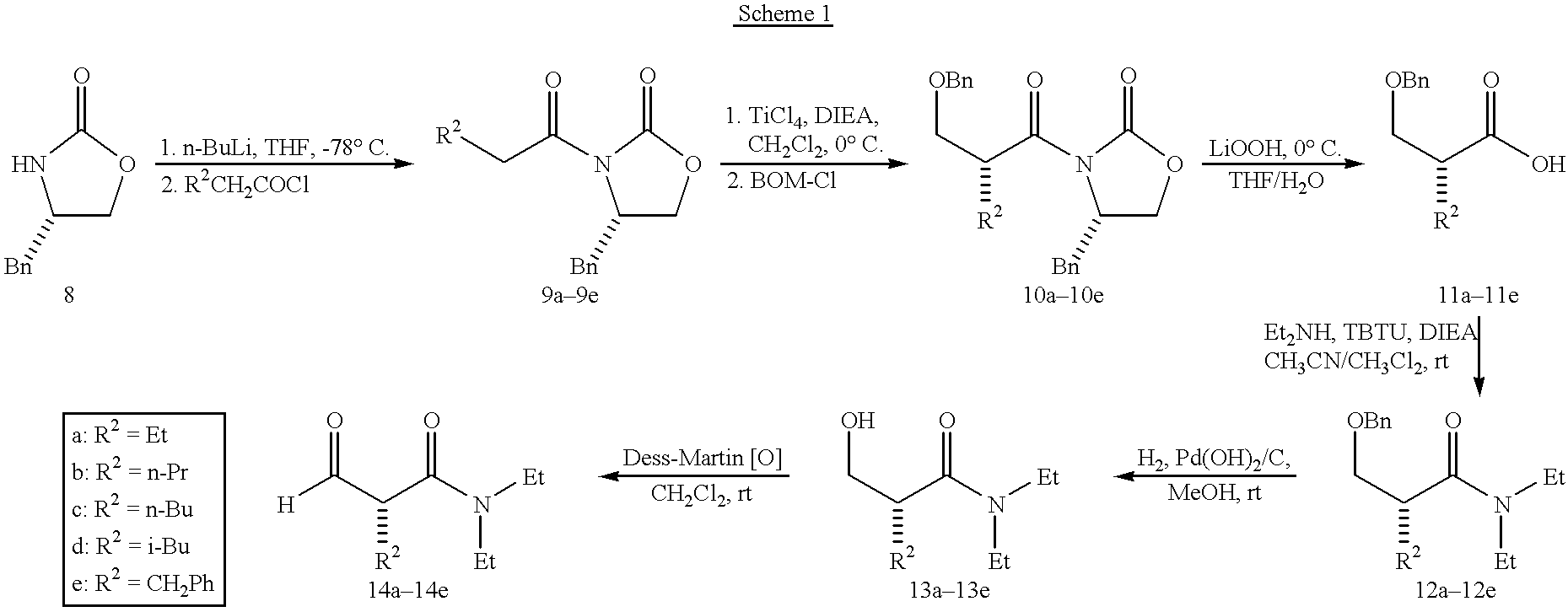
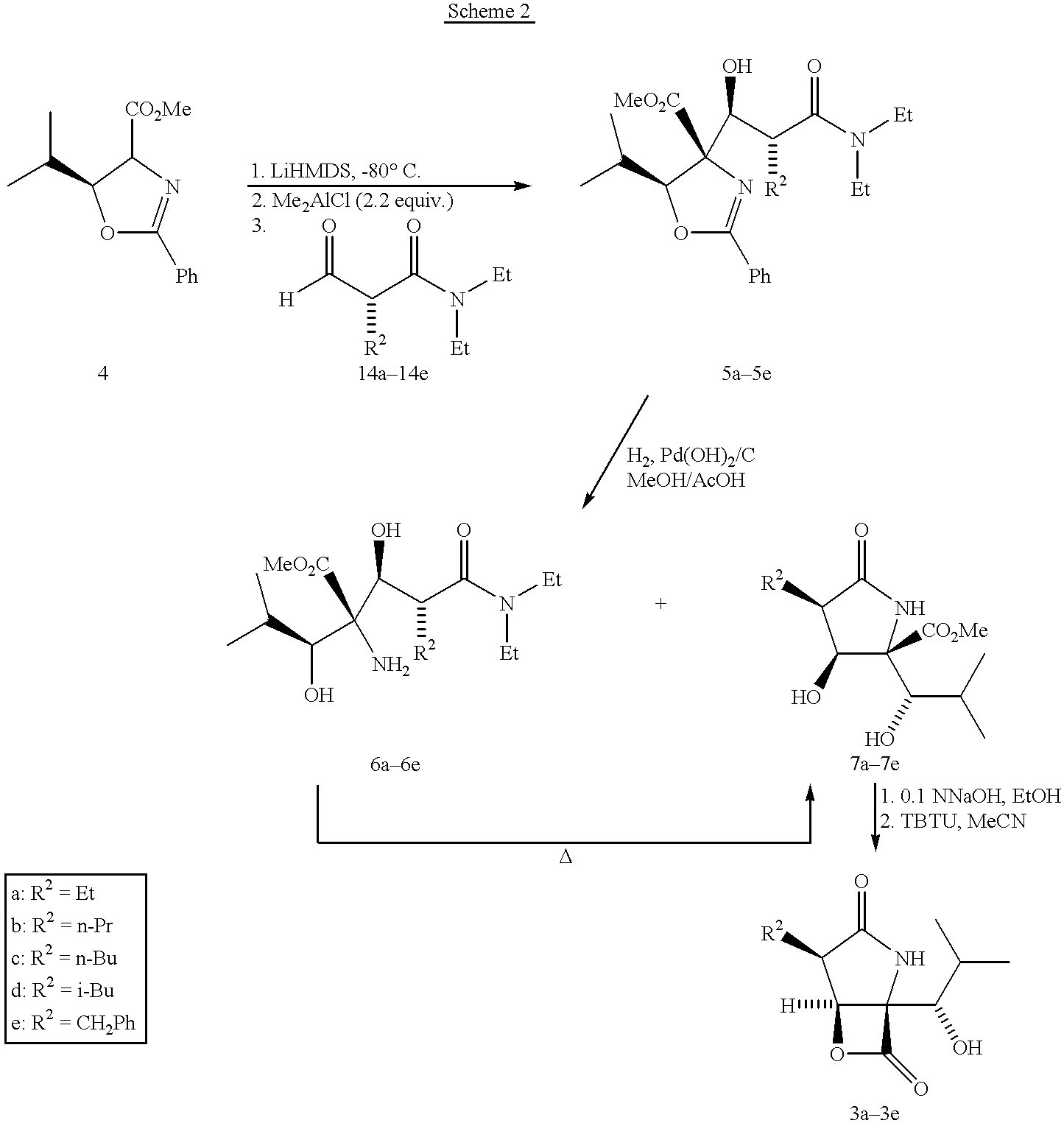
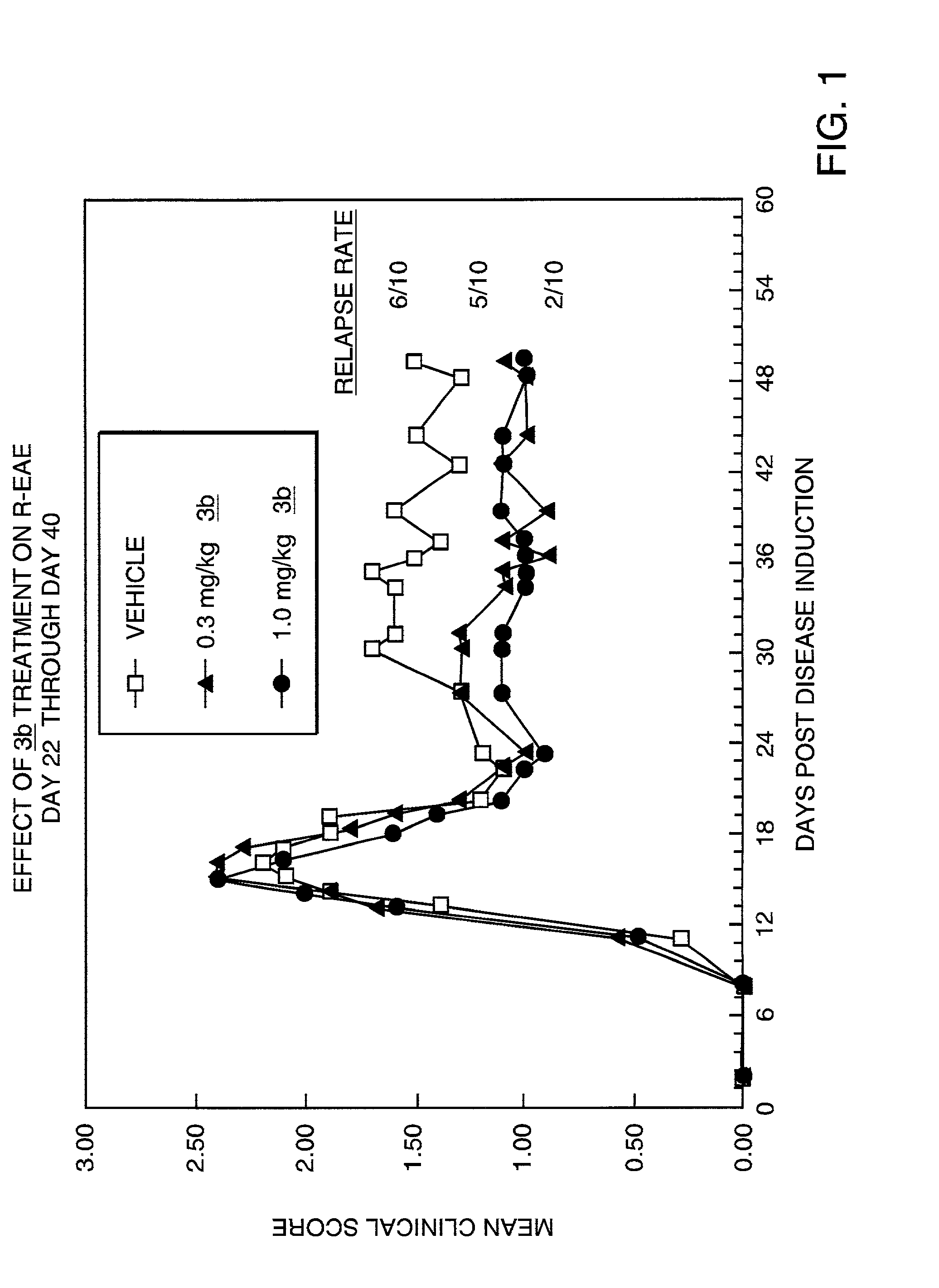
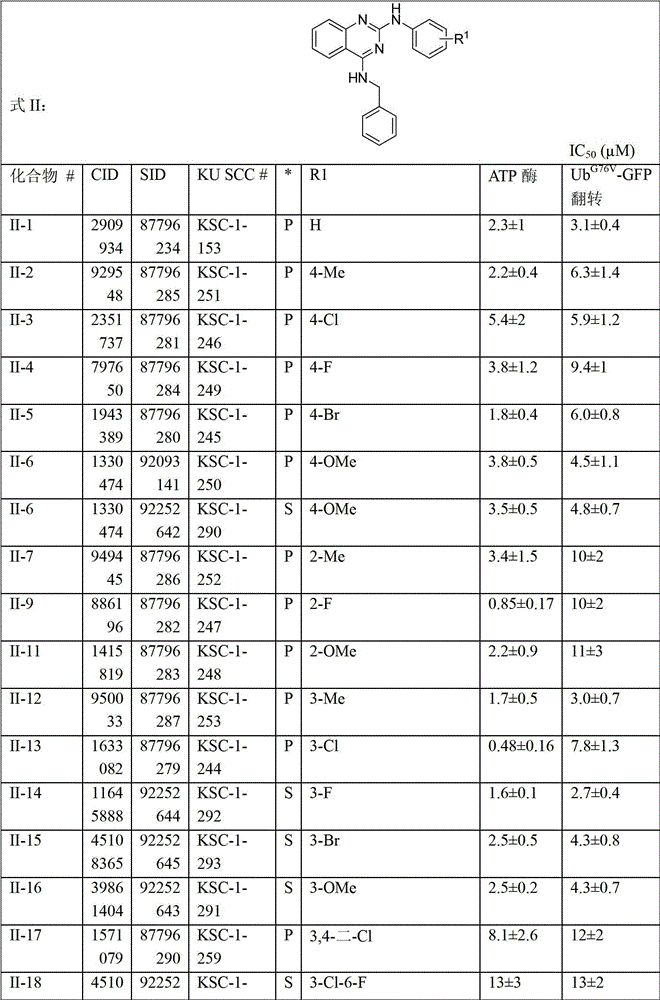
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
54 results about "Ubiquitin proteasome" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
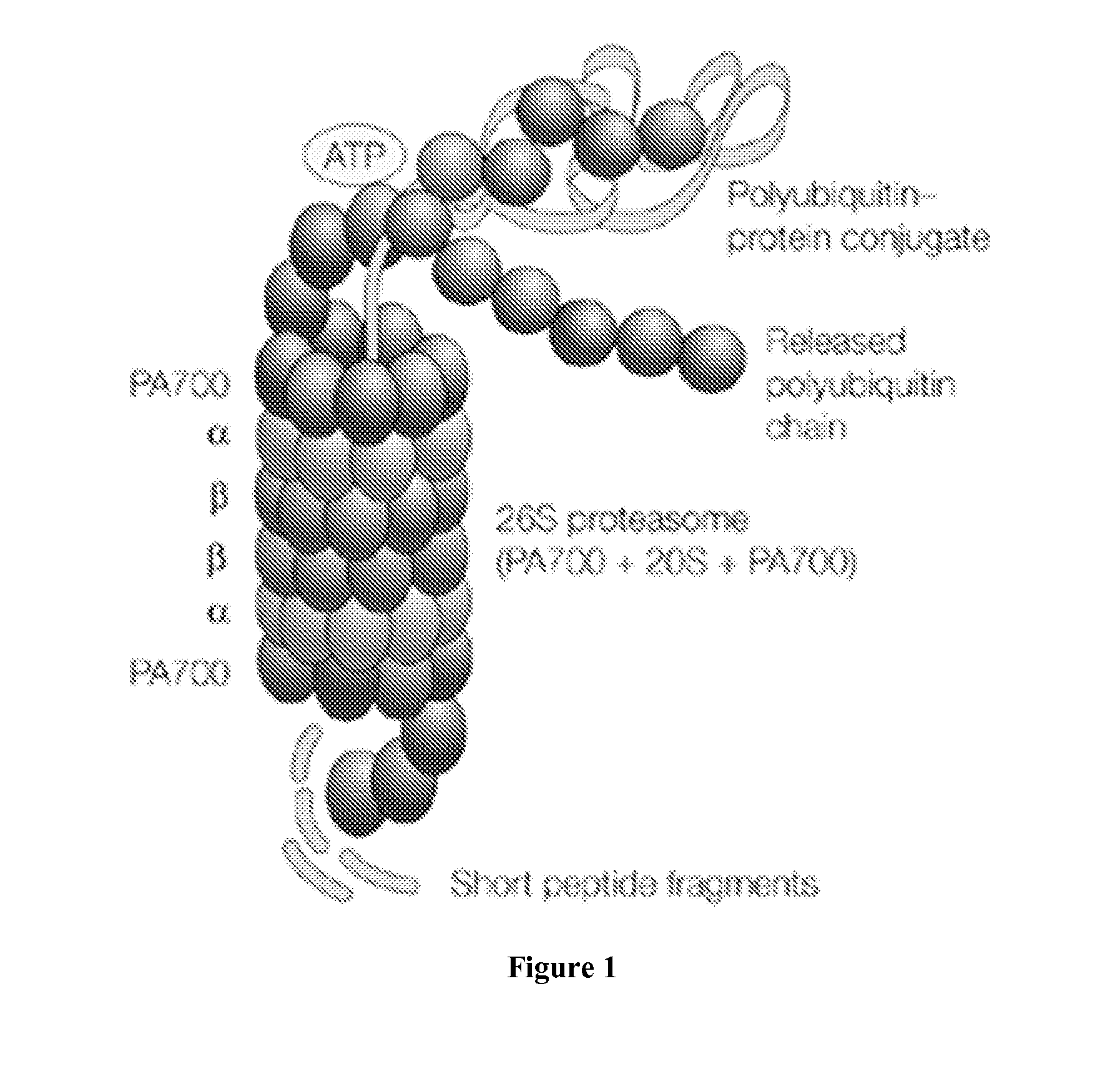
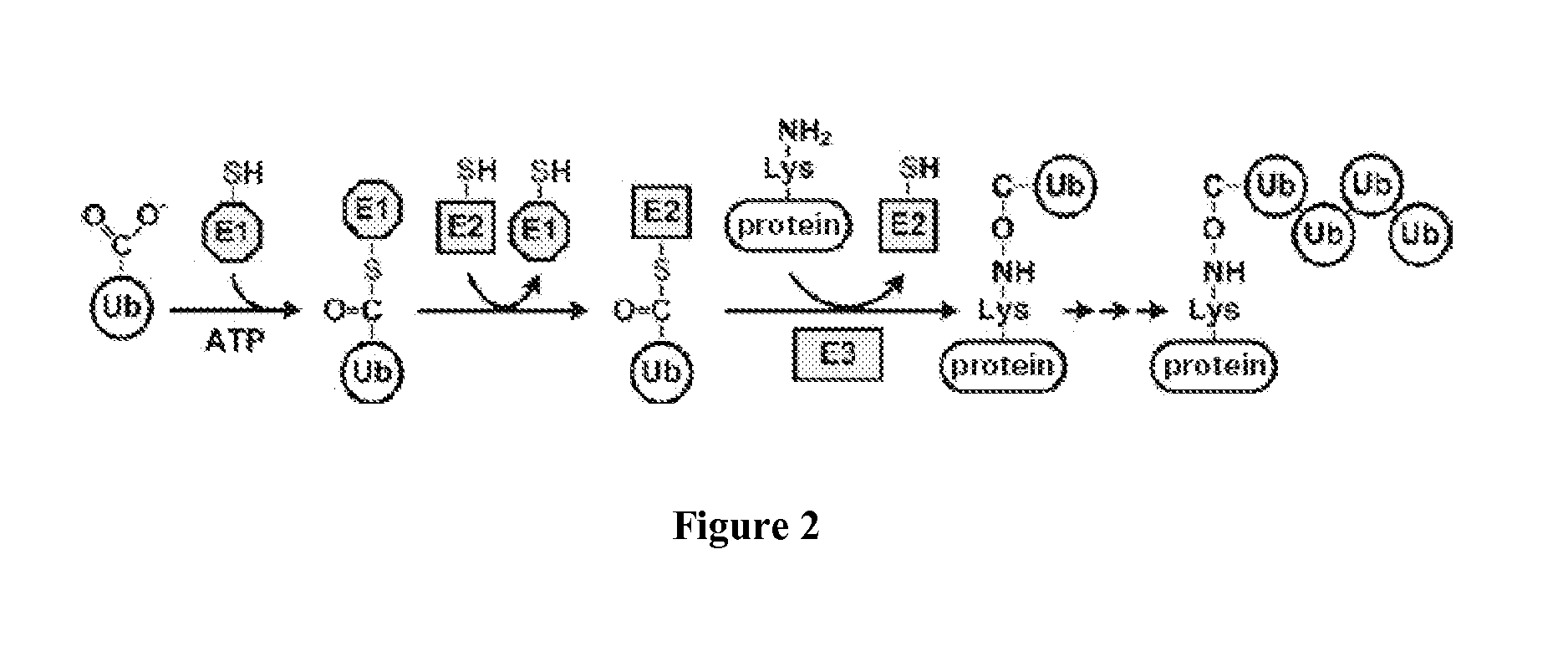
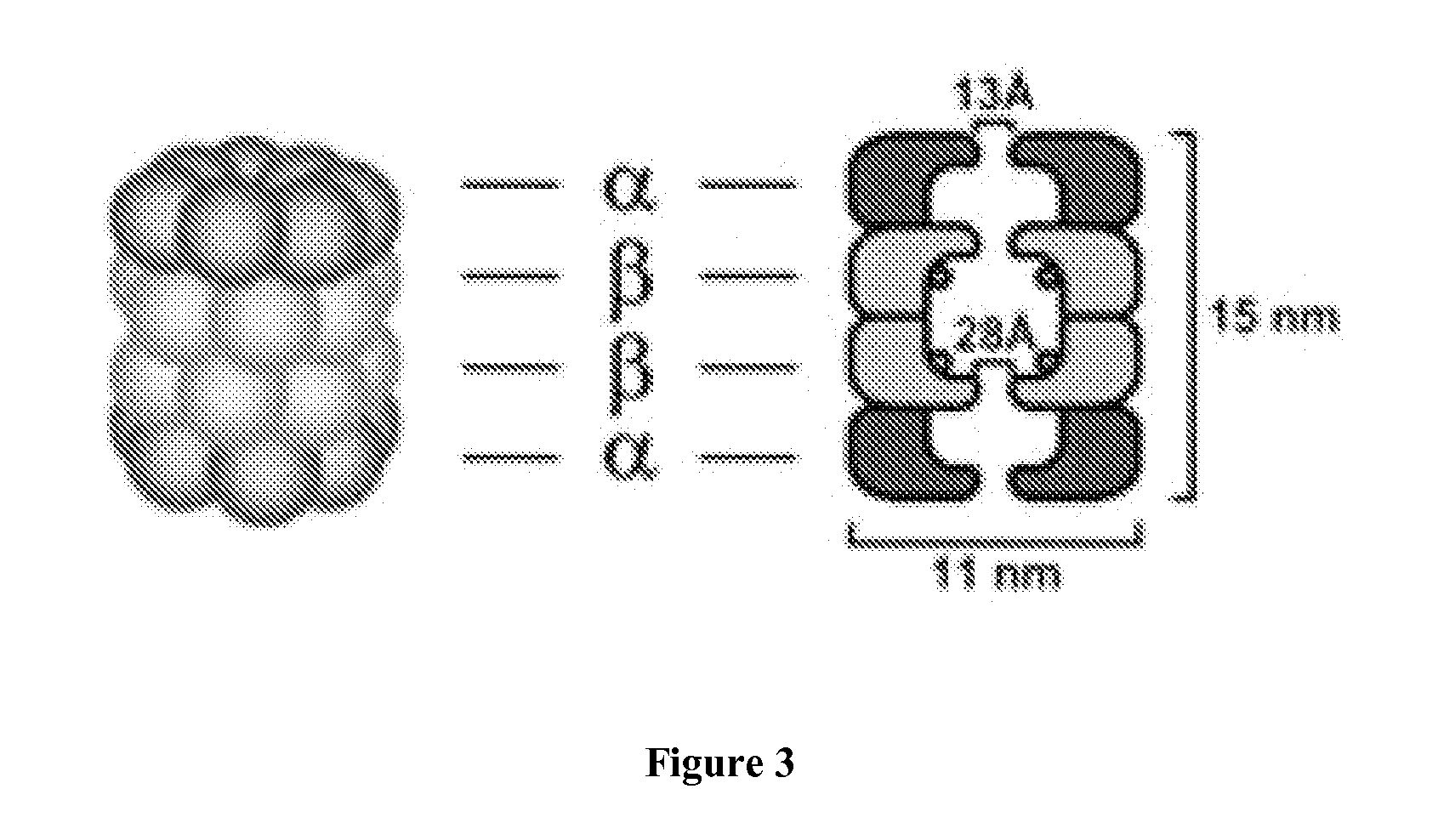
The Ubiquitin Proteasome Pathway (UPP) The Ubiquitin Proteasome Pathway (UPP) is the principal mechanism for protein catabolism in the mammalian cytosol and nucleus. The highly regulated UPP affects a wide variety of cellular processes and substrates and defects in the system can result in the pathogenesis of several important human diseases.
Treatment of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases
InactiveUS20010051654A1Low rate and severityEffective treatmentBiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsDiseaseGlucocorticoid
This invention is directed to the treatment of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases by administering proteasome inhibitors, ubiquitin pathway inhibitors, agents that interfere with the activation of NF-kappaB via the ubiquitin proteasome pathway, or mixtures thereof. The invention is further directed to the treatment of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases by administering an effective combination of a glucocorticoid and a proteasome inhibitor, ubiquitin pathway inhibitor, agent that interferes with the activation of NF-kappaB via the ubiquitin proteasome pathway, or mixture thereof. Pharmaceutical compositions comprising a combination of a glucocorticoid and a proteasome inhibitor, ubiquitin pathway inhibitor, agent that interferes with the activation of NF-kappaB via the ubiquitin proteasome pathway, or mixture thereof are also contemplated within the scope of the invention.
Owner:ELLIOTT PETER J +2
Inhibition of proteasomes to prevent restenosis
InactiveUS20040116329A1Peptide/protein ingredientsBoron compound active ingredientsSmooth musclePercent Diameter Stenosis
Restenosis of blood vessels after angioplasty is achieved by preventing of cell proliferation, particularly of smooth muscle cells, in blood vessel walls by inhibiting the ubiquitin-proteasome protein degradation pathway. The inhibition is accomplished by administering to the cells in the blood vessel walls a compound, e.g., a protein or small molecule, capable of inhibiting the ubiquitin-proteasome protein degradation pathway. The inhibiting compound is preferably administered by coating the compound on a stent and implanting the stent in the blood vessel after angioplasty.
