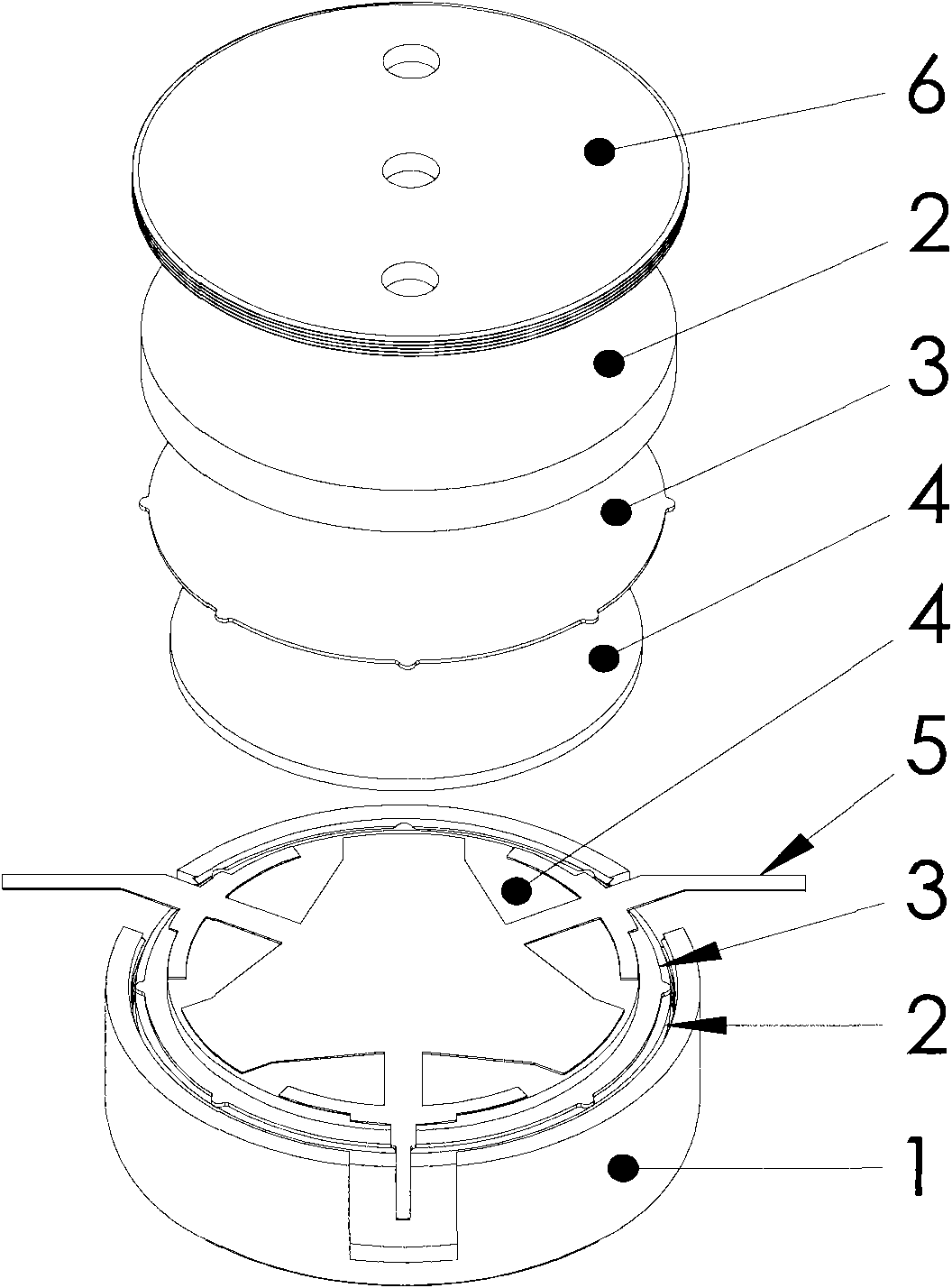
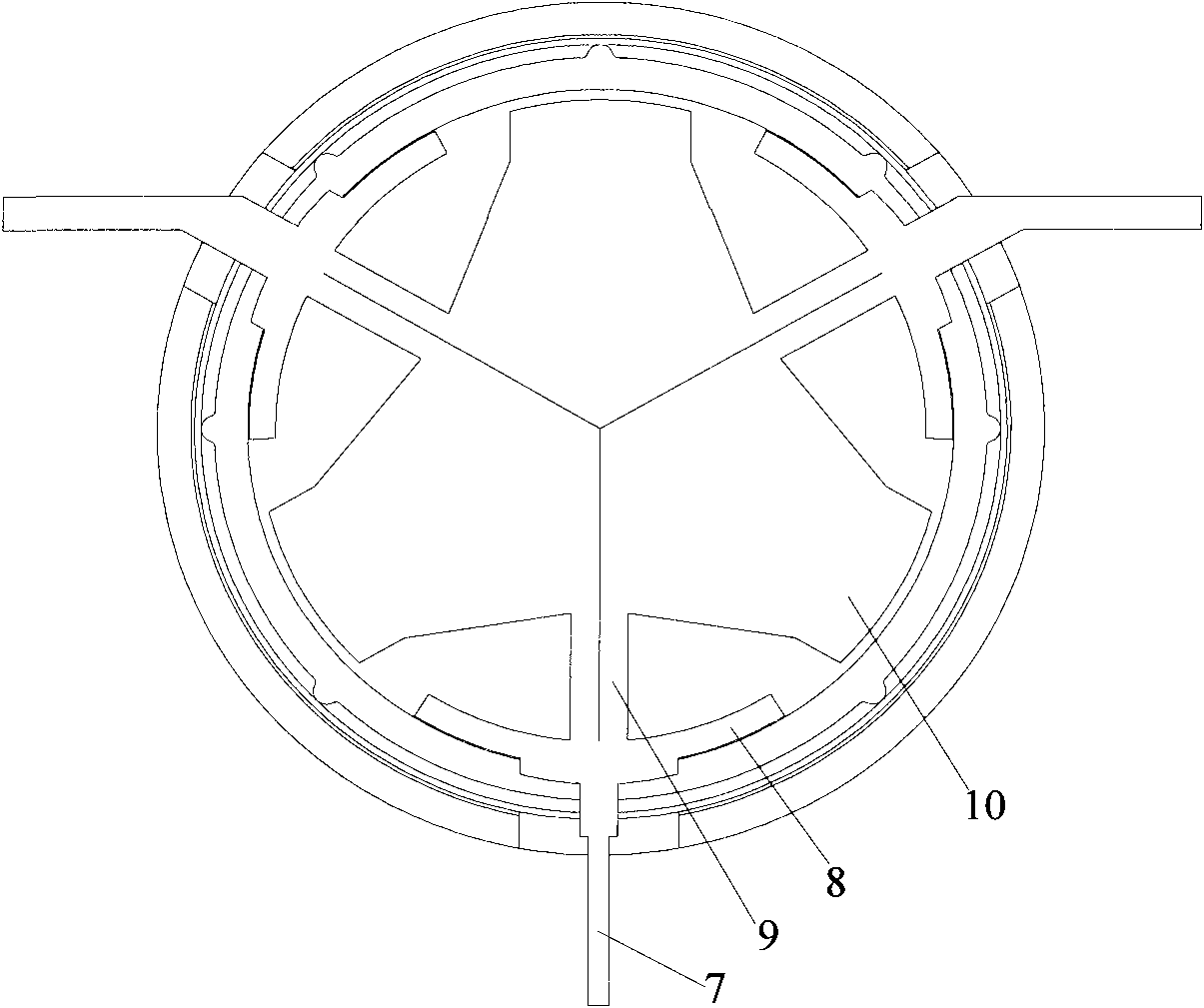
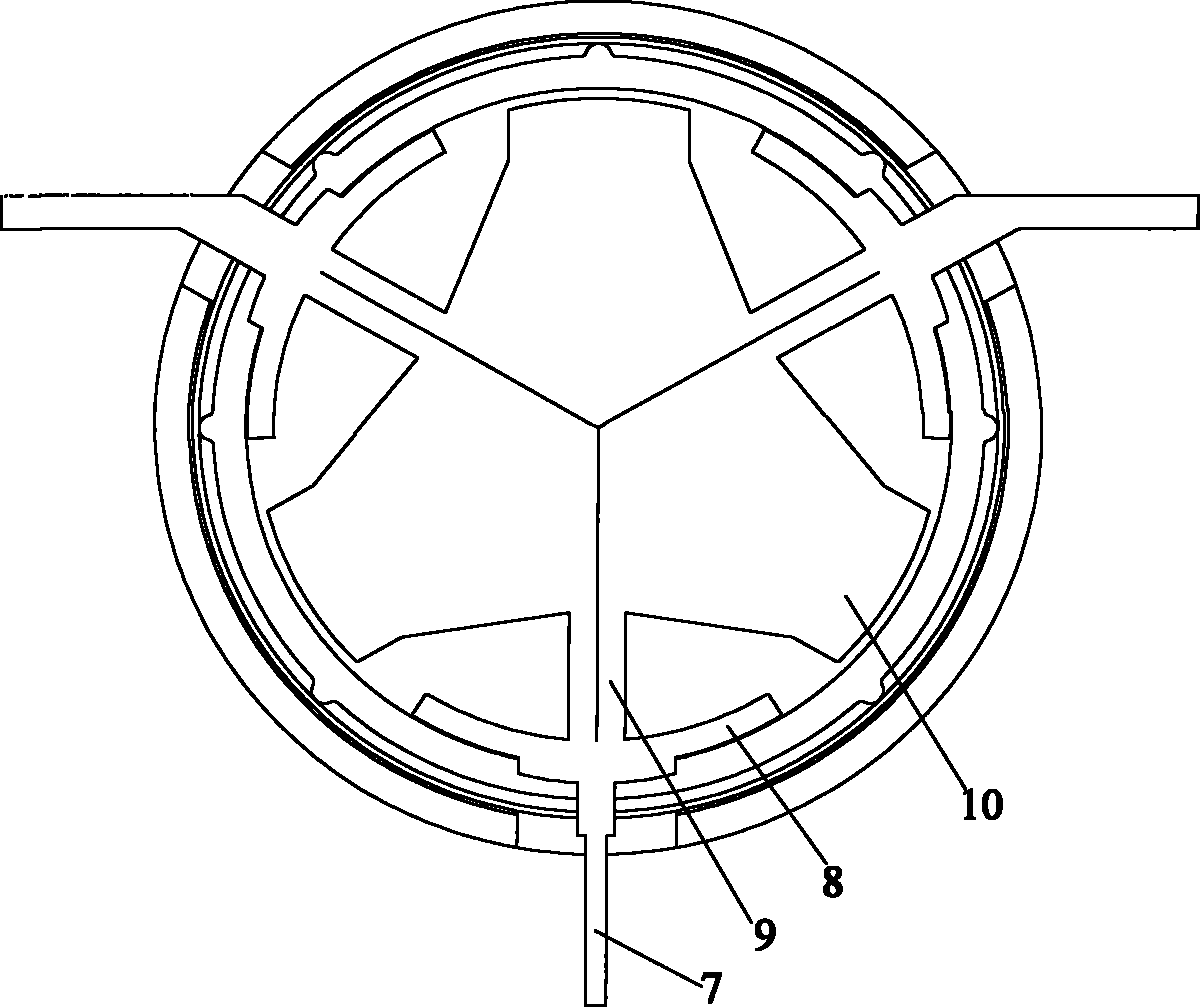
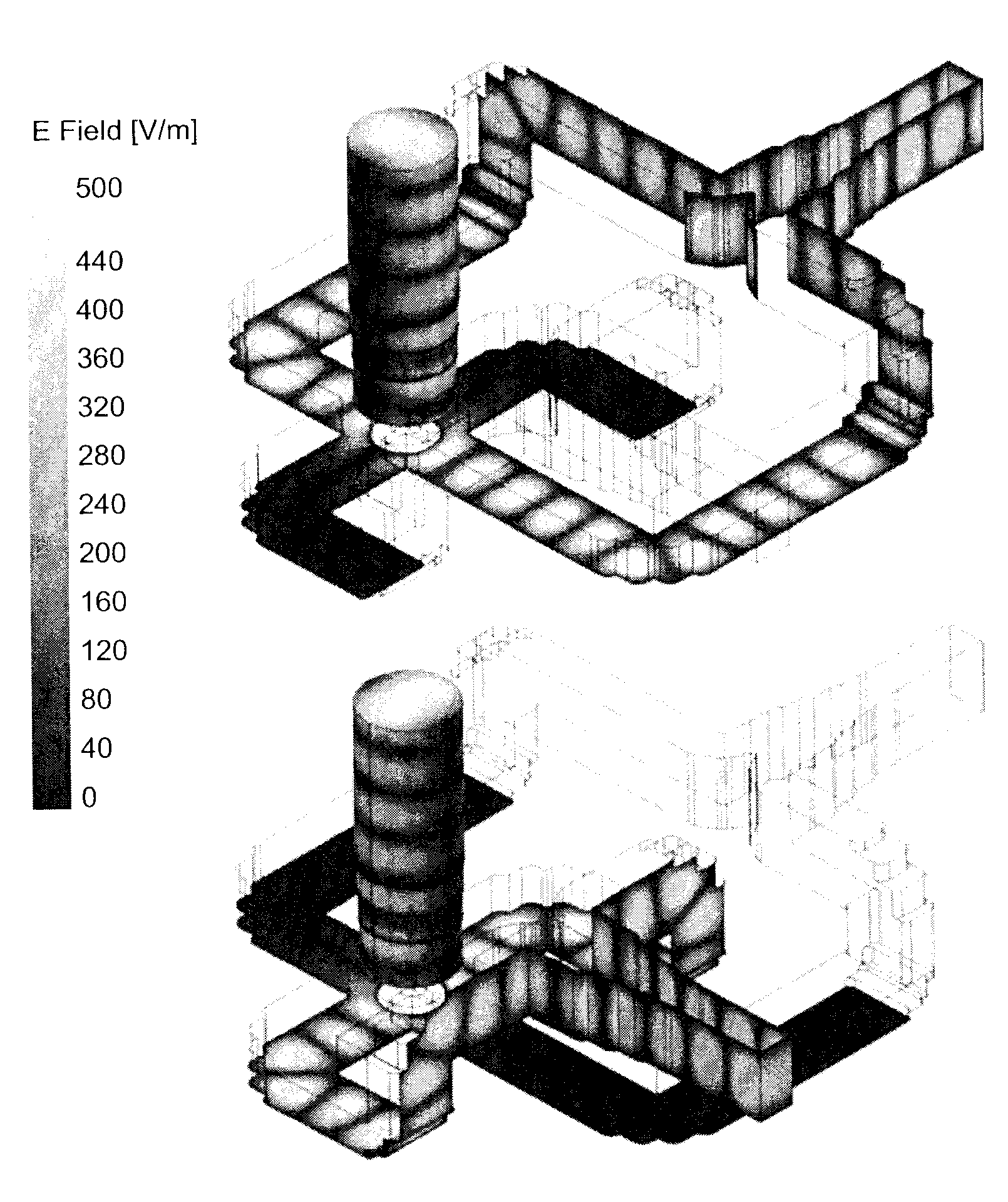
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
67 results about "Y junction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Y junction may refer to one of several things. A 3-way junction where three roads meet. A Wye (railroad) junction that takes the form of a triangle of railway lines.
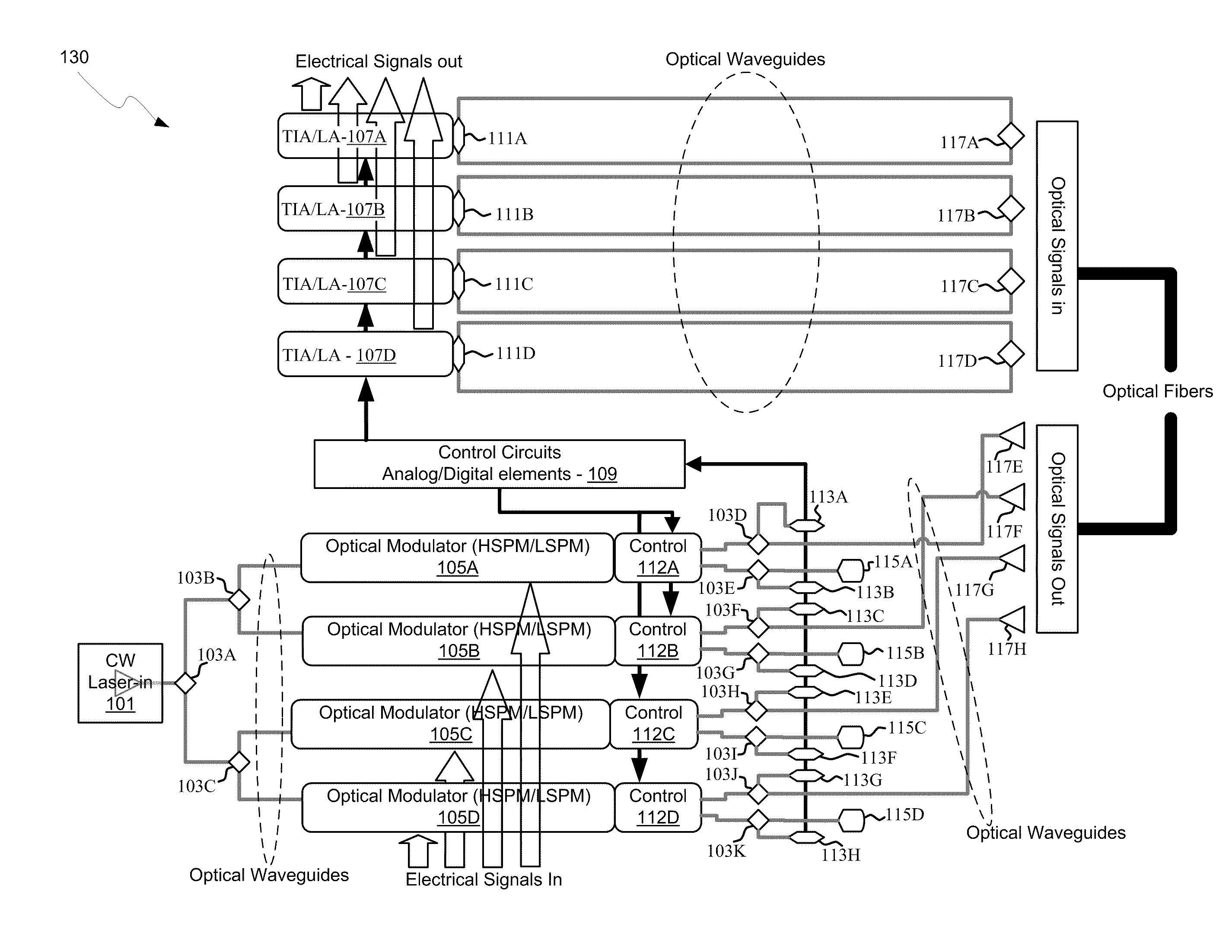
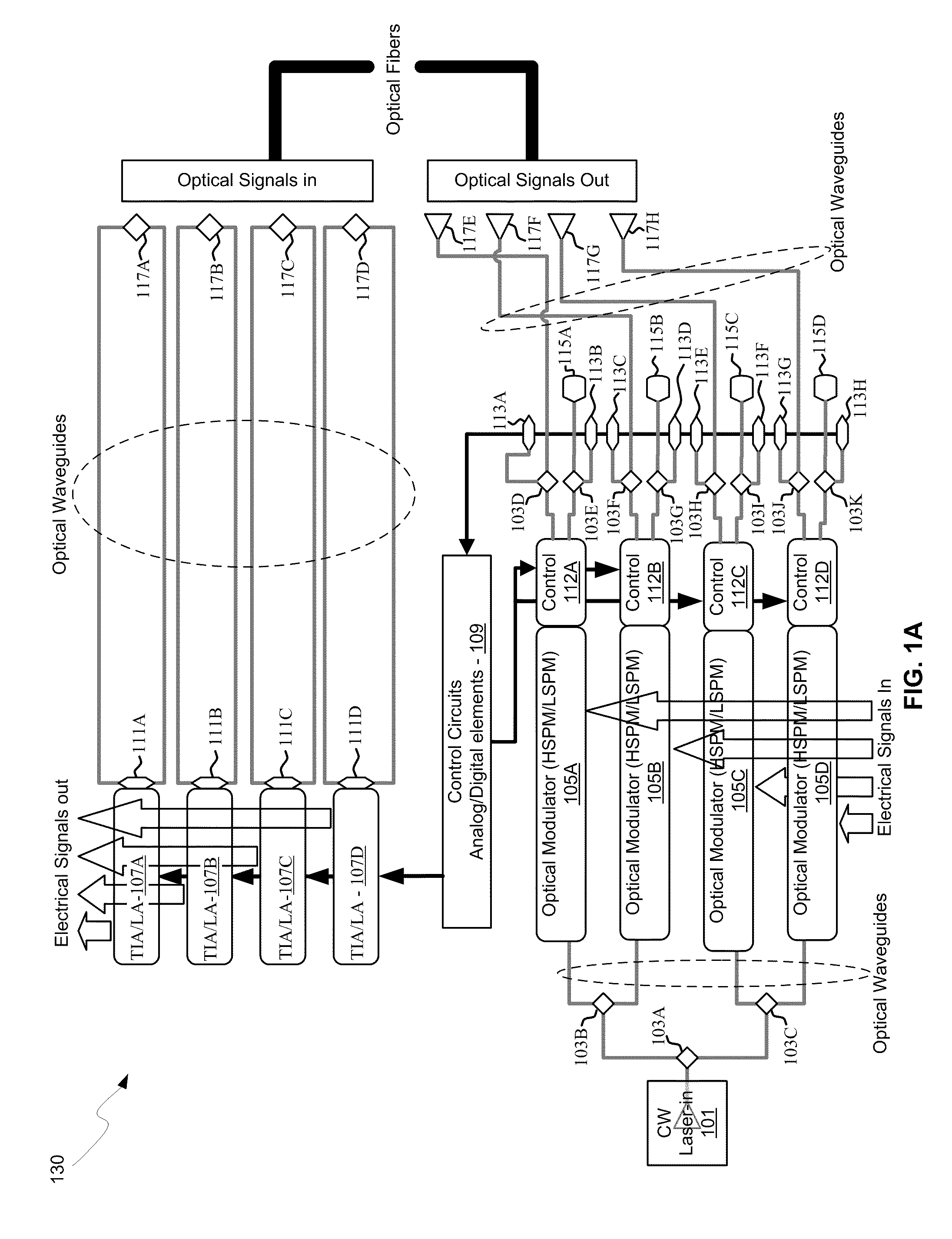
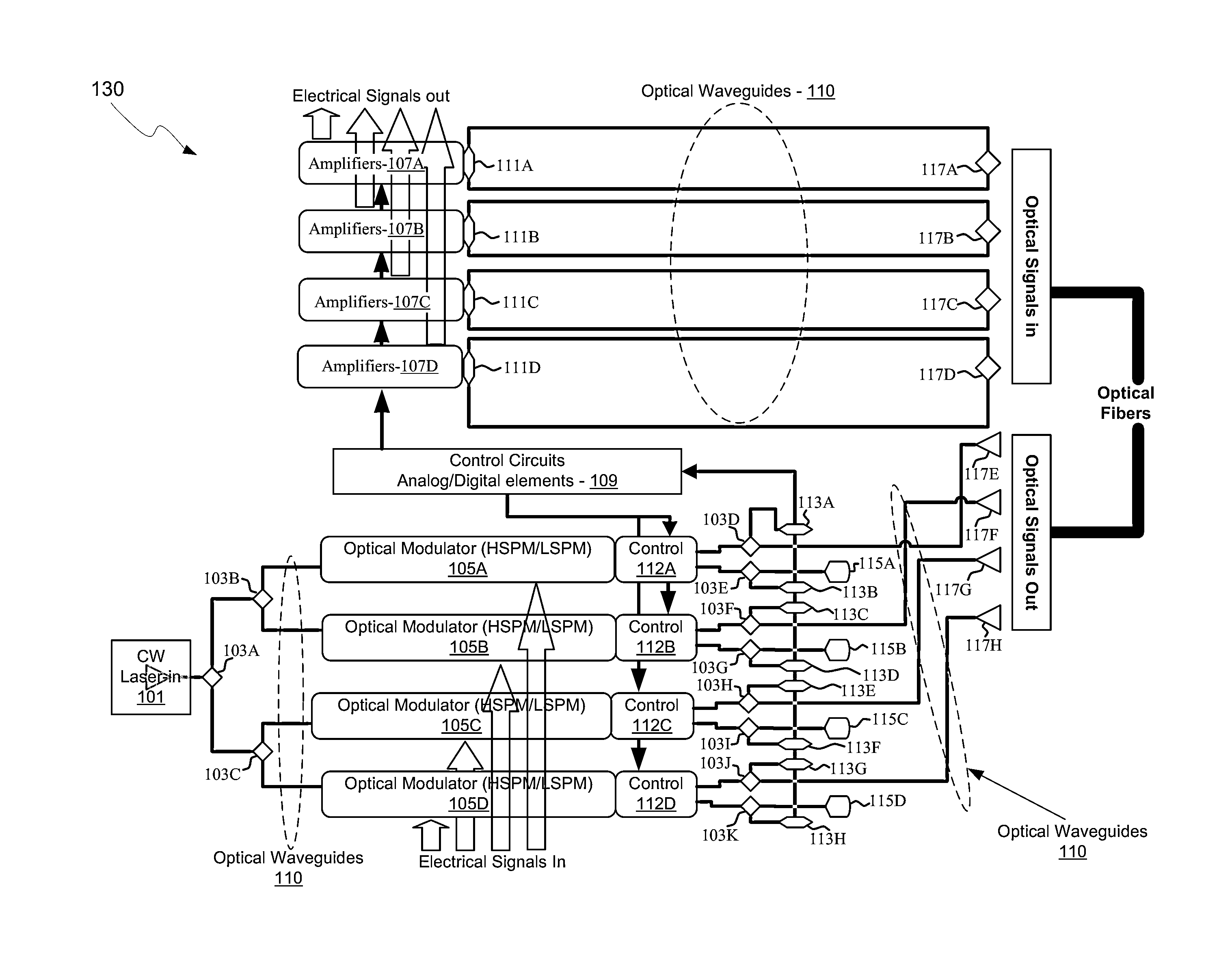
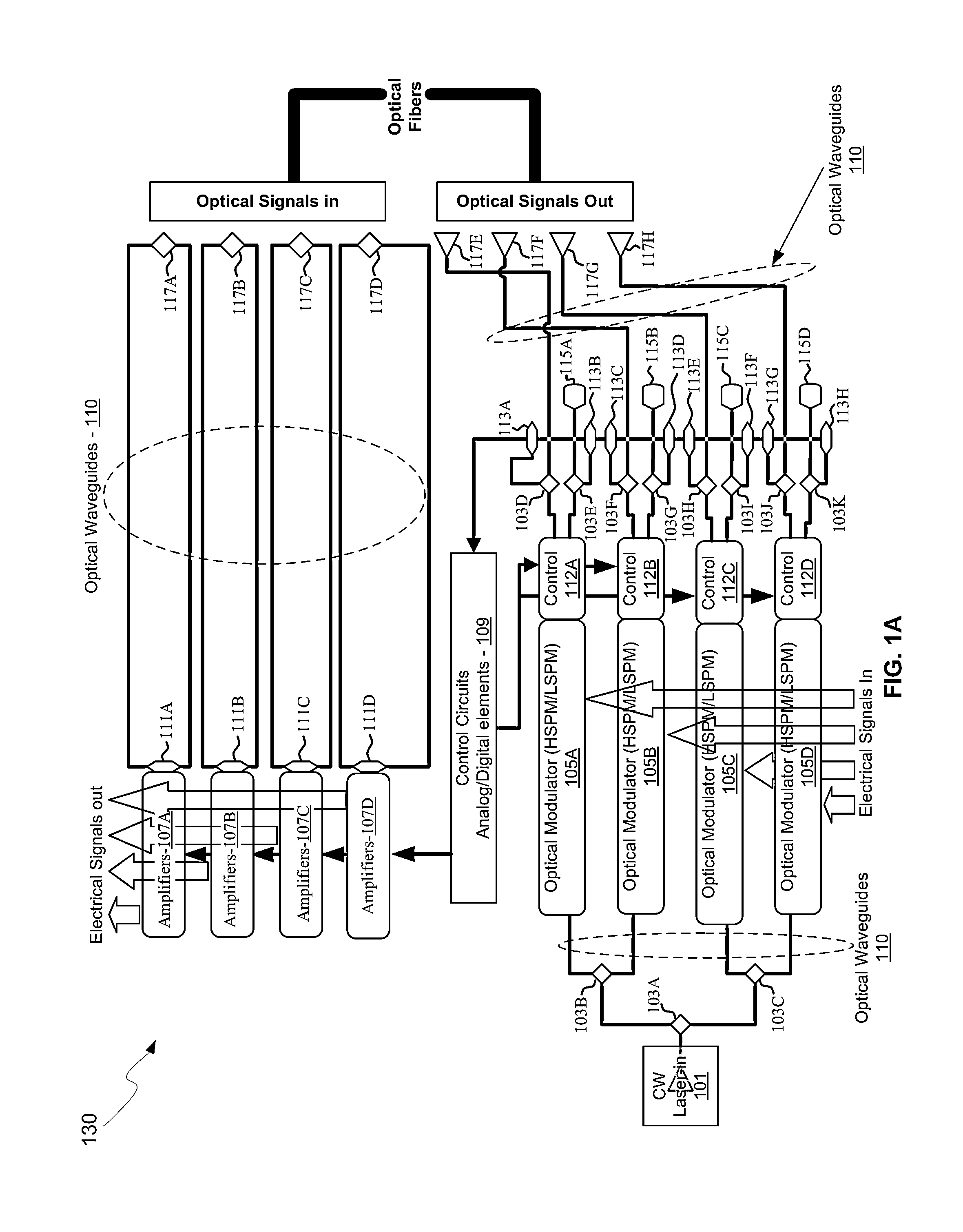
Integrated control system for laser and mach-zehnder interferometer
ActiveUS20100128336A1Electromagnetic transmissionOptical waveguide light guideLow speedMach–Zehnder interferometer
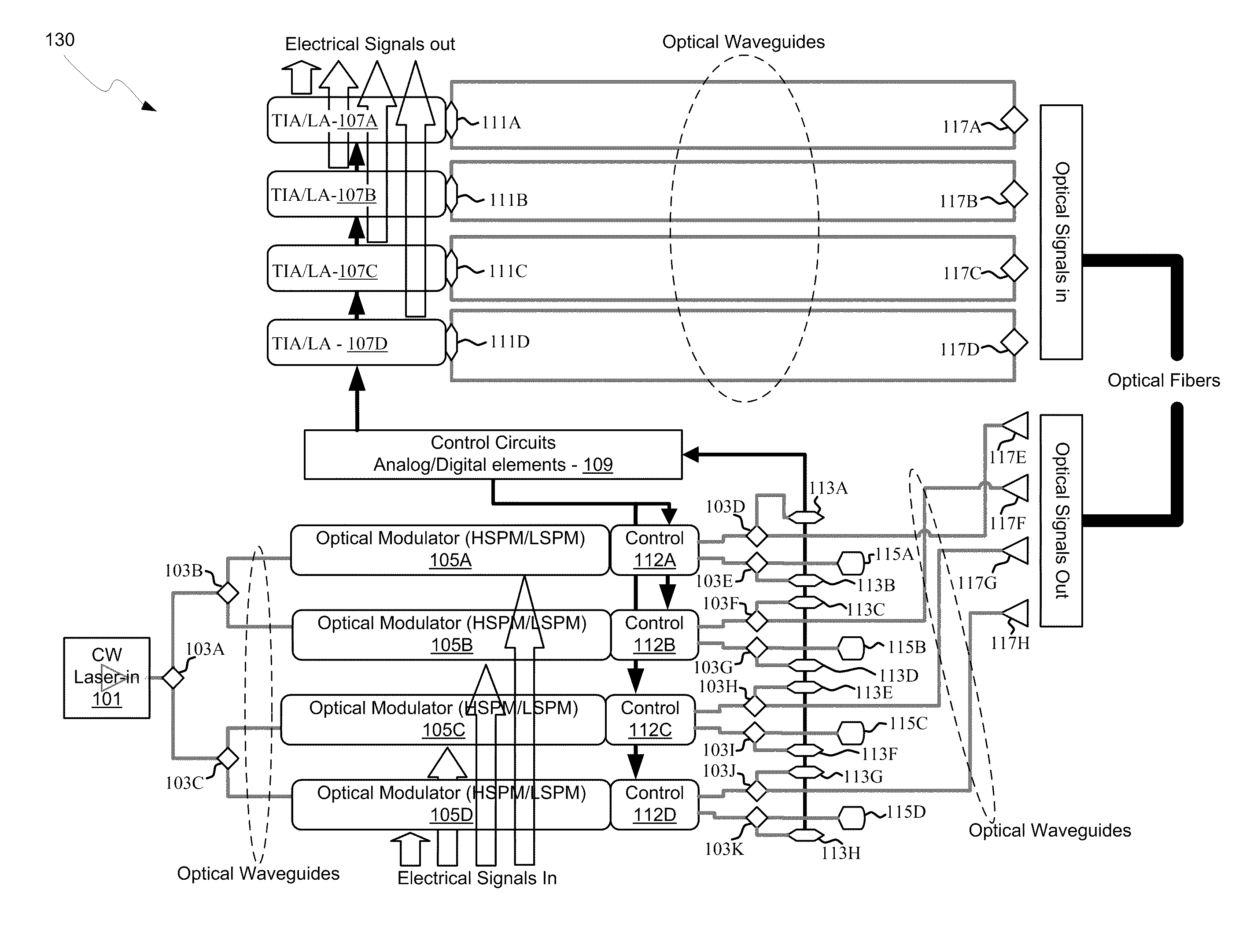
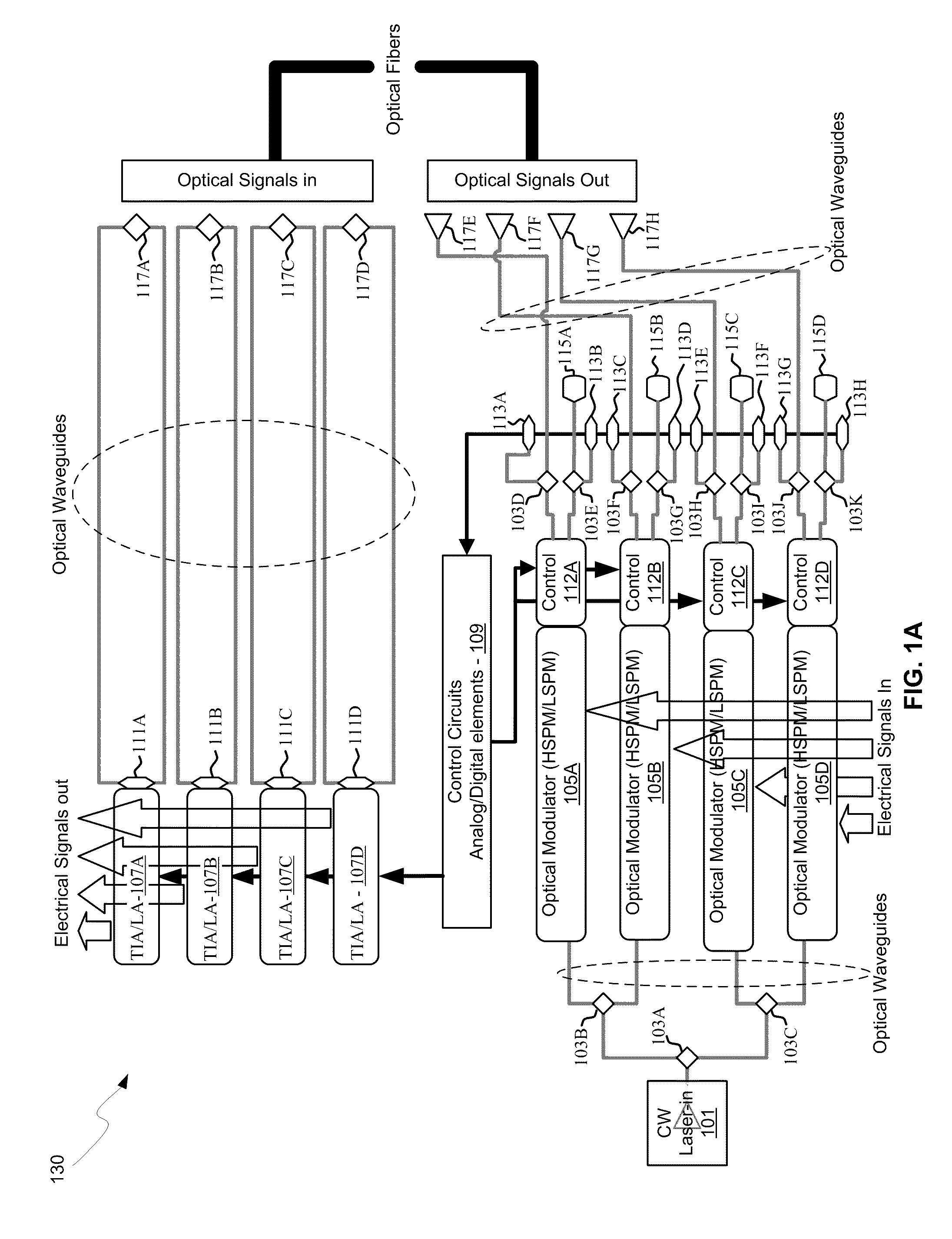
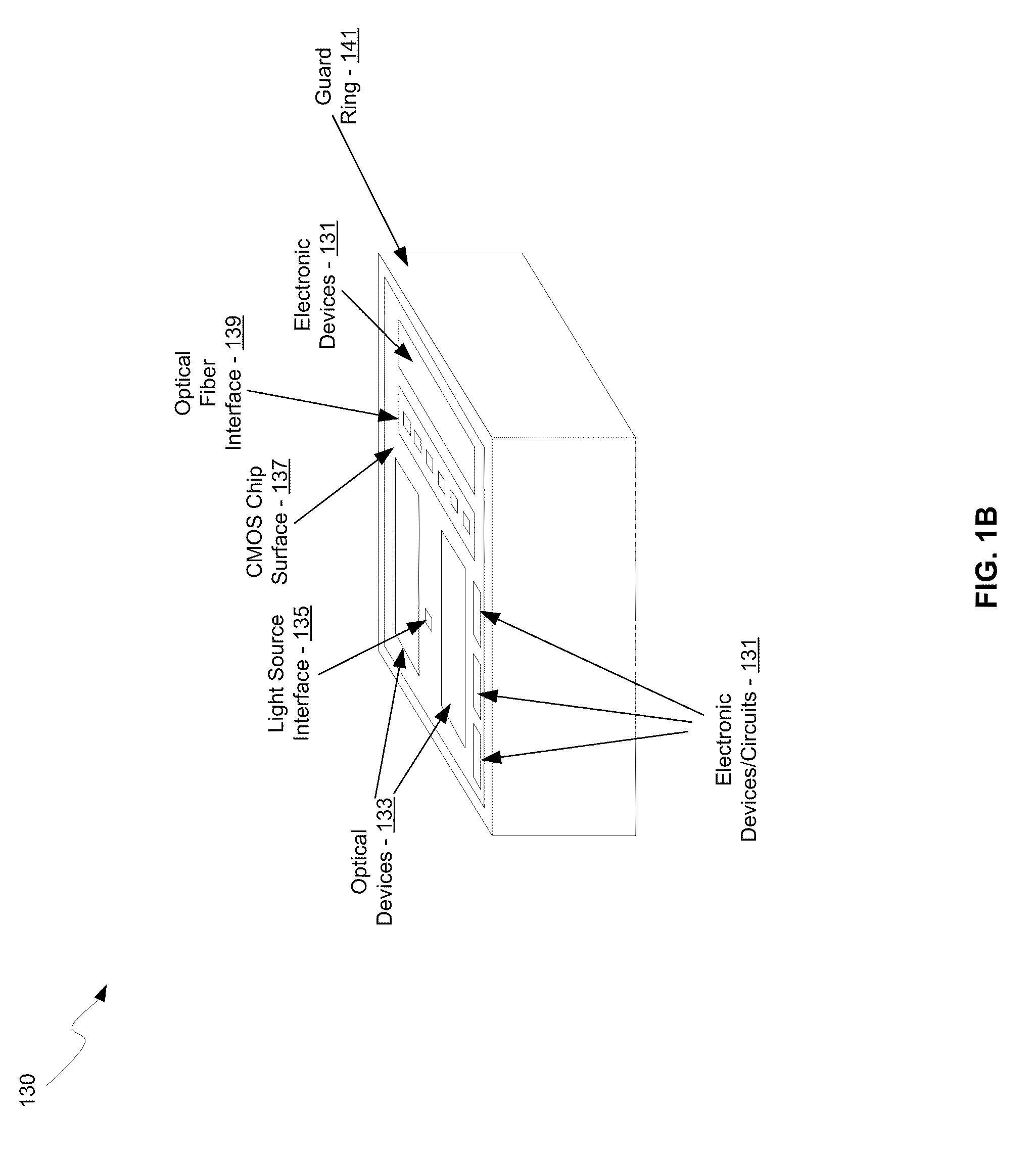
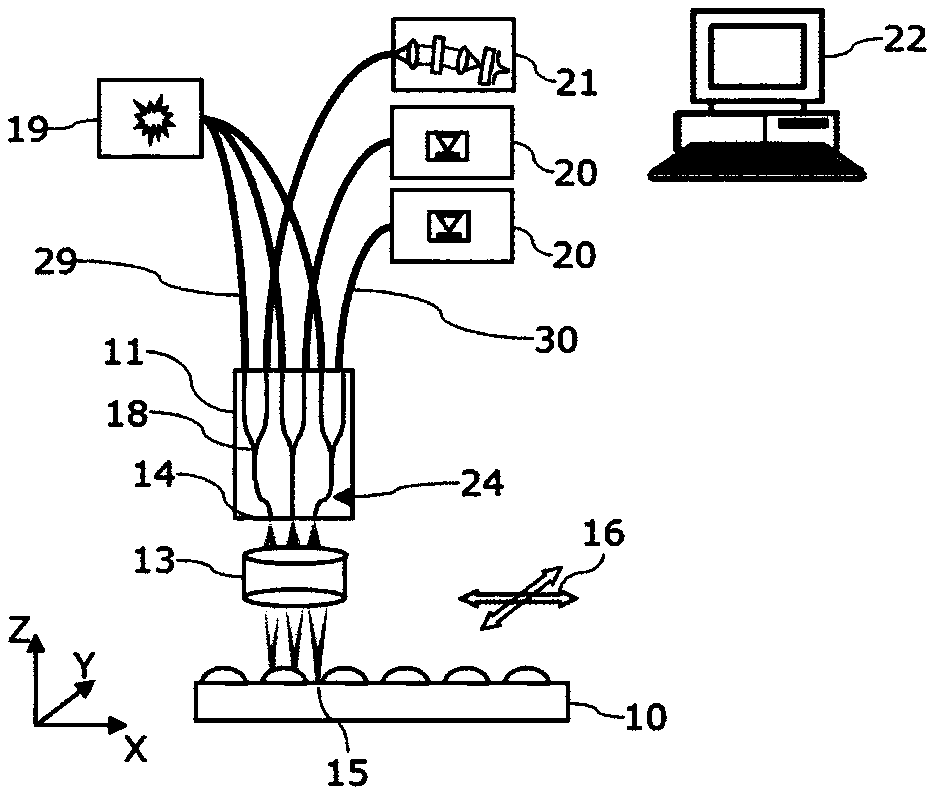
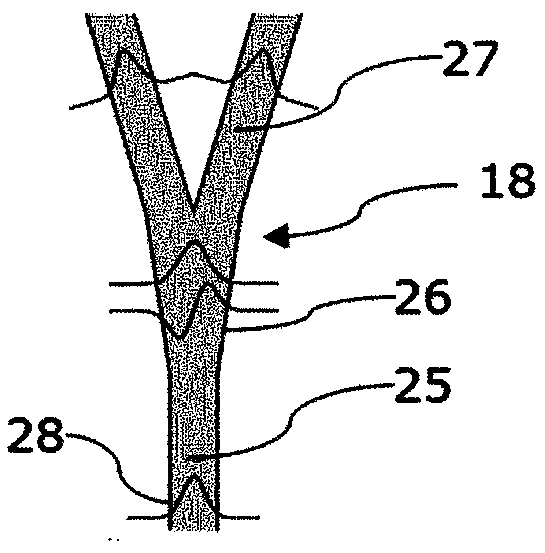
An integrated control system for a laser and Mach-Zehnder interferometer are disclosed and may include configuring a bias point for low-speed control of an optical modulator utilizing control circuitry integrated on the same CMOS die. The optical modulator may be differentially monitored. A laser source for the modulator may be controlled utilizing monitor photodiodes via optical taps on outputs of the modulator, or utilizing a monitor photodiode on one output port of the modulator, which may comprise a Mach-Zehnder interferometer. An error signal may be generated by subtracting monitor photodiode signals from optical taps on output ports of the modulator. The bias point of the modulator may be adjusted by minimizing the error signal. Calibration time of the bias point may be reduced utilizing electronic data inversion. An output of the modulator may comprise a Y-junction and a single monitor photodiode may measure both branches of the modulator.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
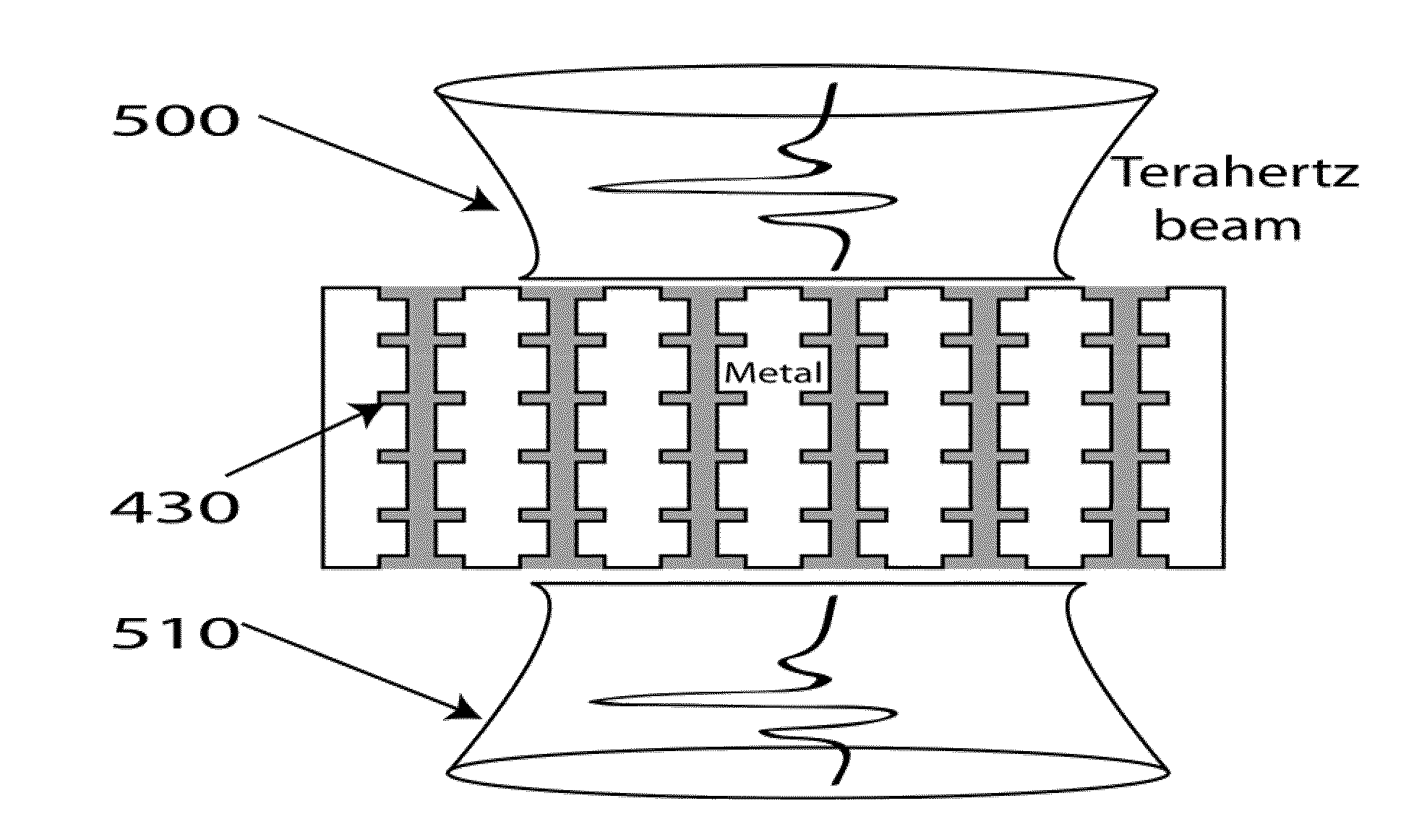
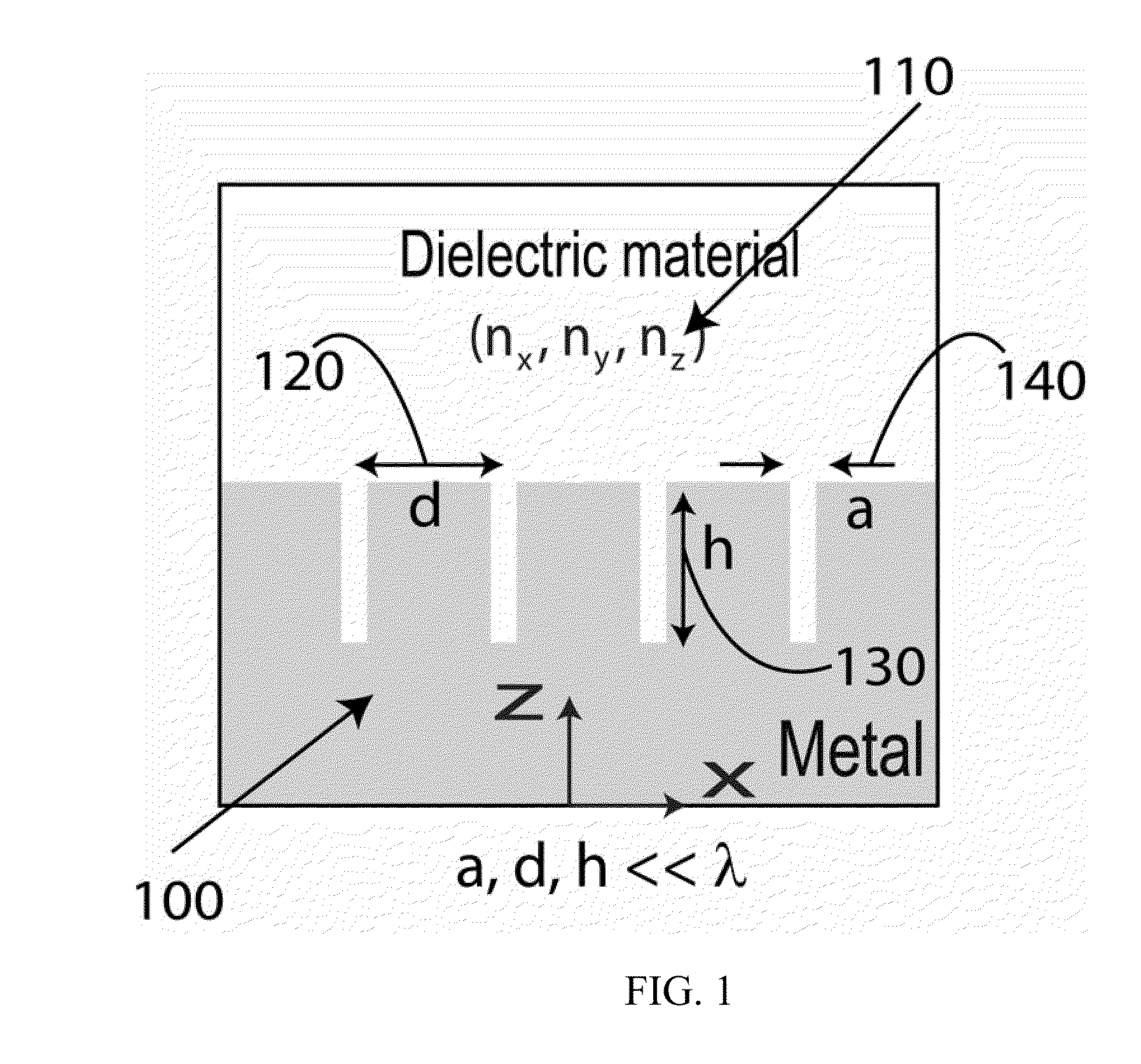
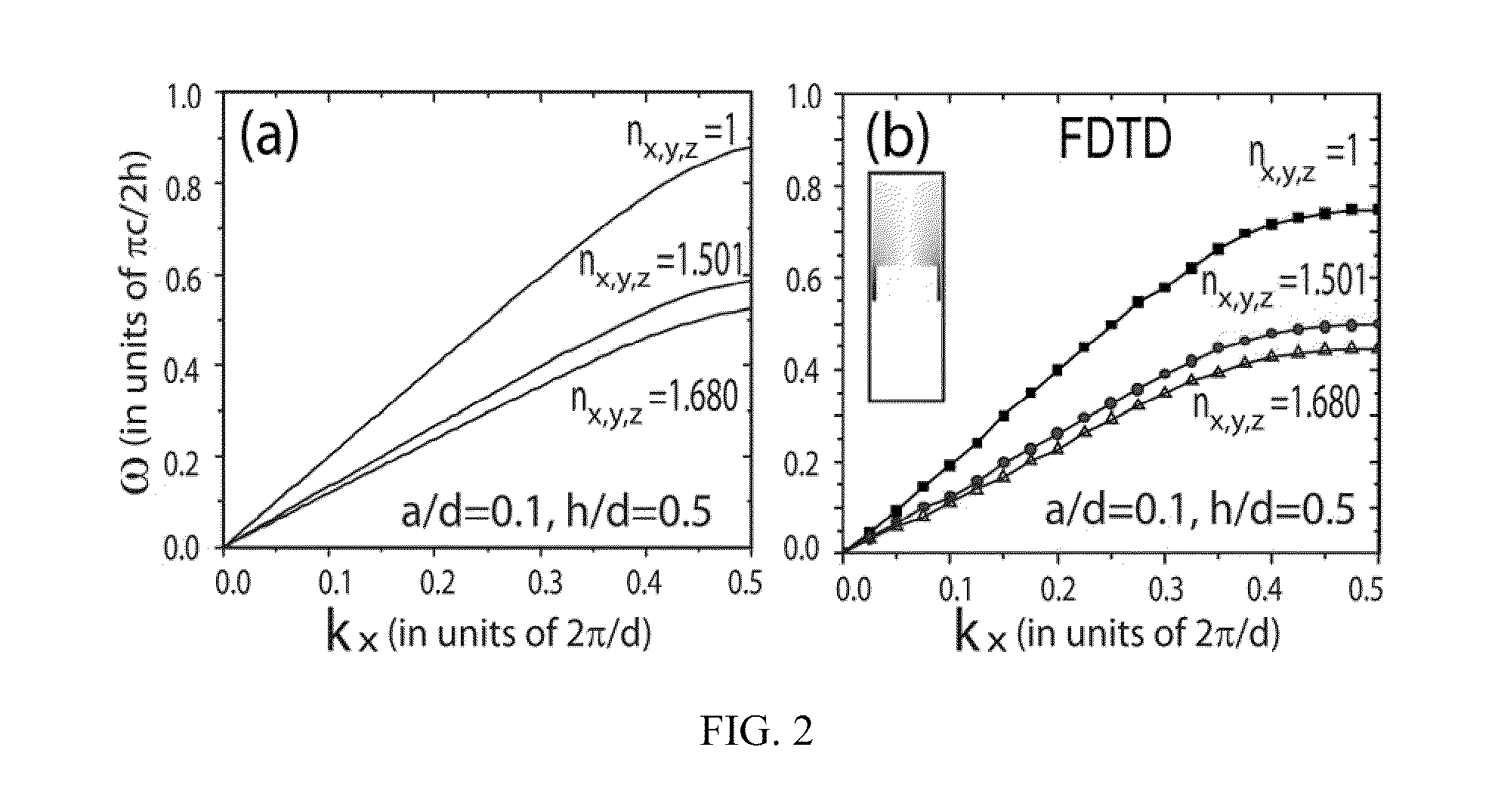
Dynamic Terahertz Switch Using Periodic Corrugated Structures
InactiveUS20120019901A1Ease of lightOptical light guidesNon-linear opticsManufacturing technologyElectrical conductor
