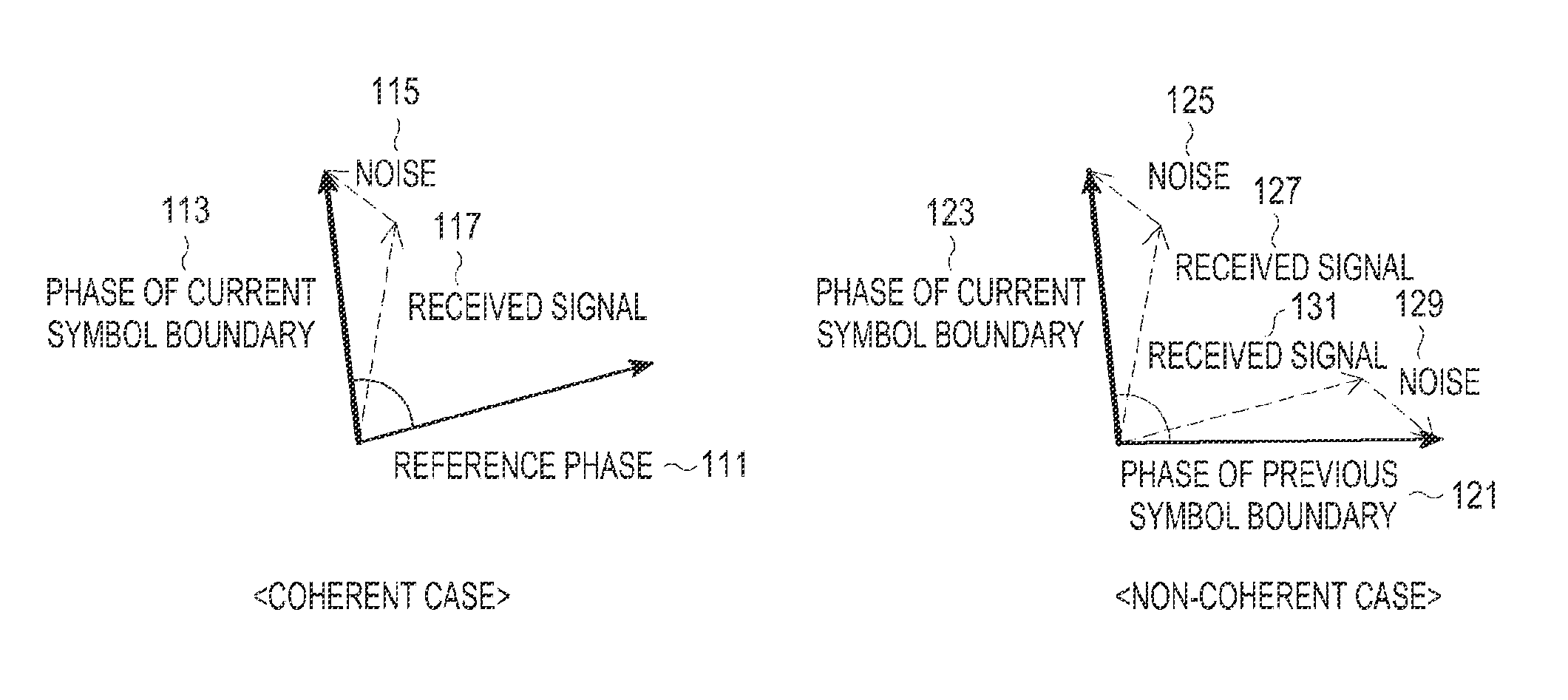Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
109results about How to "Lower implementation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
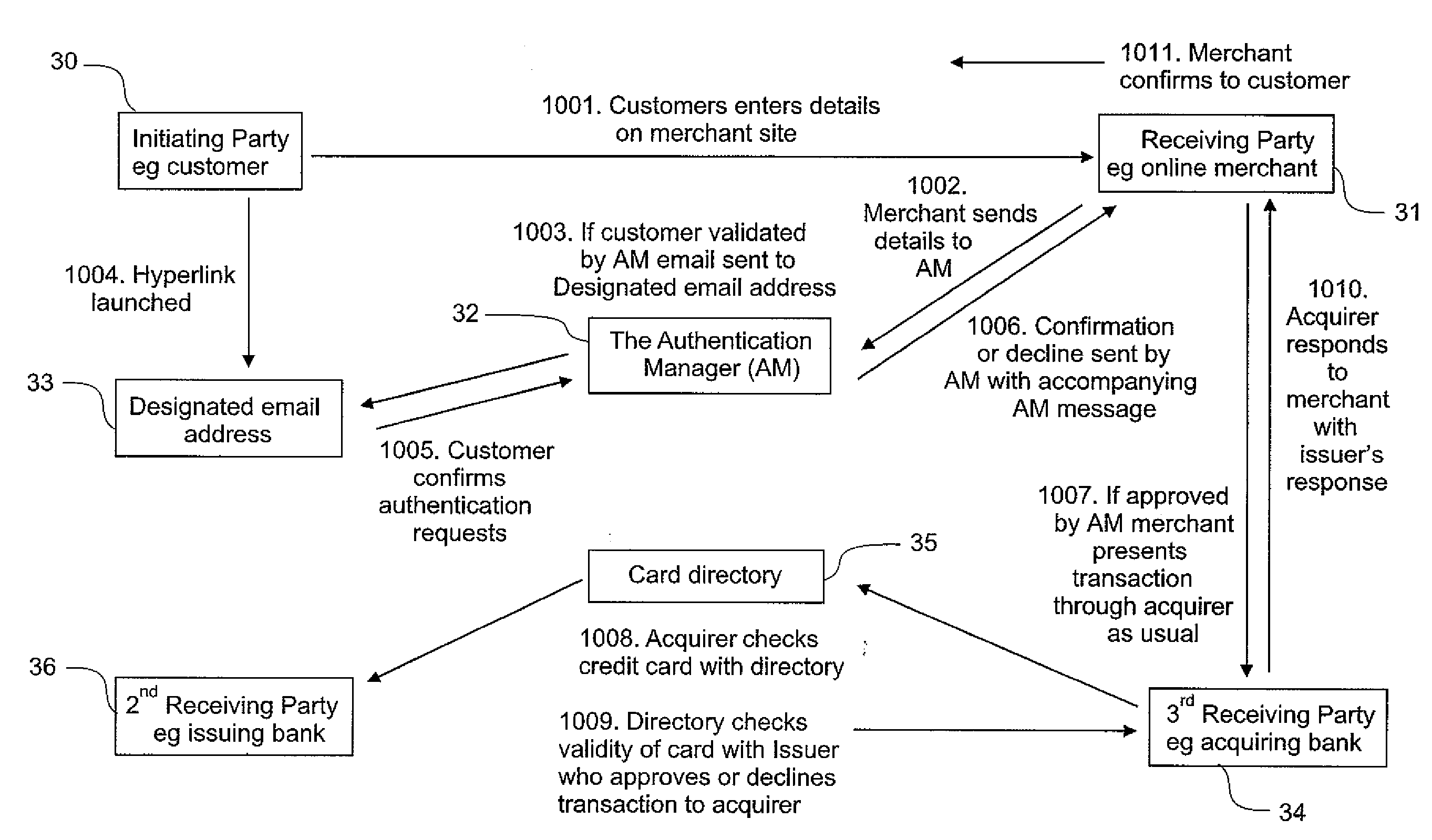
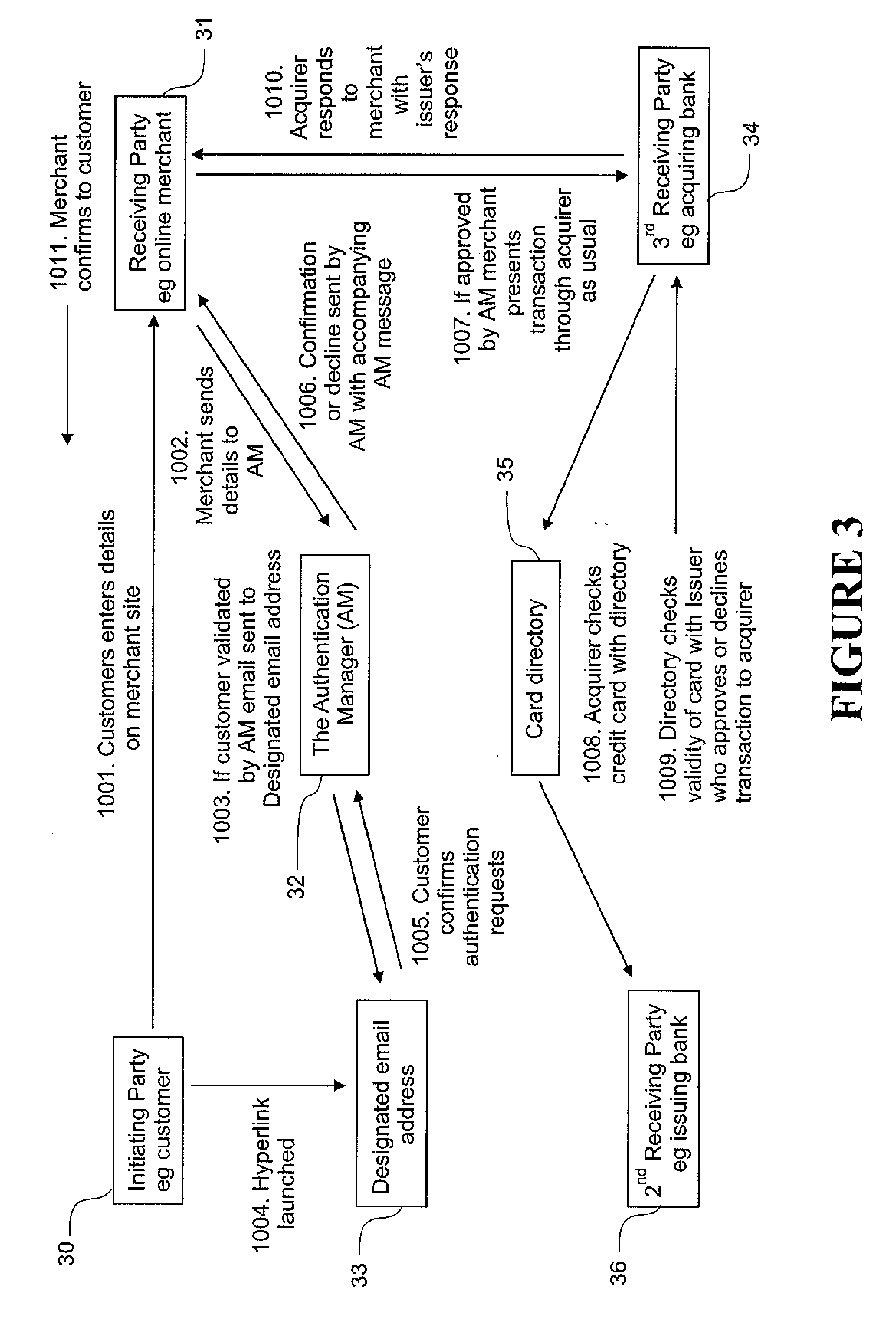
A Method of Authentication
InactiveUS20060173776A1Low cost of implementation and operationImprove securityFinancePayment architectureInternet privacyQuestion answer
The present invention relates to the authentication of parties involved in transactions performed remotely over a network, such as the Internet. When a first party initiates a transaction with a second party, the second party can request authentication of the first party. Authentication is carried out by sending a communication to the first party, which includes a redirection to a transaction specific location,. At the transaction specific location the first party is required to approve the transaction as well as answer some identifying question or questions. If the transaction is approved and the question or questions answered correctly, the second party is informed that the transaction can be approved.
Owner:SHALLEY BARRY
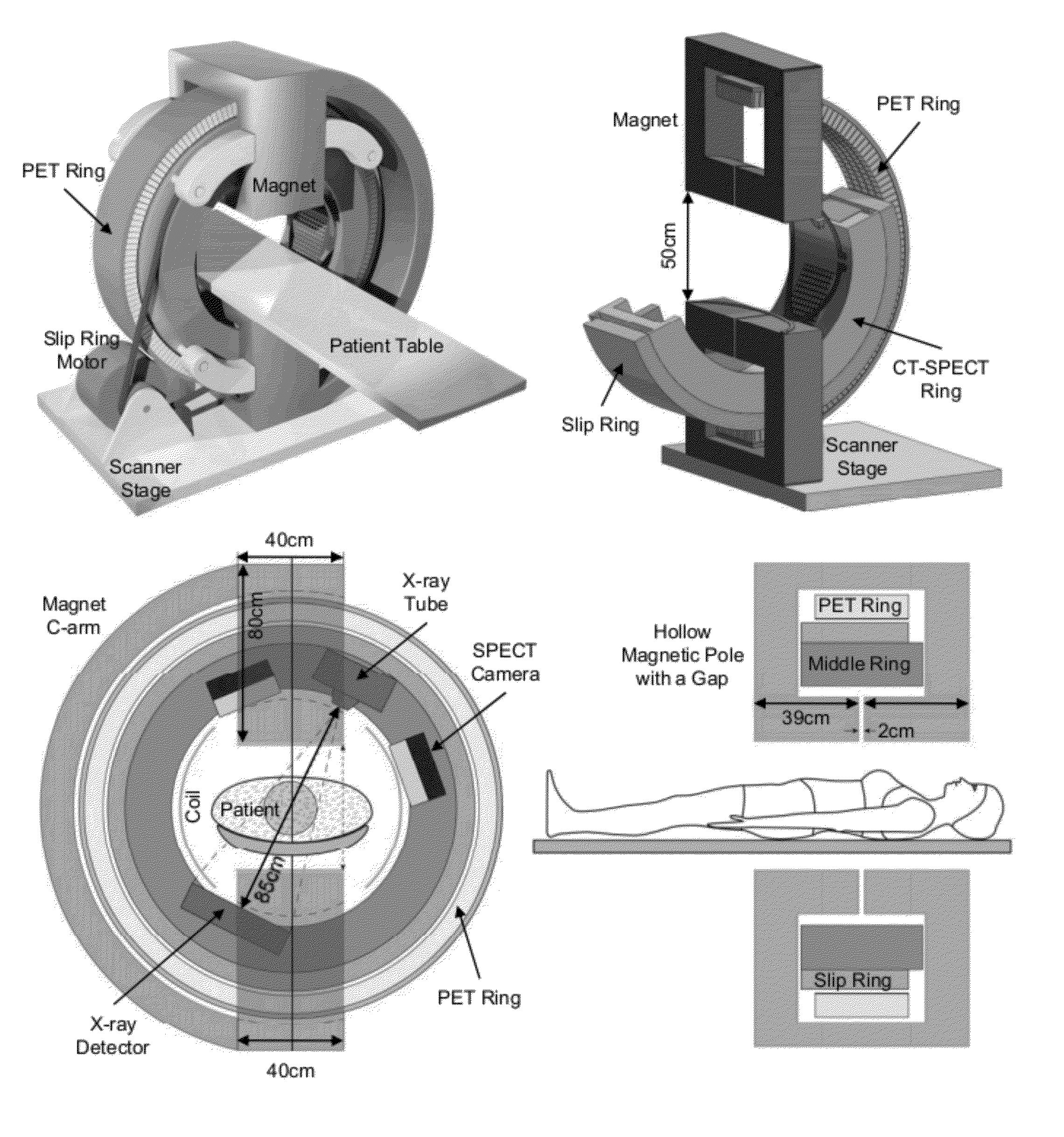
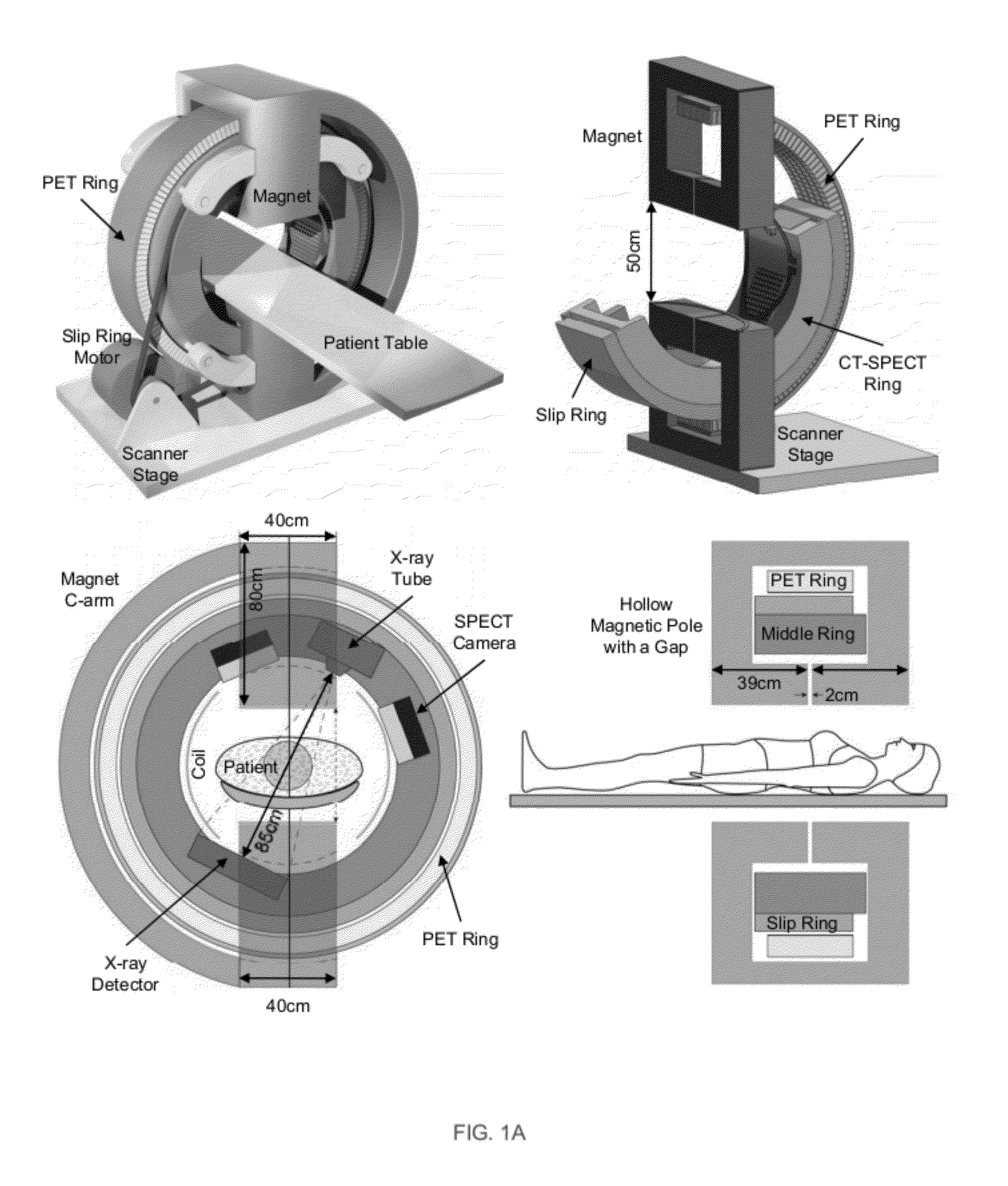
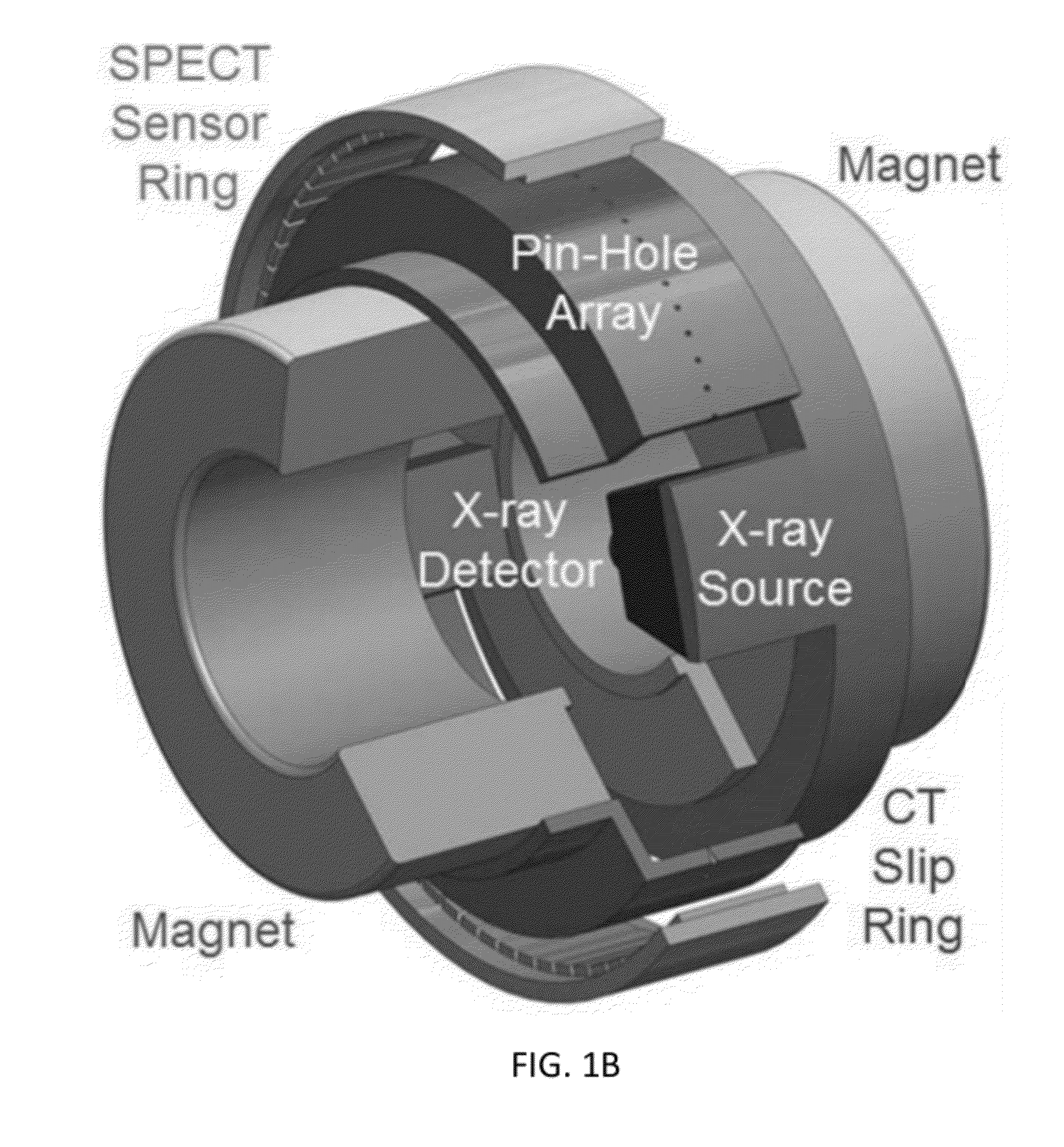
Omni-Tomographic Imaging for Interior Reconstruction using Simultaneous Data Acquisition from Multiple Imaging Modalities
InactiveUS20120265050A1Less importantLow costUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic Radiology ModalityModern medicine
Embodiments of the invention relate to omni-tomographic imaging or grand fusion imaging, i.e., large scale fusion of simultaneous data acquisition from multiple imaging modalities such as CT, MRI, PET, SPECT, US, and optical imaging. A preferred omni-tomography system of the invention comprises two or more imaging modalities operably configured for concurrent signal acquisition for performing ROI-targeted reconstruction and contained in a single gantry with a first inner ring as a permanent magnet; a second middle ring containing an x-ray tube, detector array, and a pair of SPECT detectors; and a third outer ring for containing PET crystals and electronics. Omni-tomography offers great synergy in vivo for diagnosis, intervention, and drug development, and can be made versatile and cost-effective, and as such is expected to become an unprecedented imaging platform for development of systems biology and modern medicine.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
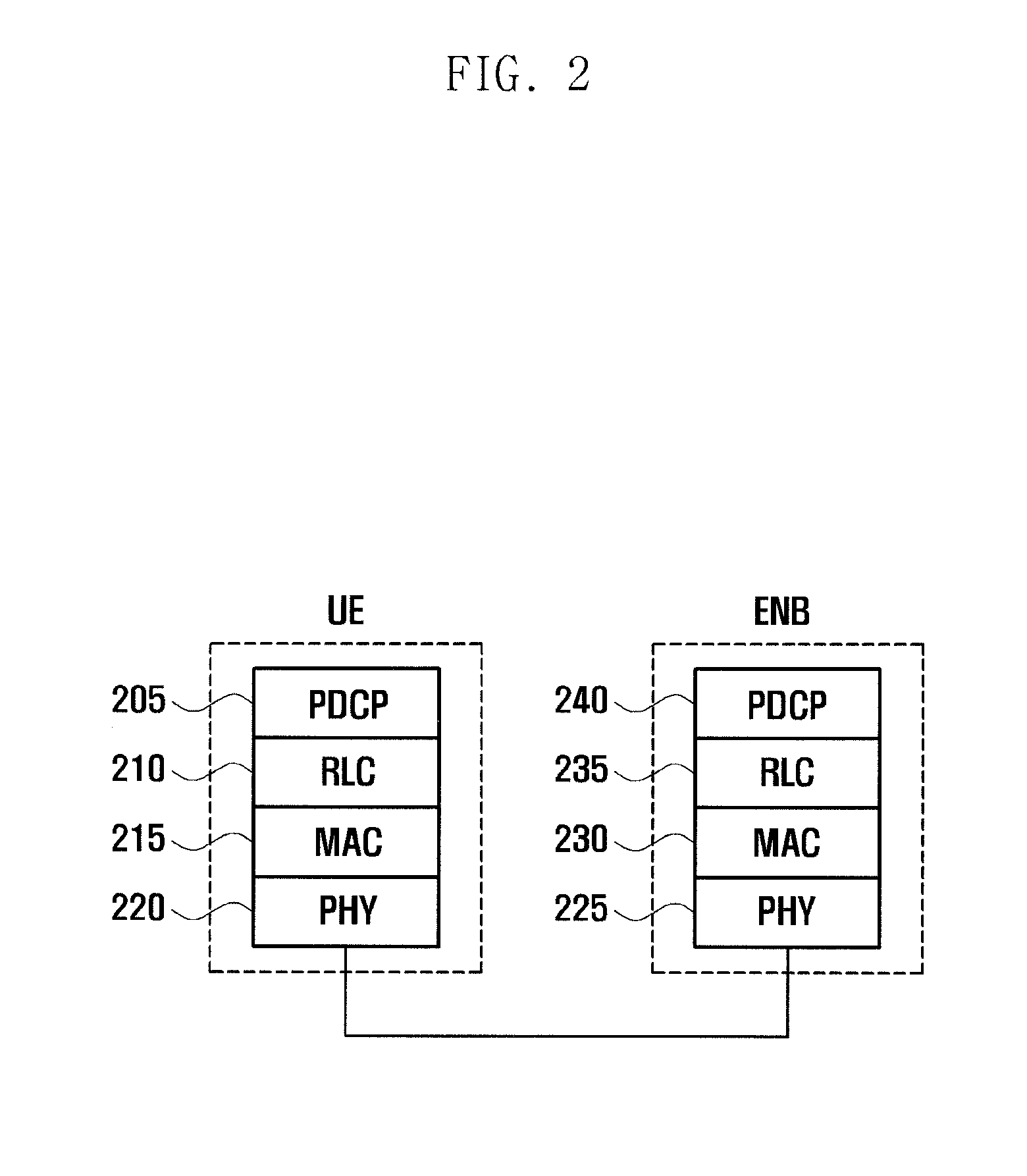
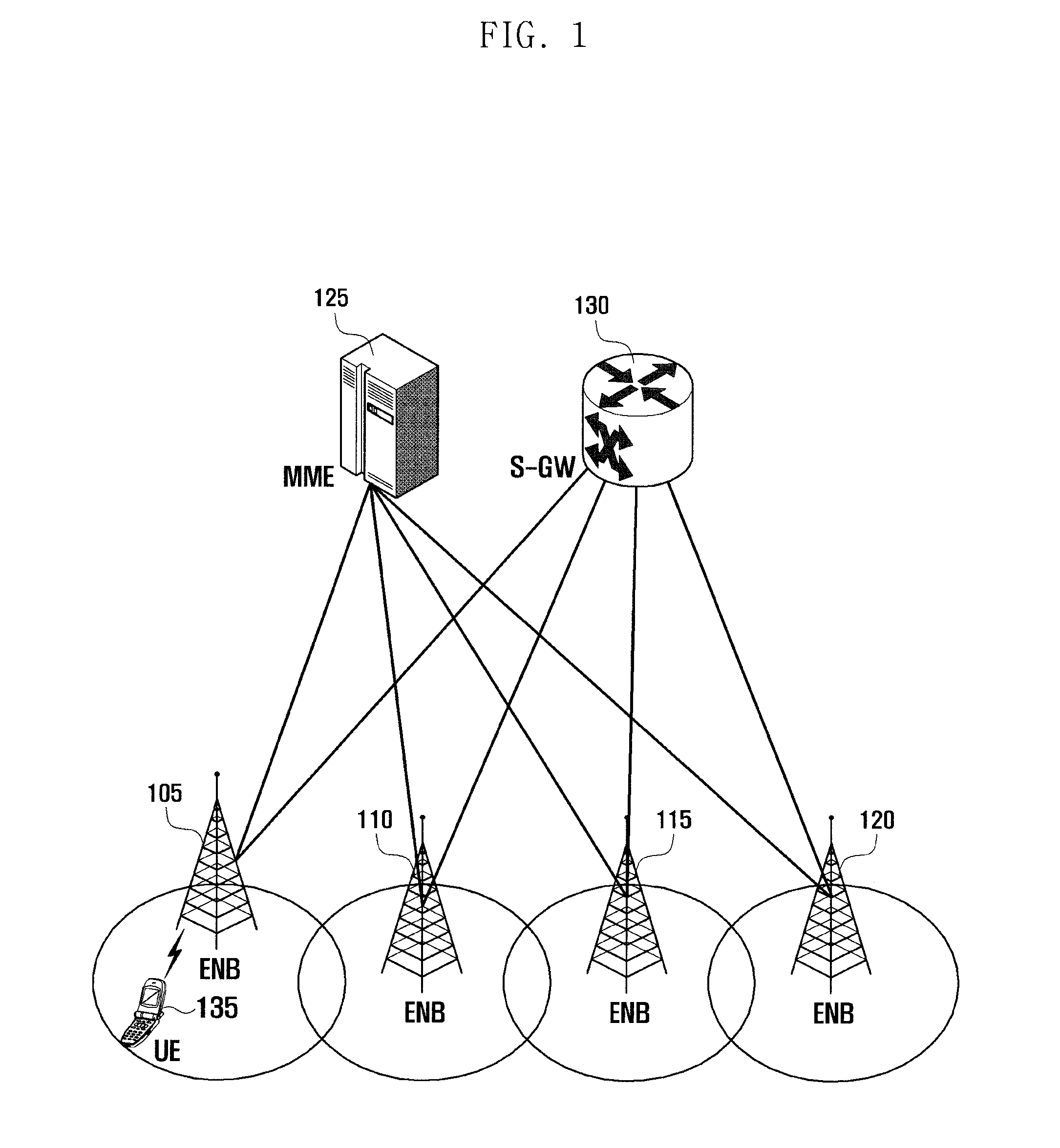
