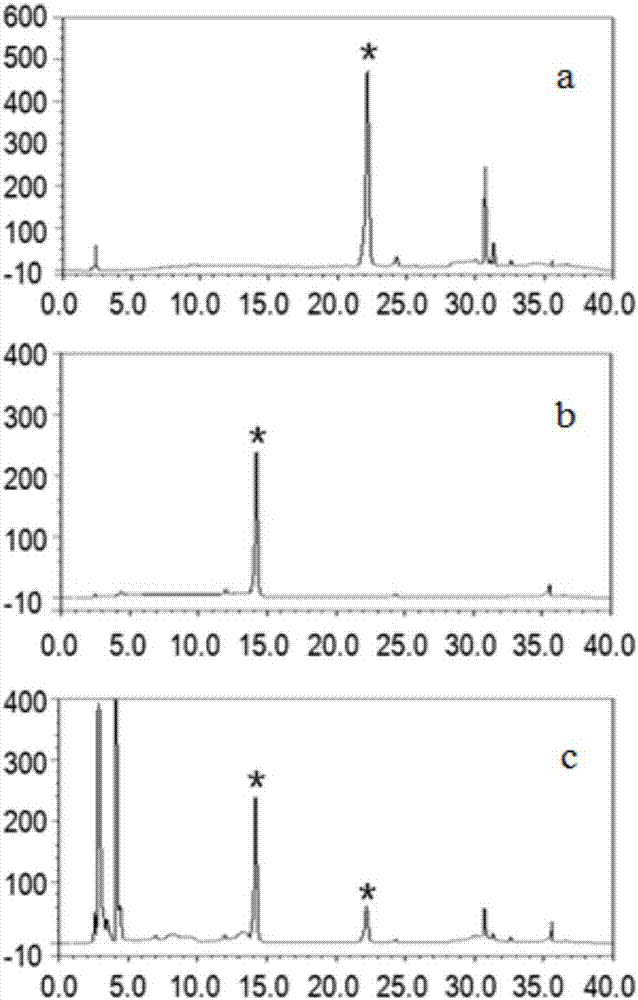
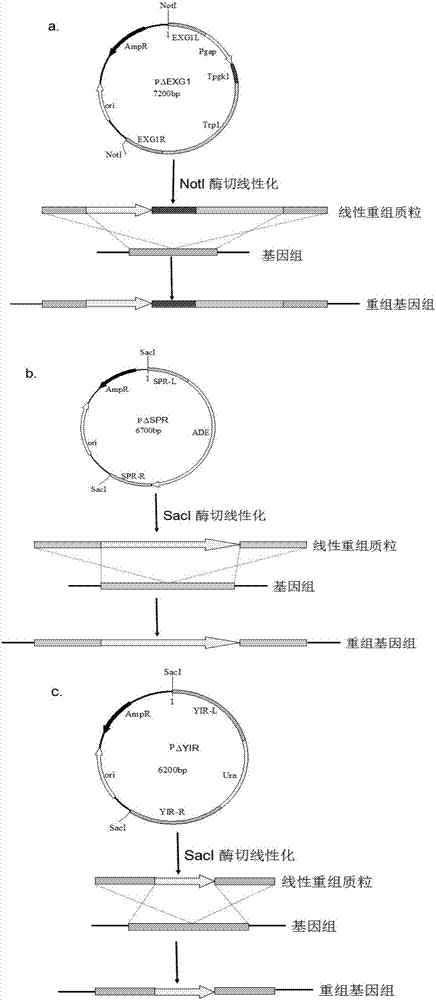
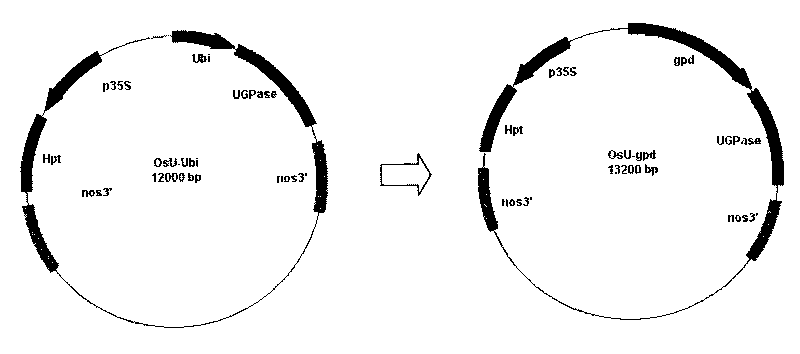
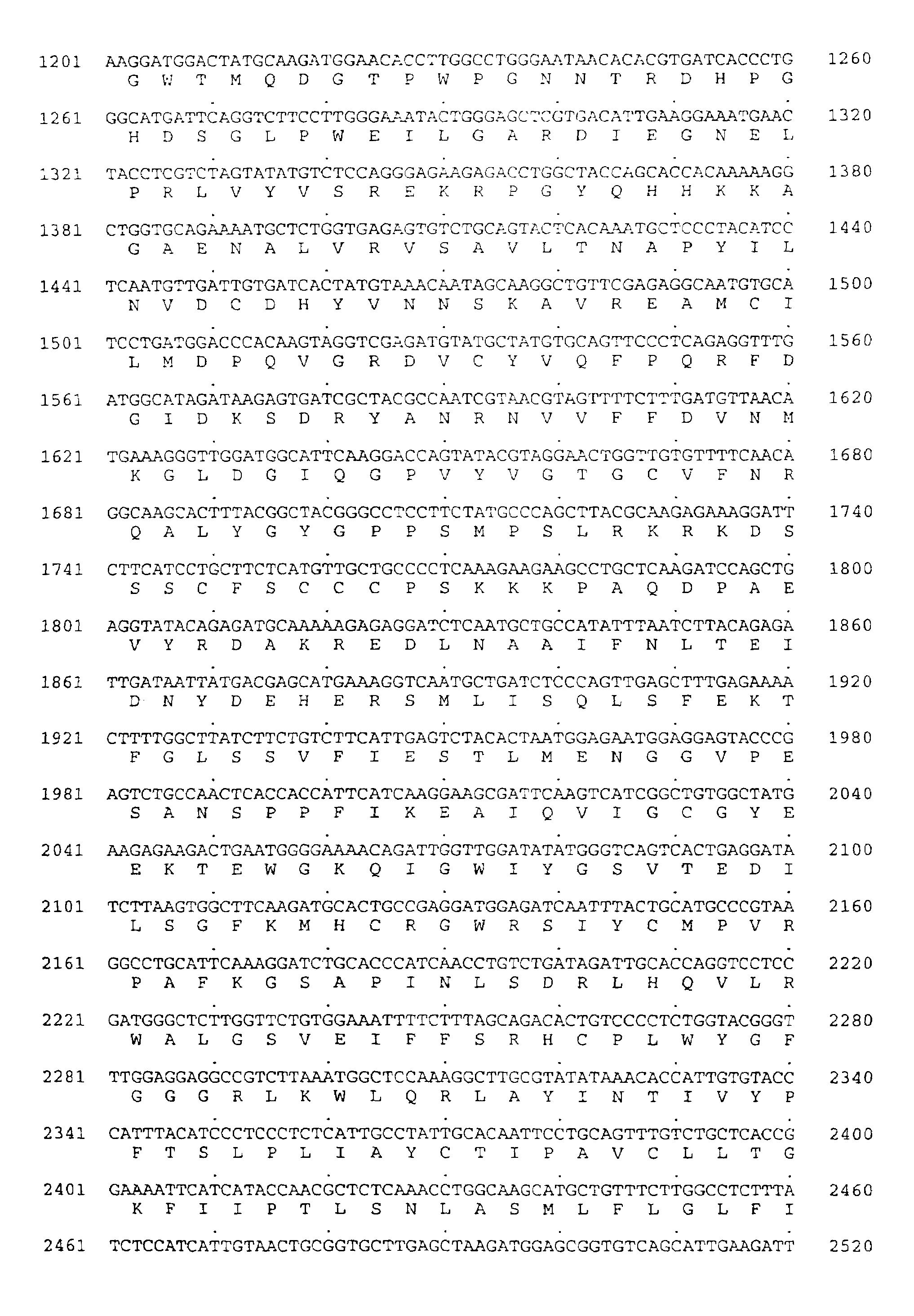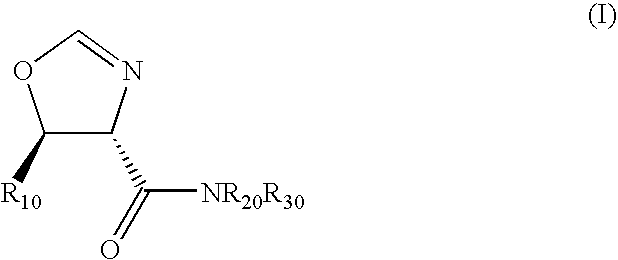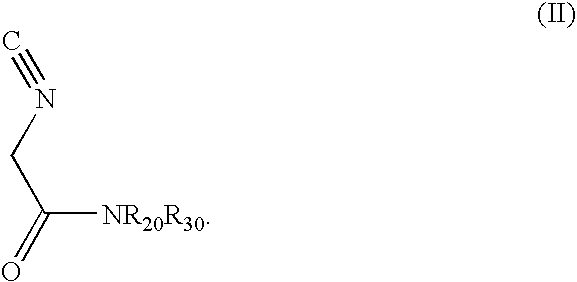Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
95 results about "UDP Glucose" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
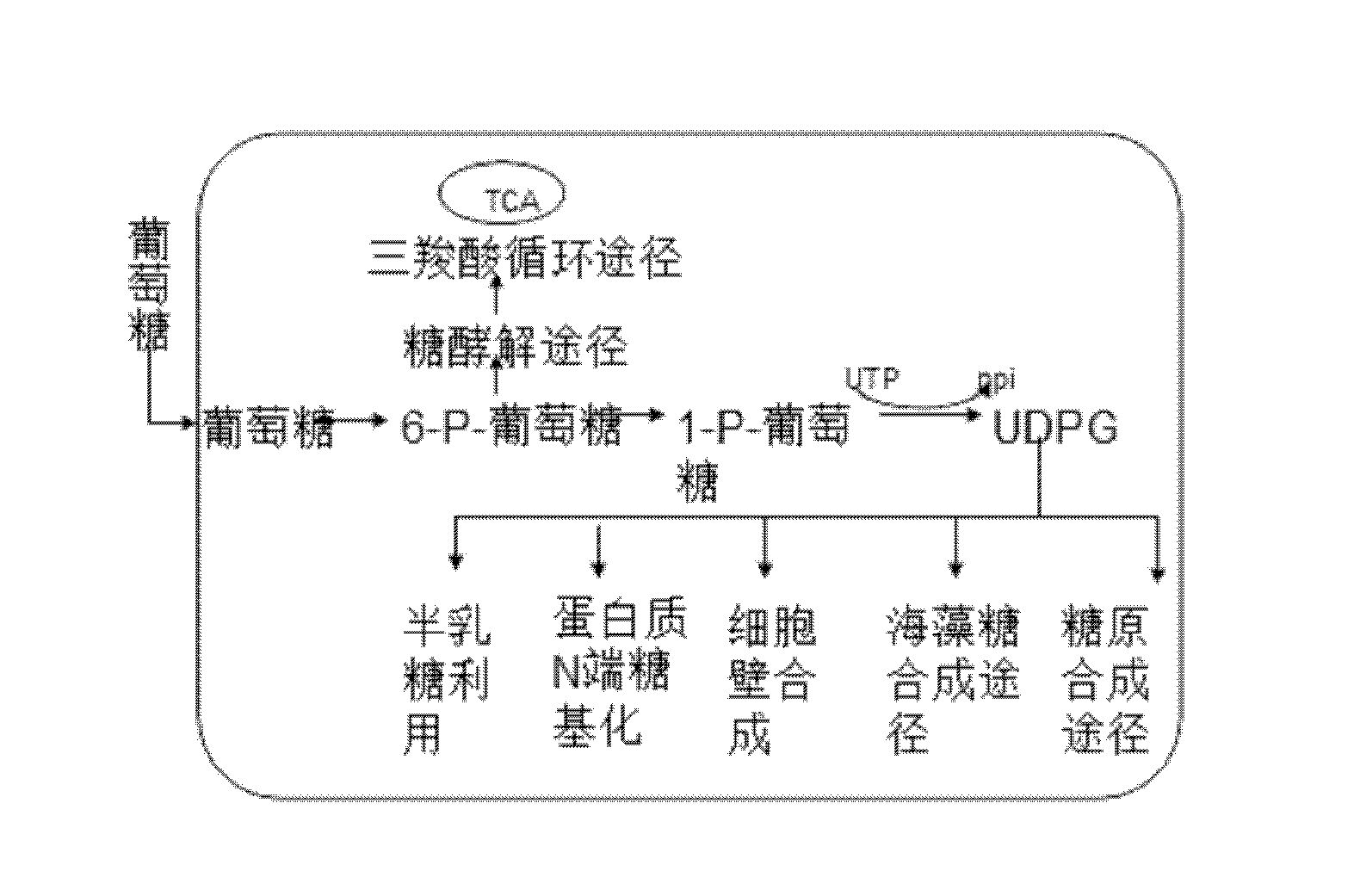
UDP-glucose is used in nucleotide sugar metabolism as an activated form of glucose, a substrate for enzymes called glucosyltransferases.
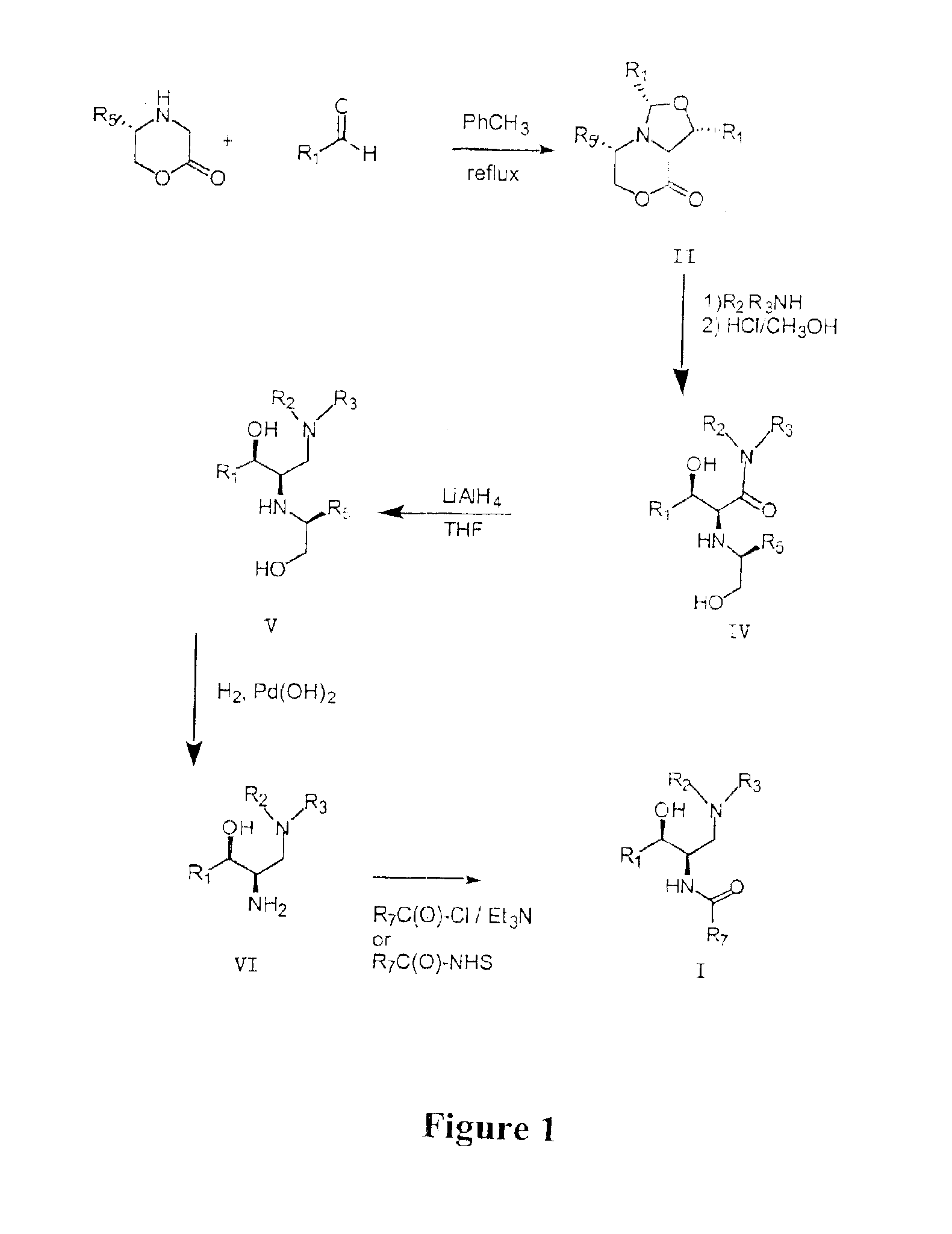
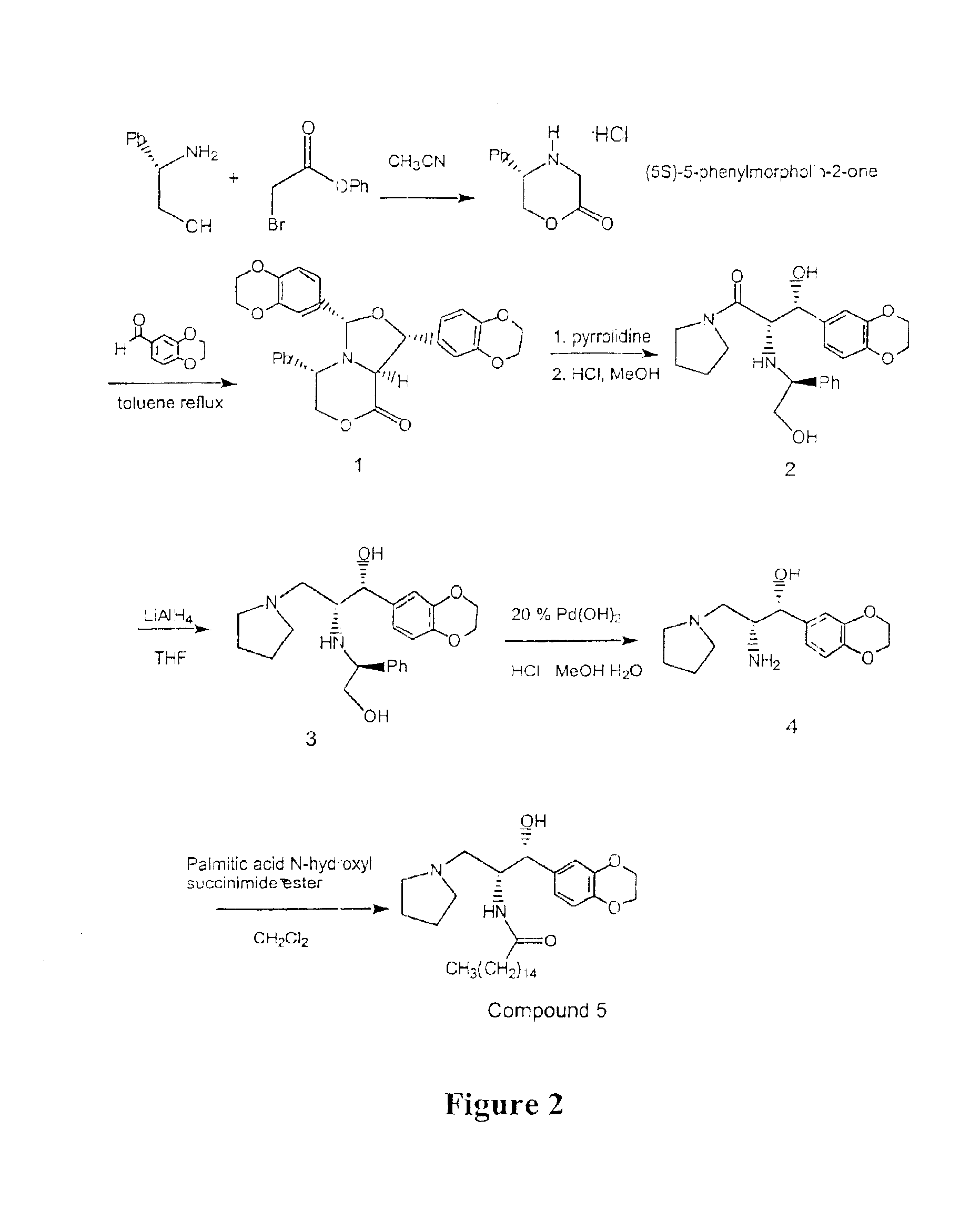
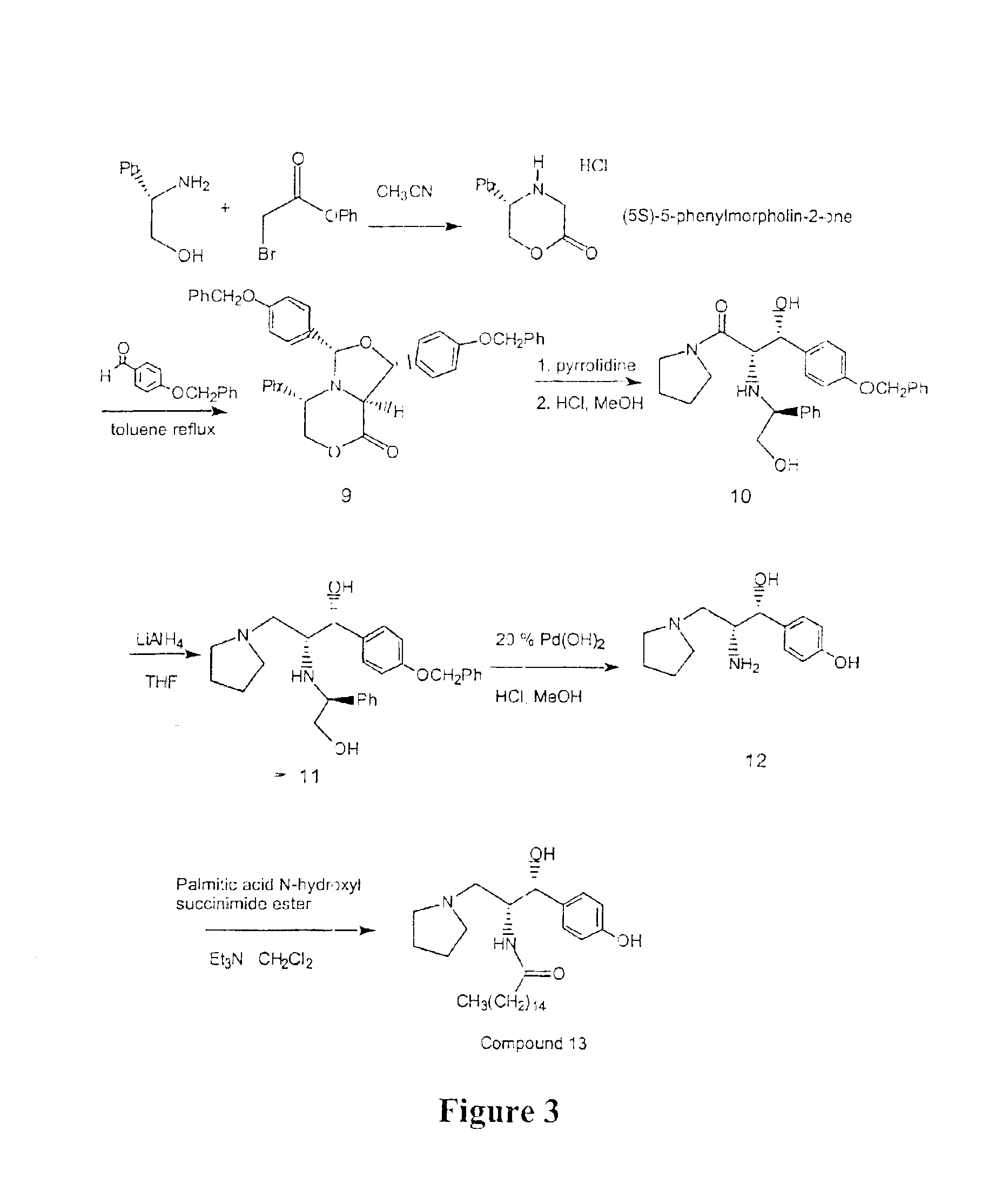
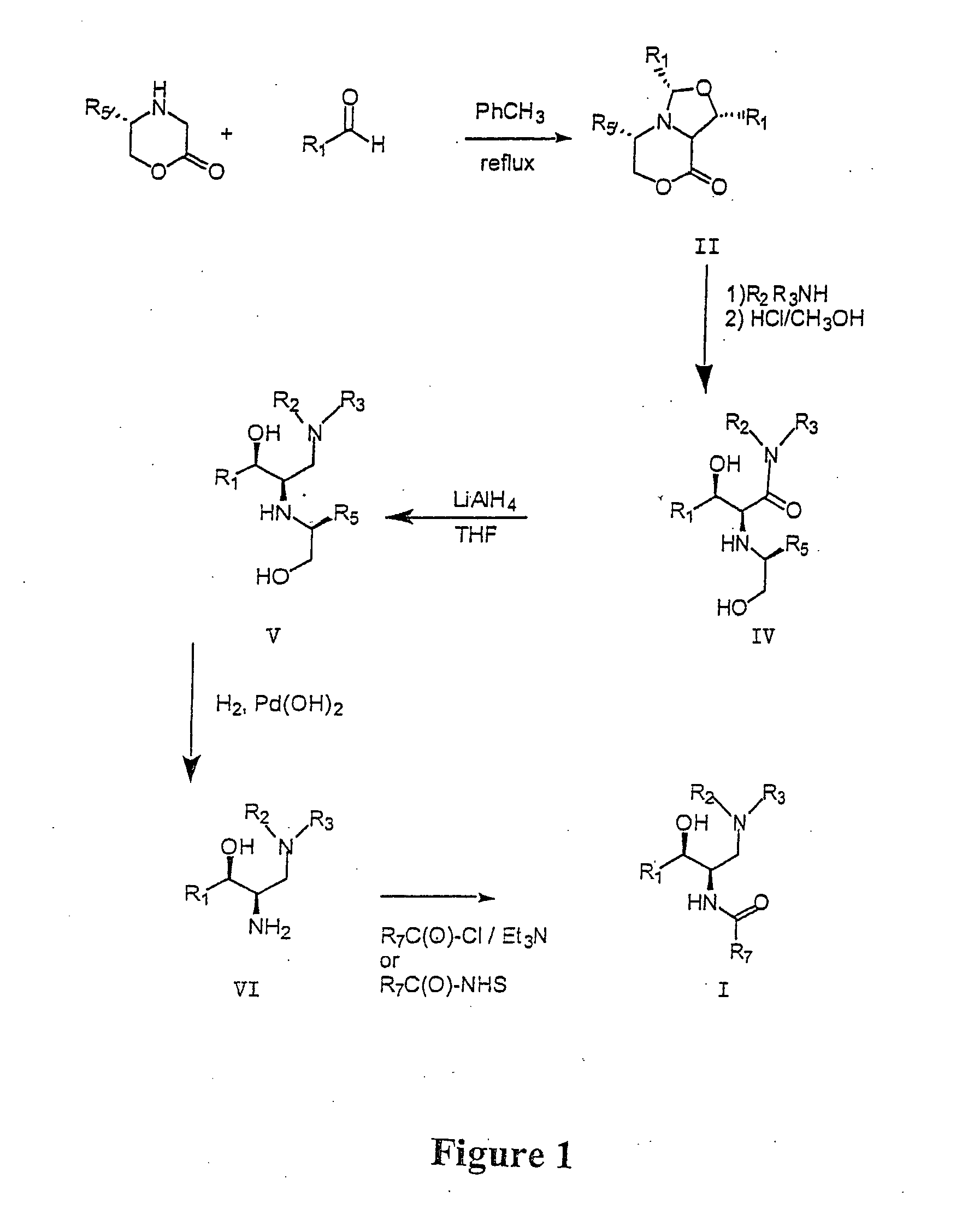
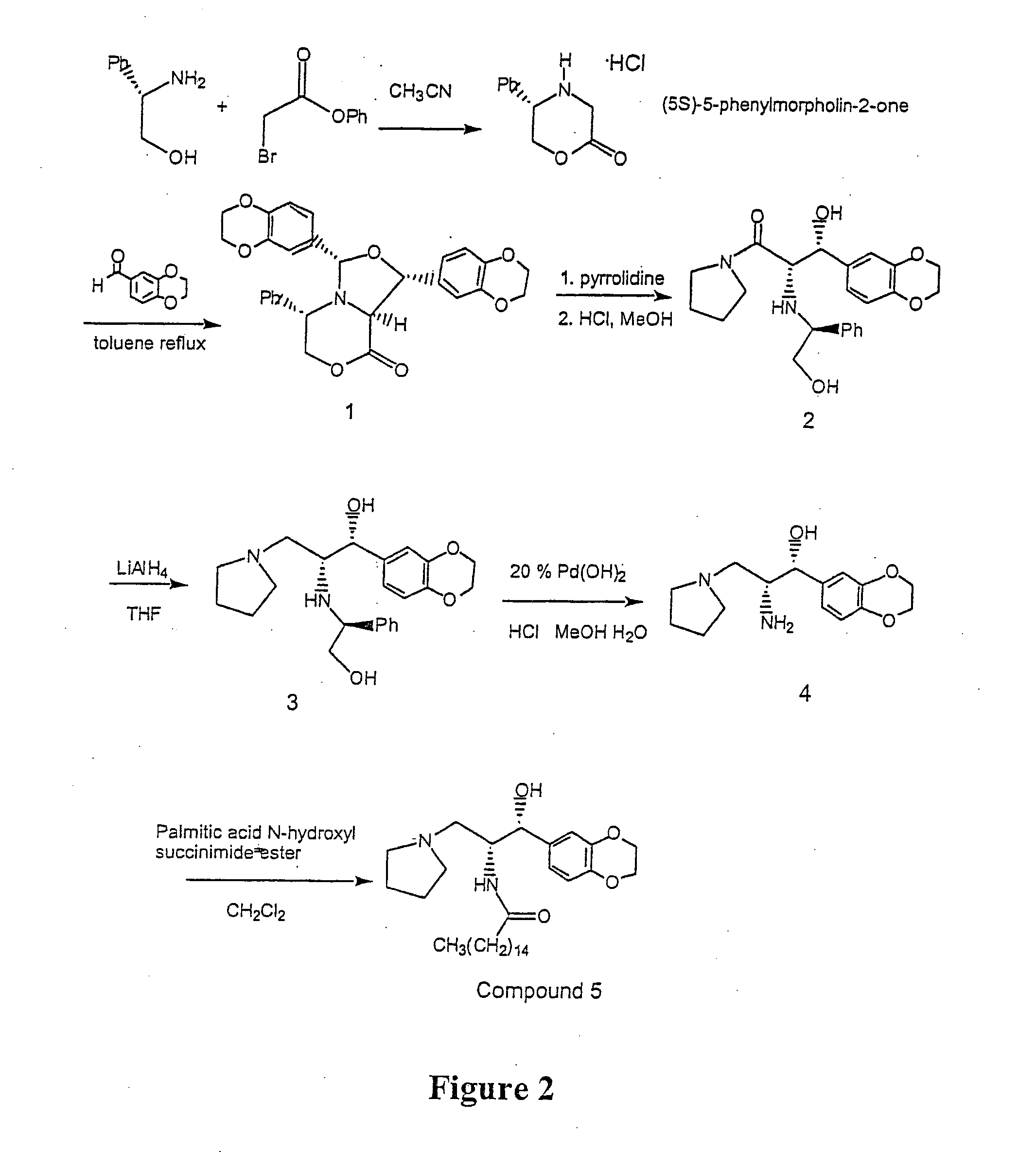
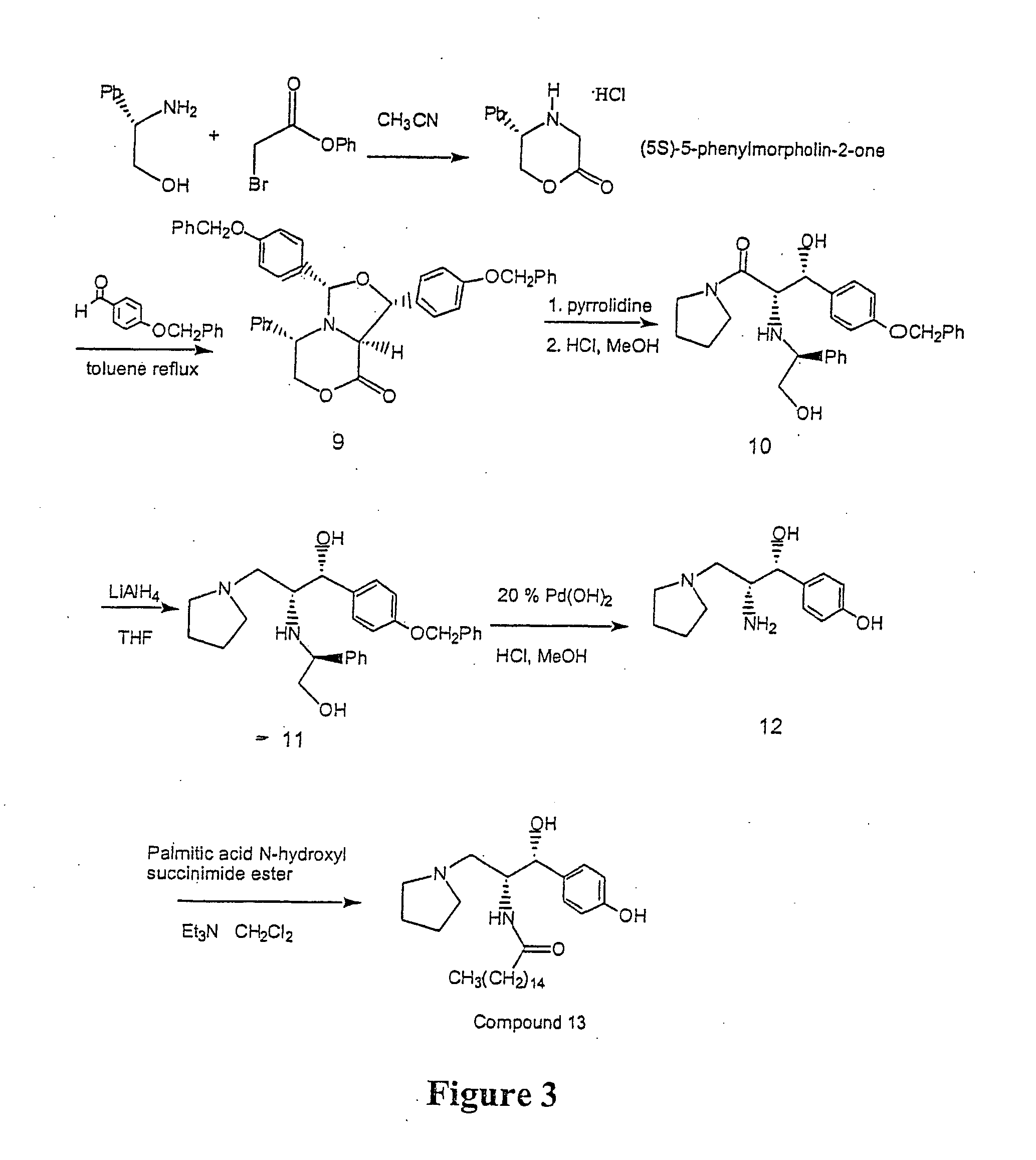
Synthesis of UDP-glucose: N-acylsphingosine glucosyltransferase inhibitors
Disclosed is a novel enantiomeric synthesis cermamide-like inhibitors of UDP-glucose: N-acylsphingosine glucosyltransferase. Also disclosed are novel intermediates formed during the synthesis.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
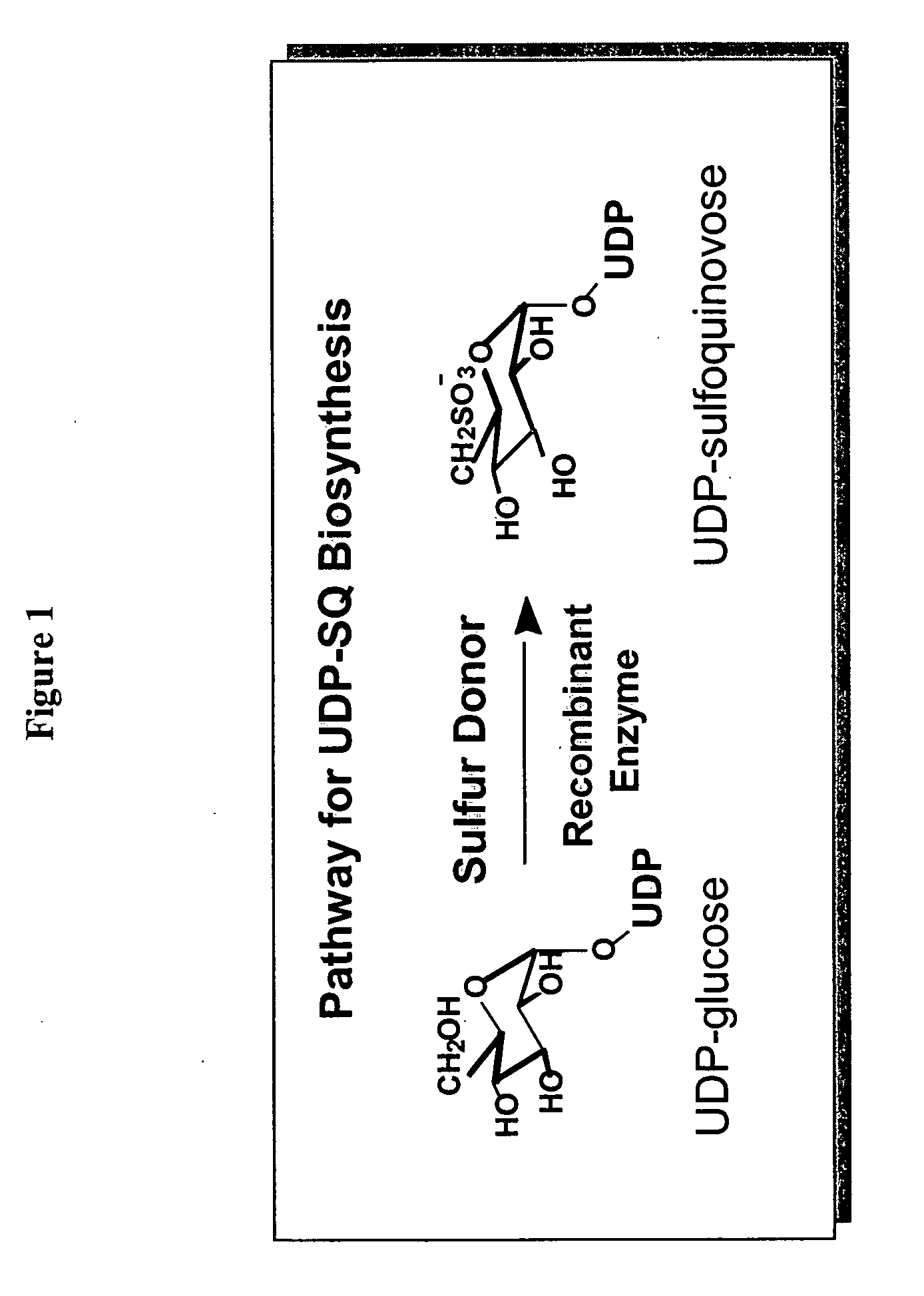
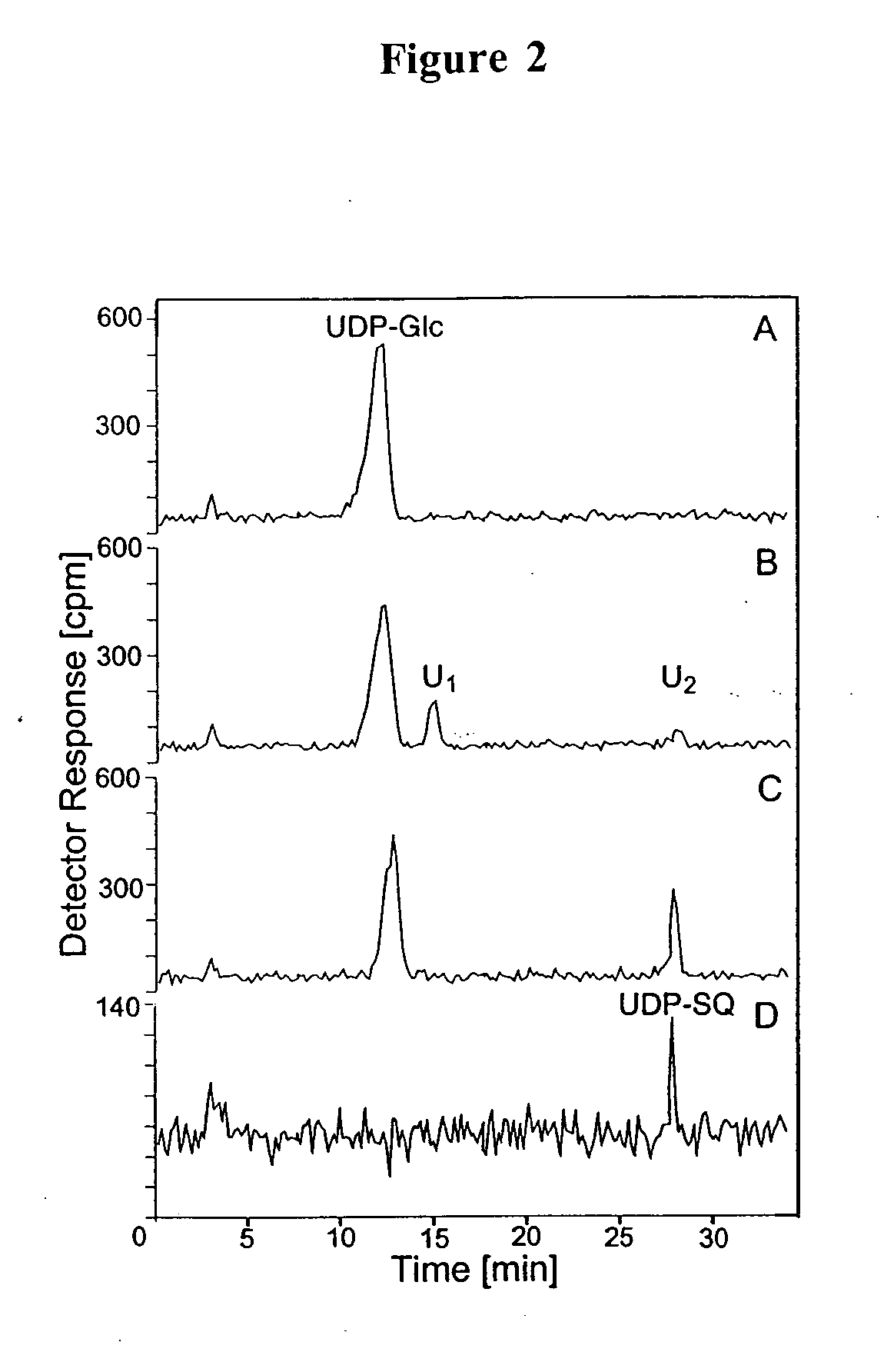
Compositions and methods for the synthesis and subsequent modification of uridine-5'-diphosphosulfoquinovose (UDP-SQ)
The present invention is directed to compositions and methods related to the synthesis and modification of uridine-5′-diphospho-sulfoquinovose (UDP-SQ). In particular, the methods of the present invention comprise the utilization of recombinant enzymes from Arabidopsis thaliana, UDP-glucose, and a sulfur donor to synthesize UDP-SQ, and the subsequent modification of UDP-SQ to form compounds including, but