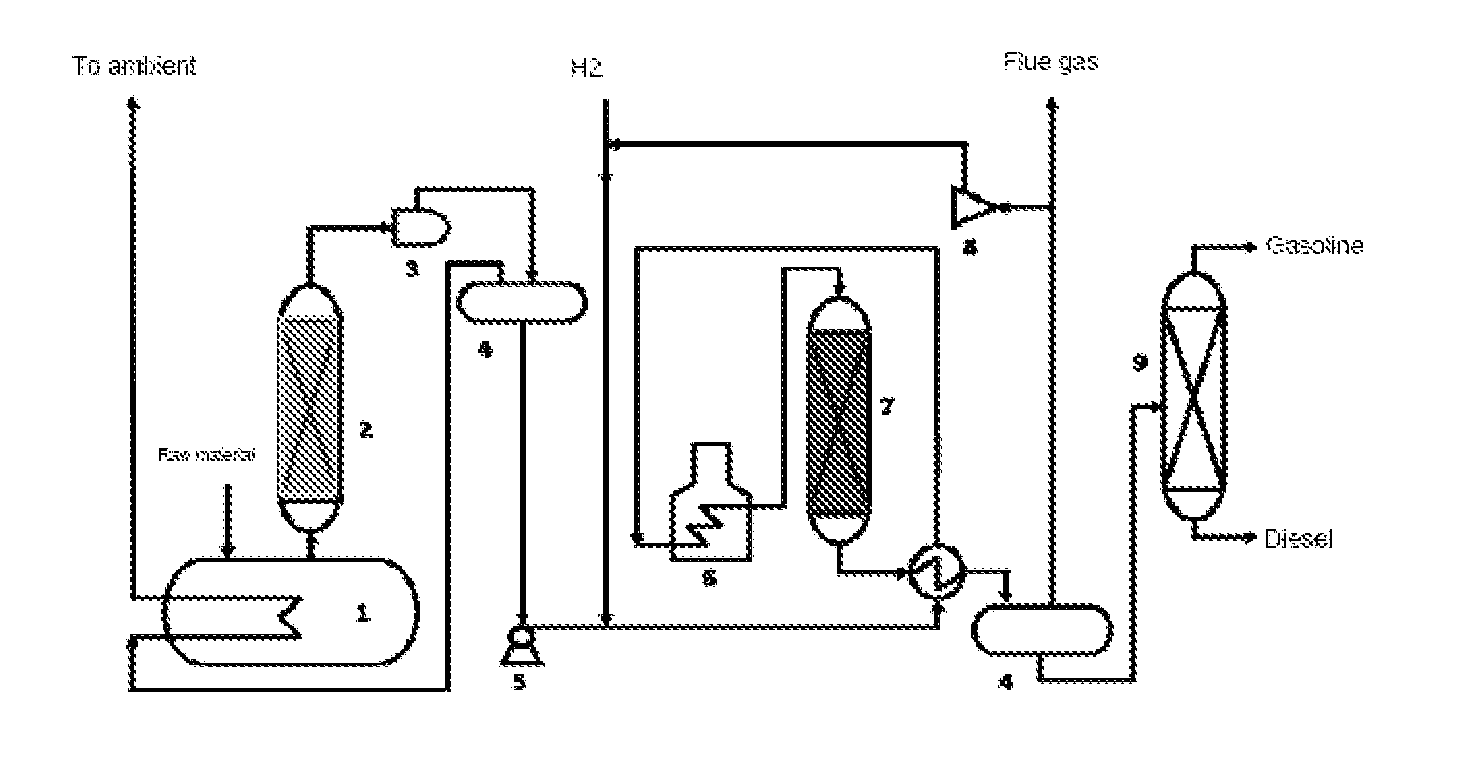
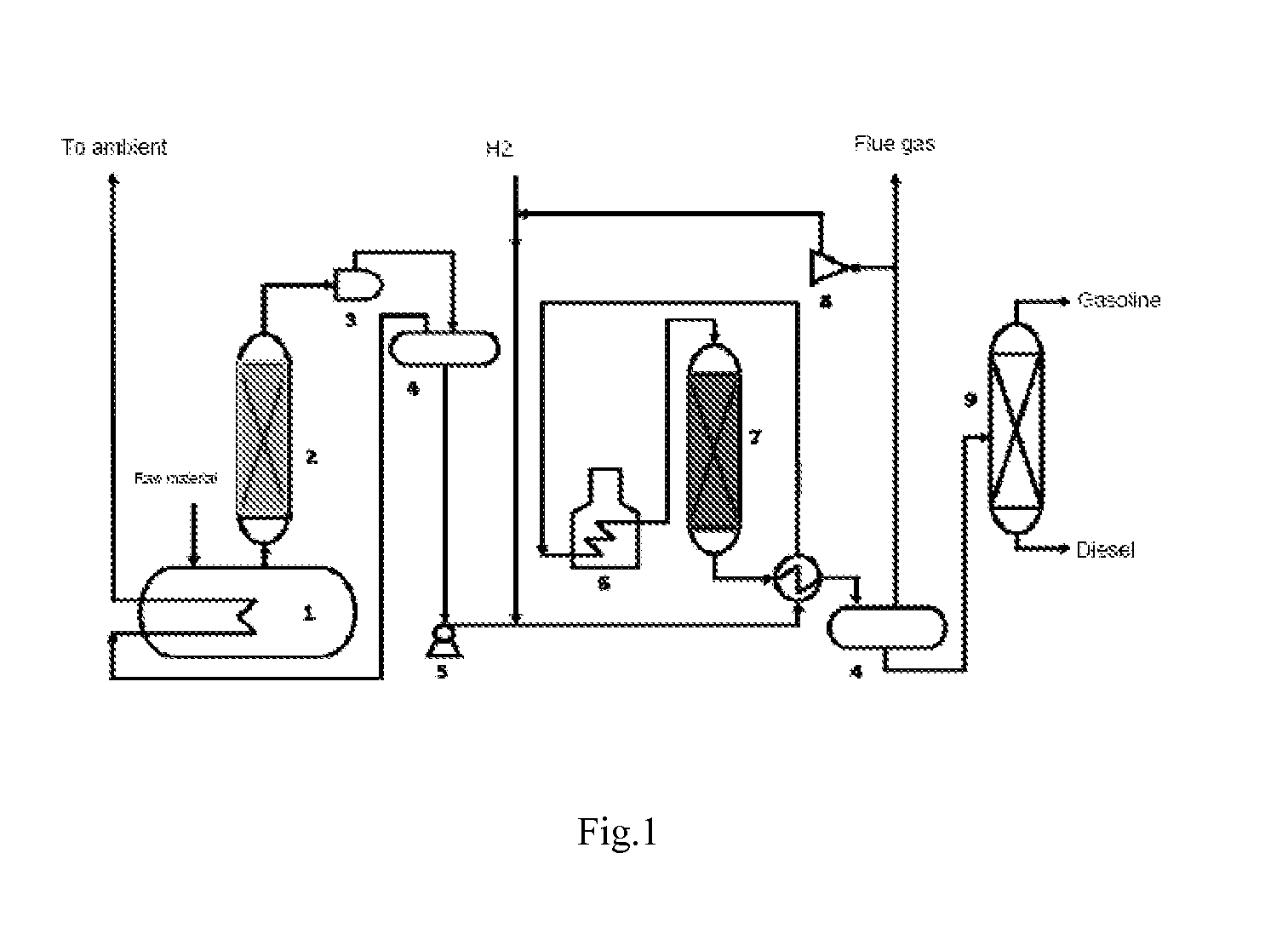
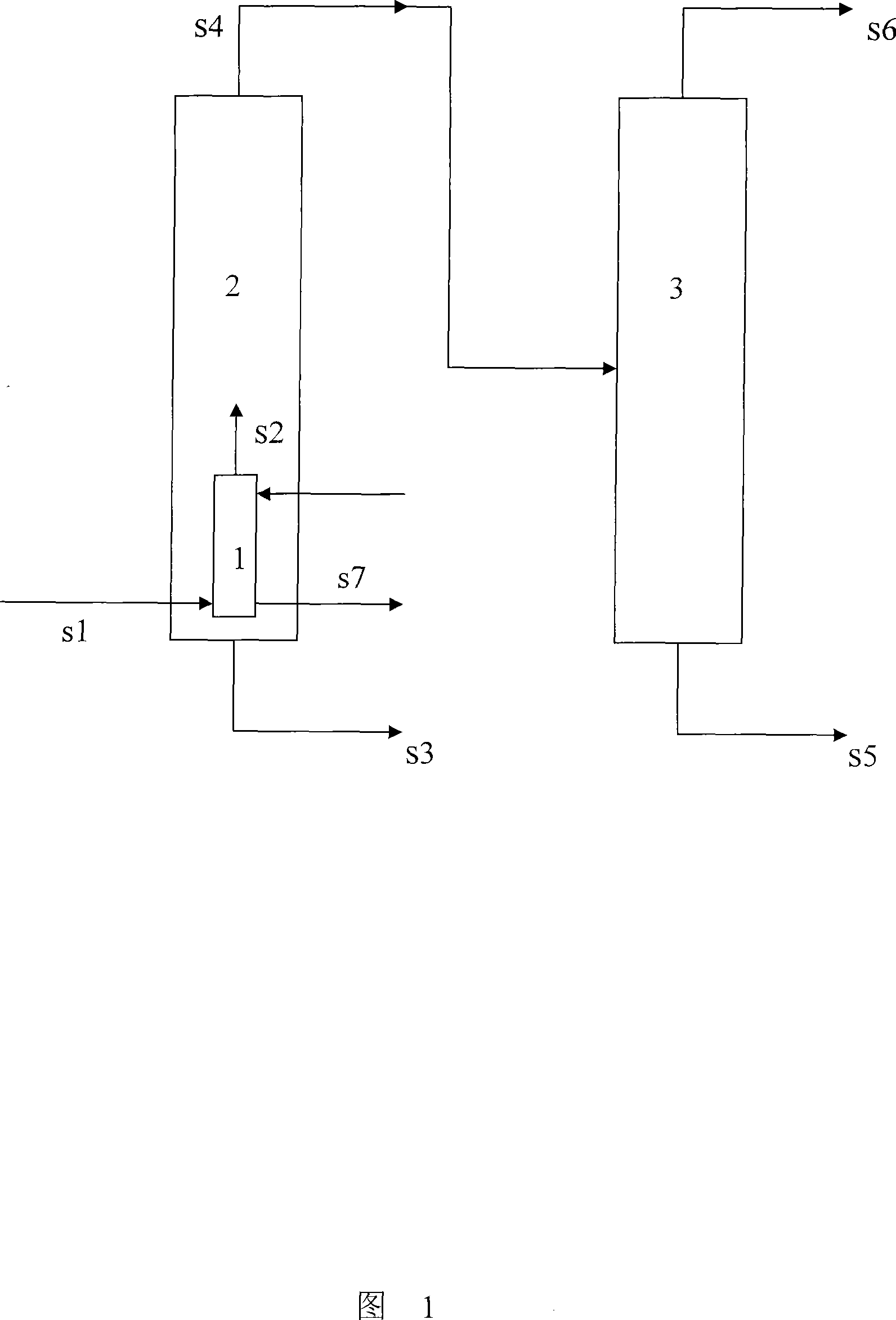
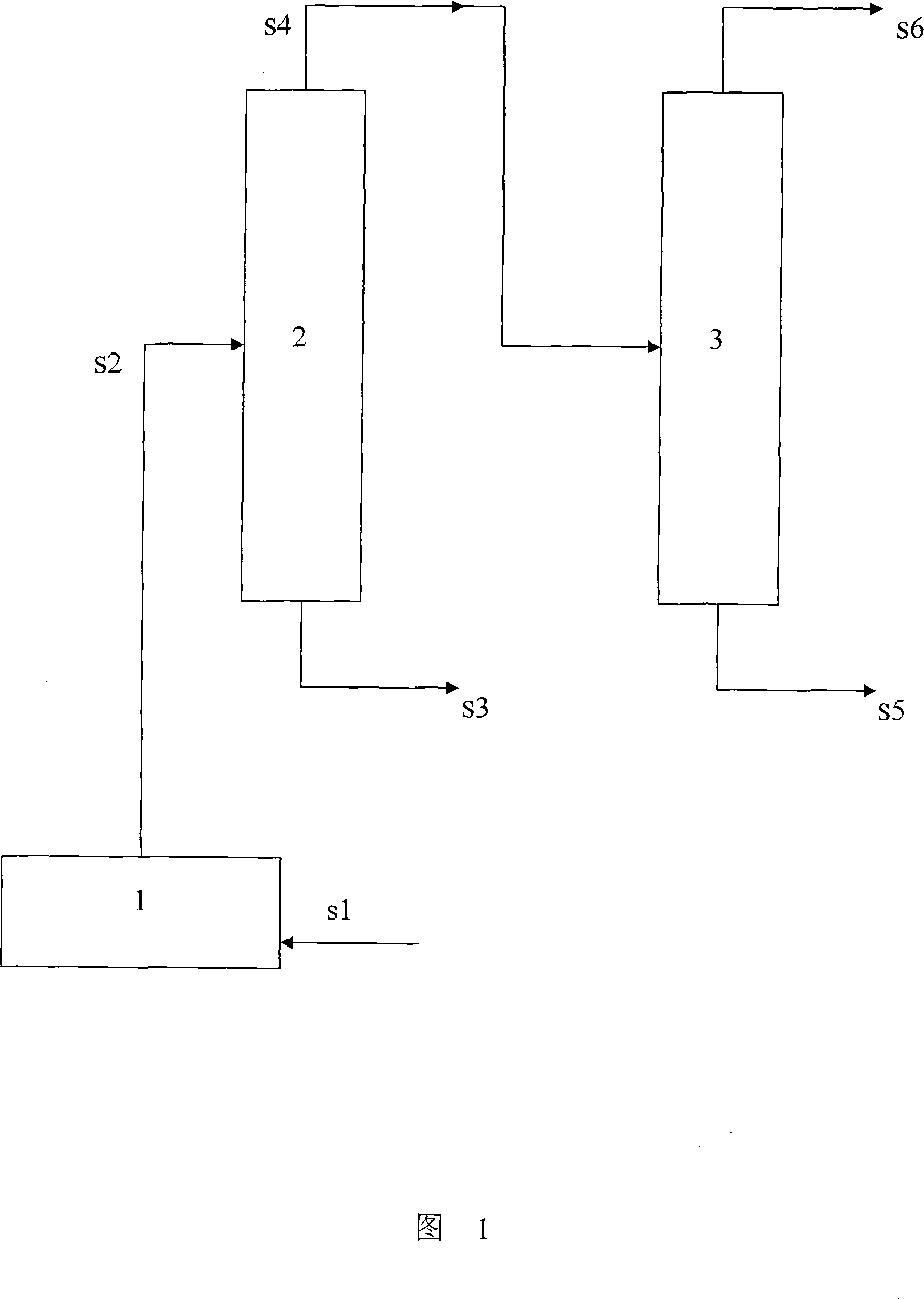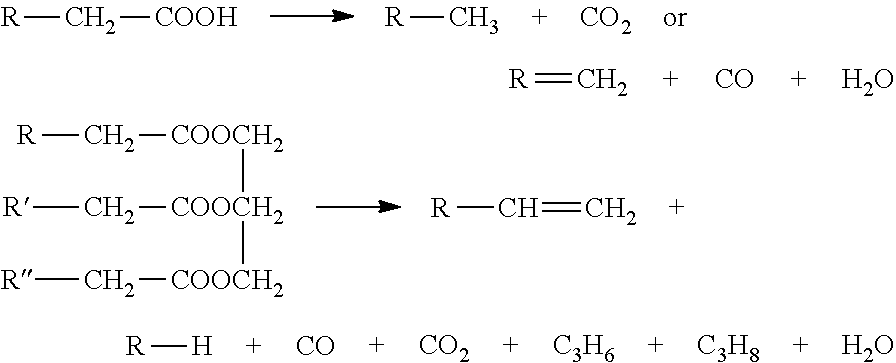Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
183results about "Hydrocarbon by depolymerisation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
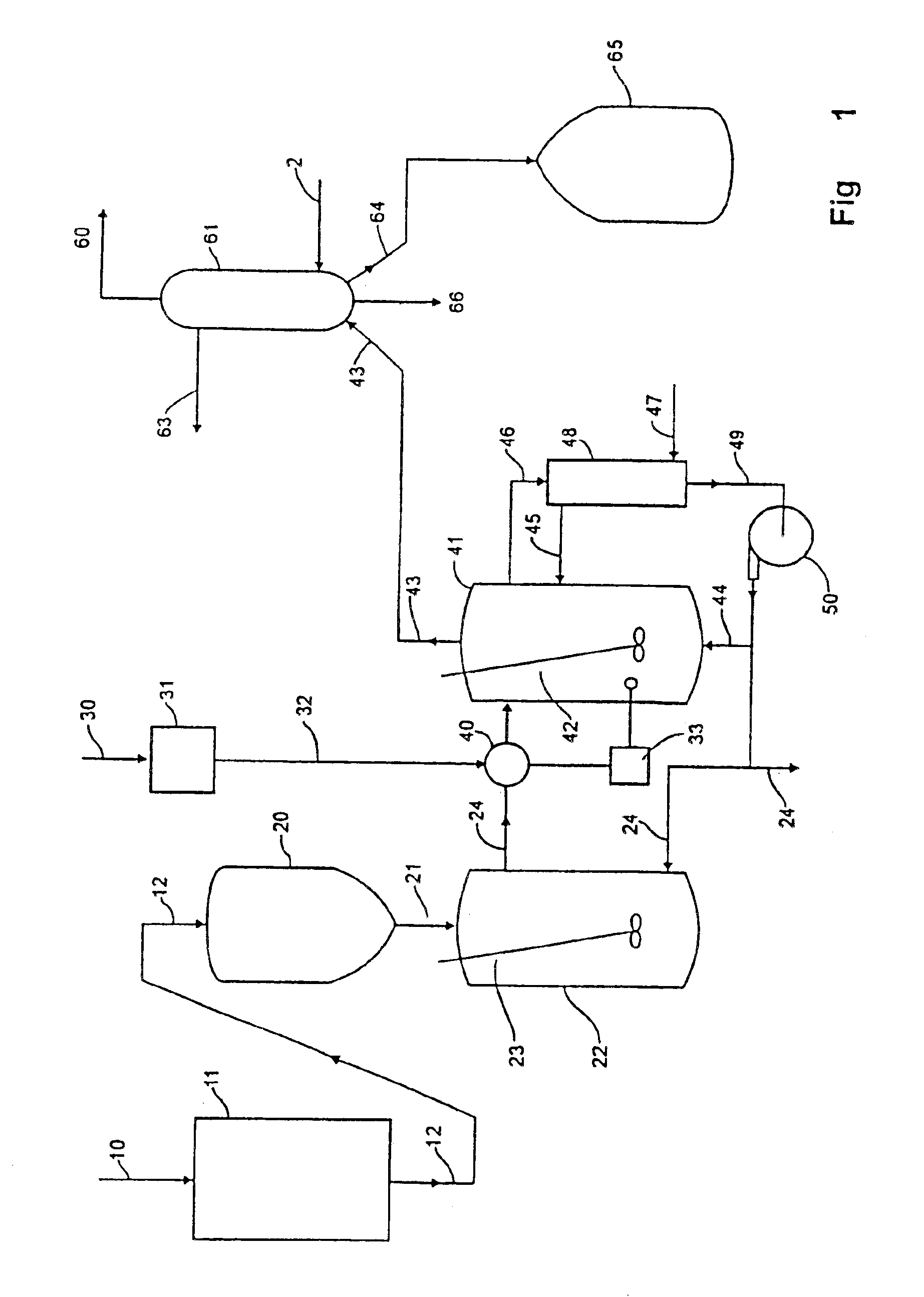
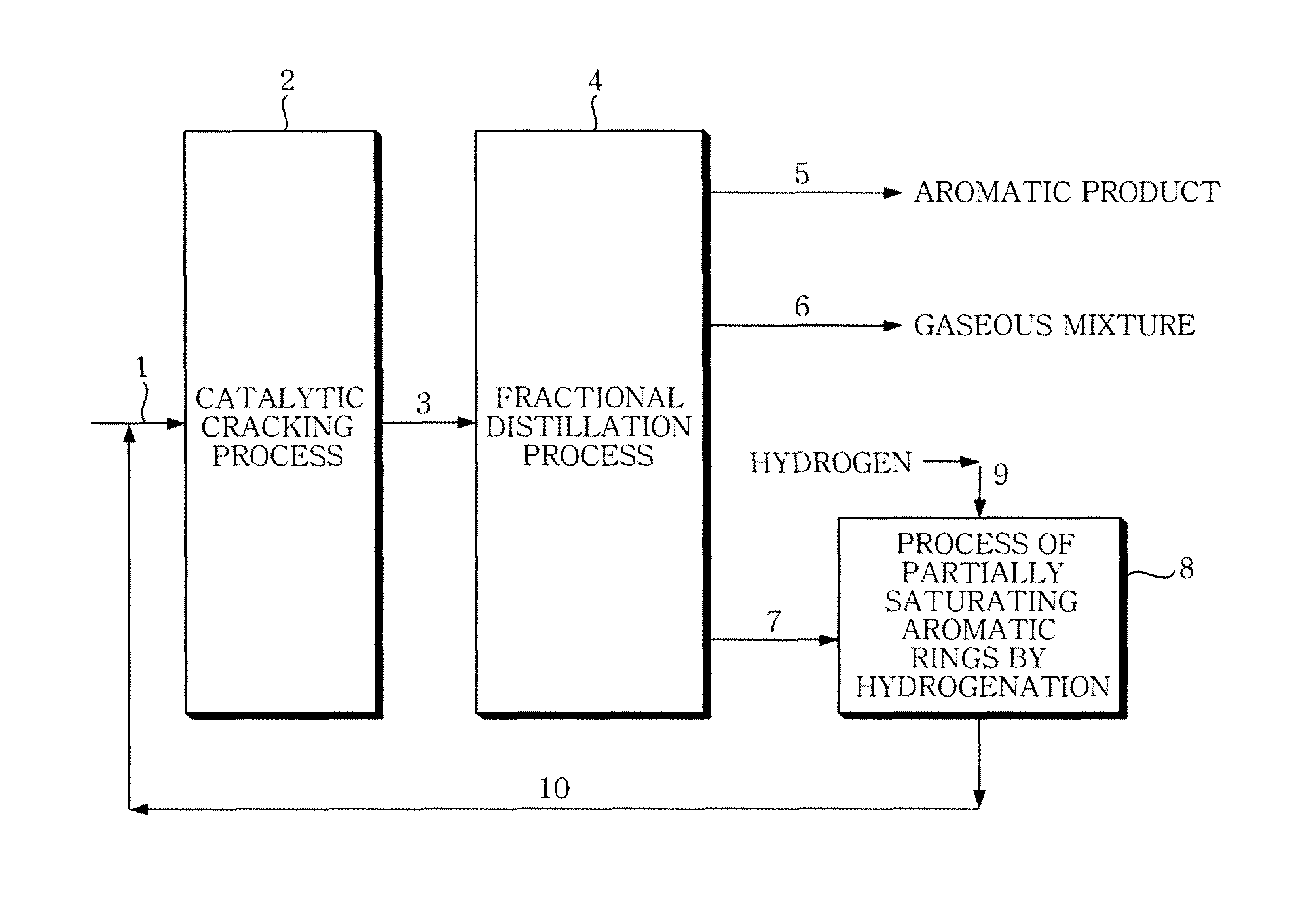
Method for producing high value aromatics and olefin from light cycle oil produced by a fluidized catalytic cracking process
ActiveUS20110207979A1Increase productionMaximize processing efficiencyCatalytic crackingHydrocarbonsHigh concentrationPetroleum
The present invention relates to a method of producing aromatic products (benzene / toluene / xylene) and olefin products from petroleum fractions obtained by fluid catalytic cracking, and, more particularly, to a method of producing products comprising high-concentration aromatic products and high value-added light olefin products from light cycle oil obtained by fluid catalytic cracking.
Owner:SK INNOVATION CO LTD
Process for waste plastic recycling
InactiveUS6861568B1Reduce demandReduce dependenceLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionHydrocarbonsPolyvinyl chlorideDiluent
A process for recycling or decomposing waste plastic where such wasteplastic is decomposed in a diluent such as hot oil through actions involvingfree radical precursor, such as polyvinyl chloride or polyurethane, is achievedat low temperature. The thermal decomposition (or pyrolysis) reaction is forabout 1 hour at 375° C., and useable products, such as distillate, coke, and oilare recovered. Additionally the diluent may be recycled within the process.