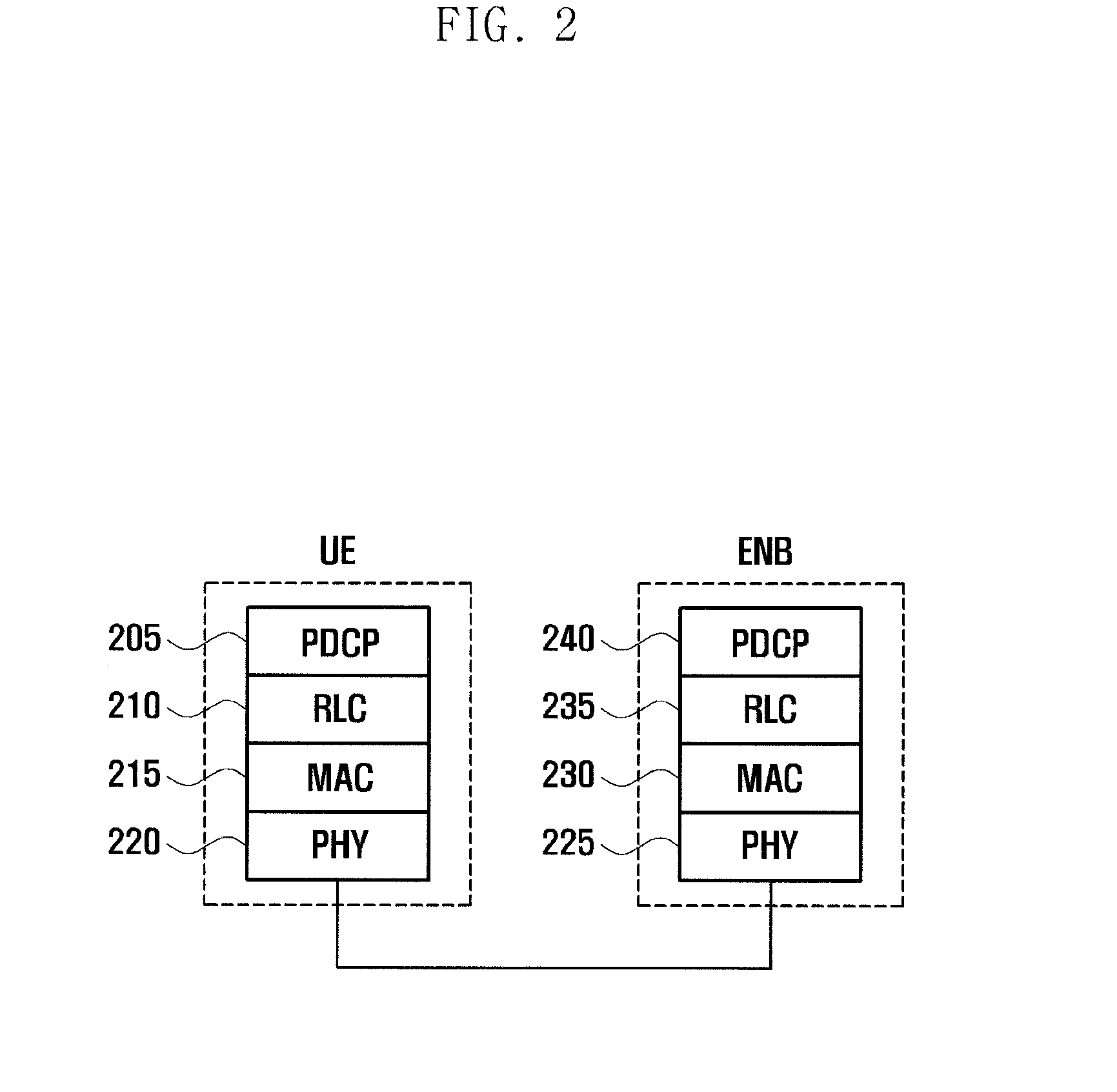
Method and apparatus for transmitting/receiving data on multiple carriers in mobile communication system
ActiveUS20130201960A1Improve uplink performanceLower implementationSynchronisation arrangementError preventionCarrier signalPrimary cell
A data transmission method and an apparatus to communicate data on multiple carriers in the mobile communication system are provided. A random access method of a terminal in a mobile communication system including primary and secondary cells operating on multiple carriers according to the present invention includes communicating data after random access in the primary cell, receiving, when the random access is triggered in the secondary cell, information for use in the secondary cell random access from the primary cell, transmitting a preamble in the secondary cell based on the received information, monitoring the primary cell to receive a Random Access Response for the secondary cell, and applying, when the Random Access Response for the secondary cell is received, the information carried in the Random Access Response to the secondary cell in which the preamble has been transmitted.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
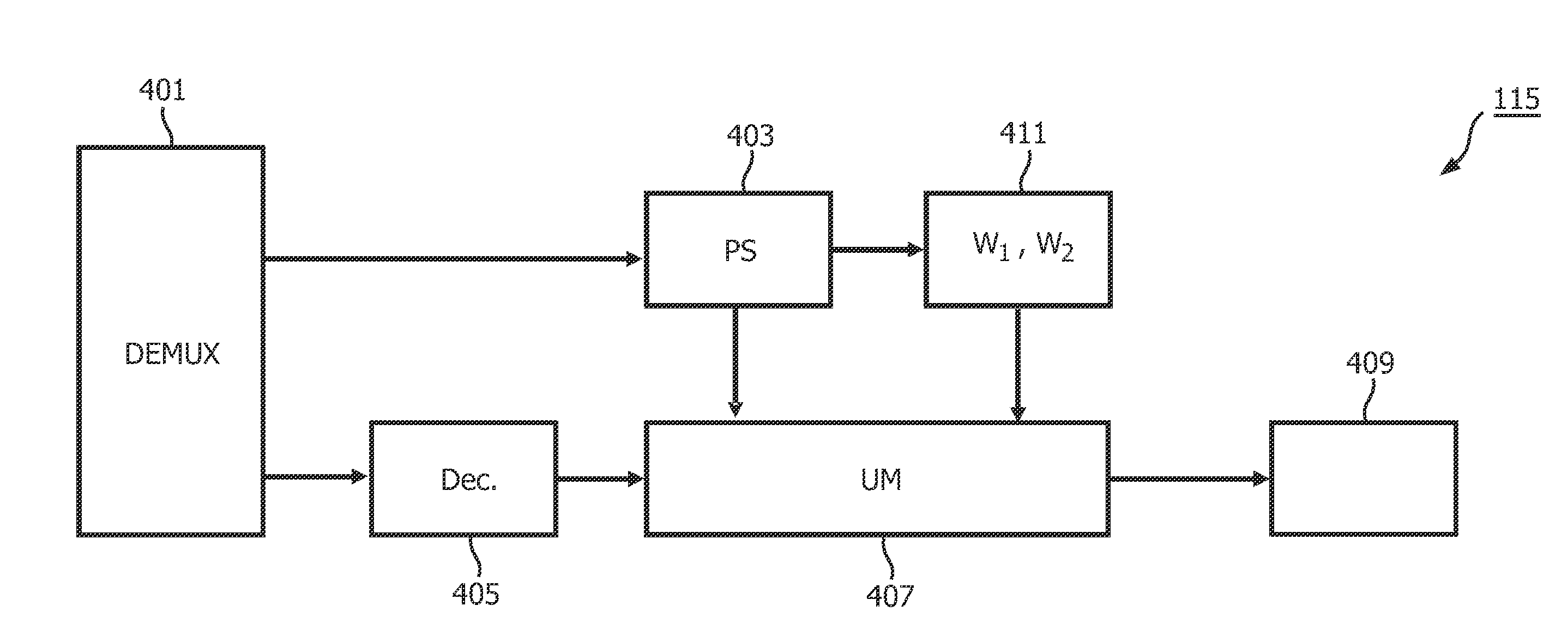
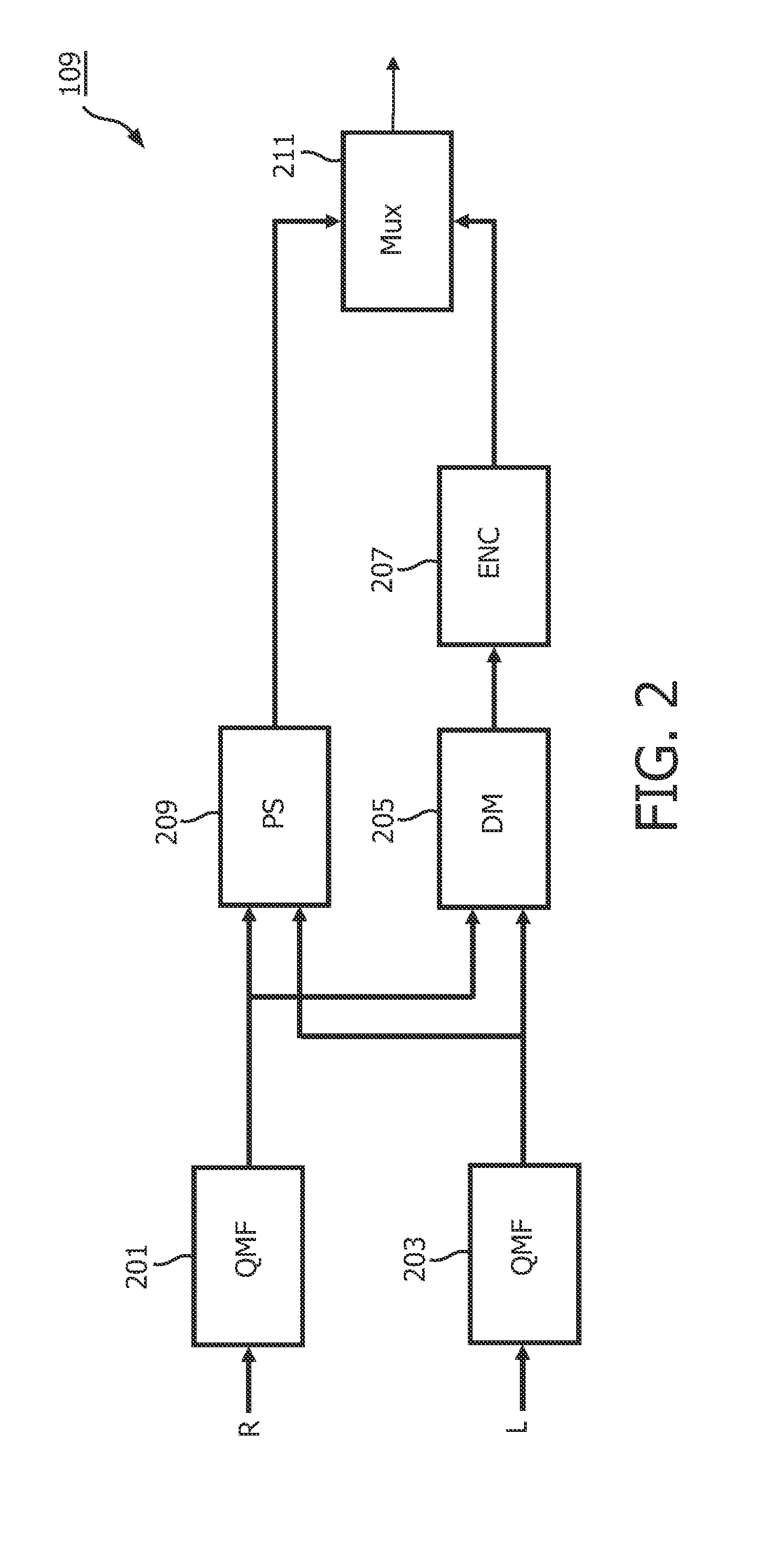
Parametric encoding and decoding
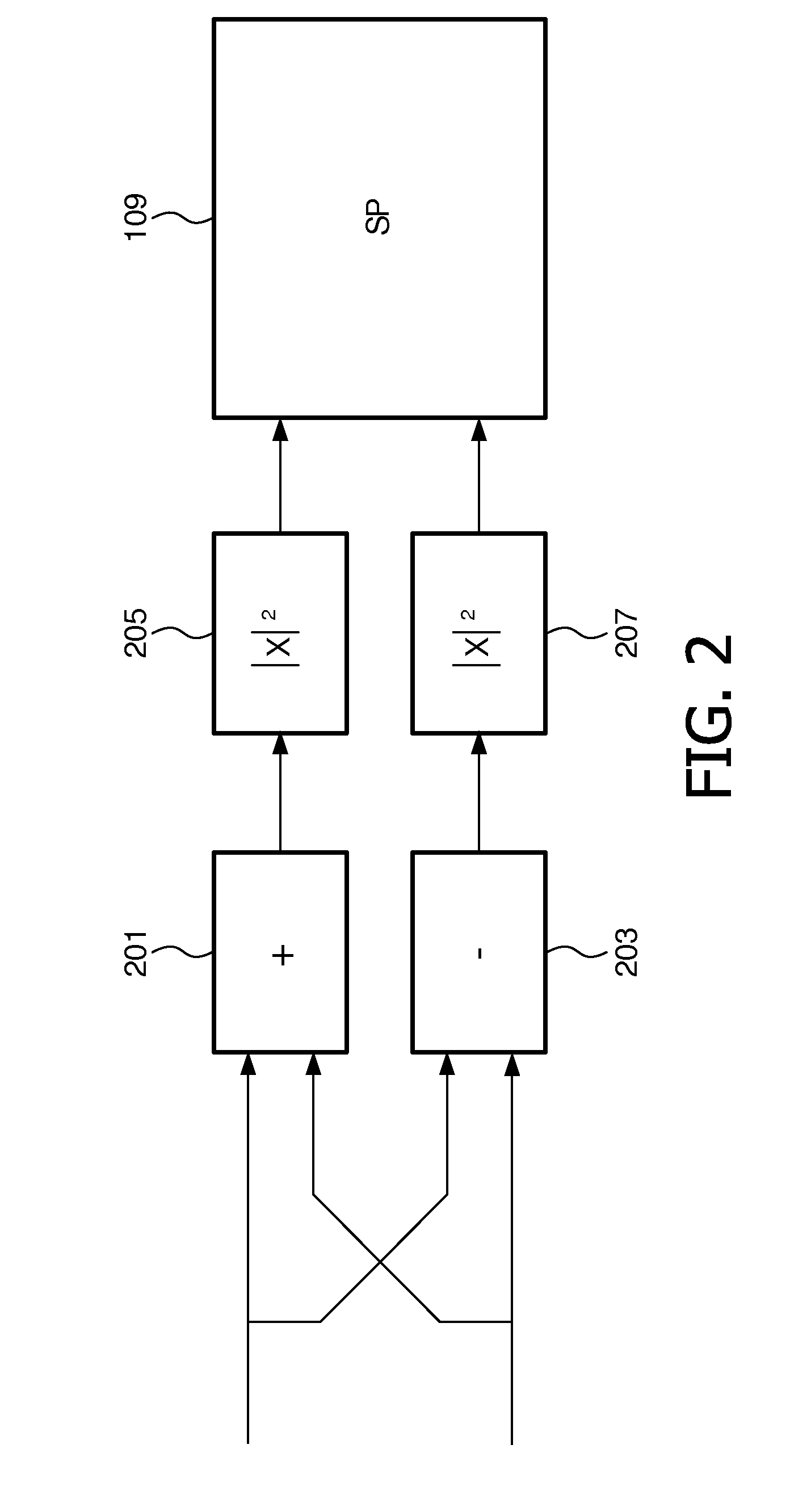
ActiveUS20120224702A1Easy to codeReduce disadvantagesSpeech analysisStereophonic systemsFrequency mixerVocal tract
An encoder for a multi-channel audio signal which comprises a down-mixer (201, 203, 205) for generating a down-mix as a combination of at least a first and second channel signal weighted by respectively a first and second weight with different amplitudes for at least some time-frequency intervals. Furthermore, a circuit (201, 203, 209) generates up-mix parametric data characterizing a relationship between the channel signals as well as characterizing the weights. A circuit generates weight estimates for the encoder weights from the up-mix parametric data; and comprises an up-mixer (407) which recreates the multi channel audio signal by up-mixing the down-mix in response to the up-mix parametric data, the first weight estimate and the second weight estimate. The up-mixing is dependent on the amplitude of at least one of the weight estimate(s).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
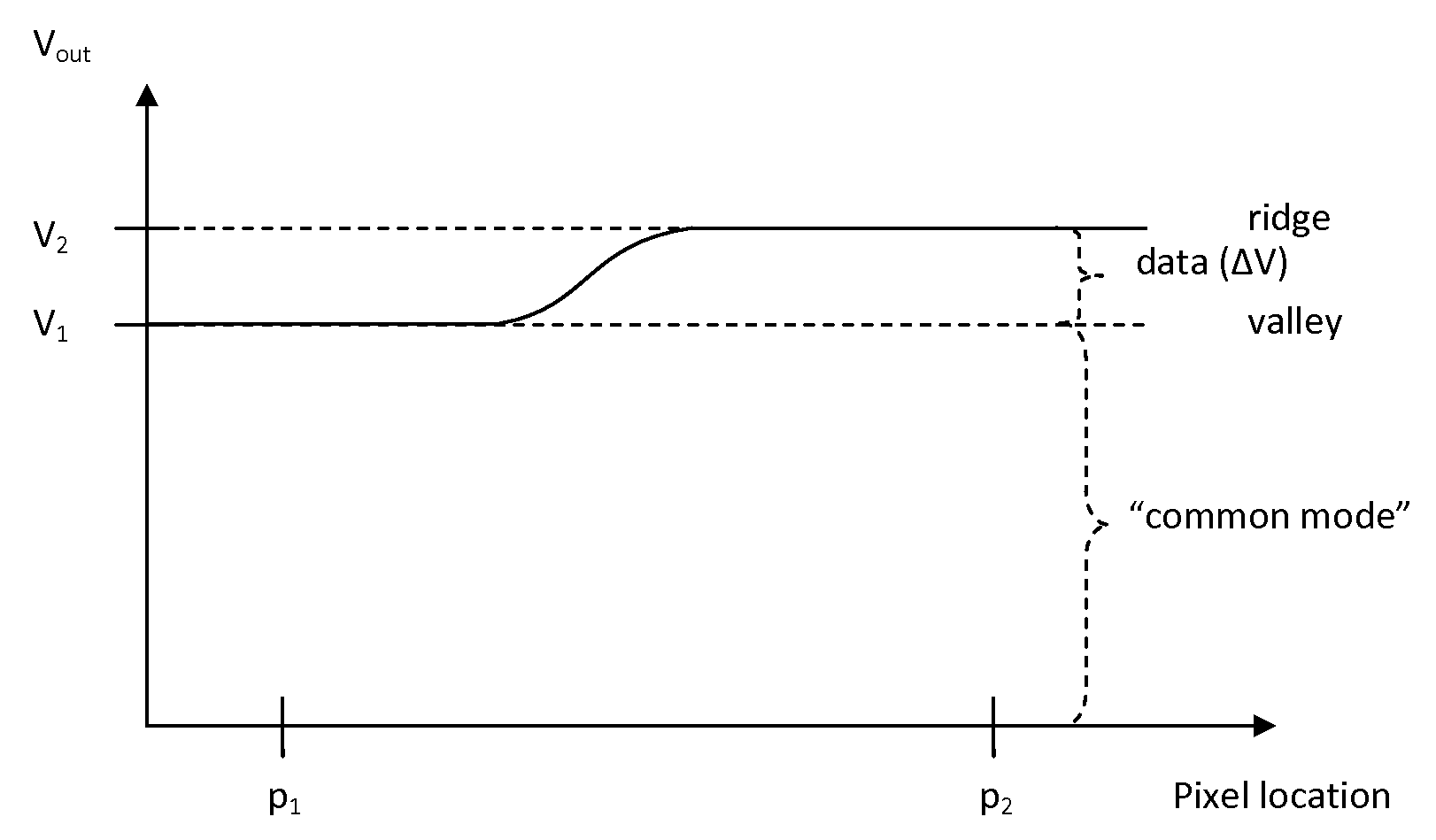
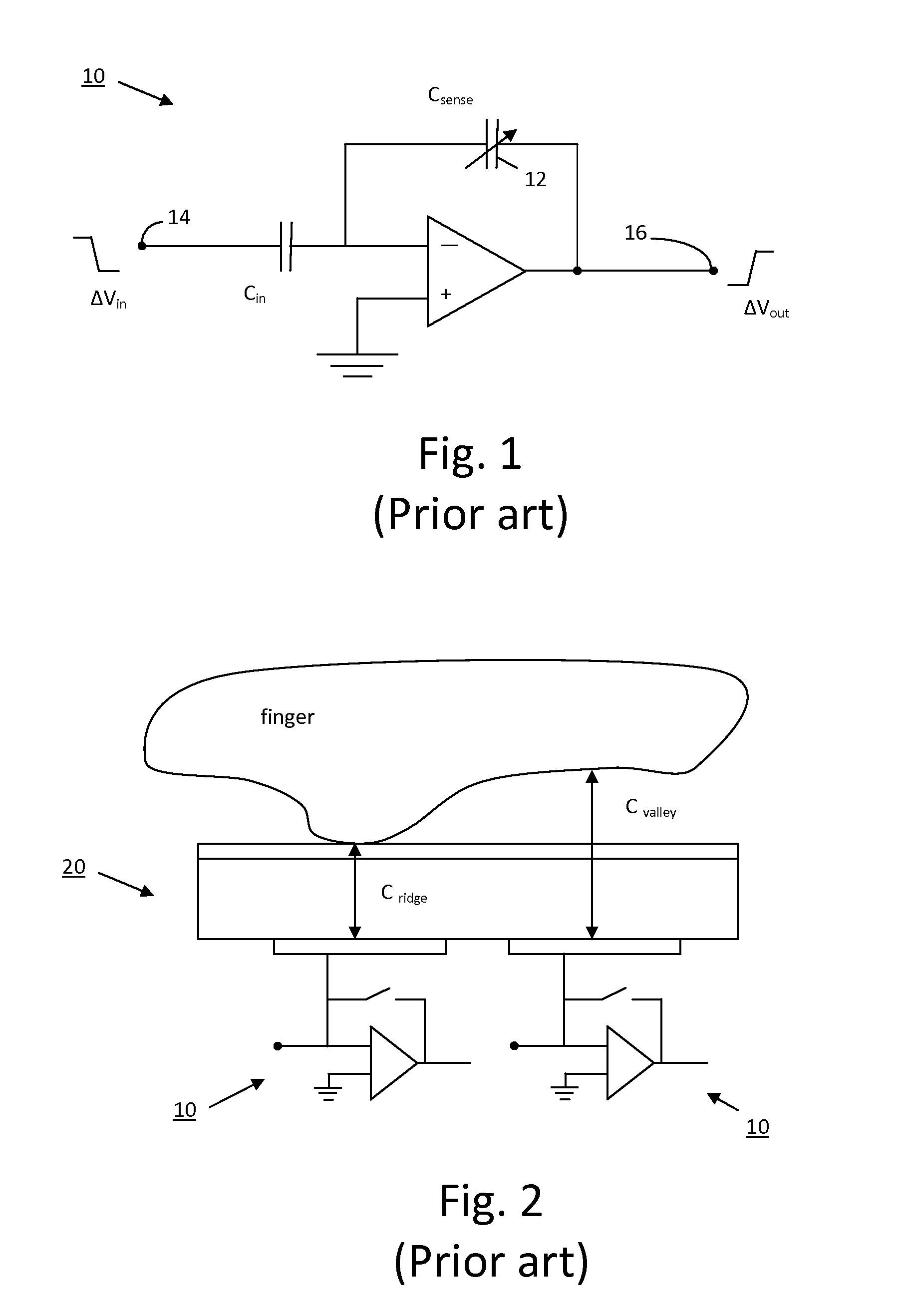
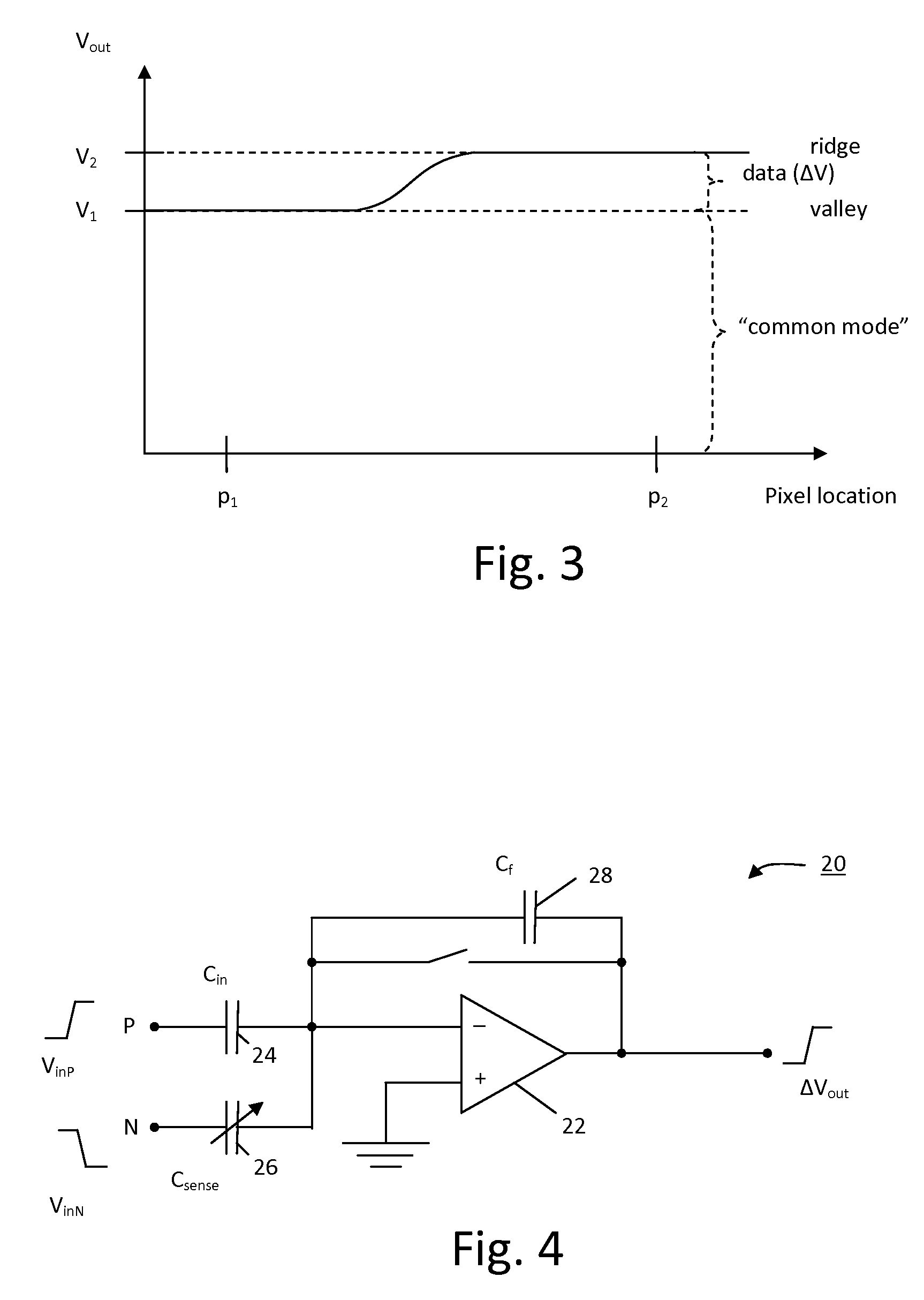
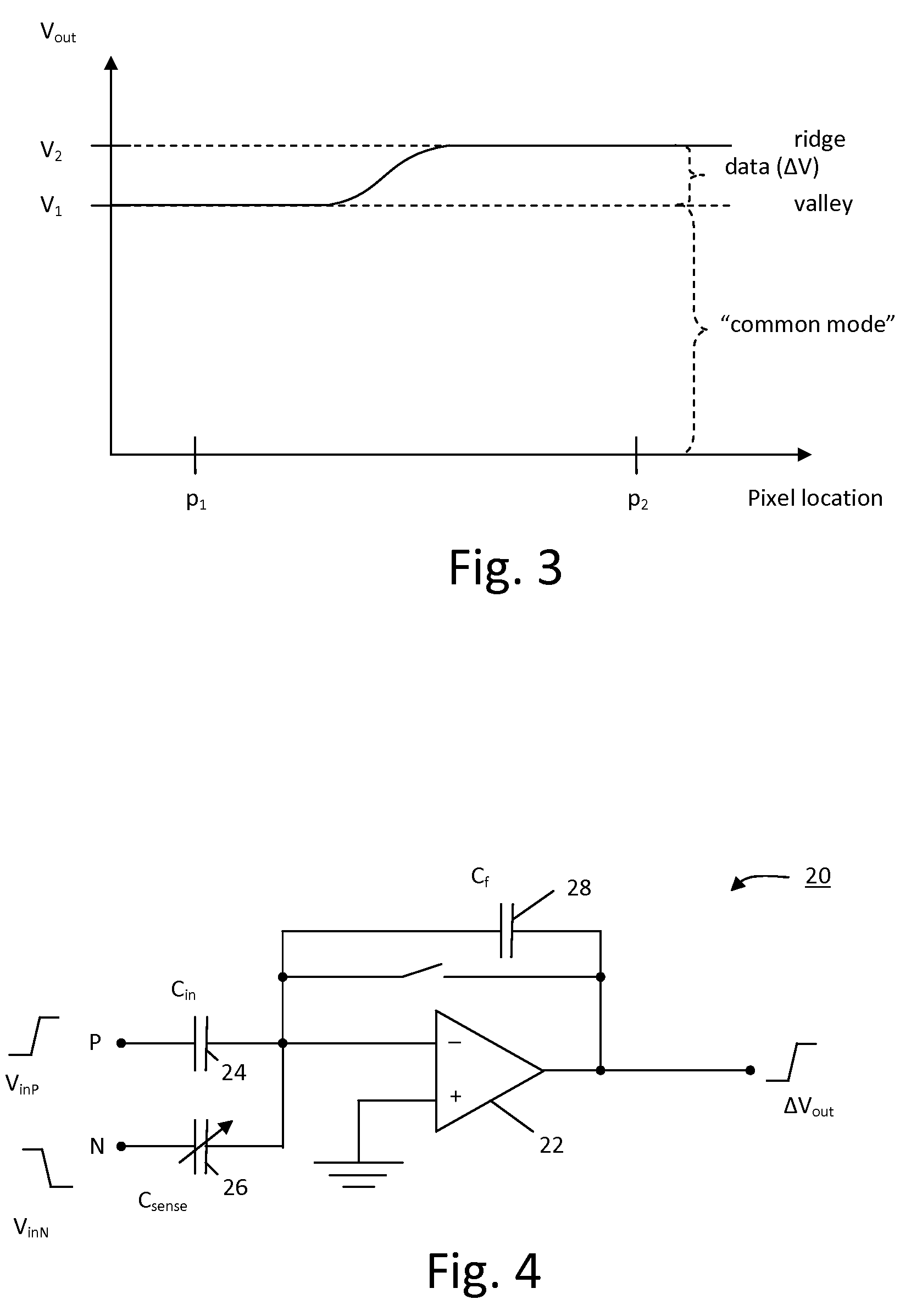
Pixel Sensing Circuit with Common Mode Cancellation
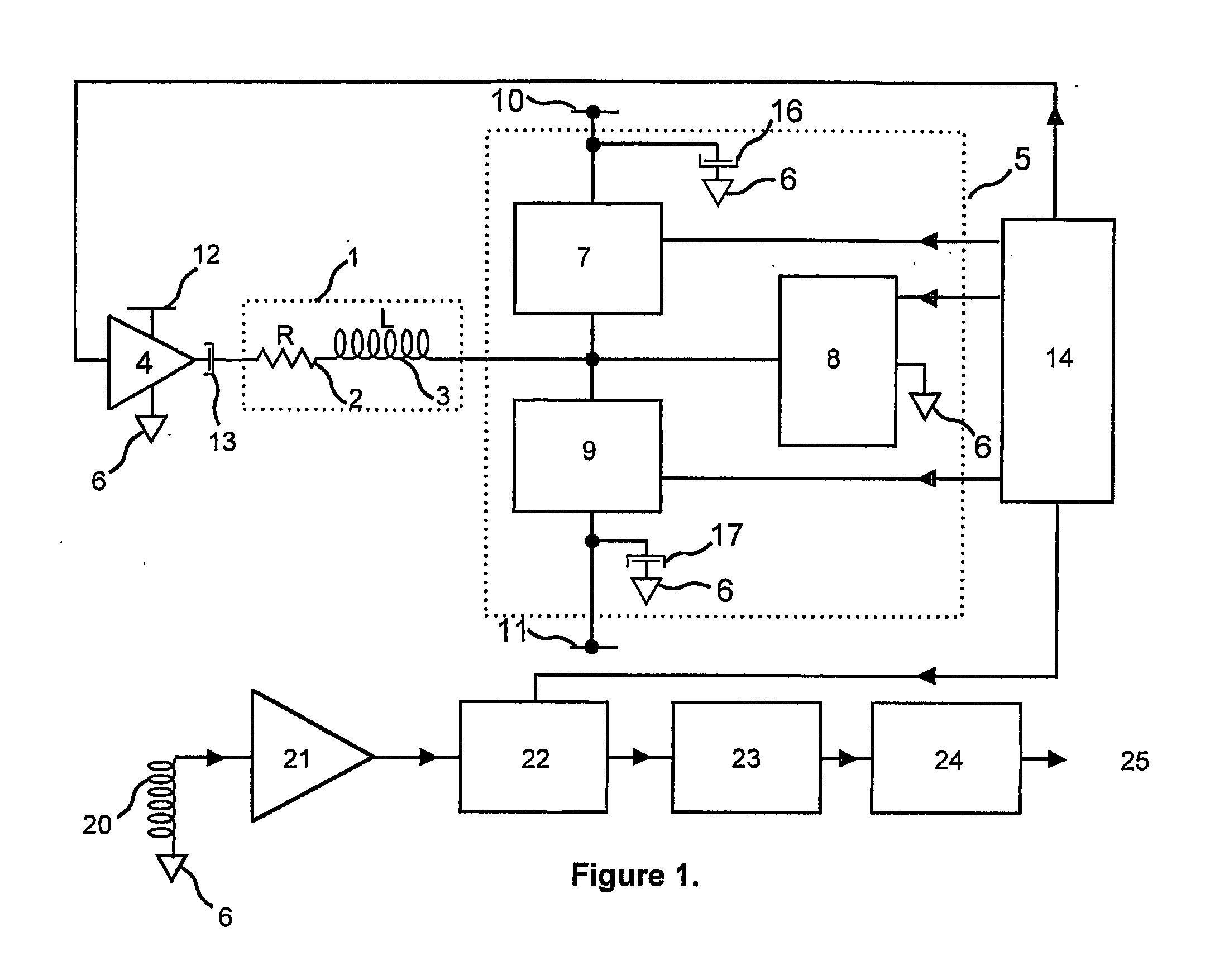