A subwavelength terahertz (THz) switch using an artificially designed conductor metamaterial is discussed in this invention. Theoretically, slow-light EM wave propagating at THz speed imitates the strongly localized surface plasmon modes and henceforth is called Spoof Surface Plasmon Polariton (SSPP) mode in this invention. The SSPP mode of slow-light EM propagation can be easily tailored by changing the refractive index of the dielectric materials inside the metallic gap structure engineered as a periodic array of grooves. Thus, the incorporation of electro-optical material which has birefringence such as a nematic liquid crystal (N-LC) or multiple-refractive indices into the metallic gap leads to a highly compact and efficient terahertz switch being controlled by a low-voltage signal. The optimal design of the SSPP switch enabled by this novel method shows many interesting properties including 1) strong subwavelength localization; 2) relatively high extinction (On / Off switching) ratio; and 3) small damping attenuation. The THz dynamic switches can be used to construct linear switches, Y junction switches and Mach-Zehnder interferometers by using micromachining and other fabrication techniques.
Owner:MAZUMDER PINAKI
Practical silicon photonic multi-function integrated-optic chip for fiber sensor applications
ActiveUS20130028557A1Reduce equipment footprintSmall sizeCoupling light guidesMetal working apparatusPolarization diversityPhotonics
This patent disclosure is based on silicon instead of LiNbO3, waveguide chip. The disclosed silicon-based multi-function integrated-optic chip comprises of unique design and fabrication features onto it. First, a unique polarization-diversity coupler is designed and fabricated to couple the external light into the silicon waveguide structure. Then TE mode is guided into a silicon slab waveguide, but TM mode is confined and diverted 90 degree in a silicon carbide structure till the chip edges for TM-mode suppression. Second, a unique two-step (vertical and lateral) taper waveguide region is designed and fabricated to bridge the polarization-diversity coupler output with the input of a multi-mode interferometer (MMI) splitter for power loss reduction. In this configuration, MMI may be a 1×2 or 2×2 structure to divide the input TE mode into a 50 / 50 splitting ratio output to form a Y-junction. Third, at either end of the Y-junction output, there is a phase modulator to achieve optical phase modulation through various physics mechanisms such as plasma dispersion, electro-optics, thermo-optics, or photo-elastic effect. With this newly-developed silicon-based multi-function integrated optic chip, the size and cost of fiber sensors including FOG's can be greatly reduced.