Owner:UNIV OF WYOMING RES
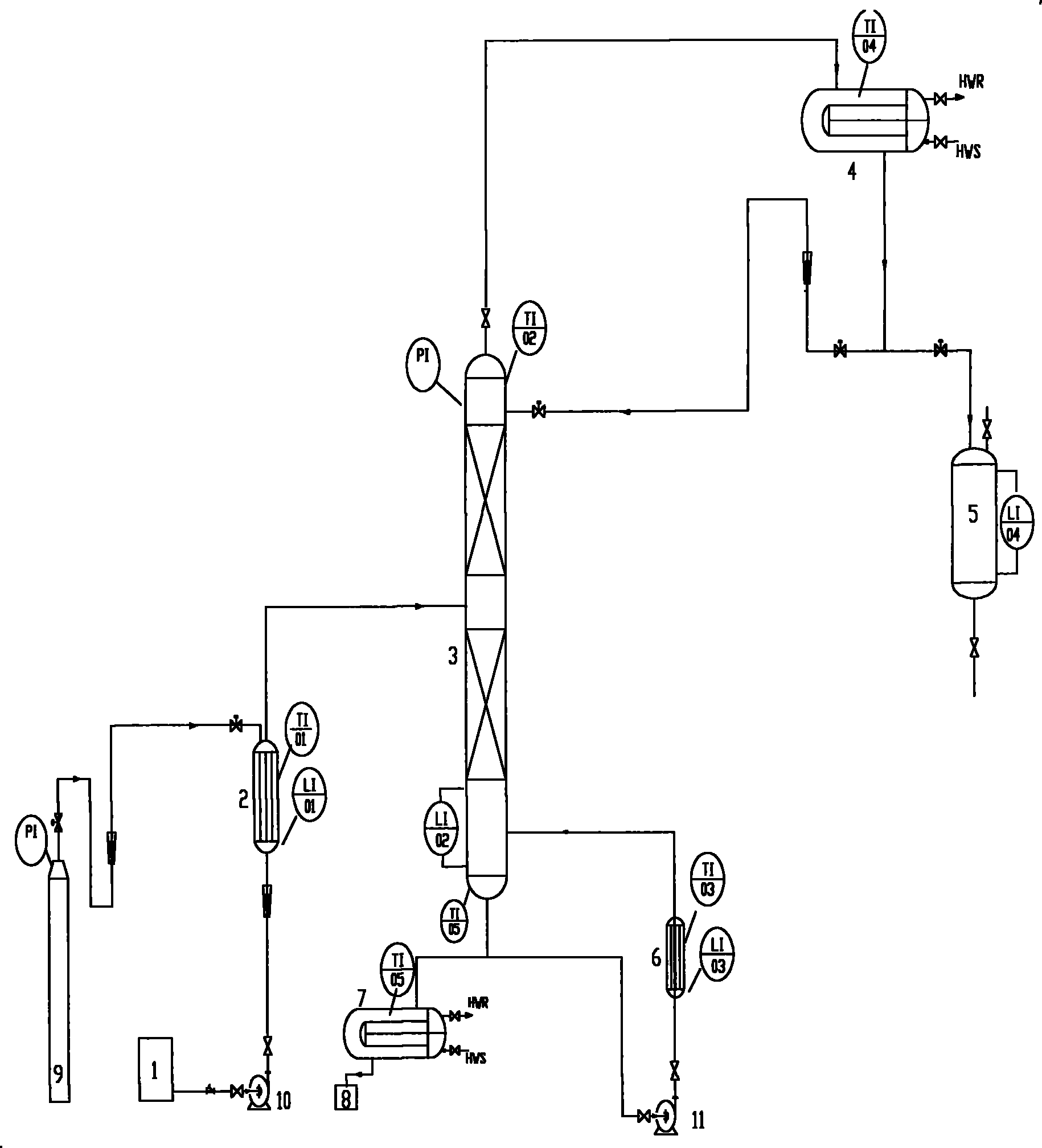
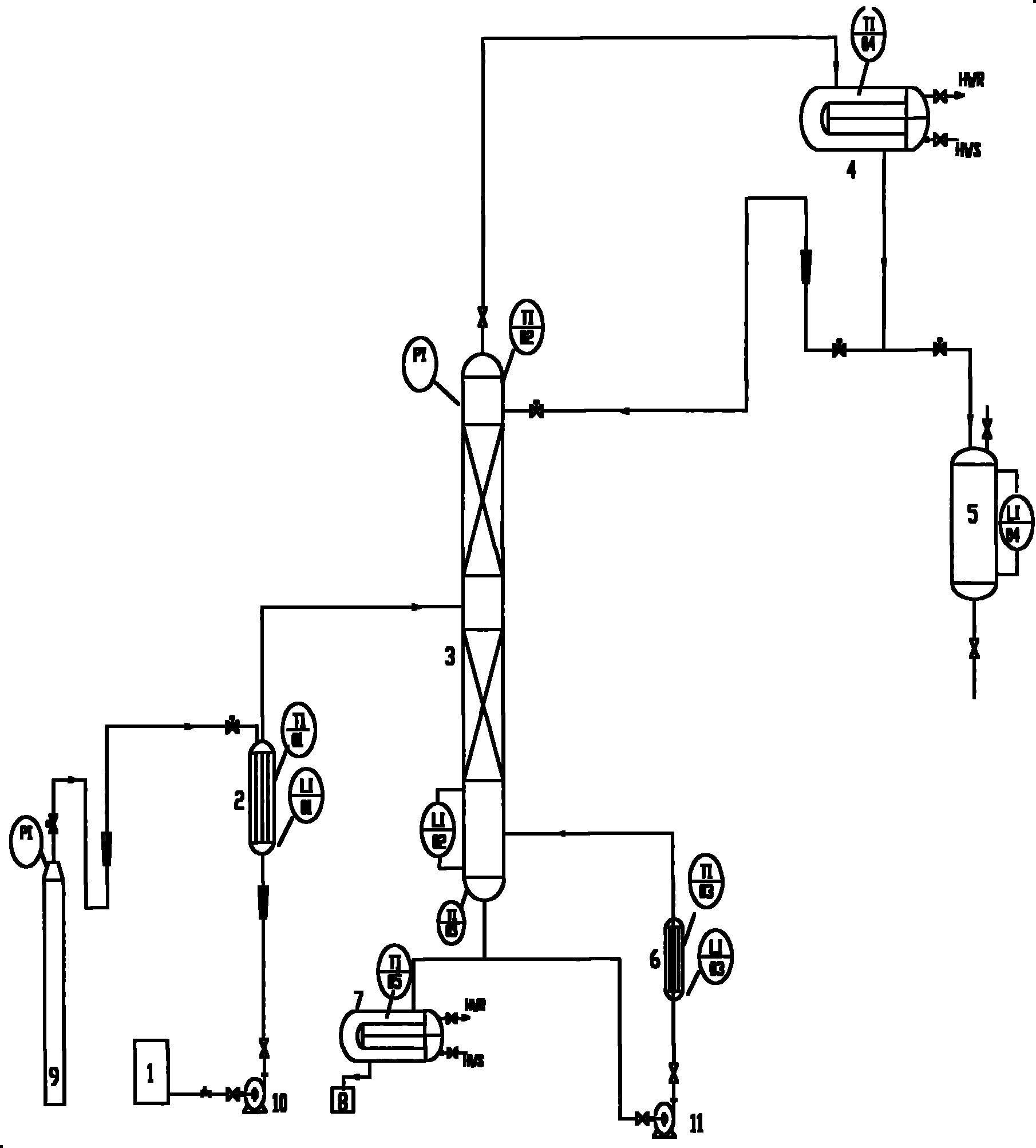
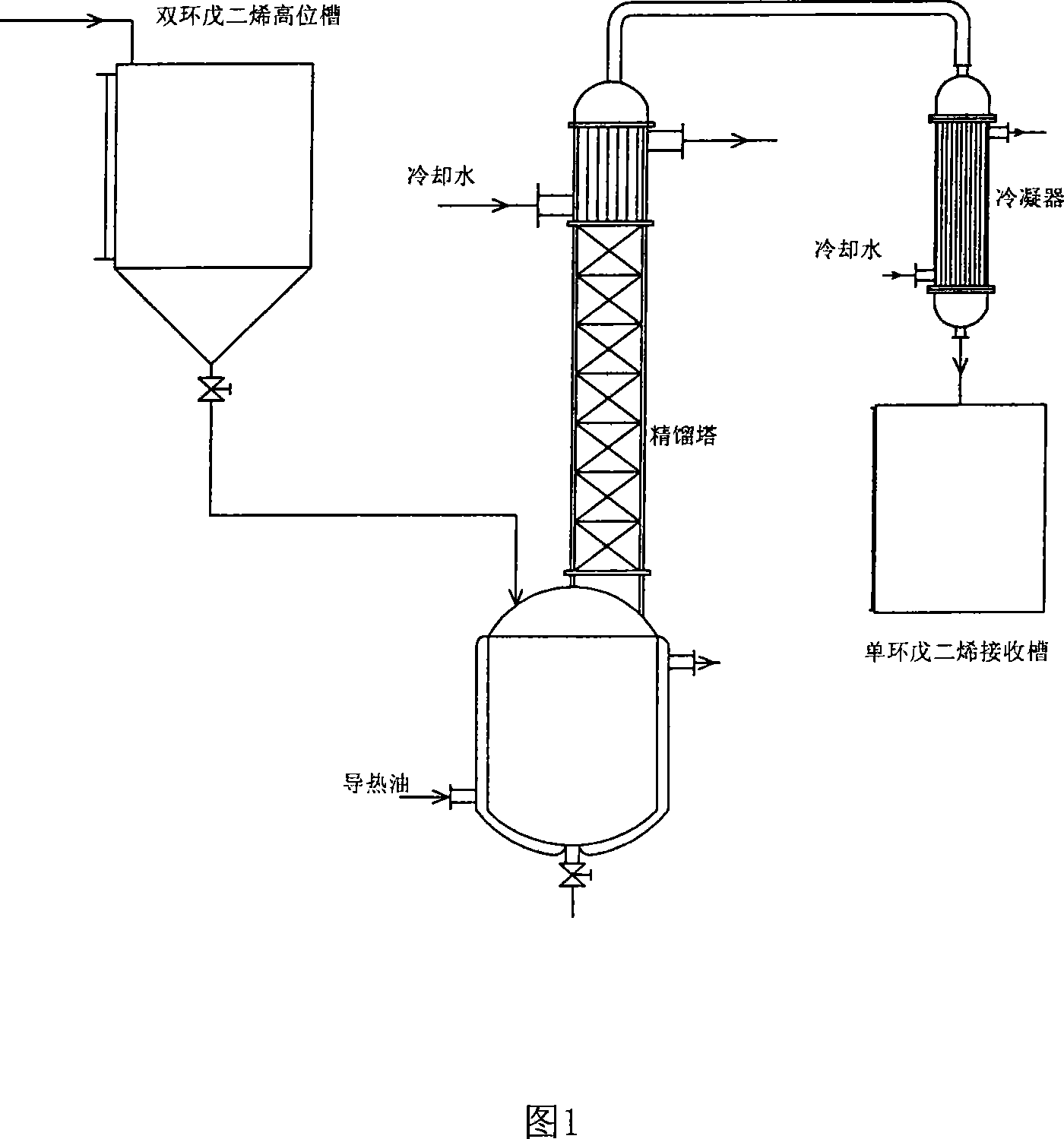
Method for preparing high-purity cyclopentadiene
ActiveCN102060649AMild reaction conditionsControllableHydrocarbon by depolymerisationReboilerNitrogen gas
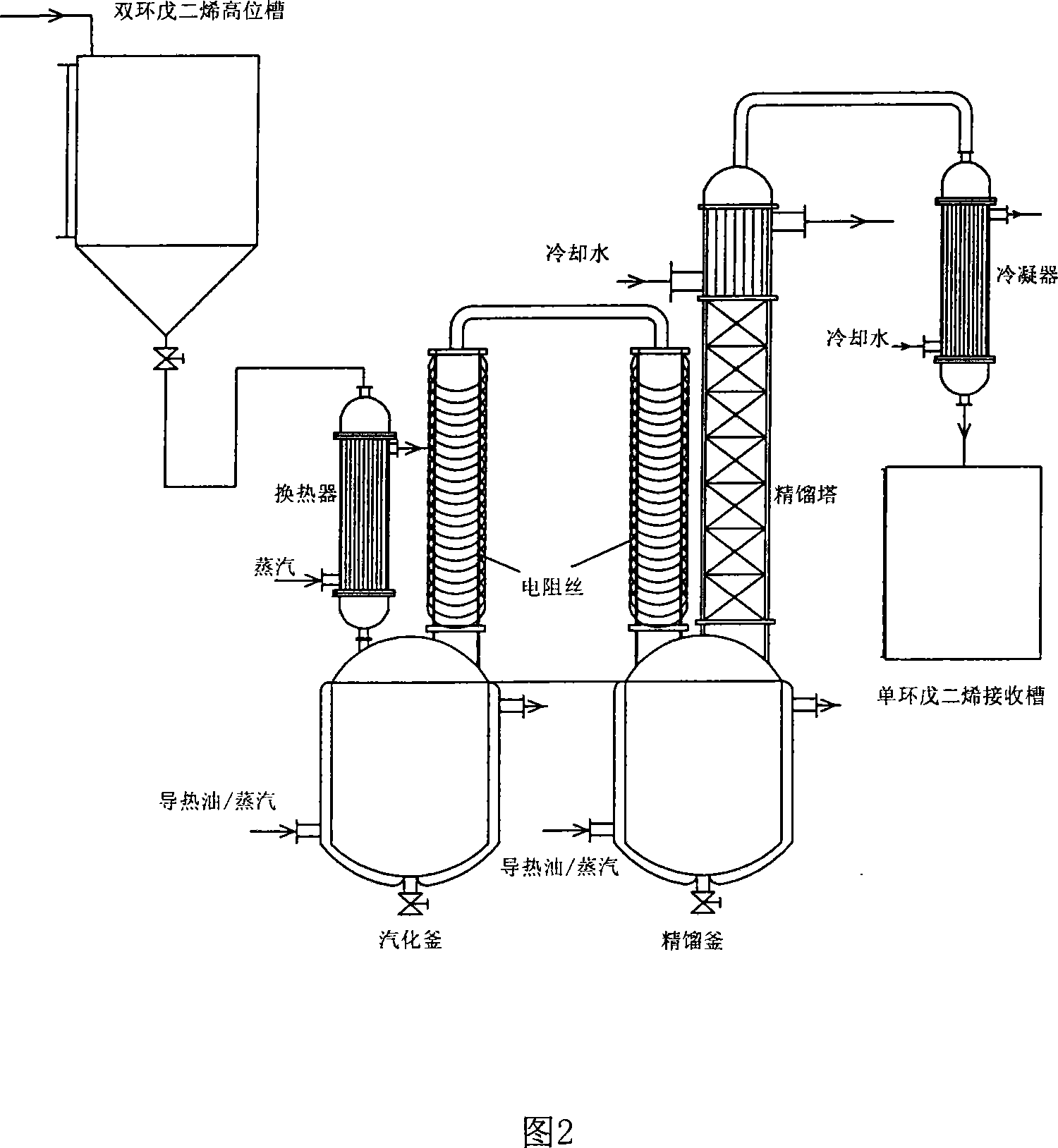
The invention relates to a method for preparing high-purity cyclopentadiene, which comprises the following steps of: heating a thermal decomposer containing purified conduction oil and a composite inhibitor and a rectifying reboiler to a specified temperature; adding dicyclopentadiene serving as a crude product into the thermal decomposer continuously and stably; allowing the depolymerized cyclopentadiene to enter a rectifying column; extracting high-purity cyclopentadiene from a tower top, heating a small amount of dicyclopentadiene and by-products by the reboiler at the tower bottom to rectify the small amount of dicyclopentadiene and by-products again, and recycling kettle liquid. The method has the advantages of simple equipment, high production capacity, little coking and long service life of the conduction oil serving as a raw material and the equipment.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Process for producing high purity dicyclo pentylene
InactiveCN1781887AHigh selectivityHydrocarbonsHydrocarbon by depolymerisationReaction rateAcid substances