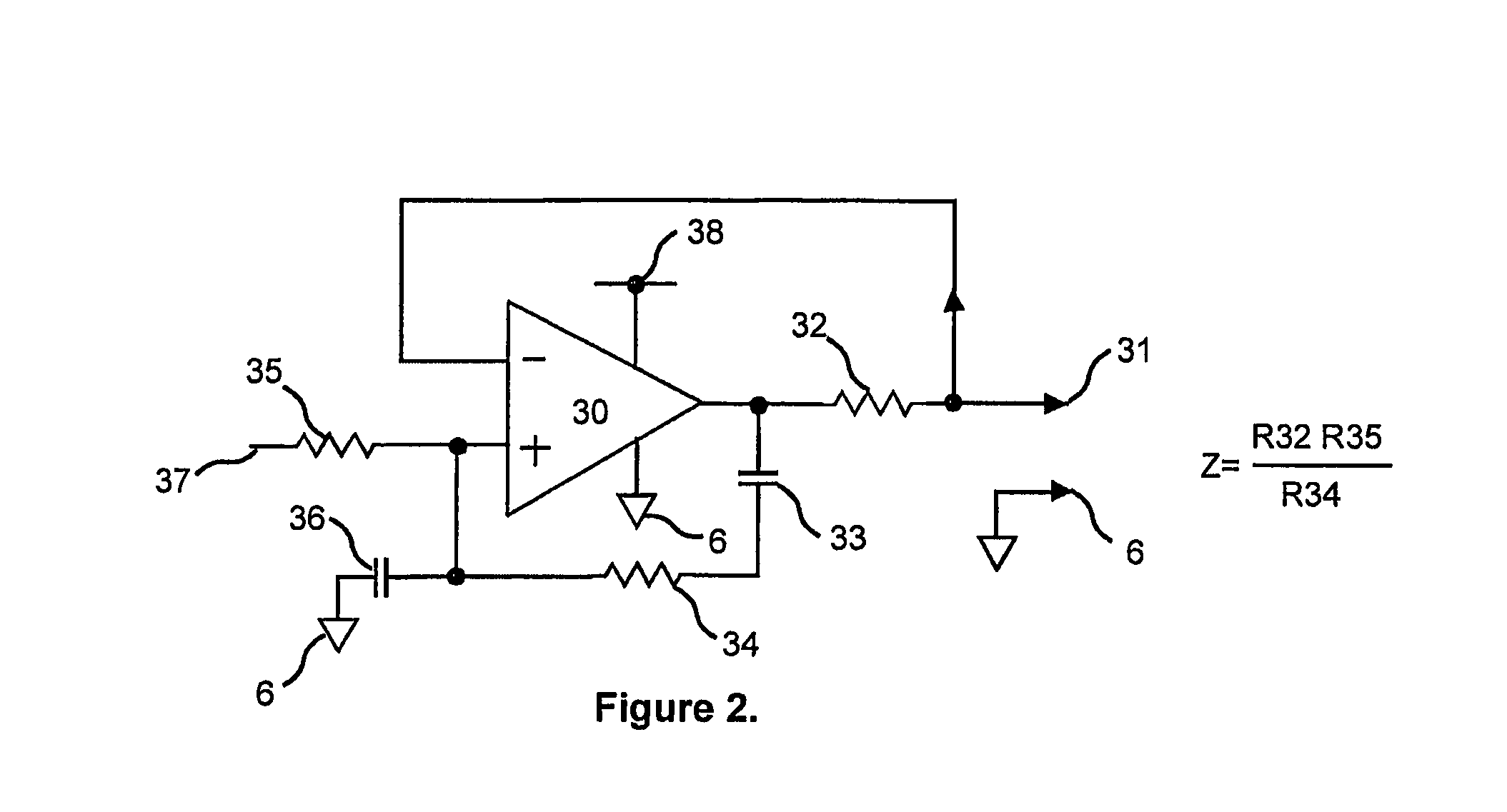
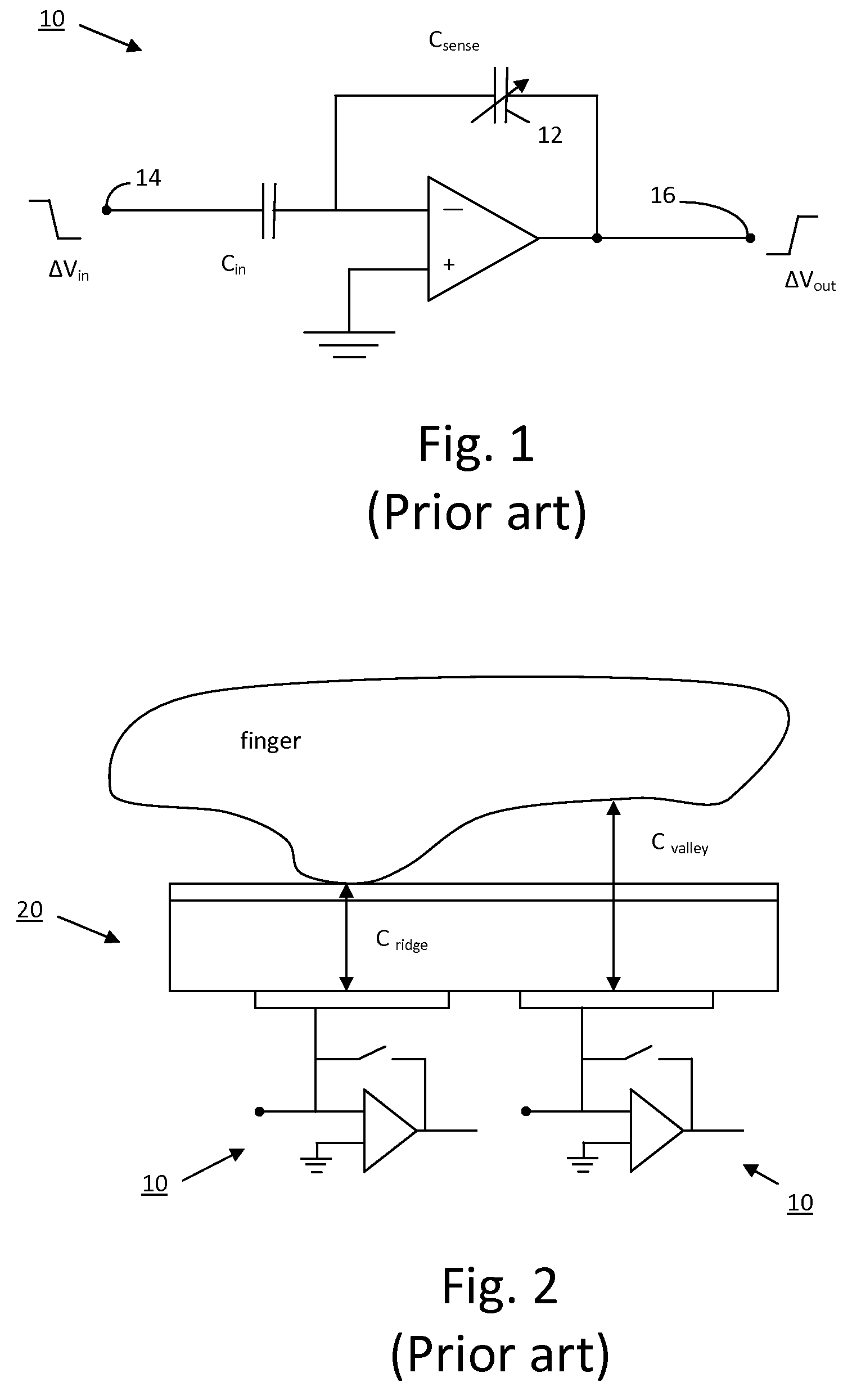
ActiveUS20090123039A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioEasy to useResistance/reactance/impedencePrint image acquisitionIntegratorBiometric data
An improved biometric data sensing circuit, for example adapted for fingerprint sensing, uses a charge subtraction technique at the input of the circuit integrator to cancel the so called “common mode” signal from the circuit output. The result is an output signal that is (a) linear, (b) free from any amplification effect due to the presence of the detected object (e.g. a finger), and (c) indicative of the detected object's fine surface geometry (i.e., indicative of the fingerprint's ridges and valleys).
Owner:APPLE INC
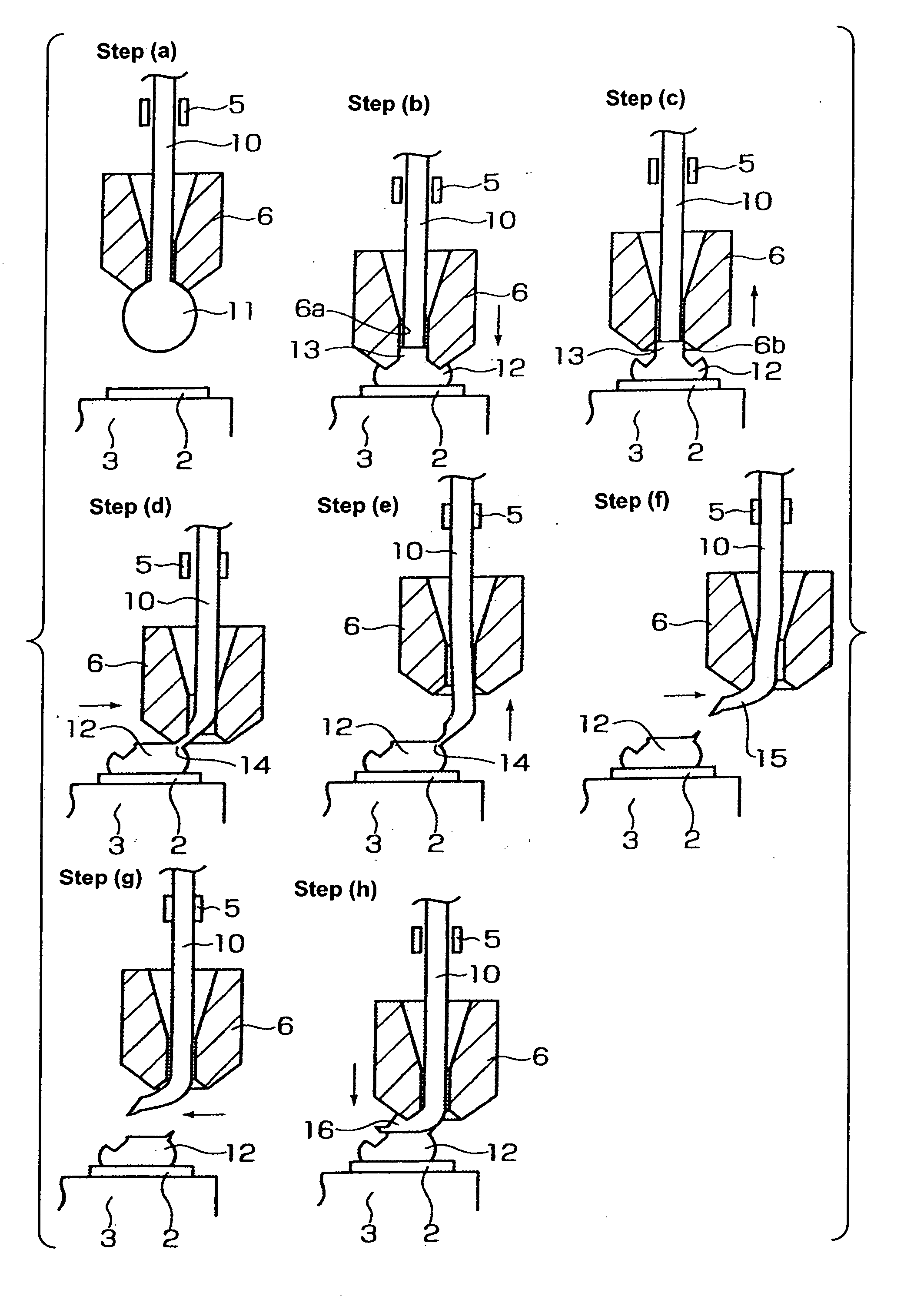
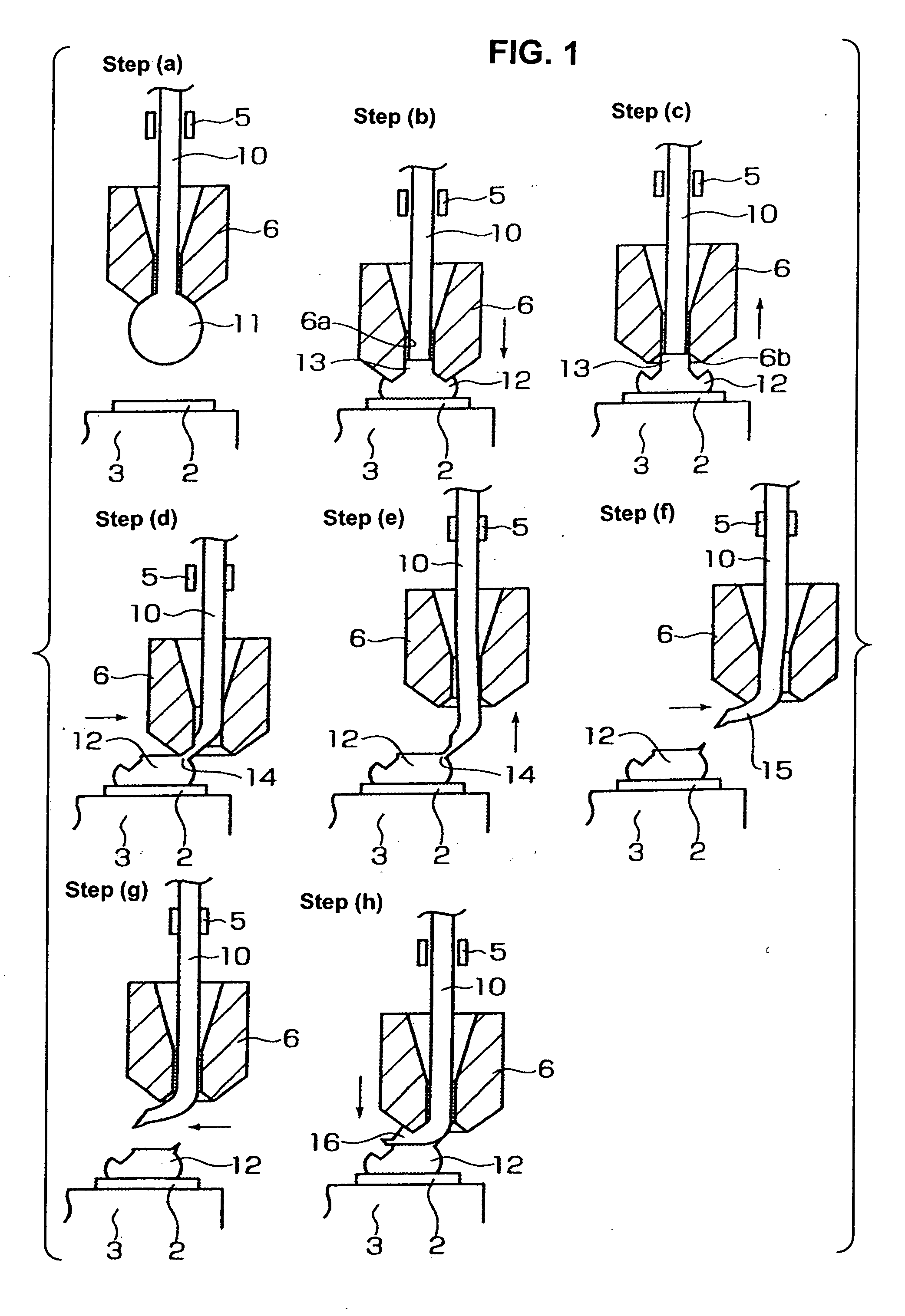
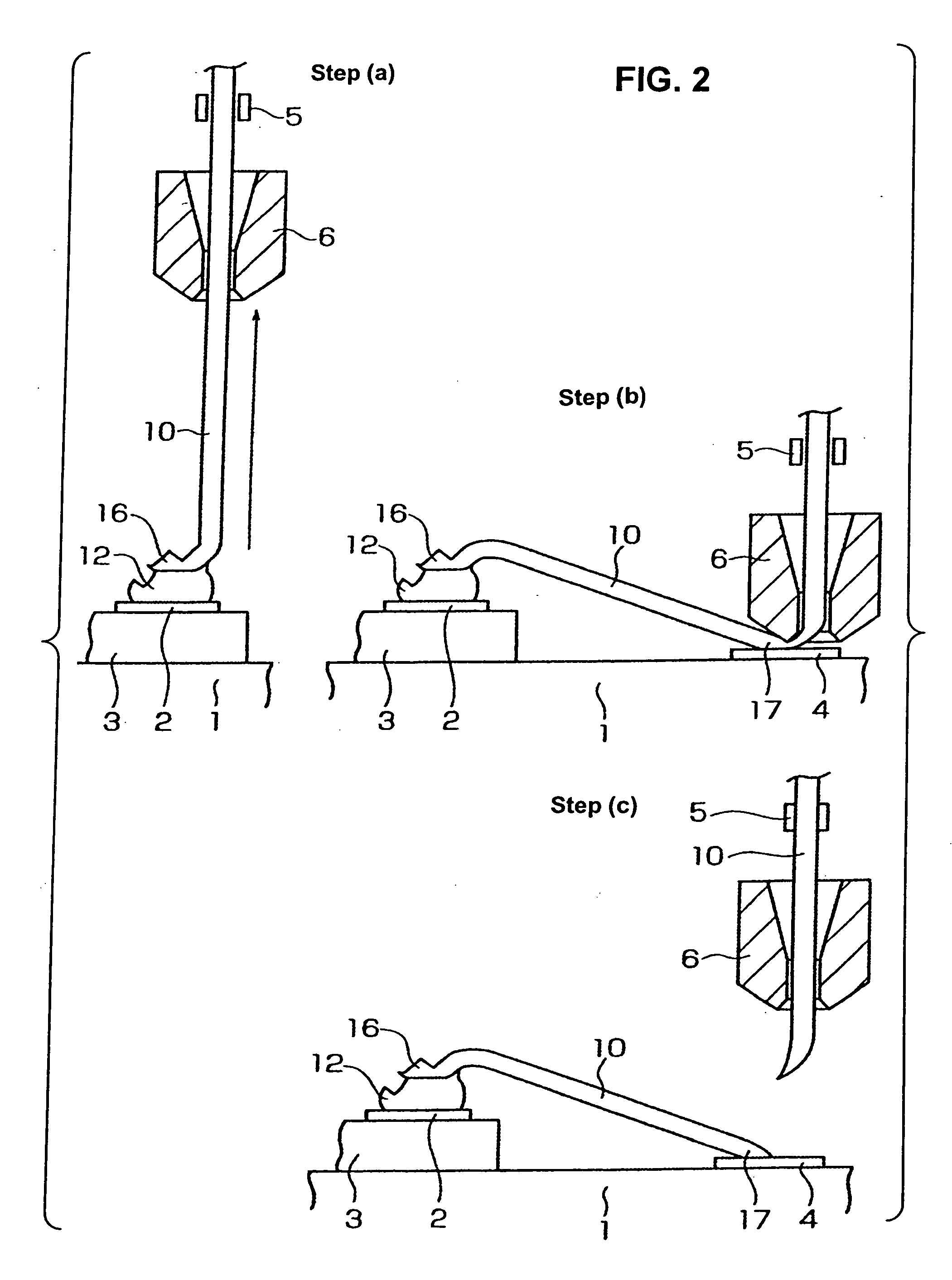
Wire bonding method
InactiveUS20060175383A1Improve implementationReduce decreaseSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesWire cuttingEngineering
A wire bonding method with the process of performing a first bonding to a pad of a die that is a first bond point, and the process of performing a second bonding to an interconnect wiring (or a lead) that is a second bond point, thus connecting the pad and the interconnect wiring with a wire. A bump is first formed on a pad, and, in a wire cutting step performed during the step of forming the bump, the wire protruding from the tip end of a capillary is bent in the lateral direction to form a bent part, and then the bent part is bonded to the bump, thus completing the first bonding process; after which the wire is bonded to the interconnect wiring, thus completing the second bonding process.
Owner:SHINKAWA CO LTD
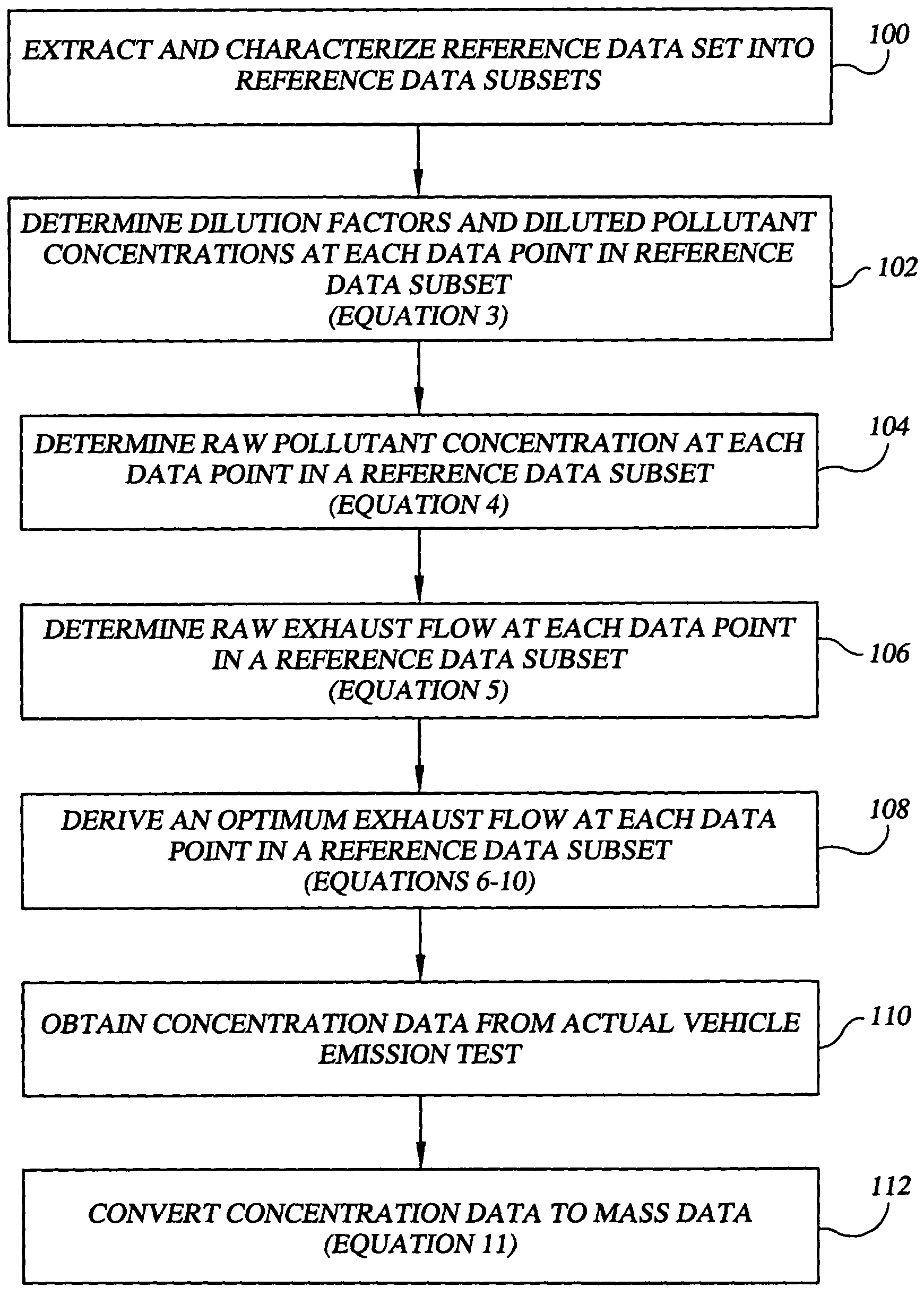
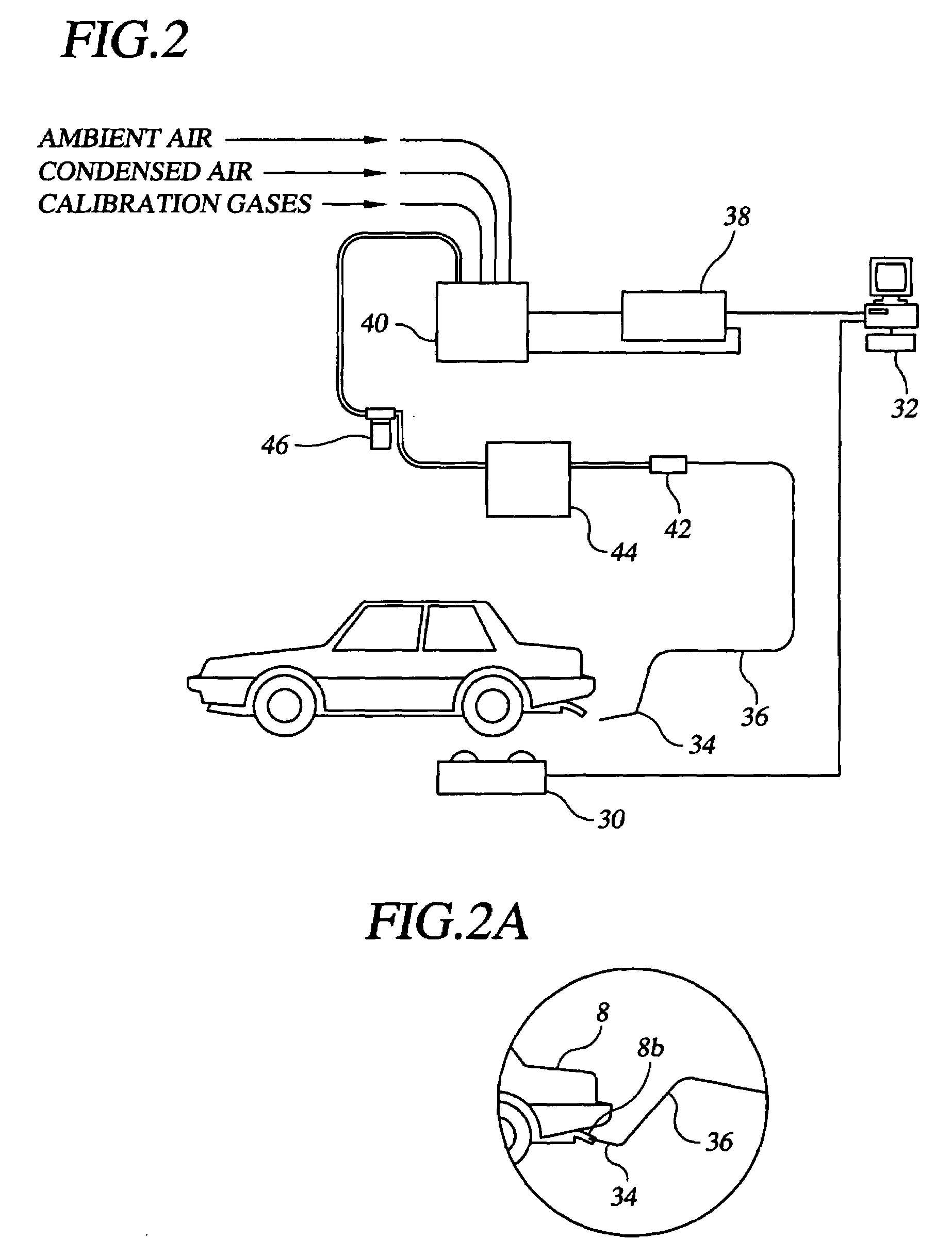
Method and system for vehicle emission testing
InactiveUS7071002B1Low implementation costReduce maintenance costsSamplingTesting/calibration apparatusReliability engineeringPollutant
A method and system for vehicle emission testing measures pollutant concentration, but then provides for conversion of the measured pollutant concentration into its corresponding pollutant mass, thereby allowing for the calculation of a vehicle's emission test scores for one or more common pollutants in units of mass per distance. Through the use of the method and system of the present invention, significantly more accurate results can be obtained as compared to prior art test methods, and without the implementation, operating, and maintenance costs of comparable test methods.
