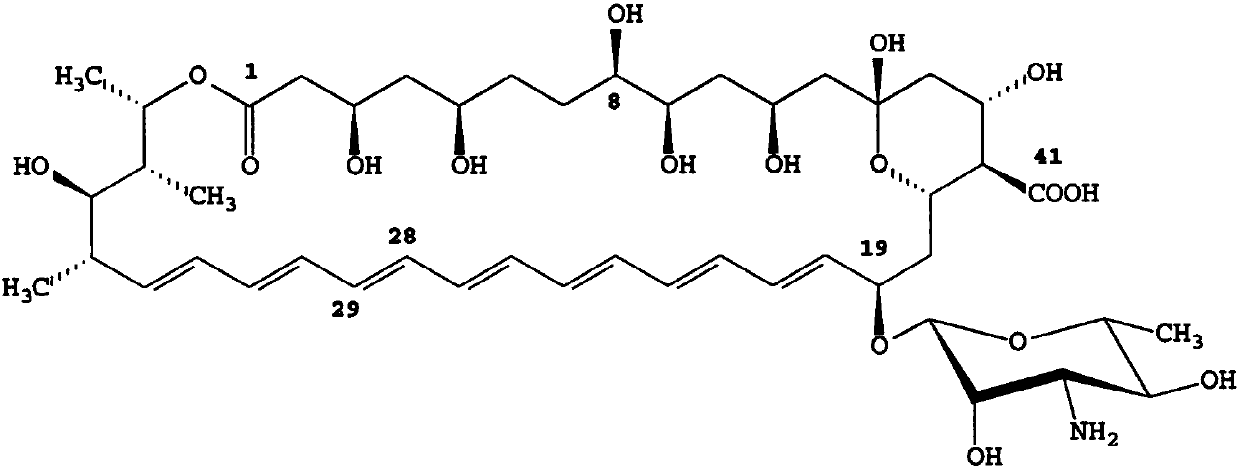
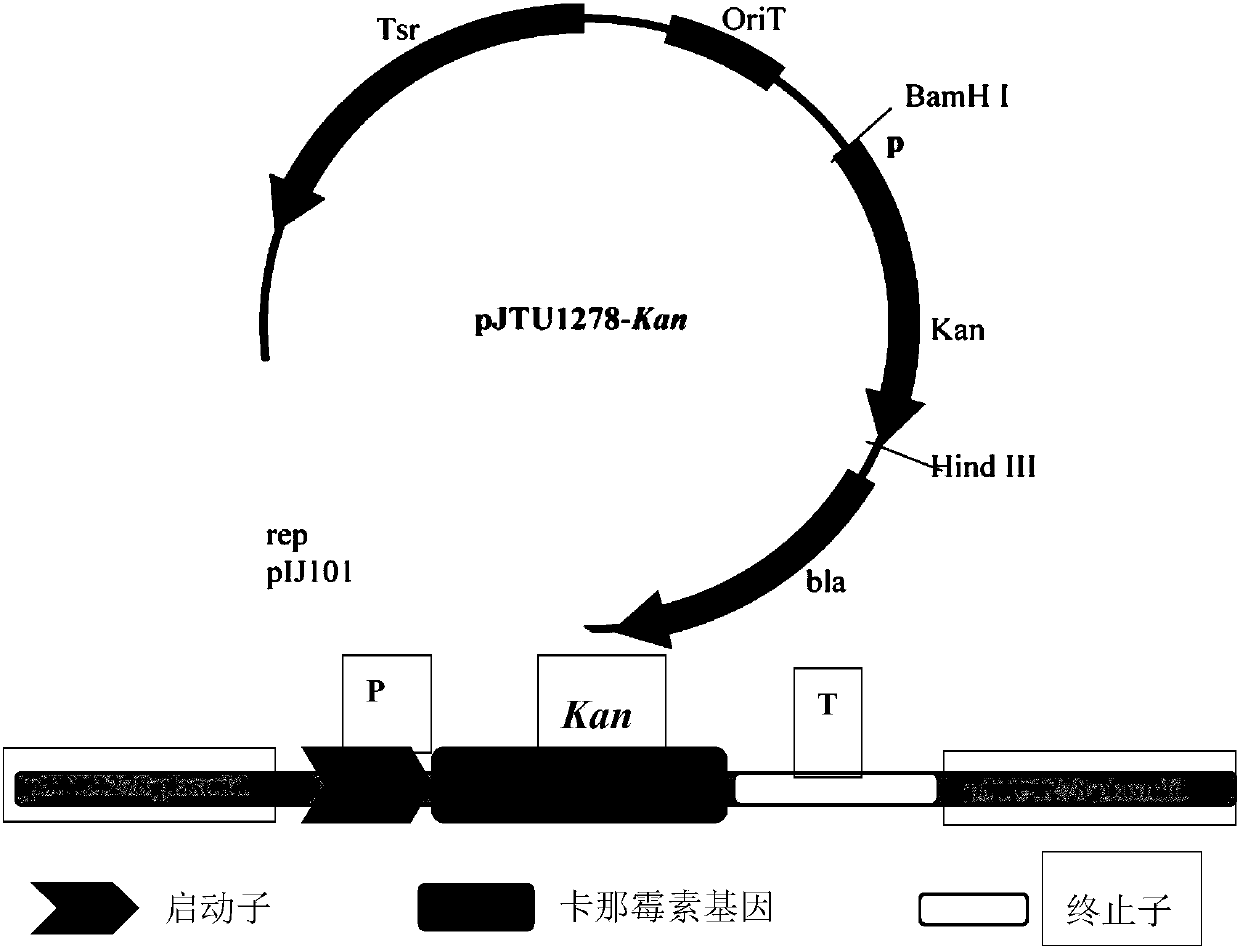
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
58 results about "Vitreoscilla hemoglobin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Gamma-polyglutamic acid production gene engineering bacterial and method for producing high-yield gamma-polyglutamic acid through gamma-polyglutamic acid production gene engineering bacterial
ActiveCN103881954AIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMonosodium glutamateGenetic engineering
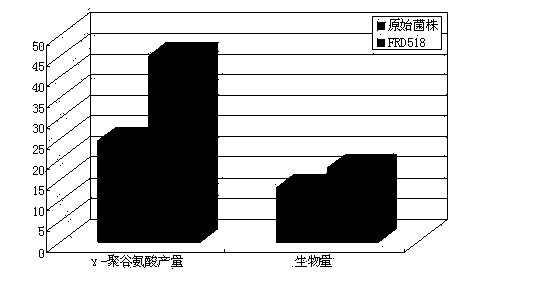
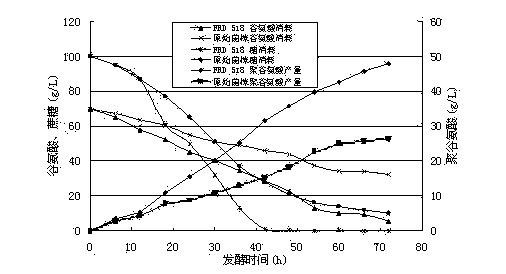
The present invention discloses a high-yield gamma-polyglutamic acid production gene engineering bacterial and a fermentation production method thereof. The gene engineering bacterial is named Bacillus subtilis FRD518, wherein the preservation number is CGMCC NO.6772, and the Vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene (vgb) is recombined and integrated on the chromosome of the gene engineering bacterial, such that the Vitreoscilla hemoglobin VHb can be successfully and highly expressed so as to significantly improve the oxygen utilization rate of the recombinant Bacillus subtilis under a low dissolved oxygen condition. According to the present invention, during a fermentation process, a carbon source, sodium glutamate, a yeast extract and other components are added in a flow manner, such that the gene engineering bacterial can efficiently produce the gamma-polyglutamic acid in a high yield manner, wherein the yield achieves more than 65 g / L, and is increased by 147% compared with the yield of the single batch culture of the original wild strain; and with the gene engineering bacterial, the problems of low yield, more by-products, long period, high energy consumption and the like of fermentation of the gamma-polyglutamic acid gene engineering bacterial under high viscosity and dissolved oxygen limiting conditions are solved, and the gamma-polyglutamic acid gene engineering bacterial can be applied for large-scale industrial production of gamma-polyglutamate acid.
Owner:SHANDONG FREDA BIOTECH
Gene recombination bacillus amyloliquefaciens and microbial inoculum preparation method
InactiveCN101717744AProtect environmentIncreased spore contentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEcological environment
The invention discloses gene recombination bacillus amyloliquefaciens and a microbial inoculum preparation method. A bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42 strain is taken as a host bacterium to construct the gene recombination bacillus amyloliquefaciens XLV09-1 with transparent vitreoscilla hemoglobin which is regulated and controlled by a P43 strong promoter by contrasting a gene recombination vector. The produced spore number of microbial inoculum prepared by fermenting the bacillus amyloliquefaciens can reach more than 100 hundred millions per milliliter, the overall yield of antibacterial lipopeptid reaches more than 1 gram per liter and prevention effect on various fungal plant diseases is improved by over 30 percent. The microbial inoculum is a green microecological preparation, of no toxic residue, safe to human and livestock, and favorable for protecting the ecological environment.