Owner:MEDSTAR RES INST
Transcriptional repression leading to parkinson's disease
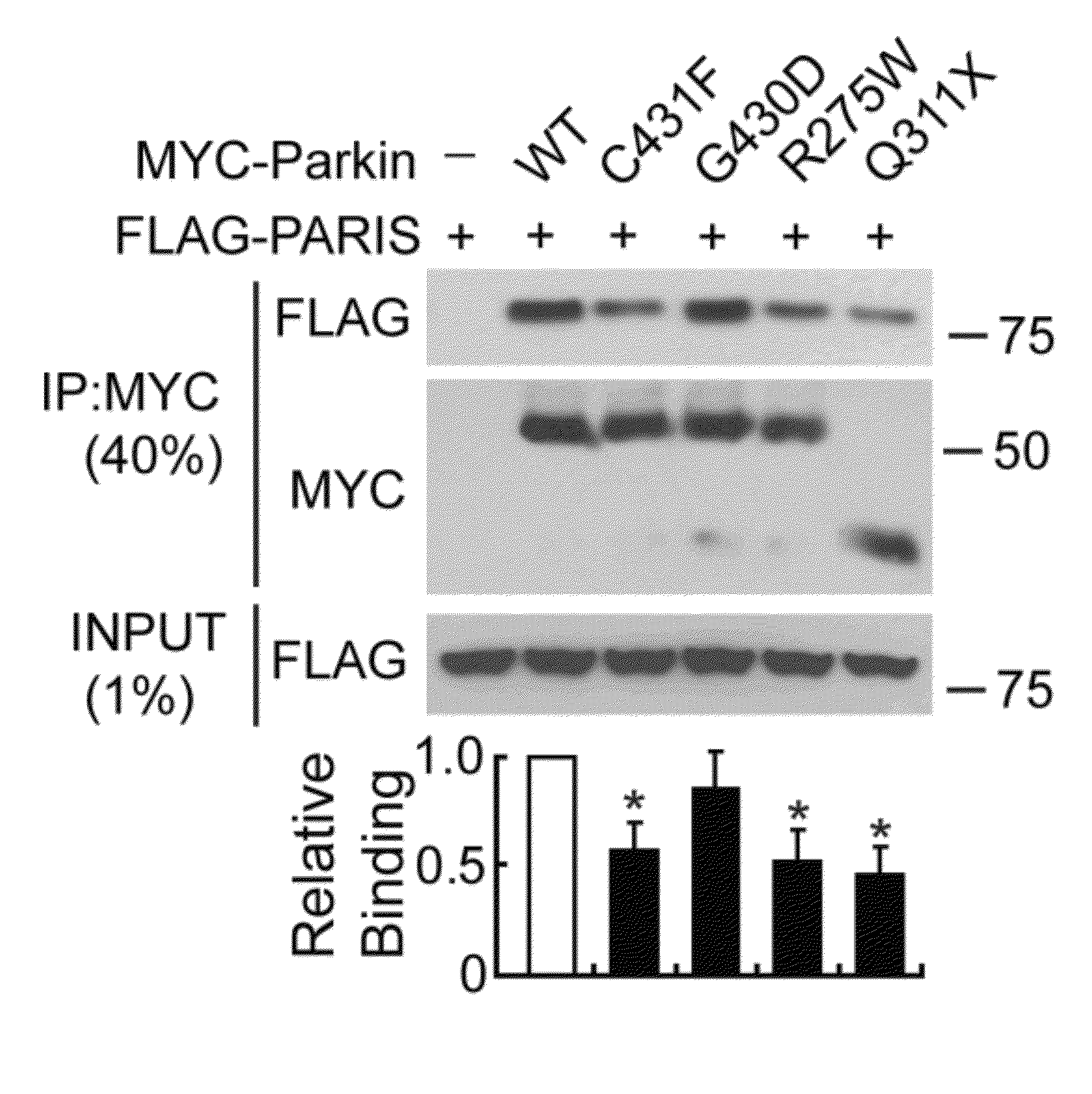
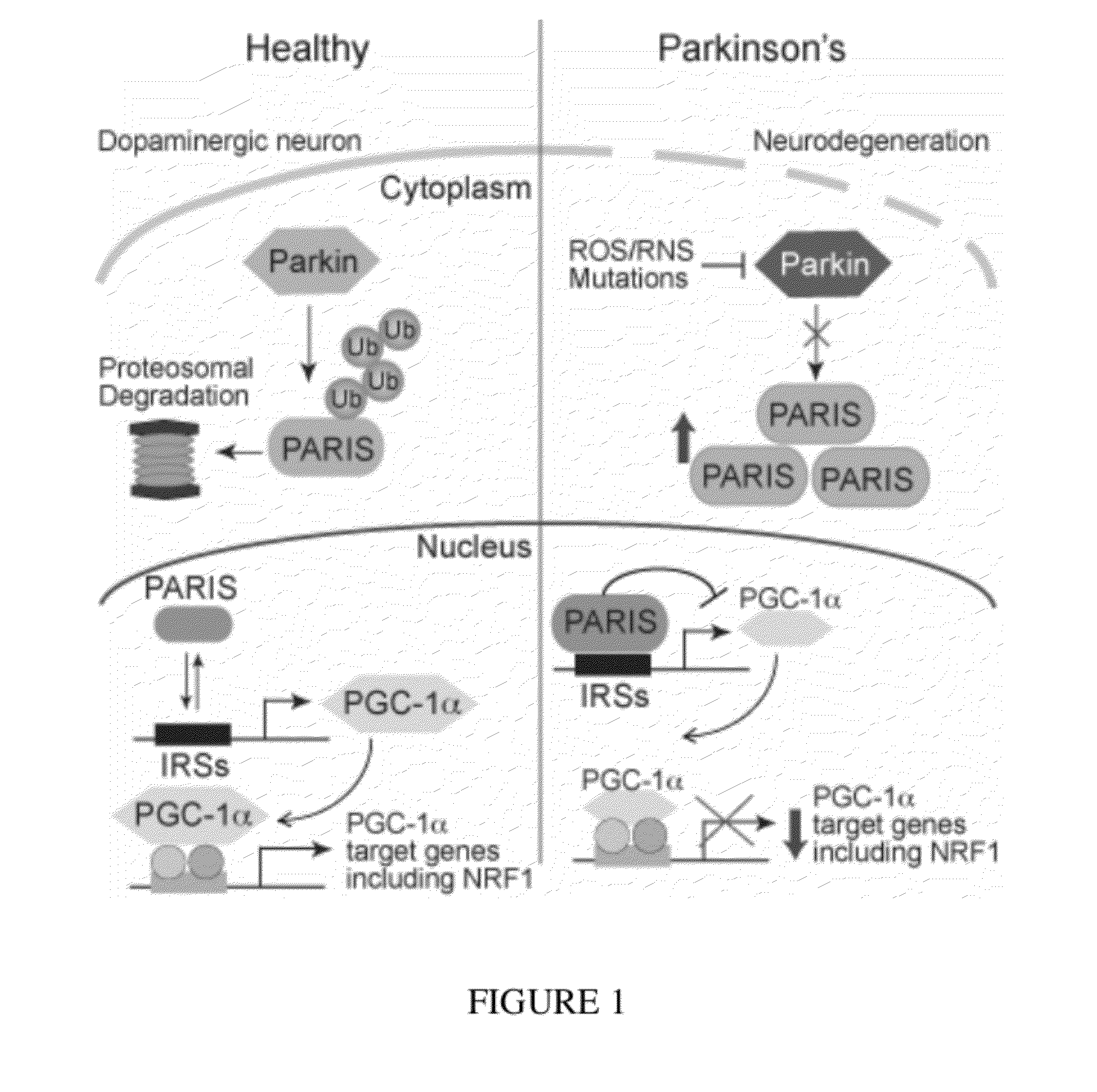
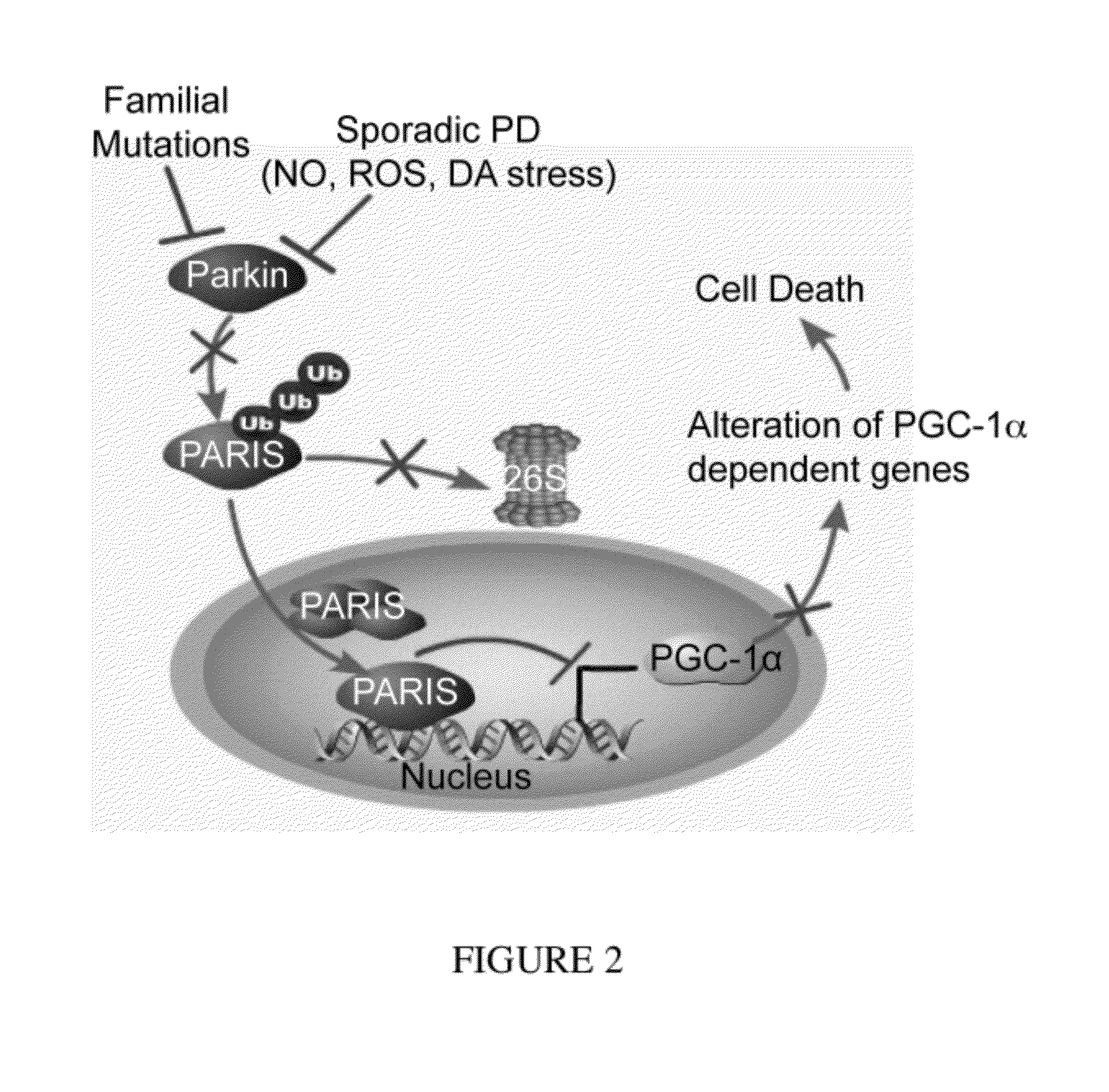
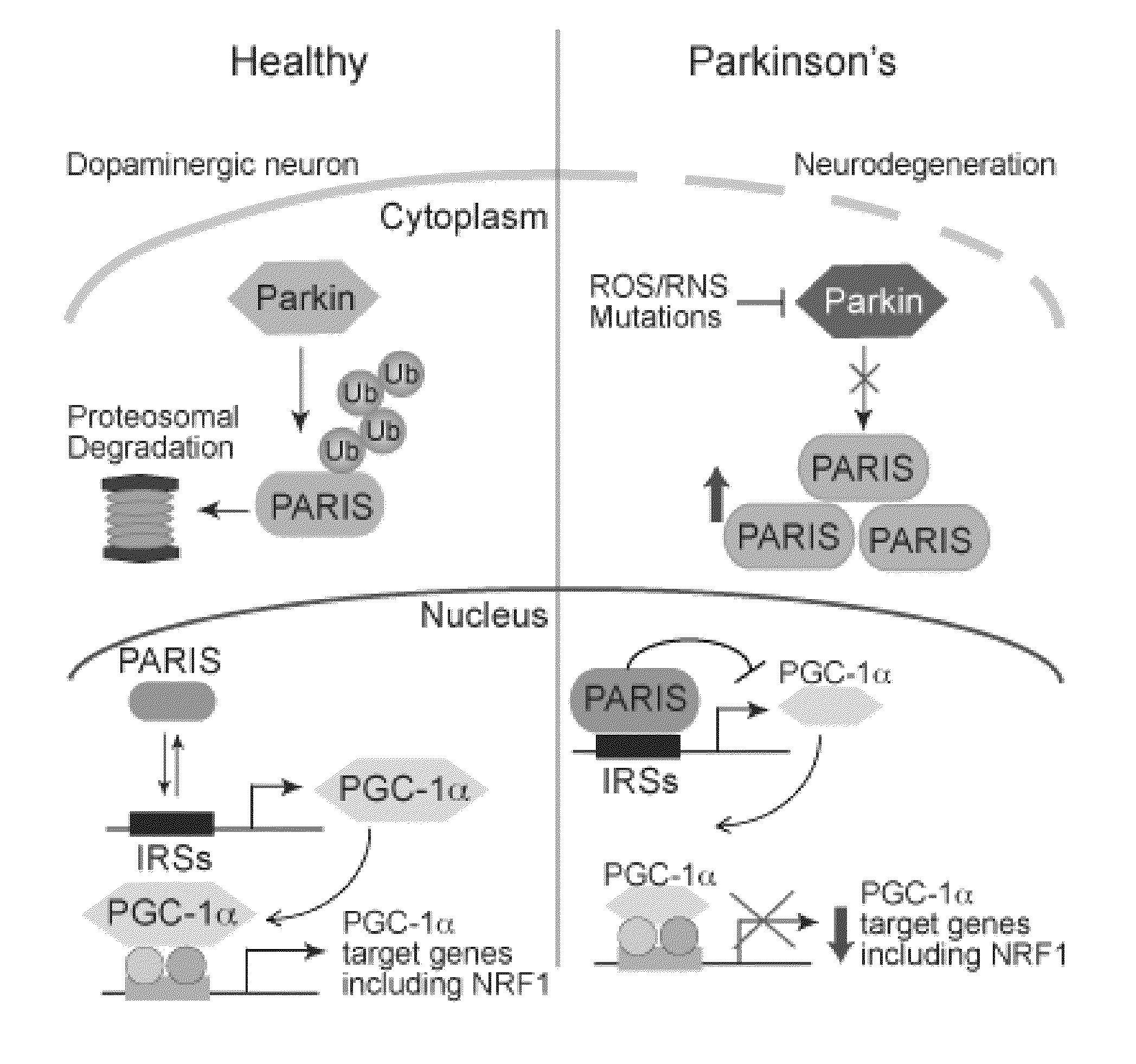
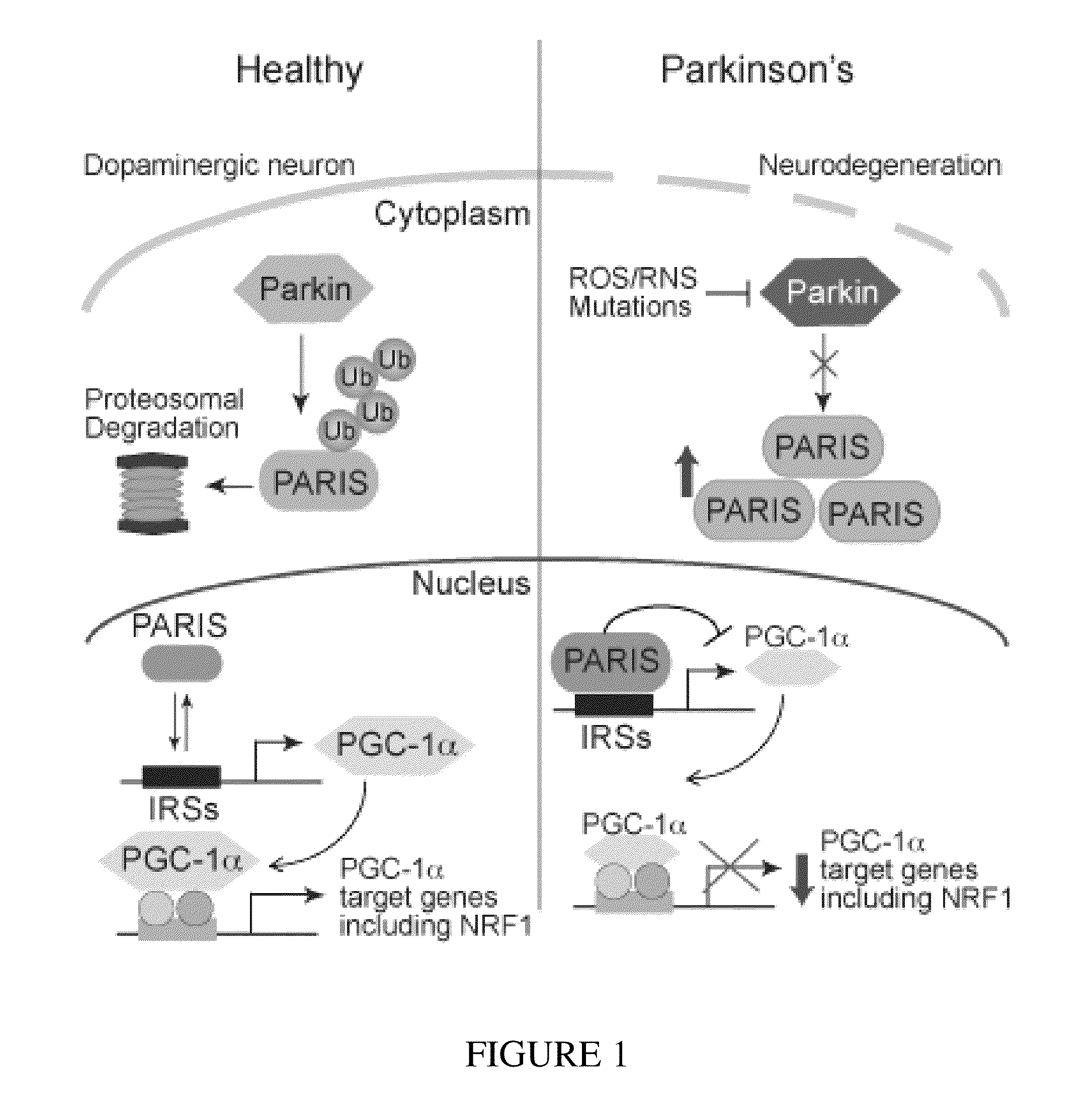
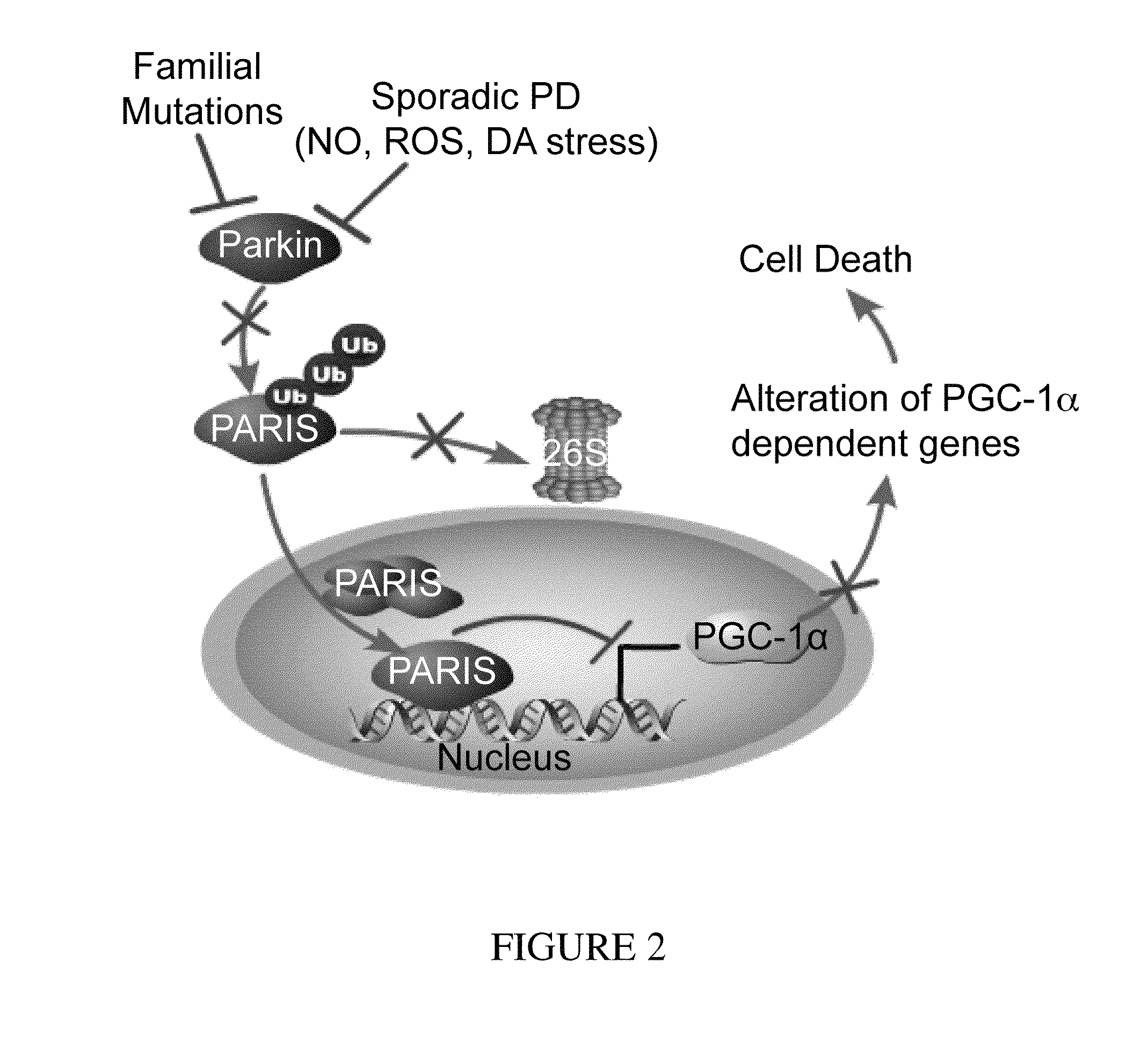
Parkinson's disease is caused by the preferential loss of substantia nigra dopamine neurons. A Parkin Interacting Substrate, PARIS (ZNF746) is identified. The levels of PARIS are regulated by the ubiquitin proteasome system via binding to and ubiquitination by the E3 ubiquitin ligase, parkin. PARIS is a KRAB and zinc finger protein that accumulates in models of parkin inactivation and in human brain Parkinson's disease patients. PARIS represses the expression of the transcriptional co-activator, PGC-1α and the PGC-1α target gene, NRF-1 by binding to insulin response sequences in the PGC-1α promoter. Conditional knockout of parkin in adult animals leads to