Owner:TAIWAN SPACE AGENCY
Integrated control system for laser and Mach-Zehnder interferometer
ActiveUS7916377B2Electromagnetic transmissionOptical waveguide light guideMach–Zehnder interferometerPhotodiode
An integrated control system for a laser and Mach-Zehnder interferometer are disclosed and may include configuring a bias point for low-speed control of an optical modulator utilizing control circuitry integrated on the same CMOS die. The optical modulator may be differentially monitored. A laser source for the modulator may be controlled utilizing monitor photodiodes via optical taps on outputs of the modulator, or utilizing a monitor photodiode on one output port of the modulator, which may comprise a Mach-Zehnder interferometer. An error signal may be generated by subtracting monitor photodiode signals from optical taps on output ports of the modulator. The bias point of the modulator may be adjusted by minimizing the error signal. Calibration time of the bias point may be reduced utilizing electronic data inversion. An output of the modulator may comprise a Y-junction and a single monitor photodiode may measure both branches of the modulator.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
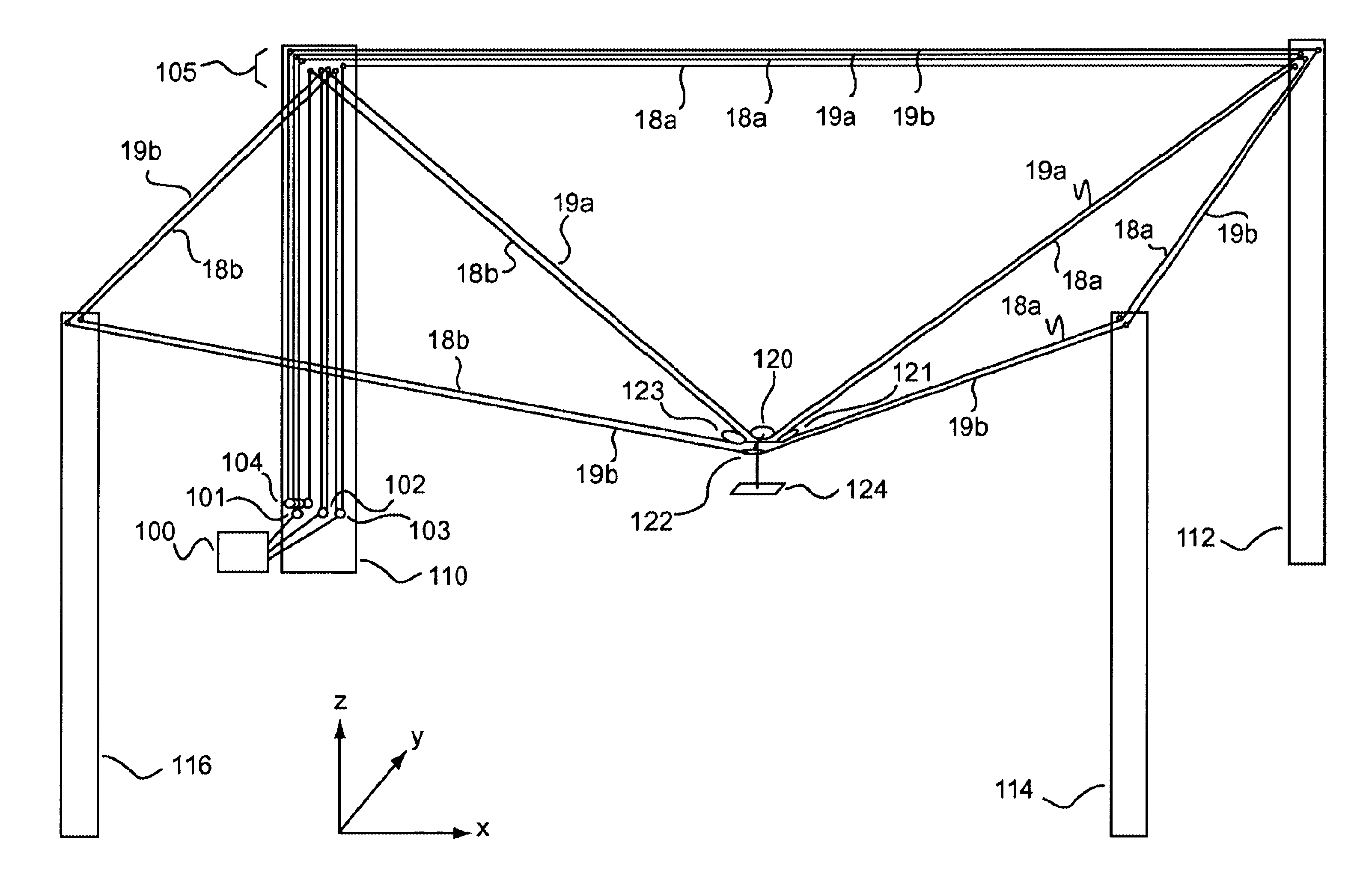
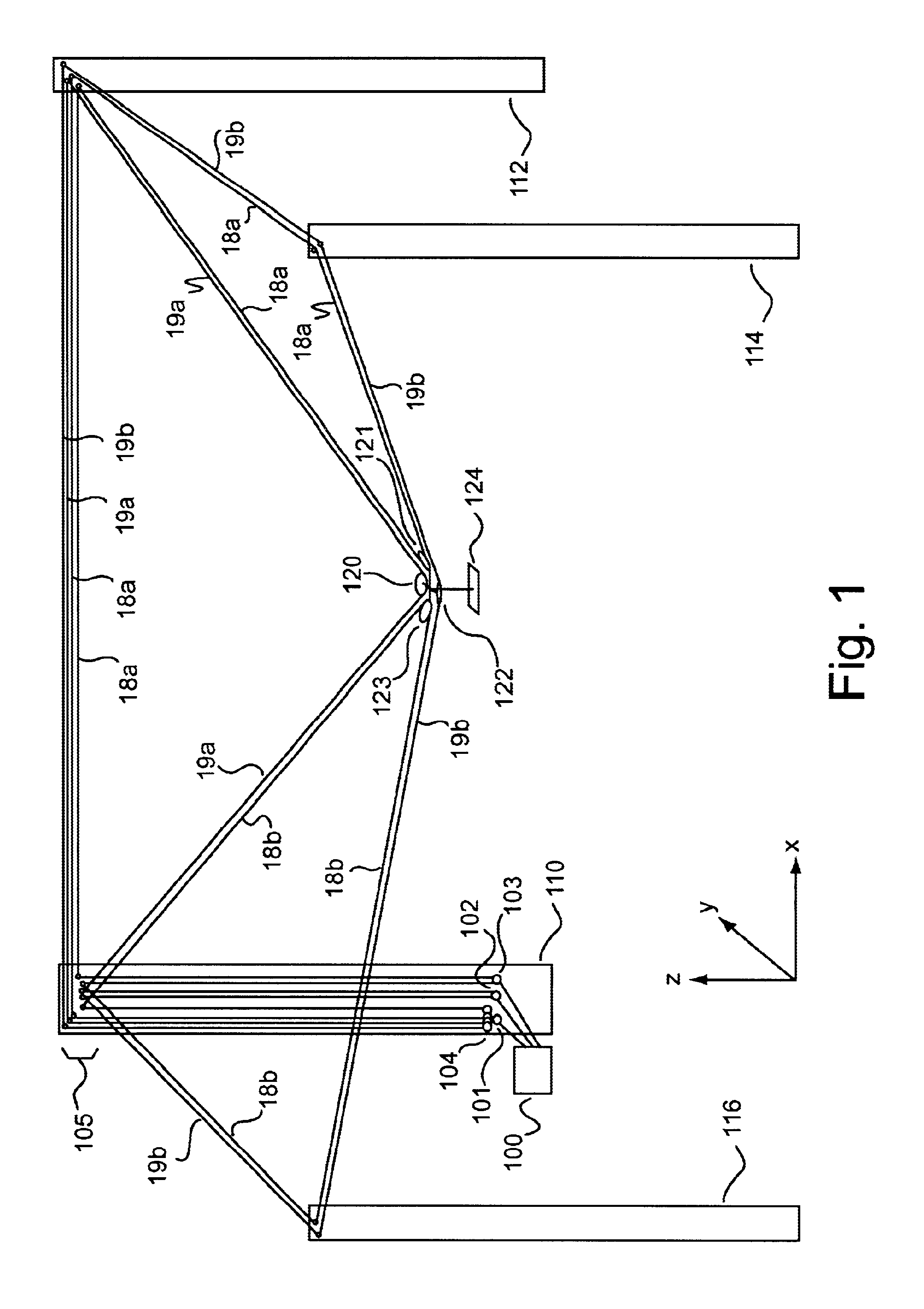
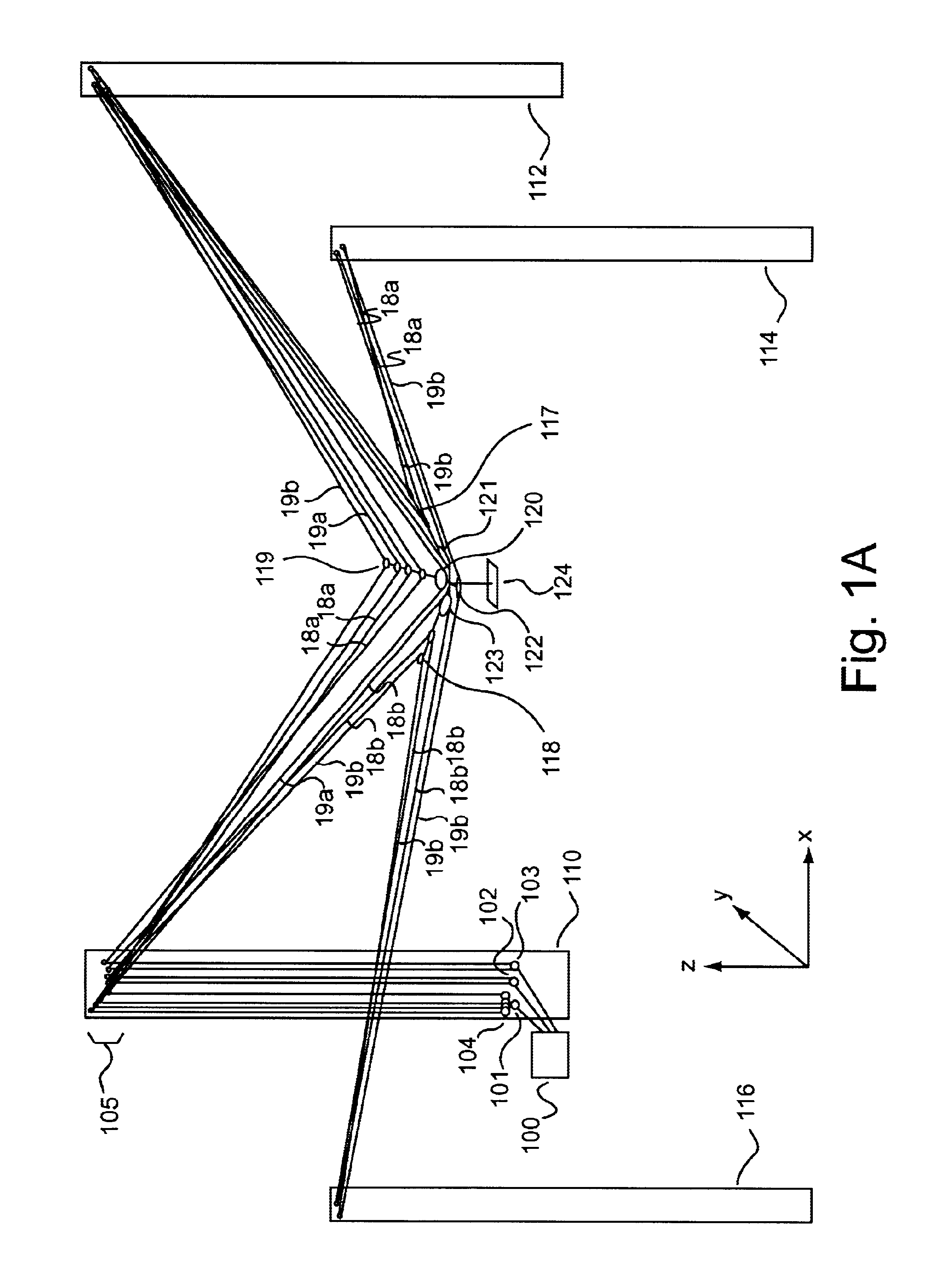
System and method for facilitating fluid three-dimensional movement of an object via directional force
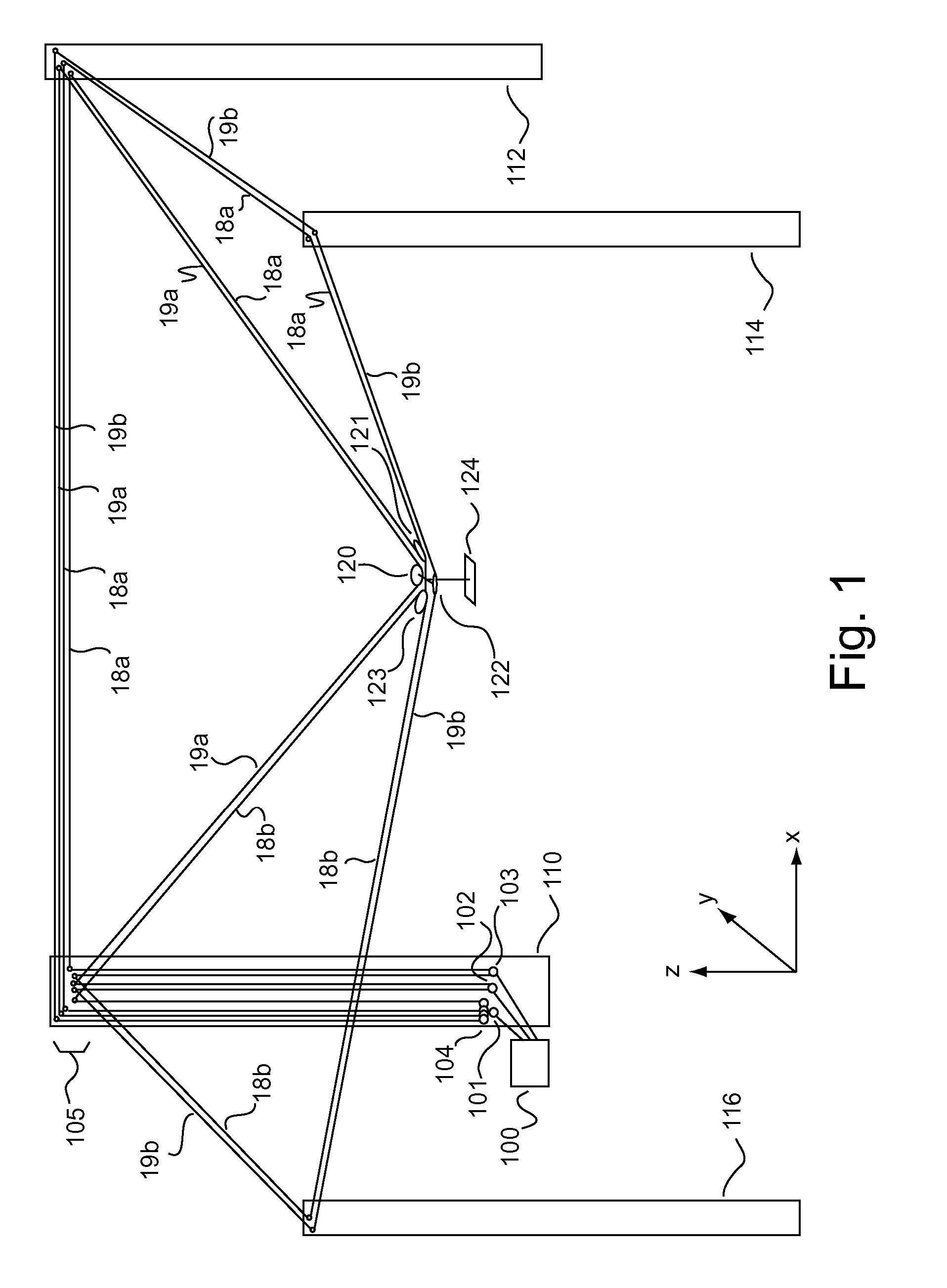
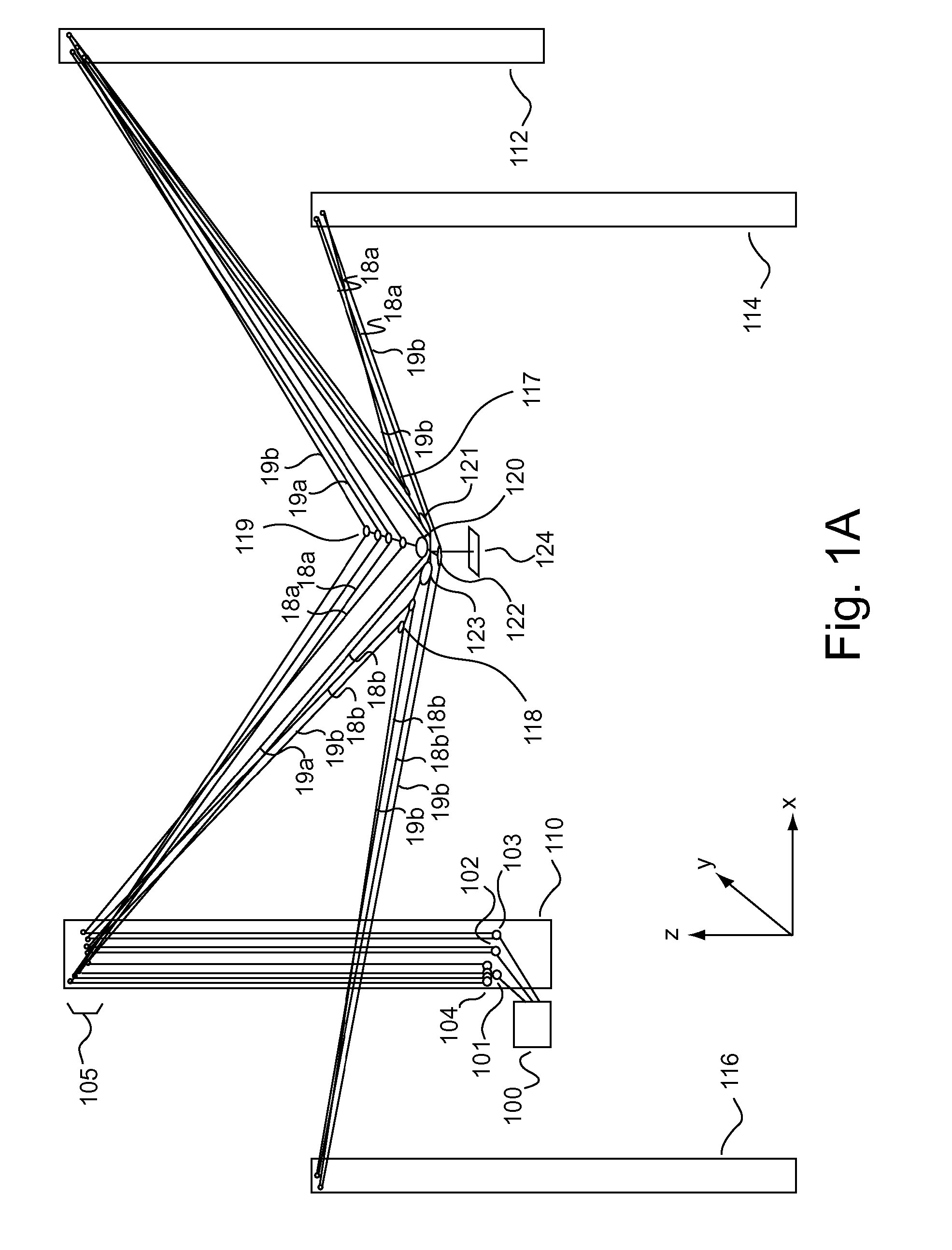
ActiveUS20050024005A1Programme-controlled manipulatorPipe supportsThree-dimensional spaceEngineering
Embodiments of the invention are ideally suited for use filming movies, sporting events, or any other activity that requires fluid movement of a camera or other object to any position within a defined volume of space. To accomplish such positioning embodiments of the invention are configured to move an object throughout three-dimensional space by relocating one or more lines that are feed through a plurality of opposing sides of the object. These line(s) (e.g., a cable, rope, string, cord, wire, or any other flexible connective element) which support the object from above or below the object within a volume of space are arranged in way that allows the object to be rapidly moved to and from any location within the defined volume of space. For instance, the system may be arranged to perform dimensional movement using one line configured as an endless loop, one line configured as a half loop, two lines configured as endless loops or two lines configured as half loops. Other embodiments which split the two lines at the X and Y junctions may yield three and four rope embodiments which are in keeping with the spirit of the invention.
Owner:FORTRESS CREDIT CORP AS AGENT
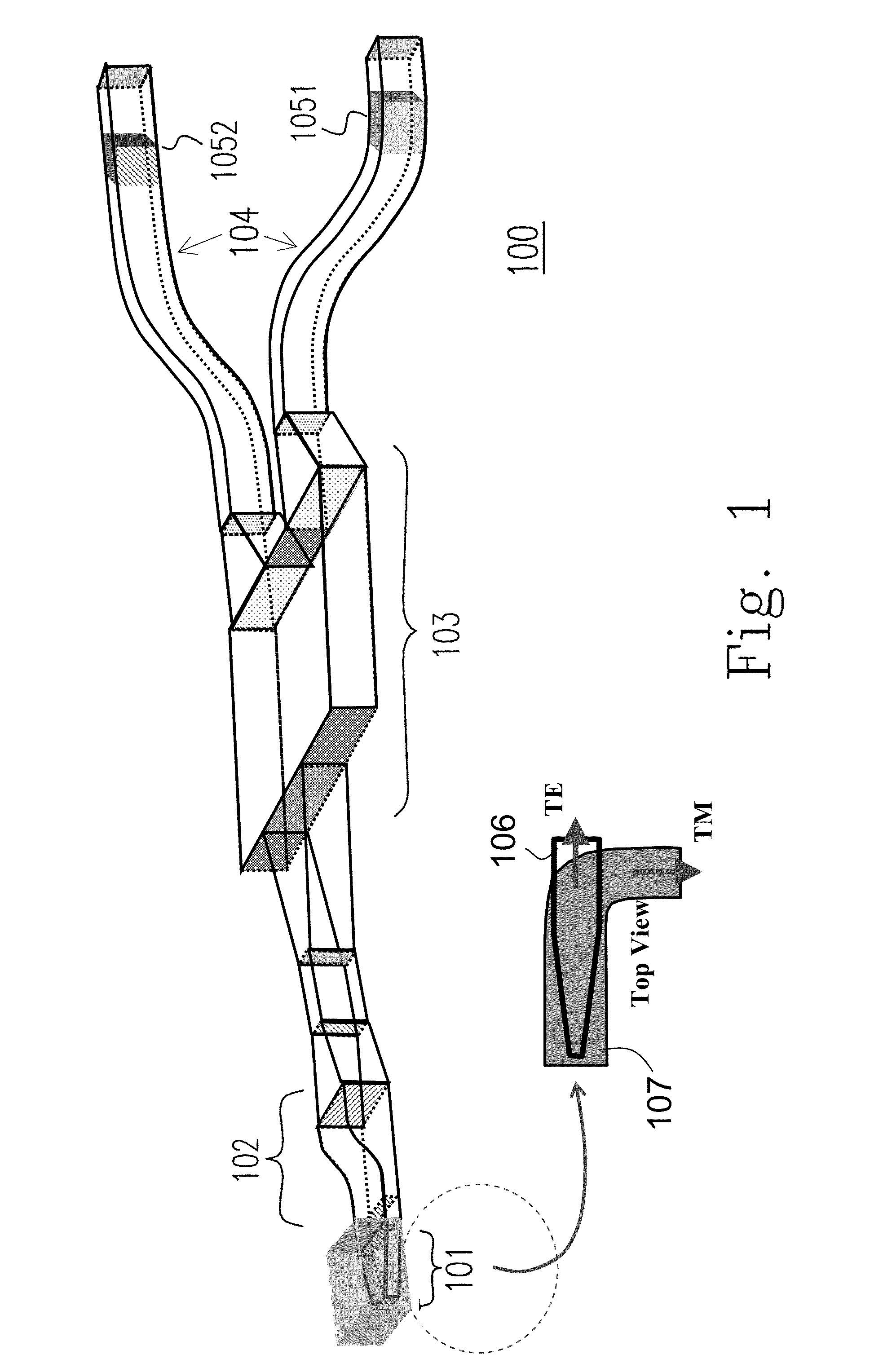
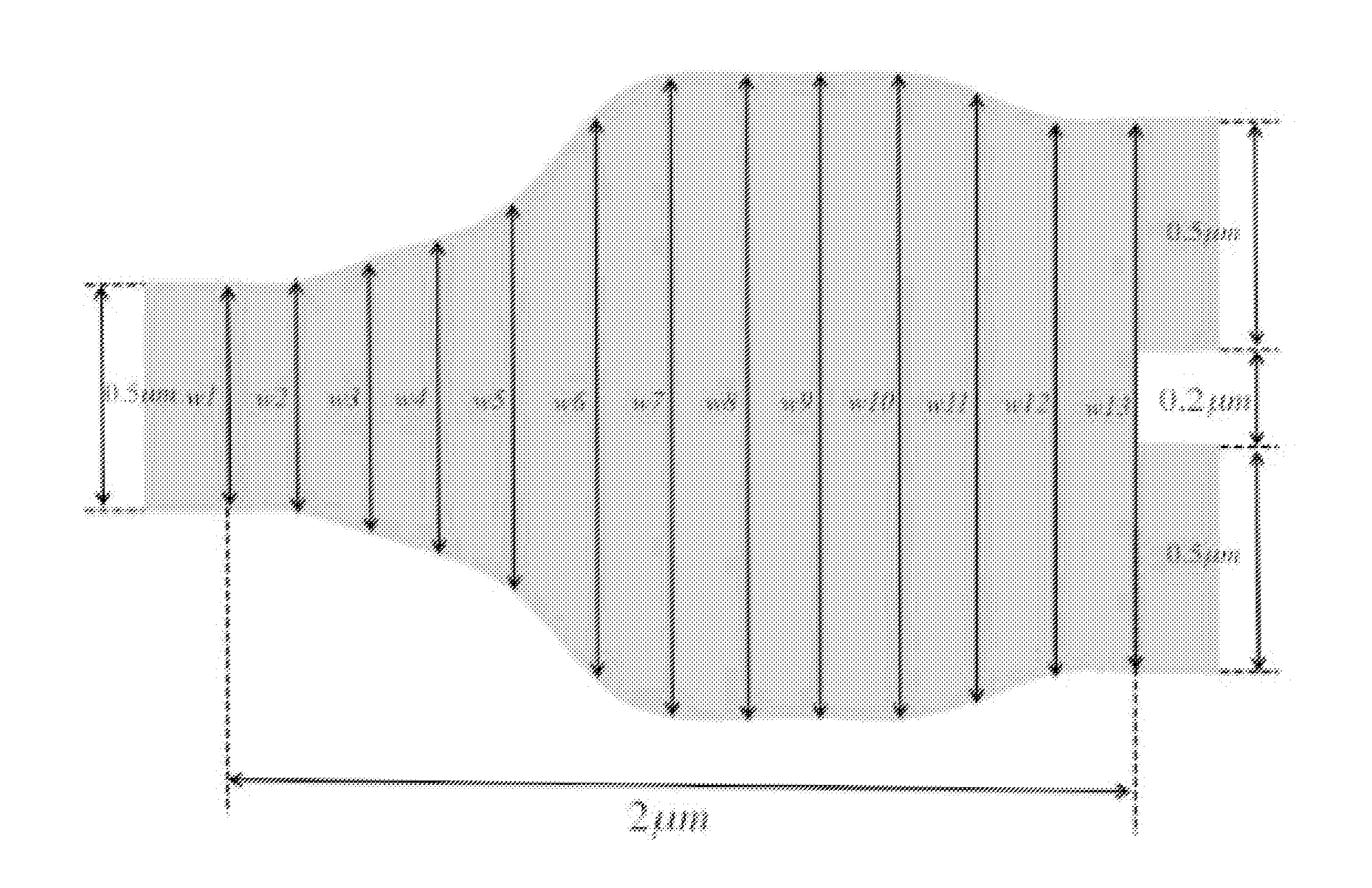
Methods for designing photonic devices
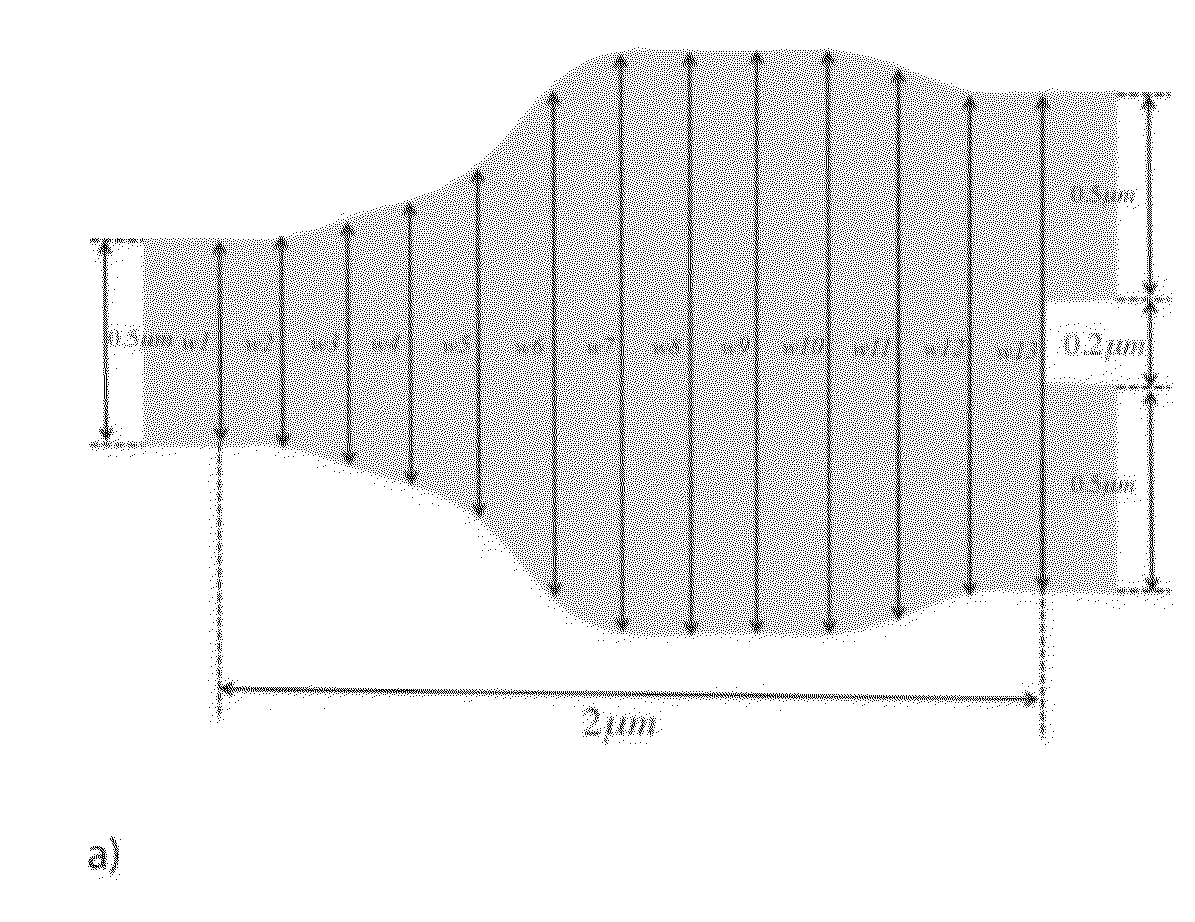
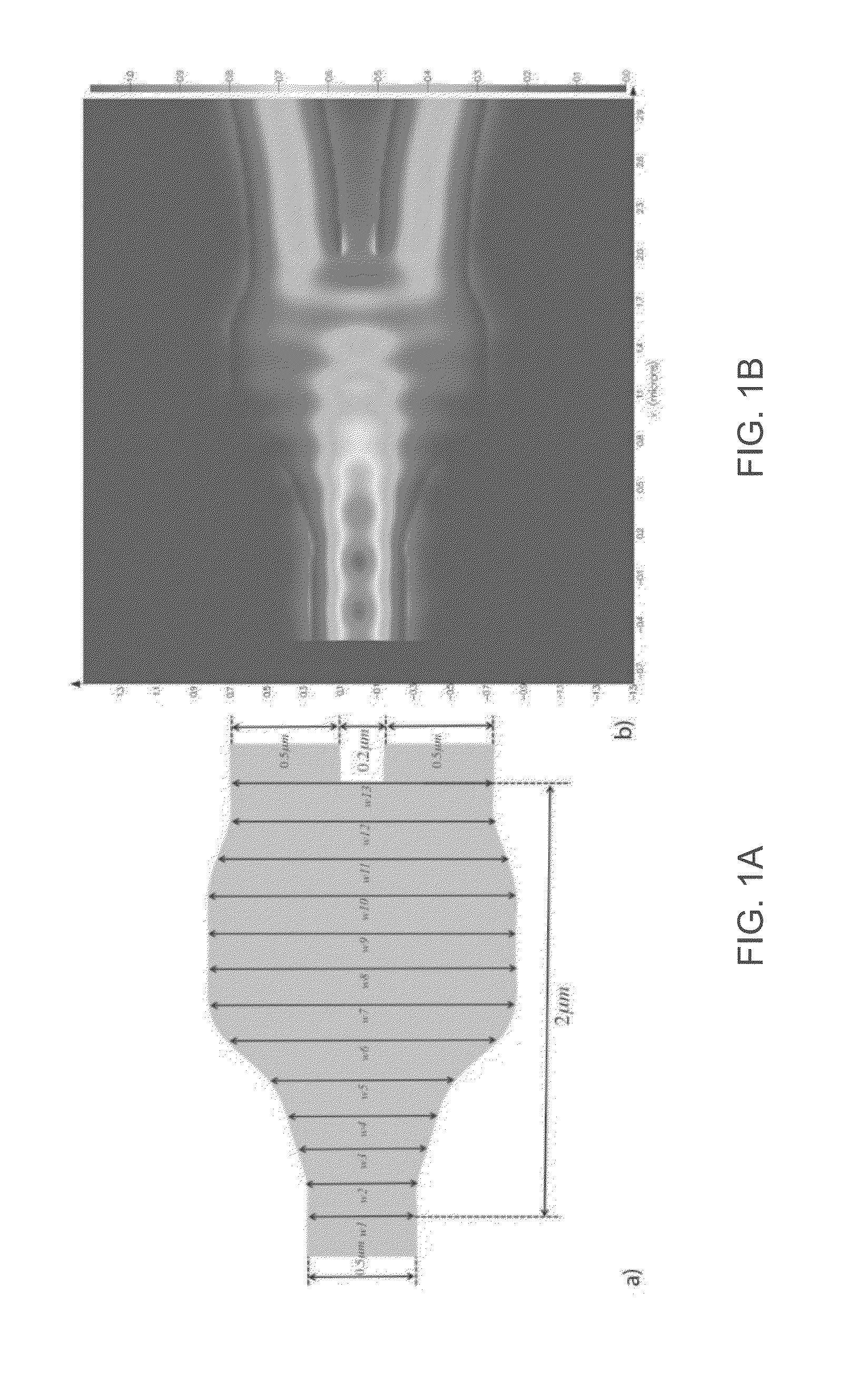
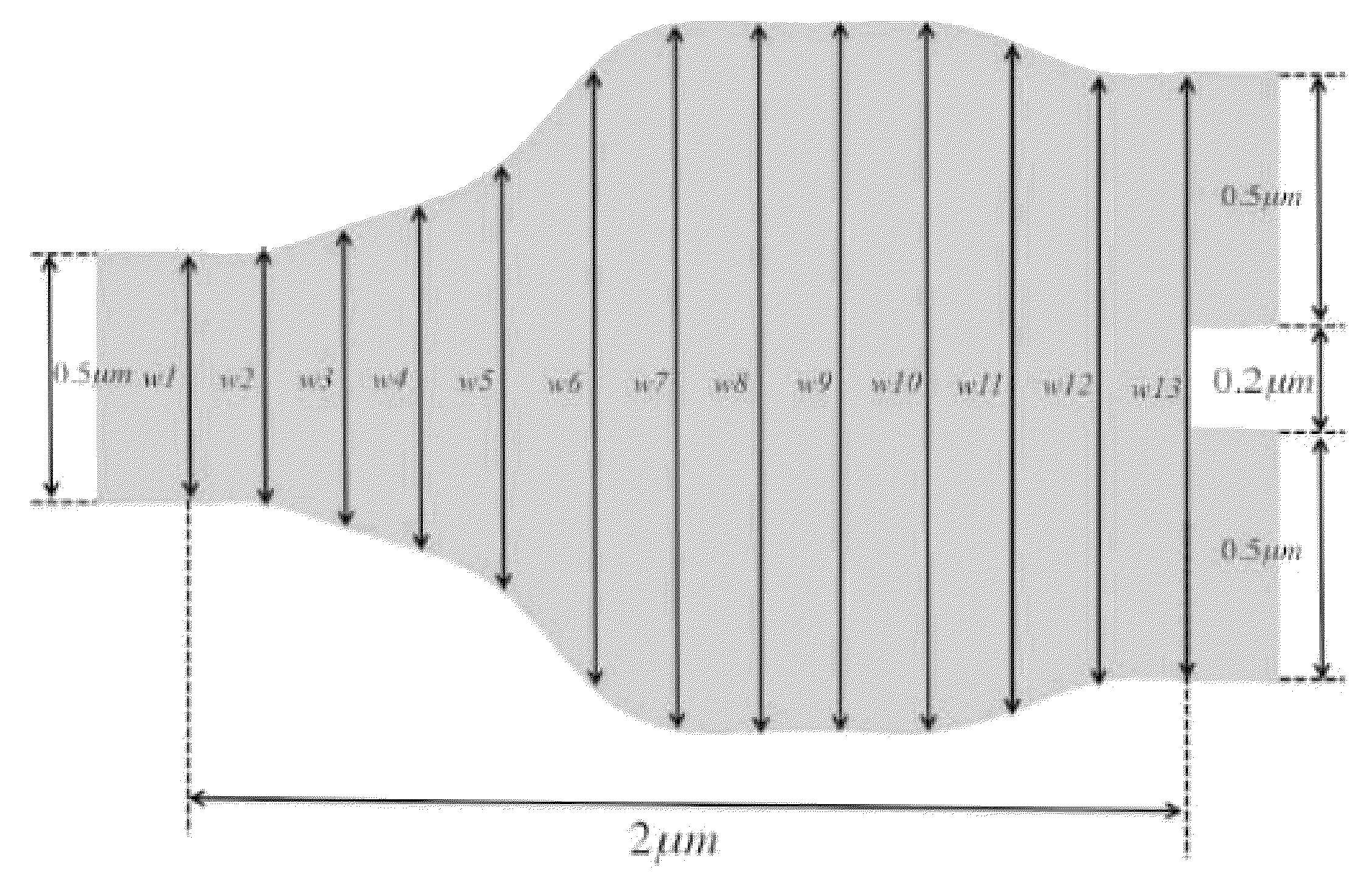
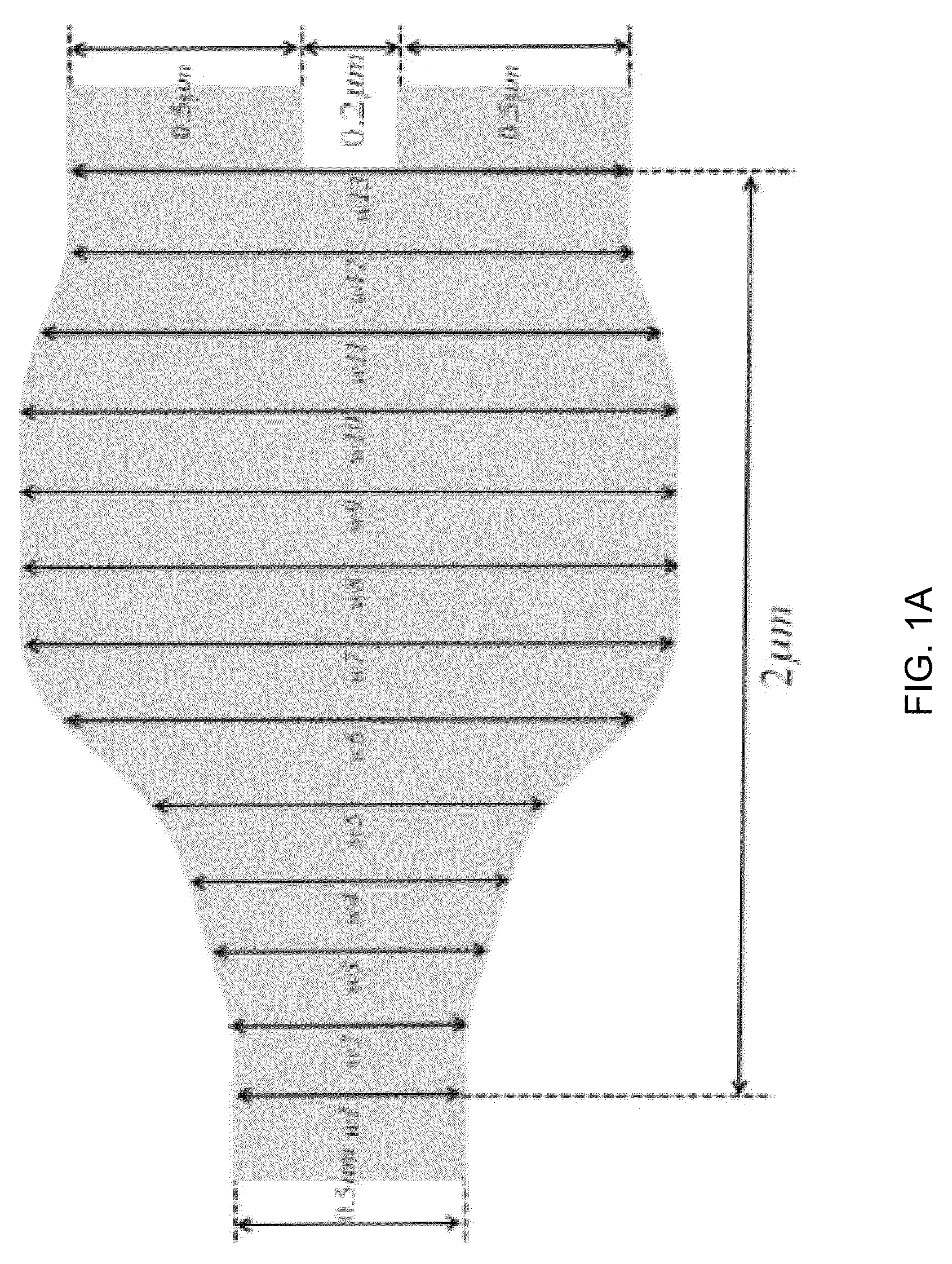
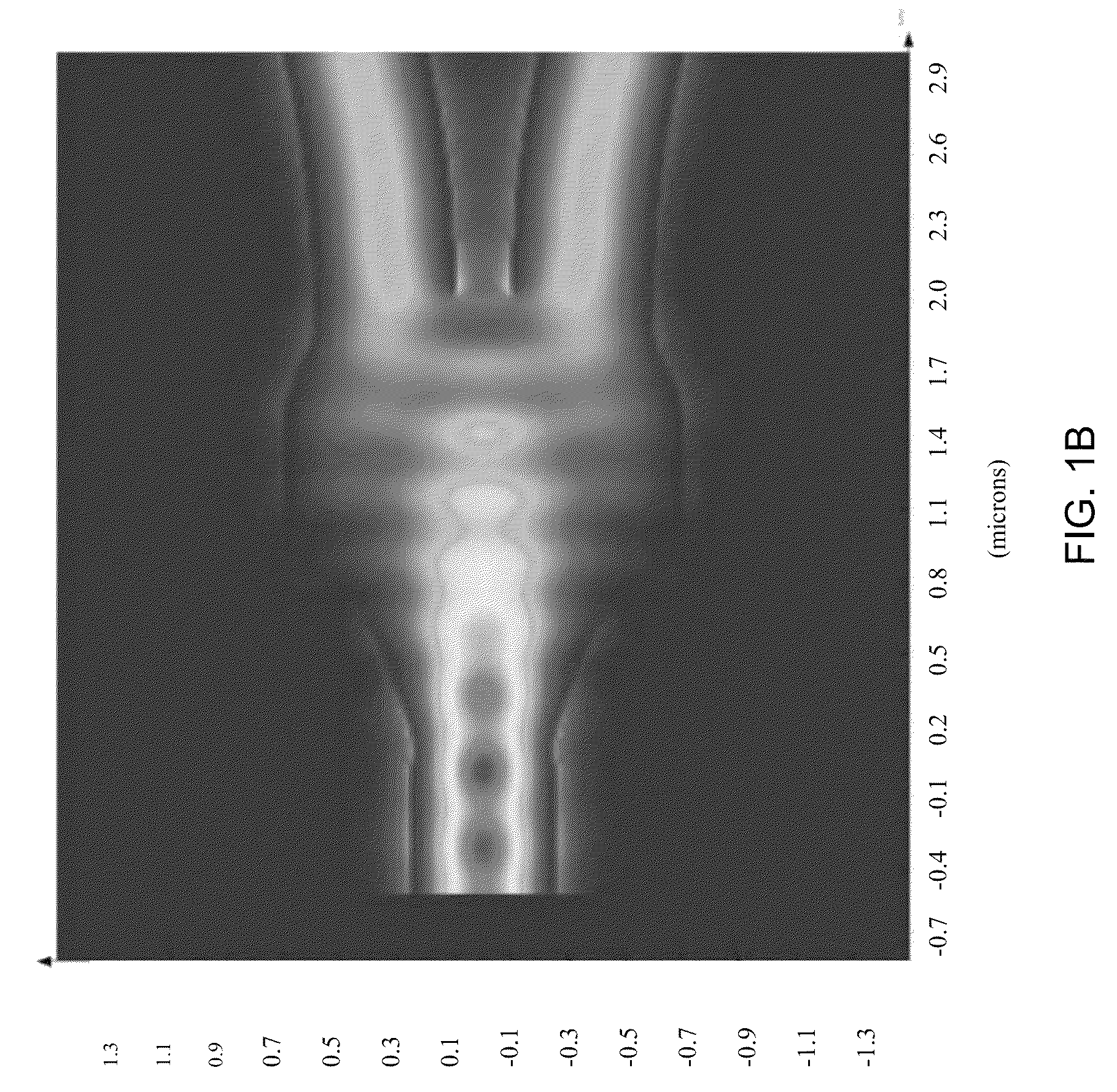
A compact, low-loss and wavelength insensitive Y-junction for submicron silicon waveguides. The design was performed using FDTD and particle swarm optimization (PSO). The device was fabricated in a 248 nm CMOS line. Measured average insertion loss is 0.28±0.02 dB across an 8-inch wafer. The device footprint is less than 1.2 μm×2 μm, orders of magnitude smaller than MMI and directional couplers.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