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
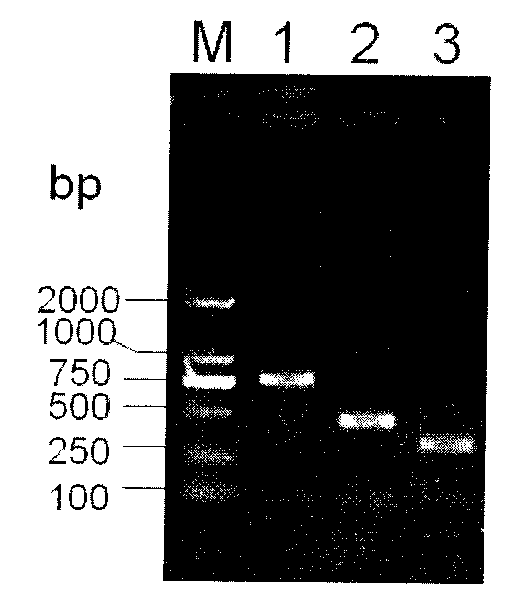
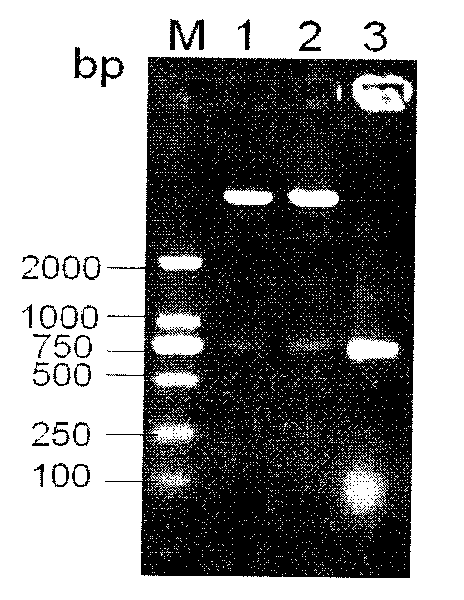
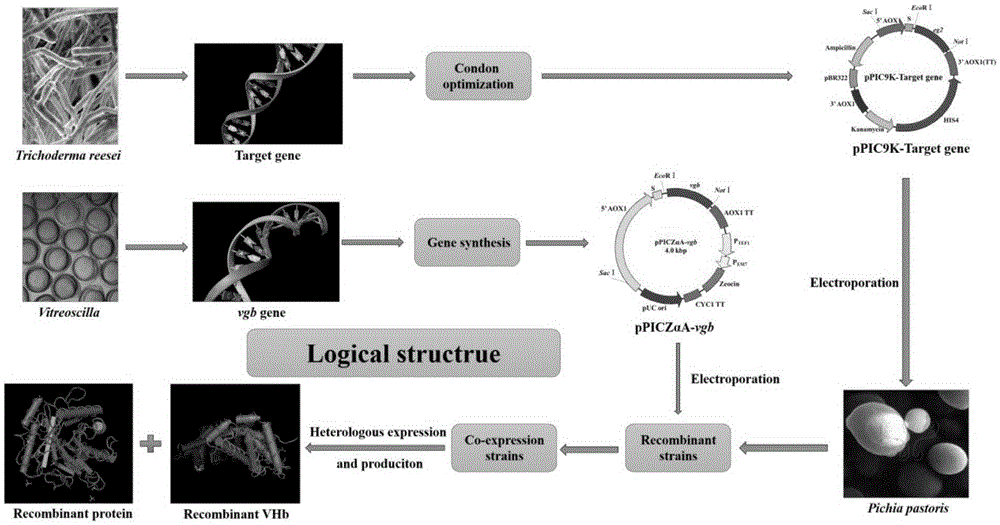
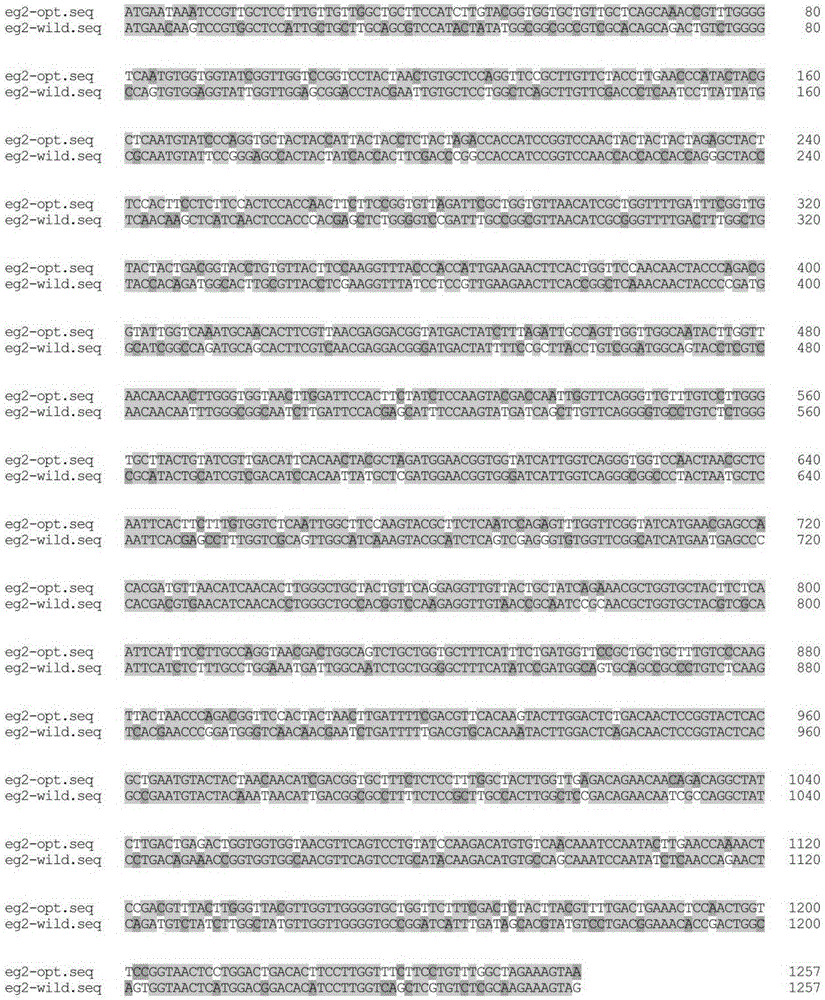
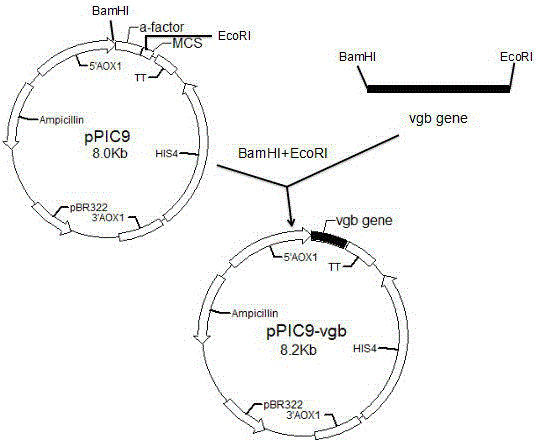
Construction method for co-expression hemoglobin VHb and cellulase protein in pichia pastoris
InactiveCN105420269AReduce GC contentImprove expression efficiencyMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionYeastNucleotide
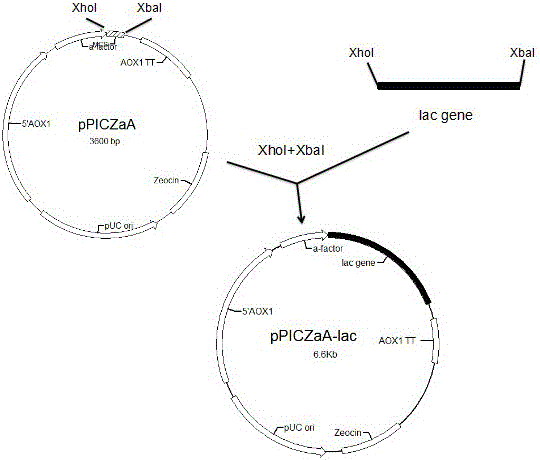
The invention relates to a construction method for co-expression hemoglobin VHb and cellulase protein in pichia pastoris, in particular to cellulase protein gene codon optimization and construction of a cellulase protein and vitreoscilla hemoglobin protein (VHb)-co-expressed pichia pastoris system. According to the construction method, codon bias optimization is performed on the nucleotide sequence of EG II (GenBank Accession No.DQ178347.1) through Gene Designer (DNA2.0, Menlo Park, CA, USA) software, a pPIC9K-eg2 expression vector is constructed, and a recombined pichia pastoris strain is obtained by taking Pichiapastoris GS115 as a host through electrotransformation. In addition, the nucleotide sequence of the VHb (GenBank Accession No.M30794.1) is obtained from NCBI and artificially synthesized into a gene, then a pPICZalphaA-vgb expression vector is constructed, and the co-expressed pichia pastoris strain is obtained by taking the recombined pichia pastoris strain containing the EG II gene as a host through electrotransformation. Detection shows that the co-expressed strain is improved on the aspects of bacterial concentration growth and enzyme activity, wherein the OD600 value is increased by 7.2%, and the enzyme activity is improved by 2.2%.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
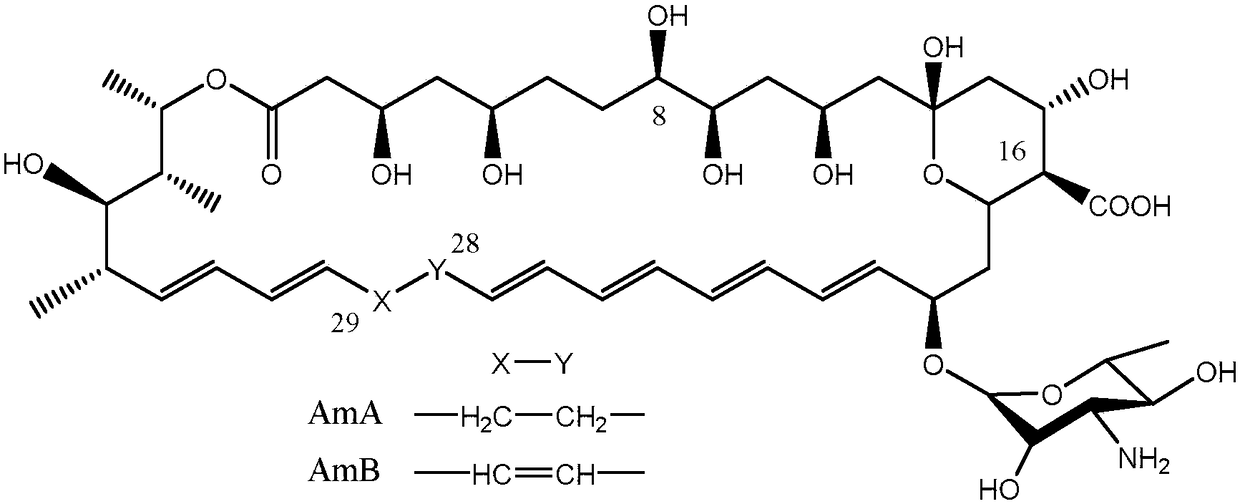
Recombined streptomyces nodosus capable of producing amphotericin B and application thereof
ActiveCN107893048AHigh purityQuality improvementBacteriaTransferasesBiotechnologyS-Adenosyl-l-methionine
The invention discloses recombined streptomyces nodosus capable of producing amphotericin B and application thereof. The recombined streptomyces nodosus is obtained by introducing a kanamycin resistance gene sequence showed in SEQ ID NO.1 into streptomyces nodosus ZJB2016050; by introducing the kanamycin resistance gene, produced strains which have no resistance previously have kanamycin resistance, the purity and quality of the strains of seed culture mediums are improved, and strain contamination phenomena can be prevented from occurring during seed cultivation in a lab. By expressing a function gene, namely vitreoscilla hemoglobin (vhb), the yield of AmB is increased by 15%; by expressing a function gene, namely the S- adenosylmethionine synthetase gene (metk), the yield of AmB is increased by about 40%.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Genetic engineering bacterium of Gluconobacter oxydans (G.oxydans) and application thereof
InactiveCN102041264ASolve the problem of insufficient oxygen supplyPromote growthBacteriaMicroorganism based processesDihydroxyacetoneGluconobacter oxydans
The invention discloses a recombinant plasmid for expressing vitreoscilla hemoglobin in a cell and a construction method of the recombinant plasmid, a genetic engineering bacterium of Gluconobacter oxydans (G.oxydans) and a construction method and application of the genetic engineering bacterium. The recombinant plasmid comprises a vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene vgb, a PtufB promoter of the Gluconobacter oxydans (G.oxydans) and a suitable carrier, wherein the genetic engineering bacterium is obtained by transforming recombinant plasmid into a host bacterium. The genetic engineering bacterium can be used for expressing the vitreoscilla hemoglobin in the cell, can be used for improving the yield of biomass and catalysate 1, 3-dihydroxyacetone under the condition of not changing the existing equipment and energy consumption pressure and provides an effective path for solving the problem of in sufficient oxygen supply in the cell cultivation and catalytic process of the Gluconobacter oxydans (G.oxydans).