progressive loss of dopamine (DA) neurons that is PARIS dependent. Overexpression of PARIS causes selective loss of DA neurons in the substantia nigra, which is reversed by either parkin or PGC-1α co-expression. The identification of PARIS provides a molecular mechanism for neurodegeneration due to parkin inactivation.
Owner:VALTED
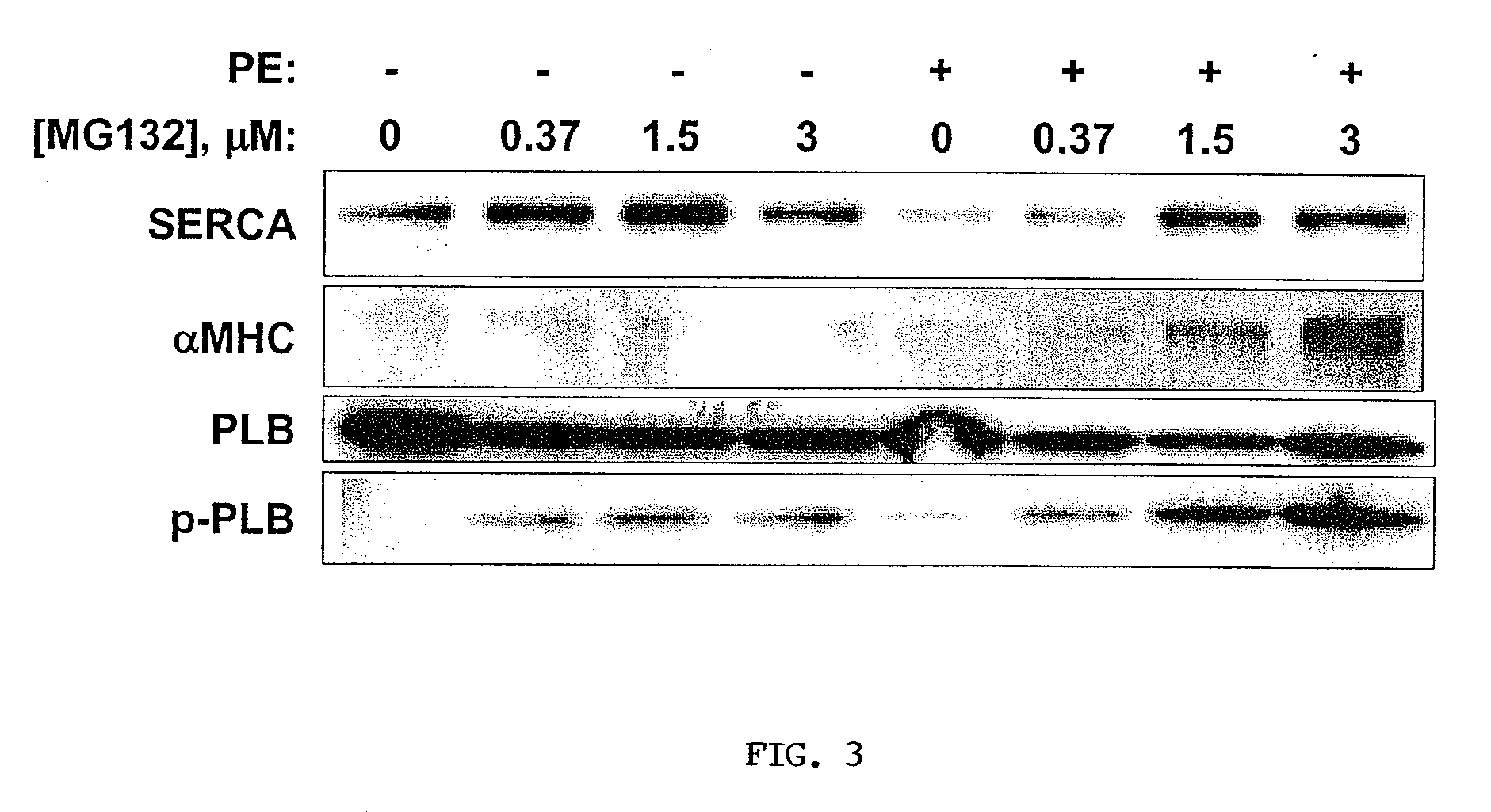
Use of Inhibitors of the Ubiquitin Proteasome Pathway as a Method of Increasing Contractility of the Heart
InactiveUS20070015777A1Increase heart contractilityIncrease contractilityBiocideTripeptide ingredientsDegradative PathwayUbiquitin proteasome
The present invention describes novel uses for inhibitors of the ubiquitin proteasome degradative pathway. In particular it describes methods for improving cardiac function, increasing alpha myosin levels in the heart, and increasing SERCA levels in the heart. The invention also provides methods for treating cardiac hypertrophy through inhibiton of the ubiquitin proteasome.