Quasi active MIMIC circulator
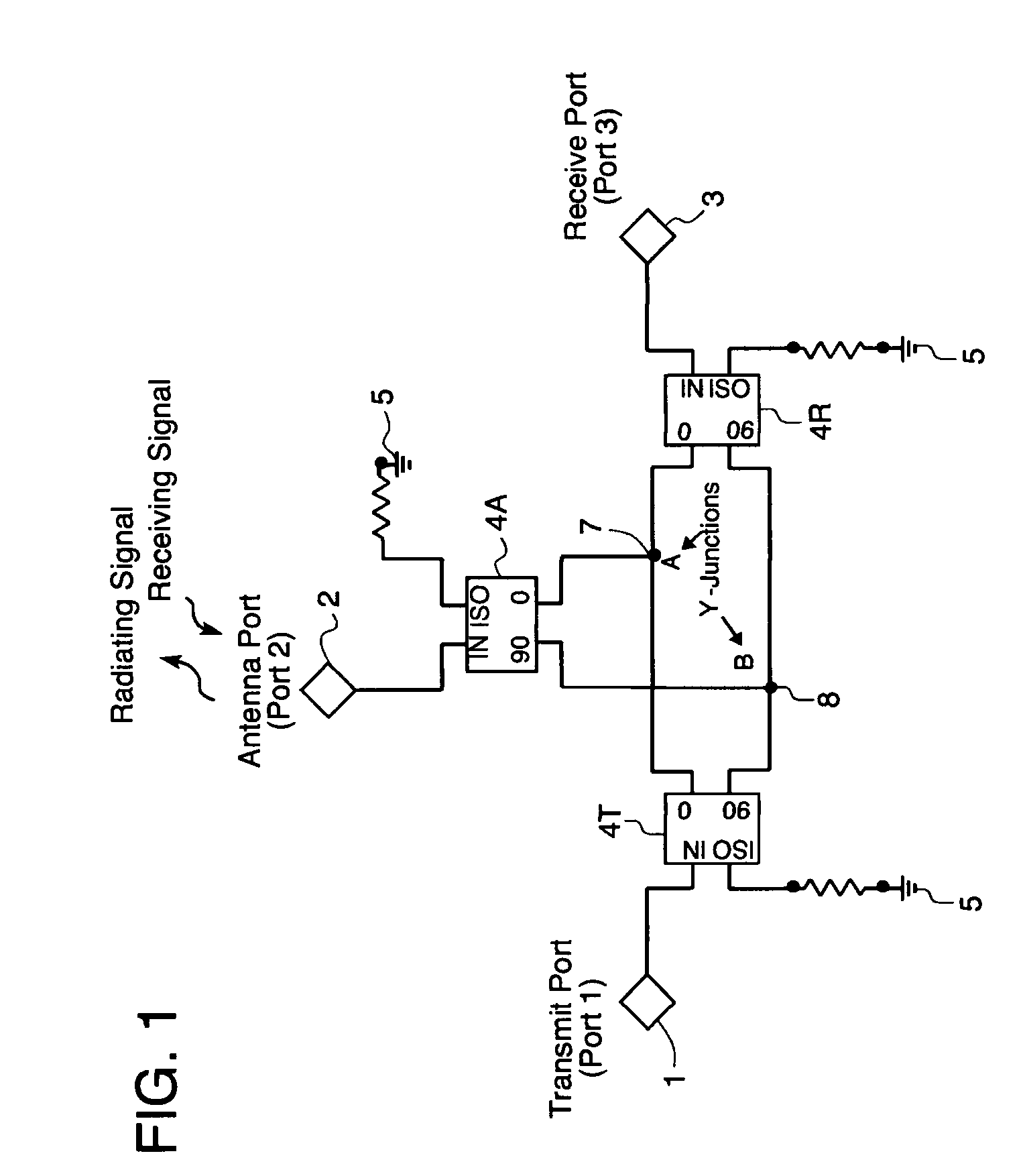
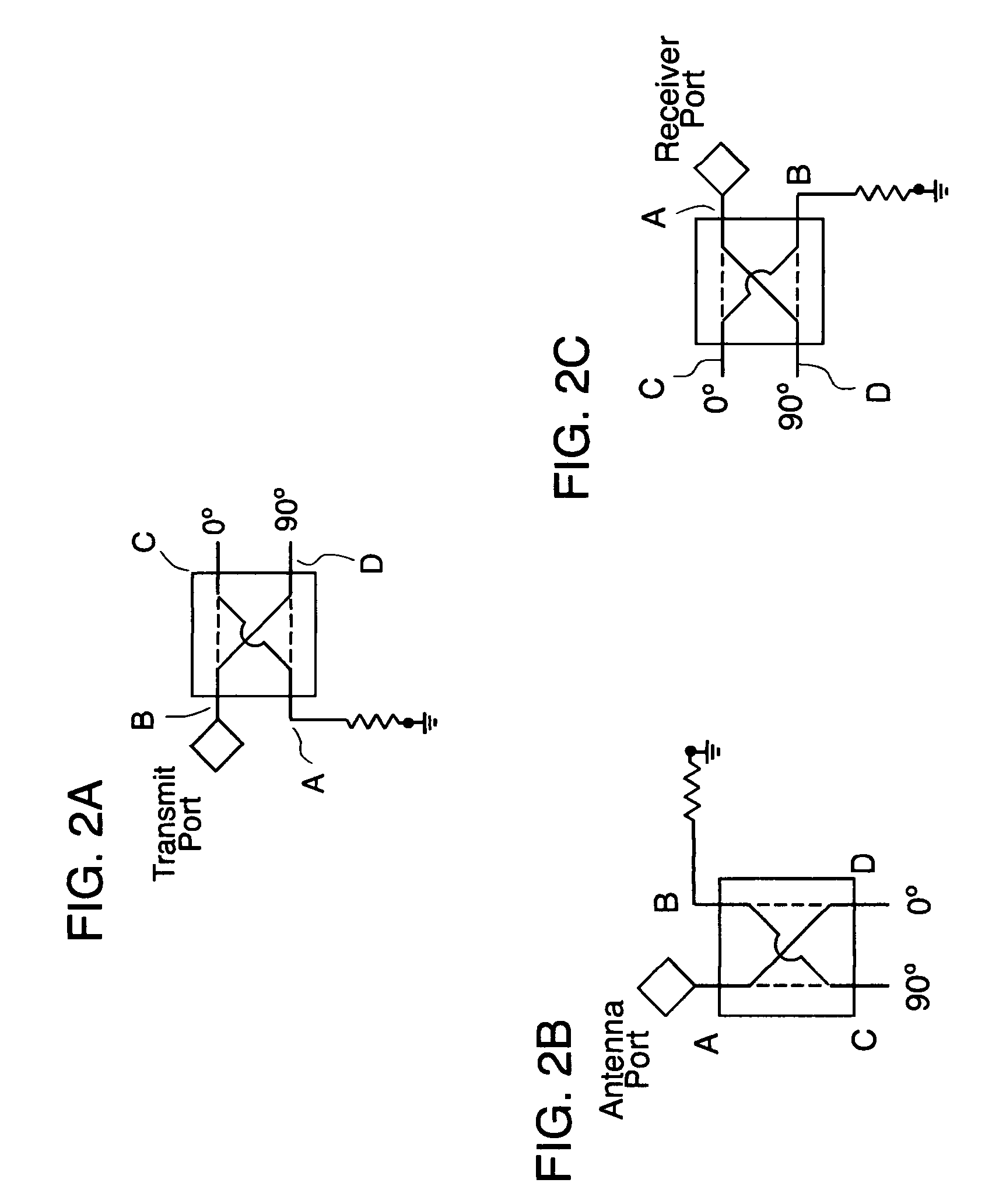
InactiveUS20090108954A1Avoid problemsPreserve energyAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesCoupling devicesLoad circuitPhase shifted
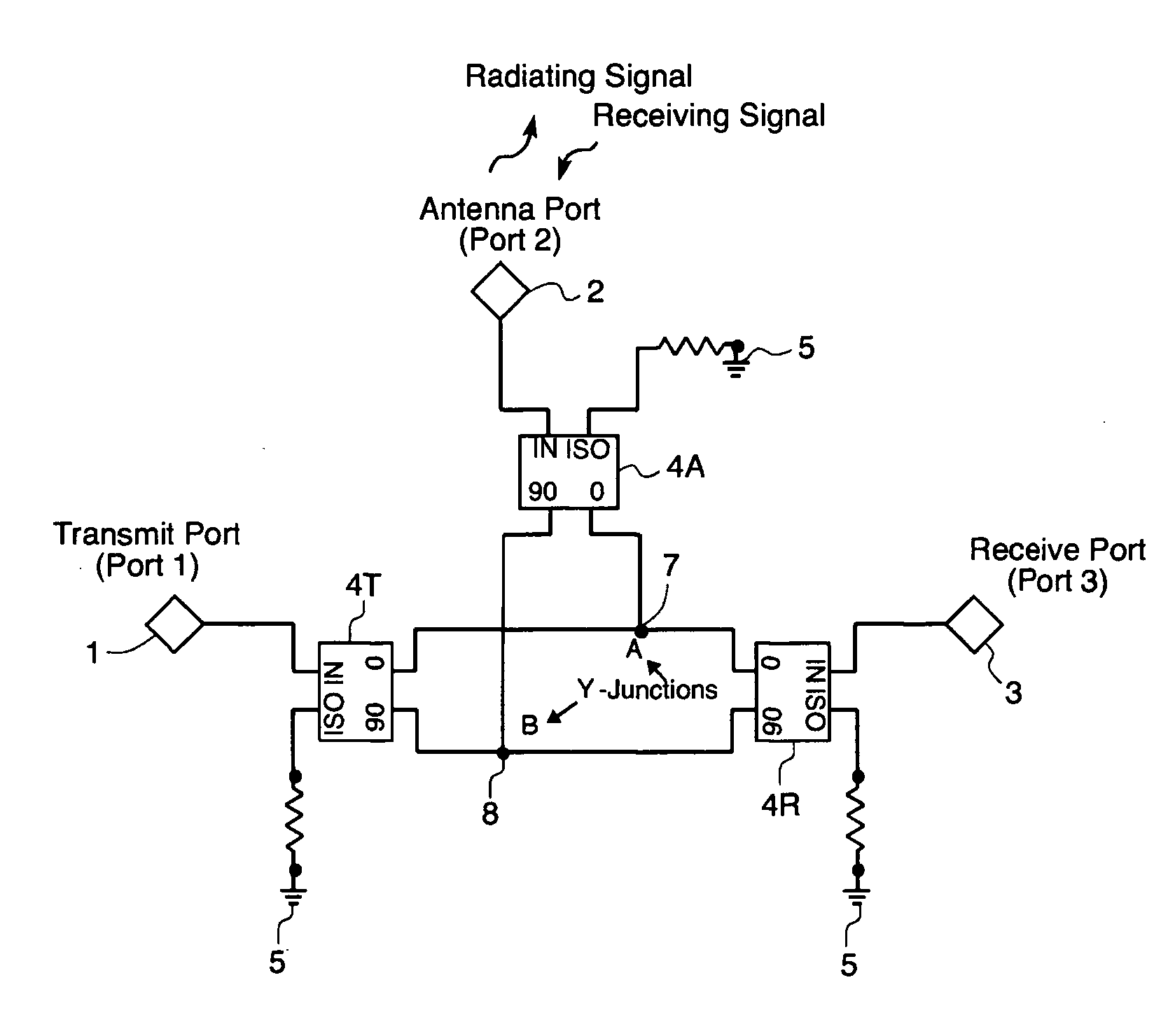
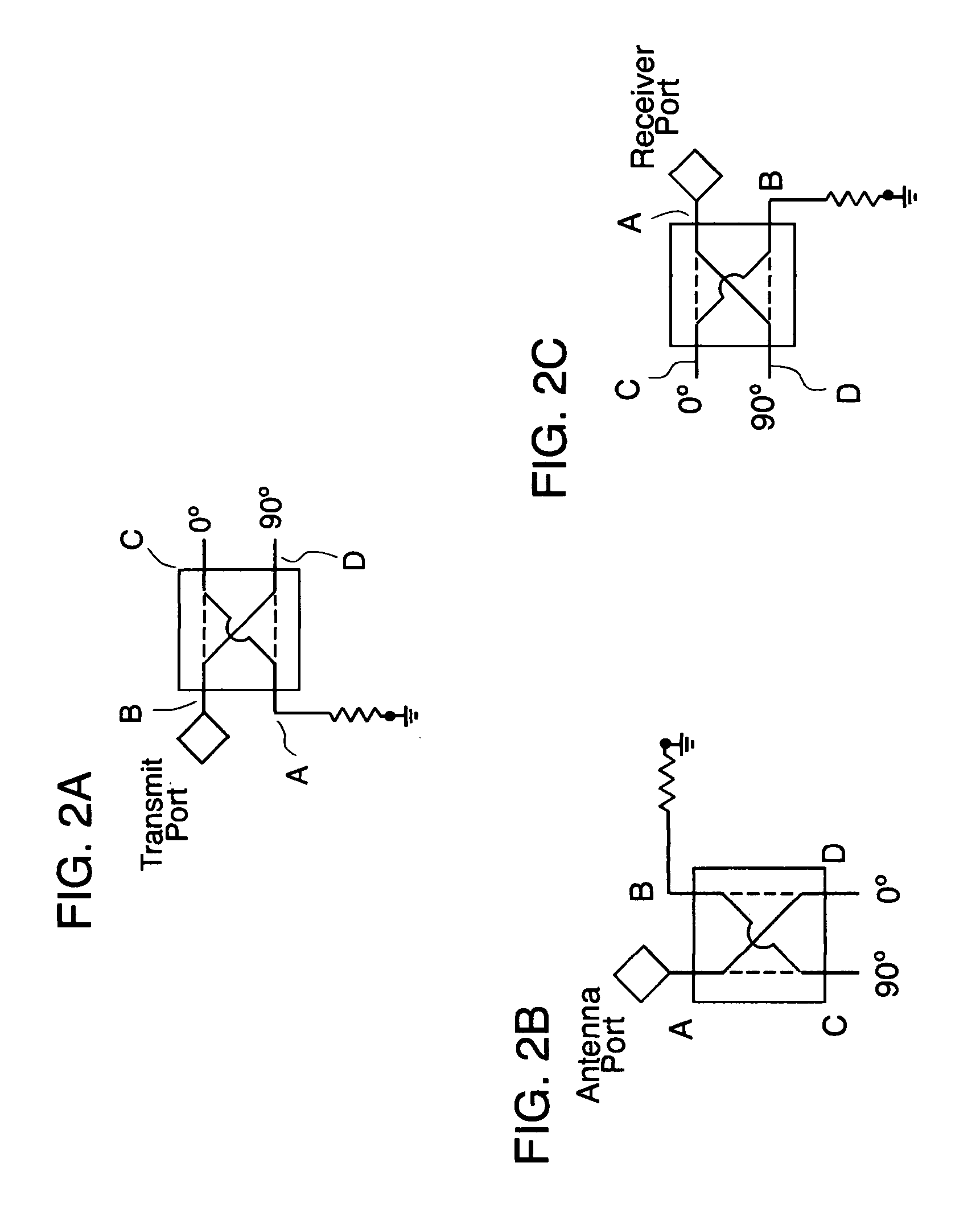
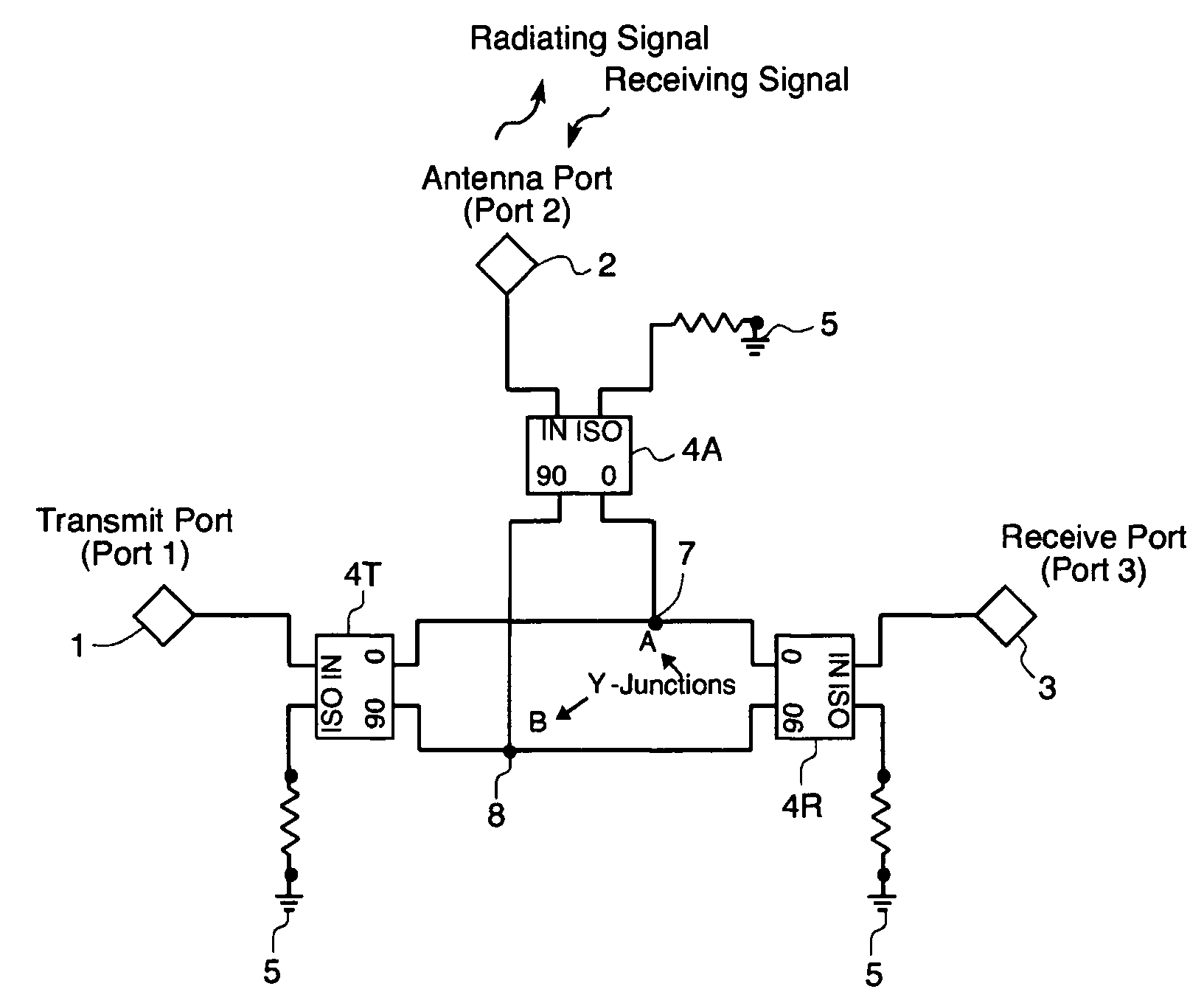
A circulator capable of simultaneous transmit and receive operations, high frequency, and high isolation and broadband performance comprising: an antenna port; a transmission port; a receiving port; wherein each port is connected to a 90 degree combiner / divider for splitting an input signal into two output components, the said output components have a ninety degrees relative phase difference to each other; each of said 90 degree combiner / dividers in addition to the connection to the above mentioned ports has at least two output connections each of which are connected to a Y-junction and if a fourth connection, said fourth connection is attached to a matching load circuit; this arrangement of circuits allows the potion of the phase shifted signals from the transmit port to enter the antenna 90 degree combiner / divider and be enhanced at the antenna port, while the rest of the signal enters the receive 90 degree combiner / divider and are phased cancelled; said arrangement allows the signals from the antenna port 90 degree combiner / divider to combine in phase at the receive port.
Owner:APPLIED RADAR
System and method for facilitating fluid three-dimensional movement of an object via directional force
Owner:FORTRESS CREDIT CORP AS AGENT
Compact and low loss Y-junction for submicron silicon waveguide
A compact, low-loss and wavelength insensitive Y-junction for submicron silicon waveguides. The design was performed using FDTD and particle swarm optimization (PSO). The device was fabricated in a 248 nm CMOS line. Measured average insertion loss is 0.28±0.02 dB across an 8-inch wafer. The device footprint is less than 1.2 μm×2 μm, orders of magnitude smaller than MMI and directional couplers.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
Method for the Preparation of Y-Branched Carbon Nanotubes
InactiveUS20070224104A1Easy to modifyMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureCombined useProcess conditions
The present invention provides a process for preparing Y-branched carbon nanotubes and the product thereby, Y-branched carbon nanotubes. More specifically, the present invention provides a process for preparing Y-branched carbon nanotubes, comprising: loading a catalyst on a carbon nanotube carrier; pre-treating the catalyst-loaded carbon nanotubes to have the catalyst bonded tightly to the surface of carbon nanotubes; and performing a synthetic reaction of carbon nanotubes using the obtained catalyst-loaded carbon nanotubes. According to the process of the present invention, Y-branched carbon nanotubes having at least one or more Y-junctions in various shapes can be prepared easily, simply and in bulk by utilizing the conventional facilities under the usual condition of process. Thus, the invention is promising industrially. The Y-branched carbon nanotubes of the invention holds great potential in regard of materials for electrodes, reinforcing agents for polymers, transistors and electrochemical products.