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Bacterial strain of bacillus licheniformis with vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene as well as construction method and application of bacterial strain
ActiveCN103146629AImprove oxygen uptakeIncrease oxygen supplyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacillus licheniformisMicrobiology
The invention relates to a bacillus licheniformis with a vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene. The bacterial strain is the bacillus licheniformis (PHY300-vgb), wherein the bacterial strain is stored in China Typical Model Cultivation Center of Wuhan, and the storage number is CCTCC NO: M2011345. The invention aims to provide the bacterial strain of the bacillus licheniformis with vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene, which can produce bacitracin in high yield, as well as a construction method and an application of the bacterial strain.
Owner:LIFECOME BIOCHEM
Method for constructing high-yield polyglutamic acid engineering strain
InactiveCN101967494AIncrease productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationA hemoglobinVitreoscilla hemoglobin
The invention provides a method for constructing a high-yield gamma-polyglutamic acid engineering strain by using gene engineering technology, and aims to greatly improve the yield of the gamma-polyglutamic acid at a lower dissolved oxygen level. In the method of the invention, a hemoglobin gene (vgb) of vitreoscilla hemoglobin is imported into a gamma-polyglutamic acid producing strain cell by using the gene engineering technology, so that the vitreoscilla hemoglobin (VHb) is successfully expressed; and thus, the utilization ratio of oxygen by a recombinant strain and the yield of producing the gamma-polyglutamic acid by a fermentation method are improved. Results show that the capacity of producing the gamma-polyglutamic acid by the recombinant strain is improved by 1.8 times during the fermentation, so that the problem of high dissolved oxygen requirement during the large-scale production of the gamma-polyglutamic acid is solved, and the feasibility is provided for the large-scale industrial production of the gamma-polyglutamic acid.
Owner:INST OF BIOPHARM OF SHANDONG PROVINCE
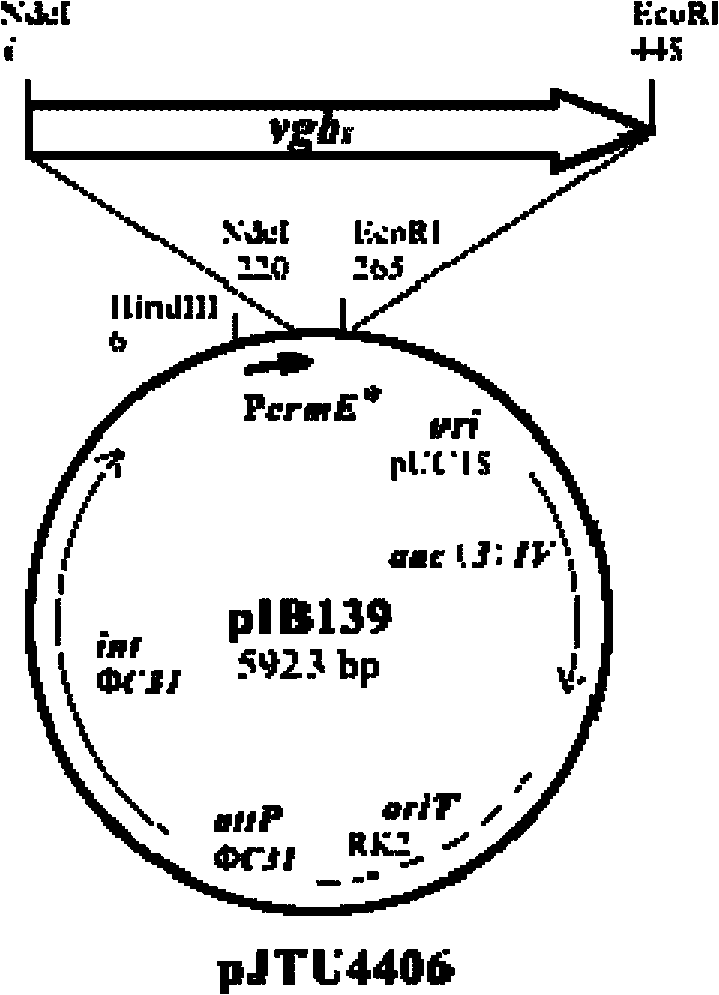
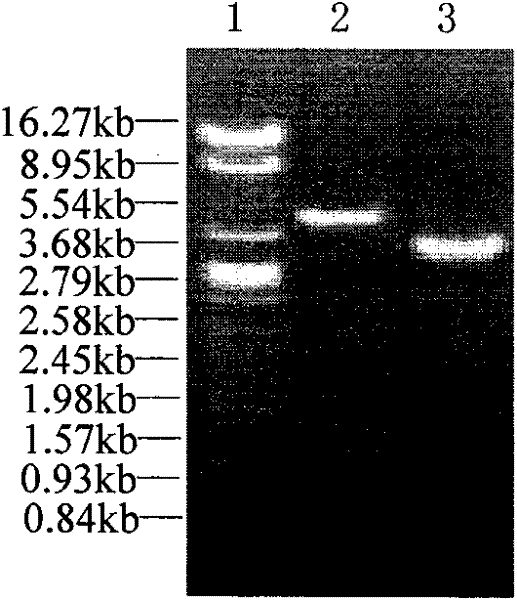
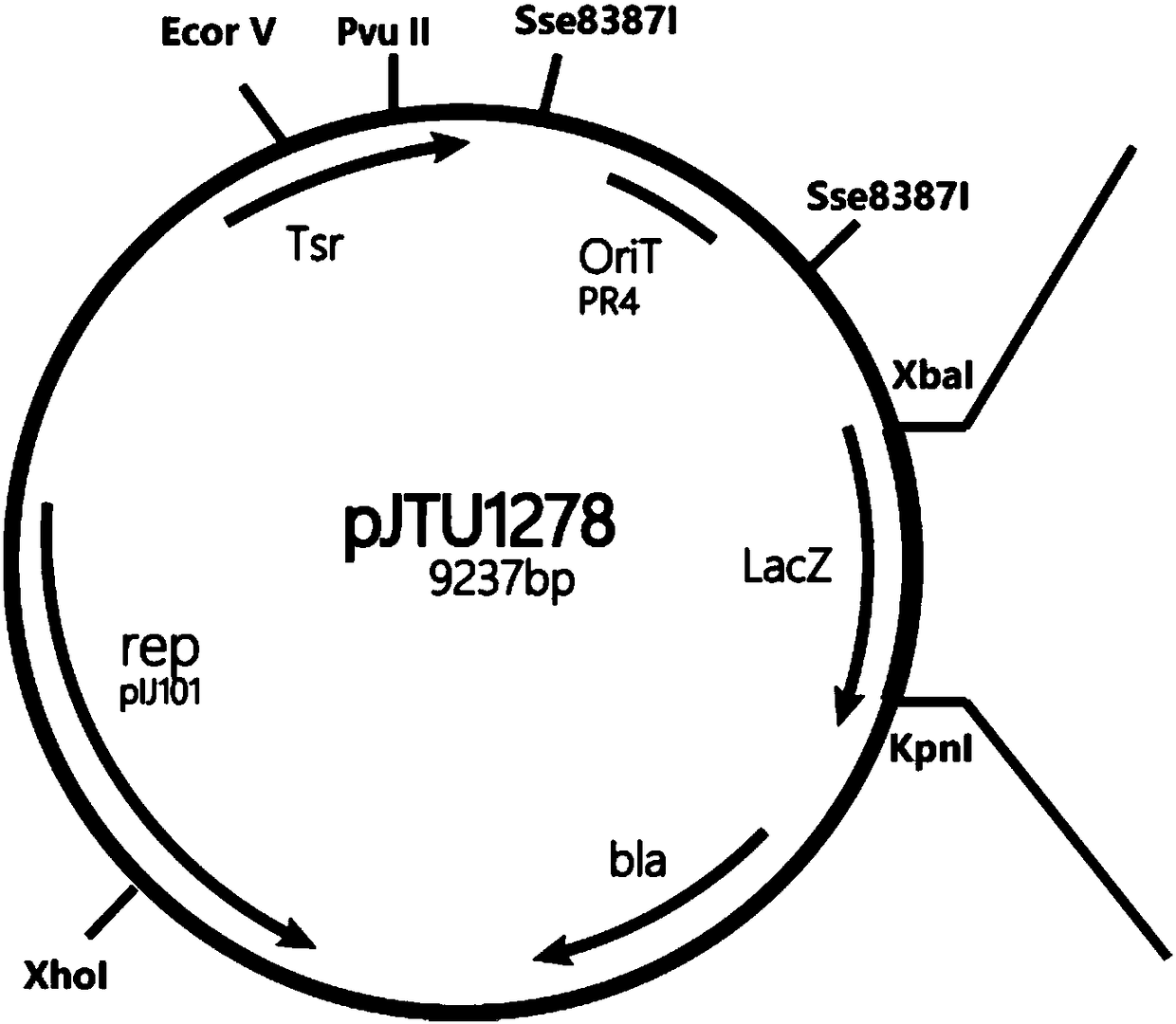
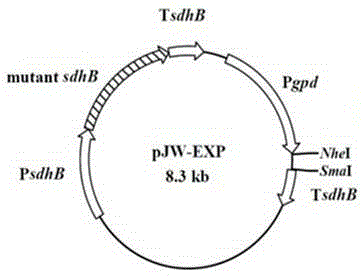
Vitreoscilla hemoglobin vgbS nucleotide sequence and plasmid and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101805742AIncrease productionBacteria peptidesFermentationRestriction Enzyme Cut SiteStreptomyces
