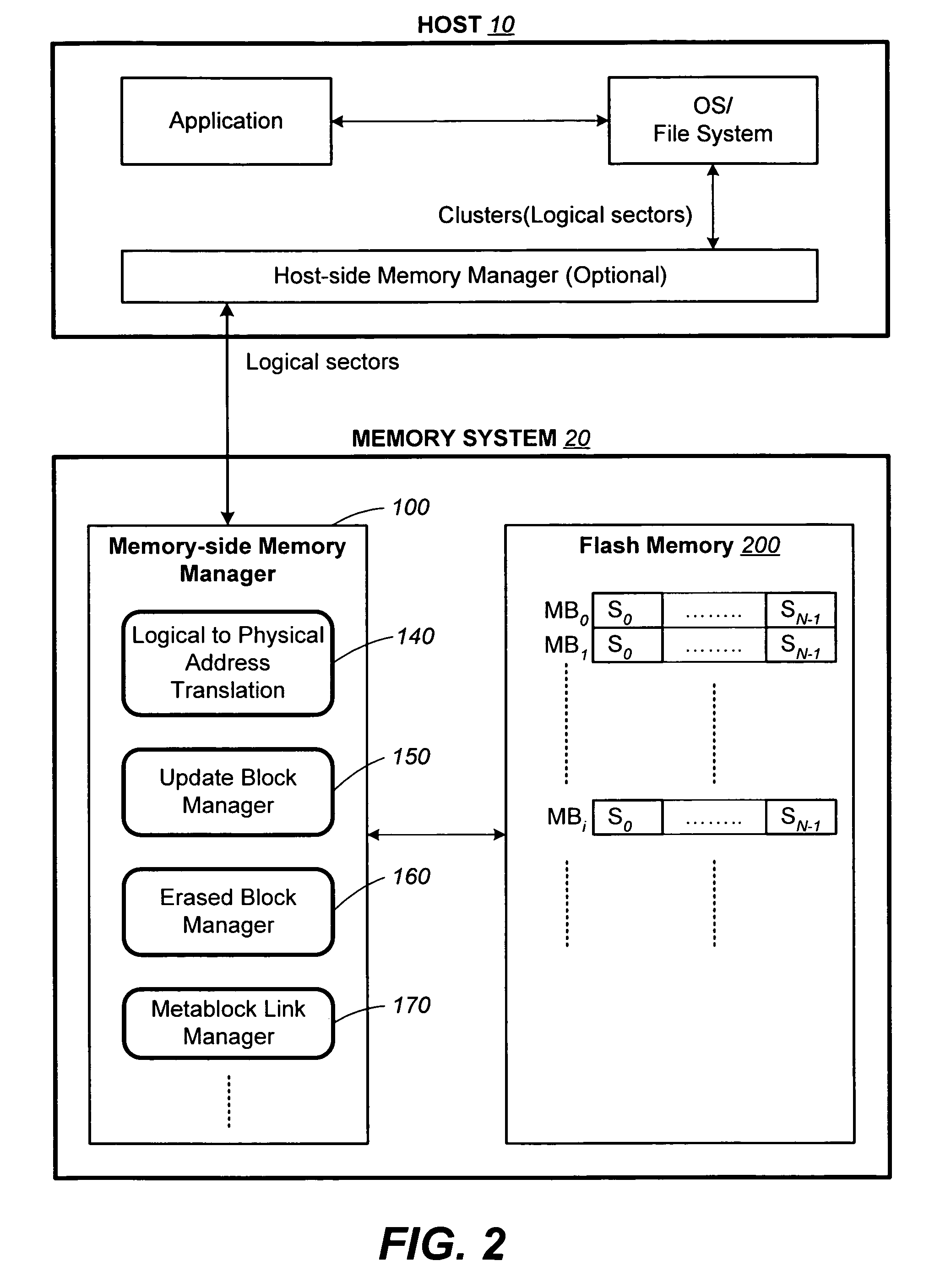
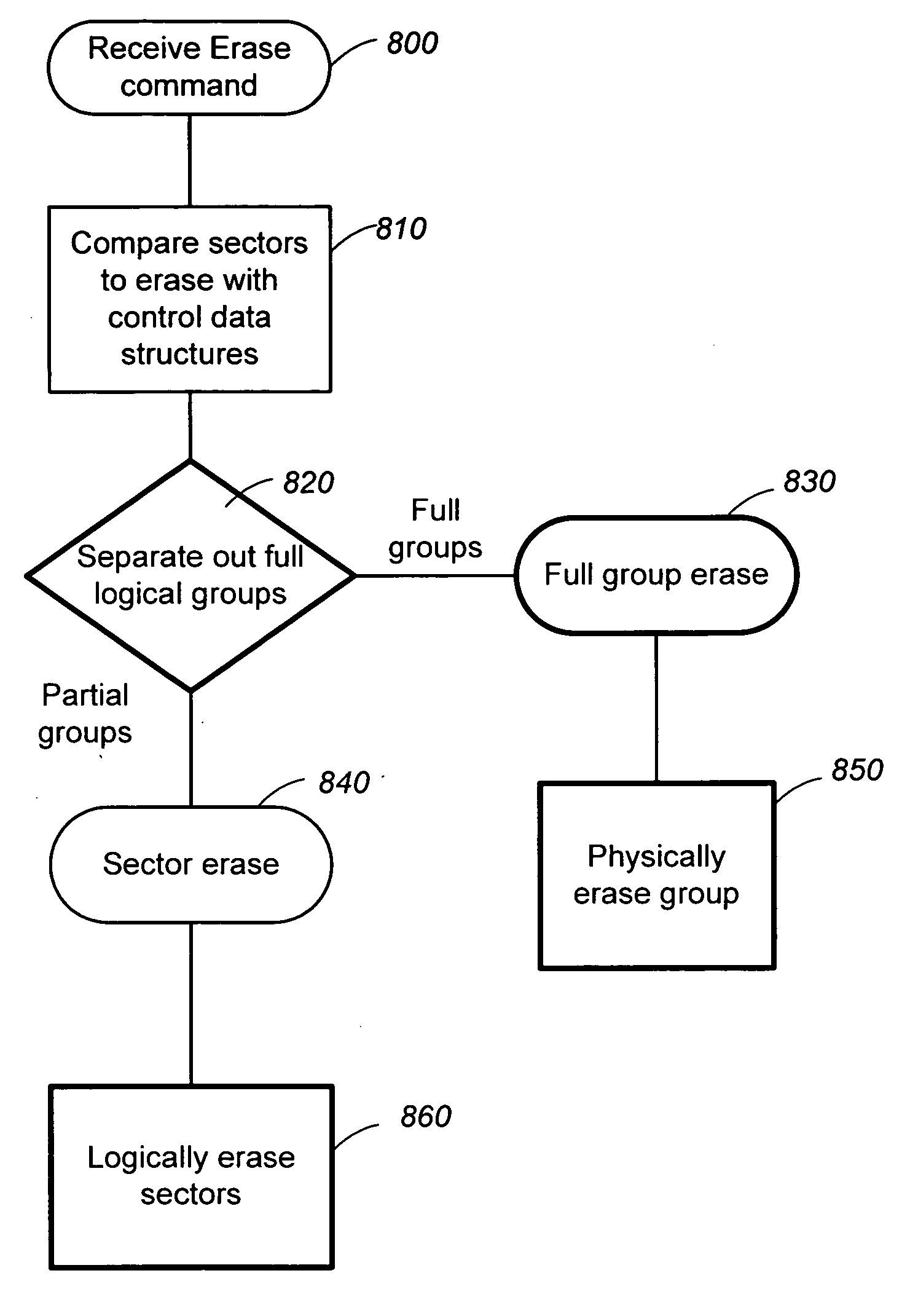
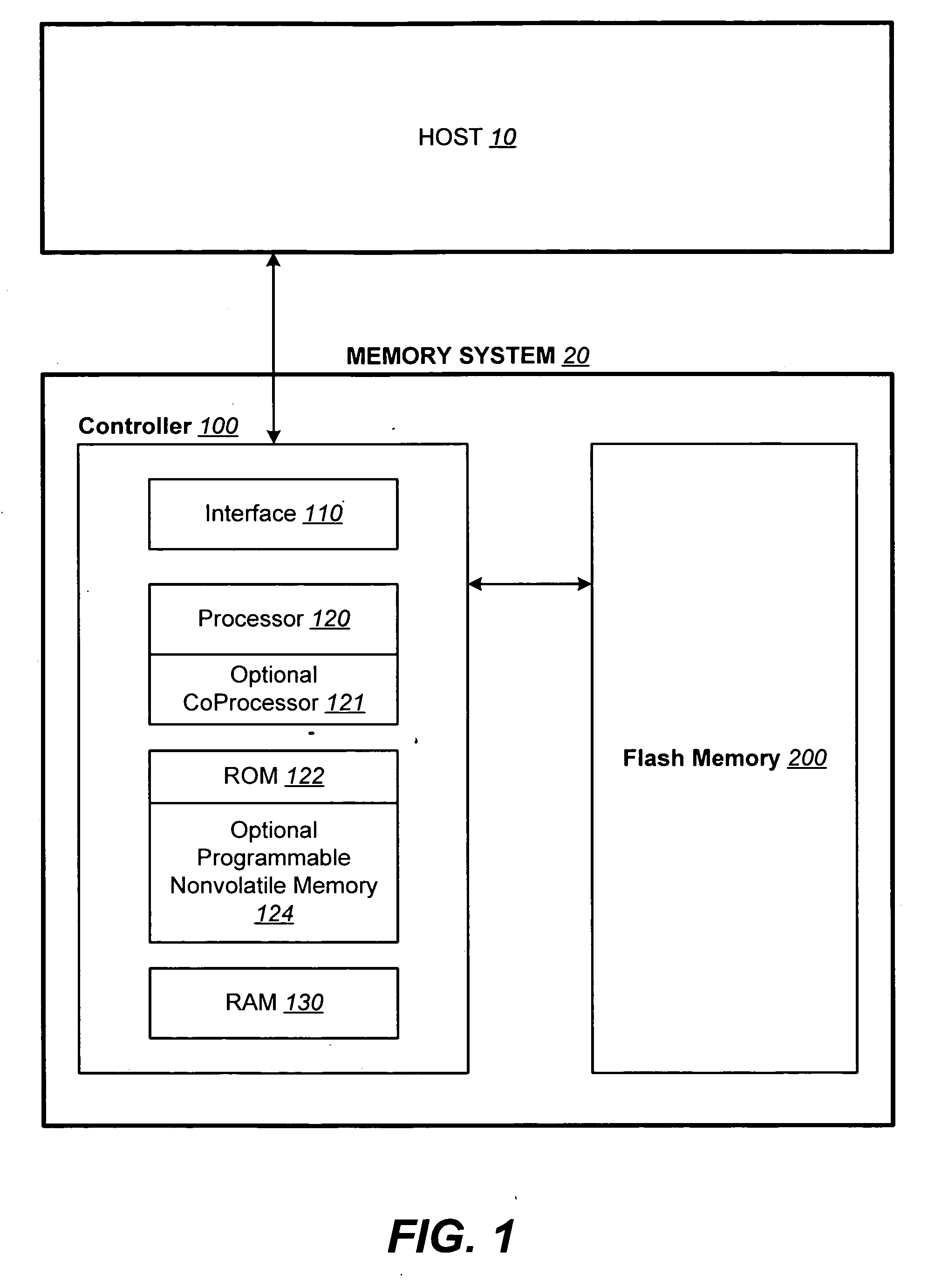
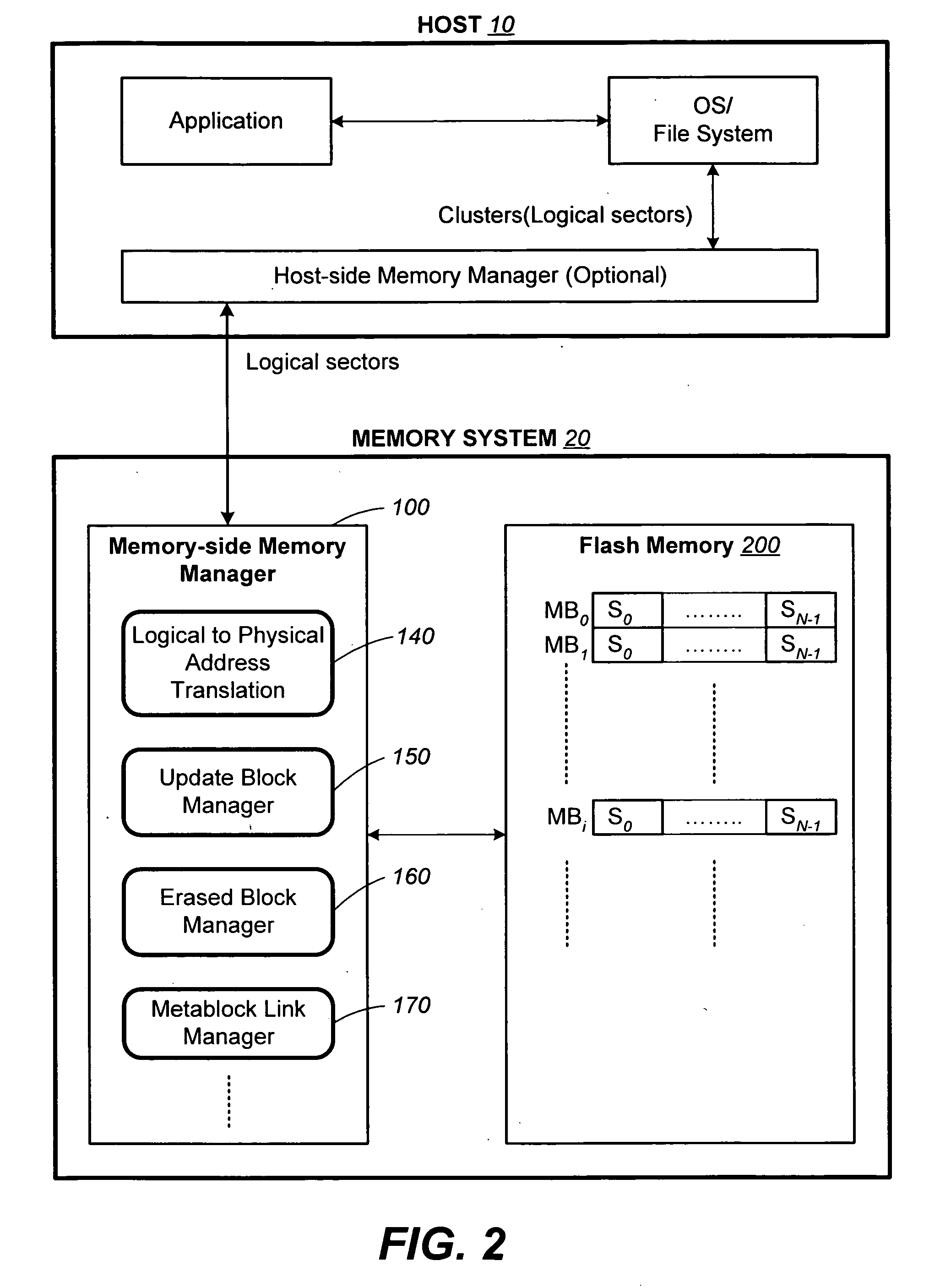
ActiveUS20070113029A1Easy to eraseExecution time can be made muchMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory systemsControl dataOperating system
The present invention presents a number of improvements for managing erase processes in non-volatile memory. Such memory systems typically manage the memory by logically organize the basic unit of physical erase (erase block) into composite logical groupings (meta-blocks or logical group), where an erase block generally consists of a number of sectors. When an erase command is received, the specified sectors are checked against the memory system's control data. If the specified sectors span any full logical grouping, the full logical groupings can each be treated a whole and erased according to one process (such as performing a true, physical erase), while other sectors are “logically” erased at the sector level by standard techniques.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Electrostatographic imaging member
InactiveUS6303254B1Improve thickness uniformityReduces undesirable dirtElectrographic process apparatusMicrometerPolymer chemistry
An electrostatographic imaging member including: a flexible supporting substrate; an imaging layer having an optional adjacent ground strip layer coated on one side of the substrate; and an anti-curl backing layer coated on the other side of the substrate which layer is comprised of a film forming polymer binder, an optional adhesion promoting polymer, and a dispersion of polytetrafluoroethylene particles which dispersion has particles with a narrow diameter particle size distribution of from about 0.19 micrometer to about 0.21 micrometer, and an average diameter particle size of about 0.20 micrometer. The optional ground strip layer can include the same dispersion of polytetrafluoroethylene particles as the anti-curl backing layer.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Methods for the management of erase operations in non-volatile memories
InactiveUS7624239B2Easy to eraseMany timesMemory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesMemory systemsVolatile memory
The present invention presents a number of improvements for managing erase processes in non-volatile memory. Such memory systems typically manage the memory by logically organize the basic unit of physical erase (erase block) into composite logical groupings (meta-blocks or logical group), where an erase block generally consists of a number of sectors. When an erase command is received, the specified sectors are checked against the memory system's control data. If the specified sectors span any full logical grouping, the full logical groupings can each be treated as a whole and erased according to one process (such as performing a true, physical erase), while other sectors are “logically” erased at the sector level by standard techniques.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Methods for the management of erase operations in non-volatile memories