Owner:KH CHEM CO LTD
Method of recovery from active port tx failure in y-cable protected pair
InactiveUS20090262790A1Enough timeShort timeError preventionDuplex signal operationCommunications systemSignal on
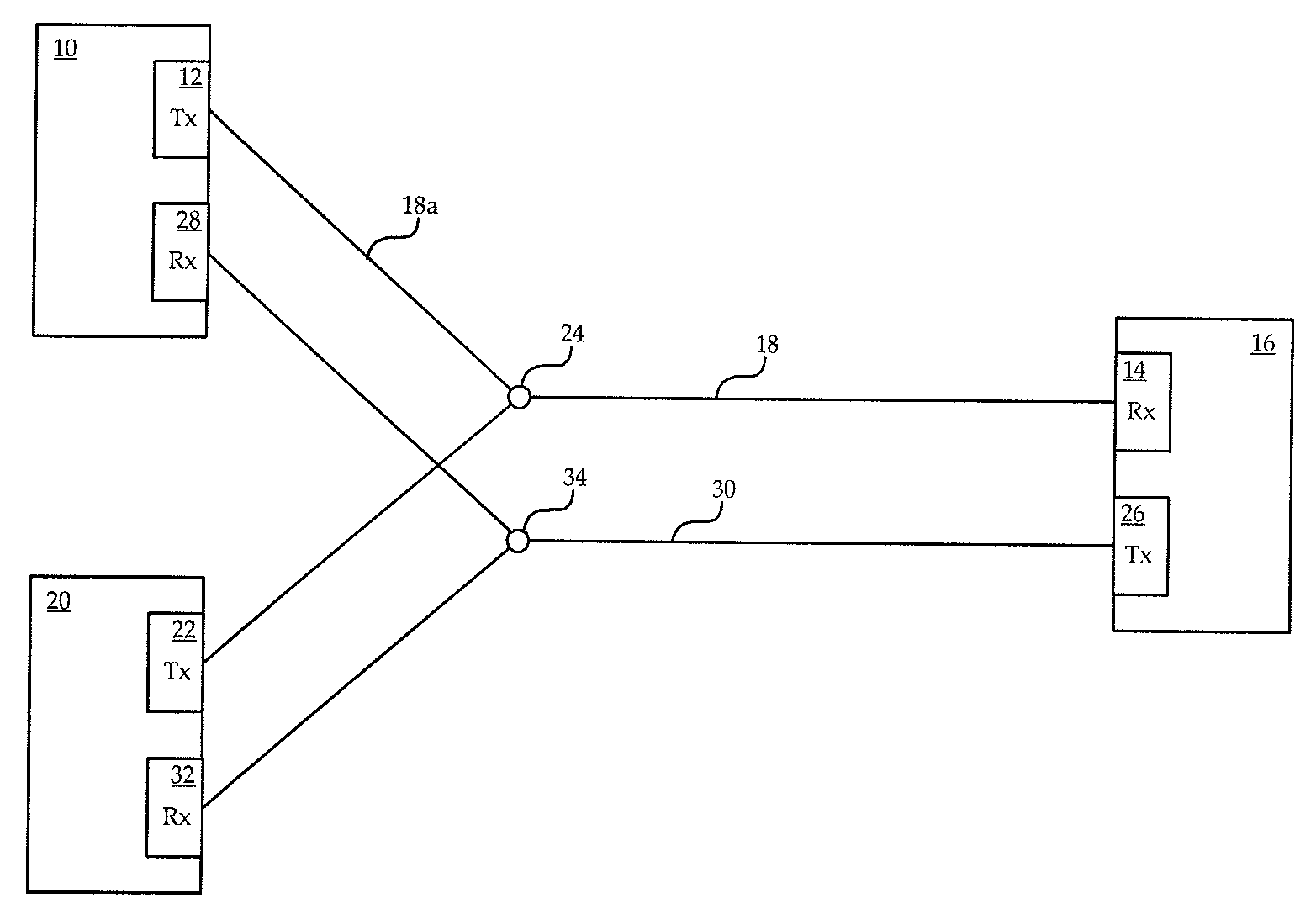
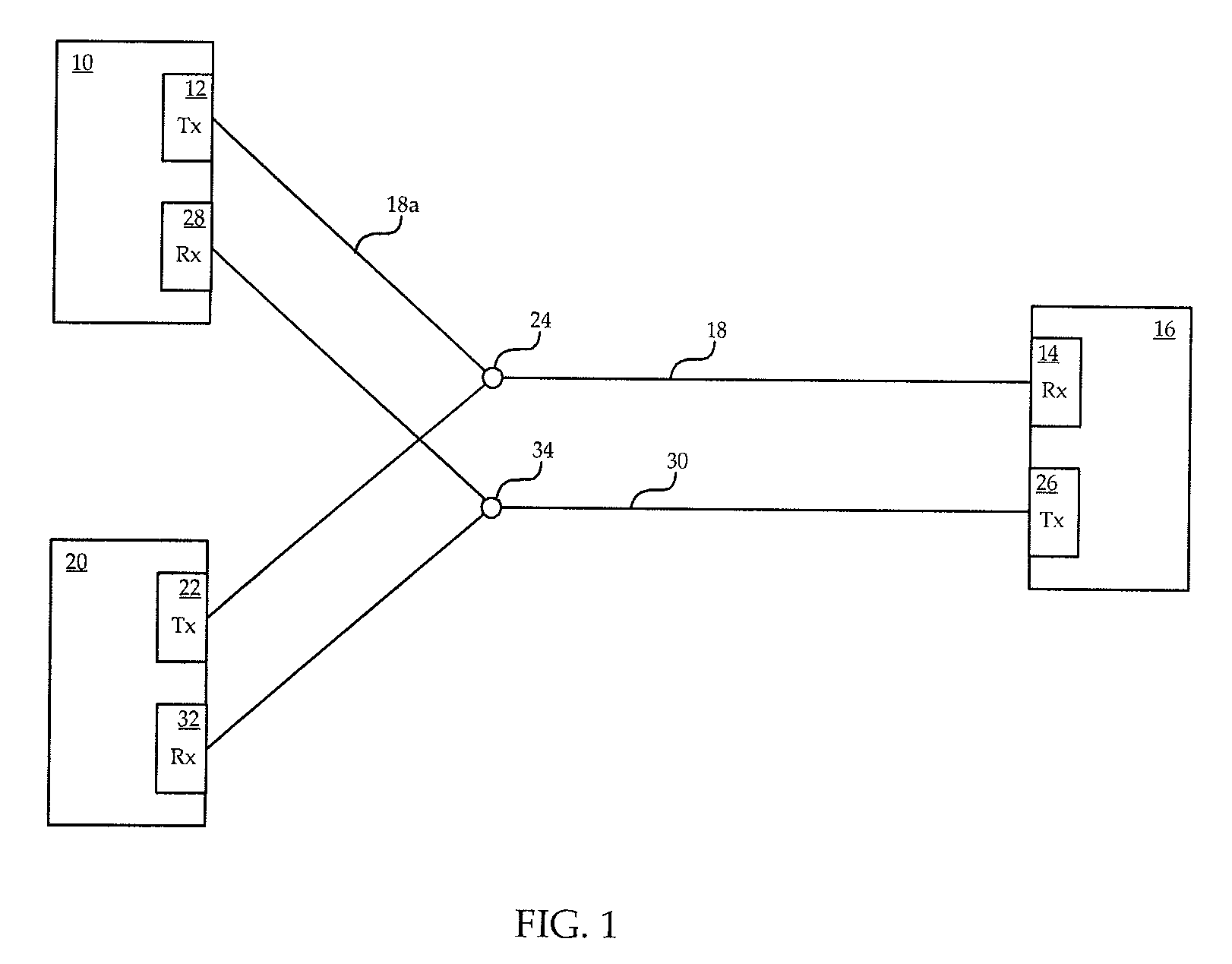
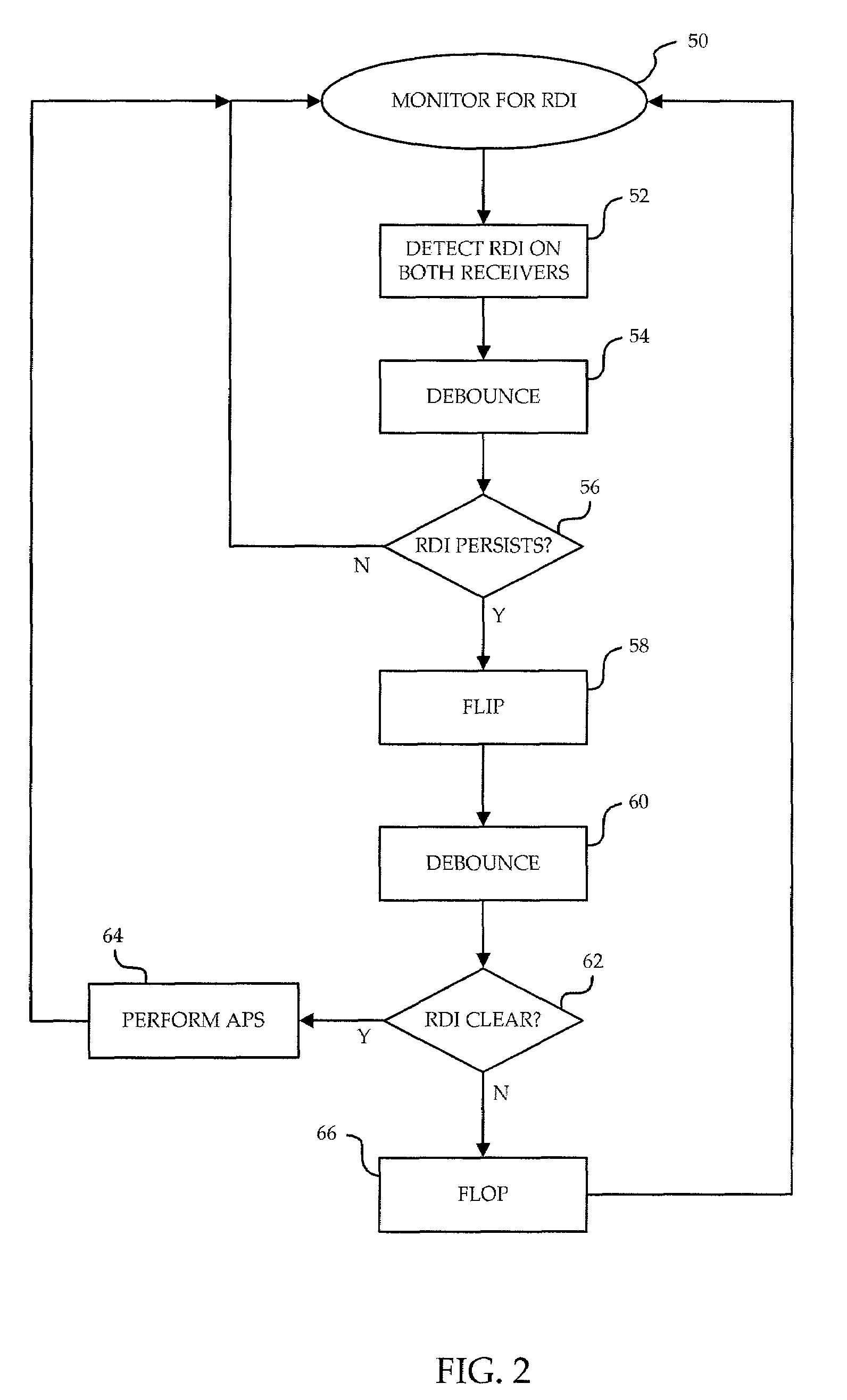
A method is provided for defect recovery in Y-cable protected pair connections in communication systems. A receiver at a remote end monitors for loss of signal on the single fiber optic cable arriving at the remote end, and transmits an RDI back to the local end where it is detected by each of two receivers, one on an active card and one on a standby card. When a persistent RDI is detected by each receiver, transmission of content is flipped from the active transmitter to the standby transmitter, without performing a full APS. If RDIs are no longer received from the remote end, then the defect was likely in the single transmitter of the active card or the single optical fiber leading from the active card to the Y-junction, and the local end realizes that switching transmission to the standby card resolved the problem and a full APS is performed. The invention allows for quick recovery from defects in portions of the Y-cable communication system which may not otherwise be correctable, or even detectable, by conventional higher level fault recovery protocols.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
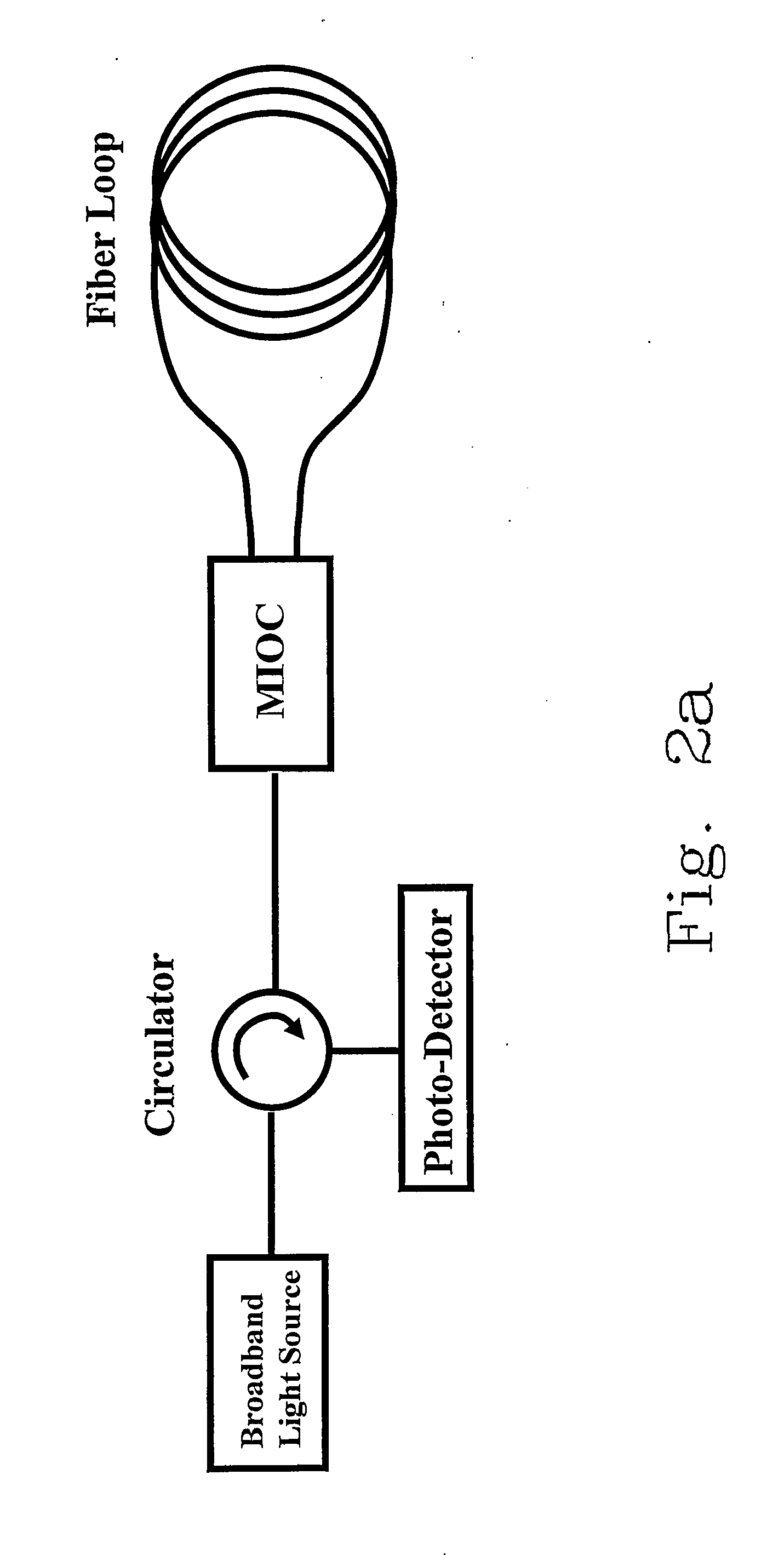
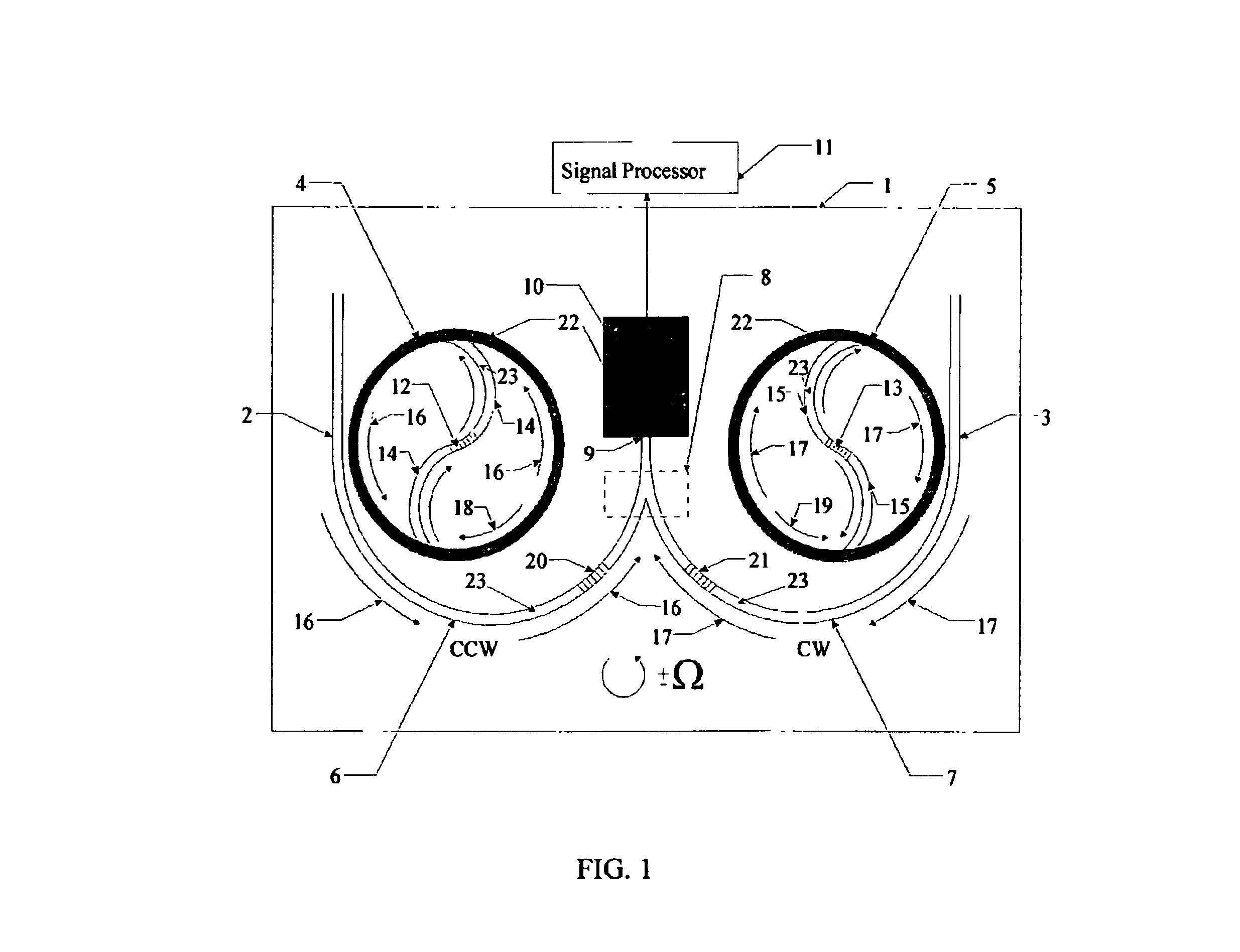
Monolithically integrated semiconductor unidirectional ring laser rotation sensor/gyroscope
InactiveUS6937342B2Reduce or eliminate the lock-in phenomenonSagnac effect gyrometersSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsPhotovoltaic detectorsGyroscope
A monolithically integrated semiconductor laser rotation sensor / gyroscope that includes at least two isolated, nonsynchronized semiconductor lasers; at least one being unidirectional and at least a further one being either a straight-line laser or a second unidirectional ring laser configured to propagate lasing light waves in the direction opposite to the first unidirectional ring laser; semiconductor directional waveguide couplers; a semiconductor Y-junction mixing region; and a semiconductor photodetector. Evanescently outcoupled signals are routed to a photodetector for detection of the Sagnac shifted frequencies to discern a beat frequency resulting from rotation of the chip structure. The straight-line semiconductor laser serves as frequency reference insensitive to rotation. Directing, filtering, and radiating unwanted reflections or backscattered light to highly absorbing regions is carried out with waveguide coupler designs and nonreciprocal couplers and filters.
Owner:NEW MEXICO UNIV OF +1
Method and system for a low-loss optical y-junction power splitter
Methods and systems for a low-loss optical Y-Junction power splitter are disclosed and may include a semiconductor die having an optical Y-junction. The optical Y-junction may comprise an input waveguide, two or more output waveguides, a taper region and a step feature. The input waveguide and the taper region may include a smooth transition between the input waveguide and the taper region, and the step feature may be between the taper region and the output waveguides. The semiconductor die may receive an optical signal in the input waveguide, and communicate substantially equal power optical signals to the output waveguides. The semiconductor die may comprise a photonically-enabled silicon CMOS integrated circuit. An optical signal may be received in each of the output waveguides and a summed output signal may be communicated to the input waveguide. The step feature may extend in a direction perpendicular to an axis of the output waveguides. Widths of the output waveguides may be different and define a splitting ratio of the Y-junction.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Integration of evaporative cooling within microfluidic systems
InactiveUS20070045880A1Provide controlMixing methodsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsProcess engineeringY junction
Evaporative cooling is an effective and efficient method for rapidly removing heat from a system device. In accordance with the disclosure herein, a microfluidic Y-junction apparatus is provided which can produce low temperatures and can be integrated into microdevices.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Y-shaped headphone / earbud cord sleeve
InactiveUS20130336515A1Cost-effective and durable and safeCost effectiveInsulated cablesEarpiece/earphone cablesEngineeringHeadphones
The present invention relates generally to a Y-shaped cord sleeve. More particularly, the invention encompasses a Y-shaped headphone / earbud cord sleeve. The present invention is also directed to a novel placement of at least one opening at or near a Y-junction of the Y-shaped cord sleeve. The present invention is also directed to a novel Y-shaped cord sleeve that has at least one accommodation or opening for a microphone and / or volume control or similar electronic input / output type device. The Y-shaped cord sleeve could also have at least one tab, medallion, or tongue to cover at least a portion of the opening for the headphone / earbud cord. The user could also personalize or individualize, or create an expression using any of the features of this invention.
Owner:CENTRILLA III ANTHONY JOHN
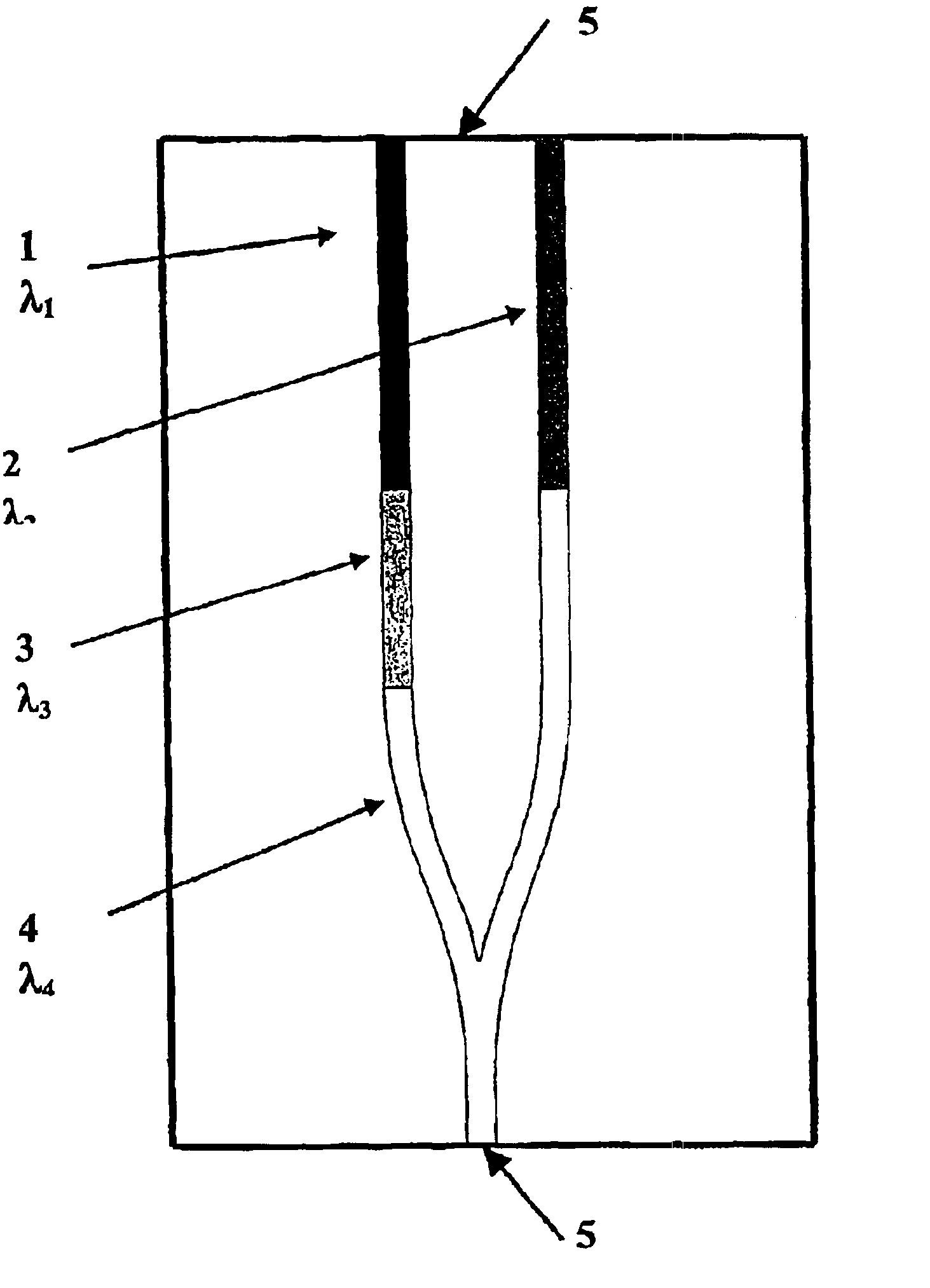
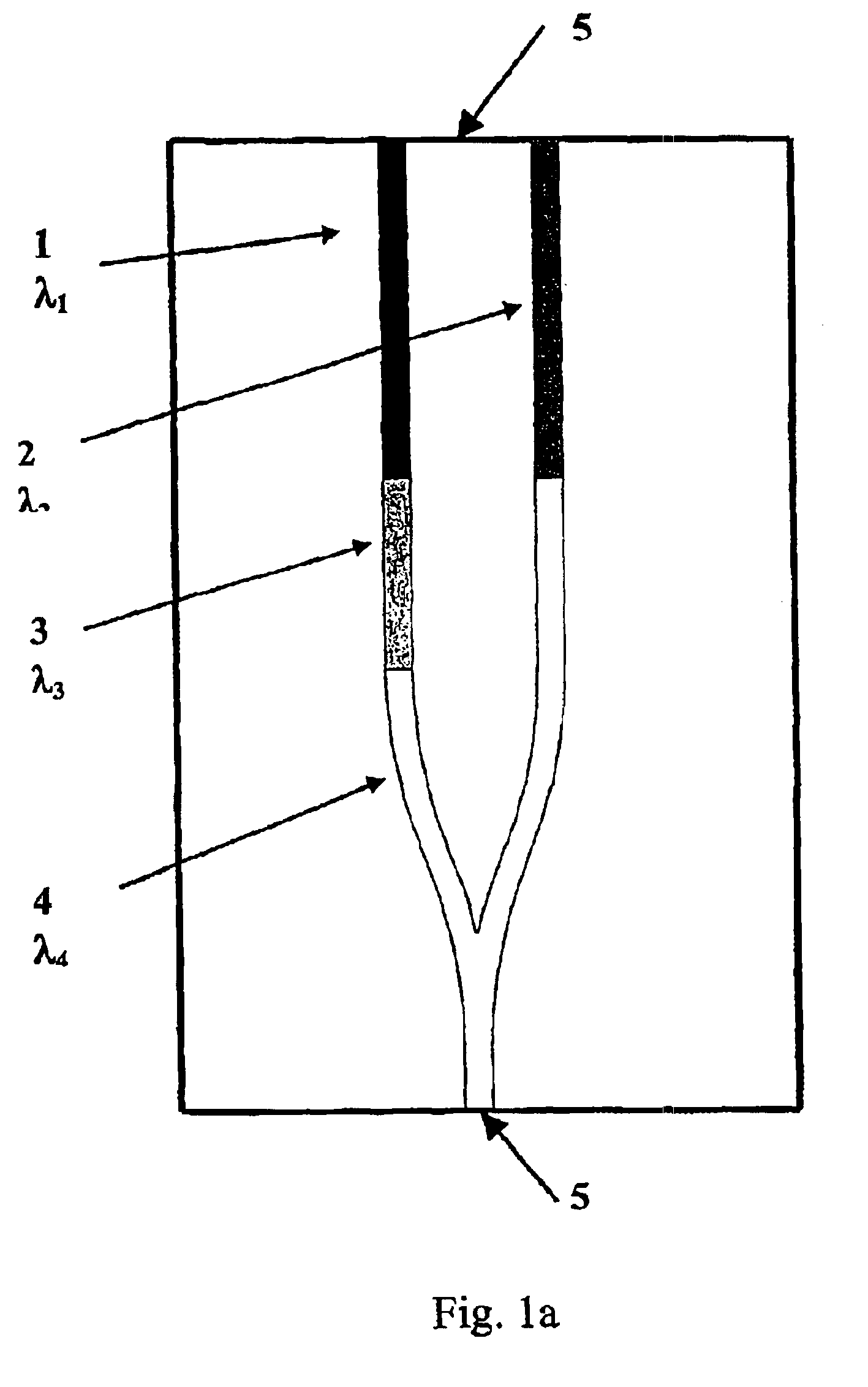
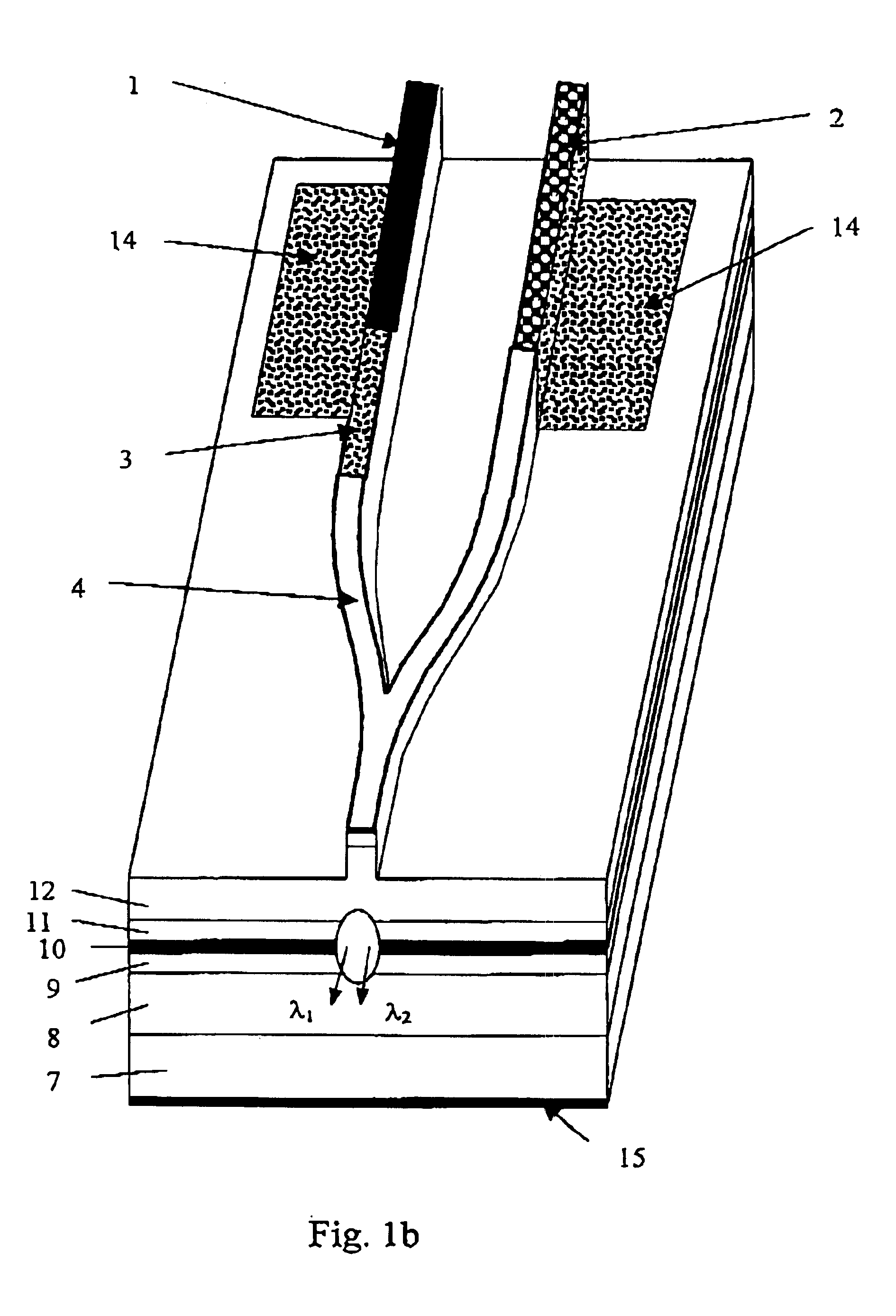
Multi-wavelength semiconductor lasers
InactiveUS6937633B2Ease of fabricationGuaranteed ease of operationSemiconductor laser arrangementsLaser output parameters controlGratingPhotonic bandgap
A multi-wavelength semiconductor laser is formed by monolithically integrating a plurality of laser diodes (1, 2) with at least one isolator section (3) and a coupler (4), which couples the different emission wavelengths λ1, λ2 into one output port (5). The isolator section can be either a light absorptive type or wavelength selective type, including a Bragg grating type isolator or a photonic bandgap crystal type isolator. The coupler is preferably a Y-junction coupler, but can also be a multi-branch waveguide coupler or a waveguide directional coupler.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Automated transportation system
InactiveUS20010037746A1Minimal costSafe and reliable and efficientAutomatic systemsTrain hauling devicesY junctionFour-wheel drive
A system is provided that includes guideways having tracks for supporting a type of vehicle which moves within the guideways and tracks for a type of vehicle which moves on top of the guideways. Guide tracks are provided within the guideways for guiding vehicles of either type and controlling movement through Y junctions. The type of vehicle that moves on top of the guideway includes auxiliary wheels which cooperate with auxiliary tracks in Y junctions to insure reliable support. Each type of vehicle includes automatic load tilting mechanisms and also a special four wheel drive arrangement.