Owner:GORDON DARBY SYST
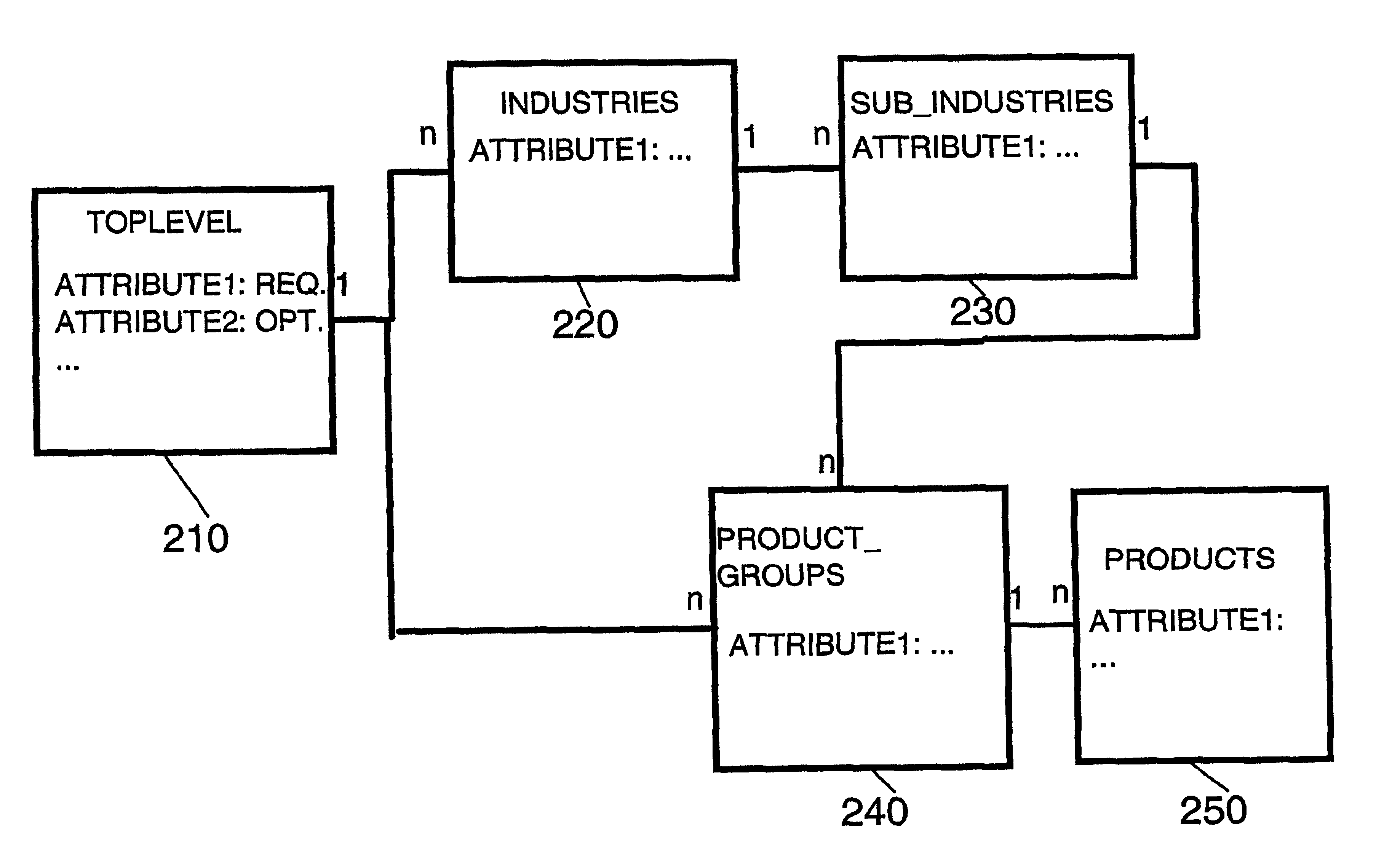
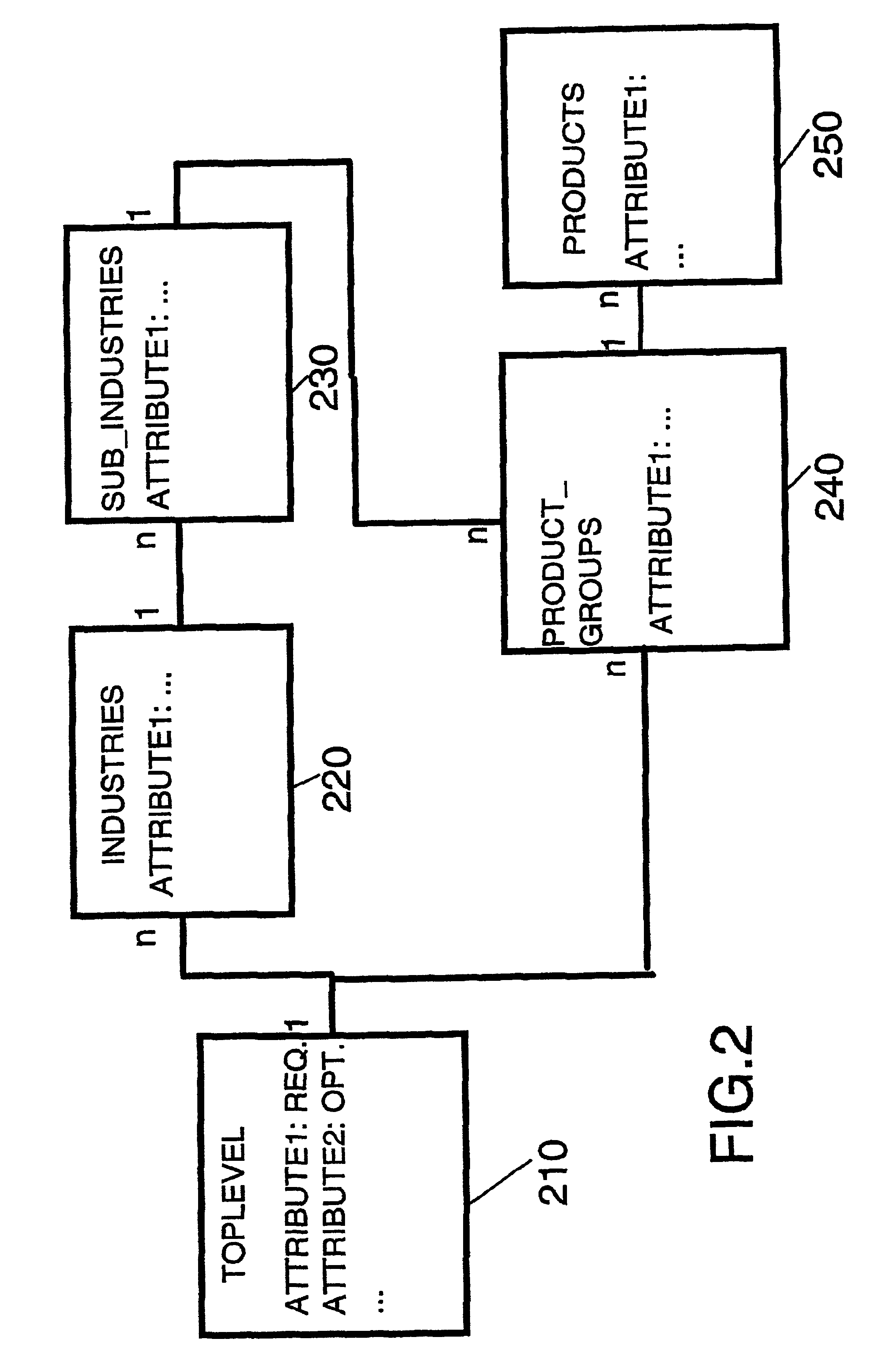
Method of structuring a catalog
ActiveUS6901408B2Simplifies useLower implementationDigital data processing detailsBuying/selling/leasing transactionsEntity relationship modellingElectronic data
The present invention relates to a method and system for electronic management of data, which can be represented in a directed graph according to an entity relationship model. Any entity relationship model compliant data pool, and particular a (web) catalog is structured by grouping catalog pages (nodes) into groups (node types) with similar properties like attributes and relationships. Catalog nodes are identified by the node type name and a node instance name that is unique for a given node type. The node type definition is advantageously enabled to be business-driven. A prior art entity relationship diagram describes the structure of the catalog by defining the node types, the node attributes and the possible relationships, and optionally access control information. The catalog structure is stored in the database in a separate set of structure tables. This set of tables is used by the inventive, generic catalog maintenance tool to customize itself by validating the user input using the structure definition stored in said structure tables.
Owner:KYNDRYL INC
Method and apparatus for transmitting/receiving data on multiple carriers in mobile communication system
ActiveUS20150043505A1Improve uplink performanceLower implementationSynchronisation arrangementError preventionCarrier signalPrimary cell
A data transmission method and an apparatus to communicate data on multiple carriers in the mobile communication system are provided. A random access method of a terminal in a mobile communication system including primary and secondary cells operating on multiple carriers according to the present invention includes communicating data after random access in the primary cell, receiving, when the random access is triggered in the secondary cell, information for use in the secondary cell random access from the primary cell, transmitting a preamble in the secondary cell based on the received information, monitoring the primary cell to receive a Random Access Response for the secondary cell, and applying, when the Random Access Response for the secondary cell is received, the information carried in the Random Access Response to the secondary cell in which the preamble has been transmitted.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
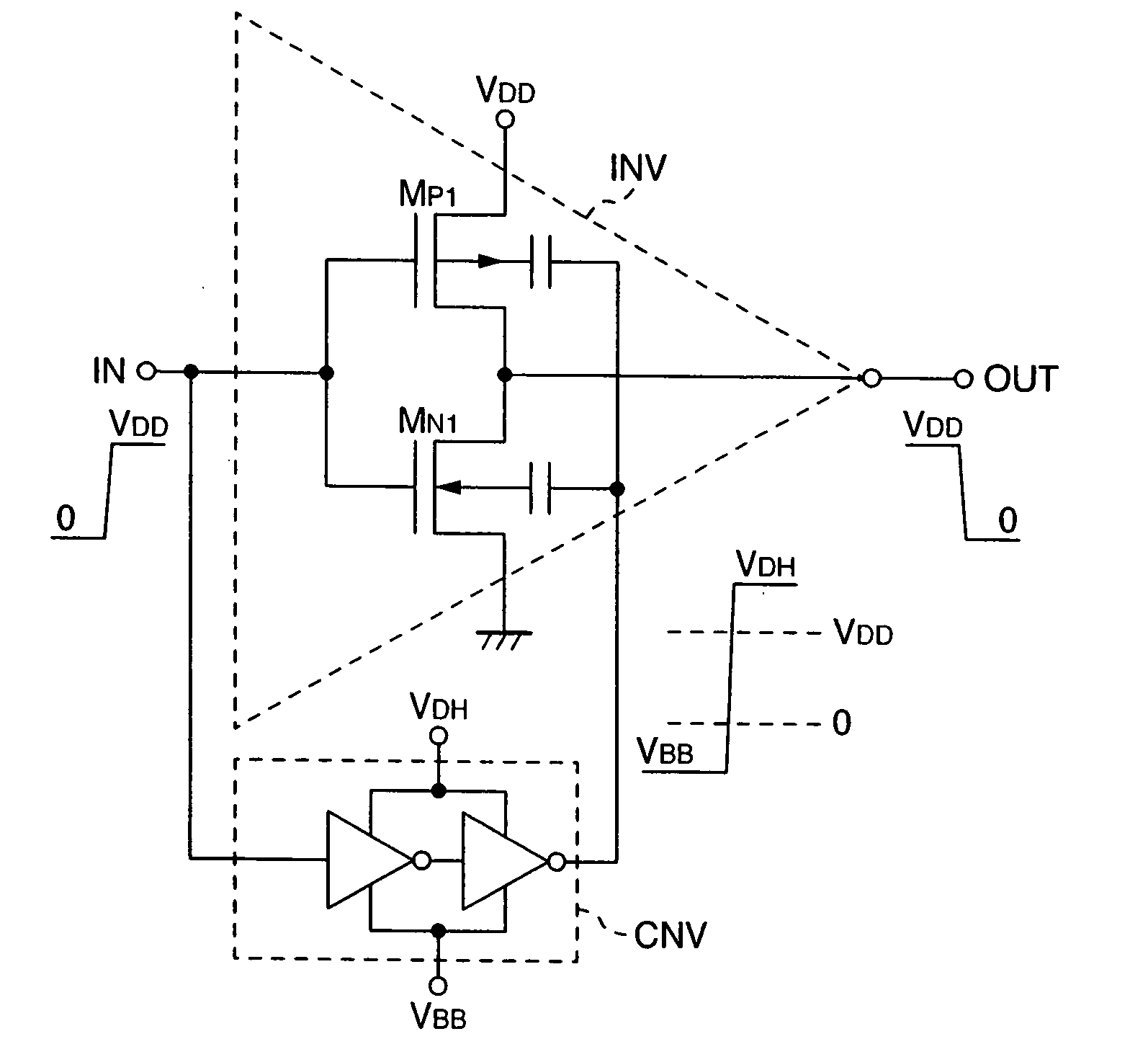
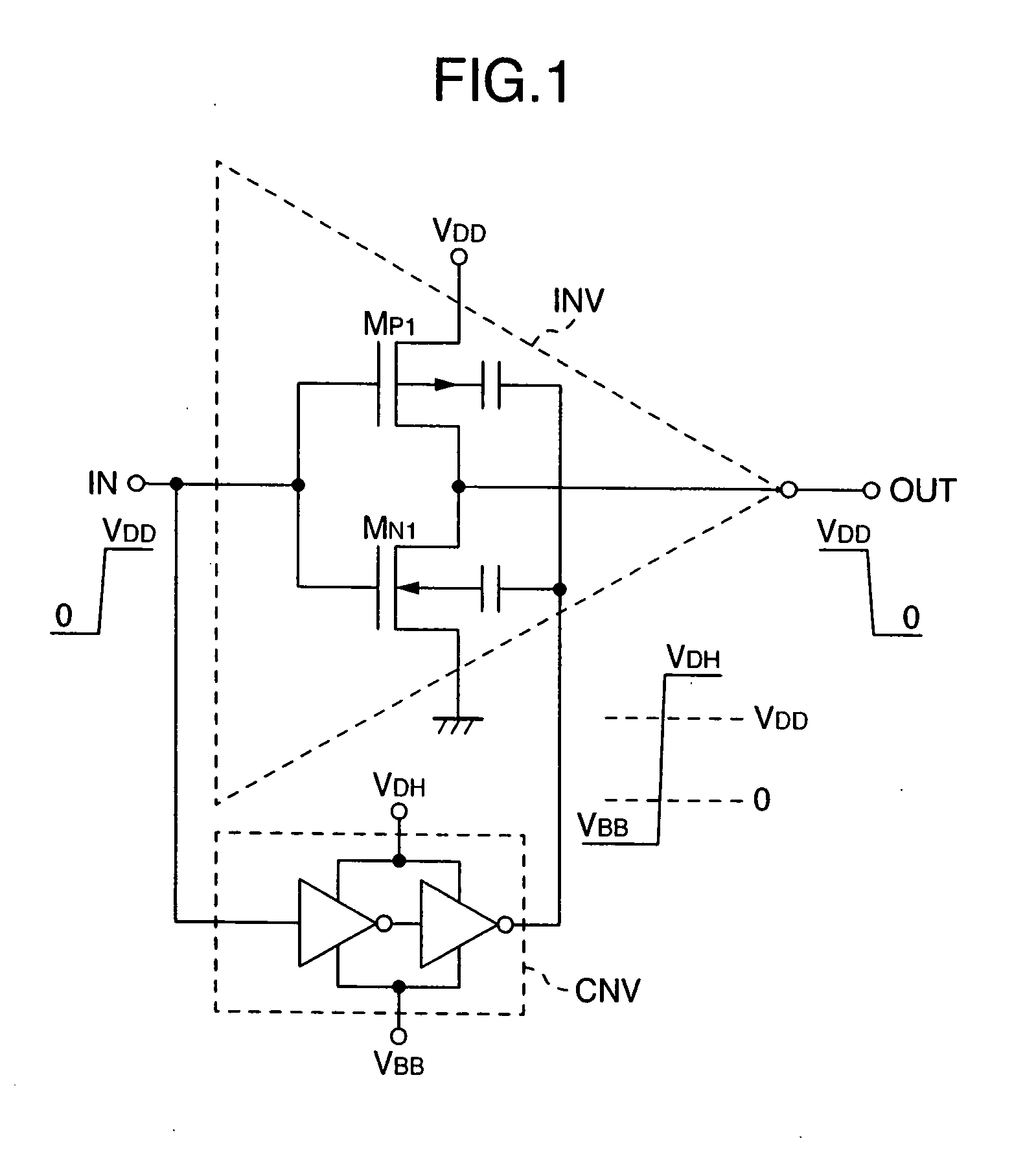
Semiconductor devices
InactiveUS20070152736A1Effective conditionsEffective structureSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSVoltage amplitude
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Standards-based formatting of flat files into markup language representations
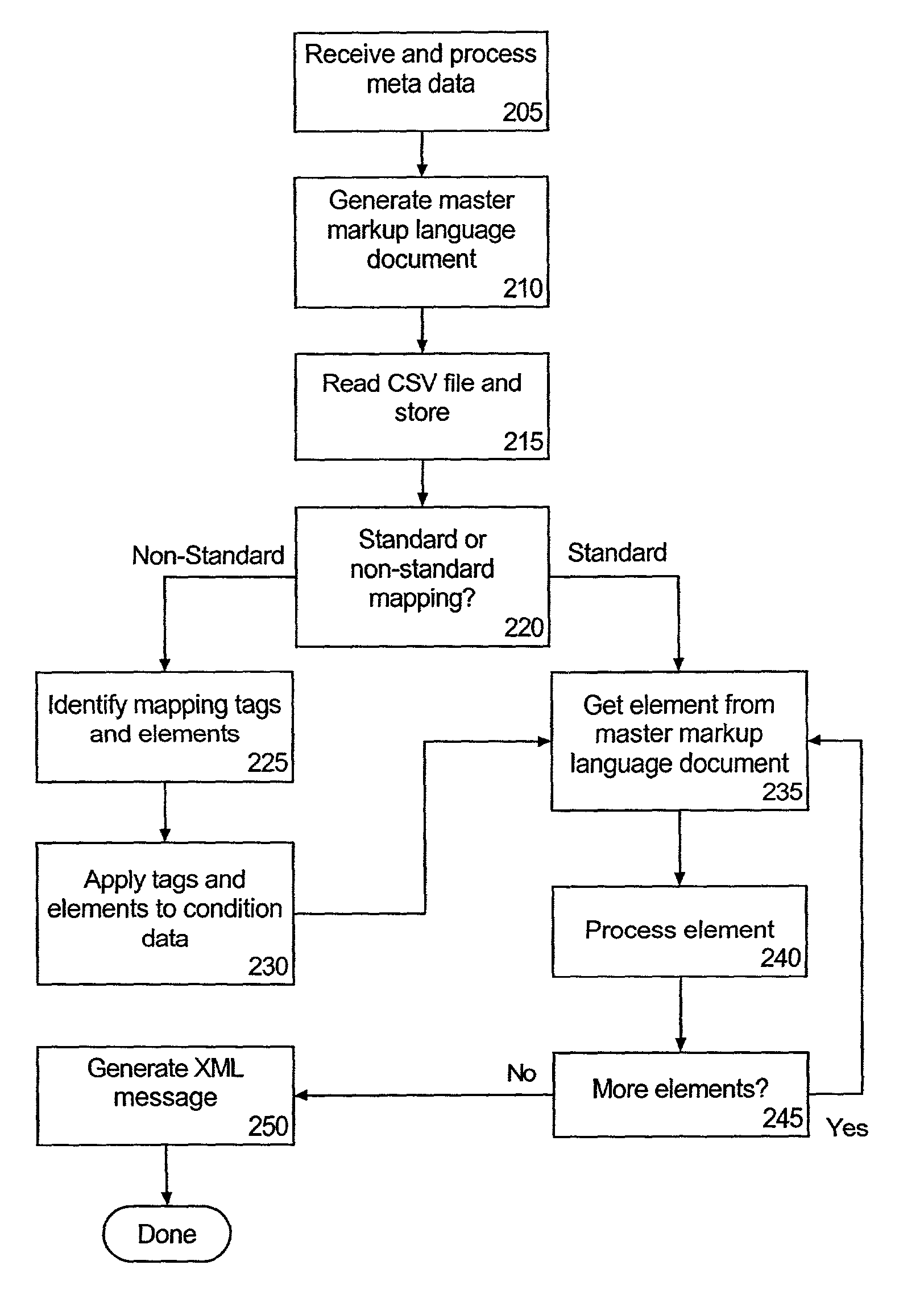
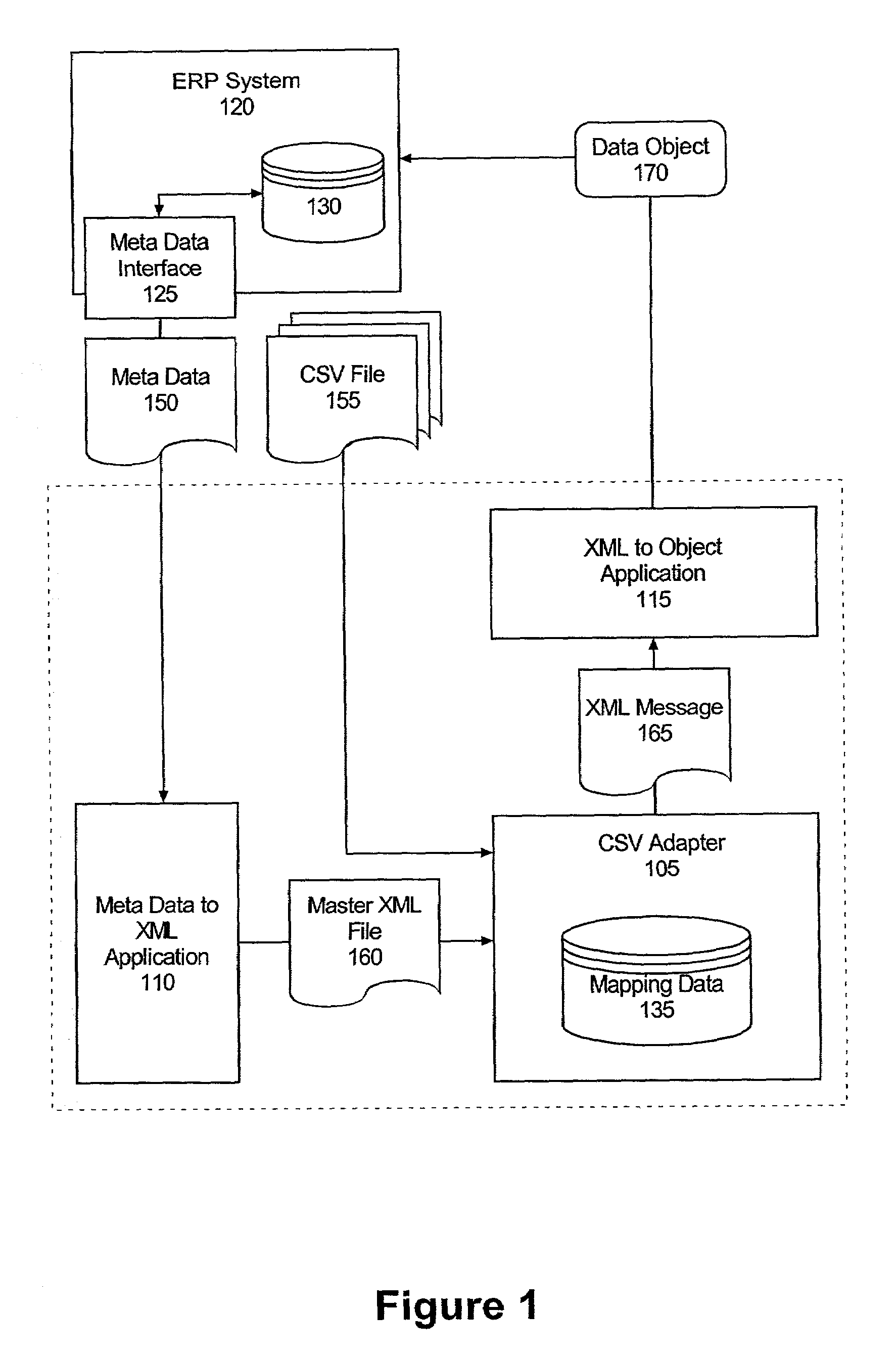
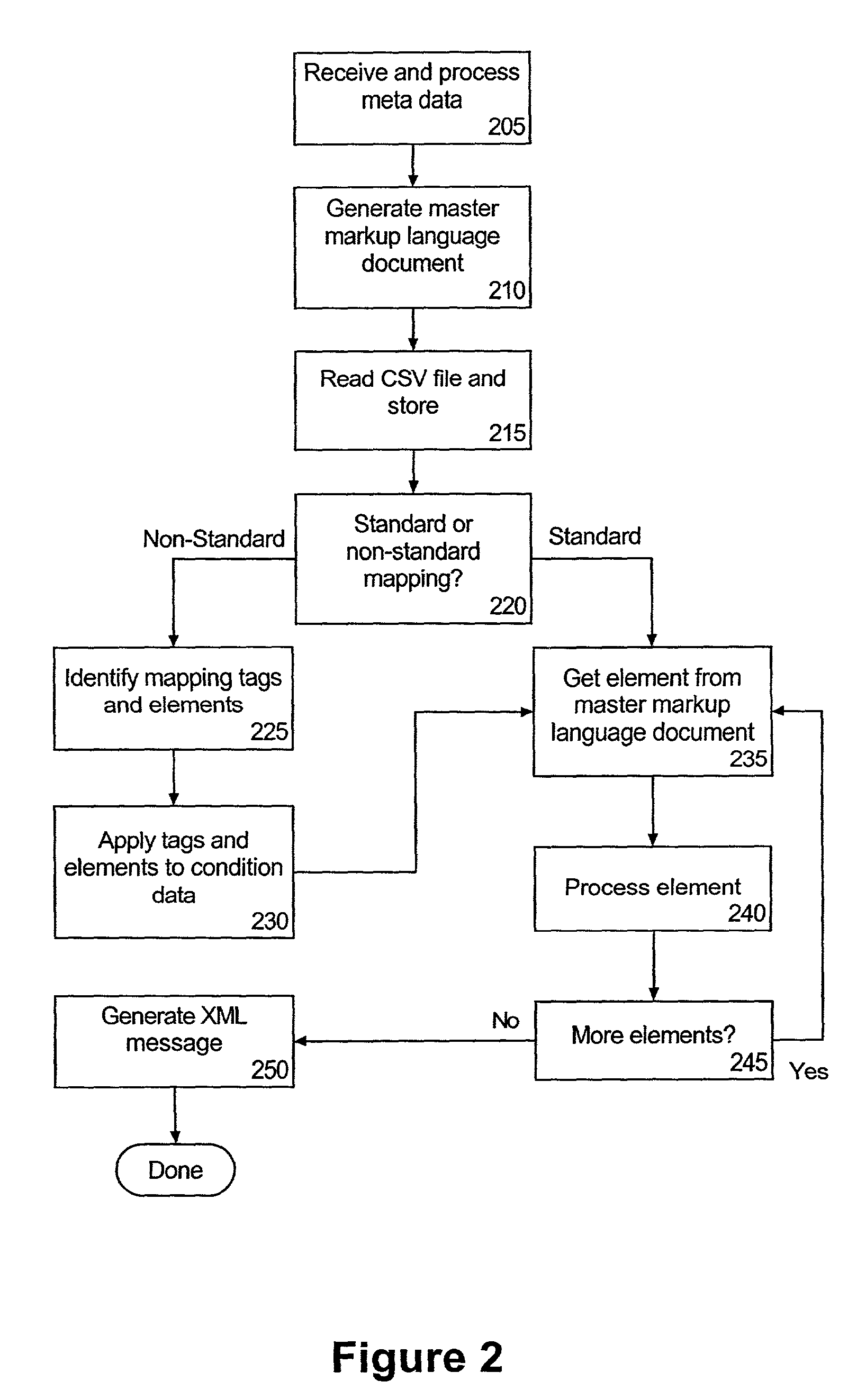
InactiveUS7093195B2Facilitate of dataFacilitate populationData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsMapping techniquesDocument preparation
A method of building an application response message can include receiving a master file specifying a message format for populating a particular data object of an application. The master document can specify element names which correspond to fields of the data object. A technique for mapping particular data items specified by at least one flat file to the element names specified in the master file can be determined; and a markup language representation of the data object can be generated according to the determined mapping technique and the specified message format.