InactiveUS20070113030A1Easy to eraseExecution time can be made muchMemory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesControl dataOperating system
The present invention presents a number of improvements for managing erase processes in non-volatile memory. Such memory systems typically manage the memory by logically organize the basic unit of physical erase (erase block) into composite logical groupings (meta-blocks or logical group), where an erase block generally consists of a number of sectors. When an erase command is received, the specified sectors are checked against the memory system's control data. If the specified sectors span any full logical grouping, the full logical groupings can each be treated a whole and erased according to one process (such as performing a true, physical erase), while other sectors are “logically” erased at the sector level by standard techniques.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Methods of operating bandgap engineered memory
ActiveUS20070268753A1Easy to eraseLarge operating windowSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesDielectric structureCondensed matter physics
Memory cells comprising: a semiconductor substrate having a source region and a drain region disposed below a surface of the substrate and separated by a channel region; a tunnel dielectric structure disposed above the channel region, the tunnel dielectric structure comprising at least one layer having a hole-tunneling barrier height; a charge storage layer disposed above the tunnel dielectric structure; an insulating layer disposed above the charge storage layer; and a gate electrode disposed above the insulating layer are described along with arrays and methods of operation.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
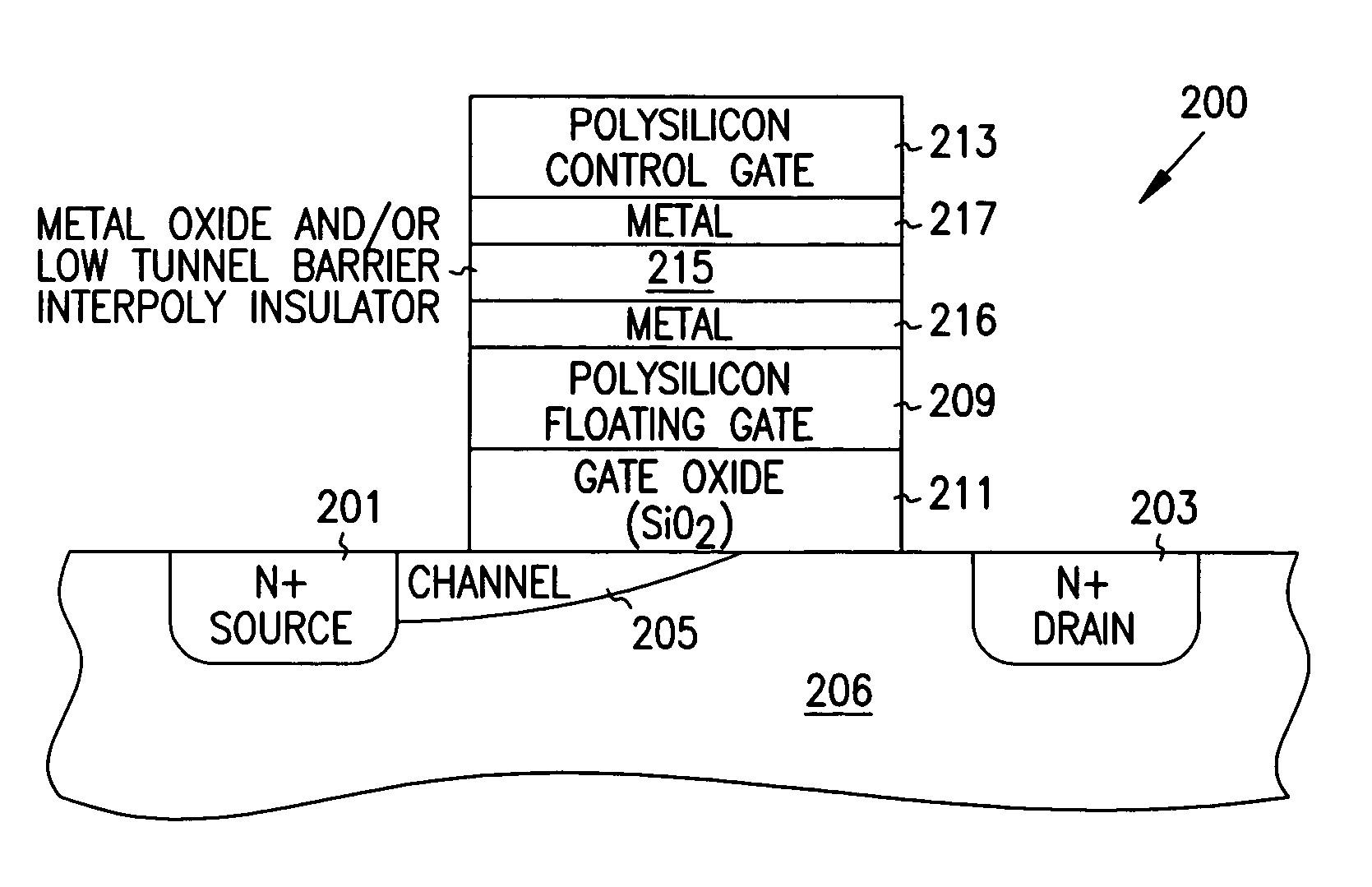
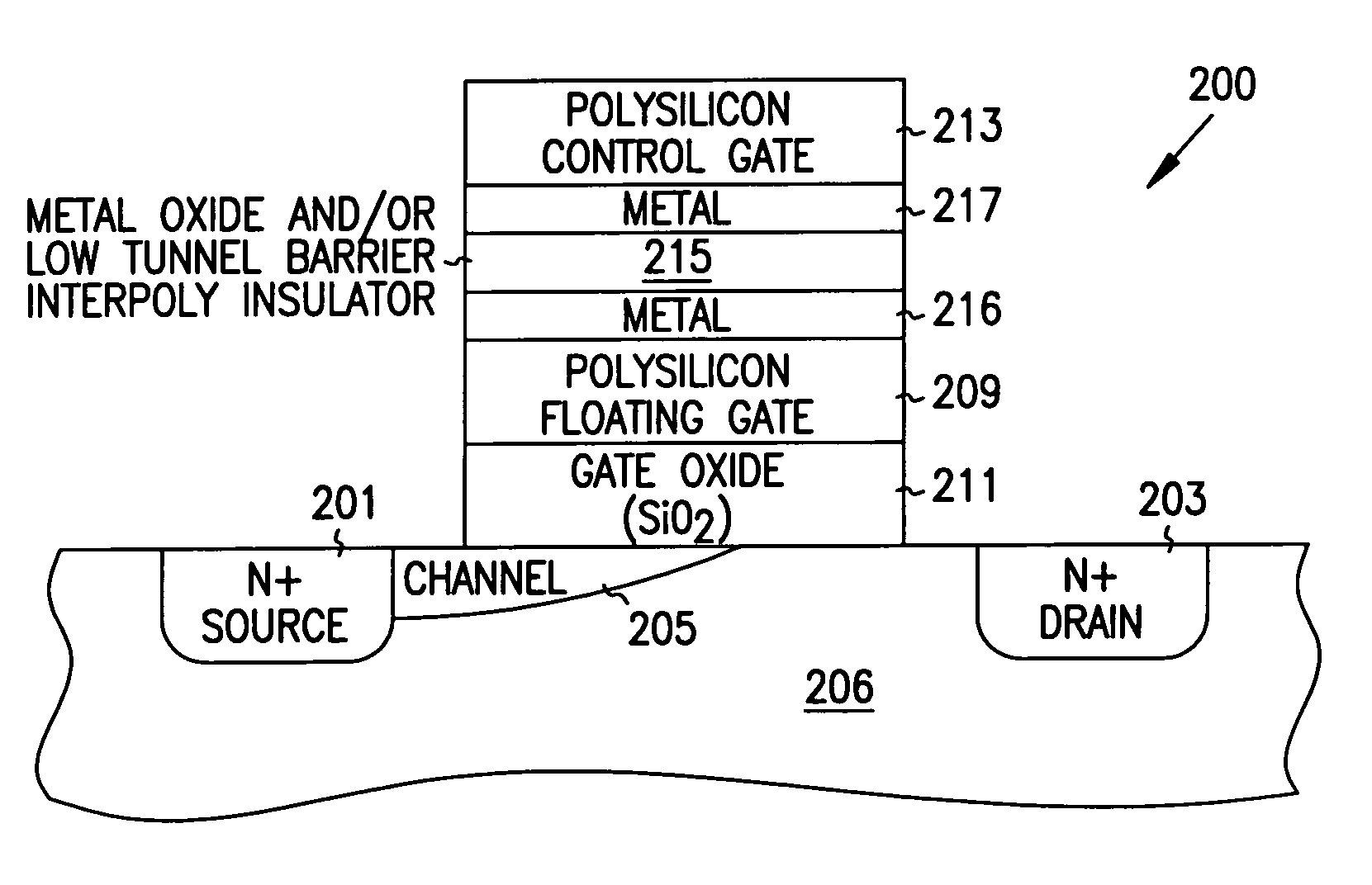
Integrated circuit memory device and method
InactiveUS20060002192A1Increase current gainEasy programmingSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesEngineeringGate oxide
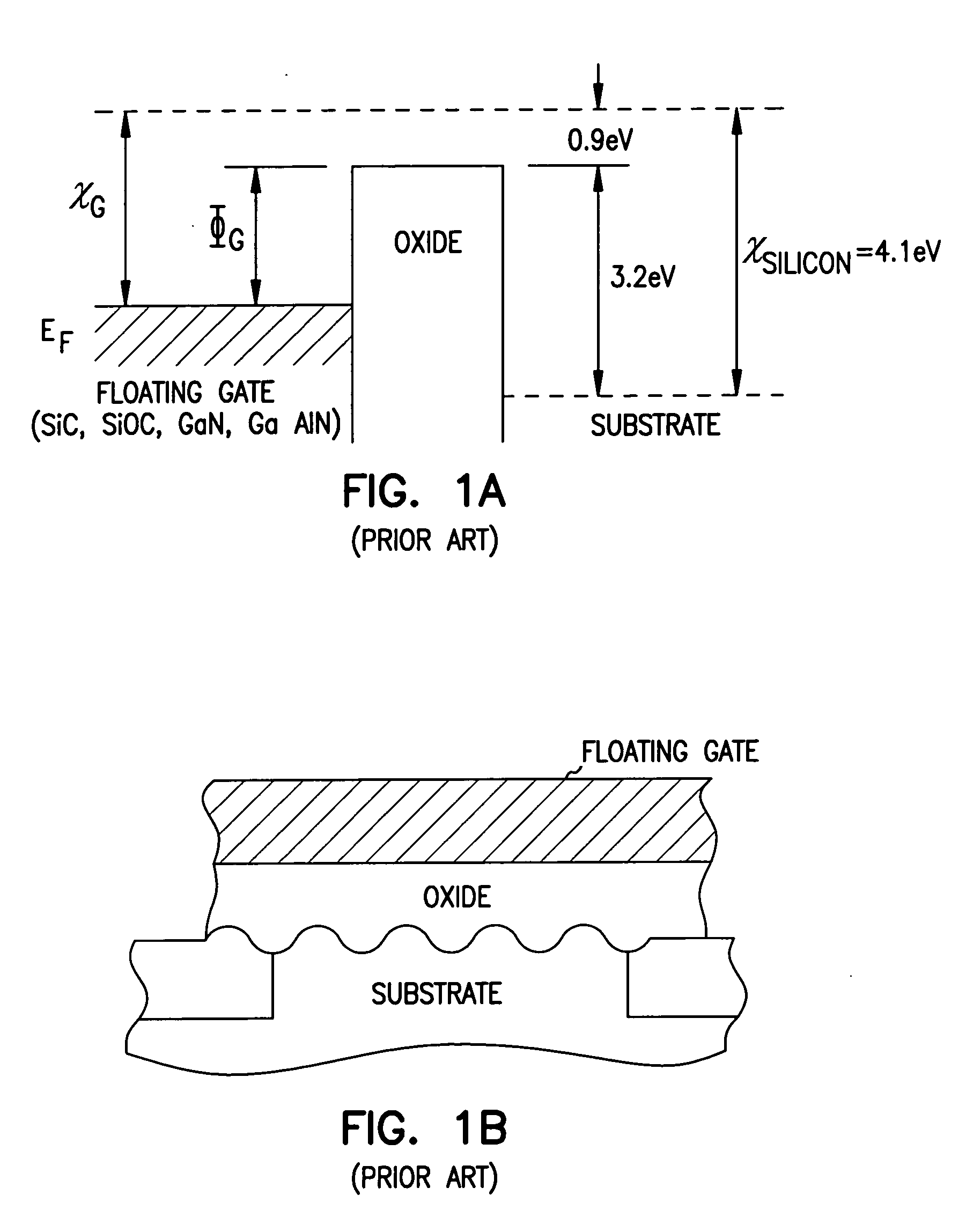
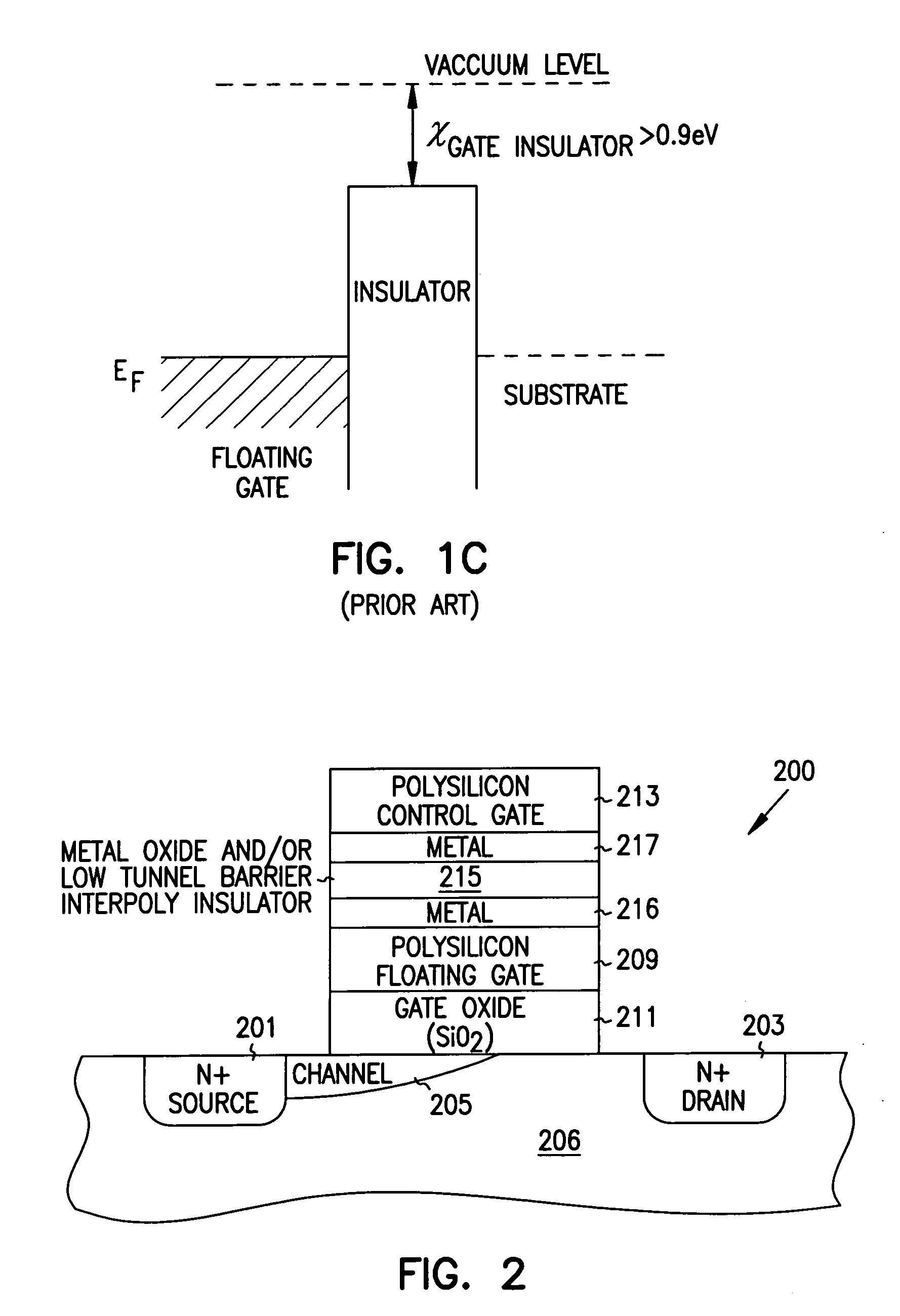
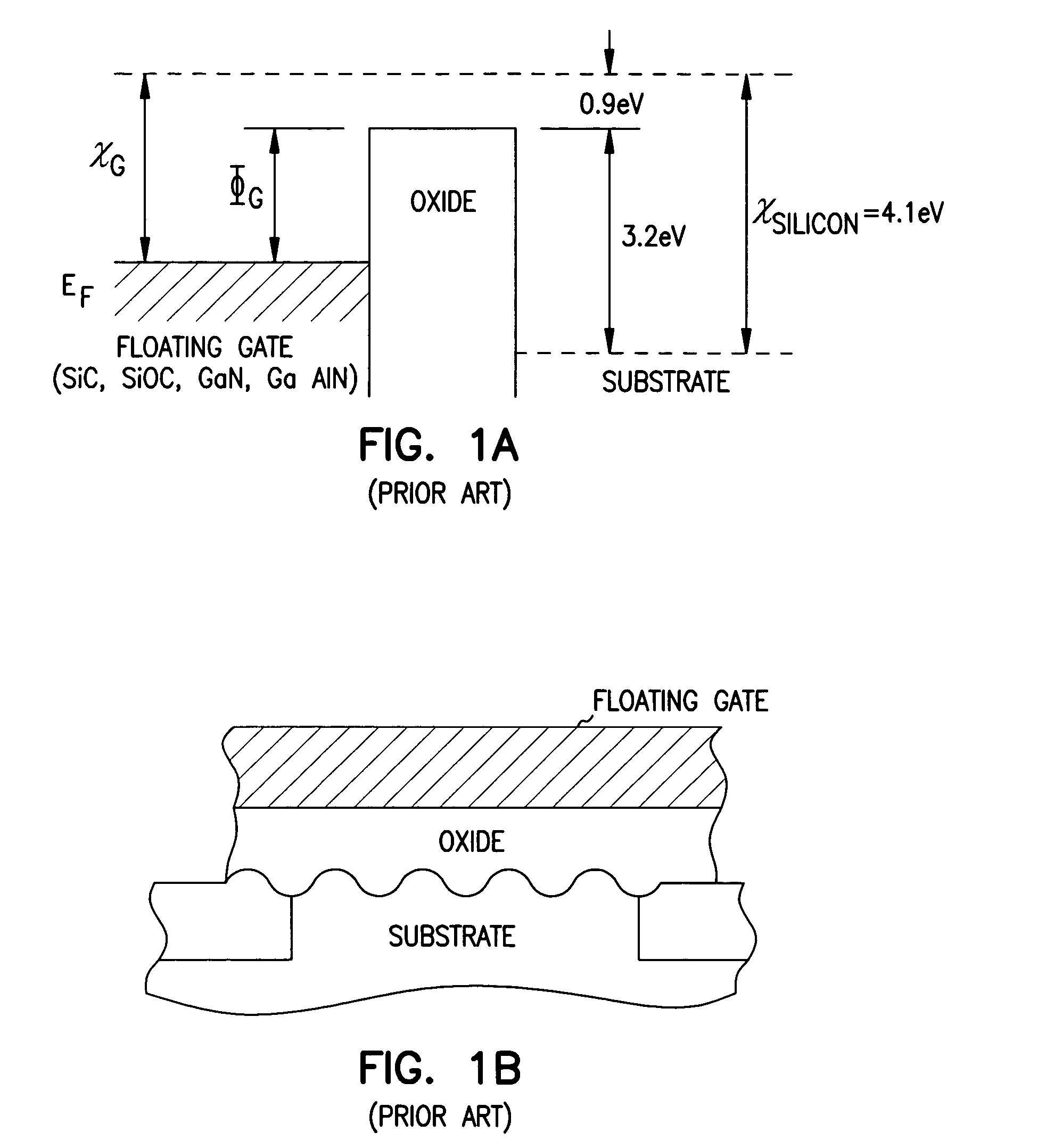
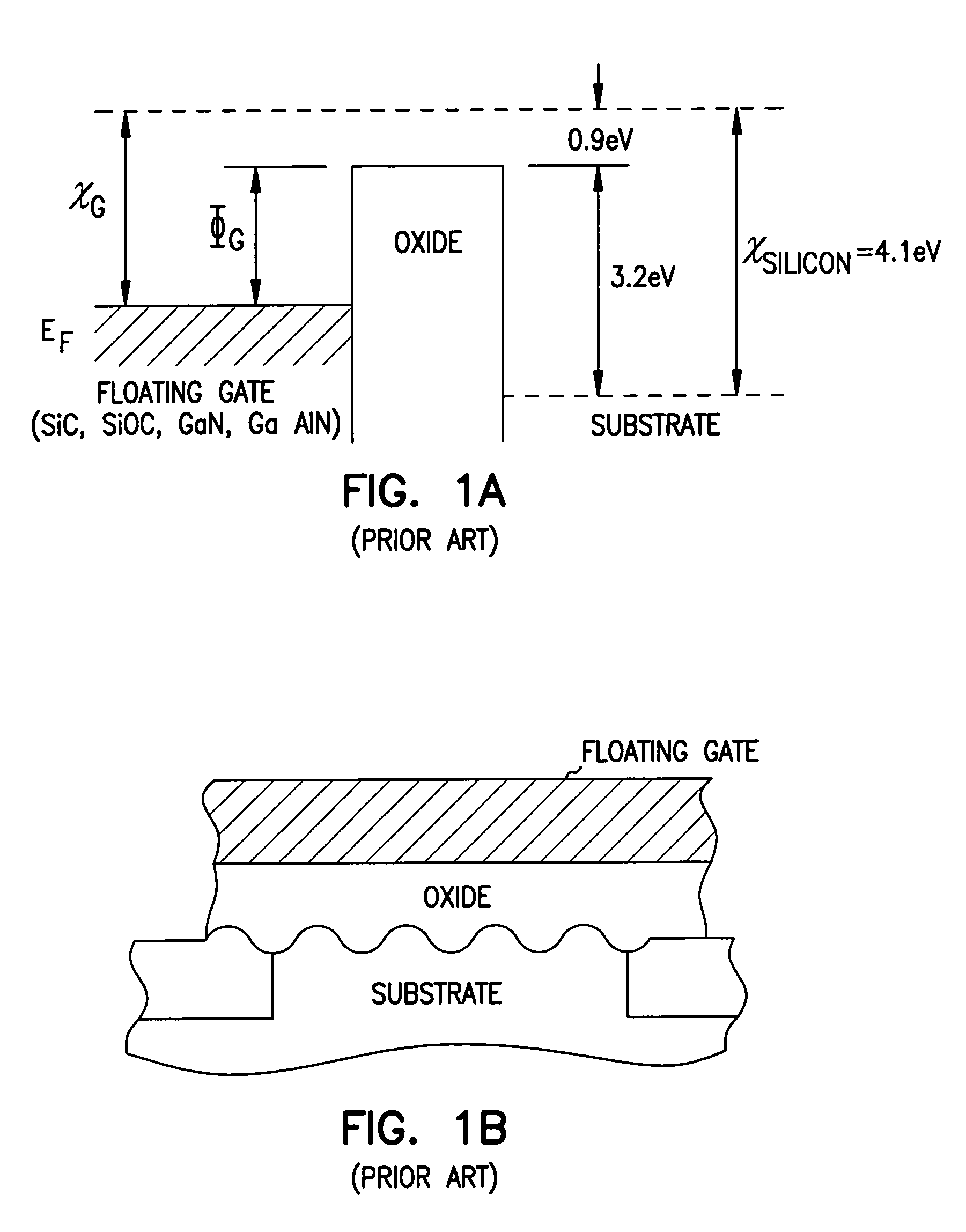
