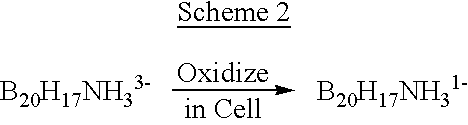Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
71results about How to "Minimise concentration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
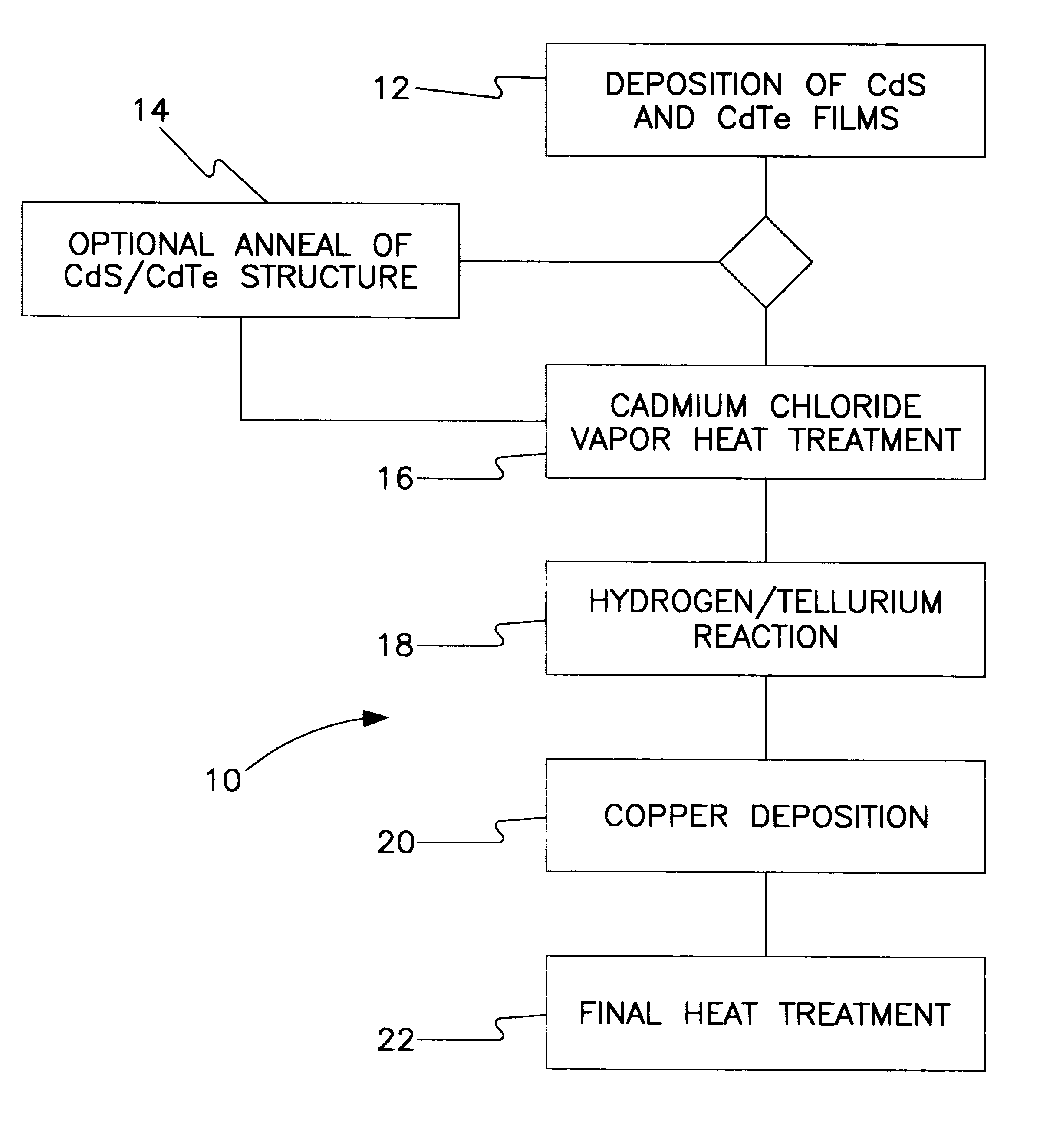
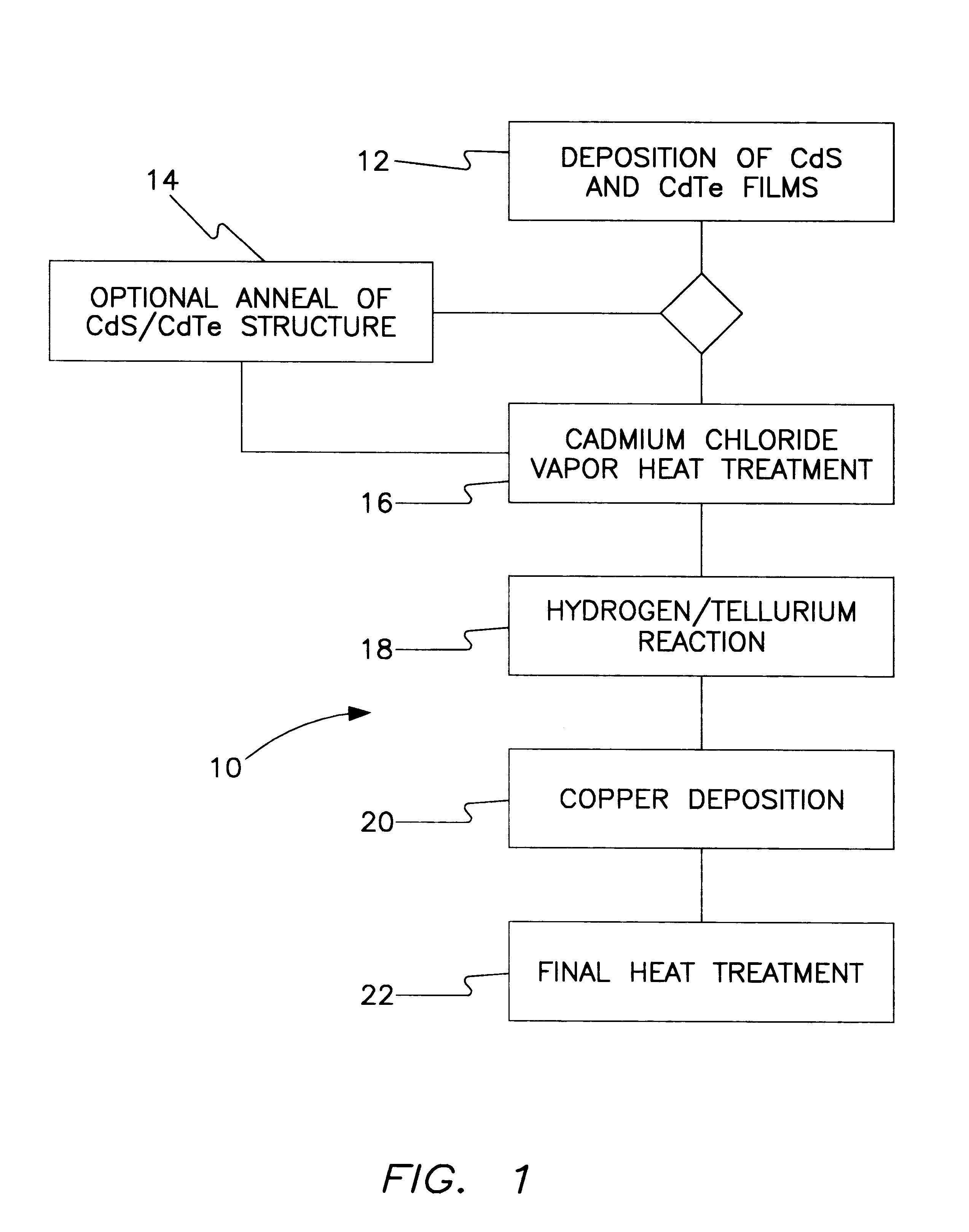
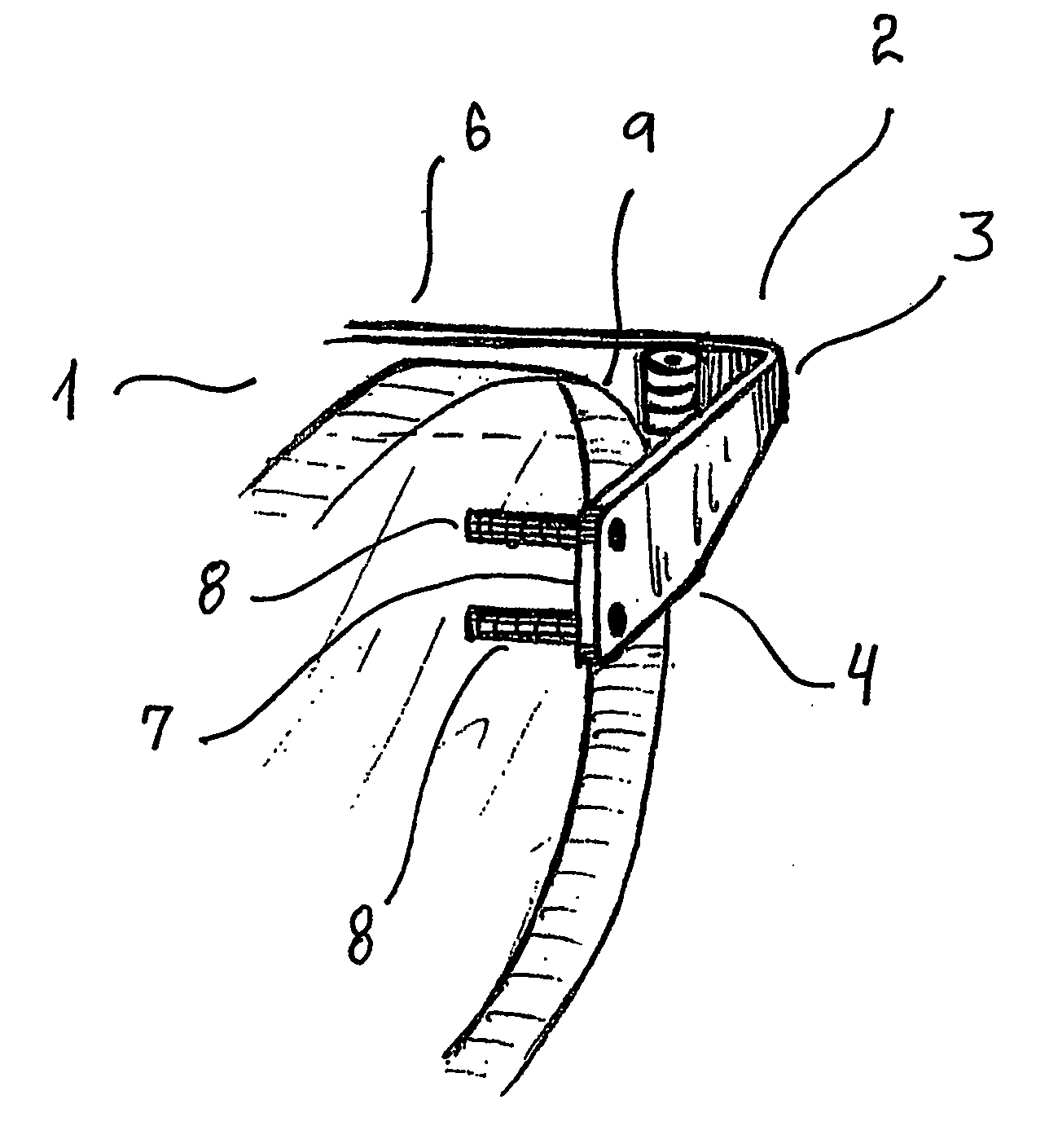
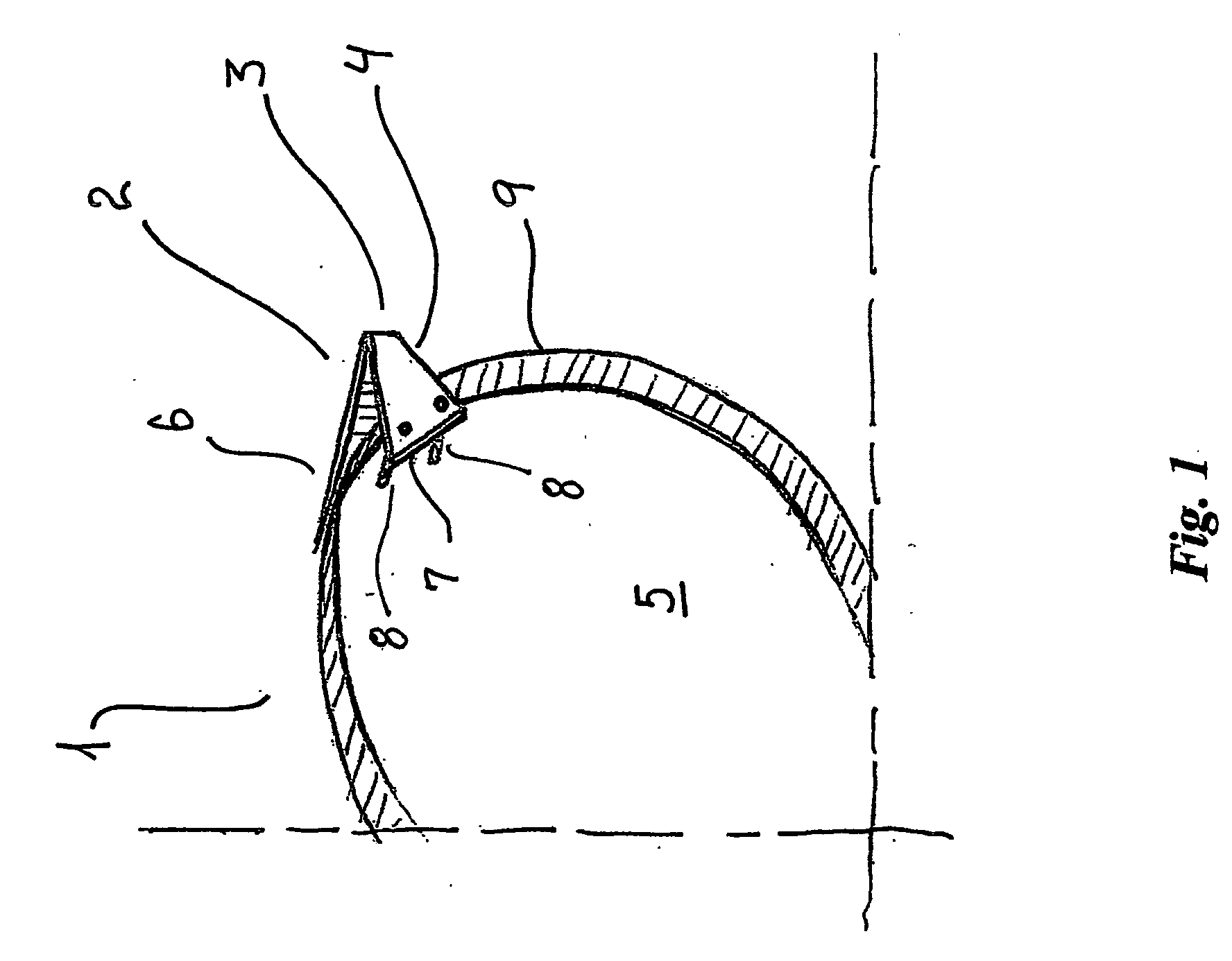
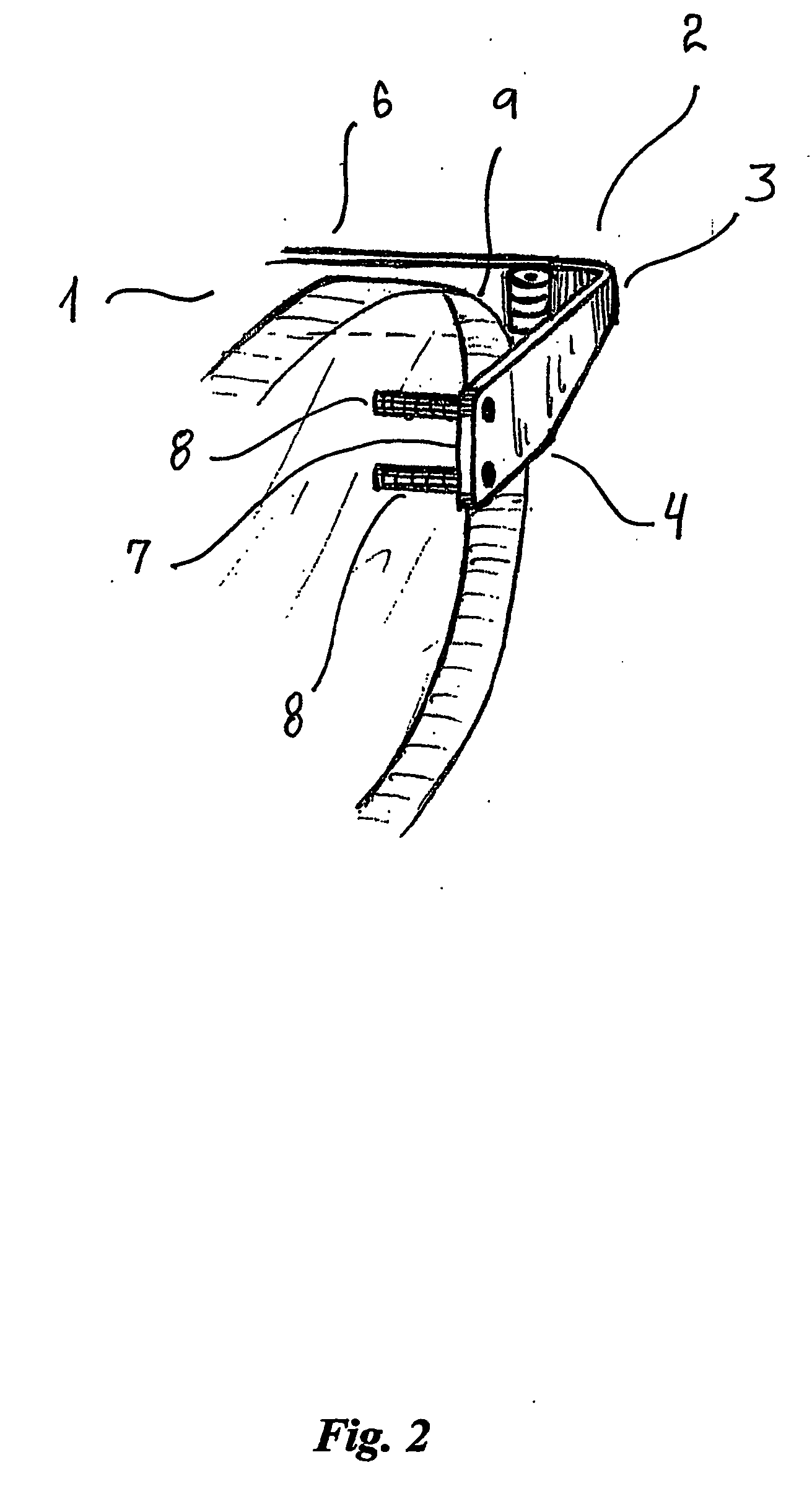
All-vapor processing of p-type tellurium-containing II-VI semiconductor and ohmic contacts thereof
InactiveUS6251701B1Reduce manufacturing costReduce pollutionFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOhmic contactTellurium compounds
An all dry method for producing solar cells is provided comprising first heat-annealing a II-VI semiconductor; enhancing the conductivity and grain size of the annealed layer; modifying the surface and depositing a tellurium layer onto the enhanced layer; and then depositing copper onto the tellurium layer so as to produce a copper tellurium compound on the layer.
Owner:U S DEPT OF ENGERGY
Apparatus and method for the production of bulk silicon carbide single crystals
ActiveUS20070283880A1Easy to controlHigh Si : C ratioAfter-treatment apparatusPolycrystalline material growthGas phaseSingle crystal
An apparatus and method for growing bulk single crystals of silicon carbide is provided. The apparatus includes a sublimation chamber with a silicon vapor species phase outlet that allows the selective passage of atomic silicon vapor species while minimizing the concurrent passage of other vapor phase species. The apparatus can provide control of vapor phase stoichiometry within the sublimation chamber, which in turn can allow the production of bulk silicon carbide single crystals with reduced intrinsic point defects concentration.
Owner:CREE INC
Cannula stent
ActiveUS7172623B2Optimize allocationIncreasing selected widthStentsBlood vesselsEngineeringUltimate tensile strength
A stent (30) formed from cannula and having flexible segments (31) and high hoop strength segments (32) alternating therealong. Longitudinal struts or tie bars (41) interconnect the segments. Minimal length reduction of the strut occurs upon expansion. In the high hoop strength segment (32), struts (37) in a zig-zag configuration (Gianturco Z-stent) are initially parallel in the unexpanded strut condition. In the flexible segment (31), struts (58) extend from a respective C-shaped bend (59) to converge at the opposite ends thereof when unexpanded. In one embodiment, certain adjacent struts (39–41) of the hoop segment are spaced apart by elongated openings or gaps (46, 48) interposed therebetween and interconnected at their respective ends (42, 44) to form a T-shaped strut interconnection (45). The selected width (50, 51) of the first and third struts (54, 57) increases toward the ends (47, 48) of the elongated openings (46, 48) adjacent the strut interconnection (45). This strut width increase about one end of the strut significantly reduces the tensile strain exhibited about the opening end when the stent is radially expanded during manufacture. The tip length (52, 55) of the struts about the interconnection (45) is also adjusted (increased) along with the other C-shaped strut interconnections (59, 71) to further distribute the tensile strain developed during radial expansion.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
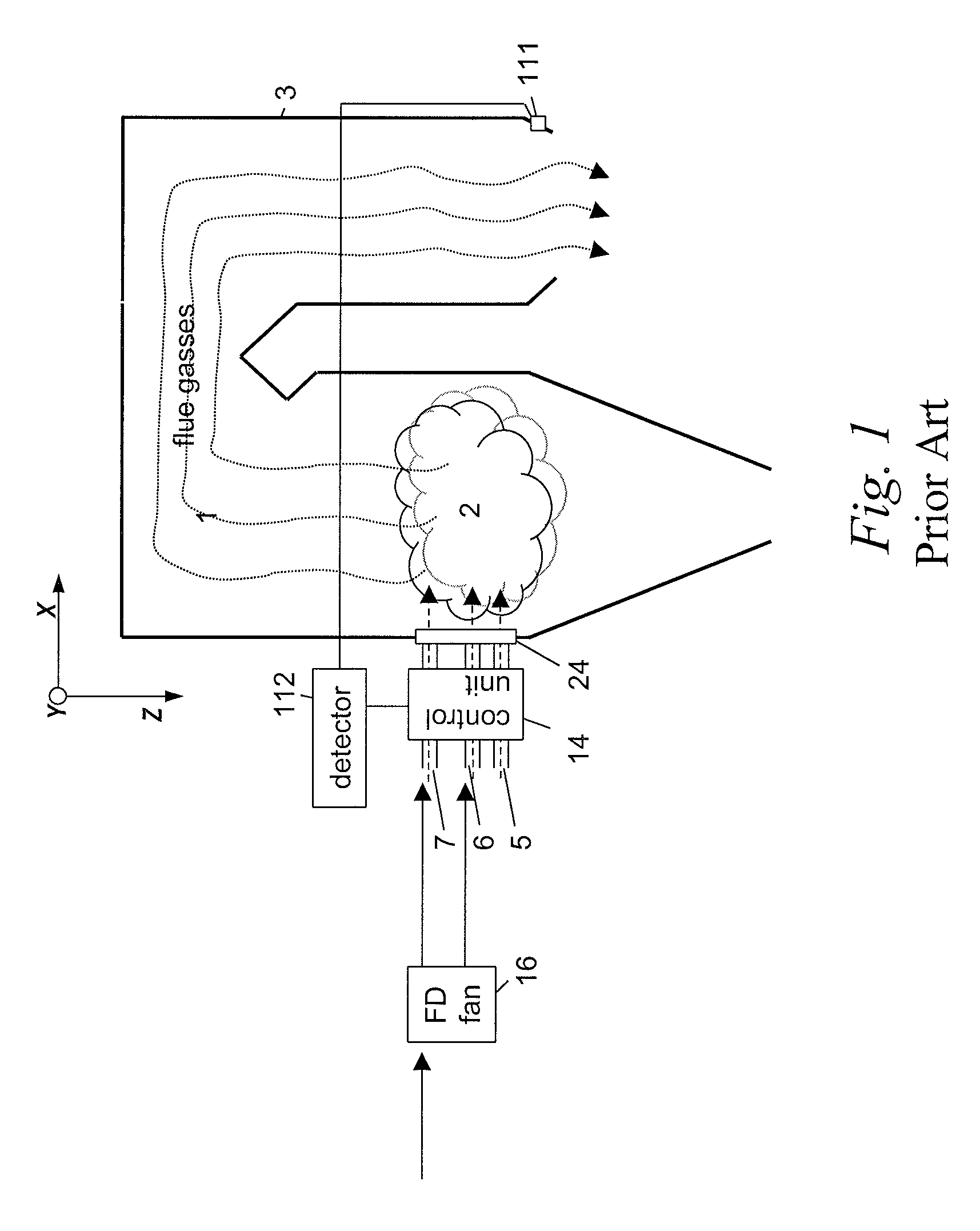
Optical flue gas monitor and control
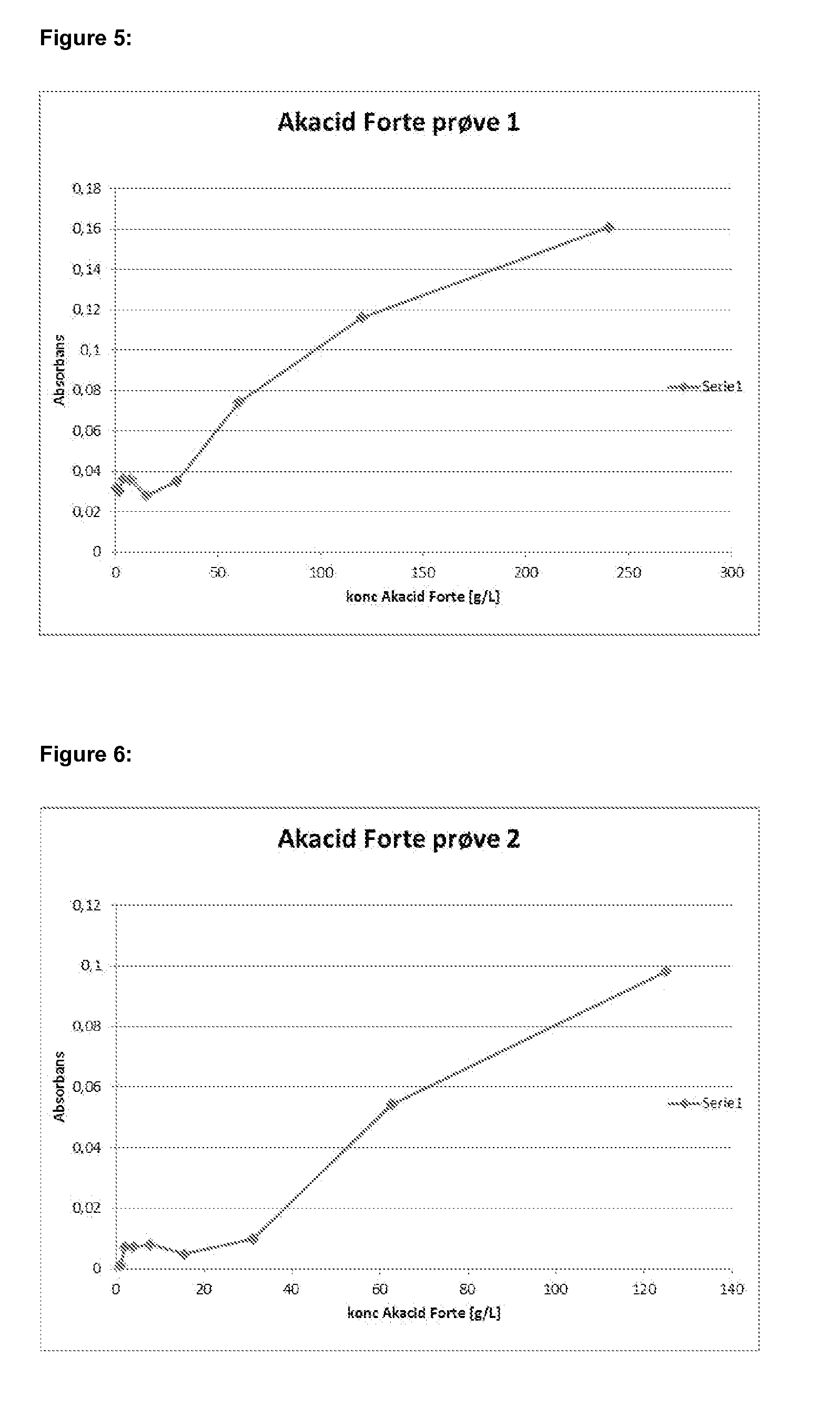
InactiveUS20110045422A1Minimise concentrationFuel supply regulationEmission preventionCombustorFlue gas
A plurality of optical monitoring systems 220,320 sense the concentration of at least one constituent in flue gasses of a furnace 1 and its emission control devices. The monitoring devices 220,320 includes at least one optical source 221 for providing beams 223 through a sampling zone 18 to create a combined signal indicating the amount of various constituents within the sampling zone 18. The combined signal may be fed forward to emission control devices to prepare them for oncoming emissions. The combined signals may also feed backward to adjust the emission control devices. They may also be provided to a control unit 230 to control stoicheometry of the burners of furnace 1. This results in a more efficient system that reduces the amount of emissions released.