Owner:IBM CORP
Apparatus for testing a power supply
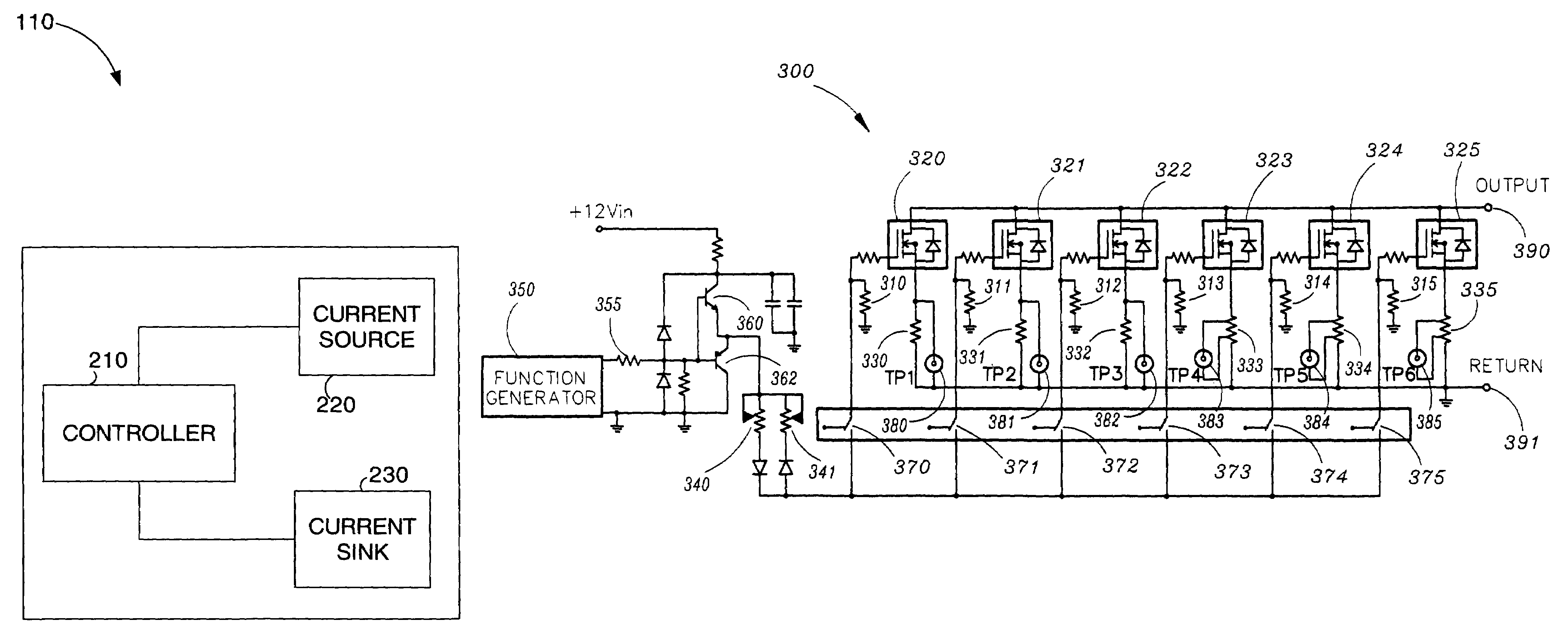
InactiveUS7436200B1Reduce weightSmall sizePower supply testingIndividual semiconductor device testingSmall form factorOperability
The present invention is an apparatus for testing a power supply. A power supply testing apparatus may include a remote load which may sink an adjustable amount of current with an adjustable slew rate and may test the response of the power supply to determine its operability with a dynamic load. Additionally, in an alternative embodiment of the invention, the testing apparatus may source an adjustable amount of current with an adjustable slew rate to the output of a power supply. In yet another embodiment of the invention, the testing apparatus may include an adjustable current sink and adjustable current source with an adjustable slew rate. The power supply testing apparatus of the present invention may be implemented with standard circuit components on a circuit board and thus provide a small form factor. Additionally, due to the small form factor and low weight implementation, the power supply testing apparatus may utilize reduced length test wires which reduce the inductance in the test wires and increases the apparatus' slew rate for more effective testing.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Optimized SCA CORBA descriptor for SCA CORBA descriptor files
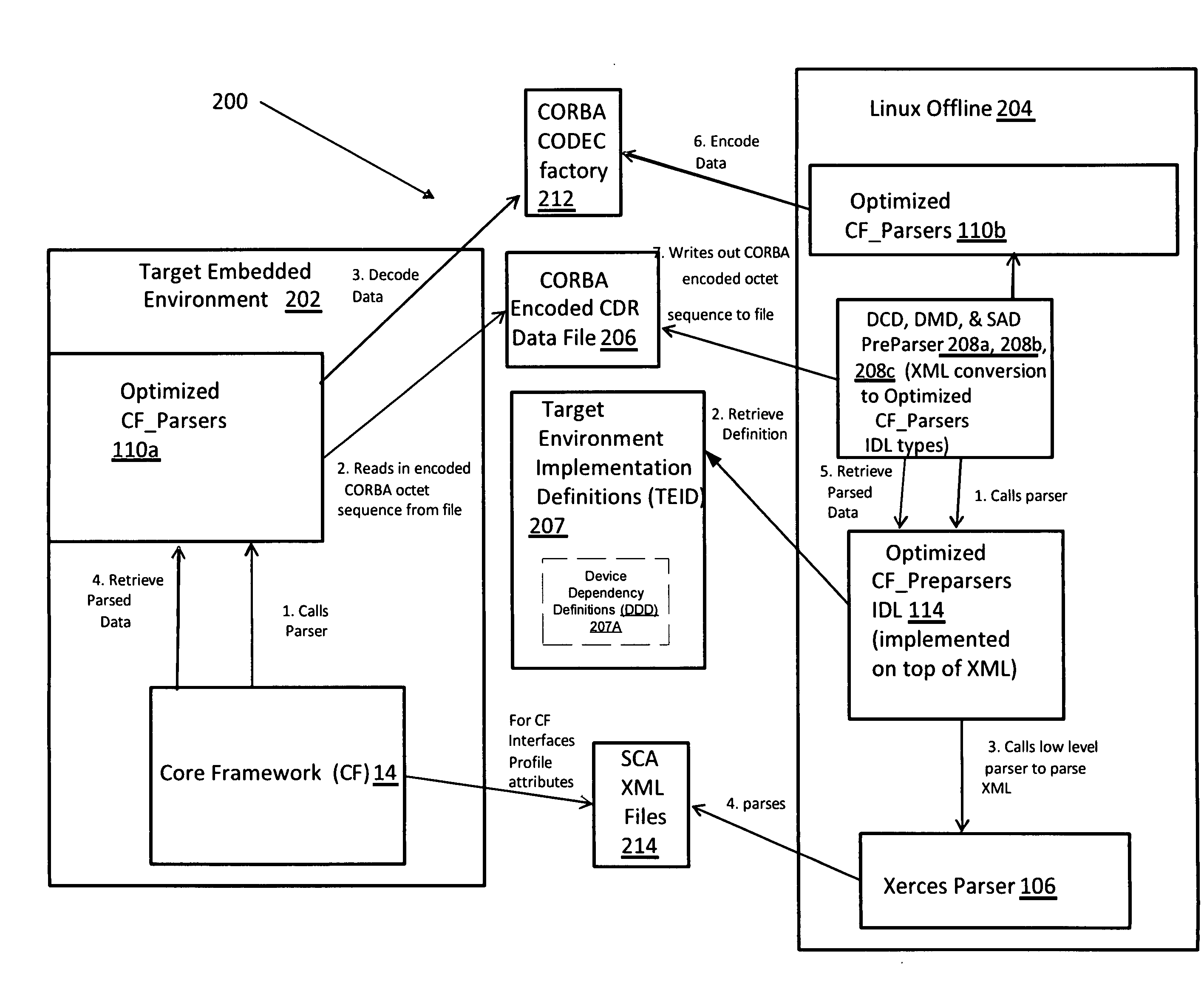
ActiveUS20130139146A1Speed up parsing processEliminate effectiveSemi-structured data mapping/conversionProgram loading/initiatingXMLStructure type
A preparsers tool is provided for converting SCA XML files into CORBA structures usable by an SCA Core Framework (CF). The preparsers tool retrieves a set of target environment implementation definitions (TEID) that define at least one characteristic of a target environment to which a CORBA CDR file is provided. For each component in the target environment, at least one of the component instantiation implementation software device dependencies, usesdevice dependencies, and deployment dependencies, are merged together into an implementation device dependencies list having a first part comprising visible device dependencies and a second part comprising external device dependencies. The parsed set of XML files is converted into a CORBA structure type, the conversion based at least in part on the TEID, such that the conversion of the parsed set of XML files results in a CORBA structure having a type and precedence order that is correct for the target environment.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Spatial sound reproduction
InactiveUS20120328109A1Enhance listening experienceImprove performancePseudo-stereo systemsStereophonic arrangmentsVocal tractShort terms
An apparatus for spatial sound reproduction comprises a receiver (101) for receiving a multi-channel audio signal. An analyzer (107) determines a spatial property of the multi-channel audio signal, such as a spatial complexity or organization. A selection processor (109) then selects a reproduction mode from a plurality of sound reproduction modes where the multi-channel sound reproduction modes employ different spatial rendering techniques. A reproduction circuit (103) then drives a set of loud-speakers (105) to reproduce the multi-channel audio signal using the selected reproduction mode. The switching between the reproduction modes may be fast (e.g. in the order of 100 ms to 10 secs) thereby allowing a short term adaptation of the reproduction mode to the signal characteristics. The approach may in particular provide an improved spatial experience to a listener.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method of establishing an oscillator clock signal
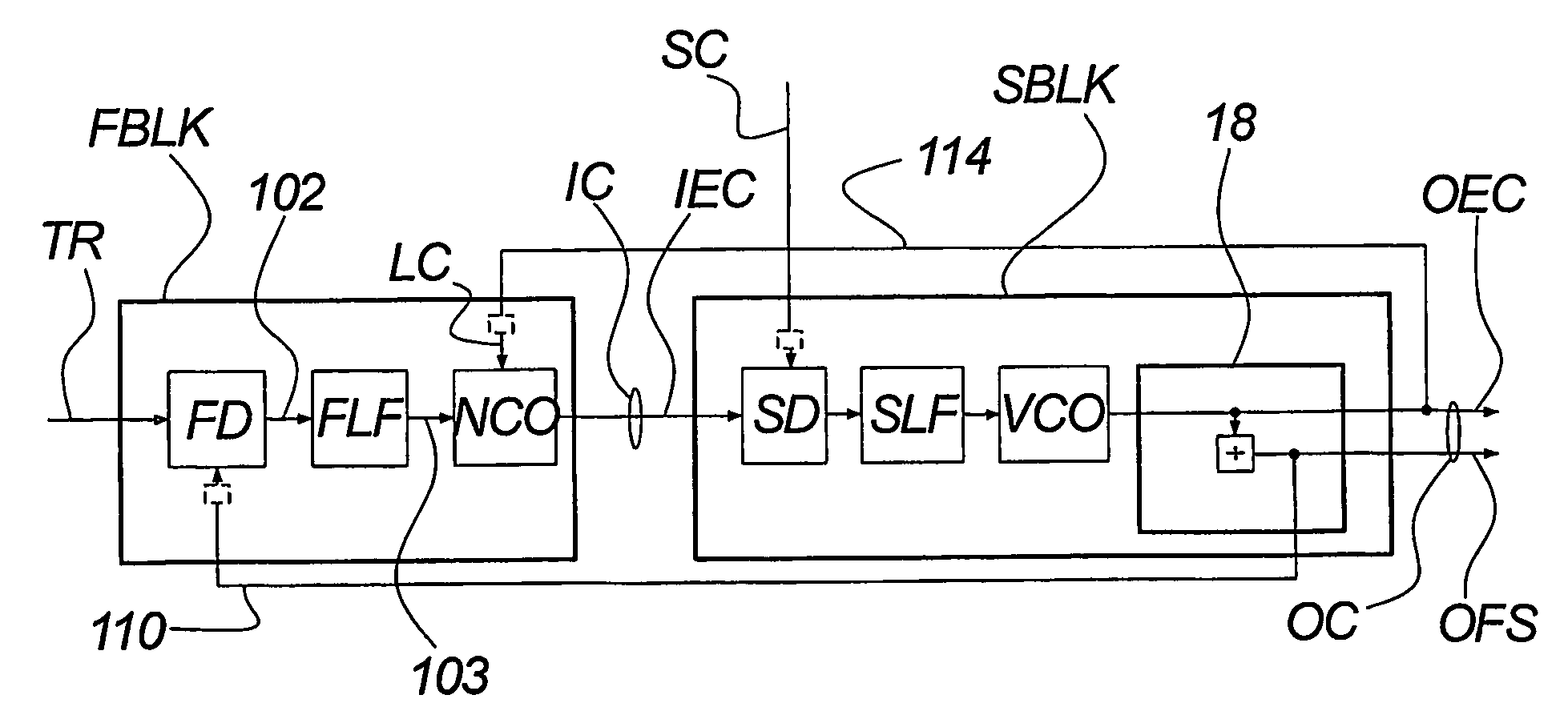
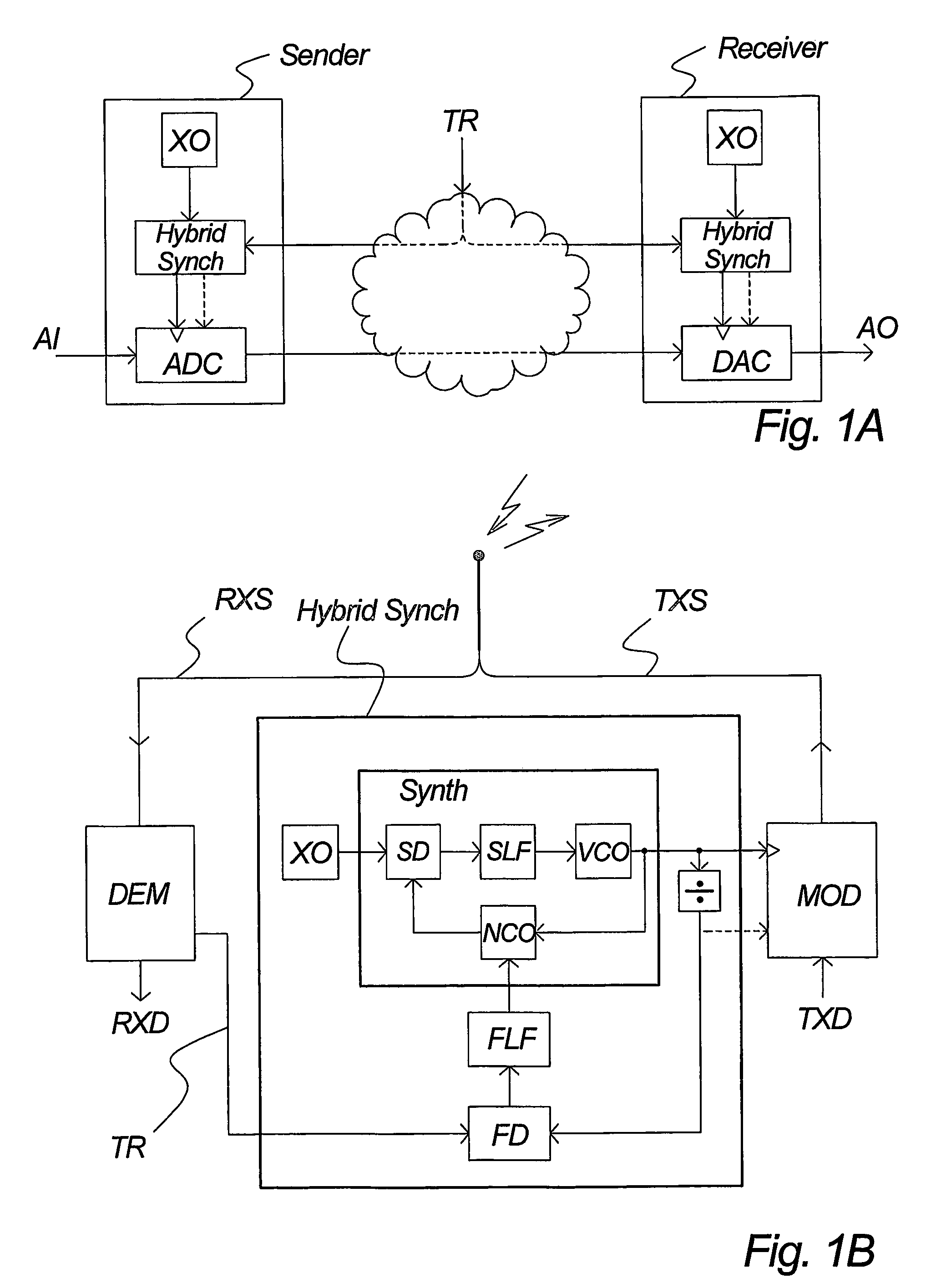
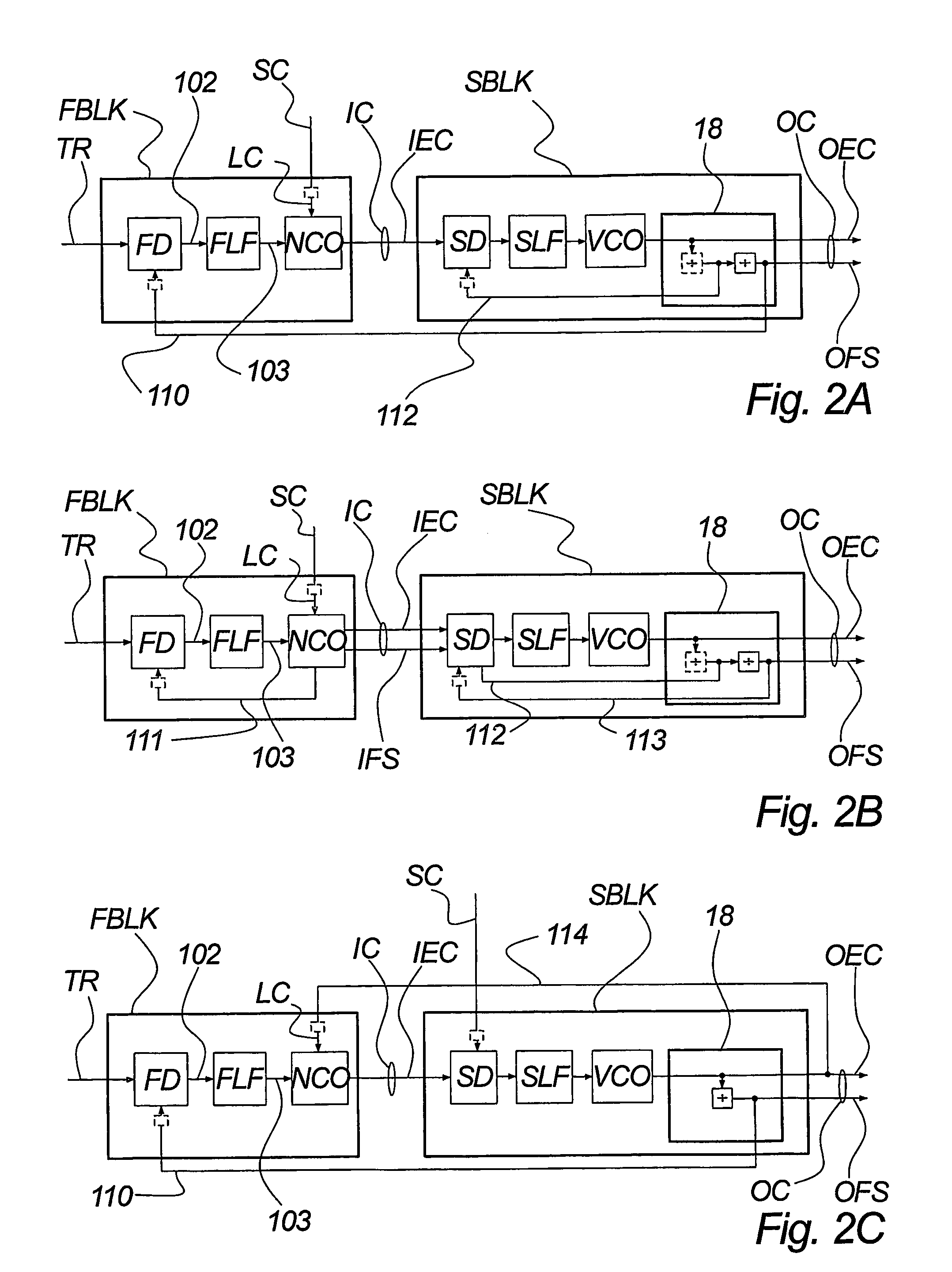
InactiveUS7495516B2Lower implementationSimple and low componentPulse automatic controlDigital data processing detailsCycle controlFrequency spectrum
A hybrid numeric-analog clock synchronizer, for establishing a clock or carrier locked to a timing reference. The clock may include a framing component. The reference may have a low update rate. The synchronizer achieves high jitter rejection, low phase noise and wide frequency range. It can be integrated on chip. It may comprise a numeric time-locked loop (TLL) with an analog phase-locked loop (PLL). Moreover a high-performance number-controlled oscillator (NCO), for creating an event clock from a master clock according to a period control signal. It processes edge times rather than period values, allowing direct control of the spectrum and peak amplitude of the justification jitter. Moreover a combined clock-and-frame asynchrony detector, for measuring the phase or time offset between composite signals. It responds e.g. to event clocks and frame syncs, enabling frame locking with loop bandwidths greater than the frame rate.
Owner:TRAVIS CHRISTOPHER JULIAN
Current limiting strategy
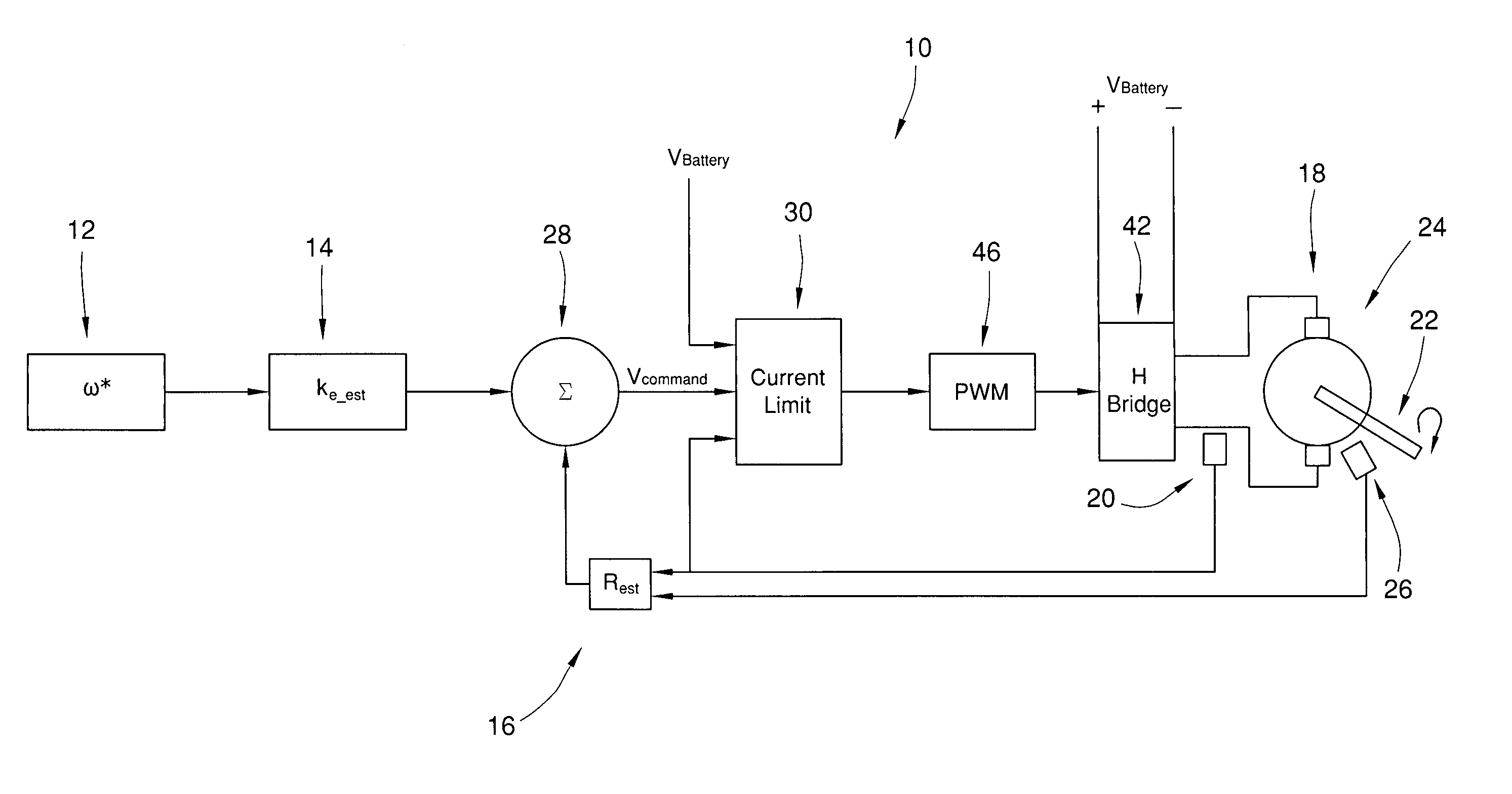
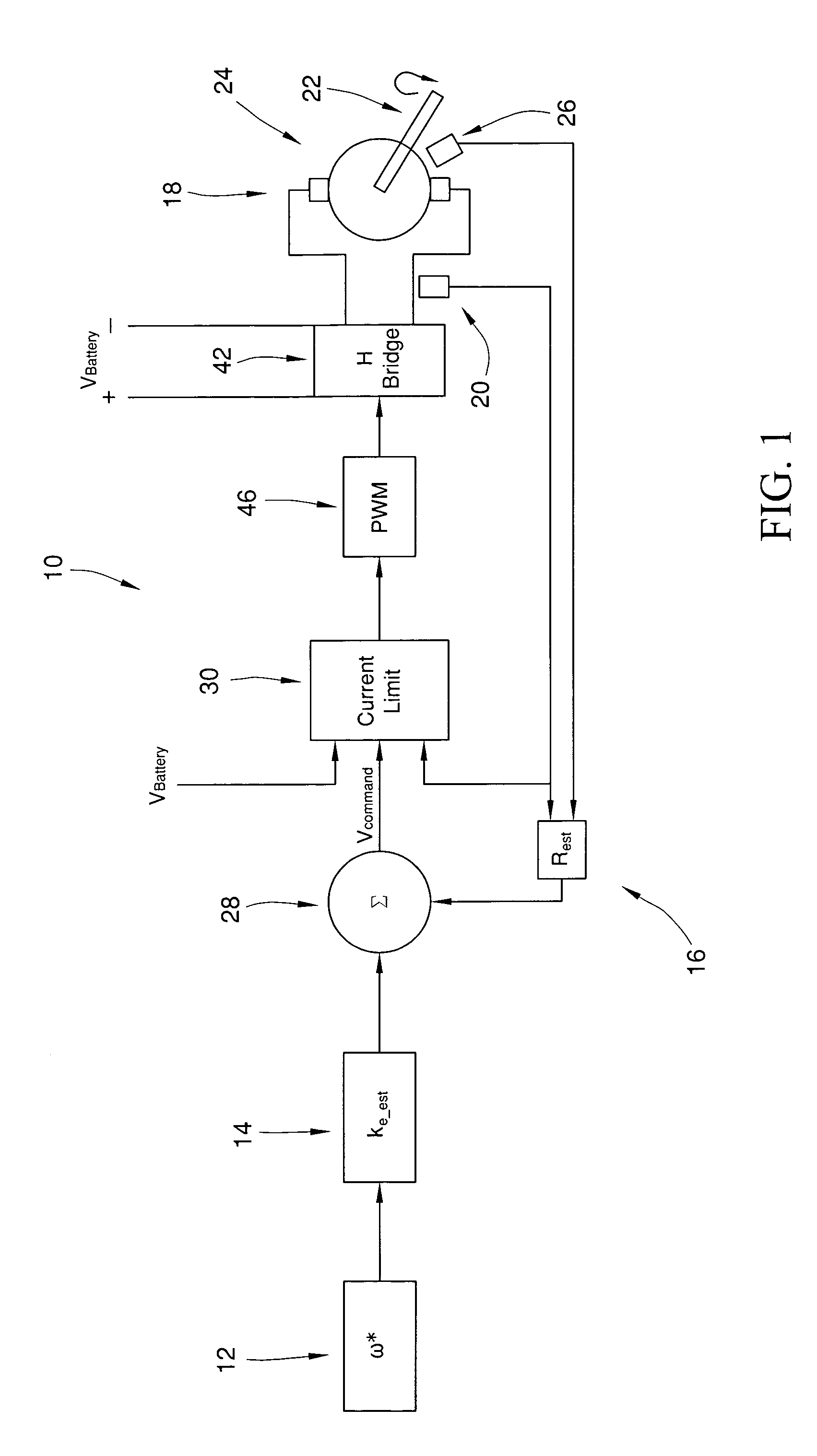
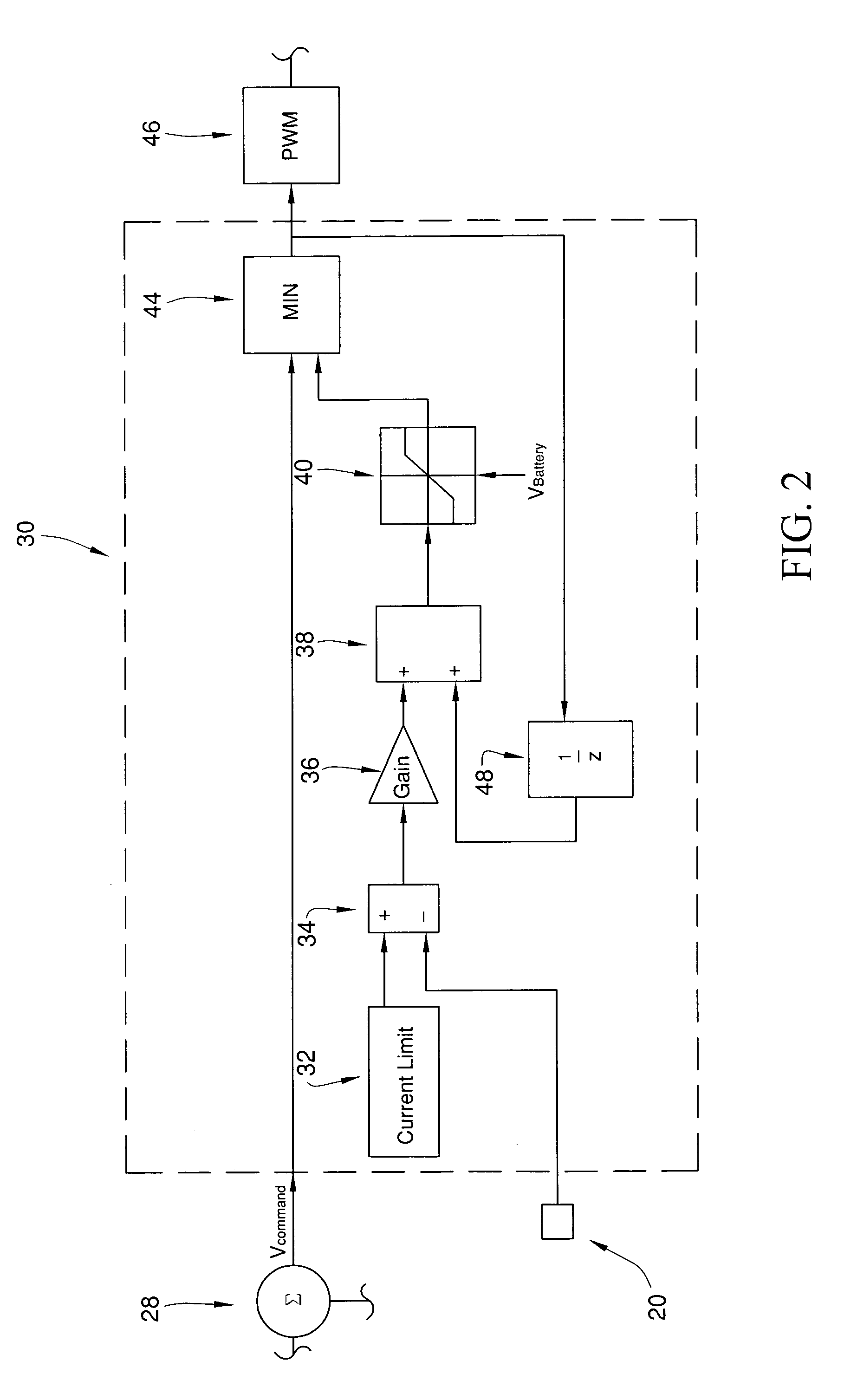
InactiveUS7026776B1Simple low cost implementationSimply and easilyAC motor controlDC motor speed/torque controlMotor speedEngineering
The invention provides a method for controlling current in a direct current motor having a back emf constant (ke), which may be a function of field current if the direct current motor is a field wound machine, and motor resistance (Rs) in all 4 quadrants of operation. The method includes the step of rotating a motor shaft of the direct current motor with a controller by applying a first voltage across the direct current motor's terminals. The first voltage corresponds to a first value of current passing through the armature windings of the direct current motor. The method also includes the step of determining a maximum value of current to pass through the armature windings of the direct current motor. The maximum value of current is selected to prevent undesirable over current conditions, such as thermal overload as one example. The method also includes the step of receiving a signal corresponding to a desired motor speed (ω*) with the controller during the rotating step. The method also includes the step of first computing a second voltage to replace the first voltage from the controller after the receiving and determining steps and in view of the estimates of the back emf constant (ke<sub2>—< / sub2>est) and the armature resistance (Rest) of the direct current motor. The method also includes the step of limiting the second voltage, if necessary to limit the current, before replacing the first voltage based at least in part on a difference between the maximum value of current and the current polarity, a gain quantity, and the first value of current and voltage in order to dynamically control current during the operating step.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC
Multi-Frequency Metal Detector Having Constant Reactive Transmit Voltage Applied To A Transmit Coil
ActiveUS20080074114A1Lower implementationSimple circuitElectric/magnetic detectionAcoustic wave reradiationMetal detectorsVoltage
An electronic metal detector having a transmit coil (1) adapted to transmit an alternating magnetic field associated with a reactive transmit voltage, wherein the transmit voltage signal is selected such that the reactive transmit voltage is approximately constant for at least a time period during which a magnetic field signal to be processed is received by the detector for processing.
