Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
120results about How to "Avoid excess performance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
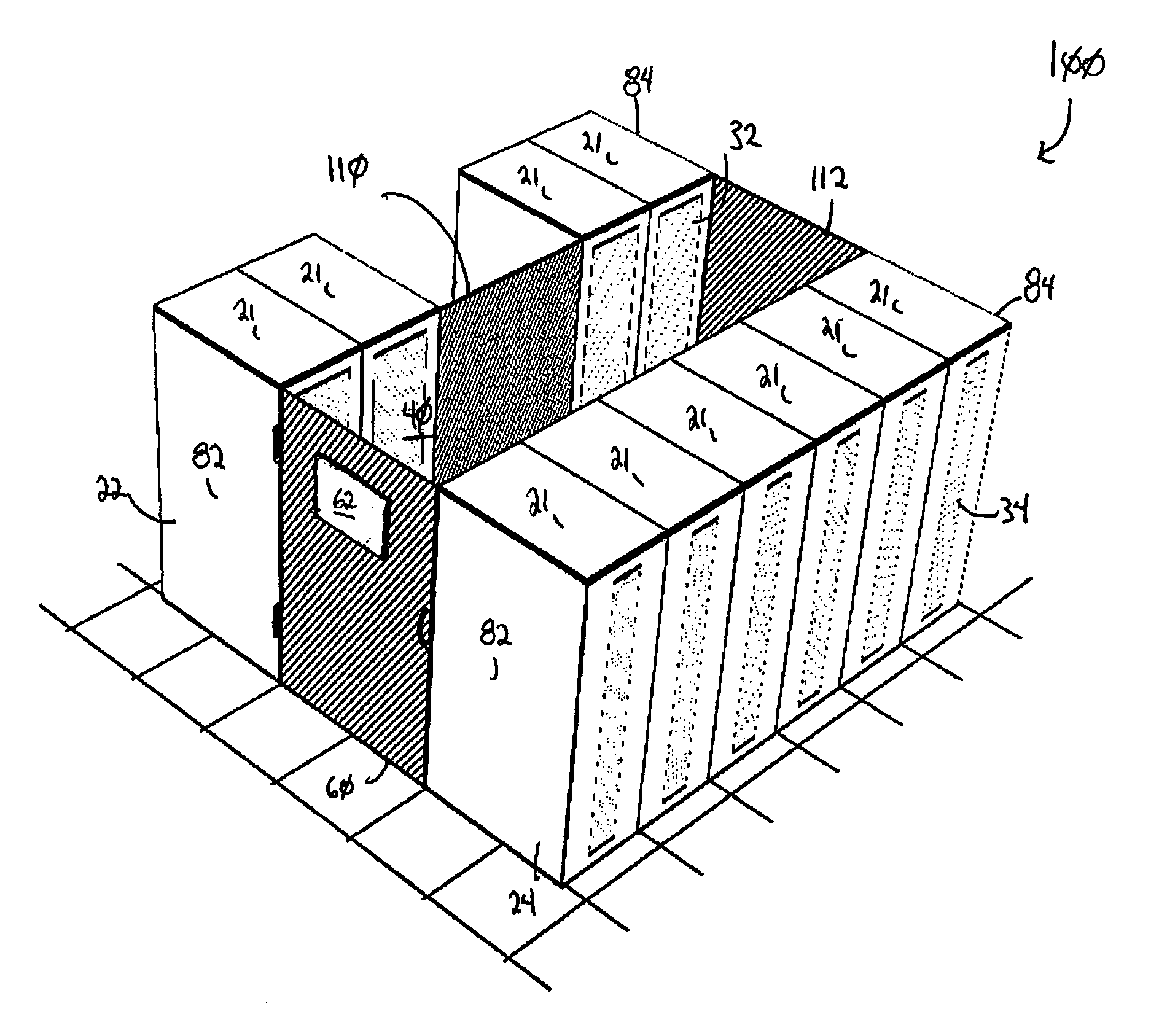
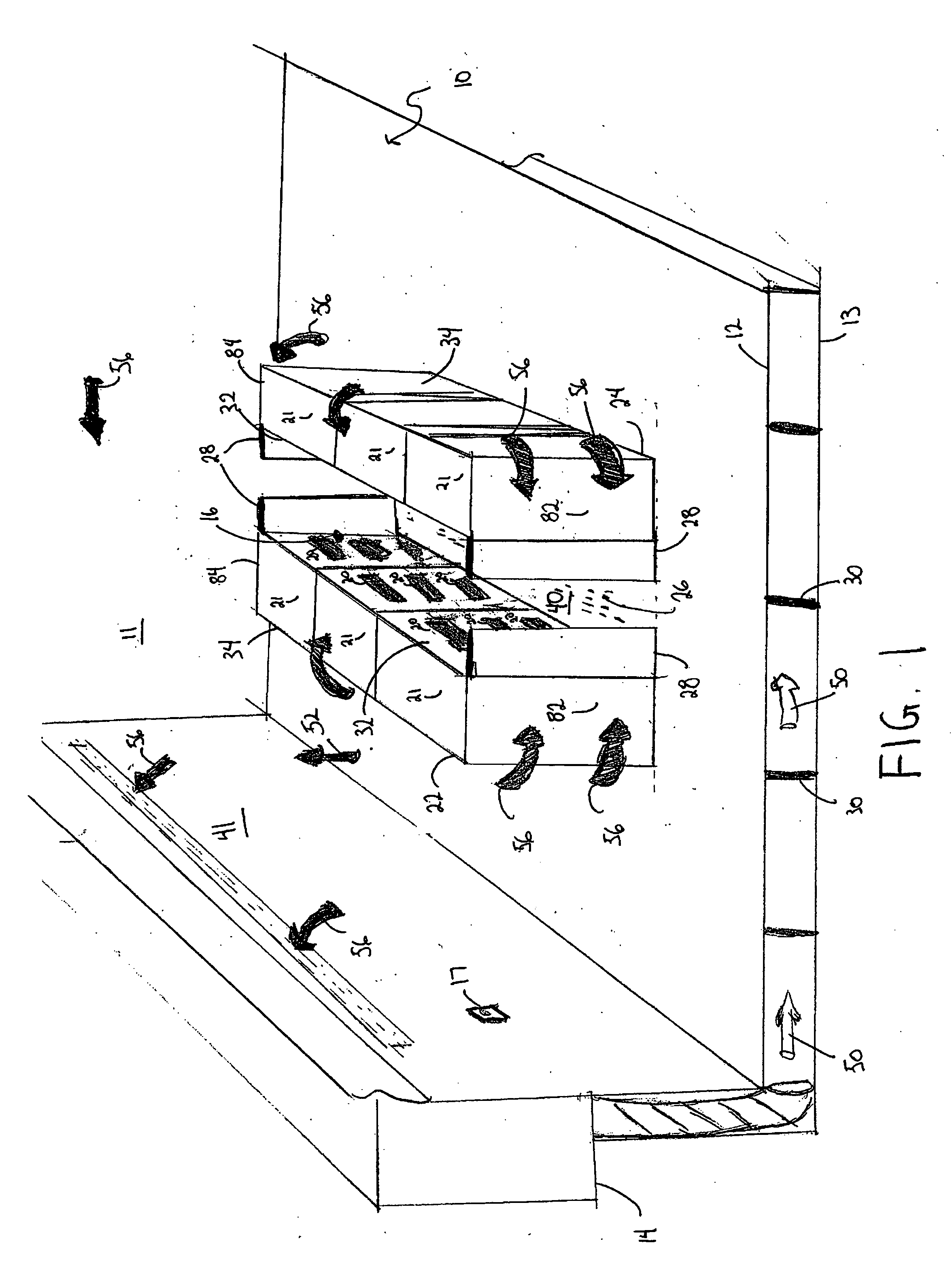
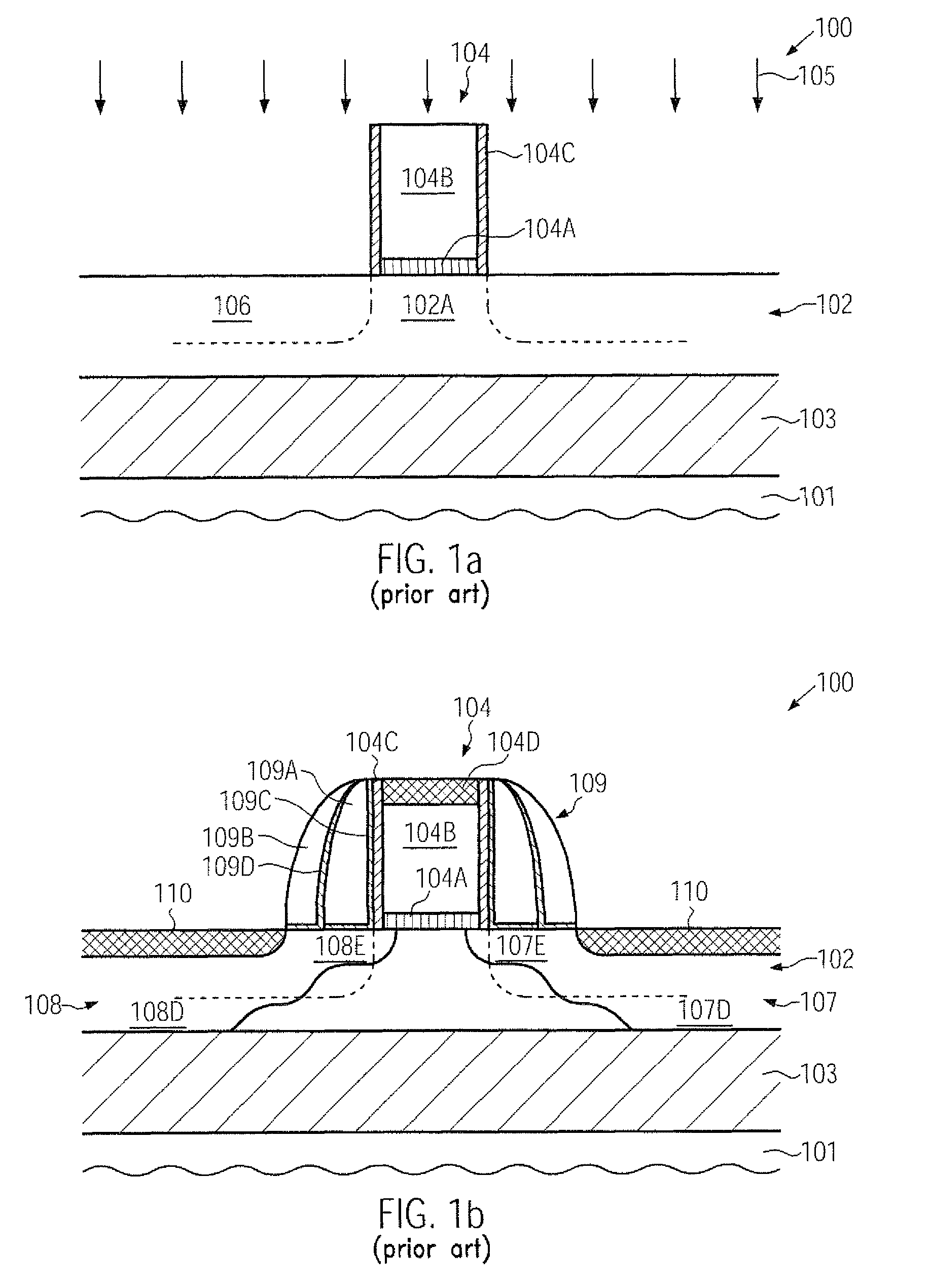
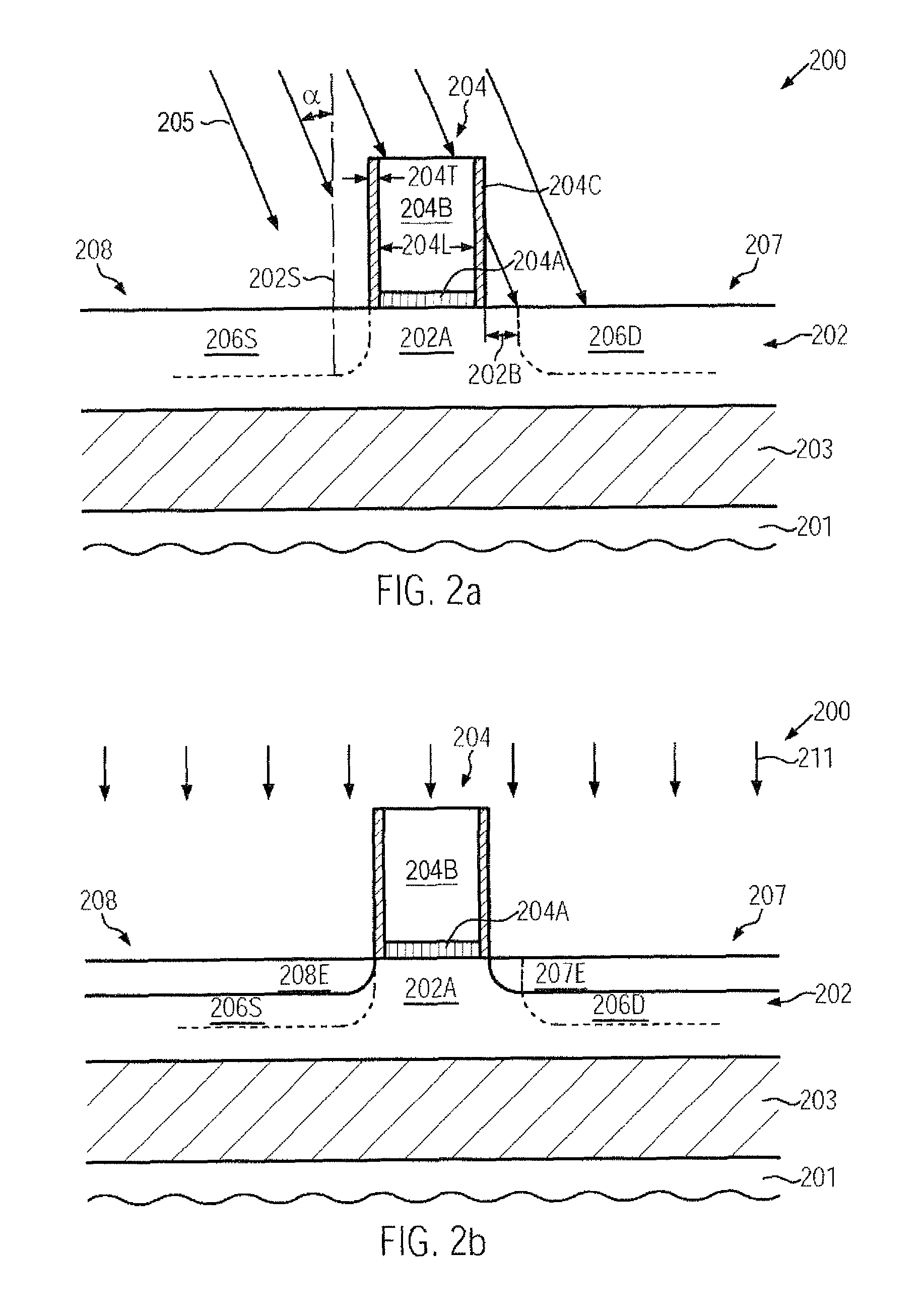
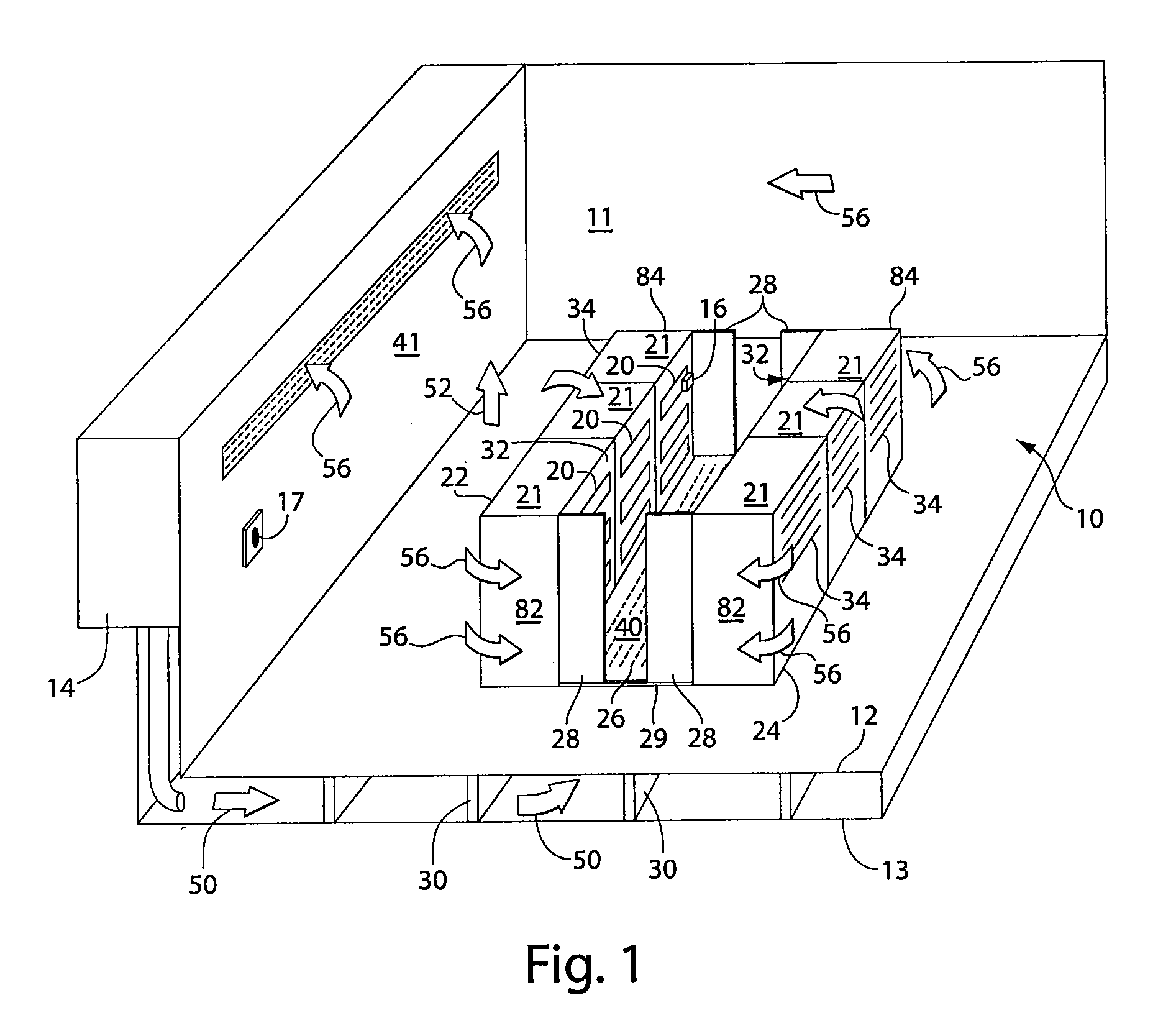
Cold aisle isolation
ActiveUS20060260338A1Easy to modifyLarge capacityLighting and heating apparatusDigital data processing detailsEngineeringAir cooling system
A data center cooling solution providing techniques for using baffles, doors and roof sections to prevent warm air from being entrained into a cold aisle in a data center, wherein the data center generally contains an air cooling system and a raised floor structure. The raised floor structure is configured to deliver cool air into the data center through a plurality of grates and perforated tiles in the floor. Electronic equipment racks are disposed around the grates and perforated tiles, such that the front faces of the equipment racks face the grates and perforated tiles. A collection of baffles, doors or roof sections inhibit the mixing of the cool air delivered by the air cooling system and the warm air exhausted by the electronic equipment.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC IT CORP
Drive current increase in transistors by asymmetric amorphization implantation
ActiveUS7855118B2Increased complexityImprove performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDriving currentNon symmetric
By providing a substantially non-damaged semiconductor region between a pre-amorphization region and the gate electrode structure, an increase of series resistance at the drain side during the re-crystallization may be reduced, thereby contributing to overall transistor performance, in particular in the linear operating mode. Thus, symmetric and asymmetric transistor architectures may be achieved with enhanced performance without unduly adding to overall process complexity.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
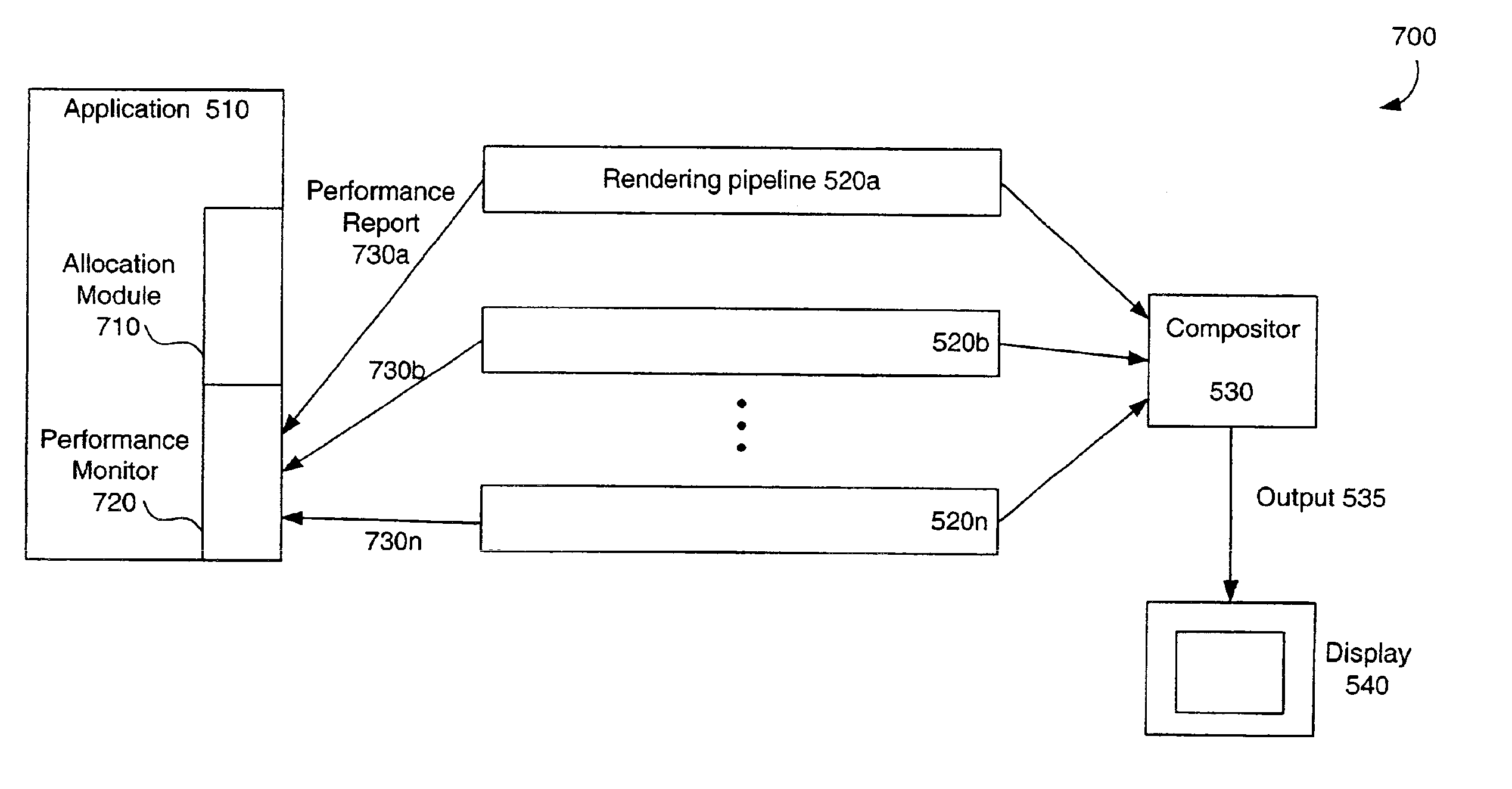
System, method, and computer program product for near-real time load balancing across multiple rendering pipelines
InactiveUS6885376B2Easy to useReduce loadMultiple digital computer combinationsProcessor architectures/configurationComputational scienceGraphics
A system, method, and computer program product for creating a sequence of computer graphics frames, using a plurality of rendering pipelines. For each frame, each rendering pipeline receives a subset of the total amount of graphics data for the particular frame. At the completion of a frame, each rendering pipeline sends a performance report to a performance monitor. The performance monitor determines whether or not there was a significant disparity in the time required by the respective rendering pipelines to render their tiles. If a disparity is detected, and if the disparity is determined to be greater than some threshold, an allocation module resizes the tiles for the next frame. This serves to balance the load across rendering pipelines for each frame.