Owner:AUTRAN CORP
Tubular carbon nano/micro structures and method of making same
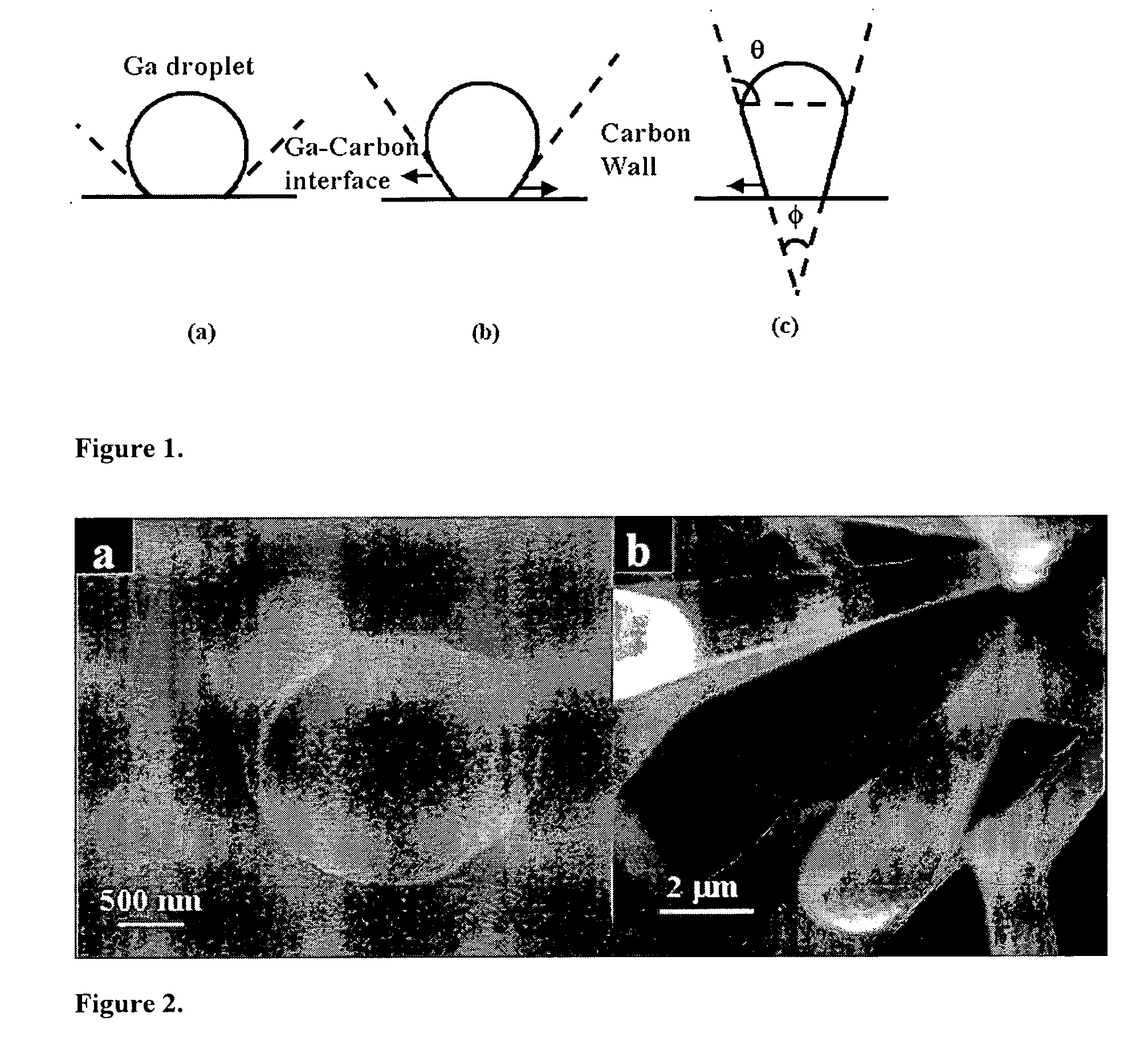
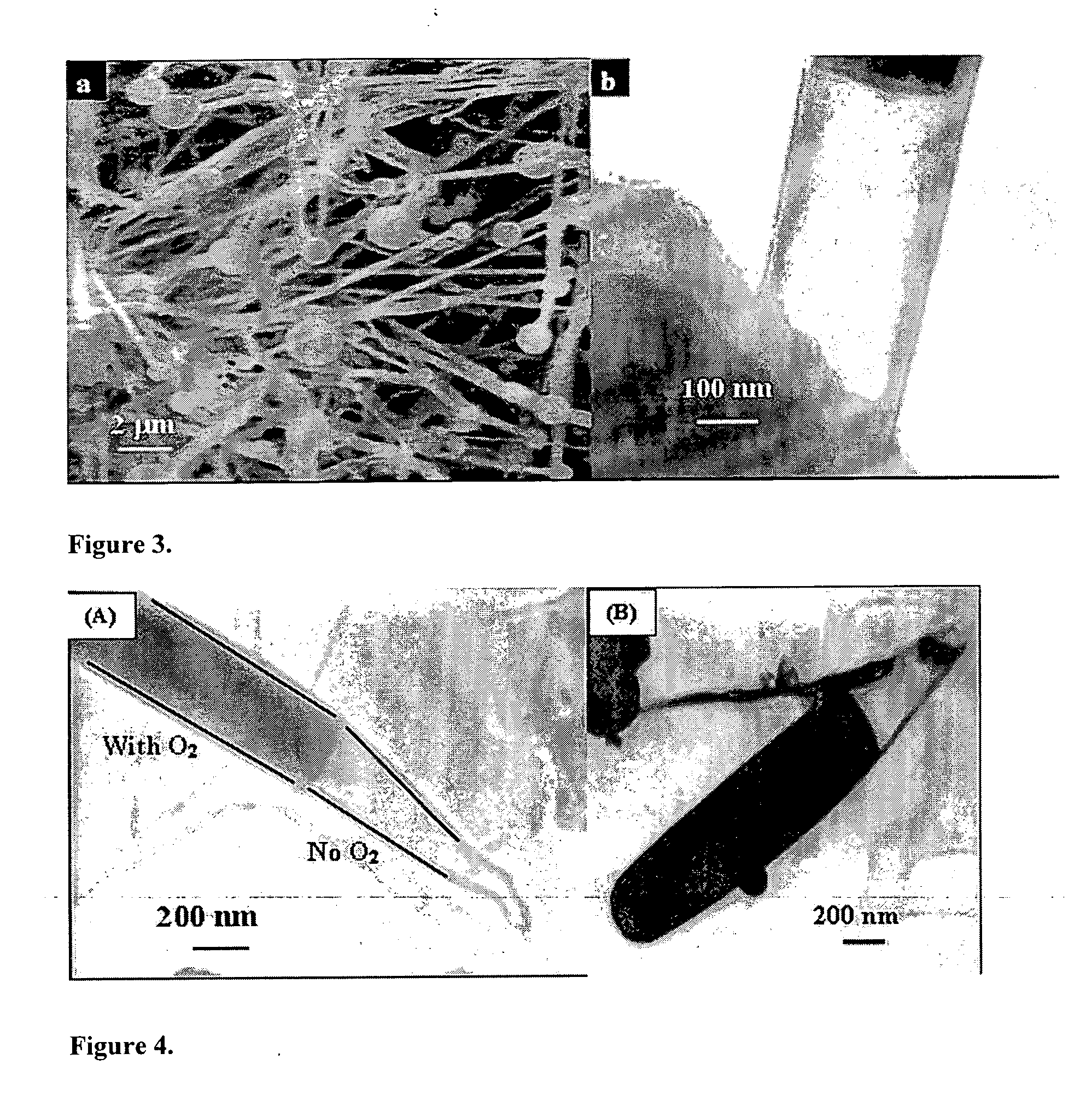
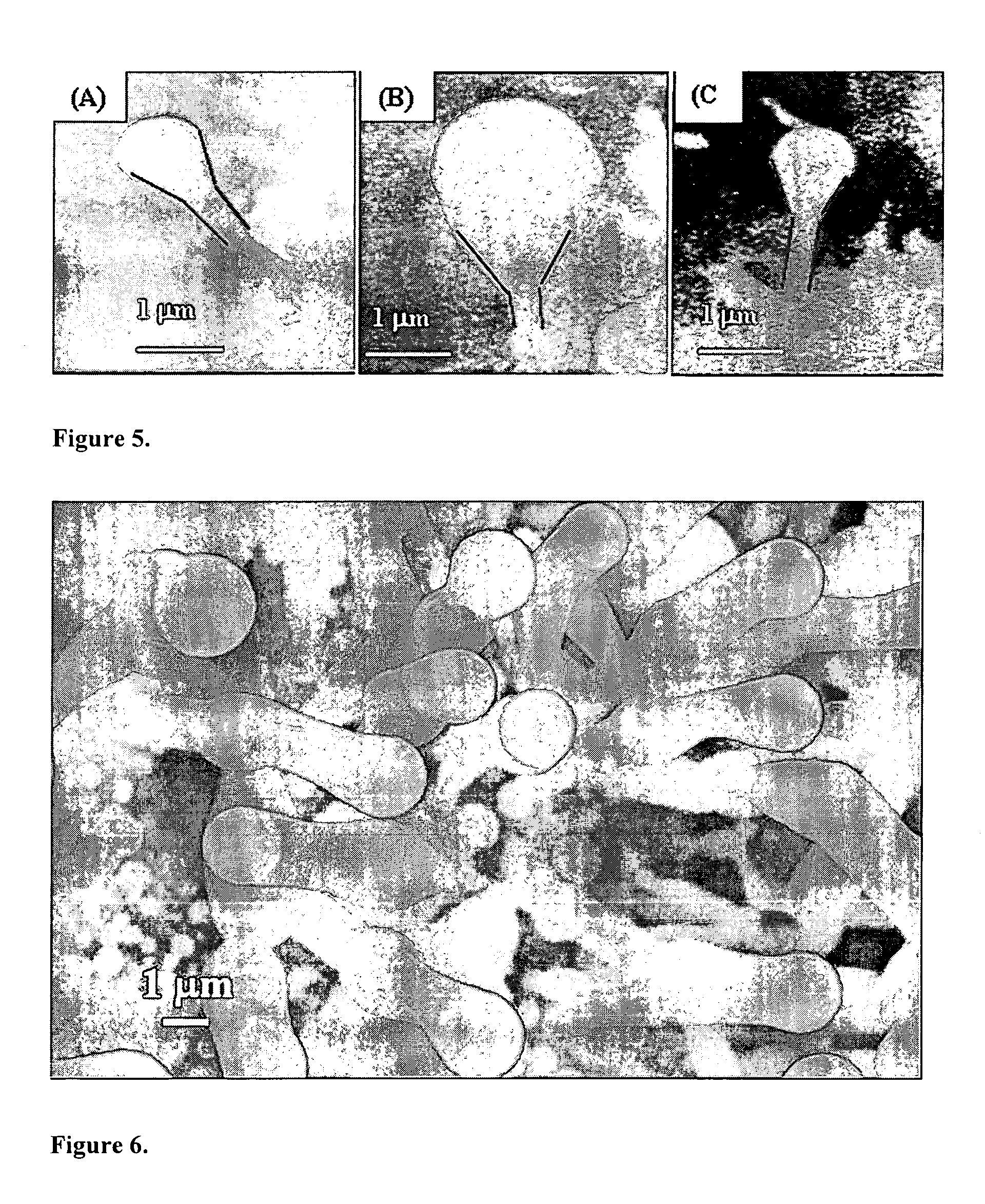
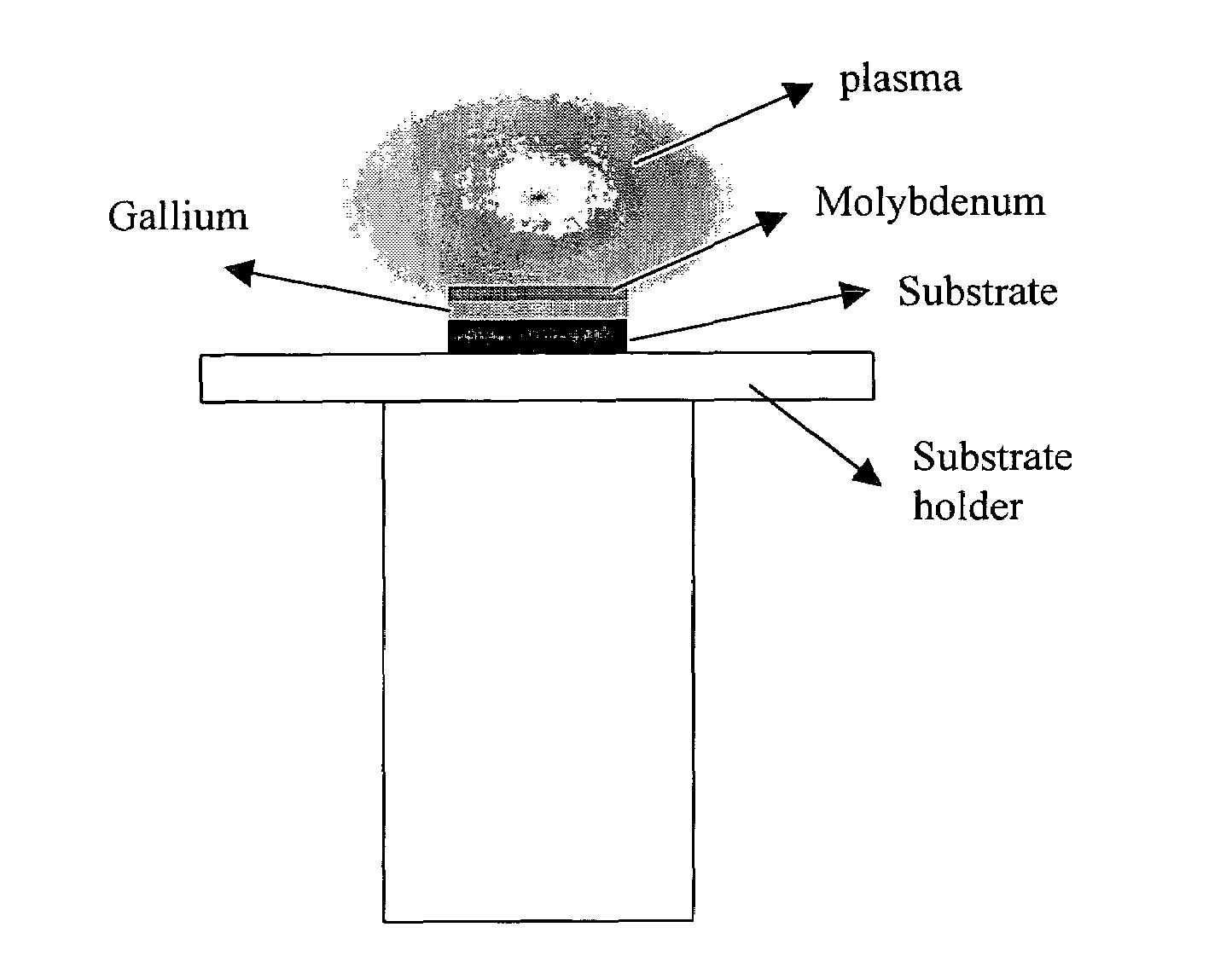
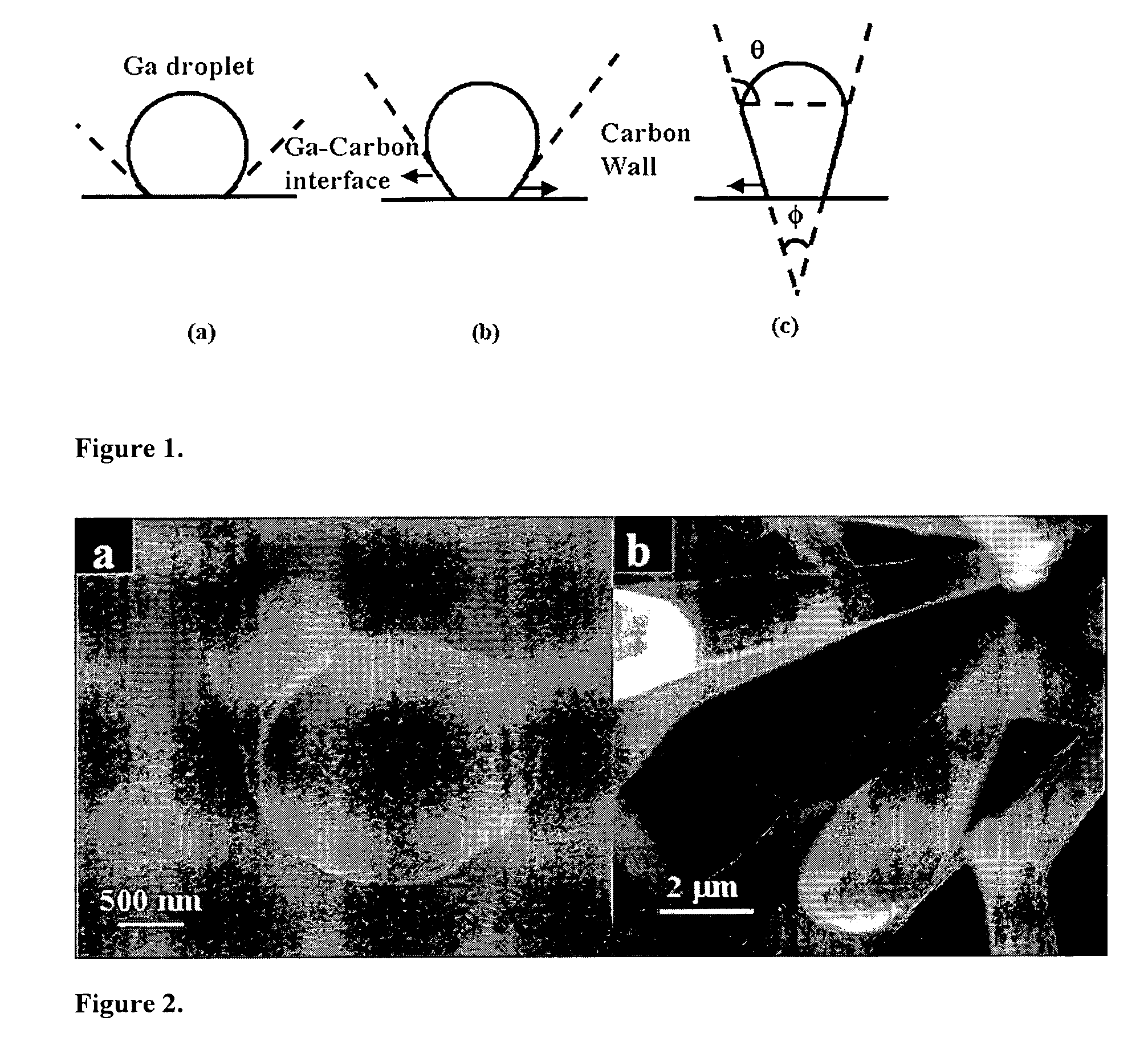
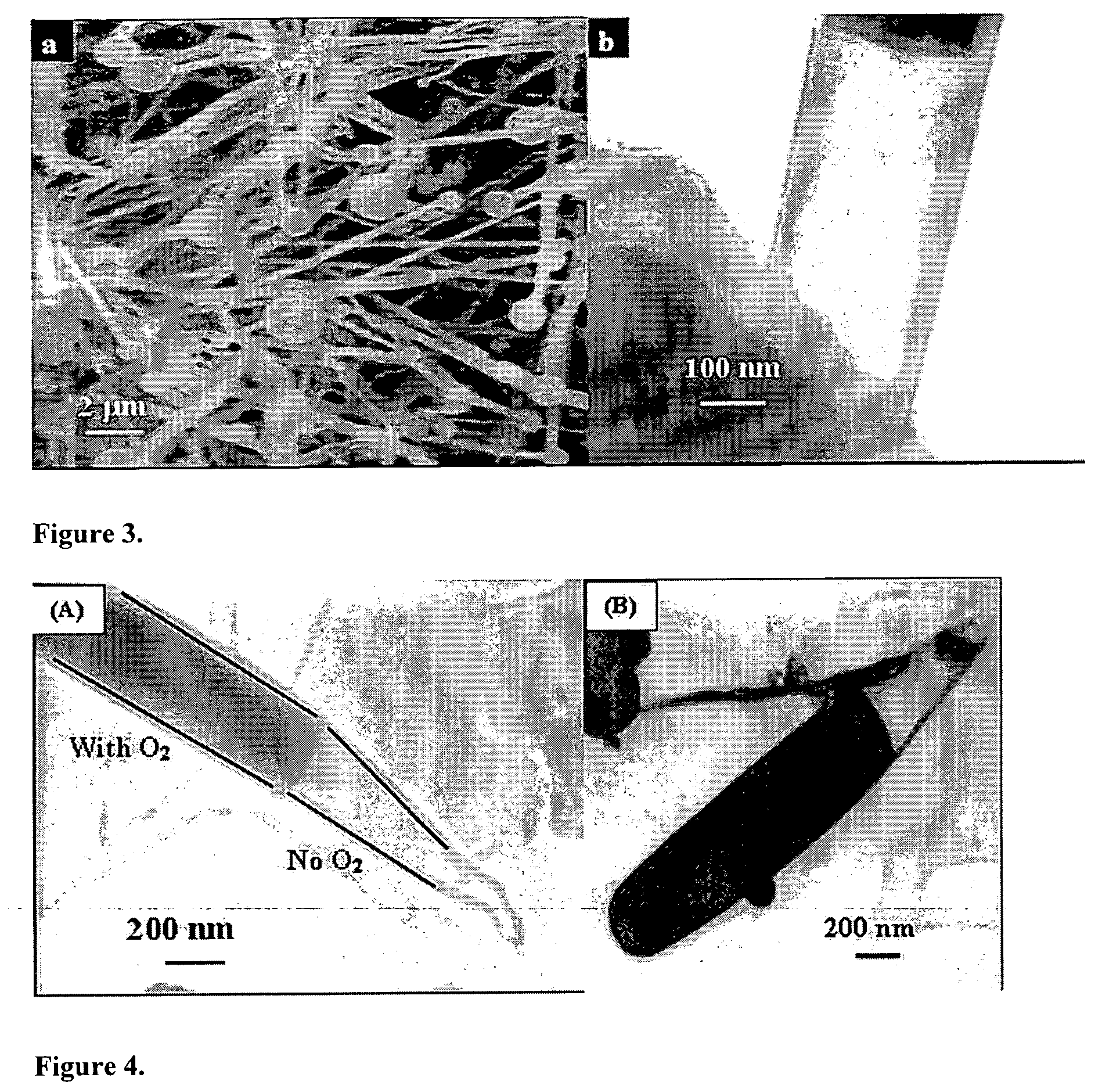
A method of synthesizing and controlling the internal diameters, conical angles, and morphology of tubular carbon nano / micro structures. Different morphologies can be synthesized included but not limited to cones, straight tubes, nozzles, cone-on-tube (funnels), tube-on-cone, cone-tube-cone, n-staged structures, multijunctioned tubes, Y-junctions, dumbbell (pinched morphology) and capsules. The process is based on changing the wetting behavior of a low melting metals such as gallium, indium, and aluminum with carbon using a growth environment of different gas phase chemistries. The described carbon tubular morphologies can be synthesized using any kind of gas phase excitation such as, but not limited to, microwave excitation, hot filament excitation, thermal excitation and Radio Frequency (RF) excitations. The depositions area is only limited by the substrate area in the equipment used and not limited by the process. The internal diameters of the carbon tubular structures can be varied from a few nm to as high as about 20 microns. The wall thickness is about 10-20 nm. The carbon tubular structures can be formed open on both ends are directly applicable to micro-fluidics. Gallium required for the growth of the carbon tubes can be supplied either as a thin film on the substrate or could be supplied through the gas phase with different precursors such as Tri-methyl gallium. Seamless Y-junctions with no internal obstructions can be synthesized without the need of templates. Multi-channeled junctions can also be synthesized without any internal obstructions. Gallium that partially fills the carbon structures can be removed from the tubes by simple heating in vacuum at temperature above 600°.