Structures and methods for DEAPROM memory with low tunnel barrier intergate insulators are provided. The DEAPROM memory includes a first source / drain region and a second source / drain region separated by a channel region in a substrate. A floating gate opposes the channel region and is separated therefrom by a gate oxide. A control gate opposes the floating gate. The control gate is separated from the floating gate by a low tunnel barrier intergate insulator having a tunnel barrier of less than 1.5 eV. The low tunnel barrier intergate insulator includes a metal oxide insulator selected from the group consisting of NiO, Al2O3, Ta2O5, TiO2, ZrO2, Nb2O5, Y2O3, Gd2O3, SrBi2Ta2O3, SrTiO3, PbTiO3, and PbZrO3. The floating gate includes a polysilicon floating gate having a metal layer formed thereon in contact with the low tunnel barrier intergate insulator. And, the control gate includes a polysilicon control gate having a metal layer formed thereon in contact with the low tunnel barrier intergate insulator.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Bandgap engineered split gate memory
ActiveUS20070267687A1Easy to eraseLarge operating windowTransistorSolid-state devicesDielectric structureCondensed matter physics
Memory cells comprising: a semiconductor substrate having a source region and a drain region disposed below a surface of the substrate and separated by a channel region; a tunnel dielectric structure disposed above the channel region, the tunnel dielectric structure comprising at least one layer having a hole-tunneling barrier height; a charge storage layer disposed above the tunnel dielectric structure; an insulating layer disposed above the charge storage layer; and a gate electrode disposed above the insulating layer are described along with arrays and methods of operation.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Fingerprint easily erasible film
ActiveUS20060035060A1Superior fingerprint erasabilityEasy to eraseRecord information storageMagnetic recordingFingerprintChemistry
A fingerprint easily erasable film formed by providing a resin layer on a substrate, in which surface of the resin layer is matted and which is formed so that the surface of the resin layer should show a wet tension (JIS-K 6768:1999) of 25 mN / m or higher. Preferably, the resin layer has a surface roughness of 0.2 to 2.0 μm in terms of the ten point mean roughness Rz (JIS-B 0601:1994). The resin layer preferably contains an ionizing radiation curable resin and a matting agent, more preferably, two kinds of matting agents having different average particle diameters. On the fingerprint easily erasable film having such a configuration, ingredients of fingerprint are unlikely to adhere, and even if ingredients of fingerprint adhere, the ingredients of fingerprint can be removed substantially completely or to such a degree that they cannot be visually observed by wiping with cloth or the like.
