Erasure method and device for nonvolatile memory
A non-volatile memory technology, applied in the field of erasing non-volatile memory, can solve problems such as complex process and time overhead
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
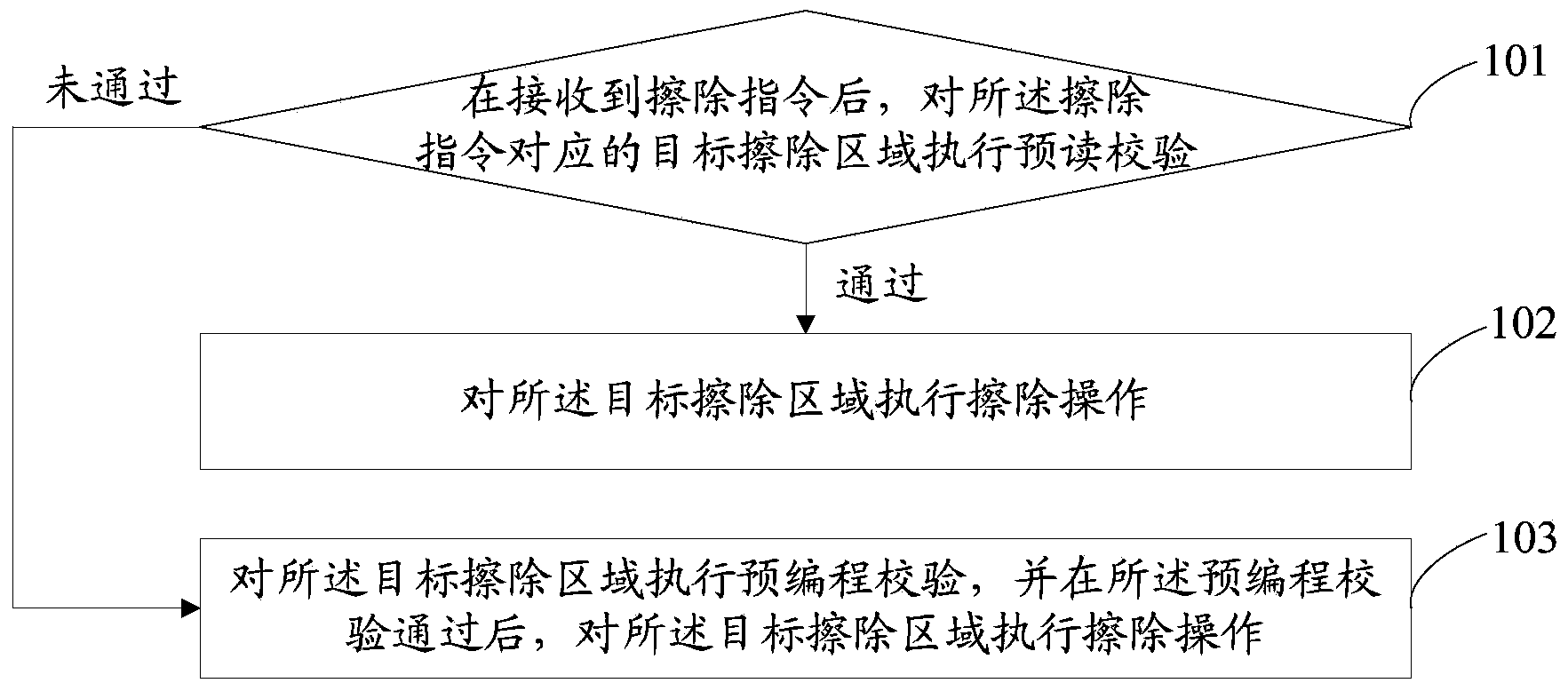
[0069] refer to figure 1 , shows a flowchart of a method for erasing a non-volatile memory according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention, and the method may specifically include the following steps:
[0070] Step 101, after receiving an erasing command, perform a read-ahead check on a target erasing area corresponding to the erasing command.
[0071] If the read-ahead check passes, execute step 102; if the read-ahead check fails, execute step 103.
[0072] In the current technology, in order to avoid both Erase cells and Pgm cells in the target erasing area before performing the erasing operation, the convergence of the threshold voltage of the memory cells in the target erasing area after the erasing operation is completed is poor In order to improve the convergence of the threshold voltage of the memory cells in the target erasing area, a pre-programming process is generally performed before performing an erasing operation. However, if the target erasing area is in th...