The invention relates to a vitreoscilla hemoglobin vgbS nucleotide sequence and a plasmid and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. The vitreoscilla hemoglobin vgbS nucleotide sequence is prepared by introducing restriction enzyme cutting sites of NdeI and EcoRI at both ends of a vgb nucleotide sequence of streptomyces serving as a host cell respectively. In addition, the plasmid pJTU4406 is generated by cutting off the vgbS nucleotide sequence on pJTU4405 through the NdeI and the EcoRI, and inserting the vgbS nucleotide sequence into corresponding sites of a carrier pIB139. An amino acid sequence of protein expressed and generated by the vgbS nucleotide sequence is totally identical to that of the natural vitreoscilla hemoglobin, and the vitreoscilla hemoglobin vgbS nucleotide sequence can improve the utilization efficiency of the streptomyces to oxygen, promote the growth velocity of thalli and improve the yield of antibiotics.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
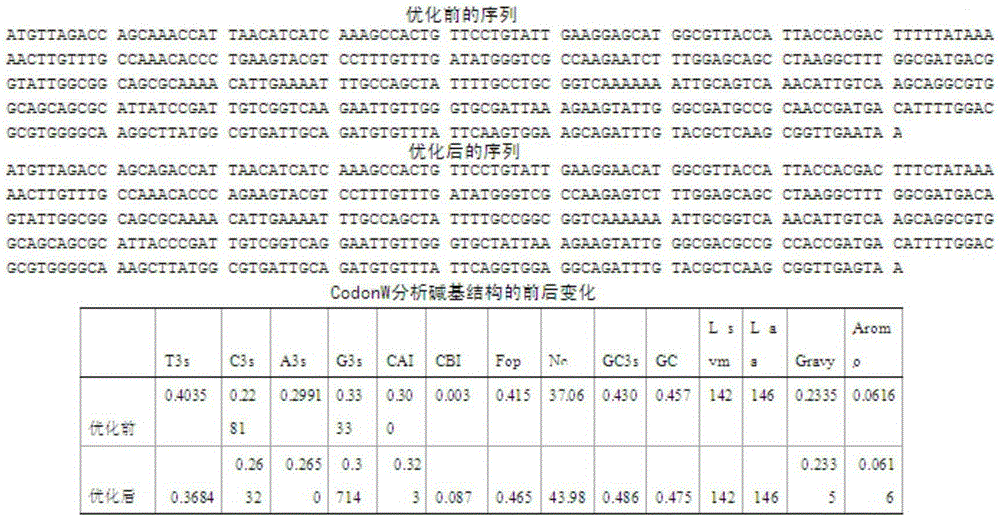
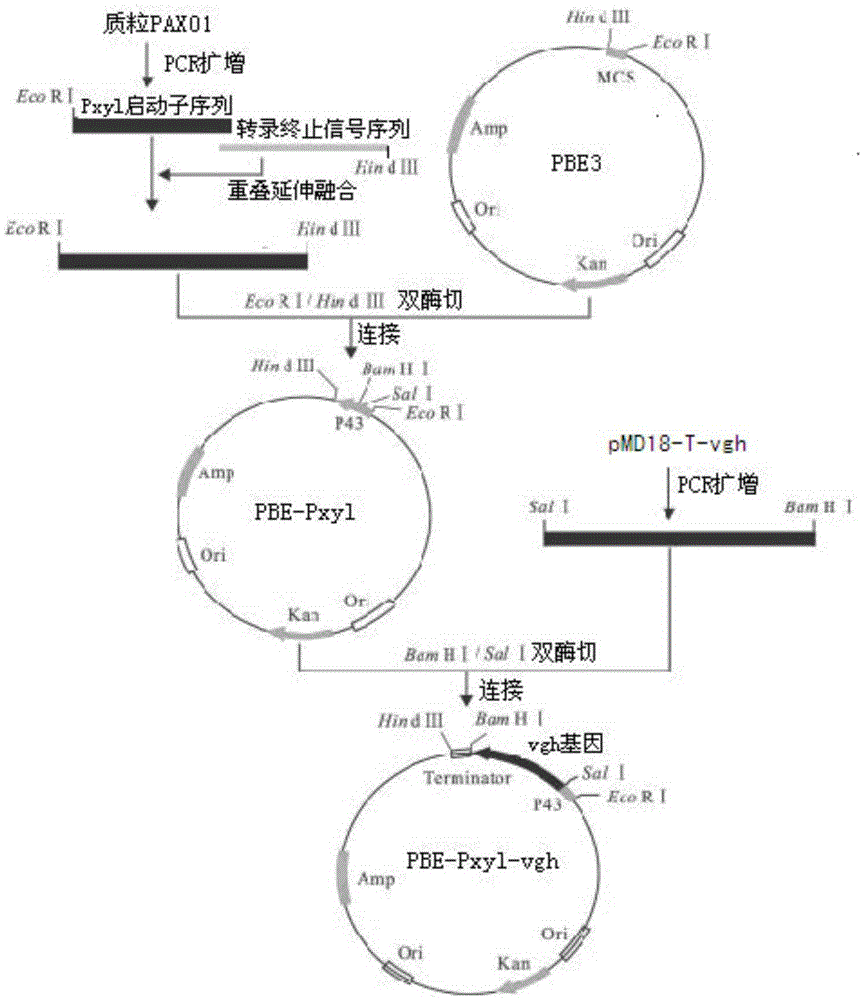
Vitreoscilla hemoglobin mutant and controllable expression of vitreoscilla hemoglobin mutant in genetically engineered bacteria
ActiveCN105348384AImprove the utilization of oxygenIncrease profitBacteriaHaemoglobins/myoglobinsAlpha-amylaseEngineered genetic
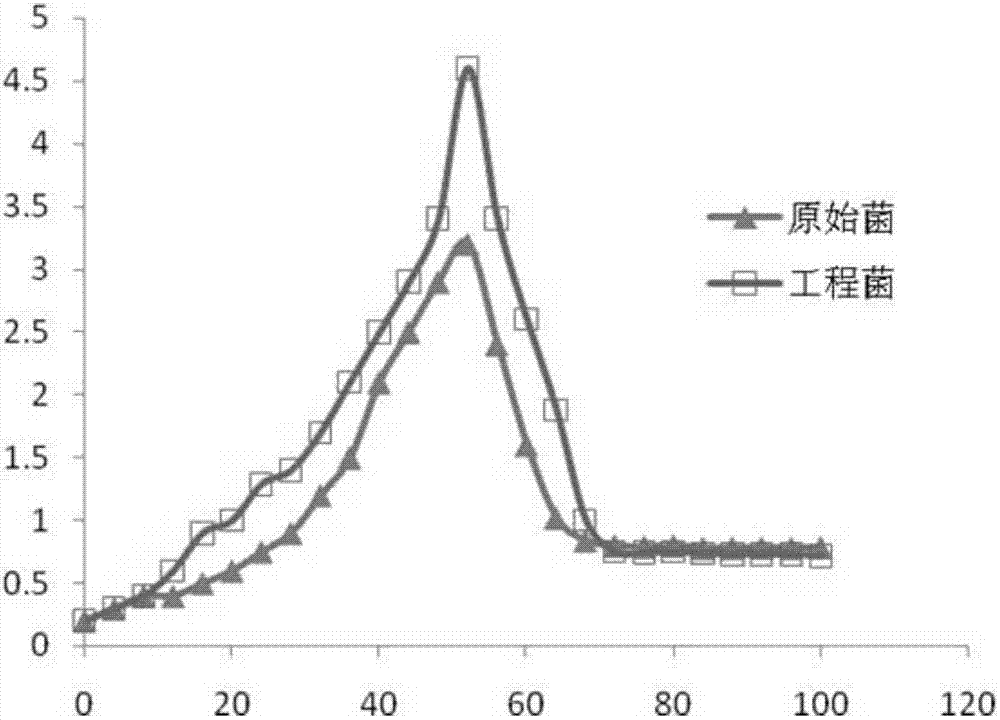
The invention discloses recombination bacillus subtilis of a vitreoscilla hemoglobin mutant gene with optimized controllable expression codon and and application thereof. A strain is the recombination bacillus subtilis / PBE-Pxyl-vgb, and the collection number is CGMCC No.10787. A bacillus subtilis expression carrier PBE-Pxyl-vgb is constructed through the vitreoscilla hemoglobin mutant gene vgh with the optimized codon; the expression carrier PBE-Pxyl-vgb is electrically transferred into bacillus subtilis, and the recombination bacillus subtilis (PBE-Pxyl-vgb) is obtained. When intermediate temperature alpha-amylase is produced with the strain, xylose is added or not added according to the requirements in the practical fermentation process to start or stop the expression of vitreoscilla hemoglobin, the controllable expression of the vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene is achieved, excessive consumption, caused by the continuous expression of the vitreoscilla hemoglobin, of nutrient substances in fermentation liquor and oxygen is avoided, and therefore the oxygen use efficiency of the recombination bacillus subtilis is improved. The result shows that the intermediate temperature alpha-amylase fermentation level of the recombination bacillus subtilis is increased by 303% compared with an original strain.