not limited to, 6-sulfo-α-D-quinovosyl diaclyglycerol (SQDG) and alkyl sulfoquinovoside. The compositions and methods of the invention provide a more simple, rapid means of synthesizing UDP-SQ, and the subsequent modification of UDP-SQ to compounds including, but not limited to, SQDG.
Owner:MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Use of mixed duplex oligonucleotides to effect localized genetic changes in plants
InactiveUS7094606B2Other foreign material introduction processesFermentationACC oxidaseGenetic Change
Owner:CIBUS
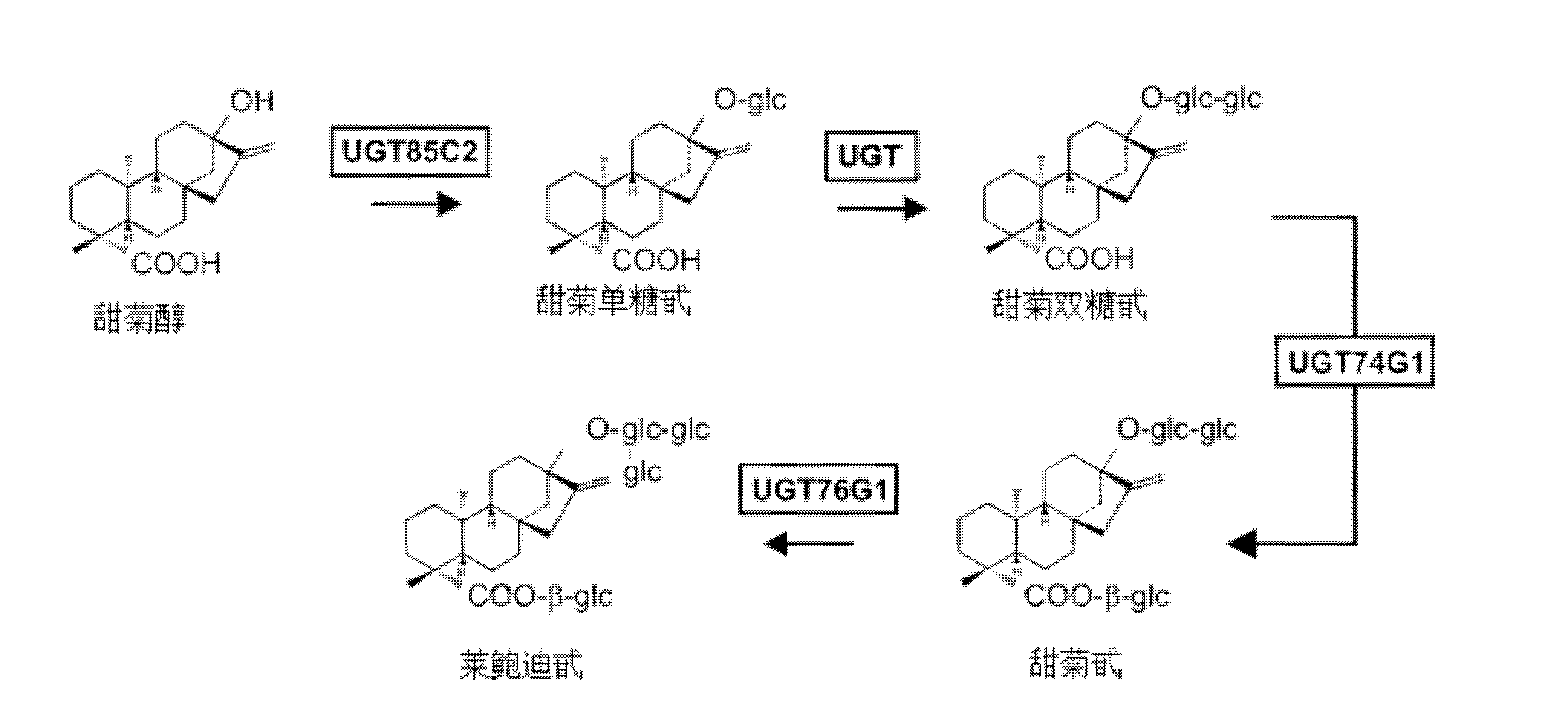
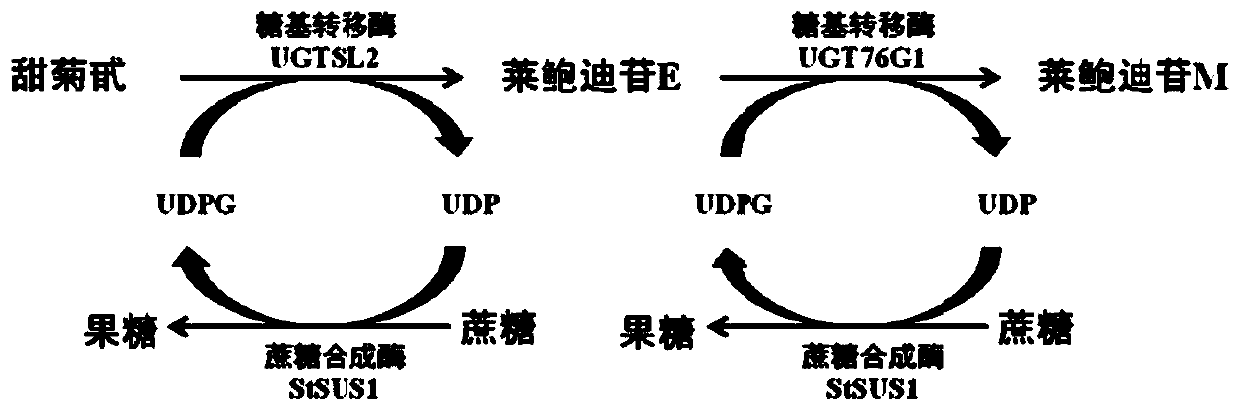
Genetically engineered bacteria used for producing stevia glycosyltransferase UGT76G1 and application thereof
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacteria used for producing stevia glycosyltransferase UGT76G1; a UGT76G1 coding gene is inserted between the restriction enzyme cutting sites EcoRI and XhoI of a PYes2 carrier, so as to construct a recombinant plasmid, and then the recombinant plasmid is introduced to expression host Saccharomyces cerevisiae YPH499 to obtain the engineered bacteria; and the coding gene of the UGT76G1 is GenBank, No. GenBank: AY345974.1, and the gene sequence of the coding gene is named as UGT (Udp Glucuronyl Transferase). The invention also discloses a construction method of the genetically engineered bacteria and the application of the bacteria to the production of rebaudioside A. According to the invention, under the condition that expensive UDPG (Uridine Diphosphate Glucose) is not added, cheap carbon source glucose is used as a substrate, the metabolic pathway of UDPG in the yeast is regulated, and then the rebaudioside A is produced from St glycosides through whole cell catalysis.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Synthesis of UDP-glucose: N-acylsphingosine glucosyltransferase inhibitors