Owner:KIMOTO CO LTD
Integrated circuit memory device and method
InactiveUS7027328B2Increase current gainEasy programmingTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringGate oxide
Structures and methods for DEAPROM memory with low tunnel barrier intergate insulators are provided. The DEAPROM memory includes a first source / drain region and a second source / drain region separated by a channel region in a substrate. A floating gate opposes the channel region and is separated therefrom by a gate oxide. A control gate opposes the floating gate. The control gate is separated from the floating gate by a low tunnel barrier intergate insulator having a tunnel barrier of less than 1.5 eV. The low tunnel barrier intergate insulator includes a metal oxide insulator selected from the group consisting of NiO, Al2O3, Ta2O5, TiO2, ZrO2, Nb2O5, Y2O3, Gd2O3, SrBi2Ta2O3, SrTiO3, PbTiO3, and PbZrO3. The floating gate includes a polysilicon floating gate having a metal layer formed thereon in contact with the low tunnel barrier intergate insulator. And, the control gate includes a polysilicon control gate having a metal layer formed thereon in contact with the low tunnel barrier intergate insulator.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Non-volatile memory cells, memory arrays including the same and methods of operating cells and arrays
ActiveUS7642585B2Easy to eraseLarge operating windowTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMemory cellDielectric structure
Memory cells comprising: a semiconductor substrate having a source region and a drain region disposed below a surface of the substrate and separated by a channel region; a tunnel dielectric structure disposed above the channel region, the tunnel dielectric structure comprising at least one layer having a small hole-tunneling-barrier height; a charge storage layer disposed above the tunnel dielectric structure; an insulating layer disposed above the charge storage layer; and a gate electrode disposed above the insulating layer are described along with arrays thereof and methods of operation.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD +1
Method and system for managing terminal loss
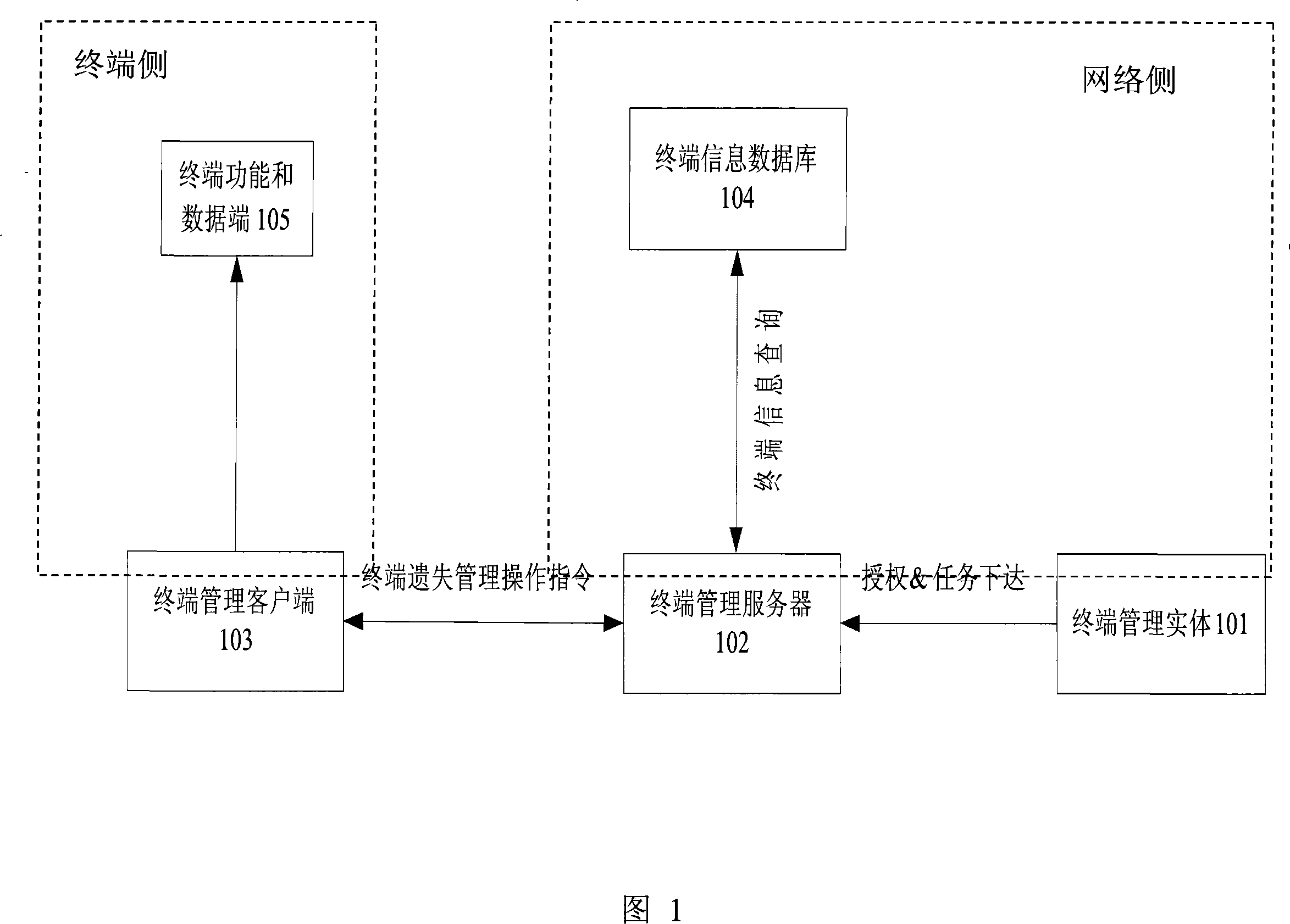
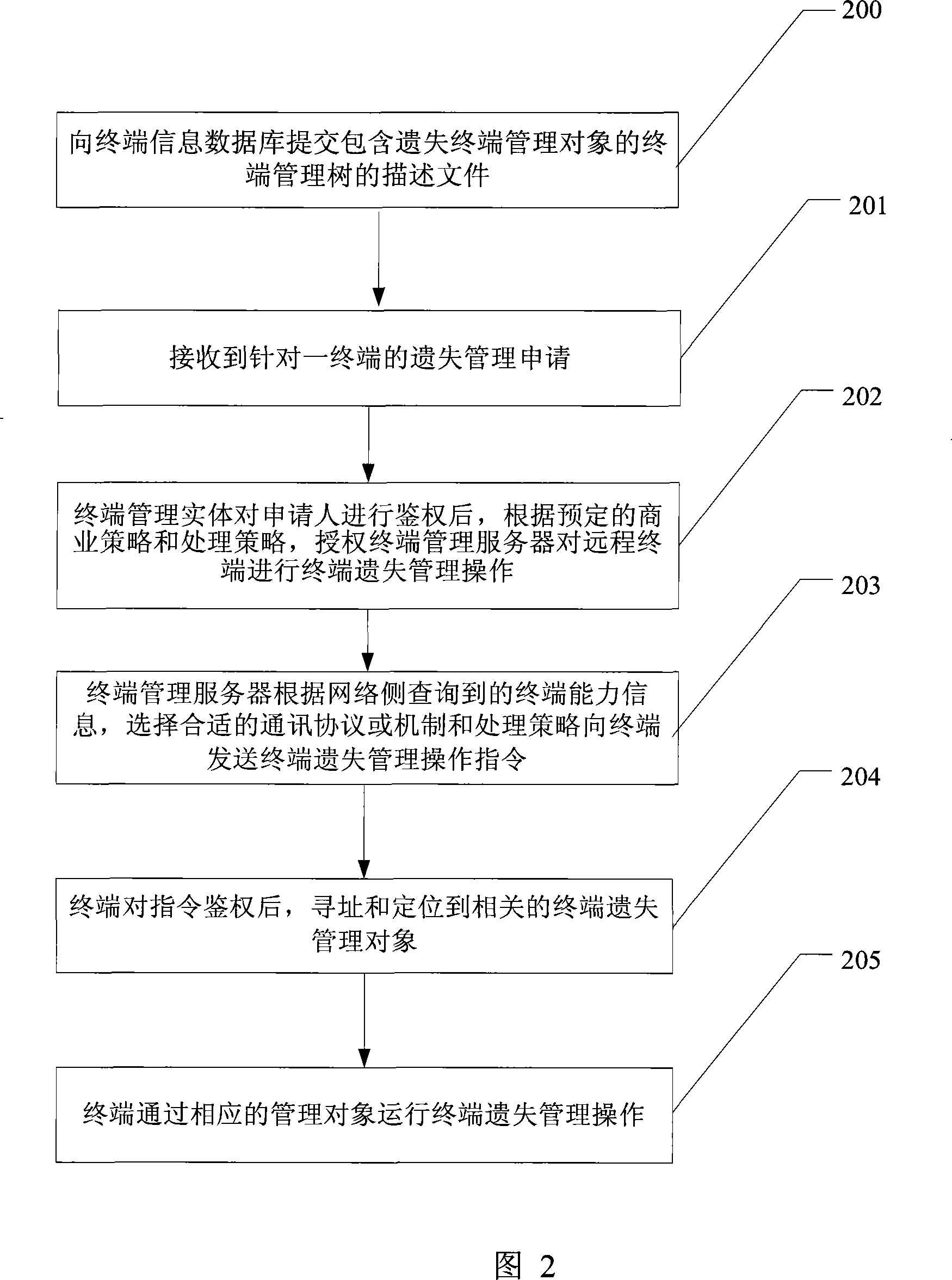
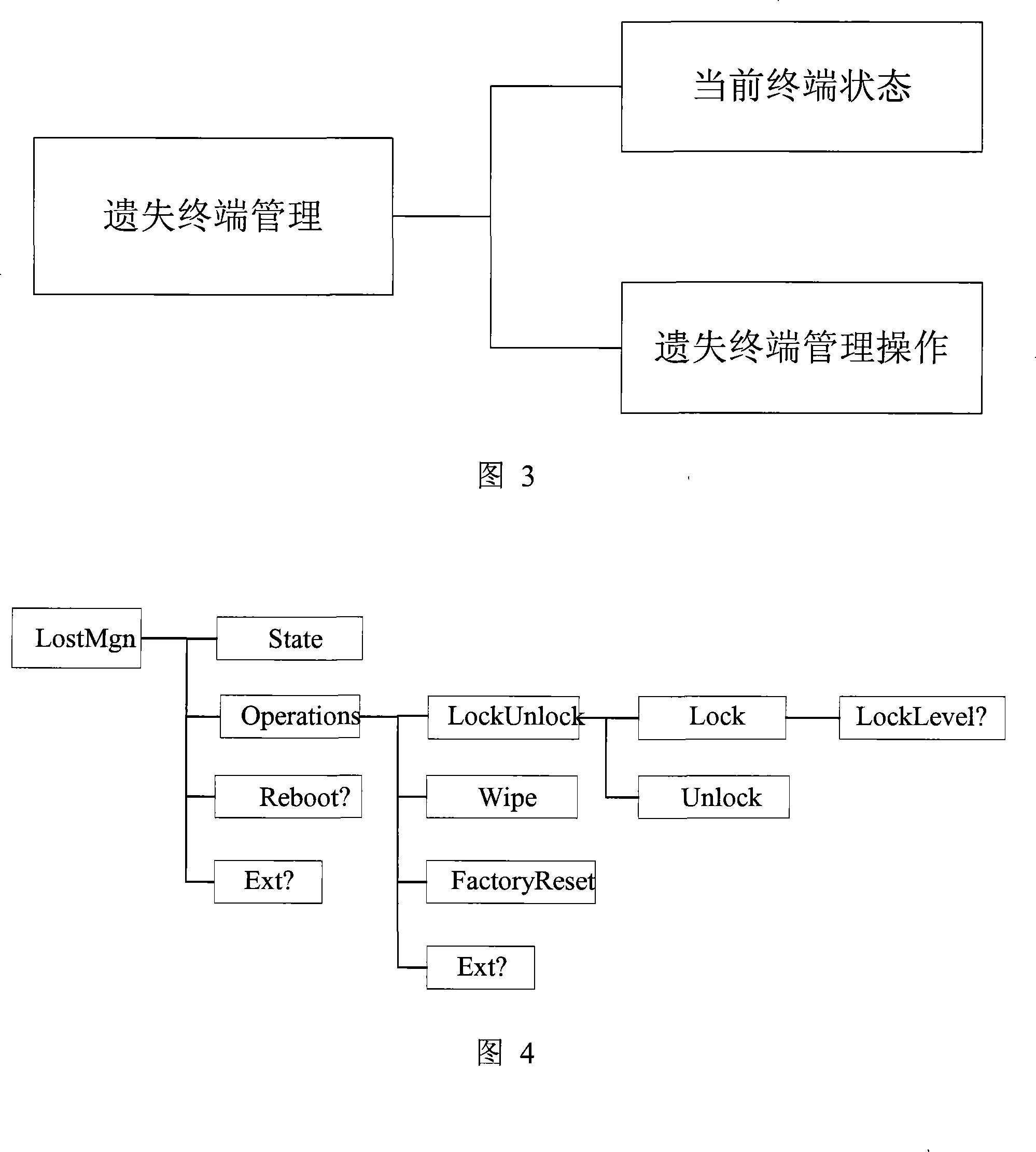
InactiveCN101179401ANo human intervention requiredEasy to eraseTelemetry/telecontrol selection arrangementsSubstation remote connection/disconnectionClient-sideAuthentication
The invention provides a method and system for terminal loss management, which relates to the field of remote protection of mobile terminal data, the processes of the method comprising that: a description file of terminal management tree is submitted to a terminal information database; a terminal management entity authenticates an applicant of terminal management operation and, after passing the authentication, authorizes a terminal management server to operate terminal functions and data through the loss management of remote terminal; the terminal management server issues operation instructions of loss management to a terminal management client; the terminal management client executes the instructions and performs the operations of terminal loss management; and the terminal management client returns operation results and states. The system comprises: a terminal side including a terminal management client and terminal functions and data; and a network side including a terminal information database, a terminal management server and a terminal management entity. The invention can remotely carry out data protection, data wiping, lock, unlock, factory state reset and other operations, to ensure the security of user data.