Owner:ALSTOM TECH LTD
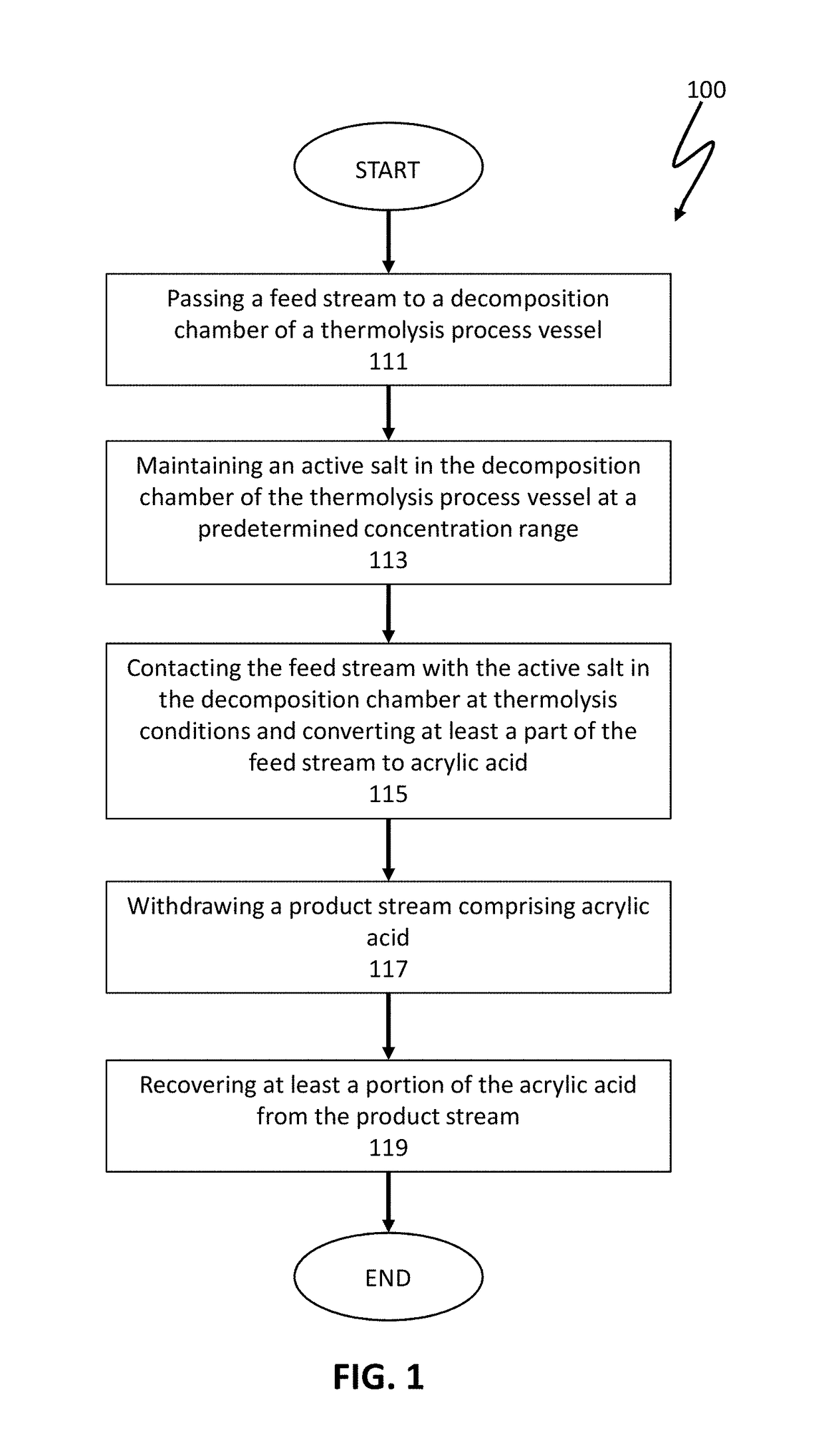
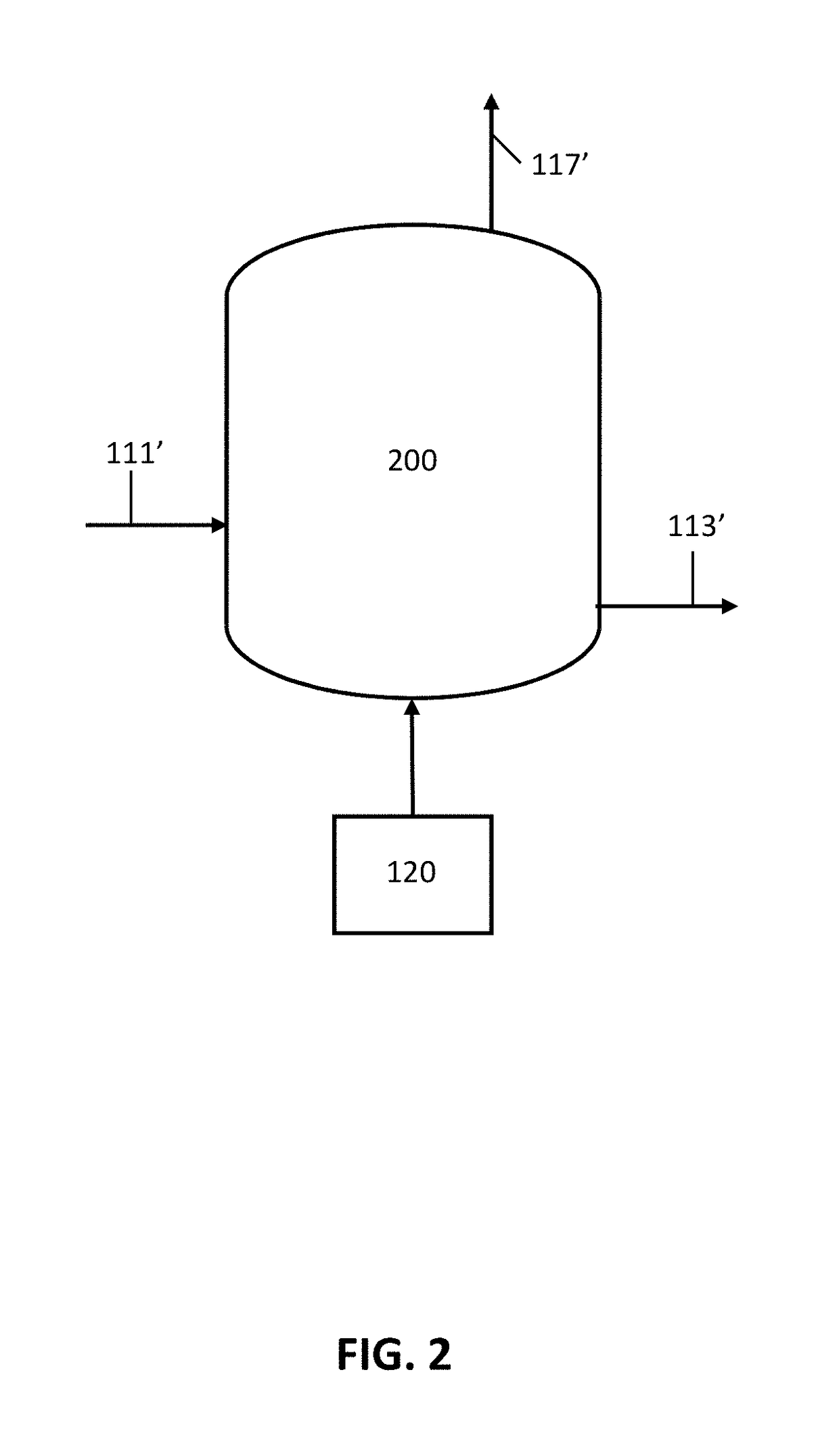
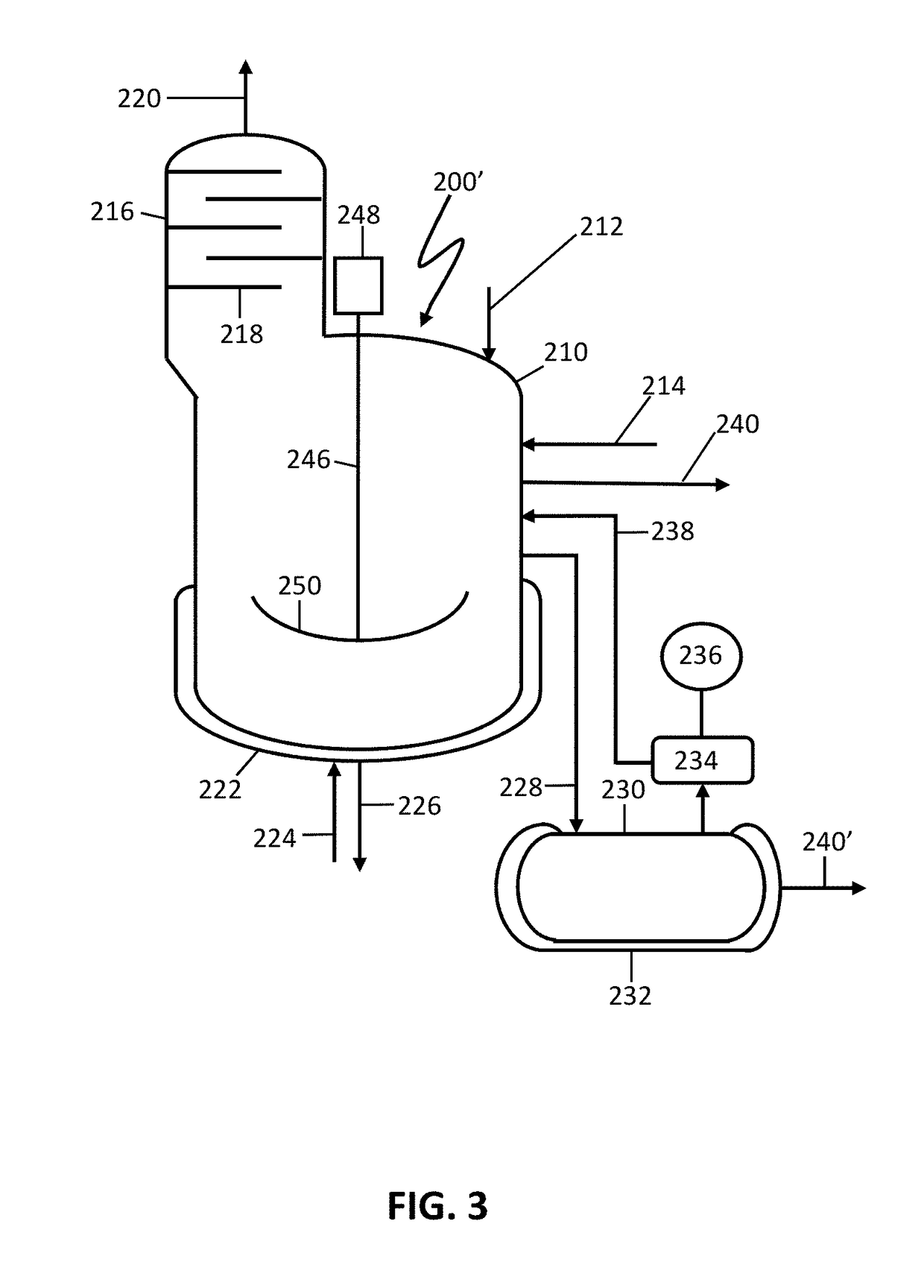
Thermolysis of polypropiolactone to produce acrylic acid
ActiveUS10065914B1High purityReduce and limit polymerizationOrganic compound preparationChemical/physical/physico-chemical stationary reactorsAcrylic acidPolymerization
The present invention is directed to reactor apparatus and processes for thermolysis of polypropiolactone to produce highly pure acrylic acid. In preferred embodiments of the present invention, the processes comprise introducing a feed stream comprising polypropiolactone to a thermolysis process vessel through an inlet; maintaining a concentration of active salt by adding and removing portions of active salt by at least one inlet and at least one outlet; heating the thermolysis process vessel; and recovering a product including acrylic acid from an outlet. In certain preferred embodiments, the active salt may be present as a catalyst used for polymerization of the polypropiolactone in the feed stream. In some embodiments, one or more active salts may be added to the feed stream and / or the thermolysis process vessel.
Owner:NOVOMER INC
Transistor, fabricating method thereof and flat panel display therewith
InactiveUS20080157083A1Control concentrationMinimise currentSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDisplay deviceFlat panel display
A transistor includes a substrate, an active region including a source region, a channel region, and a drain region which are crystallized using an SGS crystallization method and are formed on the substrate so that a grain size of a first annealed portion and a second annealed portion are different from each other, a gate insulating layer formed on the active region, and a gate electrode formed on the gate insulating layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG MOBILE DISPLAY CO LTD
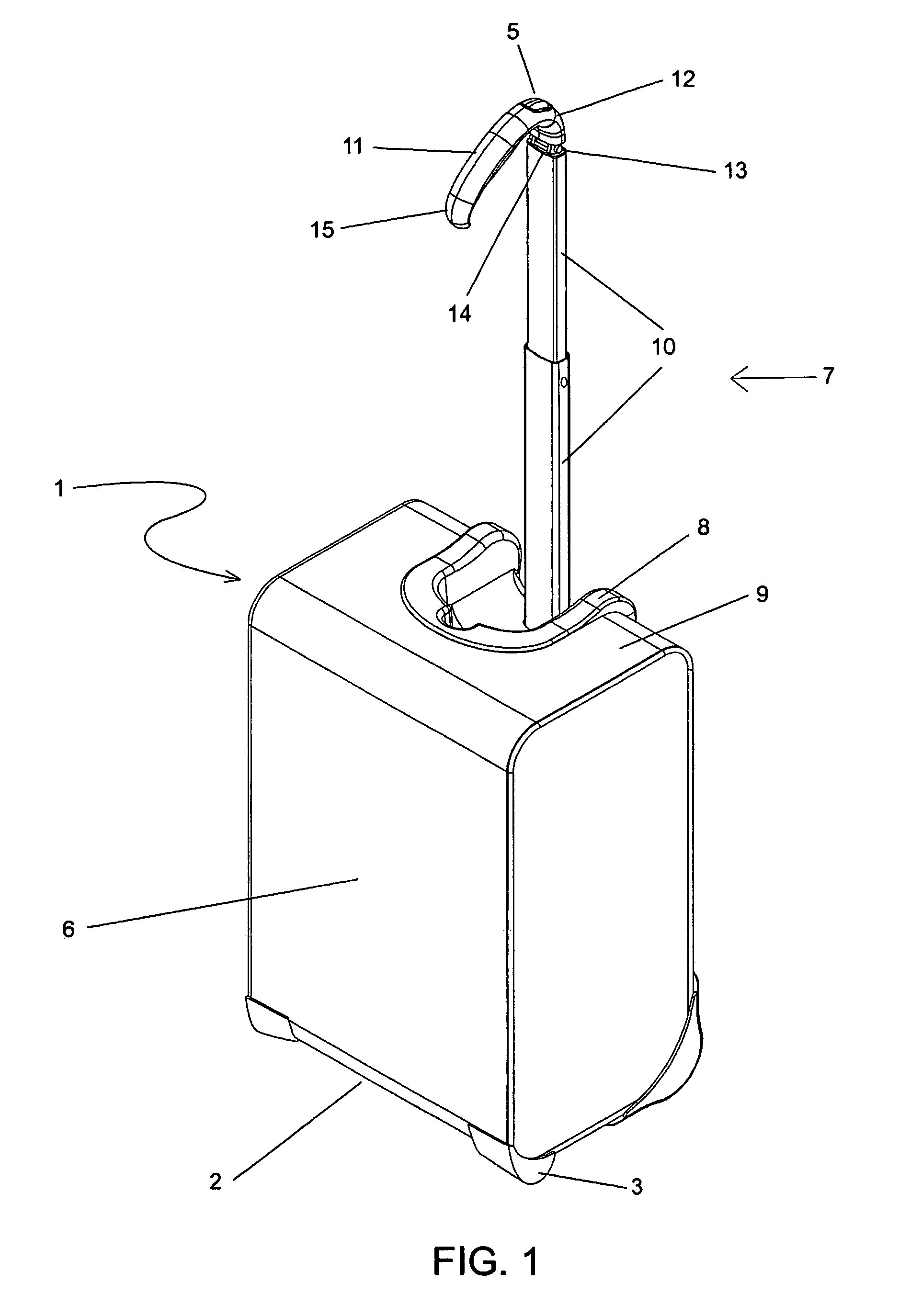
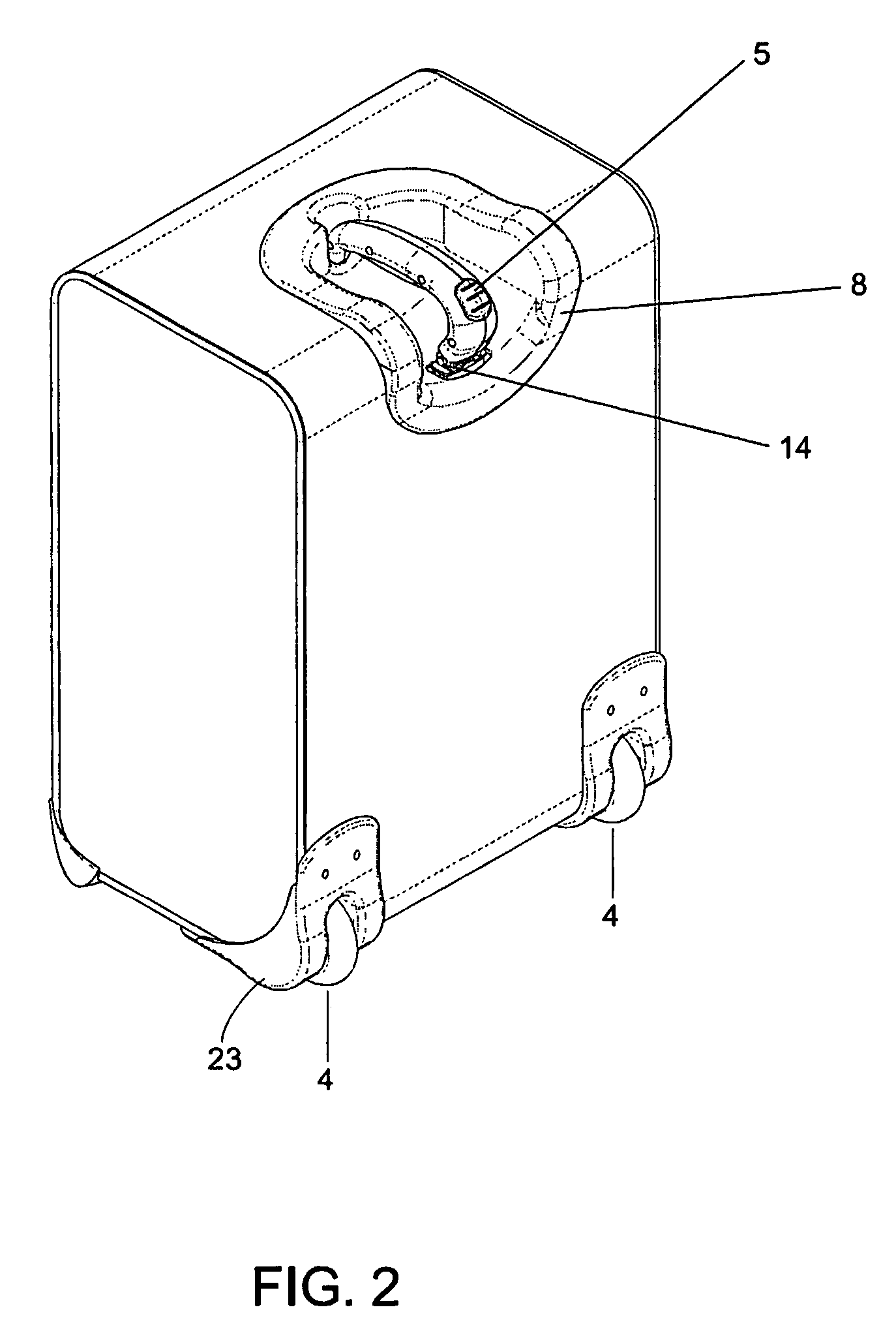