Disclosed is a novel enantiomeric synthesis ceramide-like inhibitors of UDP-glucose: N-acylsphingosine glucosyltransferase. Also disclosed are novel intermediates formed during the synthesis.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Method for preparing rebaudioside-M by enzymic method
ActiveCN104726523AHigh reaction conversion rateReduce manufacturing costFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionUdp glycosyltransferaseSucrose synthetase
The invention discloses a method for preparing rebaudioside-M by an enzymic method. The method comprises the steps of utilizing tomato UDP-glycosyltransferase and potato sucrose synthetase, and using rebaudioside-A and sucrose as raw materials for producing rebaudioside-M. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the high-yield recombinant strain of UDP-glycosyltransferase and sucrose synthase is obtained by virtue of a genetic engineering technology at first, then a bio-enzyme crude product is collected, a catalytic reaction is directly carried out, UDP or UDP-glucose is not added in the reaction system, the rebaudioside-A and the sucrose are used as the raw materials, and the rebaudioside-A is catalyzed to generate the rebaudioside-M through the efficient circulation of catalyzing the UDP-glucose by the sucrose synthase, and through the action of the tomato UDP-glycosyltransferase. Compared with the existing preparation method for rebaudioside-M, the process is short in steps, low in cost, important in application value, and good in economical efficiency.