Owner:ZTE CORP
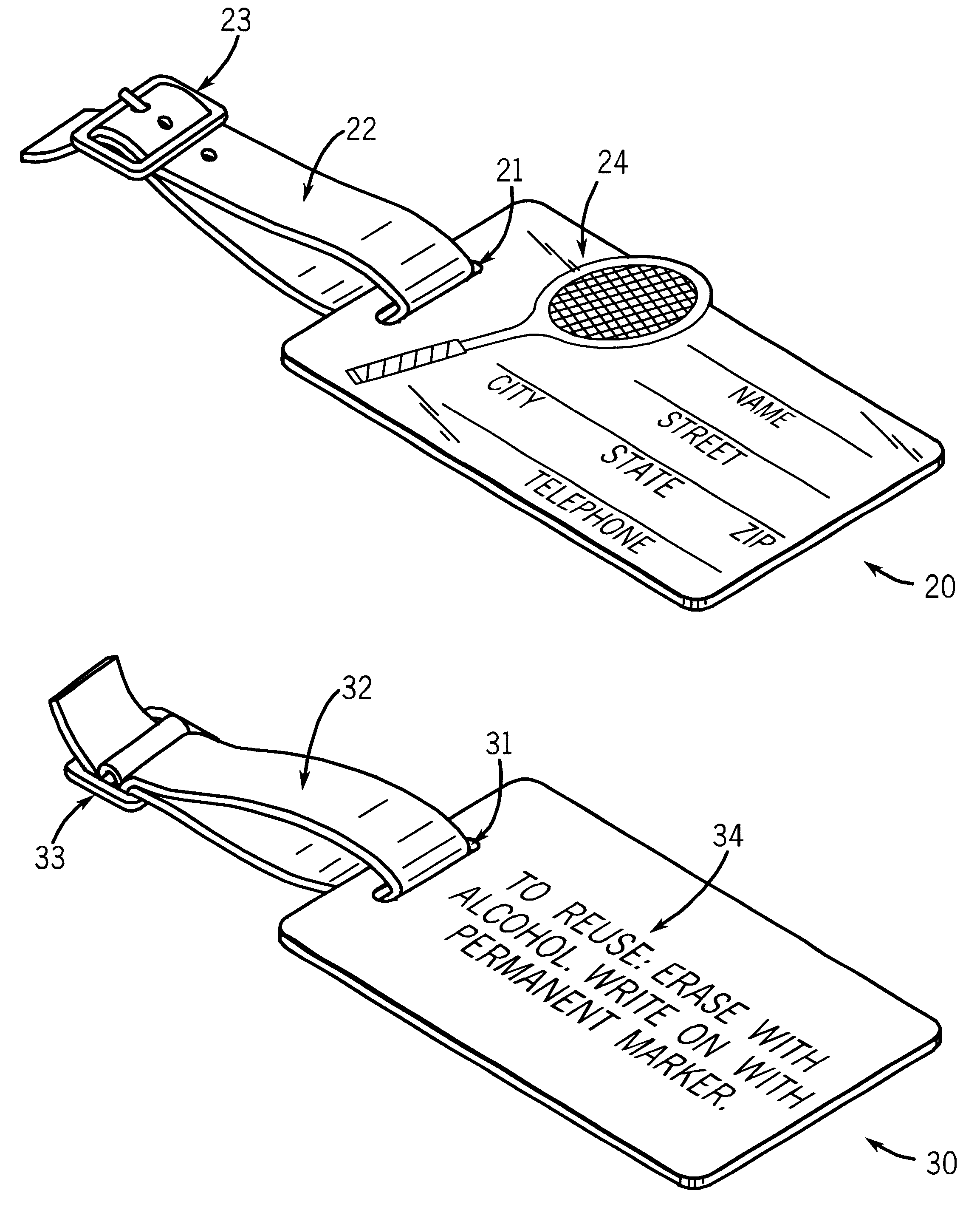
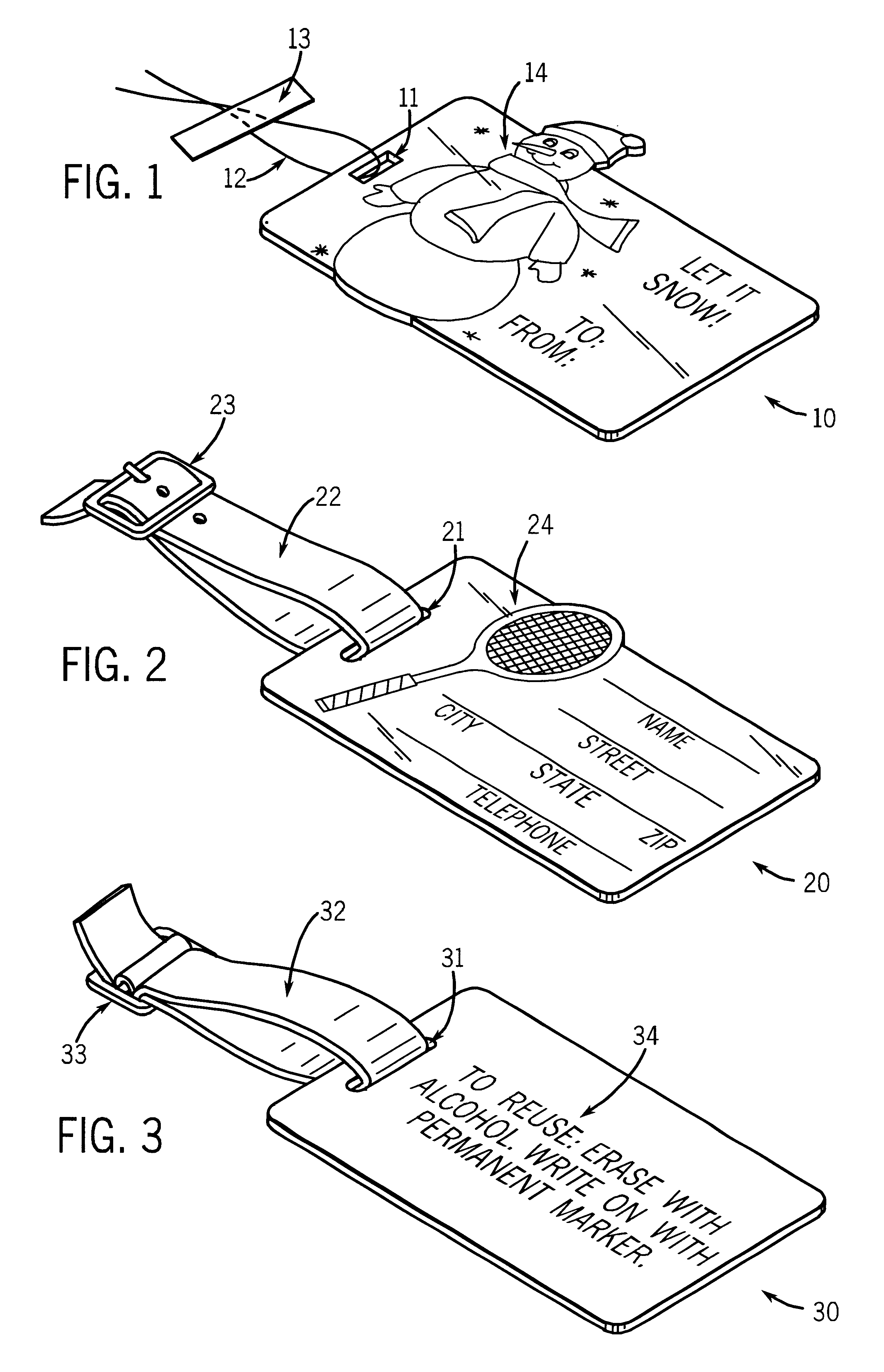
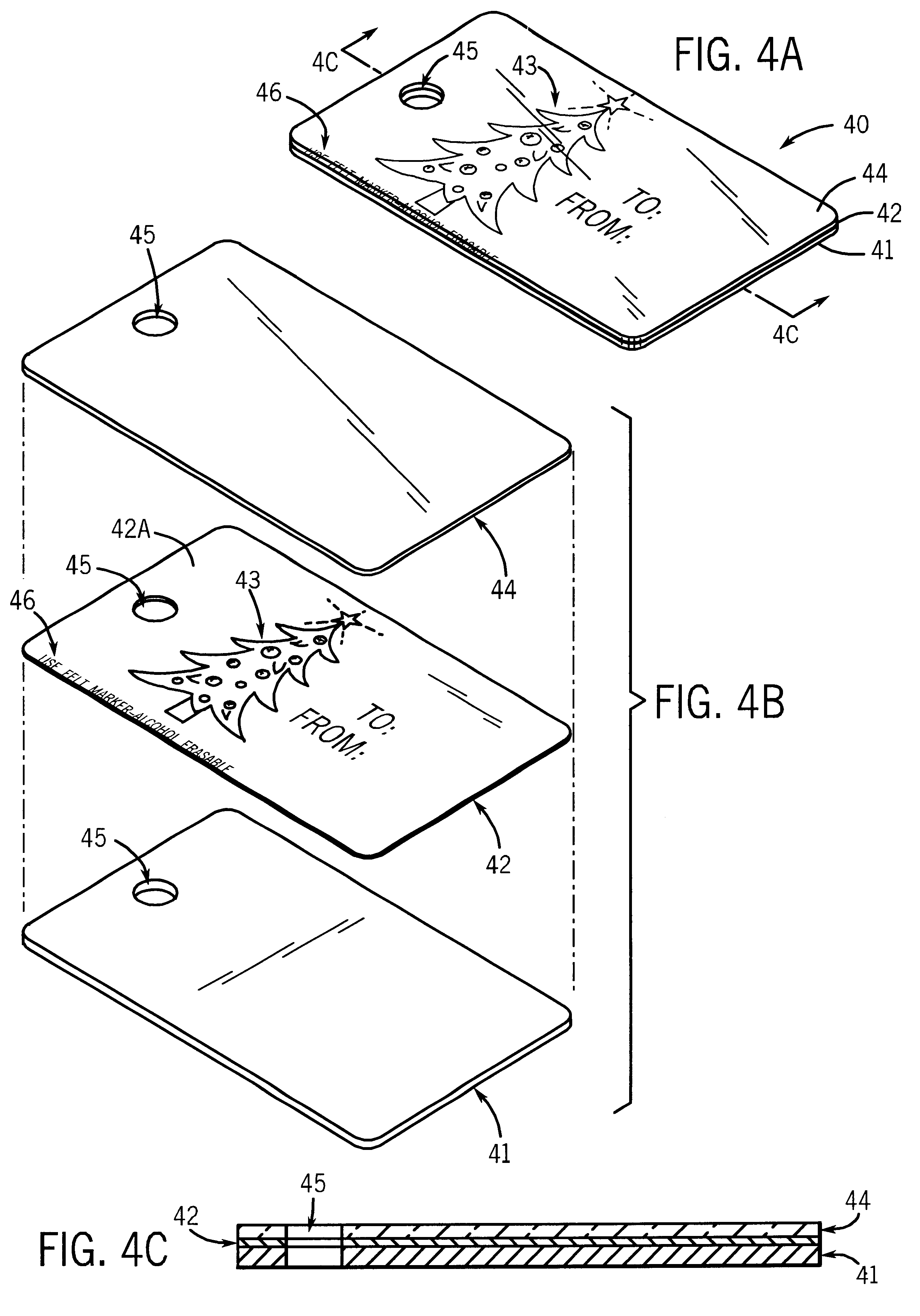
Reusable information tag
InactiveUS6550813B1Information can be easilyEasy to separateStampsOther printing matterGraphicsThin membrane
A reusable information tag is provided with a substrate bonded on its top surface to a middle layer which has graphics and indicia disposed upon its top surface, the middle layer being bonded to a transparent or translucent top layer of a nonporous writable and erasable film. A reusable means for attachment is provided. The tag may be written upon with a pen and attached to a gift, luggage or other article. It may then be easily detached, erased and reused. An unlimited variety of tags containing different graphics and indicia for every holiday, occasion, event, use and interest may be easily and inexpensively manufactured. A kit for making the tag is also provided. Alternative embodiments provide for disposing the graphics and indicia on either the top surface of the substrate or the bottom surface of the top layer.