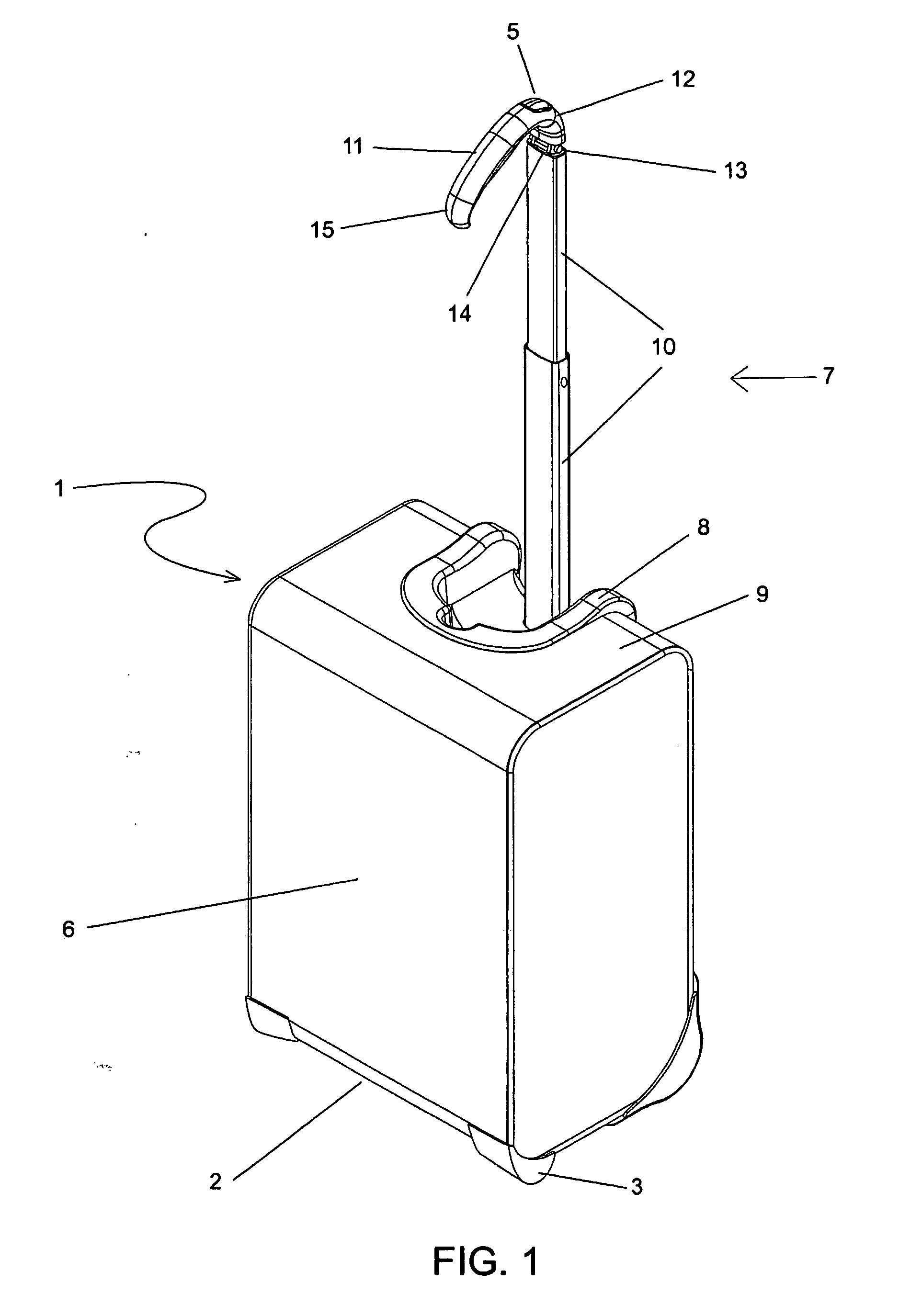
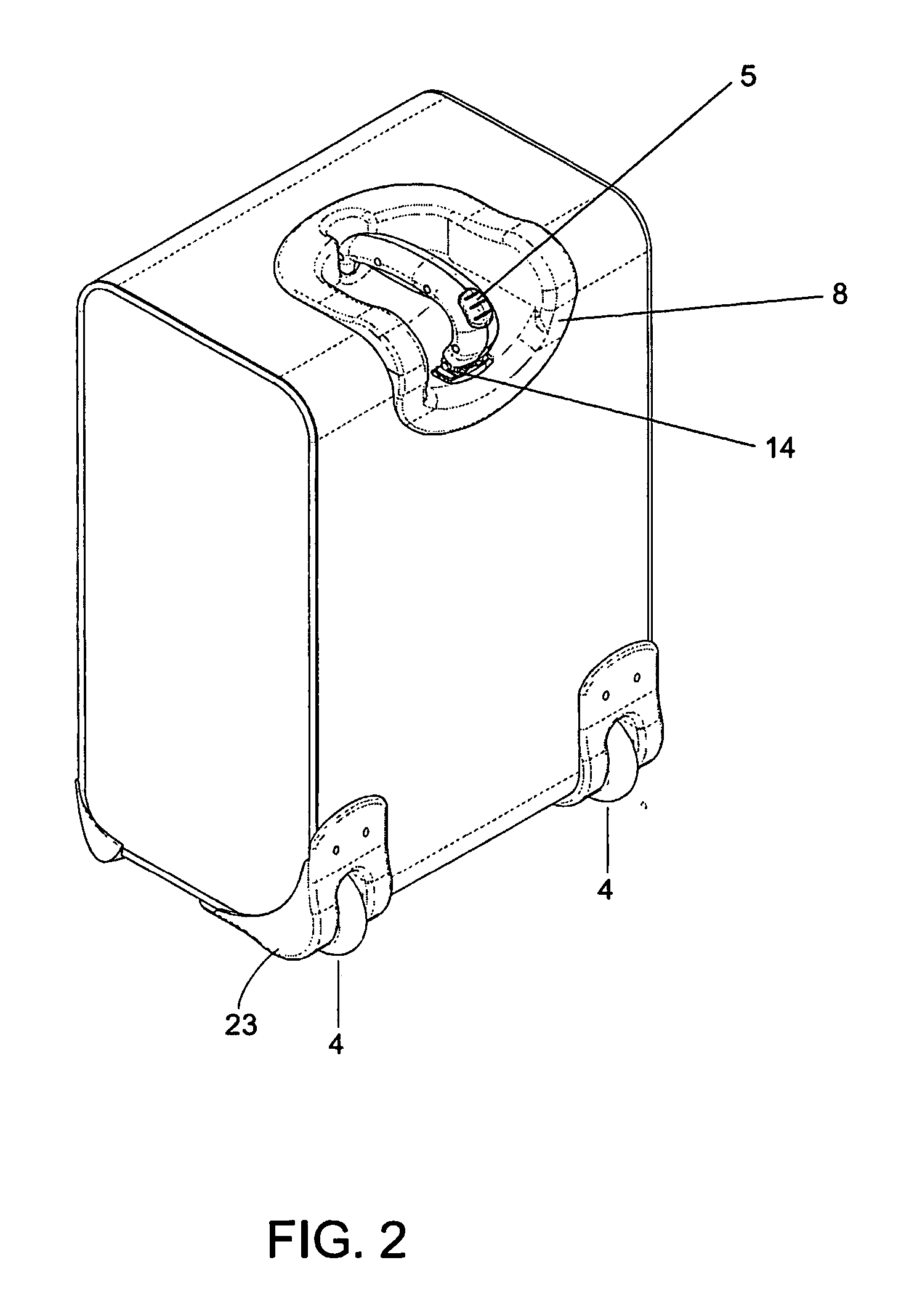
Handle apparatus with cantilevered handle grip for luggage case
InactiveUS7461730B2Prevent tippingStrong and more positionWing handlesKitchen equipmentEngineeringCantilever
A wheeled luggage case (1) has a single telescoping handle arm assembly (10) and a cantilevered handle grip (11) which is rotatably attached to the top end (13) of the handle arm assembly, such that the plane of rotation of the grip is approximately parallel to the rolling direction of the luggage case. The cantilevered handle grip (11) rotates from a position approximately perpendicular to the telescoping handle arm assembly (10) to a position approximately 30° below the horizontal, and a resilient element is provided which urges the grip to rotate downwardly while in use. The invention provides an ergonomically comfortable wheeled luggage case by allowing the user to grasp the grip in a natural position and, simultaneously, increasing the amount of leverage available to prevent the luggage case from tipping over when it is rolled over uneven ground. Further, the resilient element distributes the weight of the luggage case evenly across the user's hand.
Owner:INVENTIVE TRAVELWARE
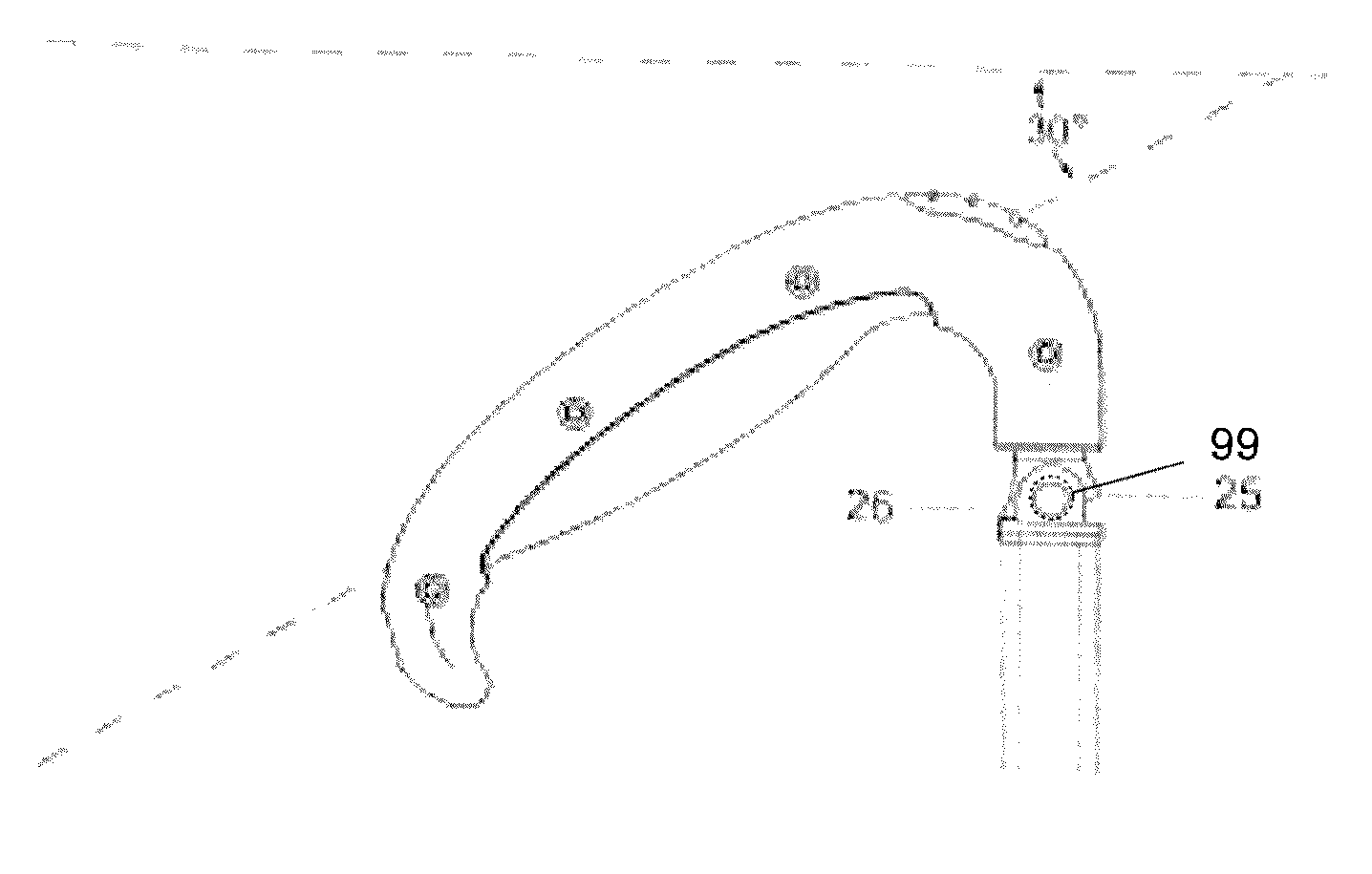
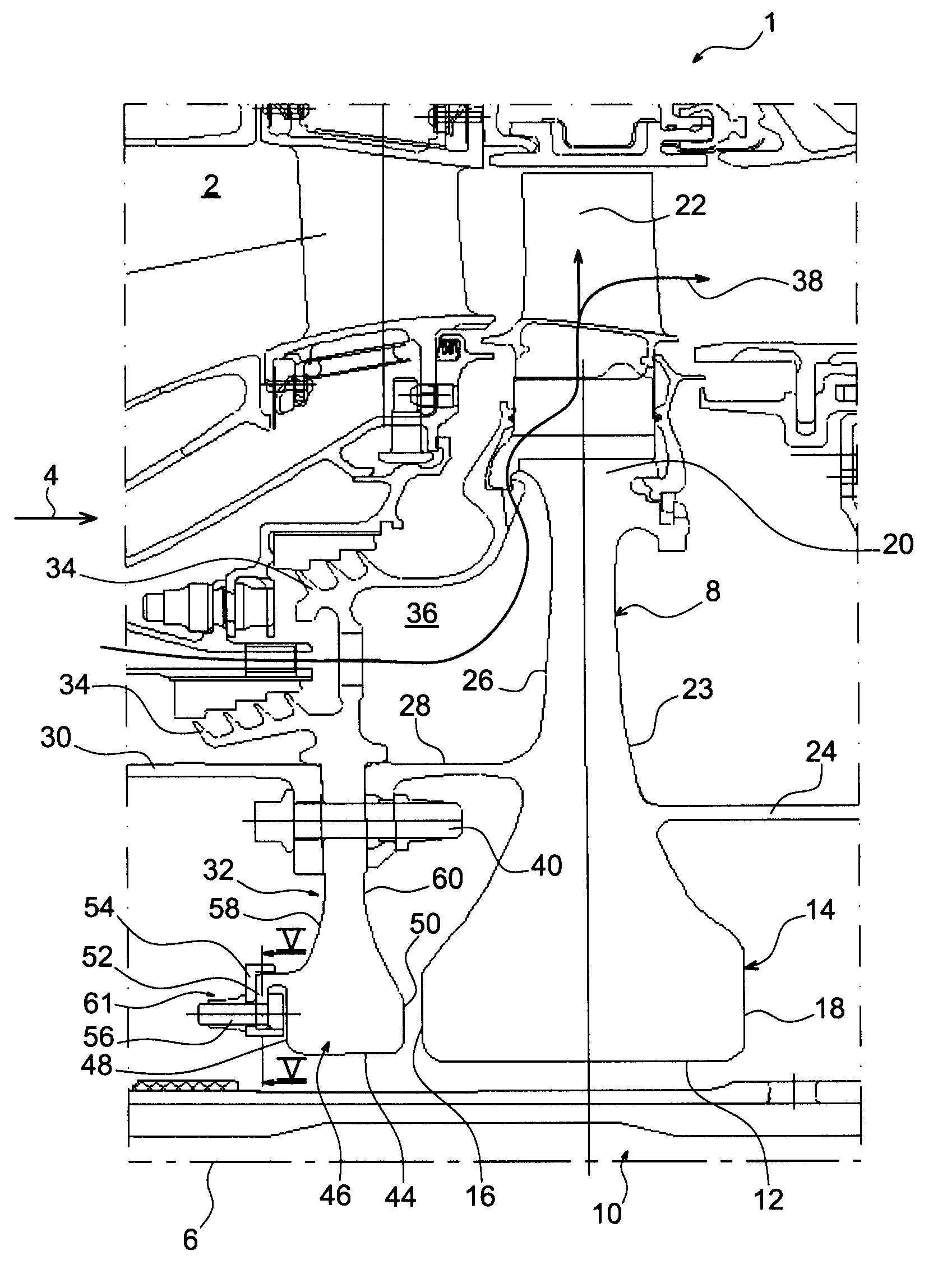
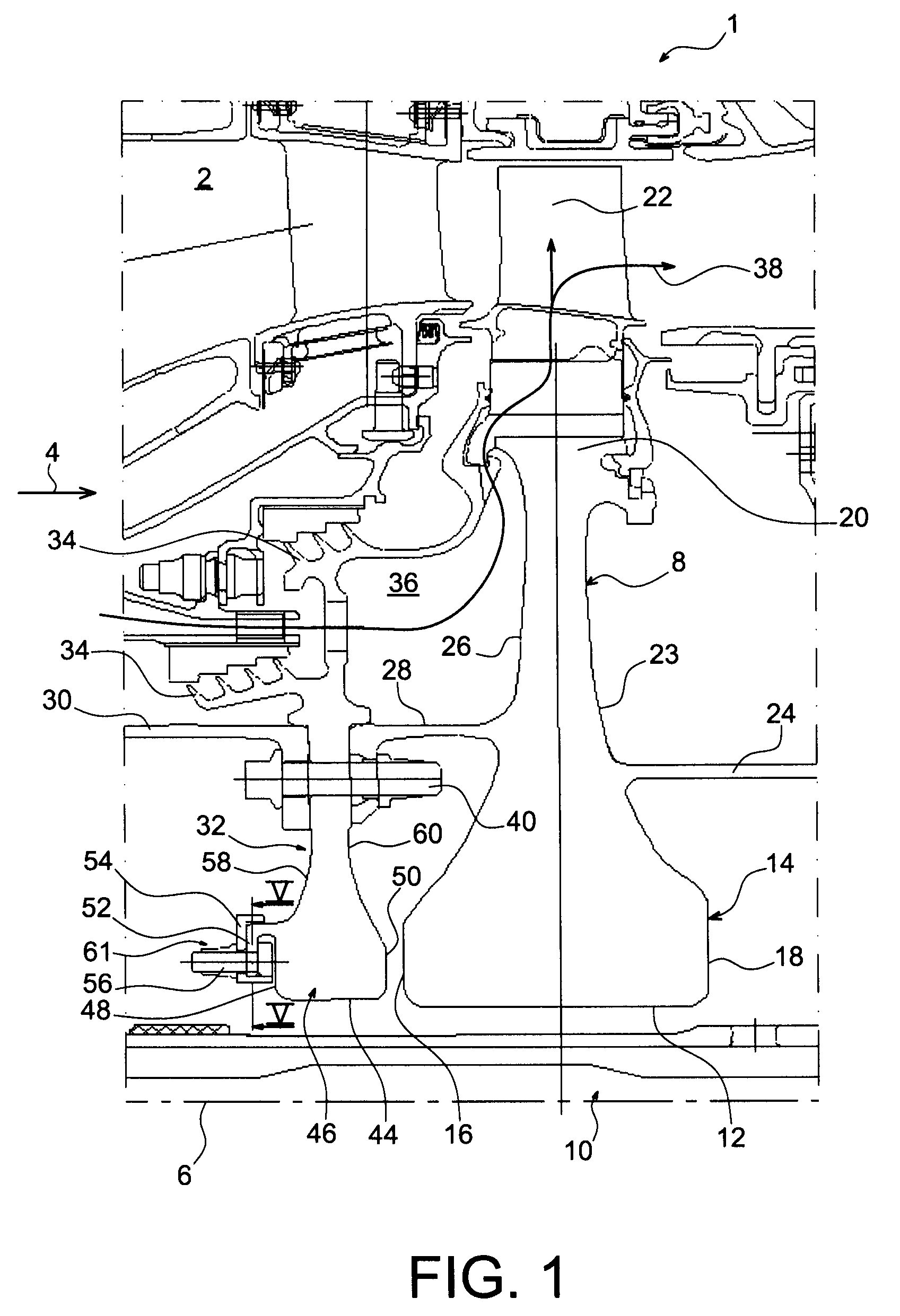
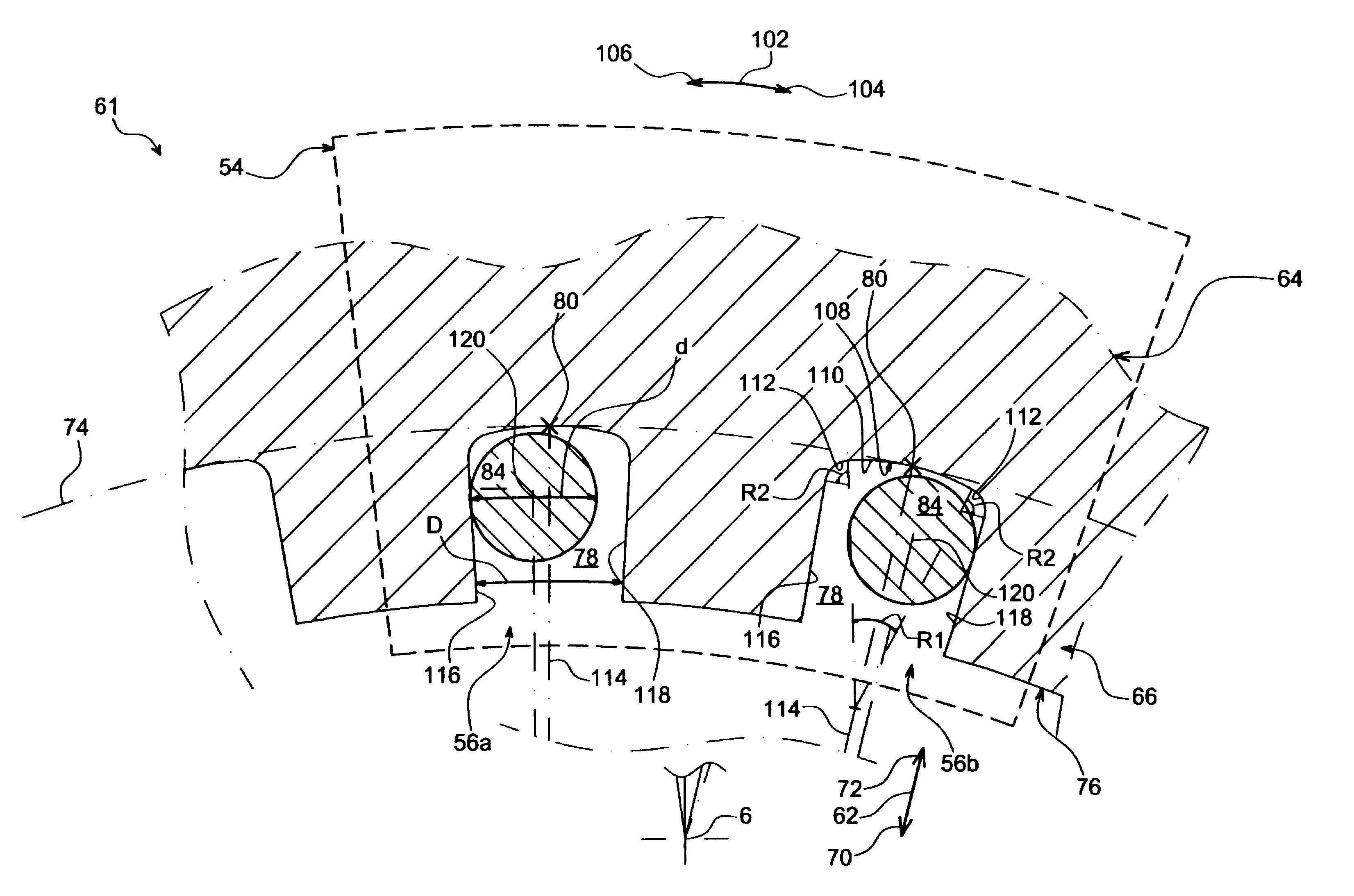
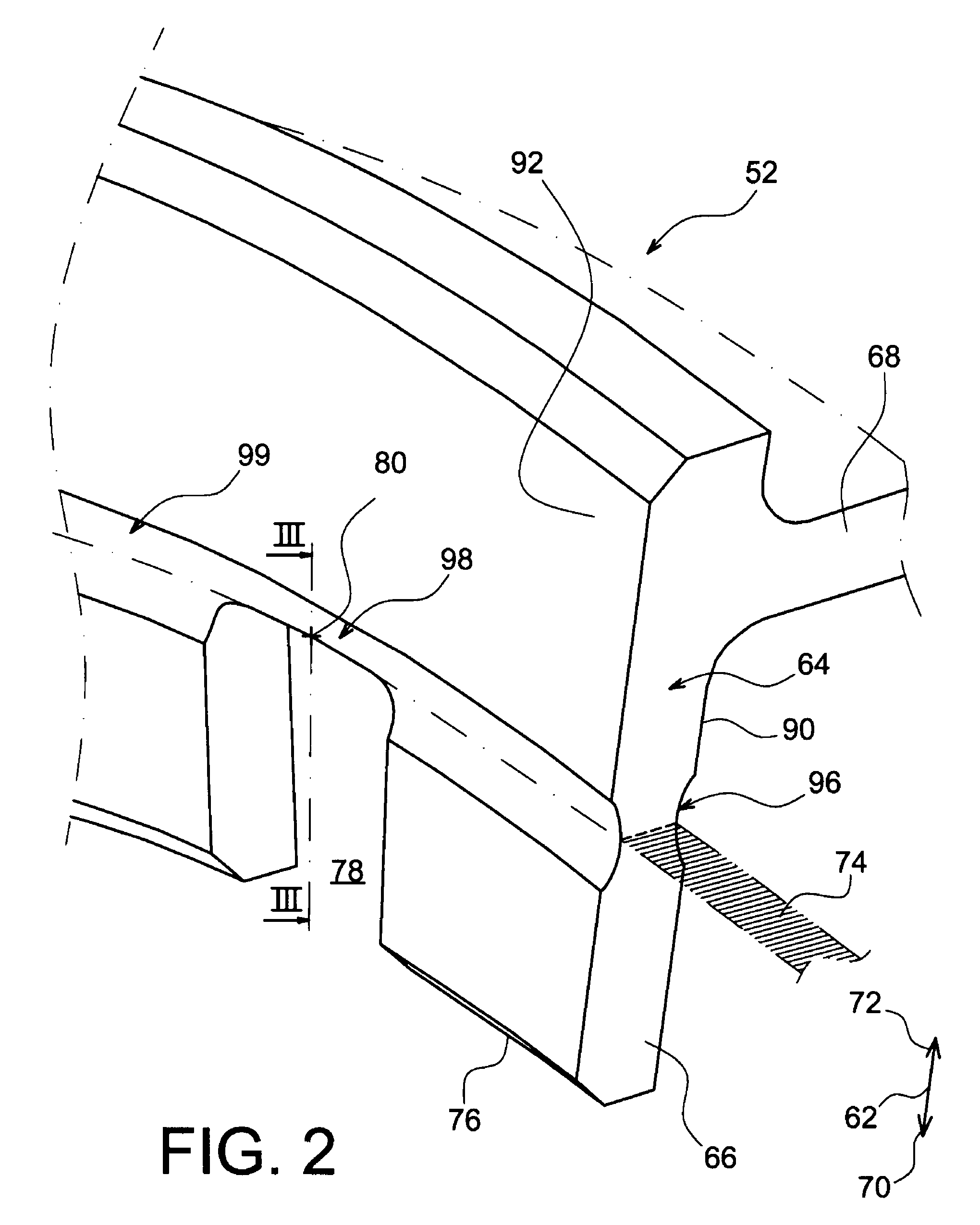
Balancing system for turbomachine rotor
The present invention relates to a turbomachine rotor balancing system comprising a balancing flange (52) provided with through-passageways (78), the system further comprising balance weights (54) each mounted fixedly on the flange (52) by means of a first and a second screw / nut assembly (56a, 56b) having a first and a second screw (84, 84) passing through a first and a second passageway (78, 78). According to the invention, said first screw is pressing against a first tangential end side (116) of the first through-passageway, and at a distance from a second tangential end side, and the second screw is pressing against a second tangential end side (118) of the second through-passageway, and at a distance from the first tangential end side.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