The present invention provides a technological process of producing high purity dicyclopentadiene (DCPD) with petroleum cracking C5 fraction as main material. The process includes the following steps: 1. dimerizing C5 fraction and eliminating light components to obtain coarse DCPD; 2. catalytically depolymerizing the coarse DCPD at 100-200 deg.c in the presence of inorganic carrier supported acid catalyst to obtain high purity CPD; and 3. dimerizing CPD and eliminating light components to obtain high purity DCPD. The present invention is a low temperature catalytic depolymerizing process with low scaling, and effectively raised depolymerizing reaction rate and depolymerizing reaction selectivity.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +2
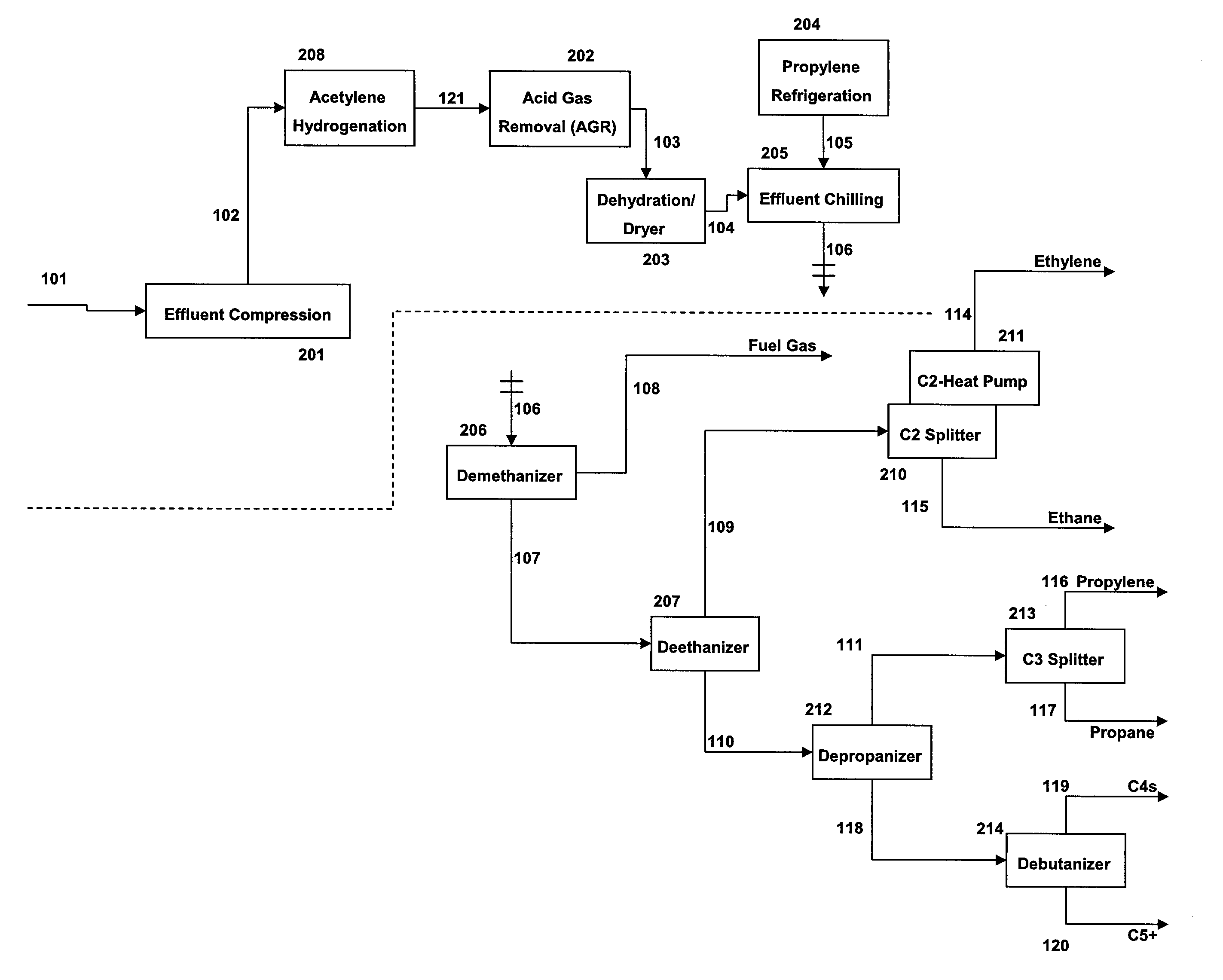
Method for contaminants removal in the olefin production process
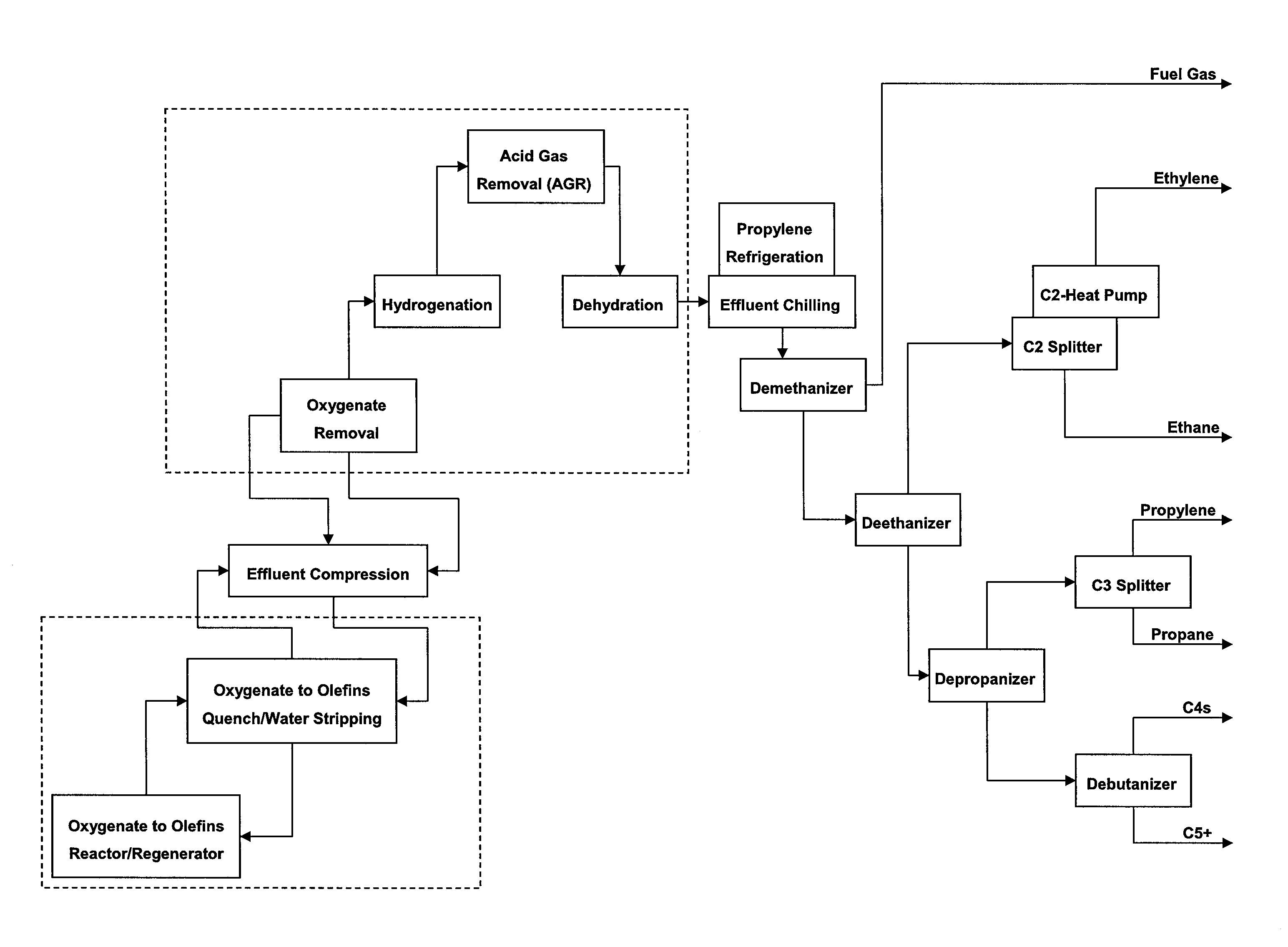
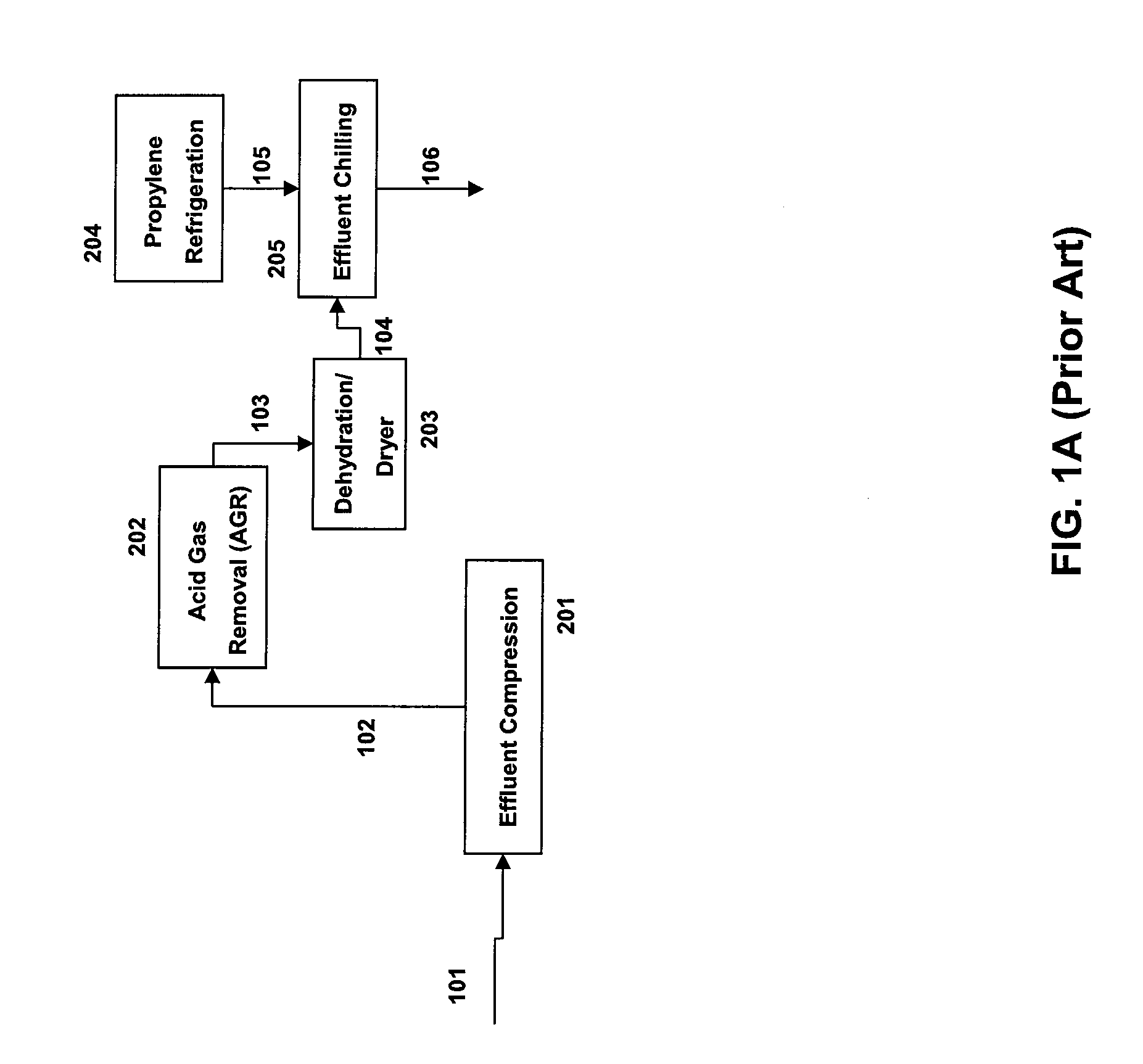
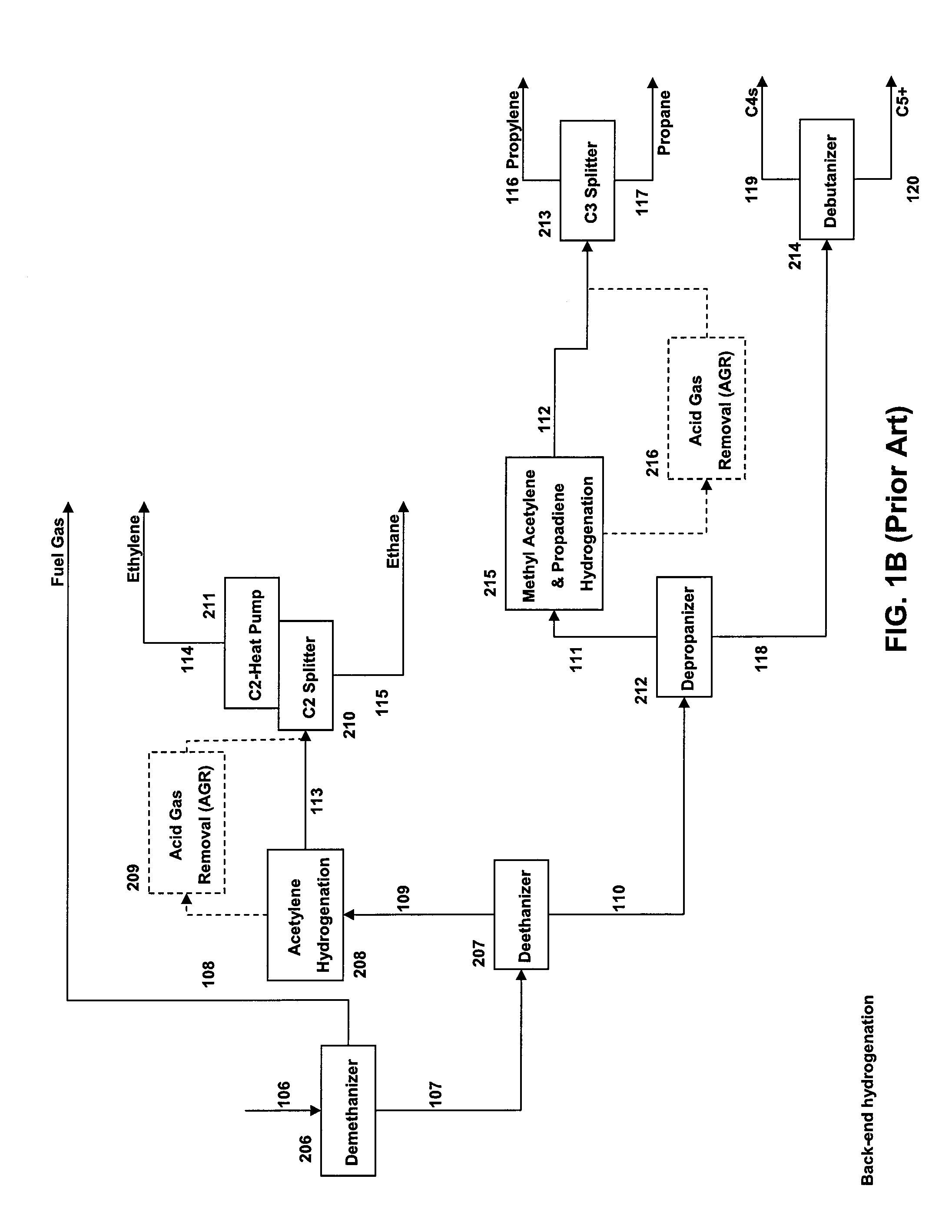
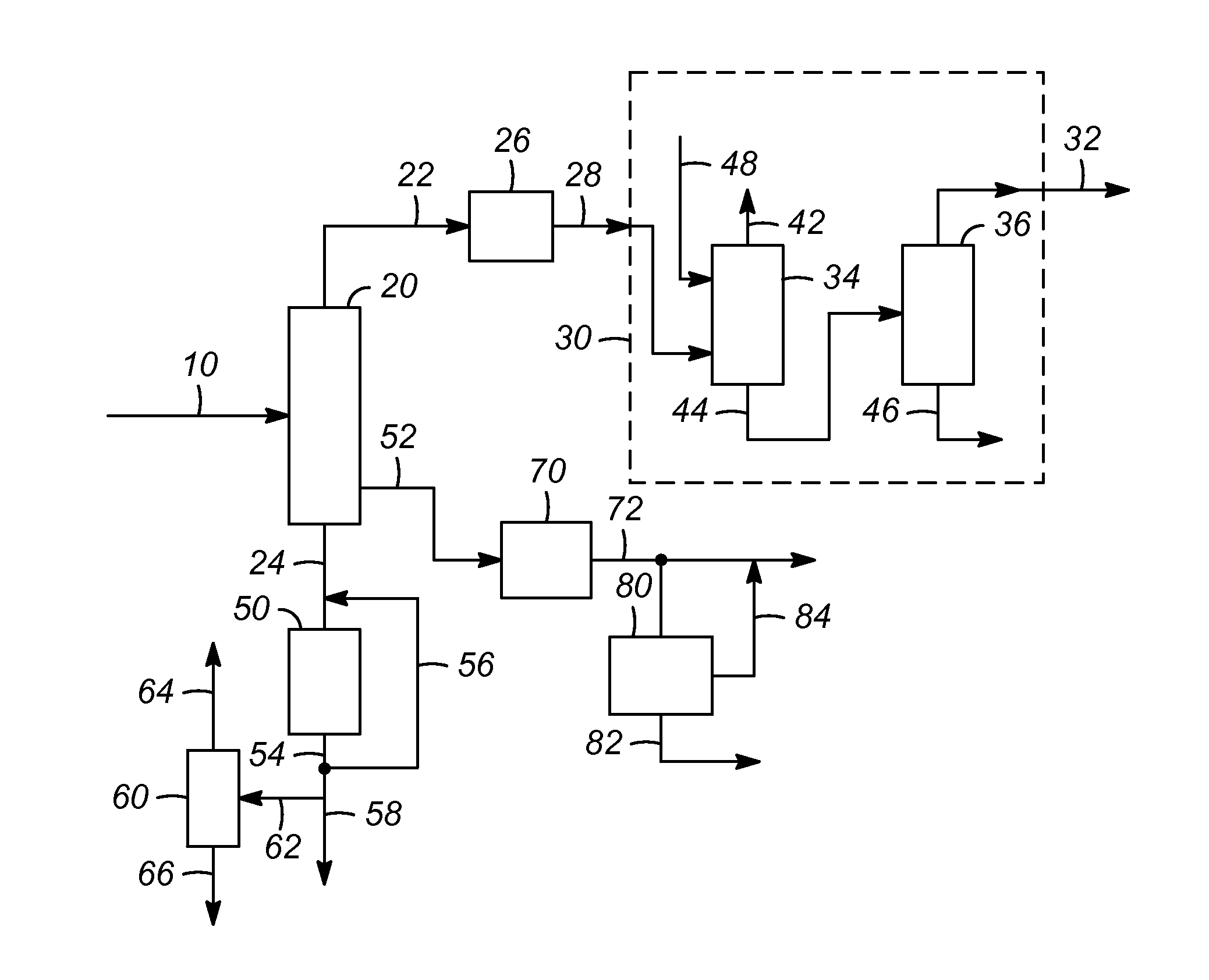
ActiveUS20110144397A1Reduce in quantityHydrocarbon by hydrogenationHydrocarbon purification/separationReactor systemDistillation
The present invention provides a method and reactor system for hydrogenating acetylenes present in the olefin stream derived from the following streams, alone or in combination: petroleum catalytic cracking process and / or oxygenate-to-olefin reactor, such as methanol-to-olefin (MTO) reactor, in an olefin production plant before the distillation steps, wherein the acetylene hydrogenation occurs before or just after the acid gas removal step.
