Method and system for a low-loss optical y-junction power splitter
a power splitter and optical y-junction technology, applied in the field of semiconductor photonics, can solve the problems of cable bulk penalties, large power requirements, and complex structure, and achieve only modest improvements in reach and limited scalability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
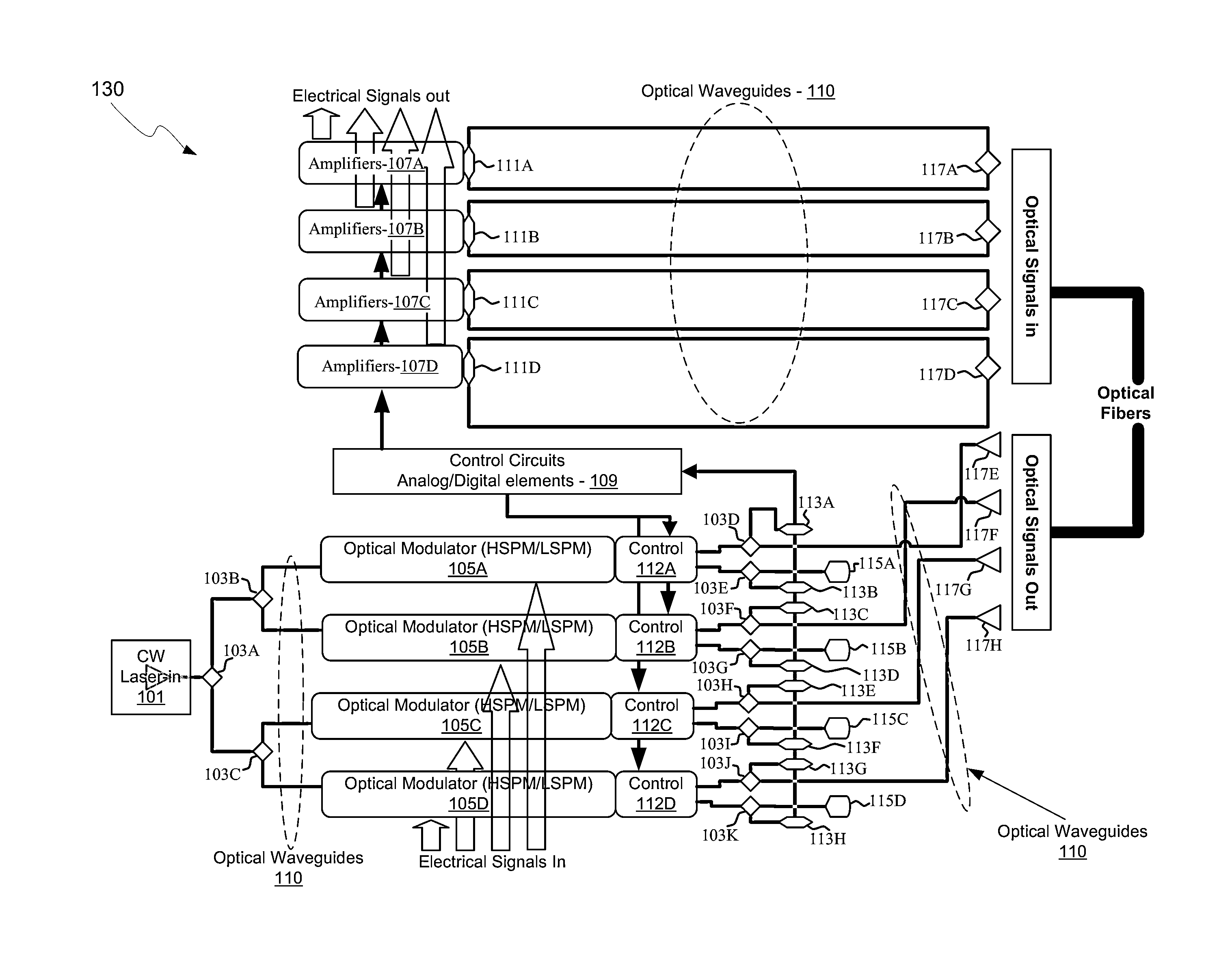
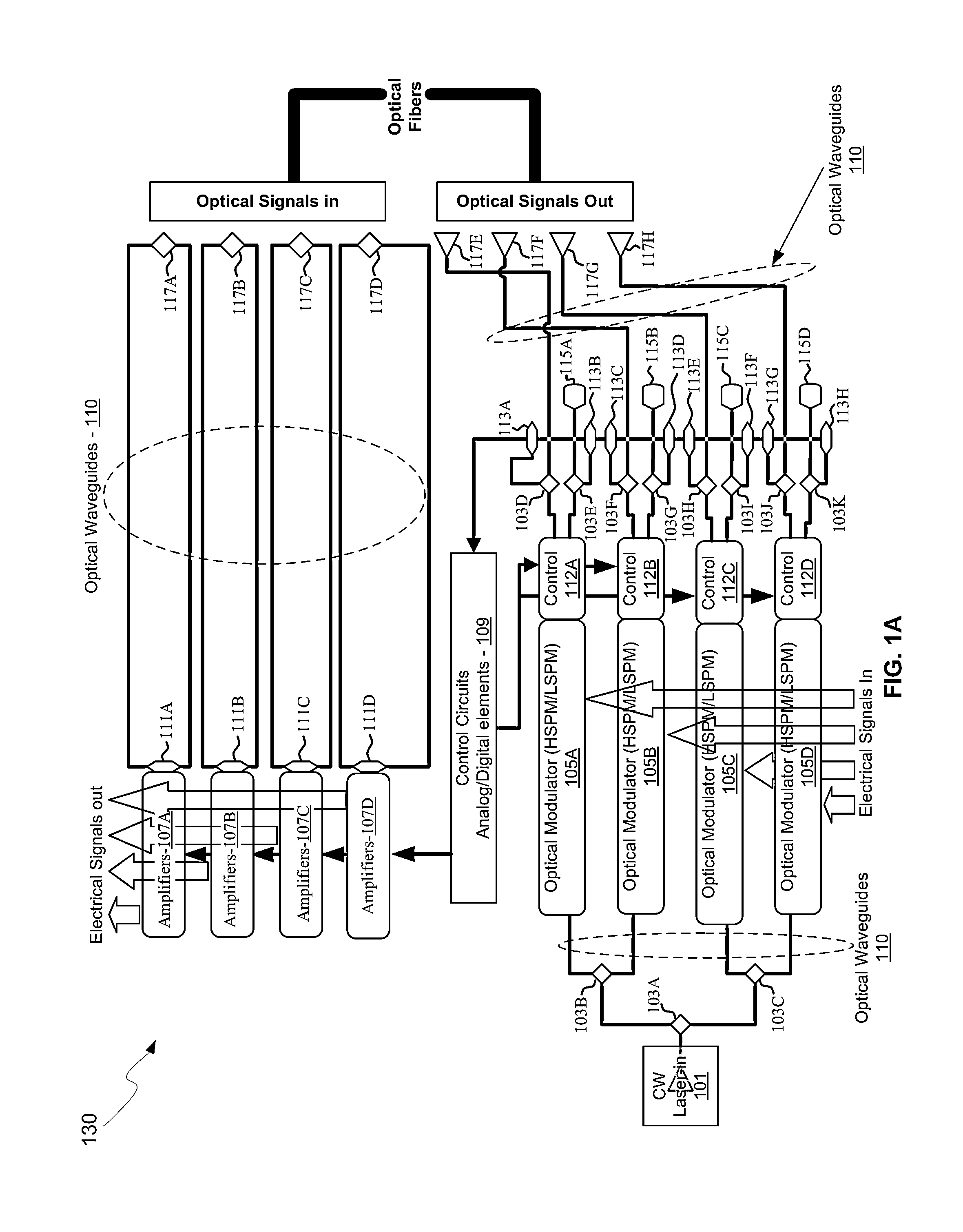
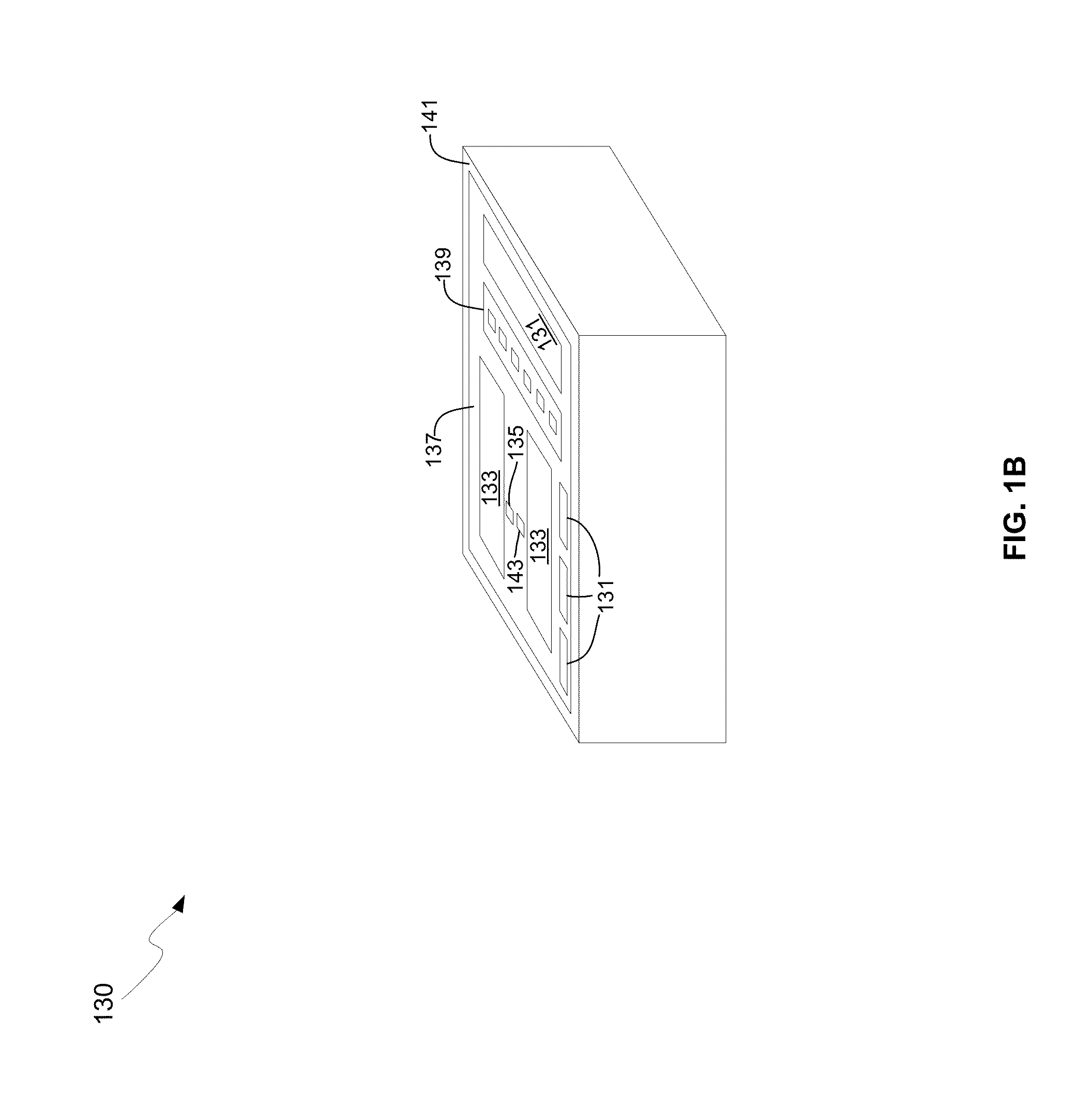
[0015]Certain aspects of the disclosure may be found in a method and system for a low-loss optical Y-Junction power splitter. Exemplary aspects of the disclosure may comprise in a semiconductor die with an optical Y-junction, where the optical Y-junction comprises an input waveguide, two or more output waveguides, a taper region and a step feature. The input waveguide and the taper region may include a smooth transition between them, and the step feature may be between the taper region and the two or more output waveguides. The semiconductor die may receive an optical signal in the input waveguide, and communicate substantially equal power optical signals to each of the two or more output waveguides. The semiconductor die may comprise a photonically-enabled integrated circuit. The semiconductor die may comprise silicon. An optical signal may be received in each of the two or more output waveguides and a summed output signal may be communicated to the input waveguide. The semiconduct...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com