Owner:XINGHUA GL STEVIA CO LTD
Method for preparing Rebaudioside E through enzyme method
ActiveCN109750072AHigh yieldTransferasesMicroorganism based processesSucrose synthetaseDecomposition
The invention discloses a method for preparing Rebaudioside E through an enzyme method. By means of the method, through tomato source UDP-glycosyl transferase and potato source sucrose synthetase, with stevioside as the raw material, the Rebaudioside E is produced through one-step glycosylation; meanwhile, by means of the fixed-point mutation technology, the UDP-glycosyl transferase is transformed, and the yield of the Rebaudioside E is further improved. By means of the method, no UDP-glucose or UDP needs to be added, the UDP-glucose is obtained as the raw material of glycosylation under the sucrose synthetase decomposition effect of the UDP in a crude extraction solution and the added sucrose, a double-enzyme circulating reaction system is established, and the stevioside is effectively catalyzed to generate the Rebaudioside E. The yield of the Rebaudioside E can reach 65% or above; through the fixed-point mutation technology in the later period, N358F beneficial mutants are obtained through screening, and the yield of the Rebaudioside E is improved through the catalysis and can reach 85% or above at most. Compared with an existing Rebaudioside E preparing method, the method is simple in processing step, low in cost and high in yield and has important application value.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Biocatalytic method for synthesis of rebaudioside M
The invention discloses a biocatalytic method for synthesis of rebaudioside M. Firstly, rebaudioside E is synthesized by a glycosylation reaction of stevioside with UDP-glycosyltransferase from tomatos and sucrose synthetase from potatoes; then, rebaudioside M is synthesized by a glycosylation reaction of rebaudioside E with UDP-glycosyltransferase from stevia rebaudiana and sucrose synthetase from potatoes. The method uses a molecular cloning technique, escherichia coli genetically engineered bacteria for heterologous expression of UDP-glycosyltransferase and sucrose synthetase are obtained,after fermentation and enzyme production, crude extract of cells is directly used for a catalytic reaction, addditionally added saccharose is decomposed with sucrose synthetase to obtain UDP-glucose,UDP in the crude extract and the UDP-glucose serve as raw materials for the glycosylation reaction, a double-enzyme cycle reaction system is established, and the rebaudioside M is produced by effectively catalyzing stevioside. The cost of raw materials is lower, the processing steps are simple, and the method has an important application value.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
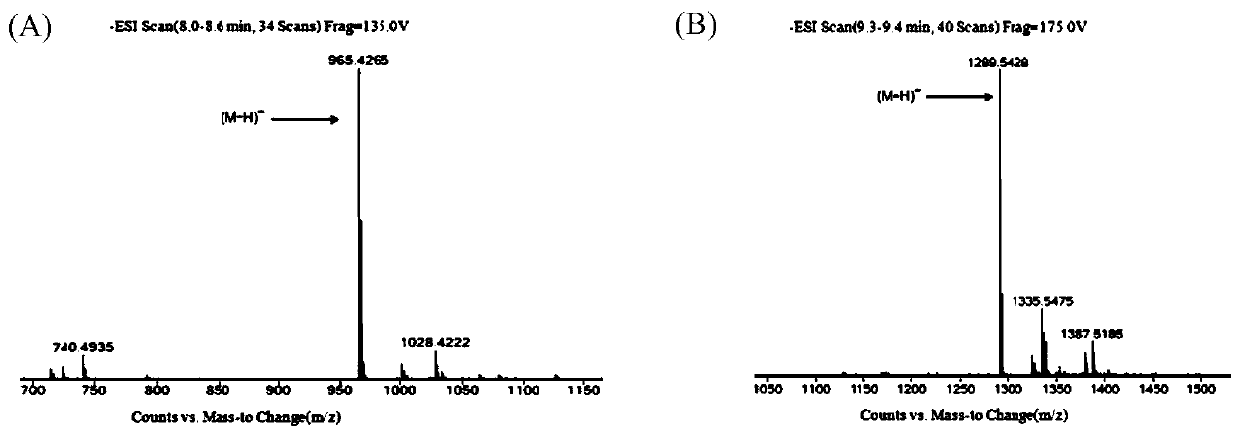
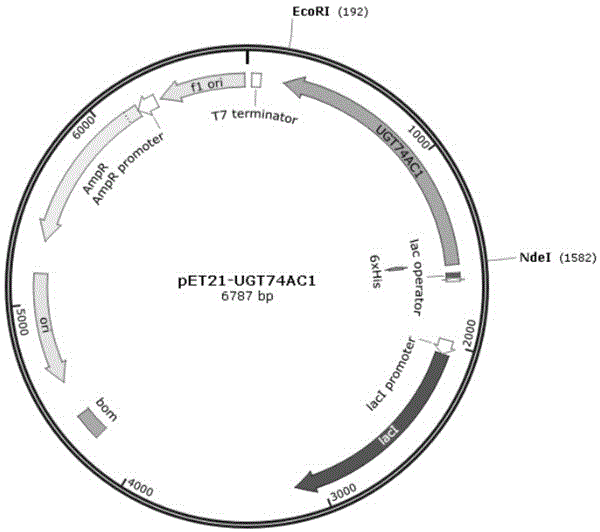
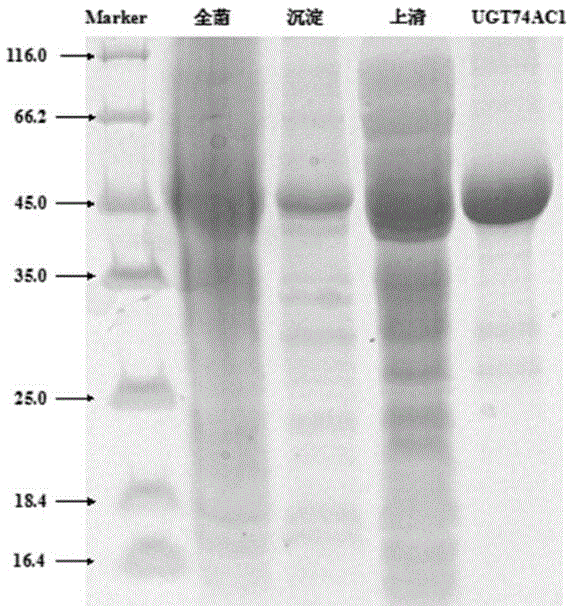
Mangosteen glycosyltransferase gene UGT74AC1 and application thereof
The invention discloses a mangosteen glycosyltransferase gene (i)UGT74AC1( / i) and application of glycosyltransferase with a gene (i)UGT74AC1( / i) code in synthetic mogrosideIE. The glycosyltransferase gene (i)UGT74AC1( / i) has a nucleotide coding sequence shown in SEQIDNO.1 and a peptide sequence shown in SEQIDNO.2. By utilization of an expression of the mangosteen glycosyltransferase gene (i)UGT74AC1( / i) in escherichia coli, the recombinant glycosyltransferase (i)UGT74AC1( / i) can catalyze mogrol and UDP-glucose to react, thereby generating the mogrosideIE. The glycosyltransferase gene (i)UGT74AC1( / i) disclosed by the invention can be applied to the artificial synthesis of the mogrosideIE. Meanwhile, the gene has an important application value in the aspect of improving momordica grosvenori by the utilization of a transgenic technology to improve the content of the mogroside.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
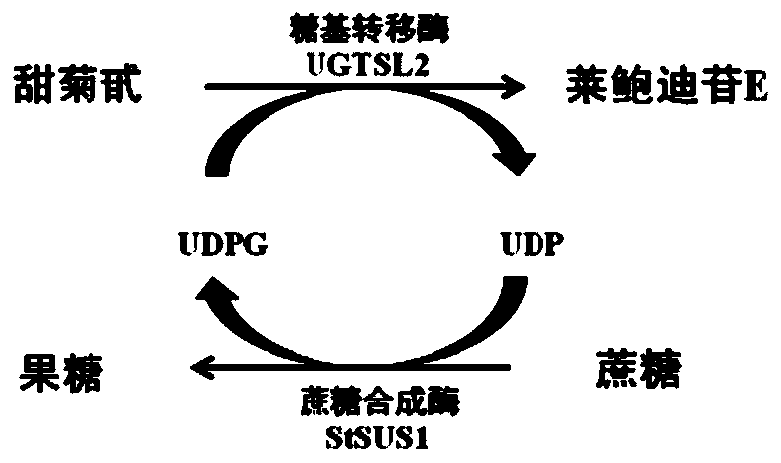
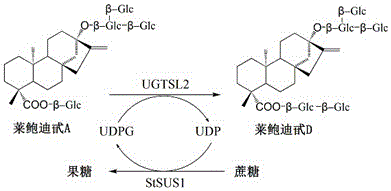
Recombinant bacterium and application of recombinant bacterium to generation of rebaudioside D by catalyzing rebaudioside A
ActiveCN106754595AAvoid separation and purificationHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSucrose synthetaseRebaudioside D
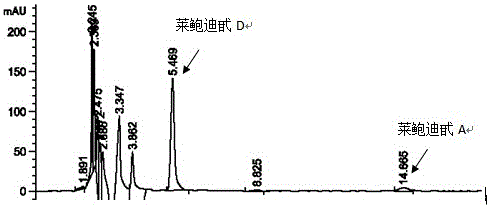
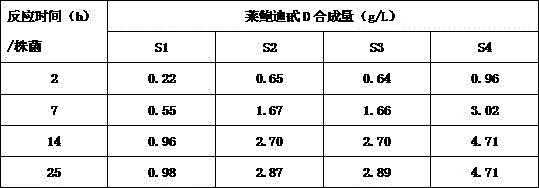
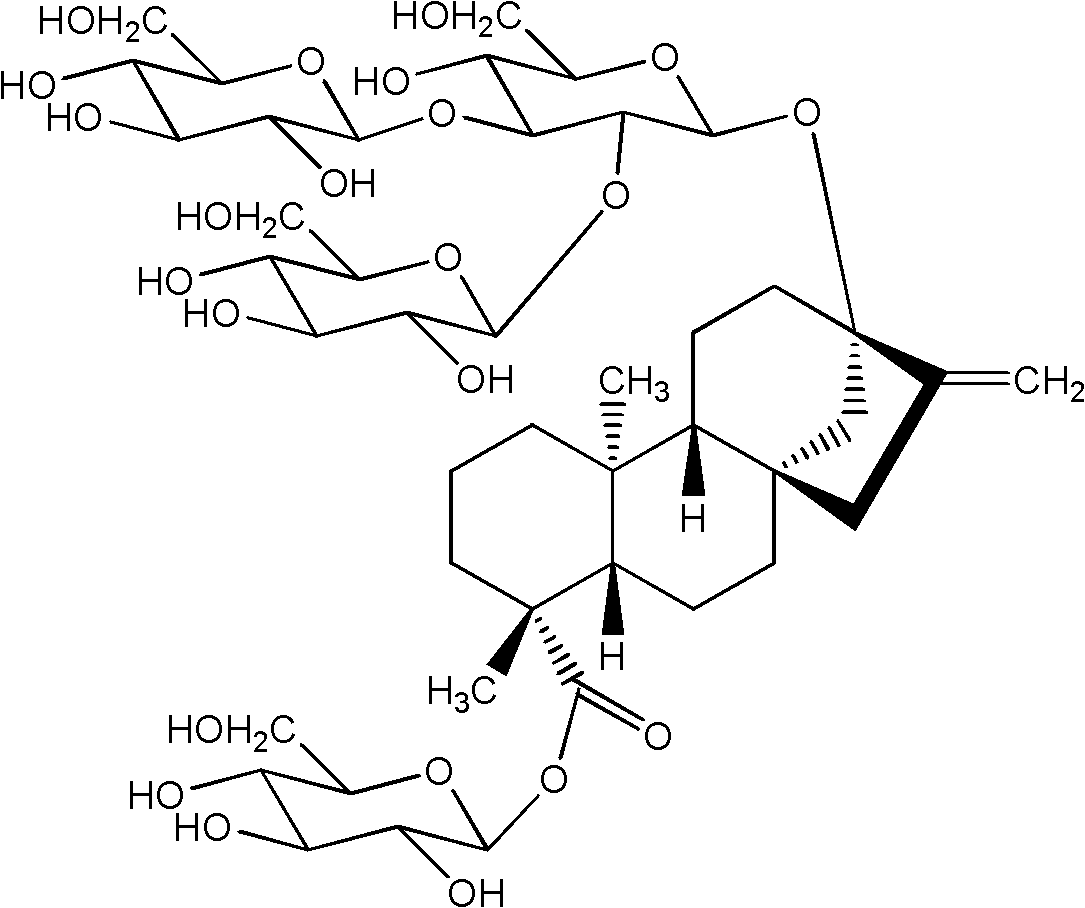
The invention discloses a recombinant bacterium and application of the recombinant bacterium to the generation of rebaudioside D by catalyzing rebaudioside A. The recombinant bacterium contains a tomato-derived glycosyltransferase UGTSL2 gene and a potato-derived sucrose synthase StSUS1 gene; the tomato-derived glycosyltransferase UGTSL2 gene is cloned between NdeI and XhoI sites of pRSFDuet-1 to construct a recombinant plasmid pRSFDuet-SL2; then the potato-derived sucrose synthase StSUS1 gene is cloned between NcoI and EcoRI sites of the pRSFDuet-SL2 to construct a recombinant plasmid pRSFDuet-SL2-SUS1; the recombinant plasmid pRSFDuet-SL2-SUS1 is transferred into a host cell to obtain the recombinant bacterium. After the recombinant bacterium is subjected to induction expression, the recombinant bacterium is added into a reaction mixture to catalyze the rebaudioside A to generate the rebaudioside D; in reaction, crude enzyme liquid obtained by crushing the recombinant bacterium is utilized and separation and purification of an enzyme are avoided; lyophilized powder does not need to be produced; UDP (Uridine Diphosphate) or UDP-glucose and any cell penetration agent or other chemical reagents do not need to be added into a reaction solution, so that the recombinant bacterium has a better environment-friendly property. The yield of the rebaudioside D can reach 10.8g / L.
Owner:XINGHUA GL STEVIA CO LTD
Stevia rebaudiana enzyme VI and method for converting rebaudioside-A into rebaudioside-D