Owner:MORGAN STANLEY +1
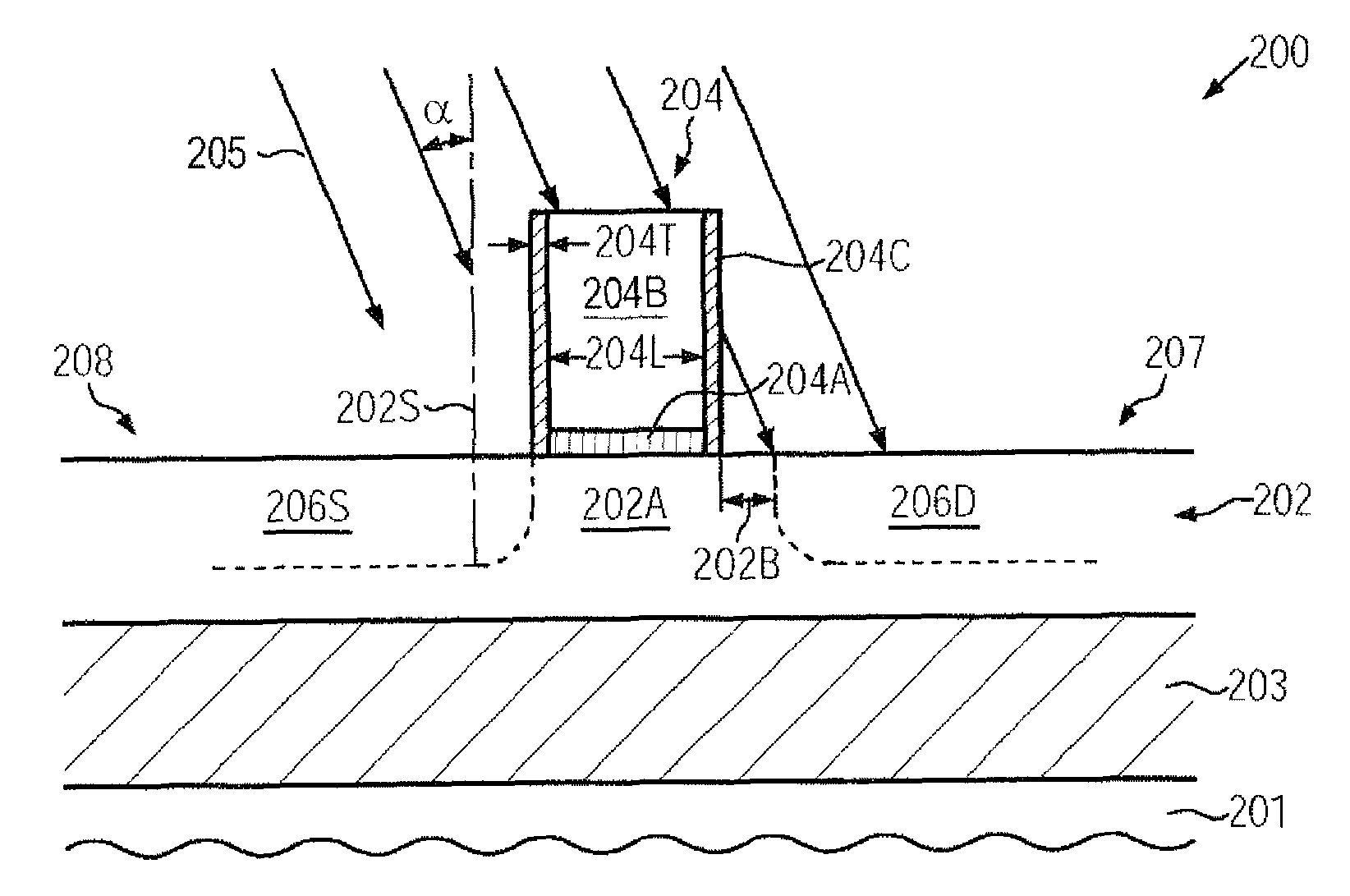
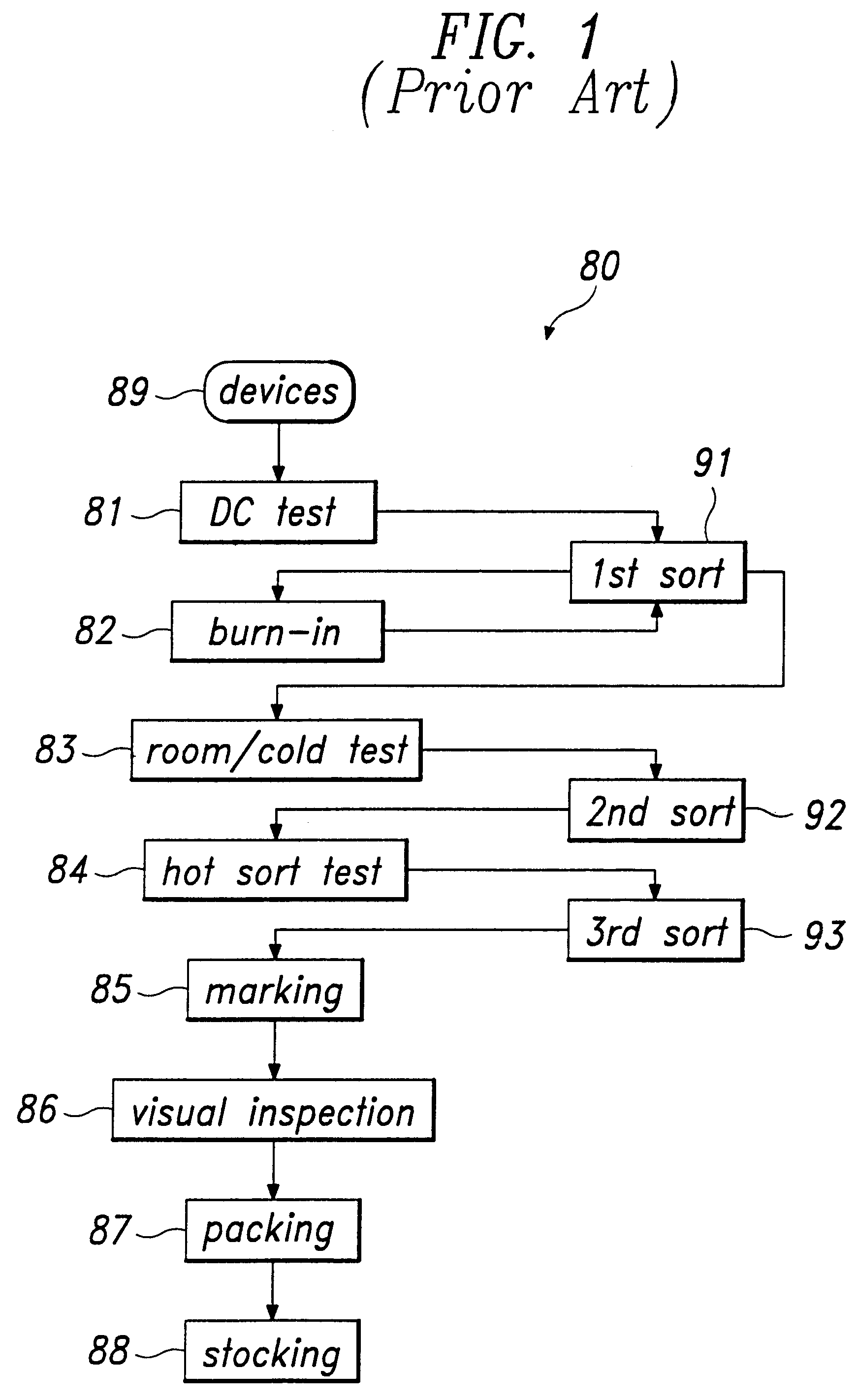
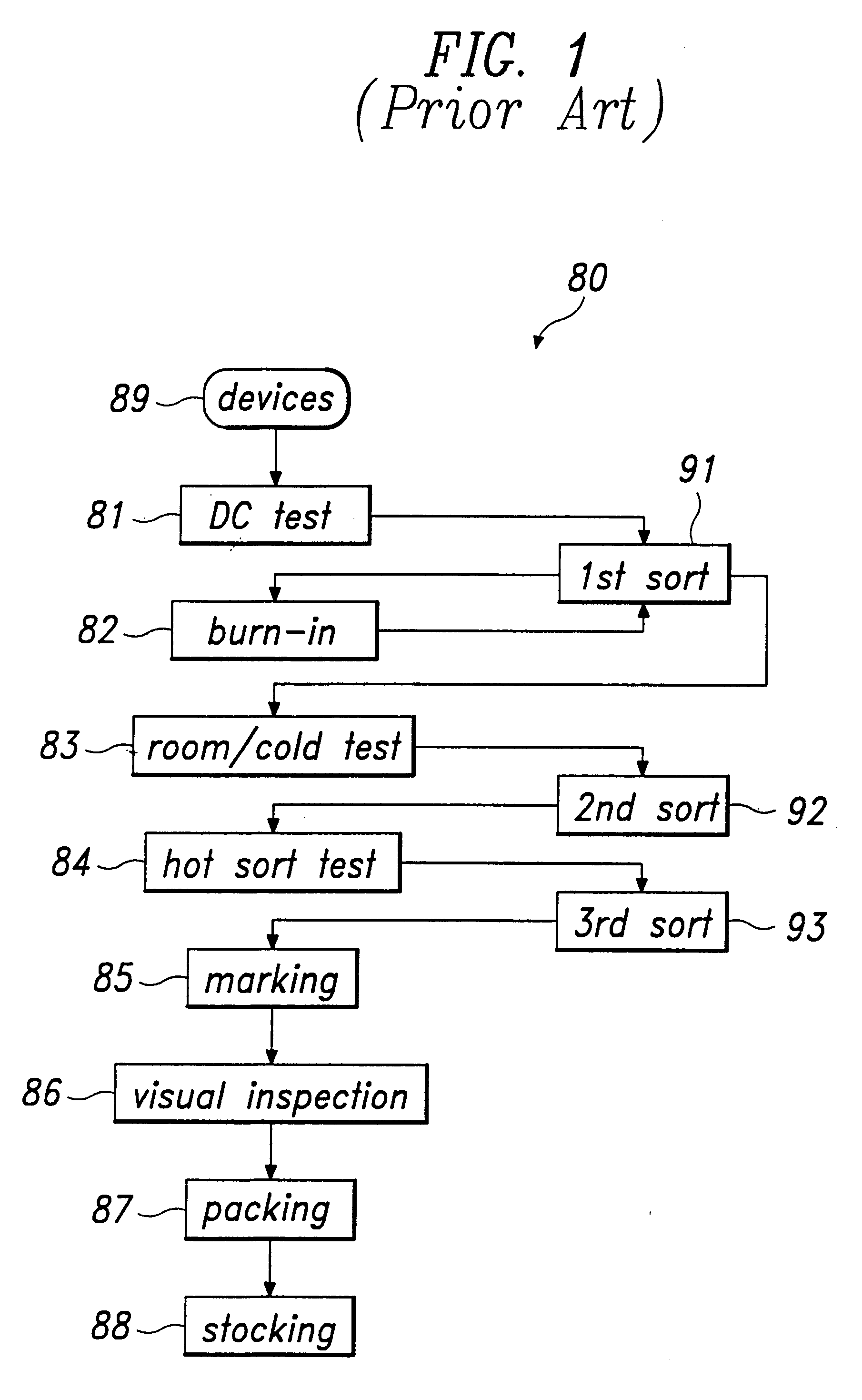
Test and burn-in apparatus, in-line system using the test and burn-in apparatus, and test method using the in-line system
InactiveUS6563331B1Reduced number of stepAvoid excess performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectronic circuit testingDevice materialTest phase
An apparatus for testing semiconductor devices allows various testing processes, including a burn-in process, to be performed at the same testing stage. Test trays which contain the semiconductor devices are used throughout an in-line system so that an entire back-end process can be performed without loading / unloading the semiconductor devices between the various tests. The in-line system includes multiple test and burn-in apparatuses as well as a single sorting unit which performs a composite sorting operation after all the testing processes. A method for testing semiconductor devices in the in-line system includes testing the semiconductor devices in the test trays using the test and burn-in apparatus, transferring the test trays to a different testing apparatus for a second testing, and finally sorting the semiconductor devices after all testing processes have been performed based on a final sorting map created by combining test tray maps generated during each of the tests.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Test and burn-in apparatus, in-line system using the test and burn-in apparatus, and test method using the in-line system
InactiveUS6313652B1Reduced number of stepAvoid excess performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectronic circuit testingGeneration processDevice material
A test and burn-in apparatus for semiconductor chip package devices, an in-line system which includes the test and burn-in apparatus, and a test method which employs the in-line system are provided. A test and burn-in apparatus for testing semiconductor devices allows various testing processes, including a burn-in process, to be performed at the same testing stage. The apparatus employs test trays which contain the semiconductor devices. These test trays are used throughout the in-line system so that an entire back-end process can be performed without the need for loading / unloading the semiconductor devices into and from device trays between the various tests. The test and burn-in apparatus according to this invention can therefore occupy less space than the prior art testing apparatuses. The in-line system includes multiple test and burn-in apparatuses as well as a single sorting unit which performs a composite sorting operation after all the testing processes have been performed. Furthermore, the method for testing the semiconductor devices in the in-line system includes testing the semiconductor devices in the test trays using the test and burn-in apparatus, generating a test tray map corresponding to results of the test, transferring the test trays to a different testing apparatus for a second testing and test tray map generation process, and finally sorting the semiconductor devices in the sorting unit after all testing processes have been performed based on a final sorting map created by combining the test tray maps of each of the tests. The benefits of this invention are reduced time and space requirements because neither transferring the devices to device trays between tests nor performing multiple sorting steps are required.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Reconfigurable ball bat and method
InactiveUS7014580B2Quickly and easily remove and replaceReduced durabilityRacket sportsBiomedical engineeringBallast
Owner:COMPOSITES DESIGN SERVICES +1
Sensor device
ActiveUS7814791B2Avoid excess performanceAcceleration measurement using interia forcesNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsGyroscopeZ-Coordinate
The present invention is related to sensor arrangements and particularly to sensor arrangements for symmetric response in a x-, y- and z-coordinate system. The arrangement comprises four gyroscopes with one axis arranged into different directions of sensitivity.
Owner:IMEGO
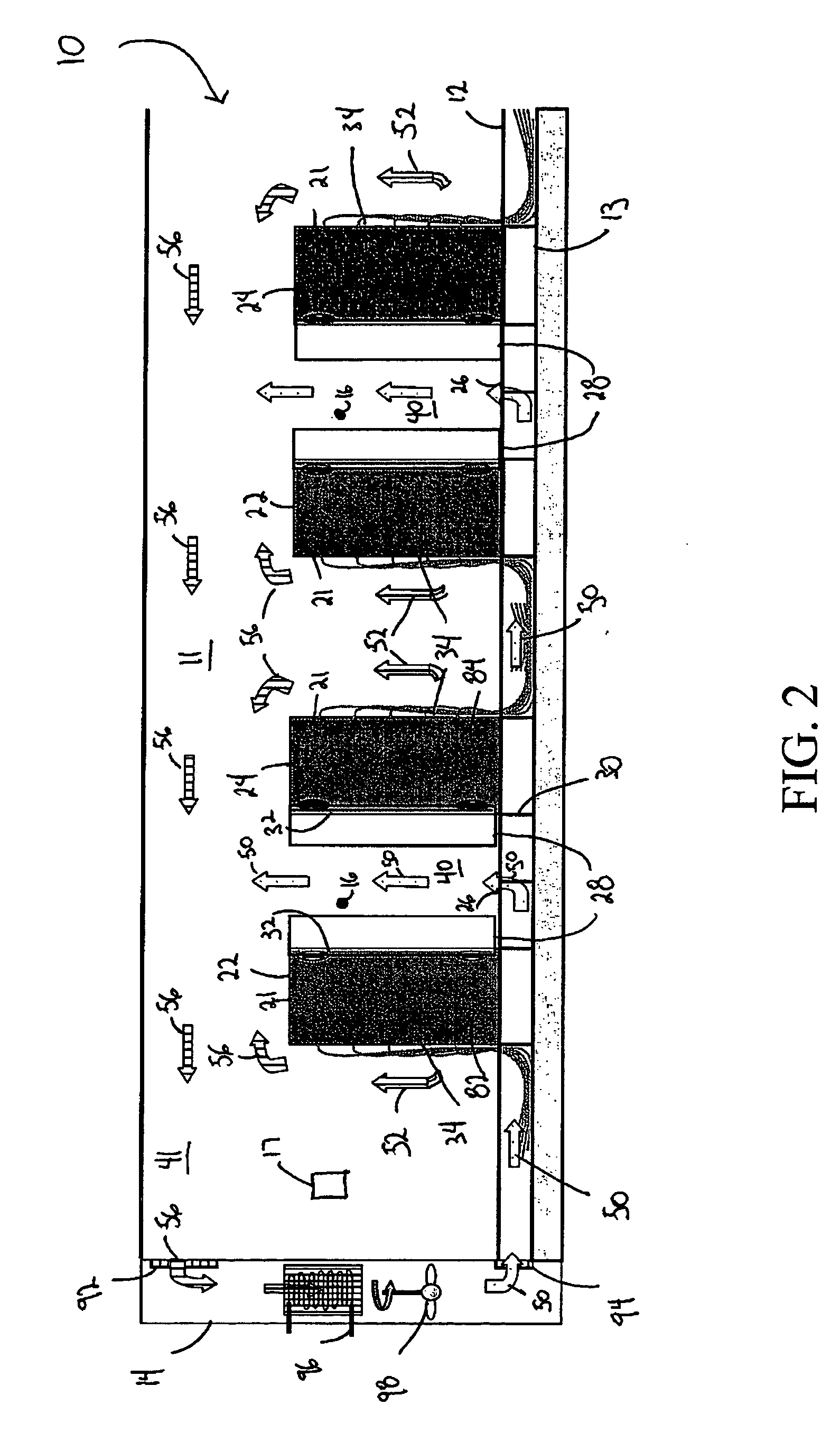
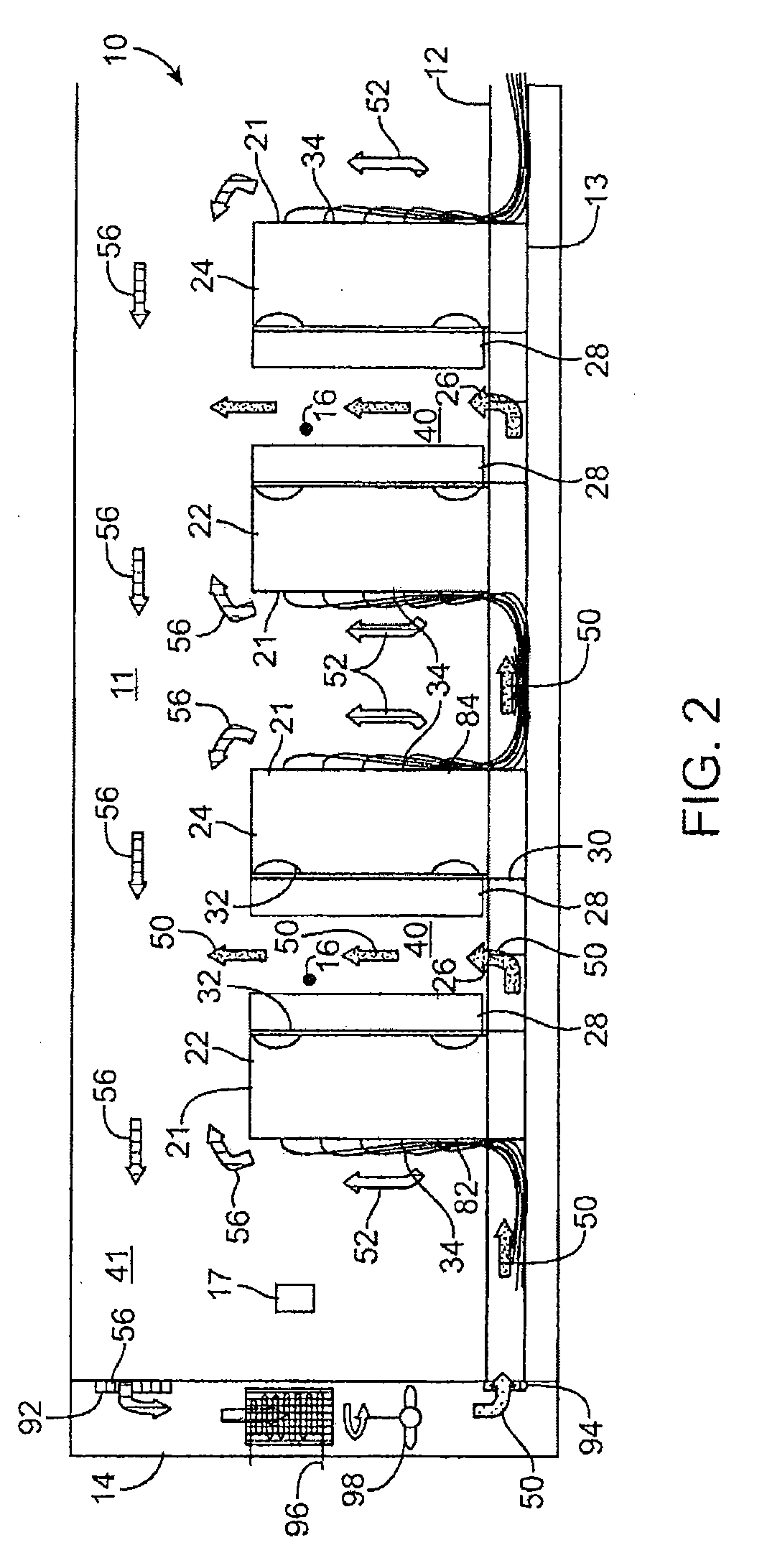
Cold aisle isolation
ActiveUS20090107652A1Easy to modifyLarge capacityDigital data processing detailsElectrical apparatus contructional detailsAir cooling systemEngineering
A data center cooling solution providing techniques for using baffles, doors and roof sections to prevent warm air from being entrained into a cold aisle in a data center, wherein the data center generally contains an air cooling system and a raised floor structure. The raised floor structure is configured to deliver cool air into the data center through a plurality of grates and perforated tiles in the floor. Electronic equipment racks are disposed around the grates and perforated tiles, such that the front faces of the equipment racks face the grates and perforated tiles. A collection of baffles, doors or roof sections inhibit the mixing of the cool air delivered by the air cooling system and the warm air exhausted by the electronic equipment.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC IT CORP
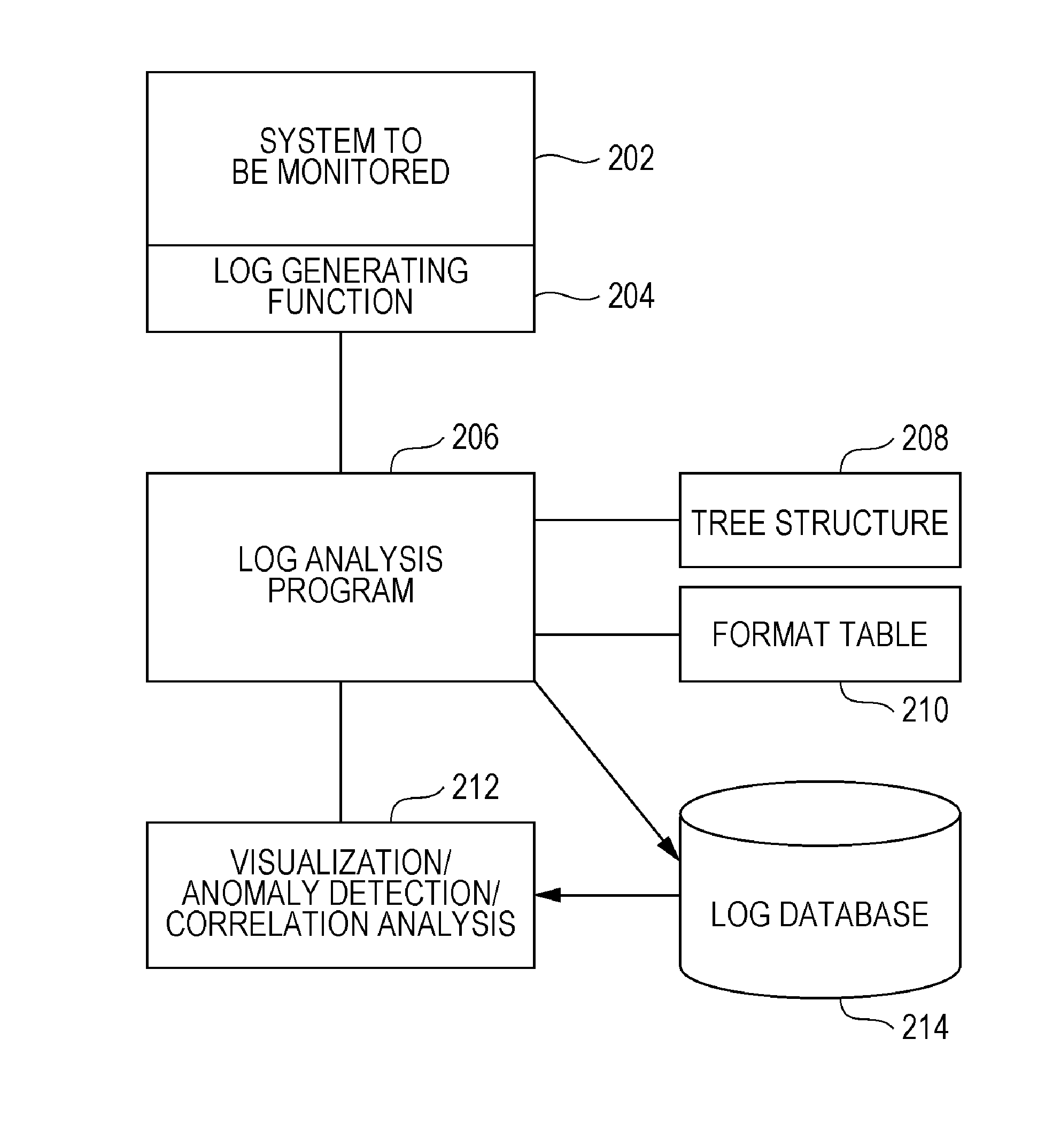
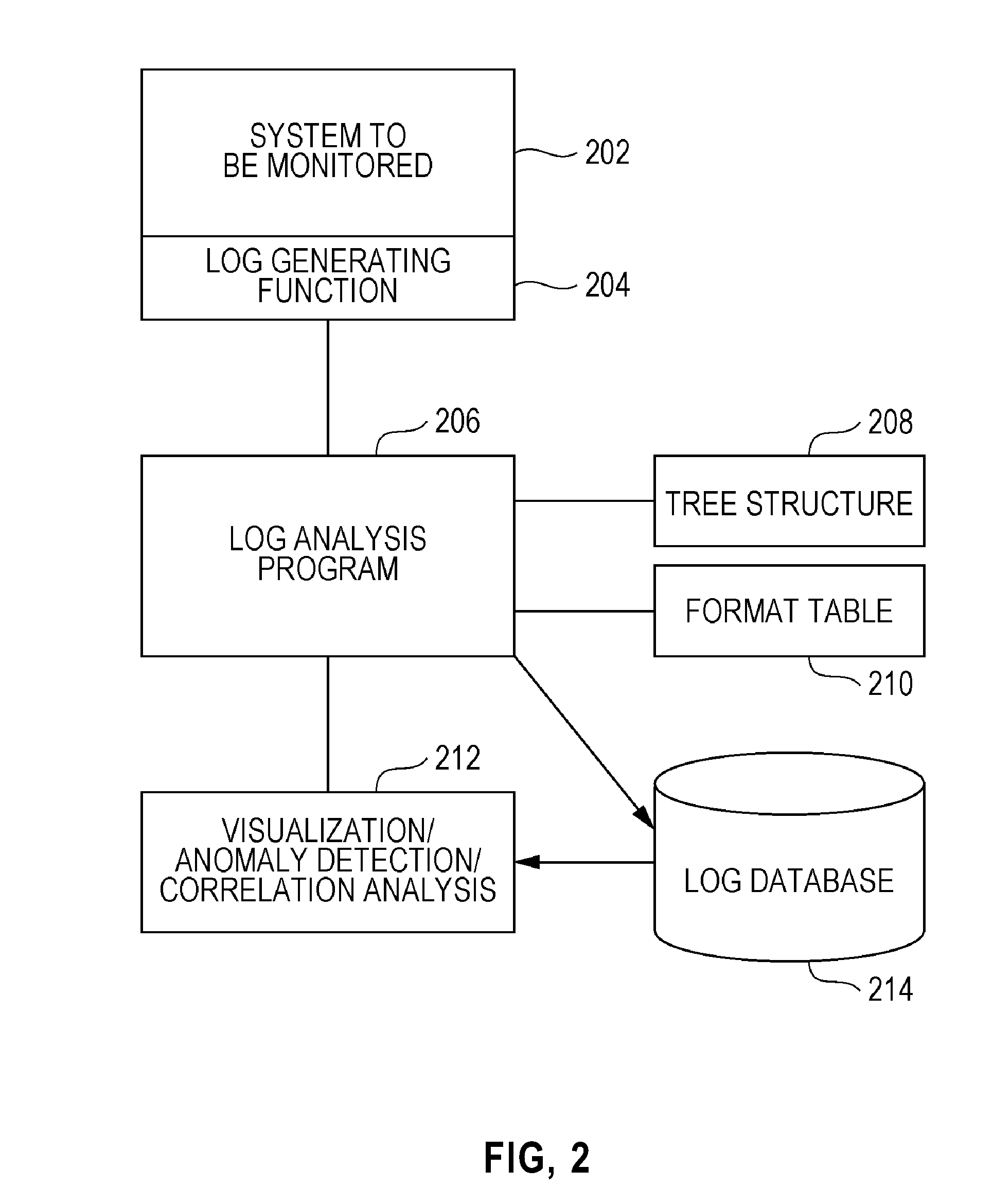
Method, program, and system for classification of system log
InactiveUS20140324865A1Avoid excess performanceEnsure effective applicationDigital data processing detailsNon-redundant fault processingData processing systemData mining
Method and system for classifying system logs. A data processing system reads a message in one line of a system log; prepares a root node of a tree structure in which each node holds a format; calculates a similarity between a log of the root node and the message; generates and stores a first format in the root node if the calculated similarity is equal to or greater than a threshold value; adds the message to a child node of the root node, in accordance with a given condition; searches for, after the first format is created, a second format similar to the first format in a format storage table; combines the first format and the similar format to produce a combined parent format, where the combined parent format holds a plurality of formats; and stores the combined parent format in the format storage table to produce a classified format.