Owner:STONE & WEBSTER PROCESS TECH
Low energy method of pyrolysis of hydrocarbon materials such as rubber
A low energy method of pyrolysis of rubber or other hydrocarbon material is provided. The hydrocarbon material is heated while maintaining a vacuum, using a clay catalyst. In an additional embodiment, the temperature of the reaction chamber and corresponding fuel input is varied either over time or spatially within the reaction chamber, to take advantage of the exothermic properties of the reaction. With the method of the present invention, a higher quality solid reaction product can be achieved, as well as a liquid having reduced polyaromatic hydrocarbons and oxidized organic contaminants.
Owner:DELTA ENERGY GRP LLC
Alternative solvents for a method of reclaiming styrene and other products from polystyrene based materials
A method of pretreating polystyrene-containing materials to form a solution of polystyrene in a processing solvent from which the styrene in the polystyrene in the materials is reclaimed. The materials are mixed with an environmentally acceptable pretreating solvent having a lower boiling point than the processing solvent, typically at a location remote from the reclamation plant. The pretreating solvent is selected from the group consisting of d-limonene, l-limonene, dipentene, and blends thereof. Prior to actual processing to reclaim styrene, the pretreating solvent is substantially replaced with the processing solvent. The pretreating solvent may be recovered for reuse.