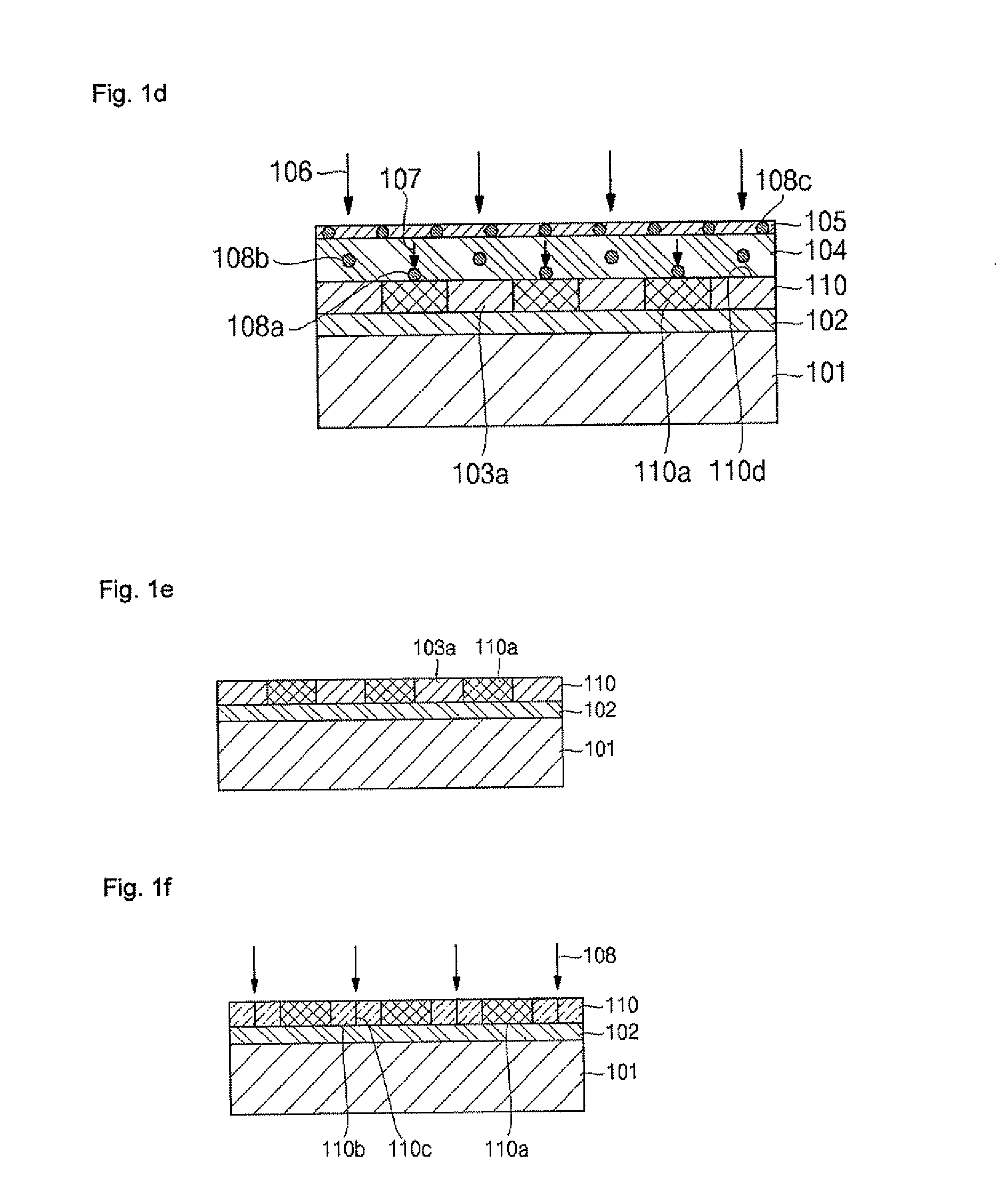
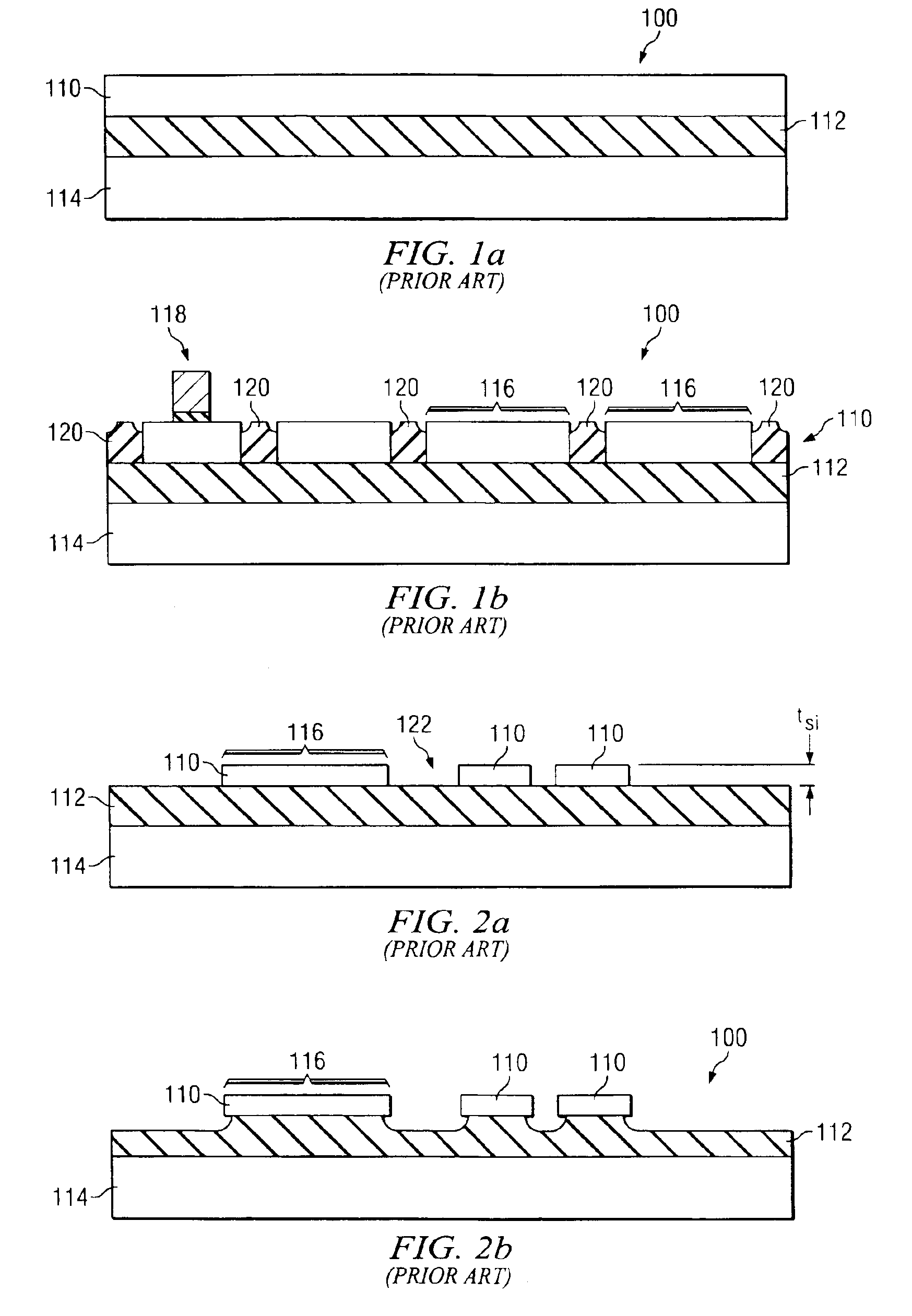
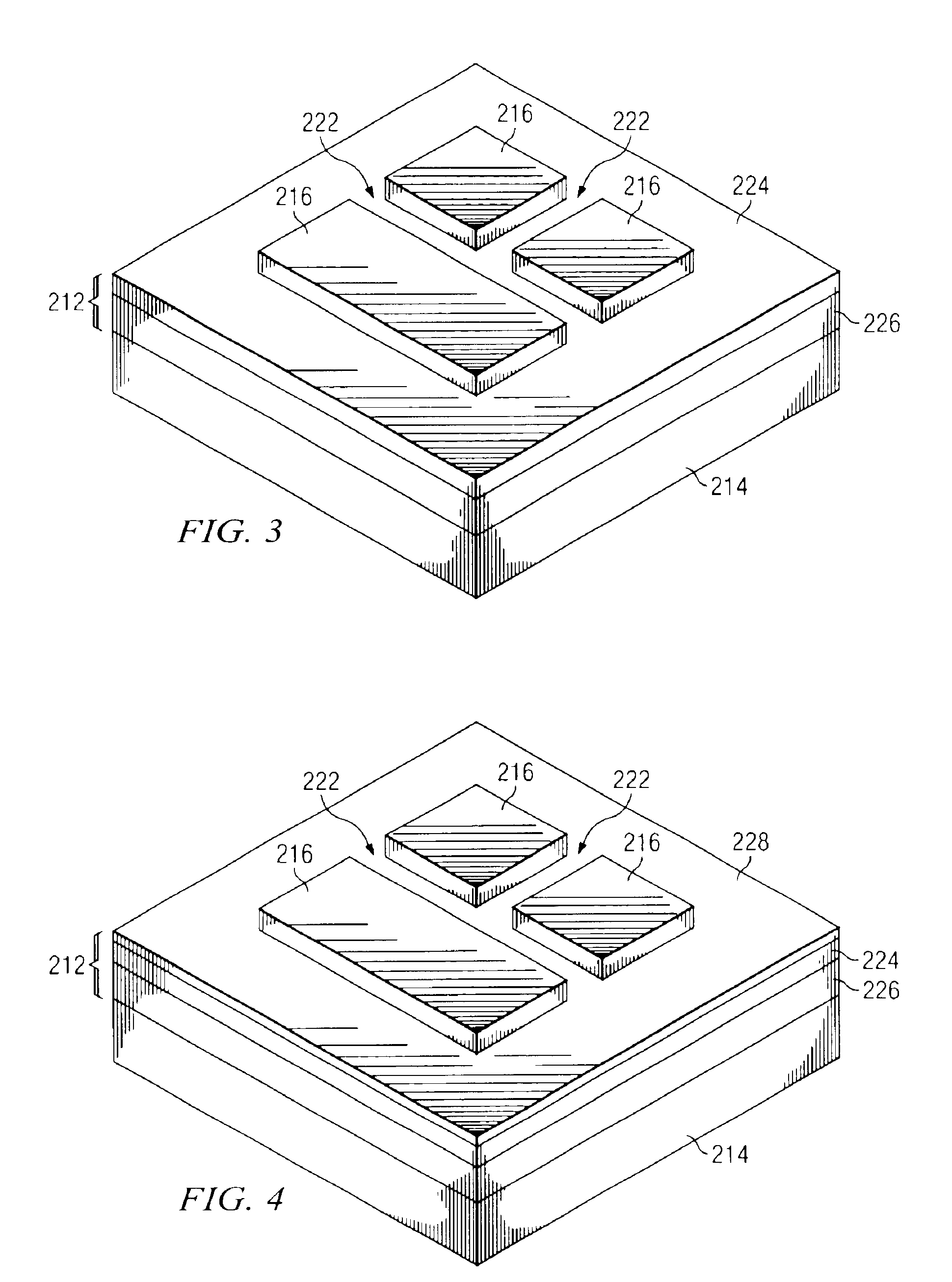
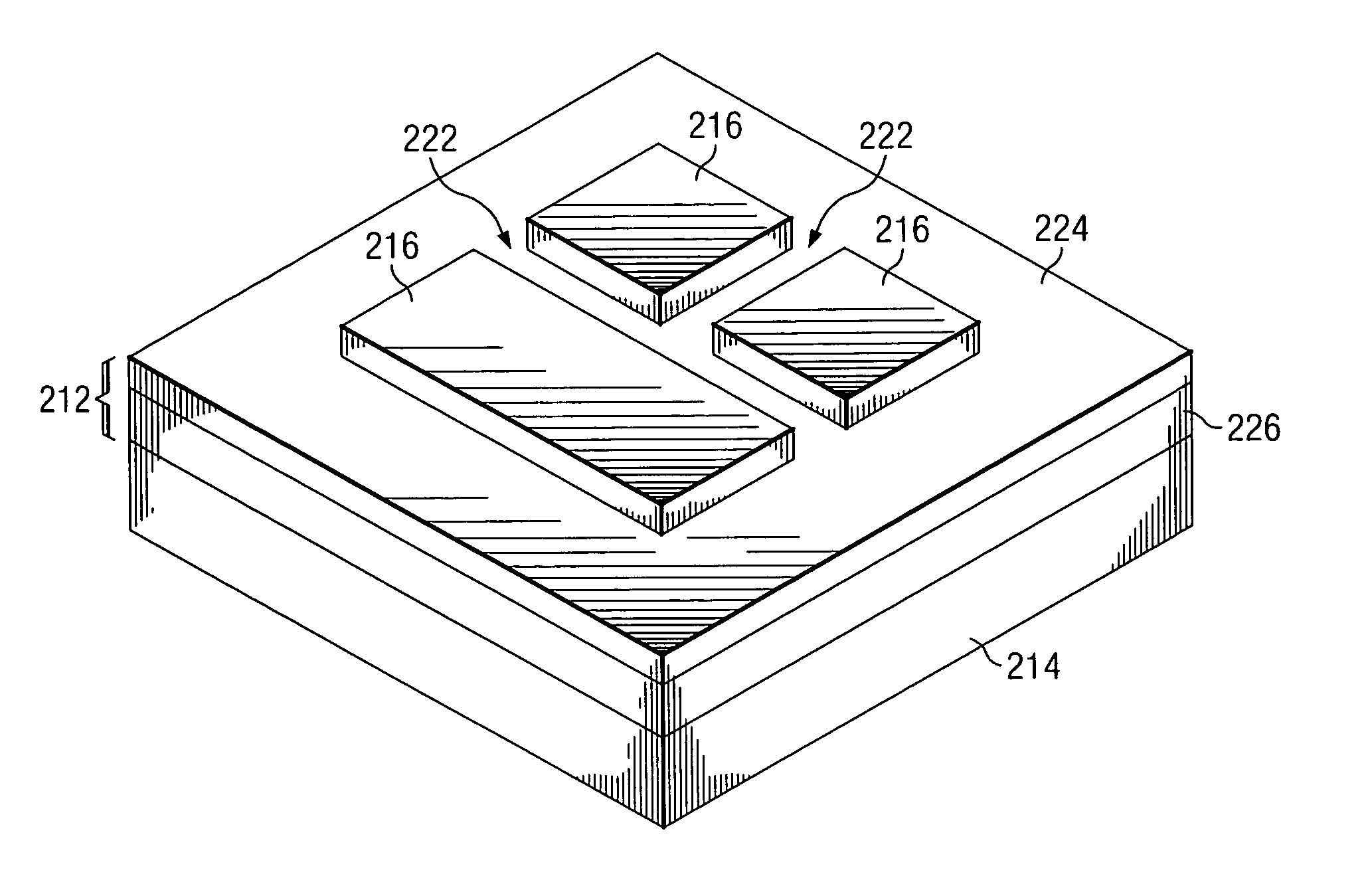
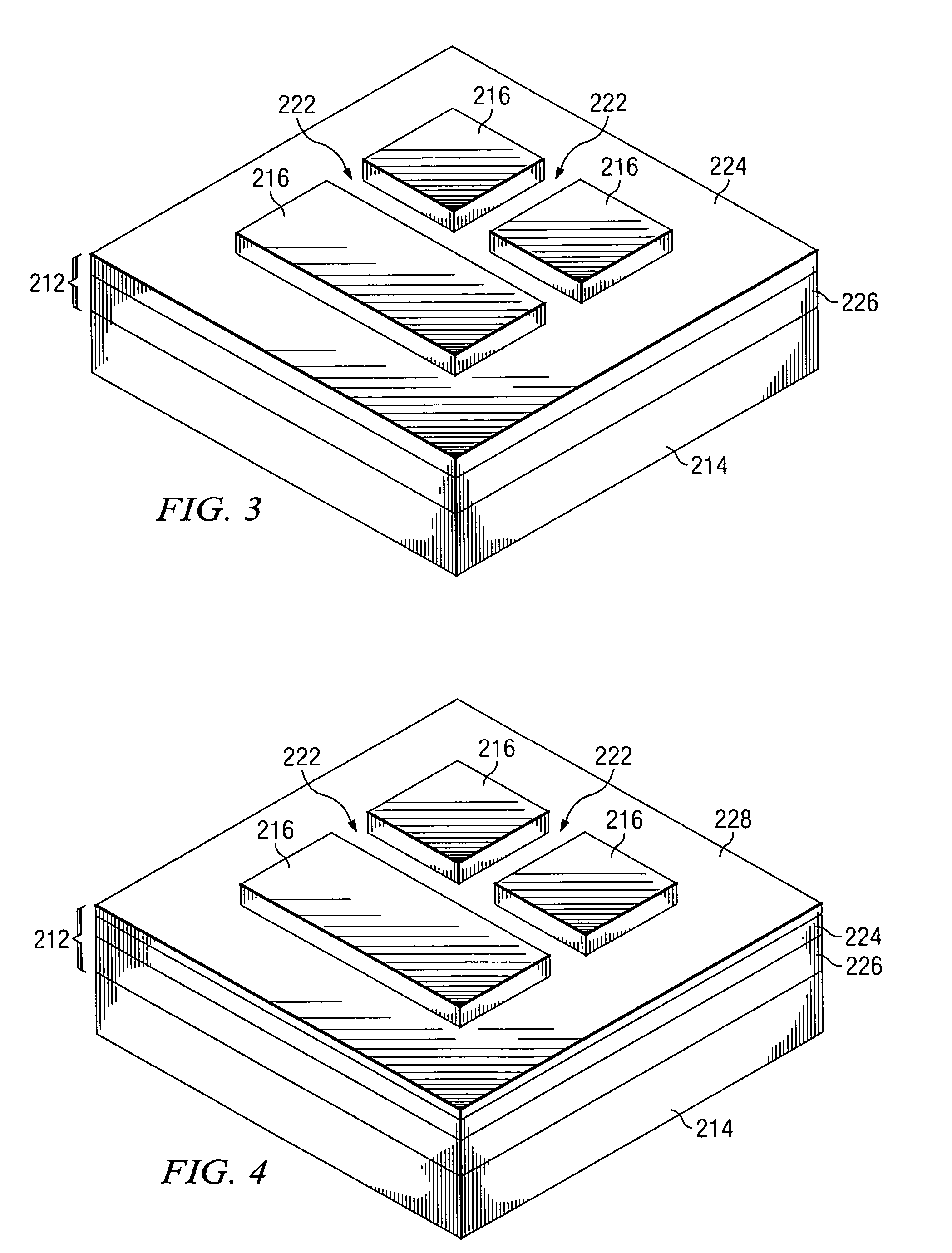
SOI chip with recess-resistant buried insulator and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS6949451B2Minimize parasitic capacitanceImprove equipment reliabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor structureDielectric layer
A semiconductor-on-insulator structure includes a substrate and a buried insulator stack overlying the substrate. The buried insulator stack includes a first dielectric layer and a recess-resistant layer overlying the first dielectric layer. A second dielectric layer can overlie the recess-resistant layer. A semiconductor layer overlying the buried insulator stack. Active devices, such as transistors and diodes, can be formed in the semiconductor layer.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Method and apparatus for mounting a sensor
InactiveUS20090084197A1Eliminate measurement resultingPrevent accidental backingForce transducersForce measurement by elastic gauge deformationEngineeringAxial force
A sensor has a body having a tapered locking surface, and engages in a component with a mounting surface having a complementary taper to the tapered locking surface of the body. The body is positioned on the component with the tapered locking surface aligned with the mounting surface, and an axial force is applied to the body to drive the tapered locking surface into engagement with the complementary taper of the mounting surface. The body is then fixed relative to the component by swaging outwards a skirt on the body into engagement with a lower surface of the component.