Owner:IBM CORP
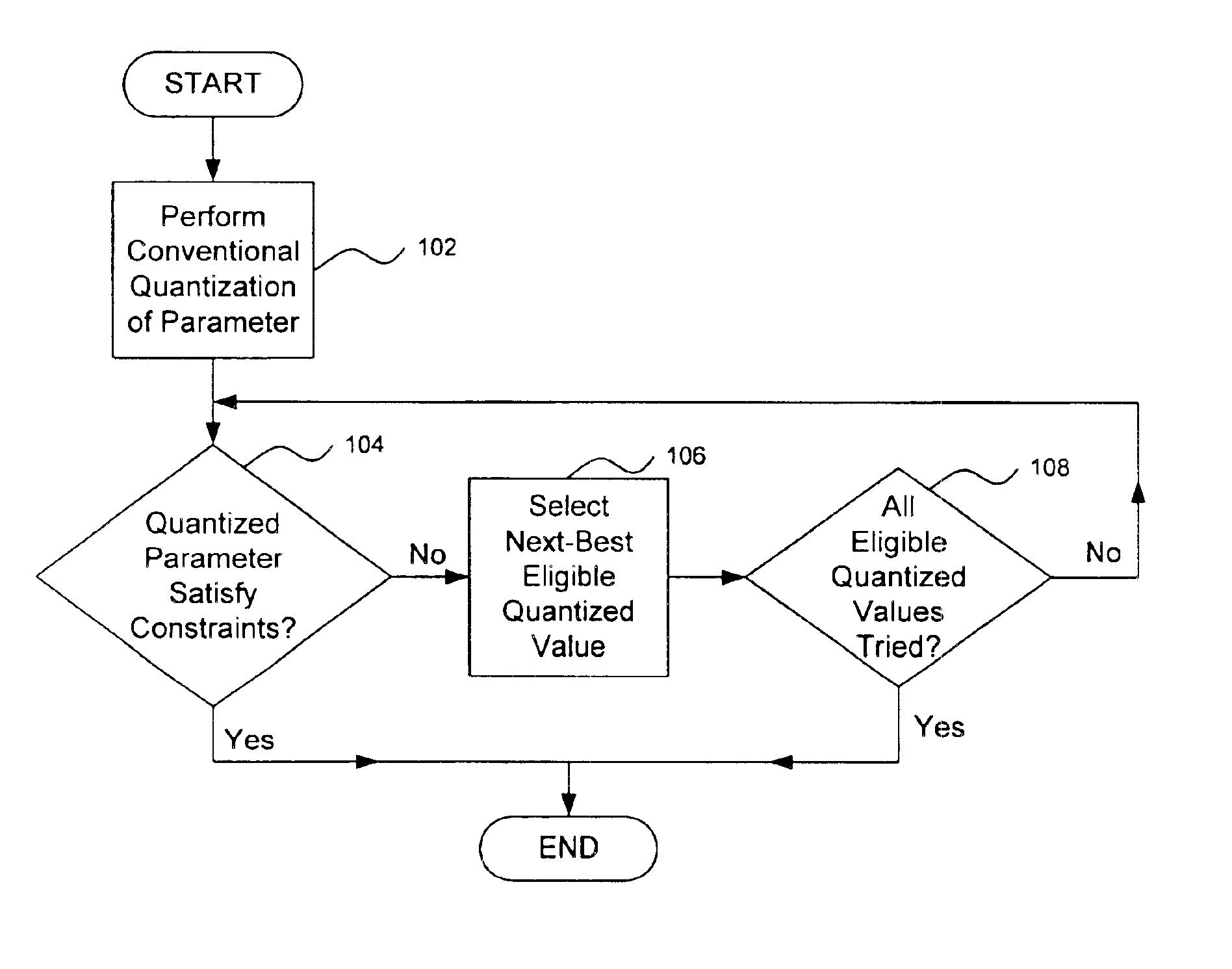
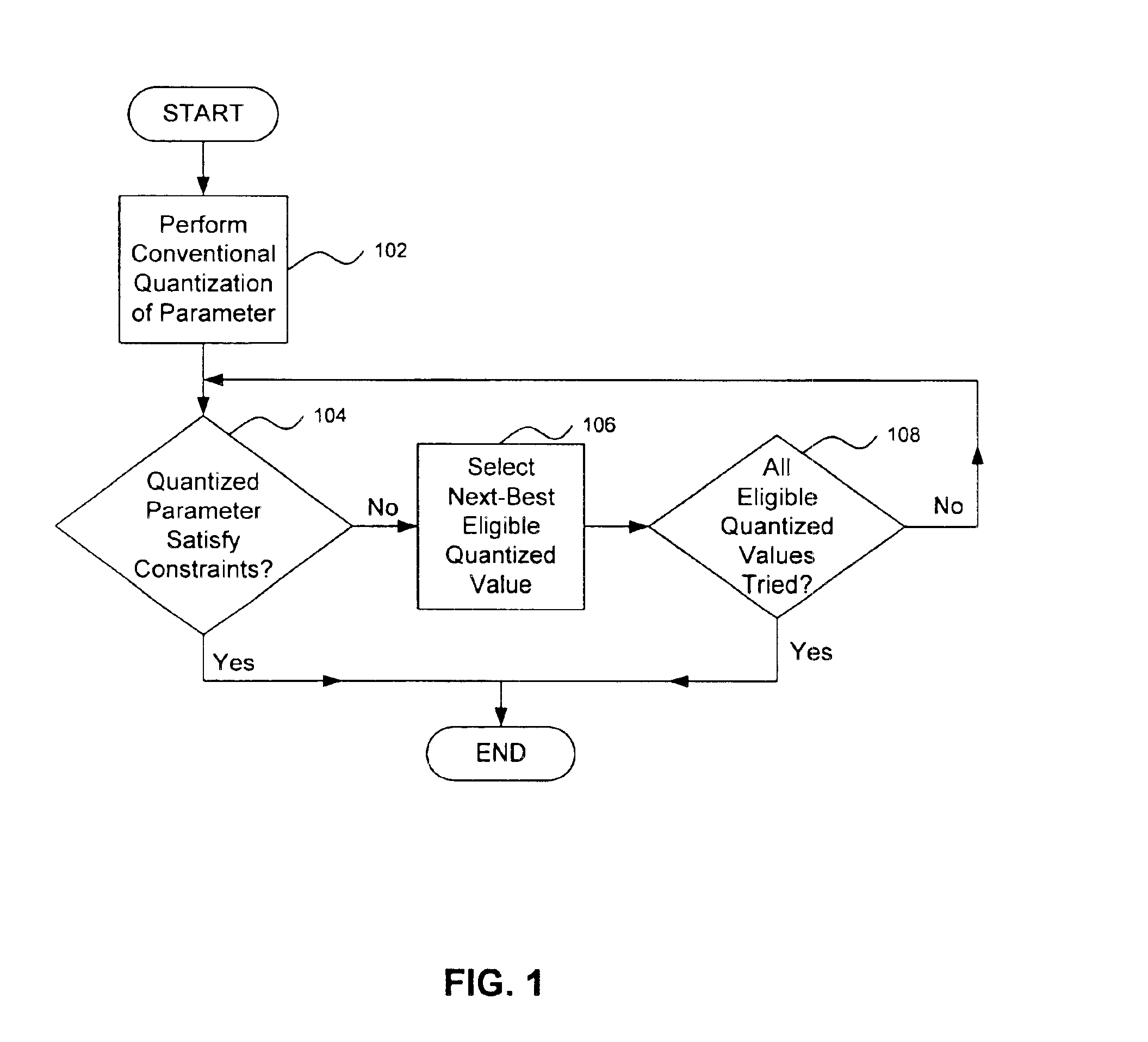
Bit error concealment methods for speech coding
InactiveUS6885988B2Error robustnessLess performance degradationOther error detection/correction/protectionSpeech analysisData segmentError concealment
A method of concealing bit errors in a signal is provided. The method comprises encoding a signal parameter according to a set of constraints placed on a signal parameter quantizer. The encoded signal parameter is decoded and compared against the set of constraints. Finally, the method includes declaring the decoded signal parameter invalid when the set of constraints is violated. Training binned ranges of gain values provide a threshold for selecting data segments to examine for violation of constraints on gain differences. Further, an additional method comprises training a threshold function T(qlg(m−1), Δqlg(m−1) used in a codec bit error detecting technique. The threshold function is based upon a first training file having N signal segments. The method includes encoding the first training file and determining gain values qlg(m) of each of the N signal segments within the encoded first training file. The gain values form a range and the range is divided into bins. Next, the gain values are stored in a second training file. The method associates each of particular ones of the gain values and gain differences within the sequence qlg(m−1) and Δqlg(m−1) with a corresponding one of the bins.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
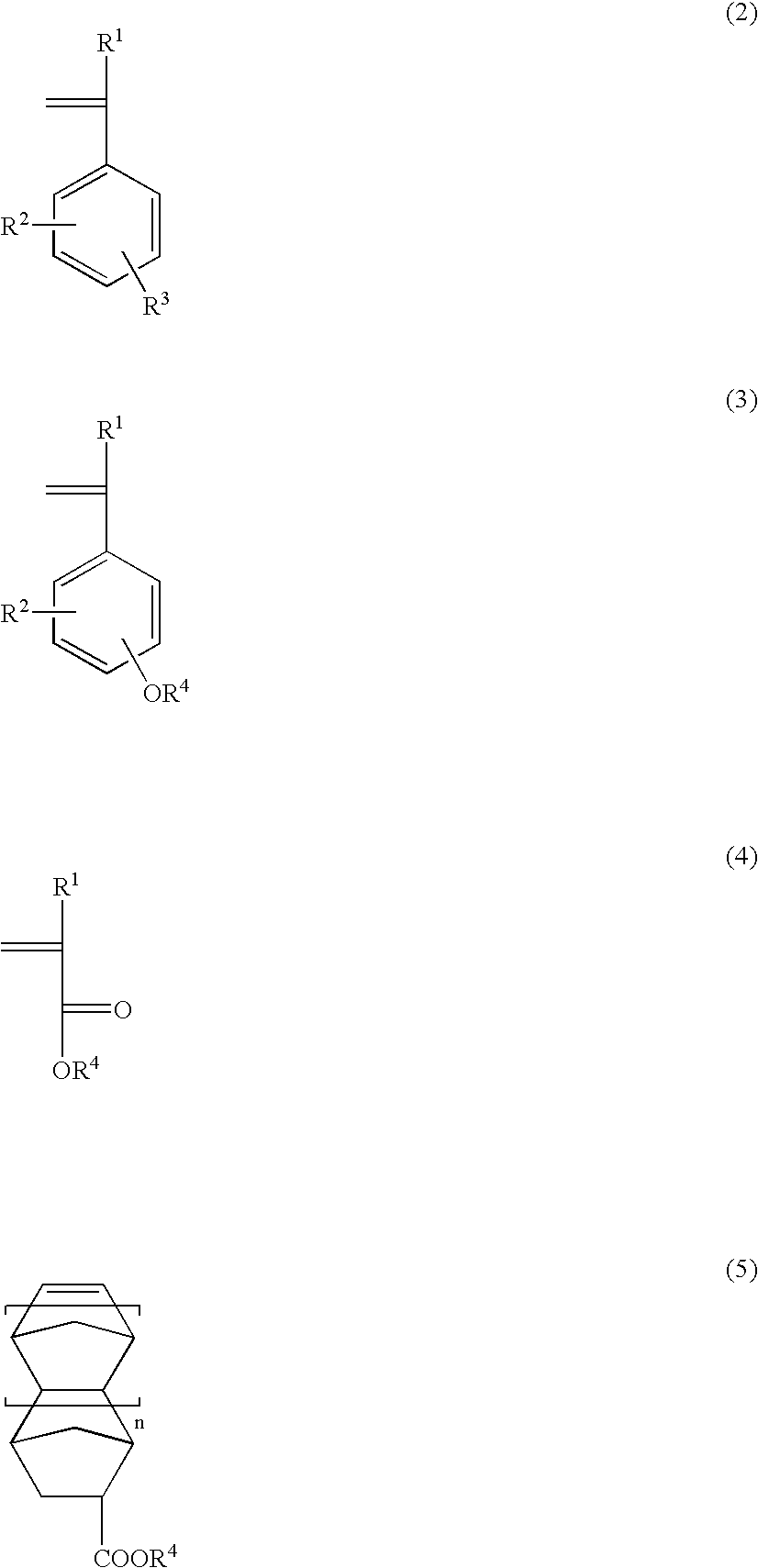
Hyperbranched polymer, production method therefor and resist composition containing hyperbranched polymer
InactiveUS20070148585A1Improve flatnessImprove solubilityPhotosensitive materialsPhotomechanical apparatusResistPolymer science
The present invention provides a hyperbranched polymer suitable as a polymer material for nanofabrication, in particular, photolithography. The hyperbranched polymer of the present invention is characterized by having a core portion prepared by a living radical polymerization of chloromethyl styrene or the like, and an acid decomposition group such as p-tert-butoxy styrene, which is linked to the core portion and present at the end of a molecule of the polymer.
Owner:LION CORP
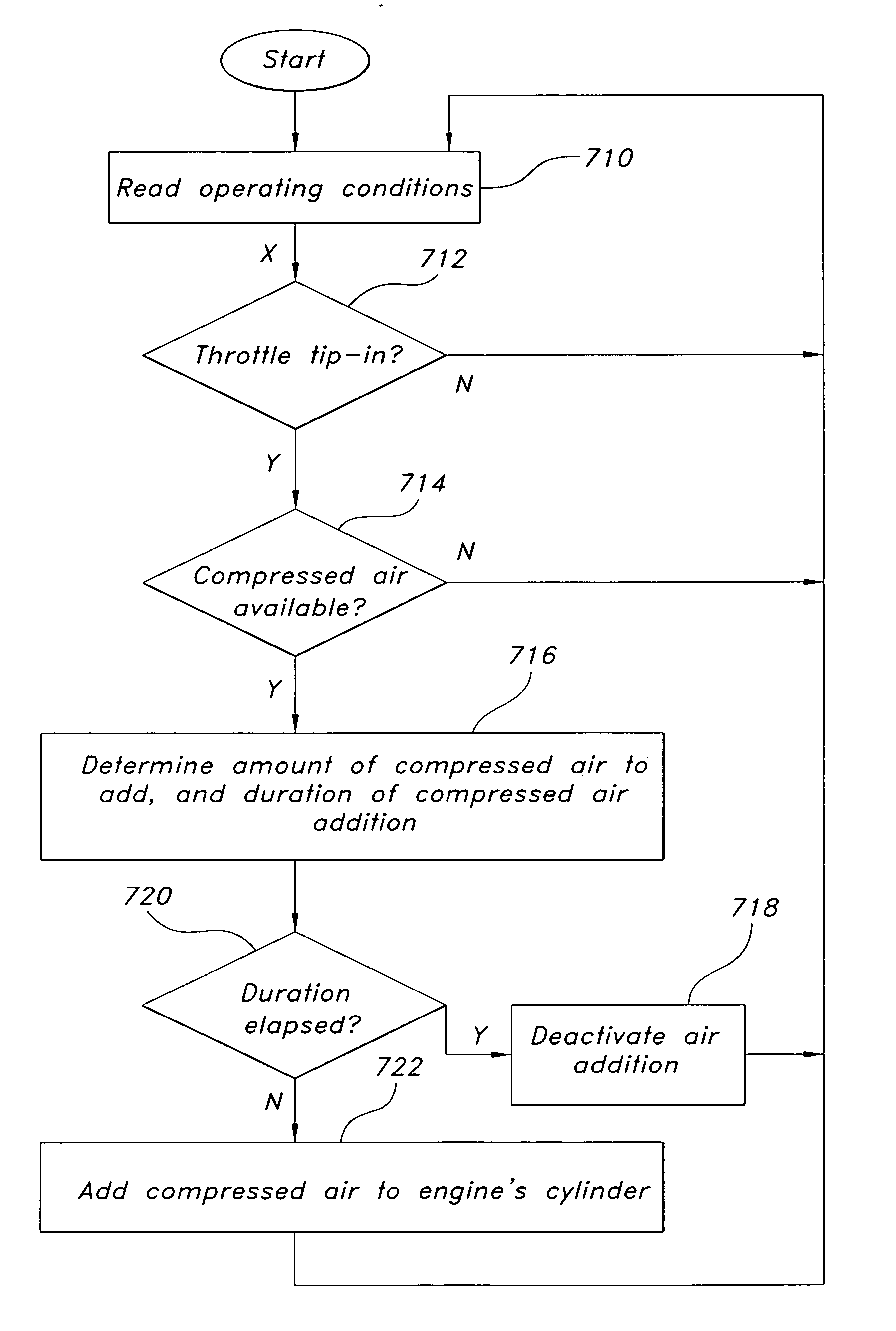
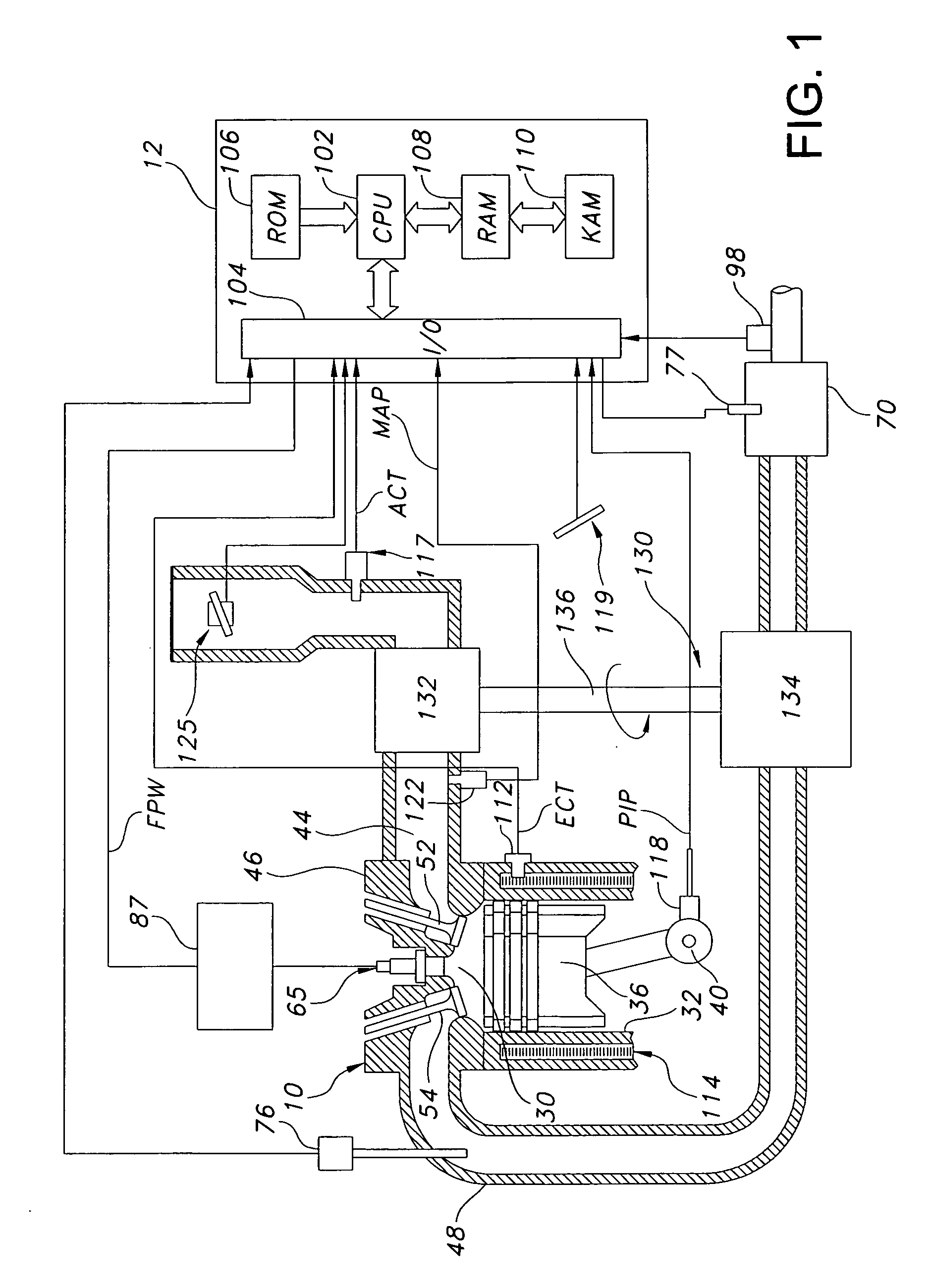
Turbo-lag compensation system for an engine
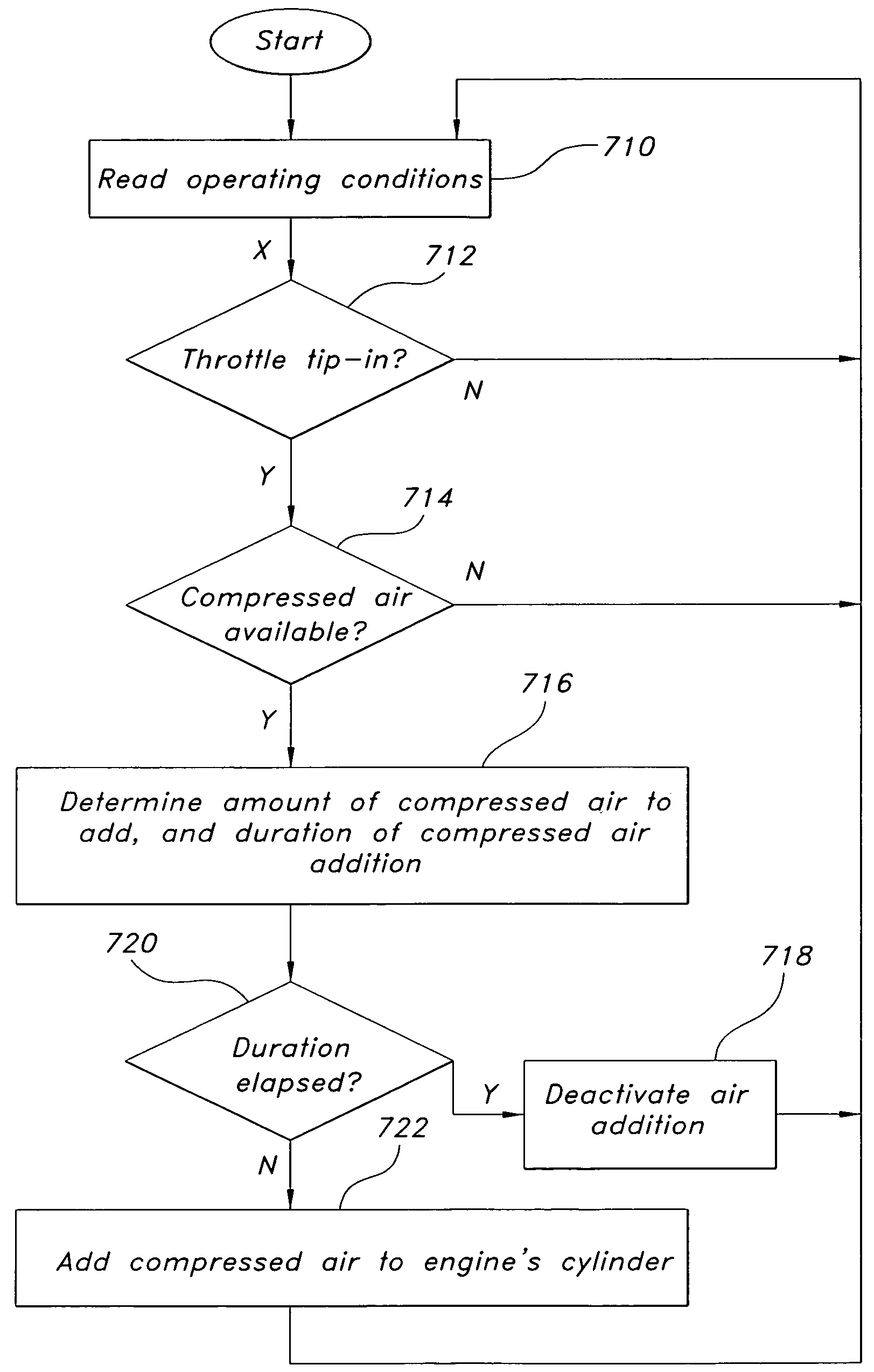
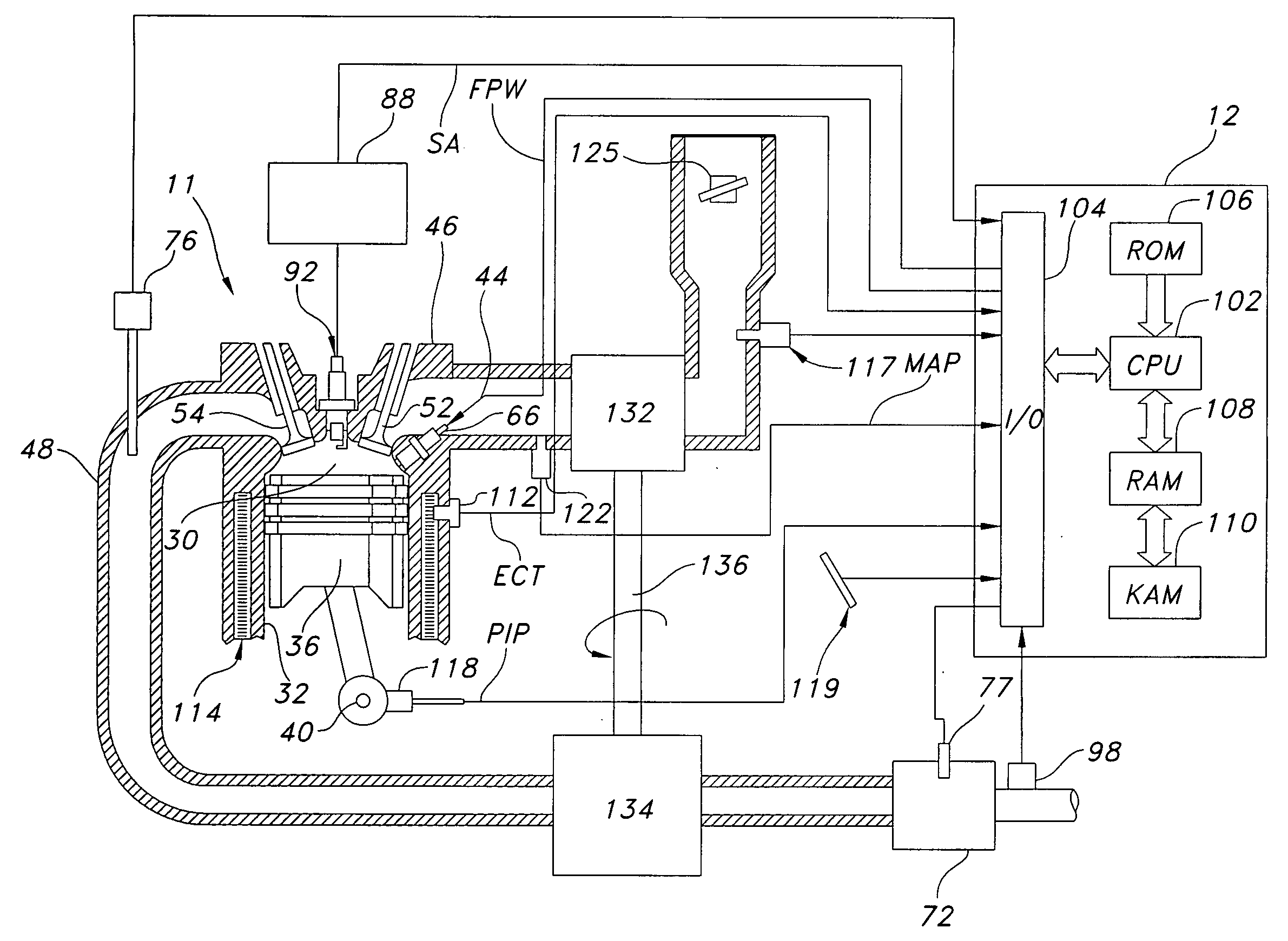
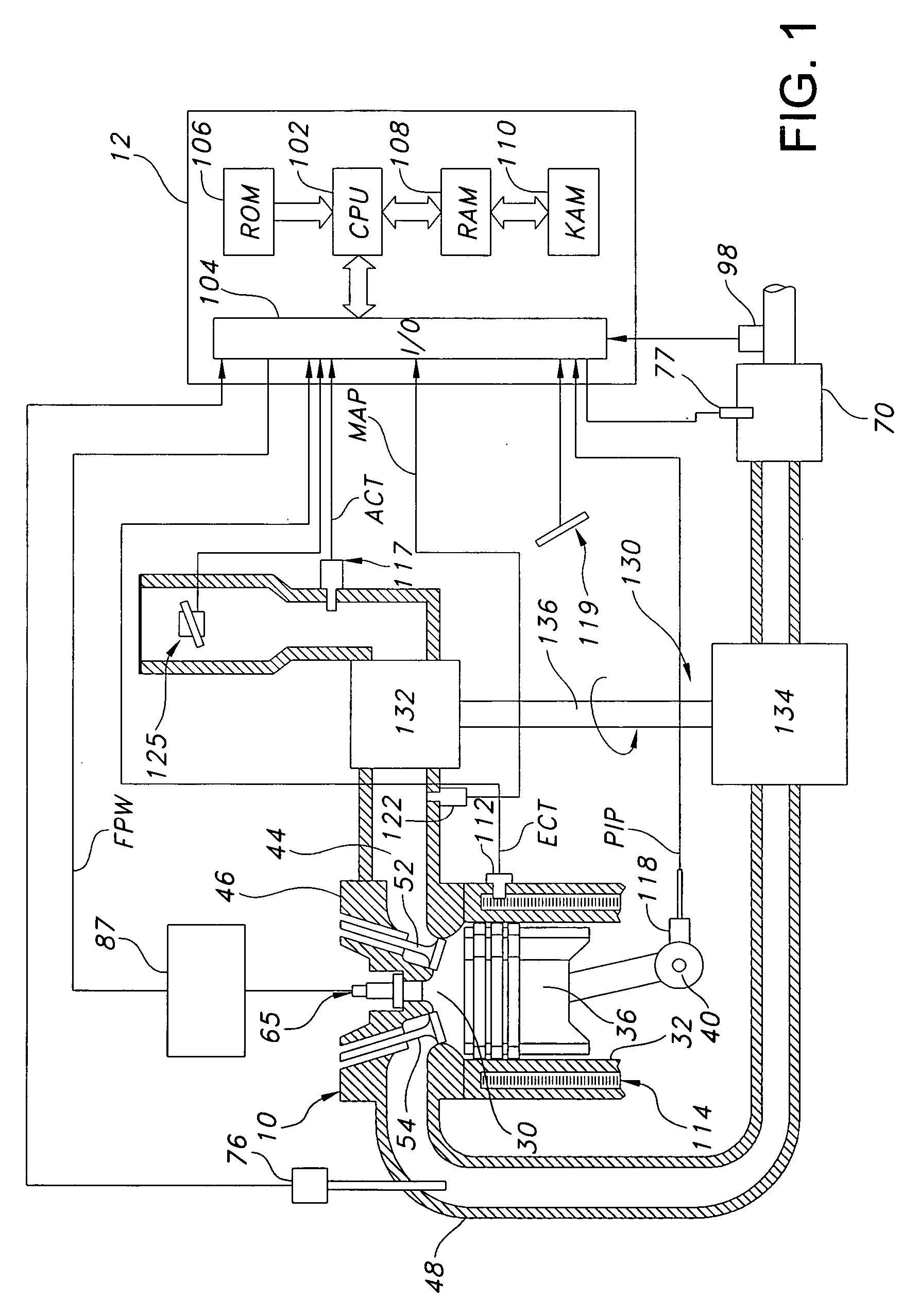
ActiveUS7314043B1Avoid excess performanceImprove power densityElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesAudio power amplifierCompression device
A boost system for an engine, comprising an engine having at least a cylinder; a fuel injector coupled to said cylinder; a compression device coupled to said engine; a compressed air storage device coupled to said compression device and configured to deliver compressed air to an air flow amplifier device located in the inlet air passageway to said cylinder; and a controller to adjust an amount of fuel injection to account for variation of air delivered to said cylinder from said flow amplifier device.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
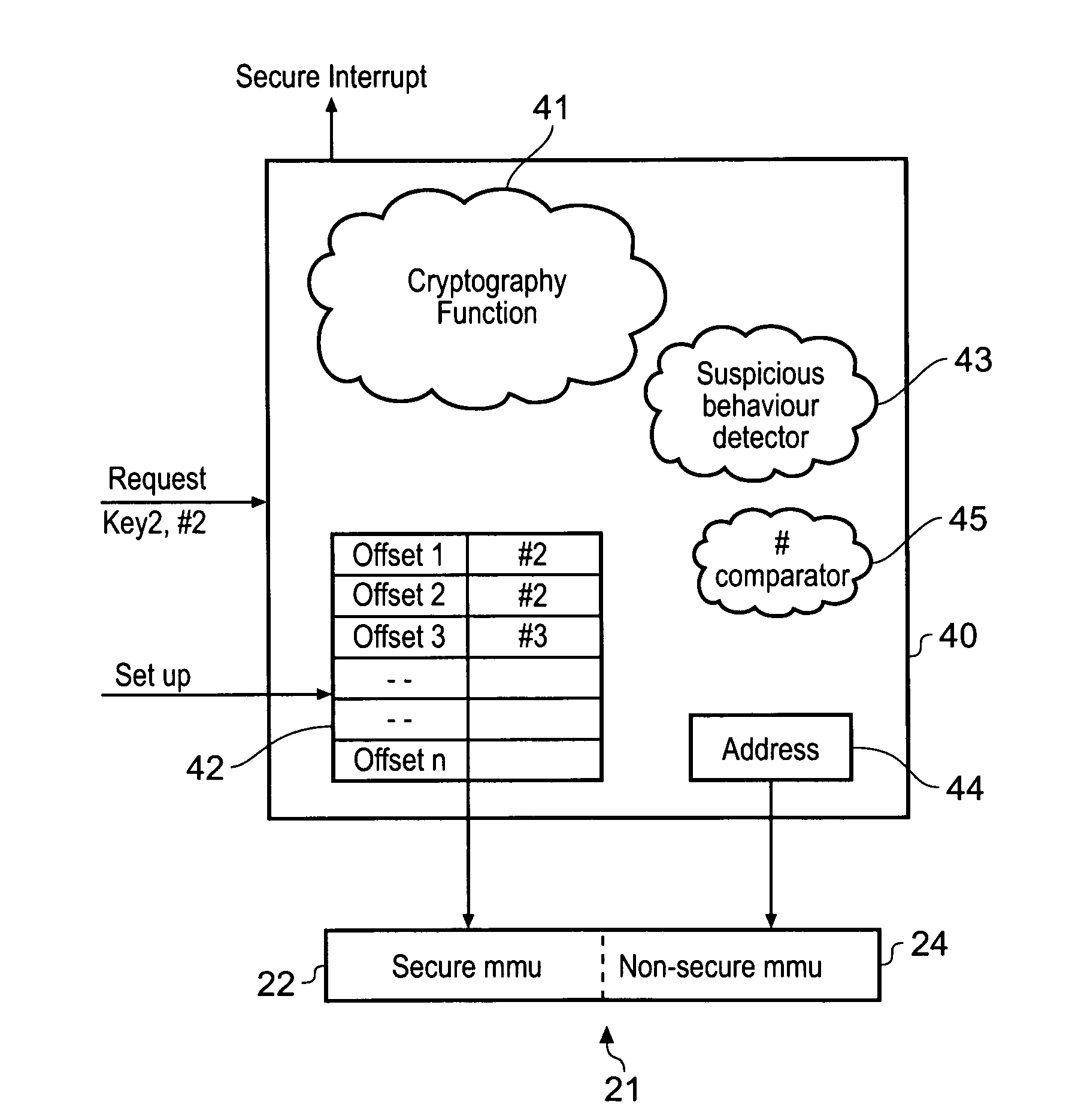
Providing secure services to a non-secure application
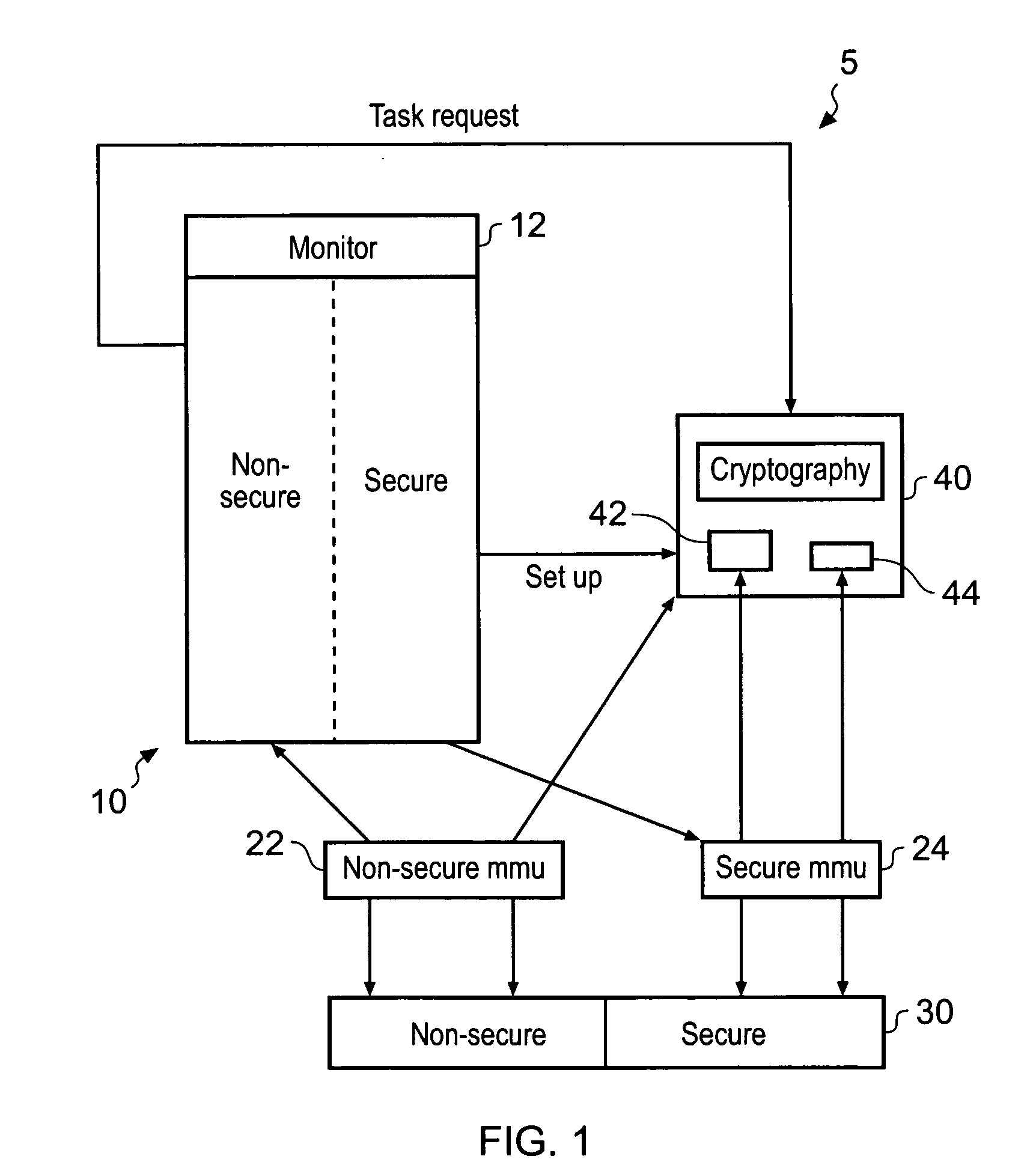
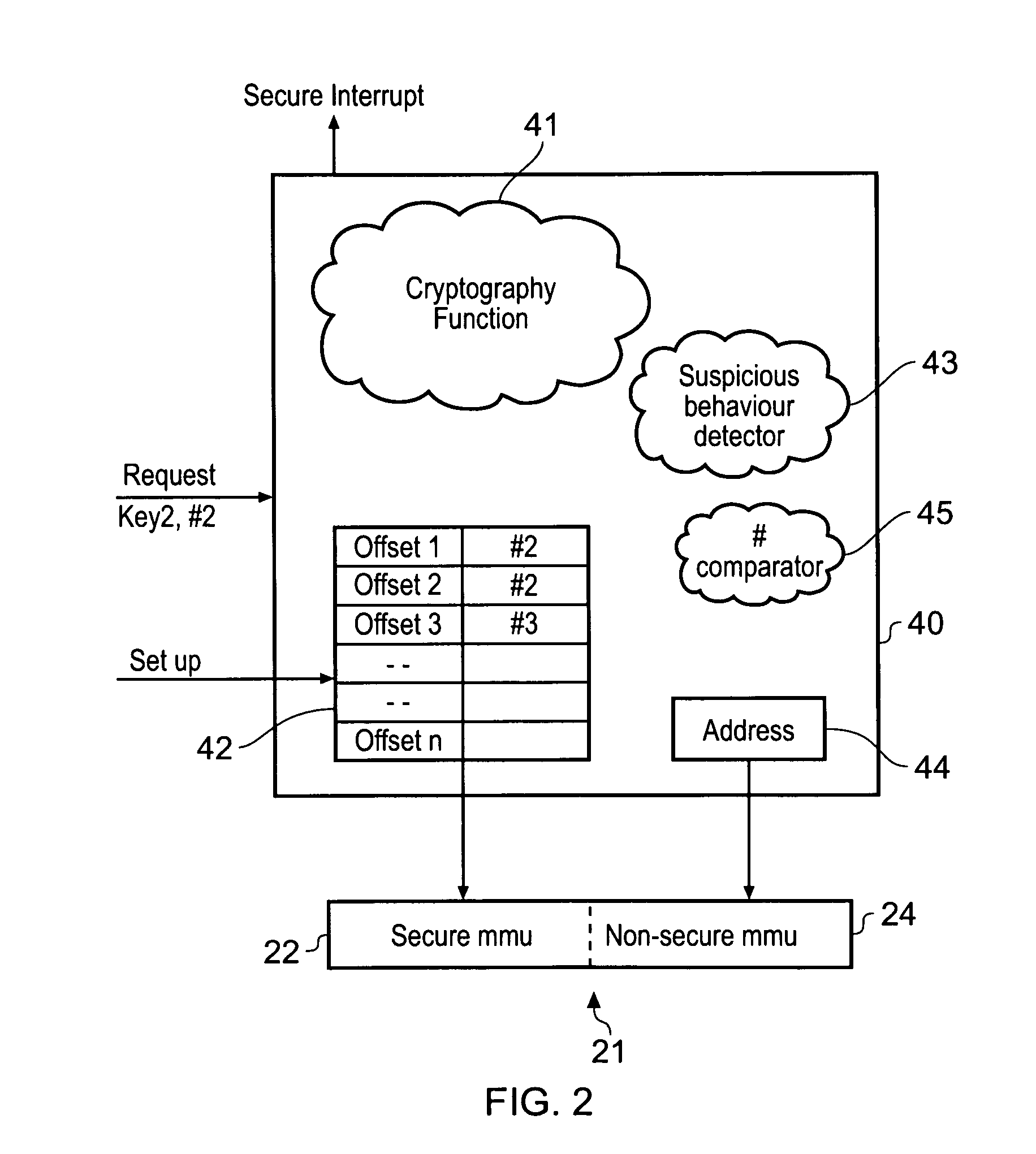
ActiveUS20090172329A1Avoid excess performanceImprove performanceDigital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionData memoryApplication software
A data processing apparatus comprising a data processor for processing data in a secure and a non-secure mode, said data processor processing data in said secure mode having access to secure data that is not accessible to said data processor processing data in said non-secure mode; and a further processing device for performing a task in response to a request from said data processor issued from said non-secure mode, said task comprising processing data at least some of which is secure data, said further processing device comprising a secure data store, said secure data store not being accessible to processes running on said data processor in non-secure mode; wherein prior to issuing any of said requests said data processor is adapted to perform a set up operation on said further data processing device, said set up operation being performed by said data processor operating in said secure mode and comprising storing secure data in said secure data store on said further processing device, said secure data being secure data required by said further processing device to perform said task; wherein in response to receipt of said request from said data processor operating in said non-secure mode said further data processing device performs said task using data stored in said secure data store to access any secure data required.