Owner:PONSFORD THOMAS E +1
Technique for separating cyclopentadiene and methylcyclopentadiene
ActiveCN101186552AHigh purityReduce investmentDistillation purification/separationHydrocarbonsSeparation technologyMethylcyclopentadiene
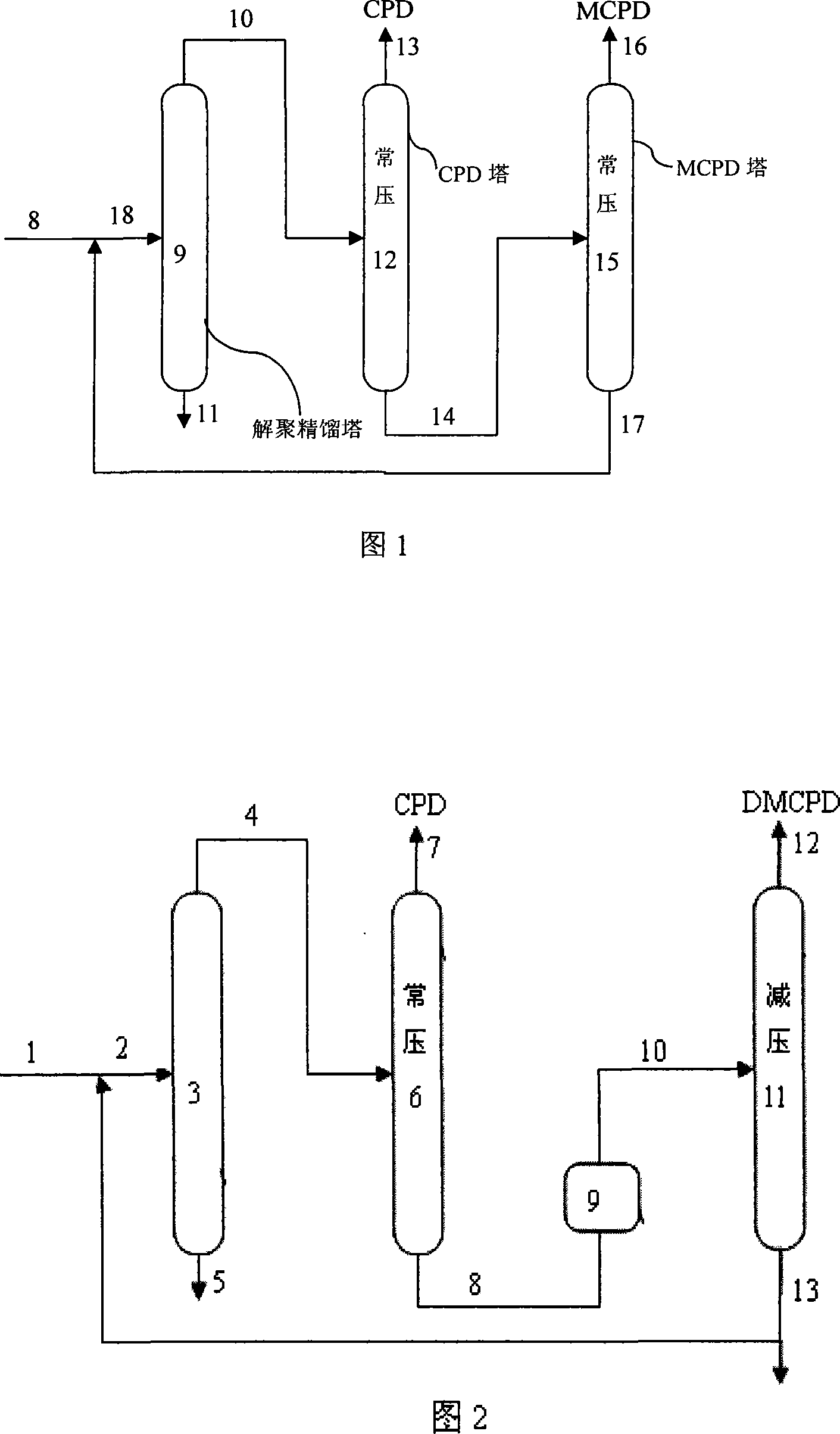
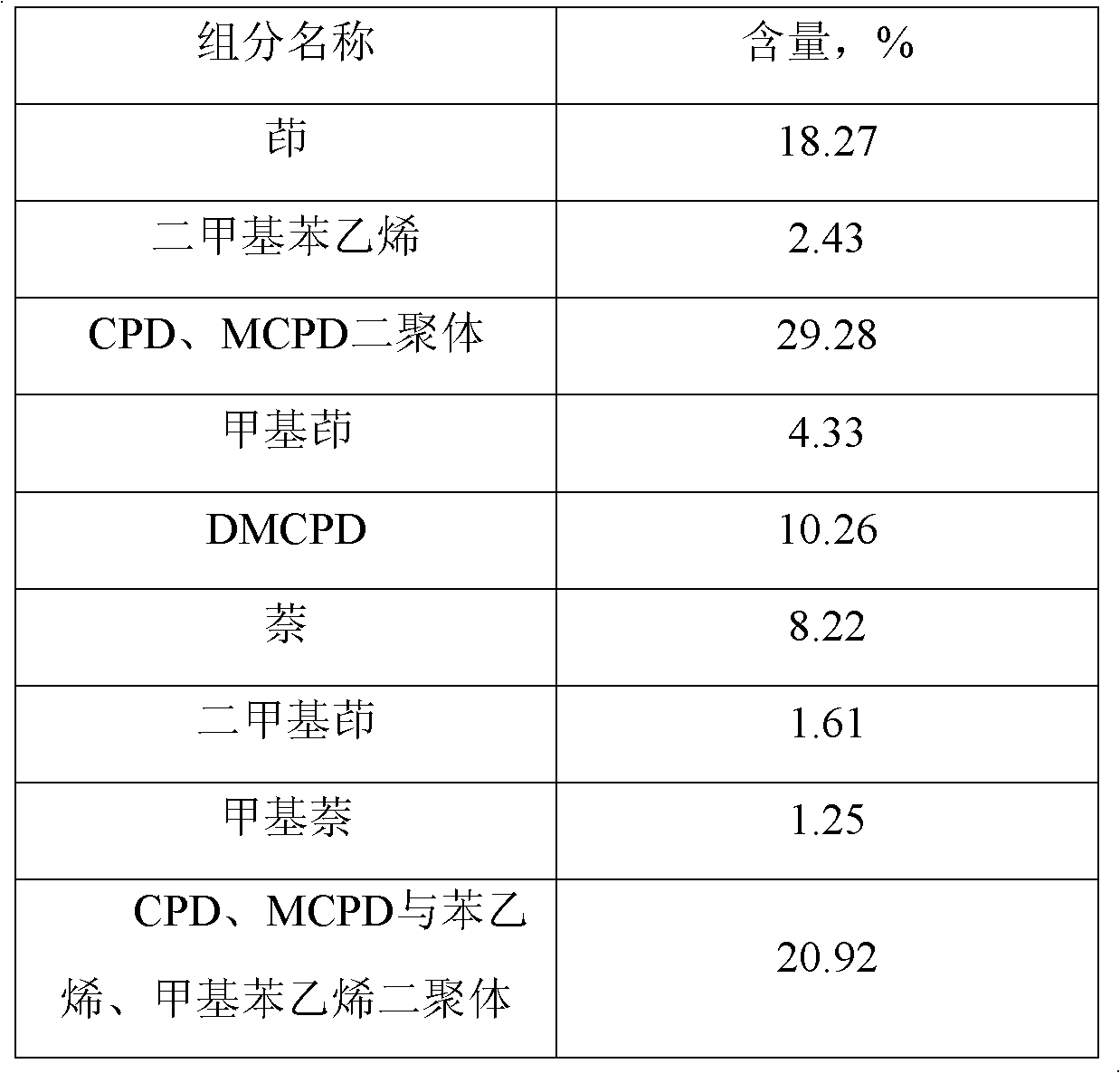
The invention relates to a separation technology of a mixture with cyclopentadiene and methyl cyclopentadiene as main ingredients, which pertains to the fine chemicals manufacturing technical field. A mixture with main ingredients of CPD and MCPD is firstly extracted from the mixture with cyclopentadiene and methyl cyclopentadiene as main ingredients from the top of a de-polymerization rectifying tower; the mixture with the main ingredients of CPD and MCPD then enters a CPD tower, and CPD is extracted from the top of a normal pressure rectifying tower; materials at the bottom of the CPD tower enter a dimerization reactor, and a mixture material with DMCPD as a main ingredient is acquired; the mixture material enters a MCPD tower to be rectified under reduced pressure, and the methyl cyclopentadiene is extracted from the top of the MCPD tower in the form of DMCPD. The invention adopts a de-polymerization normal reduced pressure separation method, which requires little supportive equipment investment and simple operation technique and can effectively overcome defects of the prior art, reduce product waste during the mixture separation process, improve extraction rate by one operation and reduce energy consumption, so that the cyclopentadiene and methyl cyclopentadiene of relatively high purity can be obtained.
Owner:山东东昌精细化工科技有限公司
Preparation method of high-purity ethylidene norbornene (ENB)
ActiveCN103483135AHigh yieldAvoid lostHydrocarbon by isomerisationHydrocarbon by depolymerisationIsomerizationDead volume
The invention relates to a preparation method of high-purity ethylidene norbornene (ENB), which comprises the following steps: 1) preparing cyclopentadiene (CPD) from cracked C9 bicyclic section distillate; 2) reacting the CPD and 1,3-butadiene (BD) in a non-dead-volume cascade tubular reactor to generate 5-vinyl-2-norbornene (VNB); 3) separating the crude VNB to obtain refined VNB, collecting the unreacted BD, CPD and circulating solvent, and returning to the front of the tubular reactor, thereby forming a circulating loop; and 4) dehydrating the refined VNB obtained in the step 3), carrying out isomerization reaction to obtain crude ENB, and removing light and heavy components from the crude ENB by a refining tower to obtain the high-purity ENB. The method has the advantages of simple and reliable process route and low facility request, and is suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:HENGHE MATERIALS & SCI TECH CO LTD
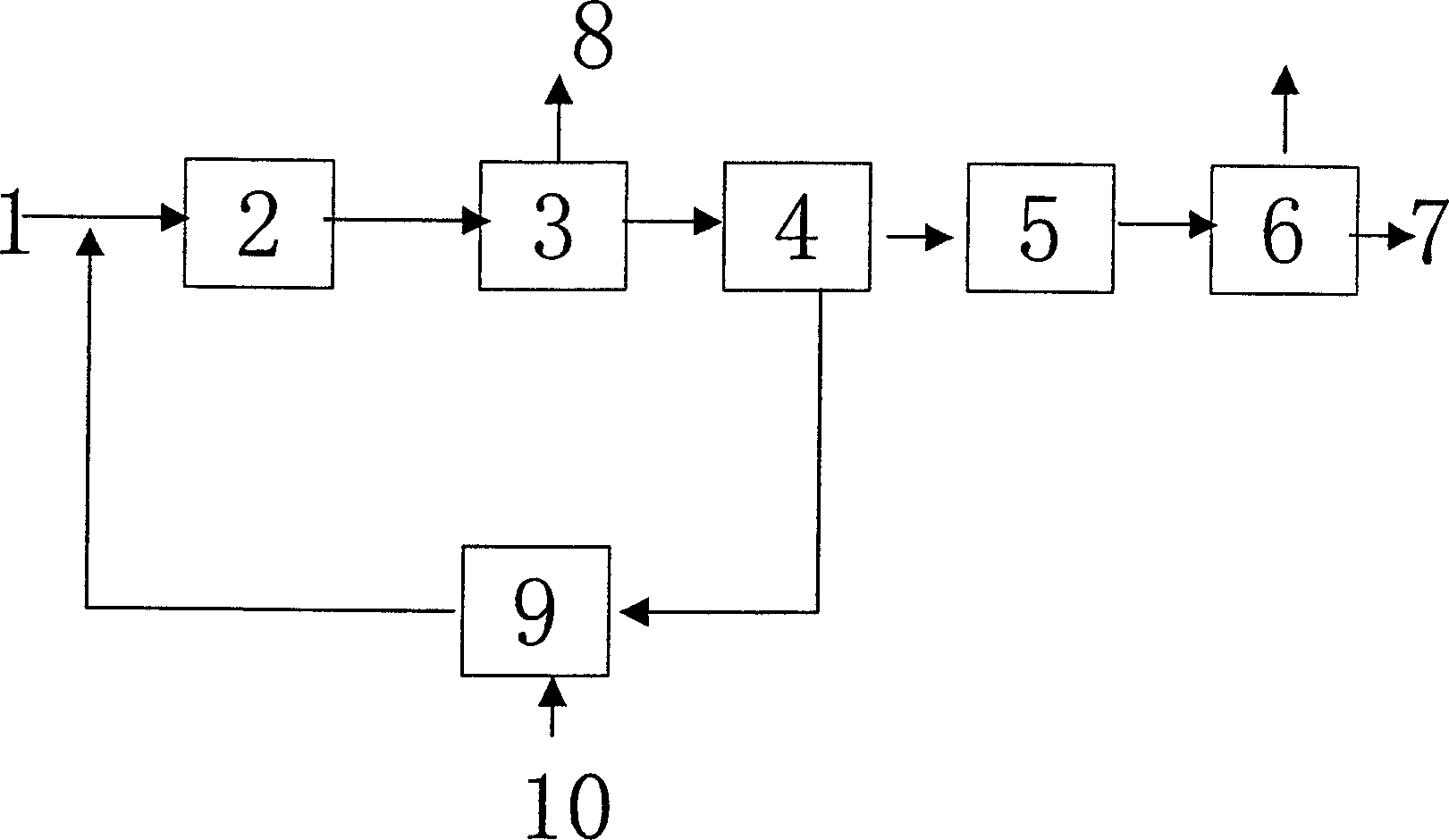
Dicyclopentadiene continuous cracking novel process
ActiveCN101070262AChange processAdjust speedHydrocarbon by depolymerisationEngineeringCracking reaction
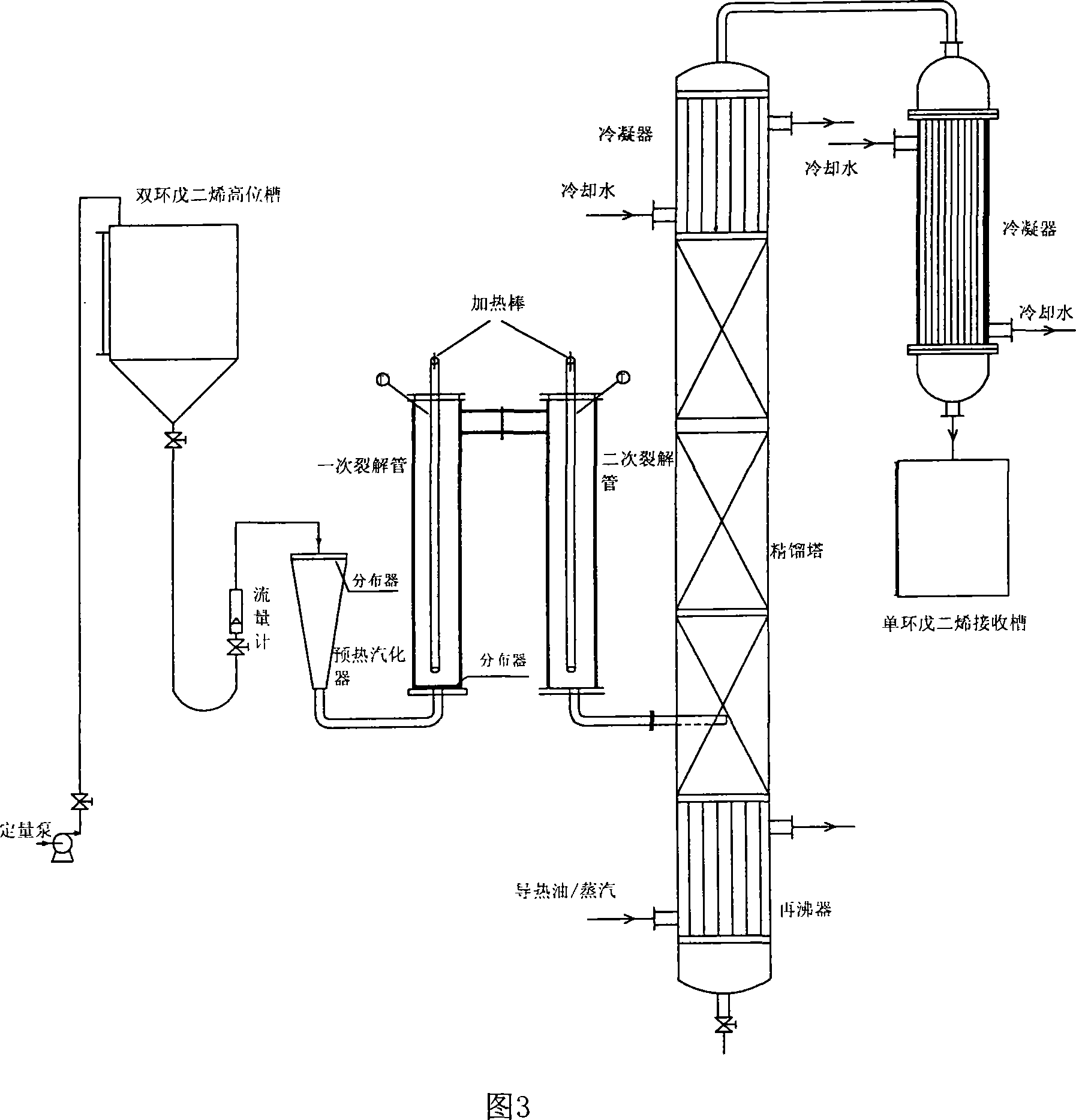
This invention relates to a new style dicyclopentadiene series lytic craft. Preheat dicyclopentadiene, then enter lytic device after vaporizing to proceed lytic response; after reaction finishing, carry out separation to gain monocyclic ring pentadiene. The heating of lytic device adopts internally fired mode. This invention through change the technical process and type of heating, internal heating instead externally heating, to advance thermal efficiency, decrease slagging, and advance productive capacity. This invention could advance double productive capacity for the same heat consumption, and decoking cycle is prolonged 4 to 5 times.
