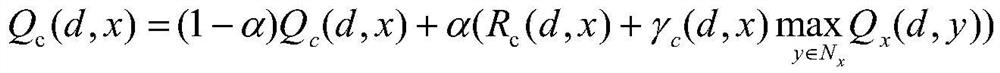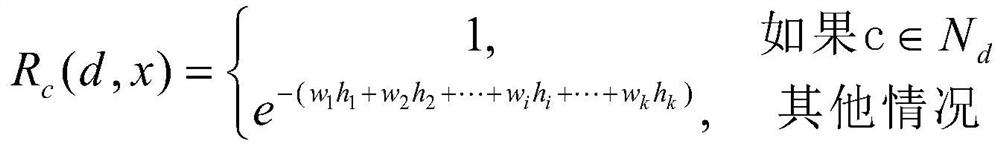Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
37results about How to "Improve Q value" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
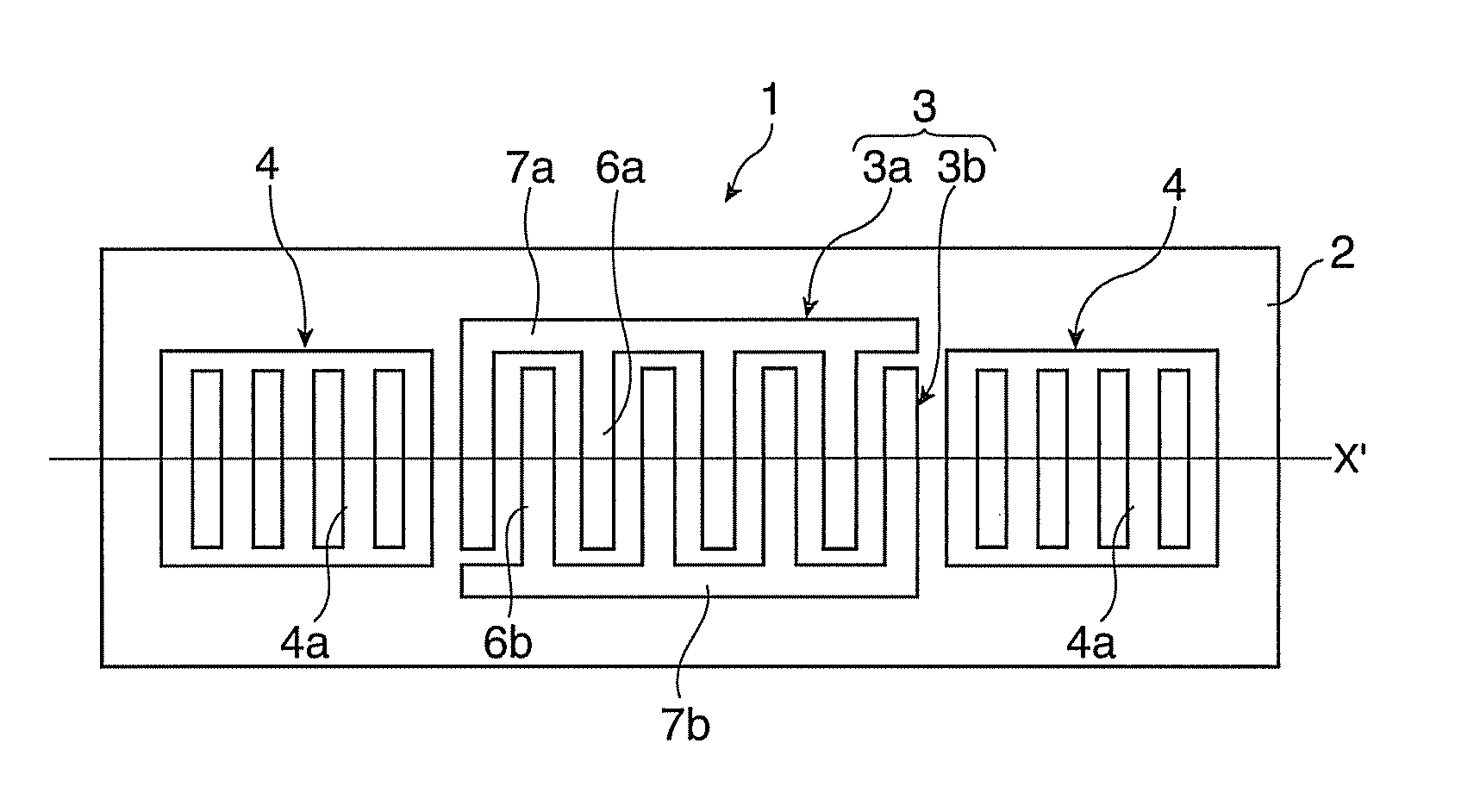
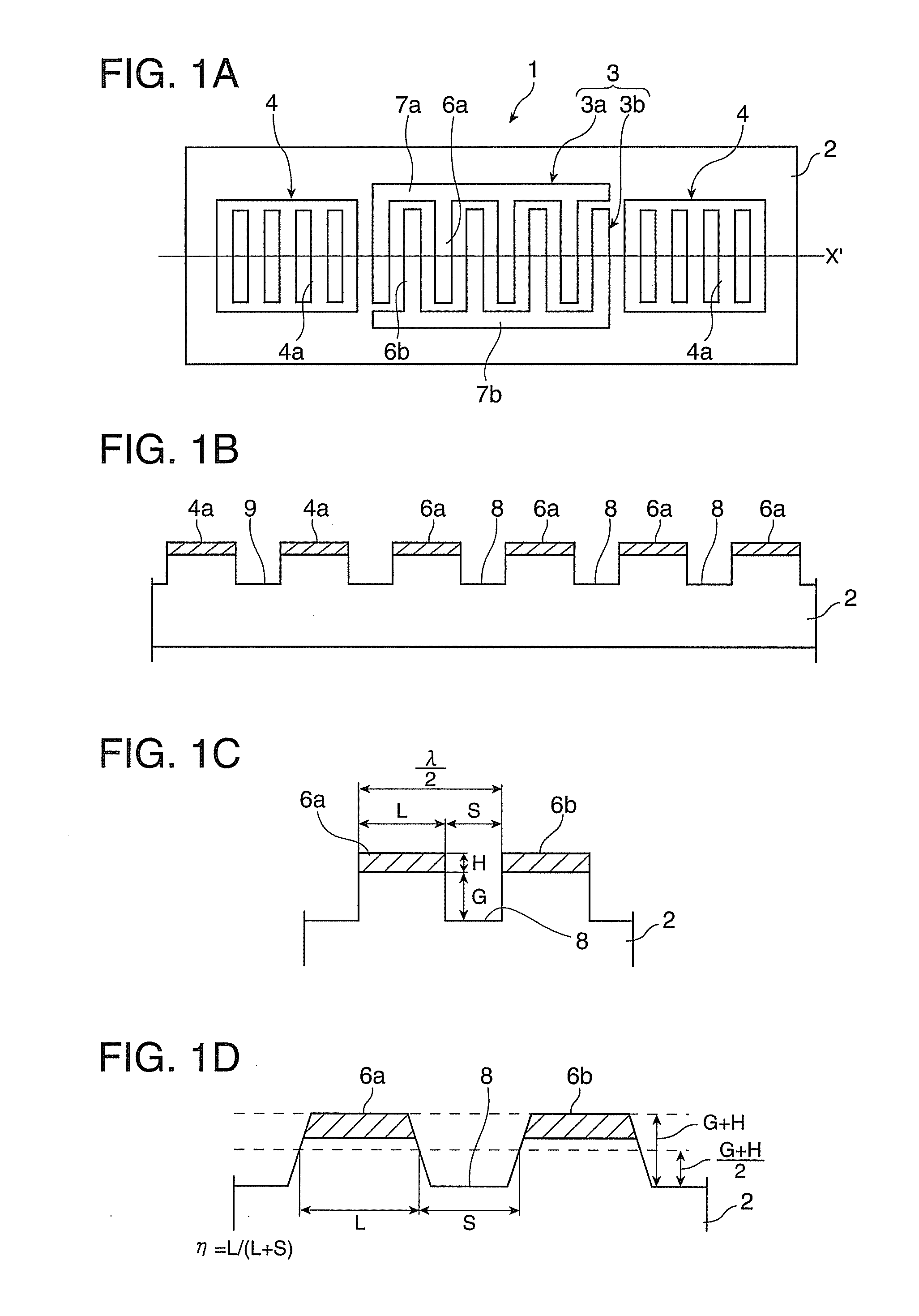
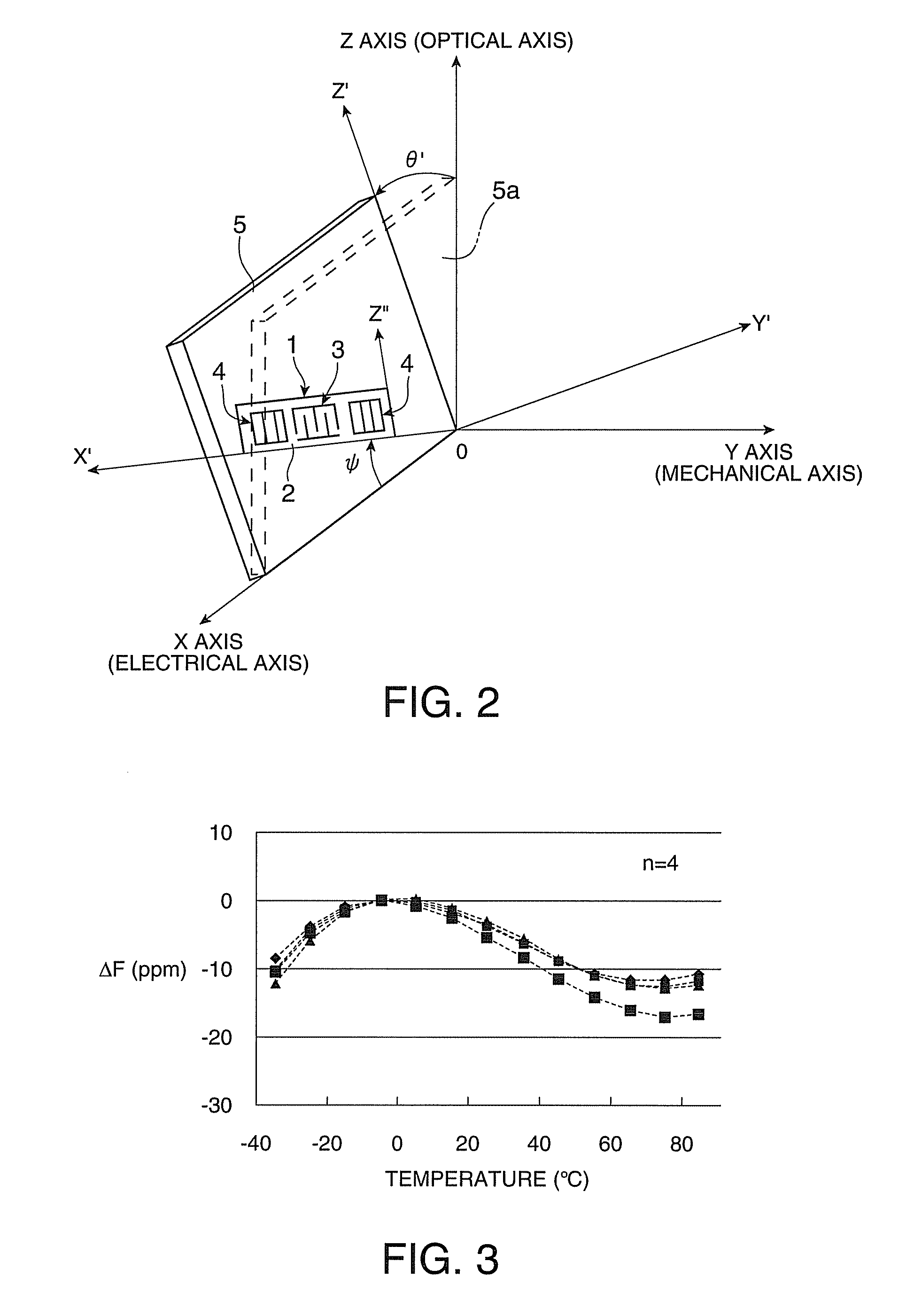
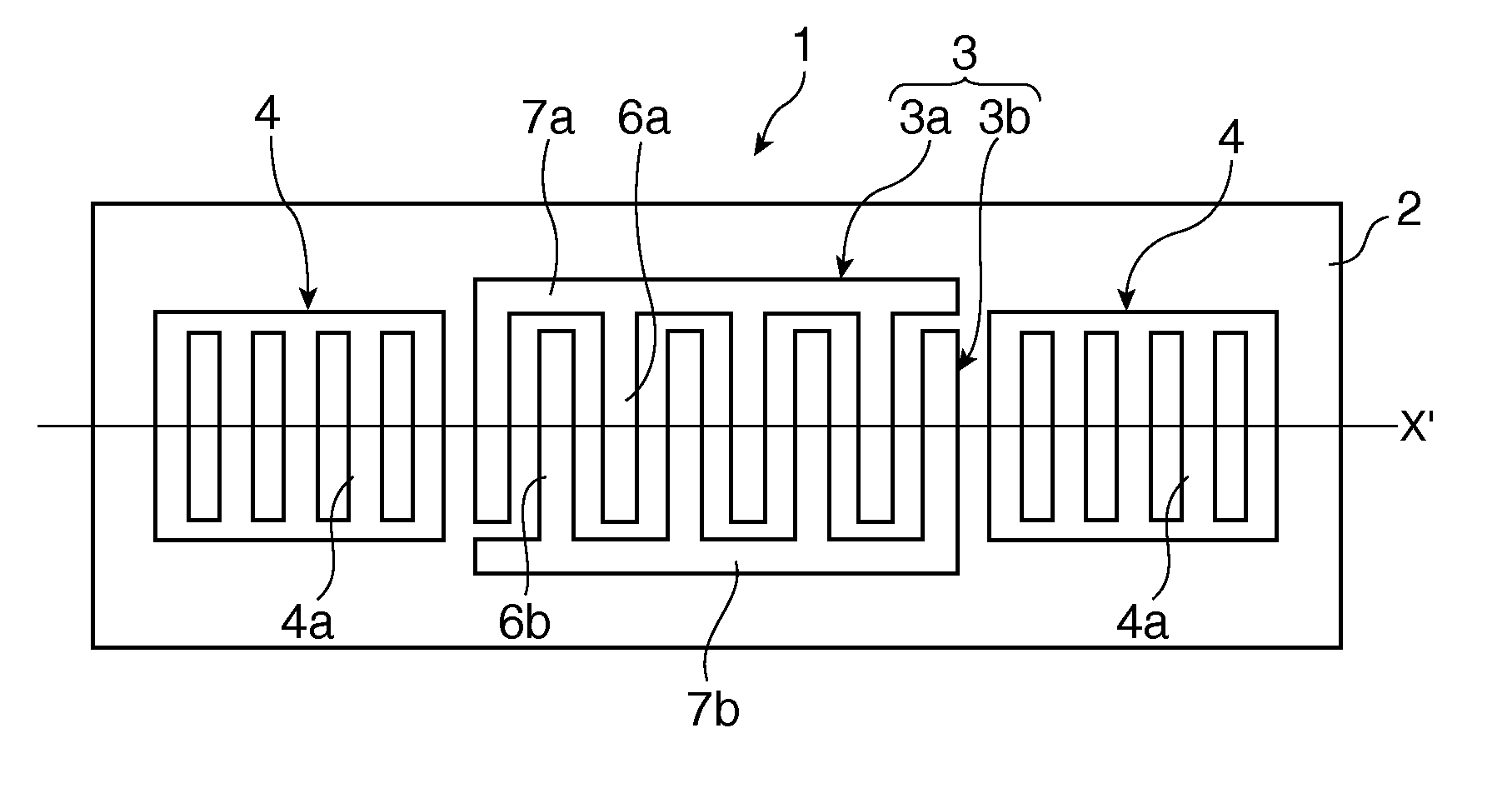
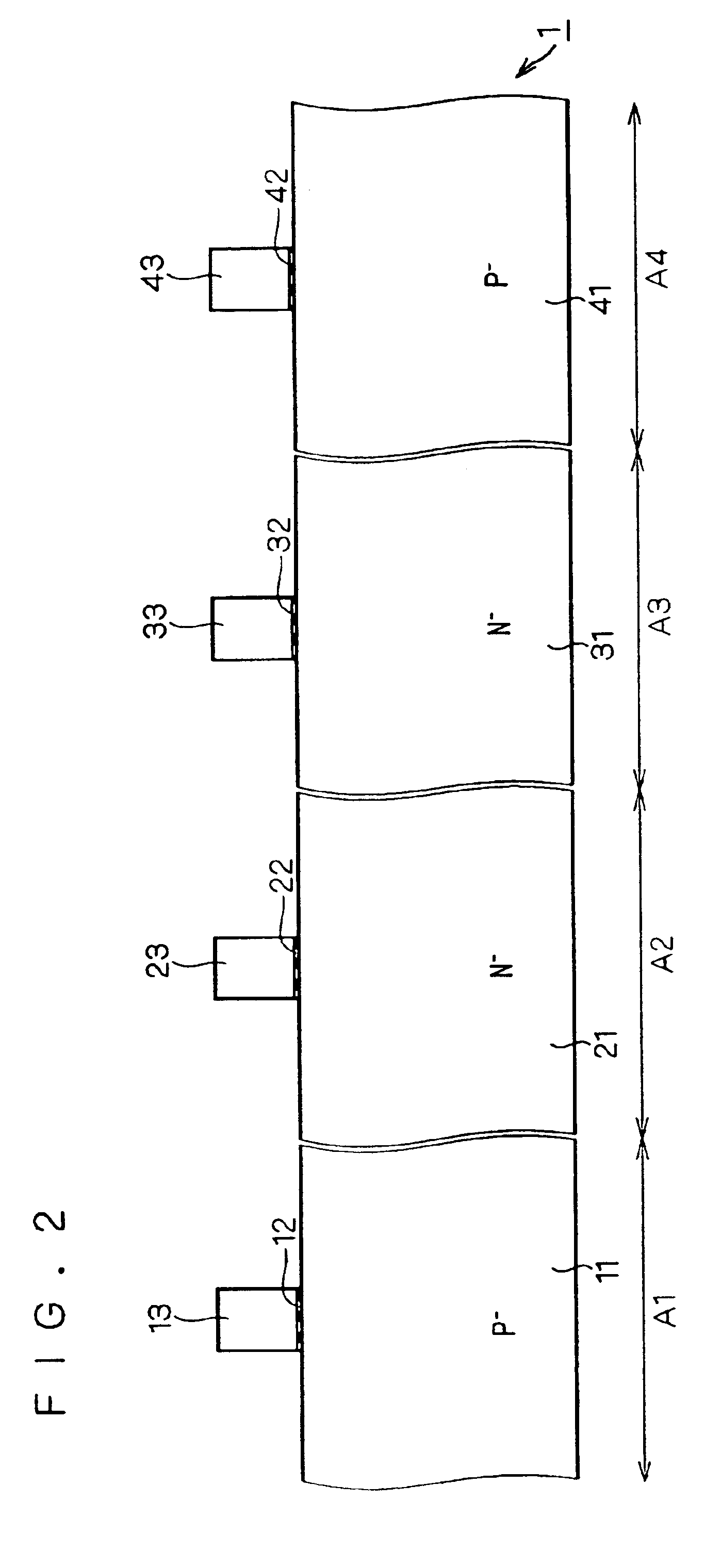
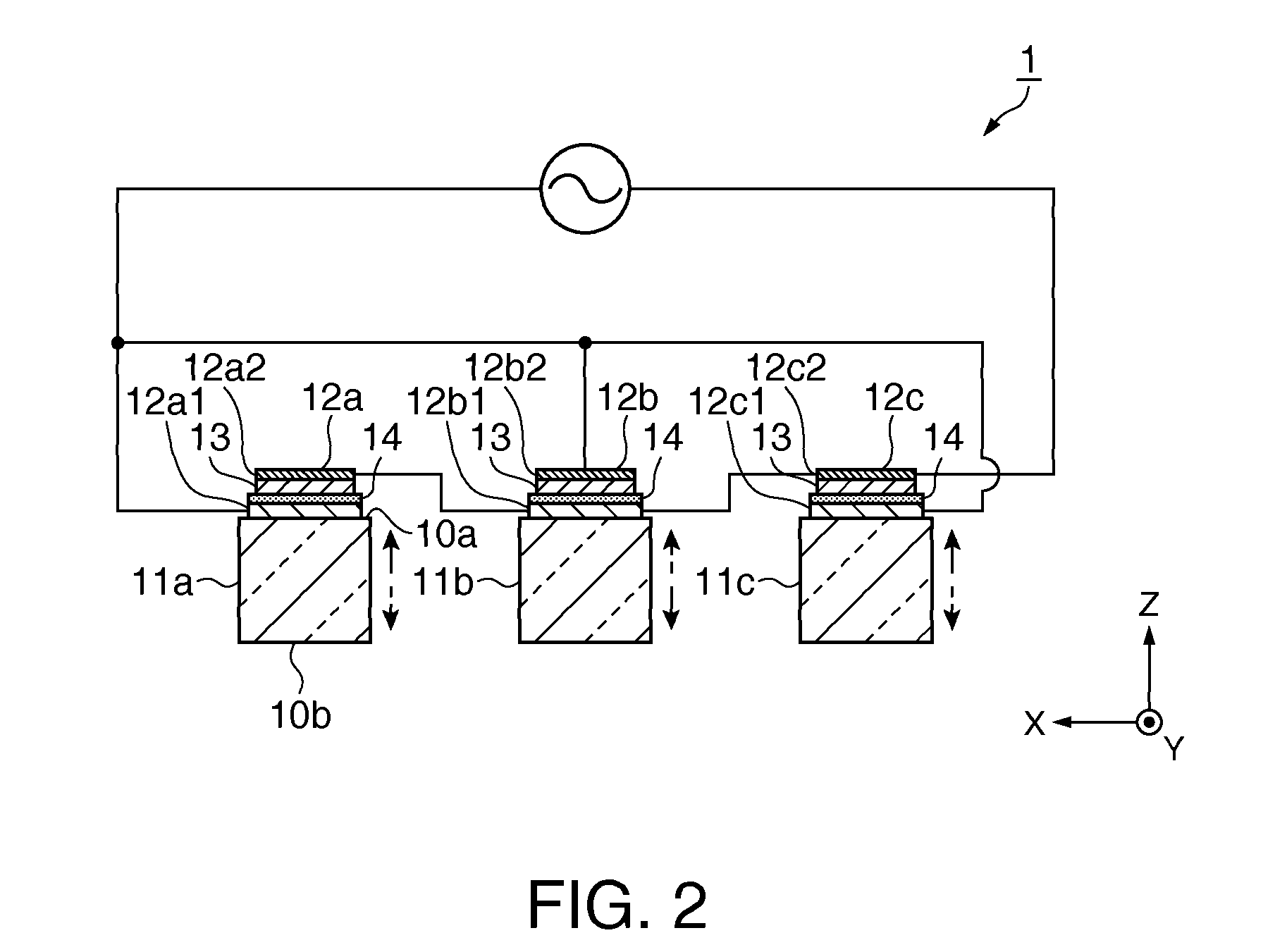
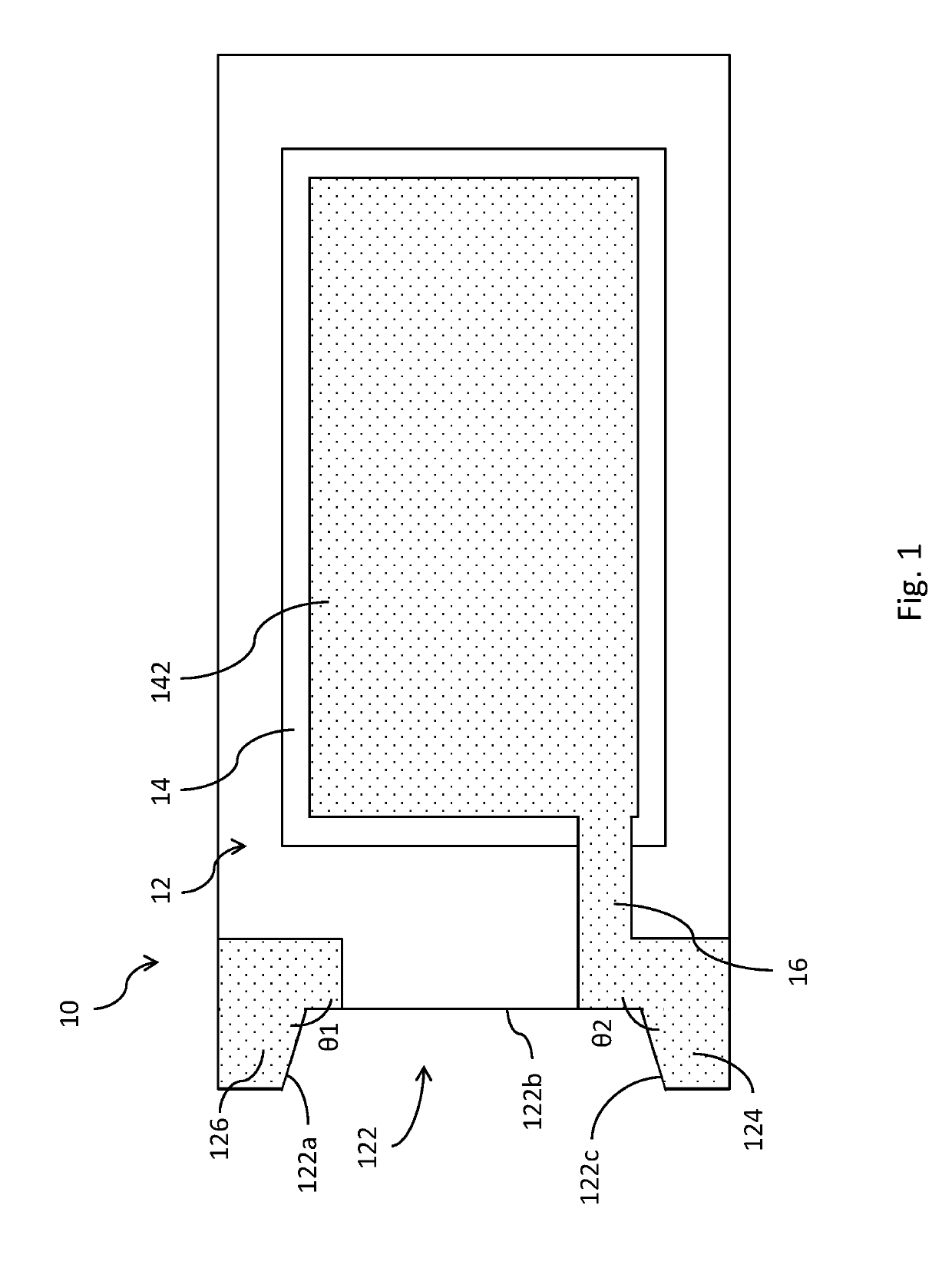
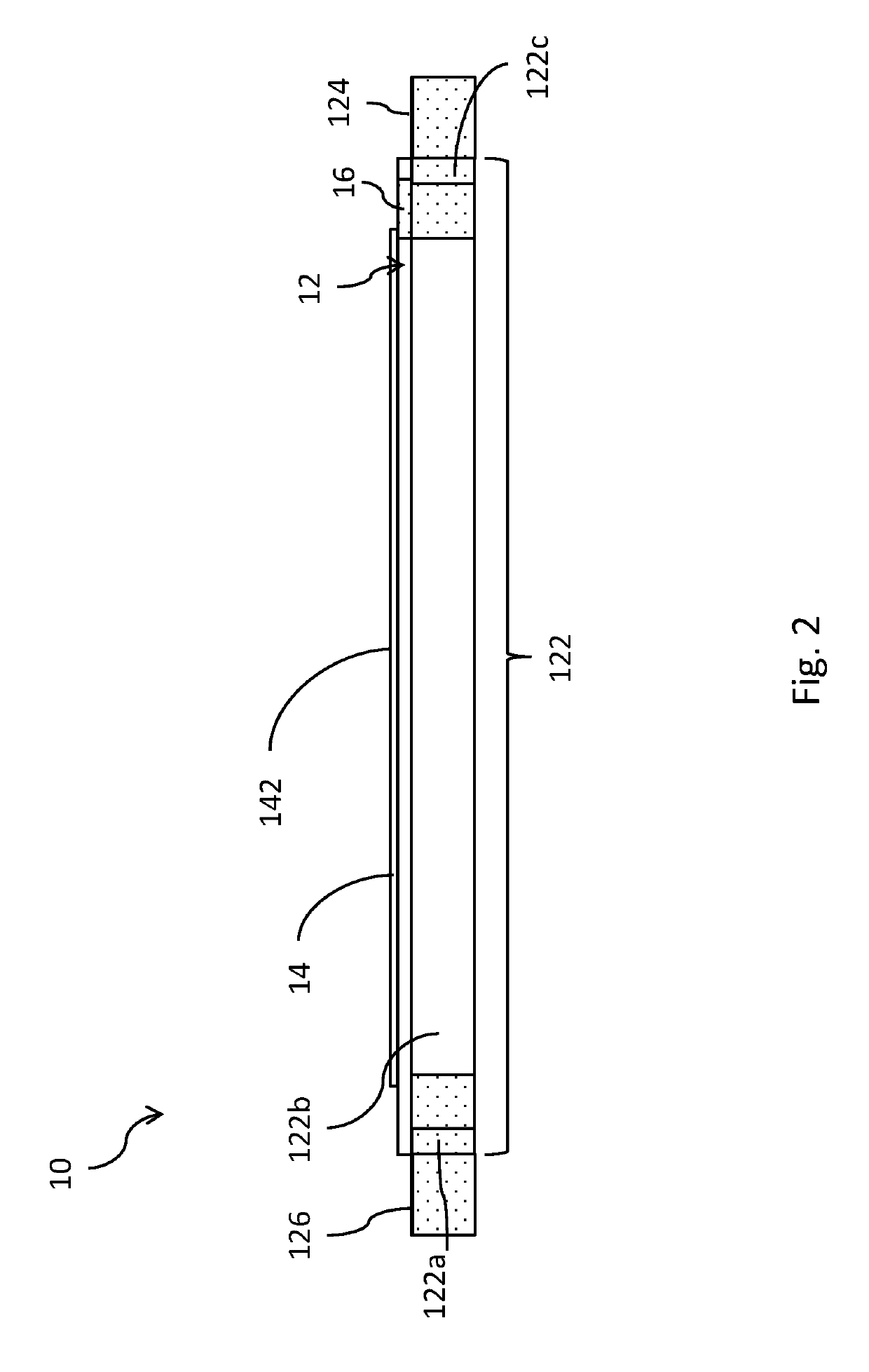
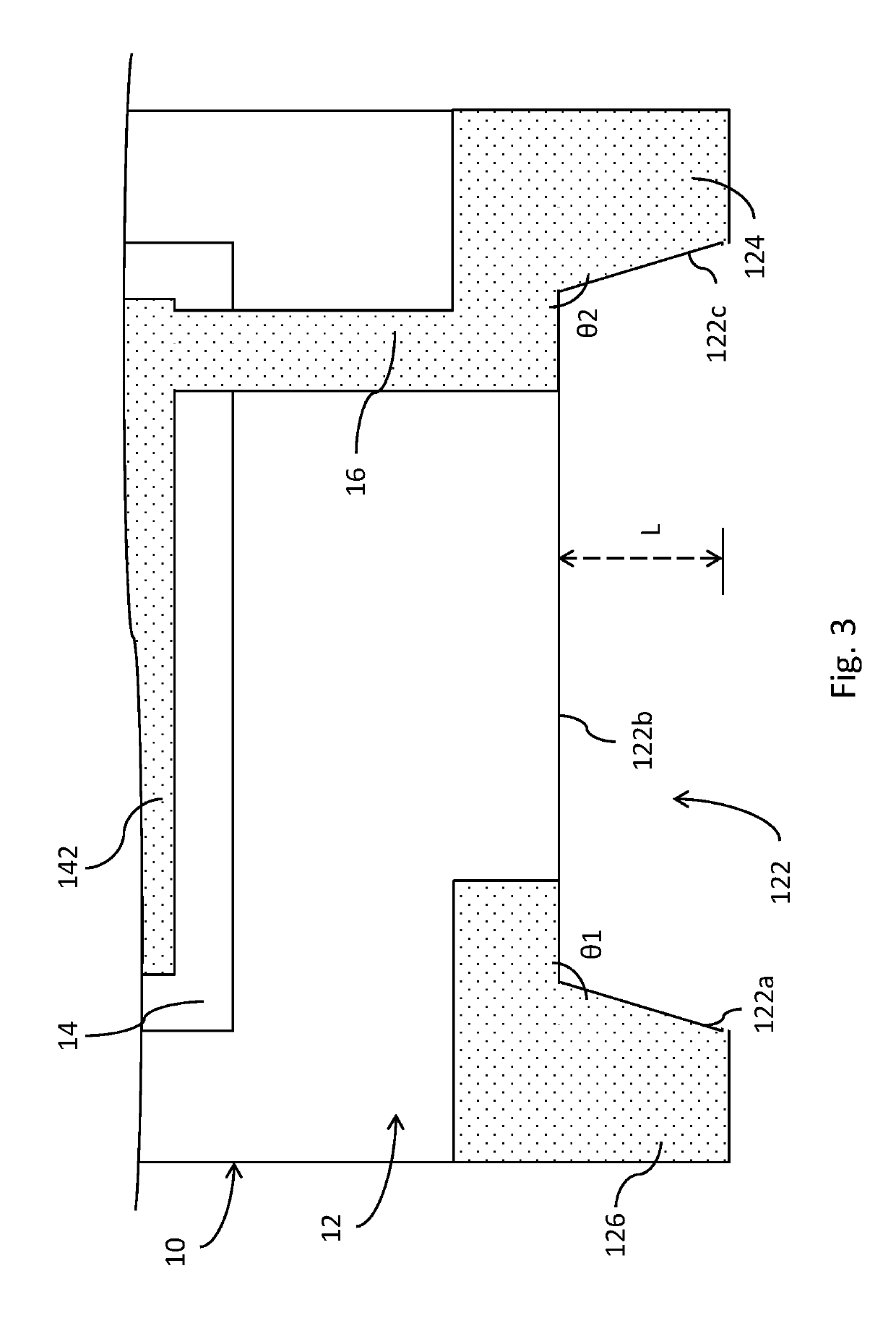
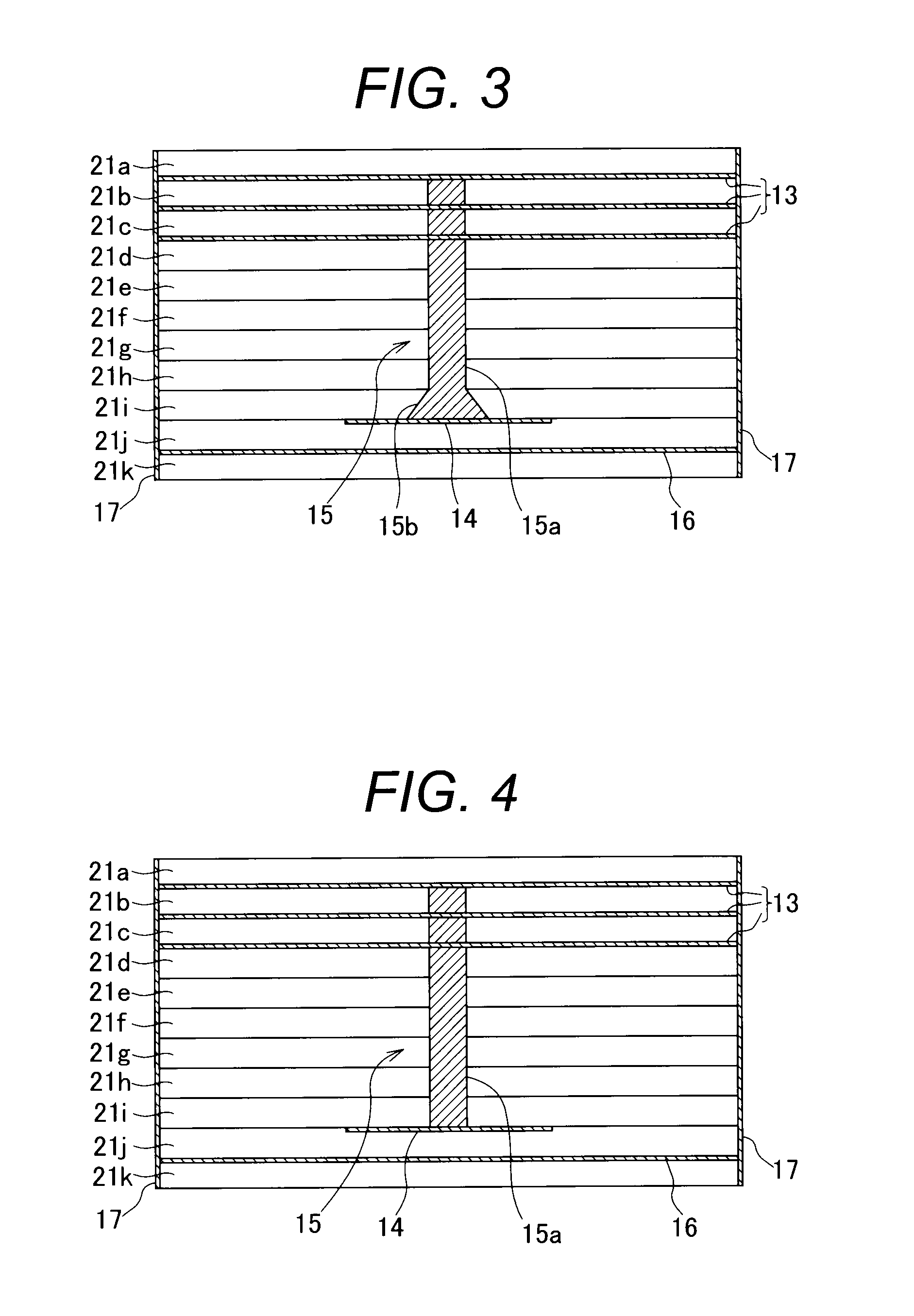
Surface acoustic wave device, electronic apparatus, and sensor apparatus
InactiveUS20120068573A1Improve Q valueSmall frequency fluctuationPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesEngineeringAcoustic wave
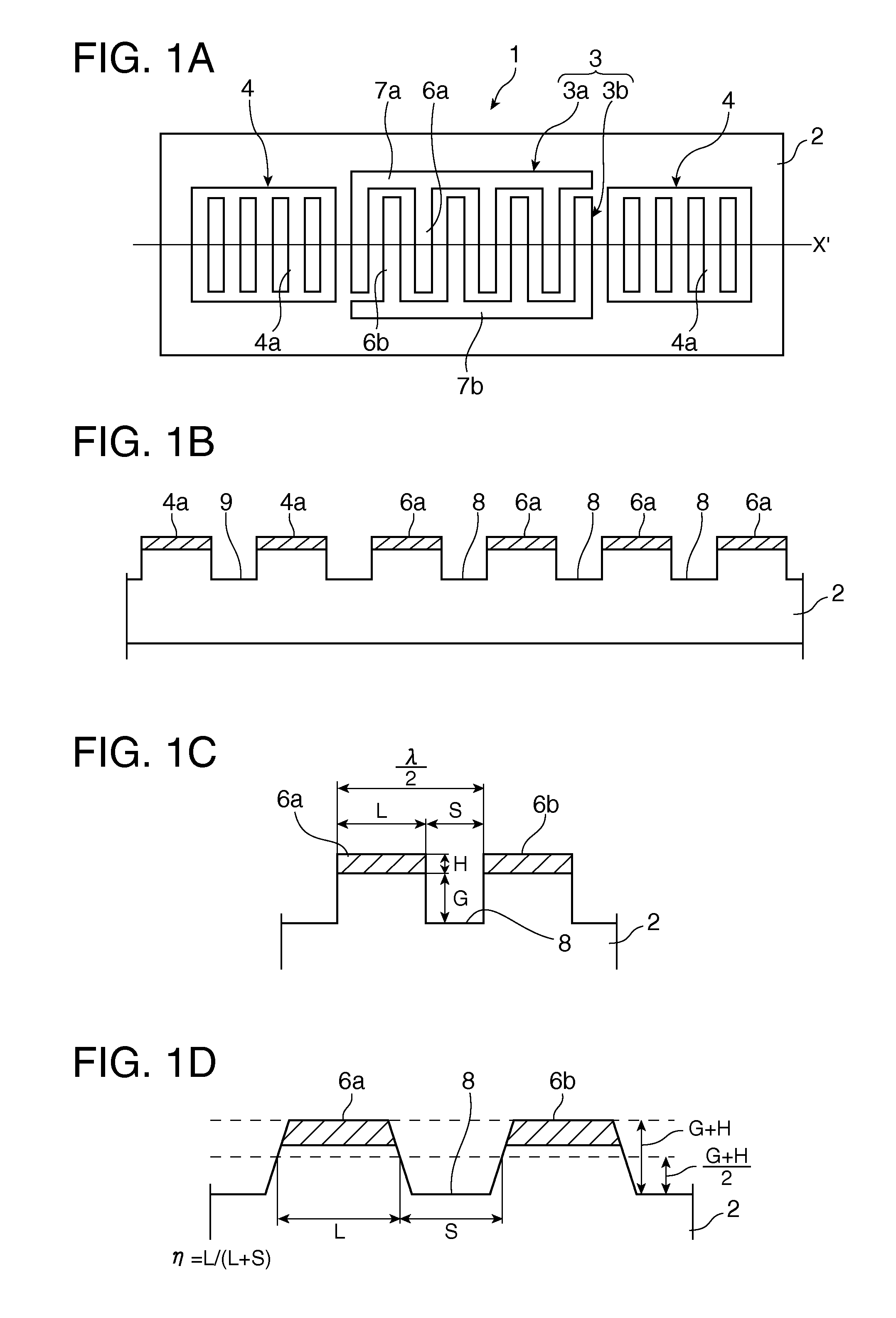
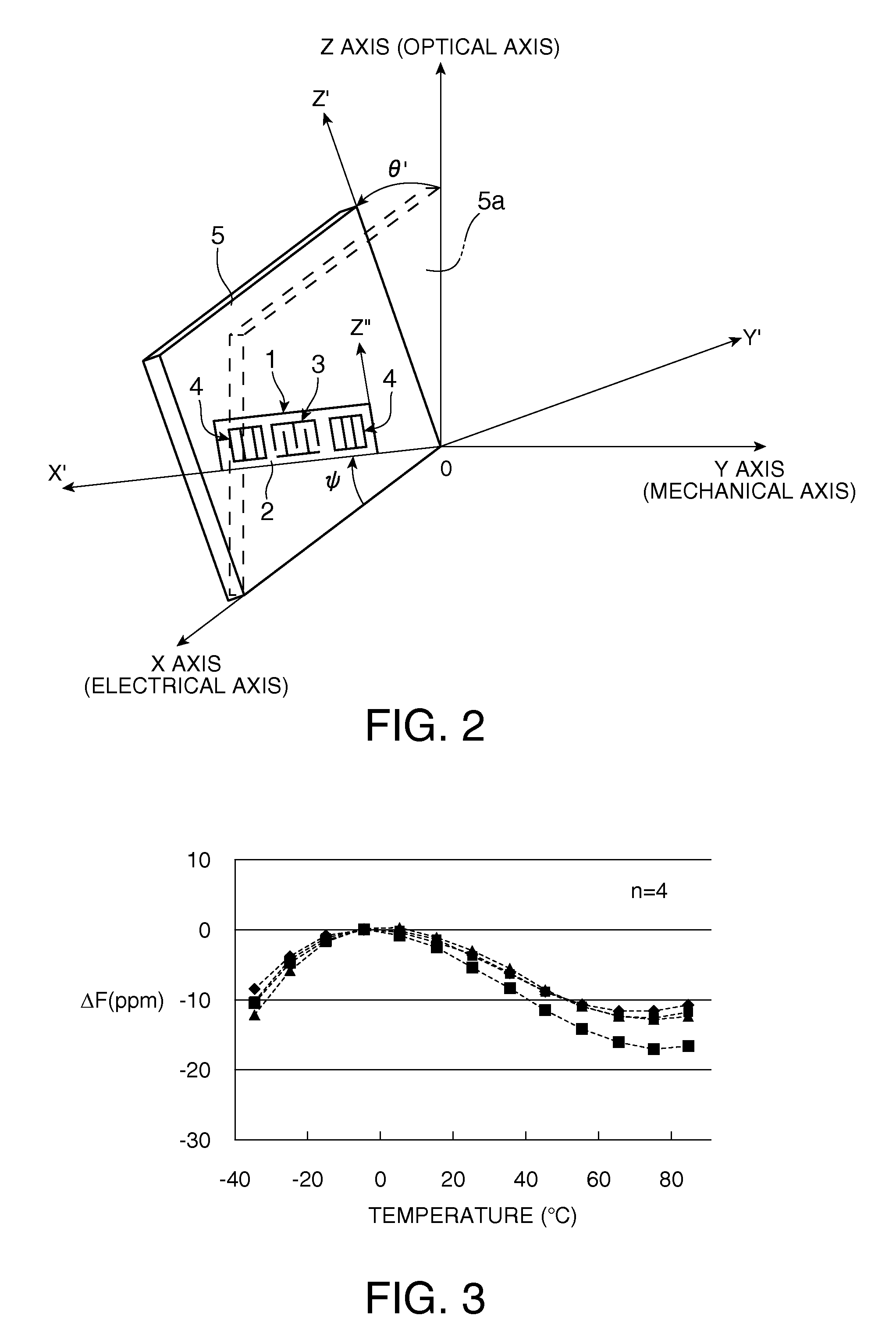
A SAW device includes an IDT which is provided on the principal surface of a quartz crystal substrate having Euler angles (−1.5°≦φ≦1.5°, 117°≦θ≦142°, |ψ|≠90°×n (where n=0, 1, 2, 3)) and excites a Rayleigh wave (wavelength: λ) in a stopband upper end mode. Inter-electrode-finger grooves are recessed between electrode fingers of the IDT. An IDT line occupancy η and an inter-electrode-finger groove depth G satisfy a predetermined relationship in terms of the wavelength λ, such that the SAW device has a frequency-temperature characteristic of a cubic curve having an inflection point between a maximum value and a minimum value in an operation temperature range. The inflection point is adjustable to a desired temperature or a desired temperature range depending on the IDT line occupancy η within an operation temperature range.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Surface acoustic wave device, electronic apparatus, and sensor apparatus
InactiveUS20120086308A1Improve Q valueSmall frequency fluctuationPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyImpedence networksEngineeringAcoustic wave
