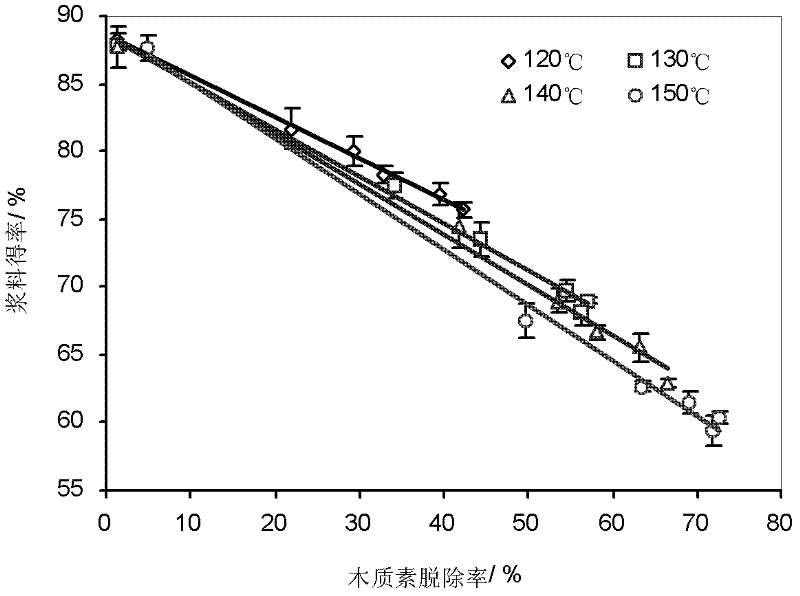
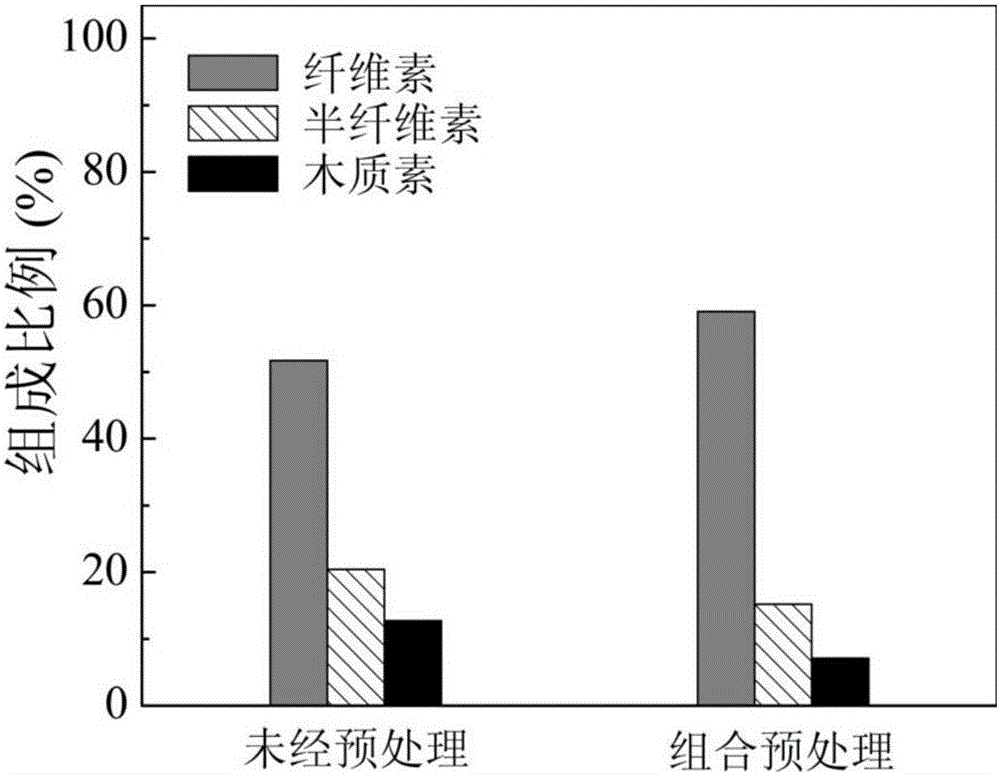
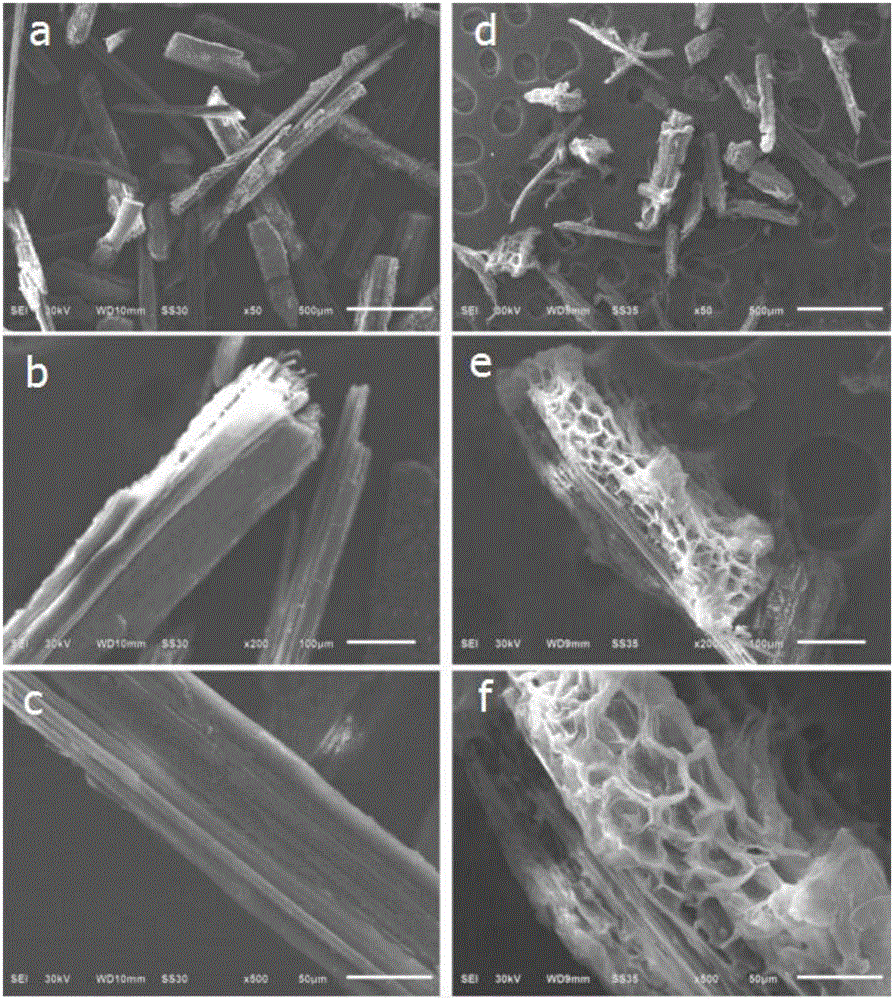
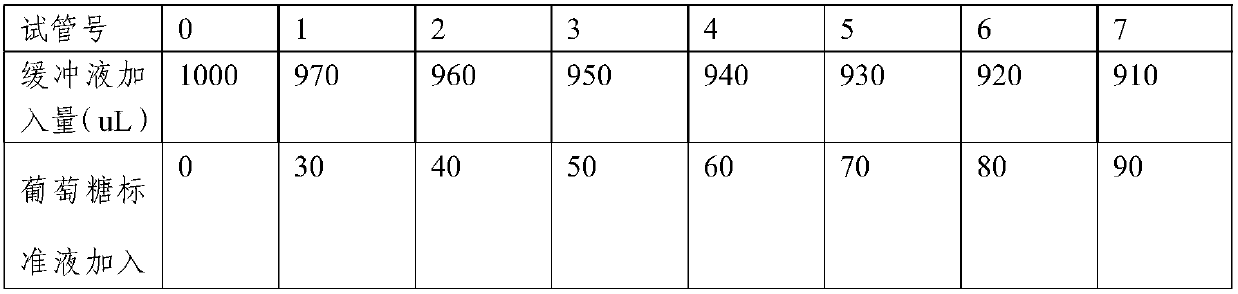
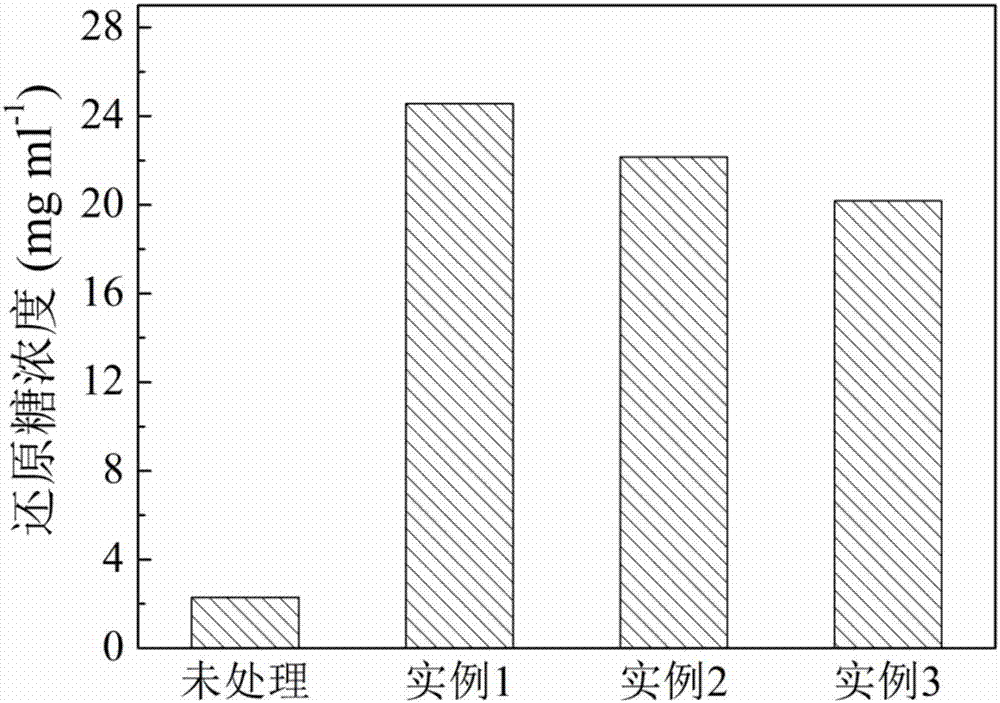
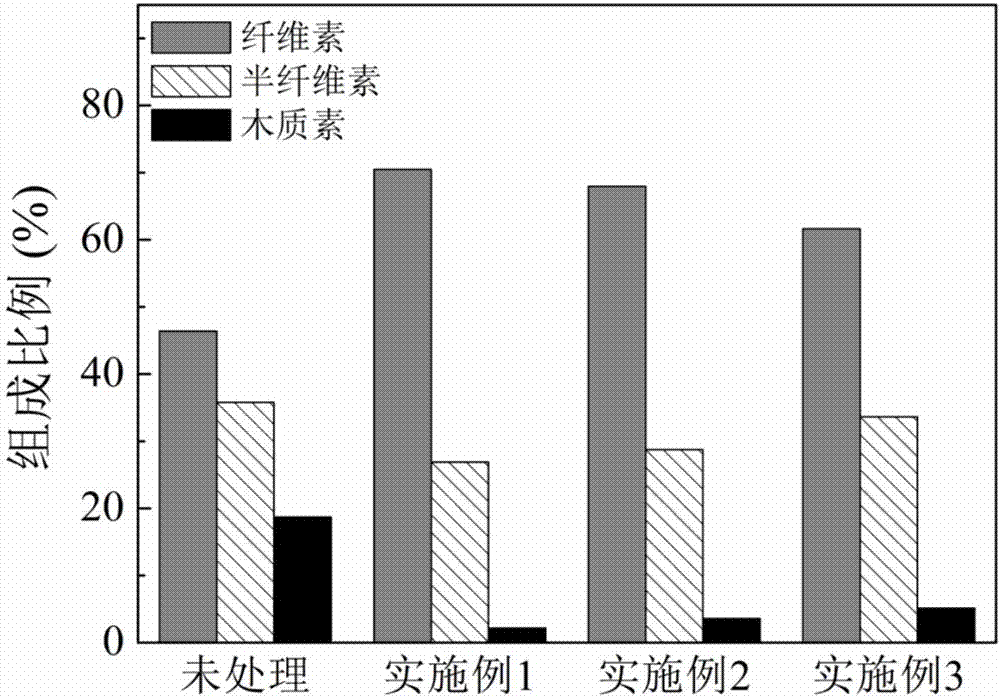
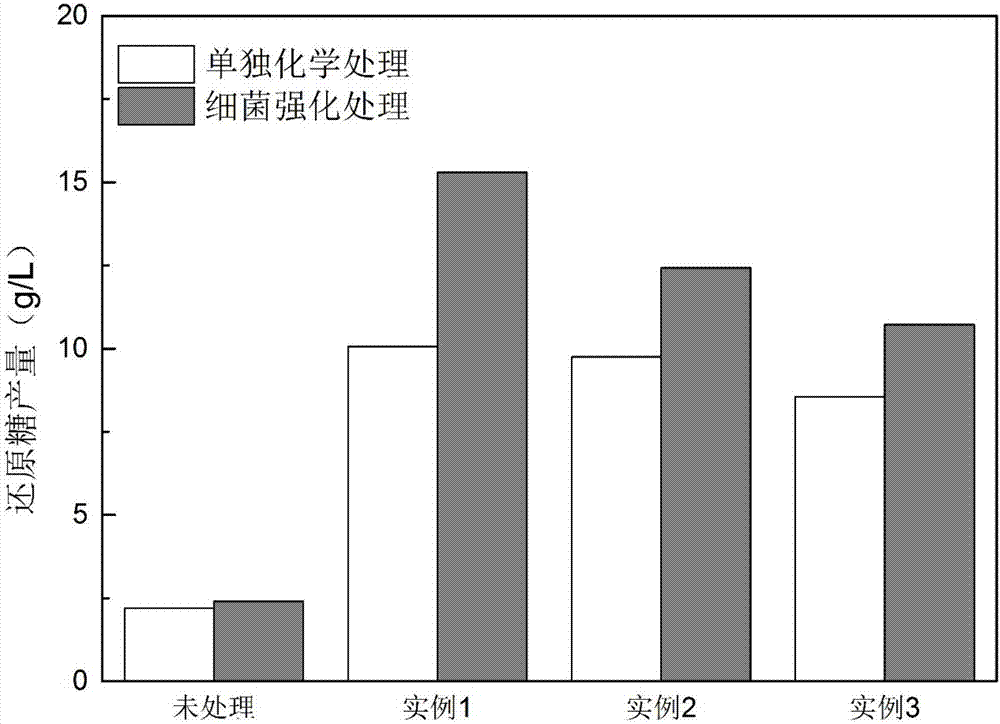
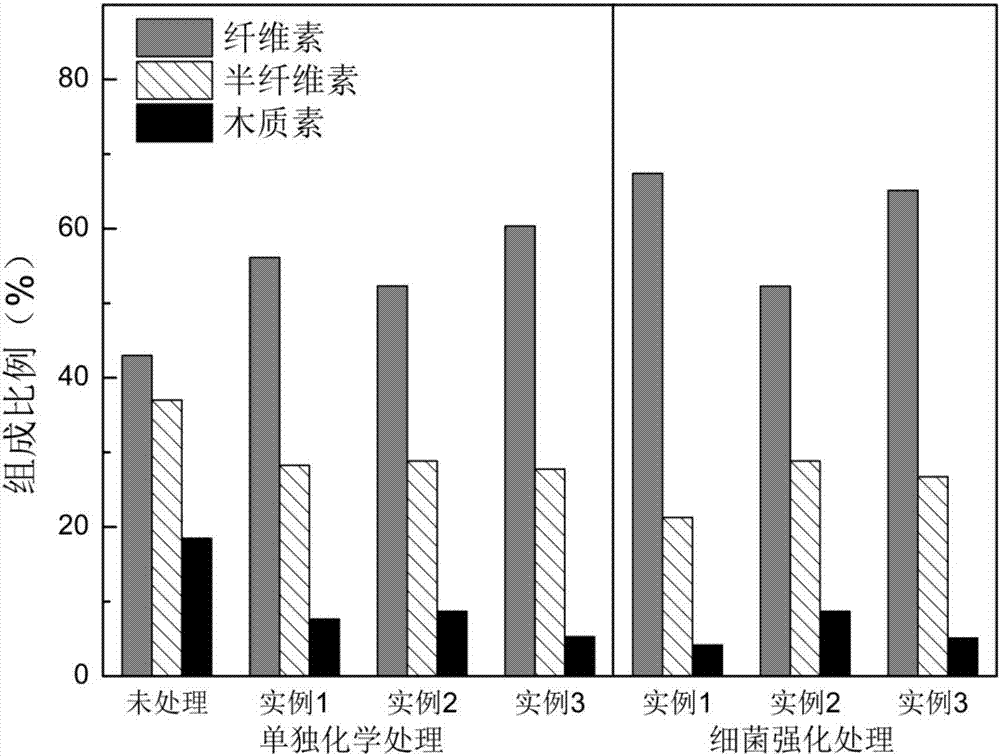
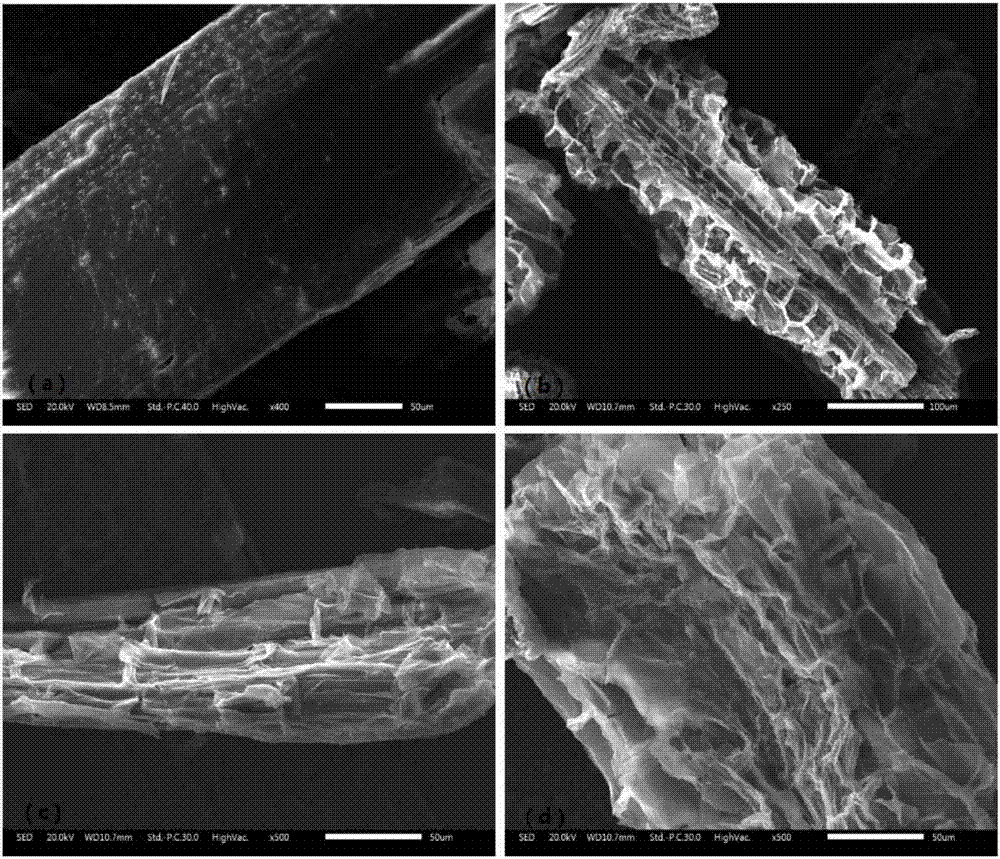
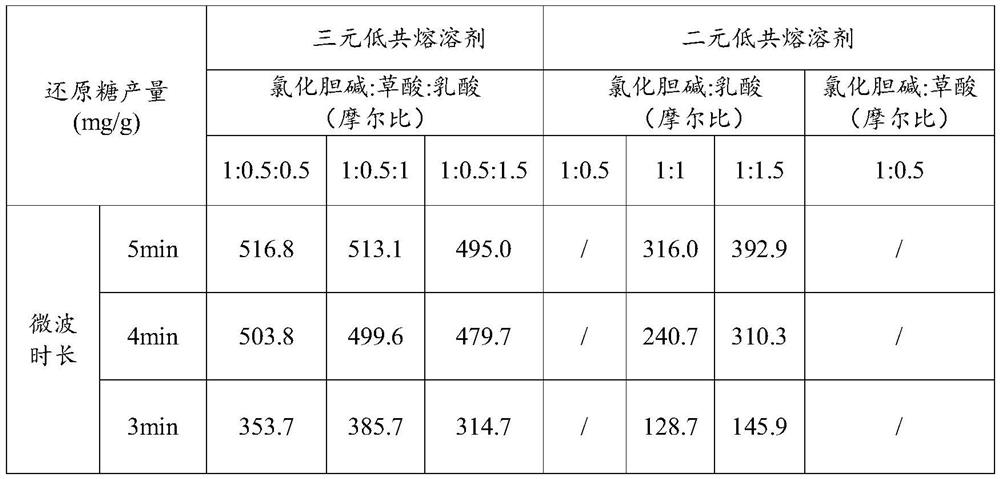
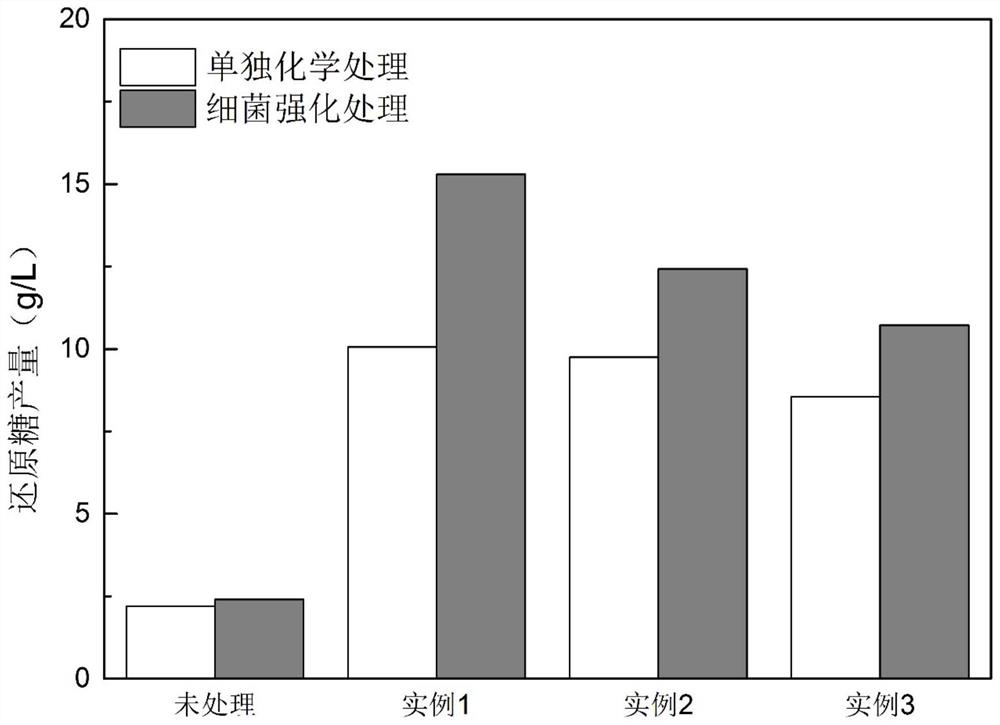
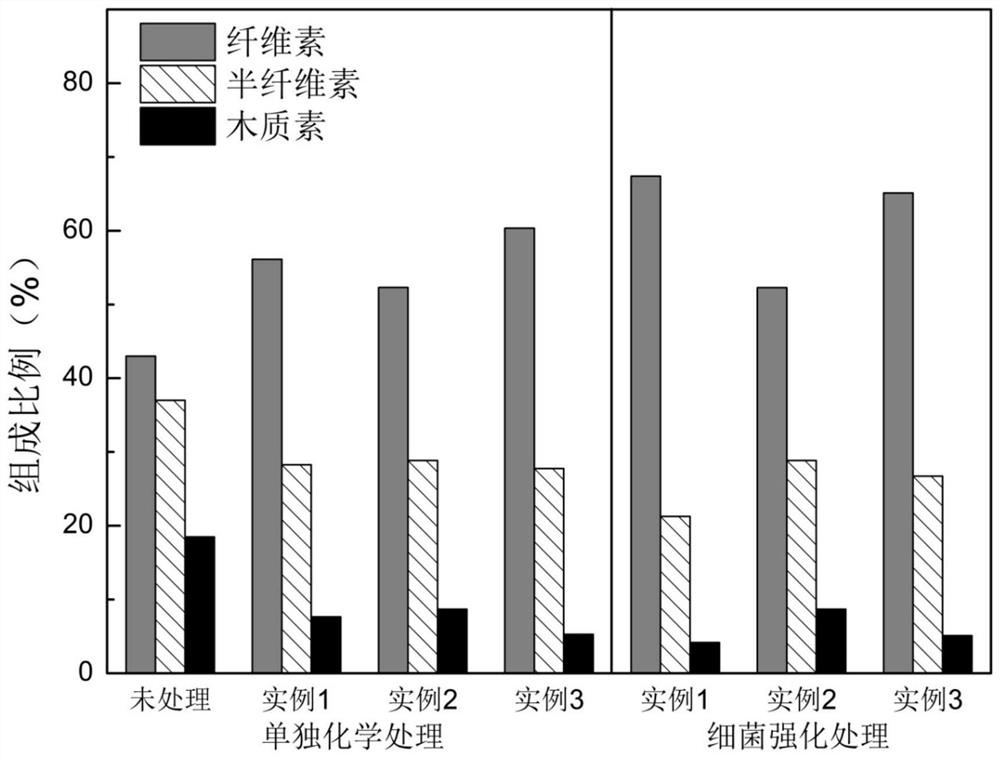
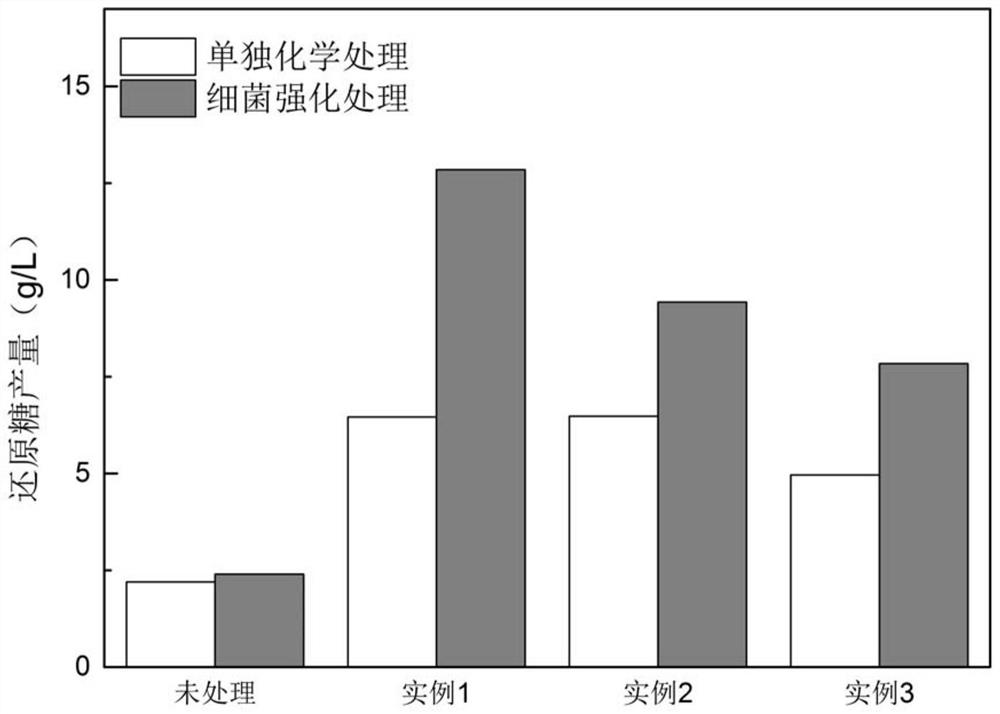
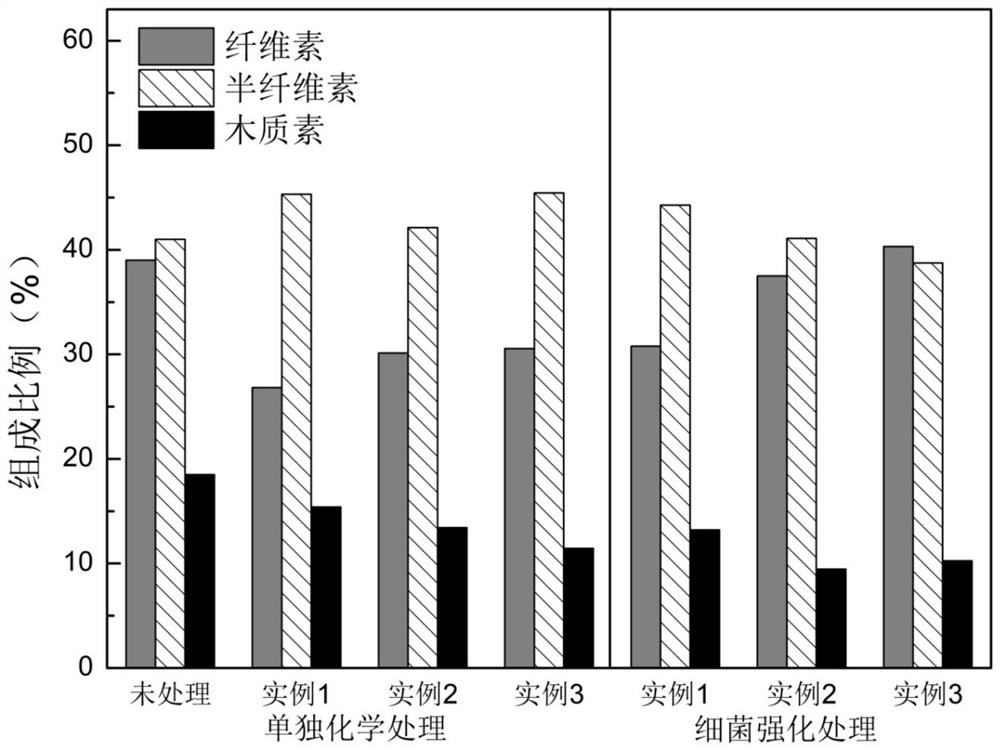
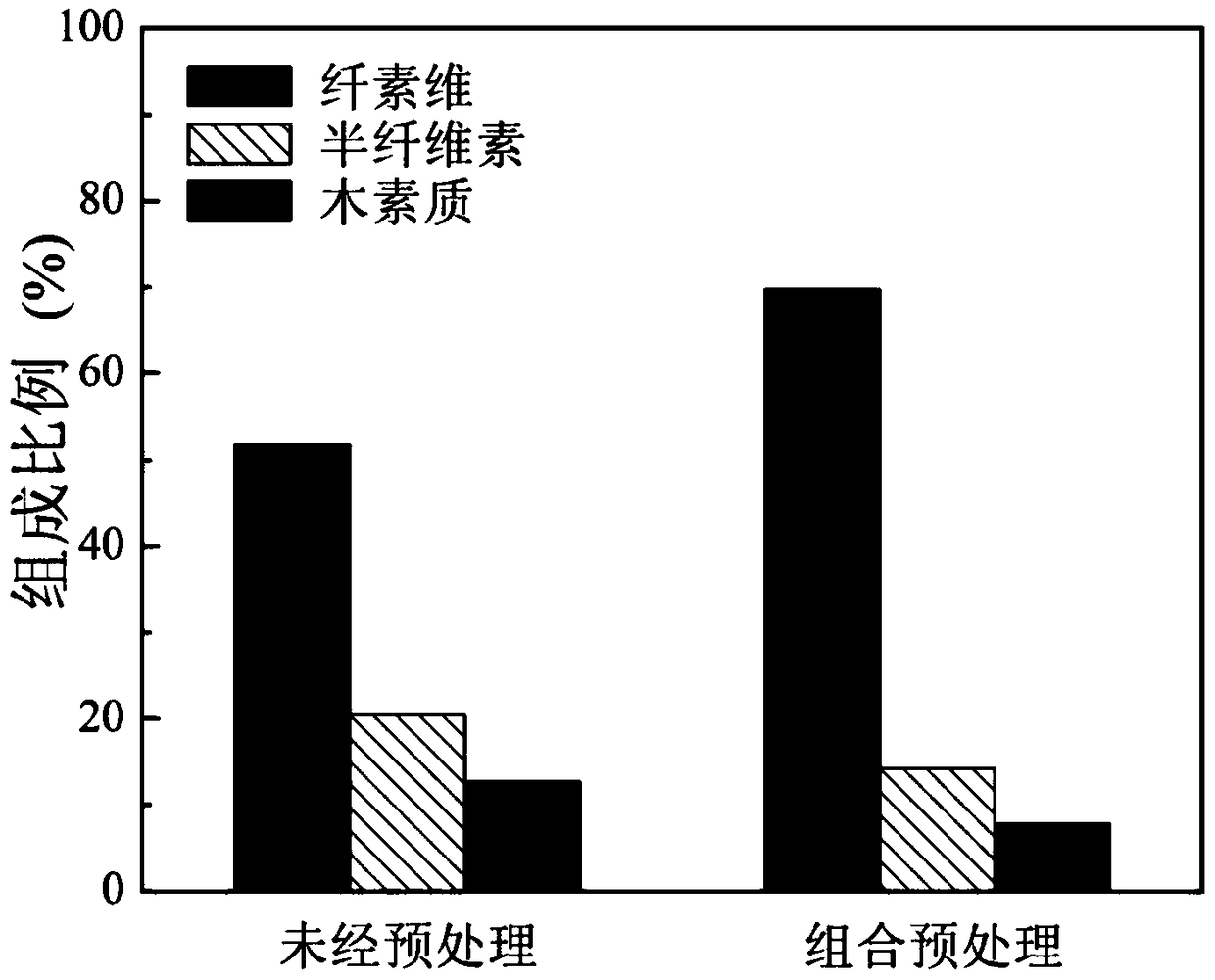
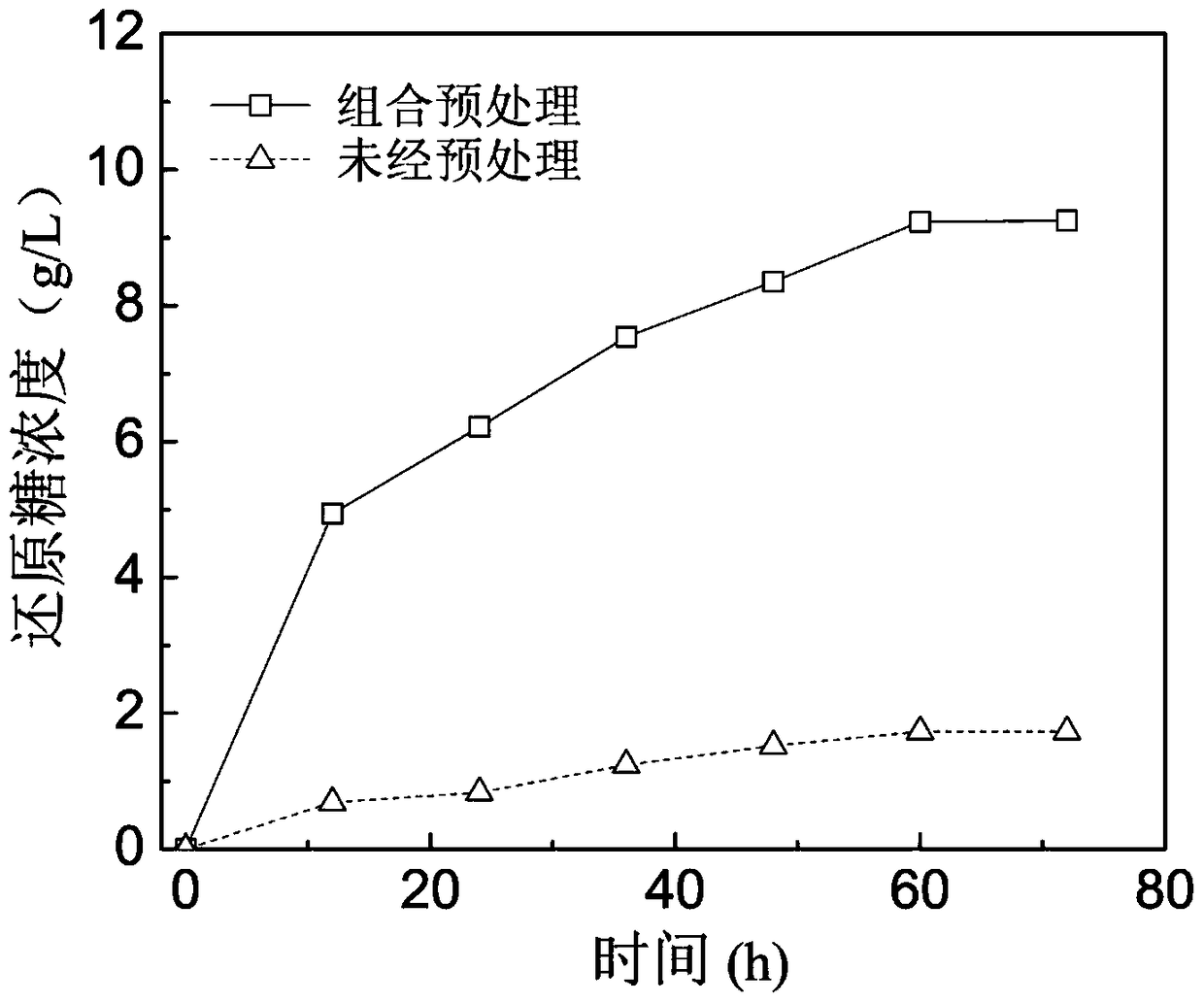
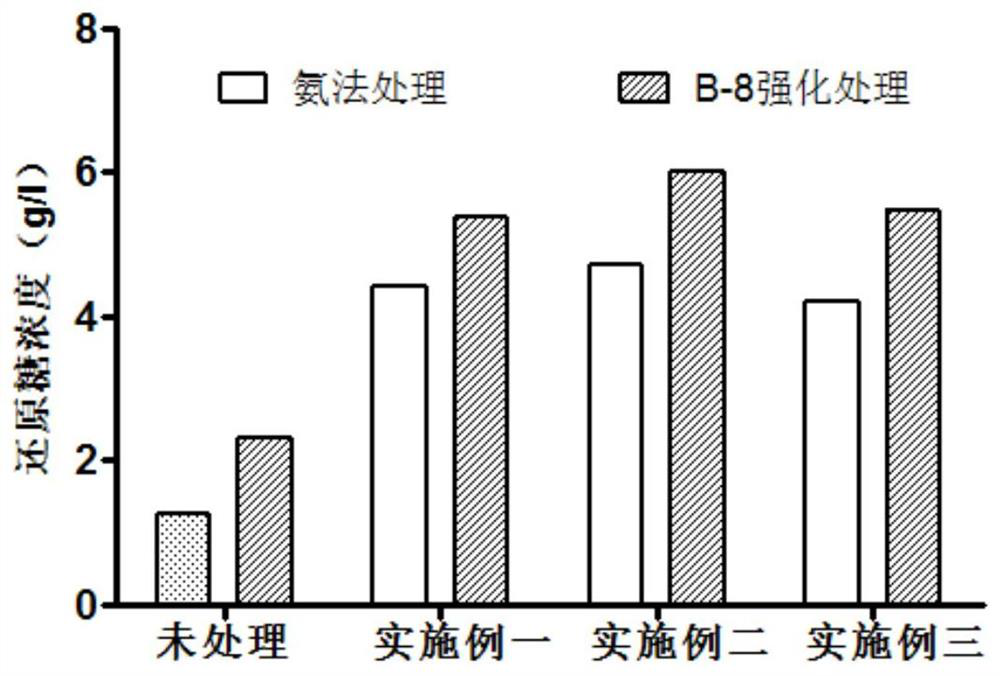
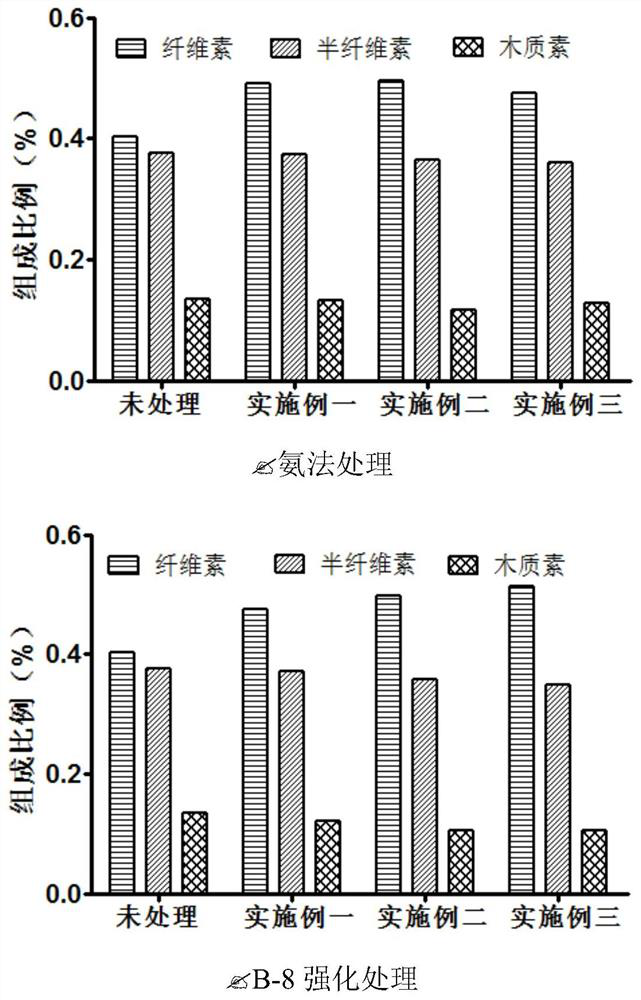
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34results about How to "Improve enzymatic hydrolysis and saccharification efficiency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Pretreatment method for improving enzymatic hydrolysis and saccharification efficiency of non-wood fiber raw material
InactiveCN102517358ARealize industrial productionImprove hydrolysis efficiencyFermentationFiberPretreatment method
The invention discloses a pretreatment method for improving enzymatic hydrolysis and saccharification efficiency of a non-wood fiber raw material. The method comprises the following steps of: mixing an aqueous solution of sodium carbonate and the non-wood fiber raw material, pre-impregnating for 30 to 120 minutes at the temperature of between 30 and 90 DEG C, heating to the temperature of between 100 and 180 DEG C, performing heat preservation reaction for 0 to 120 minutes, washing the non-wood fiber raw material by using water, defibering the raw material into fibrous pulp by using a stuff grinder, and thus completing the pretreatment process. The yield of the pretreated non-wood fiber raw material is between 50 and 90 percent, the removal rate of lignin is between 10 and 80 percent, the loss of high glycan is between 0 and 25 percent, a little silicon dioxide is dissolved from the non-wood fiber raw material in the pretreatment solution, and most silicon dioxide is preserved in the pretreated non-wood fiber raw material.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Pretreatment method capable of improving saccharification efficiency of lignocellulose
ActiveCN110760552AImprove enzymatic hydrolysis and saccharification efficiencyLow equipment requirementsPulping with organic solventsFermentationCelluloseGlycerol
The invention discloses a pretreatment method capable of improving saccharification efficiency of lignocellulose. According to the method, ethanedioic acid, choline chloride and glycerol are added towater for reaction to obtain a modified deep-eutectic solvent (DES), and a lignocellulose raw material is pretreated with the modified DES. The method can realize pretreatment of the lignocellulose under a lower-temperature condition, is more beneficial to improvement of the saccharification efficiency of the lignocellulose and can substantially increase the total quantity of carbohydrates released in a lignocellulose hydrolytic process.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Combined pretreatment process for improving lignocellulose saccharification effect