Owner:TRANSENSE TECH
Laundry Detergent
InactiveUS20130177518A1Minimise concentrationBiocideOrganic active ingredientsLaundry detergentChemistry
Owner:LIQUID VANITY
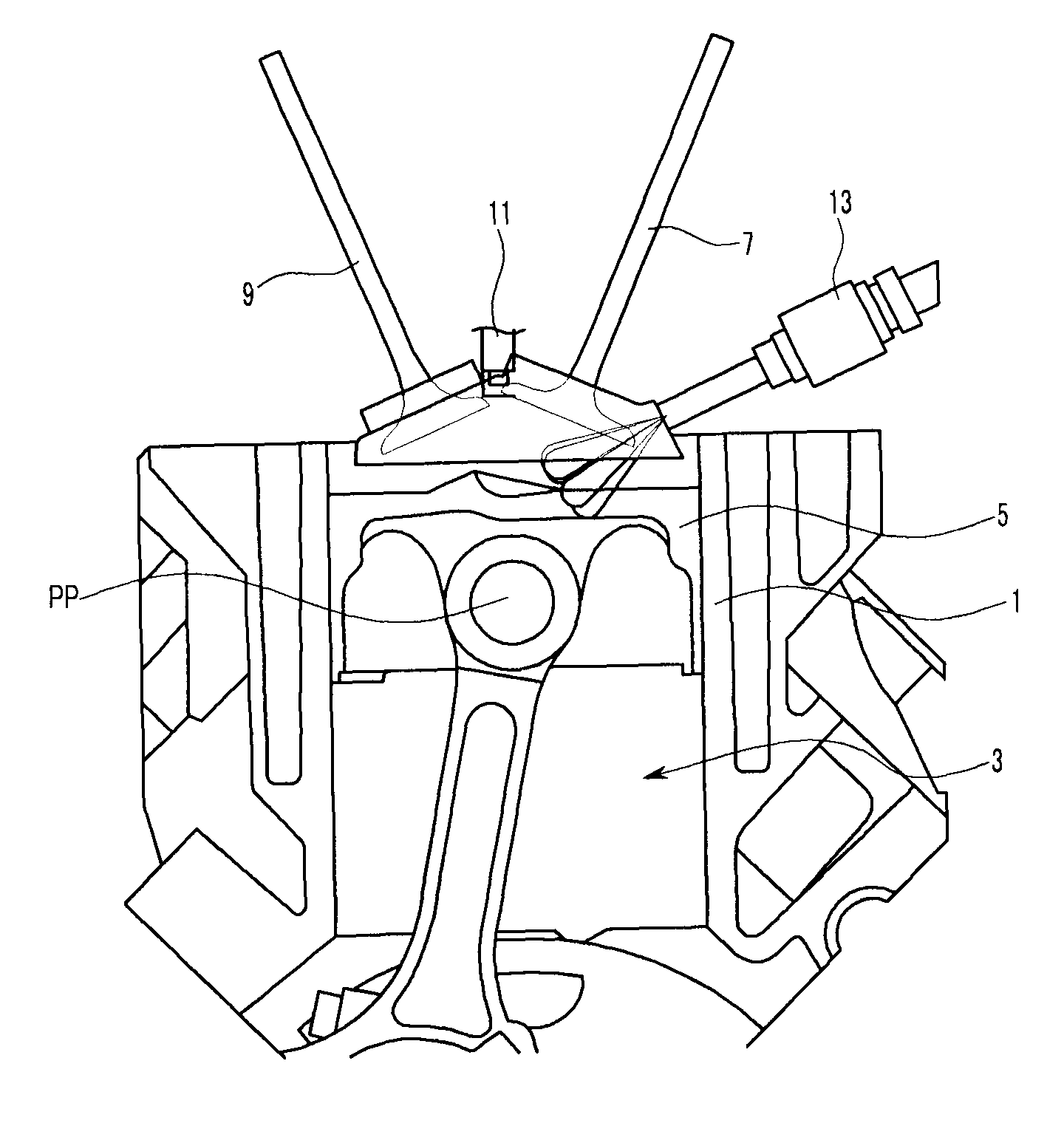
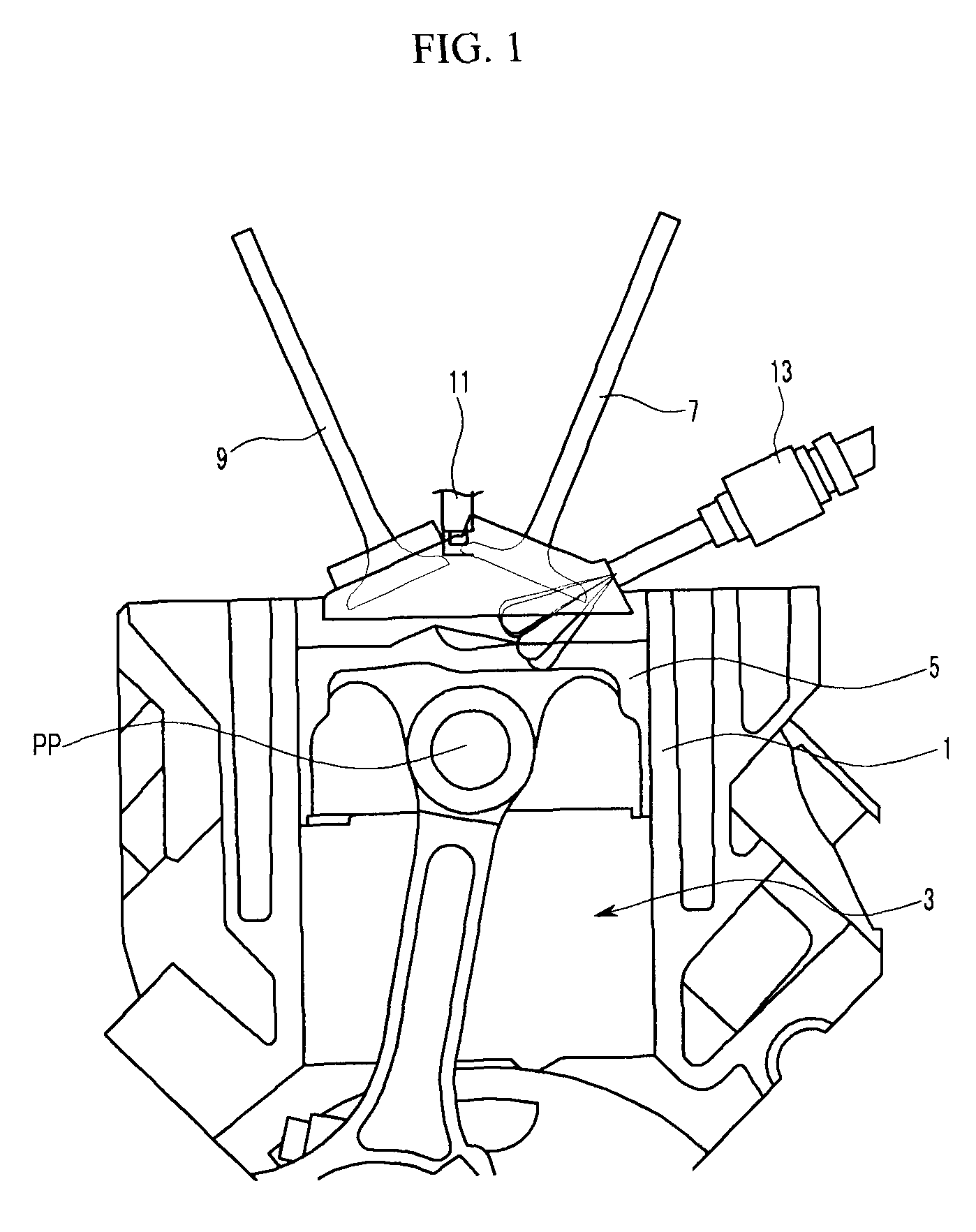
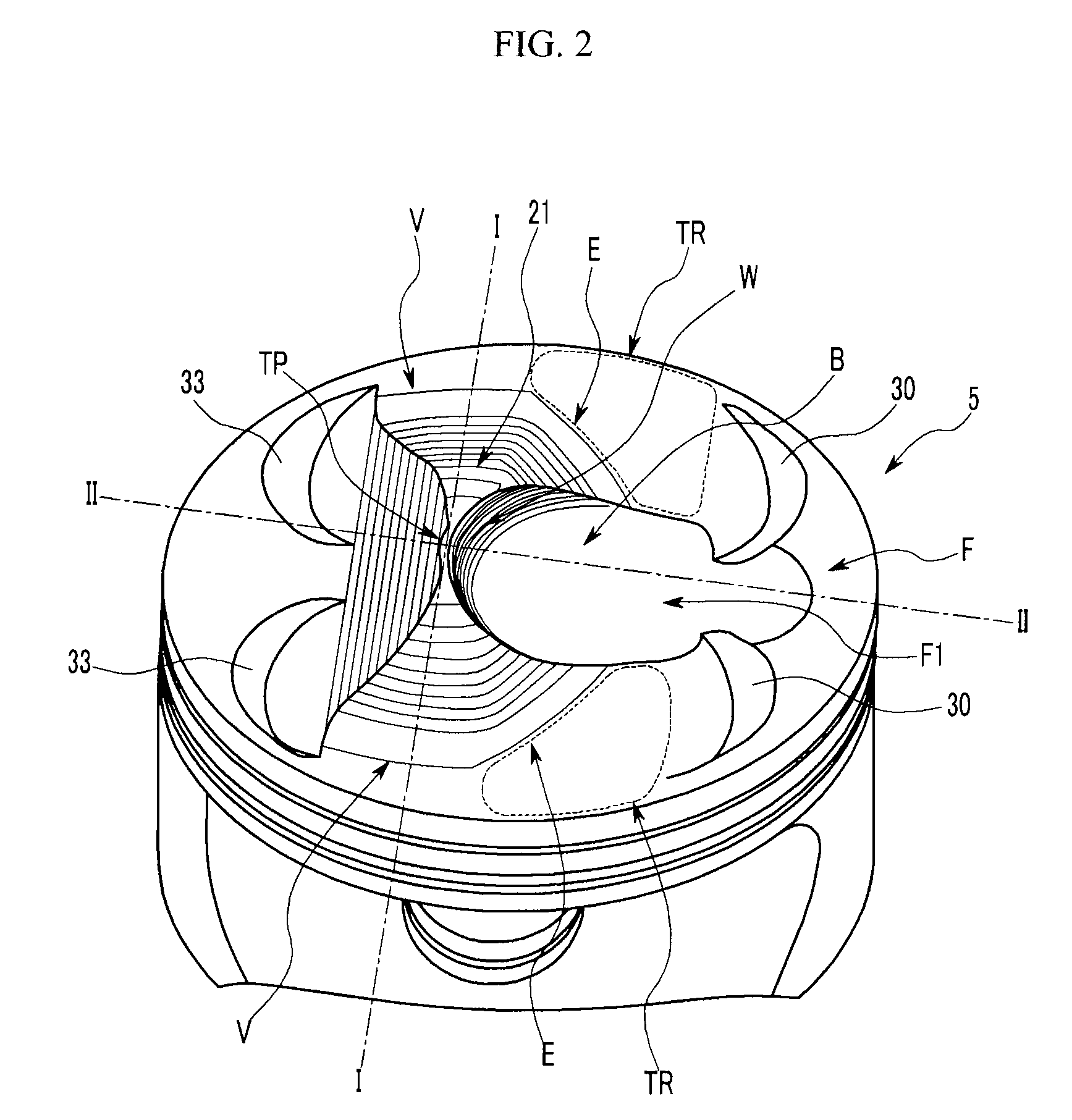
Piston of gasoline direct injection engine
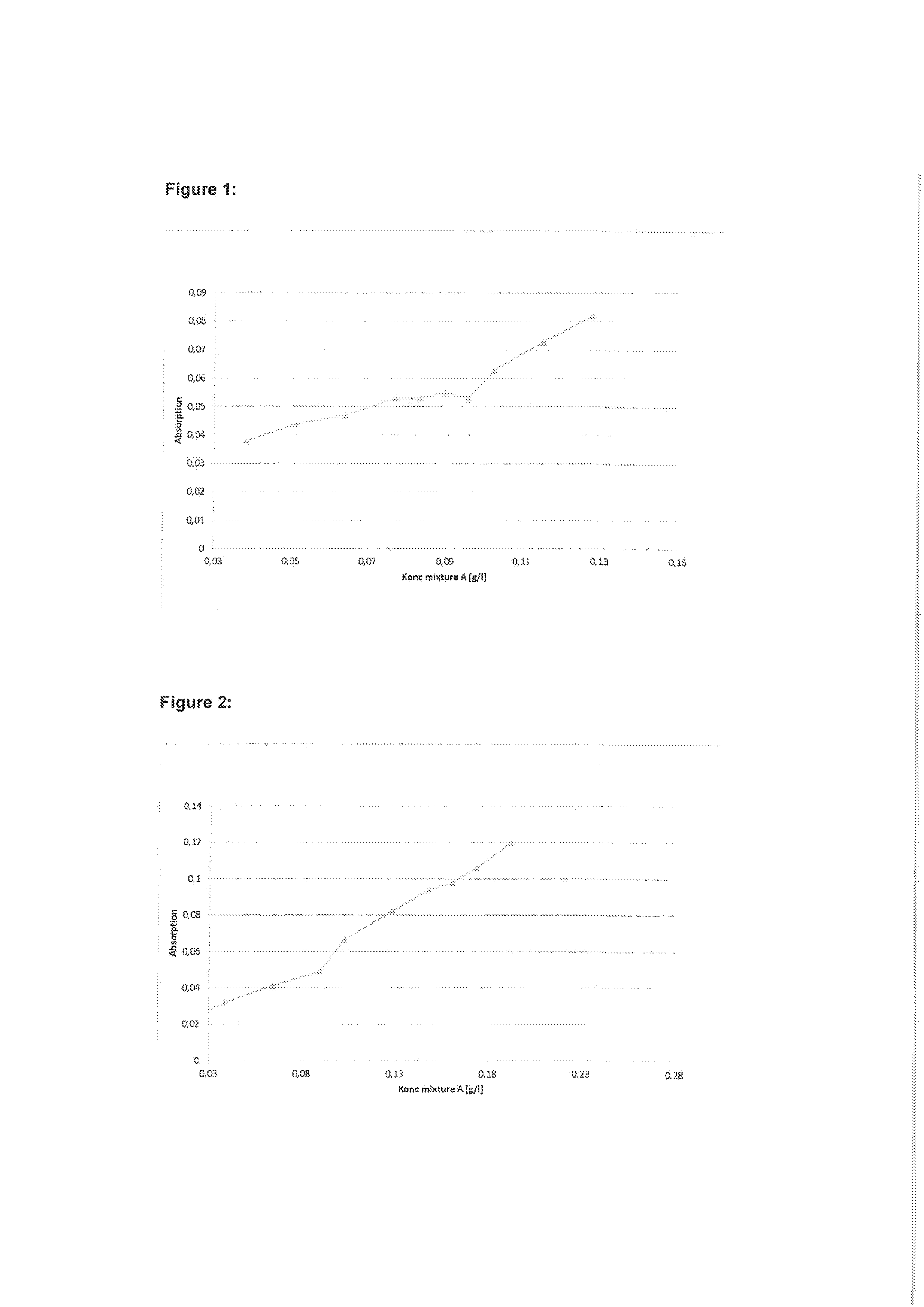
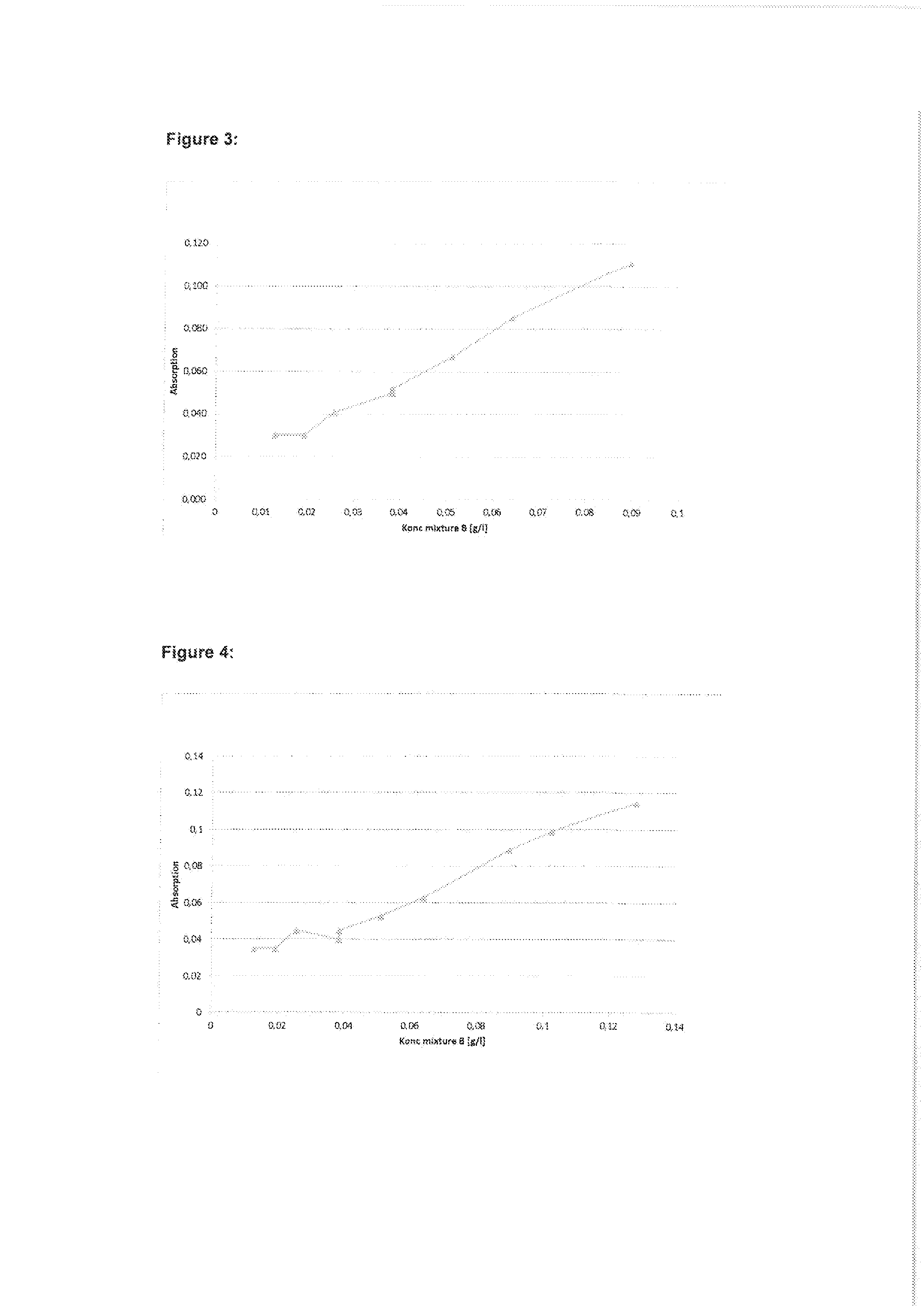
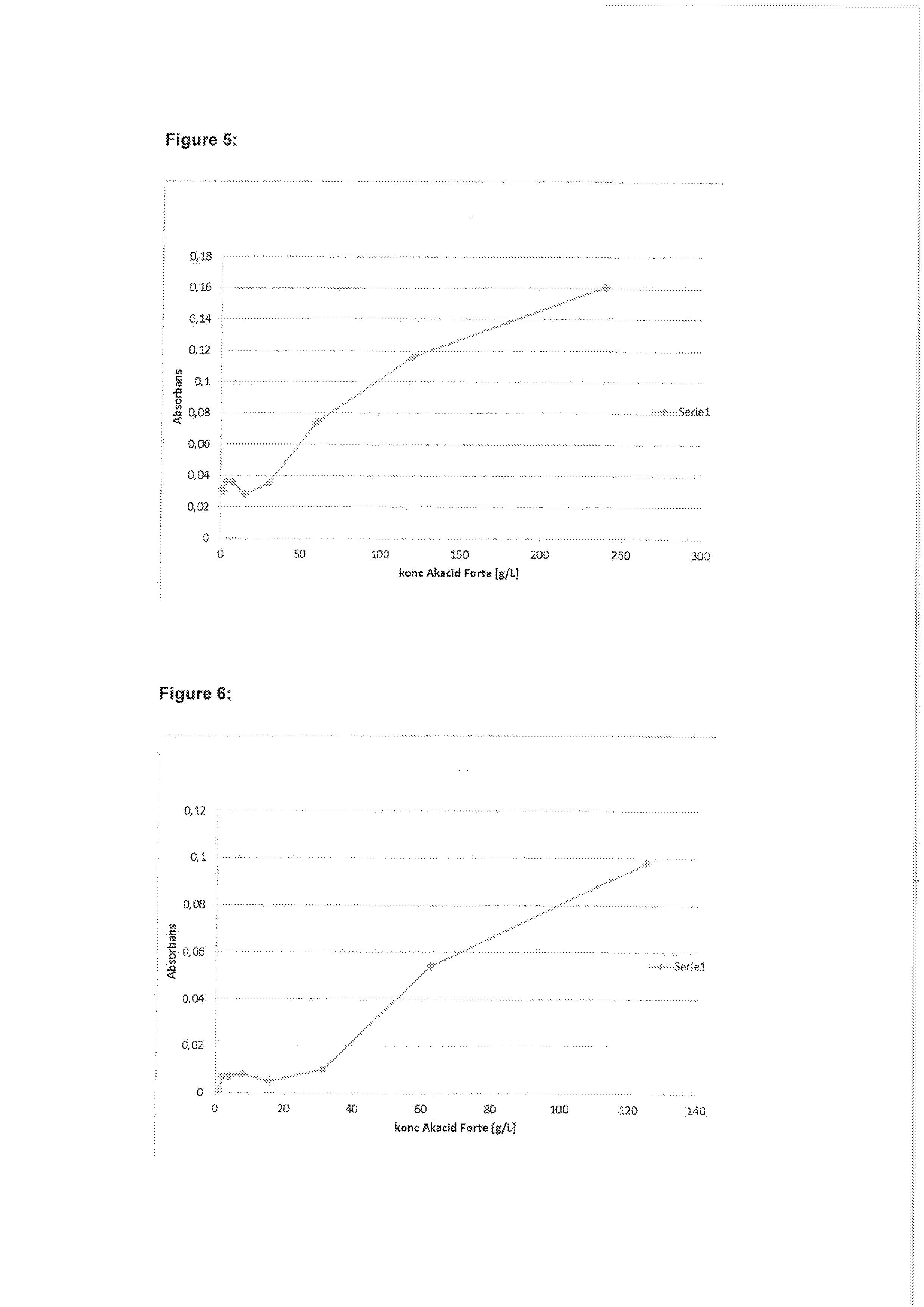
ActiveUS7971568B2Minimise concentrationReduce pollutantsInternal combustion piston enginesPistonsGasoline direct injectionSlope angle
A piston of a gasoline direct engine may include a protuberance portion protruding along a circular arc shape having a radius (R1) equal to the piston diameter to have a predetermined height (T) from the upper surface thereof, and the edge of the protuberance portion is rounded to be connected with the upper surface; a bowl (B) having a bottom surface (F1) having an asymmetrical ellipse shape from the center of the protuberance portion to the intake side direction thereof, wherein the bottom surface thereof becomes deeper in the exhaust side direction to have a predetermined slope angle (θ1), and the inner wall portion thereof has a circular arc shape to form a predetermined rising angle (θ2) at the upper part thereof; and trumpet portions (TR) of which edge ends (E) thereof are expanded in the intake side direction of the protuberance portion to be connected to the bowl (B).