A SAW device has an IDT which is provided in the principal surface of a quartz crystal substrate having Euler angles (−1.5°≦φ≦1.5°, 117°≦θ≦142°, |ψ|≠90°×n (where n=0, 1, 2, 3)) and excites a Rayleigh wave (wavelength: λ) in a stopband upper end mode. Inter-electrode-finger grooves are recessed between the electrode fingers of the IDT. The depth G of the inter-electrode-finger grooves is 0.01λ≦G≦0.07λ, and an electrode finger thickness H and an IDT line occupancy η satisfy a predetermined relationship. Thus, a frequency-temperature characteristic constantly has an inflection point between a maximum value and a minimum value in an operation temperature range, thereby suppressing a fluctuation in an inflection-point temperature due to a manufacturing variation in the IDT line occupancy η.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Surface detect cavity photonic crystal refractive index sensor containing absorption medium graphene
InactiveCN106053390AHigh sensitivityImprove Q valuePhase-affecting property measurementsOptical light guidesRing downPhotonic crystal
The invention discloses a surface defect cavity photonic crystal refractive index sensor containing absorption medium graphene. The sensor consists of a surface defect cavity (1), a periodic photonic crystal (2) and a coupling prism (3), wherein the periodic photonic crystal is formed by periodically alternatively arranging a high refractive index material (A) and a low refractive index material (B); the surface defect cavity consists of absorption medium graphene (C) and the low refractive index material (B), and the structure of the surface defect cavity is (B)-(C)-(B). The defect cavity is used for substituting a gold membrane (or silver membrane) in a traditional SPR sensor, and the absorption medium graphene is introduced into the defect cavity, so that a resonant optical signal formed in the defect cavity is gradually absorbed to form ring down, and a defect peak corresponding to the resonant wavelength is acquired in a reflective spectrum. A relationship of the resonant peak wavelength and the refractive index of a sample to be detected is established, and the refractive index of the sample to be detected is dynamically monitored by defecting the drifting of the resonant peak wavelength.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Nuclear magnetic resonance apparatus probe