Owner:JIANGSU KESHENG CROP TECH
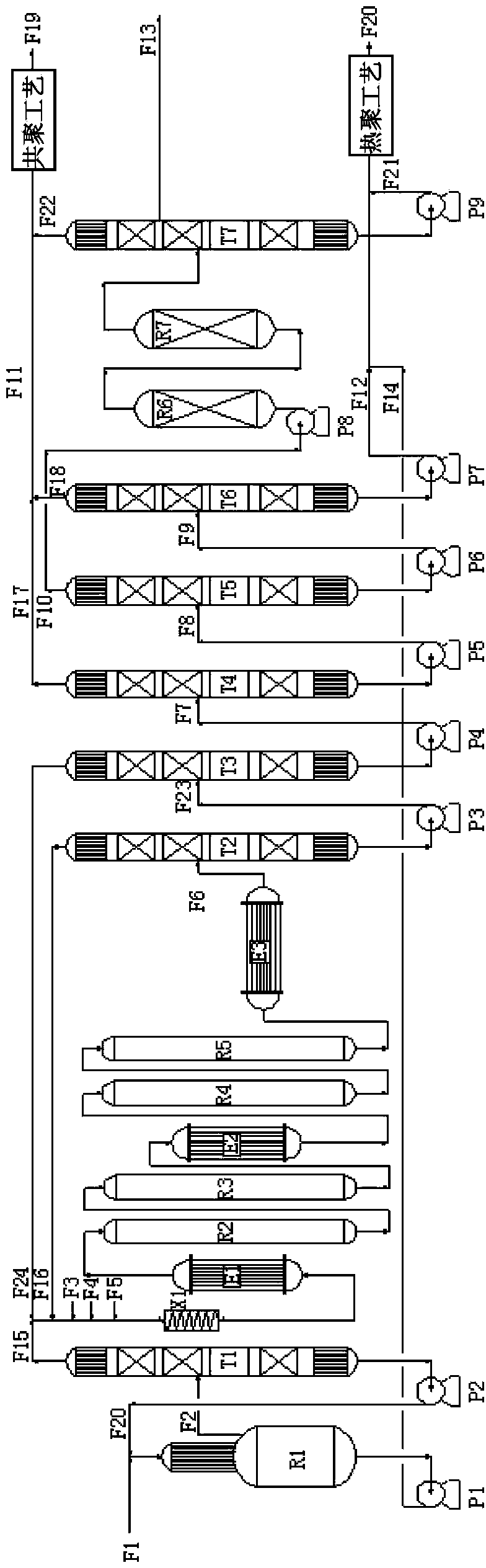
Method for extracting methyl cyclopentadiene from ethylene cracked C9 heavy fractions
ActiveCN102010285ANo preheating requiredIncrease profitDistillation purification/separationHydrocarbon by depolymerisationDepolymerizationGas phase
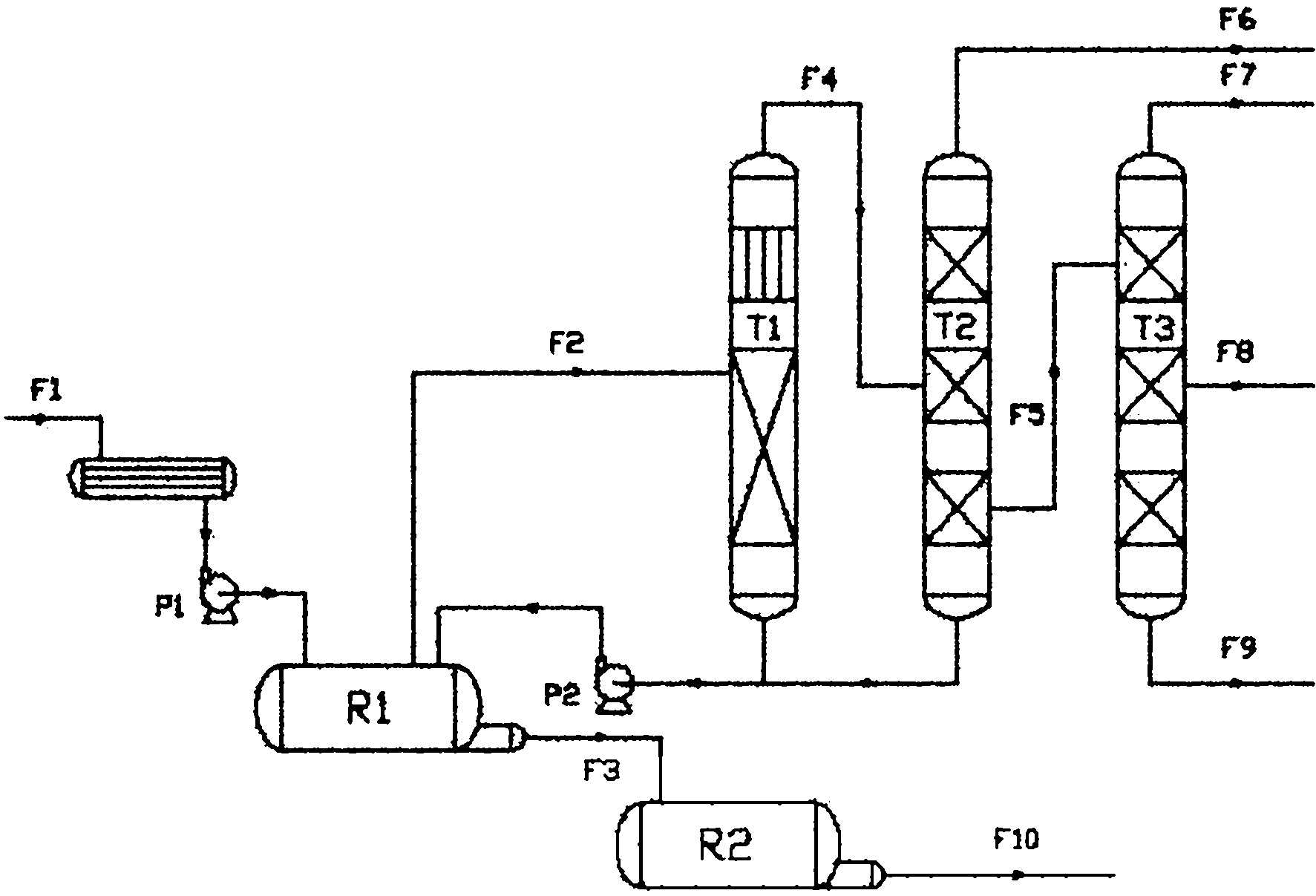
The invention relates to a method for extracting methyl cyclopentadiene from ethylene cracked C9 heavy fractions, which comprises the following steps of: (1) preheating C9 heavy fractions serving as a raw material and conveying to a depolymerizing reactor; (2) performing depolymerization reaction on the raw material; (3) adding a gas-phase material generated by depolymerization into a rectifying column T1; (4) adding a mixture of coarse cyclopentadiene and coarse methyl cyclopentadiene generated in the step (3) into a rectifying column T2 for further rectifying; (5) adding the residual material in the depolymerizing reactor into a coumarone resin reaction kettle to generate coumarone resin; (6) performing dimerization on the cyclopentadiene material to obtain dicyclopentadiene; (7) performing dimerization on the methyl cyclopentadiene material to obtain methyl cyclopentadiene dimer; and (8) adding the methyl cyclopentadiene dimer into a rectifying column T3, rectifying under reduced pressure, and removing light fractions on the tower top and heavy fractions at the tower bottom to obtain the methyl cyclopentadiene dimer on a side line. The method is simple and suitable for industrial application; and the purity of a product is not less than 98 percent.
Owner:HENGHE MATERIALS & SCI TECH CO LTD
Hydrocracking process for a hydrocarbon stream
A process for transalkylating a coal tar stream is described. A coal tar stream is provided, and is fractionated to provide at least one hydrocarbon stream having polycyclic aromatics. The hydrocarbon stream is hydrotreated in a hydrotreating zone, and then hydrocracked in a hydrocracking zone. A light aromatics stream is added to the hydrocracking zone. The light aromatics stream comprises one or more light aromatics having a ratio of methyl / aromatic available position that is lower than a ratio of methyl / aromatic available position for the hydrotreated stream. The hydrocracked stream is transalkylated in the hydrocracking zone.
Owner:UOP LLC
Process of separating cyclopentadiene and methyl cydopentadiene from ethylene side C9 product
ActiveCN101066902AExpand sourceEasy to separateFractional condensation purification/separationHydrocarbon by depolymerisationMethylcyclopentadieneEthylene
The present invention is process of separating cyclopentadiene and methyl cyclopentadiene from mixture containing dicyclopentadiene and dimethyl cyclopentadiene, and is especially suitable for separating and purifying cyclopentadiene and methyl cyclopentadiene from ethylene side C9 product or coarse cyclopentadiene product. The material, ethylene side C9 product or coarse cyclopentadiene product, is introduced into a high temperature cracking reactor, the high temperature cracked gas mixture is led to the first fractionating tower to separate out the fraction containing cyclopentadiene and methyl cyclopentadiene in the tower top, and the tower top fraction of the first fractionating tower is fed to the second fractionating tower to separate out cyclopentadiene in the tower top and methyl cyclopentadiene in the tower bottom.
Owner:天津天大天海化工新技术有限公司 +1
Depolymerization of Plastic Materials
A styrene monomer reclamation process and system is described. The styrene monomer reclamation process includes providing a waste plastic. The waste plastic includes styrenic polymers. The waste plastic is formed into polymer particles. At least a portion of the polymer particles are dissolved in a solvent to form a polymer stream. The dissolved polymer particles are depolymerized to form a styrene monomer stream.
Owner:FINA TECH
Method for removal of acetylenes from hydrocarbon streams
InactiveUS7393993B1Easy to separateEasily utilizedHydrocarbon by dehydrogenationChemical industryPurification methodsHydrogen
The process of the invention comprises contacting a hydrocarbon stream, comprising light olefins plus impurities such as acetylenes, in the absence of hydrogen with a supported copper catalyst, preferably CuO / alumina. The acetylene component undergoes a coupling reaction producing a diacetylene which can be more readily removed. Thus, the methylacetylene (MA) contaminant in liquid propylene yields at about 80° C. and 3792 kPa (550 psig) a significant amount dimethyl diacetylene (2,4-hexadiyne). Surprisingly, very little cyclization products are present. The process is useful for purification of olefin feeds. It can be used alone or in combination with known purification methods such as catalytic distillation or selective hydrogenation.
Owner:UOP LLC
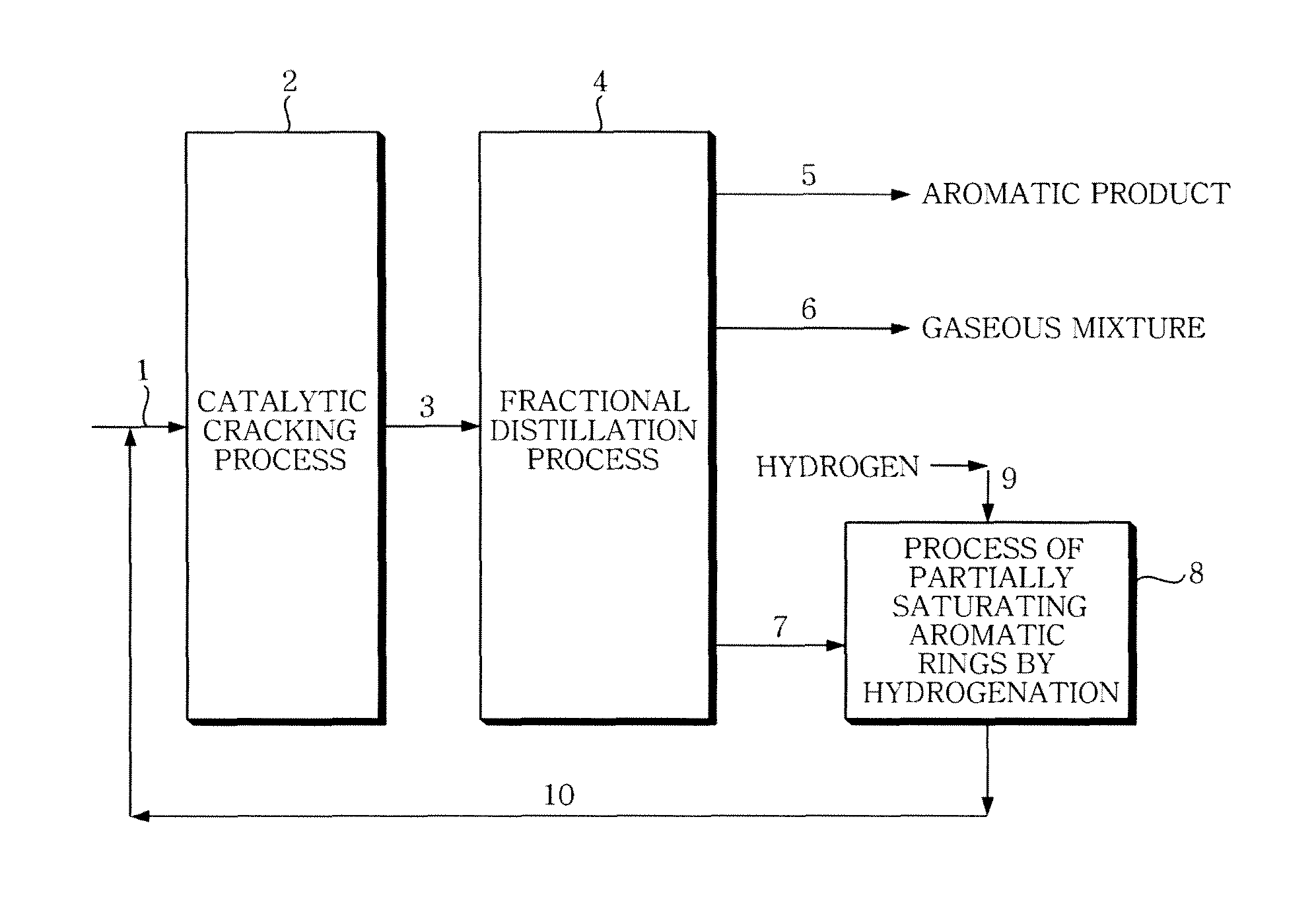
Method for producing high value aromatics and olefin from light cycle oil produced by a fluidized catalytic cracking process
ActiveUS8912377B2Increase productionMaximize processing efficiencyCatalytic crackingHydrocarbon by hydrogenationHigh concentrationPetroleum
The present invention relates to a method of producing aromatic products (benzene / toluene / xylene) and olefin products from petroleum fractions obtained by fluid catalytic cracking, and, more particularly, to a method of producing products comprising high-concentration aromatic products and high value-added light olefin products from light cycle oil obtained by fluid catalytic cracking.