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +1
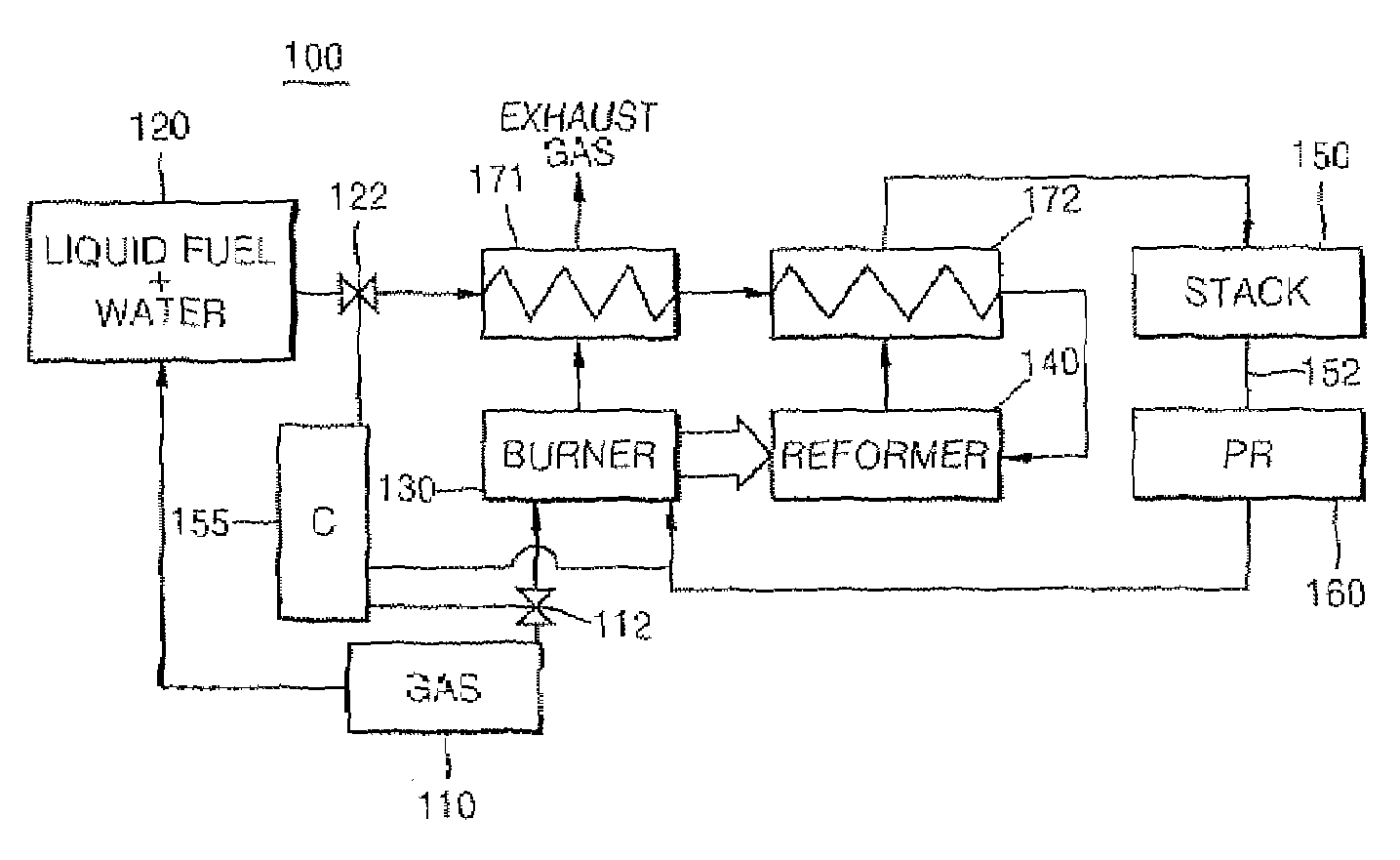
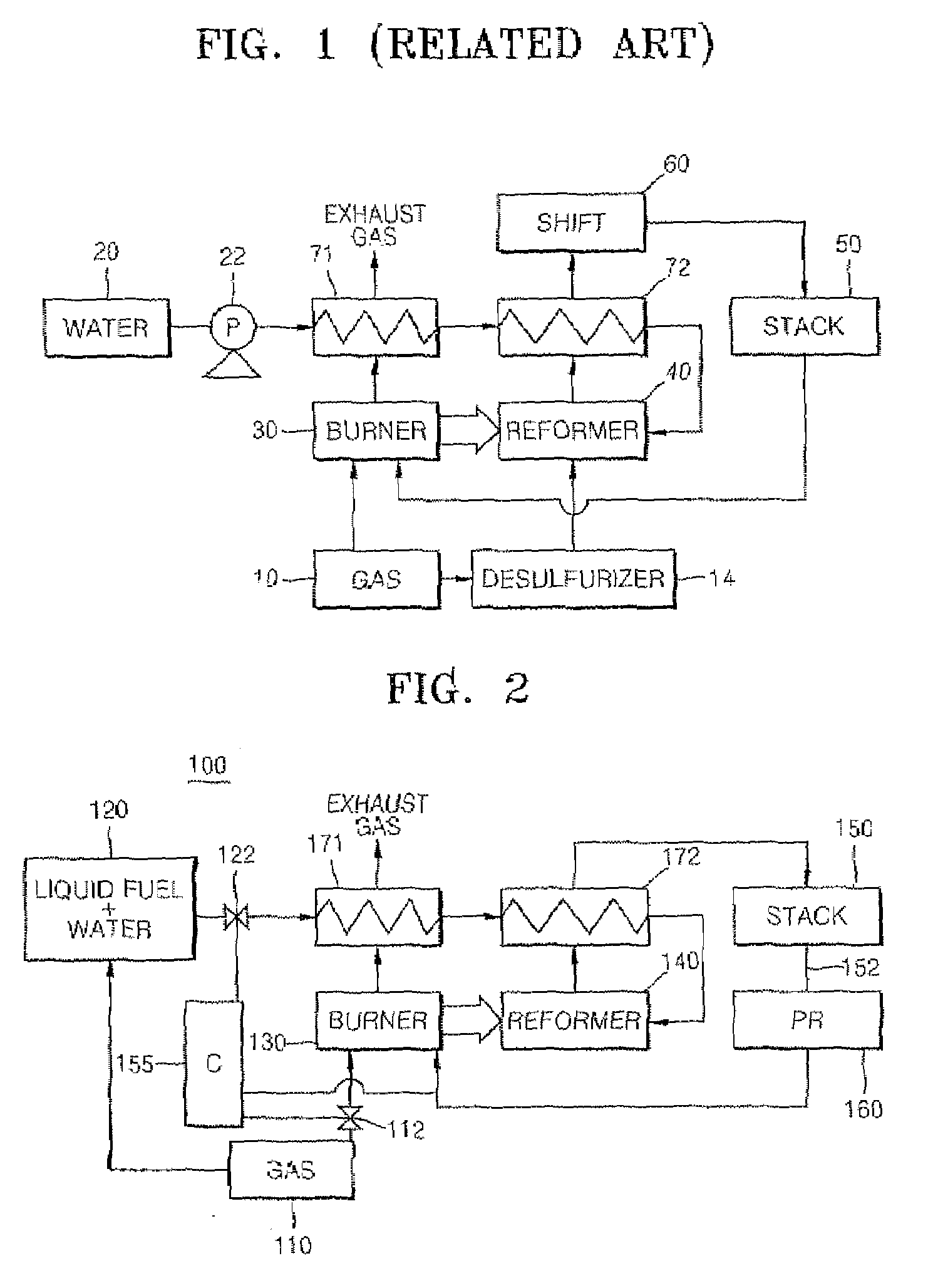
Fuel cell system
InactiveUS20070264543A1Increase supplyUniform pressureHydrogenReactant parameters controlHydrogenFuel cells
A fuel cell system that includes a liquid fuel tank containing a non-sulfur-containing liquid fuel and water; a reformer generating a hydrogen-rich gas from the liquid fuel and water received from the liquid fuel tank; a reformer burner heating the reformer by burning a gaseous fuel received from a gaseous fuel tank, and a fuel cell stack generating electrical energy from the hydrogen-rich gas received from the reformer. The liquid fuel tank is connected to the gaseous fuel tank, and the liquid fuel mixed with water is supplied to the reformer by the pressure of the gaseous fuel tank.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
SOI chip with recess-resistant buried insulator and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20050275024A1Avoid erosionMinimizes parasitic capacitanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor structureDielectric layer
A semiconductor-on-insulator structure includes a substrate and a buried insulator stack overlying the substrate. The buried insulator stack includes a first dielectric layer and a recess-resistant layer overlying the first dielectric layer. A second dielectric layer can overlie the recess-resistant layer. A semiconductor layer overlying the buried insulator stack. Active devices, such as transistors and diodes, can be formed in the semiconductor layer.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Handle apparatus for luggage case
InactiveUS20050150732A1Minimise concentrationEvenly distributedLuggageOther accessoriesEngineeringMechanical engineering
A wheeled luggage case (1) has a single telescoping handle arm assembly (10) and a cantilevered handle grip (11) which is rotatably attached to the top end (13) of the handle arm assembly, such that the plane of rotation of the grip is approximately parallel to the rolling direction of the luggage case. The cantilevered handle grip (11) rotates from a position approximately perpendicular to the telescoping handle arm assembly (10) to a position approximately 30° below the horizontal, and a resilient element is provided which urges the grip to rotate downwardly while in use. The invention provides an ergonomically comfortable wheeled luggage case by allowing the user to grasp the grip in a natural position and, simultaneously, increasing the amount of leverage available to prevent the luggage case from tipping over when it is rolled over uneven ground. Further, the resilient element distributes the weight of the luggage case evenly across the user's hand.
Owner:INVENTIVE TRAVELWARE
Laundry Detergent
ActiveUS20160017262A1Minimise concentrationOrganic active ingredientsBiocideOrganic chemistryLaundry detergent
Owner:LIQUID VANITY
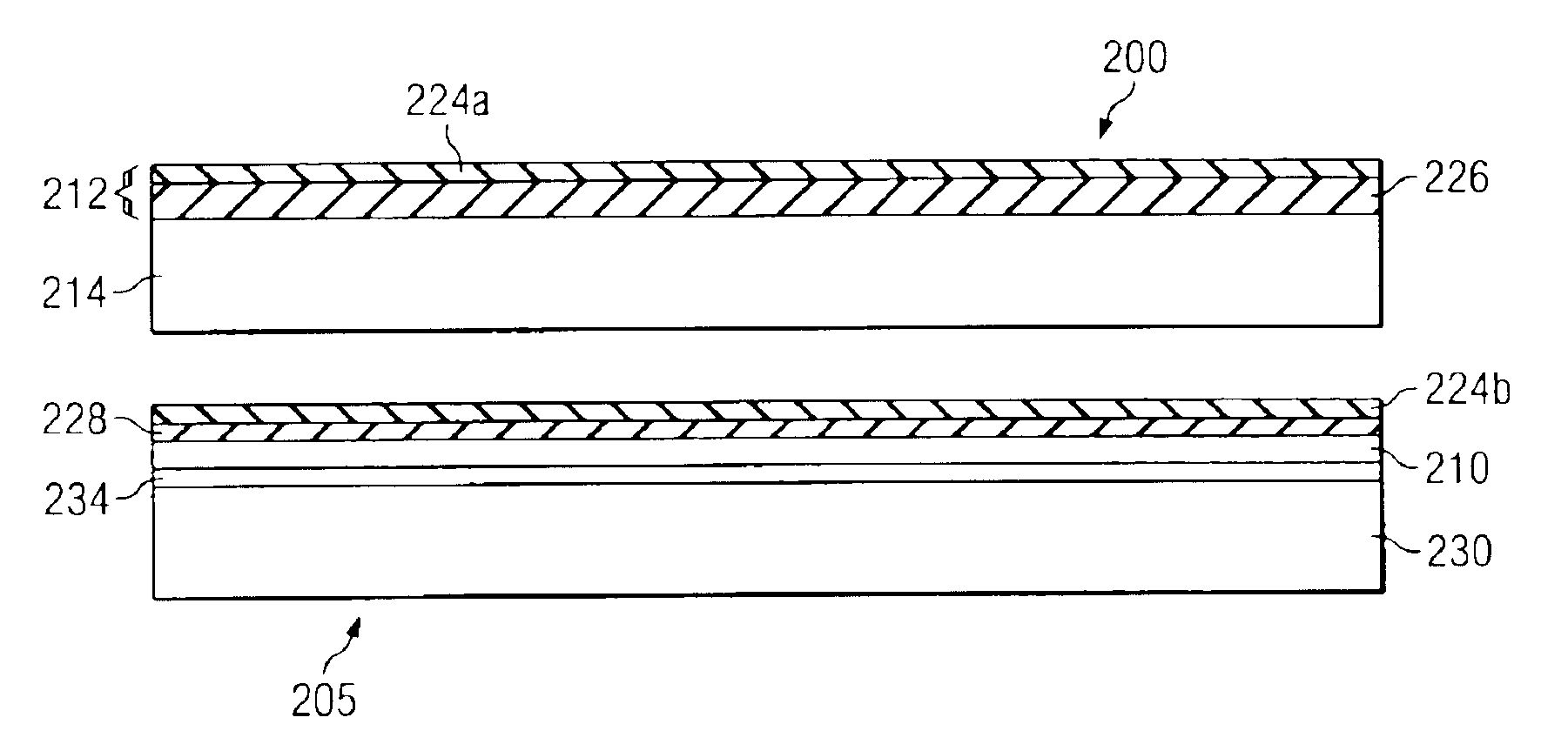
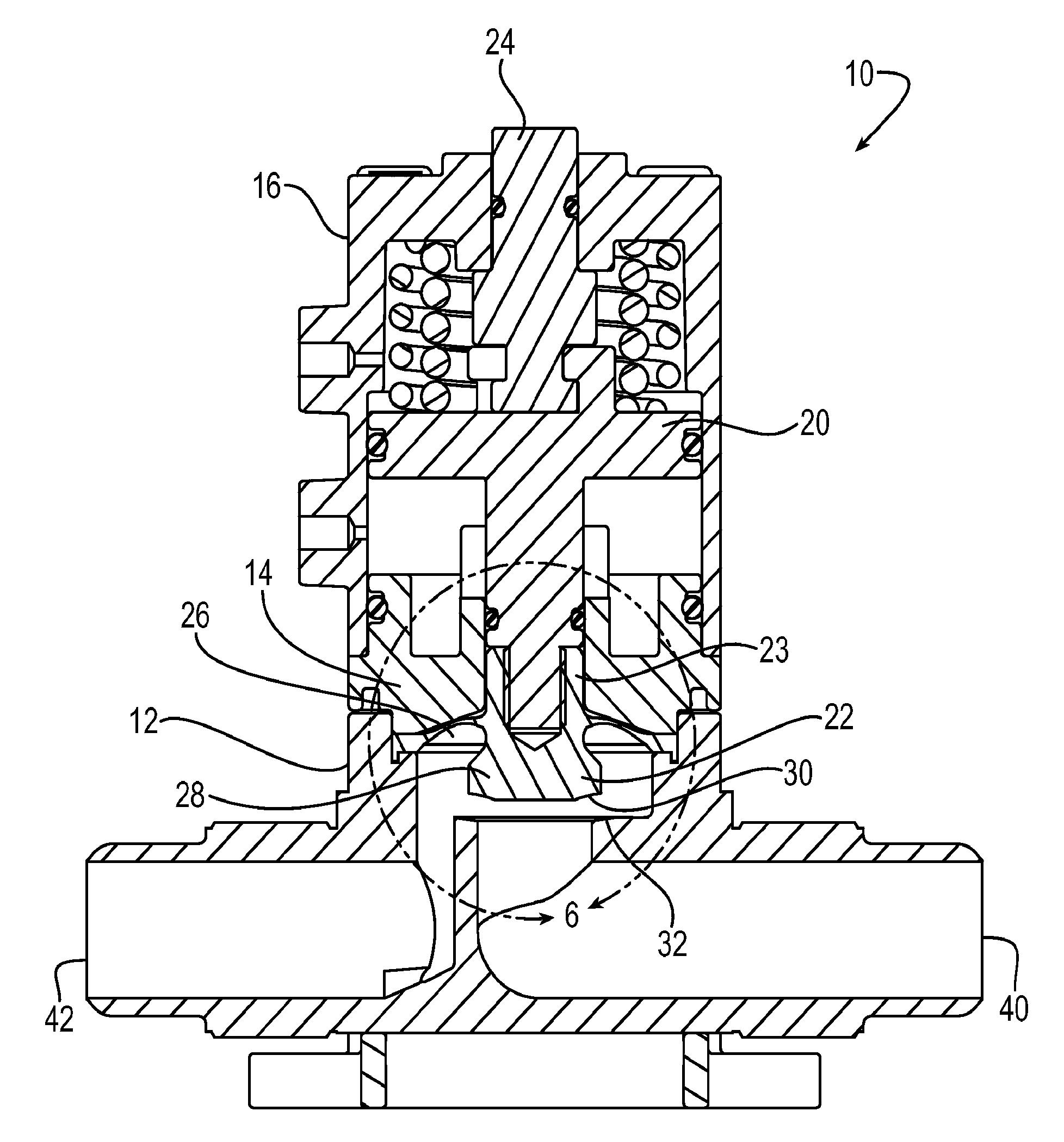
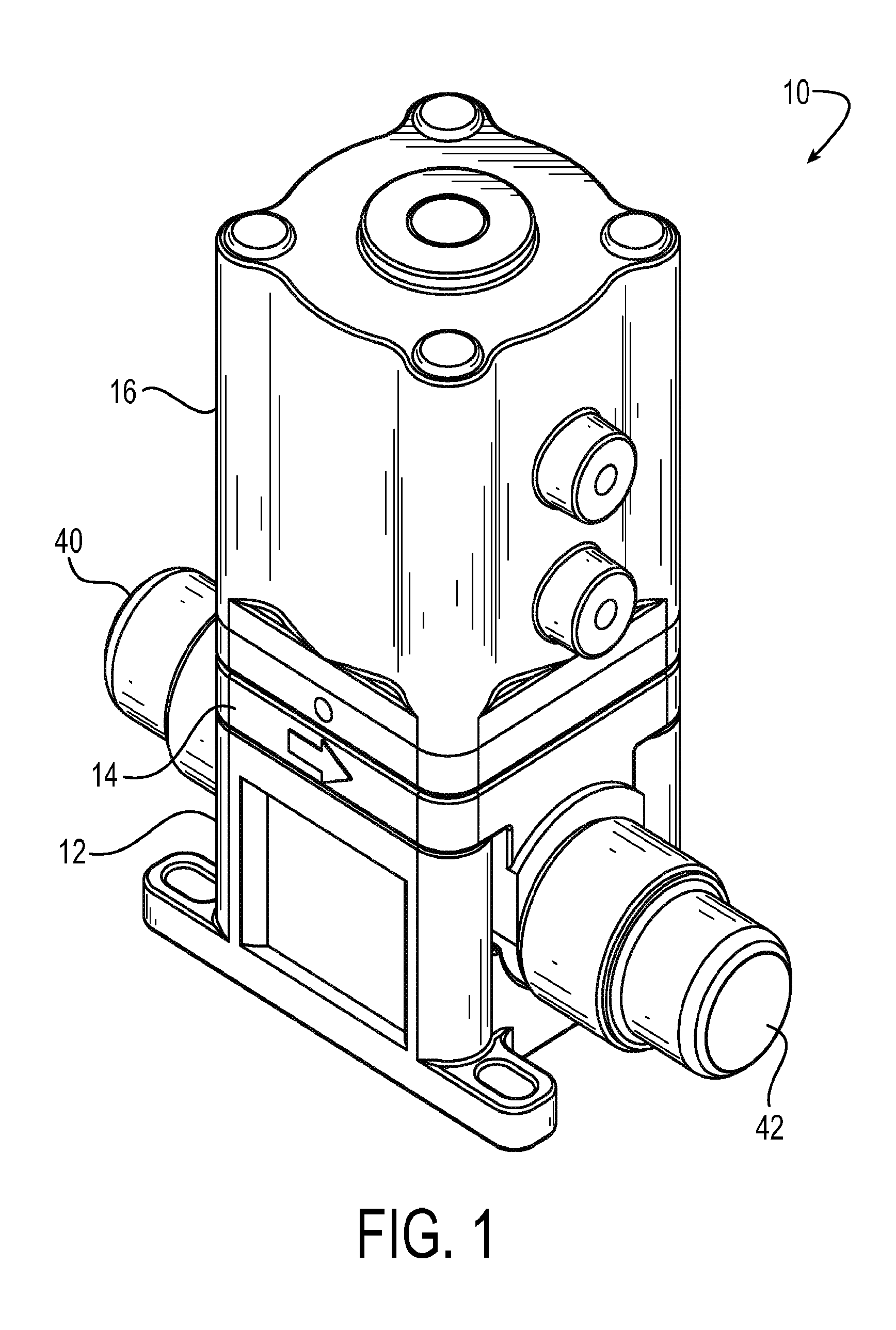
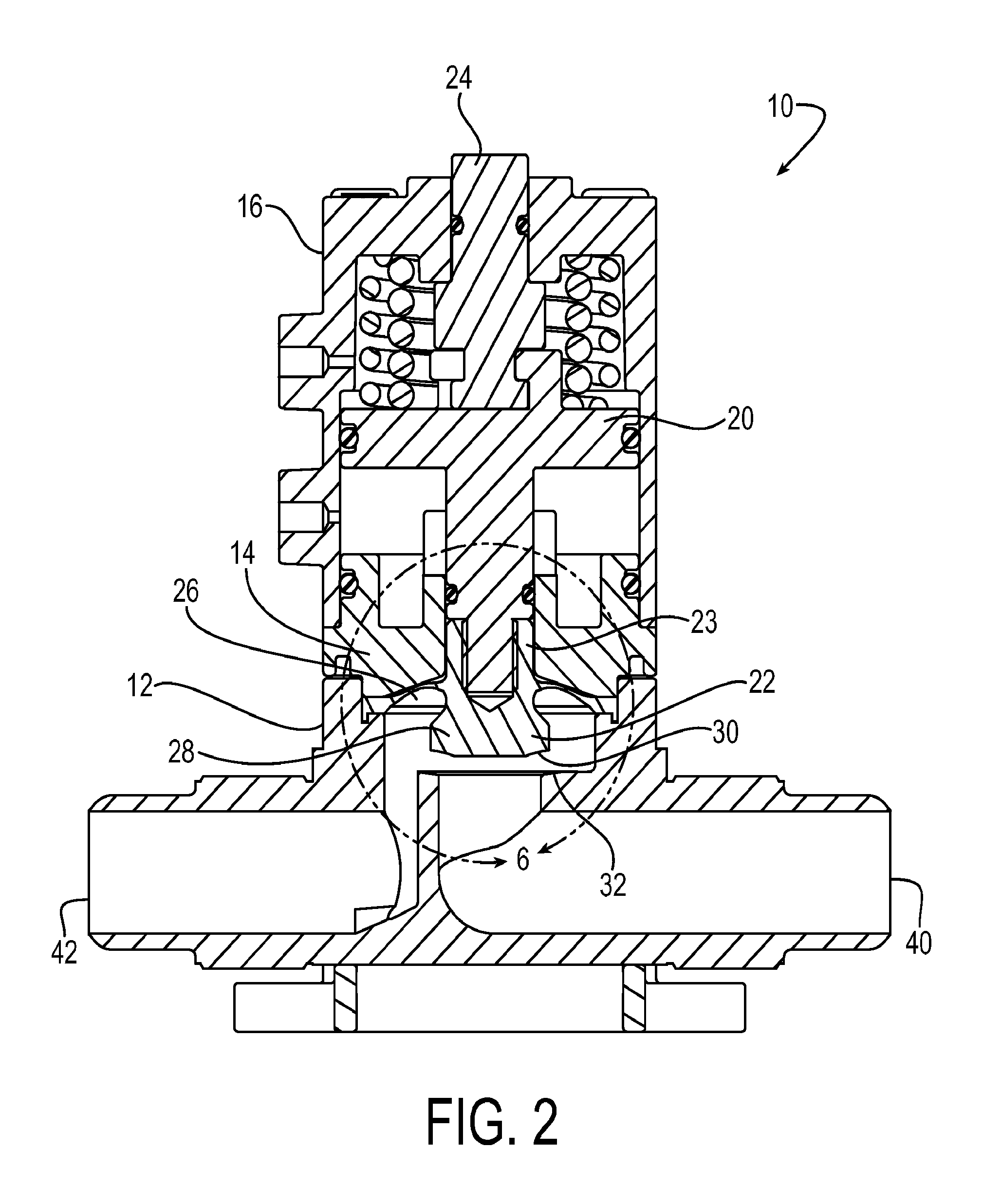
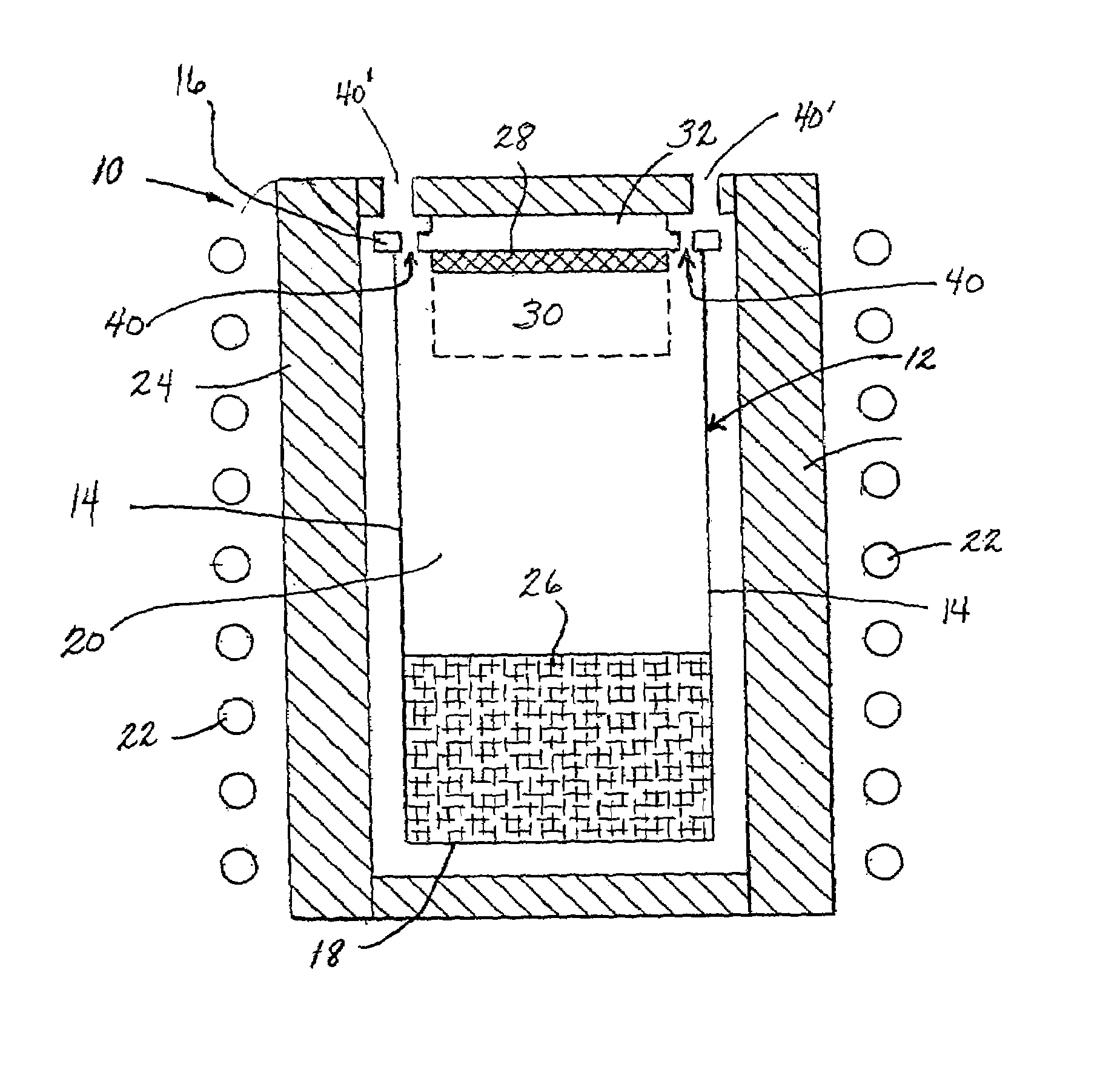
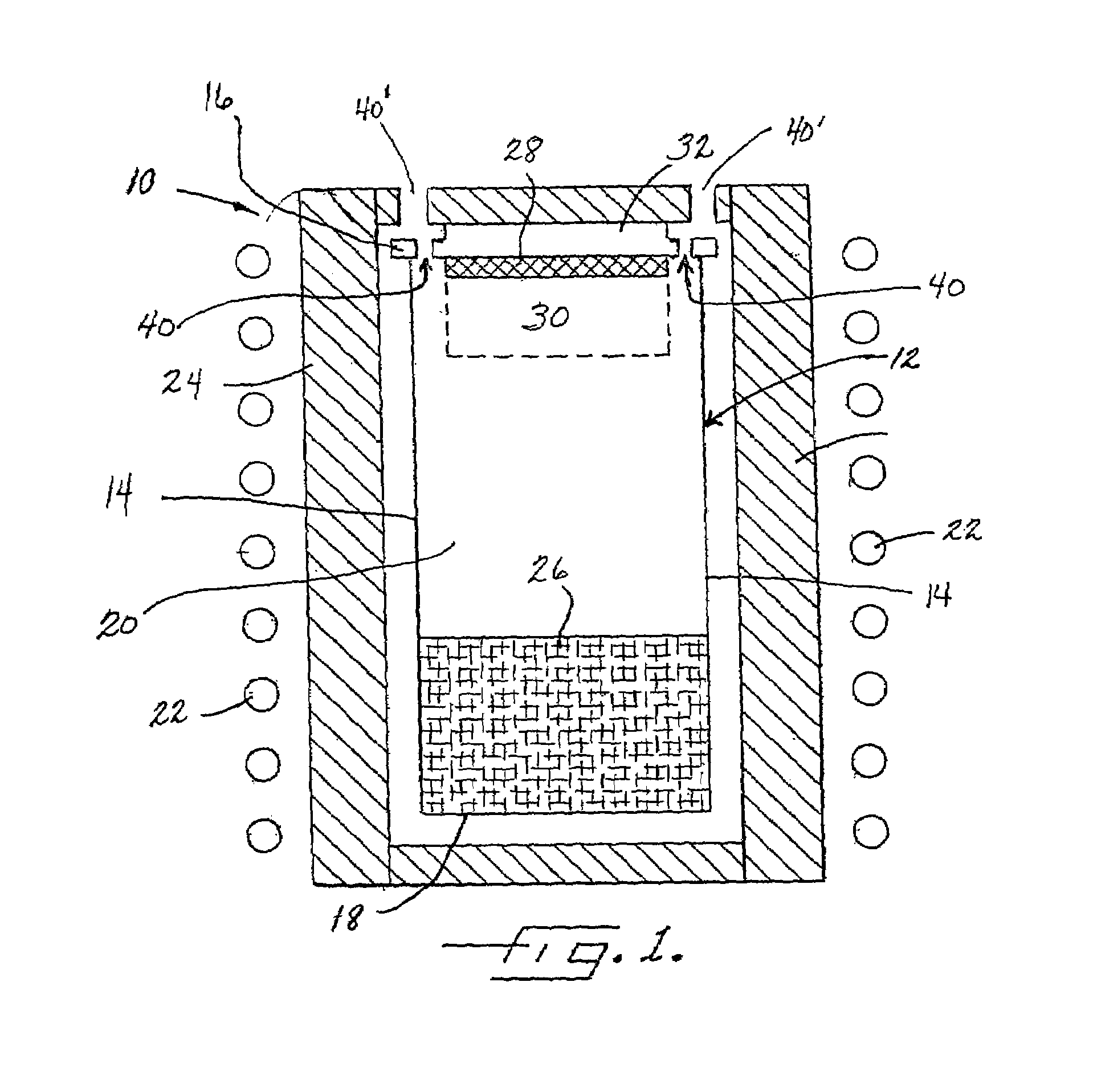
Diaphragm valve with dual point seal and floating diaphragm web
ActiveUS20150369379A1Extend valve lifeImprove reliabilitySpindle sealingsDiaphragm valvesPistonEngineering
A high purity valve (10) includes a valve body (12) having an inlet (40) and an outlet (42) separated by a valve seat (32), and a diaphragm (22) having a central stem (23) that has a first end coupled to a piston (20) for actuating the valve, and a poppet (28) for engaging the valve seat to close the valve. The poppet forms a dual point seal (50 / 52, 50′ / 52′) with the valve seat having at least two points of contact between an annular surface (30) of the poppet and the valve seat. The annular surface of the poppet may be either a concave surface or a convex surface that provides the dual point seal. The valve has a retainer (14) adjacent the diaphragm, and the diaphragm has a flexible web (26) that extends radially outward from the central stem. The retainer has a surface (60) adjacent the web, and the surface is spaced apart from the web such that the web does not contact the surface when the valve is pressurized.