InactiveUS20050083059A1High sensitivityLittle resistanceElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceAudio power amplifier
A nuclear magnetic resonance apparatus comprises a superconducting magnet that produces a static magnetic field, a probe having a probe coil that irradiates an RF pulse magnetic field and receives a free induction decay signal (FID signal) emitted therefrom, an RF power source that supplies the probe with an RF current, an amplifier that amplifies the FID signal, a detector that detects a signal, and an analyzer that analyzes the signal detected by the detector, wherein the probe coil includes a solenoid coil and a saddle type coil.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Inductor for semiconductor integrated circuit and method of fabricating the same
InactiveUS7091576B2Wide cross-sectional areaReduce resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEtchingLine width
Disclosed are an inductor for a semiconductor integrated circuit, which provides a wider cross-sectional area, significantly reduces the resistance to improve the Q value and has a highly uniform film thickness, and a method of fabricating the inductor. A spiral inductor is formed on a topmost interconnection layer of a multilayer interconnection layer formed by a damascene method. This inductor is formed by patterning a barrier metal layer on an insulation film, on which a topmost interconnection is formed, in such a way that the barrier metal layer contacts the topmost interconnection, then forming a protective insulation film on an entire surface of the barrier metal layer, forming an opening in that portion of the protective insulation film which lies over the barrier metal layer, forming a thick Cu film with the barrier metal layer serving as a plating electrode, and performing wet etching of the Cu film. This process can allow the inductor to be so formed as to be thick and have a wide line width.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Surface acoustic wave resonator, surface acoustic wave oscillator, and surface acoustic wave module unit