Owner:ARM LTD
Separator and fuel cell using thereof
InactiveUS20050221158A1Easy to assembleEasy to fabricateFuel cells groupingFuel cell auxillariesFuel cellsReactive gas
A fuel cell is provided therein with a metal separator for aiming at preventing corrosion and at reducing a contact resistance. The separator is compose of conductive passage board formed therein with passages, and a metal planar panel, the passage boards and the metal planar panel being superposed with one another. The metal planar panel is formed therein with a plurality of manifolds for passing reactive gas or cooling medium through an adjacent cell while the passage boards are formed therein with a plurality of meandering through channels for distributing the reactive gas or the cooling medium from the manifolds. Further, a part of the meandering through channels is superposed with a part or all parts of the manifolds, and a covering layer for preventing the metal planar panel from being corroded, and for restraining a growth of a nonconductive film is formed over an entire part of the metal planar panel or over at least a part thereof which makes contact with the meandering through channels.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Baseball bat with replaceable barrel
InactiveUS6905429B2Quickly and easily remove and replaceReduced durabilityRacket sportsMicrochiropteraGun barrel
A baseball or softball bat configured to allow the removal and replacement of the barrel section of the bat if the barrel is damaged or simply for enabling selection of a barrel having particular performance characteristics. Alternatively, the barrel may be selectively changed to meet certain regulation requirements. In one aspect, one or more components of the ball bat can be provided as a kit. In another aspect, the ball bat can be made by forming and assembling the components simply and inexpensively. Exemplary embodiments include a center tube or handle, a transition, and a barrel some or all of which can be separably combined during assembly.
Owner:HOONFORSYTHE TECH
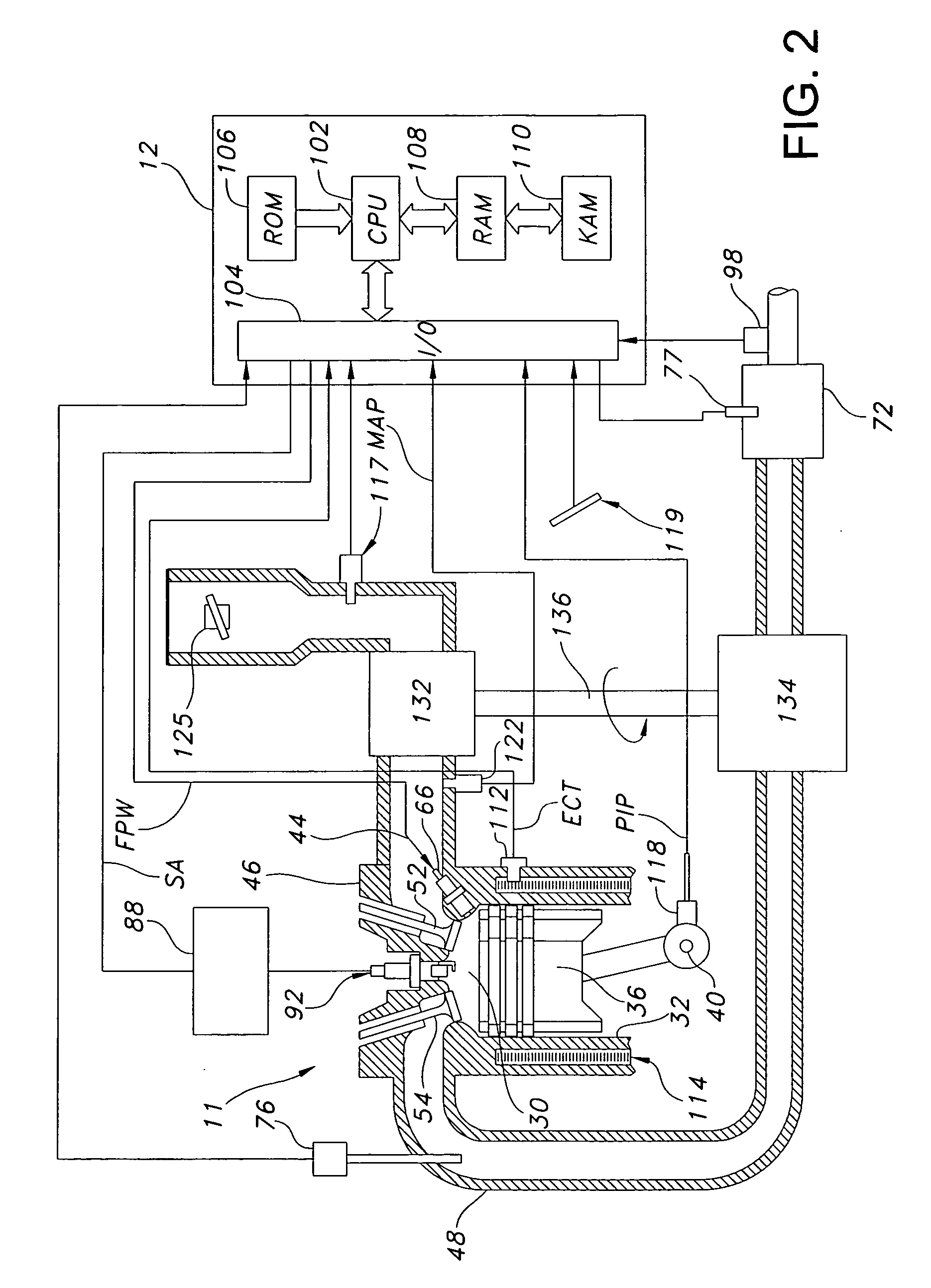
Turbo-lag compensation system for an engine
ActiveUS20070283939A1Increase engine power densityLess transient performanceElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesAudio power amplifierCompression device
A boost system for an engine, comprising an engine having at least a cylinder; a fuel injector coupled to said cylinder; a compression device coupled to said engine; a compressed air storage device coupled to said compression device and configured to deliver compressed air to an air flow amplifier device located in the inlet air passageway to said cylinder; and a controller to adjust an amount of fuel injection to account for variation of air delivered to said cylinder from said flow amplifier device.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Turbo-lag compensation system having an ejector
InactiveUS20070119169A1Reduced air storageIncrease pressureInternal combustion piston enginesEngine controllersCompression deviceLag
A boost system for an engine, comprising an engine having at least a cylinder with an intake valve configured to cover and uncover an intake opening into the cylinder, the cylinder coupled to an intake manifold; a compression device coupled to said engine; and an air delivery nozzle configured to deliver pressurized air to said cylinder via said opening, where said nozzle has a converging-diverging shape so that discharged air is at a supersonic velocity at least under some operating conditions.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
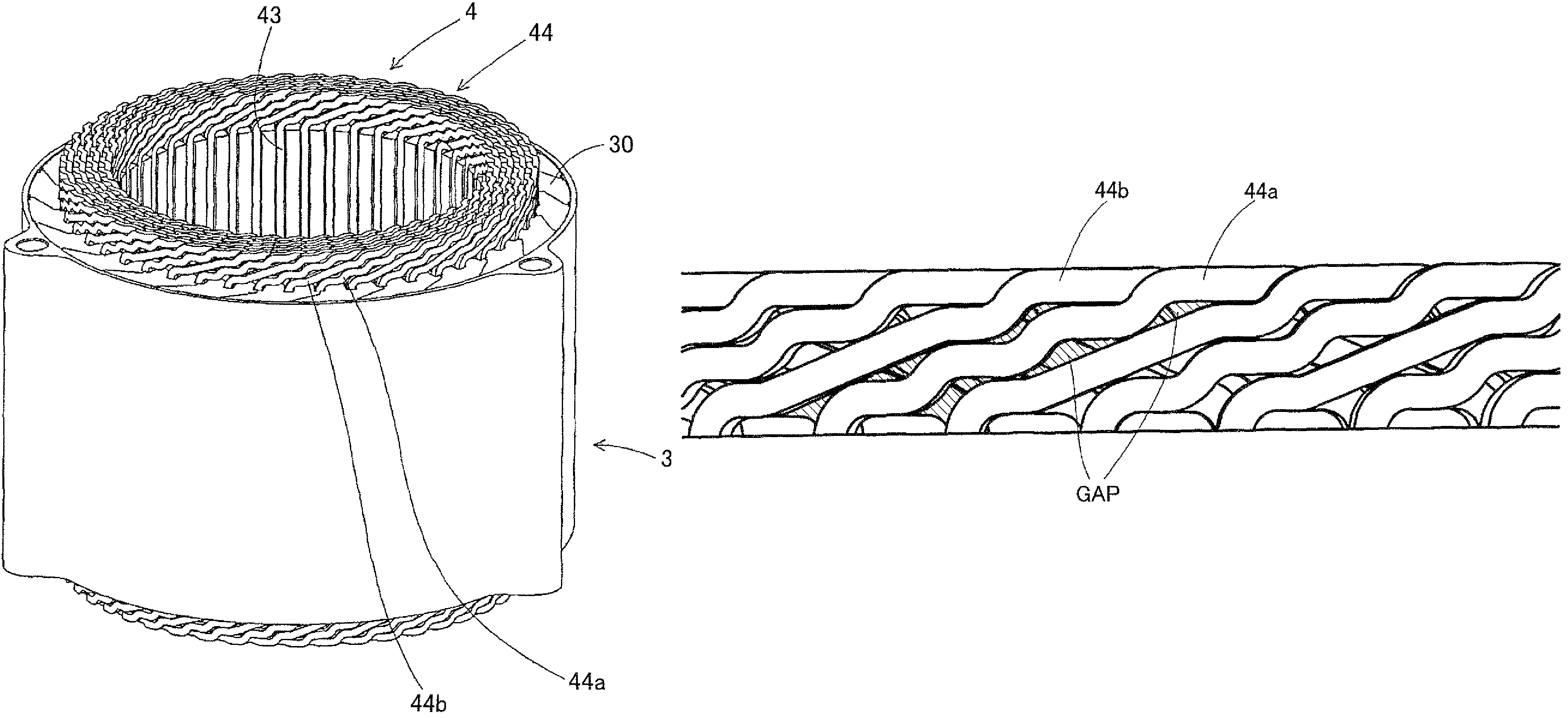
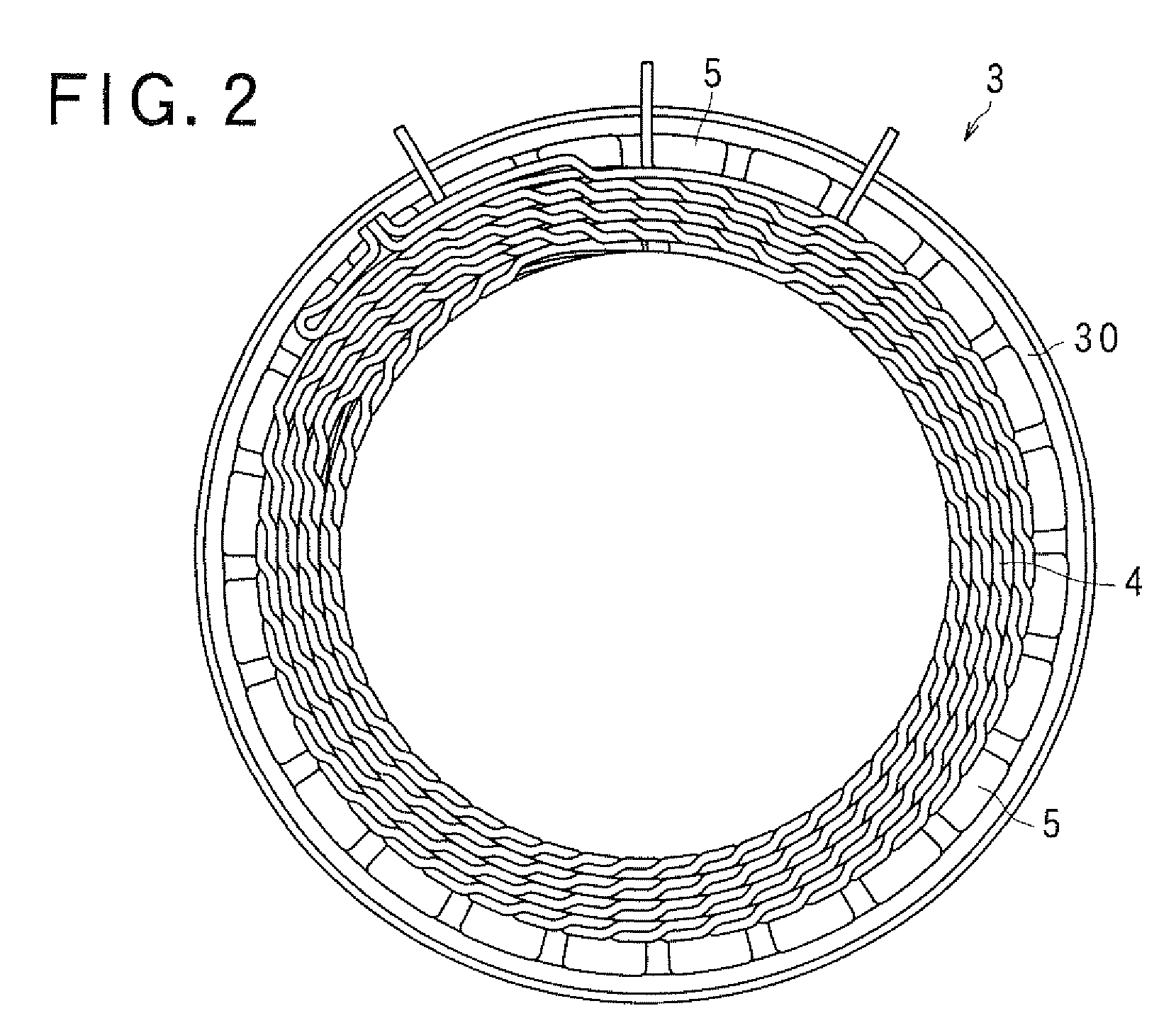
Stator of electric rotating machine and electric rotating machine
ActiveUS7812498B2Improve performanceAvoid excess performanceWindings insulation shape/form/constructionSynchronous machinesEngineeringConductor Coil
The stator of an electric rotating machine includes a stator core having slots formed therein along a circumferential direction thereof, and a stator winding formed by conductive wires wound on the slots. The stator winding includes in-slot portions accommodated in the slots and turn portions each of which connects each adjacent two of the in-slot portions outside of the slots. Each of the turn portions includes a first turn portion formed with M1 steps (m1 being a positive integer) extending along axial ends of the stator core, and a second turn portion formed with m2 steps (m2 being an integer larger than m1) extending along the axial ends.