Owner:MYOGEN INC
Methods and compositions for inhibition of the transitional endoplasmic reticulum atpase
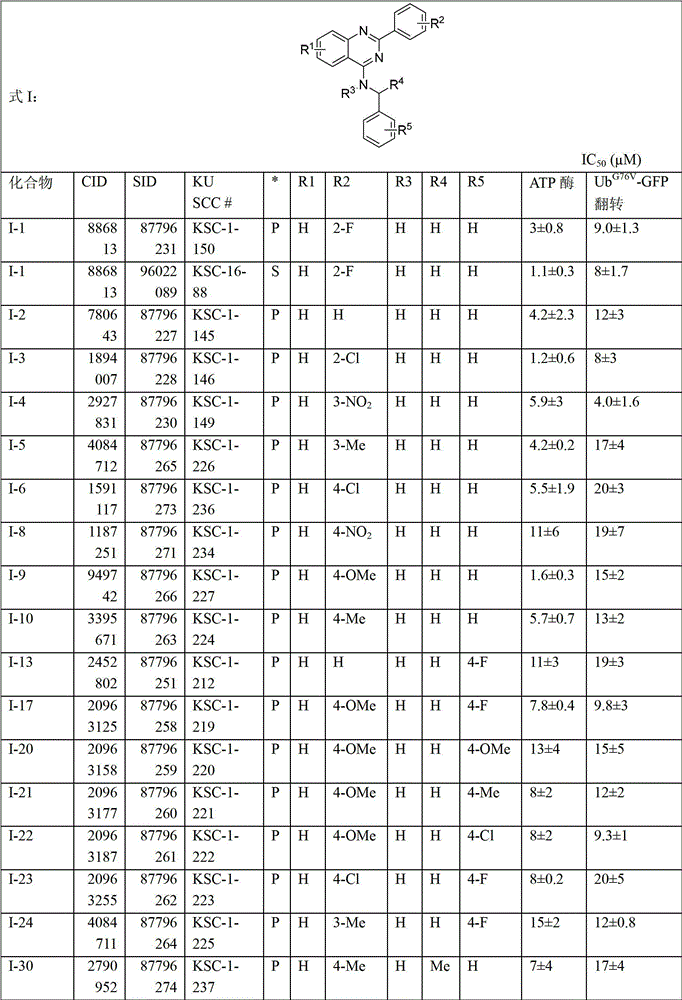
Compounds of Formulas I-XLIII are identified as direct inhibitors of p97 ATPase or of the degradation of a p97-dependent ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) substrate. Methods and compositions are disclosed for inhibiting p97 ATPase and the degradation of a p97-dependent UPS substrate, and for identifying inhibitors thereof.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +2
Regulation of HIF protein levels via deubiquitination pathway
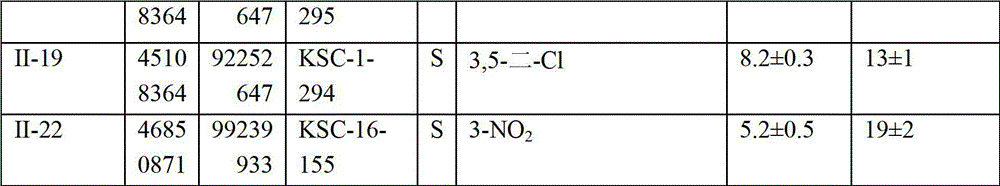
InactiveUS20050049309A1Lower protein levelReduced activityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAnticarcinogenPropanoic acid
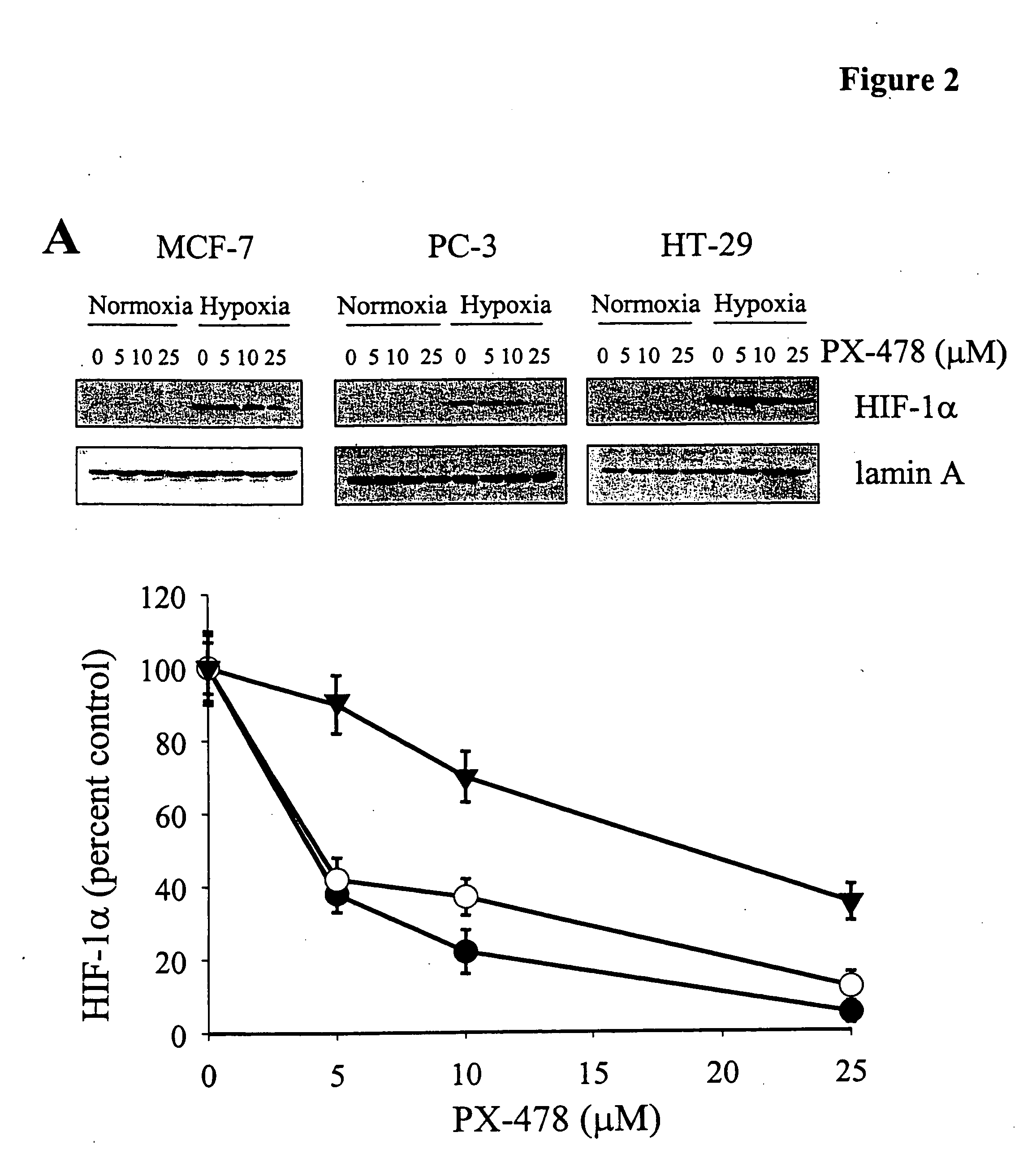
The hypoxia inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) transcription factor is an important regulator of the cellular response to hypoxia. The activity of HIF-1 is regulated by the level of the HIF-1α subunit, HIF-1α, which is rapidly degraded under normoxic conditions by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. HIF-1α levels increase under hypoxic conditions. Many human cancers also show constitutively increased HIF-1α levels. PX-478 or S-2-amino-3-[4′-N,N,-bis(2-chloroethyl)amino]phenyl propionic acid N-oxide dihydrochloride, is a novel anticancer agent, and is capably of decreasing both constitutive and hypoxia induced HIF-1α protein levels and HIF-1 transactivation in vitro and in vivo. In method embodiments, the administration of PX-478 is independent of the pathways of HIF-1α regulation involving the von Hippel-Lindau protein and p53. PX-478 causes an increase in polyubiquitinated HIF-1α levels due to inhibition of HIF-1α deubiquitination. The levels of other proteins whose proteasomal breakdown is mediated by ubiquitination are not affected by PX-478. Deubiquitination is a novel pathway for the regulation of cellular HIF-1α levels and PX-478 is a specific inhibitor of the pathway. Therapeutic compounds for regulating cellular HIF-1α levels and methods of regulating cellular HIF-1α levels are herein provided.
Owner:PROLX PHARMA +1
Prediction method for ubiquitination degradation of target protein
ActiveCN109785902AImprove the transformation effectCutting costsProteomicsGenomicsProtein targetProtein subunit
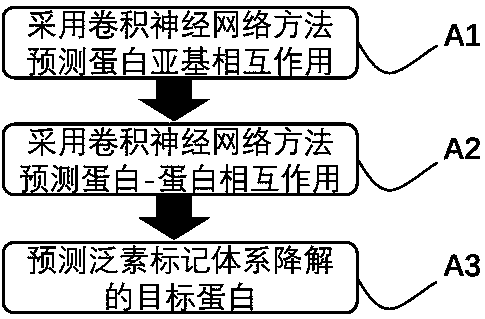
The invention relates to a prediction method for the ubiquitination degradation of a target protein. The prediction method comprises the following steps: A1, predicting the interaction of protein subunits by adopting a convolutional neural network method; A2, constructing a spatial three-dimensional structure of the ubiquitin marking system; A3, predicting a ubiquitination-degraded target protein,downloading a three-dimensional structure file of the target protein, complementing the three-dimensional structure of the target protein by using a homologous modeling method, and predicting the interaction between the target protein and a E3 ubiquitination marking system by using the convolutional neural network method; after that, optimizing an overall spatial three-dimensional structure of interaction between the E3 ubiquitin marking system and the target protein by adopting a molecular dynamics method, judging whether the target protein is possibly marked by the E3 ubiquitin marking system or not according to the stability of the system, and performing ubiquitin-target protein marking by virtue of the ubiquitin-target protein marking system, and degrading the protein by virtue of a ubiquitin-proteasome.