ActiveUS20110199160A1Improve Q valueSmall sizePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksAcoustic waveSurface acoustic wave oscillators
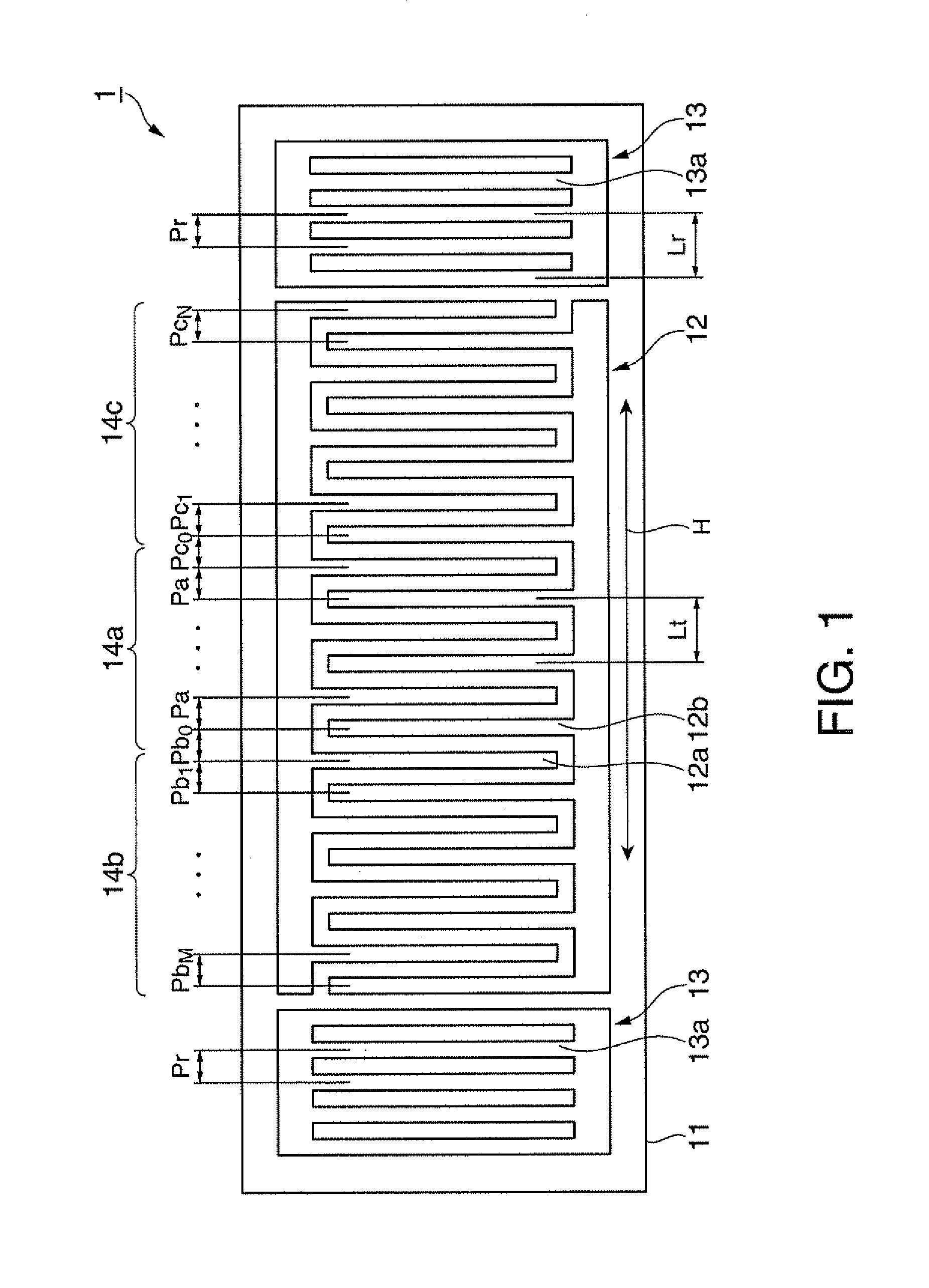
It is possible to reduce the size of a surface acoustic wave (SAW) resonator by enhancing a Q value. In a SAW resonator in which an IDT having electrode fingers for exciting SAW is disposed on a crystal substrate, the IDT includes a first region disposed at the center of the IDT and a second region and a third region disposed on both sides of the first region. A frequency is fixed in the first region and a portion in which a frequency gradually decreases as it approaches an edge of the IDT is disposed in the second region and the third region. When the frequency of the first region is Fa, the frequency at an edge of the second region is FbM, and the frequency at an edge of the third region is FcN, the variations in frequency are in the ranges of 0.9815<FbM / Fa<0.9953 and 0.9815<FcN / Fa<0.9953, respectively.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP +1
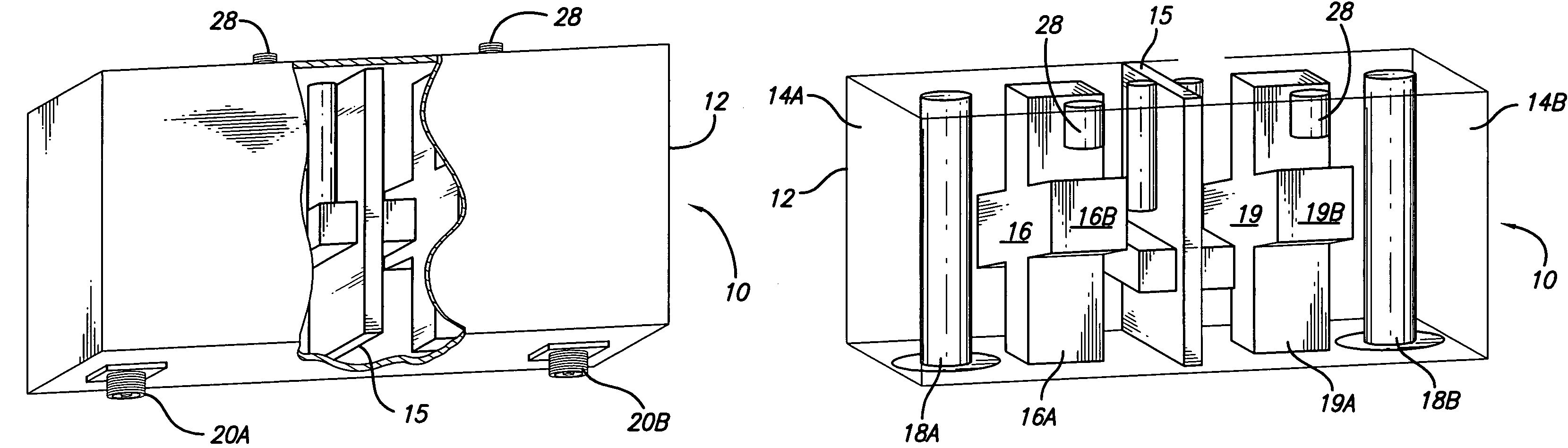
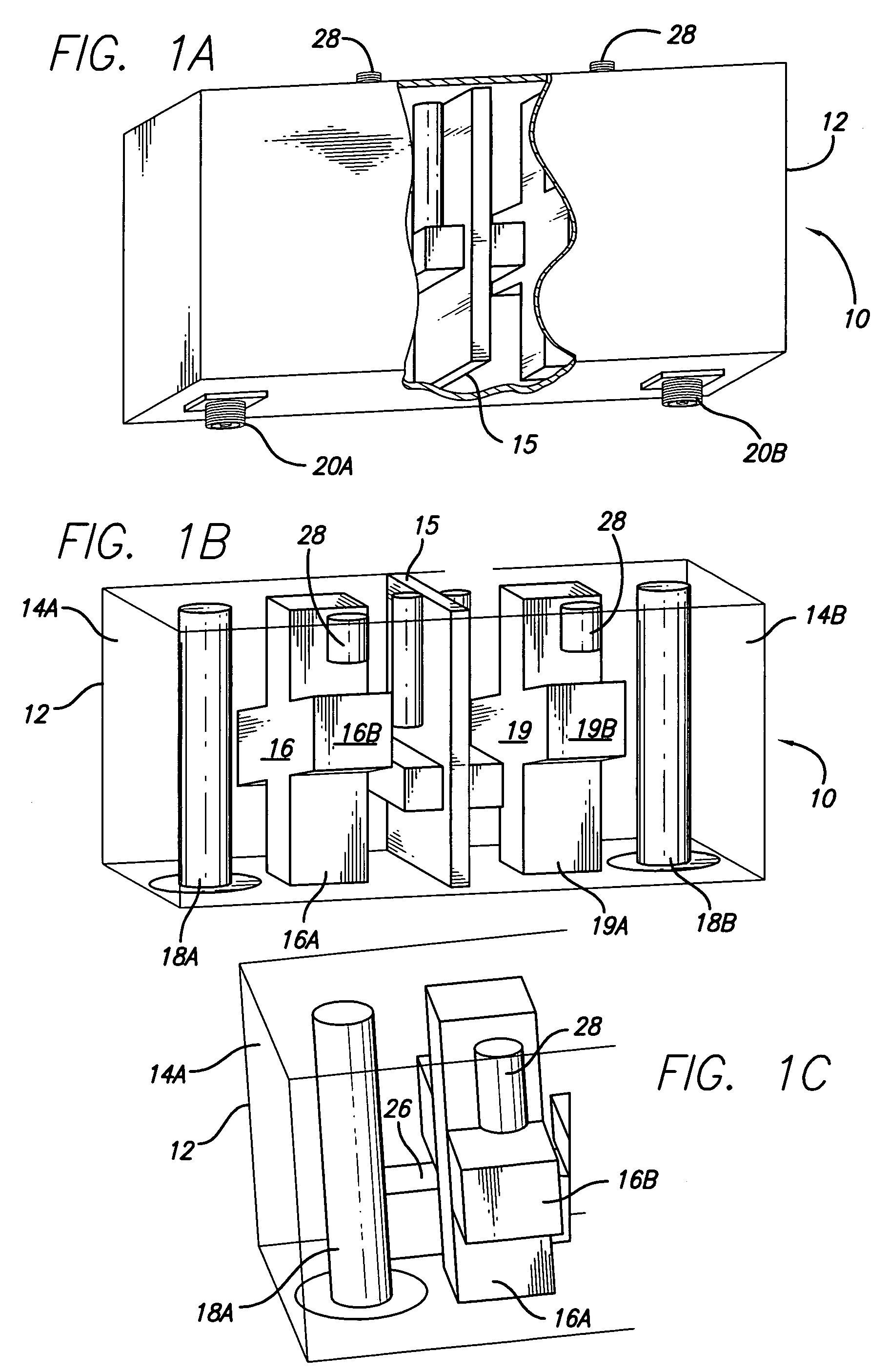
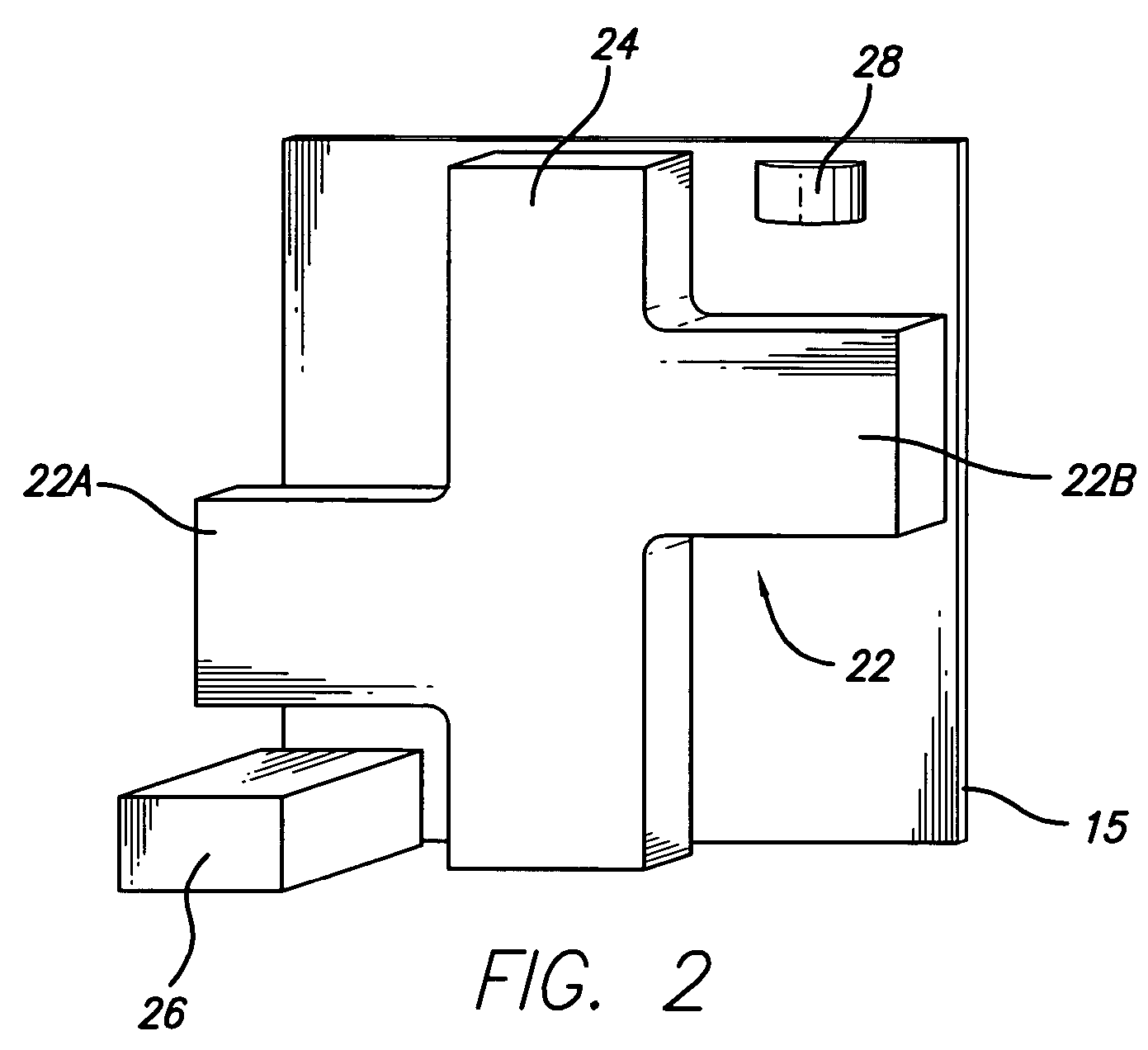
Dual mode ceramic filter
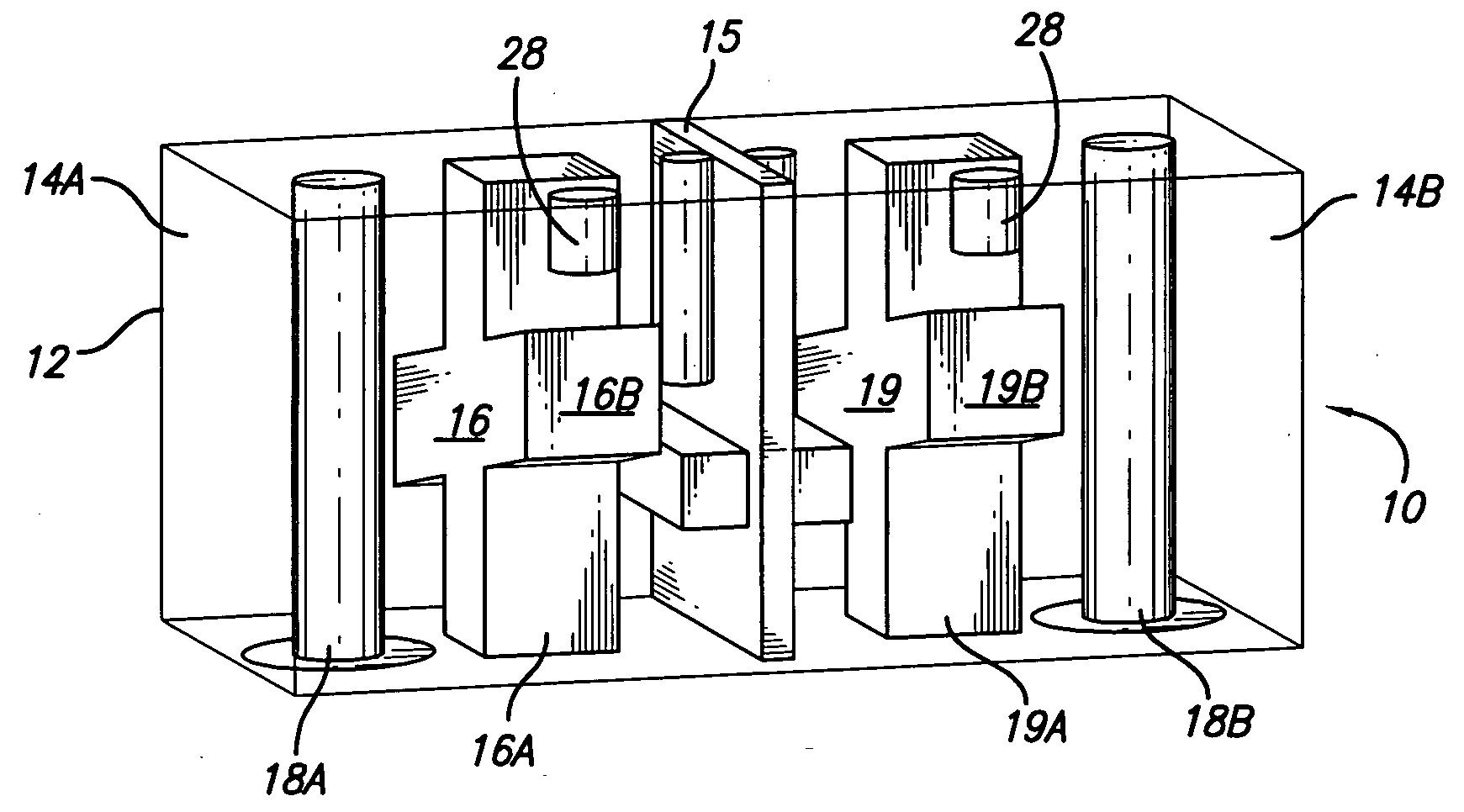
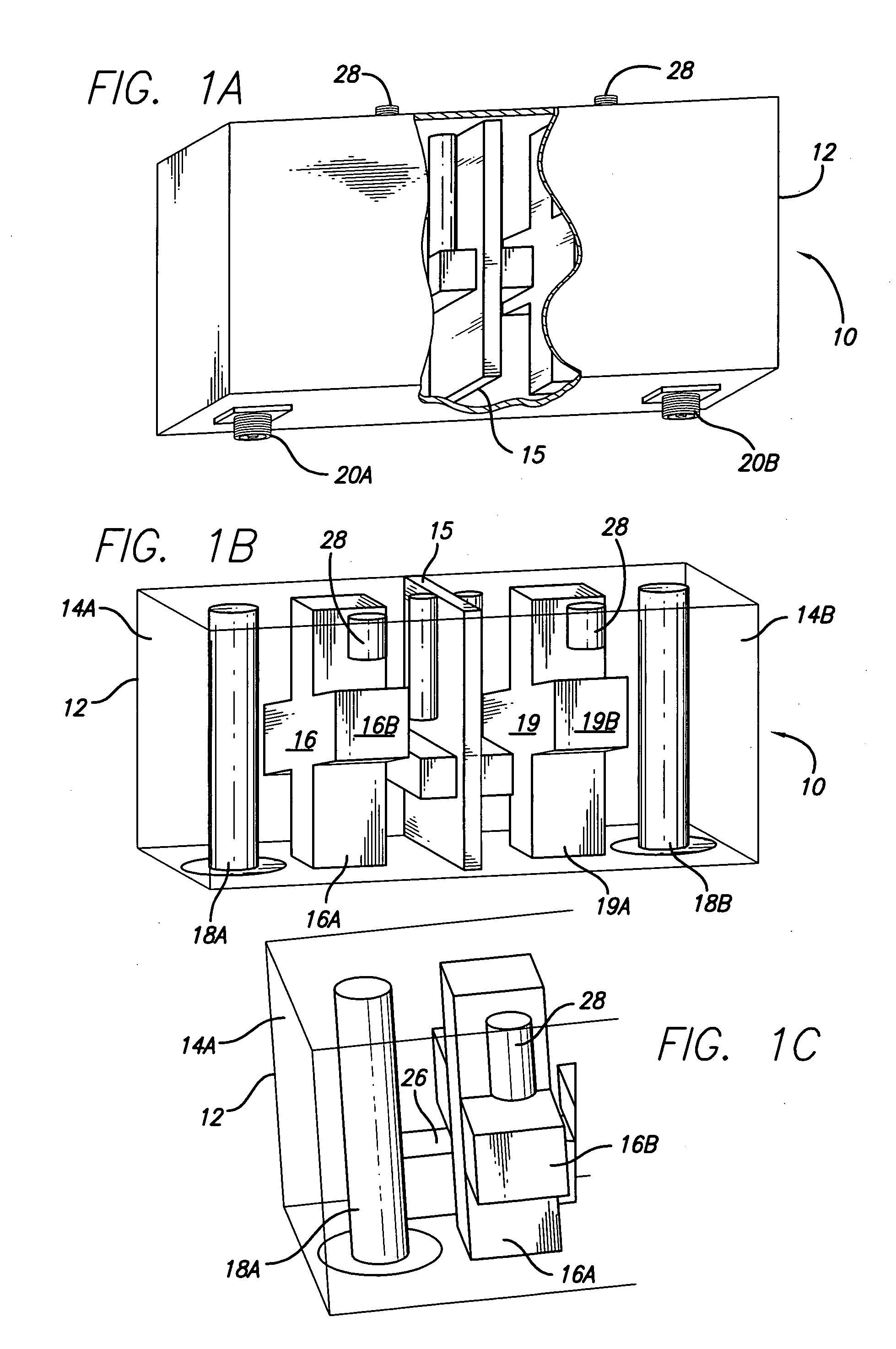
A dual mode ceramic filter has an enclosure with two cavities separated by a wall, and two TM dual-mode resonators, each TM dual-mode resonator positioned in a corresponding cavity. Each TM dual-mode resonator has first and second modes, and a body having a central portion with a plurality of arms extending outwardly from the central portion. The filter also has two input conductive members, each input conductive members positioned in a corresponding cavity. Each input conductive member is disposed proximate a corresponding TM dual-mode resonator for coupling between the input conductive member and the TM dual-mode resonator.