Owner:MINELAB ELECTRONICS
Pixel sensing circuit with common mode cancellation
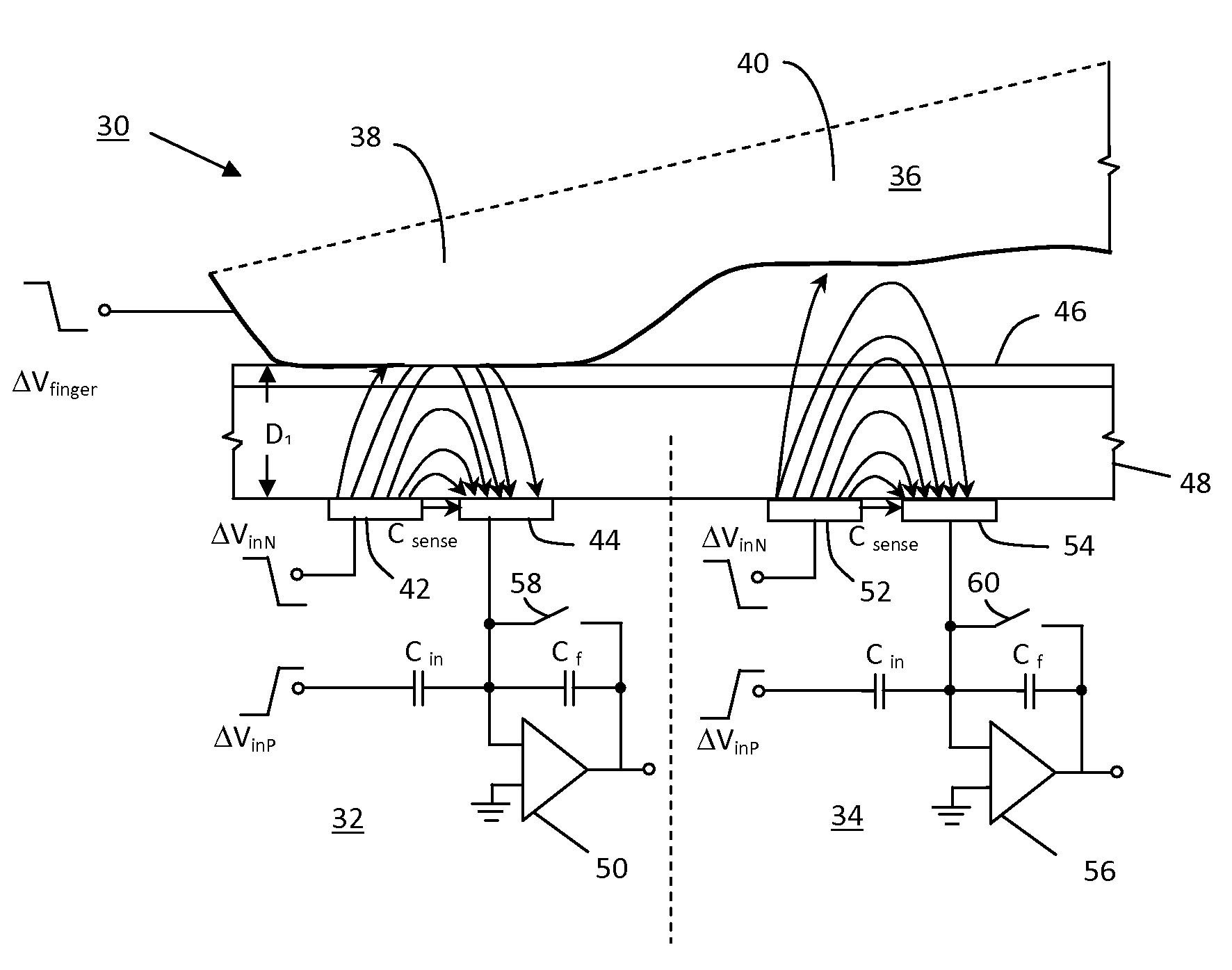
ActiveUS8115497B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioLower implementationResistance/reactance/impedencePrint image acquisitionBiometric dataIntegrator
An improved biometric data sensing circuit, for example adapted for fingerprint sensing, uses a charge subtraction technique at the input of the circuit integrator to cancel the so called “common mode” signal from the circuit output. The result is an output signal that is (a) linear, (b) free from any amplification effect due to the presence of the detected object (e.g. a finger), and (c) indicative of the detected object's fine surface geometry (i.e., indicative of the fingerprint's ridges and valleys).
Owner:APPLE INC
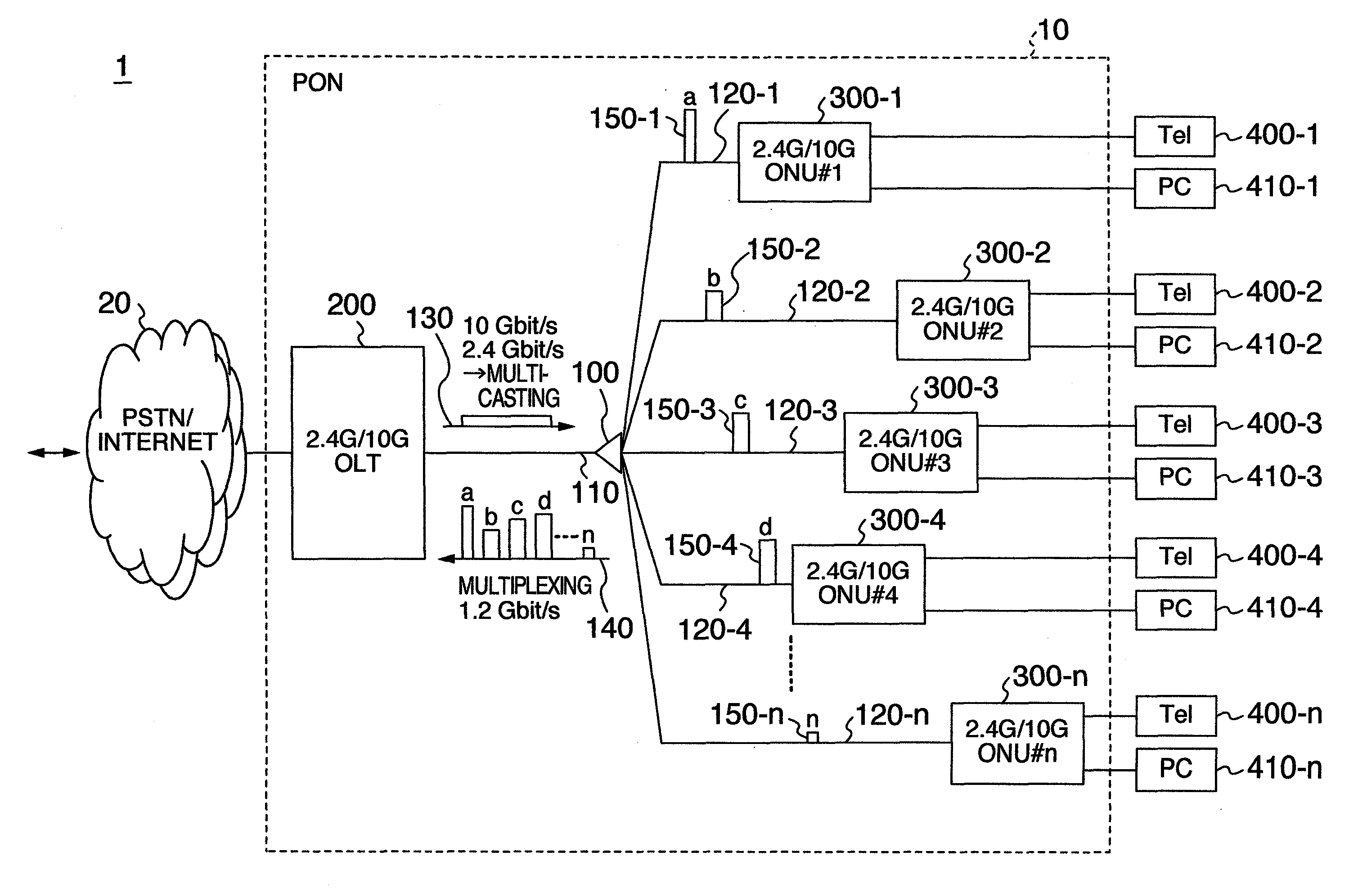
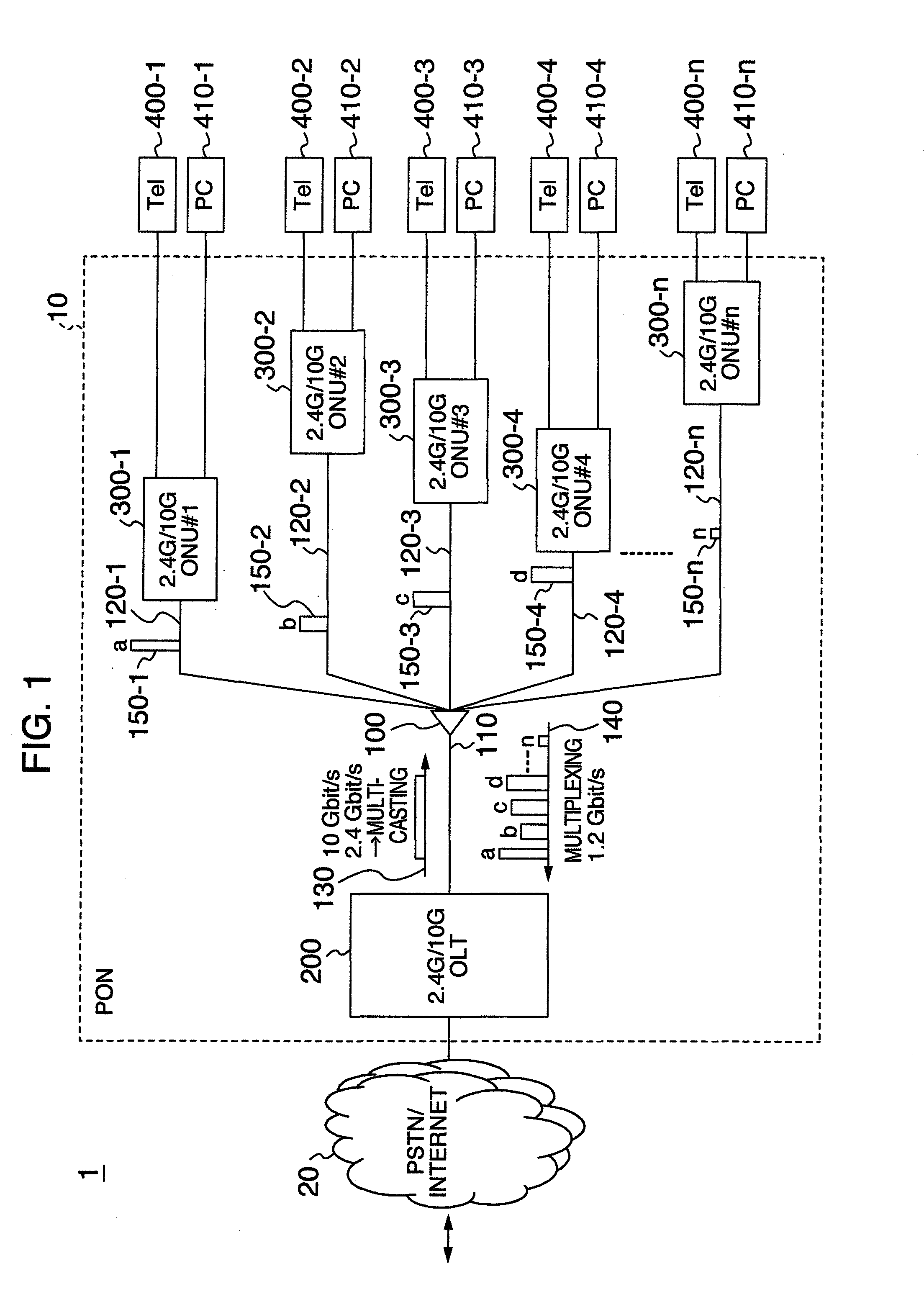
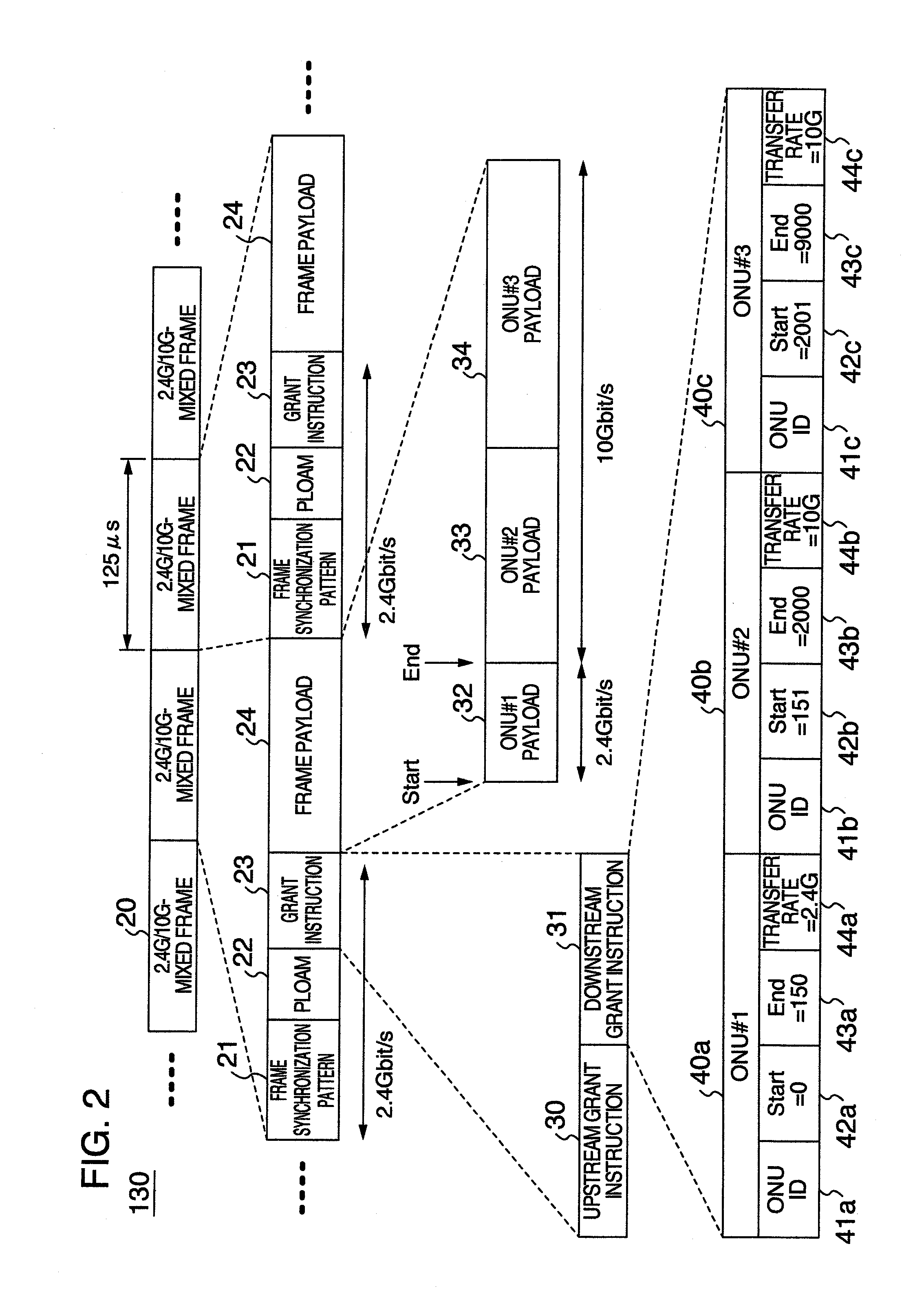
Passive optical network system and operation method thereof
InactiveUS20100290783A1Power is wastefully consumedReduce power consumptionMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division optical multiplex systemsSignal onMaster station
A master station includes an optical transmission interface for transmitting signals to a plurality of slave stations at a first transfer rate or a second transfer rate which is higher than the first one, packet buffers for accumulating the signals addressed to each of the plurality of slave stations, and a control unit for determining transmission timings and transfer rates of the signals on the basis of an amount of the signals accumulated in the packet buffers, transmitting the signals with the determined timings and rates, and notifying each of the slave stations about the determined timings and rates. Each of the slave stations includes an optical reception interface for receiving the signals of the first transfer rate or the second transfer rate, and a control unit for controlling the optical reception interface on the basis of the timings and rates which the slave stations is notified.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Ct scanning system
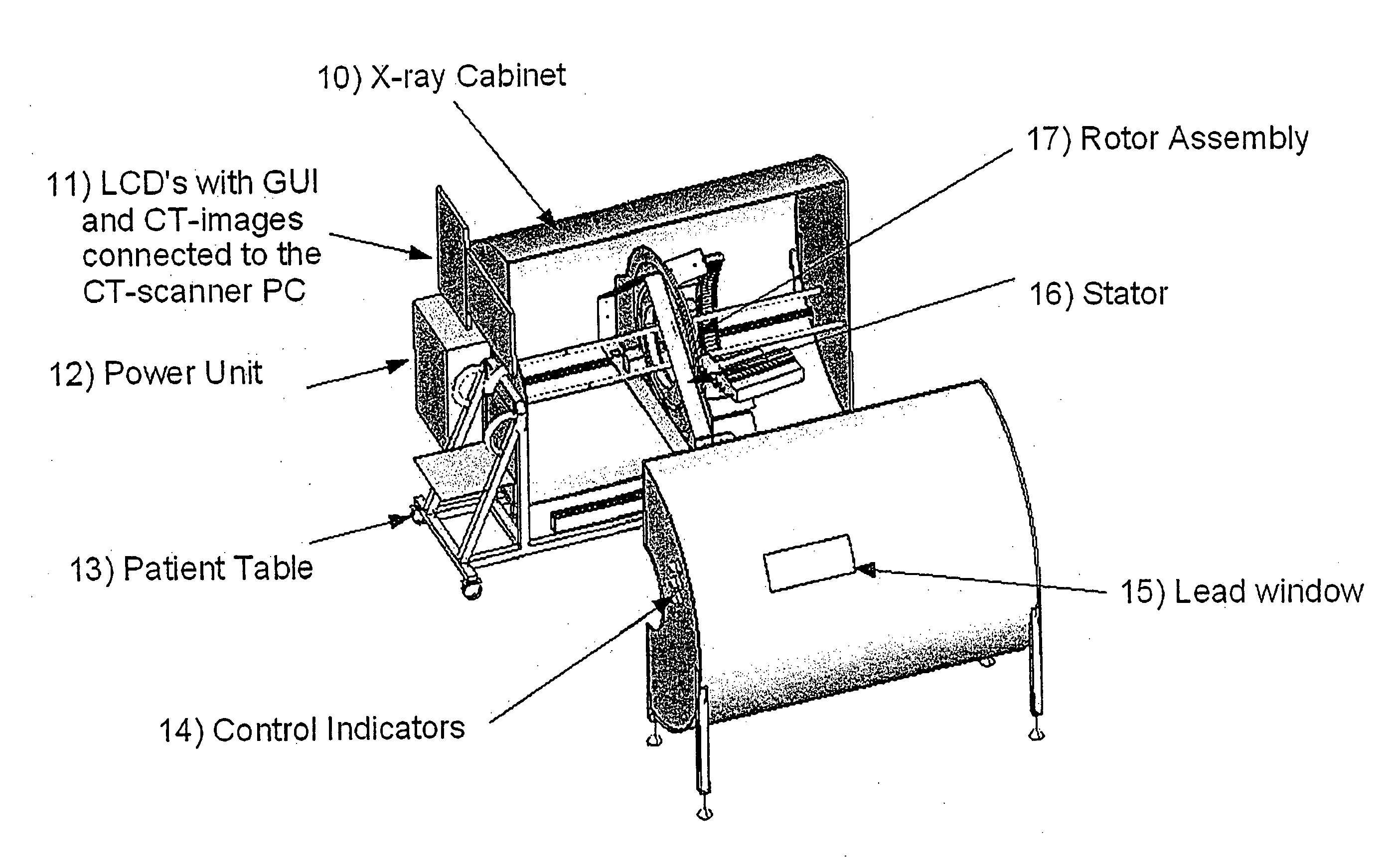
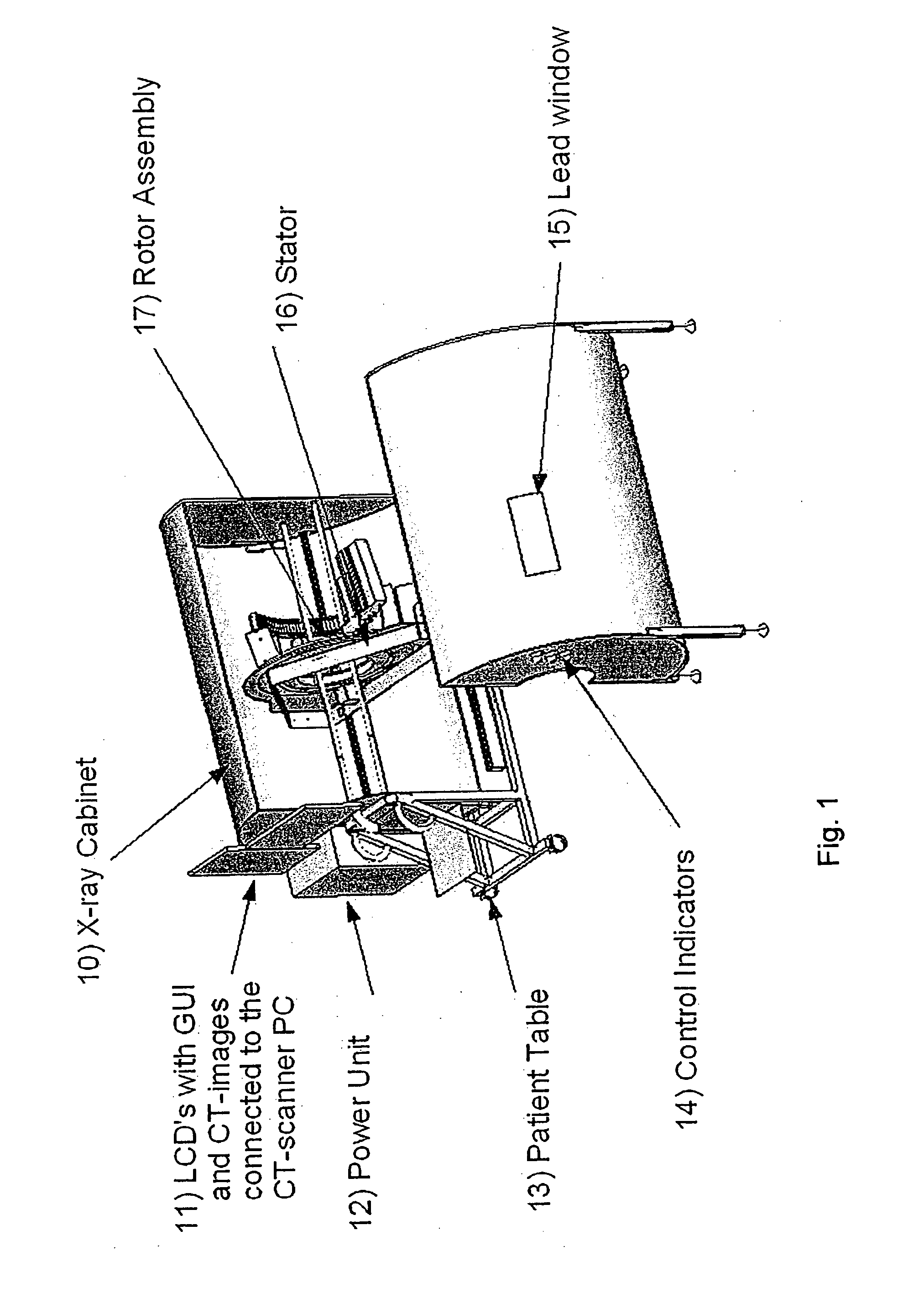
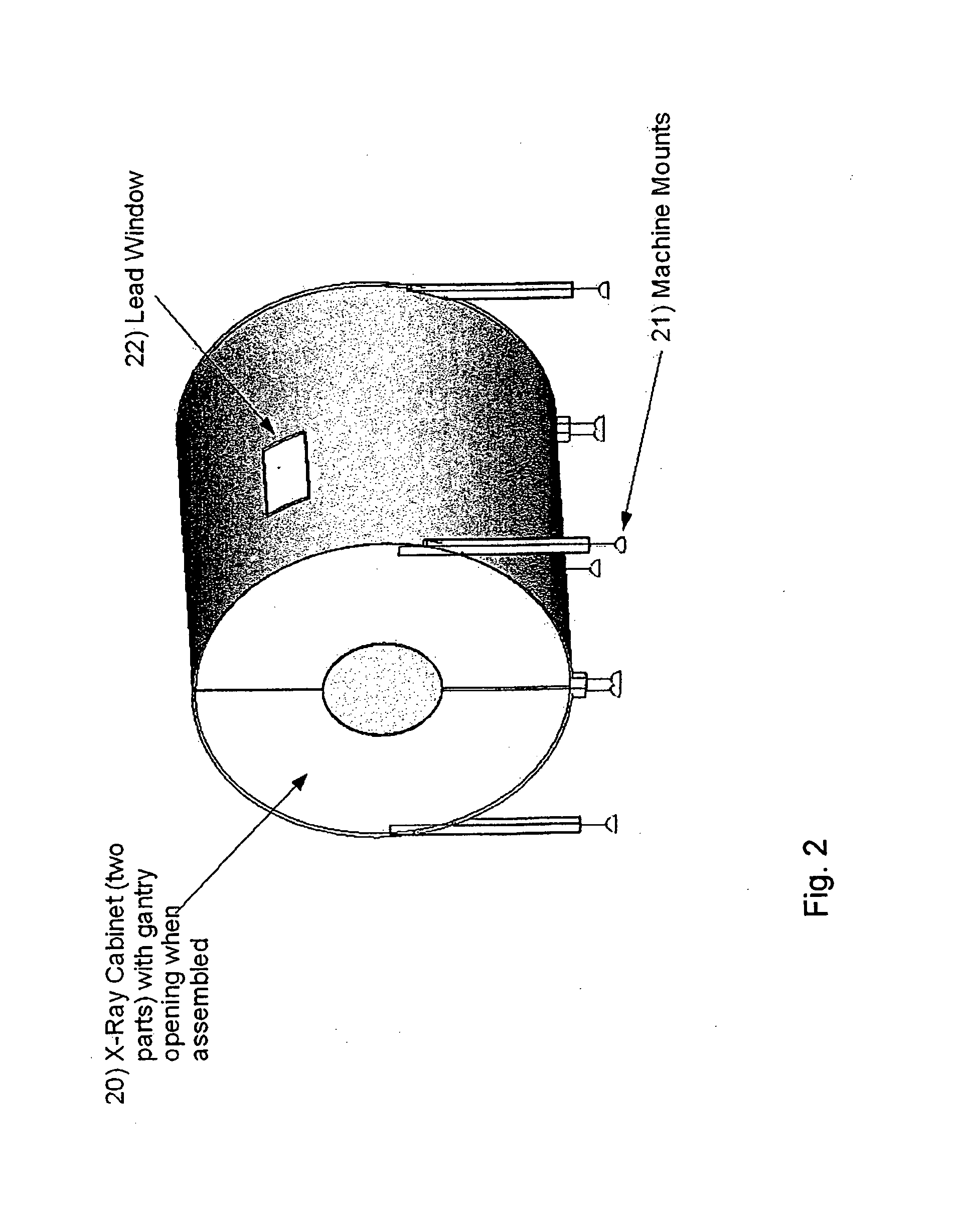
ActiveUS20110150177A1Easy to useAffordable price levelMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingComputed tomographyX-ray
The present invention provides a CT scanning system having a patient table and a gantry comprising an x-ray source configured to irradiate an x-ray beam while at least partly rotating about an object being arranged on the patient table in order to be scanned. The gantry further comprises an x-ray detector configured to receive x-rays penetrating through the object to be scanned and further configured to provide output signals representative of the received x-rays. The CT scanning system further comprises an x-ray cabinet comprising x-ray shielding material. It is preferred that the x-ray cabinet is fully surrounding the gantry. The x-ray cabinet may at least partly surround the patient table. However, it is preferred that the x-ray cabinet is fully surrounding the patient table. Thus, the patient table may be configured to be fully inserted in the x-ray cabinet, whereby the x-ray cabinet is fully surrounding the patient table. The x-ray cabinet may have an end part with a patient opening allowing the introduction of a patient into the x-ray cabinet through said opening, and the CT scanning system may further comprise a closure part or door for providing an x-ray shielding closure of the patient opening at the first end part. The x-ray cabinet may be formed by at least two parts.