The invention belongs to the field of food chemistry, and particularly relates to a method for converting RA (rebaudioside-A) which is taken as a raw material into RD (rebaudioside-D), and the key is stevia rebaudiana enzyme VI and a preparation method thereof. The converting method comprises the following steps: A, the RA of which the purity is higher than 90% is dissolved with water according to the weight measurement ratio of 1:6-1:10m / v; B, UDP-Glu (Uridine Diphosphate Glucose) is added according to the weight ratio that RA:UDP-Glu=15:5-15:9; C, the stevia rebaudiana enzyme VI is added according to the weight ratio that RA: stevia rebaudiana enzyme VI=(800-1200):1 (preferably 1000:1), and then reaction is carried out for 3-7h at the temperature of 40-60 DEG C and the pH of 6-8; and D, a reaction solution is filtered and dried to obtain RD-containing solid matter. The conversion rate of converting RA into RD is larger than or equal to 70%, and the RD content in the solid matter is 60%-70%, can achieve 80% after further separation and purification, and even can be larger than 90%.
Owner:SICHUAN INGIA BIOSYNTHETIC CO LTD
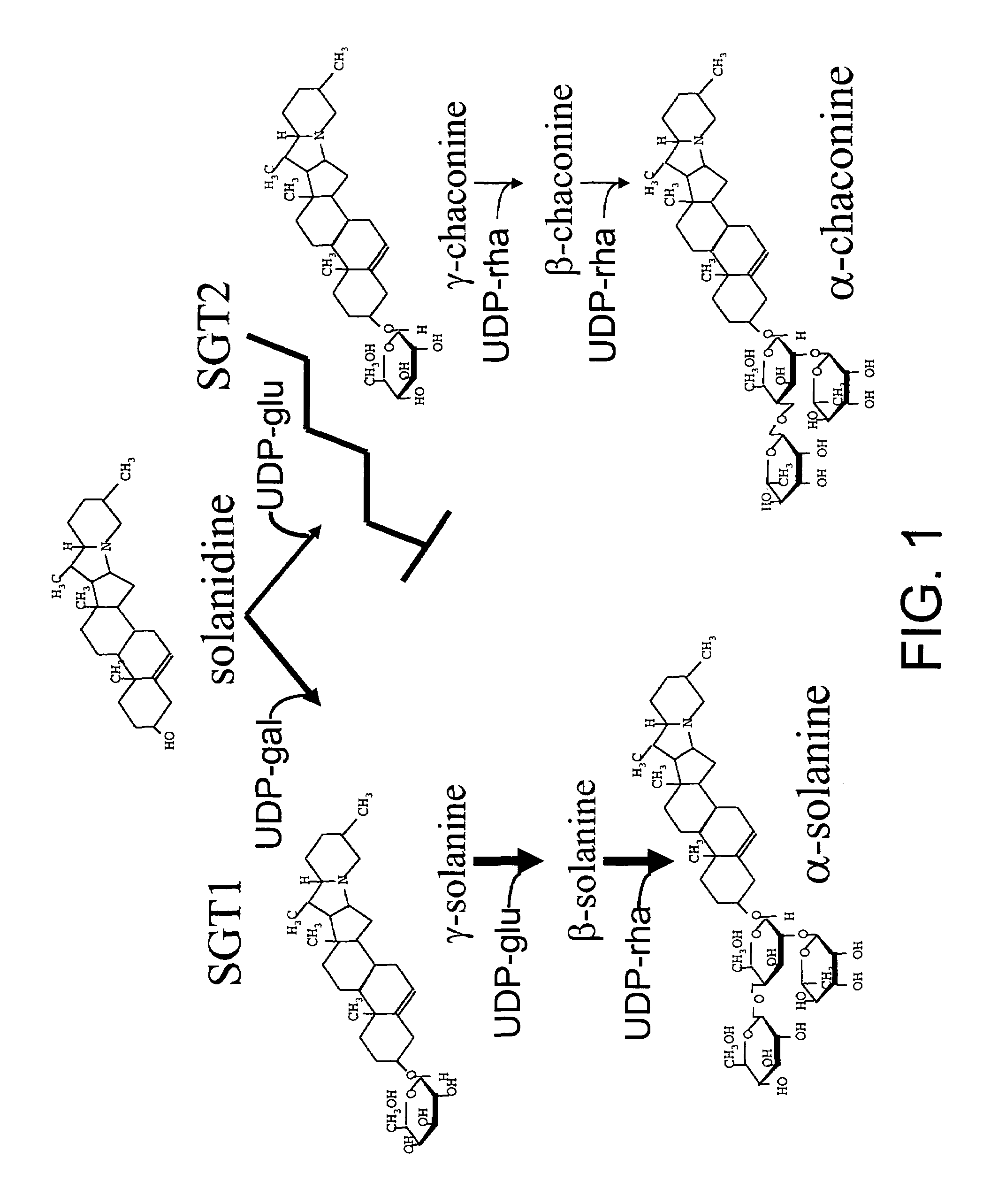
Solanum tuberosum sterol alkaloid glycosyltransferase (SGT) a novel solanidine glucosyltransferase SGT2 and uses thereof
InactiveUS7375259B1Increased glycoalkaloid biosynthesisReduce or eliminate glycoalkaloid biosynthesisBacteriaLibrary member identificationSterolSolanidine glucosyltransferase
Nucleic acid sequences from potato that encode the enzyme UDP-glucose:solanidine glucosyltransferase (SGT2) are disclosed. Recombinant DNA molecules containing the sequences, and use thereof, in particular, use of the sequences and antisense constructs to inhibit the production of SGT2 and thereby reduce the level of the more human-toxic of the two predominant steroidal glycoalkaloids α-chaconine and / or increase the level of the more insect-toxic α-solanine in Solanaceous plants such as potato are described.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
Method for preparing rebaudioside M2 by catalyzing rebaudioside A through recombinant bacterium
ActiveCN106834389AAvoid separation and purificationHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSucrose synthetaseRebaudioside D
The invention discloses a recombinant bacterium and application of the recombinant bacterium to preparation of rebaudioside M2 by catalyzing rebaudioside A. The recombinant bacterium contains a tomato-based glycosyltransferase UGTSL2 gene and a potato-based sucrose synthase StSUS1 gene at the same time; the tomato-based glycosyltransferase UGTSL2 gene is cloned between NdeI and XhoI sites of pRSFDuet-1 and is constructed to obtain a recombinant plasmid pRSFDuet-SL2; then the potato-based sucrose synthase StSUS1 gene is cloned between NcoI and EcoRI sites of the pRSFDuet-SL2 and is constructed to obtain a recombinant plasmid pRSFDuet-SL2-SUS1; the recombinant plasmid pRSFDuet-SL2-SUS1 is transferred into a host cell to obtain the recombinant bacterium. After the recombinant bacterium is subjected to induced expression, crude enzyme liquid is taken and is added into a reaction mixture to catalyze the rebaudioside A to generate the rebaudioside M2; in a reaction process, the crude enzyme liquid obtained by crushing the recombinant bacterium is utilized and separation and purification of an enzyme are avoided; lyophilized powder is also not needed and substrates including rebaudioside D and UDP or UDP-glucose and any cell penetration agent or other chemical reagents do not need to be added, so that the environmental friendliness is better. The yield of the rebaudioside M2 reaches 11.09g / L.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
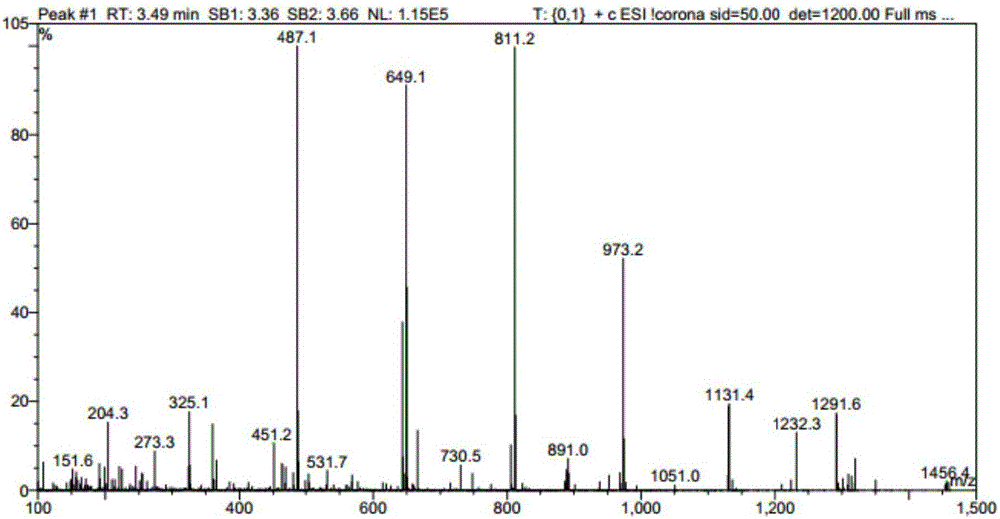
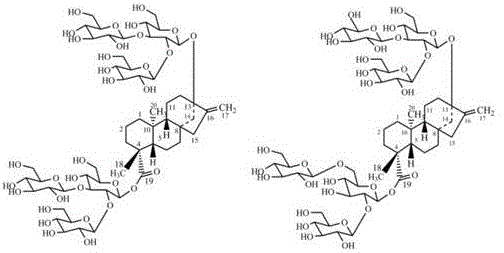
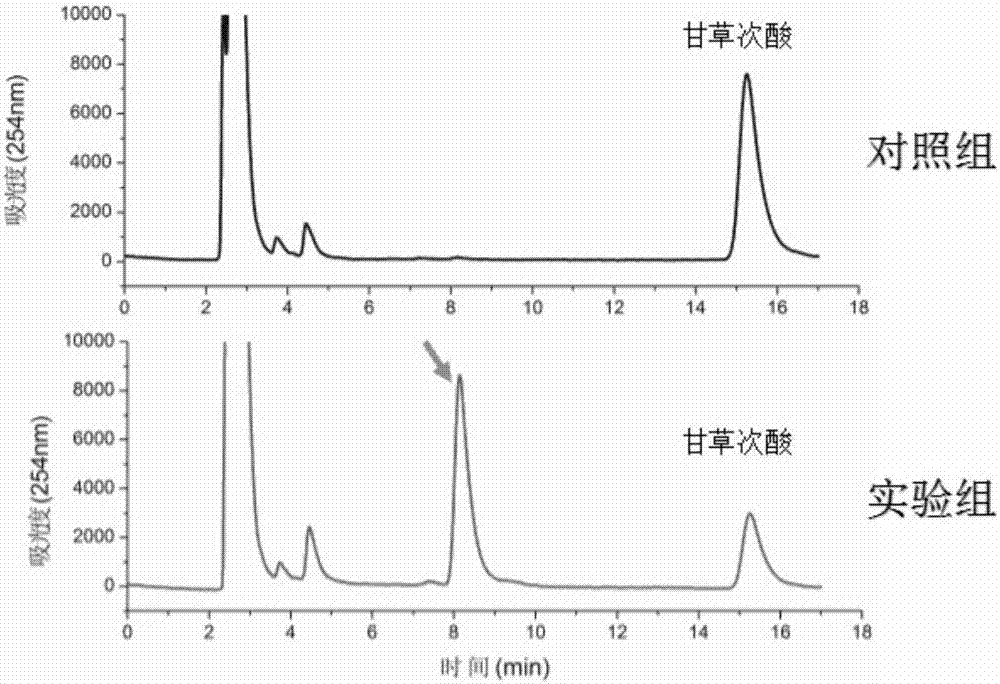
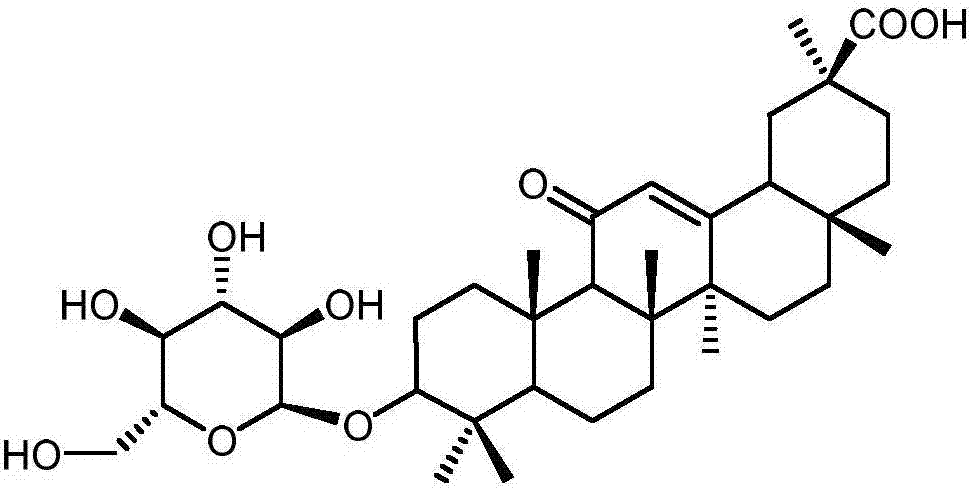
Method for synthesizing 3-O-glucose-glycyrrhetinic acid with enzymic method
ActiveCN107502599AHigh catalytic efficiencyMild reaction conditionsTransferasesGenetic engineeringChemical synthesisEscherichia coli
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing 3-O-glucose-glycyrrhetinic acid with an enzymic method and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. Glycosyltransferase gene Unigene14953, Unigene20323UGT73C11, UGT73C5 and UGT73C6 from plant licorice, barbarea vulgaris or Arabidopsis are cloned or chemically synthesized, escherichia coli is preferably selected as host bacteria, and genetically engineered bacteria containing glycosyl transferase is established; recombinant glycosyl transferase serves as glycyrrhetinic acid substrate and uridine diphosphate glucose, and 3-O-glucose-glycyrrhetinic acid can be synthesized efficiently in pH value of 5.0-11.0 and at the temperature of 25-55DEG C conditions.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
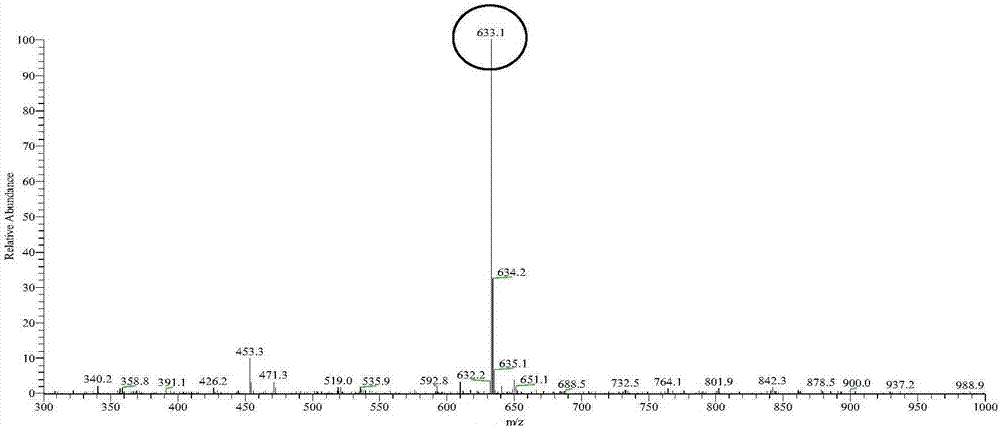
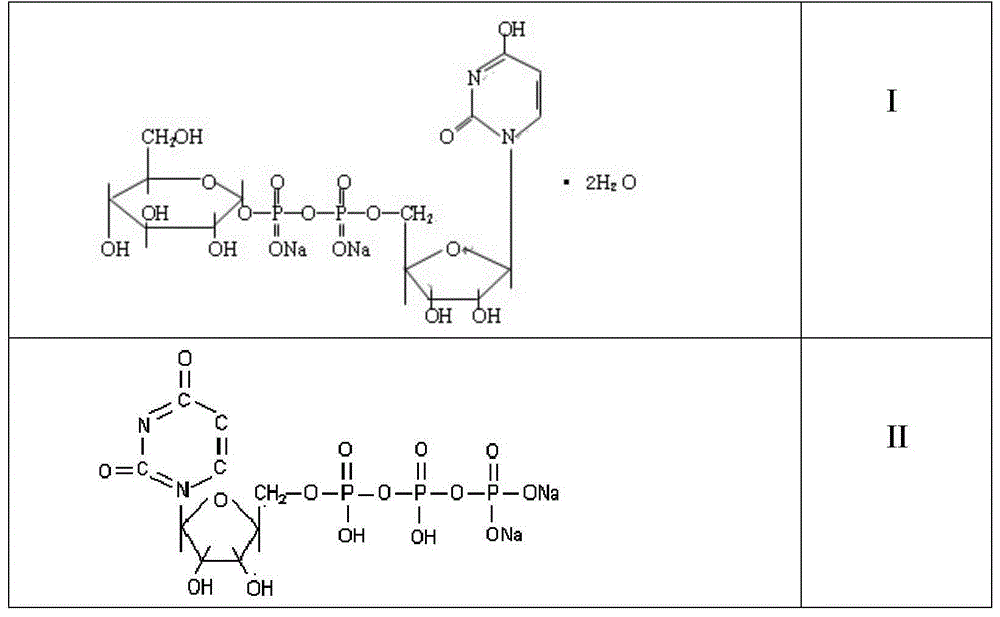
Preparation method of uridine diphosphate glucose
ActiveCN104561195AWide variety of sourcesLow priceTransferasesMicroorganism based processesAlcoholGenetically engineered
The invention relates to a preparation method of uridine diphosphate glucose (UDPG), which comprises the steps of simply, conveniently, economically, reasonably and greatly synthesizing the UDPG by the combined action of yeast and genetically engineered bacteria, performing purification via resin separation, alcohol precipitation and the like, and obtaining a target compound with very high purity.
Owner:SHANGHAI ZHAOWEI TECH DEV +1
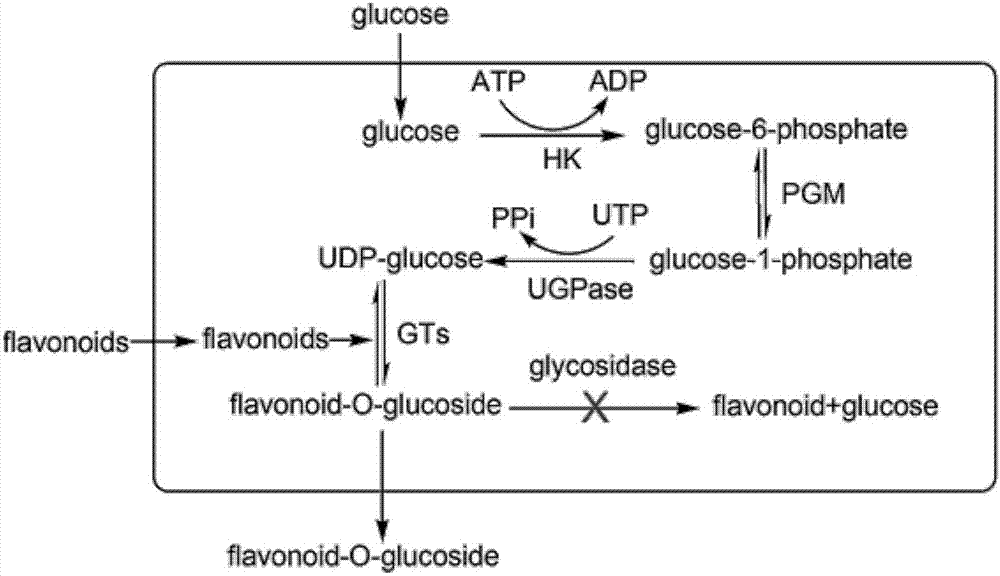
Genetically engineered bacterium for catalyzing glucose glycosylation of flavonoids compound and application thereof
ActiveCN107164253AImprove efficacyGood water solubilityFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyHydrolase Gene
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium for catalyzing glucose glycosylation of a flavonoids compound and an application thereof. Specifically, a Beta-glycoside hydrolases gene of a chassis biological cell is removed according to the genetically engineered bacterium, and endogenous degradation of a glycosylation product is reduced; the high-expression regulation is performed to two key enzymes of glucophosphomutase (PGM) and uridine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase (UGP1) of the chassis biological cell for participating in the synthesis of glycosylated-donor uridine diphosphate glucose (UDP-Glu), and a UDP-glucuronosyltransferase gene for catalyzing the flavonoid aglycones glucose glycosylation is combined so as to obtain a genetically engineered strain for effectively catalyzing the glucose glycosylation of the flavonoids compound, and finally scutellarein is used as a catalytic substrate for fermenting for 54 h in 10 L of a fermentation tank, wherein the yield of scutellarein-7-O-glucose of the glycosylation product is up to 1200 mg / L. The used strategy provides a technology reference for biologically-catalyzing chemical micromolecular glycosylation by using a microbiological method.