InactiveCN105002232AShort processing timeLower requirementFermentationChemical treatmentPre treatment
The invention provides a combined pretreatment process for improving the lignocellulose saccharification effect. According to the process, firstly, an alkali / urea solution is used for conducting first-step treatment on lignocellulose raw materials, part of lignin and hemicellulose ingredients in the lignocellulose raw materials are removed through chemical treatment, and the stable structure of lignocellulose is damaged to a certain degree; physical treatment is further conducted through ultrasonic waves, and the structure of the lignocellulose is more loosened. After pretreatment of the process, the ingredient content of the lignocellulose is obviously changed, and the proportion of cellulose is remarkably increased. In addition, the structure of the lignocellulose is remarkably changed, the raw material surface becomes rough, loosened and porous, and the accessible surface in the enzymolysis saccharification process is greatly increased. The combined pretreatment process has the advantages of being not high in equipment requirement, simple in operation, moderate in treatment condition, low in cost and the like, and can greatly improve the saccharification efficiency of the lignocellulose.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Method for improving enzymolysis saccharifying efficiency of hemp straw
InactiveCN107828832ALarge specific surface areaPromote swellingMicroorganism based processesFermentationWhite rotVolume concentration
The invention relates to a method for improving the enzymolysis saccharifying efficiency of hemp straw. The method is mainly characterized in that before enzymolysis saccharifying of hemp straw, the following pretreatment is performed: (1) crushing hemp straw, performing high-temperature sterilization, then inoculating white rot fungi into the crushed straw, and performing culture for 7-28 days toobtain biologically pre-treated hemp straw; and (2) mixing the biologically pre-treated hemp straw with a low-concentration alkali and hydrogen peroxide mixed solution, and performing treatment for 20-30 h at 40-60 DEG C to obtain pre-treated hemp straw, wherein the mass concentration of alkali in the mixed solution is 0.5-5%, and the volume concentration of hydrogen peroxide is 2.5-3.5%. Beforealkali oxygen treatment of hemp, biological pretreatment is performed at first, so that the consumption and the concentration of alkali in the alkali oxygen treatment process are reduced, the treatment time is shortened, the treatment efficiency is improved, and the pretreatment effect is improved.
Owner:INST OF BAST FIBER CROPS CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Combined pretreatment process for efficiently and environmentally friendly improving enzymolysis saccharification efficiency of lignocellulose