Owner:PARKER INTANGIBLES LLC
Solid concentrate composition for polymeric chain extension
InactiveUS20080206503A1Extension of timeMinimise concentrationProductsReagentsPolymer chemistryPolymer
A solid concentrate composition for use in promoting chain extension within a polymer, and corresponding method, includes a chain extender and a non-reactive carrier resin or a co-reactive carrier resin. The concentrate composition prevents the premature reaction of the chain extender within a molding apparatus, increasing the dispersion of the chain extender throughout the polymer, and thereby preventing gelation and promoting homogeneous chain extension.
Owner:CLARIANT FIANCE (BVI) LTD
Compositions for boron delivery to mammalian tissue
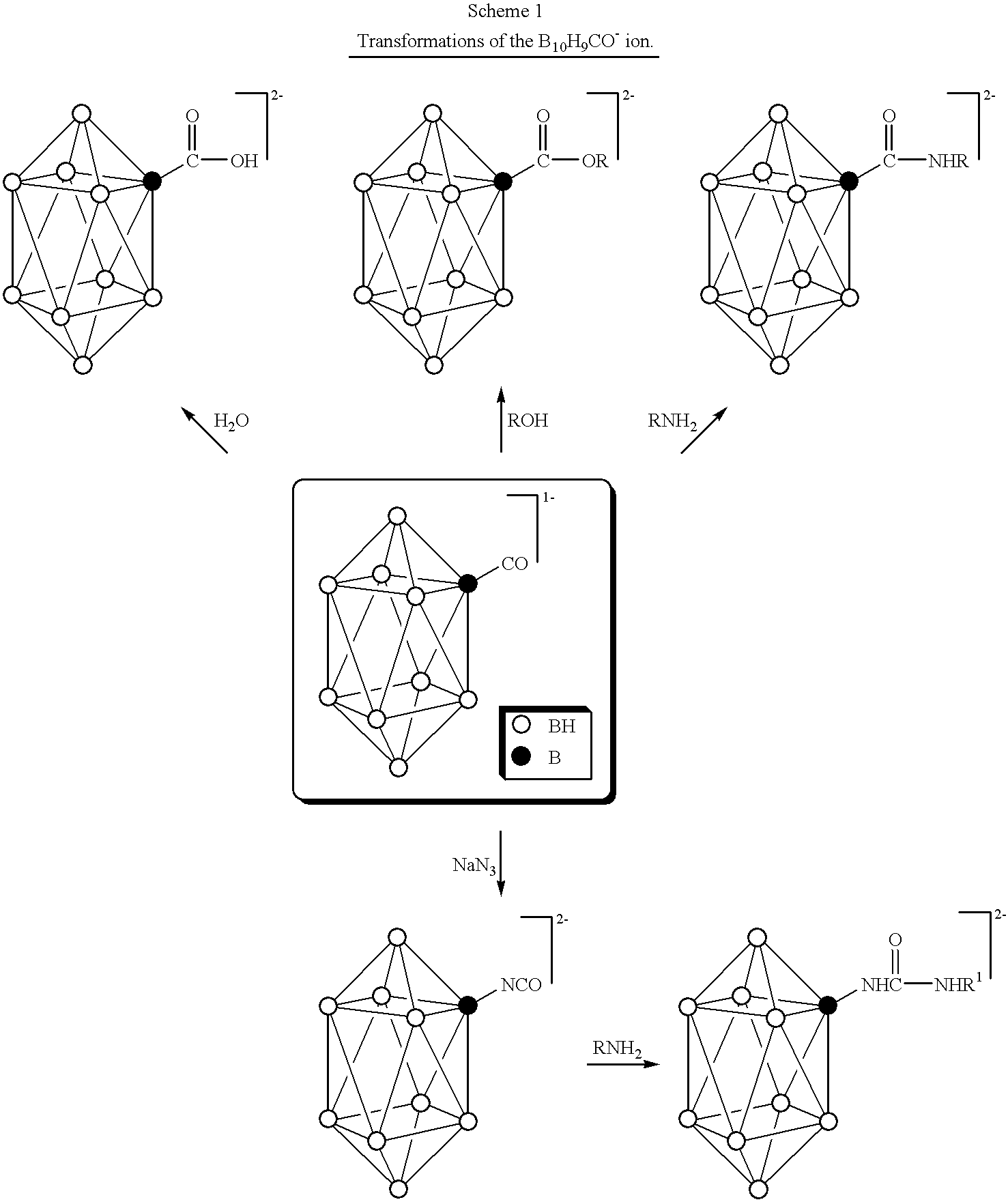
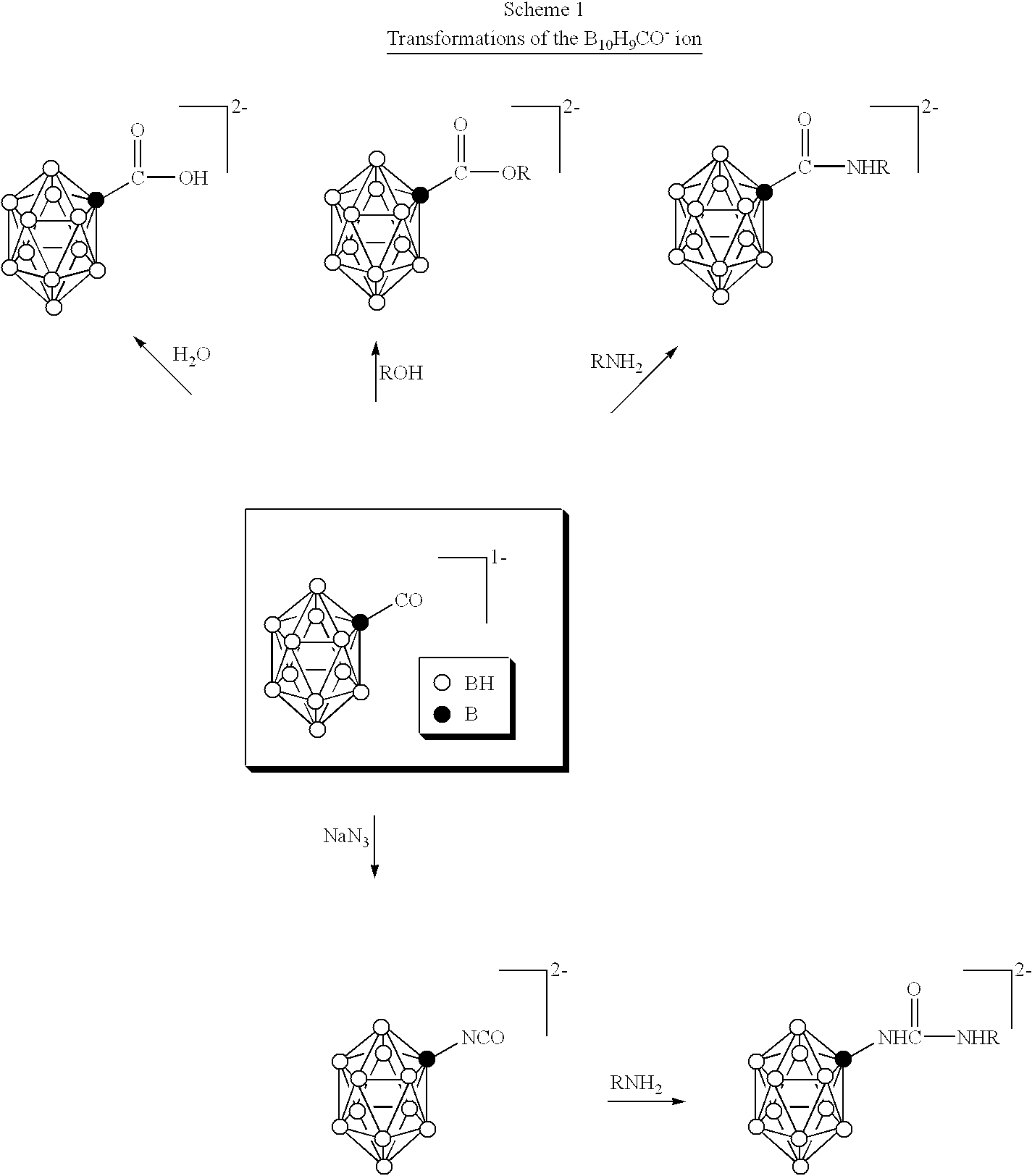
InactiveUS6274116B1Minimize concentrationMinimise concentrationIn-vivo radioactive preparationsEnergy modified materialsAbnormal tissue growthElectron donor
Boron neutron capture therapy can utilize XyB20H17L where X is an alkali metal, y is 1 to 4, and L is a two electron donor such as NH3, and Na2B10H9NCO, among others. These borane salts may be used free or encapsulated in liposomes. Liposomes may also have embedded within their bilayers carboranes to increase the amount of delivered 10B and / or to increase the tumor specificity of the liposome.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
Transistor, fabricating method thereof and flat panel display therewith
ActiveUS20100219415A1Minimise currentMinimise concentrationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDisplay deviceEngineering
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Method of fabricating thin film transistor
InactiveUS7452790B2Minimise concentrationFrom gel statePolycrystalline material growthMetal catalystAmorphous silicon
Disclosed is a method of fabricating a thin film transistor in which, in order to control the concentration of metal catalysts remaining on a polycrystalline silicon layer when an amorphous silicon layer formed on an insulating substrate is crystallized into the polycrystalline silicon layer by a super grain silicon (SGS) crystallization method, the substrate is annealed so that a very small amount of metal catalyst is adsorbed or diffused into a capping layer, and then a crystallization process is carried out, thereby minimizing the concentration of the metal catalysts remaining on the polycrystalline silicon layer, as well as forming a thick metal catalyst layer. The method includes preparing an insulating substrate; sequentially forming an amorphous silicon layer, a capping layer, and a metal catalyst layer on the substrate; first annealing the substrate to adsorb or diffuse metal catalysts into the capping layer; removing the metal catalyst layer; second annealing the substrate to crystallize the amorphous silicon layer into a polycrystalline silicon layer by means of the metal catalyst; and removing the capping layer. Thus, with the method of fabricating the thin film transistor of the present invention, it is possible to minimize the concentration of the metal catalysts remaining on the polycrystalline silicon layer, as well as to form a thick metal catalyst layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
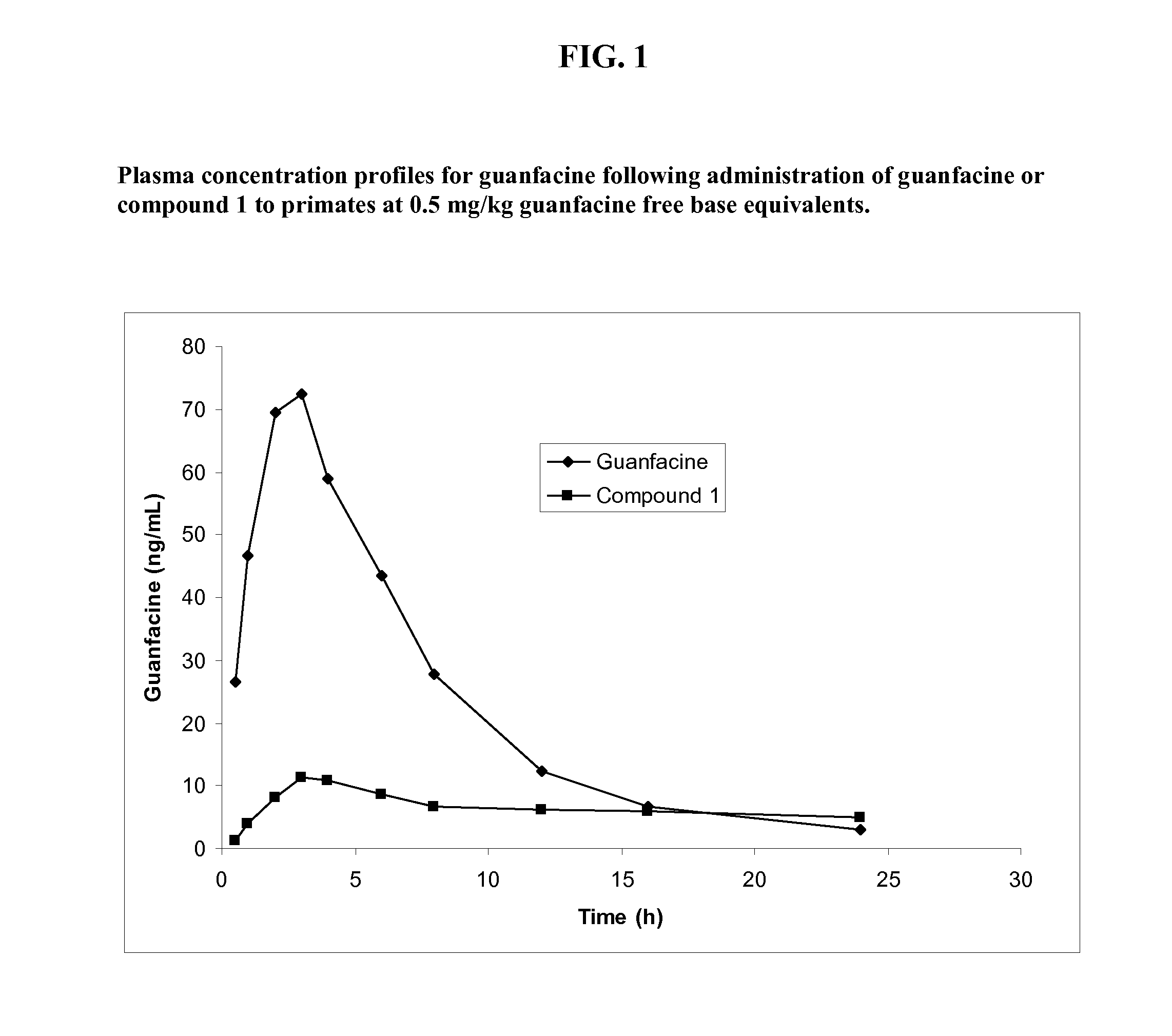
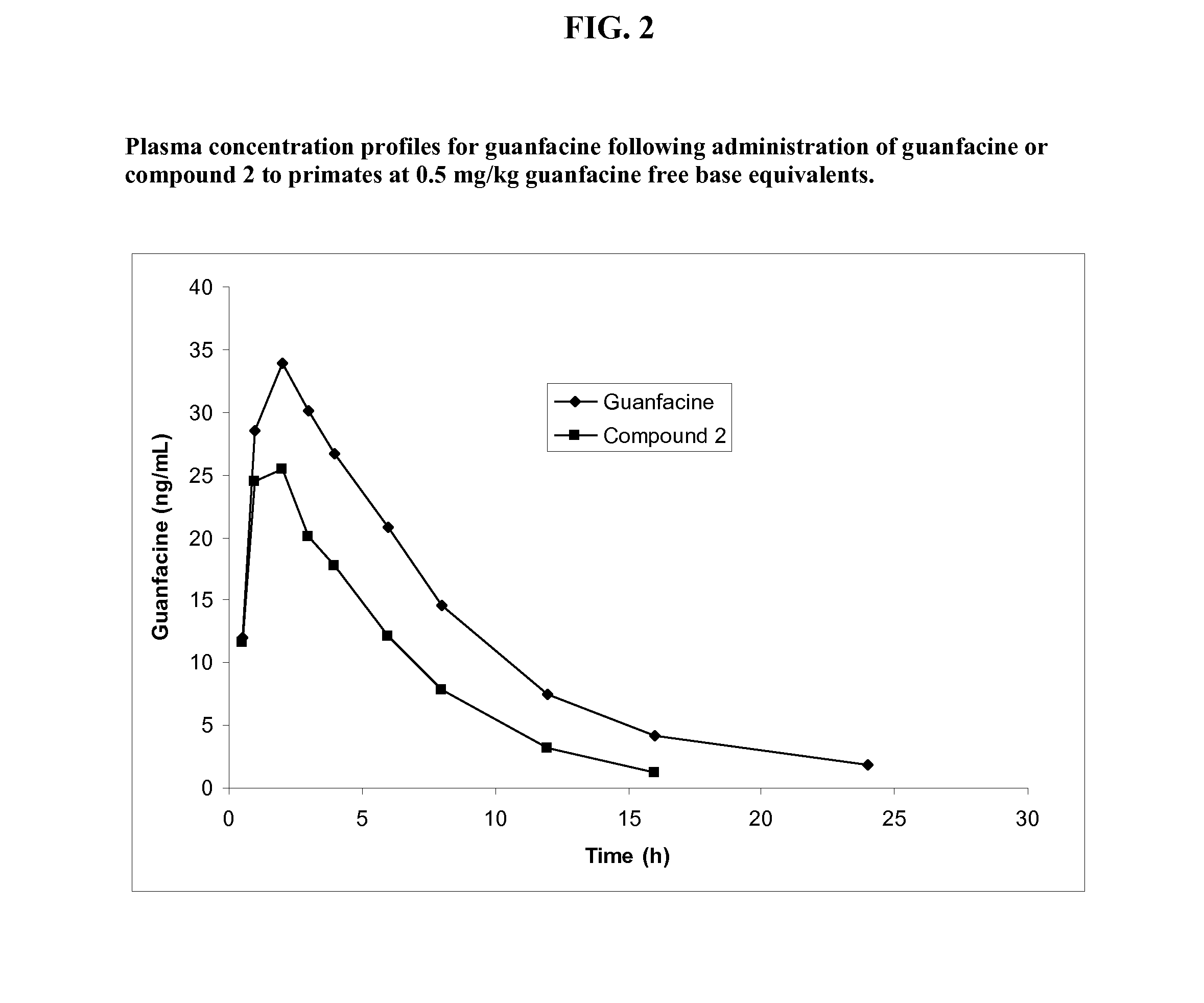
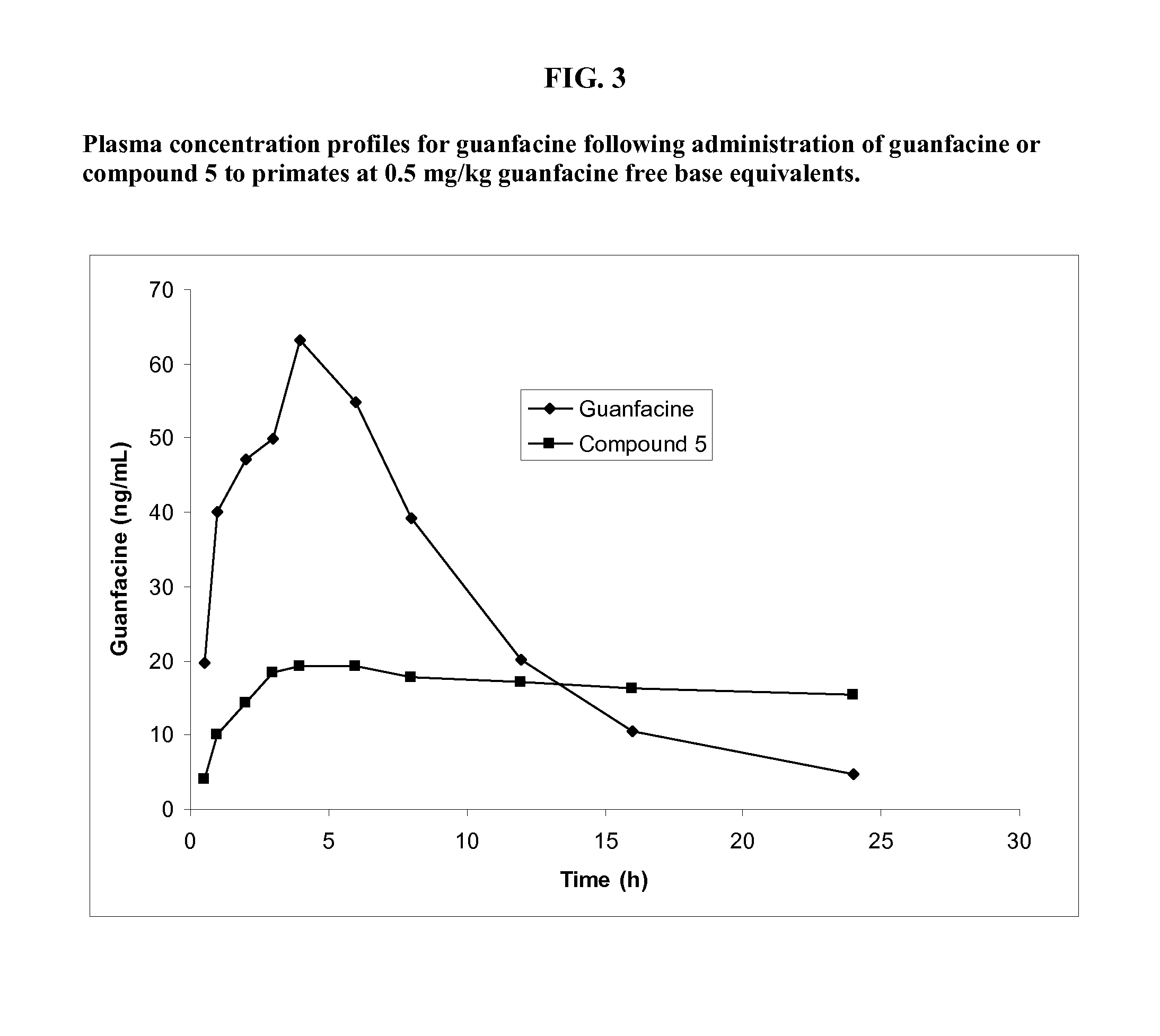
Prodrugs of guanfacine
InactiveUS20120178666A1Reducing adverse gastrointestinal side effectLower average (BiocideUrea derivatives preparationSide effectMedicine
Prodrugs of guanfacine with amino acids or short peptides, pharmaceutical compositions containing such prodrugs and a method for providing therapeutic benefit in the treatment of ADHD / ODD (attention deficient hyperactivity disorder and oppositional defiance disorder) with guanfacine prodrugs are provided herein. Additionally, methods for minimizing or avoiding the adverse gastrointestinal side effects associated with guanfacine administration, as well as improving the pharmacokinetics of guanfacine are provided herein.