Owner:DENSO CORP
3D ultrasound imaging system
ActiveUS20160038121A1Quicker and more comfortable and reliable analysisEasy to compareImage enhancementImage analysisUltrasound imagingSonification
The present invention relates to an ultrasound imaging system (10) comprising:—an image processor (34) configured to receive at least one set of volume data resulting from a three-dimensional ultrasound scan of a body (12) and to provide corresponding display data,—an anatomy detector (38) configured to detect a position and orientation of an anatomical object of interest within the at least one set of volume data,—a slice generator (40) for generating a plurality of two-dimensional slices from the at least one set of volume data, wherein said slice generator (40) is configured to define respective slice locations based on the results of the anatomy detector for the anatomical object of interest so as to obtain a set of two-dimensional standard views of the anatomical object of interest, wherein the slice generator (40) is further configured to define for each two-dimensional standard view which anatomical features of the anatomical object of interest are expected to be contained, and—an evaluation unit (42) for evaluating a quality factor for each of the generated plurality of two-dimensional slices by comparing each of the slices with the anatomical features expected for the respective two-dimensional standard view.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
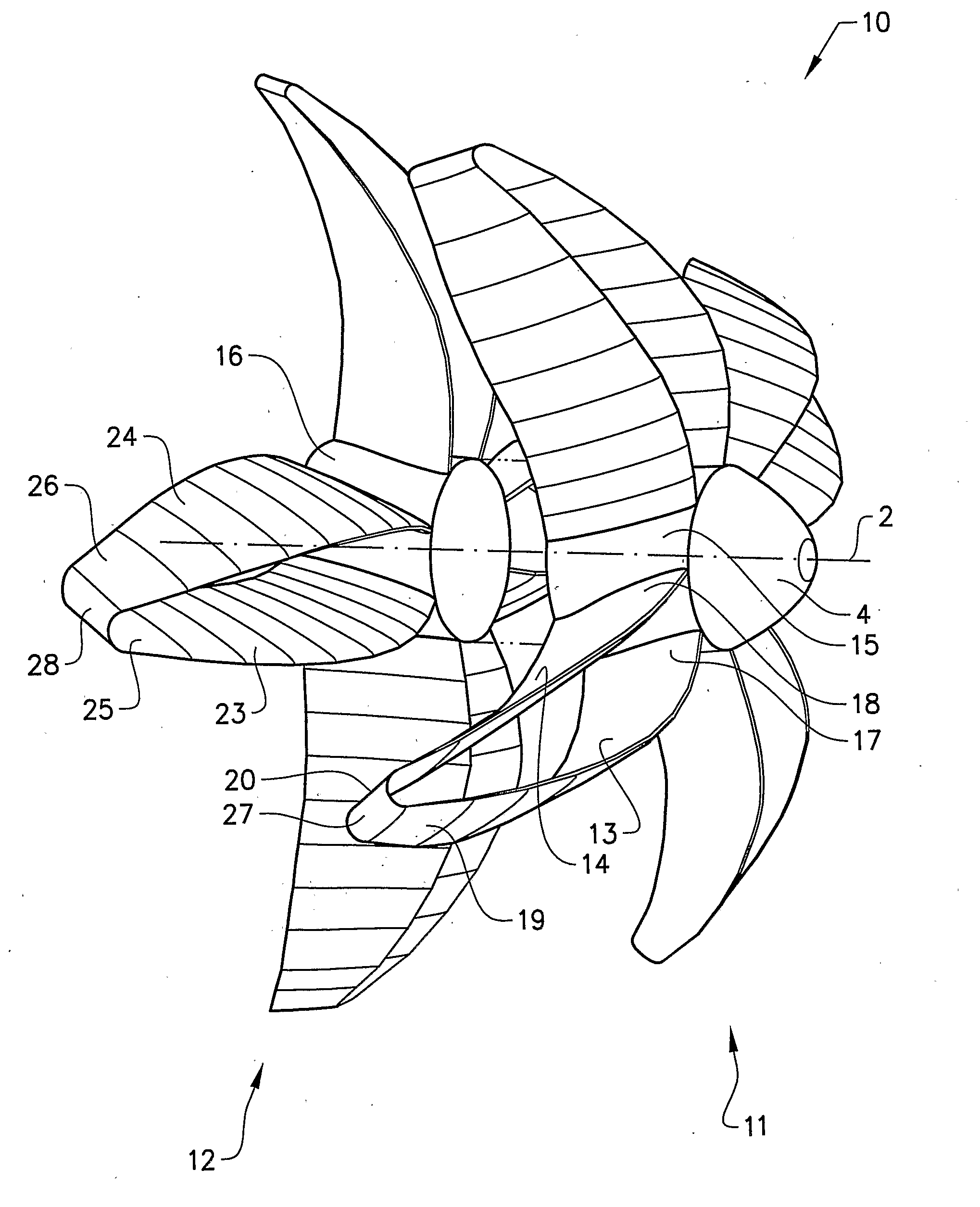
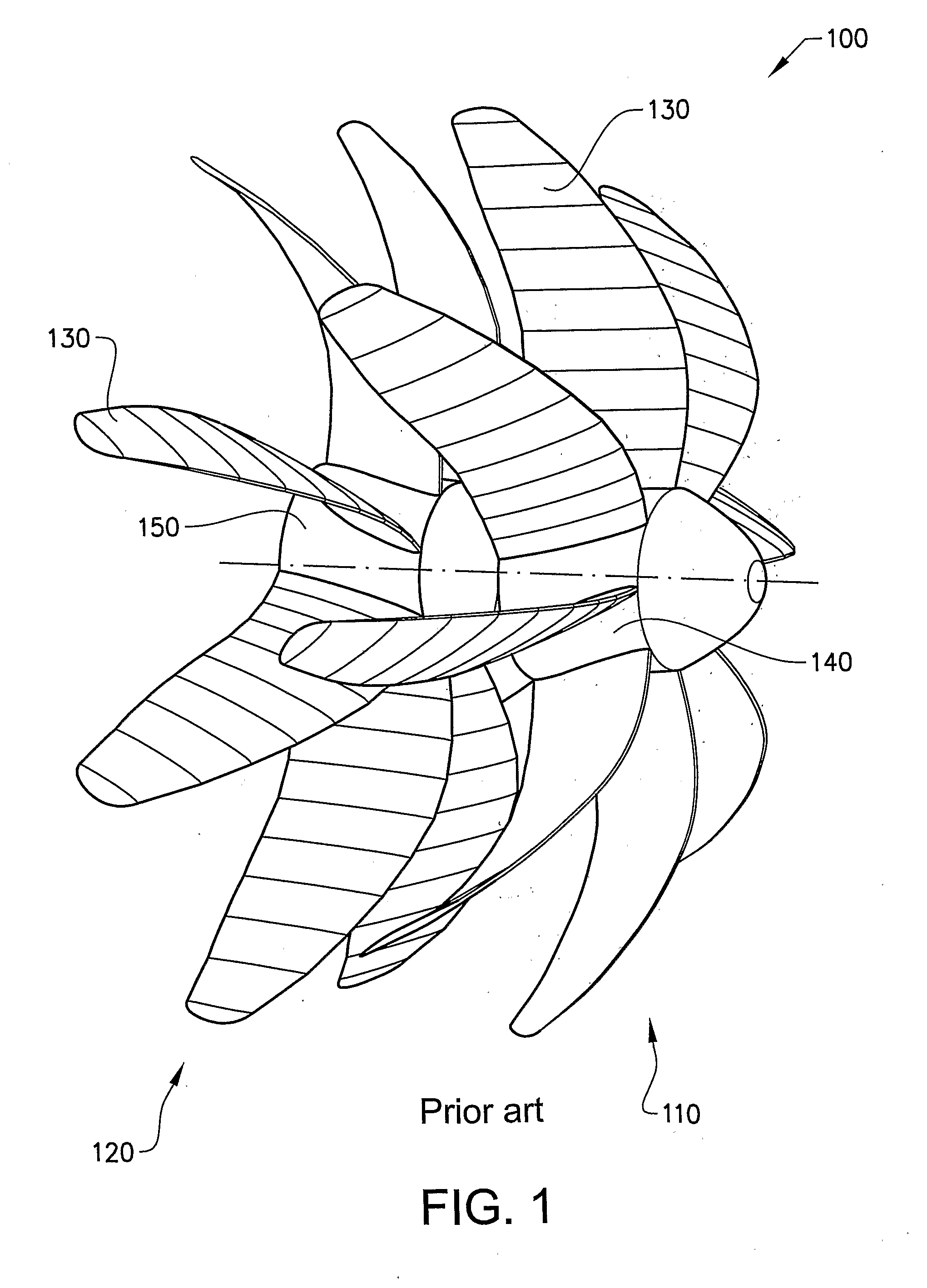
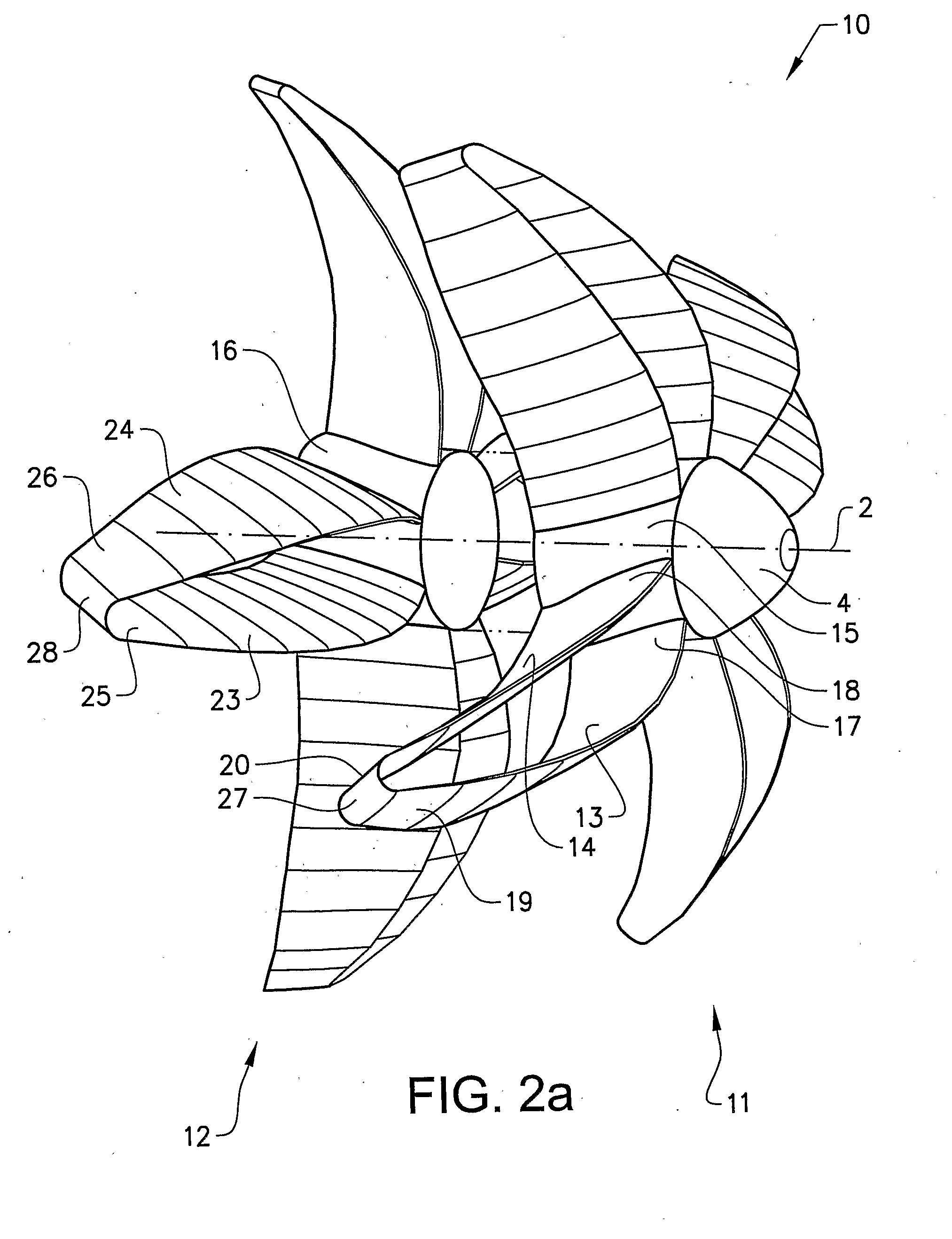
Air propeller arrangement and aircraft
InactiveUS20120288374A1Low root bend moment and tip displacementEmission reductionPropellersEfficient propulsion technologiesPropellerAirplane
An air propeller arrangement for propulsion of a fixed-wing aircraft includes a first air propeller that includes a first hub member and at least a first and a second propeller blade, the first and second blades being configured to contribute significantly to the propulsion and having a substantially equal length. Each of the blades has an inner, root end arranged at the first hub member and an outer, tip end positioned at a distance from the first hub member such that each blade extends in a radial direction from the first hub member. The first and second blades are interconnected at their outer ends. An aircraft provided with such an air propeller arrangement is also provided.
Owner:GKN AEROSPACE SWEDEN AB
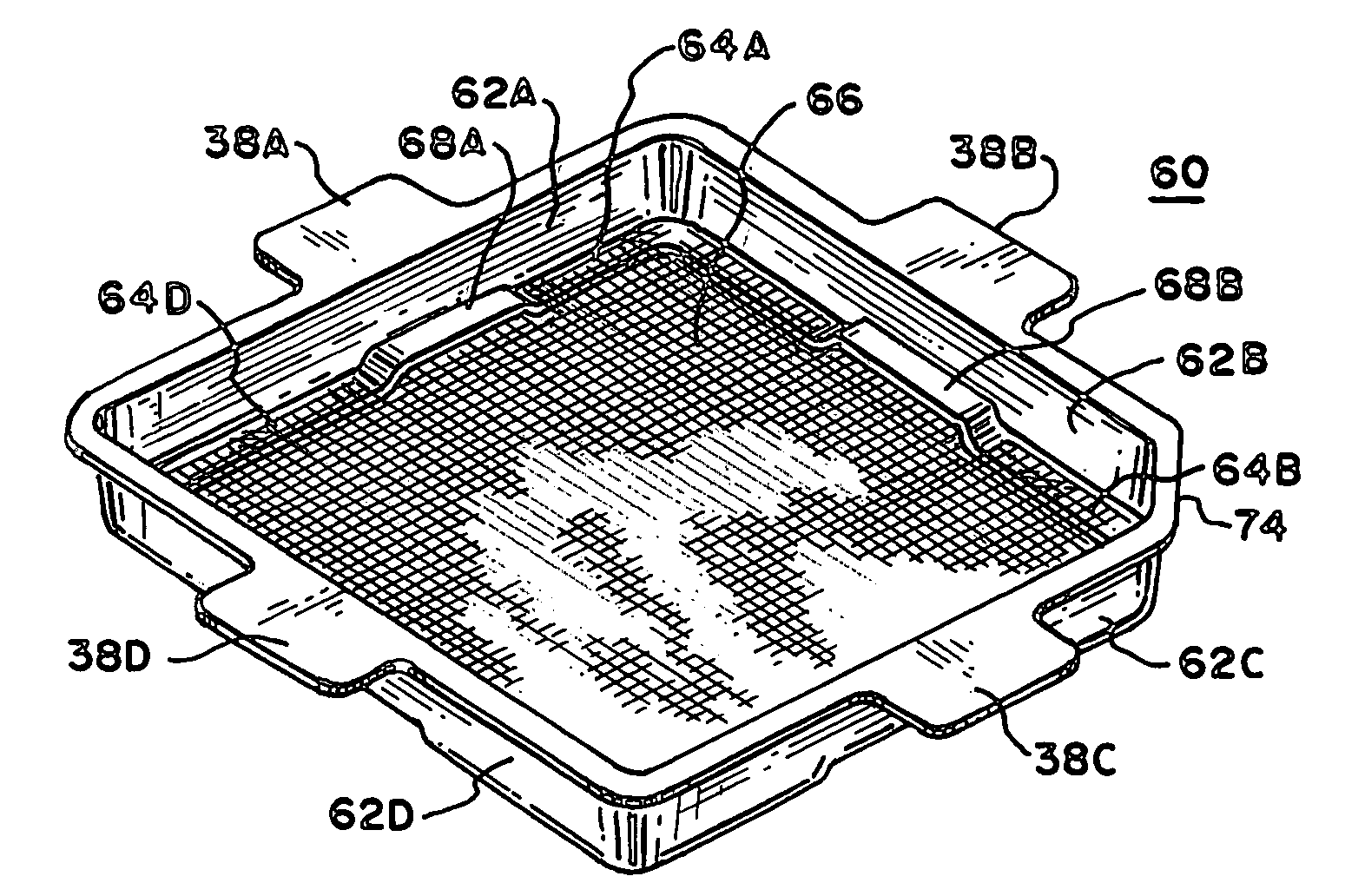
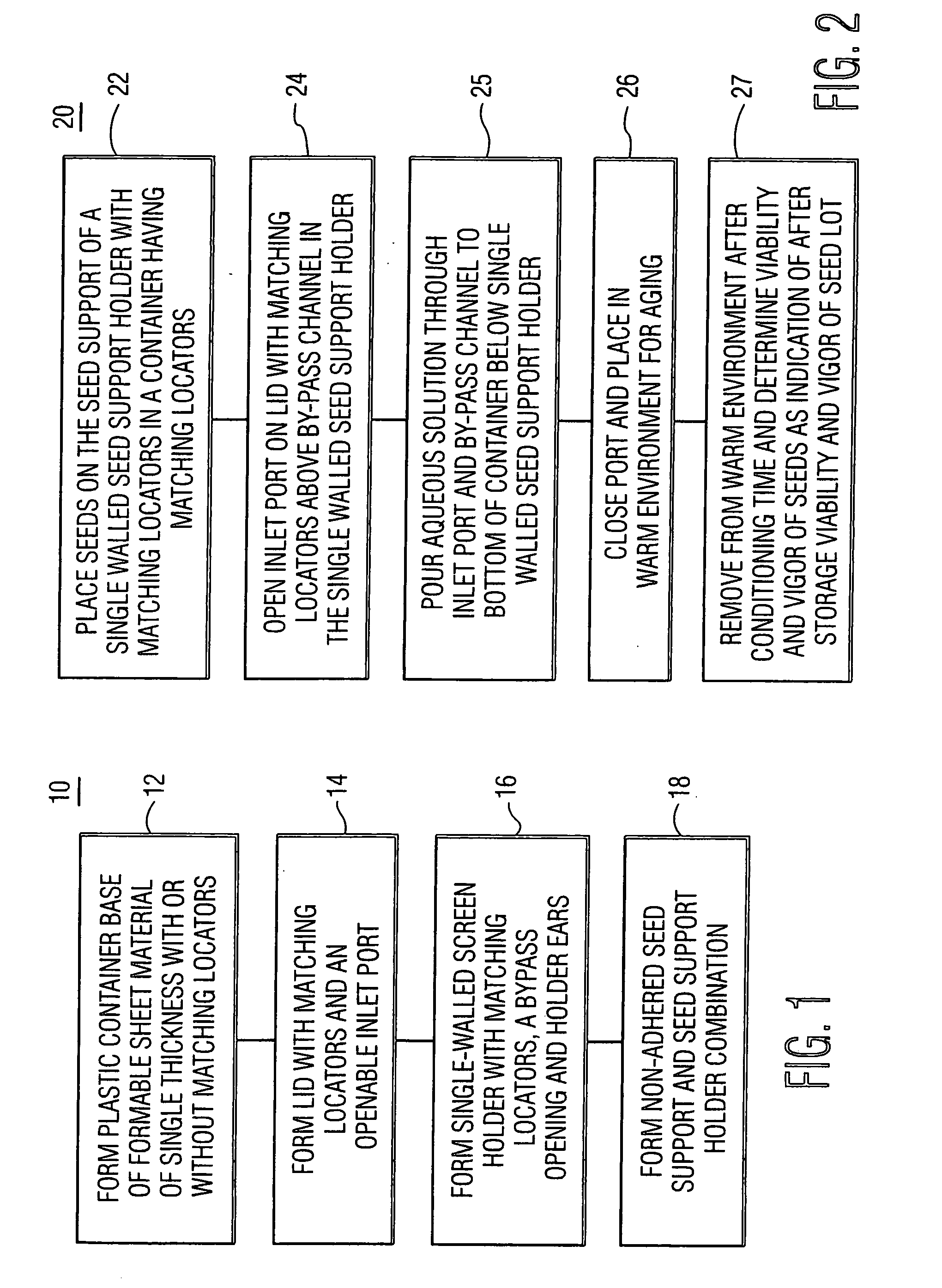
Seed testing method and apparatus
ActiveUS20090077873A1Cheap to makeDisposableAspharagus cultivationTesting plants/treesAccelerated agingEngineering
To provide an accelerated aging seed testing kit system, a single sheet of plastic or other suitable formable sheet material is pressed into the shape of a compartment base having recesses for mounting a seed holder. A seed holder that includes a seed support and a seed support holder is formed. The seed support holder is formed of a single sheet of plastic having radially extending tabs that fit into the recesses of the container to support the seed support above the bottom of the test kit. A bypass channel for addition of an aqueous solution used in the prescribed test condition is provided in the seed holder. A lid is formed out of one piece of plastic having a bendable tab to serve as a port and the openings and connecting points of the lid and seed holder are positioned so they can only fit together in one orientation having the port above the bypass channel.