Owner:GNI CO LTD
Power line decoding method for an memory array
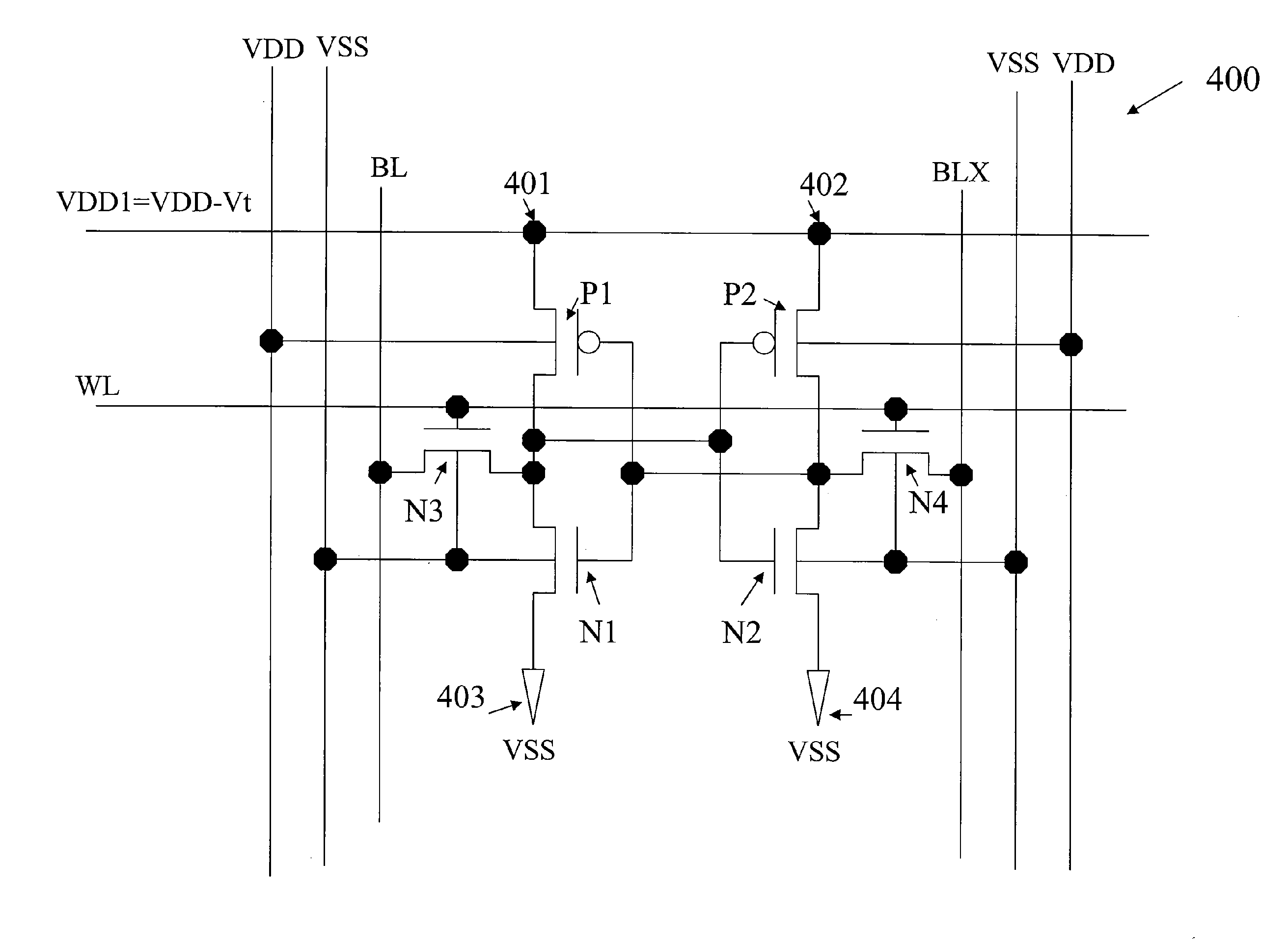
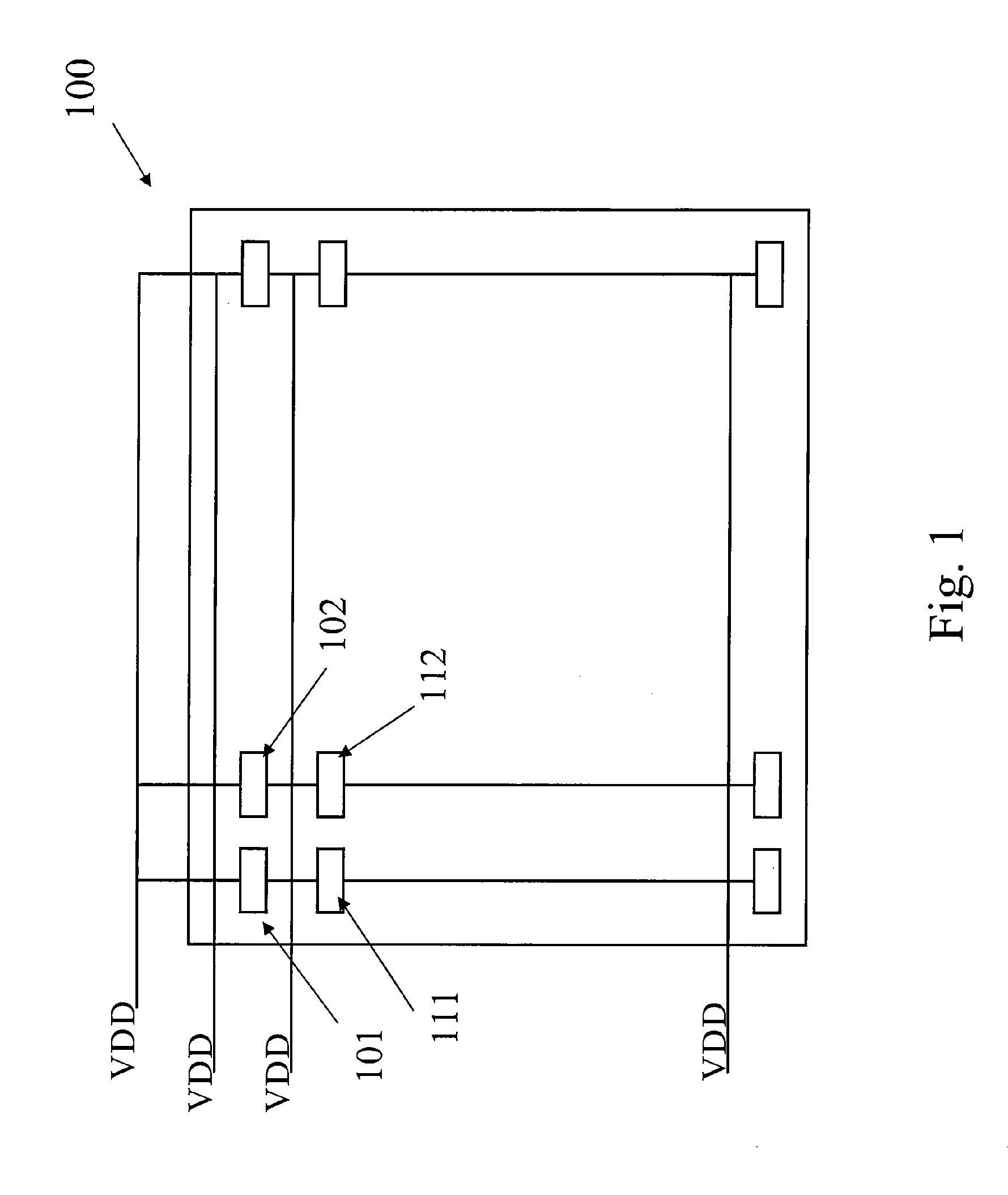
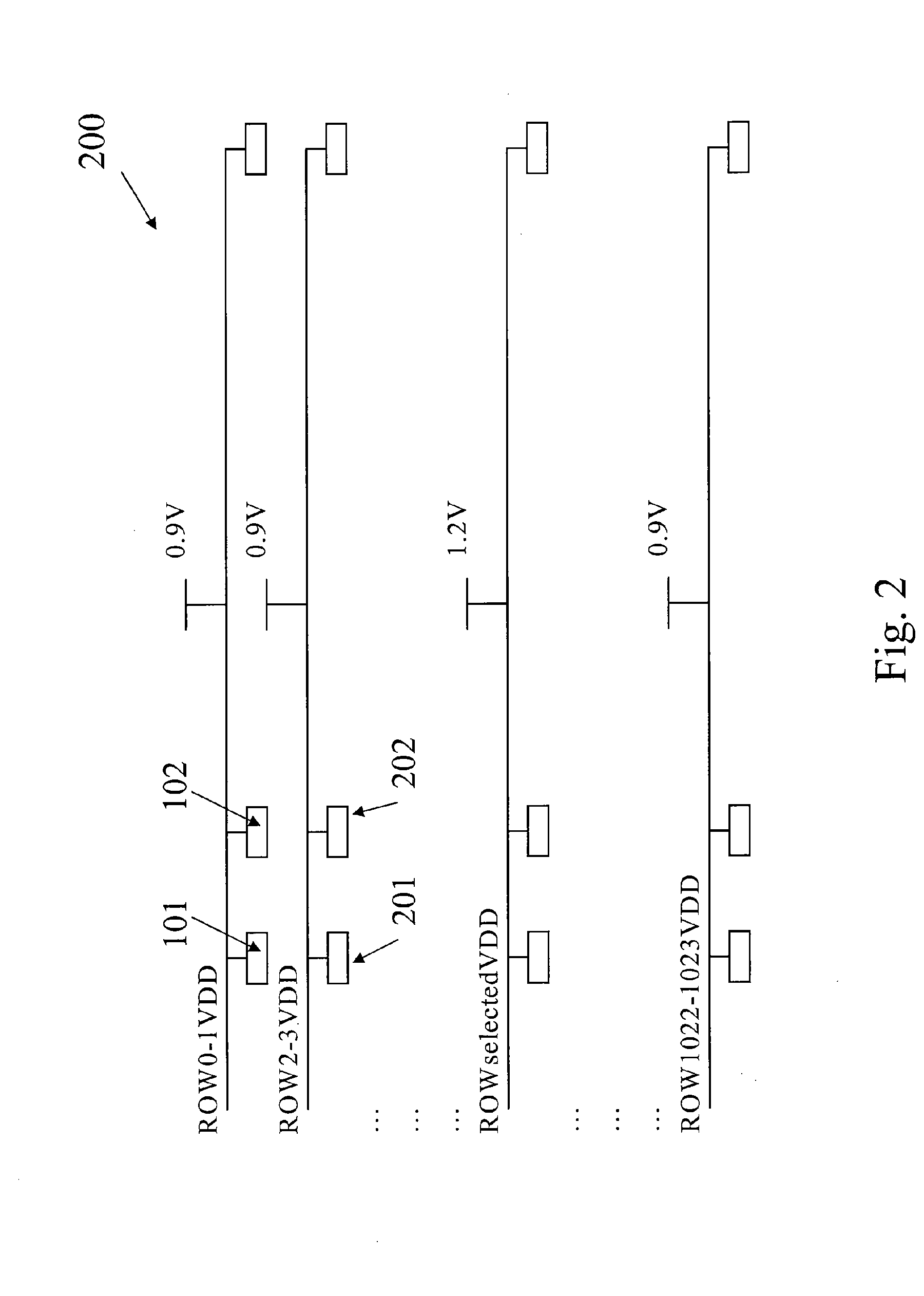
InactiveUS20100103759A1Simple designLow cost implementationDigital storageIntegrated circuitStorage cell
A method for selectively providing power supply voltage to a memory device. The method provides an integrated circuit memory device including a first plurality of memory cells. Each memory cell includes a power terminal and a ground terminal. The method includes selecting a second plurality of memory cells from the first plurality of memory cells. The method provides a first power voltage to the power terminal of each of the selected memory cells and a second power voltage to the power terminal of each of the unselected memory cells. The second power voltage is lower than the first power voltage. In an embodiment, the method applies a first ground voltage to the ground terminal of each of the selected memory cells and applies a second ground voltage to the ground terminal of each of the unselected memory cells. The second ground voltage is higher than the first ground voltage.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
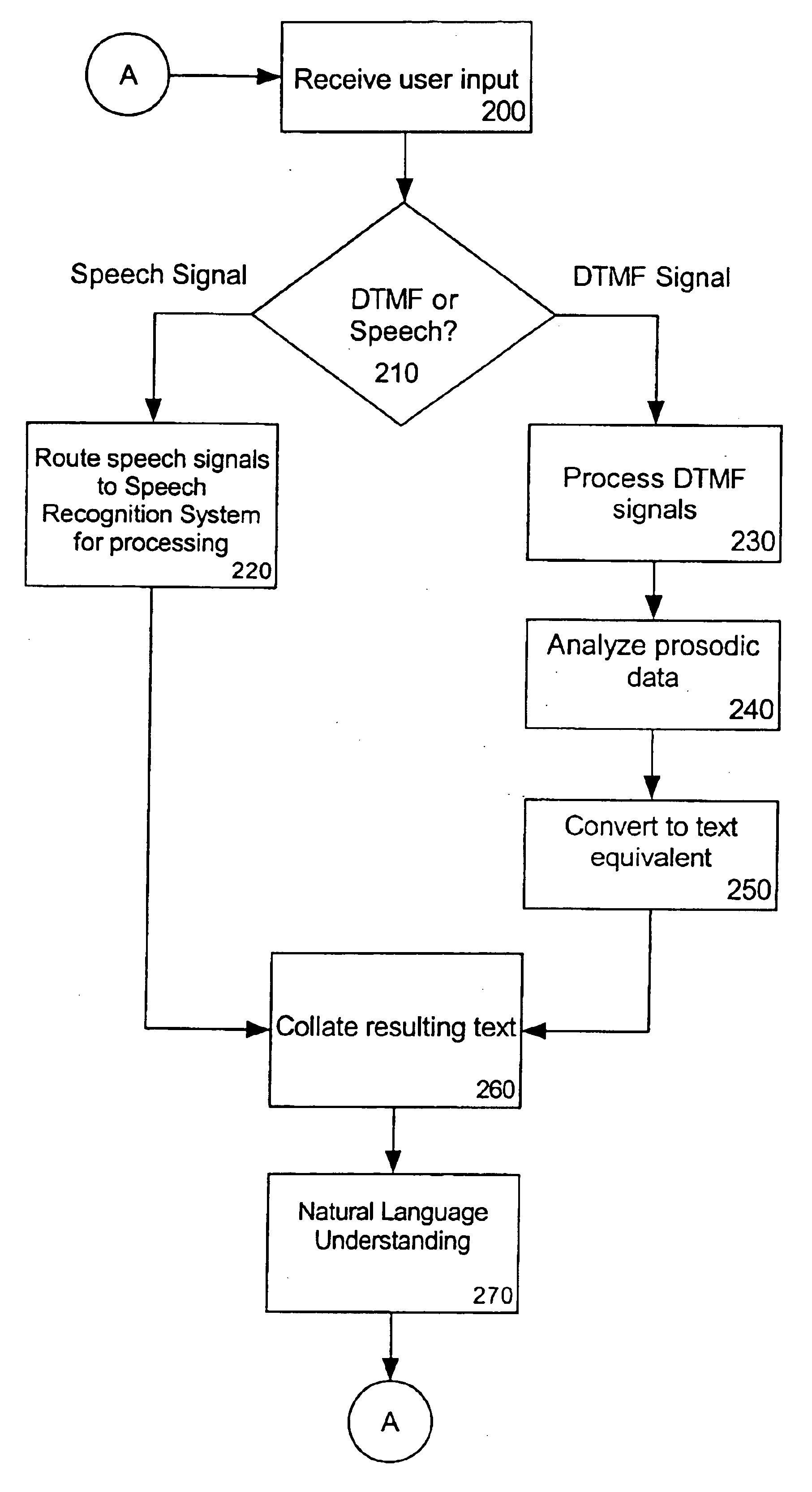
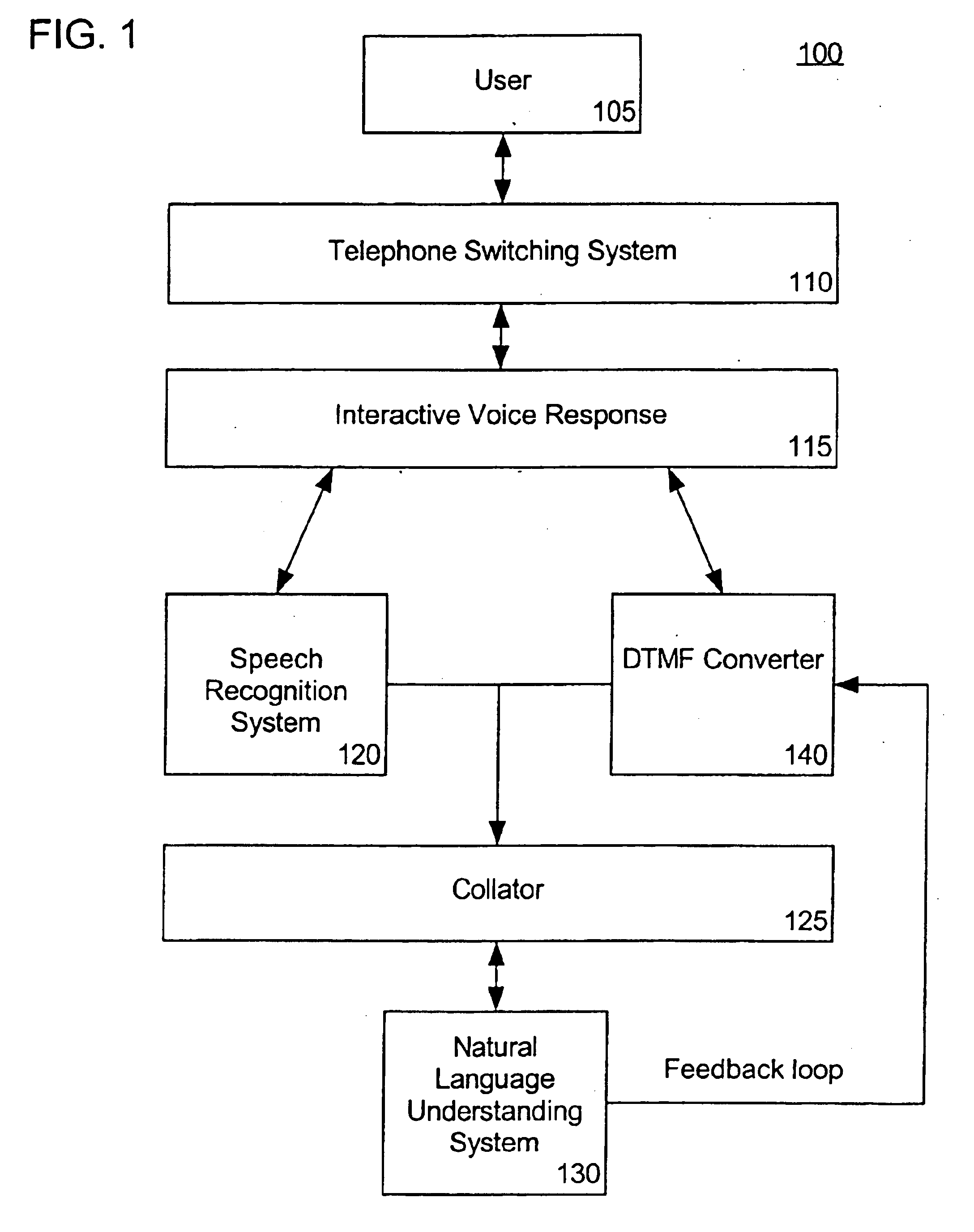
Processing dual tone multi-frequency signals for use with a natural language understanding system
InactiveUS6845356B1Lower implementationProvide feedbackSpeech recognitionNatural language understandingSpeech sound
A method for processing dual tone multi-frequency signals for use with a natural language understanding system can include several steps. The step of determining whether a audio input signal is a dual tone multi-frequency signal or a human speech signal can be included. If the audio input signal is determined to be a dual tone multi-frequency signal, the audio input signal can be converted to at least one text equivalent. Also, the step of providing the at least one text equivalent to a natural language understanding system can be included. The natural language understanding system can determine a meaning from the text equivalent.
Owner:NUANCE COMM INC
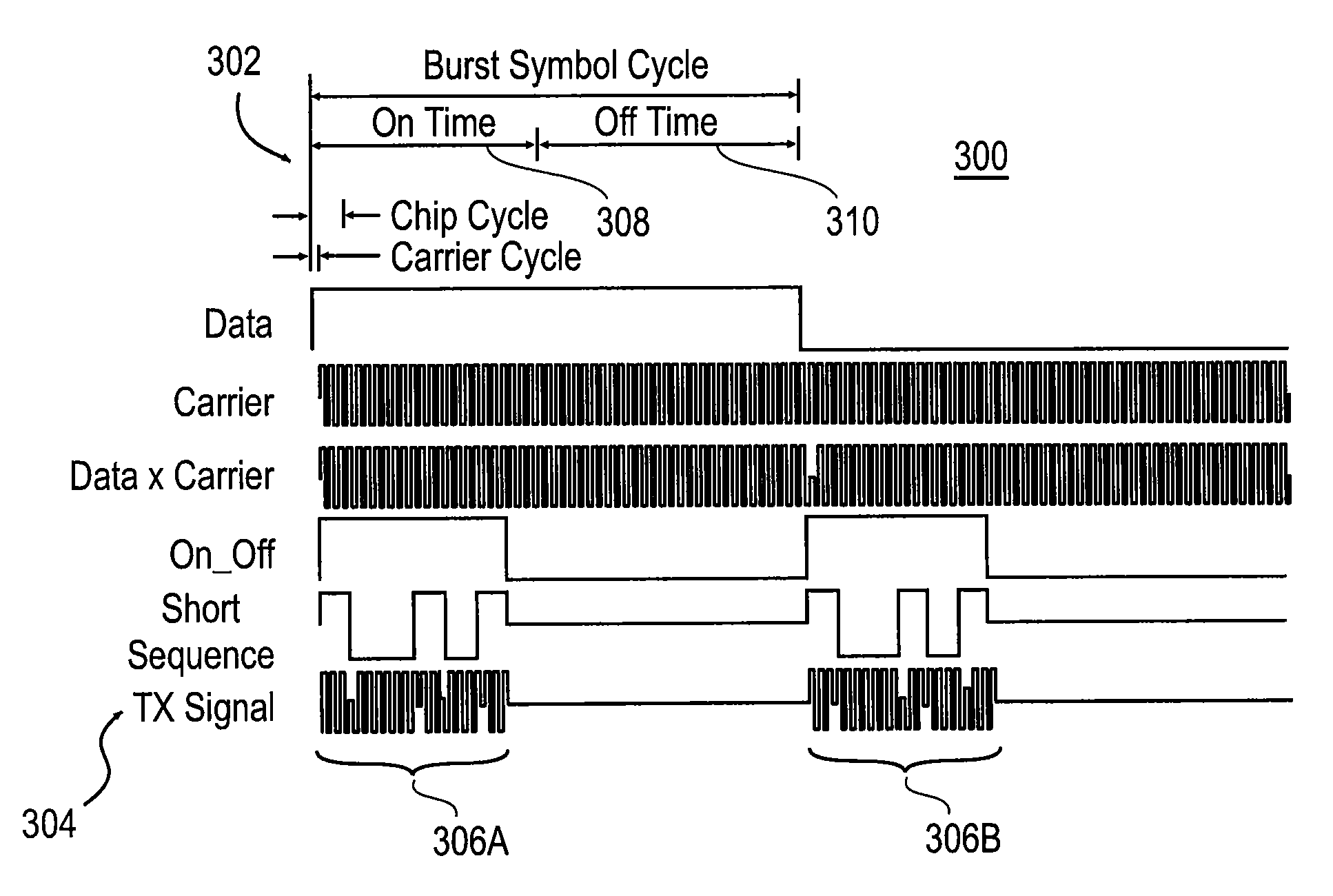
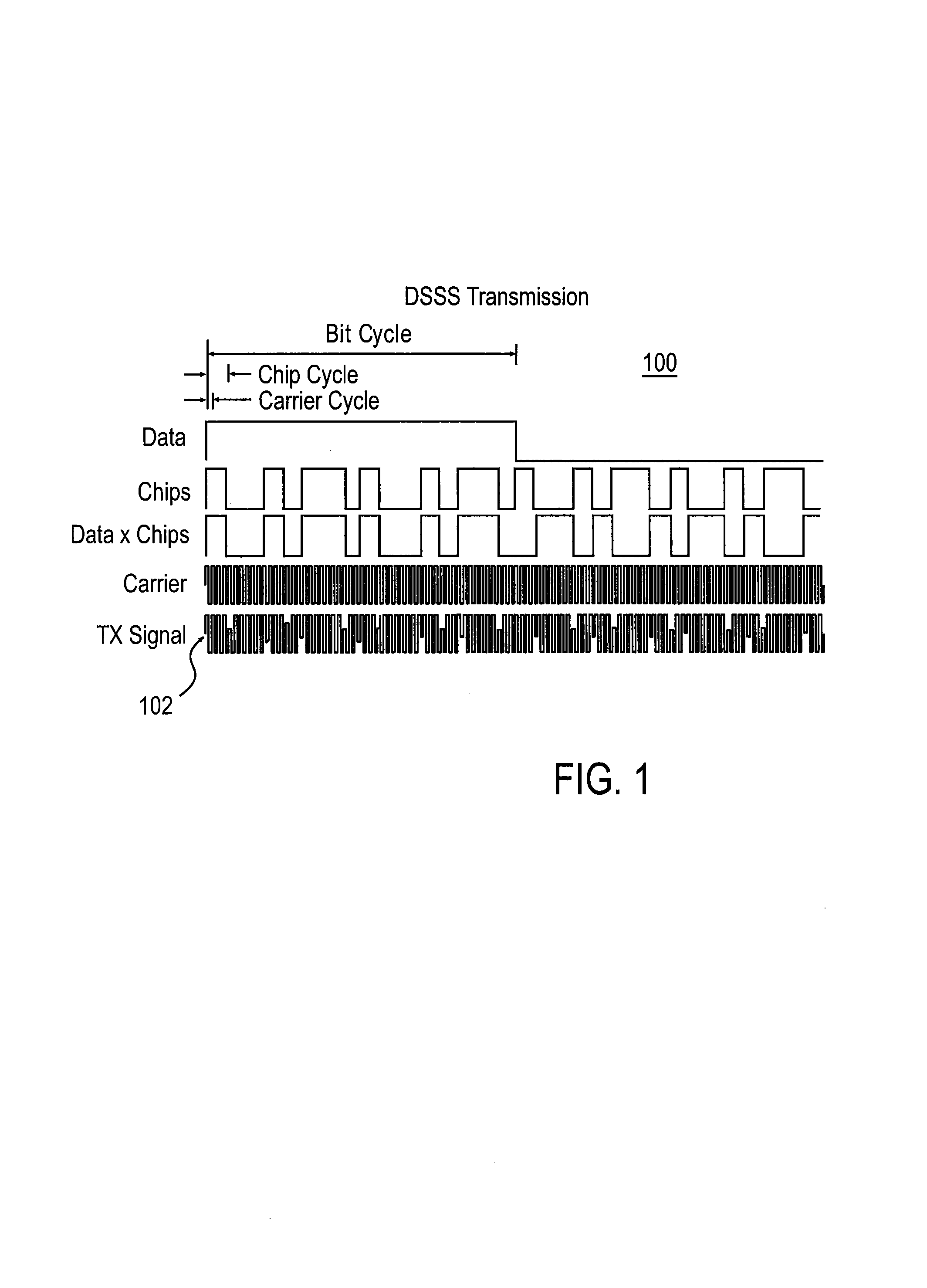
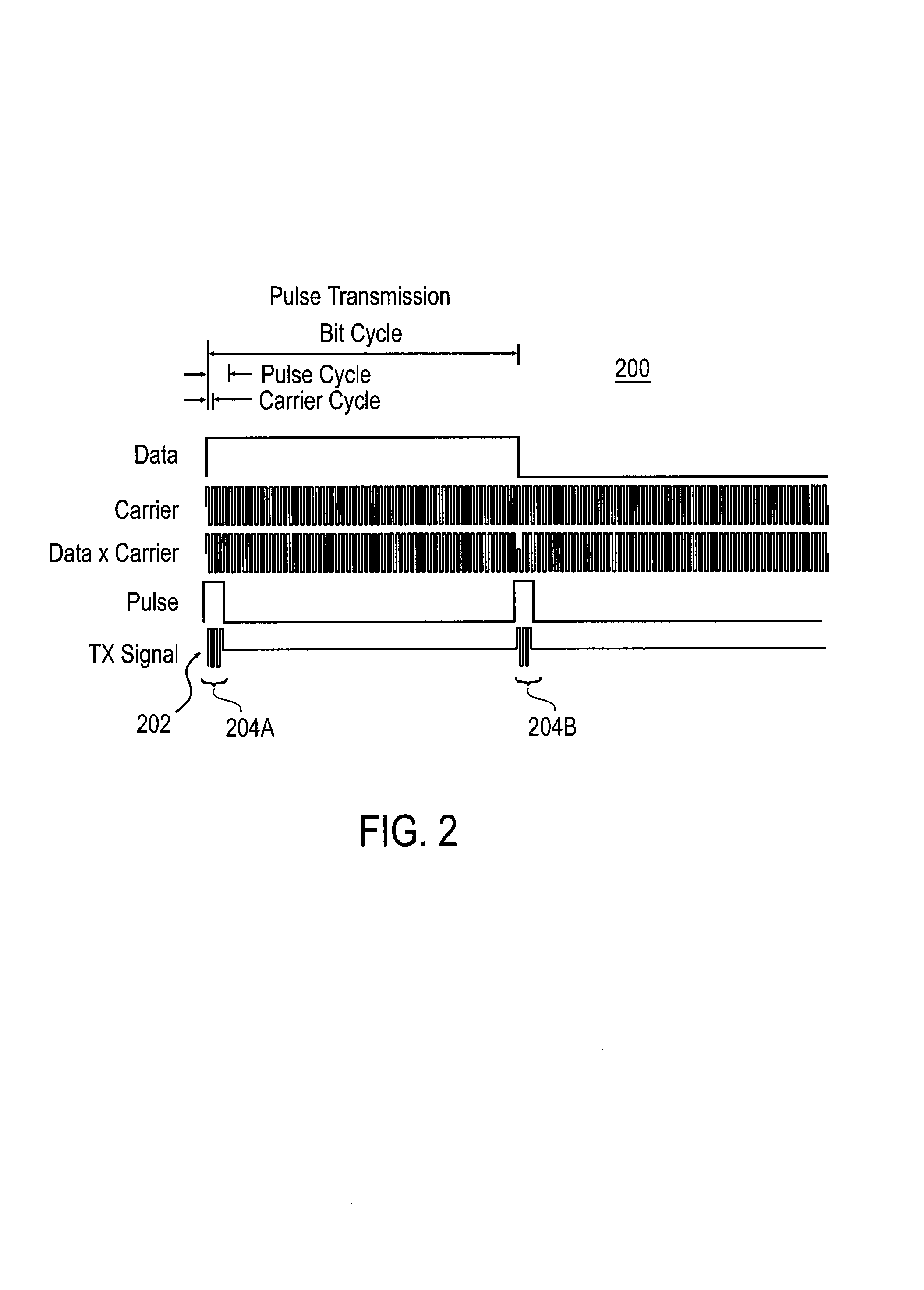
Multi-band ultra-wide band communication method and system
InactiveUS7221911B2Improve performanceHigh data transfer rate capabilityElectric signal transmission systemsFrequency/rate-modulated pulse demodulationFast Fourier transformMulti band
The present invention provides ultra-wide band communication systems and methods, including multi-band ultra-wide band communication systems and methods. Methods and systems are provided in which frequency sub-bands of an ultra-wide band spectrum are allocated for signal transmission. An ultra-wide band transmission including the information is sent, including sending a signal over each of the plurality of sub-bands.Methods are further provided in which a first data signal containing information is converted into an encoded signal using an Inverse Fast Fourier Transform. The encoded signal is converted into an encoded ultra-wide band signal that can be pulsed or transmitted using burst symbol cycles. The encoded pulsed ultra-wide band signal is decoded using a Fast Fourier Transform to obtain the information.