Owner:SIEGRIST DONNA J
Structures for the management of erase operations in non-volatile memories
ActiveUS7783845B2Easy to eraseMany timesMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory systemsControl dataComputer science
The present invention presents a number of improvements for managing erase processes in non-volatile memory. Such memory systems typically manage the memory by logically organize the basic unit of physical erase (erase block) into composite logical groupings (meta-blocks or logical group), where an erase block generally consists of a number of sectors. When an erase command is received, the specified sectors are checked against the memory system's control data. If the specified sectors span any full logical grouping, the full logical groupings can each be treated as a whole and erased according to one process (such as performing a true, physical erase), while other sectors are “logically” erased at the sector level by standard techniques.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
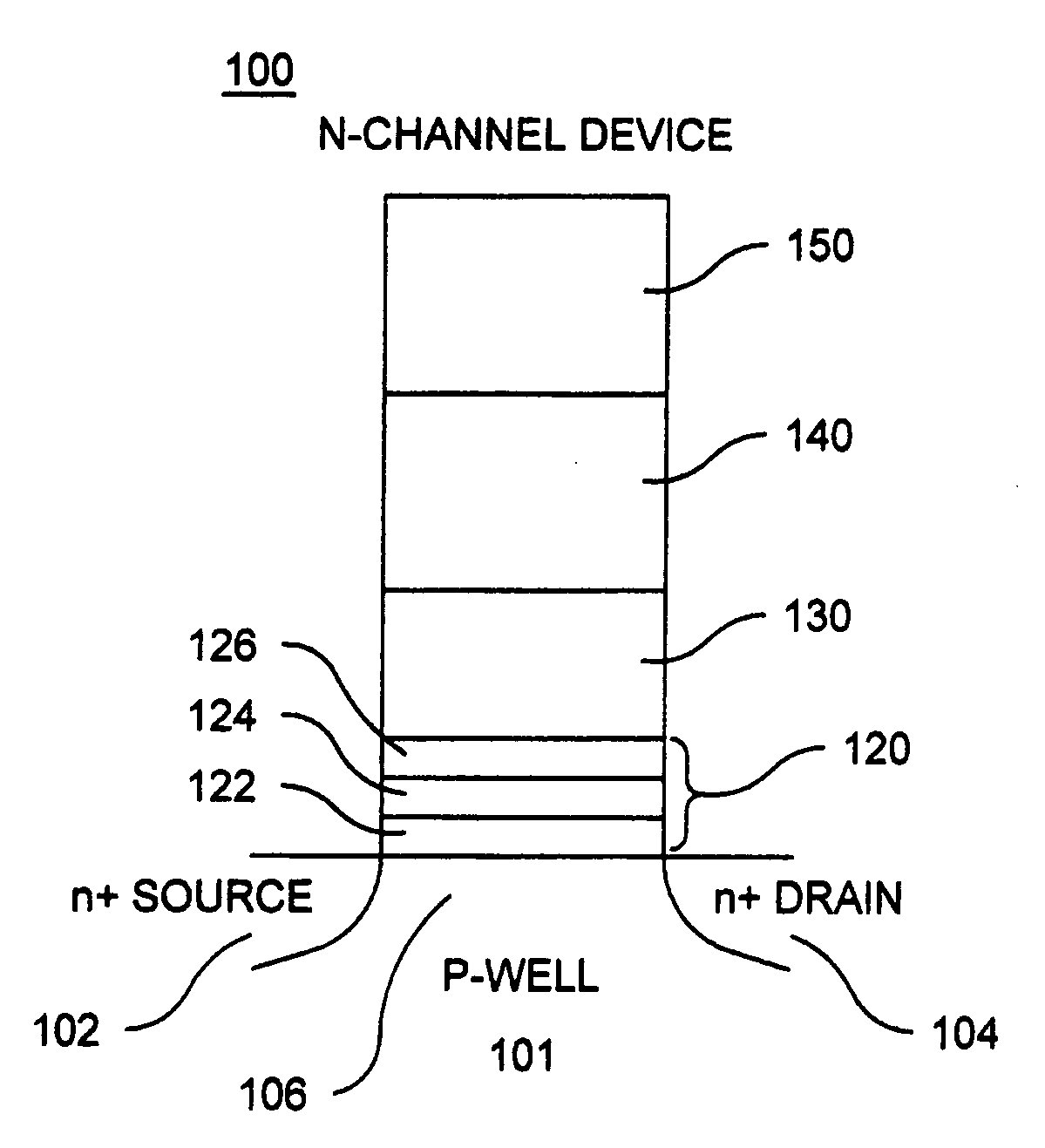
Non-volatile memory cells having a polysilicon-containing, multi-layer insulating structure, memory arrays including the same and methods of operating the same
ActiveUS20080099826A1Facilitates positive voltage erase operationReduce semiconductor layer/oxide interface damageTransistorRead-only memoriesPolycrystalline siliconSemiconductor
Memory cells including a semiconductor layer having at least two source / drain regions disposed below a surface of the semiconductor layer and separated by a channel region; a lower insulating layer disposed above the channel region; a charge storage layer disposed above the lower insulating layer; an upper insulating multi-layer structure disposed above the charge storage layer, wherein the upper insulating multi-layer structure comprises a polysilicon material layer interposed between a first dielectric layer and a second dielectric layer; and a gate disposed above the upper insulating multi-layer structure are described along with arrays thereof and methods of operation.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
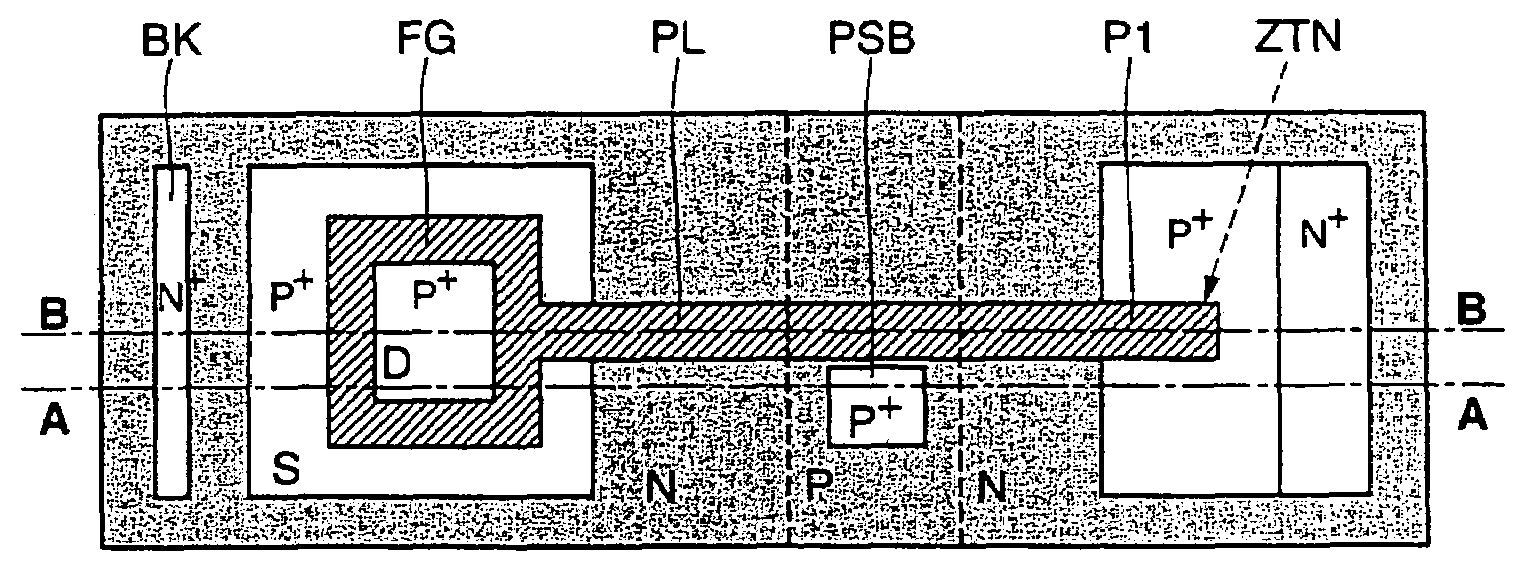
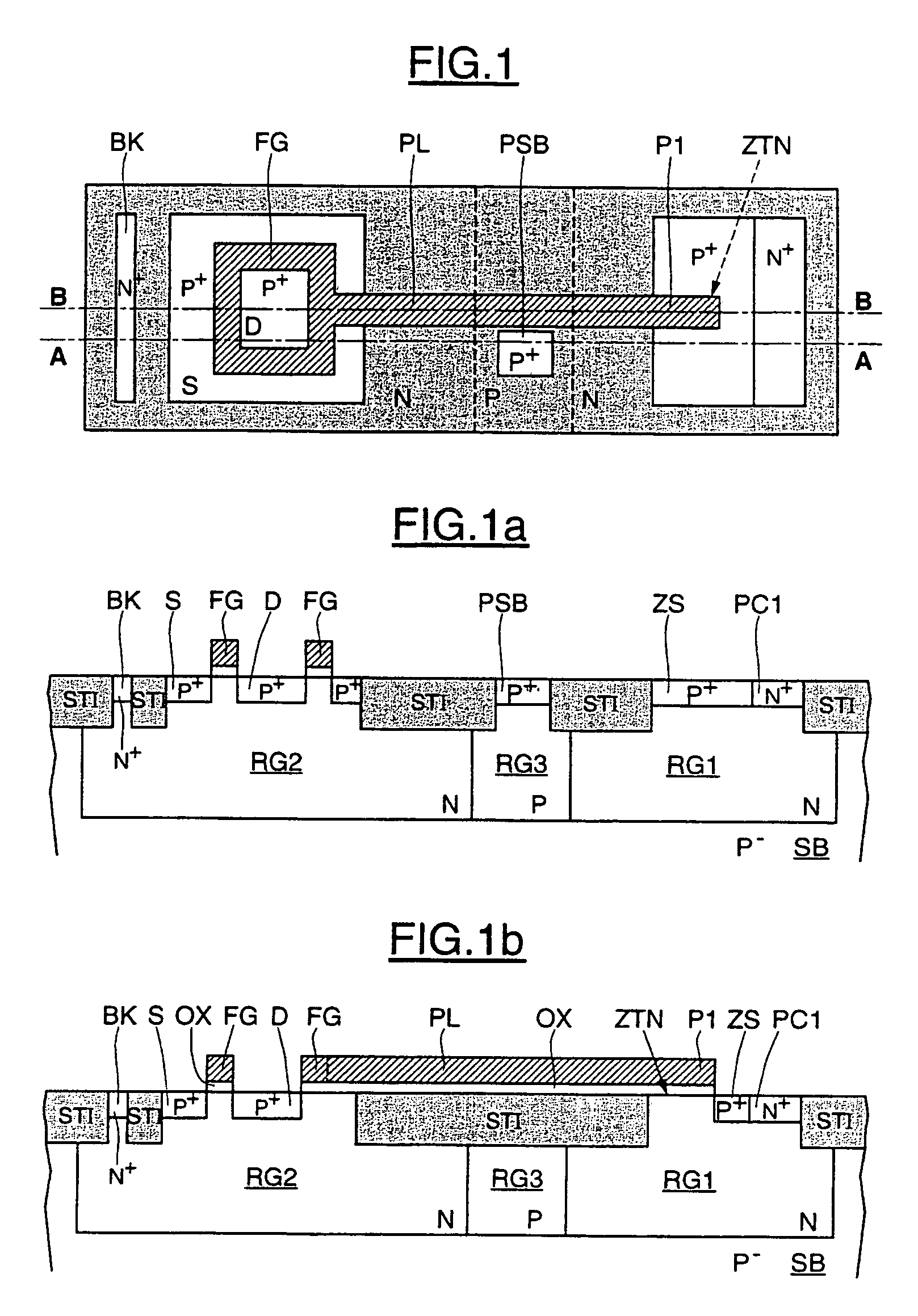
Electrically erasable and programmable, non-volatile semiconductor memory device having a single layer of gate material, and corresponding memory plane
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Erasable Ink, Method of Erasing Image Including the Same, and Method of Recycling Recording Medium Using the Erasing Method
InactiveUS20070228005A1Low costFast and easy imagingMethine/polymethine dyesDecorative surface effectsCorona dischargeEngineering
The invention provides a method for easily and promptly erasing an image (including a character) formed on a printed article with a low cost, and an apparatus employing such method. A printed article bearing an image formed on a surface including an inorganic pigment is exposed to a reactive gas generated by creeping discharge or corona discharge induced by a voltage applied between a pair of opposed electrodes, whereby the image is erased.