InactiveCN107488682AReduce crystallinityImprove saccharification efficiencyBiofuelsFermentationCellulasePre treatment
The invention relates to a process for improving enzymolysis saccharification efficiency of lignocelluloses through combined pretreatment of an NADES and NU. The process comprises the following steps: firstly, mixing choline chloride / lactic acid according to a certain ratio, and performing further treatment on a lignocelluloses raw material so as to remove a part of lignin and hemicelluloses and damage the dense structure of the lignocelluloses; further performing a second step of pretreatment on the lignocelluloses by using NU at different temperature. By adopting the process, the ratios of the lignin and the hemicelluloses can be reduced, the surfaces of the lignocelluloses are loosened and porous, the accessible areas of the lignocelluloses are increased, and the saccharification efficiency of the lignocelluloses is improved. The combined pretreatment process has the advantages of being low in equipment requirement, simple to operate, gentle in treatment condition, low in cost, environmentally friendly and the like, and the saccharification efficiency of the lignocelluloses can be greatly improved.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Biological-chemical combined treatment process for improving saccharifying effect of lignocellulose
ActiveCN105177055ALower requirementReduce investmentBiofuelsMicroorganism based processesChemical treatmentMicroorganism
The invention discloses a biological-chemical combined treatment process for improving saccharifying effect of lignocellulose. According to the process, a lignocellulose raw material is subjected to biological treatment by virtue of an efficient lignocelluloses degrading bacterium sphingobacterium sp. LD-1 (preservation number is CGMCC No.10920), so as to remove partial lignin and hemicellulose components in the lignocellulose raw material with the action of microorganisms, and to damage the stable structure of the lignocellulose to a certain degree; and furthermore, the lignocellulose undergoes chemical treatment at low temperature by virtue of alkali / urea, so that the lignocellulose is more loose in structure. The lignocellulose, which is preprocessed by the process disclosed by the invention, achieves significant change in component content and obvious increase in proportion of cellulose; in addition, the structure of the lignocellulose is significantly changed as well, and the surface of the raw material becomes rough, loose and porous, so as to greatly increase an accessible surface during enzymolysis saccharifying. The combined pretreatment process disclosed by the invention has the advantages of being not high in requirement on equipment, simple in operation, mild in processing condition, low in cost and the like, and the saccharifying efficiency of the lignocellulose is greatly improved.