Owner:INTEL CORP
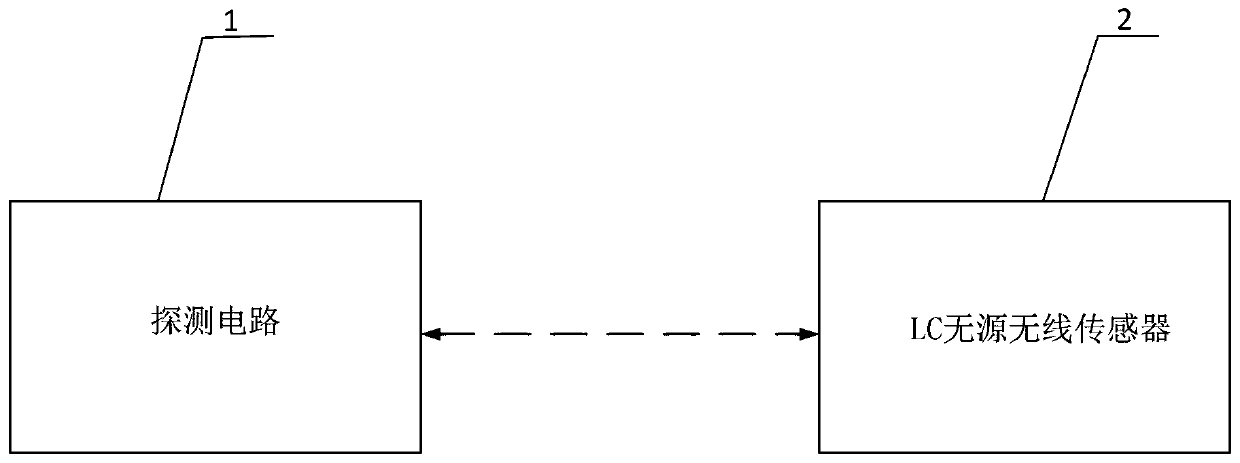
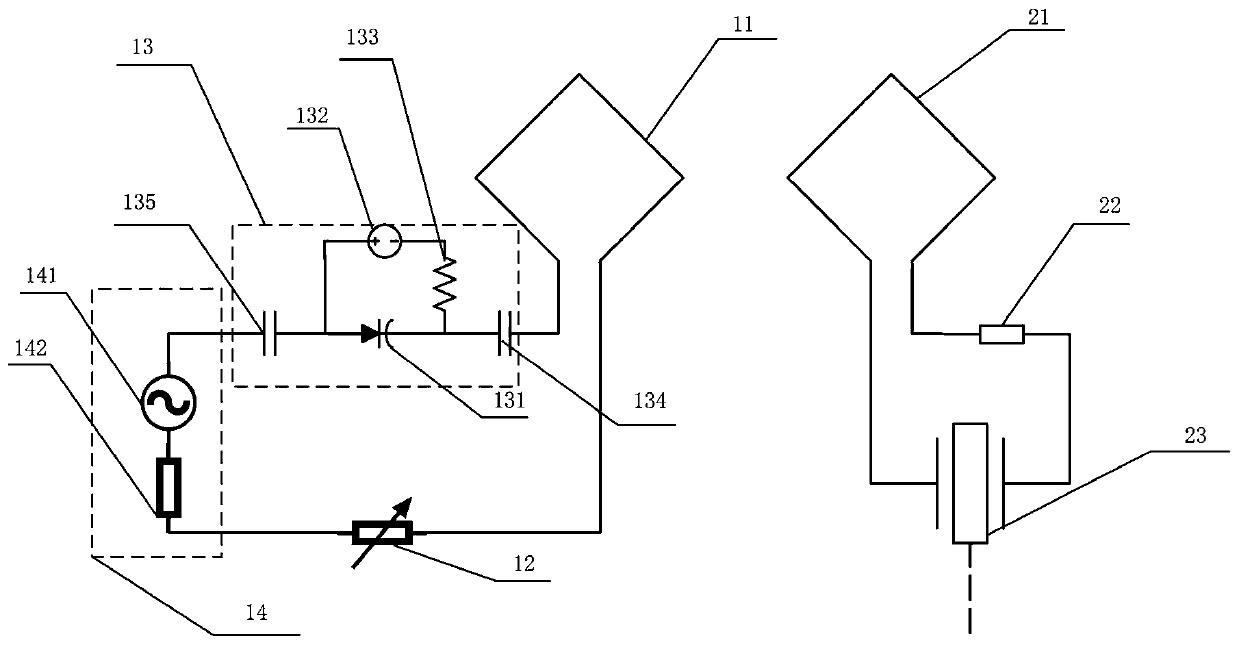
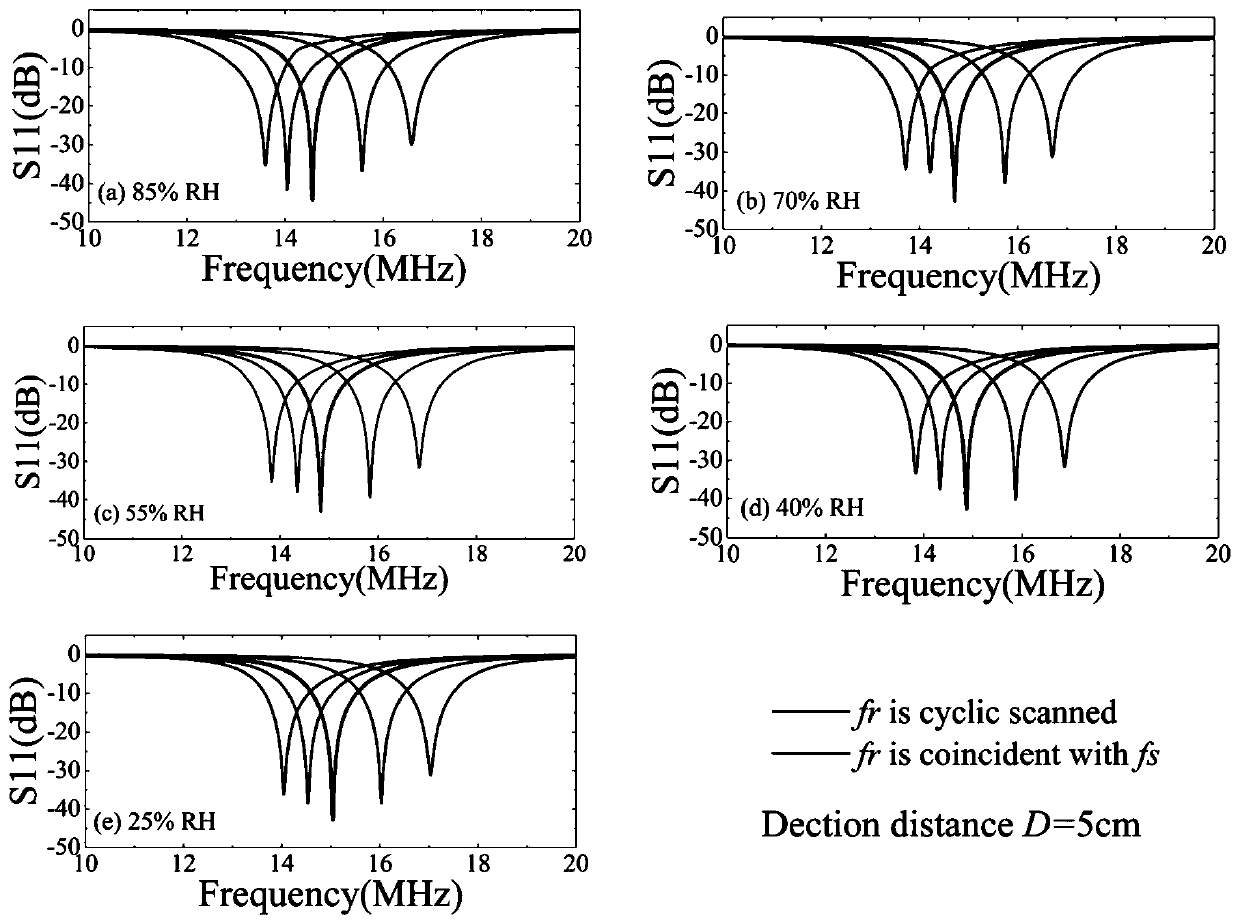
Long-distance LC passive wireless sensing system
ActiveCN110853318AImprove transmission distanceCapacitance adjustableTransmission systemsCapacitanceLine sensor
The invention provides a long-distance LC passive wireless sensing system, and relates to the technical field of wireless passive sensing systems. In the system, a detection circuit is wirelessly connected with an LC passive wireless sensor circuit through inductive magnetic resonance weak coupling. By designing the capacitance values, the inductance values and the resistance values of the detection circuit and the LC passive wireless sensor circuit, the resonance frequencies of the detection circuit and the LC passive wireless sensor circuit are equal, the gain and the loss of the system arealso equal, and therefore, the PT symmetry or PTX symmetry is met. According to the LC passive wireless sensing system provided by the invention, the frequency splitting can be avoided, and passive wireless signal enhancement and ultra-long-distance transmission are realized. The capacitance value of the detection circuit is adjustable, so the inherent frequency of the detection circuit can be consistent with the signal frequency of the sensor circuit all the time, thereby achieving the efficient transmission of full-frequency signals. An adjustable resistor is added in the detection circuit,so the signal intensity and the Q value are greatly improved. The sensing system circuit structure design satisfying PTX symmetry has more flexible requirements for inductance and capacitance.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Active inductor with high Q value, high inductance and tunable operating frequency range
InactiveCN105680822AHigh Q valueIncrease the inductance valueFrequency selective two-port networksAmplifier input/output impedence modificationCapacitanceEngineering
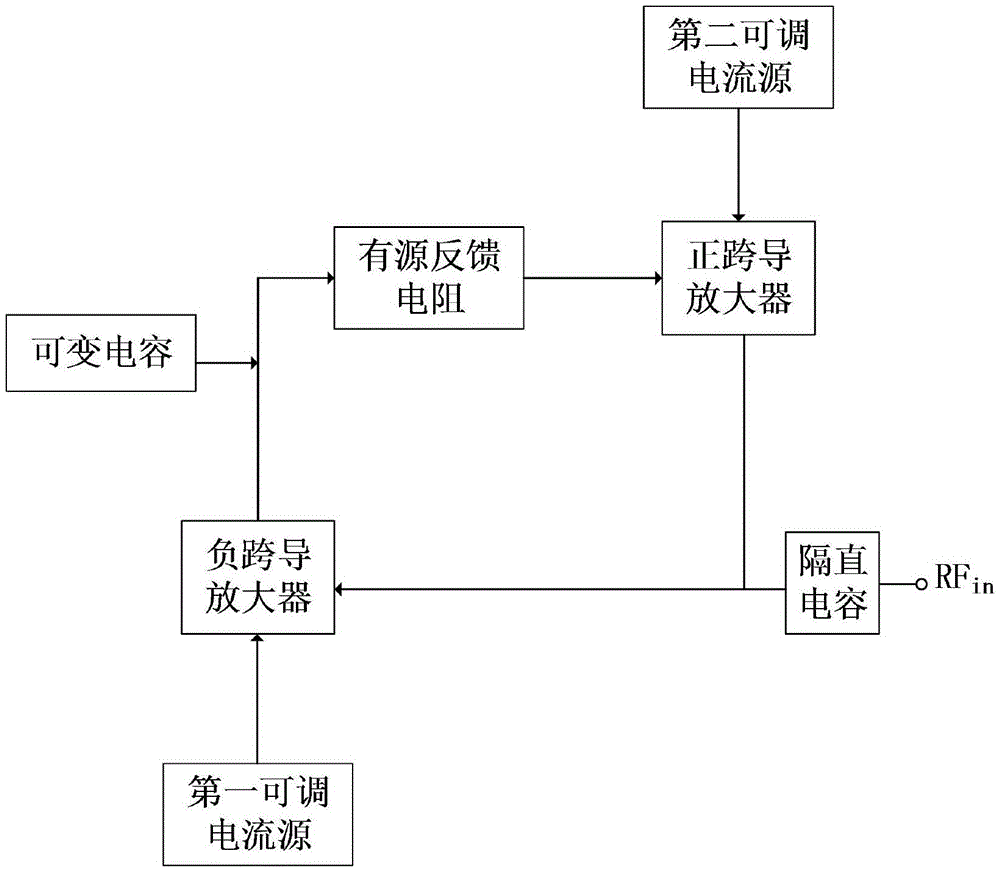
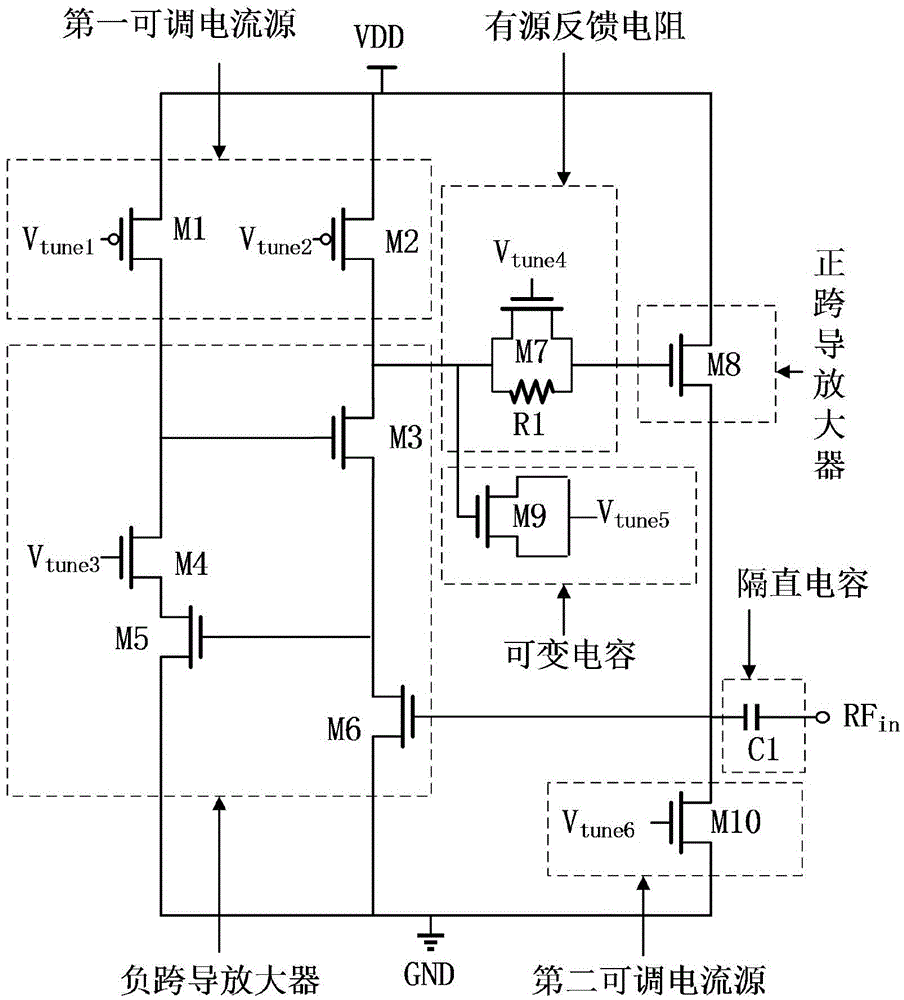
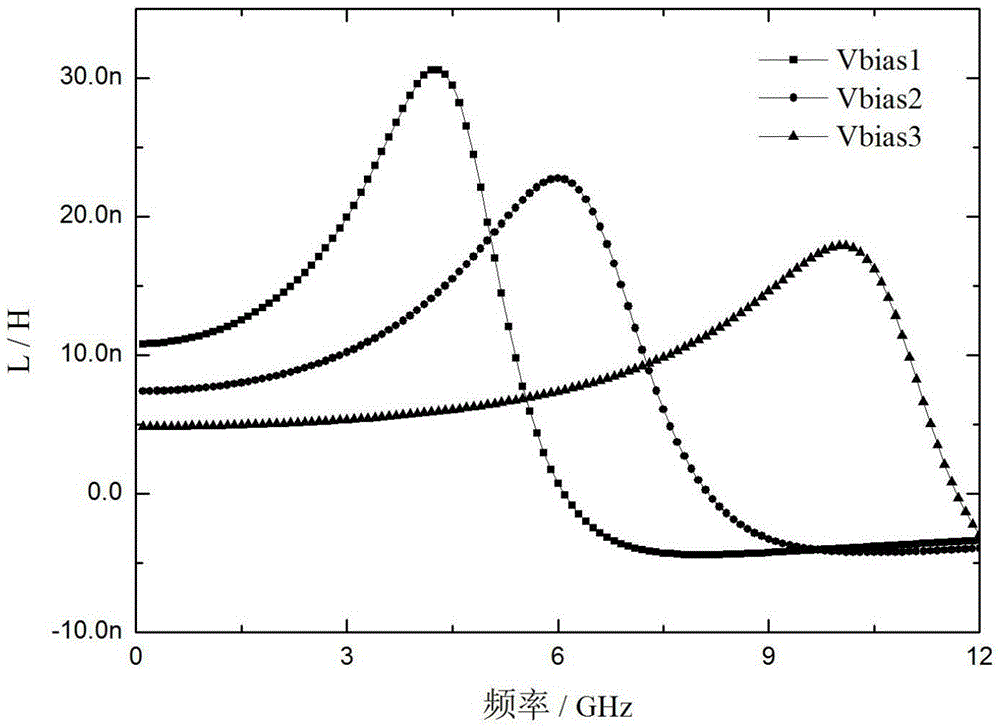
The invention discloses an active inductor with a high Q value, a high inductance and a tunable operating frequency range. The active inductor comprises a variable capacitor, an active feedback resistor, a positive transconductance amplifier, a negative transconductance amplifier, a first adjustable current source, a second adjustable current source and a stopping condenser, wherein the negative transconductance amplifier adds a multiple voltage modulation circuit on a common source-common gate structure; the adjustable active feedback resistor is connected between the positive transconductance amplifier and the negative transconductance amplifier for improving the real part loss of the active inductor to further improve the Q value; the variable capacitor is connected to the input end of the positive transconductance amplifier and the output end of the negative transconductance amplifier for adjusting the load capacitance of the active inductor to expand the adjusting range of the inductance and the Q value. Two adjustable current sources respectively provide direct current bias for the positive transconductance amplifier and the negative transconductance amplifier and can adjust the operating frequency range of the active inductor. Through the constituent parts, the operating frequency range, the inductance and the Q value of the active inductor can be all adjusted.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Integrated electromagnetic induction coil for wireless charging and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105788824AImprove wireless charging efficiencyImprove qualityTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsTransformers/inductances magnetic coresDiluentInductance
The invention belongs to the related technical field of wireless charging, and particularly relates to an integrated electromagnetic induction coil for wireless charging and a preparation method thereof. The integrated electromagnetic induction coil is formed by integral preparation of a magnetic conducting material and a coil; the magnetic conducting material is prepared from amorphous and nanocrystalline scales; and the preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, fixing the coil on a template; stacking the amorphous and nanocrystalline scales; infiltrating the amorphous and nanocrystalline scales with a coating agent diluted by a diluent; and finally preparing the integrated electromagnetic induction coil with a magnet yoke structure through drying treatment. The prepared integrated electromagnetic induction coil has the characteristics of being high in inductance, high in quality factor, simple in integral molding process, low in cost and the like.