Owner:INST OF MATERIA MEDICA AN INST OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Cellulose synthase encoding polynucleotides and uses thereof
InactiveUS7049481B1Quality improvementLow lignin contentBryophytesSugar derivativesNucleotidePlant cell
The invention relates to isolated polynucleotides encoding functional cellulose synthases and UDP-glucose binding domain thereof, transgenic plants and plant cells transformed with the polynucleotides. The invention further relates to methods of transforming plants and plant cells with cellulose synthase or UDP-encoding polynucleotides.
Owner:MICHIGAN TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
Method for improving biological output and polysaccharide content of lucid ganoderma
InactiveCN101717782AHigh in polysaccharidesLarge biomassVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyUridine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase
The invention discloses a method for improving biological output and polysaccharide content of lucid ganoderma. The UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase (OsUgp2) gene derived from rice is connected to an overexpression vector and transferred into the lucid ganoderma by a agrobacterium rhizogenes mediated method; in the obtained transgenosis lucid ganoderma strain, the expression of the OsUgp2 gene is strengthened, and the biological output and the intracellular polysaccharide and extracellular polysaccharide content of the ganoderma sinensis are obviously improved. The invention can effectively improve the biological output and the polysaccharide content in edible and medicinal fungi, such as the lucid ganoderma, and the like, provides a new approach for improving the polysaccharide content of the edible and medicinal fungi and has favorable application and development prospect.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Gene participating in forming of peach fruit combined state linalool and application thereof
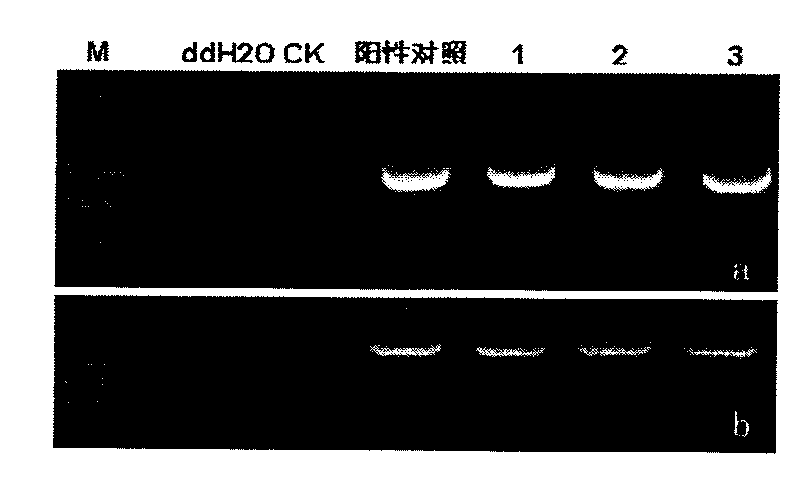
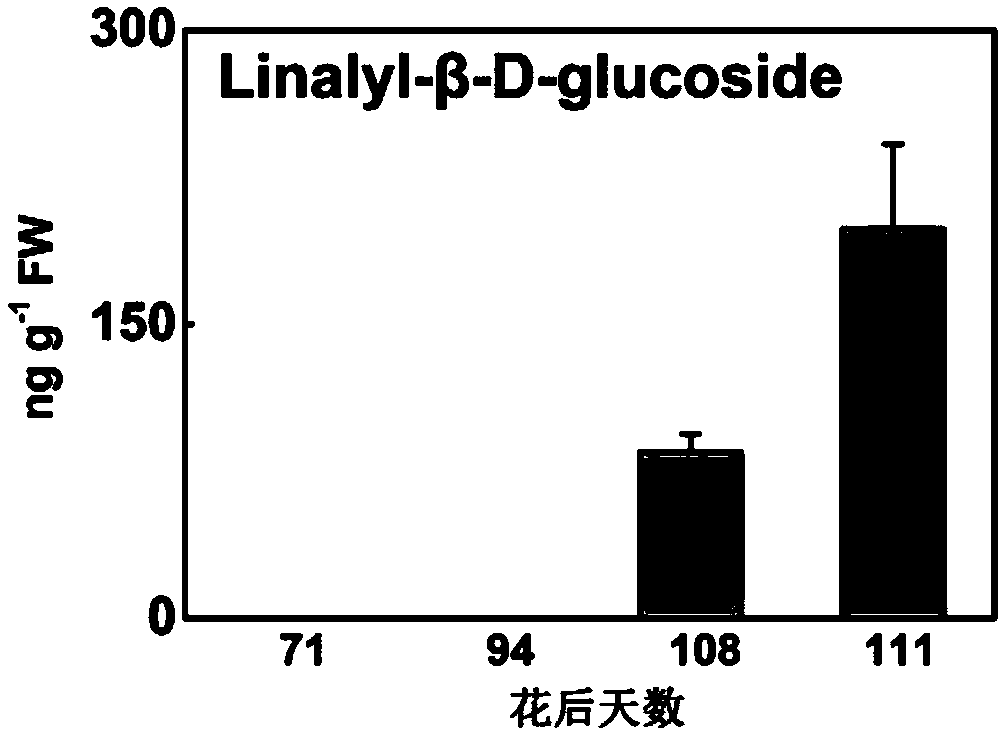
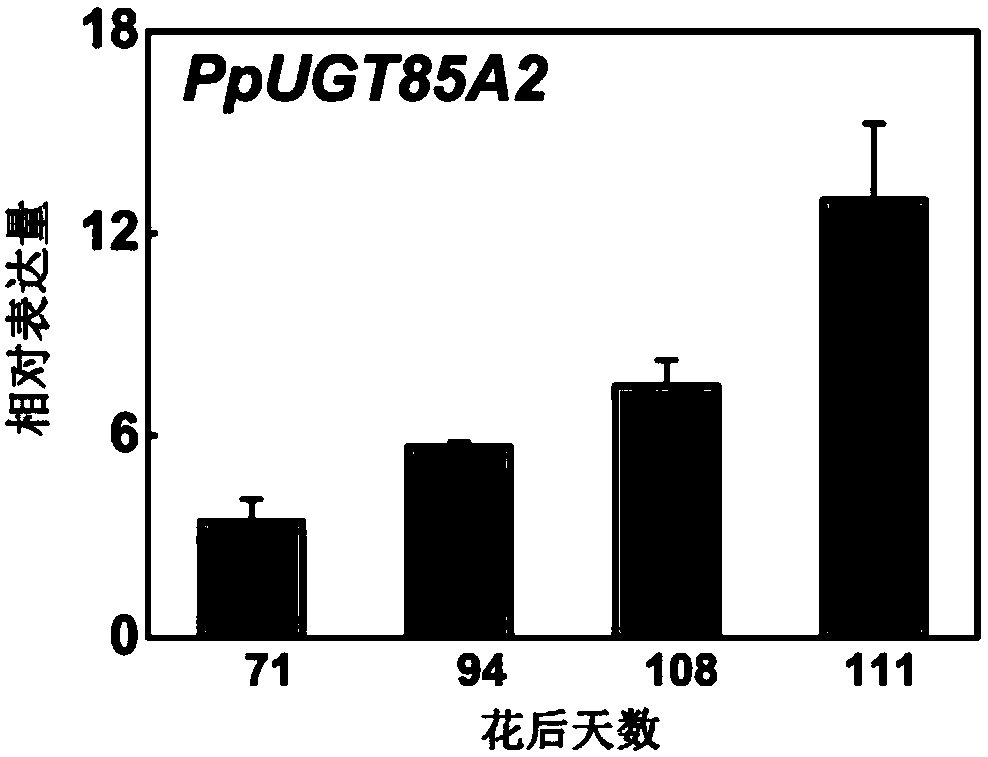
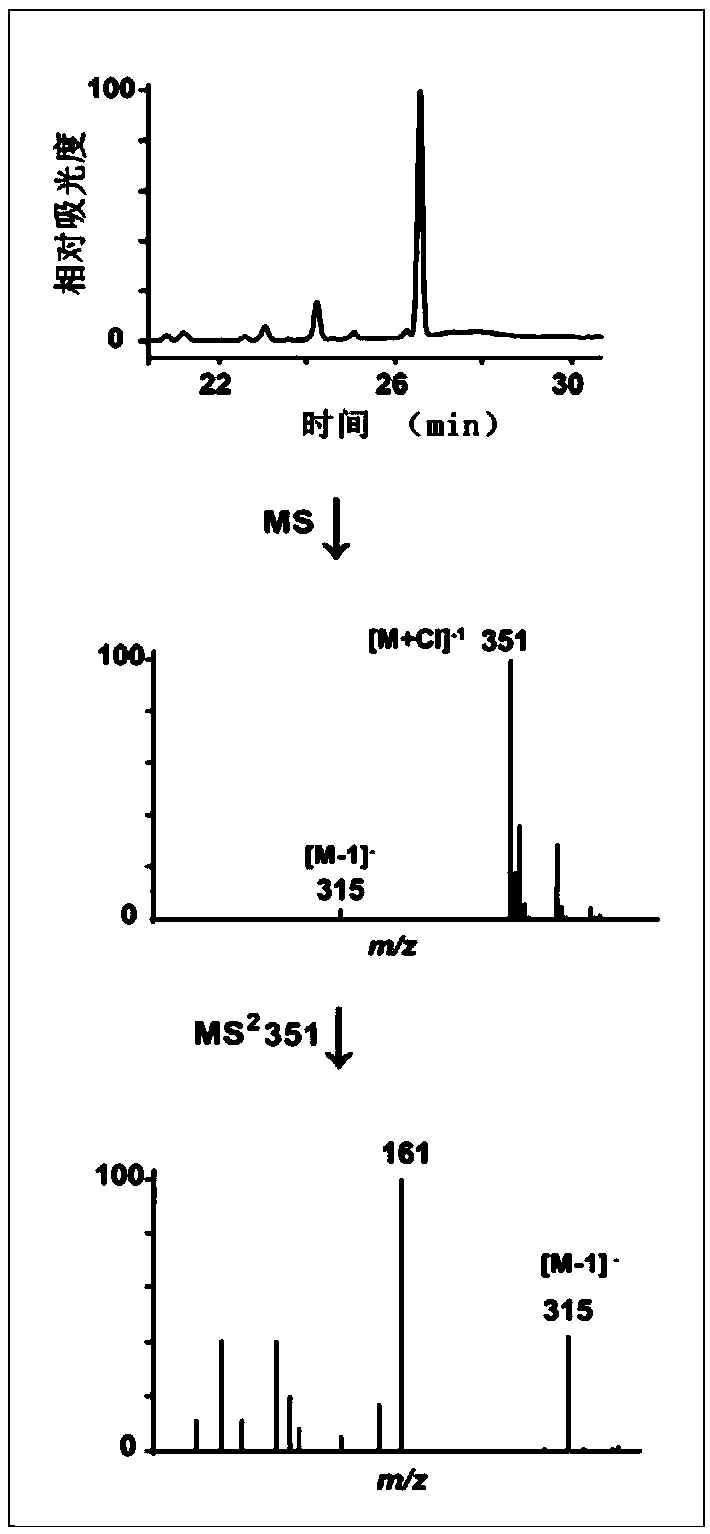
ActiveCN108251438AIncrease reservesImprove aroma qualityFermentationGlycosyltransferasesBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention provides a gene PpUGT85A2 participating in forming of peach fruit combined state linalool. A full-length sequence of PpUGT85A2 is obtained through PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification, and the situation that PpUGT85A2 is clustered in a UGT85 family is obtained through analyzing an evolutionary tree. An in-vitro functional verification conducted in escherichia coli shows thatPpUGT85A2 can convert linalool to be in a combined state mode without the volatility under the condition that UDP-glucose serves as a sugar donor. PpUGT85A2 is overexpressed in a peach fruit and tobacco, the content of linalyl-beta-D-glucoside in combined state linalool is outstandingly increased, storage of fragrant matter is increased, and thus the gene has important application value on improving the fragrance quality of processed food by adopting a hydrolase to release the combined state linalool in the processing process of agricultural products after being picked.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
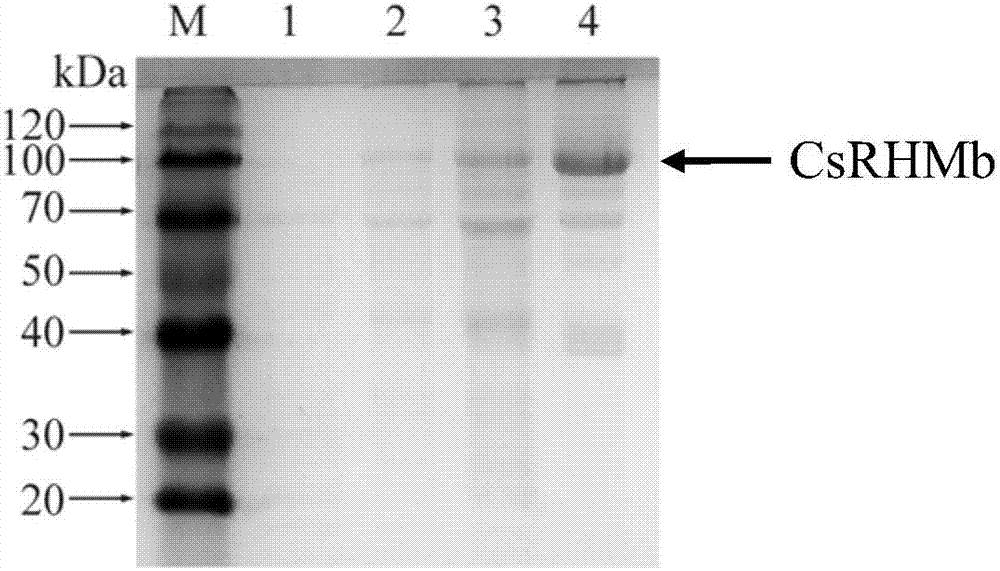
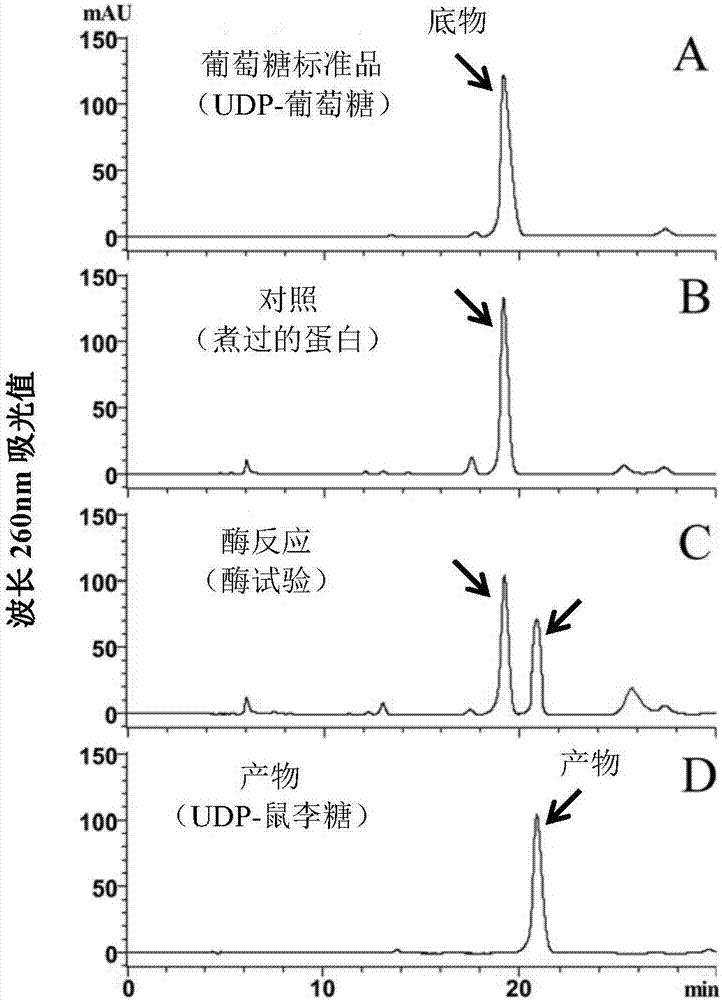
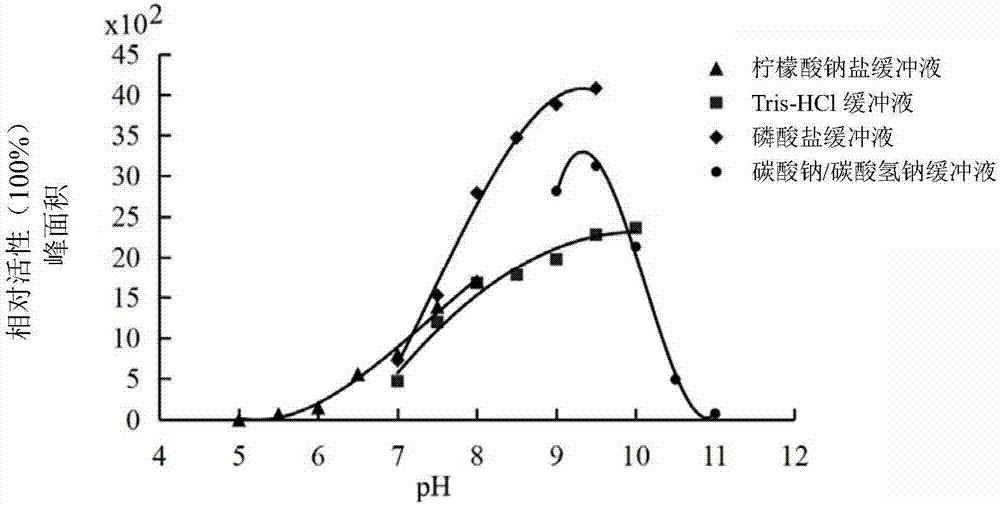
Gene CsRHMb capable of catalyzing biosynthesis of UDP-rhamnose as well as encoded protein of gene CsRHMb and applications of encoded protein
ActiveCN106916838AOptimize the most suitable reaction conditionsPharmacologically activeIsomerasesFermentationBiotechnologyReaction system
The invention provides a gene CsRHMb capable of efficiently catalyzing the biosynthesis of UDP-rhamnose as well as encoded protein and an engineered strain of the gene CsRHMb. The gene is obtained by separating and cloning fresh tea leaves, the encoded protein is in a reaction system taking UDP-glucose as the substrate and in which NADPH exists, and the protein or the recombinant protein expressed by the engineered strain can efficiently convert UDP-glucose to generate UDP-rhamnose. The invention provides the efficient and safe biosynthesis technology of UDP-rhamnose, the optimal reaction condition of enzyme is optimized through the bioengineering method, and a foundation is provided for realizing the commercial production of UDP-rhamnose.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
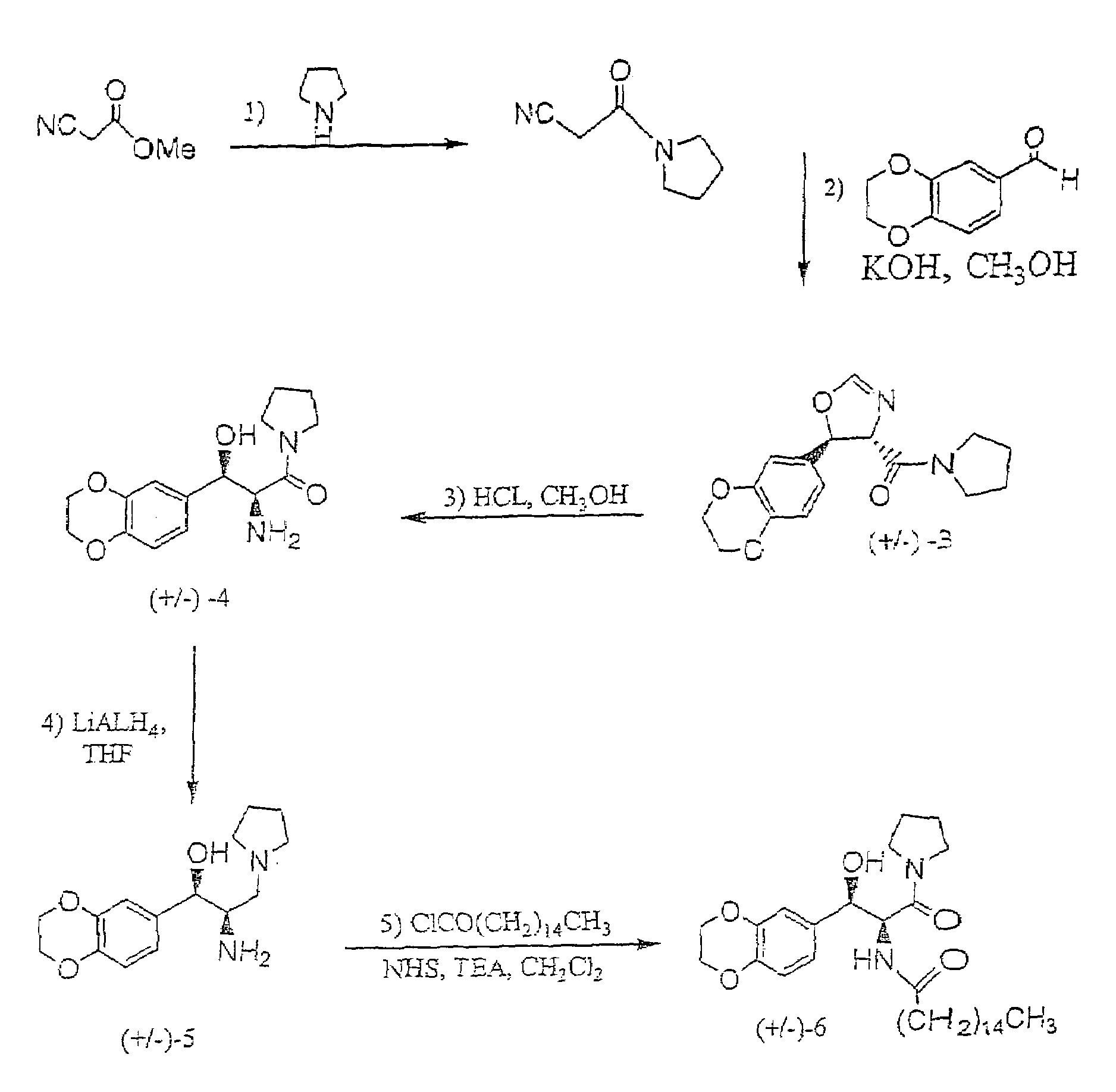
Diastereoselective synthesis of UDP-glucose: N-acylsphingosine glucosyltransferase inhibitors
InactiveUS7041831B2Efficient and highly diastereoselectiveBiocideOrganic chemistryN-Acyl SphingosineGlycosyltransferase inhibitor
Disclosed is a method of preparing a composition comprising a compound represented Structural Formula (I): The method comprises the step of reacting an aldehyde compound R10CHO with an isonitrile compound represented by Structural Formula (II):
Owner:GENZYME CORP
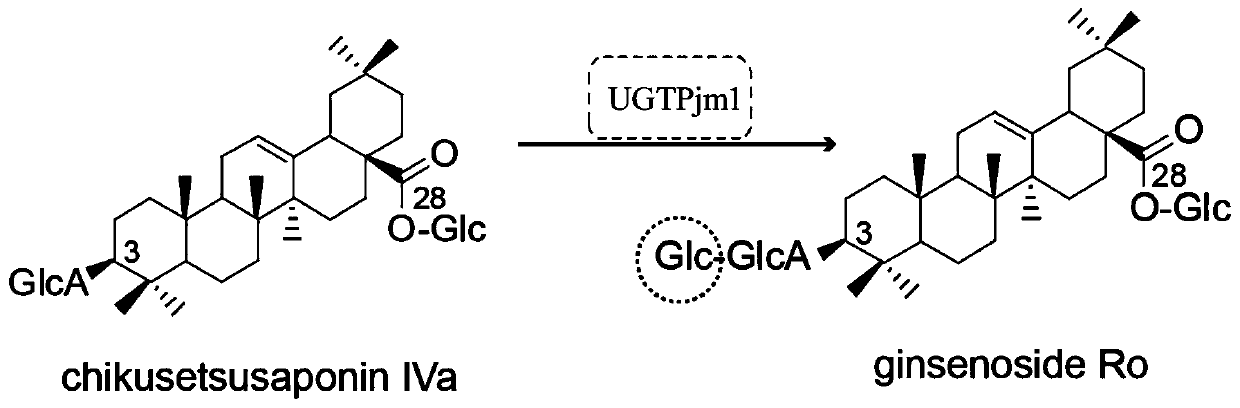
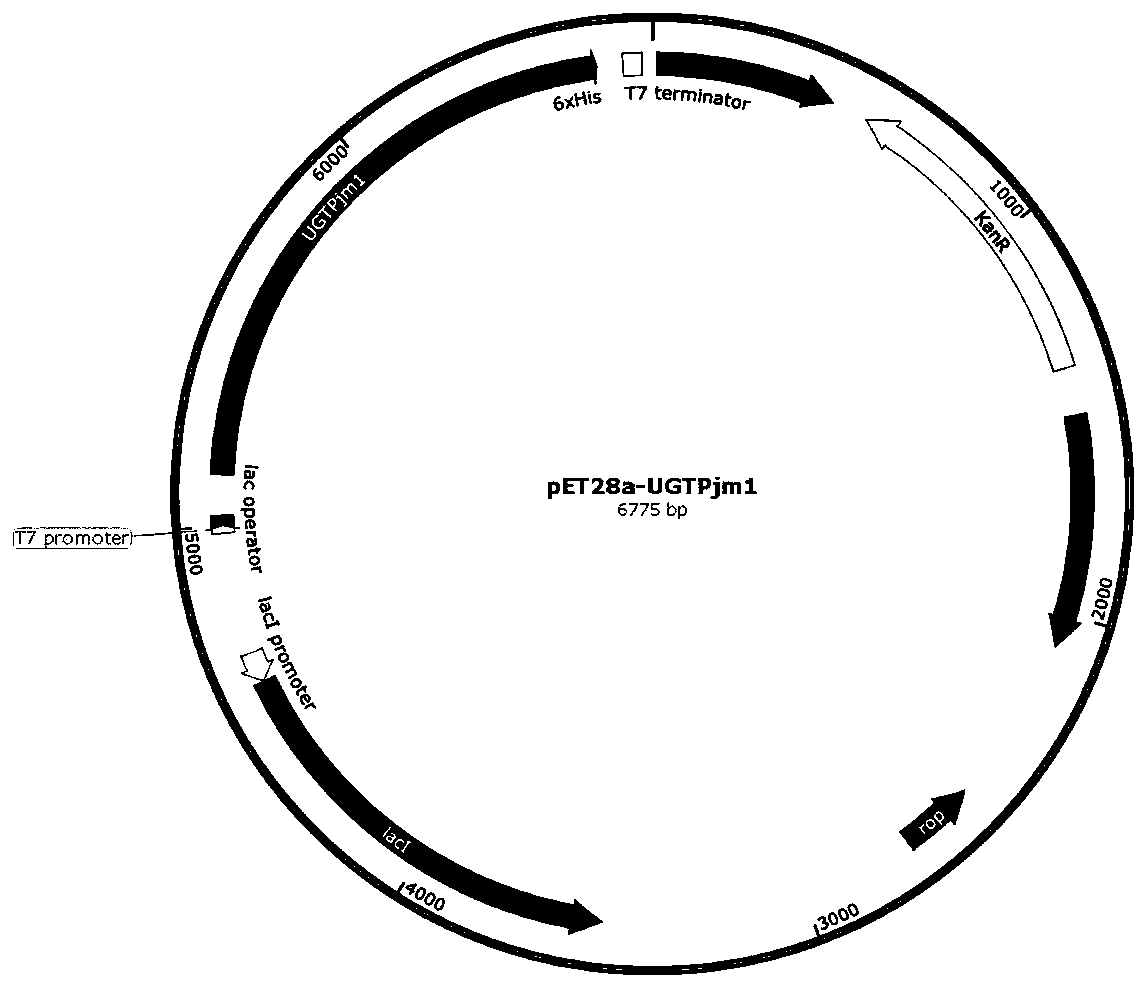
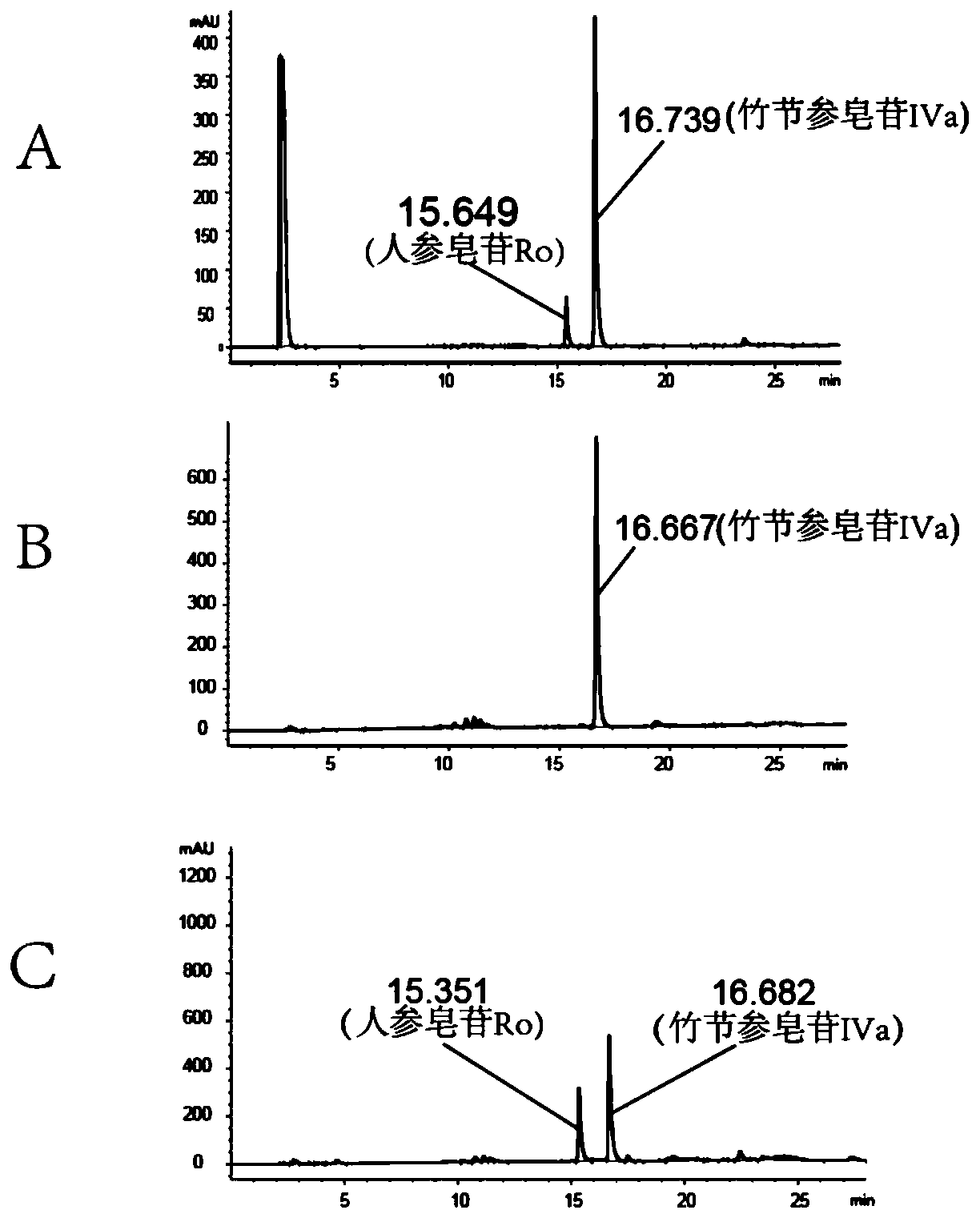
Panax japonicus var. major glycosyl transferase UGTPjm1 gene and application thereof in preparing ginsenoside Ro
