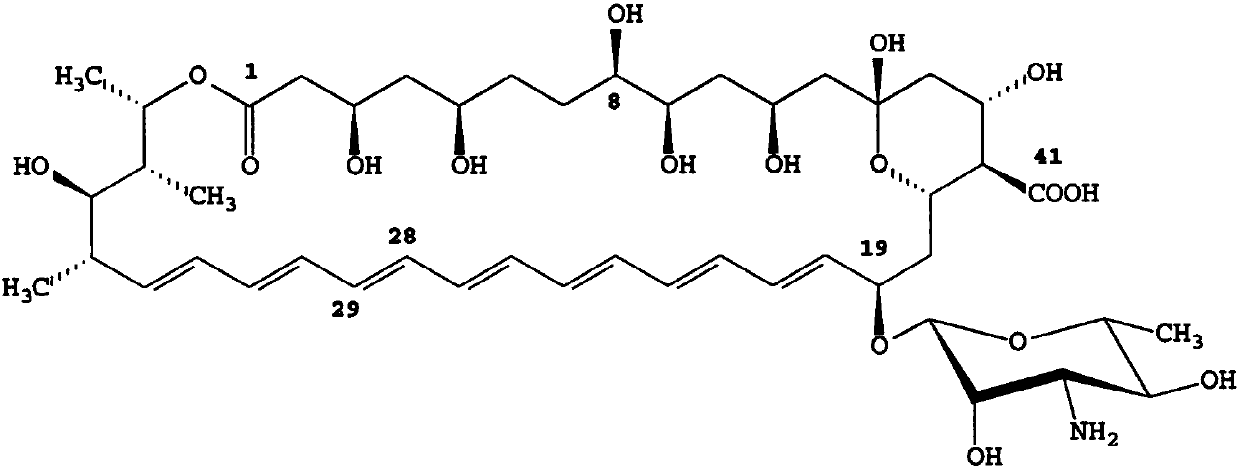
Recombined streptomyces nodosus capable of producing amphotericin B and application thereof
A technology of amphotericin and streptomyces, applied in the direction of enzymes, bacteria, bacterial peptides, etc., can solve the problems of miscellaneous bacteria pollution, no antibiotic resistance, etc., achieve low bacterial contamination rate, strong bactericidal effect, reduce human factors and environment The effect of factor influence rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Embodiment 1, the screening of high-yielding AmB mutant strain
[0045] (1) Streptomyces nodosus (Streptomyces nodosus, Caffrey P, Lynch S, Flood E, Finnan S, Oliynyk M. Amphotericin biosynthesis in Streptomyces nodosus: reductions from analysis of polyketide synthase and late genes. Chem Biol 2001; 8:713-723 .or Carmody M, Byrne B, Murphy B, Breen C, Lynch S et al.Analysis and manipulation of amphotericin biosynthetic genes by means of modified phage KC515transductiontechniques.Gene 2004; 343(1):107-115) inoculated onto GYM plate or slant Culture medium, cultivated at 28°C for 7 days, take gray-black spores, use cotton swab to elute the surface spores into 10mL sterile water, filter the washed spore suspension with a syringe containing cotton, and filter the spores at 12000rpm After centrifuging for 5 minutes, remove the supernatant, add 10 mL of sterile water to resuspend, centrifuge at 12000 rpm for 5 minutes to elute again, and resuspend with 5 mL of sterile water a...