Owner:湖南中森环境科技有限公司
Method for comprehensively utilizing lignocellulose by using polyol-based acidic eutectic solvent
PendingCN114085876AHigh purityImprove enzymatic hydrolysis and saccharification efficiencyFermentationPolyolCellulose compounds
The invention relates to the technical field of pretreatment of lignocellulose, and concretely relates to a method for improving the utilization value of lignocellulose through pretreatment of an acidic polyol eutectic solvent. The method mainly comprises the following steps: preparing a polyol-based acidic eutectic solvent, treating an extract-removed lignocellulose raw material, and hydrolyzing filter residues obtained by solid-liquid separation under the action of a cellulose compound enzyme so as to enhance the conversion efficiency of cellulose to glucose and improve the purity of glucose; and carrying out water precipitation regeneration and separation on a filtrate to obtain lignin, and recycling the residual filtrate in a new pretreatment process. According to the method, no metal catalyst is added in the technological process, wood fiber components can be rapidly dissociated through pretreatment, two components including lignin and cellulose are obtained, the cellulose serves as a conversion object, the enzymolysis saccharification efficiency is improved, the obtained glucose is high in purity, the follow-up purification cost is reduced, the solvent can be recycled, and the cost is low. The two major components of the wood fibers are separated and utilized through a green and environment-friendly method, and comprehensive utilization of the lignocellulose components is facilitated.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
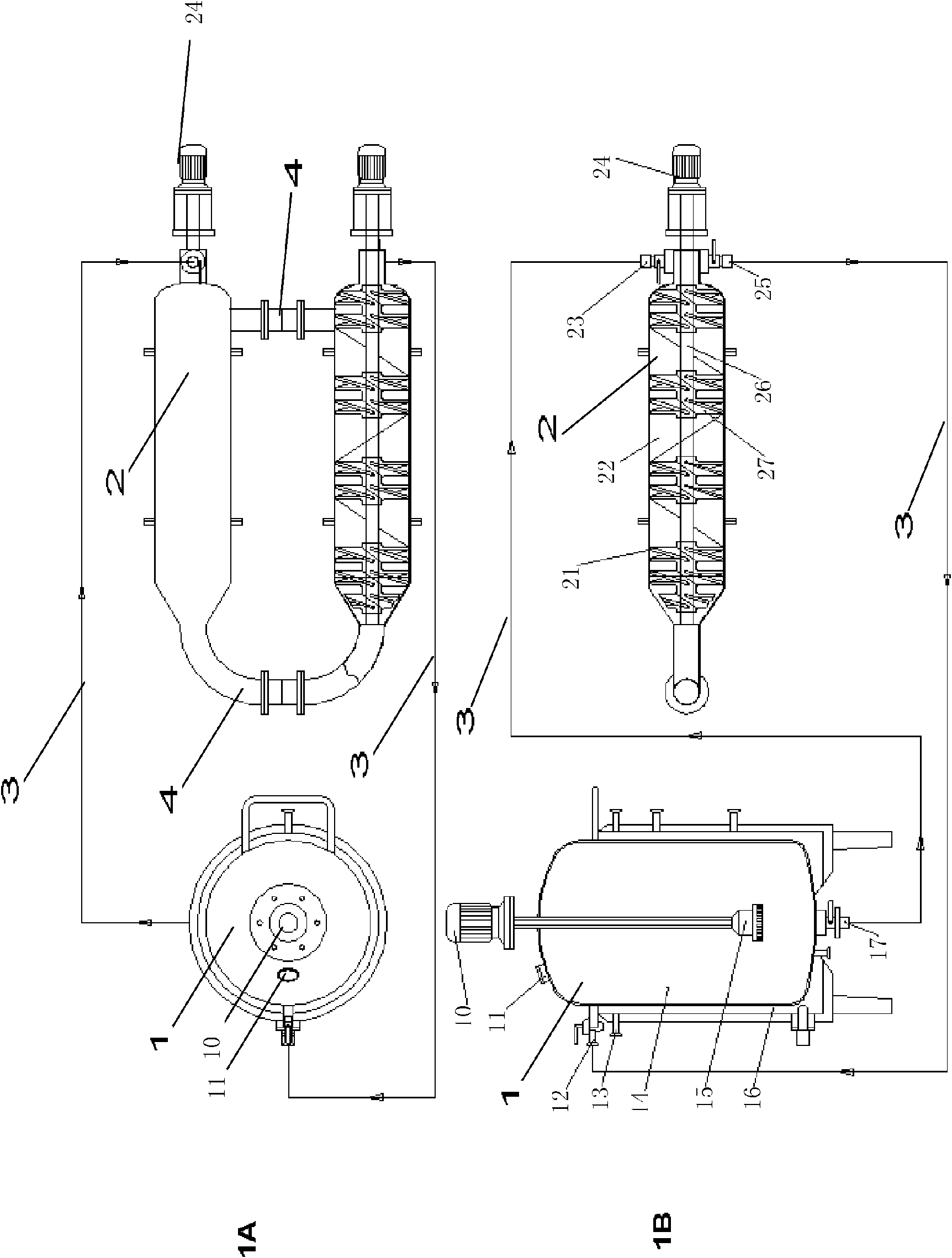
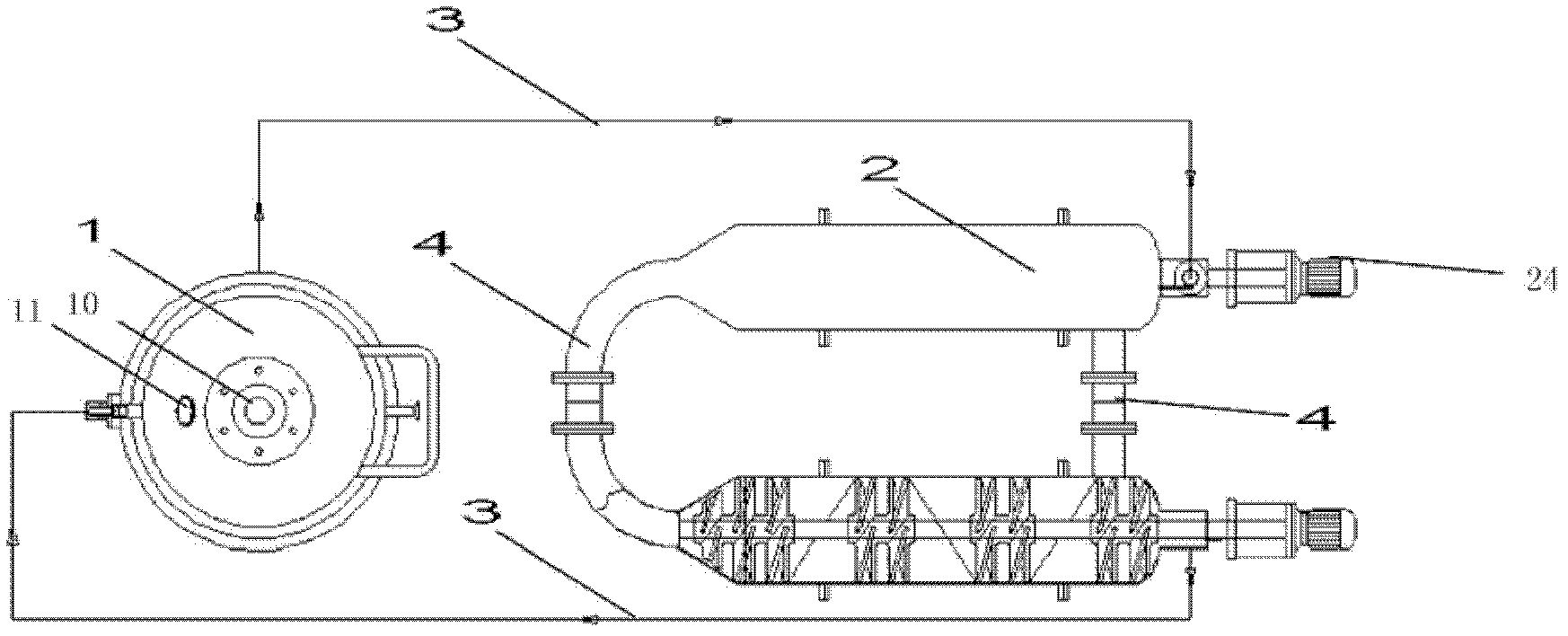
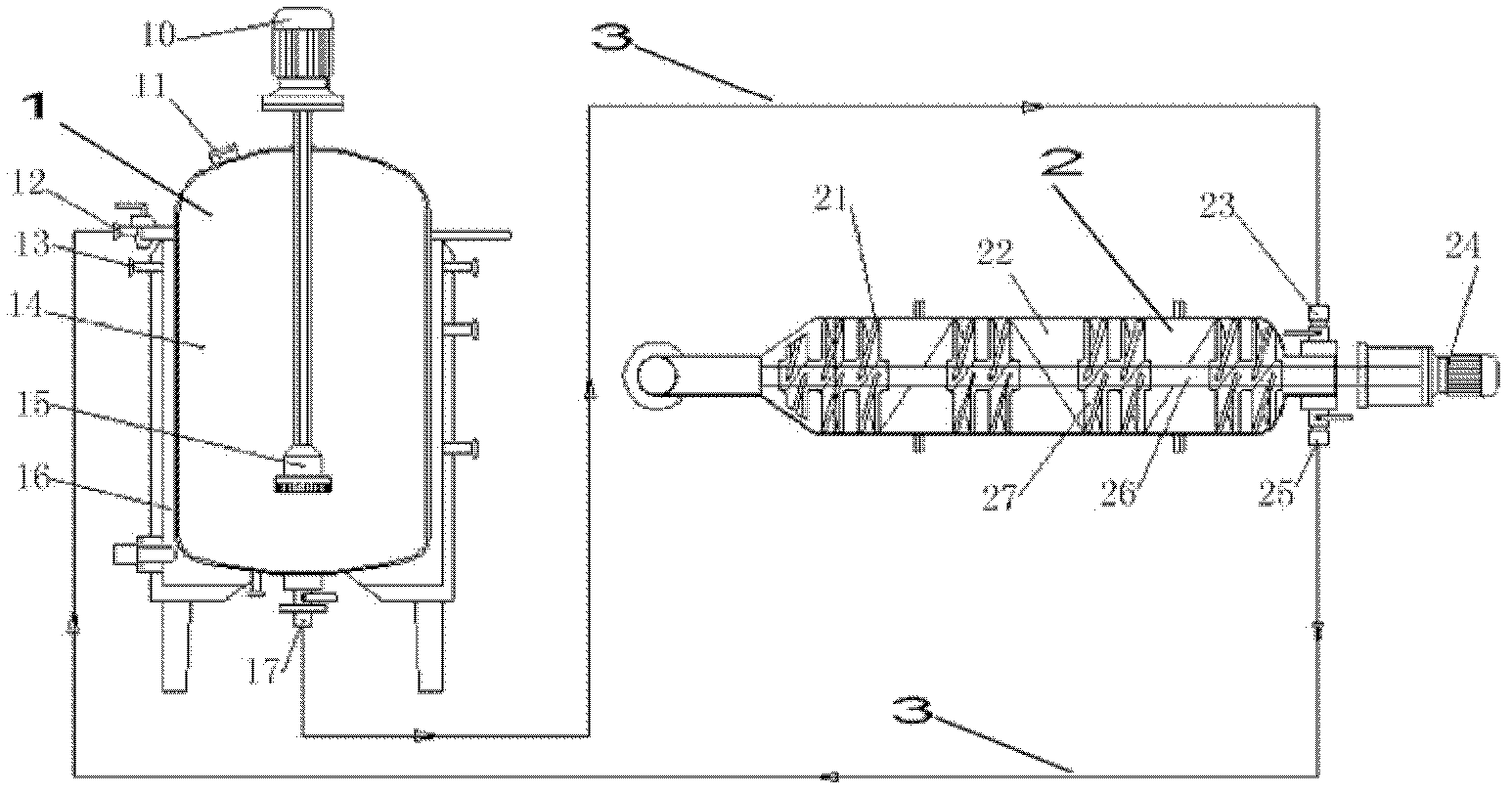
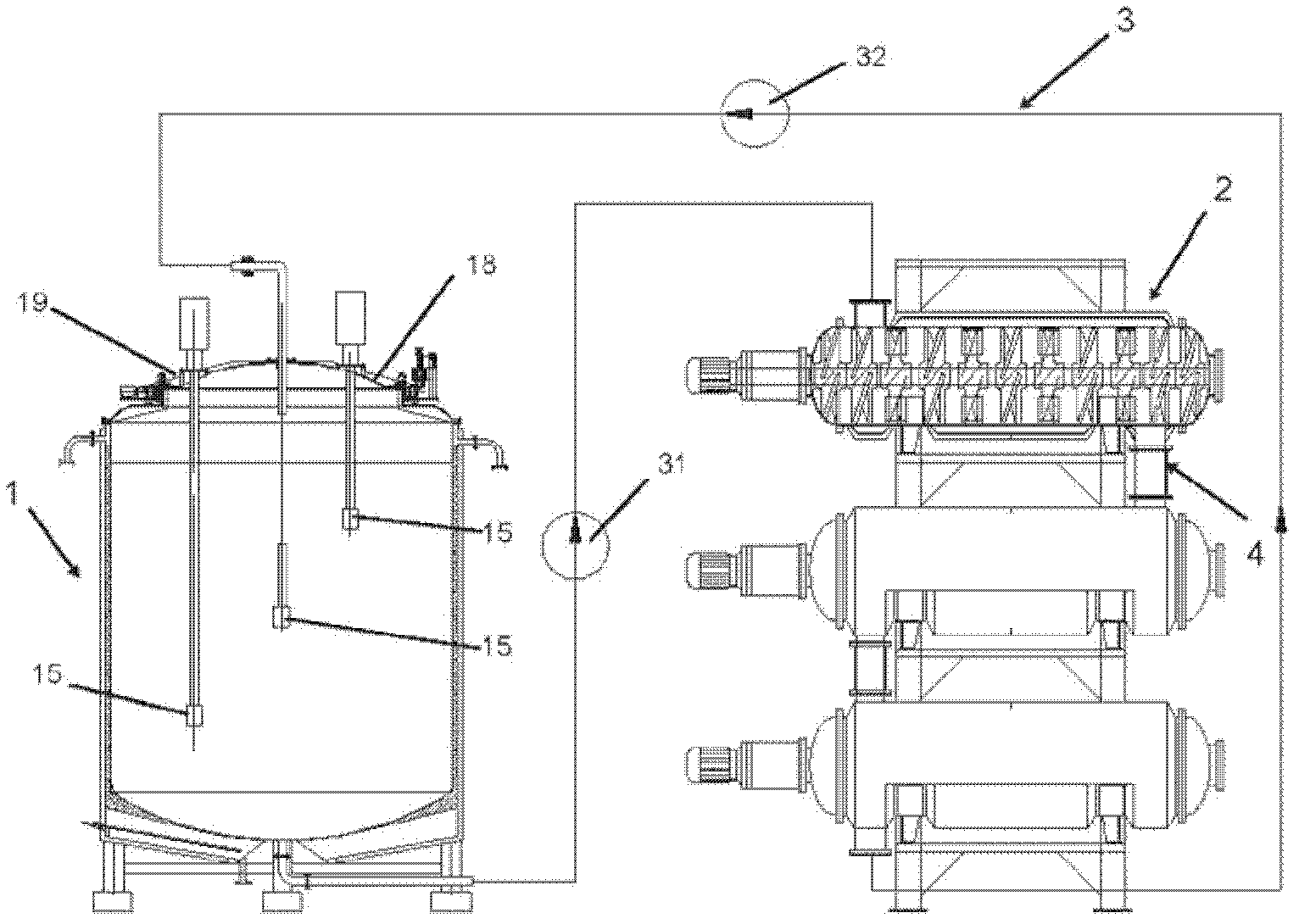
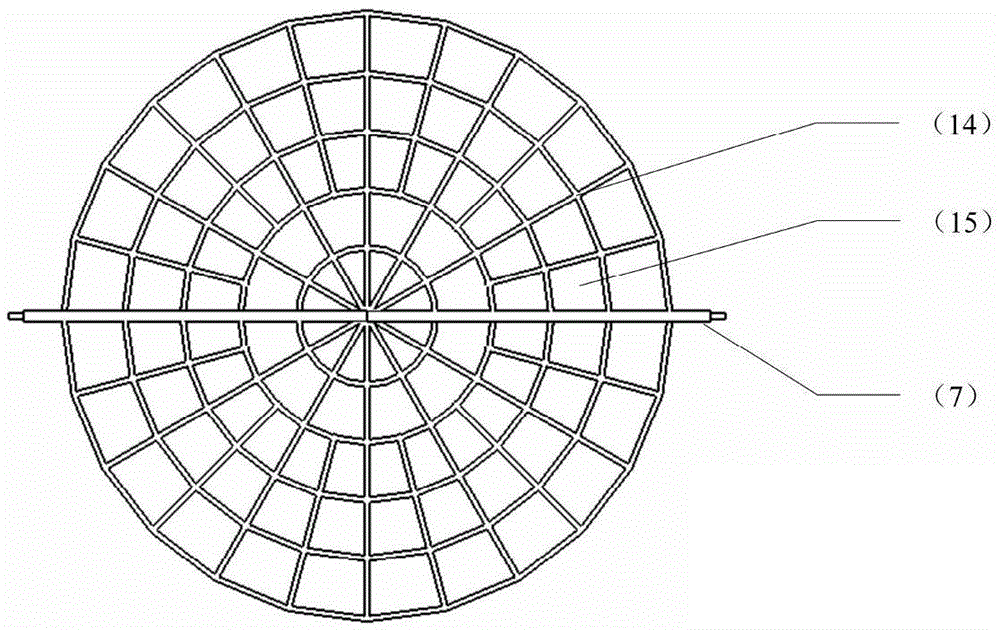
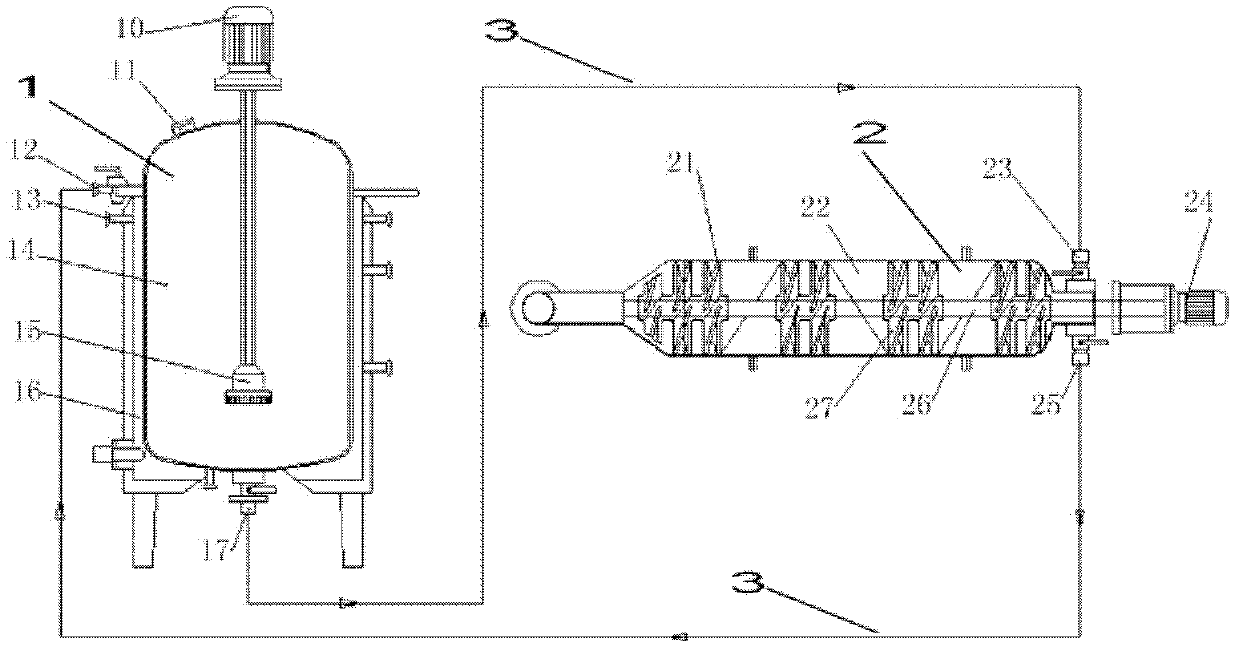
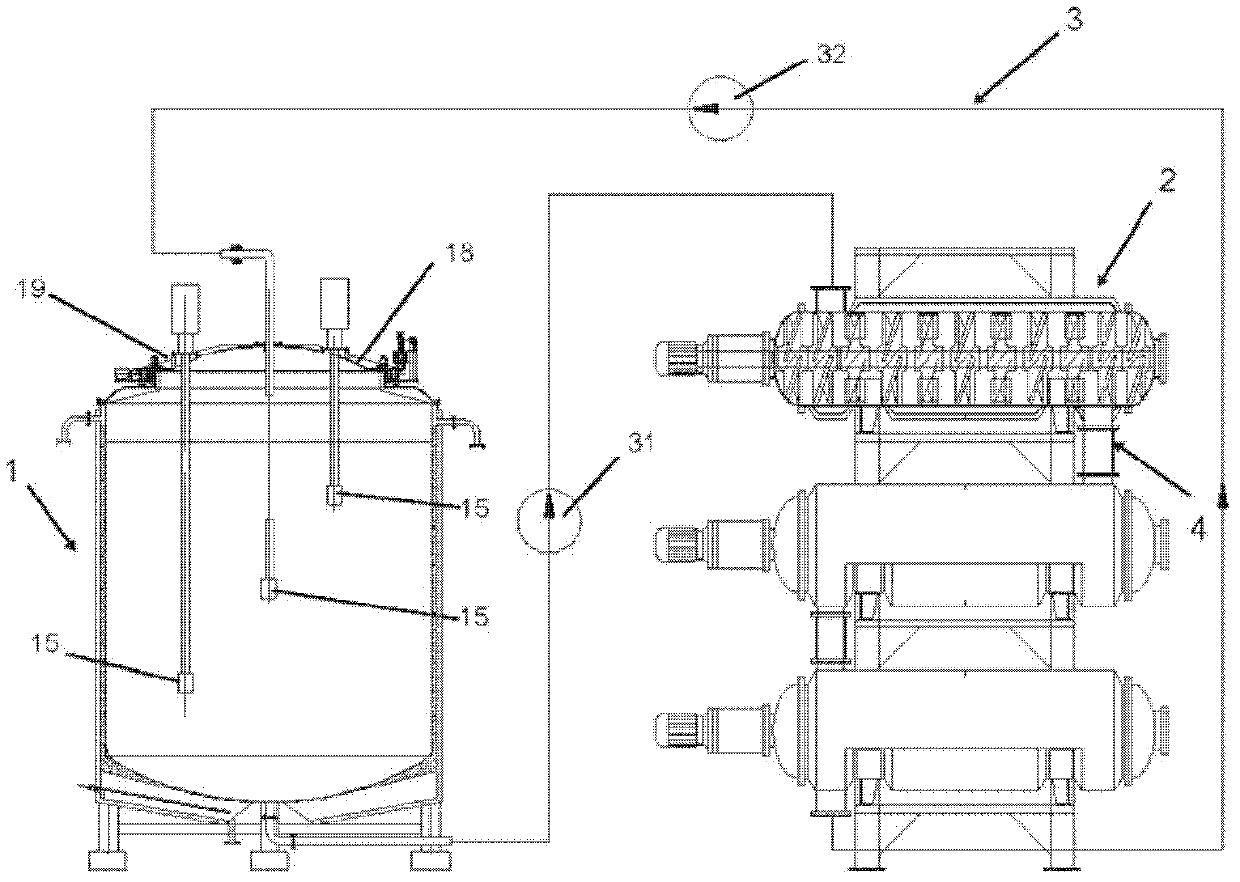
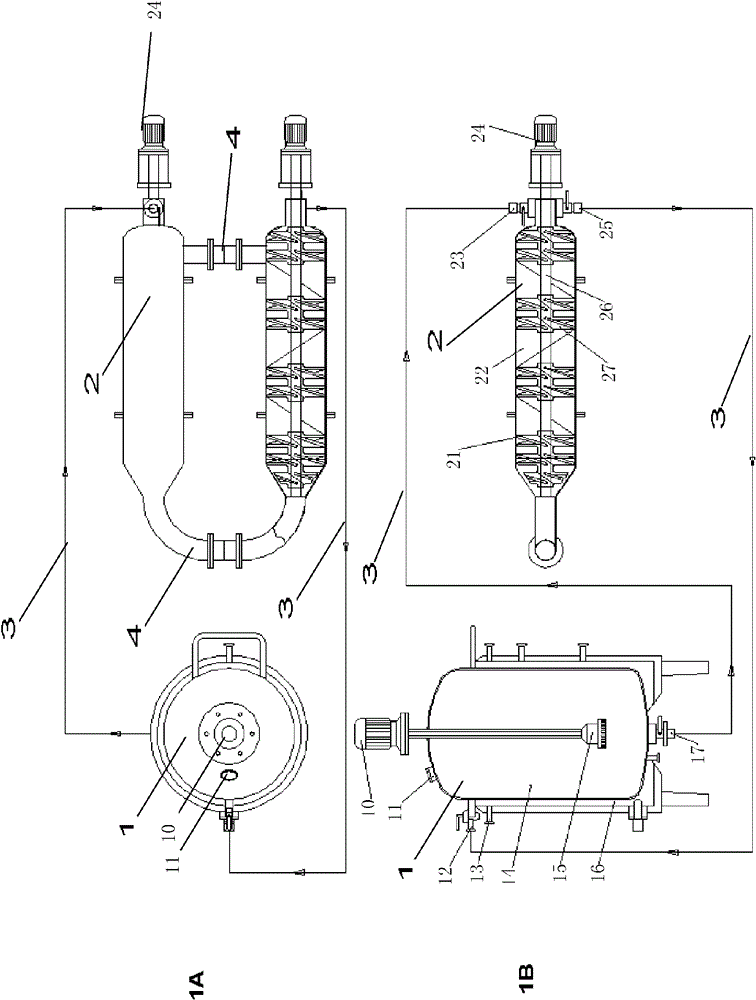
Double-body circulatory cellulose enzymatic hydrolysis reactor and application thereof
ActiveCN102604828AImprove enzymatic hydrolysis and saccharification efficiencyImprove sugar conversion rateBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCelluloseEnzymatic hydrolysis
The invention provides a double-body circulatory cellulose enzymatic hydrolysis reactor and an application of the double-body circulatory cellulose enzymatic hydrolysis reactor. The double-body circulatory cellulose enzymatic hydrolysis reactor specifically comprises a first reaction tank, a second reaction tank, a first pipe and a second pipe. The first reaction tank comprises a first reaction tank body, a shearing homogenizer, an inlet and an outlet, wherein the shearing homogenizer is arranged in the first reaction tank body, the inlet is used for feeding, and the outlet is used for discharging; the second reaction tank comprises more than two reaction pipes which are connected in series or parallel; the first pipe is used for connecting the first reaction tank with the second reaction tank; and the second pipe is used for connecting the reaction pipes in the second reaction tank. When being used for the enzymolysis and the saccharification of the cellulose such as the hemp bastuse, the double-body circulatory cellulos enzymatic hydrolysis reactor has the advantages of high conversion rate, high concentration, short conversion time and low enzyme preparation consumption, etc.
Owner:SHANGHAI ZHONGWEI BIOCHEM