Owner:UNIV OF LOUISVILLE RES FOUND INC +1
Fluid stream powered pulse generating fluidic oscillator
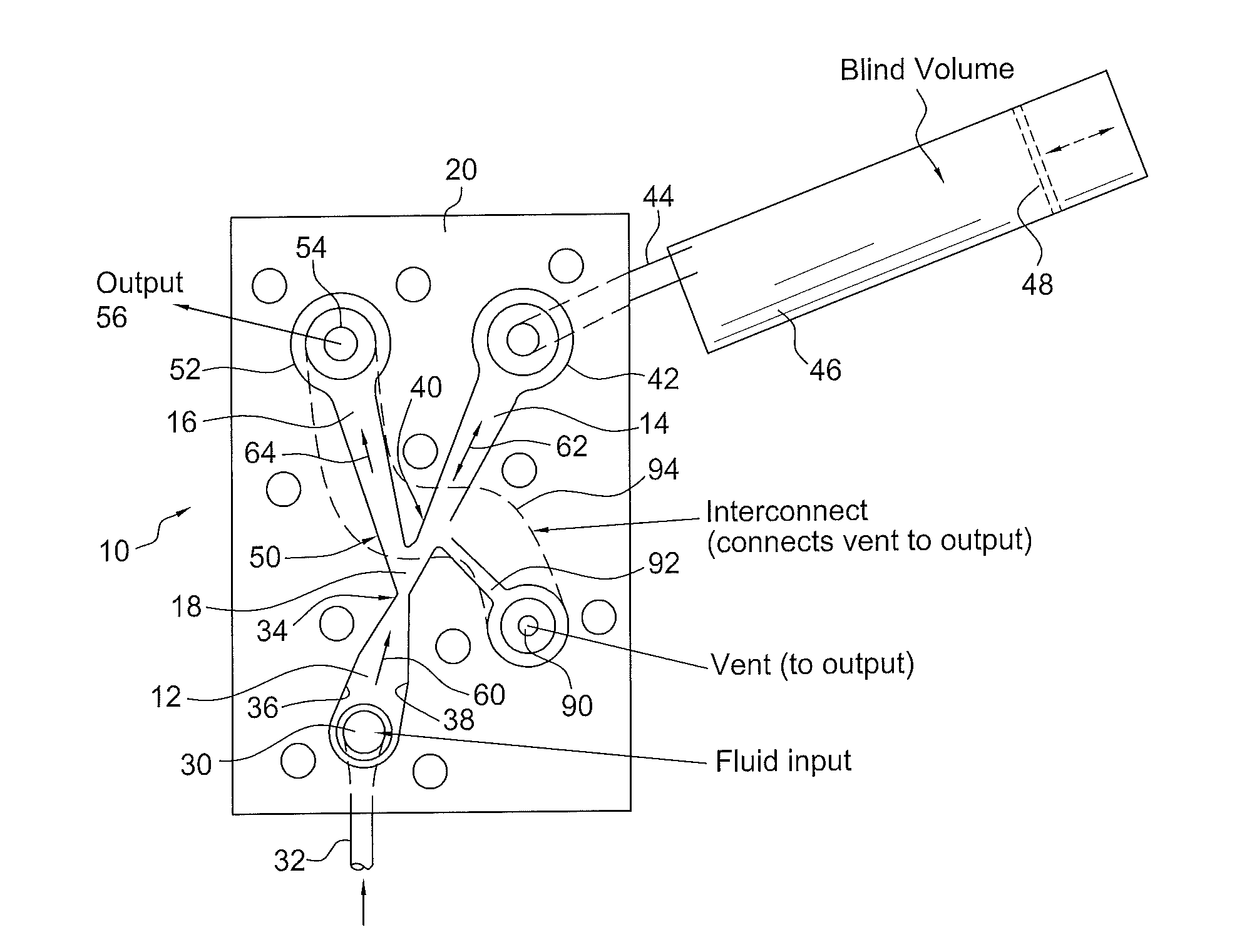
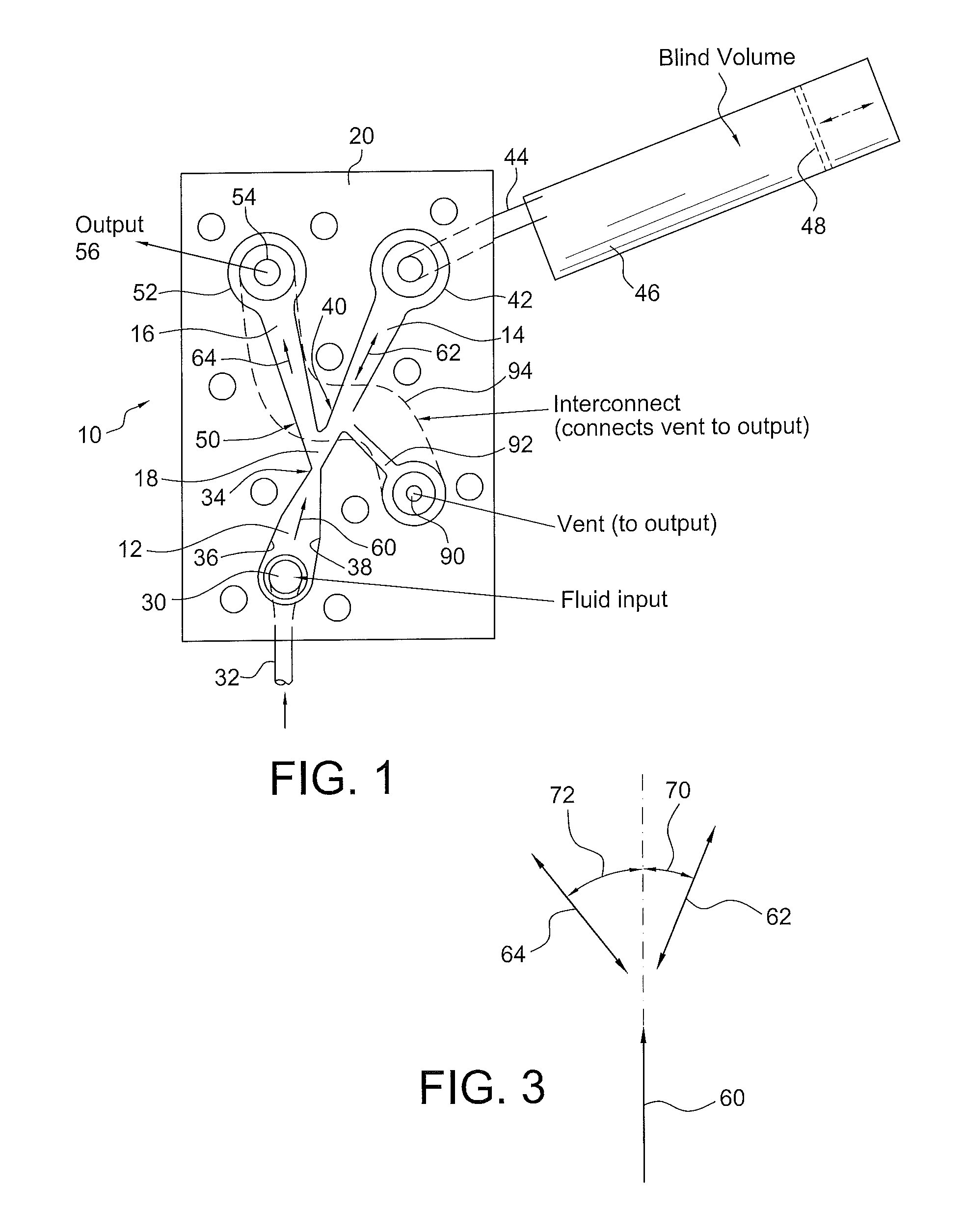
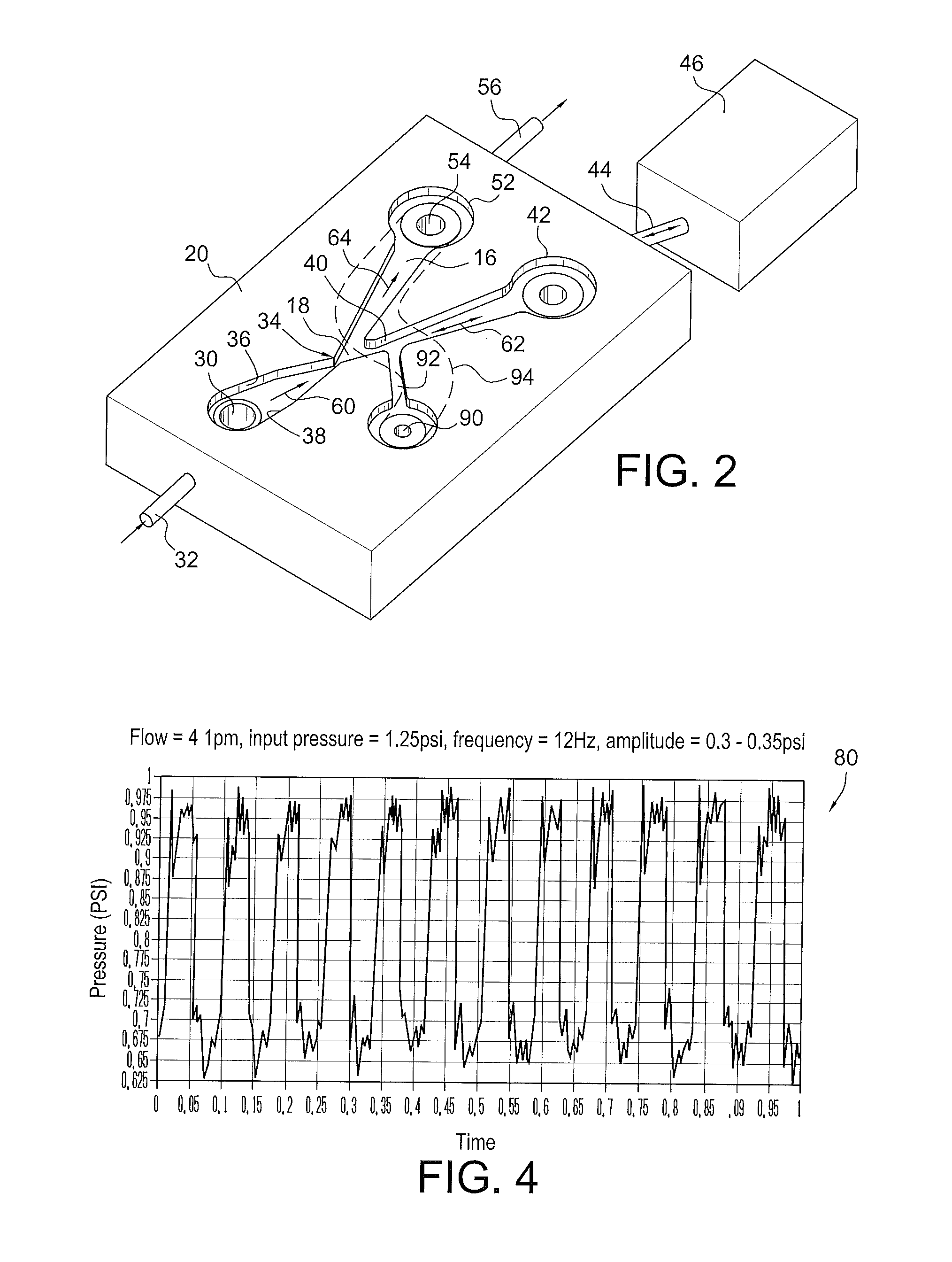
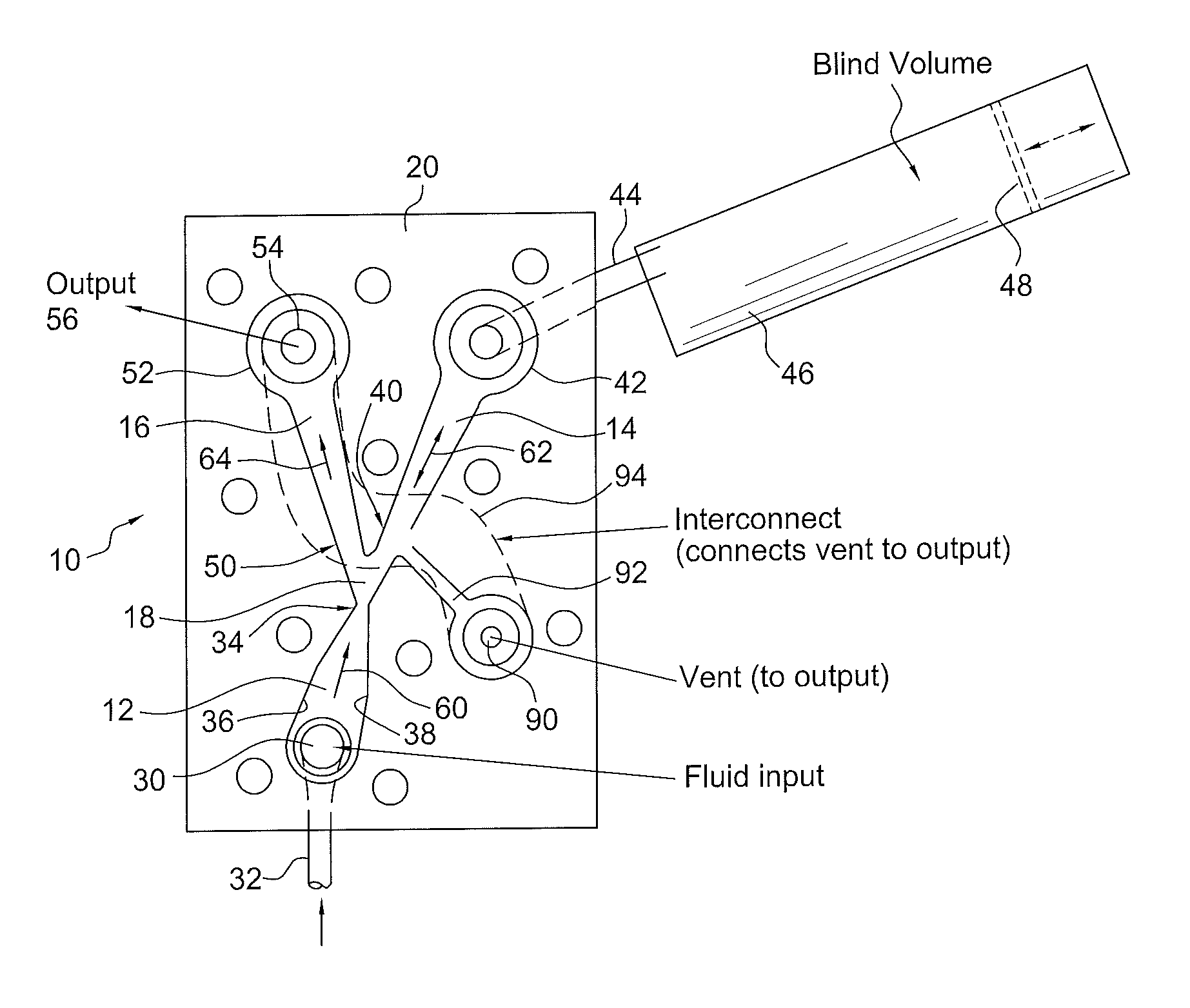
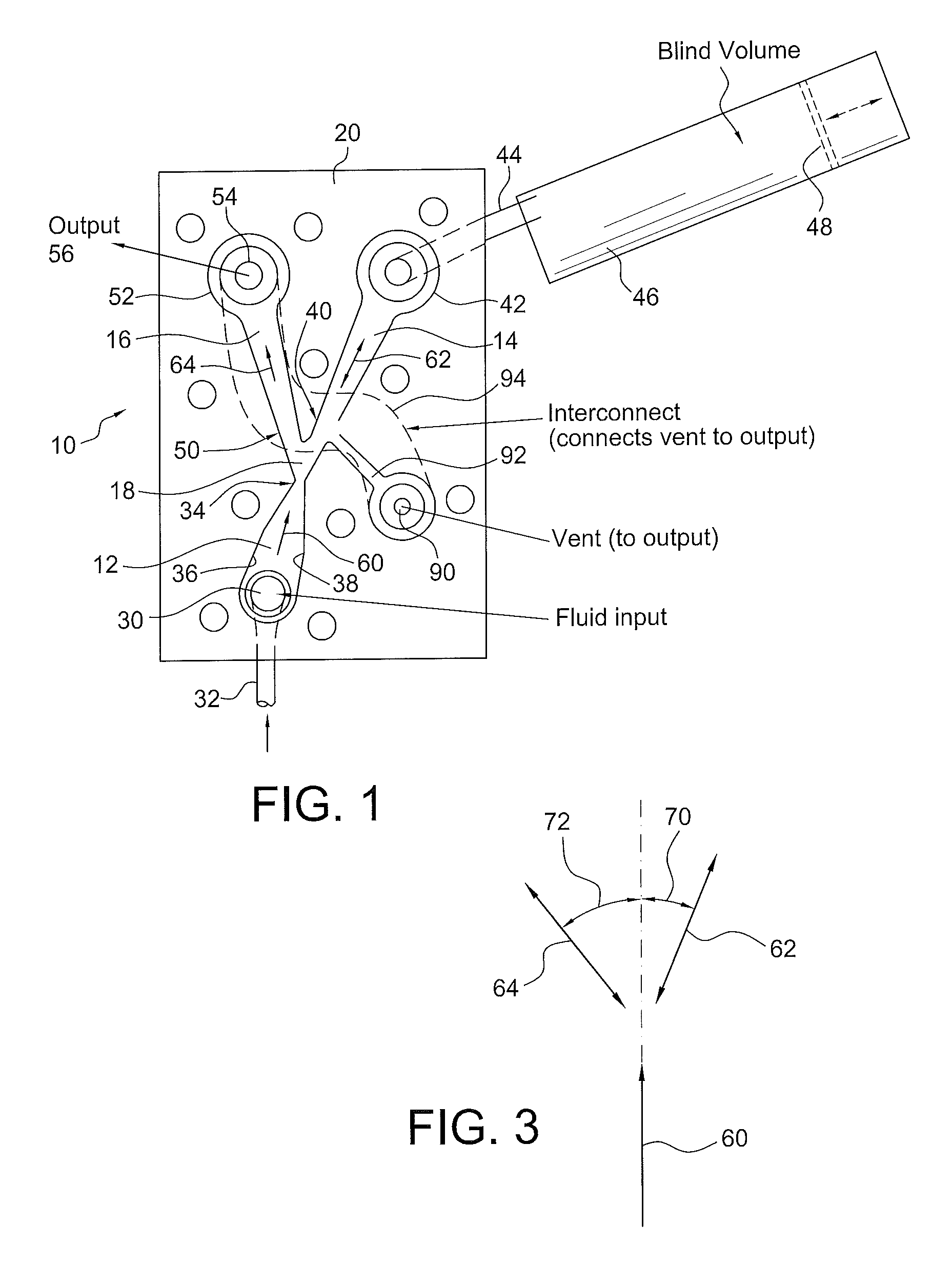
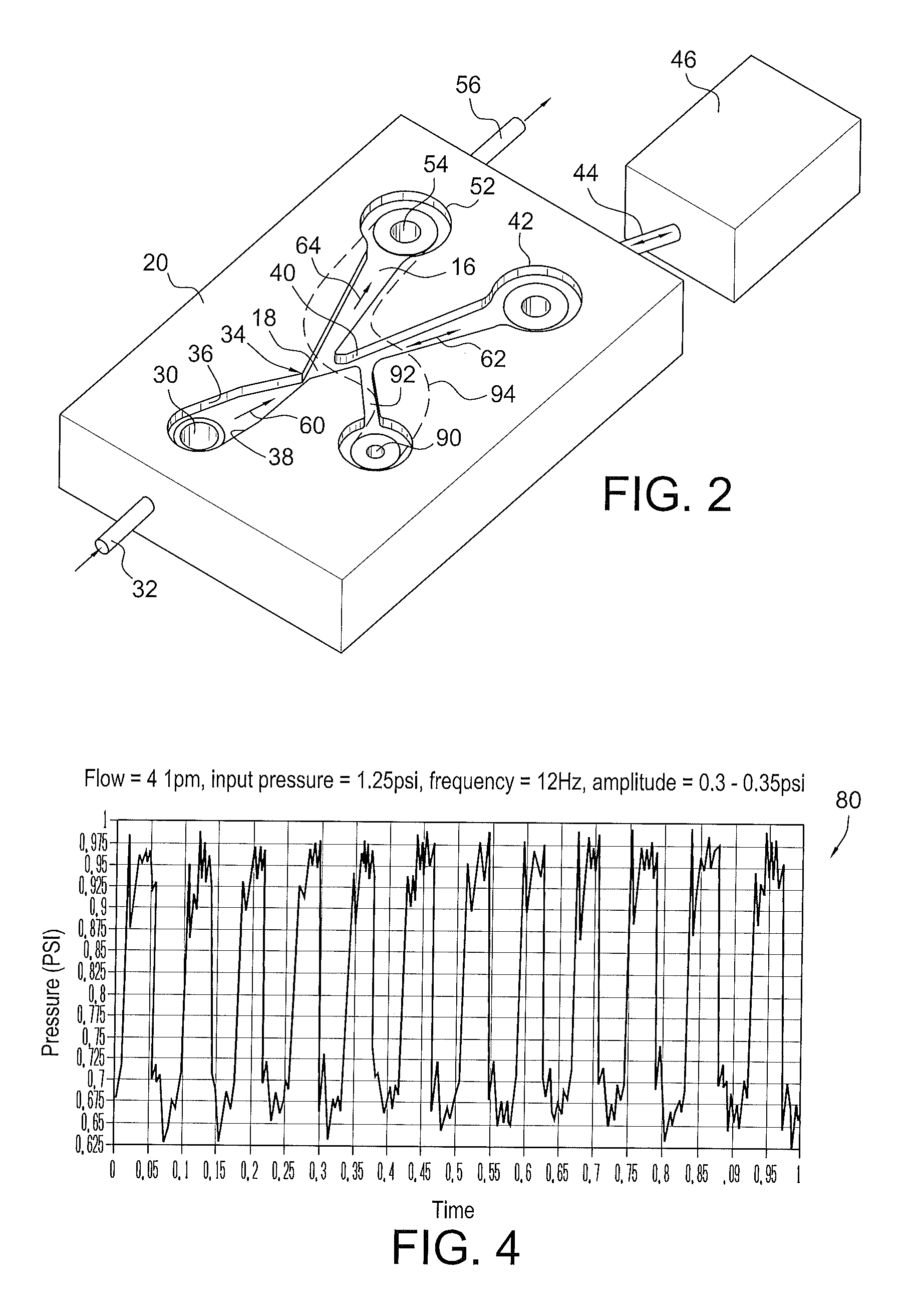
ActiveUS20120055560A1Improve stabilityLarge outputPipe supportsPhysical therapyFluidic oscillatorPulse duration
A fluidic device which produces fluid pulses having a selected pulse repetition frequency, pulse duration, pulse peak pressure and pulse peak flow rate includes first, second and third fluid flow controlling channels or lumens which converge in a junction, defining a “Y” configuration having a base leg and right and left diverging arms. The first leg portion has a fluid input and terminates downstream at the Y junction of the base and the two diverging arms. The first leg has converging walls which reduce the cross sectional area of the flow to thereby increase the fluid velocity to make a fluid jet. The second or right leg, begins at the Y junction and terminates distally in an enclosed, fluid-tight container having a selected blind volume. The third, or left leg, begins at the Y junction and terminates distally in a fluid outlet passage having a selected cross-sectional area.
Owner:DLHBOWLES INC
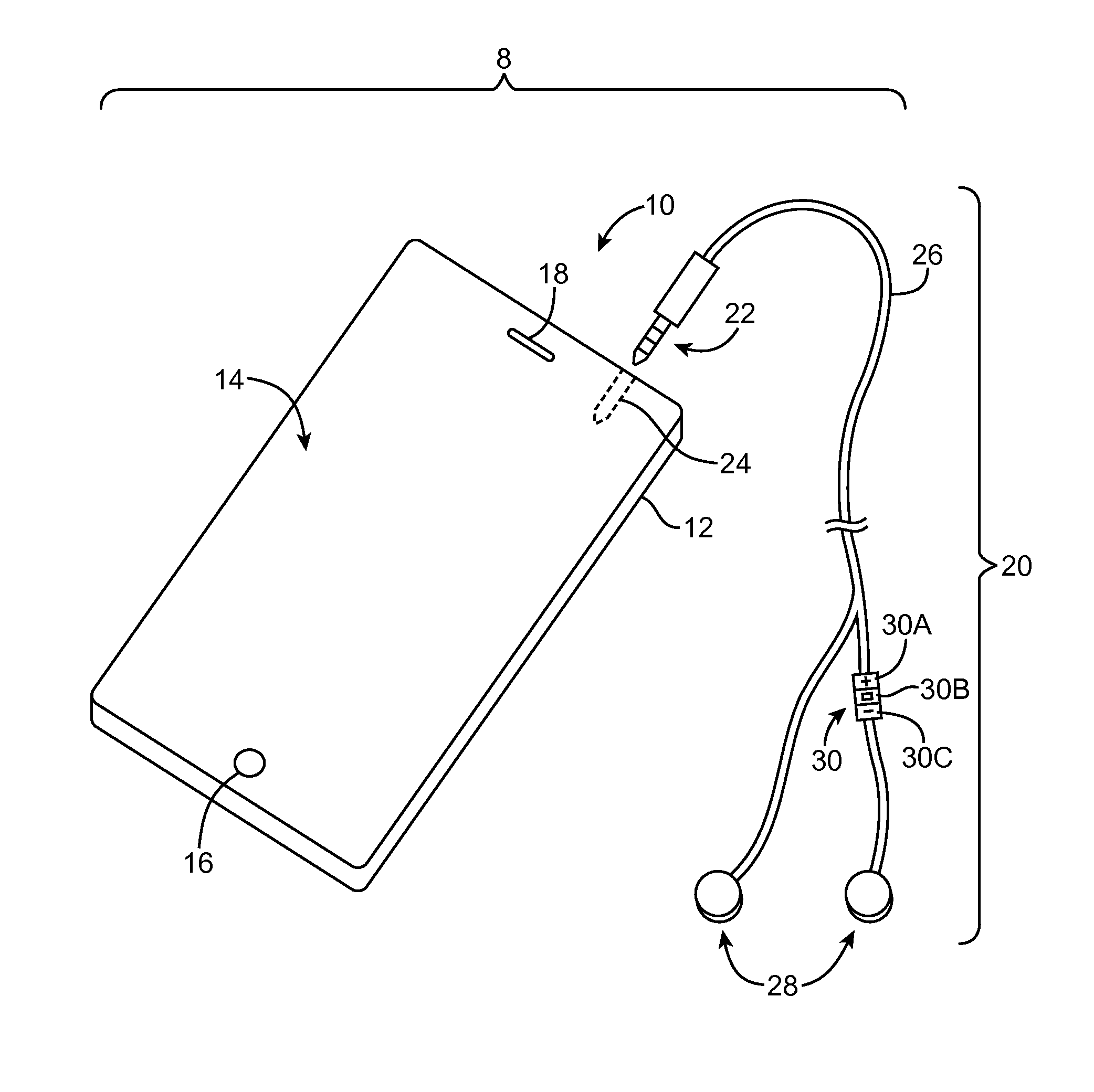
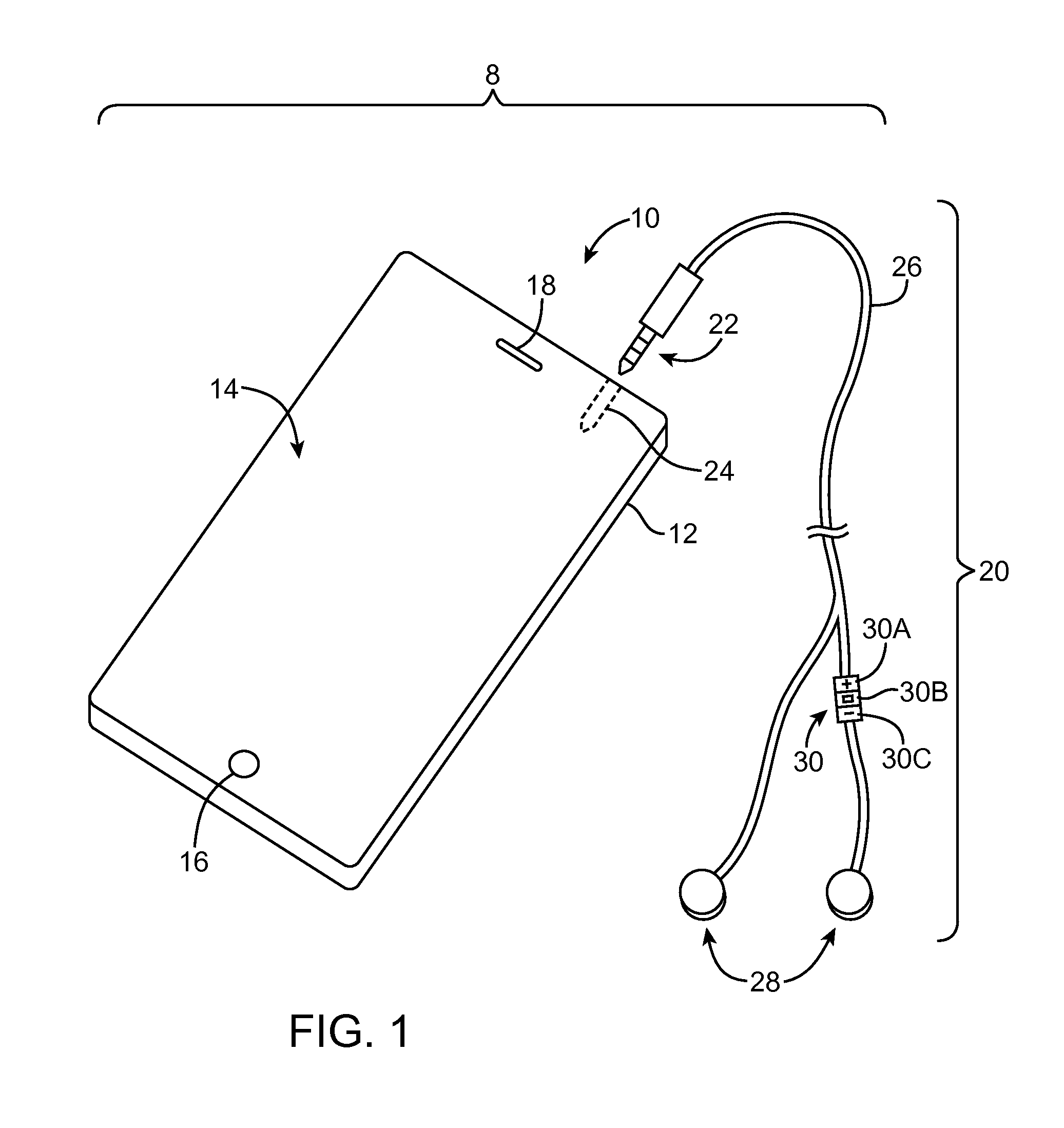
Earphones with cable orientation sensors
InactiveUS9049508B2Headphones for stereophonic communicationStereophonic circuit arrangementsHeadphonesLoudspeaker
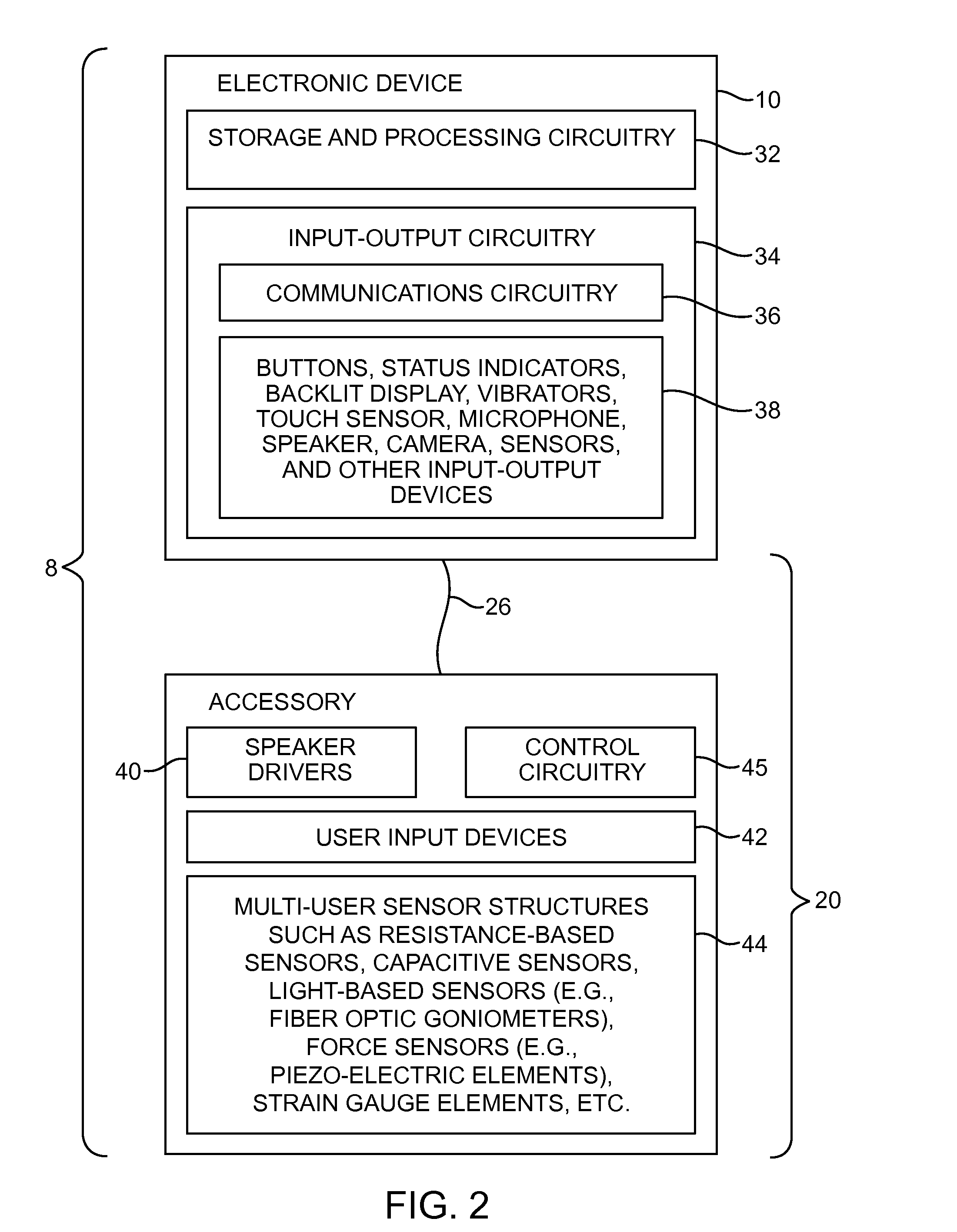
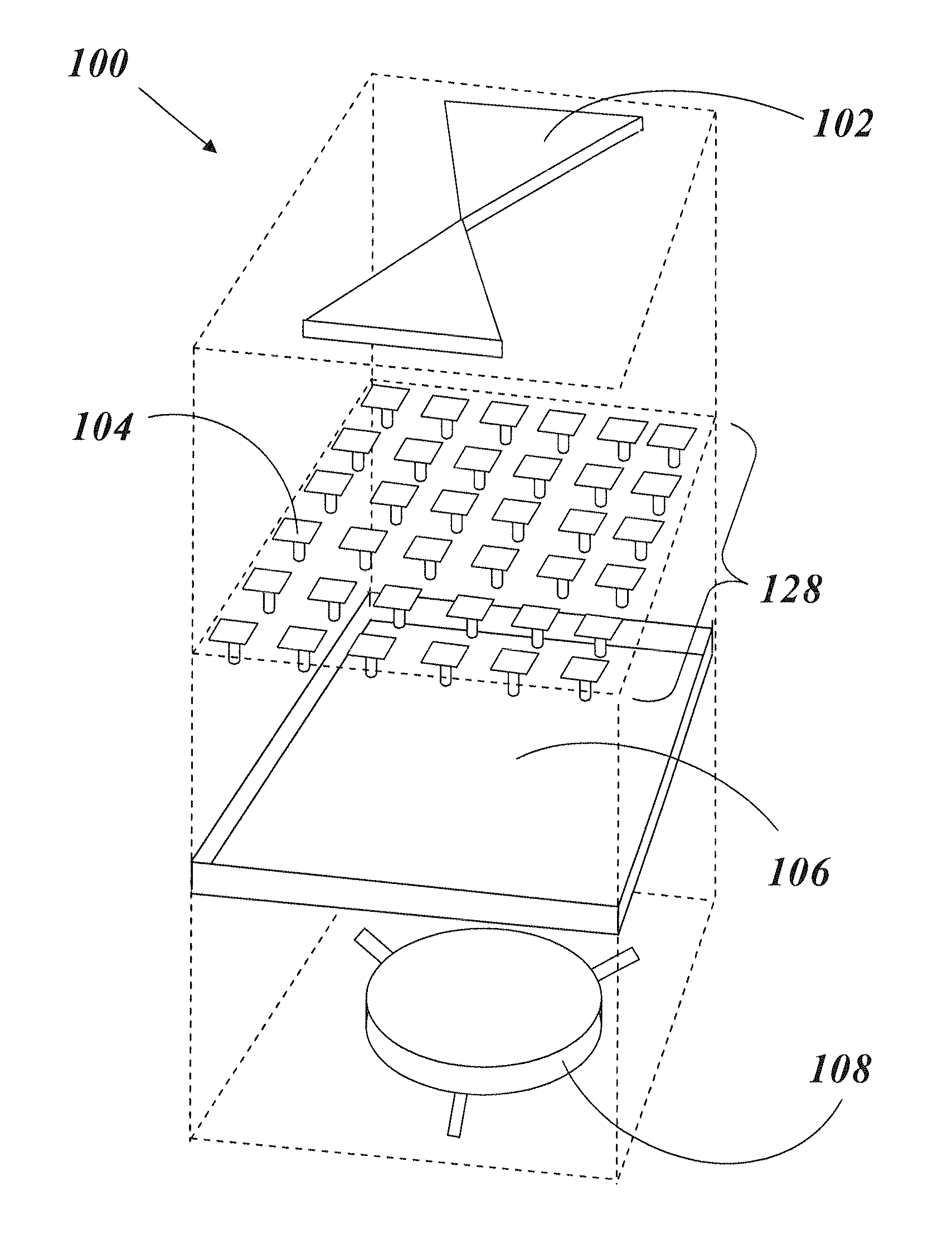
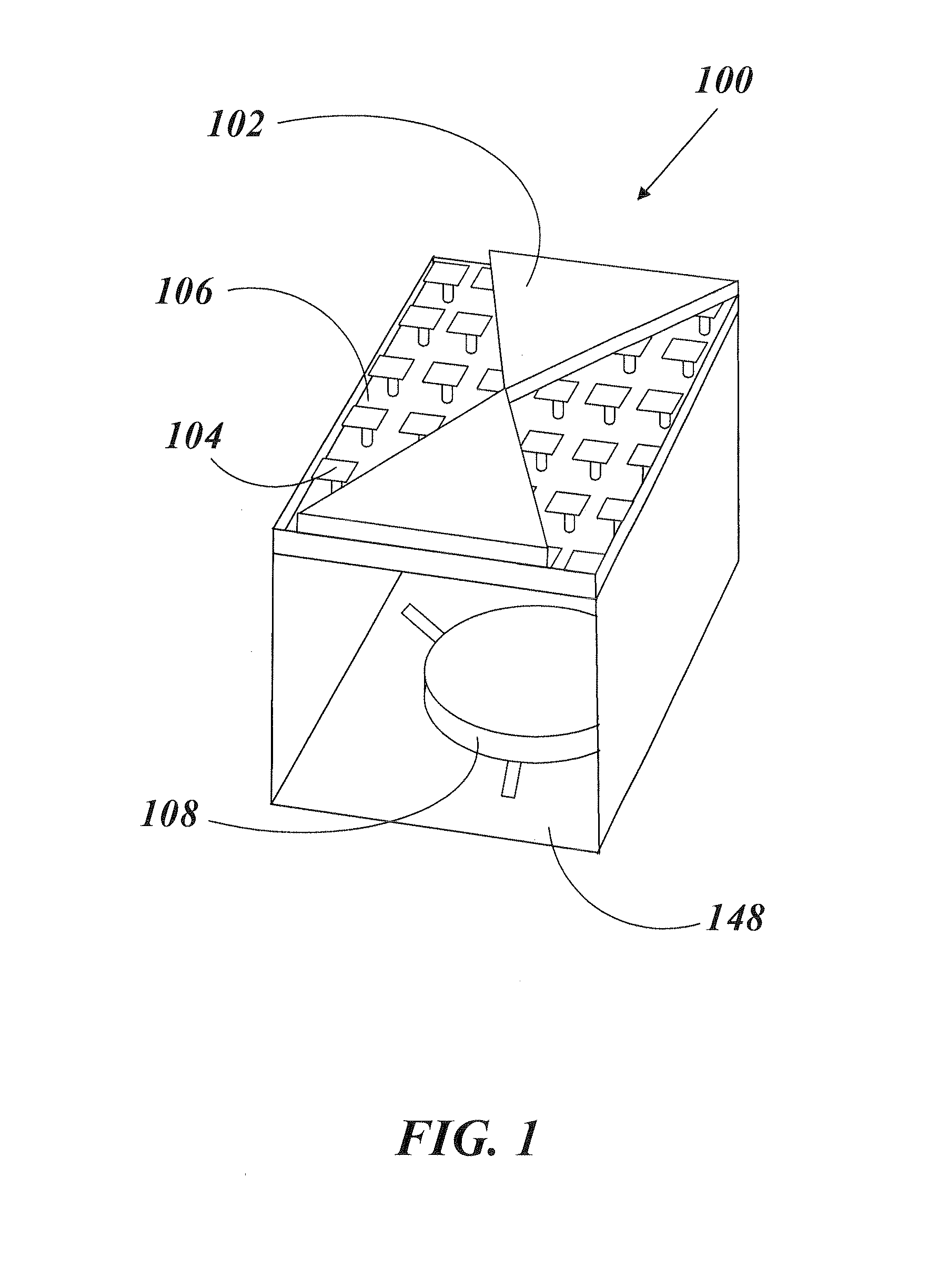
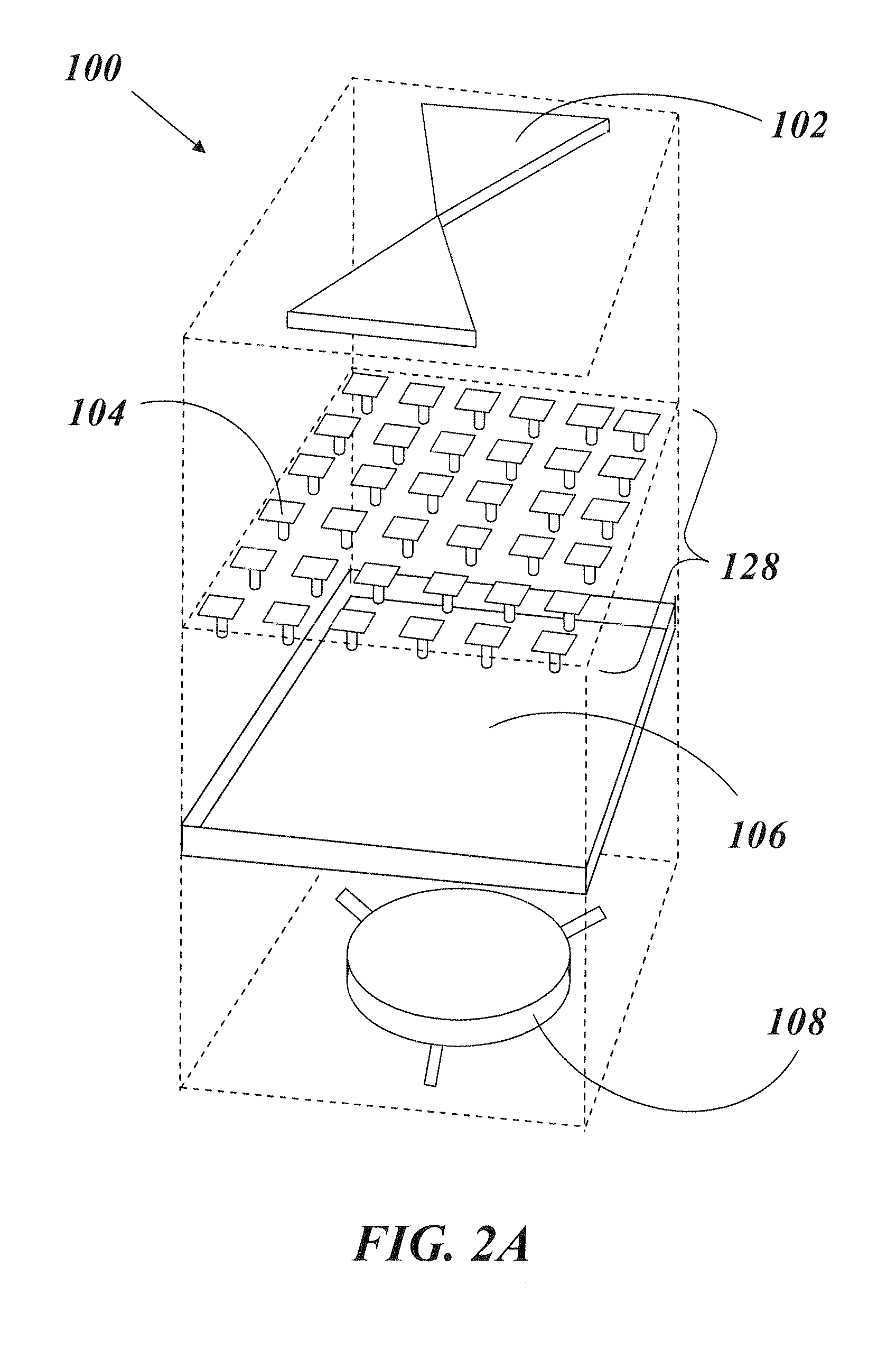
An electronic device may be coupled to an accessory such as a pair of earphones. The earphones may have multi-user sensor structures that determine whether or not the earphones are being shared by multiple users. The multi-user sensor structures may include an angle sensor configured to measure an angle at the Y-junction of a cable associated with the pair of headphones. When the first and second speakers are both located in the ears of a single user, the electronic device may perform functions such as playing audio content. When one of the speakers is located in an ear of a first user while the other of the speakers is located in an ear of a second user, the electronic device can automatically take actions such as switching from stereo to mono playback, playing a different type of audio content to each earphone, or other suitable action.