Owner:SHIRE PLC
Angiogenically effective unit dose of FGF-2 and method of use
InactiveUS20050143298A1Reduce needTherapy is also rapidOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsCoronary artery diseaseArterial disease
The present invention has multiple aspects. In particular, in one aspect, the present invention is directed to a unit dose composition comprising 0.2 μg / kg to 48 μg / kg of an FGF-2 of SEQ ID NO: 2, or an angiogenically active fragment or mutein thereof in a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. In another aspect, the present invention is directed to a method for treating a human patient for coronary artery disease, comprising administering into one or more coronary vessels or a peripheral vein of a human patient in need of treatment for coronary artery disease a safe and angiogenically effective dose of a recombinant FGF-2, or an angiogenically active fragment or mutein thereof. The single unit dose composition of the present invention provides an angiogenic effect in a human CAD patient that lasts 2 months before re-treatment is required. In another aspect, the present invention is directed to a method of administration which optimizes patient's safety. In this embodiment, fluids, heparin and / or rate of infusion all play a role. In another aspect, the present invention is directed to a pharmaceutical composition comprising a therapeutically effective amount of FGF-2, alone or in combination with heparin, in a therapeutically effective carrier. The magnitude and duration of benefit were unexpected; in addition benefit with the IV route was unexpected.
Owner:NOVARTIS VACCINES & DIAGNOSTICS INC
Rimless Spectacles And Hinge Pieces For Rimless Spectacles
InactiveUS20070216856A1Prevent angular displacementHigh strengthNon-optical partsLens assembliesCamera lensStress concentration
Rimless spectacles and hinge pieces are disclosed, where the hinge pieces each include an abutment part having an abutment surface extending parallel to and in substantial abutment with a side surface of the respective lens and at least two corresponding pins, that are fastened to the abutment part and extend into corresponding holding holes of the lenses. The pins are rigidly connected to the inner side surfaces of the corresponding holes, so that the pins substantially are prevented from gaining an angular displacement relatively to the holes in the lens. The two pins form together with the abutment part a three-sided contact area between the hinge piece and the lens. A force or torque applied to the hinge piece is distributed over this contact area, since the construction substantially prevents any mutual movements or displacements between the hinge piece and the lens, and the stresses are consequently distributed and fatal stress concentrations leading to damages and fractures of the lens are avoided.
Owner:EVA TYBRING +2
Apparatus and method for the production of bulk silicon carbide single crystals
ActiveUS7323052B2Minimise concentrationMinimize intrinsic point defects formedAfter-treatment apparatusPolycrystalline material growthGas phaseOptoelectronics
An apparatus and method for growing bulk single crystals of silicon carbide is provided. The apparatus includes a sublimation chamber with a silicon vapor species phase outlet that allows the selective passage of atomic silicon vapor species while minimizing the concurrent passage of other vapor phase species. The apparatus can provide control of vapor phase stoichiometry within the sublimation chamber, which in turn can allow the production of bulk silicon carbide single crystals with reduced intrinsic point defects concentration.
Owner:CREE INC
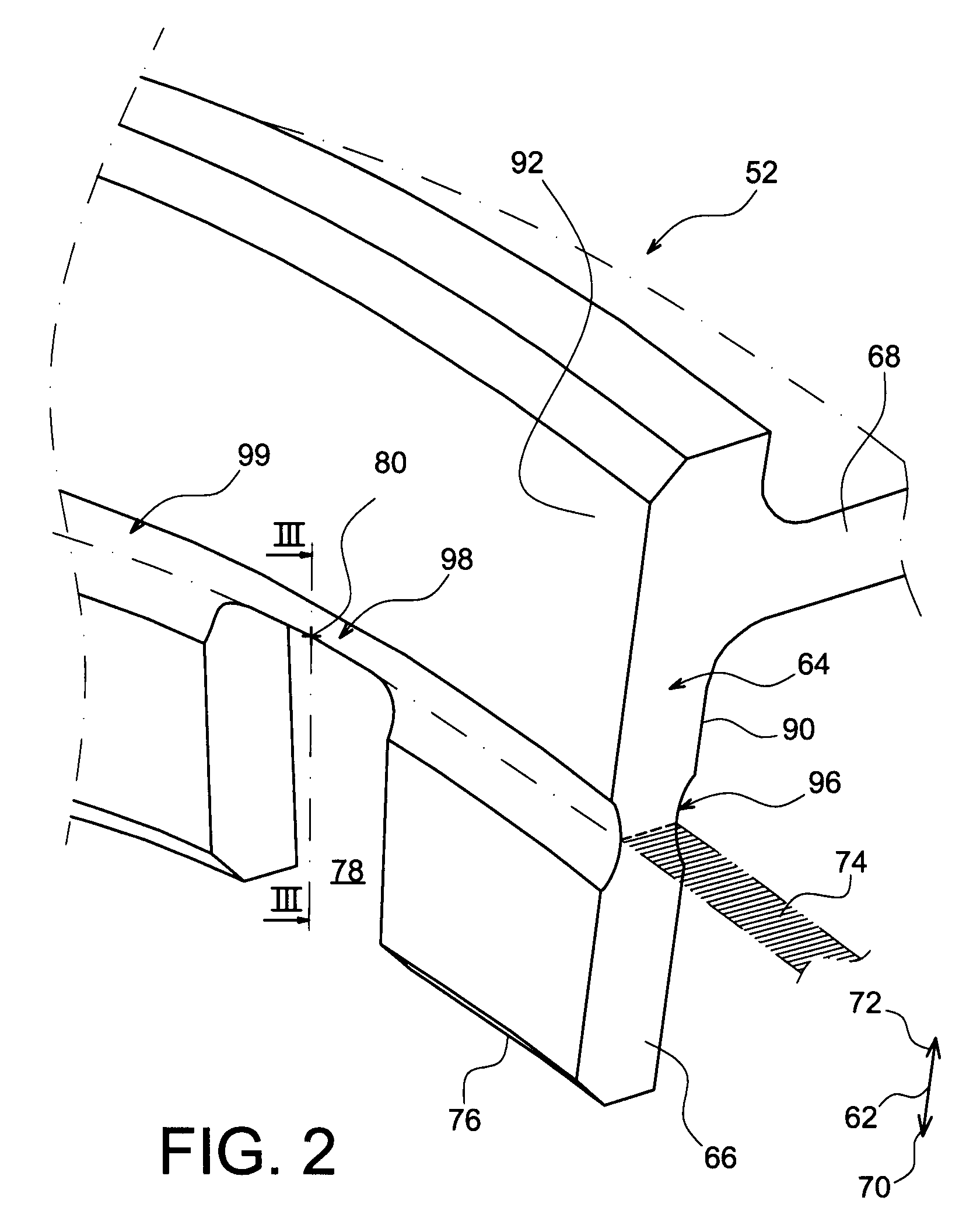
Balancing system for turbomachine rotor
The present invention relates to a turbomachine rotor balancing system comprising a balancing flange (52) provided with through-passageways (78), the system further comprising balance weights (54) each mounted fixedly on the flange (52) by means of a first and a second screw / nut assembly (56a, 56b) having a first and a second screw (84, 84) passing through a first and a second passageway (78, 78). According to the invention, said first screw is pressing against a first tangential end side (116) of the first through-passageway, and at a distance from a second tangential end side, and the second screw is pressing against a second tangential end side (118) of the second through-passageway, and at a distance from the first tangential end side.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
Enhancement of bmp retention
ActiveUS20120184490A1Increase exposurePromote cell proliferationBone-inducing factorSkeletal disorderHigh rateGold standard
The use of autogenous bone graft is the current gold standard in the 1.5 million bone-grafting surgeries performed annually in the United States. Although this practice has resulted in high rates of fusion success, it is associated with increased operative time and blood loss, along with a significant degree of donor-site morbidity. Additionally, in certain settings such as revision cases, multilevel constructs, or in patients with medical comorbidities, autogenous bone graft may exist in limited quantity and quality. This significant need for a suitable alternative to autogenous bone graft has stimulated great interest in the exploration of bone graft substitutes and extenders.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Methods for boron delivery to mammalian tissue
InactiveUS6517808B1Minimise concentrationIn-vivo radioactive preparationsEnergy modified materialsHigh concentrationAbnormal tissue growth
Boron neutron capture therapy can be used to destroy tumors. This treatment modality is enhanced by delivering compounds to the tumor site where the compounds have high concentrations of boron, the boron compounds being encapsulated in the bilayer of a liposome or in the bilayer as well as the internal space of the liposomes. Preferred compounds, include carborane units with multiple boron atoms within the carborane cage structure. Liposomes with increased tumor specificity may also be used.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
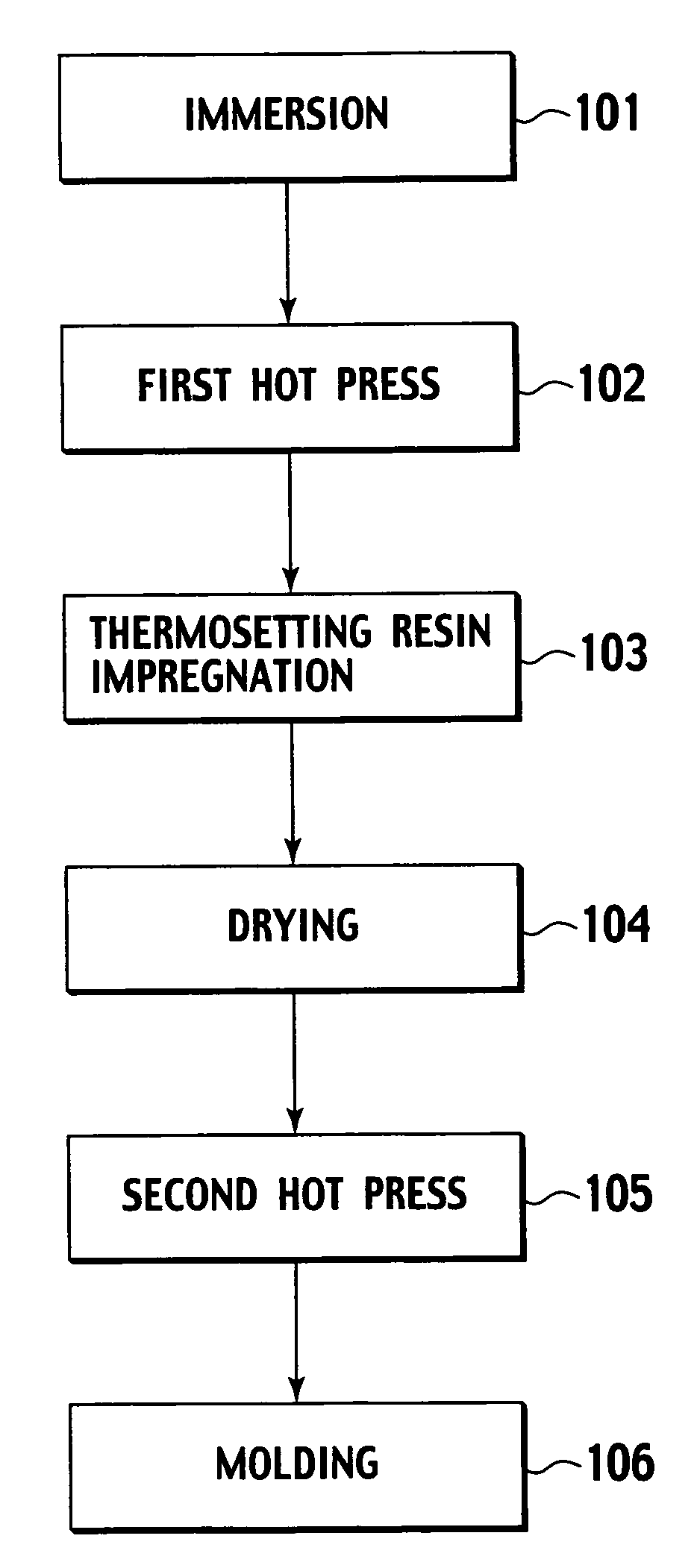
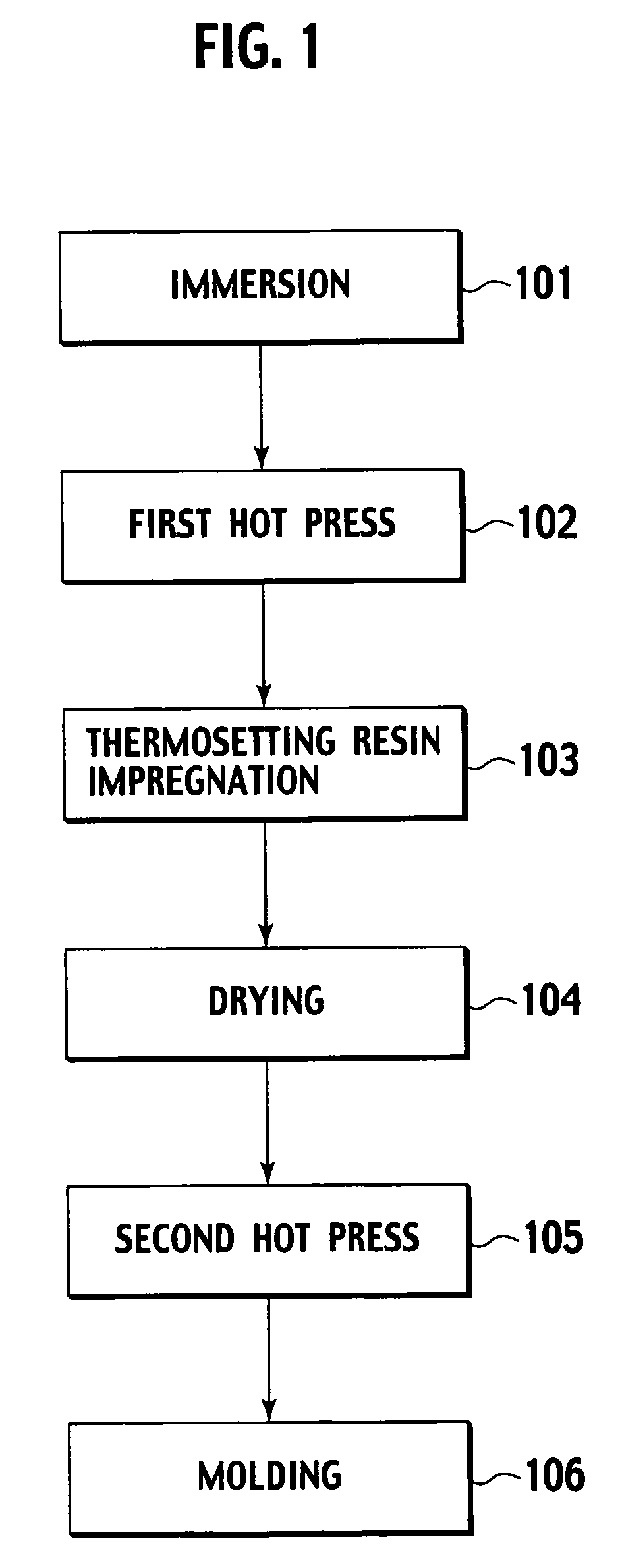
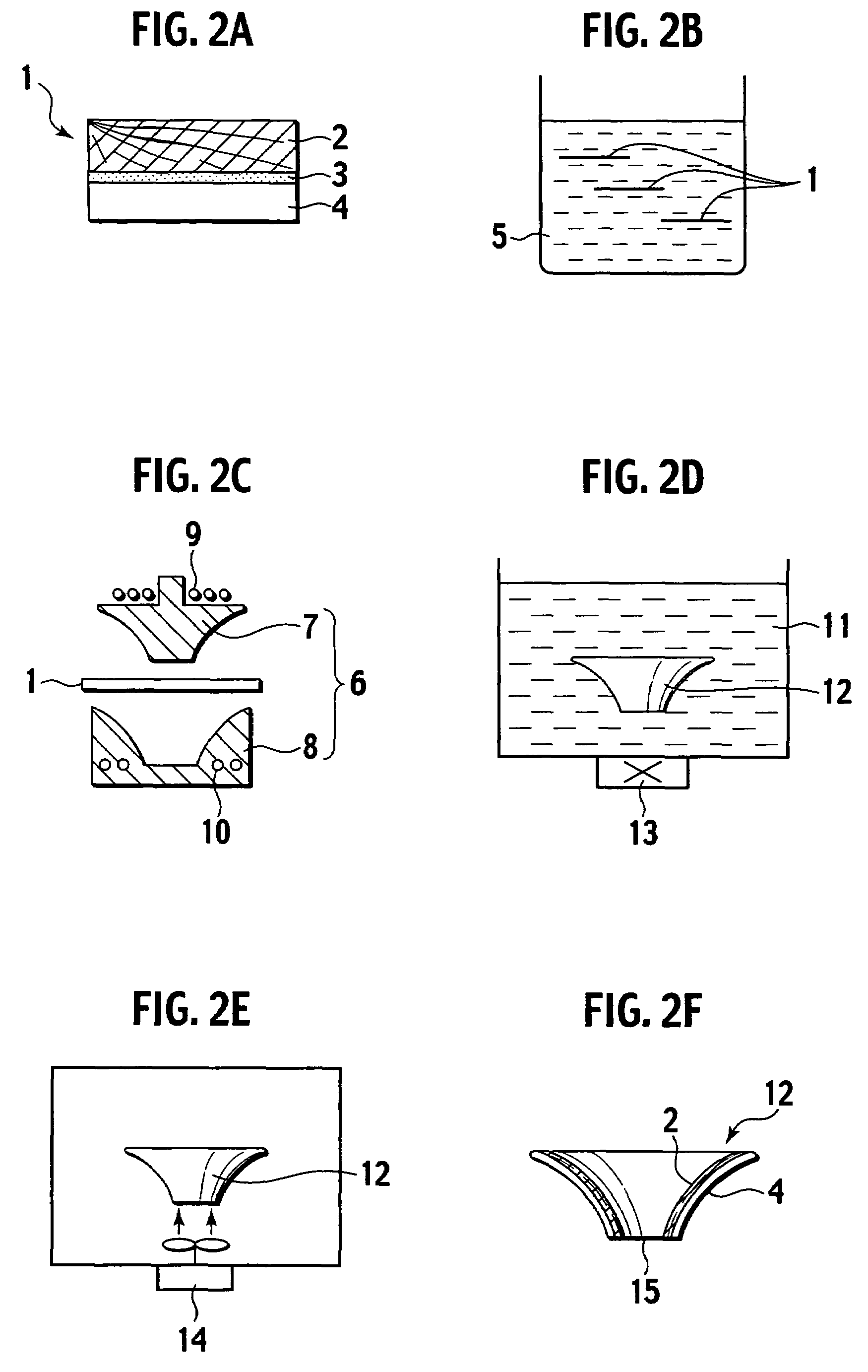
Production method of an electroacoustic transducer diaphragm, electroacoustic transducer diaphragm, and an electroacoustic transducer
ActiveUS7678218B2Minimise concentrationReduce concentrationCeramic shaping apparatusDomestic articlesTransducerEngineering
A production method for an electroacoustic transducer diaphragm includes producing an adhered sheet by adhering a sheet member on a surface of a wooden sheet having a thickness of from 0.01 mm to 3 mm, and the sheet member being made of a material different from the wooden sheet, immersing the adhered sheet into one of a solution including 0.01-1 wt % of a penetrating agent and a solution including 0.01-1 wt % of penetrating agent and 0.01-20 wt % of a wetting agent, and molding the adhered sheet obtained by the immersing step so that the immersed adhered sheet has a predetermined shape of the electroacoustic transducer diaphragm.
Owner:JVC KENWOOD CORP
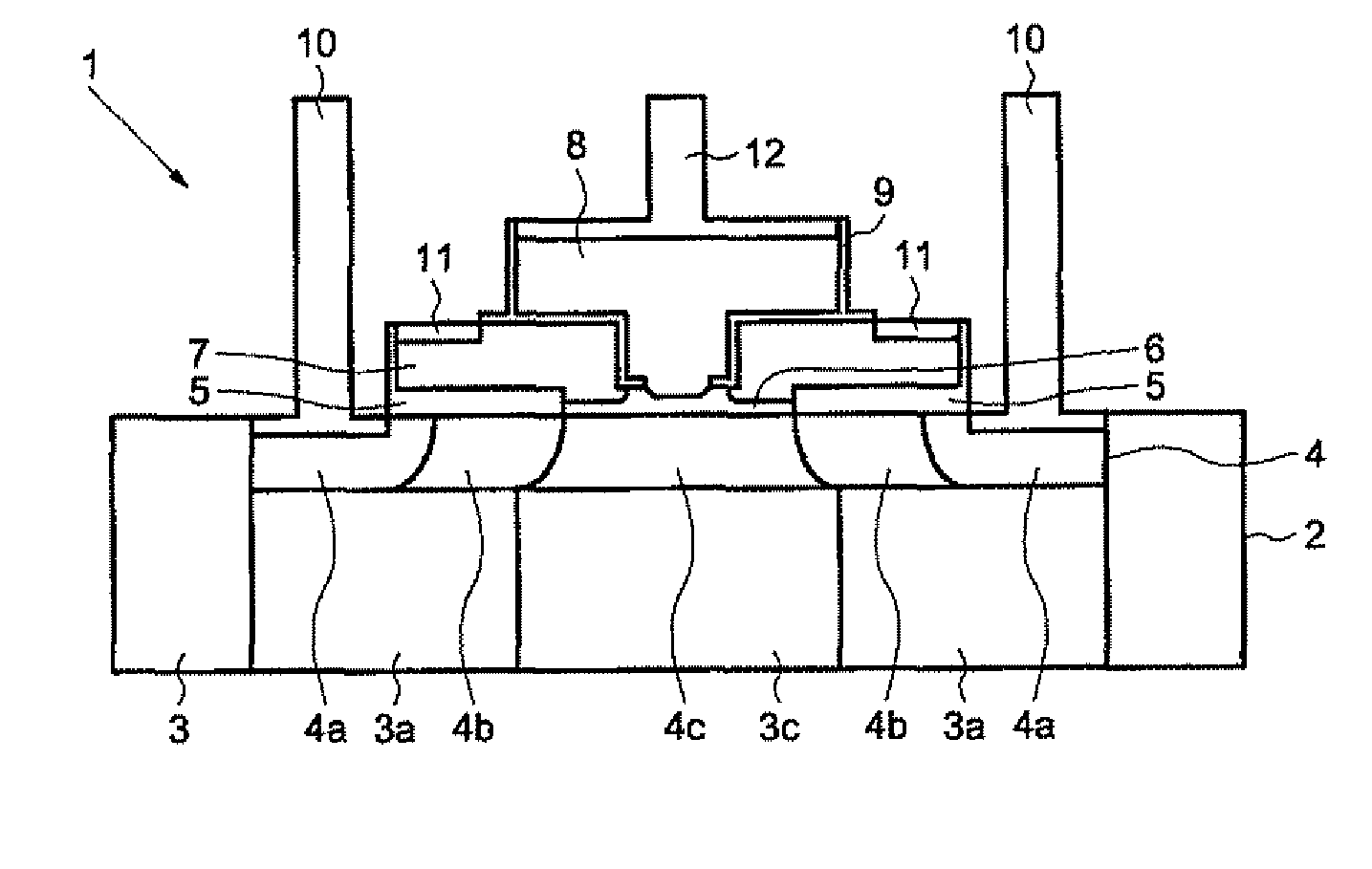
Integrated circuit comprising a gradually doped bipolar transistor and corresponding fabrication process
ActiveUS20070108555A1Efficient preparationEasy to controlSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesManufacturing technologyIntegrated circuit
An integrated circuit includes a bipolar transistor comprising a substrate and a collector formed in the substrate. The collector includes a highly doped lateral zone, a very lightly doped central zone and a lightly doped intermediate zone located between the central zone and the lateral zone 4a of the collector. The substrate includes a lightly doped lateral zone and a highly doped central zone. The dopant species in the zone of the substrate are electrically inactive.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com