Method for enhancing enzymolysis and saccharification efficiency of Chinese silvergrass by using alkaline oxydol
InactiveCN104017842APromote swellingImprove enzymatic hydrolysis and saccharification efficiencyBiofuelsFermentationWater bathsFiltration
The invention relates to a method for enhancing enzymolysis and saccharification efficiency of Chinese silvergrass by using alkaline oxydol, which comprises the following steps: irradiating Chinese silvergrass powder with 400KGy60Co-gamma rays; putting the irradiated Chinese silvergrass powder into a sodium hydroxide-oxydol solution with certain concentration, and treating in a water bath at certain temperature for some time; washing the mixed solution subjected to the water bath with dilute sulfuric acid to a neutral state, and filtering to obtain a filtration residue; putting the filtration residue in a drying oven, and drying for some time to obtain the Chinese silvergrass residue; putting the Chinese silvergrass residue into a cellulase-containing buffer solution, and oscillating in a constant-temperature oscillator for some time; treating the oscillated solution in a boiling water bath for some time, cooling, and filtering to obtain a filtrate; and determining the content of reducing sugar in the filtrate. The reducing sugar generated by treating the Chinese silvergrass with cellulase needs to be pretreated before fermentation to produce vehicle fuel ethanol, and a low-dose irradiation / dilute alkali composite technique is utilized for treatment can greatly enhance the enzymolysis and saccharification efficiency of Chinese silvergrass.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Method for improving pretreatment effect of acid catalysis ionic liquid with organic solvent-aqueous solution
ActiveCN107142291AChange rateChange structural propertiesFermentationBulk chemical productionFiberOrganic solvent
The invention discloses a method for improving the pretreatment effect of acid catalysis ionic liquid with an organic solvent-aqueous solution. The method comprises the following steps: (1) smashing a fiber raw material; (2) adding the raw material into an ionic liquid-acid system for pretreatment and catalysis; (3) regenerating with an organic solvent-aqueous solution in an amount which is 2 to 5 times the volume of the raw material; (4) continually stirring; (5) centrifuging to obtain a coarse regenerated fiber raw material; (6) washing the coarse regenerated fiber raw material with a corresponding organic solvent-aqueous solution by 4 to 6 times, and drying to obtain a regenerated fiber raw material. By adopting the method disclosed by the invention, the structural characteristic of the fiber raw material is changed. The dense cell wall structure of fibers is broken, the prepared regenerated fiber raw material is porous on the surface, is less in sediment, and is lower in lignin content, and the problem of adhesion of a large amount of lignin sediment to the surface of a conventional regenerated fiber raw material and the problem of inhibition of enzymatic saccharification are solved.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
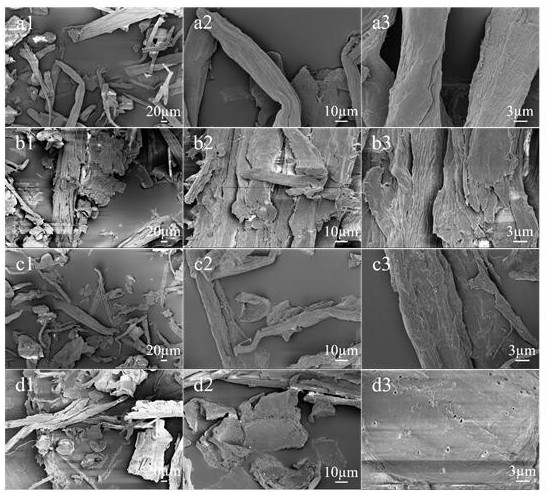
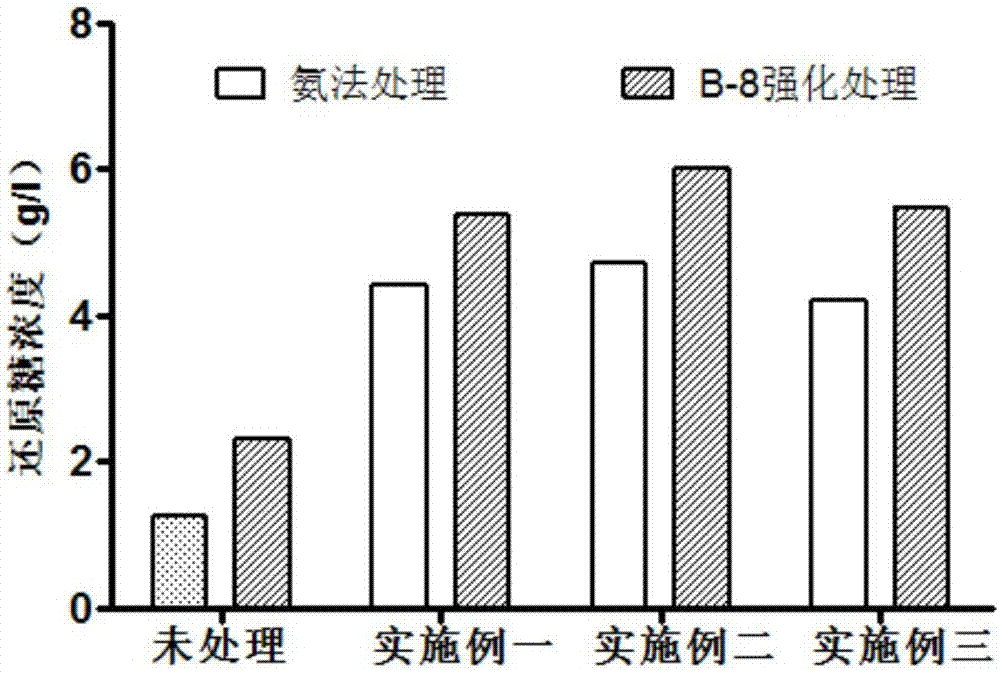
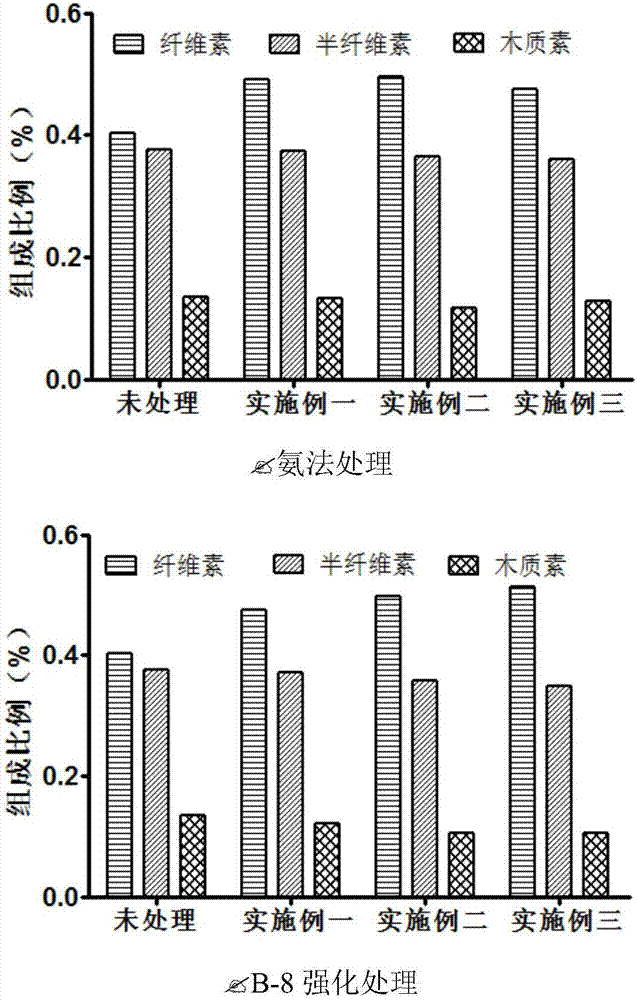
Method for strengthening ammonia pretreatment of waste biomass by means of lignin-degrading bacteria
ActiveCN107058427AIncreased accessible surfaceImprove enzymatic hydrolysis and saccharification efficiencyMicroorganism based processesFermentationCelluloseCupriavidus basilensis
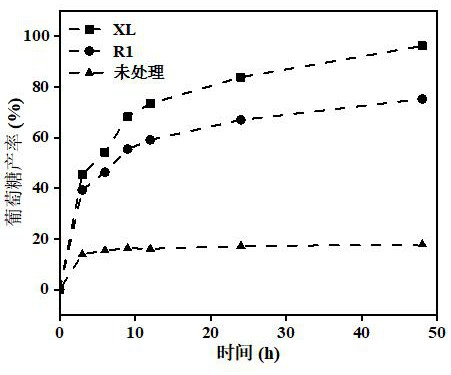