Owner:ADVANCED TECHNOLOGY & MATERIALS CO LTD
Multilayer inductor
InactiveCN102473504AIncrease the inductance valueDC superposition characteristics do not degradeInductance with magnetic coreSpiral coilInductor
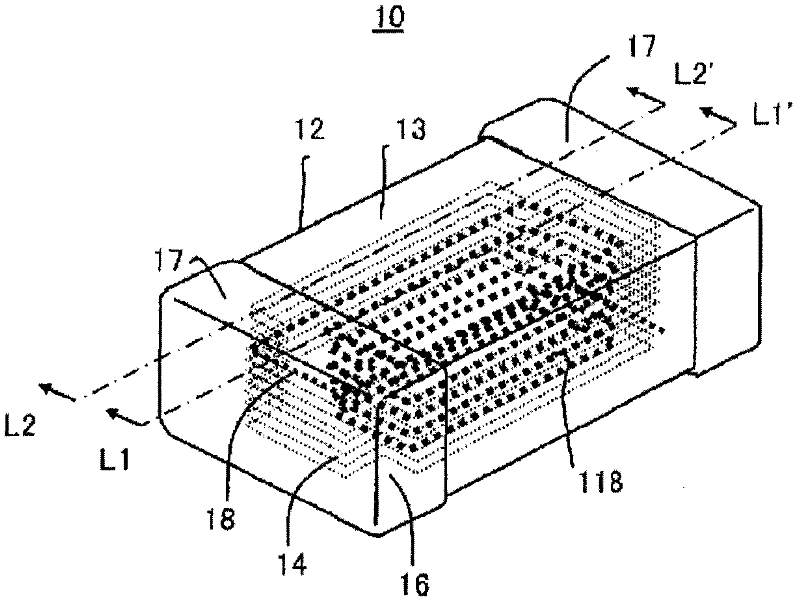
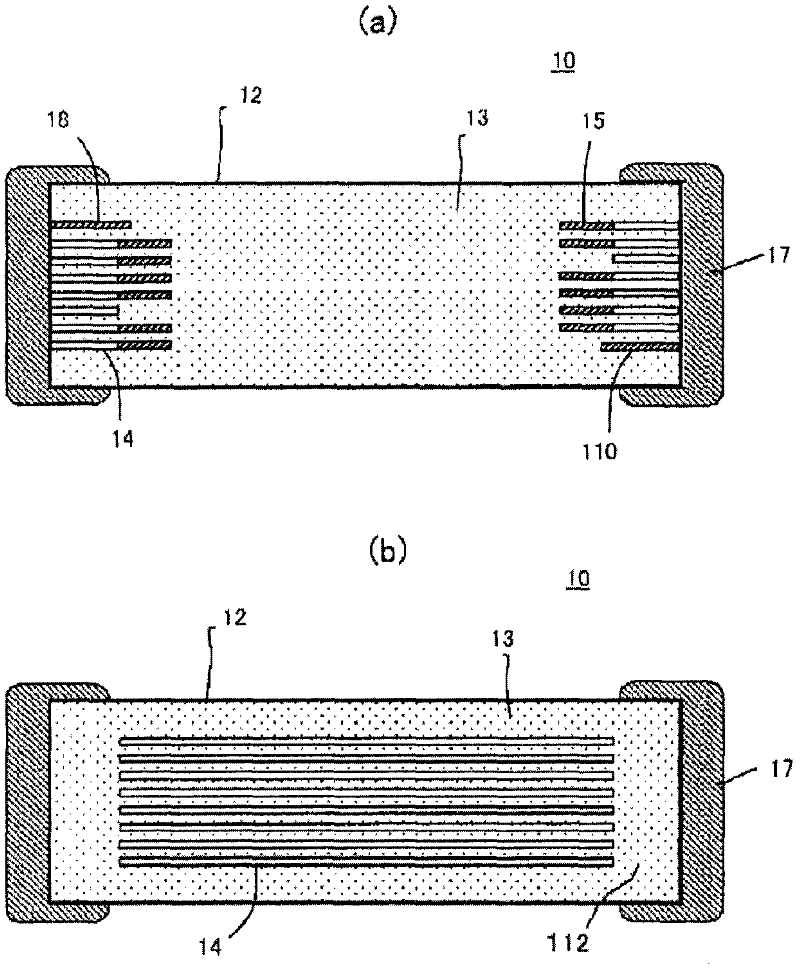
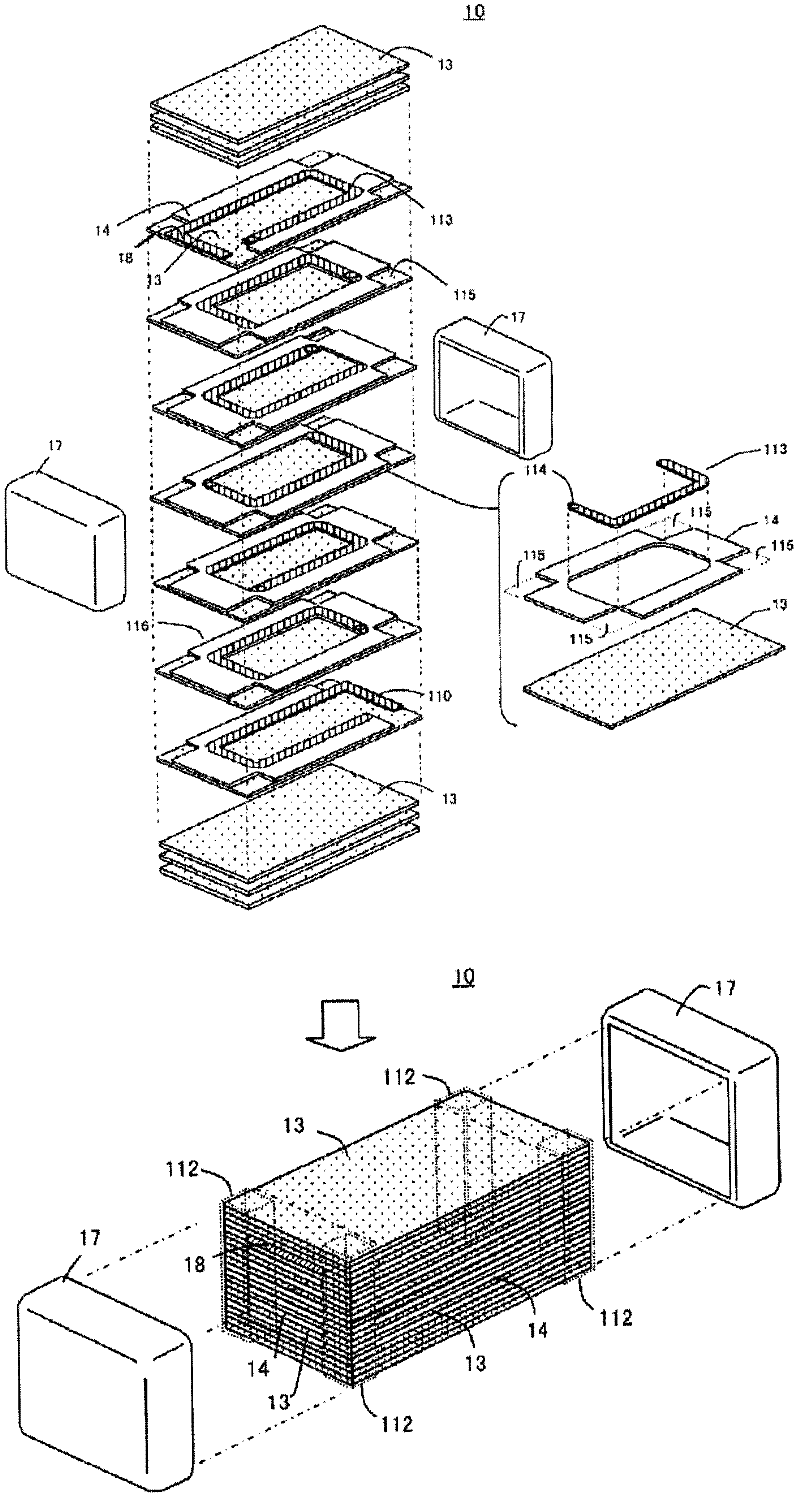
Provided is a multilayer inductor which can increase the inductance value (L) and can prevent the Q-value from decreasing without losing direct current superposition characteristics. The multilayer inductor (10) has a multilayer chip (12) shaped like a rectangular parallelepiped, and a pair of external electrodes (17) formed on the end surfaces of the multilayer chip. The multilayer chip is provided with a plurality of magnetic layers (13), coil conductors (15), and nonmagnetic layers (14). Each nonmagnetic layer is provided between adjacent magnetic layers, rectangular notched portions (115) are formed at four corners of the outer periphery of each nonmagnetic layer in the outside area of a spiral coil (118), and columnar areas (112) consisting of magnetic layers are formed at the notched portions. This structure introduces magnetic flux to the columnar areas, so magnetic saturation tends not to occur, and the direct current superposition characteristics are not lost. Further, the notched portions to be formed on the nonmagnetic material are disposed so as to be brought into contact with the external electrodes, so the Q-value is improved.
Owner:TAIYO YUDEN KK
Laminated differential inductor with top layer metal and second layer metal of equal thickness
InactiveCN102087912ARaise the sensory valueImprove Q valueSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsInductorInductance
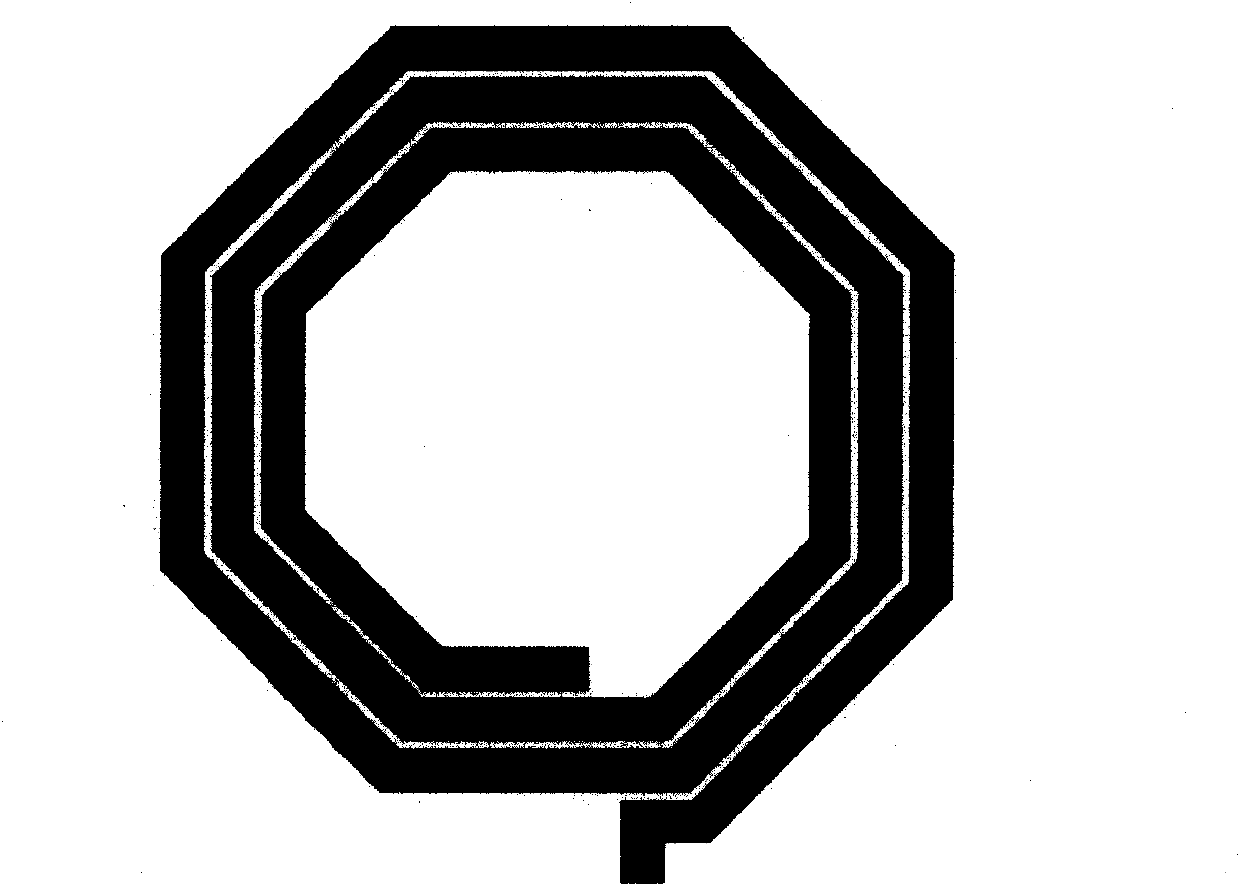
The invention discloses a laminated differential inductor with a top layer metal and a second layer metal of equal thickness. The laminated differential inductor has a multilayer structure and comprises an upper layer metal coil and a lower layer metal coil, wherein the upper layer metal coil and the lower layer metal coil have symmetric patterns and equal thickness; the metal coils are provided with inductance ports; in the inductor, the first layer of metal coil is spirally wound to the innermost end from one inductance port and then is connected with the other layer of metal coil through an interlayer through hole; the other layer of metal coil is spirally wound to the outermost end; and the upper layer metal coil is interconnected with the lower layer metal coil through the interlayer through hole. Since the mutual inductance between the symmetric upper layer metal and lower layer metal is fully utilized, the inductance of the inductor is effectively improved under the same area condition compared with the inductance of the conventional differential inductor. Both quality (Q) factor and inductance are obviously improved under the same area condition.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUA HONG NEC ELECTRONICS