Embodiment 2
[0058] Embodiment 2, the construction of AmB genetically engineered bacteria resistant to kanamycin
[0059] 1. Construction of recombinant vector
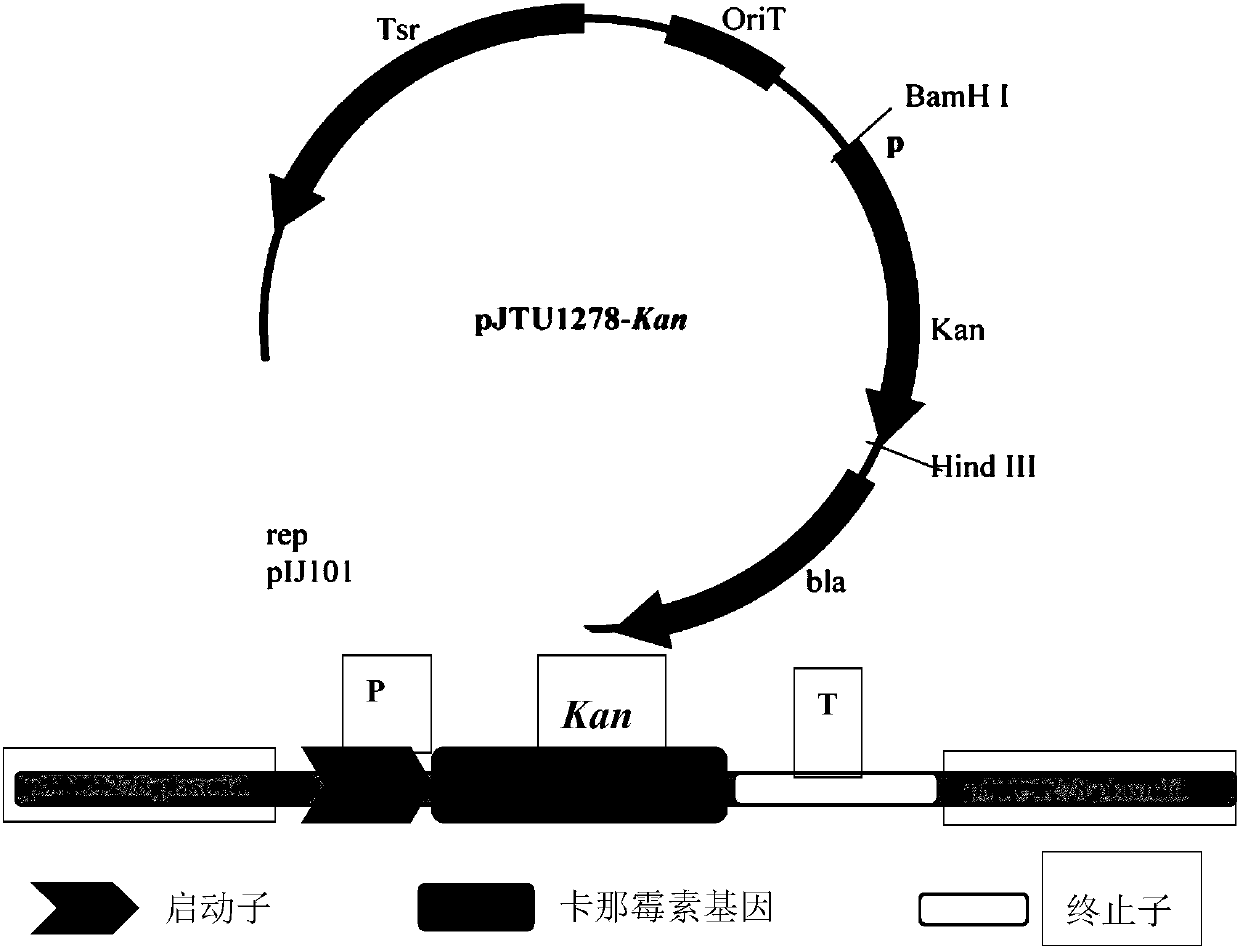
[0060] 1. Construction of recombinant vector pJTU1278-Kan
[0061] Using the pEC-XK99E plasmid as a template (the plasmid was purchased from BioVector NTCC Plasmid Vector Strain Cell Gene Collection Center, GenBank accession No. AY219682.1, Kirchner O, Tauch A. Tools for genetic engineering in the amino acid-producing bacterium Corynebacterium glutamicum. J Biotechnol 2003; 104(1-3):287-299.), design primers 99E-Kan-F and 99E-Kan-R, 99E-Kan-F is the forward primer for Kan resistance-related genes, 99E-kan- R is the reverse primer for Kan resistance-related genes, and the related genes containing kanamycin resistance genes are cloned and amplified from the template, including the kanamycin resistance gene (i.e. aph(3')-IIa gene), Promoter and RBS, the fragment size is about 1100bp, which is consistent with the target fragment. Af...
Embodiment 3
[0100] Embodiment 3, Streptomyces tuberculosis genetically engineered bacteria construction carrying vhb gene
[0101] Using the Vitiligo hyaline hemoglobin (vhb) gene as a template (GenBank accession No. JN418989.1), design primers vhbF and vhbR, vhbF is the forward primer for the vhb gene, vhbR is the reverse primer for the vhb, cloned from the template The vhb was amplified, and the fragment size was about 450bp. It was confirmed by sequencing analysis that it was consistent with the target fragment. The nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQID NO.7. After cutting this fragment with endonuclease BamHI and HindIII, clean-up this fragment for later use. The vector pJTU1278-Kan constructed in Example 2 was also digested with the same BamHI and HindIII endonuclease to recover the gel. The recovered gene fragment was ligated with the pJTU1278-Kan vector after digestion. The obtained recombinant plasmid vector was named pJTU1278-Kan-vhb, and the schematic diagram is shown in Figu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com