Owner:CANON KK +2
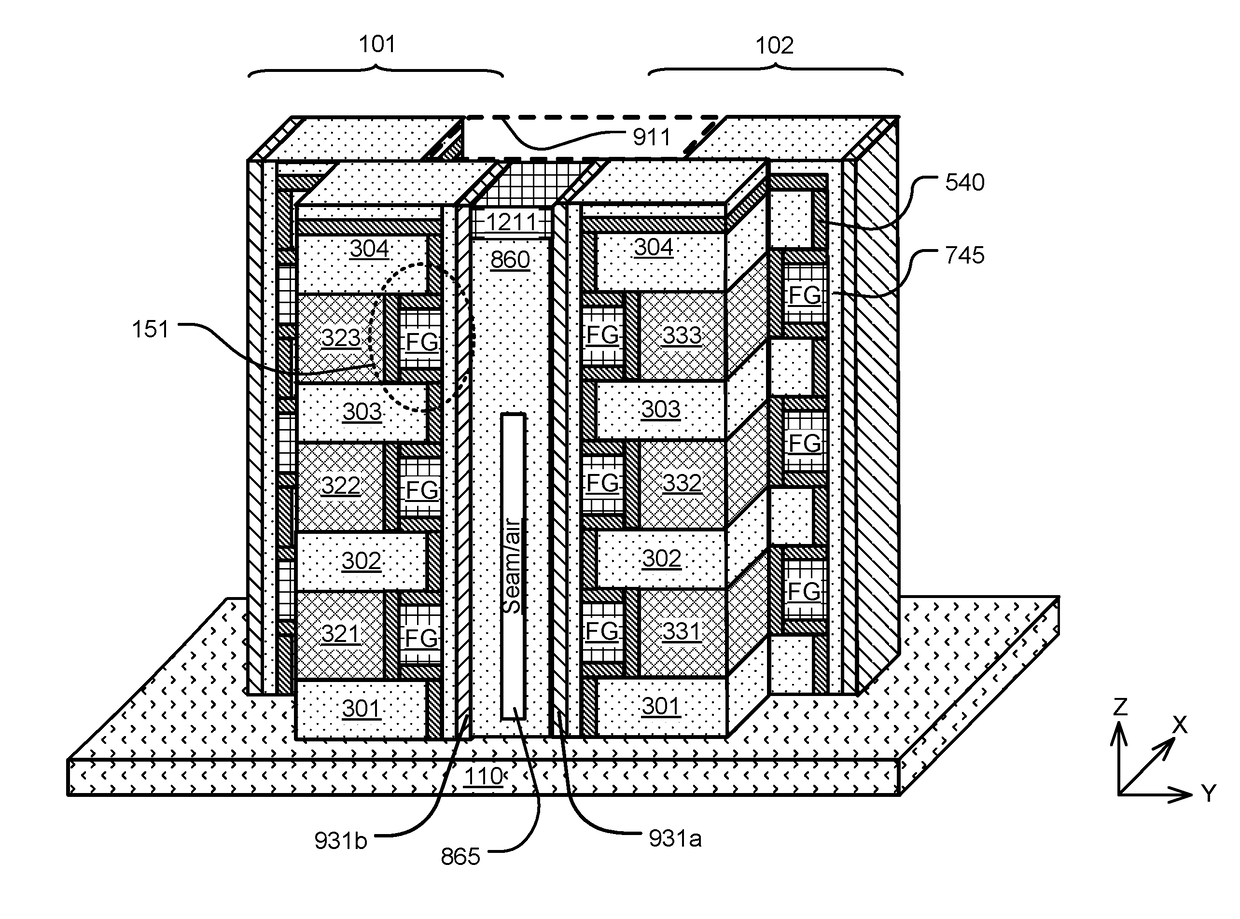
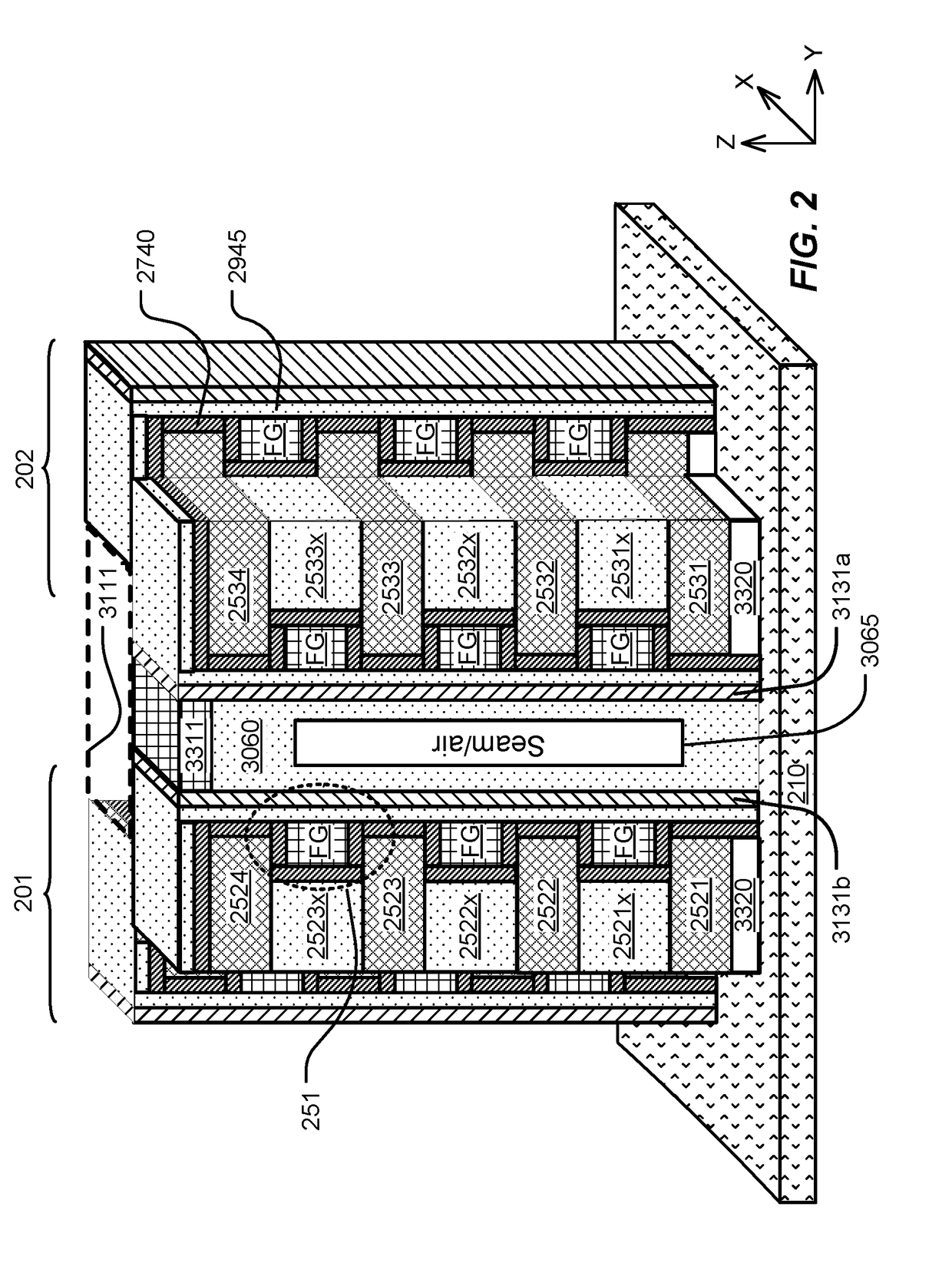
Sgvc 3D architecture with floating gate device in lateral recesses on sides of conductive strips and insulating strips
ActiveUS20170194340A1Easy to eraseLow erase saturation thresholdSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLateral recessEngineering
A memory device is provided that includes a plurality of memory cells. The memory device includes a plurality of stacks of conductive strips separated by insulating strips. Data storage structures including floating gates are disposed along the conductive strips in the stacks. Vertical channel films are disposed on sidewalls of the stacks. Memory cells in the plurality of memory cells have channels in the vertical channel films, and control gates in the conductive strips. A tunnel oxide layer is disposed between the vertical channel films and the floating gates. The floating gates can be coplanar with conductive strips in the plurality of stacks, or be disposed between the conductive strips in the plurality of stacks.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
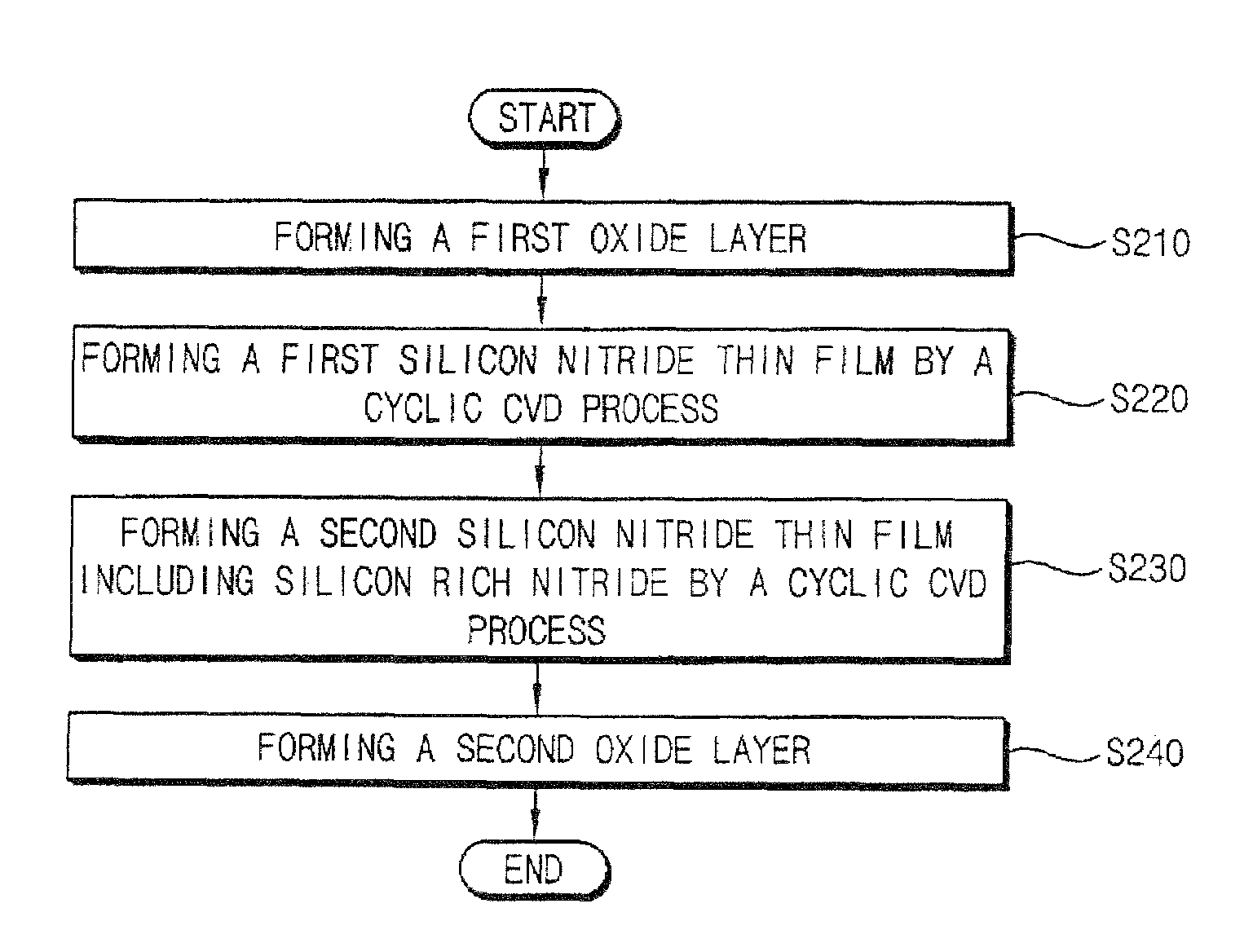
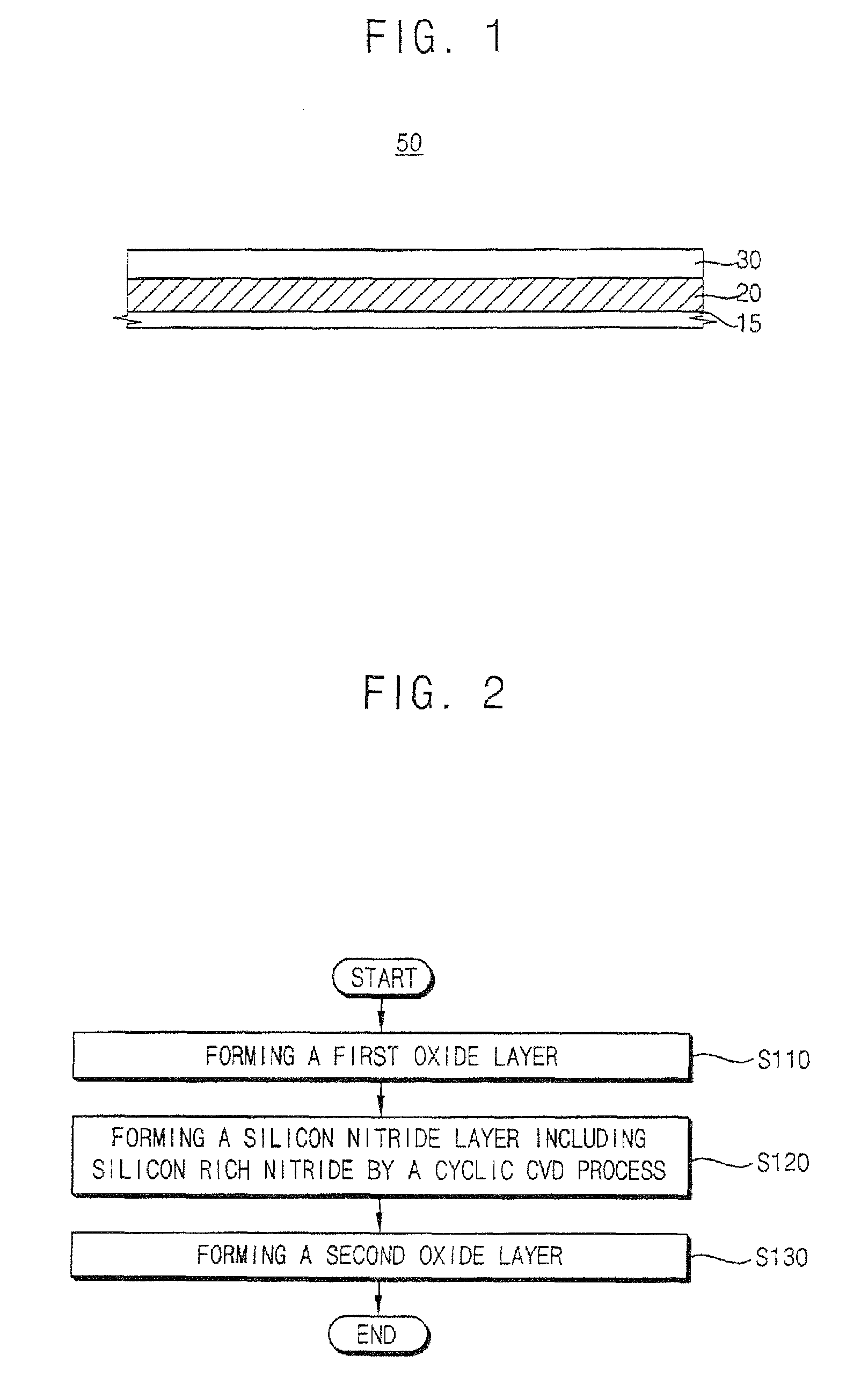
Method of manufacturing a charge-trapping dielectric and method of manufacturing a sonos-type non-volatile semiconductor device
ActiveUS7510935B2High electron trap densityEasy to eraseSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDielectricDevice material
In an embodiment, a method of manufacturing a charge-trapping dielectric and a silicon-oxide-nitride-oxide-silicon (SONOS)-type non-volatile semiconductor device includes forming the charge-trapping dielectric, and a first oxide layer including silicon oxide. A silicon nitride layer including silicon-rich nitride is formed by a cyclic chemical vapor deposition (CVD) process using a silicon source material and a nitrogen source gas. A second oxide layer is formed on the silicon nitride layer. Hence, the charge-trapping dielectric having good erase characteristics is formed. In the SONOS-type non-volatile semiconductor device including the charge-trapping dielectric, a data erase process may be stably performed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
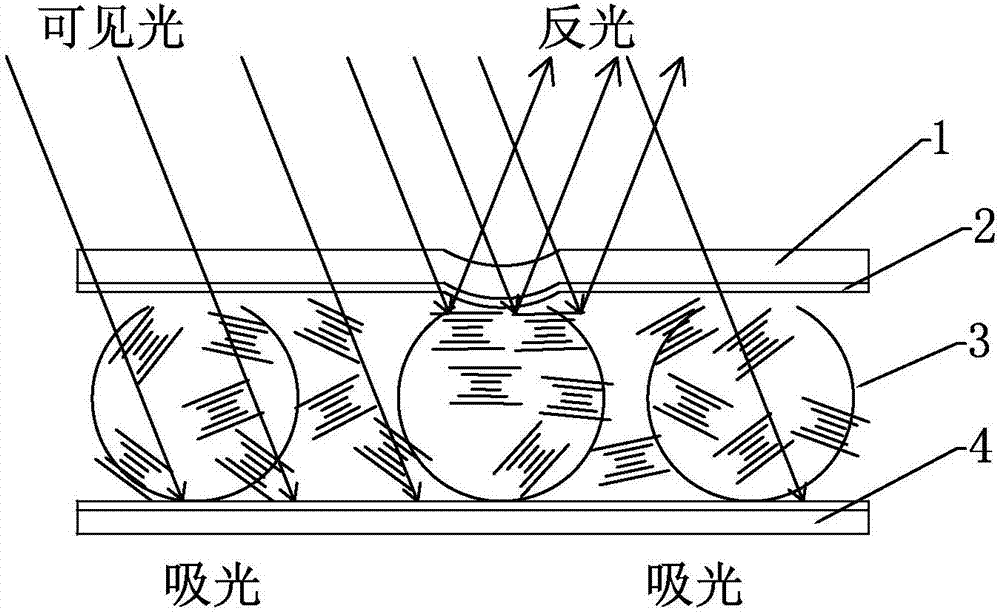
Liquid crystal composite film with writing display function and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107300818ABig advantageIncrease frictionNon-linear opticsComposite filmLiquid-crystal display
The invention belongs to the field of liquid crystal display and particularly discloses a liquid crystal composite film with a writing display function and a preparation method thereof. The liquid crystal composite film with the writing display function comprises a PET transparent film, a PVA insulating orientation layer, a liquid crystal / polymer / interval microsphere composite layer and a PET black film sequentially from top to bottom. The lower surface of the PET transparent film is coated with an ITO layer, and the upper surface of the PET black film is coated with an ITO layer. The liquid crystal composite film with the writing display function and the preparation method thereof have advantages that due to addition of the PVA insulating orientation layer, short circuit risks of two conductive layers are avoided, and accordingly the rate of finished products is sharply increased, service lives of the products are greatly prolonged, production cost is reduced, and the driving voltage of the liquid crystal film is lowered to increase key technical indexes such as brightness and contrast ratio of the film.