Owner:KAMTERTER PROD LLC
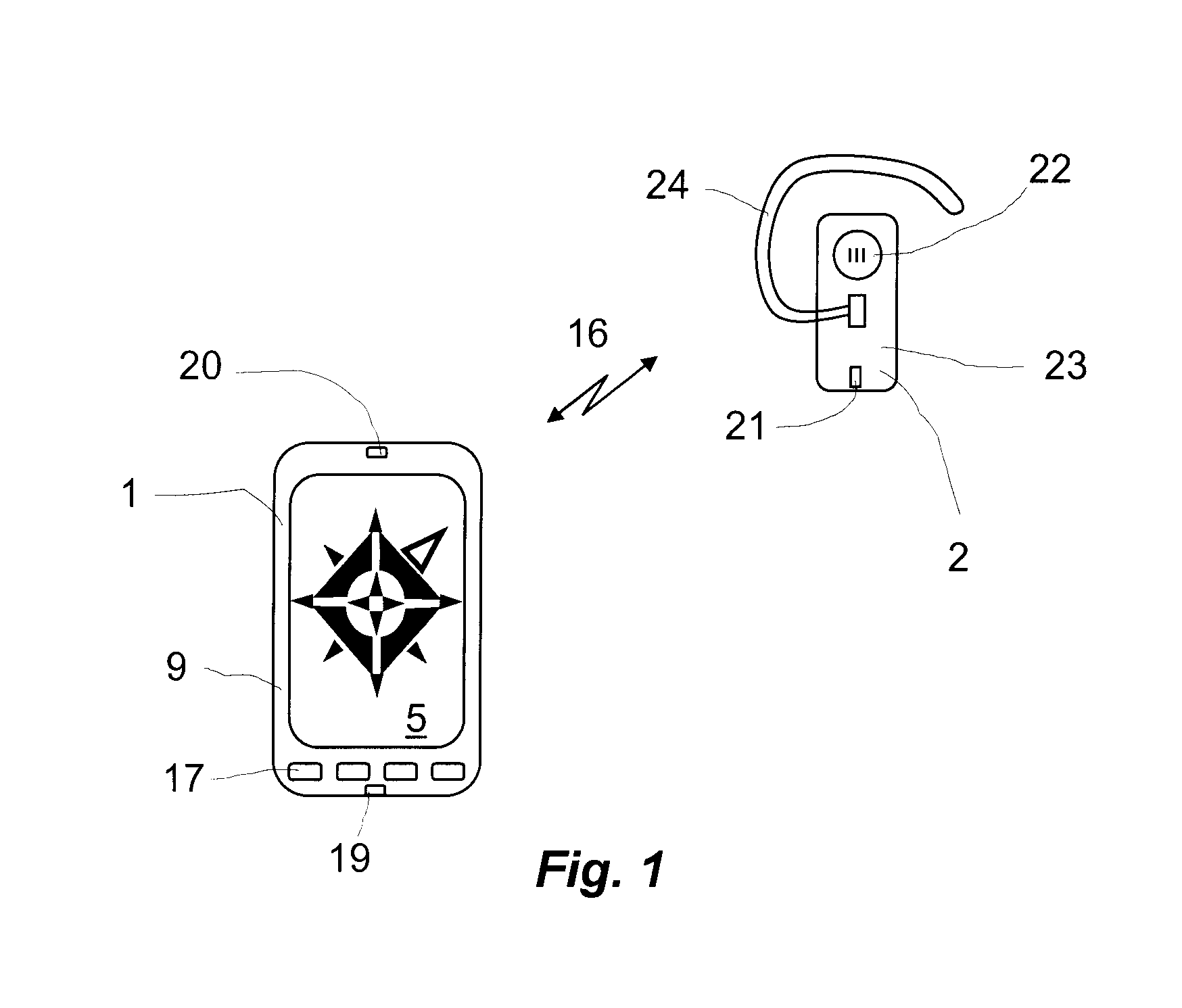
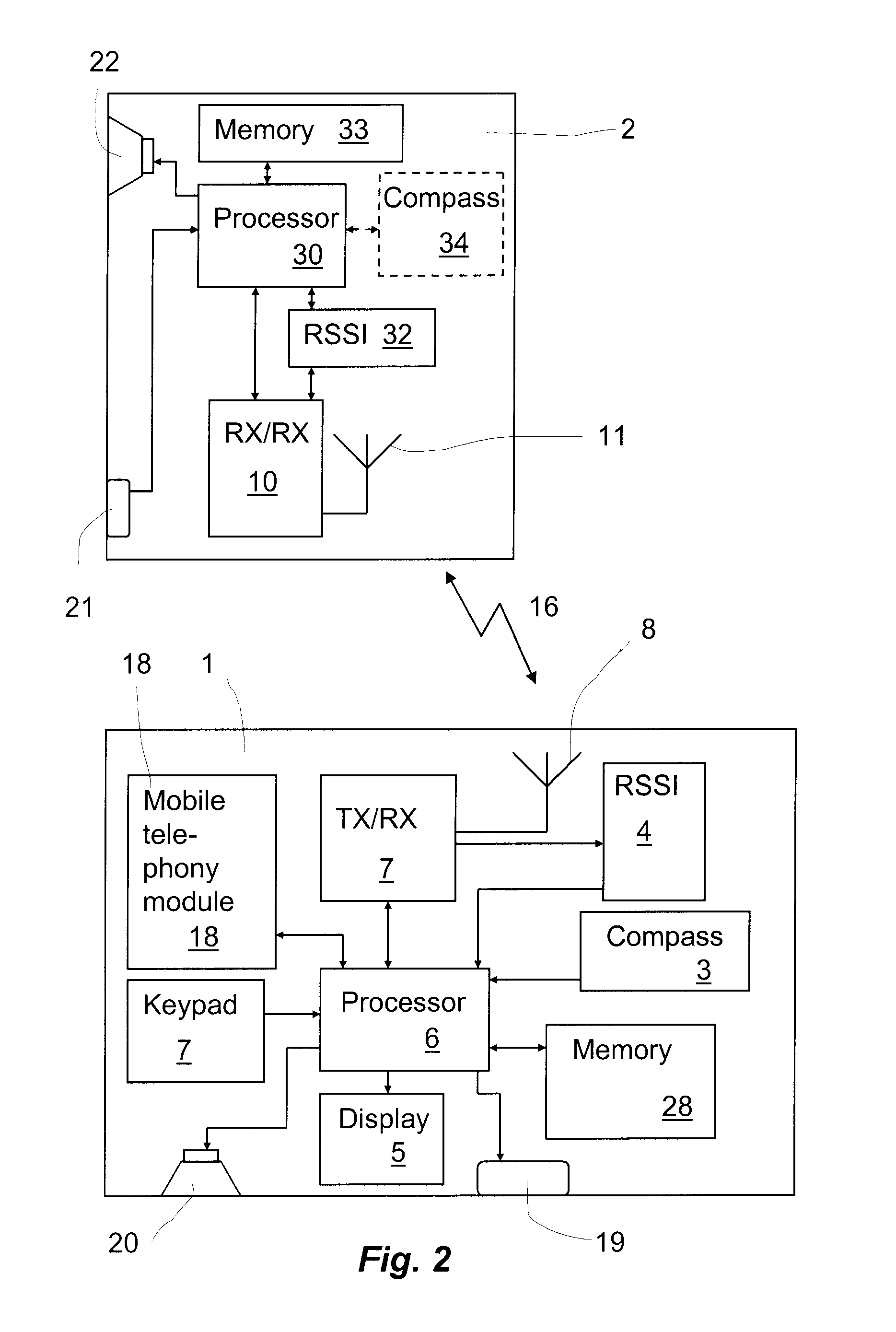
Method For Locating A Wirelessly Connected Device
InactiveUS20120088452A1Improve signal qualityAvoid excess performanceNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesTelecommunicationsConnected device
A handheld or wearable first communication device (1; 2) for locating a second handheld or wearable communication device (1; 2). The first communication device (1) is wirelessly connected to the second device (2) and comprises a processor (6), an orientation sensor (3; 34) and a readout device (5; 20; 22). The first communication device (1; 2) is adapted to store link values representing the bit error rate of the wireless link (16) between the first communication device (1; 2) and the second communication device (1; 2) as a function of the orientation of the first communication device (1; 2). The readout device (2; 20; 22) is adapted to inform the user of the specific direction (15), at which the second communication device (1; 2) is located relative to the first communication device (1,2). The invention also relates to a method of locating a second communication device and a computer program for locating a second communication device (1; 2).
Owner:GN NETCOM
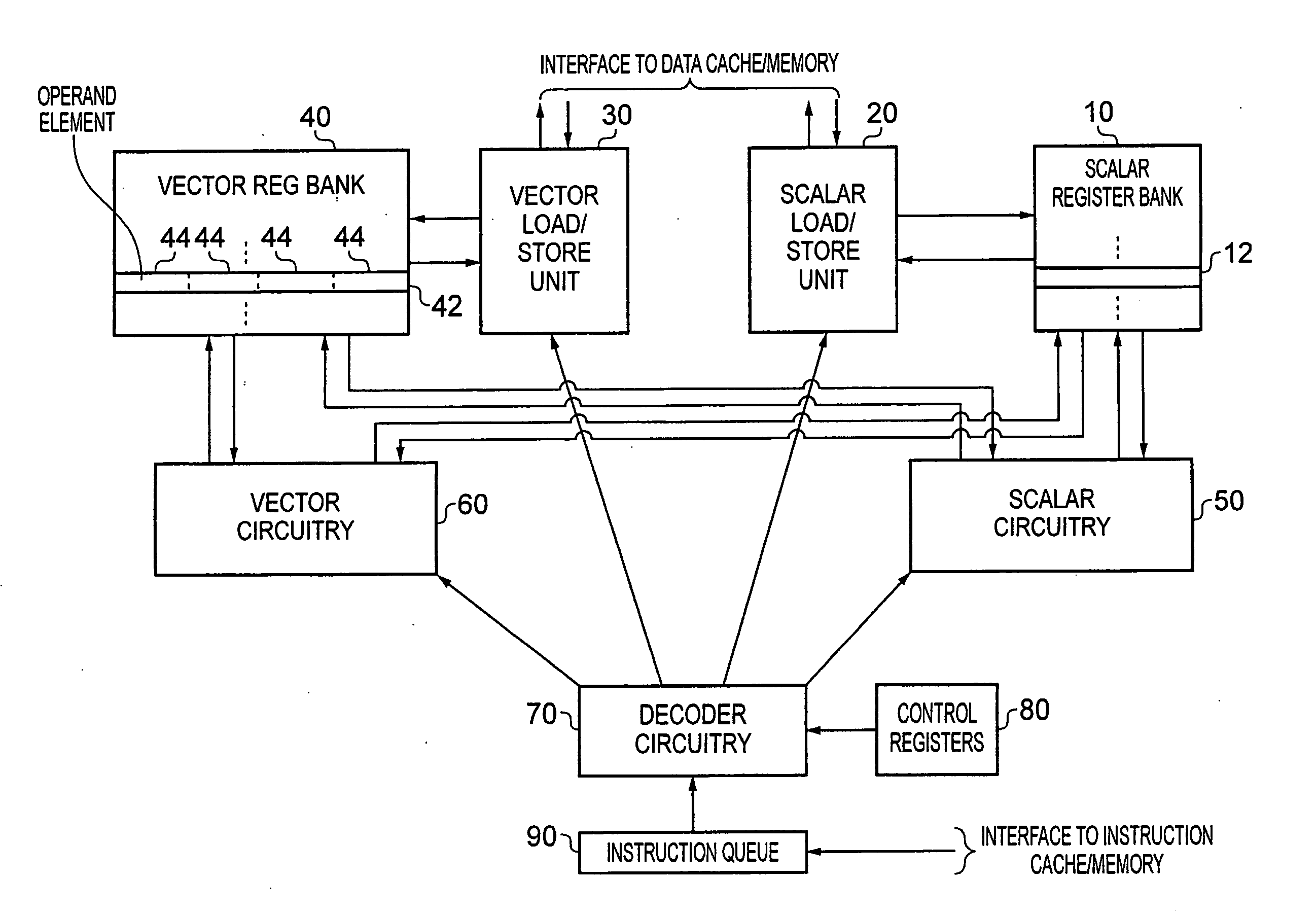
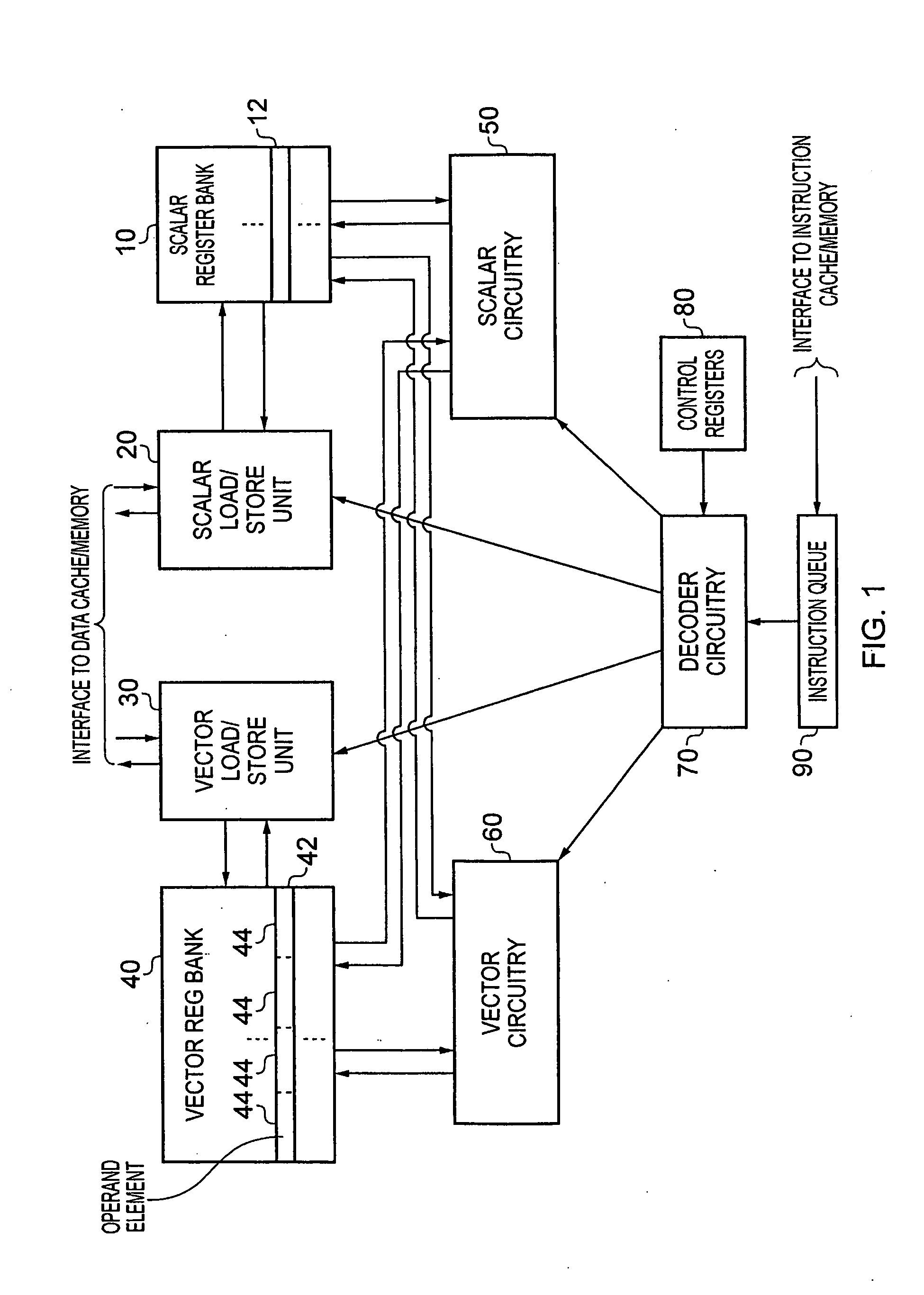
Data processing apparatus and method for performing vector operations
ActiveUS20120260061A1Improve performanceReduce pressureSingle instruction multiple data multiprocessorsRegister arrangementsControl signalOperand
A data processing apparatus having processing circuitry, a scalar register bank and a vector register bank, including decoding circuitry arranged to decode a sequence of instructions to generate control signals for the processing circuitry. The decoding circuitry is responsive to a decode modifier instruction within the sequence of instructions to alter decoding of a subsequent scalar instruction in the sequence by mapping at least one scalar operand specified by the subsequent scalar instruction to at least one vector operand in the vector register bank, and, in dependence on the scalar operation specified by the subsequent scalar instruction, determining a vector operation to be performed on at least a subset of the operand elements within the at least the one vector operand. Such an approach enables a wide variety of vector operations to be specified without the need to individually define separate vector instructions for those vector operations.
Owner:ARM LTD
Zoom lens system and camera having same
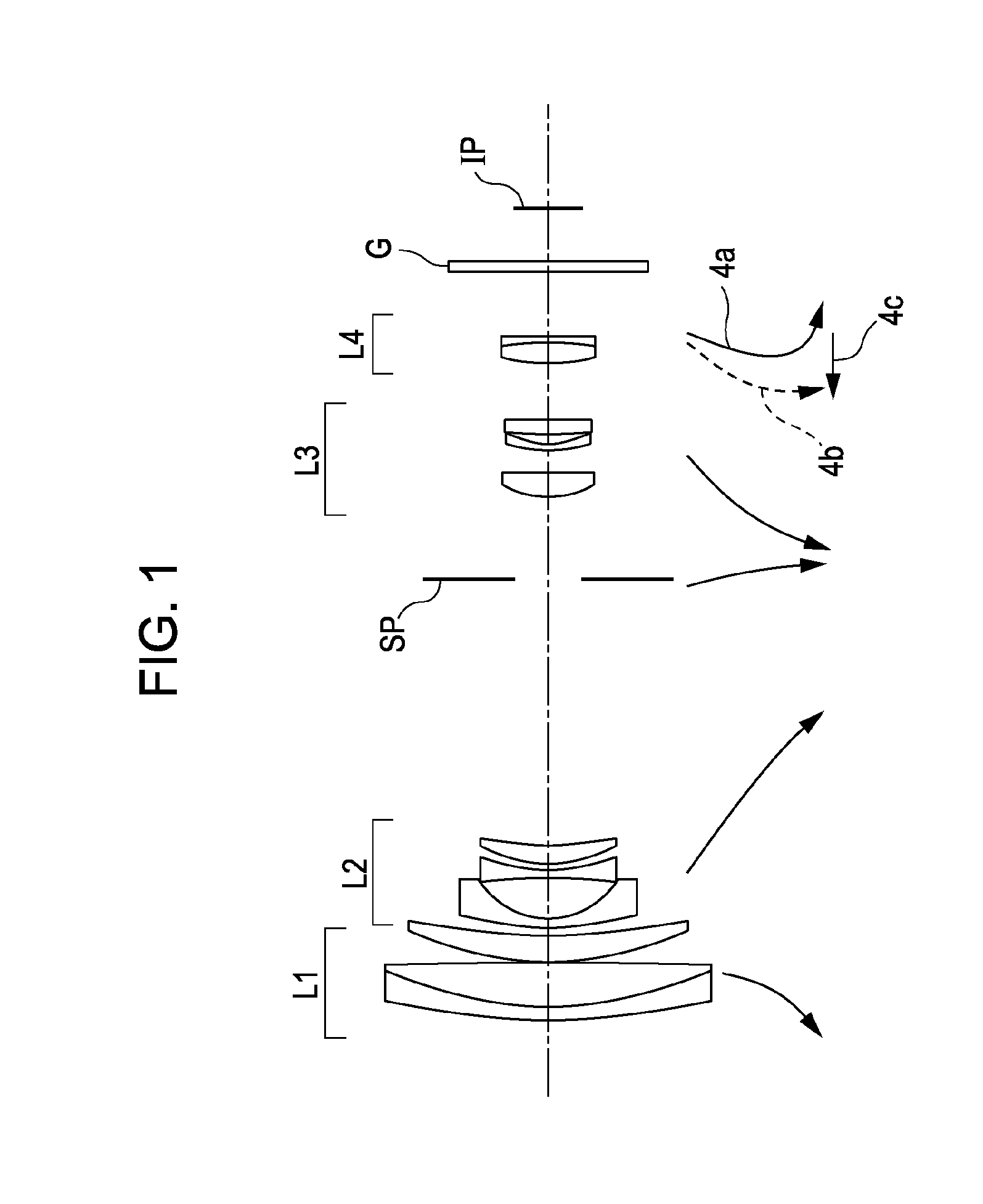
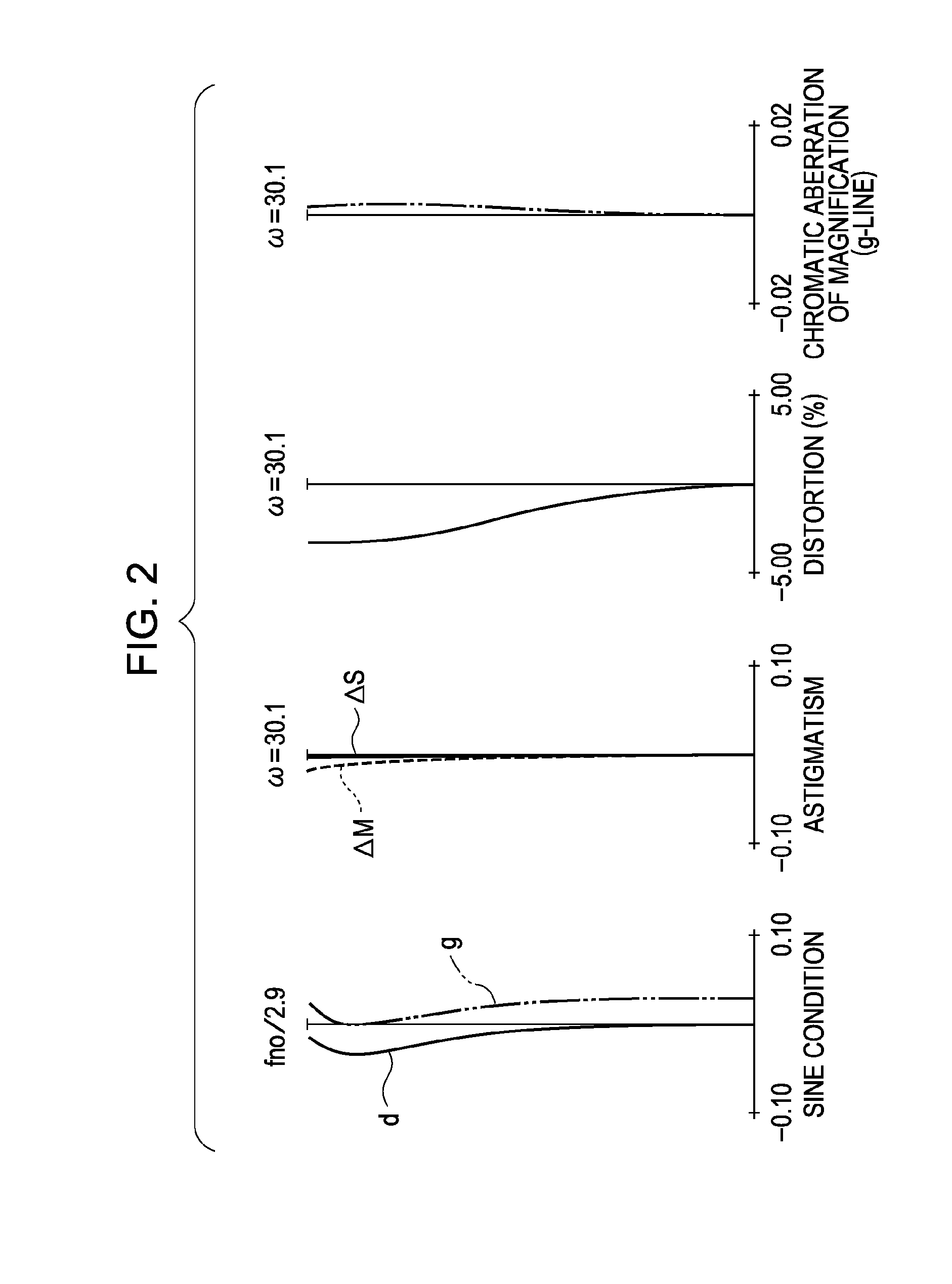
InactiveUS20080291547A1High zoom ratioAvoid excess performanceOptical elementsOptical powerMagnification
A zoom lens system includes, in order from an object side to an image side, a first lens unit having positive optical power, a second lens unit having negative optical power, a third lens unit having positive optical power, and a fourth lens unit having positive optical power. Each lens unit moves during zooming. In particular, the first lens unit moves so as to be closer to an object at a telephoto end than at a wide-angle end during zooming, and the fourth lens unit moves in a locus convex toward the object side during zooming. The sharing of magnification variation between the third lens unit and the fourth lens unit is appropriately set.
Owner:CANON KK
Silicon-carbon nanostructured composites
InactiveUS20180269480A1Avoid excess performanceGreat tendencySiliconNegative electrodesCarbon compositesLithium-ion battery
Provided herein are silicon-carbon nanostructured composites, precursors thereof, and processes for manufacturing such materials. Also provided herein are applications of such silicon-carbon composites, including uses in lithium ion batteries and anodes thereof.