The invention discloses a method for strengthening the ammonia pretreatment of waste biomass by means of lignin-degrading bacteria. Particularly, on the basis of the ammonia pretreatment of the waste biomass, the lignin-degrading bacteria, namely Cupriavidus basilensis B-8, with the preservation number of CGMCC No.4240 are used, residual lignin in the waste biomass is further removed by improving culturing conditions, and the cellulose accessible surface is improved in the enzymolysis and saccharification processes. By using the method, the enzymolysis efficiency of the pretreatment of a single ammonia method is improved by about 30%, and the method has the advantages of being short in treatment time, simple in operation, small in secondary pollution, low in cost and the like.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
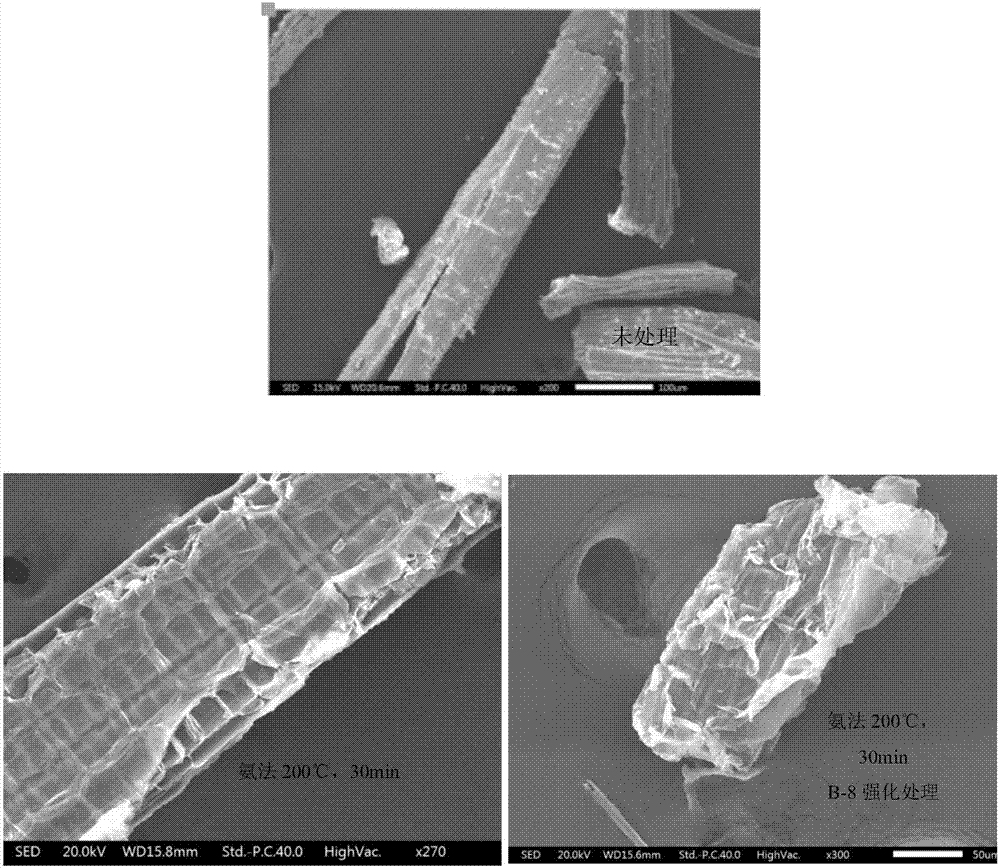
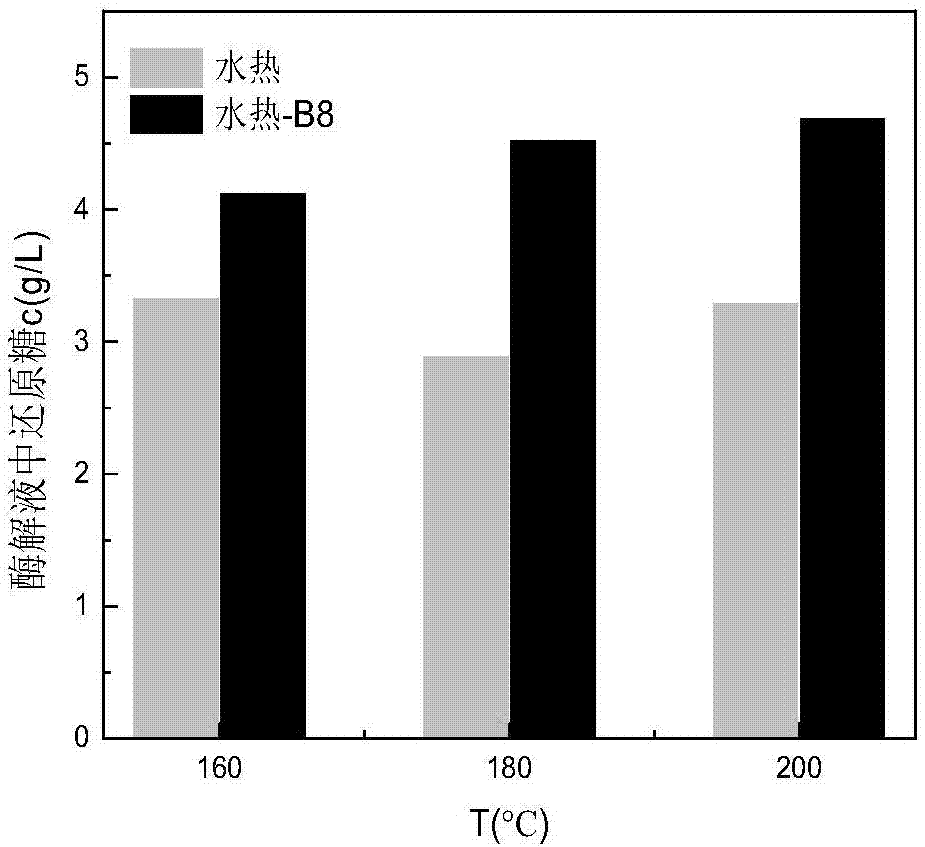
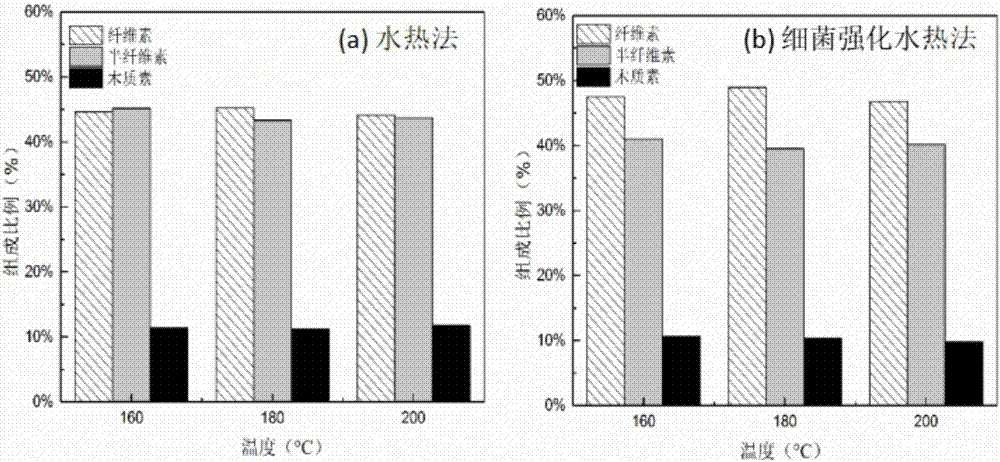
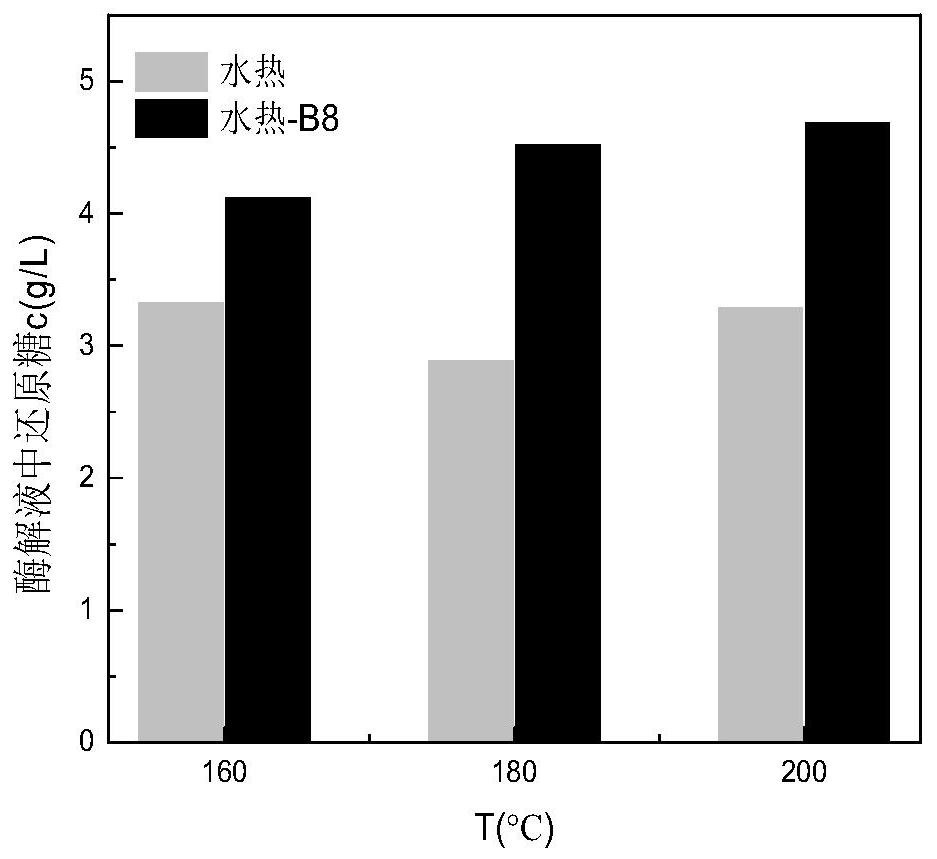
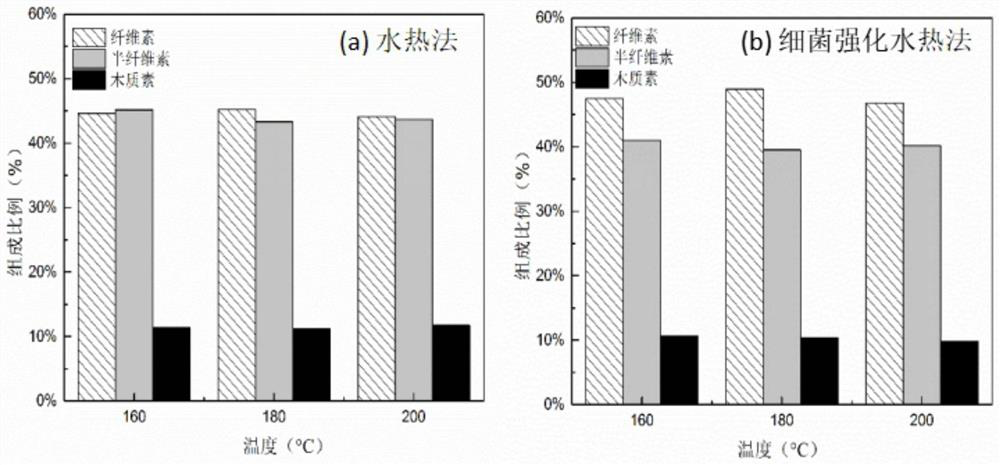
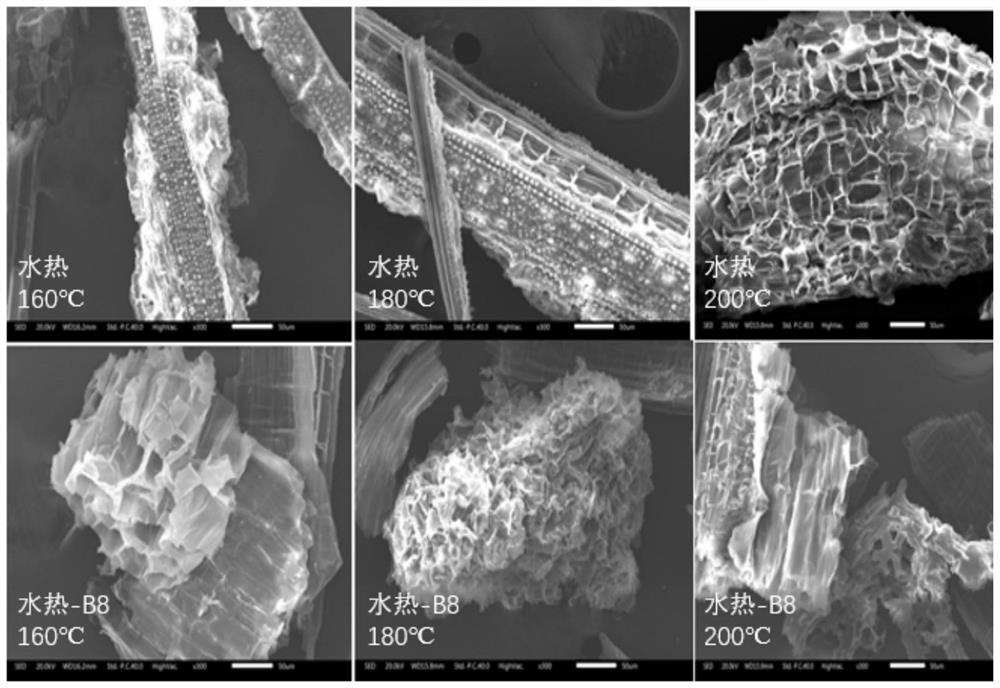
Method for enhancing waste biomass hydro-thermal pretreatment by using lignin degrading bacteria
ActiveCN107513545AImprove stabilityLoose structureMicroorganism based processesFermentationEnzymatic hydrolysisCupriavidus basilensis
The invention discloses a method for enhancing waste biomass hydro-thermal pretreatment by using lignin degrading bacteria, and concreatly relates to a method that based on pretreatment of waste biomass by a hydrothermal method, the lignin degrading bacteria (Cupriavidus basilensis B-8, a preservation number is CGMCC No.4240) is used, the culture condition is improved, and the residual lignin in the waste biomass is removed, and the accessible surfaces while enzymatic hydrolysis and saccharification can be greatly increased. The enzymatic hydrolysis efficiency for hydrothermal method pretreatment is increased by about 56%, and the method has the advantages of short processing time, simple operation, no secondary pollution, and low cost.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
High-capacity double-systematic-circulation cellulose enzymolysis reactor and its application
ActiveCN102876571AImprove enzymatic hydrolysis and saccharification efficiencyImprove sugar conversion rateBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCelluloseHigh concentration
The invention provides a high-capacity double-systematic-circulation cellulose enzymolysis reactor and its application. The high-capacity double-systematic-circulation cellulose enzymolysis reactor concretely comprises: a first reaction tank (a) comprising a tank body, shearing homogenizers positioned in the tank body, an inlet used for adding a feed material, and an outlet used for discharging the material; a second reaction tank (b) comprising above two series or parallel reaction tubes; a pipeline (c) connecting the first reaction tank with the second reaction tank; and a pipeline (d) connecting all tubes in the second reaction tank, wherein the number of the shearing homogenizers is two or more; and the volume of the first reaction tank is 3-150t, and preferably 30-100t. The enzymolysis reactor has the advantages of high conversion rate, high concentration, short conversion time, low enzyme preparation consumption, low energy consumption and the like when the enzymolysis saccharification of celluloses comprising fibrilia and the like is carried out by the enzymolysis reactor, so the enzymolysis reactor is especially suitable for high-capacity cellulose enzymolysis reaction systems.