Owner:成都分迪科技有限公司
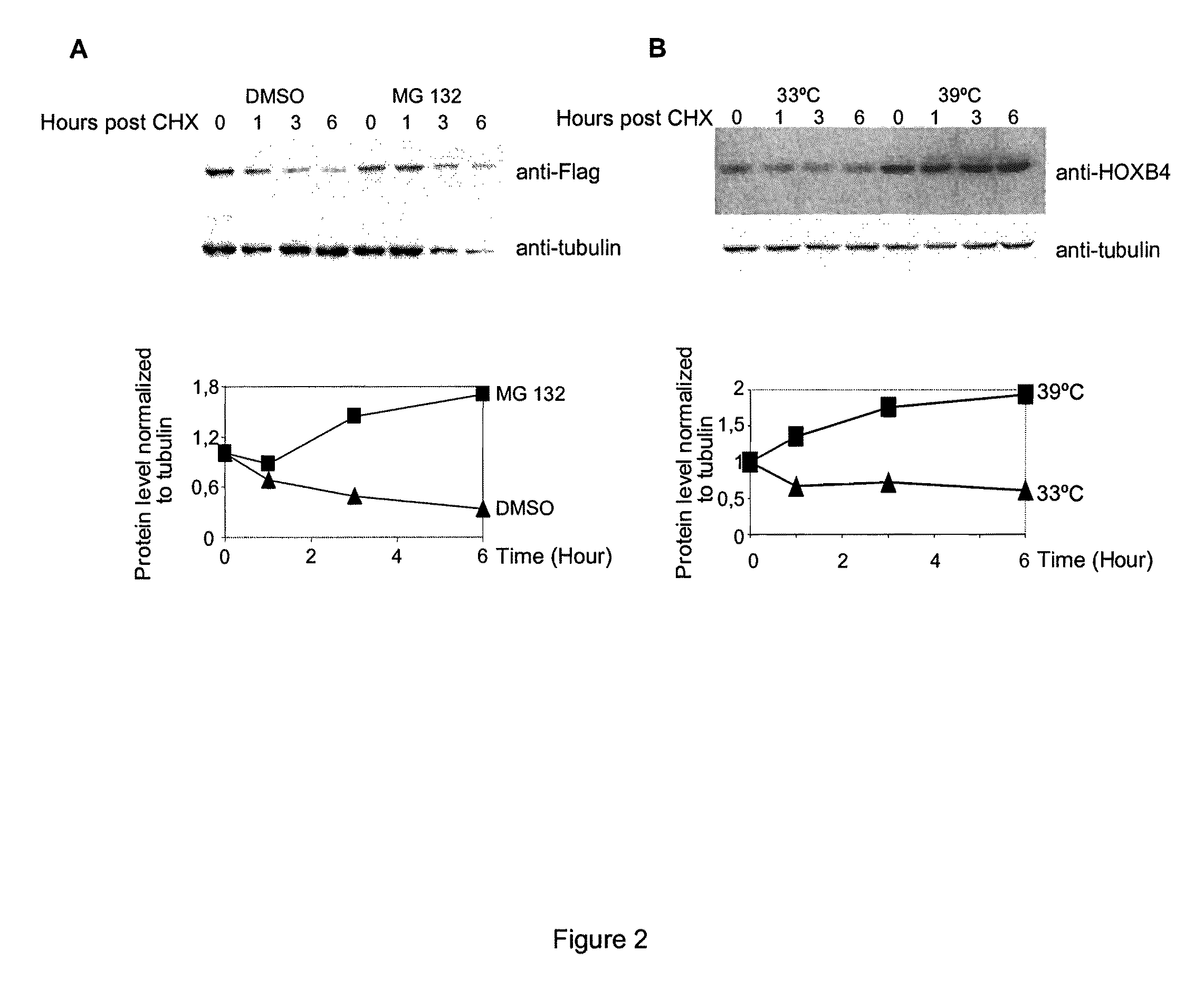
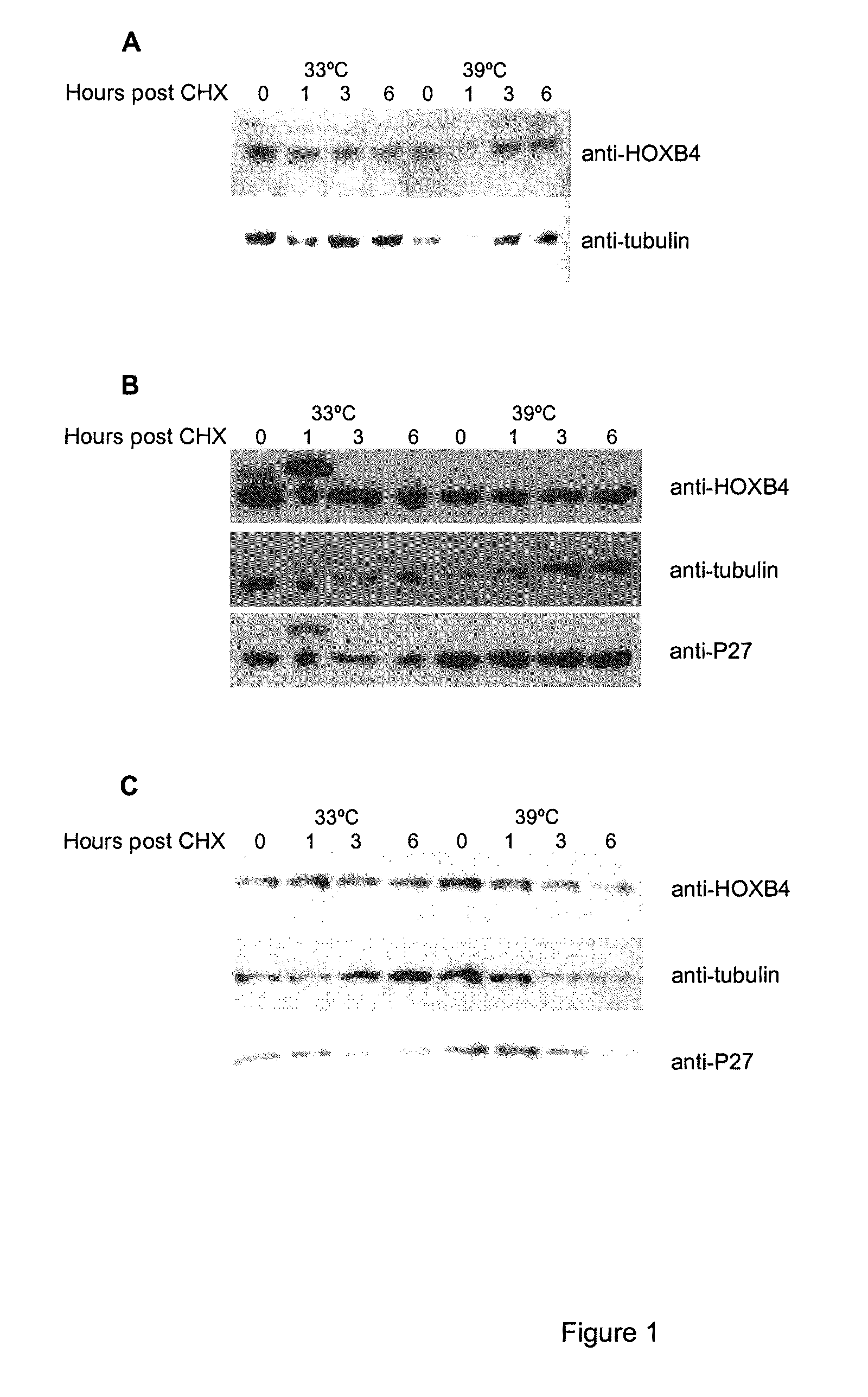
Mutated hoxb4 proteins with improved stability, and methods of use thereof
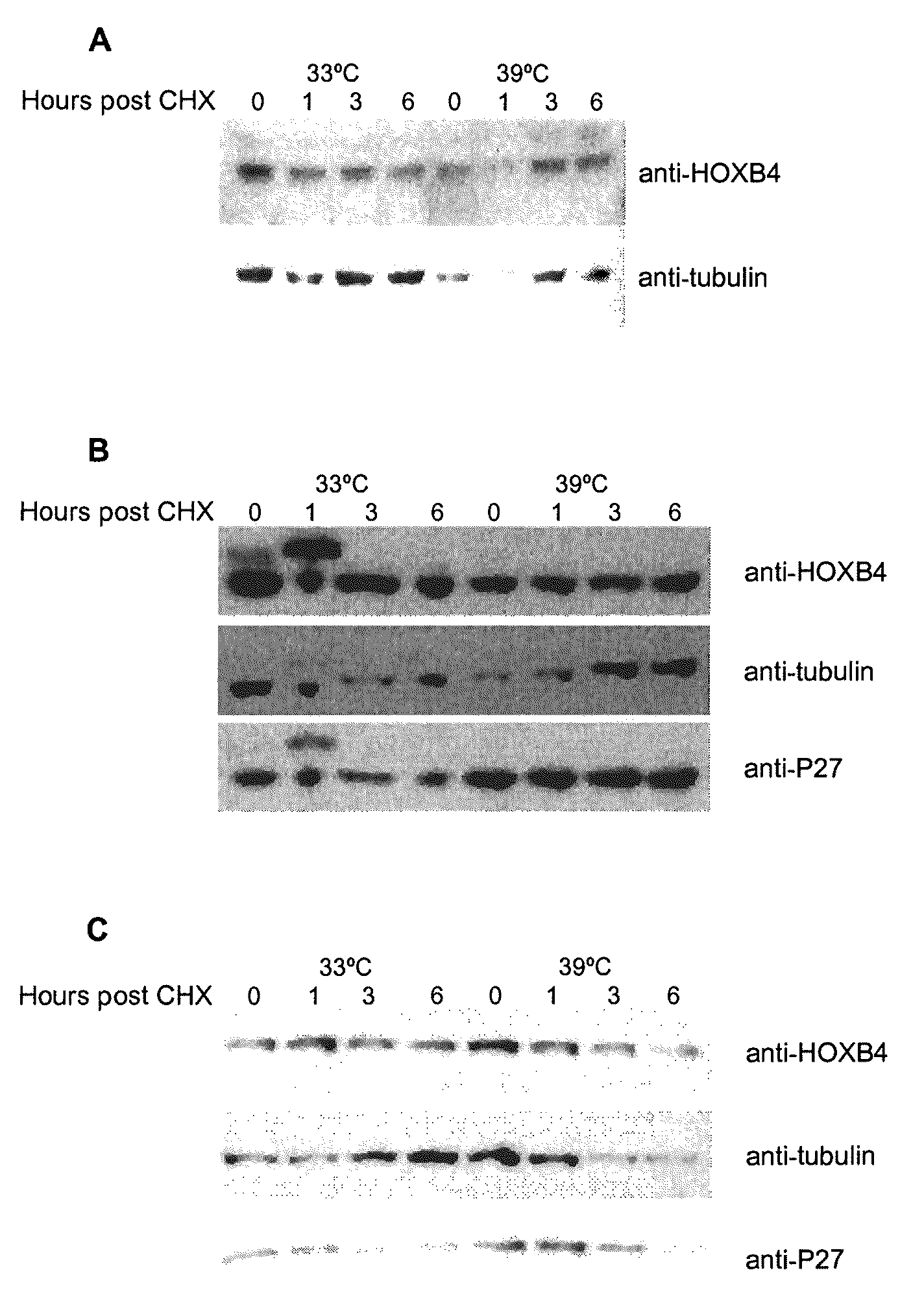
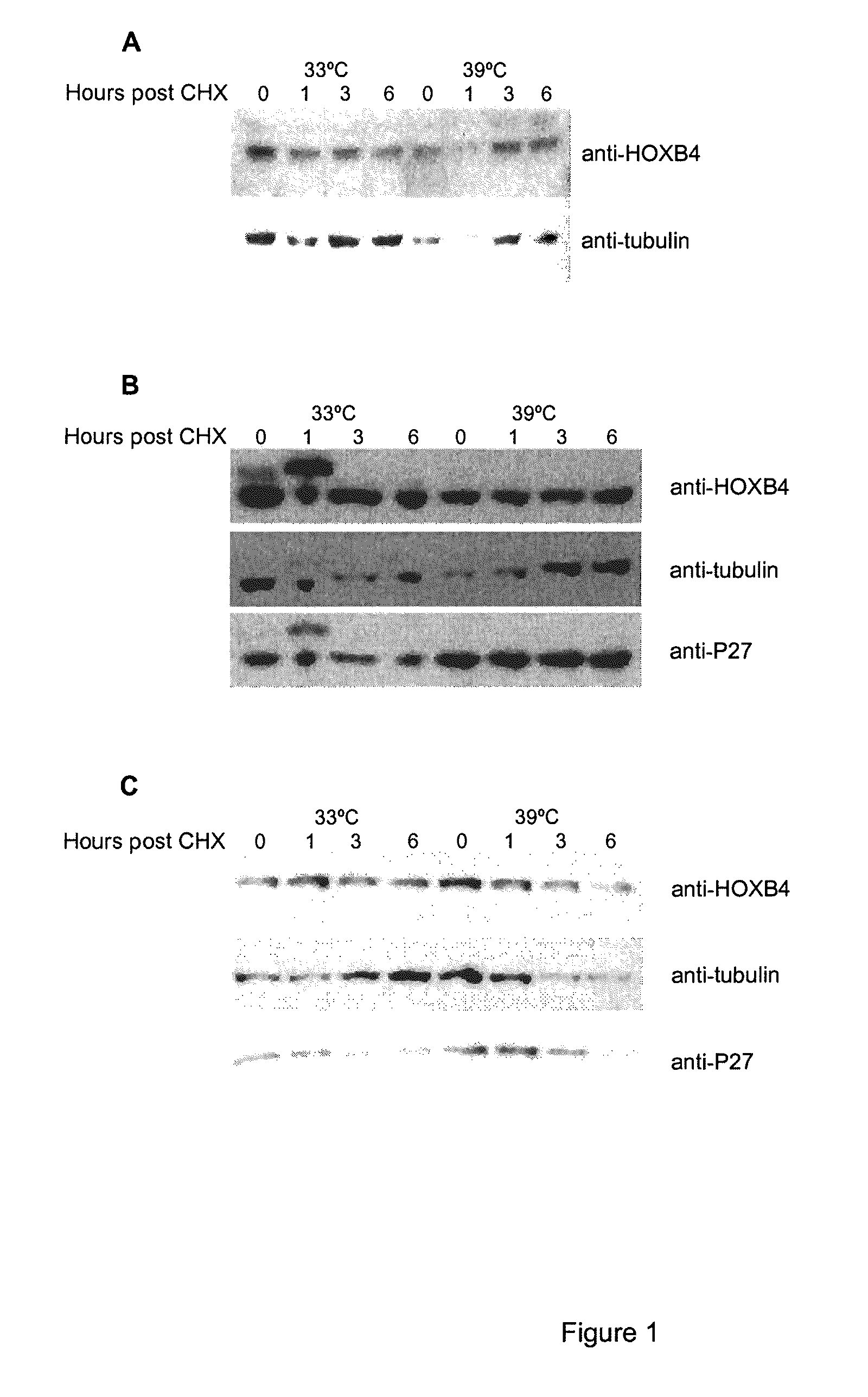
InactiveUS20080300187A1Prevent adverse side effectsIncrease dosePeptide/protein ingredientsFermentationUbiquitin proteasomeBioinformatics
A polypeptide, the amino acid sequence of which comprises a sequence as set forth in SEQ ID NO:2, including at least one mutation within the degron domain of the polypeptide encompassed between positions 1 and 35 of the sequence, wherein said at least one mutation reduces the susceptibility of the polypeptide to ubiquitin-proteasome degradation.