Owner:SK INNOVATION CO LTD
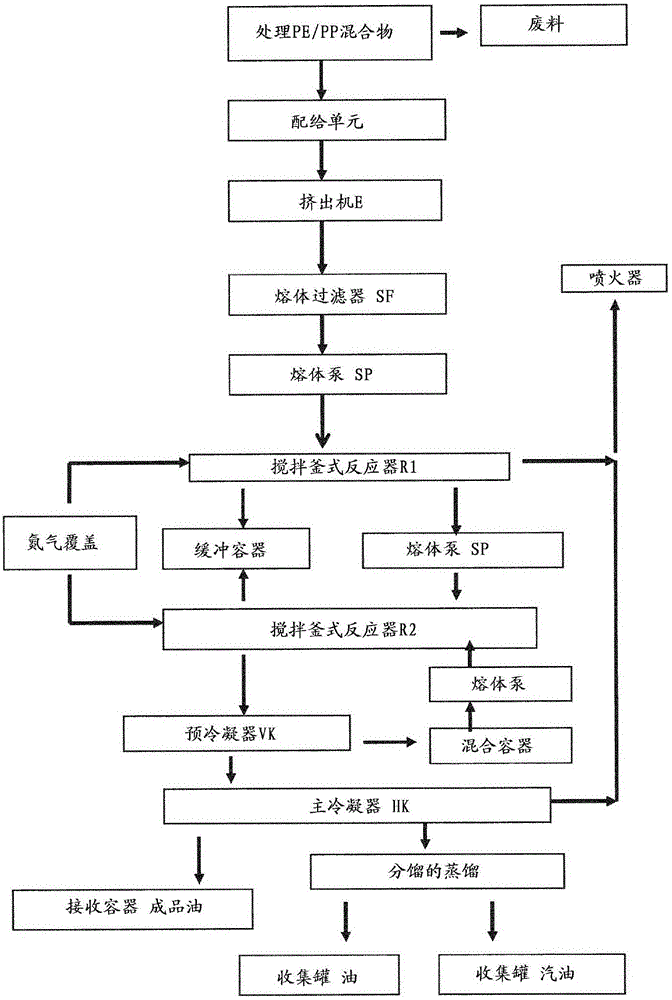
Method for the degrading of synthetic polymers and device for carrying out said method
The present invention relates to a method for degrading synthetic polymers, in particular polyolefines, comprising the following steps a) the synthetic polymers, in particular dried, synthetic polymers, are melted in at least one extruder (E), b) the polymer melt is purified by guiding said polymer melt through at least one melt filter (SF), c) the purified polymer melt is transferred into at least one first reactor (R1), said purified polymer melt in the at least one first reactor (R1) is guided from a lower region into an upper region of the reactor (R1) by heating to temperatures of between 300 and 370° C, preferably 330° C to 360° C, in particular 350° C, the polymers in the at least one first reactor (R1) are cleaved into oligomers, d) the oligomer mixture formed in the at least one first reactor (R1) is transferred into at least one second reactor (R2), the oligomer mixture in the at least second reactor (R2) is guided from a lower region into an upper region of the reactor (R2) by heating to a temperature of between 380 to 450° C, preferably 400° C to 430° C, in particular 410° C, the oligomers in the at least one second reactor (R2) being degraded into short-chained hydrocarbons, in the presence of at least one clay mineral as a depolymerisation catalyst, e) the short-chained hydrocarbons formed in the at least one second reactor (R2) are discharged into at least one precondenser (VK), the short-chained hydrocarbons emerging from the at least one second reactor (R2) are cooled in the at least one precondenser (VK); and f) the short-chained hydrocarbons cooled in the at least one precondener (VK) are guided into at least one main condenser (HK), the short-chained hydrocarbons emerging from the at least one precondenser (VK) are liquefied in the at least one main condenser (HK). The invention also relates to a system for carrying out said method and to the product oil produced according to said method.
Owner:ACHIM METHLING JOSEF RANFTL
Method for contaminants removal in the olefin production process
ActiveUS8309776B2Hydrocarbon by hydrogenationHydrocarbon purification/separationReactor systemDistillation
Owner:STONE & WEBSTER PROCESS TECH
Depolymerization processes, apparatuses and catalysts for use in connection therewith
ActiveUS20130317238A1High purityLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionPreparation by hydroxy group additionDepolymerizationPhysical chemistry
The present disclosure generally relates to processes, apparatuses and custom catalysts designed to depolymerize a polymer. In one embodiment, the present invention relates to a de-polymerizing apparatus, catalysts and reaction schemes to obtain useful monomers including fuel products by “in situ” reactions using coupled electromagnetic induction.
Owner:MOHANTY PRAVANSU S +1
Method for preparing dicyclopentadiene through gas-liquid phase depolymerization of C9 raw material
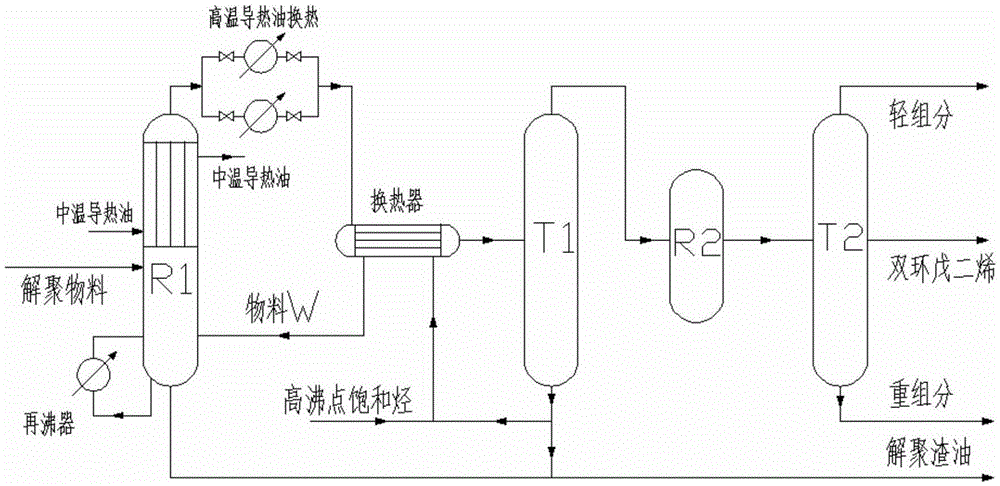
ActiveCN105399590AImprove conversion rateAdvanced technologyHydrocarbons from unsaturated hydrocarbon additionHydrocarbon by depolymerisationGas phaseTower
The invention relates to a method for preparing dicyclopentadiene through gas-liquid phase depolymerization of a C9 raw material. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out reduced pressure rectification division on the C9 raw material to obtain a thermal depolymerization raw material, preheating the thermal depolymerization raw material, and conveying the preheated thermal depolymerization raw material into a depolymerization kettle R1; carrying out liquid phase to obtain a gasification material, and carrying out a gas phase depolymerization reaction on the gasification material in the upper portion of the depolymerization kettle to obtain a gas phase depolymerization material; adding the gas phase depolymerization material to a tubular heater, heating, carrying out gas phase depolymerization, adding the obtained material to a cooling heat exchanger, carrying out heat exchange to cool in order to obtain a gas phase material and a liquid phase material, allowing the gas phase material and the liquid phase material to enter a rectifying tower T1, obtaining CPD at the top of the rectifying tower T1, allowing CPD to enter a dimerization reactor R2, and dimerizing to obtain DCPD; and allowing the DCPD to enter a rectifying tower T2, carrying out reduced pressure recitification, removing light fraction from the top of the rectifying tower T2, and removing heavy fraction from the bottom of the rectifying tower T2 to obtain dicyclopentadiene. The method has the advantages of advanced process, high conversion rate of the C9 raw material for preparing the DCPD, full recycling of system waste heat, and suitableness for industrial application, and the purity of the obtained DCPD product is not lower than 99%.
Owner:HENGHE MATERIALS & SCI TECH CO LTD
Method of reclaiming styrene and other products from polystyrene based materials
A method of reclaiming styrene from polystyrene-containing materials contaminated with animal fats and / or vegetable oils. A solution of polystyrene from such materials in a solvent is heated in distillation equipment to depolymerize the polystyrene and produce a styrene fraction and a heavier fraction, the styrene fraction being separated from the heavier fraction. Prior to heating, an inert gas is used to purge the distillation equipment of oxygen. The method preferably is carried out at the lowest temperature which will achieve the desired rate of depolymerization.
Owner:PONSFORD THOMAS E +1
Method for preparing aromatic hydrocarbon compound through blending pyrolysis of lignin and low-density polyethylene or polycarbonate or polystyrene
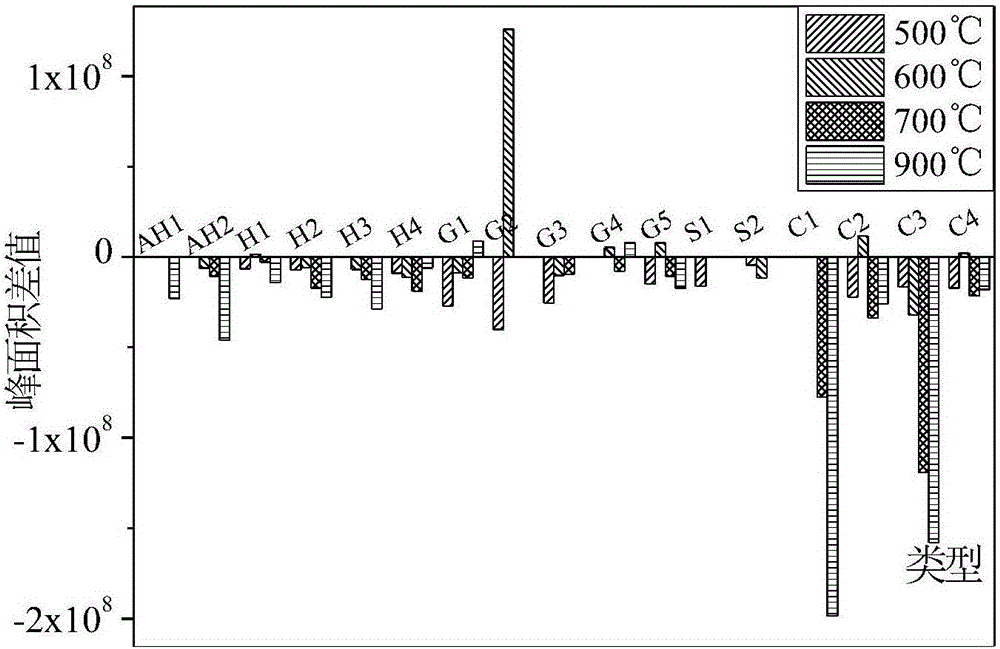
InactiveCN106431802ARealize resource utilizationPromote generationOrganic compound preparationHydrocarbonsLow-density polyethyleneResource utilization
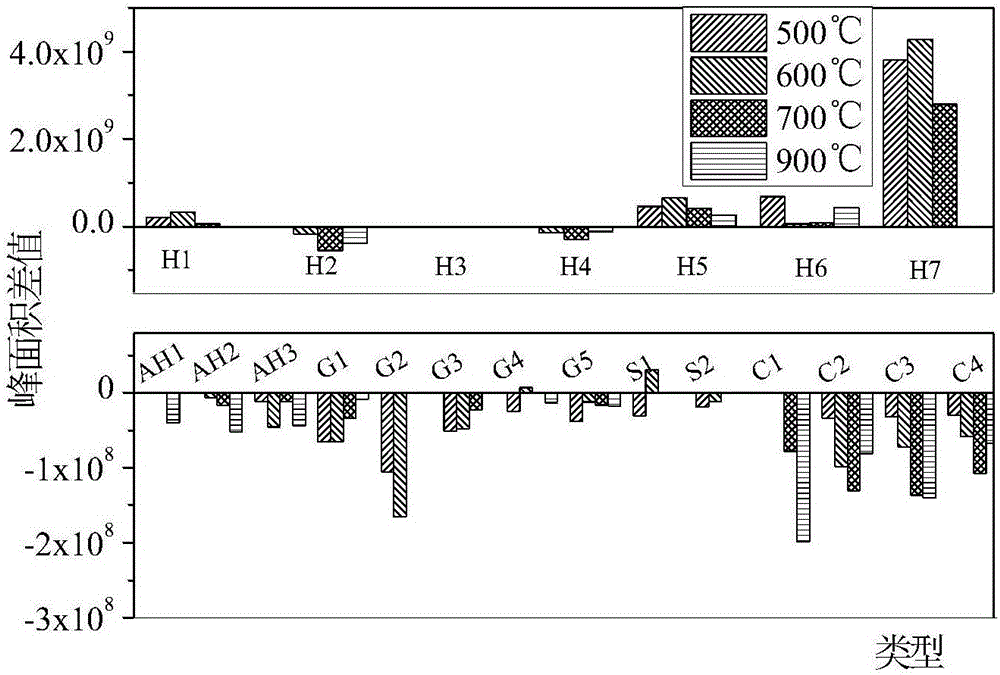
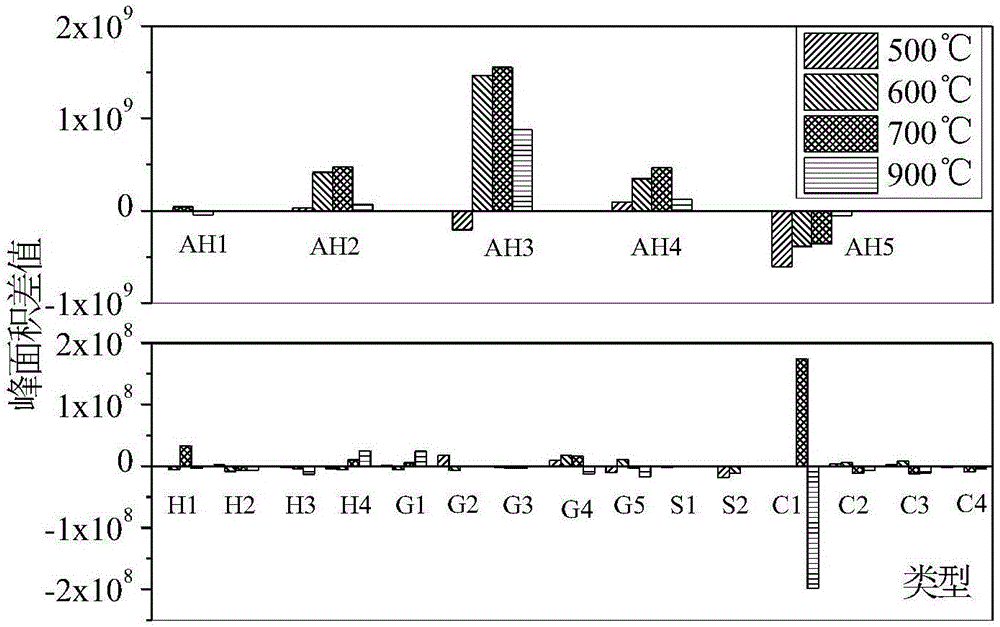
The invention discloses a method for preparing an aromatic hydrocarbon compound through blending pyrolysis of lignin and low-density polyethylene or polycarbonate or polystyrene. After the lignin and a high-molecular polymer is mixed according to a certain mass ratio, the distribution condition of blending pyrolysis products is inspected by adopting a Py-GCMS analytical means, wherein the temperature is set at 500 DEG C to 900 DEG C, and the temperature increasing rate is set at 20 DEG C / ms; the yield of aromatic hydrocarbon in the blending pyrolysis products of the lignin and polystyrene is obviously increased. Further, the weight loss condition and the small molecule escaping condition in the blending pyrolysis process of the lignin and polystyrene is inspected by adopting a TG-FTIR analytical means, wherein the temperature increasing range is set at to range from 20 DEG C to 900 DEG C, and then the blending pyrolysis mechanism is analyzed. The mode that the lignin is subjected to blending pyrolysis with low-density polyethylene or polycarbonate or polystyrene is low in cost and clean in process; meanwhile, by means of blending pyrolysis of the lignin and polystyrene, the generation amount of monomeric aromatic hydrocarbon can be effectively promoted, and directive guidance is provided for resource utilization of papermaking waste liquid and waste plastic.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Process for the Purification of 1,3-Butadiene from an Oxidative Dehydrogenation Process
ActiveUS20140296589A1Simple purification processEasy to purifyHydrocarbon by hydrogenationDistillation purification/separationButadiene DioxideDehydrogenation
A process is presented for the purification of 1,3 butadiene. The process is for treating a butadiene stream from an oxidative dehydrogenation unit, where a butane stream is dehydrogenated, generating a butadiene rich stream. The butadiene rich stream is fractionated and passed through a butadiene recovery unit. Additional C4 compounds recovered from the fractionation bottoms stream are further processed for increasing yields of butadiene.