Owner:SHANGHAI ZHONGWEI BIOCHEM
Method for preparing modified soybean straw pig fodder and pig fodder prepared by means of method
The invention discloses a method for preparing modified soybean straw pig fodder and the pig fodder prepared by means of the method. The method comprises the following steps that 1, soybean straw, soybean hulls, soybean meal, soybean oil and soybean bran are placed in an ultrafine crusher to be crushed into fine powder with the particle size of 500-600 mesh; 2, a modifier is added to the fine powder in the step 1, wherein the modifier is prepared from, by weight, yeast, ceriporiopsis subvermispora, phanerochaete chrysosporium, variegated coriolus versicolor, pleurotus ostreatus, hirschioporuslacteus and coriolopsis gallica; a mixture is formed after the addition of the modifier and poured into a fermentation tank, water is added for stirring, and the moisture content of the mixture is controlled within 15%-30%; 3, after the water is added for stirring and the temperature rises to 30-40 DEG C, and fermentation is conducted for 12-20 hours; 4, the fermented material in the step 3 is taken out and placed in a granulation dryer for drying granulation, and the finished pig fodder is obtained after the granulation is completed.
Owner:张掖市金农源生物科技有限公司
Dry-method ozone pretreatment pretreater capable of increasing straw enzymolysis saccharification ratio and method
ActiveCN105624022APrevent loss of straw polysaccharide componentsImproving the efficiency of straw enzymatic hydrolysis and saccharificationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSieveConical surface
The invention relates to a dry-method ozone pretreatment pretreater capable of increasing the straw enzymolysis saccharification ratio. The dry-method ozone pretreatment pretreater comprises a vertically arranged pretreater body, a feed hopper located on the top of the pretreater body and a discharge port formed in the bottom of the pretreater body; the feed hopper is located in the center of the pretrater top, and a diffuser is arranged under the portion beside the feed hopper in the direction perpendicular to the pretreater body; the diffuser is shaped like a circular conical surface, the vertex of the circular conical surface vertically upwards points to the center of the feed hopper, and rod-like protrusions which are perpendicular to the circular conical surface bus direction are distributed on the circular conical surface in a staggered mode; a plurality of sieve plates perpendicular to the direction of the pretreater body are arranged in the middle of the pretreater body; the sieve plates are each shaped like a mesh, and the rod-like protrusions with different heights are evenly distributed on the sieve plates and are perpendicular to the surfaces of the sieve plates. The dry-method ozone pretreatment pretreater facilitates pretreatment of semi-continuous, automatic and intelligent operation; lignin of straw subjected to ozone treatment is removed, the biodegradation rate is obviously increased, sundry bacteria and pests are killed, the storage property and fermenting property of the product are improved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
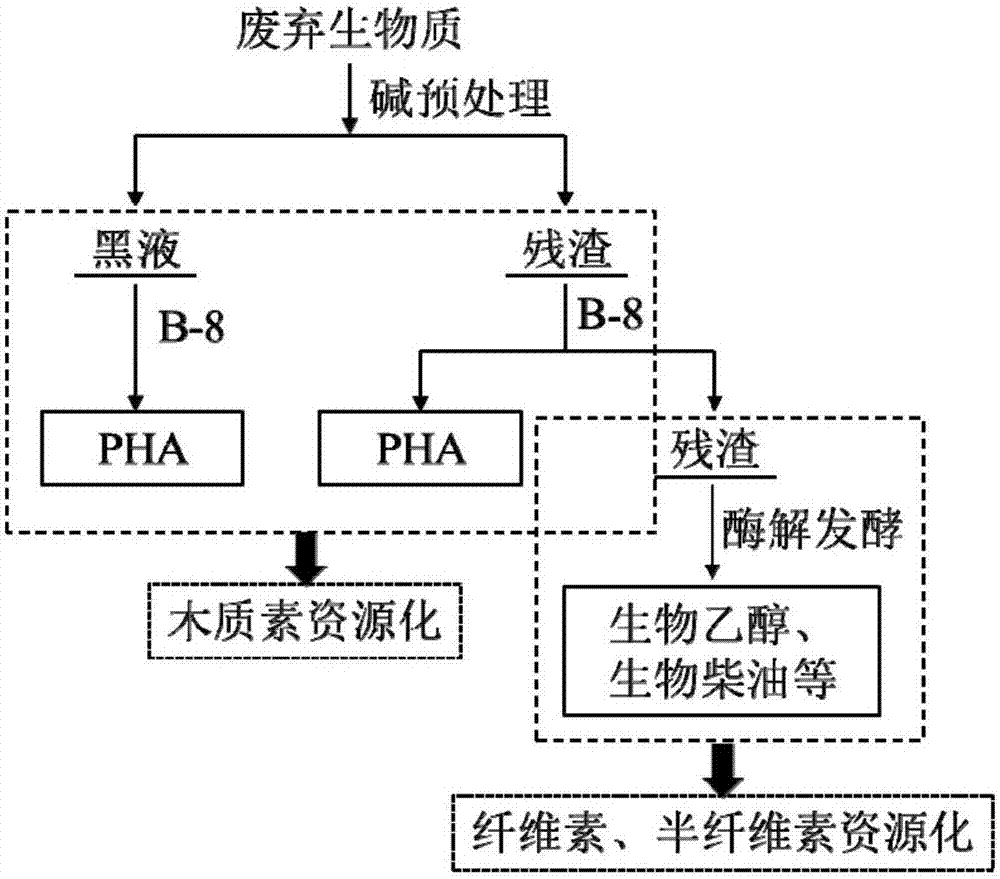
Waste biomass recycling method
ActiveCN107287251AIncreased accessible surfaceLoose structureMicroorganismsSolid waste disposalBlack liquorCupriavidus basilensis
The invention discloses a waste biomass recycling method which comprises the following specific steps: (1) performing pre-treatment by means of a waste biomass alkali method to obtain black liquor and alkali pre-treated residues; (2) after actiononthe black liquor by Cupriavidus basilensis B-8, the preservation number of which is GCMCC No.4240, separating and purifying a polyhydroxyalkanoate biological plastic in the thalli thereof; (3) treating the alkali pre-treated residues by the Cupriavidus basilensis B-8 so as to deeply remove residual lignin and converting the same into the biological plastic; and (4) performing enzymolysis on alkali-biological treatment residues to obtain high purity sugar as a follow-up biological fermenting raw material. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the sugar yielding amount by enzymolysis of waste biomass is improved by about 10 times, and lignin in residues and black liquor can be converted into the biological plastic at the same time, so that the environmental pollution problem caused by the pre-treated black liquor is solved, and the economical benefit of the process is also remarkably improved, and the method has the advantages of short treatment time, simplicity in operation, small secondary pollution, low cost and the like.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
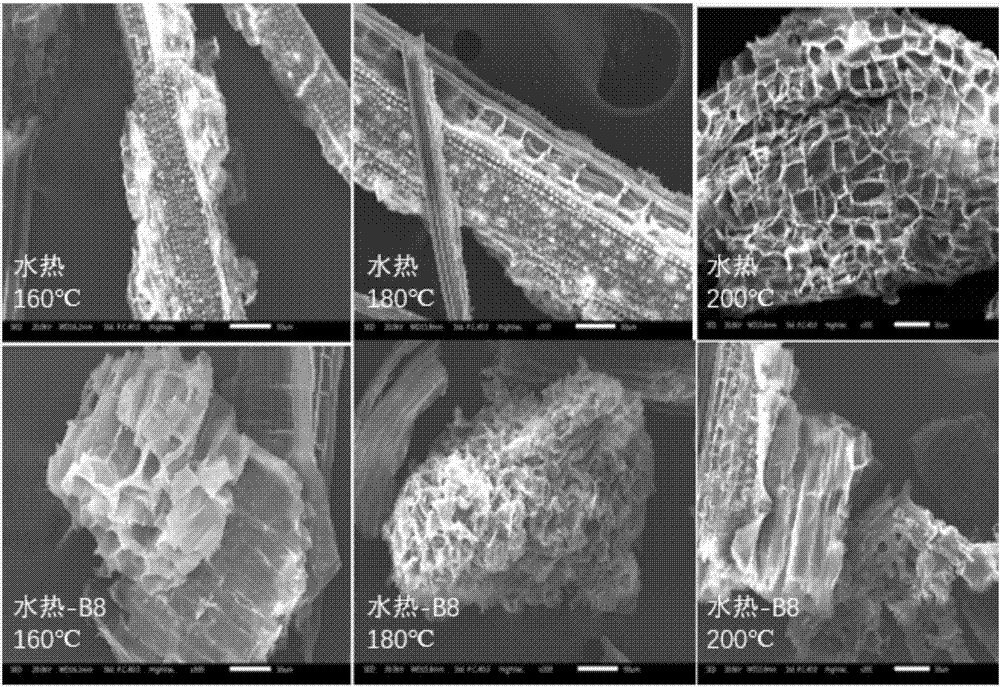
Method for reinforcing waste biomass sodium carbonate pretreatment by utilizing lignin-degrading bacteria
ActiveCN107034255AIncreased accessible surfaceAchieve deep removalMicroorganism based processesFermentationCupriavidus basilensisHemicellulose
The invention discloses a method for reinforcing the waste biomass sodium carbonate pretreatment by utilizing lignin-degrading bacteria. According to the method, based on waste biomass sodium carbonate pretreatment, residual lignin and hemicellulose in waste biomass are further removed by utilizing the lignin-degrading bacterium Cupriavidus basilensis B-8 having a preservation number of CGMCC No.4240 and improving the culture condition, steady straight rod state of waste biomass is loosened, and the surface of the waste biomass shows a porous flake shape, so that the accessible surface during enzymolysis saccharification is greatly improved. The method can be used for improving the enzymolysis rate of sodium carbonate sodium pretreatment by nearly 40 percent with remarkable effect, and has the advantages of being short in treatment time, simple in operation, small in secondary pollution, low in cost and the like.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for ultra-fast pretreatment of lignocellulose in biomass
PendingCN113046400AImprove enzymatic hydrolysis efficiencyImprove enzymatic hydrolysis and saccharification efficiencyFermentationOXALIC ACID DIHYDRATEEnvironmental chemistry
The invention provides a method for ultra-fast pretreatment of lignocellulose in biomass. The method comprises the following steps: S1, adding waste biomass into a ternary low-eutectic solvent, and sequentially carrying out microwave treatment and solid-liquid separation treatment to obtain to-be-treated filter residues, wherein the ternary low-eutectic solvent comprises a solvent prepared from choline chloride, oxalic acid and lactic acid in a molar ratio of 1:0.5:(0.5-1.5); the solid-to-liquid ratio of the waste biomass to the ternary low-eutectic solvent is 1g:(25-45)mL; and S2, cleaning the to-be-treated filter residues until the pH value is neutral, and then carrying out freeze-drying treatment to obtain the waste biomass subjected to lignocellulose pretreatment. By means of the pretreatment method, the enzymolysis efficiency can be improved; the pretreatment speed can be increased; and the treatment cost is reduced.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
A method of using lignin-degrading bacteria to strengthen sodium carbonate pretreatment of waste biomass
ActiveCN107034255BIncreased accessible surfaceLoose structureMicroorganism based processesFermentationCupriavidus basilensisEnvironmental engineering
The invention discloses a method for reinforcing the waste biomass sodium carbonate pretreatment by utilizing lignin-degrading bacteria. According to the method, based on waste biomass sodium carbonate pretreatment, residual lignin and hemicellulose in waste biomass are further removed by utilizing the lignin-degrading bacterium Cupriavidus basilensis B-8 having a preservation number of CGMCC No.4240 and improving the culture condition, steady straight rod state of waste biomass is loosened, and the surface of the waste biomass shows a porous flake shape, so that the accessible surface during enzymolysis saccharification is greatly improved. The method can be used for improving the enzymolysis rate of sodium carbonate sodium pretreatment by nearly 40 percent with remarkable effect, and has the advantages of being short in treatment time, simple in operation, small in secondary pollution, low in cost and the like.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
A method of using lignin-degrading bacteria to strengthen the hydrothermal pretreatment of waste biomass
ActiveCN107513545BImprove stabilityLoose structureMicroorganism based processesFermentationEnzymatic hydrolysisCupriavidus basilensis
The invention discloses a method for enhancing waste biomass hydro-thermal pretreatment by using lignin degrading bacteria, and concreatly relates to a method that based on pretreatment of waste biomass by a hydrothermal method, the lignin degrading bacteria (Cupriavidus basilensis B-8, a preservation number is CGMCC No.4240) is used, the culture condition is improved, and the residual lignin in the waste biomass is removed, and the accessible surfaces while enzymatic hydrolysis and saccharification can be greatly increased. The enzymatic hydrolysis efficiency for hydrothermal method pretreatment is increased by about 56%, and the method has the advantages of short processing time, simple operation, no secondary pollution, and low cost.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
A kind of organic solvent-aqueous solution improves the method of acid-catalyzed ionic liquid pretreatment effect
ActiveCN107142291BChange structural propertiesResolve attachmentFermentationBulk chemical productionFiberOrganic solvent
The invention discloses a method for improving the pretreatment effect of acid catalysis ionic liquid with an organic solvent-aqueous solution. The method comprises the following steps: (1) smashing a fiber raw material; (2) adding the raw material into an ionic liquid-acid system for pretreatment and catalysis; (3) regenerating with an organic solvent-aqueous solution in an amount which is 2 to 5 times the volume of the raw material; (4) continually stirring; (5) centrifuging to obtain a coarse regenerated fiber raw material; (6) washing the coarse regenerated fiber raw material with a corresponding organic solvent-aqueous solution by 4 to 6 times, and drying to obtain a regenerated fiber raw material. By adopting the method disclosed by the invention, the structural characteristic of the fiber raw material is changed. The dense cell wall structure of fibers is broken, the prepared regenerated fiber raw material is porous on the surface, is less in sediment, and is lower in lignin content, and the problem of adhesion of a large amount of lignin sediment to the surface of a conventional regenerated fiber raw material and the problem of inhibition of enzymatic saccharification are solved.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
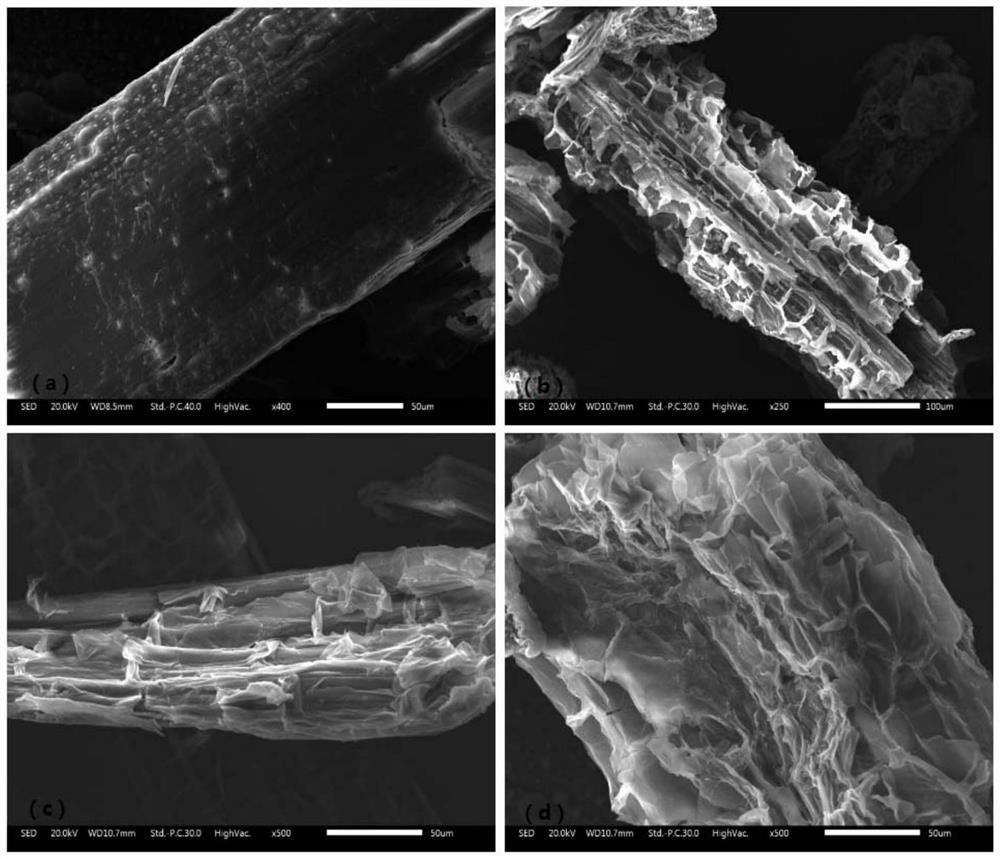
A method of using lignin-degrading bacteria to strengthen the fenton reaction pretreatment of waste biomass
ActiveCN107119094BLoose structureIncreased accessible surfaceMicroorganism based processesFermentationFenton reactionCupriavidus basilensis
The invention discloses a method for strengthening Fenton reaction pre-treatment of waste biomasses by utilizing a lignin-degrading bacterium. Specifically, on the basis of the Fenton reaction pre-treatment of the waste biomasses, residual lignin in the waste biomasses is further removed by utilizing the lignin-degrading bacterium (Cupriavidus basilensis B-8 with the preservation number of CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No. 4240) and improving culture conditions; a stable straight rod shape of the waste biomasses is changed into a loose laminar shape, so that an accessible surface in an enzymolysis and saccharification process is improved. By adopting the method disclosed by the invention, the enzymolysis efficiency of the Fenton reaction pre-treatment can be improved by about 60 percent and can be improved by about 120 percent at maximum; the method has the advantages of short treatment time, simple operation, small secondary pollution, low cost and the like.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
A bio-chemical combined treatment process to improve lignocellulose saccharification effect
ActiveCN105177055BIncreased accessible surfaceImprove enzymatic hydrolysis and saccharification efficiencyBiofuelsMicroorganism based processesChemical treatmentMicroorganism
Owner:湖南中森环境科技有限公司
Biomass pretreatment method and application
ActiveCN114438152AHigh removal rateHigh recovery rateBiofuelsFermentationPulp and paper industryCellulase
The invention provides a pretreatment method and application of biomass. The method comprises the following steps: 1) crushing and screening biomass raw materials; 2) performing benzene-alcohol extraction; (3) pretreating the biomass by using the mixed solution; and 4) carrying out vacuum filtration to realize solid-liquid two-phase separation. The application mainly comprises application of the biomass pretreatment method in lignin recovery and cellulose conversion. According to the biomass pretreatment method and application, efficient separation of biomass components can be achieved under the normal pressure and mild conditions, and meanwhile the purposes of being environmentally friendly and reducing cost and energy consumption are achieved. The biomass pretreatment method based on the green solvent, provided by the invention, has the remarkable advantages of environmental friendliness, mild conditions, high lignin removal rate and yield, stable solvent, high cellulose enzymolysis saccharification efficiency, easiness in defibration of cellulose and the like.