Owner:WISAIR
Apparatus and method for receiving signal in communication system supporting gaussian frequency shift keying modulation scheme
ActiveUS20150280951A1Reduce processLower implementationFrequency-modulated carrier systemsAngle demodulationCommunications systemEngineering
An apparatus and a method are provided for receiving a signal in a communication system supporting a Gaussian frequency shift keying (GFSK) modulation scheme. The method includes receiving the signal; and estimating a codeword vector by performing a signal detecting operation based on a GFSK-maximum likelihood sequence estimation (MLSE) scheme, which is based on a GFSK modulation scheme and an MLSE scheme, on the received signal. States of a Viterbi trellis that are used in the GFSK-MLSE scheme are determined based on the GFSK modulation scheme.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and System for Equalization and Decoding Received Signals Based on High-Order Statistics in Optical Communication Networks
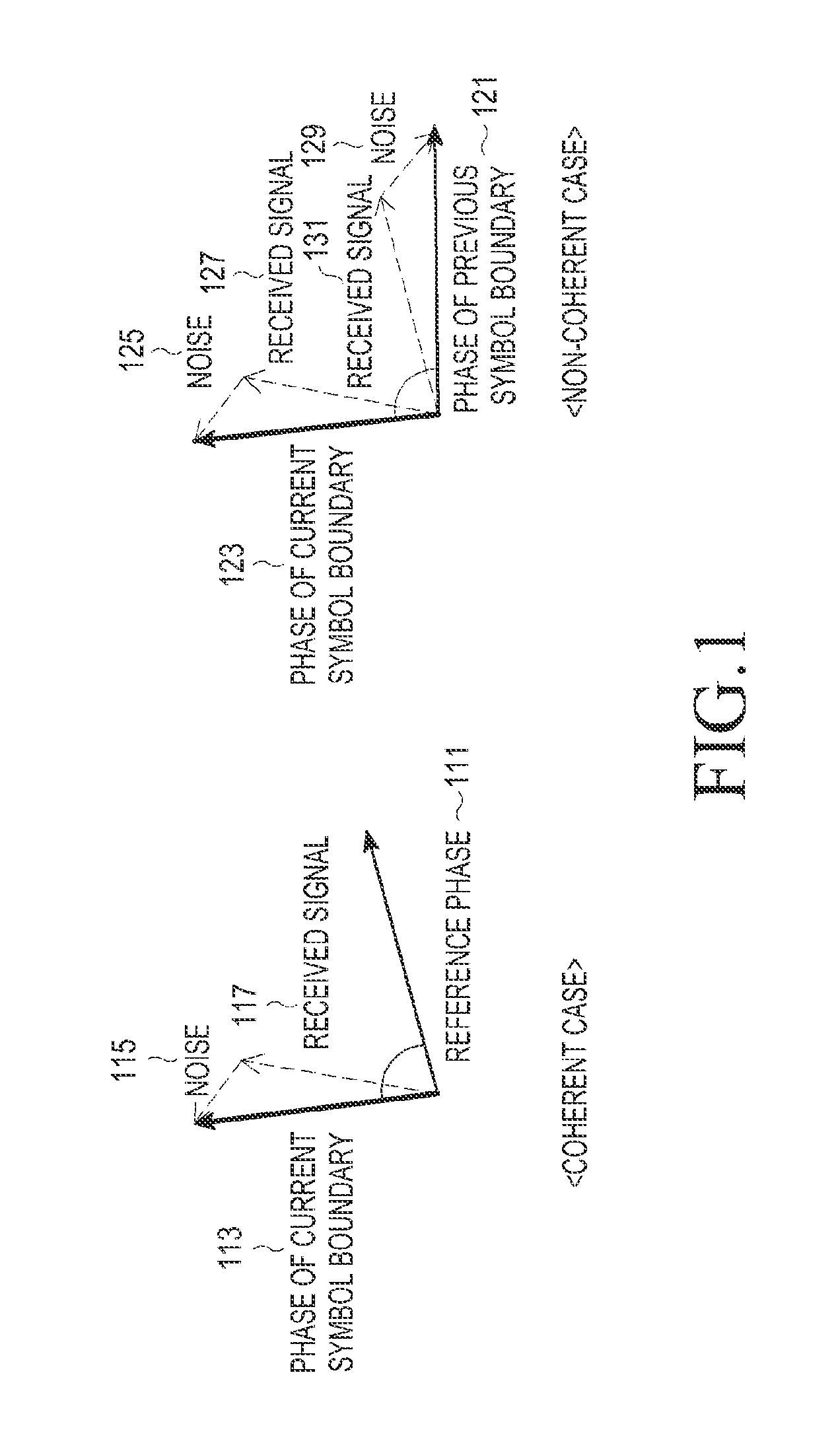
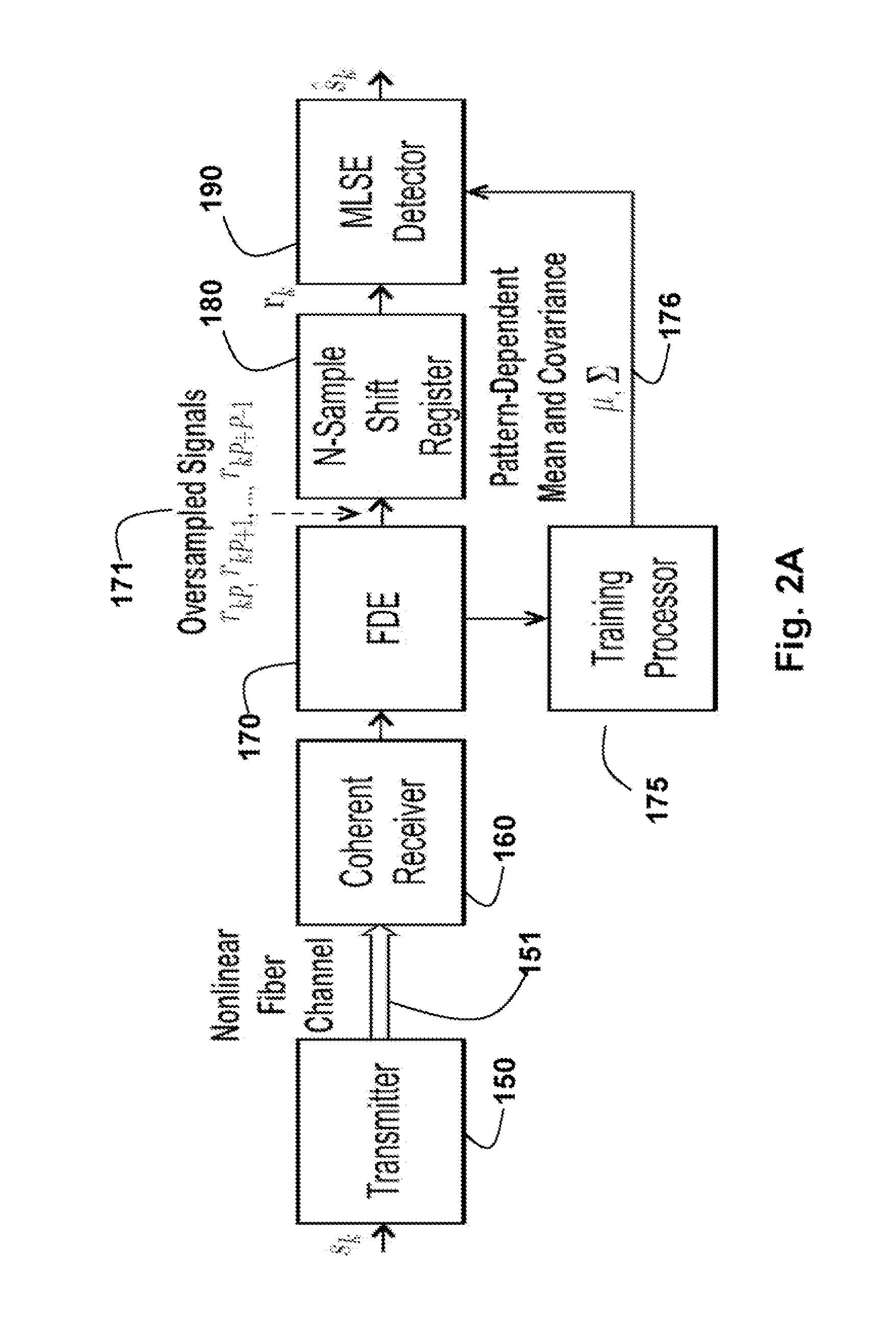
InactiveUS20130170842A1Improve receiver performanceLower implementationElectromagnetic receiversBaseband systemsHigher-order statisticsTime shifting
A method equalizes and decodes a received signal including a sequence of symbols. Subsequences of the signal are selected, wherein the subsequences are overlapping and time shifted. For each subsequence, statistics of the channel corresponding to a pattern in the subsequence are selected, wherein the statistics include high-order statistics. A transmitted signal corresponding to the received signal is then estimated based on the statistics.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Soft bit computation for a reduced state equalizer
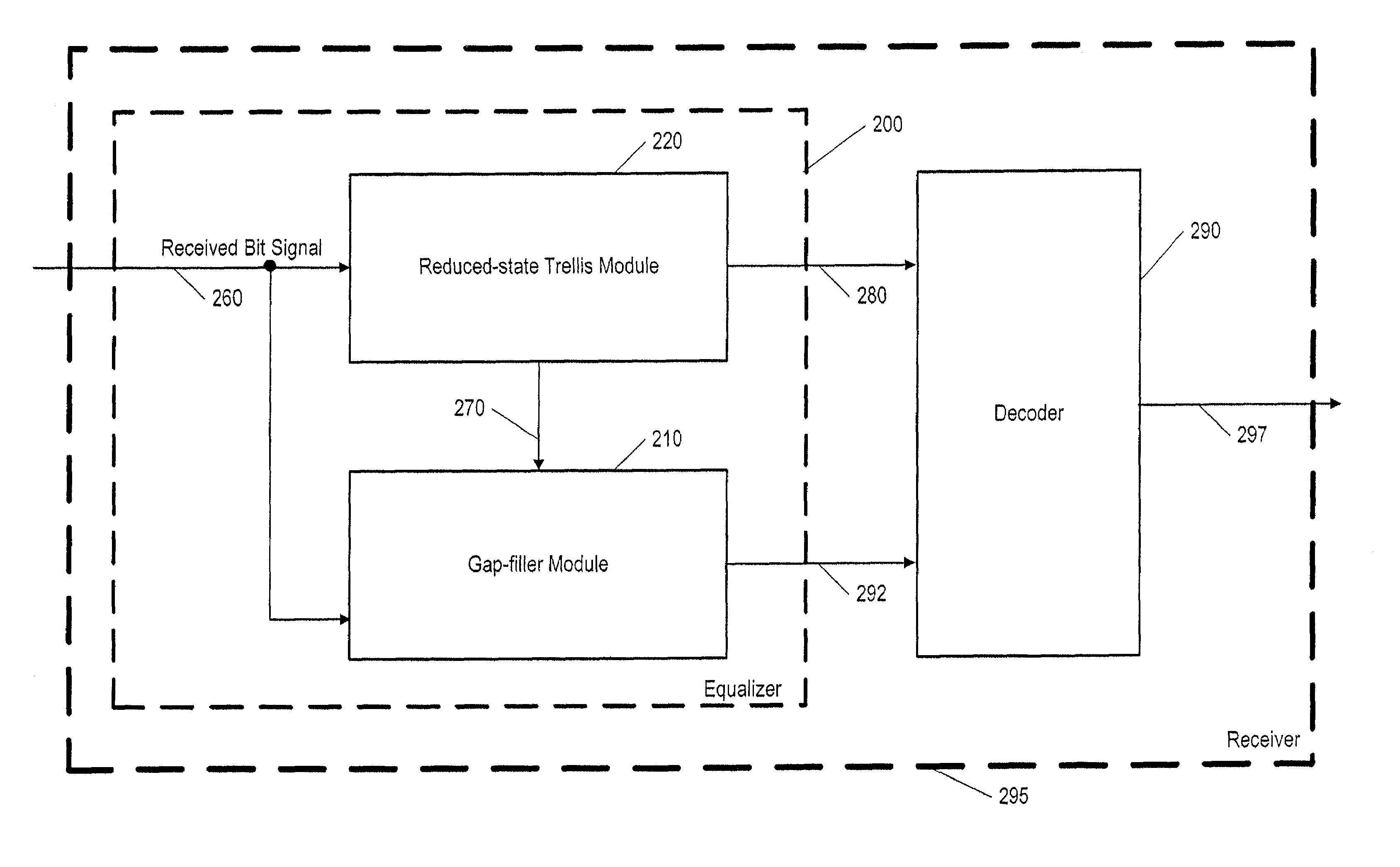
InactiveUS7042938B2Improve performanceReduce implementation complexityMultiple-port networksData representation error detection/correctionEqualizationComputer engineering
Method and apparatus for soft bit computation with a reduced state equalizer. The method assures that the number of states in the equalizer is reduced to obtain acceptable complexity, while also ensuring that soft bit computation is performed for substantially all bits. The method involves computing a first set of soft bits from bits transmitted in a received signal, using a reduced-state trellis with finite non-zero delay, calculating hard decisions in response to the received signal, and also ensuring that substantially all soft bits are computed by employing zero-delay soft decision-making or decision-feedback equalization to compute a second set of soft bits. Furthermore, the hard decisions are used to compute the second set.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC +1
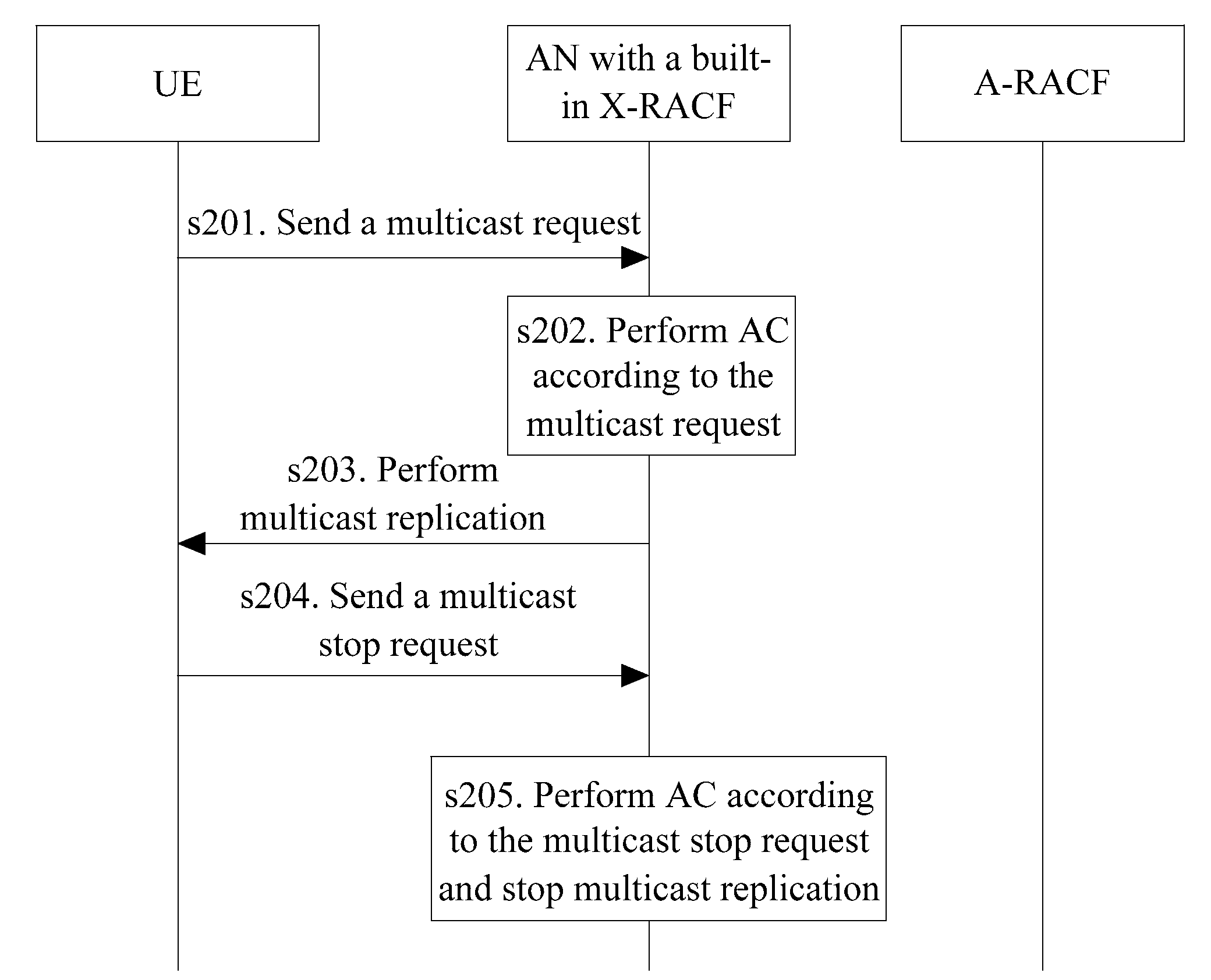
Method, system and apparatus for admission control of multicast or unicast
InactiveUS20100103934A1Reduce complexityFast channel switchingData switching by path configurationAdmission controlUnicast
The embodiment of this invention discloses a method, a system and an apparatus for admission control of multicast or unicast. The method for admission control of multicast comprises: a network device receives a multicast request and executes admission control operation of multicast resources according to the multicast request; when multicast resources are not sufficient, the network device sends an outer resources request to a resources admission control device, and executes multicast operation according to the results of admission control operation returned by the resources admission control device responsive to said outer resources request. The method for admission control of unicast comprises: a resources admission control device receives a unicast resources request and executes admission control operation of unicast resources according to the unicast resources request; when the unicast resources are not sufficient, the resources admission control device sends an outer resources request to a network device; the resources admission control device executes unicast operation according to the results of admission control operation returned by the network device responsive to said outer resources request. The embodiment of this invention guarantees fast handoff of multicast service channel in the case of implementing resources share of multicast services and unicast services, and the implementation is simple.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Location-Based Telecommunications Redundancy Protocol
InactiveUS20070281703A1Lower implementationService provisioningSpecial service for subscribersMobile phoneTelecommunications Device
A protocol for location-based telecommunications redundancy, operable at a data-communications topology juncture having at least two telecommunications media thereat, and the protocol includes the steps of: (1) On the occurrence of a call-processing request from a caller to a recipient—e.g. using a last known present location of the recipient's mobile phone; and (2) Using the current location, second software at-the-juncture propagating the request to “ring” at two call-receiving devices closest to the current location—wherein one of the devices is a mobile telecommunications device of the recipient and the other of the devices is a terrestrial device of the recipient that is closest to the current location of the recipient.
Owner:BROADPHONE
Broadband modulation/demodulation apparatus and a method thereof
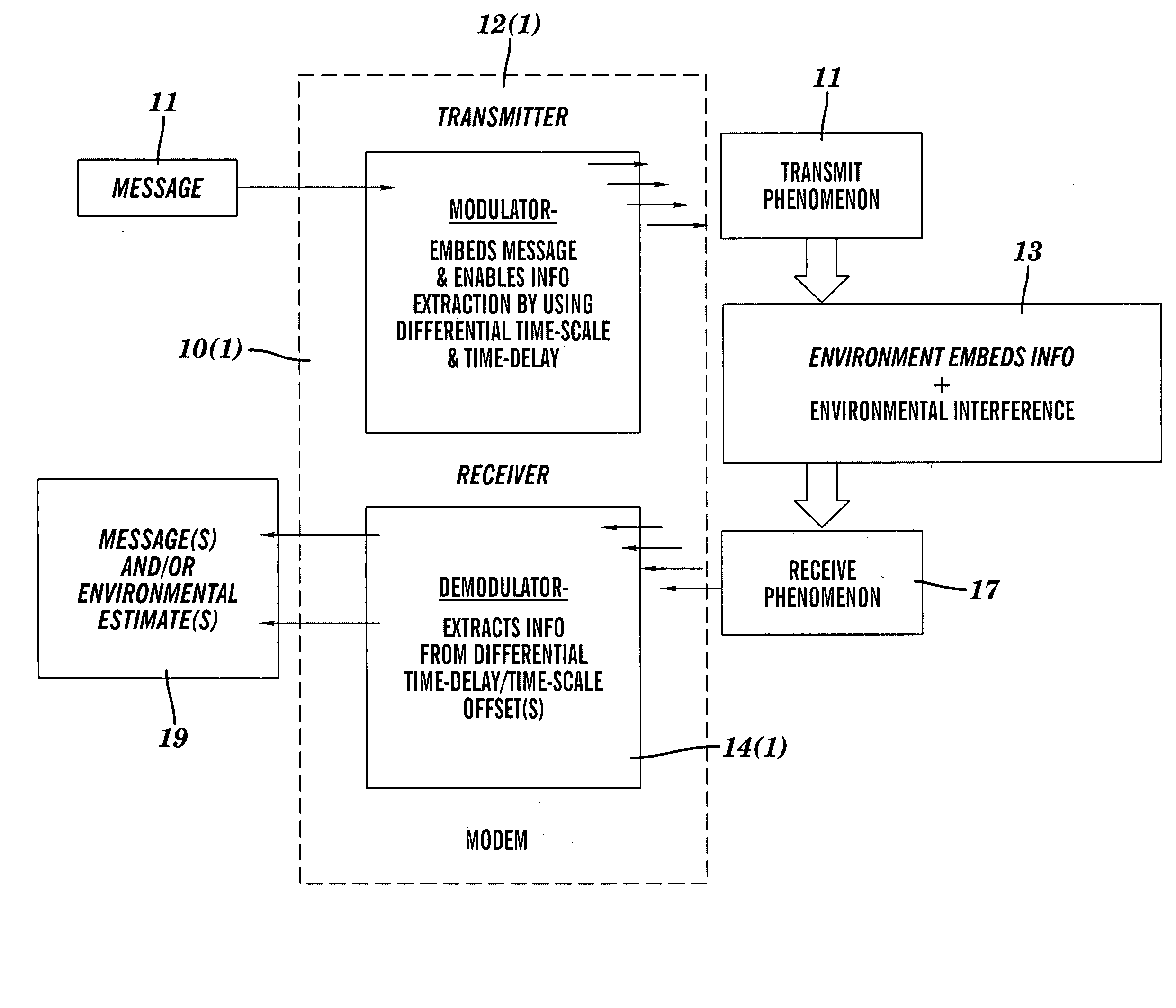
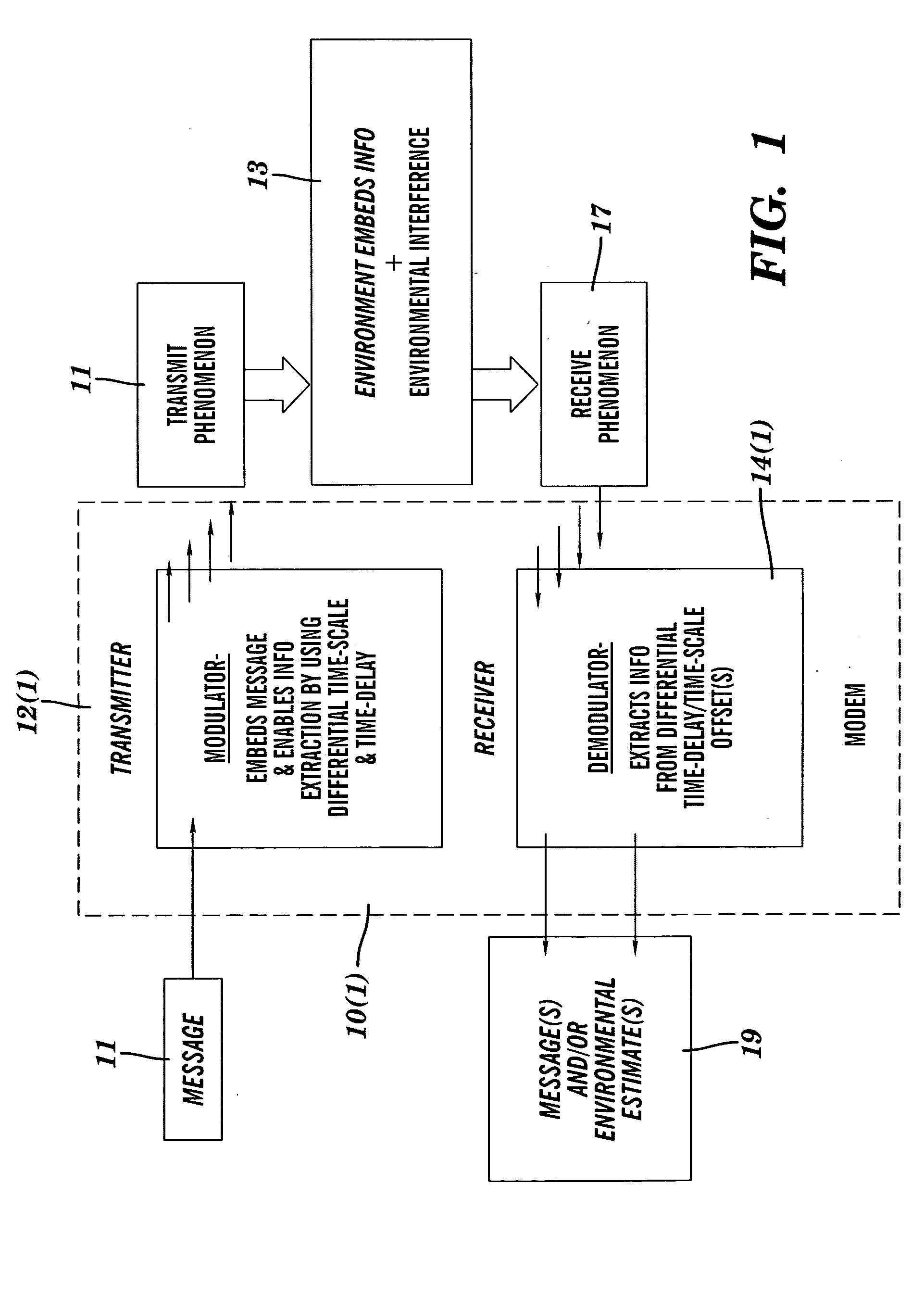
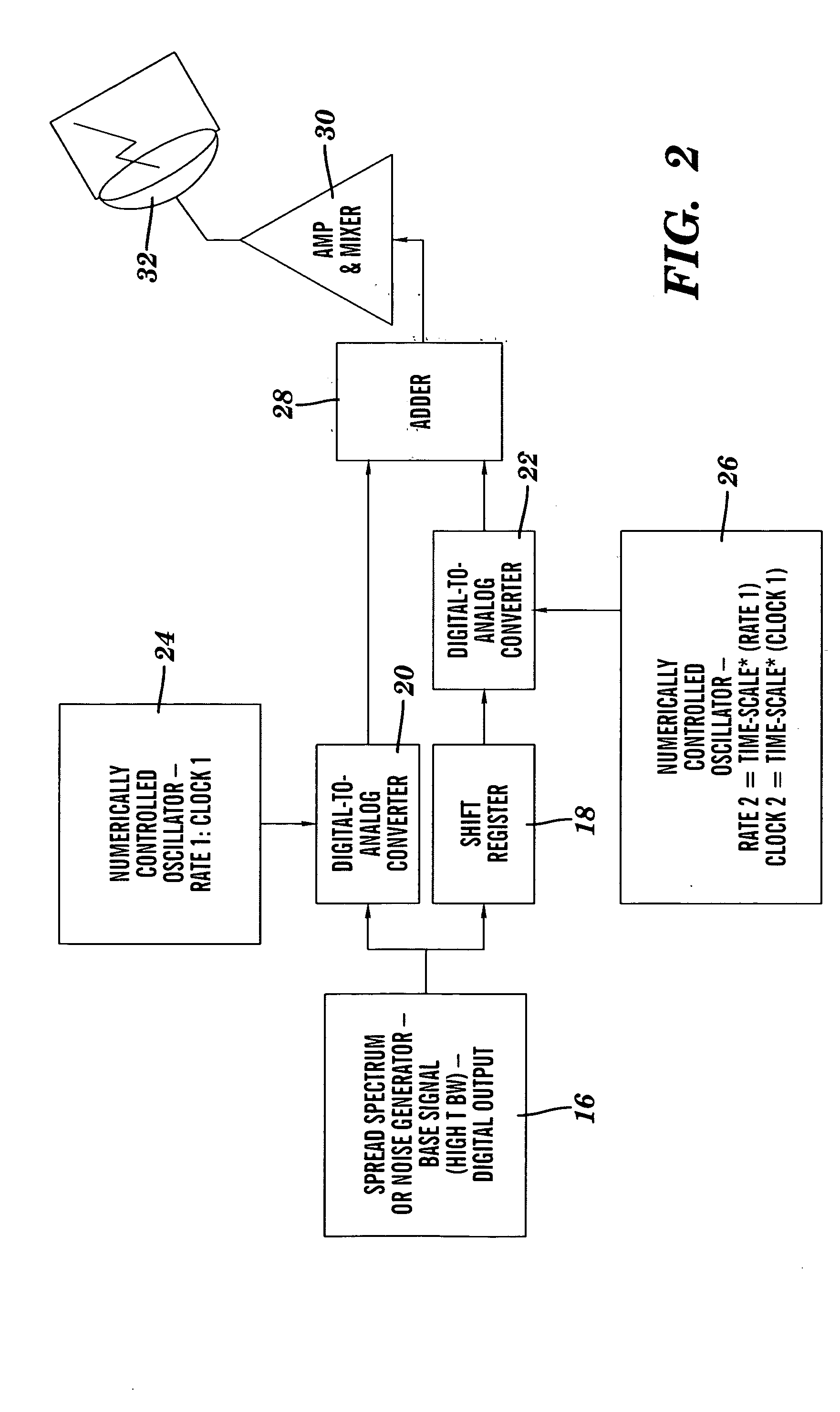
InactiveUS20050094719A1Easy to detectAccurately and precisely estimatedModulated-carrier systemsPolarisation/directional diversityTime delaysRadar
A modulator / demodulator apparatus and method for applications, such as communications, active sensing and navigation is disclosed. The modulator time-delays and time-scales (compresses or dilates) an arbitrary, noise-like “base signal,” then it sums this time-scaled and time-delayed version of the base signal with the original base signal to create a “signal pair” or doublet. The two signals in the doublet are completely overlapped in time and frequency. This doublet creation process can be repeated (with different base signals and / or different time-scale / time-delay parameters) and multiple doublets can be summed together and simultaneously transmitted. This demodulator uses the applied differential time-scale and differential time-delay to extract information, such as a message or a radar image, from the doublet.
Owner:YOUNG RANDY K
Steering control leading apparatus using landmark and method thereby
InactiveUS20110102579A1Provide accuratelyLow cost implementationCharacter and pattern recognitionColor television detailsSteering controlEngineering
Disclosed is a steering control leading apparatus using a landmark when a car travels. The steering control leading apparatus includes: a coordinate controller that analyzes images obtained by photographing the landmark installed on a road by a photographing apparatus installed in a car to generate current coordinate data and current driving lane data of a car; a lane controller that compares the current driving lane data or the current coordinate data received from targeted coordinate data and a coordinate controller to generate determined result data determining whether the car is normally driven; and a display unit that displays the current coordinate data, and the targeted coordinate data, or the data indicating whether the car is normally driven
Owner:UNION CARBIDE CHEM & PLASTICS TECH CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com