Owner:UOP LLC
Method for preparing cyclopentadiene by thermaldepolymerization of dicyclopentadiene
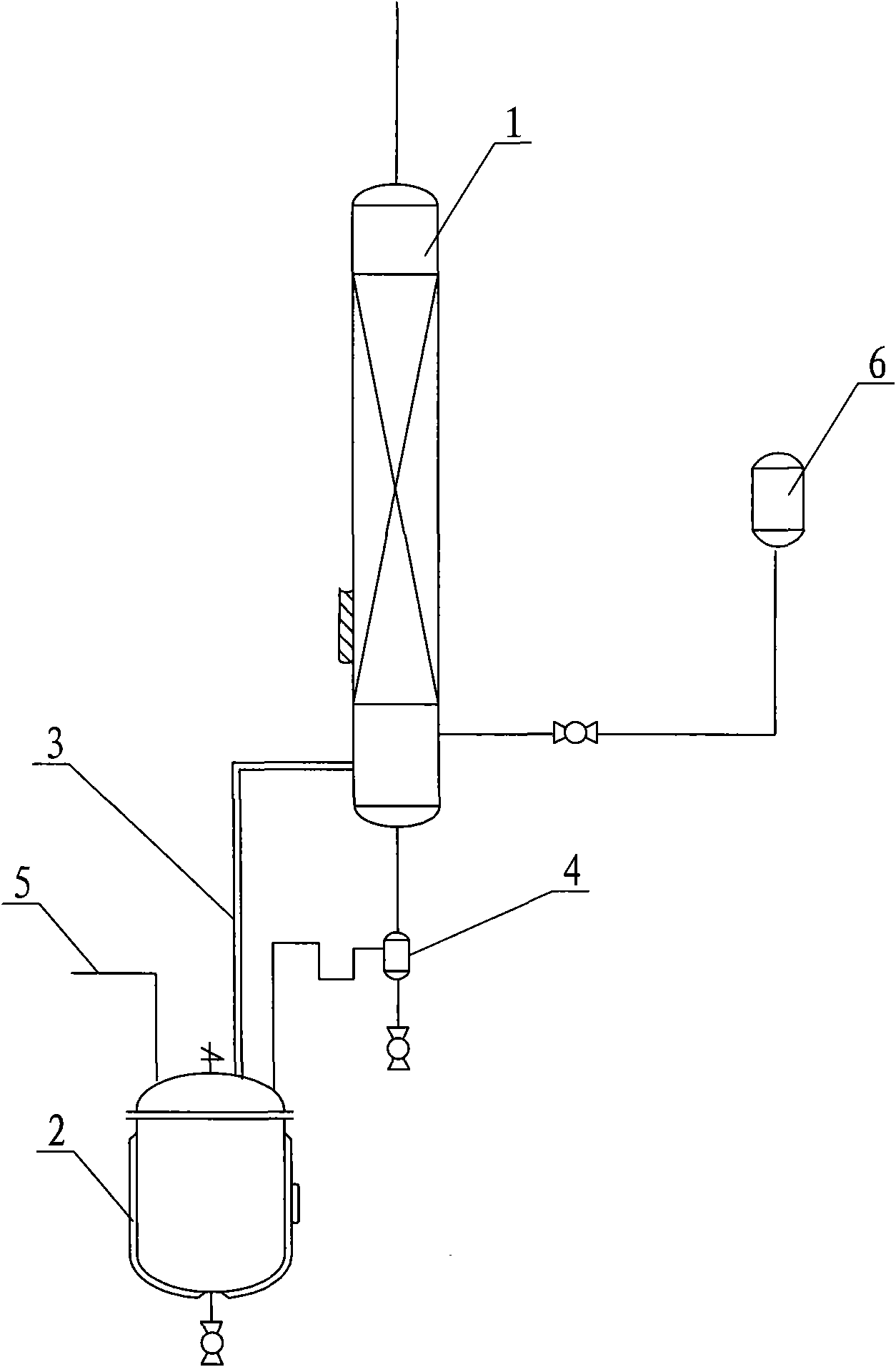
ActiveCN101613248AFully depolymerizedReduce aggregationHydrocarbon by depolymerisationDepolymerizationDiluent
The invention discloses a method for preparing cyclopentadiene by decomposing dicyclopentadiene through a liquid-phase depolymerization method. The existing liquid-phase depolymerization method has the defects that the energy consumption is high, the speed is low, the dicyclopentadiene is easy to polymerize into tripolymer or larger polymer when staying at the high temperature for a long time, etc. The method is characterized in that 1) the dicyclopentadiene is taken as raw material and is heated to be 150-240 DEG C in a reactor, so that the dicyclopentadiene is vaporized, and part of the dicyclopentadiene is decomposed to be the cyclopentadiene; 2) a volatilization tube is arranged between the top of the reactor and the bottom of a rectifying tower, the high temperature mixed gas of the dicyclopentadiene and the cyclopentadiene enters into the volatilization tube for reducing the temperature, cooling diluent is injected towards the end of the volatilization tube by the bottom of the rectifying tower, and the gas flow flowing out of the end of the volatilization tube is mixed with the cooling diluent. The method ensures the dicyclopentadiene to be fully depolymerized, reduces the polymerization phenomenon of the cyclopentadiene, improves the production efficiency, reduces the energy consumption of liquid-phase depolymerization, and remarkably increases the yield of the cyclopentadiene.
Owner:SHANDONG NHU PHARMA +1
Heavy Alkylbenzene Production Through Oligomerization
InactiveUS20130253239A1Thermal non-catalytic crackingLiquid hydrocarbon mixtures productionAlkyl transferAlkene
A process for producing heavy alkyl aromatics is presented. The process utilizes low molecular weight hydrocarbons for generating larger alkyl groups. The hydrocarbons can be generated from a variety of sources including Fischer-Tropsch liquids. The process includes oligomerization of low molecular weight olefins to larger olefins. The larger olefins are passed to an alkylation reactor to alkylate aromatic compounds.
Owner:UOP LLC
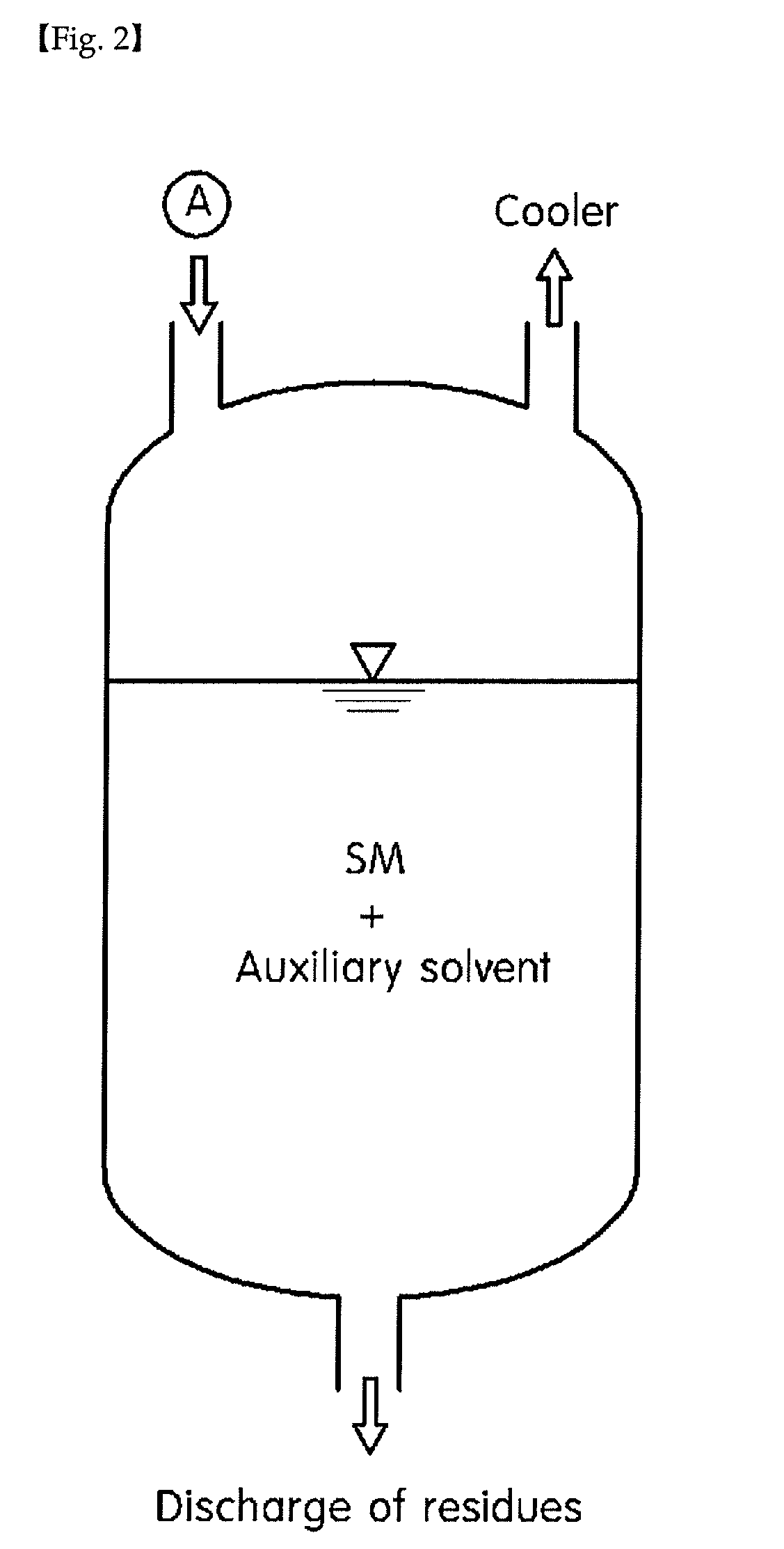
Apparatus for recovering styrene monomer and method of recovering styrene monomer using auxiliary solvent
InactiveUS20110067992A1High yieldIncrease productionMechanical conveying coke ovensProductsPolystyreneSolvent
Disclosed are an apparatus and a method for recovering styrene monomer using an auxiliary solvent, more particularly an apparatus and a method for recovering styrene monomer through pyrolysis of waste polystyrene capable of improving recovery ratio of styrene monomer using an auxiliary solvent such as steam, preventing repolymerization of pyrolyzed styrene monomer and effectively preventing production of unwanted high molecular weight materials.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF CHEM TECH
Production method for maximizing ethylene or propylene
The invention discloses a production method for maximizing ethylene or propylene. The method comprises the following main steps of: crude oil and distillate oil thereof, urban mixed waste plastics andthe like are used as raw materials, the raw materials are pretreated and then enter a catalytic cracking reactor, and high-temperature oil gas after reaction is cooled by a two-stage pre-washing tower to remove impurities and is subjected to related separation to obtain light distillate oil and heavy distillate oil; hydrogenation reaction operation is carried out on the heavy distillate oil; light distillate oil separation treatment: olefin is subjected to recombination operation, alkane enters a steam cracking device to produce ethylene in a rich manner, and aromatic hydrocarbon components are separated to serve as byproducts; and a product of the hydrogenation and recombination reaction and distillate oil of steam cracking are circulated to the catalytic cracking reactor. According to the production method disclosed by the invention, the yield of ethylene and propylene is 45-75m% of that of the raw material, and the yield of aromatic hydrocarbon is 15-30m% of that of the raw material; particularly, when the urban mixed waste plastic is used as a raw material, ethylene or propylene is produced by the urban mixed waste plastic, new plastic is reproduced by a conventional polymerization process, and the chemical cyclic utilization of the waste plastic is realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG COMY ENVIRONMENT TECH CO LTD
Method for preparing fuel by using biological oils and fats
ActiveUS20140135542A1Large heat releaseFast inactivationFatty acid hydrogenationCatalytic crackingOil and greaseHydrogen
A new method of producing fuel from biological oils and fats is provided, which comprises following steps: (a) proceeding with a catalytic cracking-deoxygenation reaction for the biological oils and fats under heating in the presence of a cracking-deoxygenation catalyst; (b) mixing the product of step (a) with hydrogen gas; and (c) proceeding with a catalytic hydrodeoxygenation reaction for the mixture from step (b) under heating in the presence of a hydrodeoxygenation catalyst. By means of the method of the present invention, clean fuel produced by using biological oils and fats as raw materials is compatible to the fuel composition produced from crude oil refining.
Owner:ECO BIOMASS TECH CO LTD +1
Method for separating cyclopentadiene and methylcyclopentadiene from ethylene by-product C9
InactiveCN101186553AExpand sourceSolve the problem of carbon accumulationDistillation purification/separationHydrocarbon by depolymerisationMethylcyclopentadieneEthylene
The invention relates to a method of separating cyclopentadiene and methyl cyclopentadiene from a mixture with ingredients of dicyclopentadiene and dimethyl cyclopentadiene. The method is particularly suitable for purifying and separating the cyclopentadiene and methyl cyclopentadiene from ethylene byproduct C9 or crude cyclopentadiene. Ethylene byproduct C9 or crude dicyclopentadiene that contains dicyclopentadiene and dimethyl cyclopentadiene is put into a high-temperature cracking reactor that is arranged in a tower boiler of a rectifying tower 1; pyrolyzed mixture gas under high temperature runs upwards through the rectifying tower to lead distillate that contains the cyclopentadiene and the methyl cyclopentadiene to be separated at the top of the tower; the mixture distillate of the cyclopentadiene and methyl cyclopentadiene that is extracted at the top of the rectifying tower 1 enters a rectifying tower 2, and the cyclopentadiene is extracted from the top of the tower and the methyl cyclopentadiene is extracted from the bottom of the tower.
Owner:天津天大天海化工新技术有限公司 +1
Method for preparing thermal-reversible cross-linking polyisobutene rubber capable of being processed repeatedly
InactiveCN105733110ASave raw materialsHigh reactivityProductsOrganic compound preparationCross-linkBenzoyl bromide
The invention relates to a method for preparing thermal-reversible cross-linking polyisobutene rubber capable of being processed repeatedly. According to a rubber matrix, a bromination poly(isobutene-co-p-methylstyrene) copolymer containing benzyl bromide functional groups is adopted, and the benzyl bromide functional groups generate a cross-linking reaction with a cross-linking agent easily; dimeric cyclopentadiene carboxylic acid sodium salt or dimeric cyclopentadiene carboxylic acid kali salt is adopted, by the adoption of a blended vulcanization mode, the thermal-reversible cross-linking agent generates an esterification reaction with the rubber matrix to form a dicyclopentadiene cross-linking bridge key, and then the rubber is prepared after hot press is performed. The prepared rubber is equivalent to traditional vulcanized rubber in stretchability and heat resistance, the tensile strength of the rubber is stabilized to be about 70% of original performance, the elongation at break is stabilized to be about 60% of original performance, rubber raw materials can be obviously saved, meanwhile, leftover materials can be reprocessed to be finished products, reutilization of the leftover materials is achieved, in this way, the utilization rate of resources is increased, and environmental friendliness and saving are achieved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF PETROCHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
Popular searches
Treatment with hydrotreatment processes Refining by aromatic hydrocarbon hydrogenation Hydrocarbon by hydrocarbon cracking Hydrocarbon oils treatment products Reagents Educts Hydrocarbon oil cracking process Indirect heating destructive distillation Special form destructive distillation Hydrocarbon preparation catalysts
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com