Owner:SHANDONG LONGKETE ENZYME PREPARATION
Method for constructing saccharopolyspora erythraea expression plasmid (pBlueV) containing vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene (vgb)
InactiveCN102234660AIncrease intakeImprove utilizationFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionPrimary metabolismProtein
The invention provides a method for cloning a saccharopolyspora erythraea expression plasmid (pBlueV) containing a vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene (vgb), belonging to the technical field of gene engineering. In the method, based on the fact that VHb (hemoglobin) can be combined with oxygen to form an oxygenated state, the VHb intervenes the oxygen related metabolic pathway of cells, thereby changing the original biological metabolism mode of the cells under oxygen-limited conditions, promoting the cell growth and protein synthesis under oxygen-deficient conditions, directly or indirectly affecting the action principles of primary metabolism and secondary metabolism of aerobes, firstly constructing an Escherichia coli expression plasmid pQEV, expressing the VHb with biological activity, and further constructing the saccharopolyspora erythraea expression plasmid (pBlueV). In order to realize high-density culture of cells and high-yield fermentation of metabolic products under oxygen-limited conditions, the invention provides an important pathway for homologous recombination of vgb gene elements and saccharopolyspora erythraea chromosome genomes.
Owner:邢安辉 +2
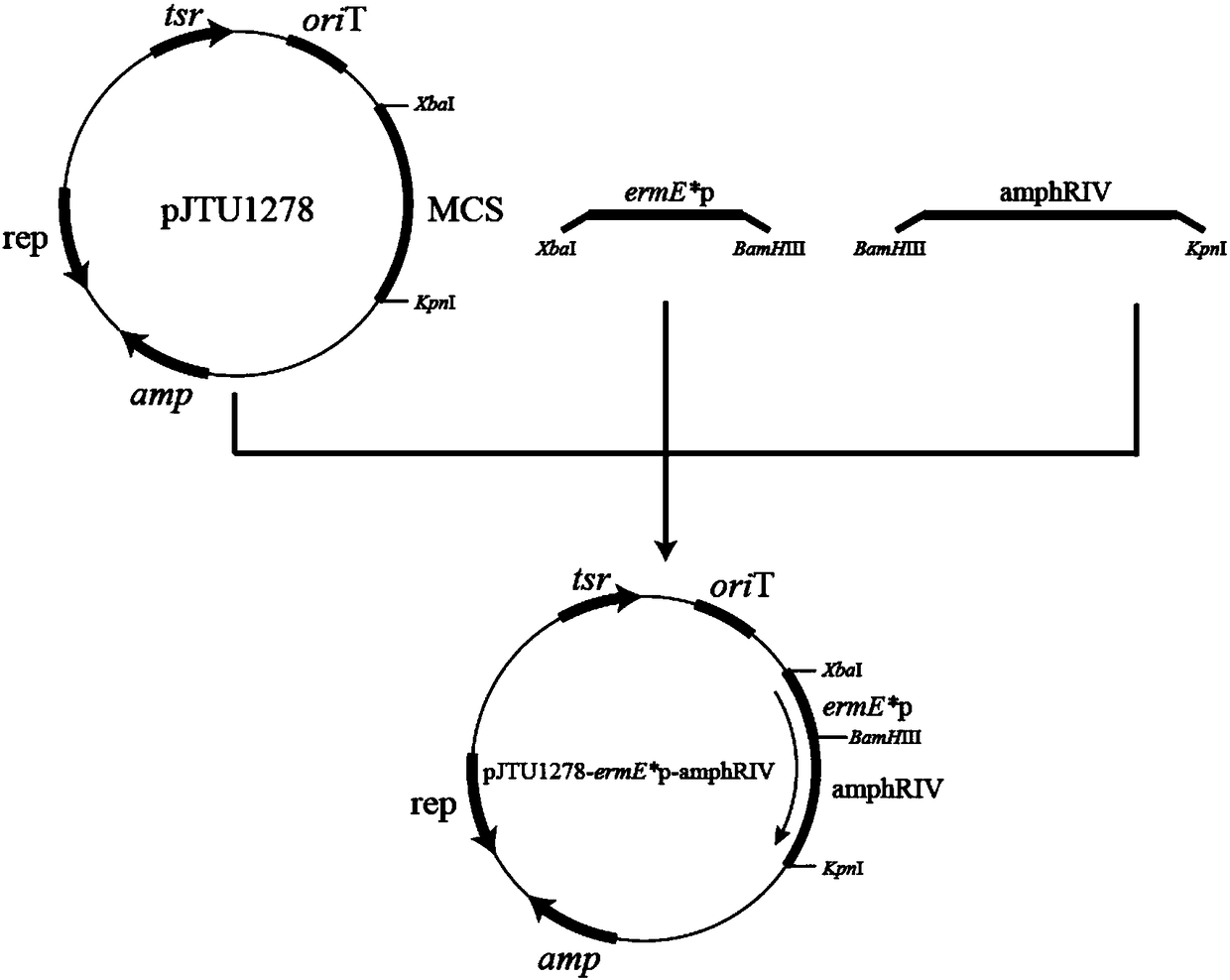
Recombinant streptomyces nodosus with high yield of amphotericin B and applications of recombinant streptomyces nodosus
ActiveCN108441459AQuality improvementIncrease production capacityBacteriaHaemoglobins/myoglobinsS-Adenosyl-l-methionineSecondary metabolite
The invention discloses recombinant streptomyces nodosus capable of producing amphotericin and applications of the recombinant streptomyces nodosus. The recombinant streptomyces nodosus is obtained byimporting vitreoscilla hemoglobin (Vhb), S-adenosylmethionine synthetase (Metk), amphotericin synthetic gene cluster regulating factor (AmphRIV), secondary metabolite global regulation factor (AraC)and erythrocin strong promoter ermE*p sequences as shown in SEQ ID NO.1, SEQ ID NO.2, SEQ ID NO.3, SEQ ID NO.4 and SEQ ID NO.5 into streptomyces nodosus ZJB2016050. Through importing and overexpression of the gene, in recombinant streptomyces nodosus, the yield of amphotericin B is improved by about 45%, the yield of the by-product amphotericin A is reduced by 60%, meanwhile, the growth cycle of the thallus during the fermentation process is shortened, and thus the purpose of improving the production efficiency is achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Ganoderic acid high-producing engineering strain kmust-VGB-1
ActiveCN105296367ALabor savingShorten the production cycleFungiMicroorganism based processesGanoderic acidMicrobacterium
The invention discloses a ganoderic acid high-producing engineering strain kmust-VGB-1, which is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center with preservation number of CGMCC NO. 11301. The lucid ganoderma engineering strain kmust-VGB-1 for high production of ganoderic acid is prepared by expressing a vitreoscilla hemoglobin VGB gene through a lucid ganoderma strong promoter P-gpd; through a fermentation experiment in a shaking flask, under the circumstance of avoiding influence on cell growth, yield of monomer ganoderic acids GA-Me, GA-T, GA-Mk and GA-S produced by the VGB converter strain are respectively 3.1 times, 3.2 times, 2.1 times and 3.6 times that of monomer ganoderic acids produced by a WT strain; therefore, the high-producing strain, as an engineering strain for producing the ganoderic acid, has a broad application prospect.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
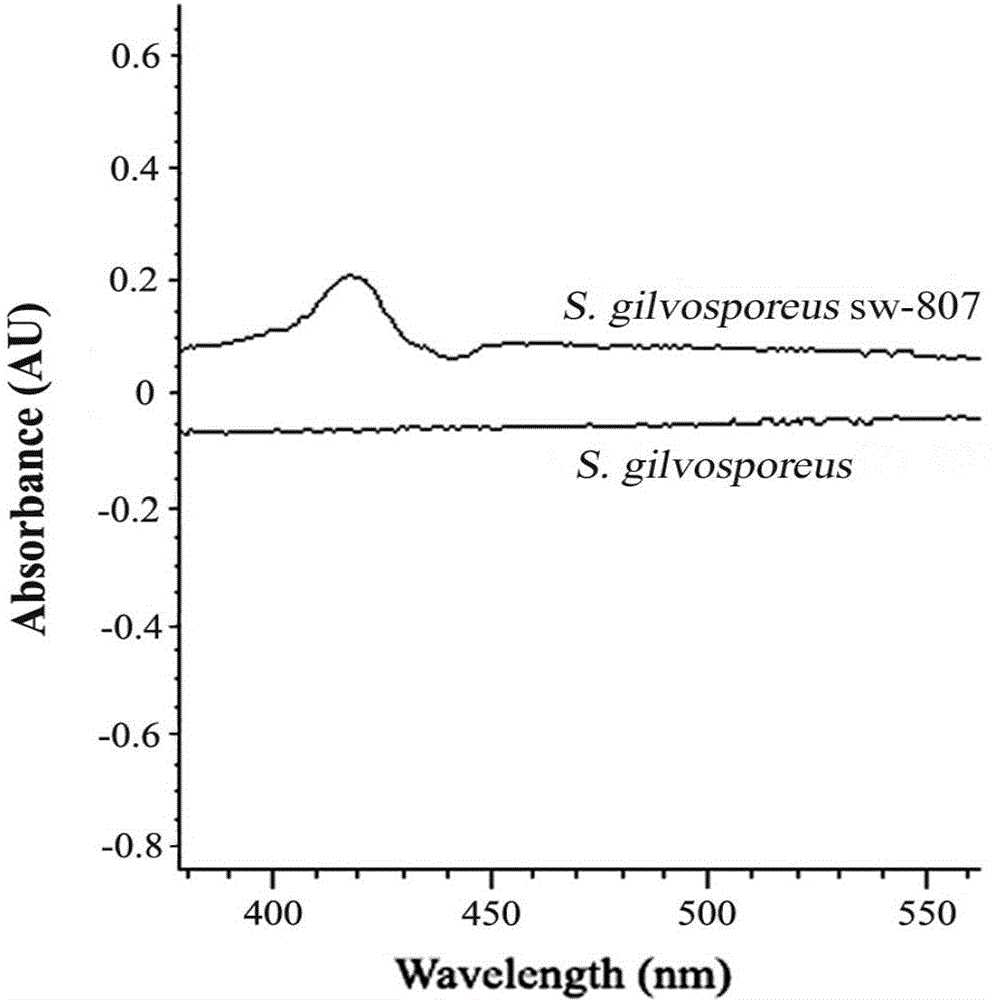
Poor oxygen resistance high density fermentation natamycin gene engineering strain constructed by using vgb gene, and application thereof
InactiveCN103555755AReduce manufacturing costImprove oxygen uptakeBacteriaFermentationBiotechnologyHigh density
The invention relates to a poor oxygen resistance high density fermentation natamycin gene engineering strain (Streptomyces gilvosporeus sw-807, CGMCC No.6890) constructed by using vgb gene, and an application thereof. According to the present invention, vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene vgb is adopted to construct recombinant plasmid, a conjugal transfer manner is adopted to integrate the vgb gene into Streptomyces gilvosporeus genome to obtain the recombinant gene engineering strain capable of being directly used for natamycin fermentation production, and VHb expression in the recombinant strain can be provided for effectively solving oxygen supply and demand contradiction in natamycin fermentation production so as to substantially increase natamycin yield, reduce production cost and bring great economic benefits.