Owner:SHANDONG LANBEISITE EDUCATIONAL EQUIP GRP +1
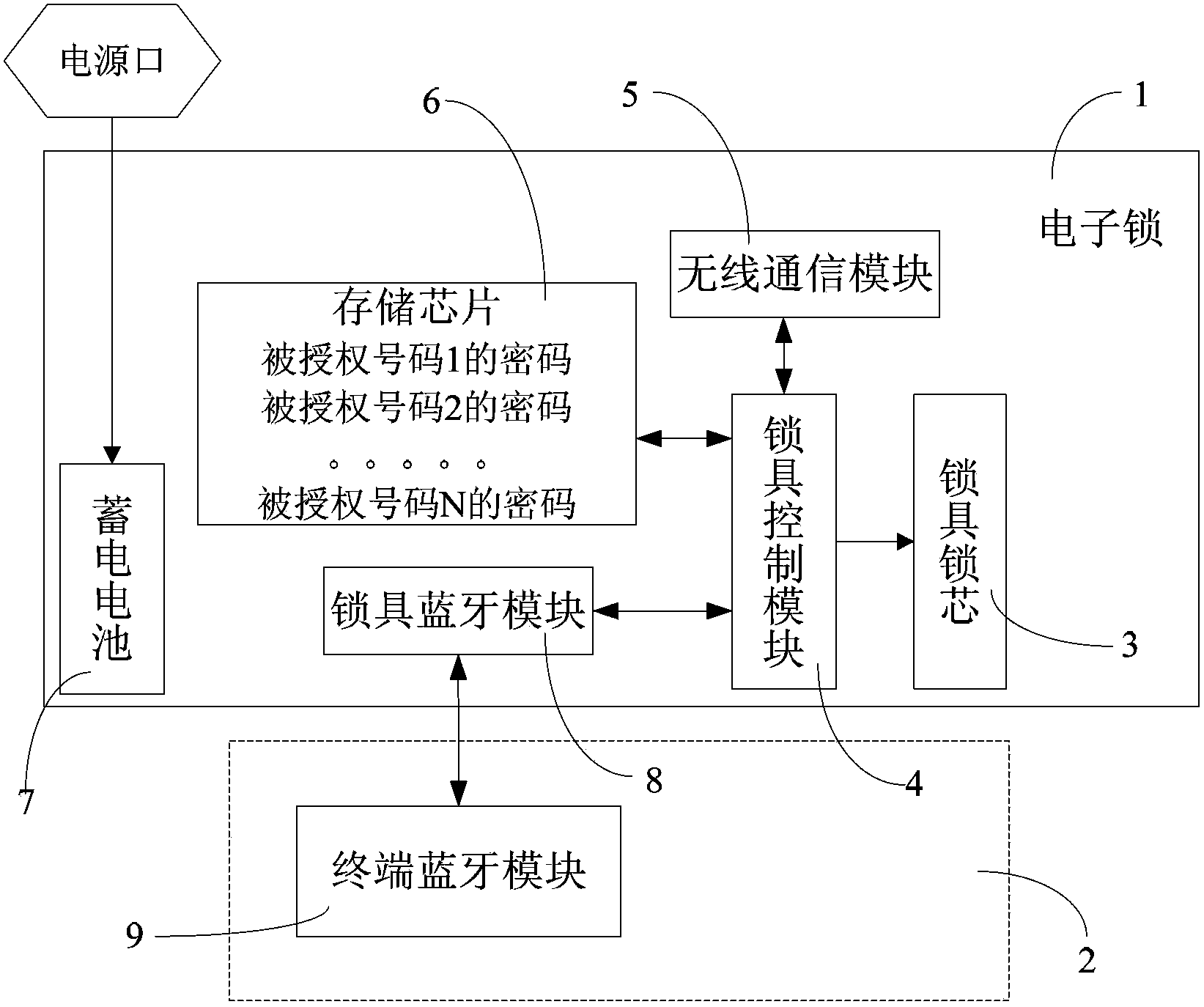
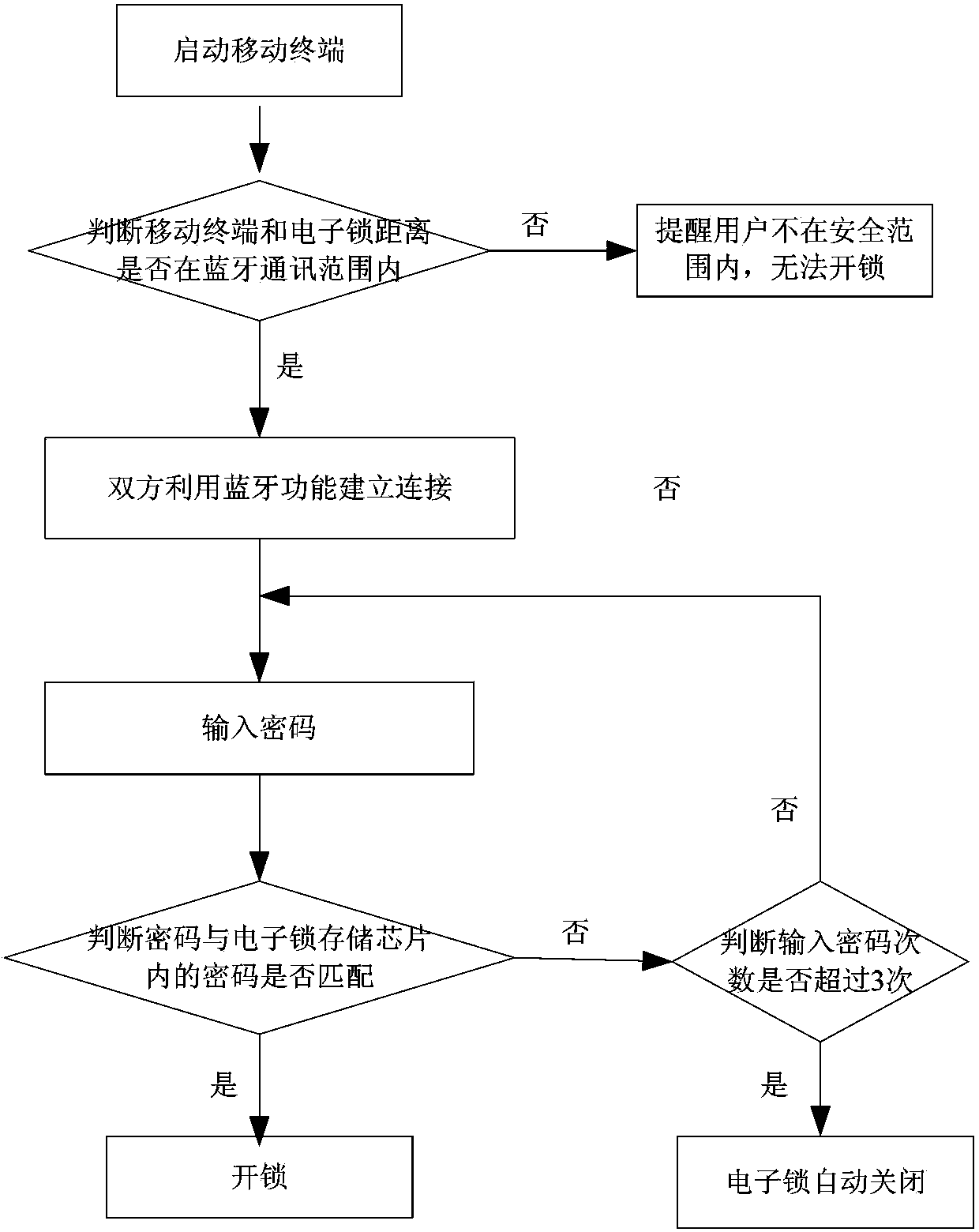
Intelligent mobile terminal control electronic lock system
InactiveCN103353997AEasy to useReduce use costIndividual entry/exit registersComputer terminalBluetooth
The invention relates to an intelligent terminal control electronic lock system which comprises an electronic lock and a mobile terminal connected with the electronic lock in a matching manner, wherein the electronic lock comprises a lockset cylinder and a lockset control module connected with the lockset cylinder in a matching manner; the lockset control module is connected with a storage chip and a lockset bluetooth module; the lockset control module can be connected with a terminal bluetooth module in the mobile terminal by the lockset bluetooth module in a matching manner; the mobile terminal can input unlocking information to the lockset control module through the terminal bluetooth module and the lockset bluetooth module; the lockset control module receives the unlocking information, and compares the unlocking information with unlocking verification information prestored by the storage chip; and when the unlocking information is matched with the unlocking verification information, the lockset control module drives to control the lockset cylinder to open the electronic lock. The electronic lock system is simple and compact in structure, convenient to use, wide in application scope, safe and reliable.
Owner:JIANGSU HILLSUN INFORMATION IND
Transmission screen
InactiveUS20070091073A1Easy to writeHigh specular glossWriting boardsBuilt-on/built-in screen projectorsComputer graphics (images)Projector
A transmission screen having a writable and erasable surface for one side is provided. This transmission screen is constructed so that the writable and erasable surface should have a specular gloss (JIS K5600-4-7:1999) of 70 to 135%, the transmission screen as a whole should have a haze (JIS K7136:2000) of 80% or more, and the surface opposite to the writable and erasable surface should have a specular gloss (JIS K5600-4-7:1999) of 10% or less. With this transmission screen, writing with a marker for white boards and erasing can be easily done while seeing images projected on the transmission screen, and the images from a projector do not become hard to see due to projection of the images on the body of a writer.
Owner:KIMOTO CO LTD
Semiconductor memory device
ActiveUS20110134680A1Reduce areaSimple equipmentSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesPhoto irradiationUltraviolet lights
To provide a semiconductor memory device including an oxide semiconductor that can deal with instability of a threshold characteristic, in which writing is possible by a simple method. The semiconductor memory device functions by utilizing a characteristic that a threshold shifts when a thin film transistor including an oxide semiconductor is irradiated with ultraviolet light. Readout can be performed by setting a readout voltage between the threshold before the ultraviolet light irradiation and the threshold after irradiation. The threshold characteristic of an initial characteristic can be controlled by providing a back gate or by using two thin film transistors.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Integrated circuit memory device and method
InactiveUS7136302B2Increase current gainEasy programmingTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringGate oxide
Structures and methods for DEAPROM memory with low tunnel barrier intergate insulators are provided. The DEAPROM memory includes a first source / drain region and a second source / drain region separated by a channel region in a substrate. A floating gate opposes the channel region and is separated therefrom by a gate oxide. A control gate opposes the floating gate. The control gate is separated from the floating gate by a low tunnel barrier intergate insulator having a tunnel barrier of less than 1.5 eV. The low tunnel barrier intergate insulator includes a metal oxide insulator selected from the group consisting of NiO, Al2O3, Ta2O5, TiO2, ZrO2, Nb2O5, Y2O3, Gd2O3, SrBi2Ta2O3, SrTiO3, PbTiO3, and PbZrO3. The floating gate includes a polysilicon floating gate having a metal layer formed thereon in contact with the low tunnel barrier intergate insulator. And, the control gate includes a polysilicon control gate having a metal layer formed thereon in contact with the low tunnel barrier intergate insulator.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com