Owner:WESTLAKE UNIV
High-capacity double-systematic-circulation cellulose enzymolysis reactor and its application
ActiveCN102876571BImprove enzymatic hydrolysis and saccharification efficiencyImprove sugar conversion rateBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHigh concentrationCellulose
Owner:SHANGHAI ZHONGWEI BIOCHEM
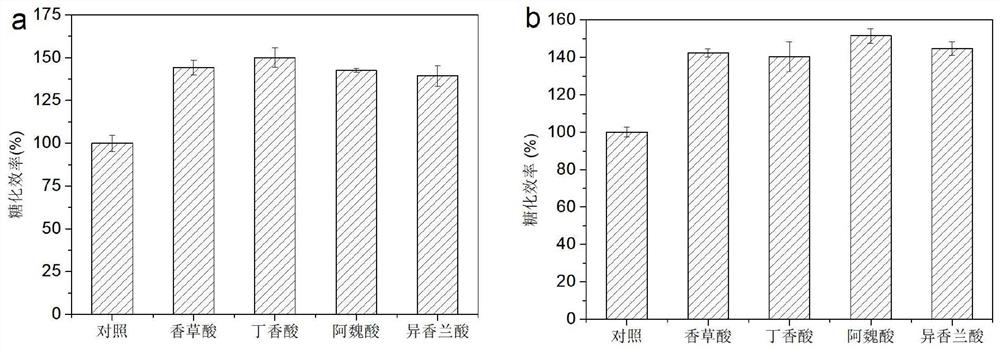
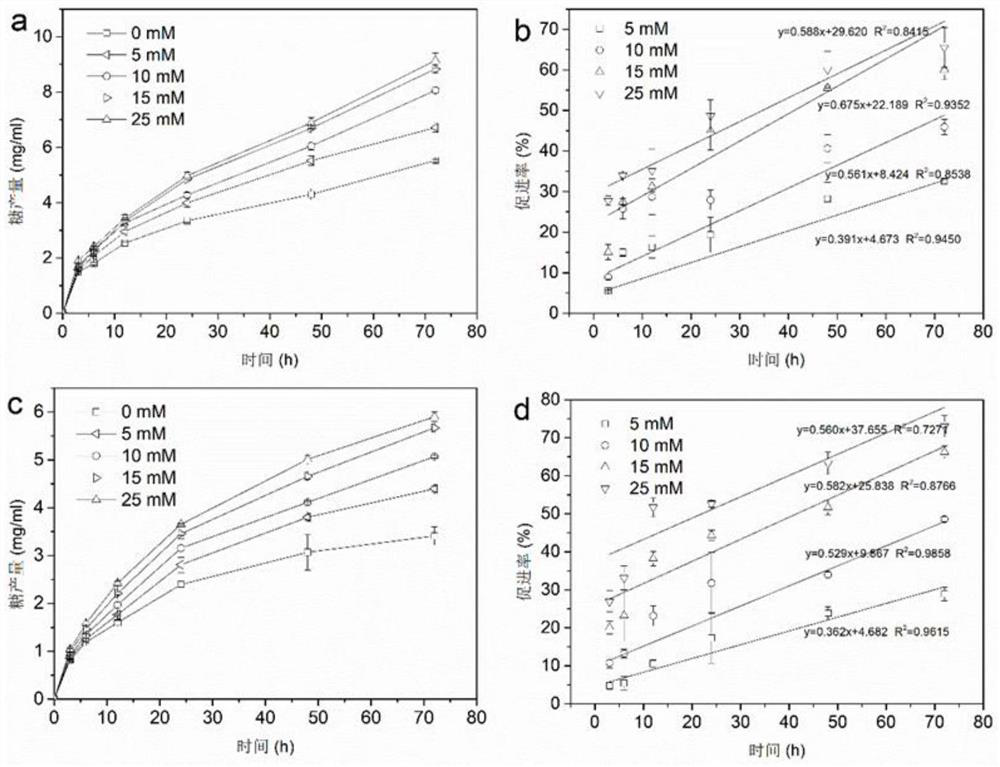
Method for improving specific activity of cellulase and application of method
ActiveCN114058605AImprove enzymatic hydrolysis and saccharification efficiencyHigher than vitalityBiofuelsEnzymesLignin degradationCellulase
The invention relates to a method for improving the specific activity of cellulase and application of the method. In particular, cellulase with improved specific activity is obtained after cellulase is incubated with phenolic acid, and the cellulase with improved specific activity can be used for improving the biomass enzymolysis saccharification efficiency. Efficient biorefinery of lignocellulosic biomass is limited due to the negative impact of expensive cellulase and lignin degradation products on cellulase hydrolysis. A lignin-derived phenolic acid compound, vanillic acid, syringic acid, ferulic acid, isovanillic acid and the like can effectively improve the specific activity of cellulase, the saccharification efficiency of different biomass is effectively improved under the condition that the enzyme dosage is not increased, and the enzyme use cost of biomass enzymolysis saccharification can be effectively reduced.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
A kind of production process of glutinous corn rice wine
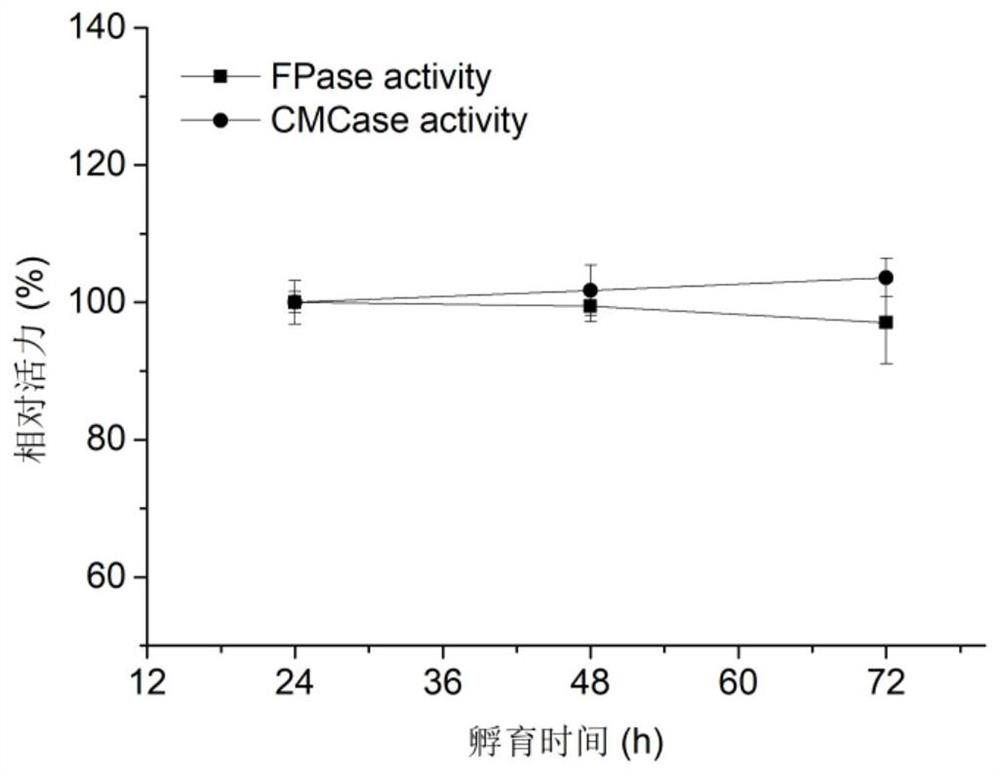
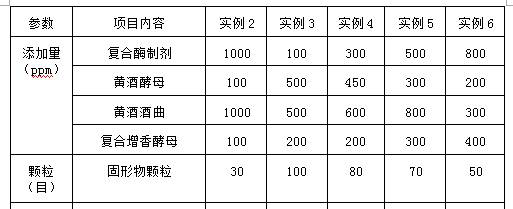
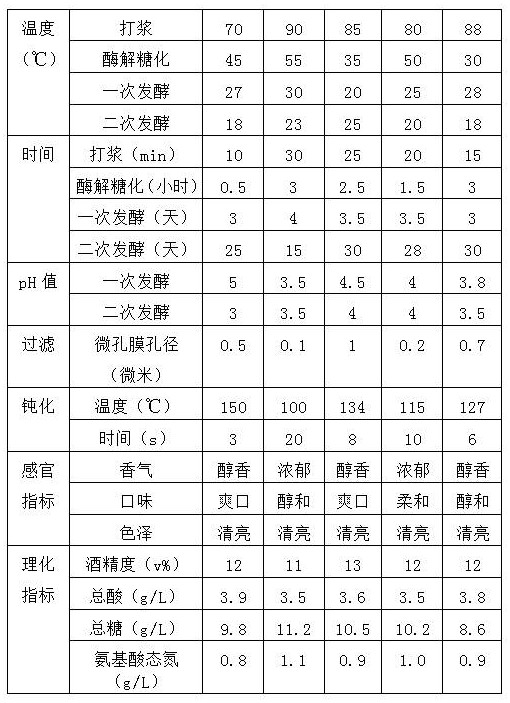
ActiveCN108660025BImprove enzymatic hydrolysis and saccharification efficiencyEnsure controllabilityMicroorganism based processesAlcoholic beverage preparationBiotechnologyWaxy corn
The invention relates to a production process of waxy corn rice wine, which specifically includes the following steps: 1), cleaning waxy corn seeds, beating, and sieving; 2), adding a compound enzyme preparation for enzymatic hydrolysis and saccharification; 3), adding activated corn Yellow rice wine yeast and yellow rice wine koji, add lactic acid to adjust the pH value and then carry out primary fermentation; 4) Add compound aroma-enhancing yeast for secondary fermentation; 5) Filter through diatomite, then filter through a ceramic microporous membrane filter, and finally pass through a tube Type sterilizer high temperature instant sterilization passivation, after sealing enters the aging stage. The invention solves the problem of high content of urethane while improving the production efficiency, ensures rich nutritional value and good taste of rice wine products, and is suitable for large-scale automatic production.
Owner:RES INST OF AGRO PROD PROCESSING SHANXI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Double-body circulatory cellulose enzymatic hydrolysis reactor and application thereof
ActiveCN102604828BImprove enzymatic hydrolysis and saccharification efficiencyImprove sugar conversion rateBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCelluloseFiber
Owner:SHANGHAI ZHONGWEI BIOCHEM
A dry ozone pretreatment pretreatment tower and method for improving the enzymatic hydrolysis and saccharification rate of straw
ActiveCN105624022BEasy to stackReduce thicknessBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEnzymatic hydrolysisPre treatment
The invention relates to a dry-method ozone pretreatment pretreater capable of increasing the straw enzymolysis saccharification ratio. The dry-method ozone pretreatment pretreater comprises a vertically arranged pretreater body, a feed hopper located on the top of the pretreater body and a discharge port formed in the bottom of the pretreater body; the feed hopper is located in the center of the pretrater top, and a diffuser is arranged under the portion beside the feed hopper in the direction perpendicular to the pretreater body; the diffuser is shaped like a circular conical surface, the vertex of the circular conical surface vertically upwards points to the center of the feed hopper, and rod-like protrusions which are perpendicular to the circular conical surface bus direction are distributed on the circular conical surface in a staggered mode; a plurality of sieve plates perpendicular to the direction of the pretreater body are arranged in the middle of the pretreater body; the sieve plates are each shaped like a mesh, and the rod-like protrusions with different heights are evenly distributed on the sieve plates and are perpendicular to the surfaces of the sieve plates. The dry-method ozone pretreatment pretreater facilitates pretreatment of semi-continuous, automatic and intelligent operation; lignin of straw subjected to ozone treatment is removed, the biodegradation rate is obviously increased, sundry bacteria and pests are killed, the storage property and fermenting property of the product are improved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
A method of using lignin-degrading bacteria to strengthen the ammonia pretreatment of waste biomass
ActiveCN107058427BIncreased accessible surfaceImprove enzymatic hydrolysis and saccharification efficiencyMicroorganism based processesFermentationCelluloseCupriavidus basilensis
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com