Owner:INST OF BIOPHARM OF SHANDONG PROVINCE
Recombinant bacillus subtilis, construction method and applications thereof
InactiveCN103421725ASolve the problem of dissolved oxygenIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicrobiologyBacillus sp. BI
The invention relates to a recombinant bacillus subtilis, a construction method and applications thereof. The invention discloses a bacillus subtilis containing vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene vgb, and the bacillus subtilis can generate gamma-polyglutamic acid. The invention also discloses a construction method that recombinant plasmid containing the vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene vgb sections is transferred into the bacillus subtilis to obtain the recombinant bacillus subtilis, which contains the vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene vgb and is capable of expressing gamma-polyglutamic acid. The recombinant bacillus subtilis can achieve the goal of high yield production of gamma-polyglutamic acid under the conditions of high viscosity culture medium and low dissolved oxygen, solves the problem of requirement on high dissolved oxygen in mass production of gamma-polyglutamic acid, and thus the production cost is effectively reduced.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene expression box and method for improving yield of saccharifying enzyme produced by aspergillus niger
InactiveCN102061295ASolve the problem of insufficient dissolved oxygenReduce energy consumptionFungiMicroorganism based processesGlyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase GeneSubmerged fermentation
The invention relates to the field of genetic engineering, and discloses a vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene expression box and a method for improving yield of saccharifying enzyme produced by aspergillus niger. The expression box comprises a transparent vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene, and a promoter and a terminator of a glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene. In the invention, aspergillus brasiliensis is subject to molecular modification, the problem of oxygen depletion of the aspergillus niger under the oxygen-limiting condition is solved from the molecular level and the energy consumption is reduced in a process of producing the saccharifying enzyme by the deep fermentation of the aspergillus niger liquid.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Vitreoscilla hemoglobin mutant and gene and application thereof
ActiveCN101134967AIncrease biomassIncrease productionBacteriaBacteria peptidesHeterologousGene conversion
The present invention discloses mutational Vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene sequence and its coded Vitreoscilla hemoglobin mutant, as well as the transformant obtained through transforming heterogenous host with the mutational Vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene and its application in fermentation. The mutational Vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene consists of 438 nucleotides and codes one segment of protein comprising 146 amino acids. The gene expressed protein can raise the biomass of the host cell in the condition of insufficient environmental oxygen dissolution, so that it may be applied for promoting the growth of the host cell in fermentation industry to raise the yield of the target product and lower production cost.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HISUN PHARMA CO LTD +1
Tylosin gene engineering strain and application thereof
InactiveCN102690775AIncrease productionIncrease contentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesShuttle vectorEnzyme Gene
The invention relates to a tylosin gene engineering strain. The construction method for the tylosin gene engineering strain comprises the following steps: cloning tylosin through polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to synthesize crucial rate-limiting enzyme gene TylF and Vitreoscilla hemoglobin VHb gene, constructing a recombinant plasmid by using an E. coli-streptomyces shuttle vector, importing the recombinant plasmid into Escherichia coli ET12567 / pUZ8002, performing conjugal transfer culture on the Escherichia coli ET12567 / pUZ8002 and streptomyces fradiae spores, converting streptomyces, screening a converter through apramycin resistance, further confirming the converter by using PCR, and finally obtaining the gene engineering strain. The tylosin gene engineering strain can be directly used in the industrial production of tylosin; and compared with the tylosin gene engineering strain used in the conventional industrial production, the tylosin gene engineering strain has the advantages that the yield of the tylosin can be obviously improved to be 17,000-18,000u / ml and the content of a component A in the tylosin is effectively improved to be 94-95 percent.
Owner:宁夏泰瑞制药股份有限公司
Method for improving yield of S-adenosylmethionine through gene expression regulation
InactiveCN104031959AIncrease productionFungiMicroorganism based processesS-Adenosyl methionineS-Adenosyl-l-methionine
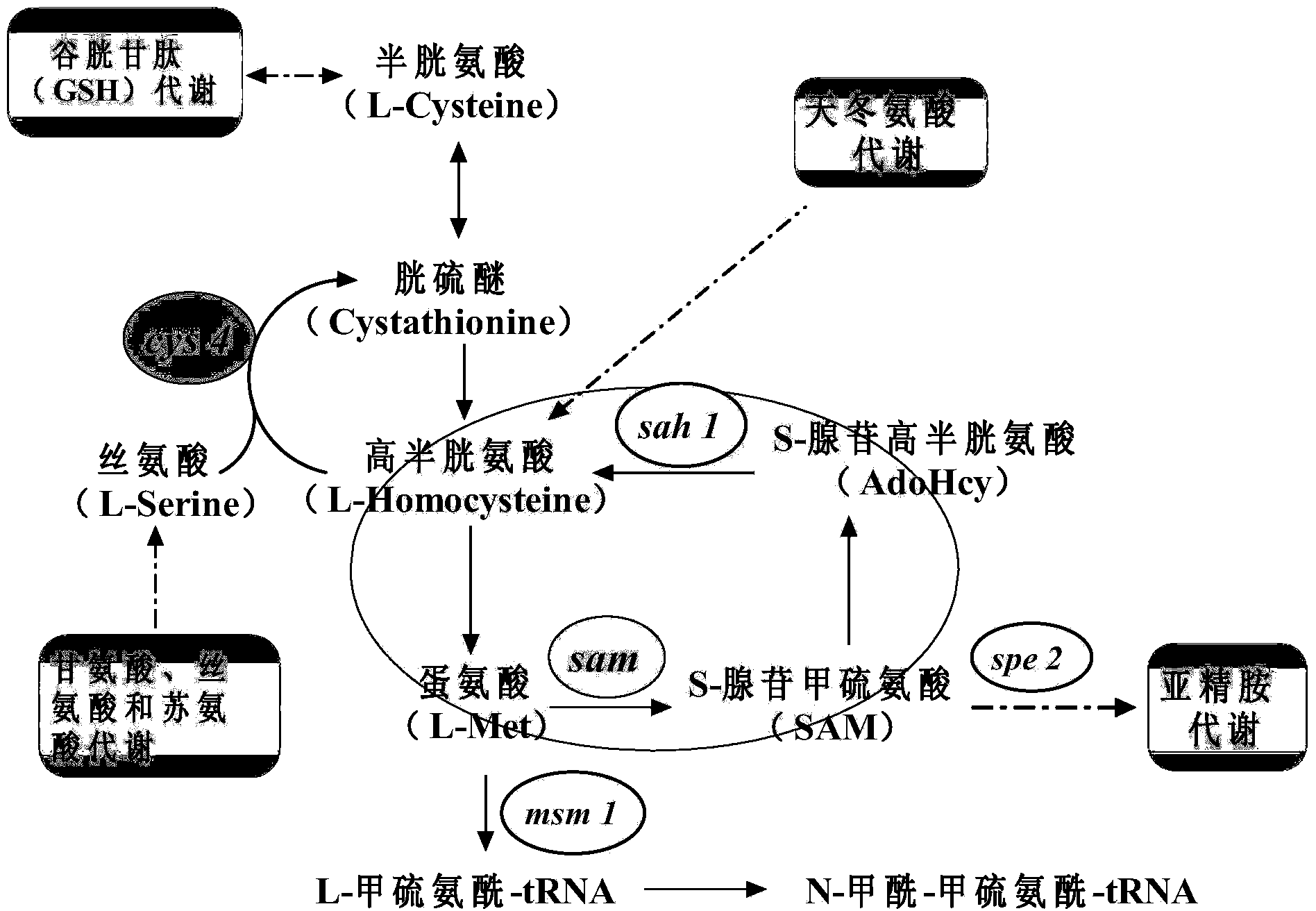
The invention relates to a method for improving the yield of S-adenosylmethionine through gene expression regulation. Coding genes of Vitreoscilla hemoglobin (VHb) are transformed into an S-adenosylmethionine production strain, and after S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase spe2 genes are removed, the yield of the S-adenosylmethionine of the S-adenosylmethionine production strain can be obviously improved.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for improving moisture resistance of cabbage type rape
ActiveCN102676576AUncertainTime consumingFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionMoisture resistanceSelfing
The invention discloses a method for improving the moisture resistance of cabbage type rape. The method comprises the following steps of: (A), constructing a glufosinate-ammonium resistant expression vector containing vitreoscilla hemoglobin (vgb), namely, (1) obtaining a target fragment, (2) recovering a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) product, transforming and sequencing, (3) preparing transferred-deoxyribonucleic acid (T-DNA), (4) preparing Vector, (5) preparing the expression vector, and (6) preparing bacterial liquid of agrobacterium tumefaciens; (B), breeding a recovery line of the moisture-resistant cabbage type rape, namely transforming the vgb into R2 by an agrobacterium tumefaciens mediated method to obtain a T0 recovery line, and performing continuous selfing to obtain a T2 recovery line; (C), breeding a maintainer line of the moisture-resistant cabbage type rape, namely (a) transforming the vgb into 6098B by the agrobacterium mediated method to obtain a T0 maintainer line, and performing continuous selfing to obtain a T2 maintainer line, and (b) hybridizing a T1 recovery line single plant serving as a male parent with the 6098B, performing continuous backcrossing by taking the 6098B as a recurrent parent to obtain BC3, and performing selfing to obtain the T2 maintainer line; and (D), obtaining a sterile line of the moisture-resistant cabbage type rape. The method is easy and convenient to operate and obvious in effect, the cost can be reduced, and the breeding progress can be shortened.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for improving sorangium cellulosum's epothilone B yield by genetic engineering
InactiveCN103834707AIncrease productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyEpothilone B
The invention discloses a method for improving sorangium cellulosum's epothilone B yield by genetic engineering. The method includes: introducing a Vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene vgb into an expression vector PBEP43 to obtain a recombinant plasmid PBEP43-vgb, and then subjecting the recombinant plasmid PBEP43-vgb to electrotransformation into sorangium cellulosum So ce M4, thus obtaining a sorangium cellulosum So ce M4 recombinant strain, and realizing improving the sorangium cellulosum So ce M4's epothilone B yield. According to the invention, the electrotransformation method is employed to transform the gene of sorangium cellulosum So ce M4, thereby greatly improving the yield of epothilone B. The method provided by the invention has broad application prospects, and research in the aspect is not reported to date.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROORGANISM
Artificially-synthesized vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene, corresponding engineered strain and application
InactiveCN110106191AIncrease productionHaemoglobins/myoglobinsMicroorganism based processesStreptomycesNucleotide
The invention relates to an artificially-synthesized vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene. The nucleotide sequence of the gene is shown in SEQ ID No.1, and the gene is marked as vgbL. The invention further provides a corresponding genetically-engineered strain for producing enramycin. The invention further provides a method for constructing the genetically-engineered strain for producing the enramycin. The artificially-synthesized vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene, the strain and the method have the advantages that the nucleotide sequence of the novel vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene vgbL which can be efficiently expressed in streptomyces is obtained, and the gene is artificially synthesized and transferred into fungicidal streptomyces ATCC21013; compared with an original wild strain, by means of the genetically-engineered strain, the yield of the enramycin is increased by 16.6%, and therefore, it can be seen that the vgbL can become an effective means of increasing the yield of antibiotics in variousstreptomyces.