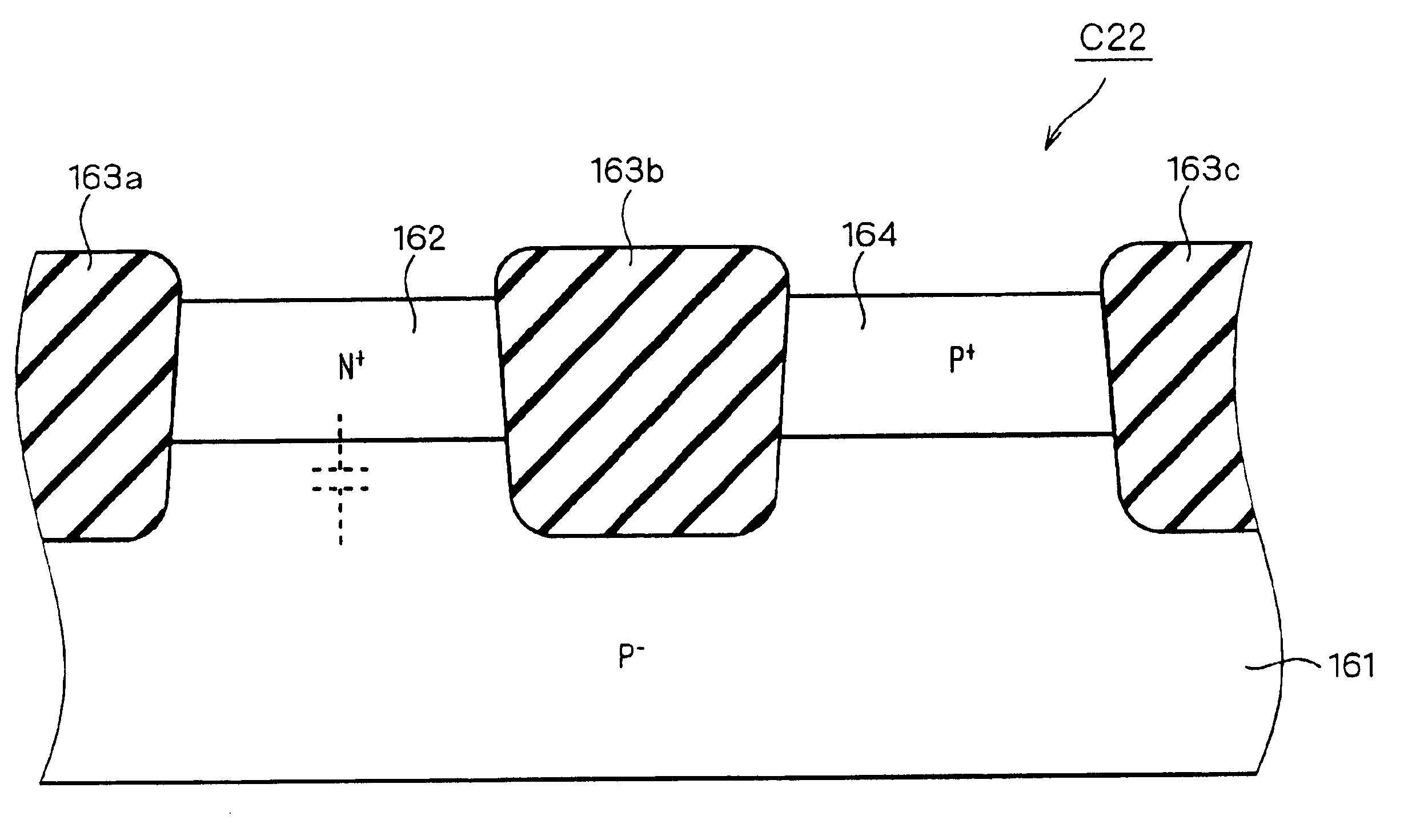
Semiconductor device including a capacitance
InactiveUS6858918B2Improve Q valueReduce the valueTransistorSolid-state devicesCapacitanceDevice material
Owner:TESSERA ADVANCED TECH
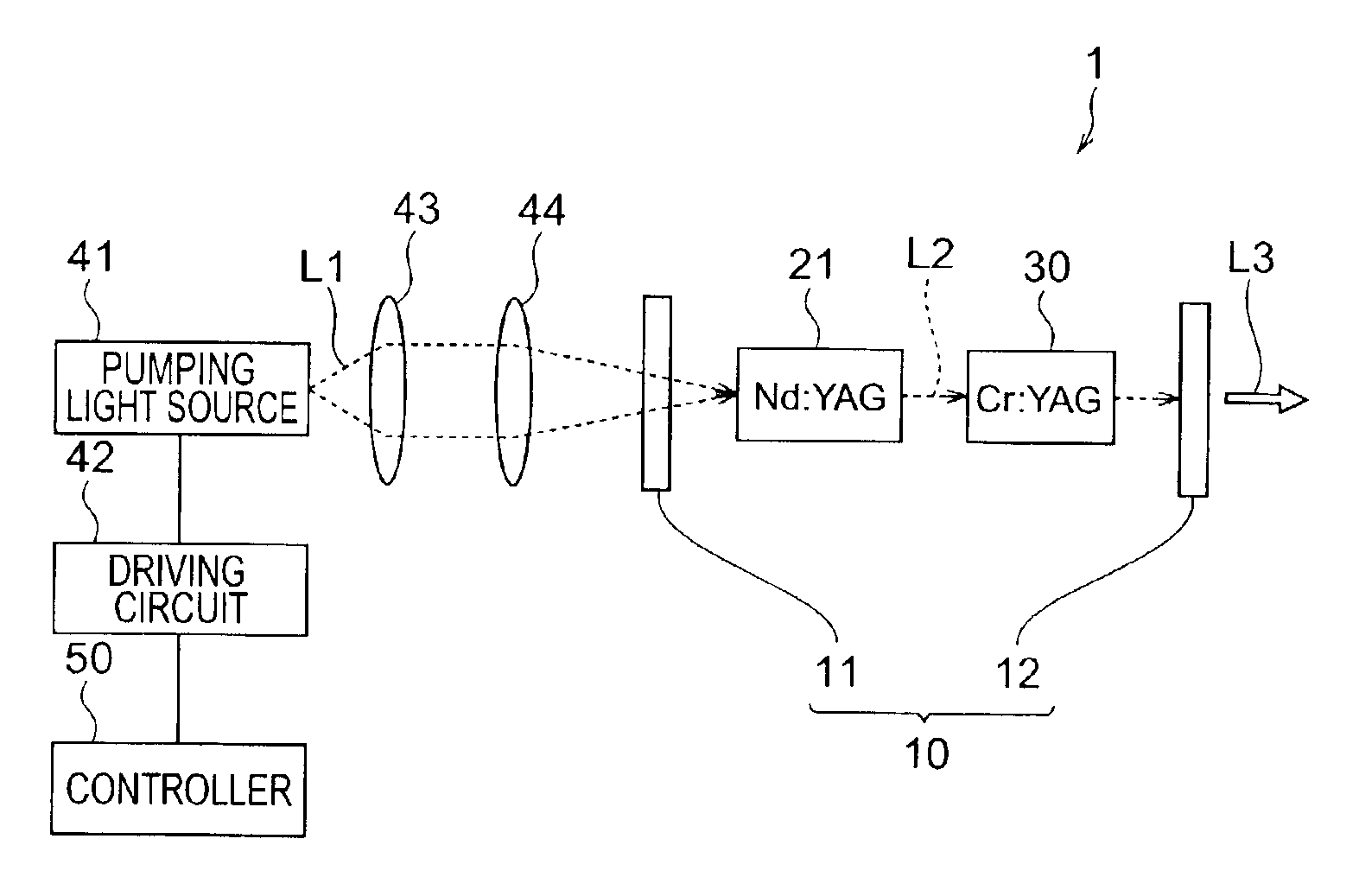
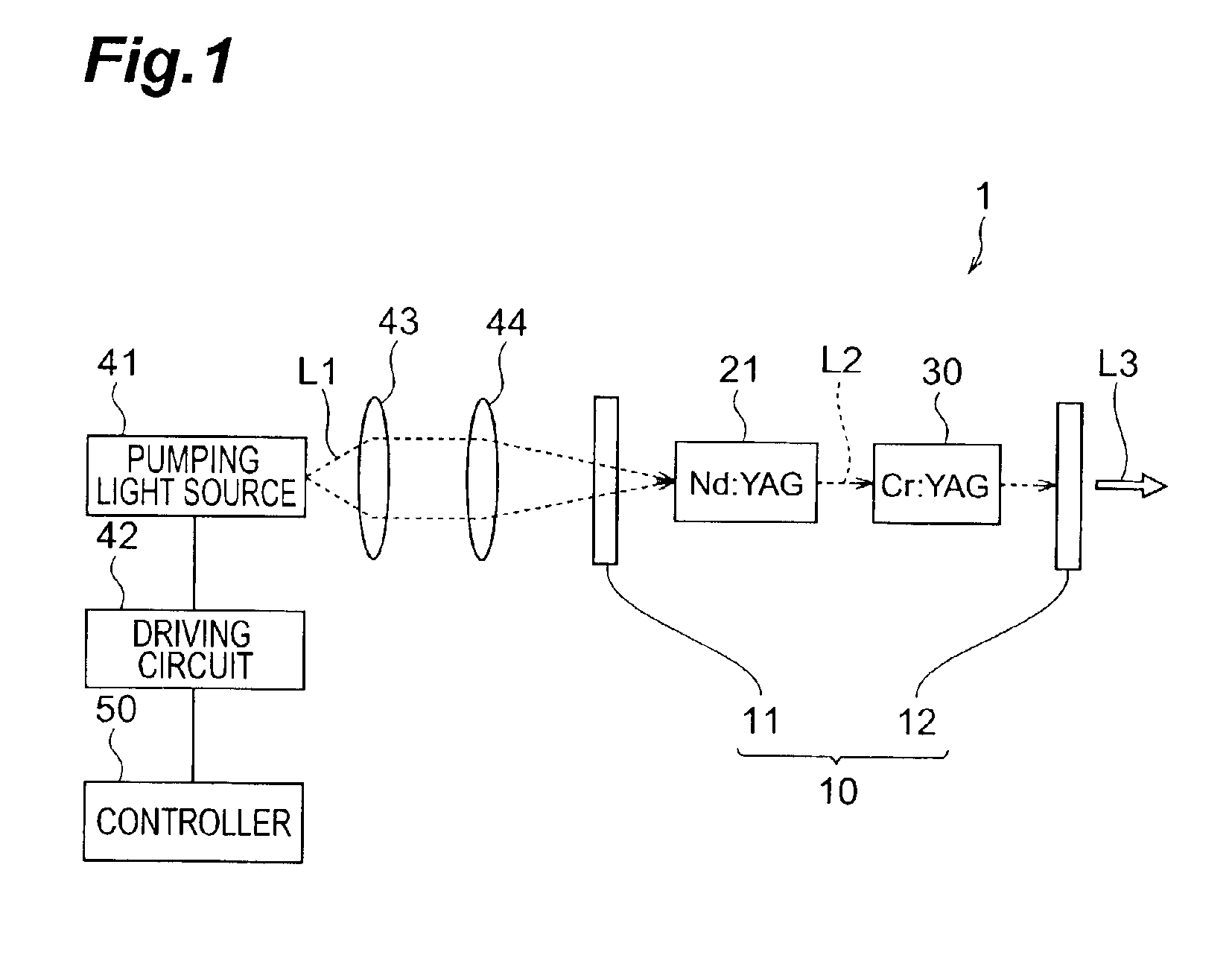
Laser light source
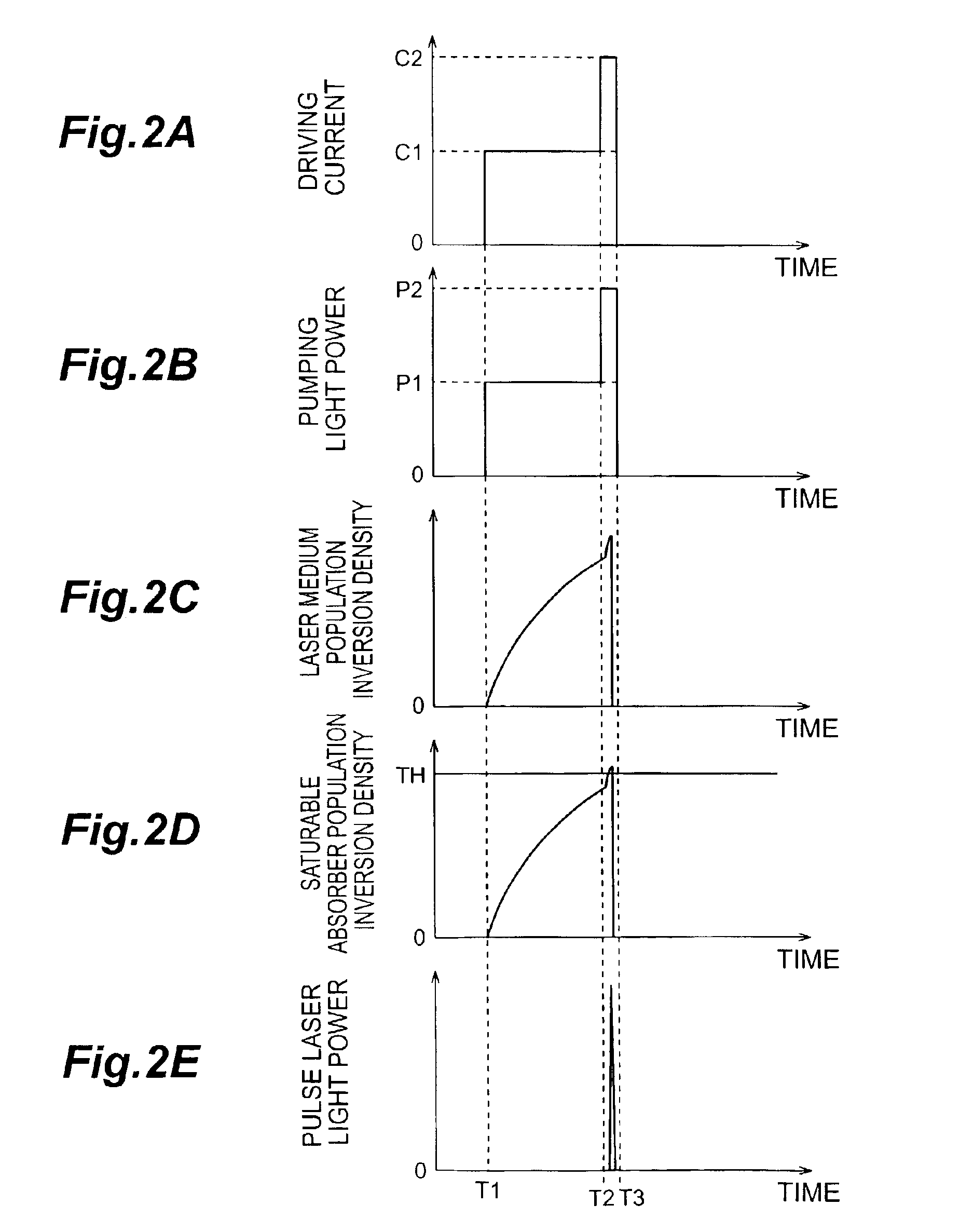
InactiveUS6931047B2High outputImprove Q valueExcitation process/apparatusStart timeIrradiation laser
In the first period from pumping start time T1 to time T2 in a laser light source 1, the power of pumping light L1 outputted from a pumping light source 41 so as to irradiate a laser medium 21 is at value P1 whereas the power of light L2 incident on a saturable absorber 30 after being emitted from the laser medium 21 is at an absorption saturation threshold or lower, which causes a resonator 10 to lower its Q-value, thereby suppressing the laser oscillation. Immediately before time T2, the power of light L2 is slightly lower than the absorption saturation threshold. In the second period subsequent to the first period, the power of light L2 is at value P2 greater than the above-mentioned value P1, whereas the power of light L2 exceeds the absorption saturation threshold, which causes the resonator 10 to increase its Q-value, whereby a mirror 12 outputs pulse laser light L3 to the outside.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
TE mode dielectric resonator device
ActiveCN105552496AEven by forceSolve the disadvantages of long-term stressResonatorsArchitectural engineeringDielectric resonator
The invention provides a TE mode dielectric resonator device. A limiting groove is arranged at the bottom of a cavity; the surface and the underside of a TE01 mode dielectric resonance rod are each provided with a clamping groove; an upper support base and a lower support base are respectively clamped on the clamping groove; the lower support base is clamped in the limiting groove; the top of the upper support base and the top of the cavity are horizontally collinear; a cover plate comprises an inner cover plate and an outer cover plate; a groove is arranged at the bottom of the outer cover plate; an elastic body is arranged in the groove; and the outer cover plate is installed on the inner cover plate through a connecting part. By being supported by the upper and lower support bases, a TE01 mode dielectric resonator is stressed uniformly; the long-term stressed disadvantage of the traditional TE01 mode dielectric resonator while being installed laterally and installed reversely can be solved; due to support through the upper and lower support bases, heat generated by the TE01 mode dielectric resonance rod can be effectively transferred to the cavity and the cover plate, such that heat dissipation of the cavity body is easily carried; and in addition, due to improvement of the cover plate, the problem that the cavity and a TE01 mode medium are in poor contact due to the machining tolerance can be solved.