Owner:AXIUM IP LLC
Data communications system with splitterless operation
InactiveUS6639911B1Improve performanceUndesirable level of noiseAutomatic exchangesOrthogonal multiplexTransceiverCommunications system
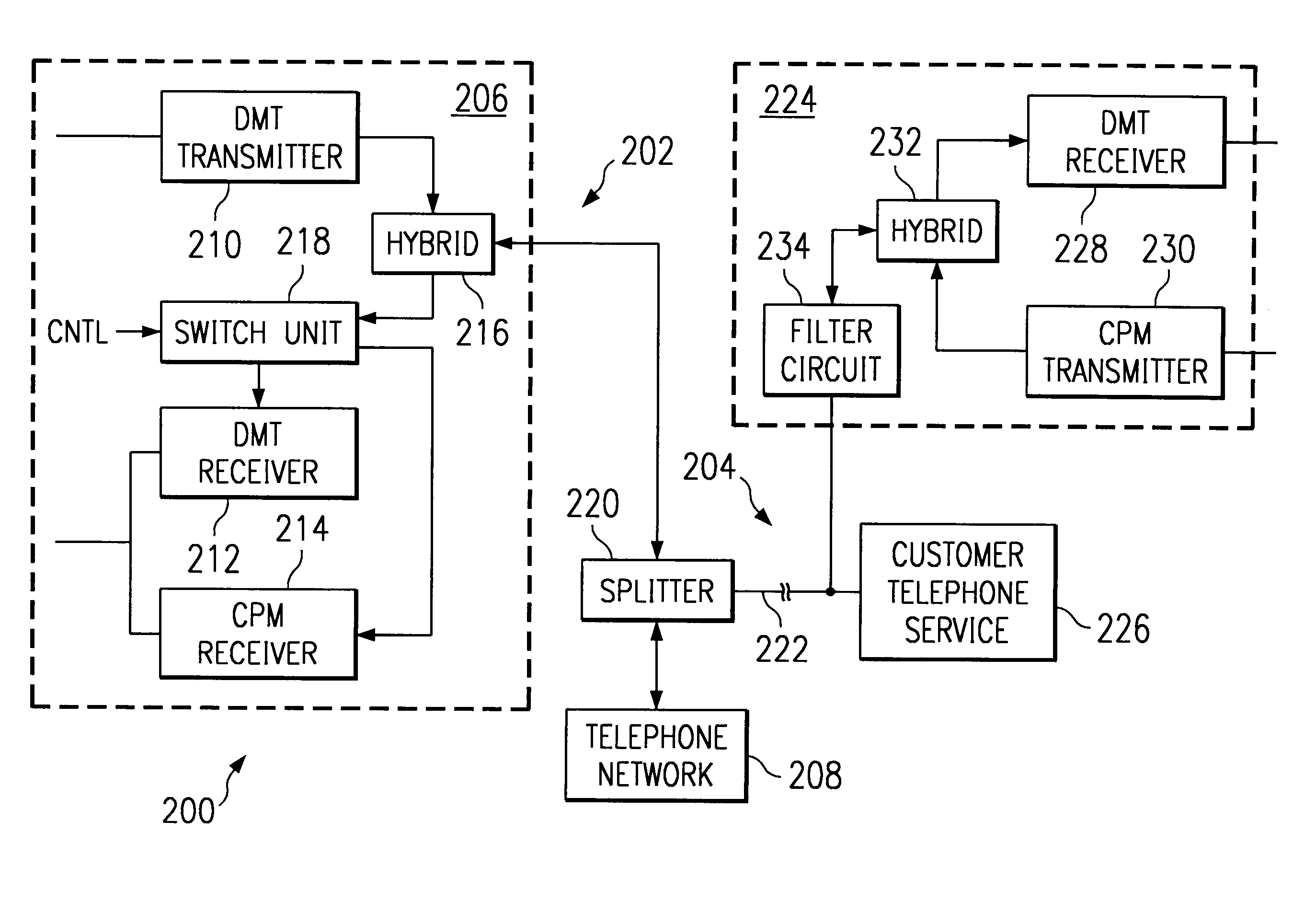
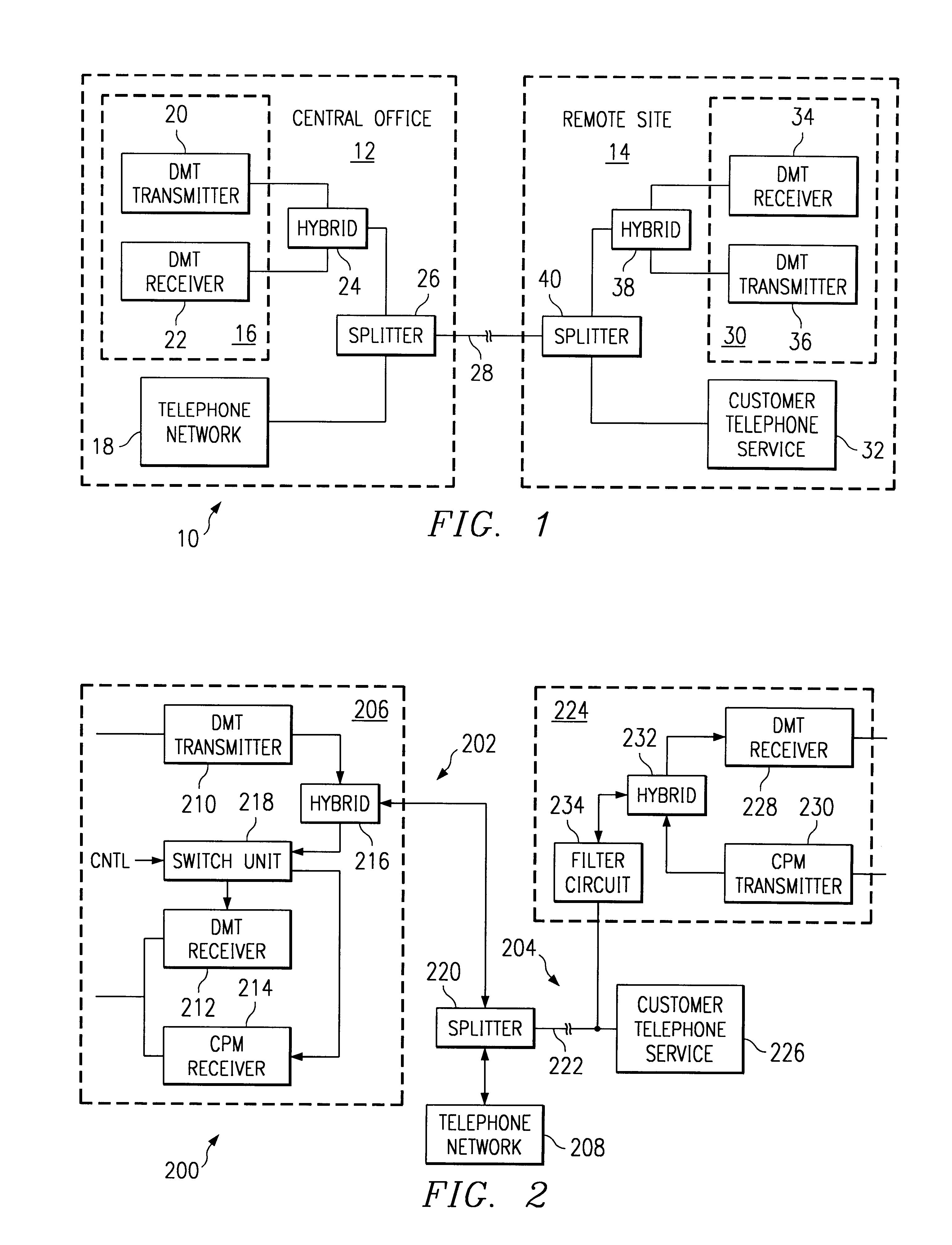
A data communication system that provides different types of service (e.g., telephone services and high-speed data transmission services) to a remote site even when the remote site lacks a splitter is disclosed. A central site (e.g., central office) is able to communicate with at least two different types of remote sites. One type of remote site includes a full splitter (i.e., both low-pass and high-pass filters), and the other type of remote site has only a partial splitter (i.e., includes high-pass filter but lacks a low-pass filter). Although conventionally the transceivers (e.g., ADSL transceivers) at these remote sites would be of the same design and use the same modulation technique for upstream as for downstream transmissions, here the remote site that lacks a low-pass filter (i.e., partial splitter type remote site) uses a different modulation technique for upstream transmissions. As an example, in a data communication system where a remote site lacks a complete splitter, a high peak-average-ratio (PAR) technique like discrete multi-tone (DMT) can be used with downstream transmissions that do not lead to noise at the telephone service even in the splitterless design, and a lower PAR technique (e.g., CPM, QAM, FSK, etc.) can be used with upstream transmissions so that the noise levels produced at the telephone service are vastly reduced. The central site is able to communicate with both the different types of remote sites. The central site selects from various receiver units depending on the type of modulation (e.g., low PAR technique) used.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
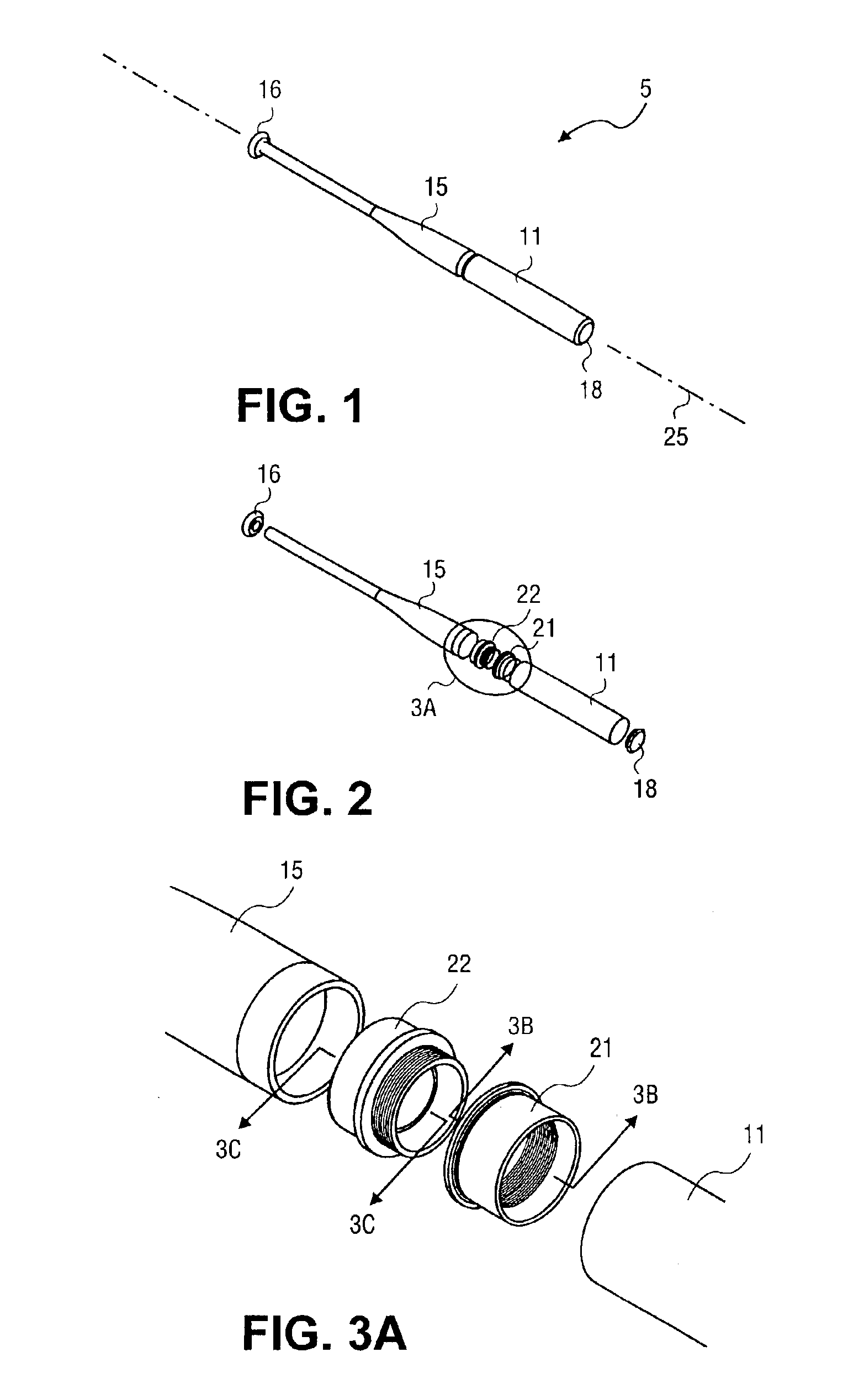
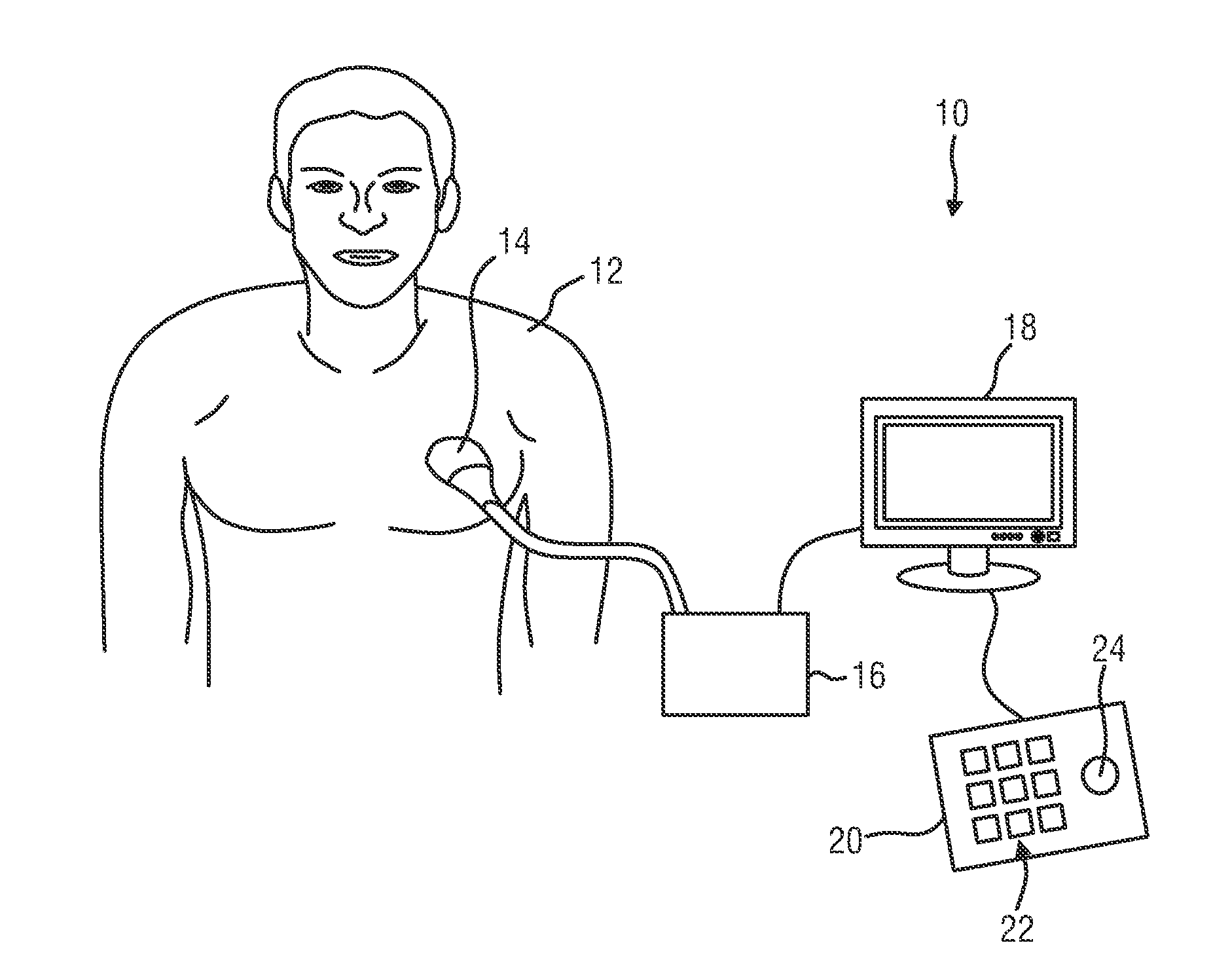
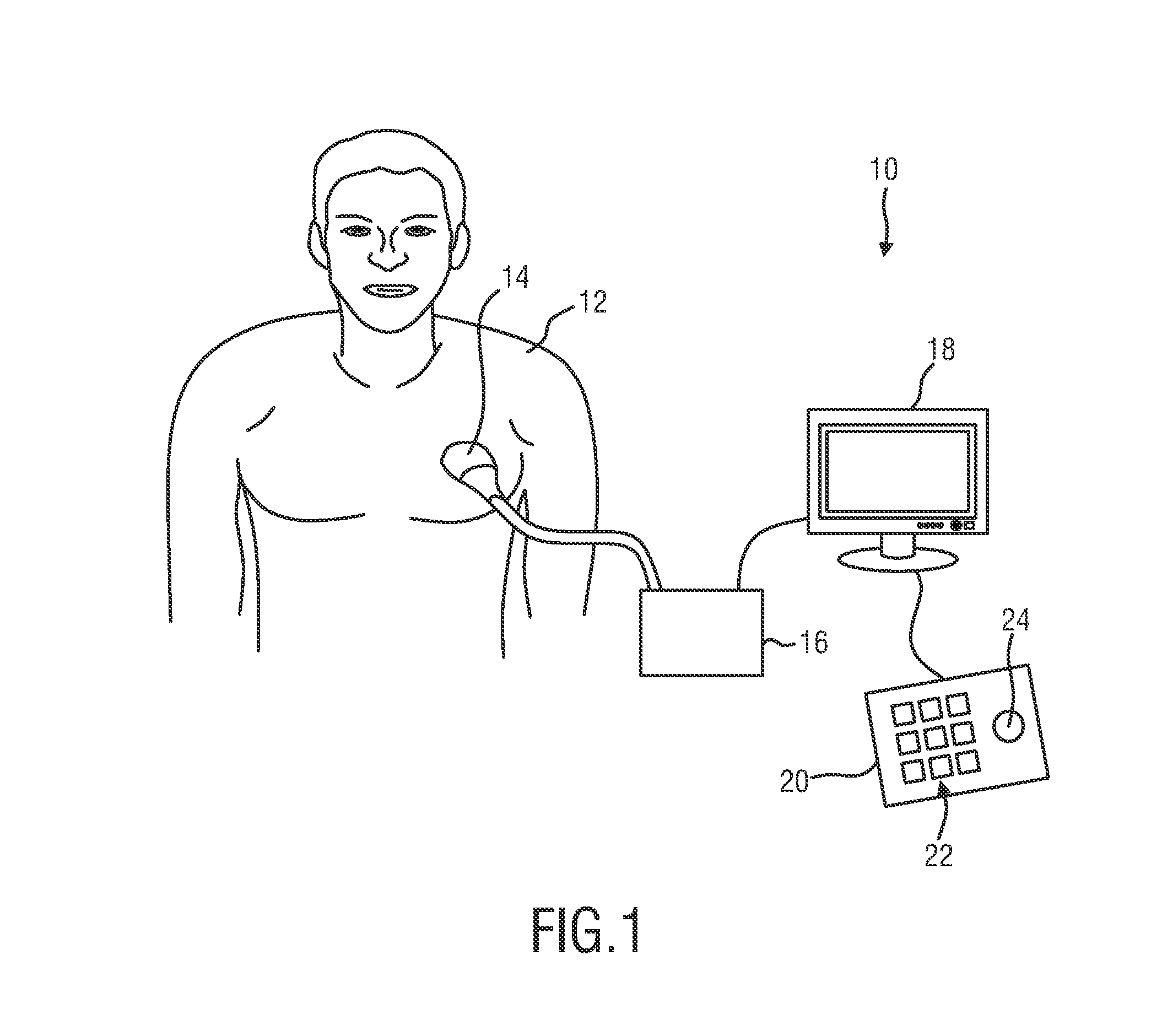
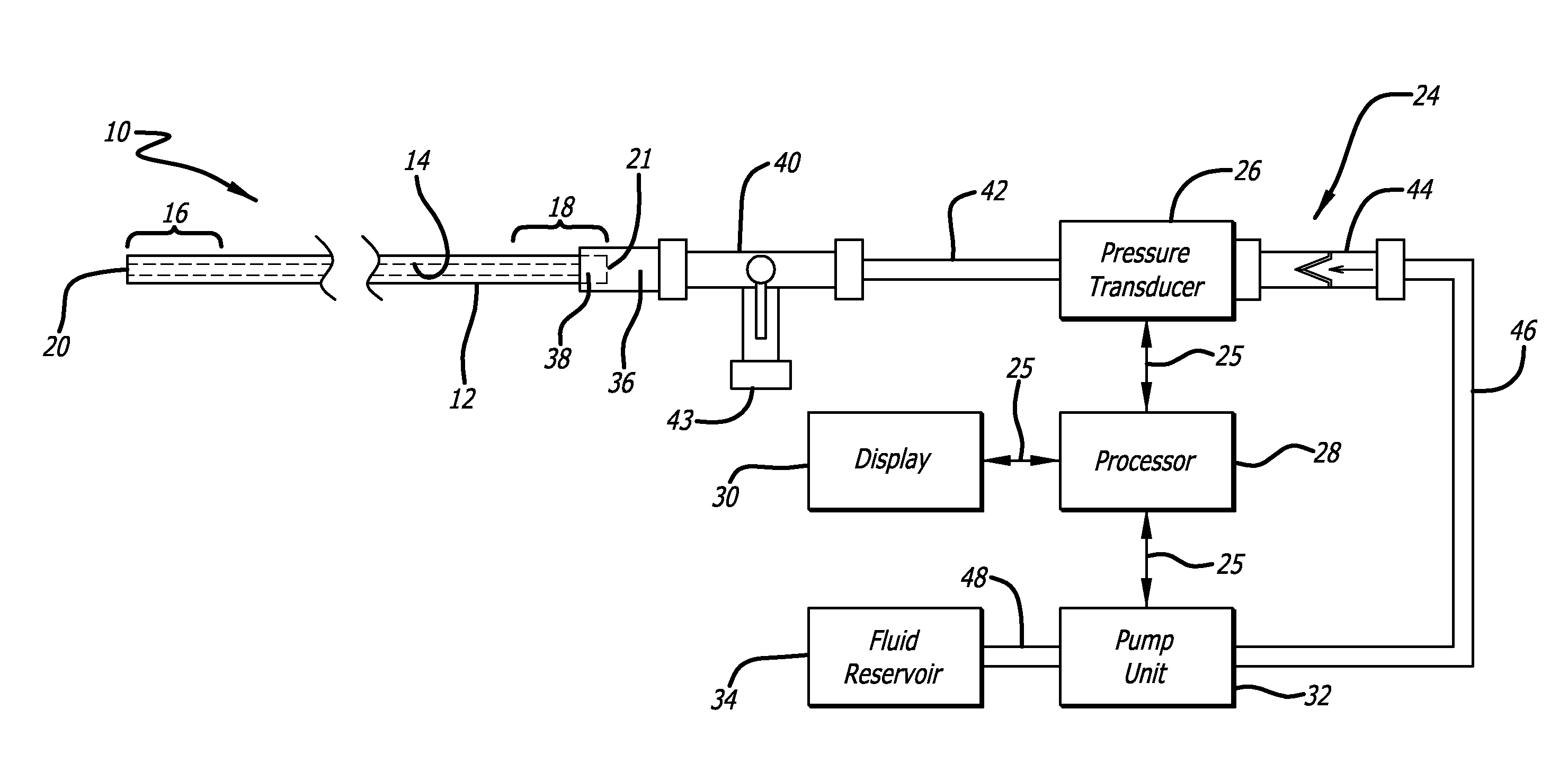
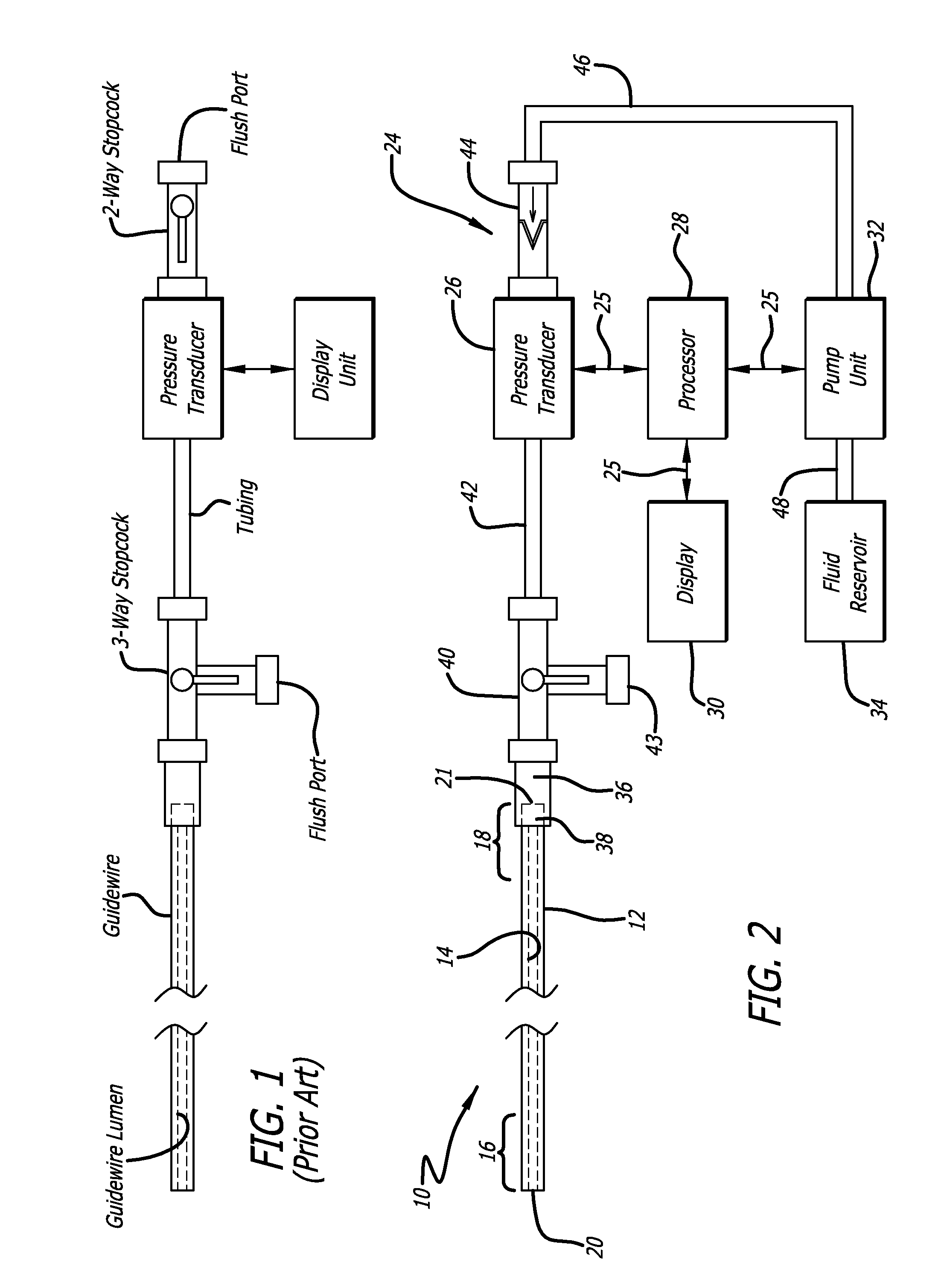
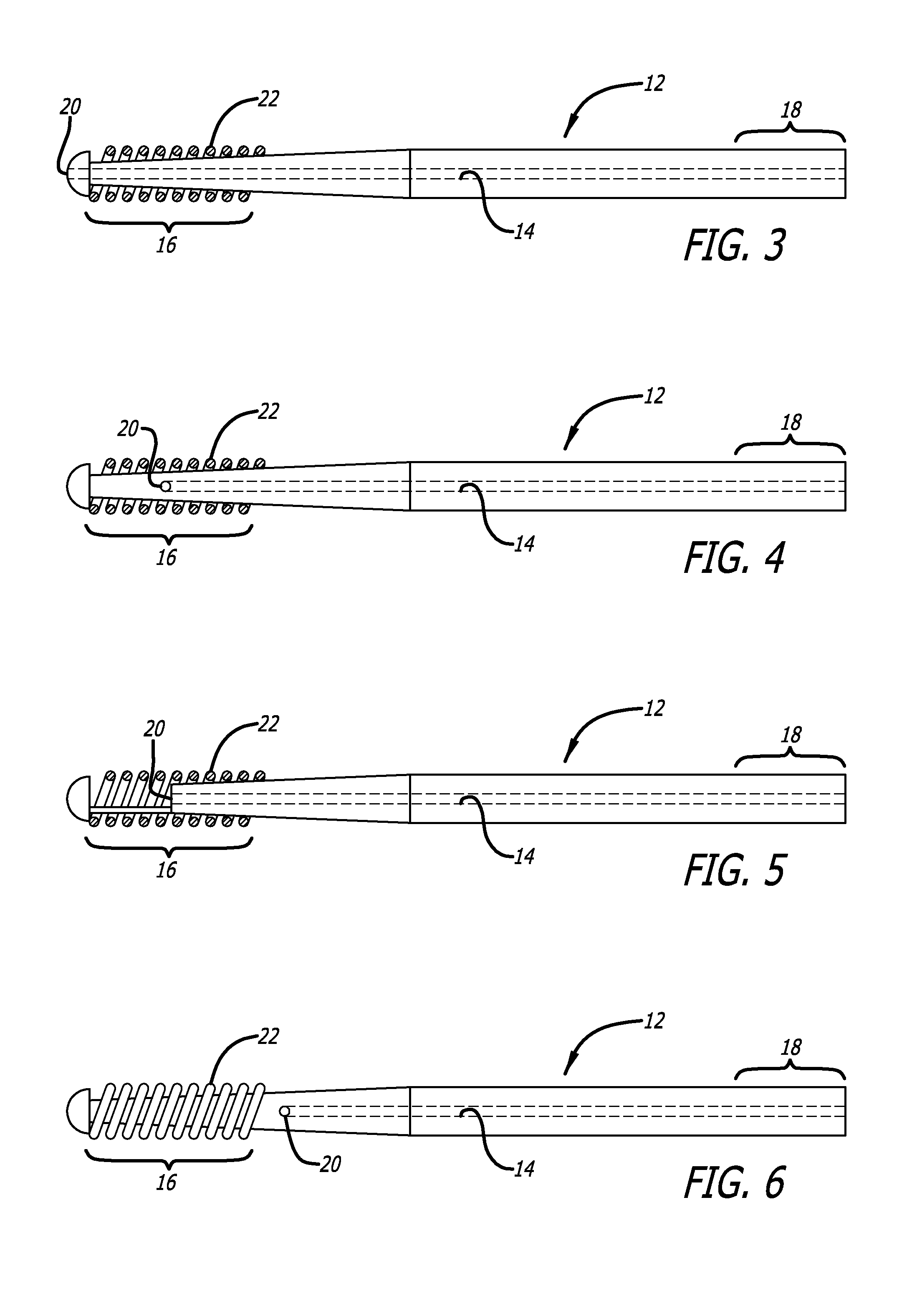
Lumen based pressure measurement guide wire system for measuring pressure in a body lumen
InactiveUS20150112210A1Accurate measurementAvoid clotsCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringBiomedical engineeringTransducer
A medical system utilizes a guide wire with a fluid filled internal lumen and a pressure measurement system to measure blood pressure in a body vessel. The guide wire includes an internal lumen with a distal opening for admitting fluid flow. The internal lumen is filled with a fluid or other media which can transmit pressure along the guide wire. The pressure measurement system includes a pressure transducer in fluid communication with the internal lumen of the guide wire. Pressure waveform in the body vessel are transmitted through the fluid or media from the distal opening of the internal lumen to the pressure transducer. The pressure transducer is in communication with a processor (with display) for determining the pressure acting on the pressure transducer. A pump with a fluid reservoir in fluid communication with the internal lumen of the guide wire is controlled by the processor. The pump introduces additional fluid into the guide wire lumen.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Electrically-Conductive Laminated Film, Touch Panel Electrode Plate, Touch Panel, and Pressure-Sensitive Adhesive for Use in Electrically-Conductive Laminated Film
InactiveUS20080213583A1High solubility parameterLess to adhesive performanceConductive layers on insulating-supportsSynthetic resin layered productsSkin appearanceMeth-