Owner:枣庄市杰诺生物酶有限公司 +1
Recombinant bacterium for promoting bacillus subtilis to synthesize menadione-7 and gene modification method thereof
PendingCN111560383AImprove utilization efficiencyEasy transferBacteriaHaemoglobins/myoglobinsBiotechnologyMicrobiology
The invention discloses a gene modification method for promoting bacillus subtilis to synthesize menadione-7. The gene modification method comprises the following steps: (1) constructing an original strain BSMK_9; and (2) carrying out overexpression of the vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene vgb. According to the invention, BSMK_9 derived from bacillus subtilis 168 is used as an original strain, and by overexpression of vitreoscilla hemoglobin, transmission of intracellular oxygen in cells is promoted, the utilization efficiency of oxygen is improved, and the influence on MK-7 synthesis is investigated; the maximum synthesis amount of MK-7 is promoted by optimizing carbon source combination and tank fermentation, and a theoretical basis is provided for construction of an MK-7 high-yield strain bygenetic modification and fermentation optimization of bacillus natto in the future.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV MARINE TECH RES INST
Yeast engineering bacterial strain capable of producing glutathione and application thereof to production of glutathione
ActiveCN102559529AIncrease productionHigh yieldFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMolecular level
The invention discloses a yeast engineering bacterial strain capable of producing glutathione, which has the bacterial strain name of 101-V and the classification name of Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain collected in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on February 15, 2012, with the collection number of CGMCC NO. 5758. The invention also discloses a method for establishing an engineering bacterial strain capable of producing glutathione at a high yield. The method comprises the following steps: integrating a Vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene vgb into a yeast genome capable of producing glutathione, and screening to obtain a recombinant yeast capable of expressing transparent Vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene. Therefore, the oxygen utilizing capability of the hemoglobin gene recombinant strainis improved in a molecular level, the contradiction between supply and demand of oxygen in the microbiological fermenting process is solved, the consumption of oxygen and energy is lowered, and the yield of glutathione is increased.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Streptomyces clavuligerus, as well as preparation method and application
ActiveCN101434930AImproved production characteristicsImprove transfer efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismStreptomyces
The invention belongs to the field of microbial engineering, provides a streptomyces clavuligerus strain LNSC with low oxygen consumption and high fermentation yield, a strain preparation method and application of the strain, and particularly relates to a method. The method utilizes genetic engineering methods, researches the application aspect of vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene (vhb), transfers the gene into the streptomyces clavuligerus culture that is used for clavulanic acid production, obtains high expression of VHB protein, thus improving the production characteristics of the streptomyces clavuligerus, and lowering the energy consumption of zymolytic production.
Owner:LUNAN PHARMA GROUP CORPORATION
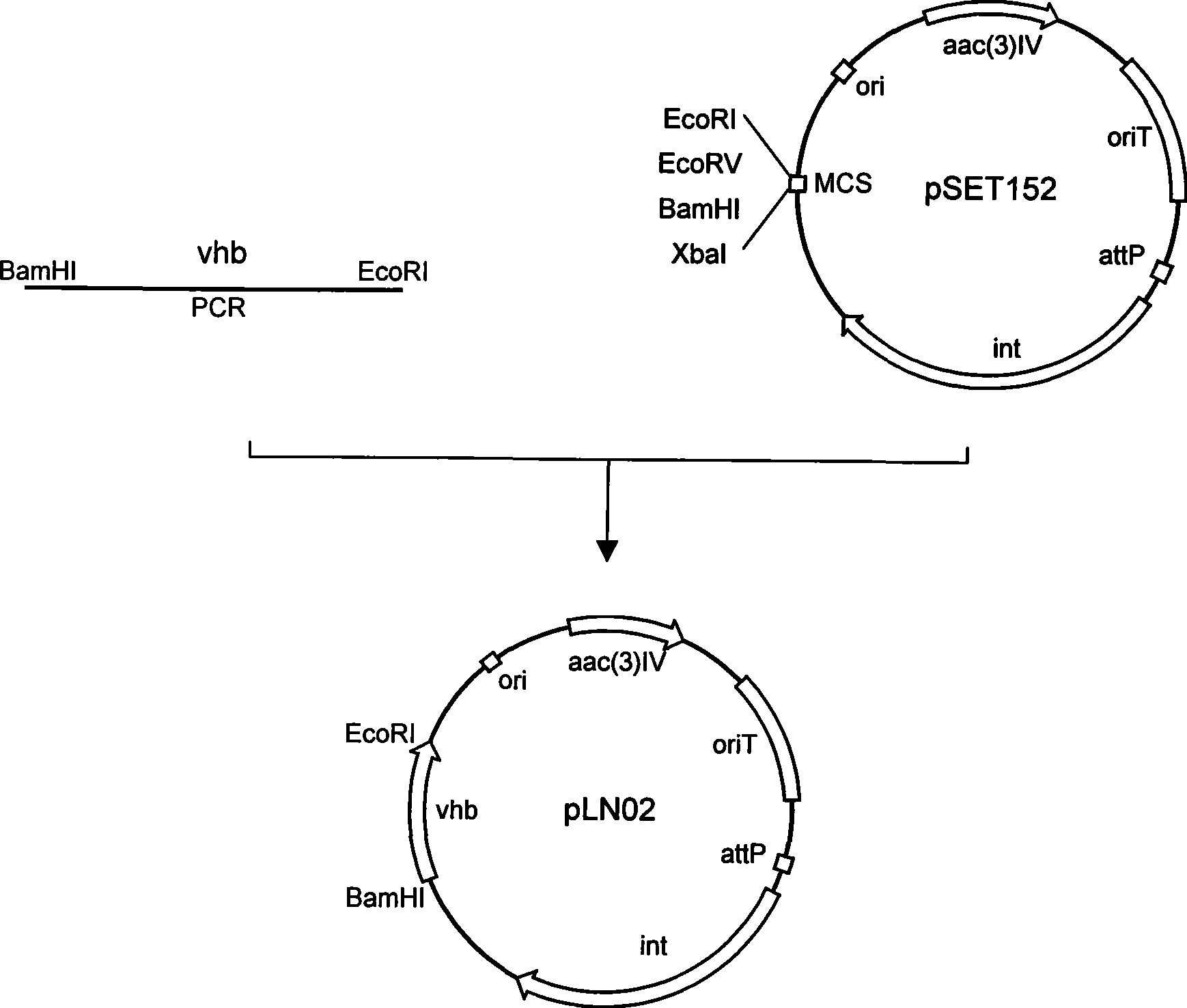
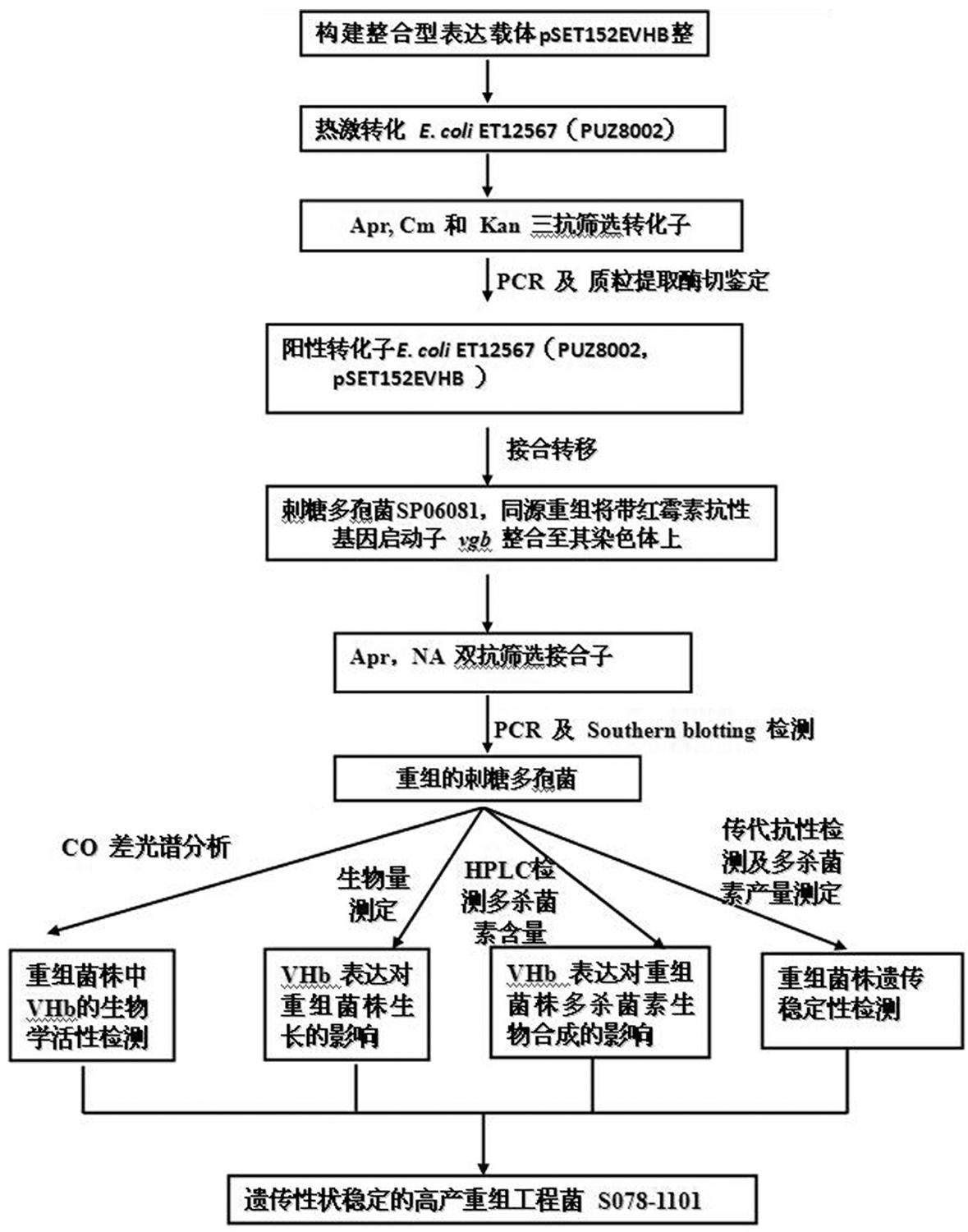
Pleocidin engineering bacteria capable of enhancing oxygen absorptive capacity, and construction method and fermentation method thereof
ActiveCN102559569APromote biosynthesisStable productivityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSpinosadSaccharopolyspora
The invention relates to pleocidin engineering bacteria capable of enhancing oxygen absorptive capacity, and a construction method and a fermentation method thereof. The pleocidin engineering bacteria are gene recombinant pleocidin engineering bacteria constructed by integrating vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene (vgb) into saccharopolyspora genome, wherein the class name is actinomycetes saccharopolyspora S078-1011; and the collection number is CCTCC NO: 2011400. The invention further comprises a construction method for the pleocidin engineering bacteria and a fermentation method for producing pleocidin by using the pleocidin engineering bacteria. The actinomycetes saccharopolyspora S078-1011 can improve the dissolved oxygen absorptive capacity of the bacteria and can obviously promote biological synthesis of the pleocidin under the conditions of normal dissolved oxygen and limited oxygen.
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Dysoxia-resistant lactase yeast strain and construction method thereof
InactiveCN106085893AIncrease productionIncrease profitFungiMicroorganism based processesPichia pastorisHigh density