Owner:VALORISATION RECH LLP +3
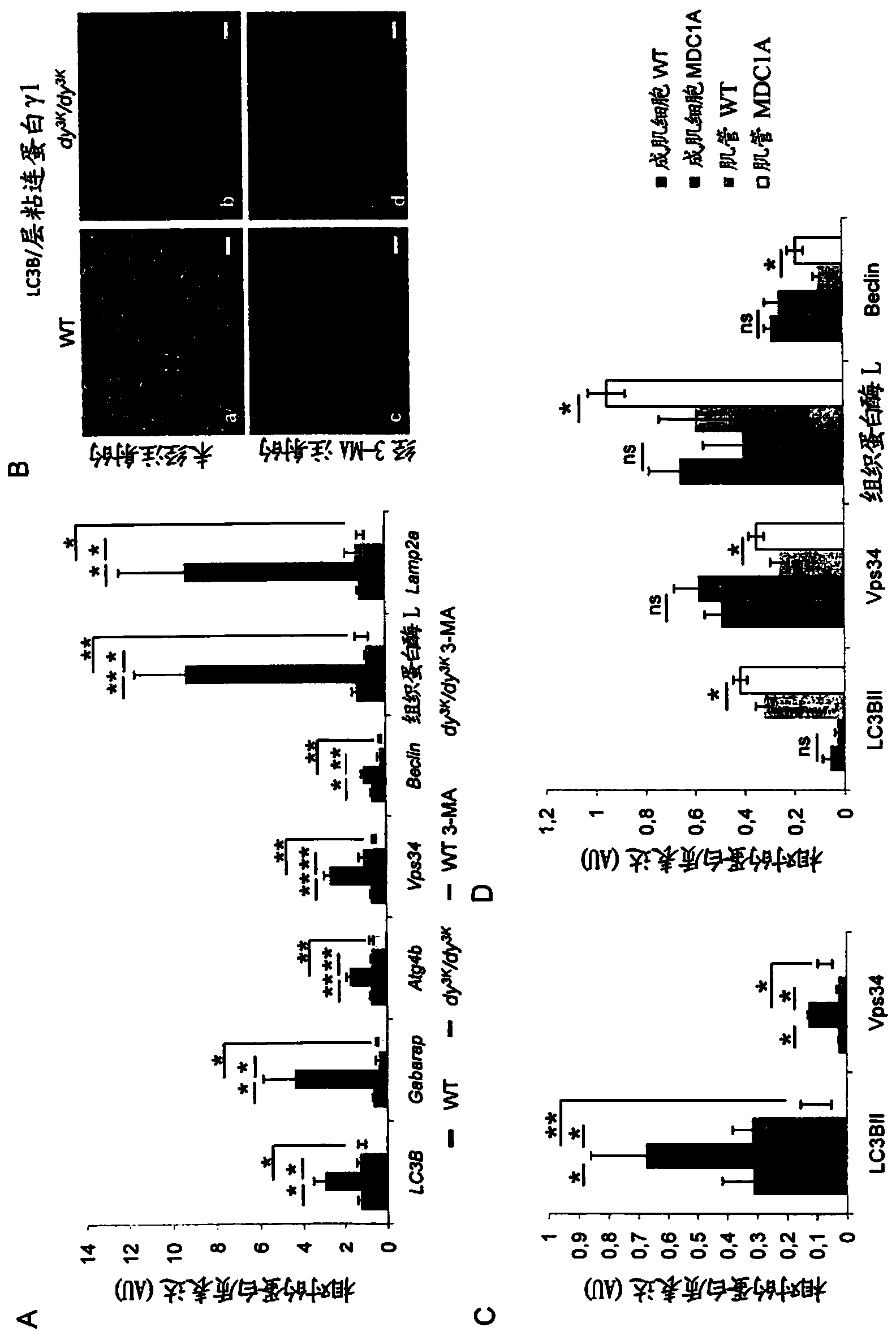
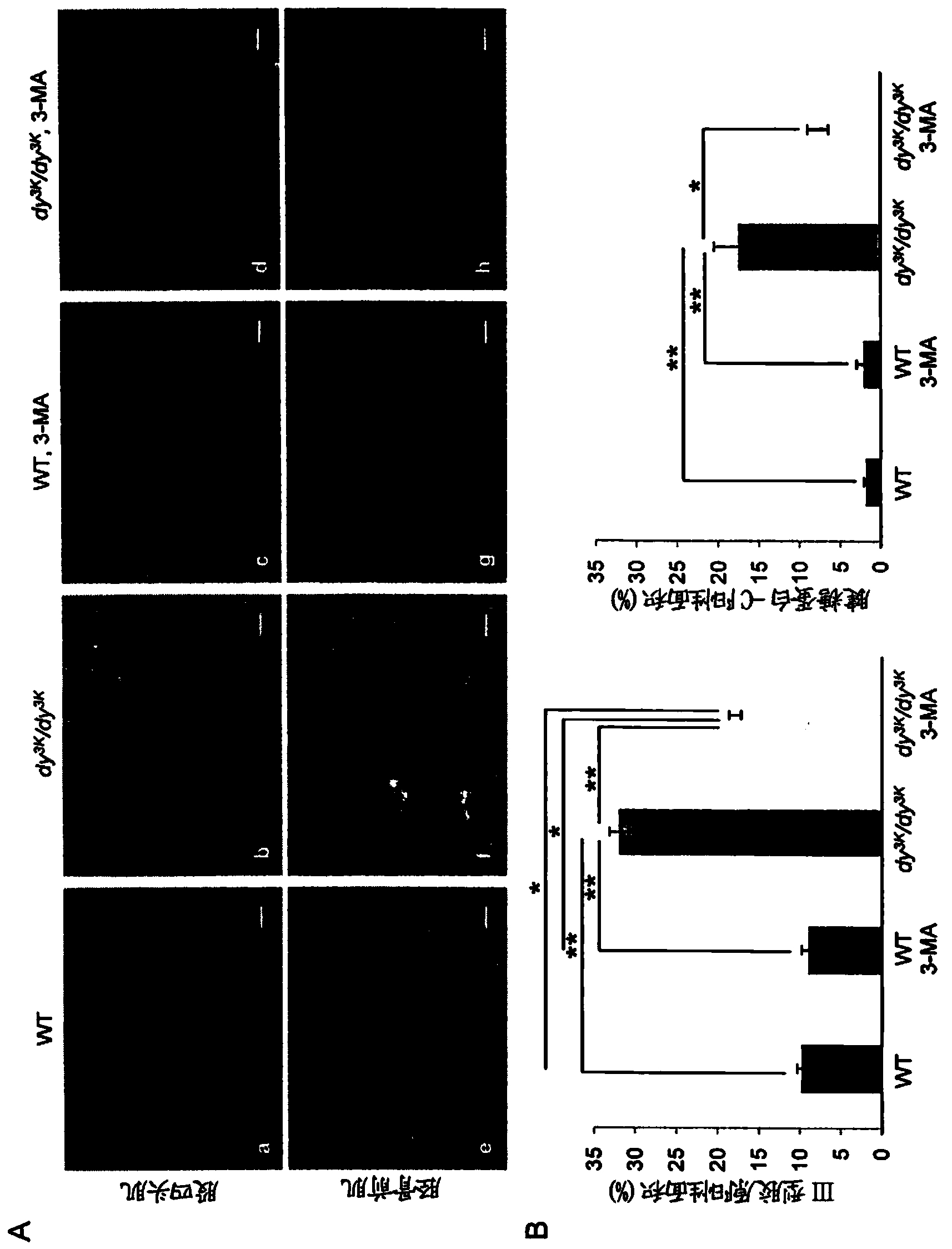
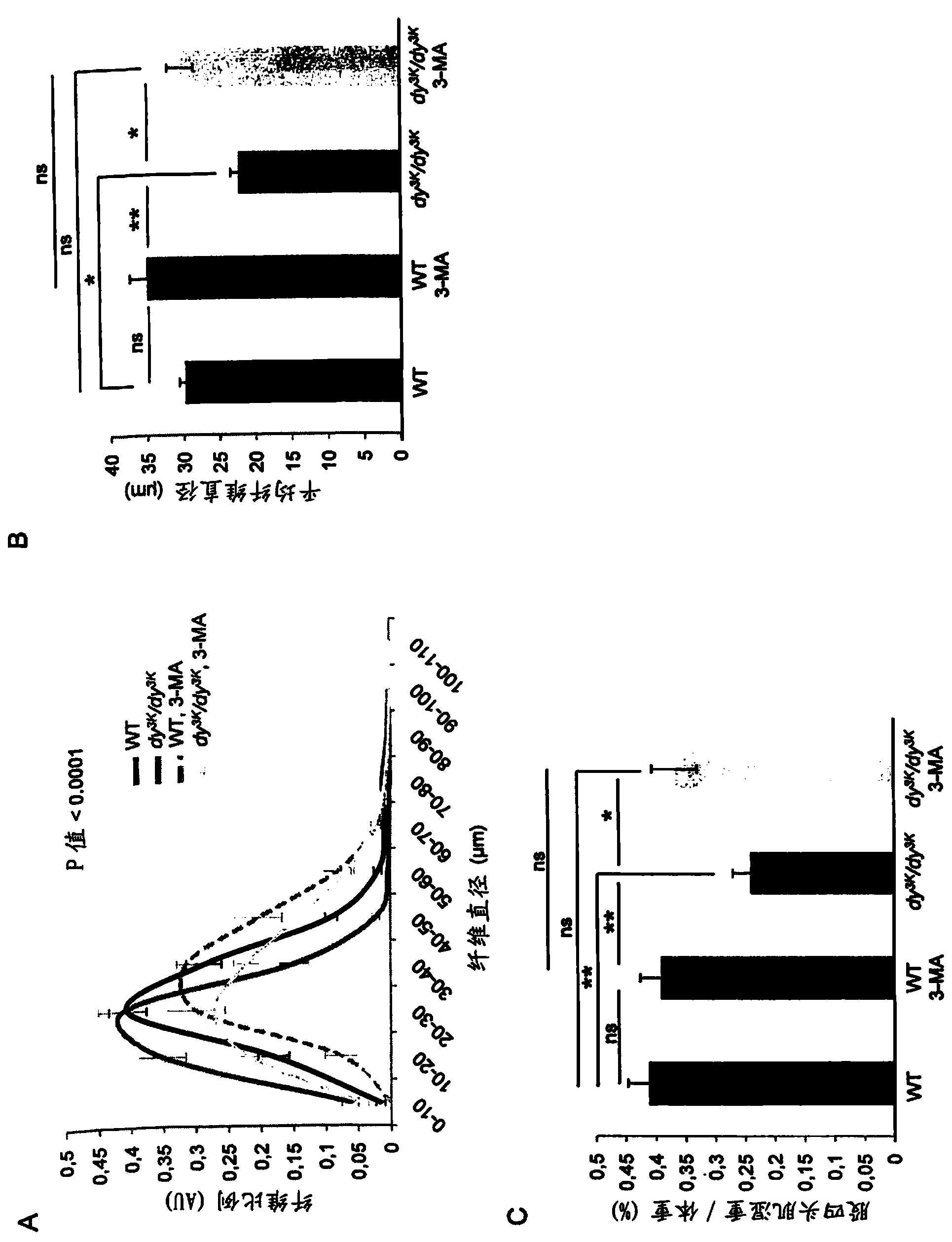
Novel treatments
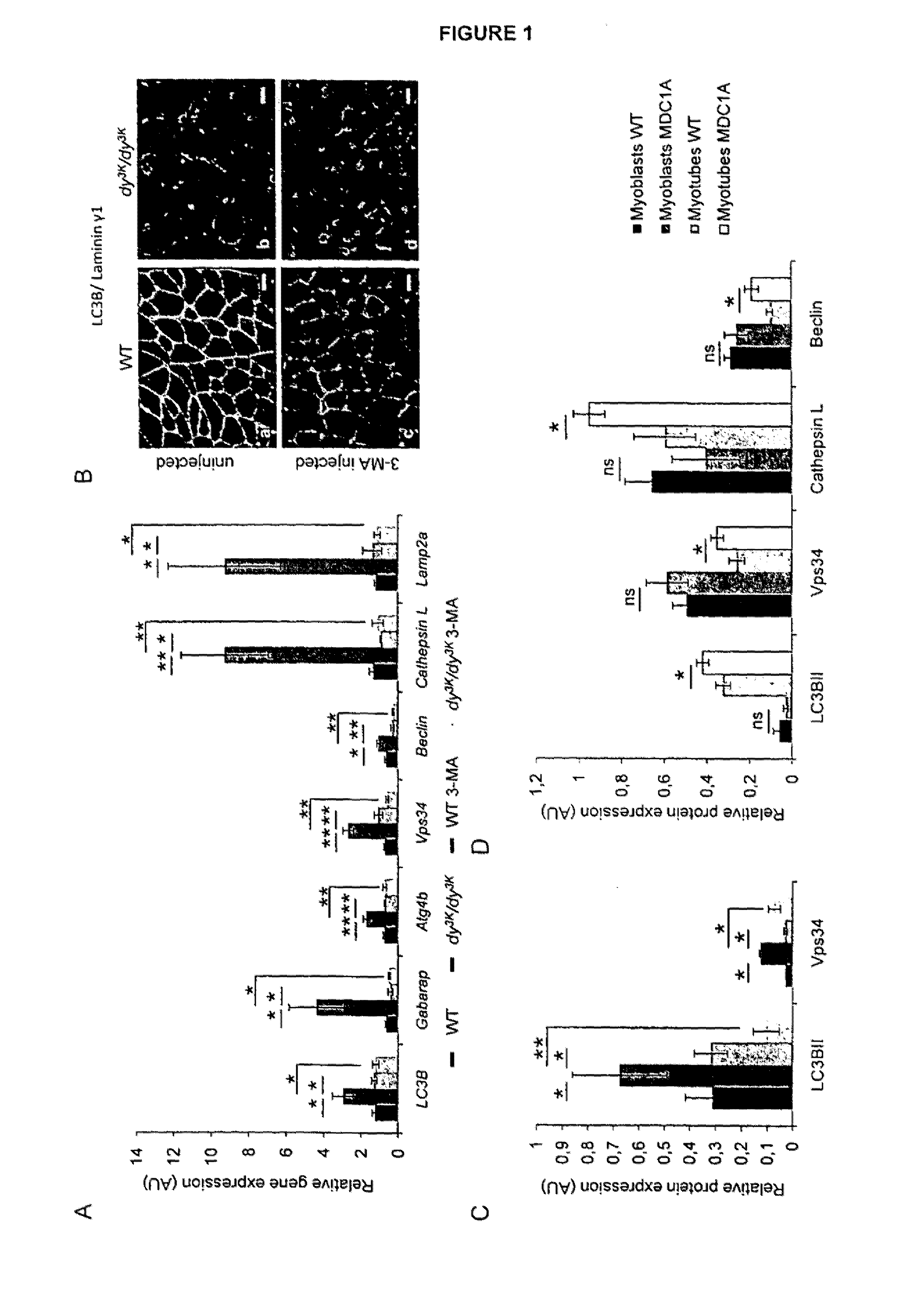
The present invention provides an inhibitor of intracellular protein degradation for use in the treatment and prevention of muscular dystrophy in a mammal. In particular, the invention provides an autophagy inhibitor and / or an inhibitor of the ubiquitin-proteasome system (such as a proteasome inhibitor) for use in the treatment and prevention of muscular dystrophy (such as congenital muscular dystrophy [e.g. MDC1A) and Duchenne muscular dystrophy [DMD]). The invention further provides corresponding methods of treatment and prevention of muscular dystrophy.
Owner:MD PHARMA
Proteolysis targeting virus, live vaccine thereof, preparation method of proteolysis targeting virus, preparation method of live vaccine, application of proteolysis targeting virus, and application of preparation method
PendingCN112175914AControl copyAbundant backup resourcesSsRNA viruses negative-senseSsRNA viruses positive-senseVirus ProteinUbiquitin proteasome