Owner:SUZHOU ZIBO ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Vibrator element, vibrator, oscillator, and electronic apparatus
ActiveUS8581669B2Q-value can be improvedDegradation is more suppressedPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyImpedence networksEngineeringElectrode
A vibrator element includes a base section, vibration arms, and excitation electrodes provided to the respective vibration arms, the excitation electrodes each include a first electrode disposed on a principal surface side of the vibration arm, a second electrode disposed so as to be opposed to the first electrode, and a piezoelectric body extending between the first electrode and the second electrode, and ITO is used as at least one of the first electrode and the second electrode.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
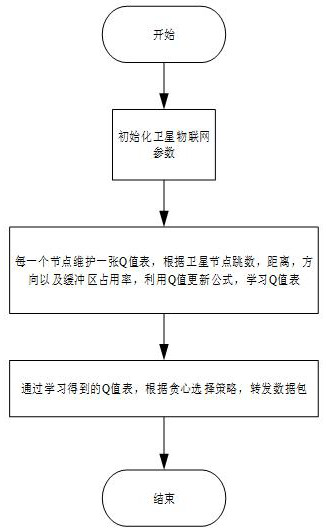
Satellite Internet of Things routing strategy based on Q-Learning
ActiveCN111770544AEfficient routingImprove reward valueNetwork topologiesMachine learningData packSpaceflight
The invention discloses a satellite Internet of Things routing strategy based on Q-Learning. Aiming at a satellite Internet of Things routing problem in a complex environment, a satellite Internet ofThings topological structure and node state dynamic changes are considered, the whole satellite Internet of Things is regarded as a reinforcement learning environment, and satellite nodes and ground nodes are regarded as intelligent agents., A method for implementing the strategy comprises the following stepsL firstly, initializingand satellite Internet of Things parameters are initialized firstly; secondly, maintaining a Q value table by each node, and learning the Q value table by utilizing a Q value updating formula according to the hop count, the distance, the direction and the buffer areaoccupancy rate of the satellite nodes; and finally, forwarding the data packet according to a greedy selection strategy through a Q value table obtained by learning. Moreover, the reward value is improved by considering the hop count of the satellite nodes, and the discount factor is improved by considering the distance and direction of the satellite nodes and the occupancy rate of the buffer area, so that the Q value is optimized, and the purpose of efficient routing of the satellite Internet of Things is achieved. Therefore, the satellite Internet of Things routing strategy has good conversion and application prospects in the fields of aviation, spaceflight, social economy and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Dual mode ceramic filter
A dual mode ceramic filter has an enclosure with two cavities separated by a wall, and two TM dual-mode resonators, each TM dual-mode resonator positioned in a corresponding cavity. Each TM dual-mode resonator has first and second modes, and a body having a central portion with a plurality of arms extending outwardly from the central portion. The filter also has two input conductive members, each input conductive members positioned in a corresponding cavity. Each input conductive member is disposed proximate a corresponding TM dual-mode resonator for coupling between the input conductive member and the TM dual-mode resonator.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Terahertz microfluidic sensor with metal square resonance array
ActiveCN113049524AImprove Q valueHigh detection sensitivityMaterial analysis by optical meansParticle physicsMaterials science
The invention discloses a terahertz microfluidic sensor with a metal square resonance array. The terahertz microfluidic sensor comprises a cover layer, a metal rectangular resonance array, a metal reflecting mirror surface and a substrate, wherein the metal reflecting mirror surface is arranged on the surface of the substrate; the metal reflecting mirror surface and the cover layer are oppositely arranged, and a gap between the metal reflecting mirror surface and the cover layer forms a microfluidic channel; and the metal rectangular resonance array is arranged in the microfluidic channel and located on the surface of the cover layer. The metal rectangular resonant array is composed of a plurality of metal rectangular resonant units, each metal rectangular resonant ring unit comprises two same metal rectangular resonant rings, and the metal rectangular resonant rings are spirally wound; outer rings of the two metal rectangular resonant rings are connected; and the two metal rectangular resonant rings are rotationally symmetrical. The microfluidic channel is used for reducing the strong absorption effect of moisture on terahertz waves, and the metal square resonance array is located in the microfluidic channel, so that the contact area between liquid to be detected and the metal square resonance array is increased, and the Q value and the detection sensitivity of the sensor are improved.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Radio frequency inductor element based on silicon substrate on insulator, and preparation method for radio frequency inductor element
ActiveCN105789189ASuppression of inductance lossImprove Q valueSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCMOSCapacitance
The invention discloses a radio frequency inductor element based on a silicon substrate on an insulator, and a preparation method for a radio frequency inductor element, and the method comprises the steps: 1), preparing the silicon substrate on the insulator, wherein the silicon substrate comprises a bottom silicon layer, an insulating layer and a top silicon layer, wherein the bottom silicon layer, the insulating layer and the top silicon layer are stacked together. A part, corresponding to a position where a radio frequency inductor element is prepared, of the lower part of the insulating layer is provided with a groove which at least reaches the bottom silicon layer; 2), defining a device region at a position corresponding to the groove through mask photoetching, removing the top silicon layer of the device region through etching, and exposing the upper surface of the insulating layer; 3), preparing the radio frequency inductor element in the device region based on the CMOS technology. The radio frequency inductor element is based on the patterned silicon substrate on the insulator, and the radio frequency inductor element with a substrate cavity is obtained through the later etching. The radio frequency inductor element can effectively inhibit the inductance loss caused by the silicon substrate, reduces the stray capacitance, and facilitates the improvement of the Q value and resonant frequency of the inductor.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Inductor component
PendingUS20210027937A1Enhanced strengthHigh strengthTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsGlass shaping apparatusComposite materialInductor
An inductor component includes an element assembly formed of an insulator material and an inner electrode arranged in the element assembly. The insulator material contains a base material formed of an amorphous material containing B, Si, O, and K and a crystalline filler and includes a filler-poor glass portion in a region along the inner electrode. The content of the crystalline filler in the filler-poor glass portion is lower than the content of the crystalline filler in the element assembly excluding the filler-poor glass portion.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Radio frequency filter on basis of variable transconductance operational amplifier
InactiveCN102420583ARealize controllable filteringImprove Q valueFrequency selective two-port networksCapacitanceRadio frequency
The invention discloses a radio frequency filter on the basis of a variable transconductance operational amplifier, which comprises a negative resistance matrix and an active LC (inductance capacitance) filter which are connected in parallel, wherein the the active LC filter is formed in a mode that an active inductance matrix is connected in parallel with a capacitance; an active inductance variation range of the active inductance matrix is configurated by a digital control signal provided by an external controller, and the active inductance matrix is controlled by an analog control signal provided by the external controller to continuously change in the currently selected active inductance variation range, so that the aim of continuously changing an active inductance value is fulfilled; and a negative resistance variation range of the negative resistance matrix is configurated by the digital control signal provided by the external controller, the negative resistance matrix is controlled by the analog control signal to continuously change in the negative resistance variation range, the loss of the active LC filter is counteracted, and the Q value of the active LC filter is ensured. After the radio frequency filter is adopted, the defects of low Q value and single working frequency range of the active filter are overcome. The radio frequency filter can work in the wide frequency band range. The Q value of the radio frequency filter is kept at a high level in the whole frequency band.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Preparation method of film bulk acoustic resonator with electrodes provided with double-ring and bridge-shaped structures
PendingCN113839638AHigh Q valueImprove leakage problemImpedence networksThin-film bulk acoustic resonatorThin membrane
The invention discloses a preparation method of a film bulk acoustic resonator with electrodes provided with double ring-shaped and bridge-shaped structures, and the method specifically comprises the following steps: sequentially depositing a stripping layer, a piezoelectric layer and a lower electrode on a substrate, and depositing an inner ring-shaped bulge, an outer ring-shaped bulge and a lower sacrificial layer wrapping the two bulges on the lower electrode, depositing a lower protection layer wrapping the lower sacrificial layer and a to-be-bonded layer II wrapping the lower protection layer on the piezoelectric layer; bonding the to-be-bonded layer I and the to-be-bonded layer II on the substrate, and removing the stripping layer and the substrate; depositing two long-strip-shaped upper sacrificial layers on the piezoelectric layer, depositing two bridge-type structures on the two long-strip-shaped upper sacrificial layers, depositing an upper electrode with the two sides connected with the two bridge-type structures respectively on the surface of the piezoelectric layer, and depositing an upper protection layer on the upper electrode and the two bridge-type structures; and forming a through hole in the piezoelectric layer, and removing the strip-shaped upper sacrificial layer and the strip-shaped lower sacrificial layer. The surface of the lower electrode of the resonator is provided with the inner annular protrusion and the outer annular protrusion, and the two side walls of the upper electrode are each provided with a bridge-type structure, so that the film bulk acoustic wave resonator has a higher Q value.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Preparation method of single crystal film bulk acoustic wave resonator with annular grooves and strip-shaped protrusions on electrodes
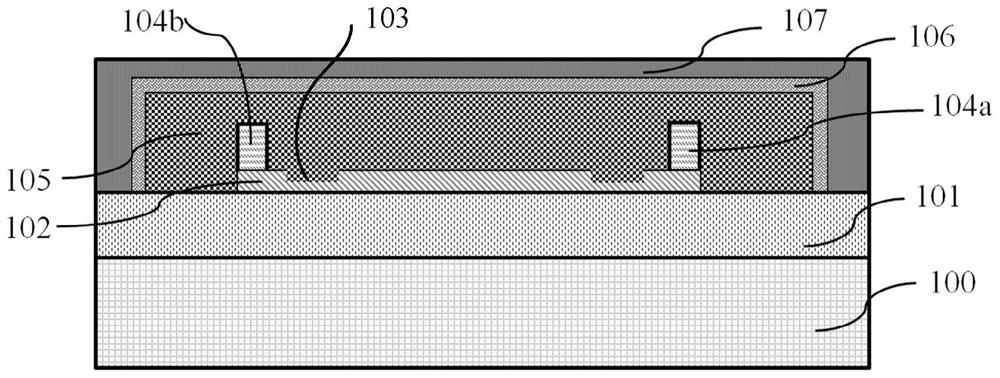
The invention discloses a preparation method of a single crystal film bulk acoustic resonator with an electrode provided with an annular groove and strip-shaped protrusions, and the method specifically comprises the following steps: sequentially depositing a stripping layer and a piezoelectric layer on a substrate, depositing a lower electrode on the piezoelectric layer, preparing an annular groove on the lower electrode, and depositing two strip-shaped protrusions and a sacrificial layer wrapping the two strip-shaped protrusions, depositing a protective layer wrapping the sacrificial layer on the piezoelectric layer, and depositing a to-be-bonded layer II wrapping the protective layer on the piezoelectric layer; then, bonding a to-be-bonded layer I and a to-be-bonded layer II on the substrate, removing the stripping layer and the substrate, depositing an upper electrode on the piezoelectric layer, preparing an annular groove on the upper electrode, and depositing two strip-shaped bulges on the upper electrode; finally, forming a through hole in the piezoelectric layer, wherein the bottom of the through hole is opened in the surface of the sacrificial layer, and the sacrificial layer is removed through the through hole to form a cavity. The lower ring groove, the first lower strip-shaped protrusion and the second lower strip-shaped protrusion are arranged on the lower electrode of the resonator, the upper ring groove, the first upper strip-shaped protrusion and the second upper strip-shaped protrusion are arranged on the upper electrode, and the frequency and the Q value of the resonator are improved.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
A micromechanical resonator, its preparation and frequency fine-tuning correction method
The invention discloses a micromechanical resonator, a preparation method thereof and a frequency fine tuning correction method. The micromechanical piezoelectric resonator comprises a substrate silicon wafer with a cavity structure, a resonant oscillator, a frequency modulation layer, a packaging film layer and a metal bonding pad structure. A wafer-level vacuum packaging method is adopted to seal a substrate silicon wafer concave cavity, a resonant oscillator, frequency modulation and other structures in a vacuum cavity. According to the frequency fine tuning method of the piezoelectric resonator provided by the invention, the frequency change of the resonator is monitored in real time by adopting the control host, and the frequency is fine tuned to the target frequency by adjusting the magnitude of the current introduced into the suspended frequency modulation layer or the surface frequency modulation layer of the auxiliary frequency modulation structure; and the position of a test platform of the probe station is automatically moved through a control bus of the automatic test probe station, so that wafer-level automatic frequency fine tuning of the micromechanical resonator is realized. Wafer-level vacuum packaging of the micromechanical resonator and accurate fine tuning of the frequency after packaging are realized, the method is simple and efficient, and technical support is provided for practicability and commercialization of the micromechanical resonator.
Owner:武汉敏声新技术有限公司
Quartz oscillating plate
ActiveUS20190245511A1Increased signal lengthImprove Q valueImpedence networksQuartzElectrical and Electronics engineering
A quartz oscillating plate comprises a substrate having a notch. Two sides of the notch respectively have a first side-electrode and a second side-electrode. The first side-electrode receives an external signal. The external signal is transmitted along the perimeter of the substrate. The notch of the substrate can increase the length of the transmission path of oscillation energy. The present invention can improve the Q value of the quartz oscillator using the quartz oscillating plate and optimize the performance of the products using the quartz oscillator.
Owner:TXC CORP
Cross-coupled filter
PendingCN112350038AReduce lossImprove harmonic characteristicsWaveguide type devicesResonanceMiniaturization
The invention discloses a cross-coupled filter, which comprises a minimum resonance structure, the minimum resonance structure is composed of four resonators, in the minimum resonance structure, two resonators in the same row form a group, and the two resonators in the same row are mainly electrically coupled or magnetically coupled; the two resonators in the same column are electromagnetically mixed and coupled; and the coupling polarities of the two groups of resonators of the two rows of resonance units are opposite, and at least one cross coupling is formed. According to the invention, miniaturization and light weight are realized in terms of structural characteristics, and low loss and good harmonic characteristics are realized in terms of electrical performance.
Owner:PROSE TECH CO LTD
Laminated electronic devices with conical vias
ActiveUS8922304B2Excellent electrical propertiesImprove Q valueElectrical connection printed elementsMultilayer circuit manufactureElectrical conductorEngineering
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
A micromechanical resonator
ActiveCN110289823BOptimize geometryReduce energy lossImpedence networksCollapsed cavityMicromachinery
The invention discloses a micromechanical resonator. By optimizing the design of the geometric dimensions of the micromechanical resonator, the mechanical vibration at the boundary between the resonator of the micromechanical resonator and the support beam is reduced, thereby reducing the energy loss of the micromechanical resonator; by designing an isolation frame structure at the resonator structure layer, And a groove or cavity structure is etched at the bottom of the substrate silicon wafer of the resonator, so as to reduce the influence of packaging stress on the performance of the resonator and improve the long-term stability of the micromechanical resonator. For a micromechanical resonator with a specific material, a specific frequency, and a specific mode, when the length of the resonator is at a certain value, the mechanical vibration at the boundary between the resonator and the support beam is the smallest. When the thickness of a certain layer of material in the resonant oscillator is changed, the length of the resonant oscillator is another optimized value.
Owner:武汉敏声新技术有限公司
An Electric Field-Induced Method for Ordered Domain Structures in Complex Perovskites
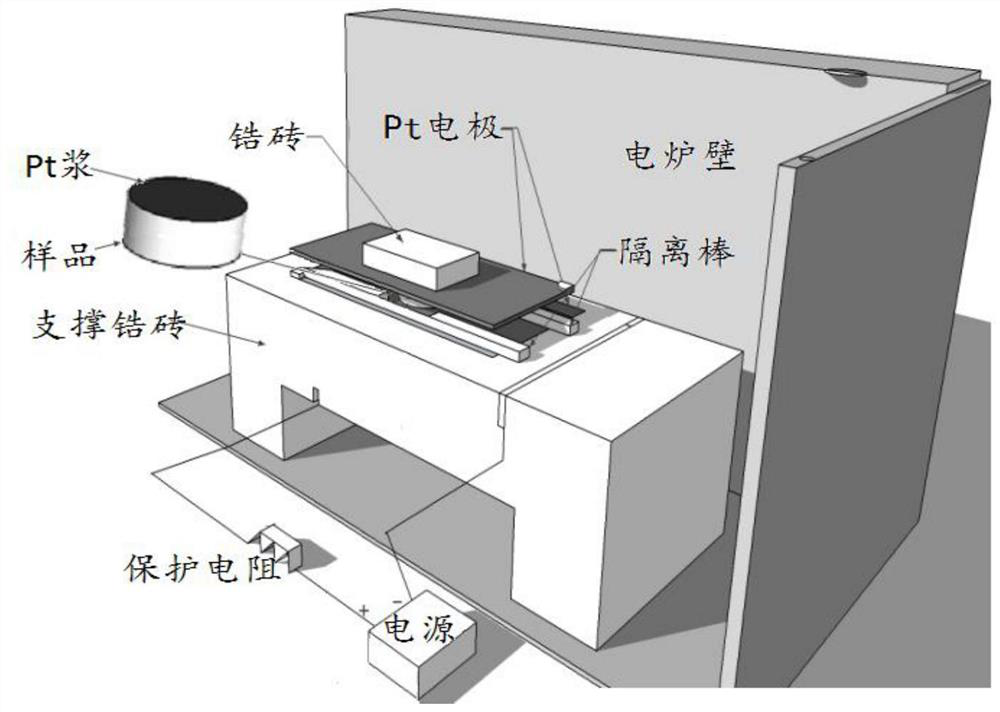
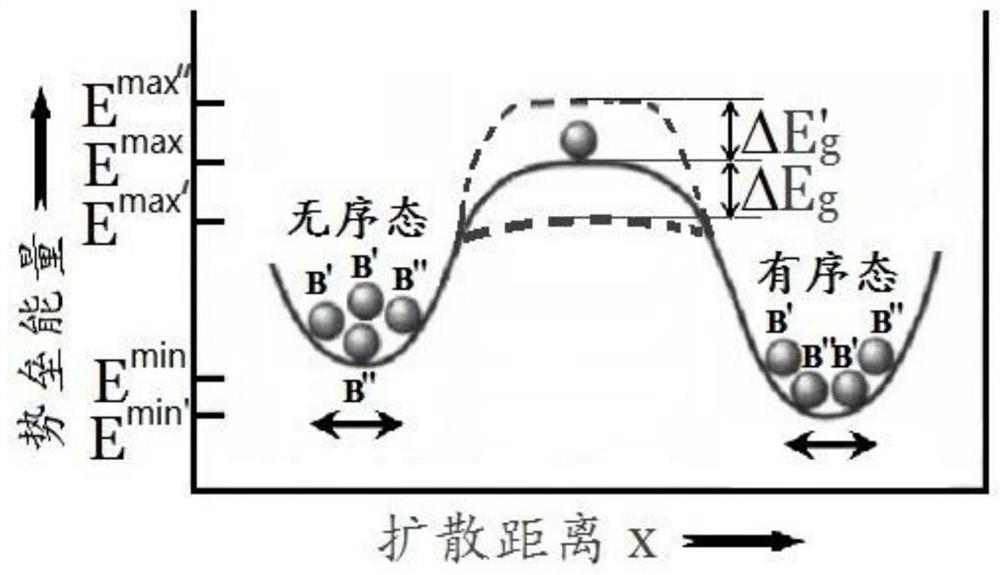
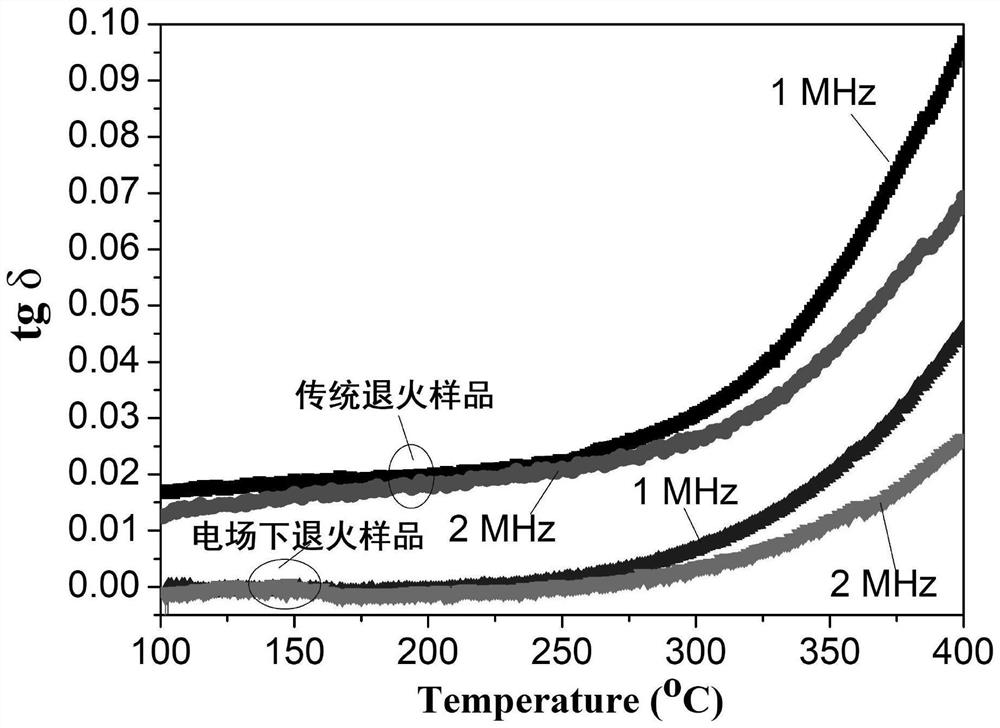
ActiveCN109180222BImprove Q valueLong-range ordered domain structure optimizationGalvano-magnetic material selectionTitaniumAlternating current
The invention discloses a method for inducing an ordered domain structure in a complex perovskite by an electric field. Carry out according to the following steps: a. prepare composite perovskite ceramics according to the conventional process; b. anneal the composite perovskite ceramics prepared in step a, specifically as follows: coat Put Pt slurry on both sides of the composite perovskite ceramics and put Pt wire electrodes on both sides and press them with zircon bricks. After supporting the above composite perovskite ceramics with zircon bricks, lead the Pt wire electrodes out of the electric furnace and connect them to AC power Positive and negative electrodes, then apply an alternating electric field through an AC power supply, and at the same time, anneal the composite perovskite ceramics at a temperature of 700°C to 900°C for 100 to 180 minutes. After the annealing is completed, the desired finished product is obtained. The invention has the advantages of low annealing temperature, short annealing time and obvious improvement of the Q value of ceramics.
Owner:GUIZHOU MINZU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com