The invention discloses a dysoxia-resistant lactase yeast strain with a preservation number of the dysoxia-resistant lactase yeast strain is CCTCC NO:M2016252. The invention further discloses a construction method of the dysoxia-resistant lactase yeast strain, wherein the construction method comprises the following steps: sequentially transferring expression vectors in vitreoscilla hemoglobin cells and lactase secretory expression vectors into pichia pastoris; screening a strain with high lactase activity to obtain the dysoxia-resistant lactase yeast strain. The strain disclosed by the invention can be used for preparing recombinant lactase protein by high-density fermentation; a utilization rate, on oxygen gas, of cells is increased by synthesizing hemoglobin (VHB) in cells, and growth, under an oxygen-lean condition, of the cells is promoted, so that the expression yield of extracellular recombinant lactase is increased.
Owner:SHANDONG ACADEMY OF PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES
Gene-recombined peoriae paenibacillus, and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN102776147AIncrease profitImprove liquidityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEngineered geneticPromoter
The invention discloses a gene-engineered bacterium of gene-recombined peoriae paenibacillus, and a construction method and application of the gene-engineered bacterium. Gene-recombined peoriae paenibacillus BC39 with vitreoscilla hemoglobin regulated and controlled by a P43 strong promoter is constructed by constructing a gene-recombination integrative vector with a peoriae paenibacillus LXH-B-1 strain as host bacteria. The gene-engineered bacterium of the gene-recombined peoriae paenibacillus is capable of intracellularly expressing the vitreoscilla hemoglobin, so that the utilization rate of oxygen by the peoriae paenibacillus, the cell biomass liveweight and the yield of catalysate polypeptide antibiotics can be improved; and the yield of the catalysate polypeptide antibiotics of the engineering strain is increased by 45% compared with that of the original strain; and therefore, an effective way is provided for solving the problem of insufficient oxygen supply in the cell culture and catalysis process of the peoriae paenibacillus.
Owner:杨凌静玥生物科技有限公司
Gene recombination bacillus amyloliquefaciens and microbial inoculum preparation method
InactiveCN101717744BIncreased spore contentHigh sporulationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEcological environment
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for increasing content of astragalus methglycoside through exogenous gene transfer technology
InactiveCN1699578AImprove pharmacological activityImprove survival ratePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsAstragalosideBacillus coli
The invention discloses a method for increasing content of astragalus methglycoside through exogenous gene transfer technique, which comprises transforming vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene (vgb), inserting the vgb gene into plasmid pBI121 by employing enzyme cutting technology in combination with PCR, obtaining intermediate expression vector pBI121-vgb using 35s-CaMV strong promotor as the starting element, and transferring into bacillus coli DH5 alpha, employing three-parent hybridizing method (pRK2013, DH5 alpha and LBA9402), obtaining trans-vgb gene Agrobacterium rhizogenes LBA9402-vgb, disseminating astragalus root sprout, thus obtaining transgenic Radix Astragali hairy-root, whose Radix Astragali Astragaloside content is five times higher then the non-transgenic hairy-root.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV OF T C M
Self-organized recombinant vitreoscilla hemoglobin and gene and application thereof
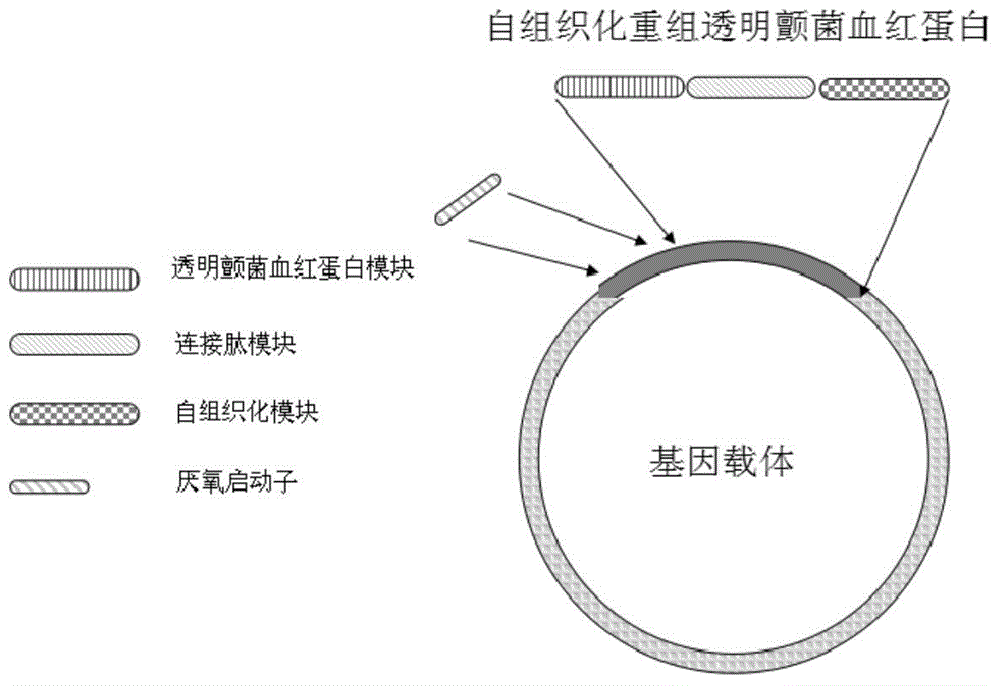
ActiveCN104892751AReserved codon substitutionImproved oxygen capture functionFungiBacteriaOxygenGene engineering
The invention discloses self-organized recombinant vitreoscilla hemoglobin with self-organizing ability and application of a gene thereof in gene engineering product production and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering. The self-organized recombinant vitreoscilla hemoglobin is composed of a vitreoscilla hemoglobin module, a connecting peptide module and a self-organized module, amino acid sequence of the vitreoscilla hemoglobin module is SEQ ID NO.1, amino acid sequence of the connecting peptide module is (SEQ ID NO.2)n, n value refers to number of series-connection repeating times of the connecting peptide module, and n is an integer from 2 to 10; amino acid sequence of the self-organized module is SEQ ID NO.3 or SEQ ID NO.4. Compared with vitreoscilla hemoglobin, protein expressed by the gene has self-organizing ability, the self-organized recombinant vitreoscilla hemoglobin has higher plasmalemma combining performance, biomass and gene engineering product yield of host cells can be increased under the circumstance that dissolved oxygen in environment is insufficient, and production cost is lowered.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com