Embodiment 2
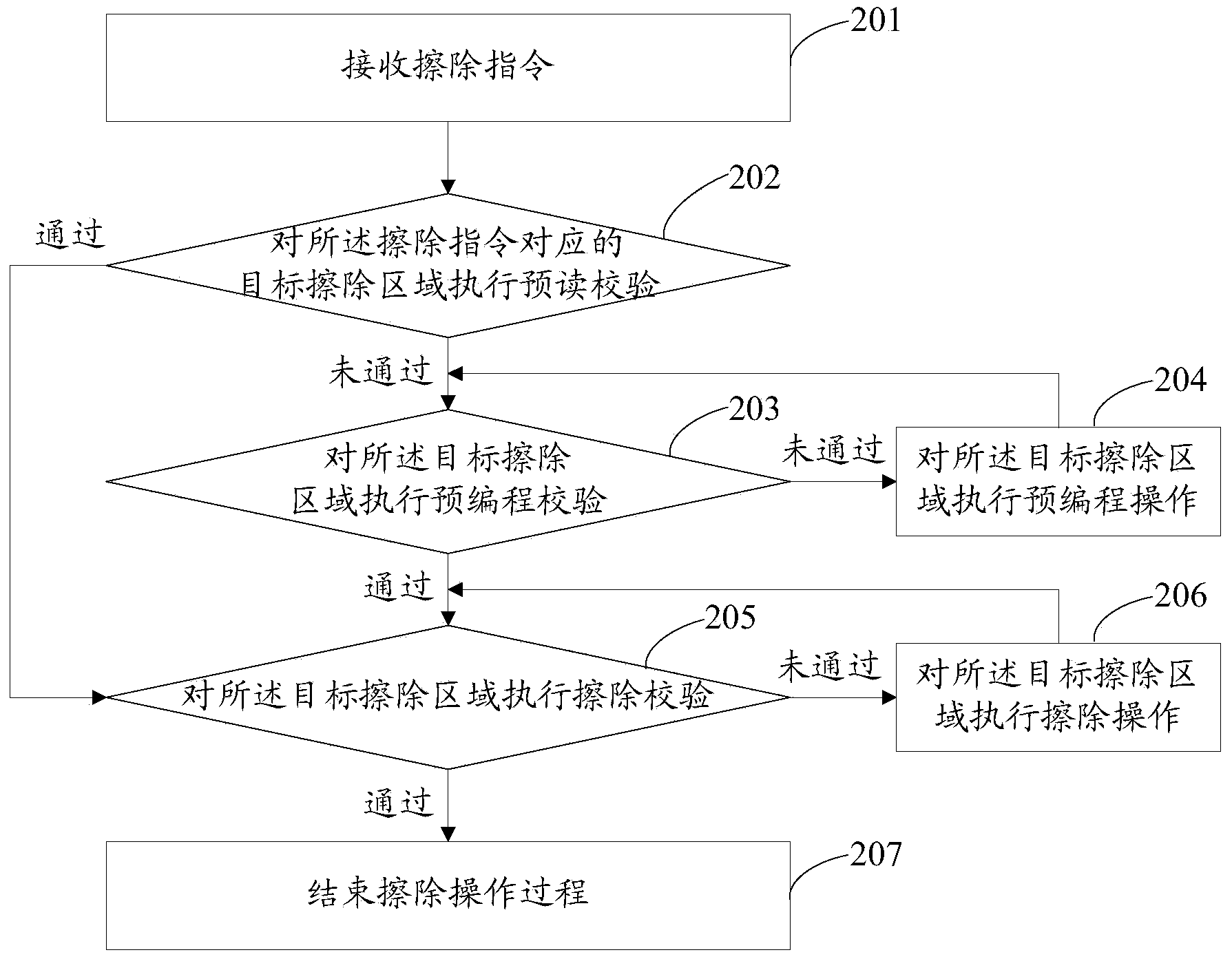
[0080] refer to figure 2 , shows a flowchart of a method for erasing a non-volatile memory according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention, and the method may specifically include the following steps:
[0081] Step 201, receiving an erase instruction.
[0082] Step 202, perform read-ahead verification on the target erasing area corresponding to the erasing instruction.
[0083] If the read-ahead check fails, execute step 203; if the read-ahead check passes, execute step 205.
[0084] During the normal operation of the non-volatile memory, if it needs to be erased, it will receive an erase command, which can include information such as the address of the target erase area, according to the target erase area The address can be used to find the target erase area corresponding to the erase command. In the embodiment of the present invention, the target erasing area may be a chip, a block or a sector.
[0085] After receiving the erasing command, firstly, a pre-read verific...
Embodiment 3
[0138] refer to Figure 4 , which shows a structural block diagram of a device for erasing a non-volatile memory according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention. The device may specifically include the following modules:
[0139] The pre-read verification module 401 is configured to perform pre-read verification on the target erase area corresponding to the erase command after receiving the erase command;
[0140] An erasing module 402, configured to perform an erasing operation on the target erasing area when the pre-read verification is passed;
[0141] A pre-program verification module 403, configured to perform a pre-program verification on the target erasing area when the pre-read verification fails;
[0142] The erasing module is further configured to perform an erasing operation on the target erasing area after the pre-program verification is passed.
[0143] In a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the device may also include the following modules:
[...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com