The present invention discloses a panax japonicus var. major glycosyl transferase UGTPjm1 gene and an application thereof in preparing ginsenoside Ro. A nucleotide sequence of the panax japonicus var.major glycosyl transferase UGTPjm1 gene is represented by SEQ ID NO:1. Panax japonicus saponin IVa and a glycosyl donor UDP-glucose are used as raw materials and a glucuronic acid group at a C3 position of the panax japonicus saponin IVa is once further glycosylated to form the ginsenoside Ro catalyzed by panax japonicus var. major glycosyl transferase encoded by the panax japonicus var. major glycosyl transferase UGTPjm1 gene. The biosynthesis regulation gene UGTPjm1 of the ginsenoside Ro is first identified and successfully verified. By synthesizing the ginsenoside Ro in vitro, management is more convenient, controllability is strong, demand for raw material planting can be reduced, agricultural land is saved, a production product is single, and separation and purification of the ginsenoside Ro in a late stage are facilitated. The panax japonicus var. major glycosyl transferase UGTPjm1 gene is used as a key gene for the biosynthesis of the ginsenoside Ro and can also be used for breeding studies of panax japonicus var. major and other plants.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
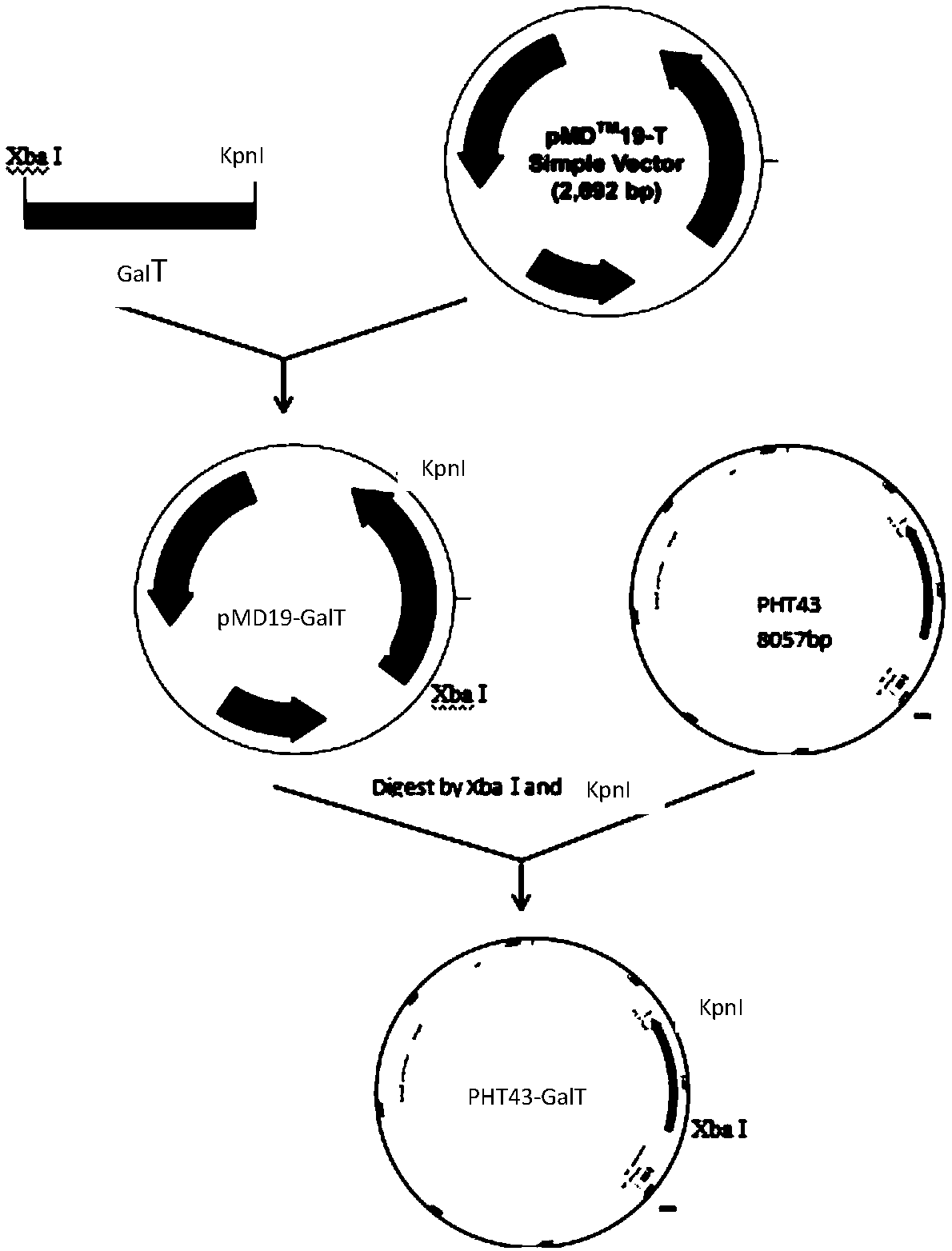
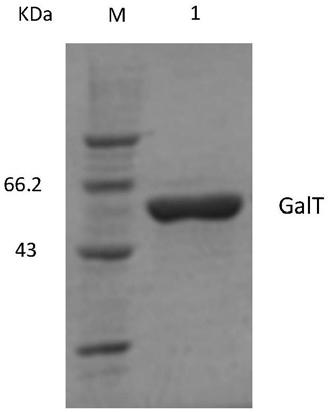
Method for efficient expression preparation of UDP-glucose-hexose-1-phosphate uridyltransferase
ActiveCN109295087AStrong ability to secrete proteinEasy to trainBacteriaTransferasesBiotechnologyFood industry
The invention relates to a method for efficient expression preparation of UDP-glucose-hexose-1-phosphate uridyltransferase. According to the method, a recombinant expression vector is constructed fromUDP-glucose-hexose-1-phosphate uridyltransferase (GalT) gene and Bacillus subtilis by using a vector; the recombinant expression vector is transformed into Bacillus subtilis to construct a recombinant engineered strain; the recombinant engineering strain is subjected to induced culture in a liquid culture medium; and the obtained bacterial liquid is subjected to centrifugation, and the supernatant is taken. According to the present invention, the method has advantages of high yield of UDP-glucose-hexose-1-phosphate uridyltransferase, pure protein, easy recovery and purification and simple production operation, provides the convenience in the industrial large-scale production of GalT, further has advantages of yield improving, time saving, labor saving and cost saving, particularly provides the safety assurance in the application of the enzyme in the food industry, and has great significance.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
Kelp uridine diphosphate (UDP)-glucose pyrophosphorylase (UGPase) gene
ActiveCN103710365AActive functionIn-depth understanding of the synthesis mechanismHydrolasesGenetic engineeringSucroseADAMTS Proteins
The invention relates to the field of a genetic engineering technology, and particularly relates to a kelp uridine diphosphate (UDP)-glucose pyrophosphorylase (UGPase) gene. The nucleotide sequence of the gene and the amino acid sequence of the coding protein are SEQ ID No.1 and SEQ ID No.2 respectively. According to the invention, the gene sequence is cloned through the gene cloning technology, and a prokaryotic expression vector is established; and enzyme activity detection on recombinant protein proves that the gene has the function of catalyzing UDP-glucose and pyrophosphoric acid to form glucose-1-phosphoric acid and UTP and belongs to a key enzyme coding gene of the synthesis path of agar-agar, starch, cellulose, trehalose, sucrose and the like. The gene has an important application value in increasing the content of economic components including algae agar-agar, starch, cellulose, trehalose, sucrose and the like.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Recombinant bacillus subtilis for synthesizing lacto-N-neotetraose based on balanced UDP-sugar supply and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN109825465AIncrease productionEfficient synthesisBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGlutamineTransferase Gene
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing lacto-N-neotetraose based on balanced UDP-sugar supply. Recombinant bacillus subtilis is obtained by integrating two beta-1,4-galactosyltransferases,integrating a glucose-6-phosphate isomerase gene, a glutamine-fructose-6-phosphate aminotransferase gene, a UTP-glucose-1-phosphate uridyl transferase gene and a UDP-glucose-epimerase gene, knocking out a UDP-glucose 6-dehydrogenase gene and exogenously expressing a beta-1,3-N-glucosamine transferase gene on a genome of a host bacterium bacillus subtilis 168 delta amyE: P43-lacY, P43-lgtB and PxylA-comK. The recombinant bacillus subtilis synthesizes the lacto-N-neotetraose, and the yield on a shake flask can reach 1800 mg / L, and the efficient synthesis of the lacto-N-tetraose is achieved.
Owner:BRIGHT DAIRY & FOOD
Biosynthesis method of uridine diphosphate glucose and uridine diphosphate glucuronic acid
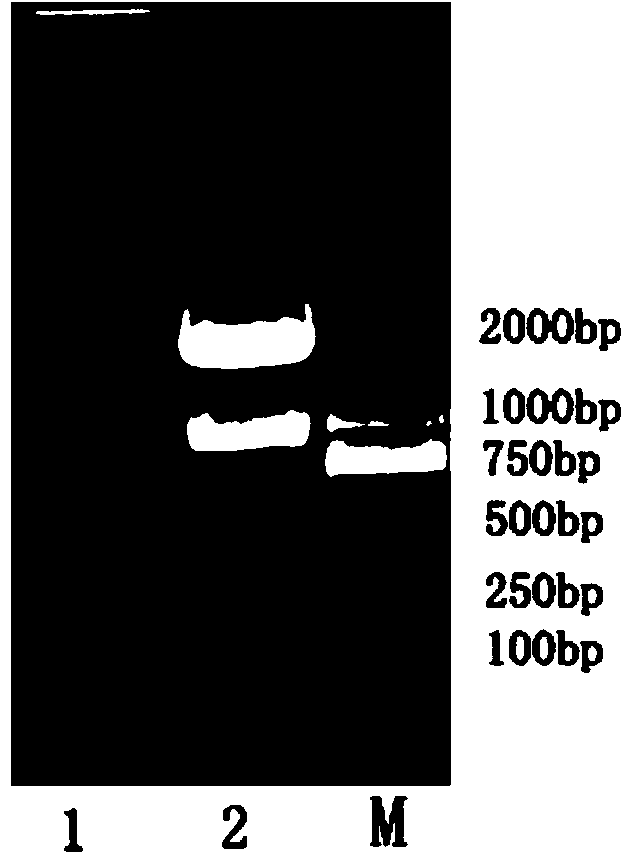
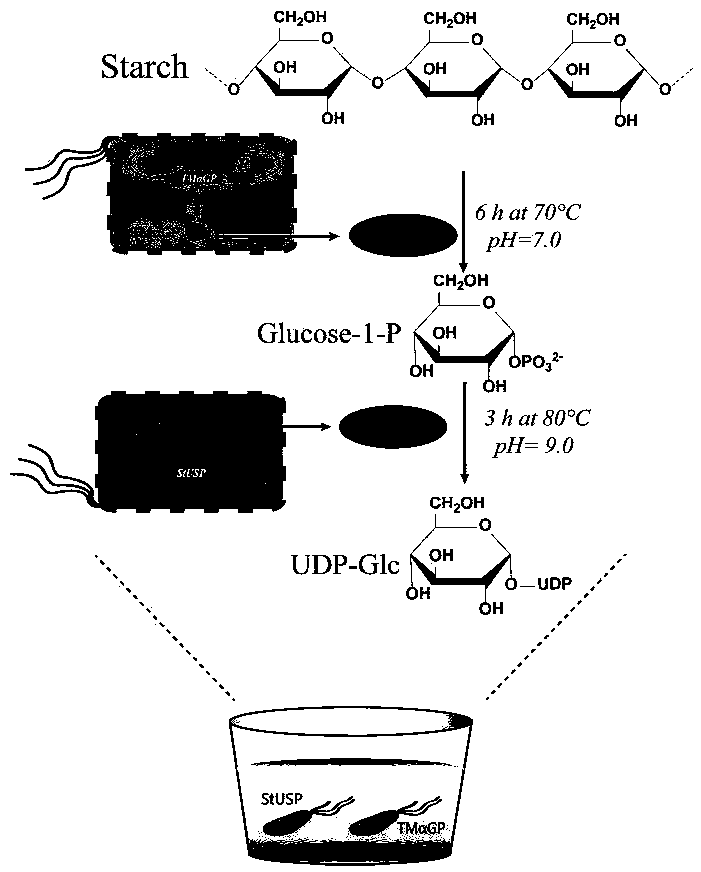
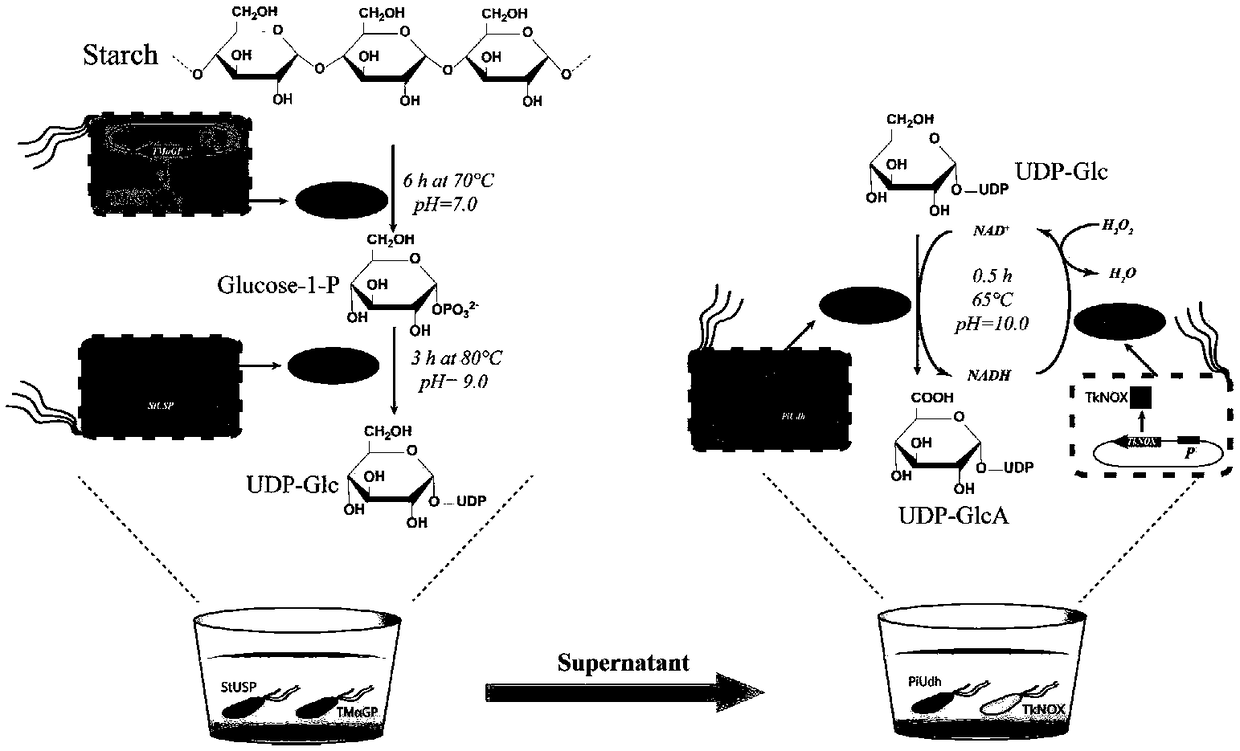
ActiveCN109371079AEasy to transformSynthetic interferenceMicroorganism based processesFermentationEscherichia coliUridine diphosphate N-acetylglucosamine
The invention discloses a biosynthesis method of uridine diphosphate glucose and uridine diphosphate glucuronic acid. The method includes adopting soluble starch as a main initial raw material, conducting recombinant expression on high-temperature alpha-glucan phosphorylase and high-temperature sugar-1-nucloside phosphorylase in escherichia coli respectively, and utilizing high-temperature whole cell catalysis of expressed bacteria to synthesize uridine diphosphate glucose; on this basis, conducting recombinant expression on high temperature uridine diphosphate glucose dehydrogenase in the escherichia coli, coupling a synthesis system of the uridine diphosphate glucose to conduct high temperature whole cell catalysis to synthesize the uridine diphosphate glucuronic acid, and introducing awhole cell catalysis system of high temperature NADH oxidase into the synthesis system of the uridine diphosphate glucuronic acid to form a high temperature NAD+ / NADH circulating system to reduce theuse of coenzyme NAD+. The high temperature whole cell catalysis method is utilized to successfully avoid the interference of various metabolic pathways of the bacteria in the synthesis process and reduce the purification difficulty.