An electrically-conductive laminated film of the invention comprises a first transparent substrate having first and second surfaces; an electrically-conductive film comprising a second transparent substrate having first and second surfaces and a transparent electrically-conductive thin layer provided on the first surface of the second transparent substrate; and a pressure-sensitive adhesive layer, wherein the first transparent substrate and the electrically-conductive film are arranged in such a manner that the second surface of the first transparent substrate is opposed to the second surface of the second transparent substrate, wherein the first transparent substrate and the electrically-conductive film are bonded to each other with the pressure-sensitive adhesive layer interposed therebetween; wherein each of the first and second transparent substrates is formed of a plastic material, wherein the pressure-sensitive adhesive layer is formed of a pressure-sensitive adhesive comprising an acrylic polymer comprising 1 to 35% by weight of a methyl (meth)acrylate monomer unit, 60 to 98% by weight of an alkyl (meth)acrylate monomer unit having an alkyl group of 2 to 12 carbon atoms, and 0.1 to 10% by weight of a functional group-containing monomer unit. The electrically-conductive laminated film can suppress to become the pressure-sensitive adhesive layer a pear skin appearance.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
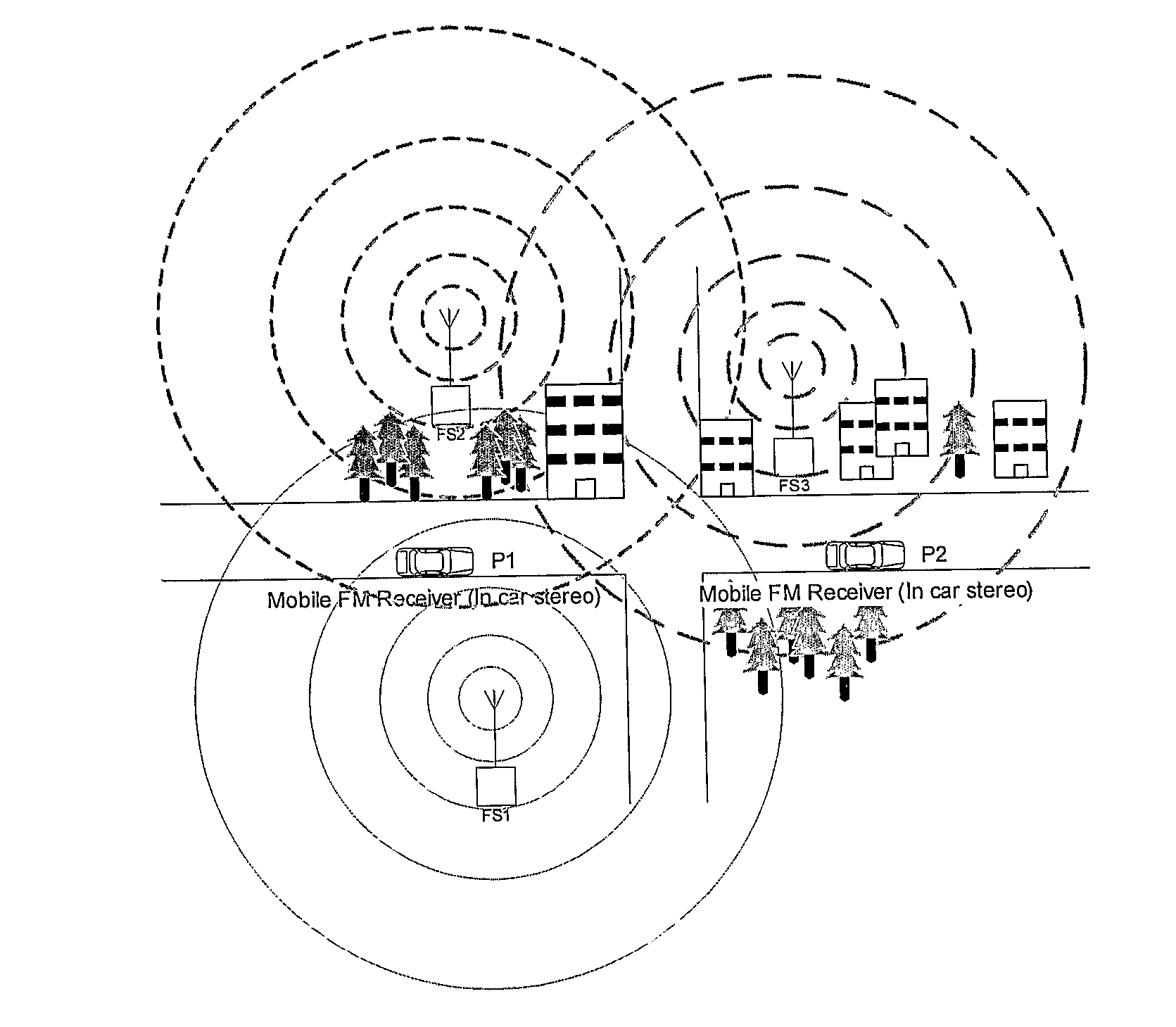
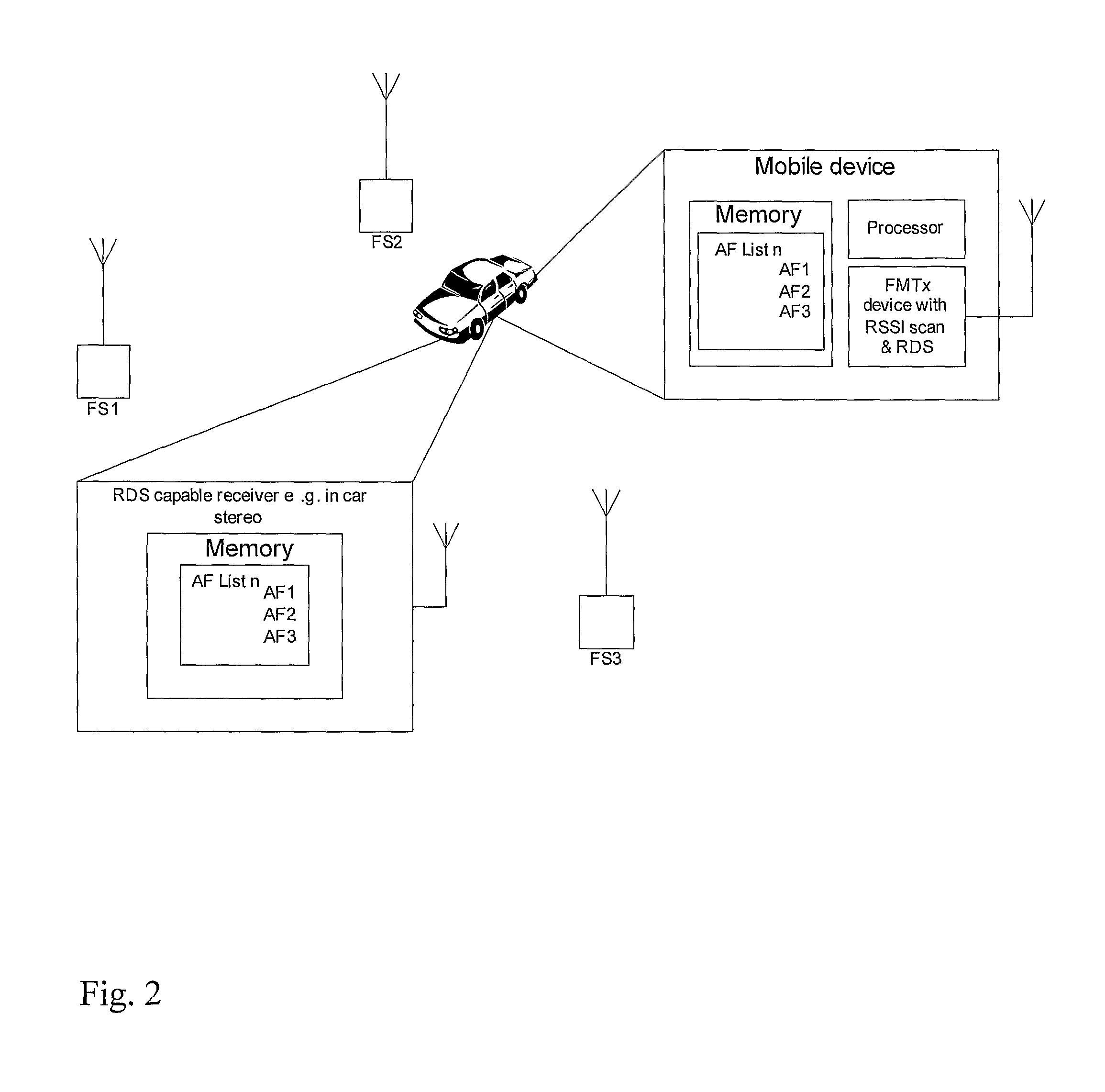
Seamless Handover of Radio Broadcasts
InactiveUS20100285732A1Avoid excess performanceBroadcast specific applicationsBroadcast transmission systemsRadiotransmitterRadio frequency
The invention provides a method for broadcasting via radio transmission, comprising the steps broadcasting data on a first radio frequency, transmitting an indication of a second frequency via said broadcast on said first frequency, establishing a synchronous second broadcast of said data on said second frequency, and discontinuing transmission of said broadcast on said first frequency. Also provided is an electronic device for broadcasting via radio transmission, comprising a receiver adapted for scanning a plurality of radio frequencies, at least first and second radio transmitters, a controller adapted for detecting available radio frequencies on which no interfering broadcasts or signals are currently received using said receiver, selecting a first detected available frequency, establishing a broadcast of data on said first frequency using said first transmitter, selecting a second detected available frequency, transmitting an indication of said second frequency via said broadcast on said first transmitter, establishing a synchronous second broadcast of said data on said second frequency using said second transmitter, and discontinuing the transmission on said first transmitter.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
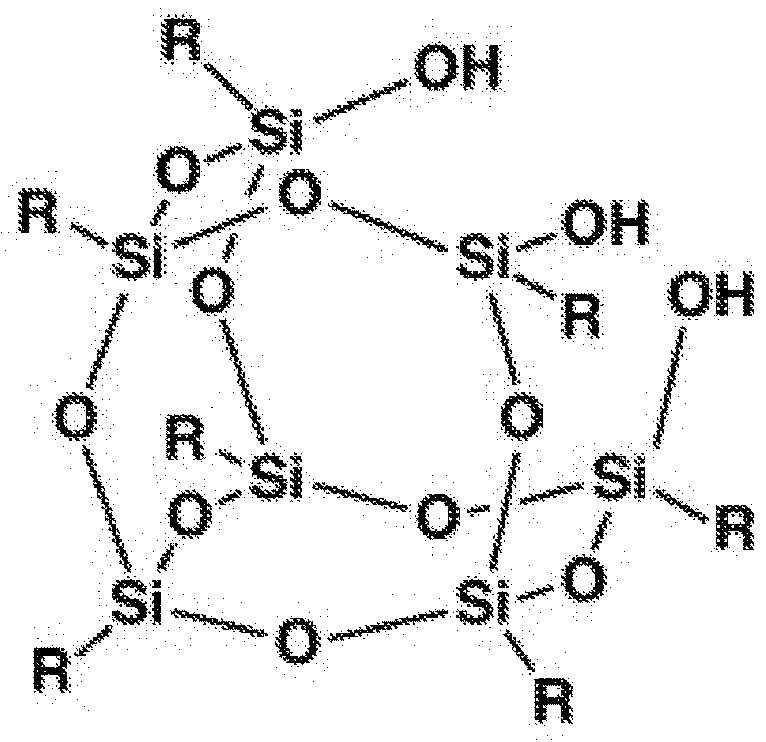
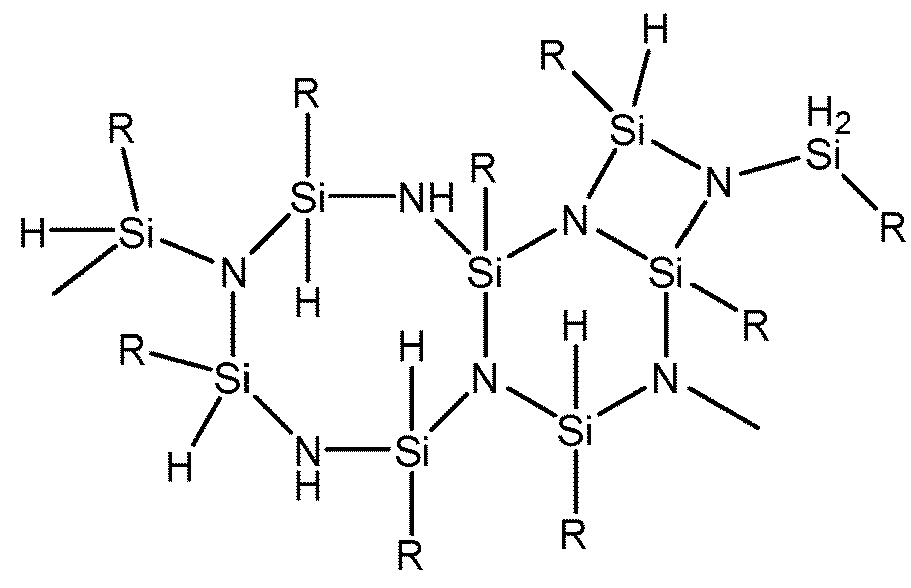
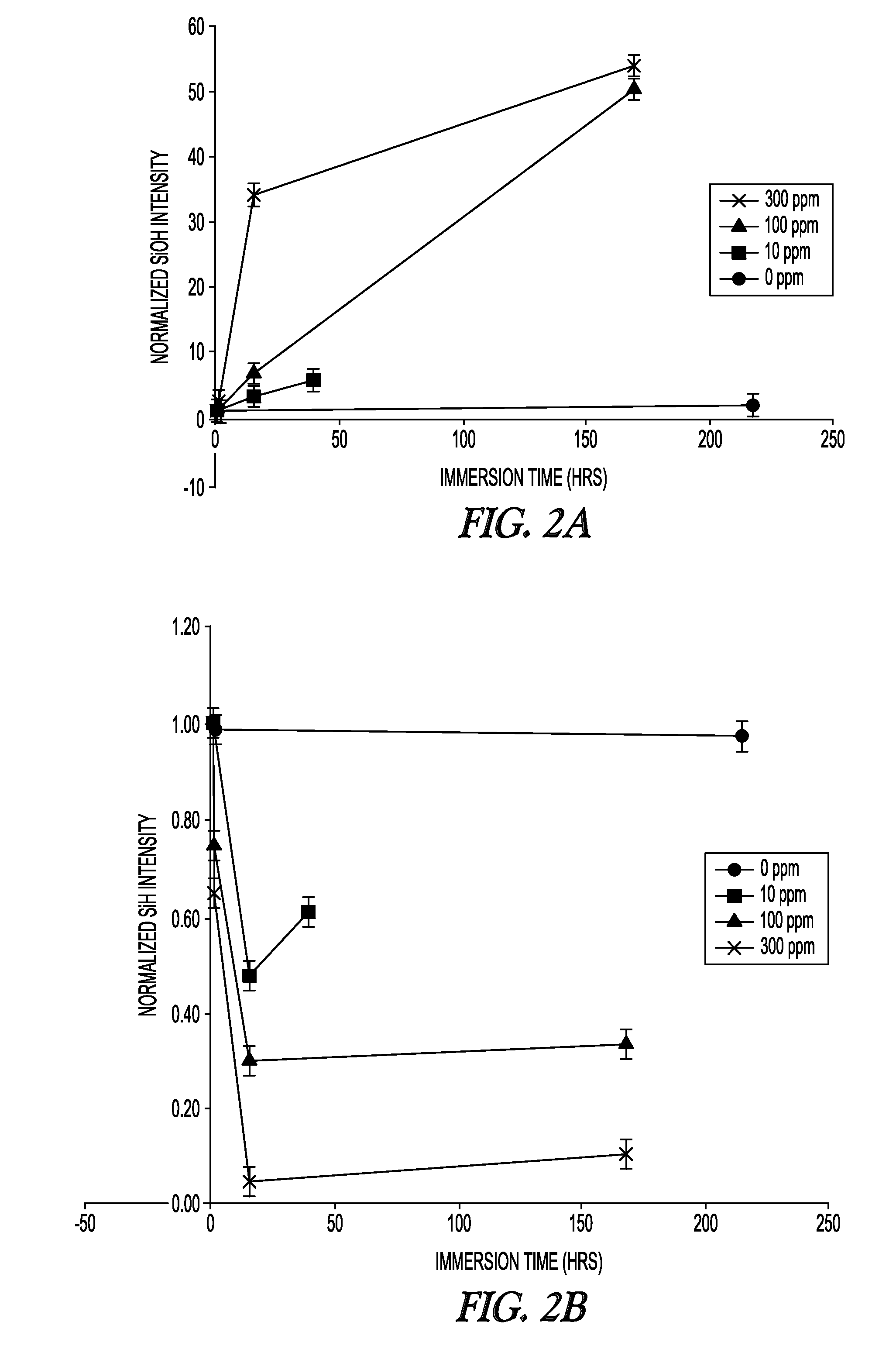
Organopolysiloxane compositions and surface modification of cured silicone elastomers
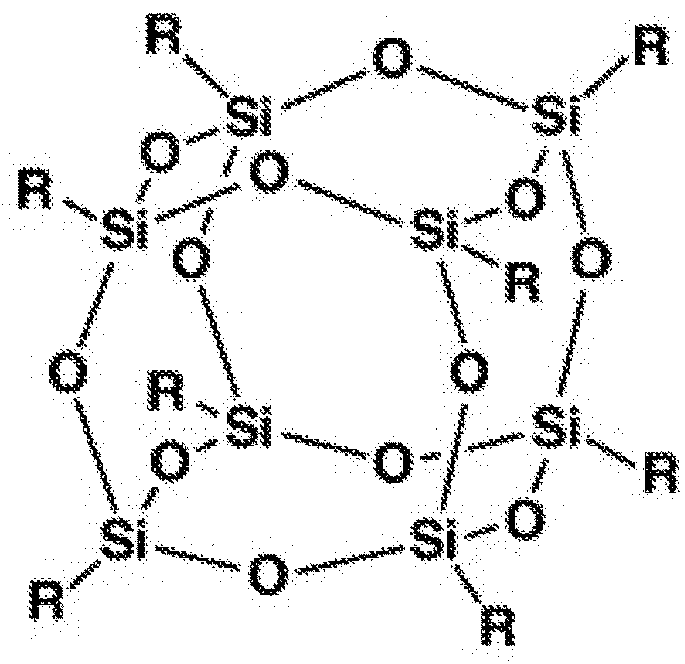
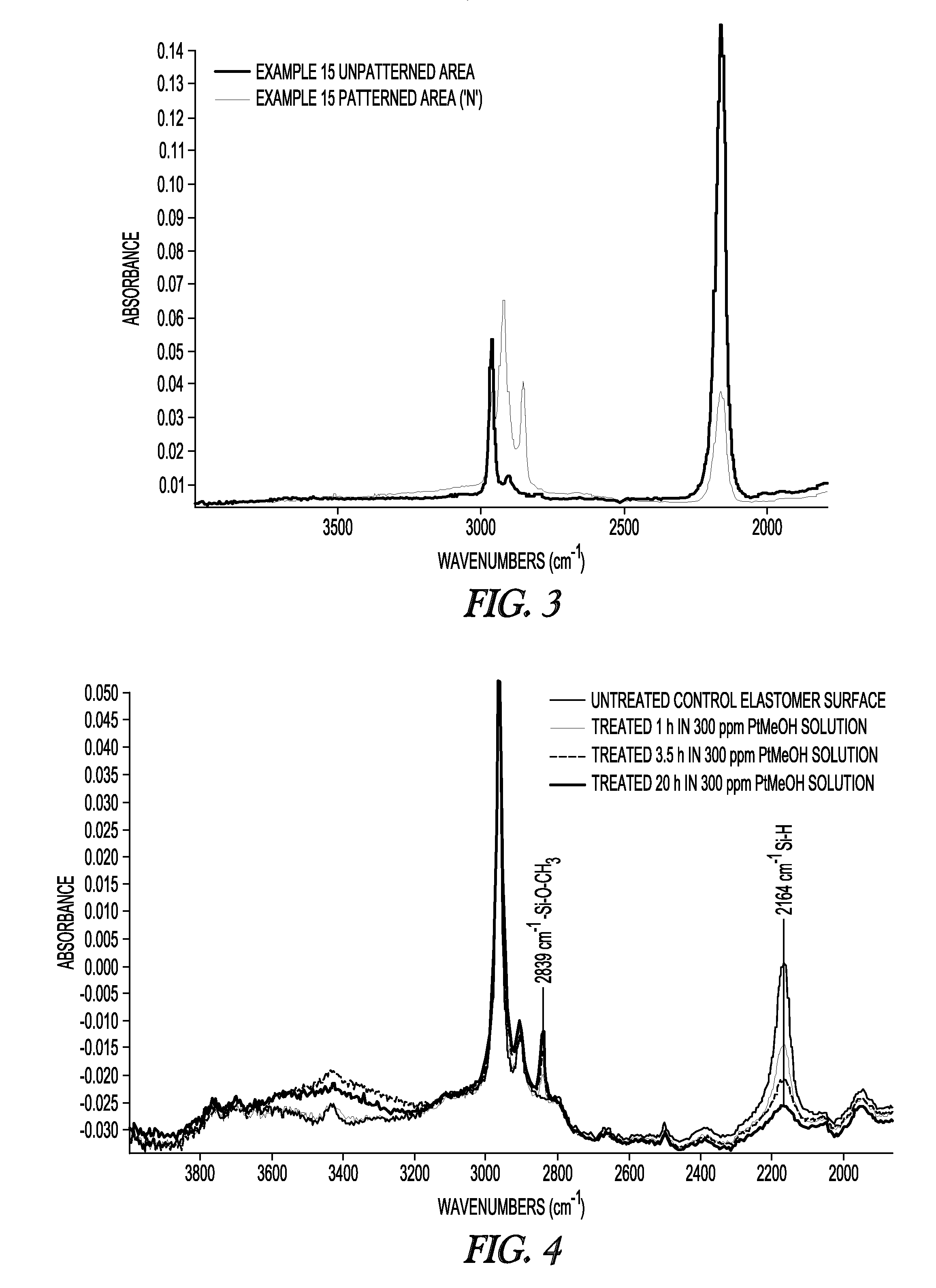
InactiveUS20140322519A1Improve hydrophilicityAmenable to patterningSemi-permeable membranesMembranesPolymer sciencePtru catalyst
The present invention relates to a method of treating a surface comprising a silicone elastomer having a plurality of Si—H groups by contacting at least one region of the surface with a solution comprising a surface treatment compound, to give a treated surface with Si—OH, Si—OR, or Si—C groups. The present invention relates to a hydrosilylation-curable silicone composition. In some examples, the hydrosilylation-curable silicone composition includes an organohydrogen-polysiloxane having an average of at least forty silicon-bonded hydrogen atoms per molecule, a cross-linking agent having an average of at least two aliphatic unsaturated carbon-carbon bonds per molecule, and a hydrosilylation catalyst, wherein the mole ratio of silicon-bonded hydrogen atoms in the composition to aliphatic unsaturated carbon-carbon bonds in the composition is at least 20:1. The invention also relates to membranes, methods of making membranes, gas permeable supports for membranes, and methods of gas separation using membranes.
Owner:DOW CORNING CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com