Owner:APPLE INC
Antenna module having reduced size, high gain, and increased power efficiency
InactiveUS8395552B2Reduce weight and sizeImprove power efficiencySimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsFerrite substrateBarium hexaferrite
A broadband integrated circulator antenna (BICA) module for receiving and transmitting signals with high efficiency and high gain. The BICA can have a bandwidth of over 70% of a radar band and can operate in frequencies from UHF to S-band and above. The BICA has a stack configuration that includes a low profile antenna, a reflecting layer or a metamaterial substrate layer, and a circulator. The circulator is placed proximal to antenna, which greatly reduces the size of the BICA. The circulator can be a stripline Y-junction ferrite circulator and the antenna can be a coaxial center fed bow-tie antenna. The reflecting layer or metamaterial substrate layer can comprise electronic bandgap metamaterial and a high permeability ferrite substrate. The high permeability ferrite substrate can be cobalt substituted Z-type barium hexaferrite.
Owner:METAMAGNETICS +1
Integrated optical switch array
InactiveCN1348108AMultiplex system selection arrangementsCoupling light guidesCouplingMiniaturization
An optical switch array is provided in which at least three input waveguides are coupled to at least three output waveguides. Each of the input waveguides is coupled in the same order to each of the output waveguides by a coupling element such as a y-junction combiner, via an intermediate waveguide and a switching mechanism that includes a coupling element such as a 1 x 2 switch. For compactness, the coupling elements that couple to the same input waveguide are mutually displaced along the output waveguides.
Owner:LYNX PHOTONIC NETWORKS
Quasi active MIMIC circulator
InactiveUS7541890B2High frequency and high bandwidthSmall sizeMultiple-port active networksOne-port networksLoad circuitPhase shifted
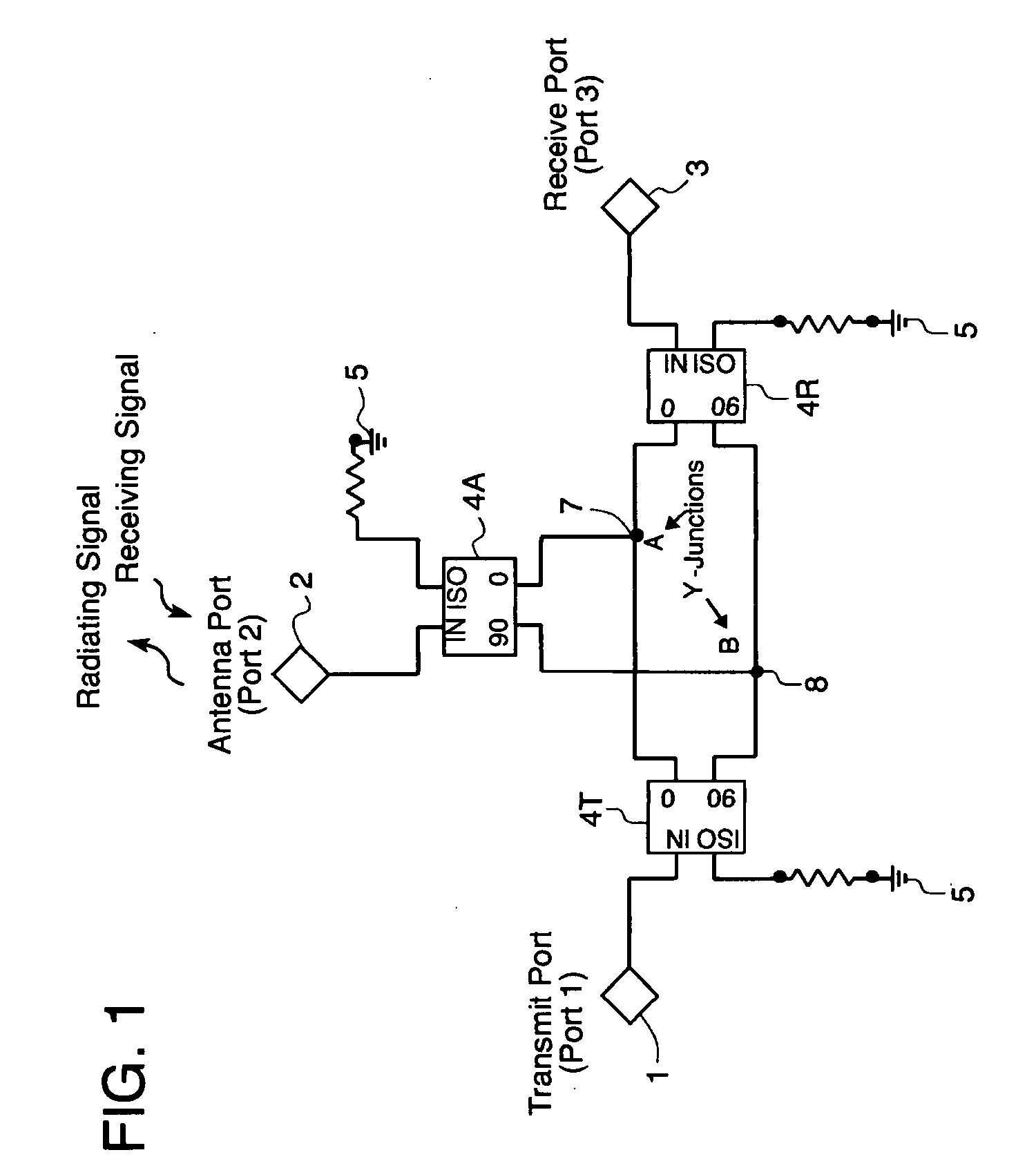
A circulator capable of simultaneous transmit and receive operations, high frequency, and high isolation and broadband performance comprising: an antenna port; a transmission port; a receiving port; wherein each port is connected to a 90 degree combiner / divider for splitting an input signal into two output components, the said output components have a ninety degrees relative phase difference to each other; each of said 90 degree combiner / dividers in addition to the connection to the above mentioned ports has at least two output connections each of which are connected to a Y-junction and if a fourth connection, said fourth connection is attached to a matching load circuit; this arrangement of circuits allows the portion of the phase shifted signals from the transmit port to enter the antenna 90 degree combiner / divider and be enhanced at the antenna port, while the rest of the signal enters the receive 90 degree combiner / divider and are phased cancelled; said arrangement allows the signals from the antenna port 90 degree combiner / divider to combine in phase at the receive port.
Owner:APPLIED RADAR
Automated transport control system
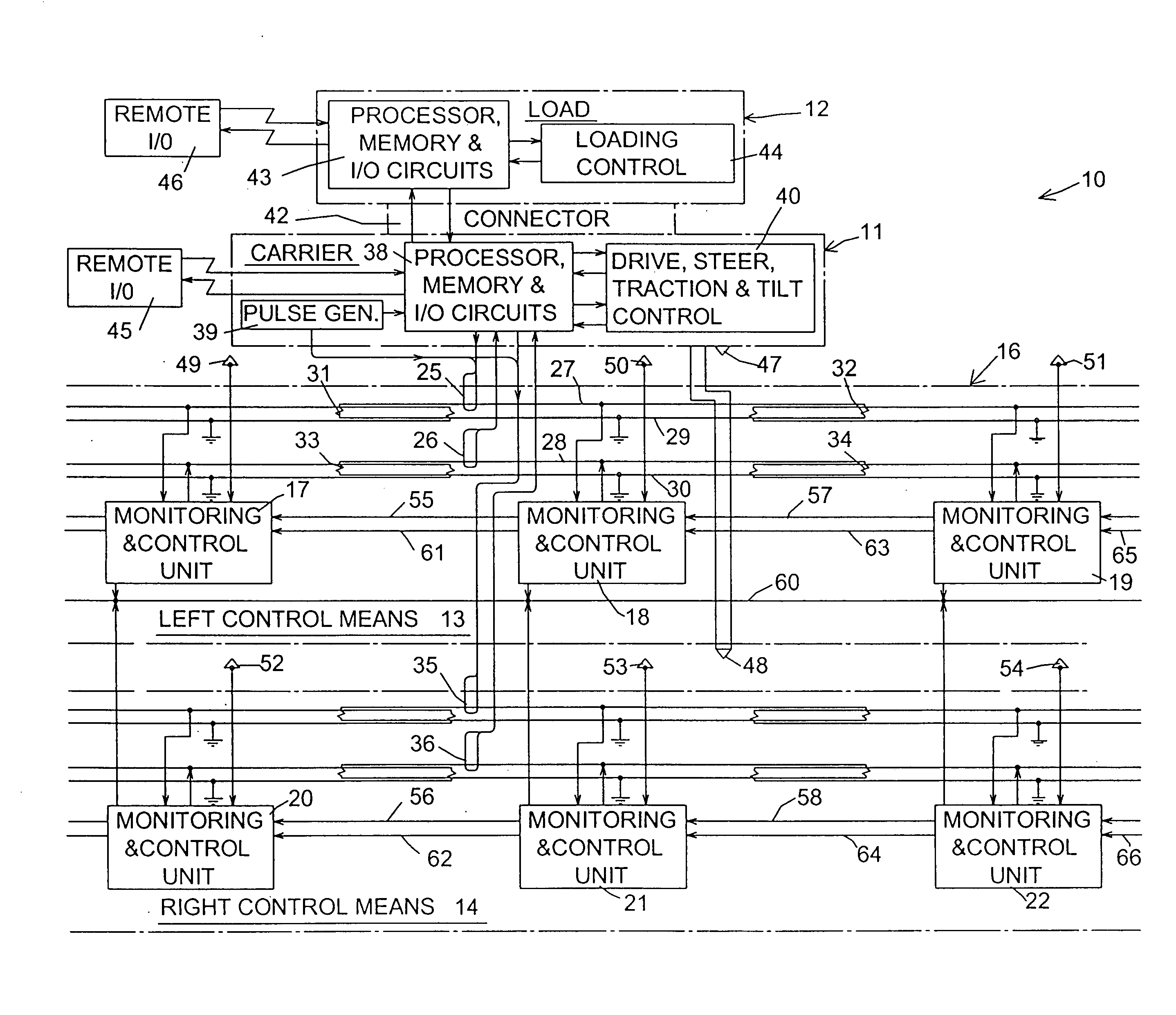
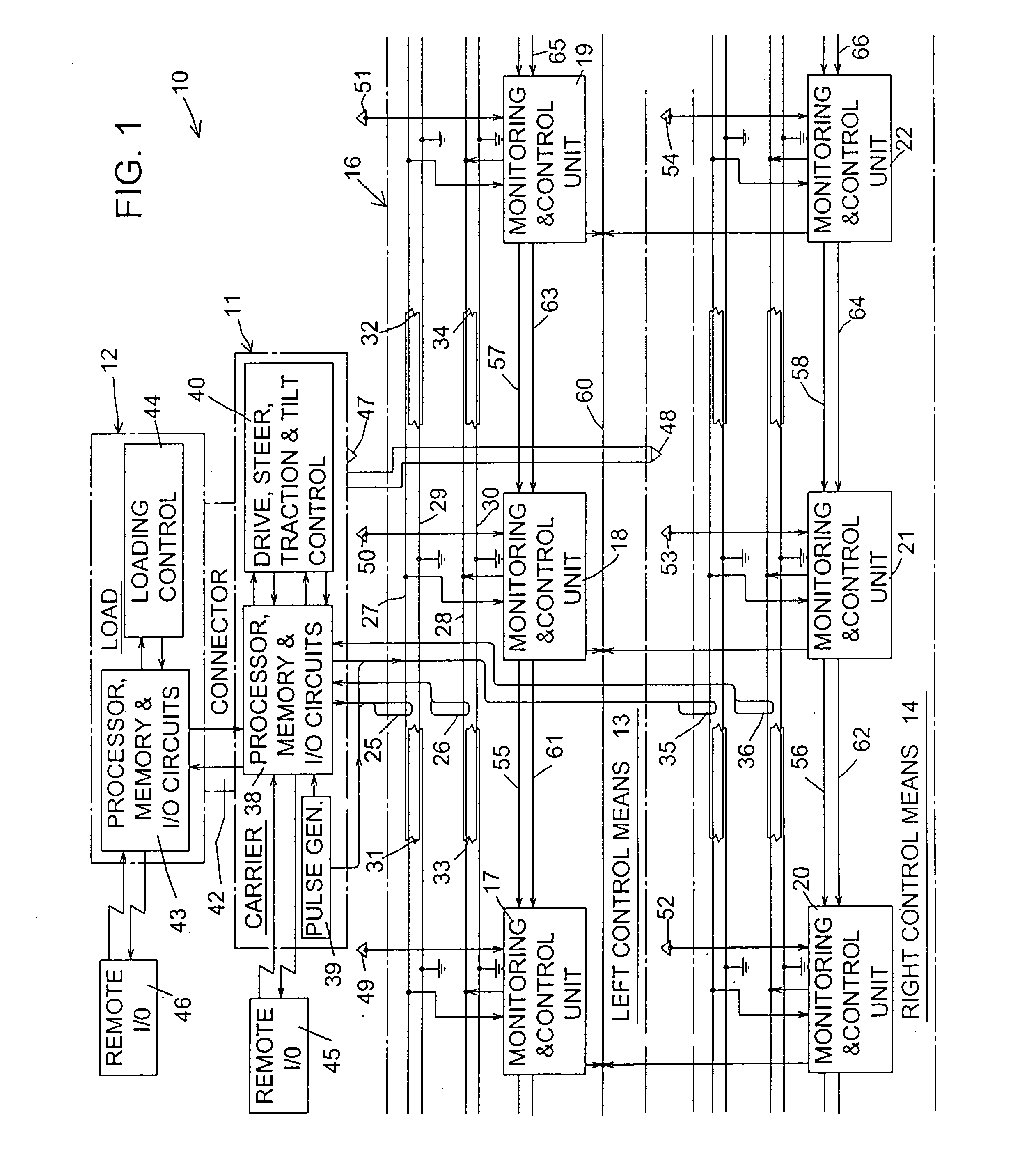
InactiveUS20100204833A1Eliminate the effects ofShorten speedDigital data processing detailsTemperatue controlControl systemCarrier signal
Each load-carrier of a system is always controlled by one of a series of MCUs (monitoring and control units) that are assigned to contiguous regions along guideways. Each carrier is slowed down to maintain a safe distance behind a carrier ahead, or to avoid collision with another carrier when approaching a merge point of a convergent Y-junction or when otherwise desirable. Distance measurements take into account the lengths of carriers and of assigned regions and the counts of speed pulses sent to MCUs since entry of carriers into their respective regions. For merge control, arrival data are developed that include the times and speeds to and at arrival of two carriers at a merge point. Through repeated comparisons of arrival data developed from one carrier with arrival data previously developed and stored as to the other carrier, the one carrier is gradually slowed down as necessary to avoid a collision.
Owner:AUTRAN CORP
Tubular carbon nano/micro structures and method of making same
A method of synthesizing and controlling the internal diameters, conical angles, and morphology of tubular carbon nano / micro structures. Different morphologies can be synthesized included but not limited to cones, straight tubes, nozzles, cone-on-tube (funnels), tube-on-cone, cone-tube-cone, n-staged structures, multijunctioned tubes, Y-junctions, dumbbell (pinched morphology) and capsules. The process is based on changing the wetting behavior of a low melting metals such as gallium, indium, and aluminum with carbon using a growth environment of different gas phase chemistries. The described carbon tubular morphologies can be synthesized using any kind of gas phase excitation such as, but not limited to, microwave excitation, hot filament excitation, thermal excitation and Radio Frequency (RF) excitations. The depositions area is only limited by the substrate area in the equipment used and not limited by the process. The internal diameters of the carbon tubular structures can be varied from a few nm to as high as about 20 microns. The wall thickness is about 10-20 nm. The carbon tubular structures can be formed open on both ends are directly applicable to micro-fluidics. Gallium required for the growth of the carbon tubes can be supplied either as a thin film on the substrate or could be supplied through the gas phase with different precursors such as Tri-methyl gallium. Seamless Y-junctions with no internal obstructions can be synthesized without the need of templates. Multi-channeled junctions can also be synthesized without any internal obstructions. Gallium that partially fills the carbon structures can be removed from the tubes by simple heating in vacuum at temperature above 600°.
Owner:UNIV OF LOUISVILLE RES FOUND INC +1
Fluid stream powered pulse generating fluidic oscillator
ActiveUS8770229B2Inexpensive and adjustable and reliableImprove stabilityPhysical therapyCircuit elementsFluidic oscillatorPulse duration
A fluidic device which produces fluid pulses having a selected pulse repetition frequency, pulse duration, pulse peak pressure and pulse peak flow rate includes first, second and third fluid flow controlling channels or lumens which converge in a junction, defining a “Y” configuration having a base leg and right and left diverging arms. The first leg portion has a fluid input and terminates downstream at the Y junction of the base and the two diverging arms. The first leg has converging walls which reduce the cross sectional area of the flow to thereby increase the fluid velocity to make a fluid jet. The second or right leg, begins at the Y junction and terminates distally in an enclosed, fluid-tight container having a selected blind volume. The third, or left leg, begins at the Y junction and terminates distally in a fluid outlet passage having a selected cross-sectional area.
Owner:DLHBOWLES INC
Compact and low loss Y-junction for submicron silicon waveguide
A compact, low-loss and wavelength insensitive Y-junction for submicron silicon waveguides. The design was performed using FDTD and particle swarm optimization (PSO). The device was fabricated in a 248 nm CMOS line. Measured average insertion loss is 0.28±0.02 dB across an 8-inch wafer. The device footprint is less than 1.2 μm×2 μm, orders of magnitude smaller than MMI and directional couplers.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
Integrated chromatic confocal sensor
ActiveCN109073367ASemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSpectrum generation using diffraction elementsBroadband light sourceY junction
Owner:UNITY SEMICON
Microwave strip transmission line circulator with harmonic suppression function
InactiveCN101958448AWork around size limitationsGood harmonic suppression effectWaveguide type devicesHarmonic mitigationElectrical conductor
The invention provides a microwave strip transmission line circulator with a harmonic suppression function, which comprises a permanent magnet, a metal pole piece, microwave ferrites and an outer case. One strip line central conductor is installed among the microwave ferrites and comprises three 120 DEG Y-junction resonators and three matching circuits, and each matching circuit comprises an open parallel circuit and an inductance type transmission line. The three inductance type transmission lines of the strip line central conductor are respectively connected with an electrical conductor at a port of the circulator radially at the equal intervals of 120 degrees. The microwave strip transmission line circulator is provided with a built-in open parallel circuit with one quarter wavelength and provides the functions of a trap filter to suppress harmonic waves.
Owner:SDP TELECOM SUZHOU
Orthomode transducer
InactiveUS20130088307A1Quality improvementFacilitates miniaturization and productionCoupling devicesBroadbandCross polarization
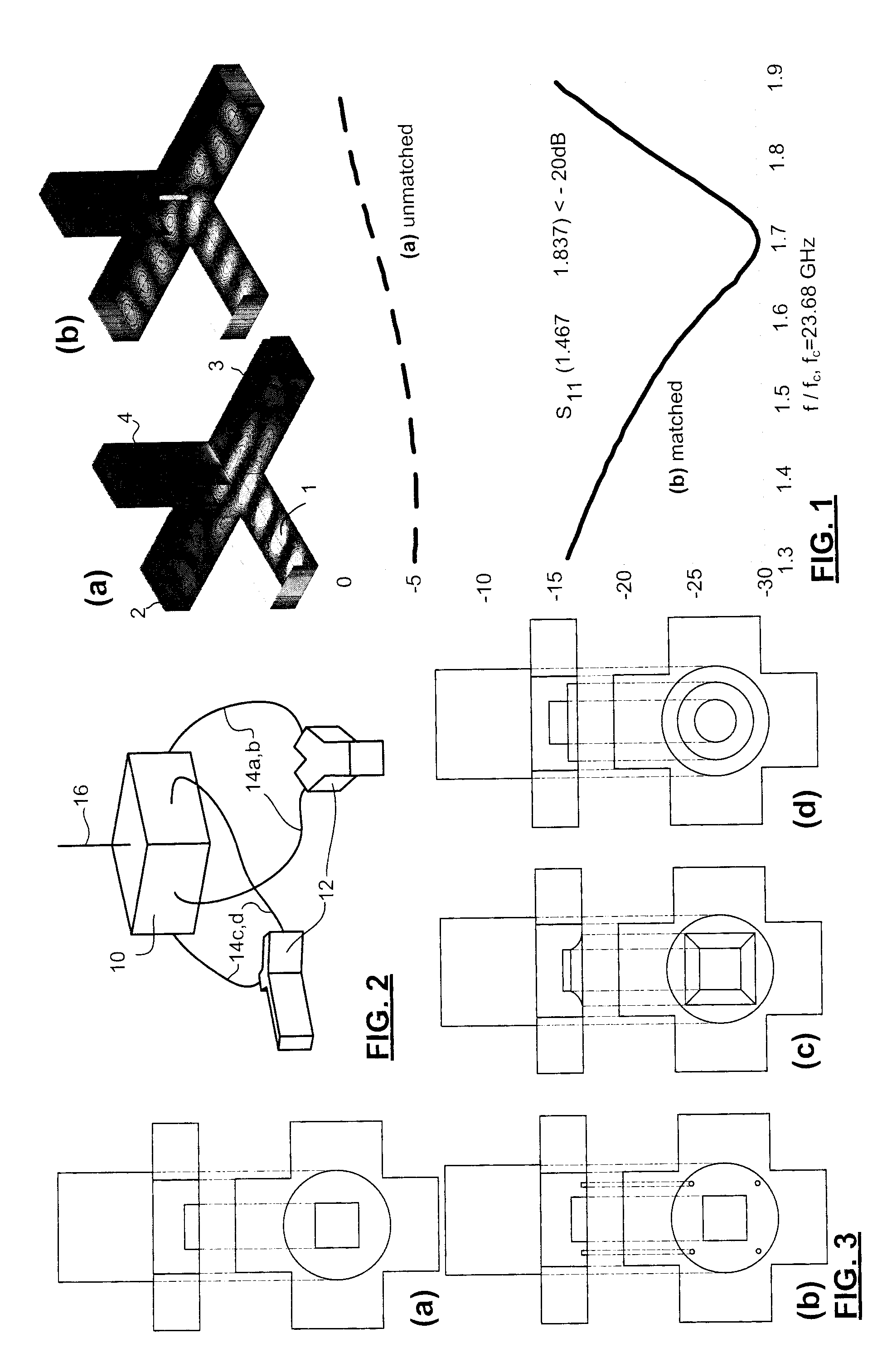
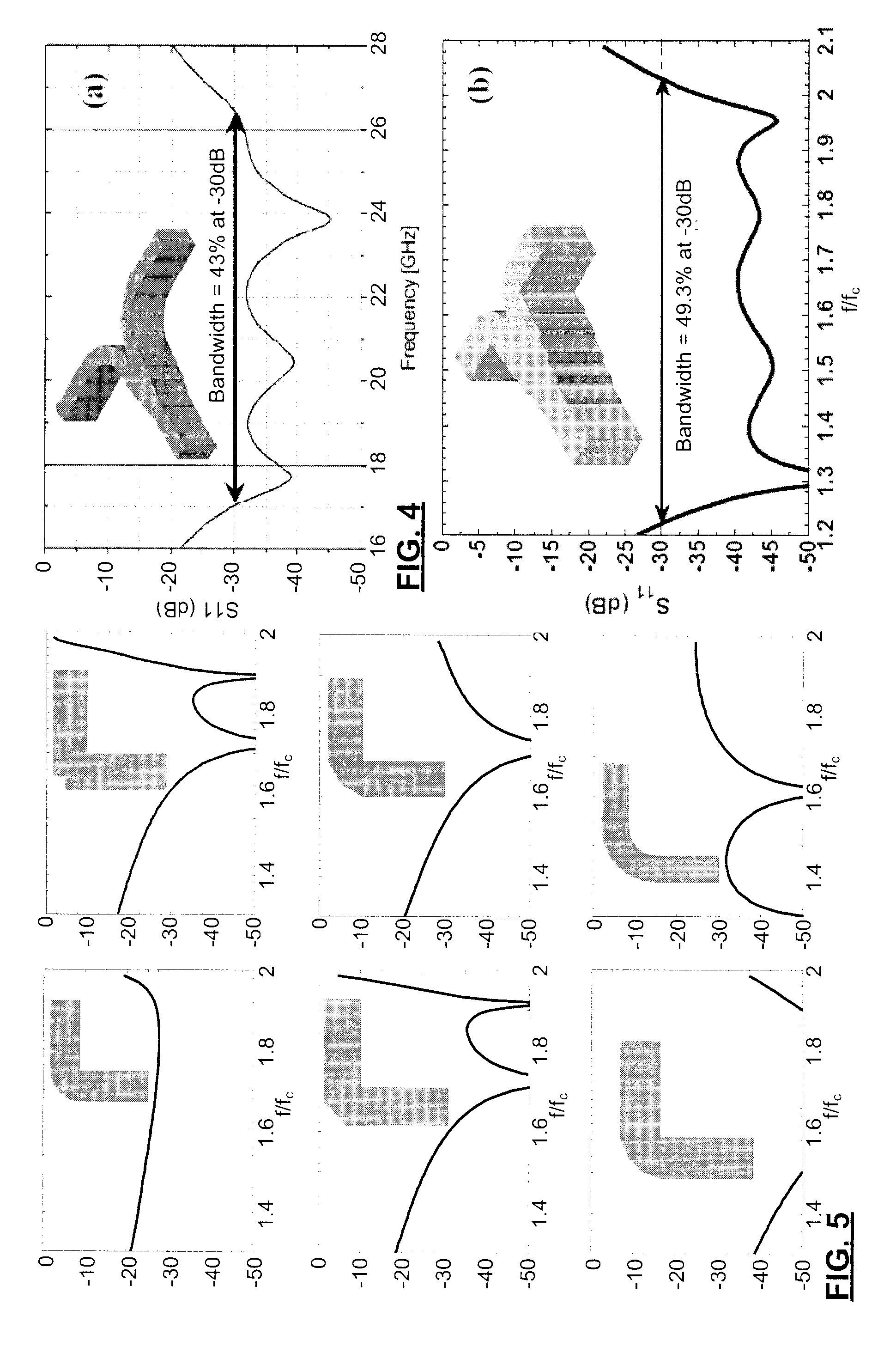
An orthomode transducer (OMT) operable in a broadband (e.g. >30%), including a frequency above ˜30 GHz, with an isolation better than −50 dB, cross-polarizations better than −40 dB, an insertion loss between −0.1 and −0.3 dB for both polarizations, and return losses better than −25 dB can be produced substantially or entirely from CNC machining, comprises a turnstile for coupling a polarization diplexed waveguide with four waveguide paths; and two E-plane Y junctions each for coupling initially oppositely directed pairs of the waveguide paths such that each waveguide path has a same electrical length from the turnstile to the E-plane Y junctions as the waveguide path with which it is paired, such that the OMT is formed in 3-6 blocks, including a single block having a substantially planar mating surface that includes the matching feature, and defines one side of initial segments of the four waveguide paths. Reproducibility of these OMTs has been shown.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com