Owner:安徽禾庚生物技术有限公司
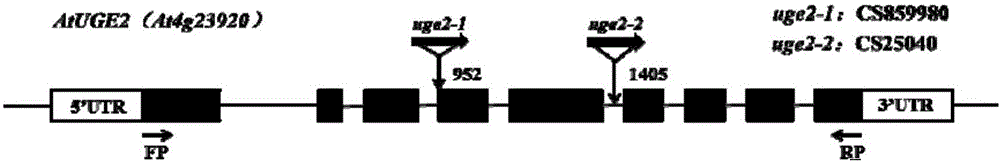
Application of arabidopsis thaliana gene At-UGE2, overexpression mutant strain and deletion mutant strain in plant character adjustment
The invention provides application of arabidopsis thaliana UDP-glucose 4-isomerase gene At-UGE2, an overexpression mutant strain 35S:UGE2 and a deletion mutant strain uge2 in adjustment of plant yield correlated characters, adversity resistance characters and the like. The function of biological synthesis and conversion of the UDP-glucose and UDP-galactose, which are catalyzed by UDP-glucose 4-isomerase, in adjustment of plant growth and development as well as adversity stress response is disclosed, a high-quality gene is provided for plant variety improvement, a new method and a new mechanism for improving plant yield characters and adversity resistance abilities are explained, and important economic significance and application value are achieved.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF BOTANY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for synthesizing soybean oligosaccharides through biological catalysis
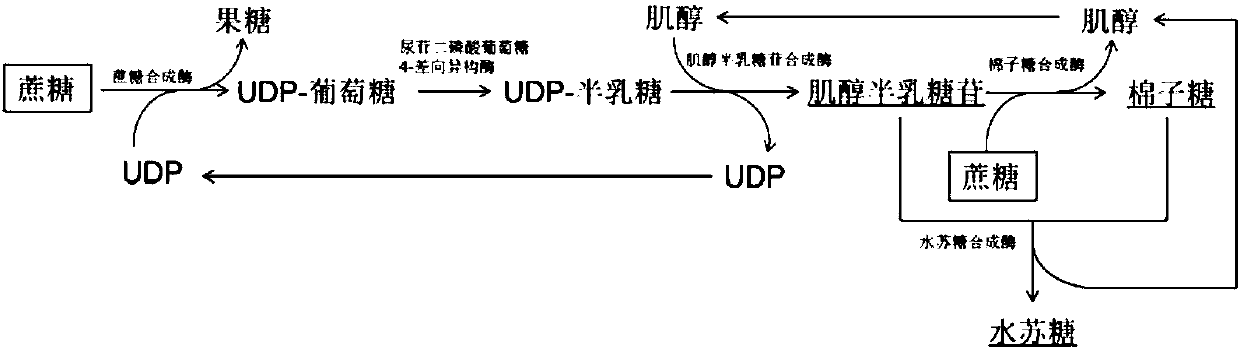
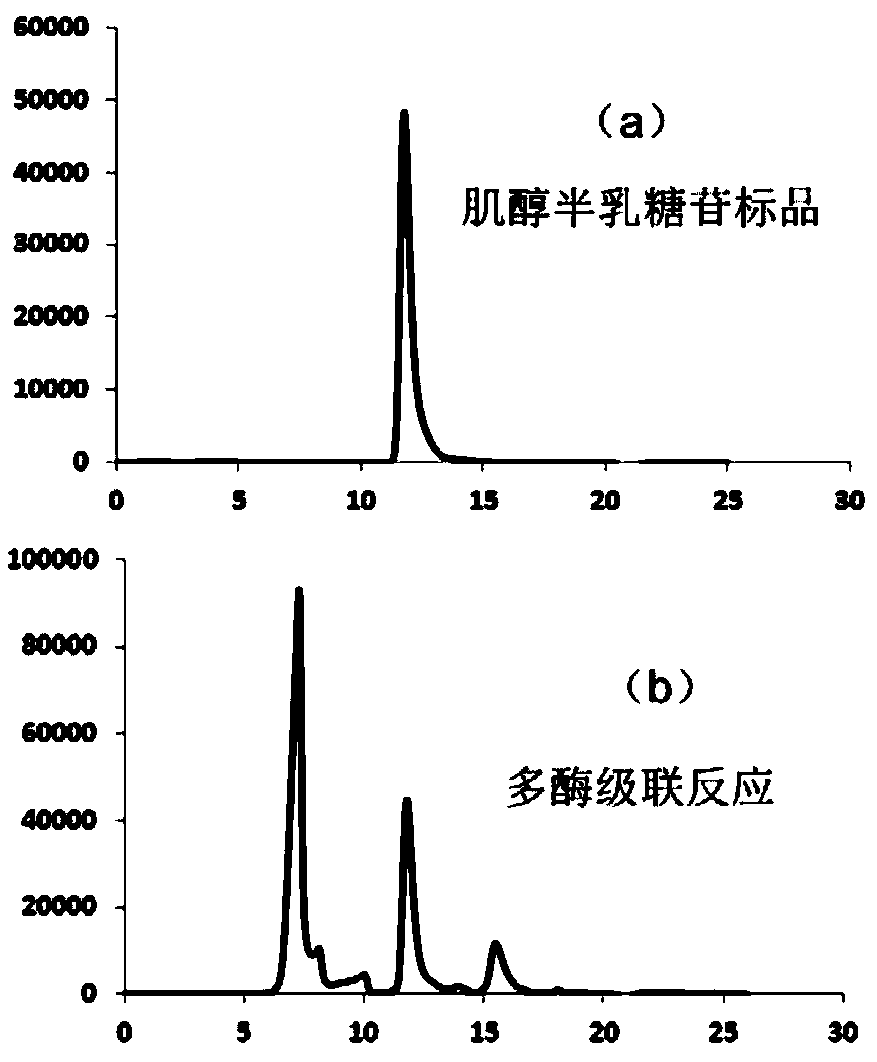
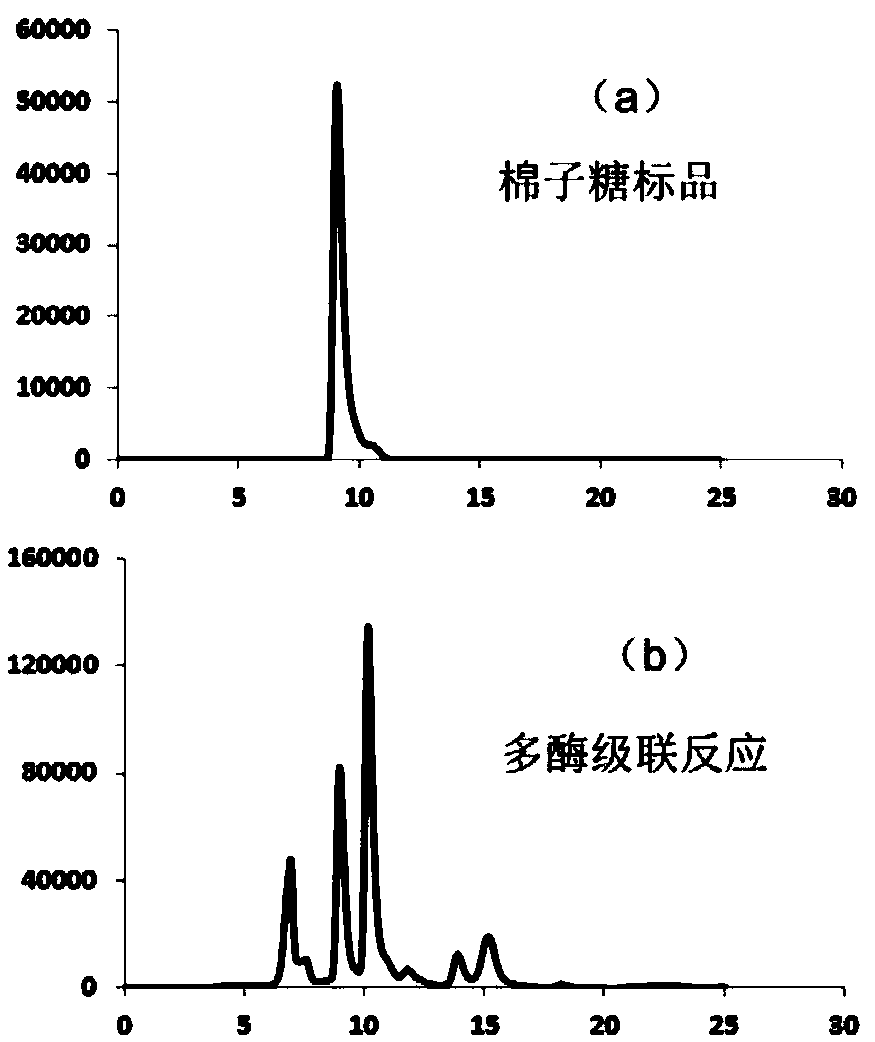
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing soybean oligosaccharides through biological catalysis. The method has the beneficial effects that that through establishing an in-vitro multi-enzyme cascade reaction system composed of sucrose synthetase, uridine diphosphate glucose 4-differential isomerase, inositol galactoside synthase, raffinose synthase and threonose synthase, sucrose is takenas a substrate to synthesize a single component or a mixed component in inositol galactoside, raffinose and threonose; the method realizes the recycling conversion of uridine diphosphate and inositol,and a crude enzyme solution added in the system contains a small amount of uridine diphosphate, so that the expensive uridine diphosphate can be avoided; the inositol galactoside yield reaches 50 g / L, the conversion rate is 70 percent, the raffinose yield reaches 20 g / L, the threonose yield reaches 10 g / L, and the obtained inositol galactoside, raffinose and threonose can be used in the fields offood, medicines and the like; the method disclosed by the invention is of great significance in the utilization of high attachment values of the sucrose and a biomass rich in the sucrose.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
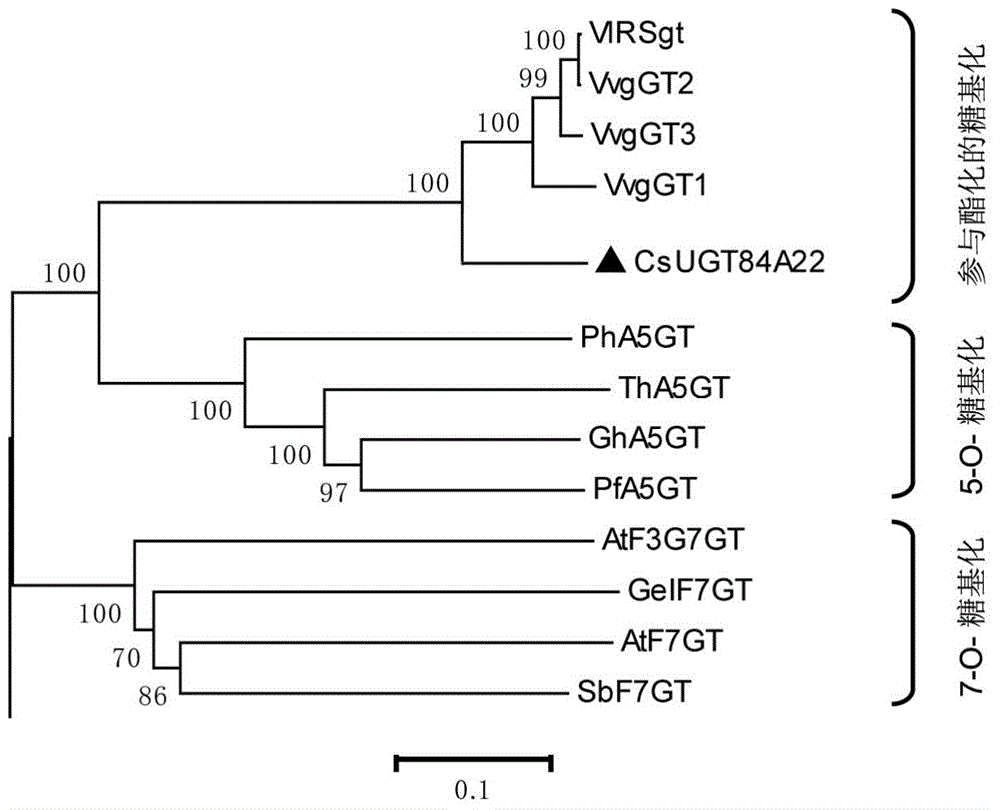
Galloyl glucosyltransferase CsUGT84A22 gene and encoded protein thereof and application
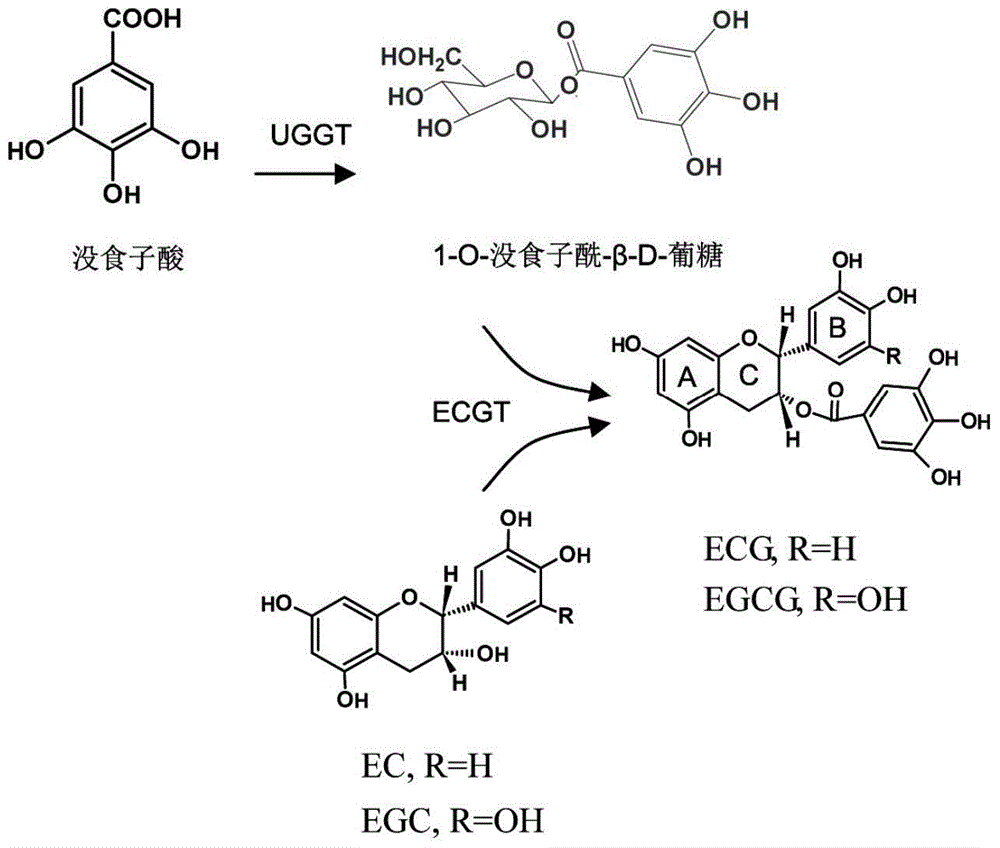
The invention discloses a galloyl glucosyltransferase CsUGT84A22 gene with a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: 1. An encoded protein of the galloyl glucosyltransferase CsUGT84A22 gene is in an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: 2. Compared with the prior art, the galloyl glucosyltransferase CsUGT84A22 gene has the advantages that the galloyl glucosyltransferase CsUGT84A22 gene for formation of uridine diphosphate glucose related to 1-O-galloyl-beta-D-glucoside are functionally cloned and verified for the first time, recombinant proteins, transgenic engineering bacteria and recombinant plasmids containing the CsUGT84A22 gene are provided, and mass synthesis of 1-O-galloyl-beta-D-glucoside is realized by means of bioengineering to lay the foundation for researches on biosynthesis regulation of ester catechins.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Improvement of Astragaloside content by endogenous gene overexpression technology
InactiveCN1699566AImprove pharmacological activityImprove survival rateOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationBiotechnologyUridine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase
The invention discloses an improvement of Astragaloside content by endogenous gene overexpression technology, wherein the two metabolism reaction coupled key enzyme genes of the polysaccharide metabolic pathway, i.e., ugp gene (uridine diphosphate glucose phosphorylase gene) and gbss gene (adenosine diphosphate glucose glycoside transferase gene) are modified in vitro, so as to reinforce the enhanced expression regulation element and construct intermediate carrier, and electrical perforation method is employed to transfer the expression intermediate carrier pBI-UG into Agrobacterium rhizogenes LBA-9402, thus obtaining polysaccharide synthesize double gene Radix Astragali hairyroot.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV OF T C M
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com