The invention provides a proteolysis targeting virus. The virus comprises one or more proteolysis targeting molecules capable of being recognized by a ubiquitin-proteasome system at one or more different protein sites; the virus protein and the proteolysis targeting molecule are connected through one or more connecting chains; and the connecting chains can be selectively cut. The invention also provides a preparation method of the proteolysis targeting virus. Specifically, the invention provides the proteolysis targeting influenza virus and a preparation method thereof. The proteolysis targeting virus and the preparation method thereof provided by the invention can be widely applied to live vaccines, attenuated vaccines, inactivated vaccines, virulent safety models and the like. Compared with the prior art, the proteolysis targeting virus and the preparation method thereof provided by the invention are used for designing the vaccine with different inactivation degrees, and have safe controllability, and the vaccine has good immunogenicity.
Owner:司龙龙 +2
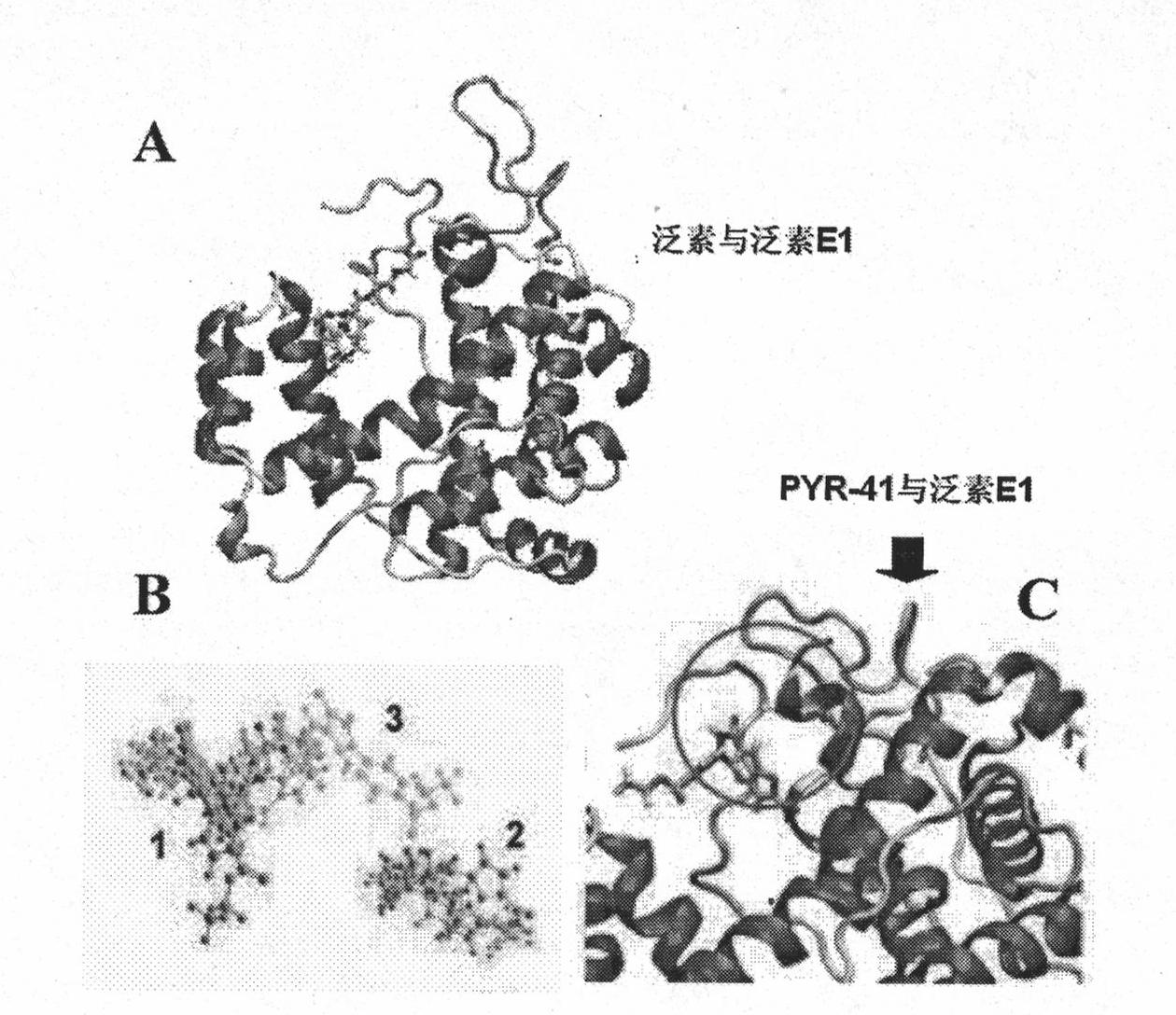
Ubiquitin E1 inhibitor and preparation method thereof
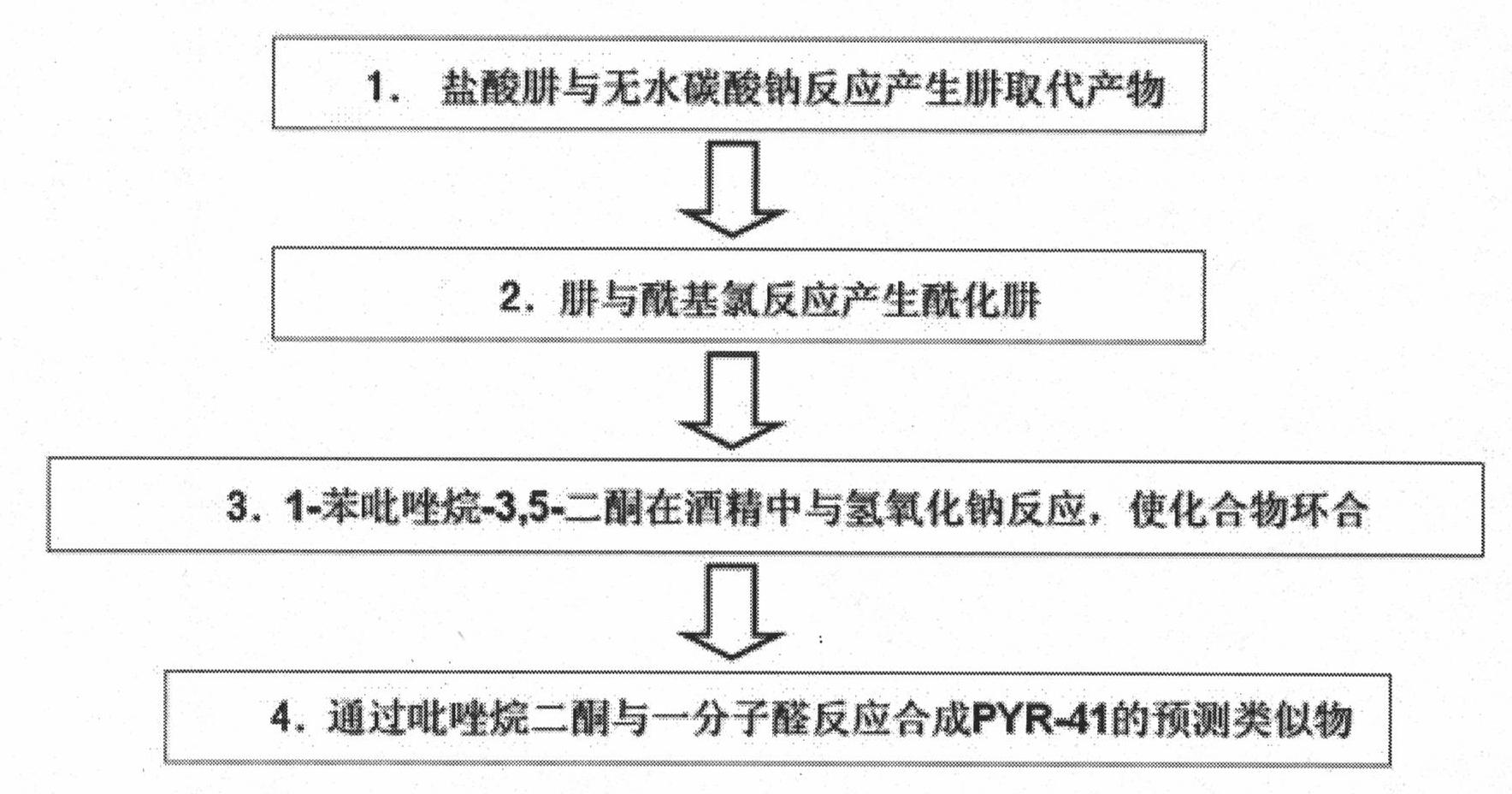
InactiveCN101961331AEasy to passGood water solubilityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryFuranProtein Degradations
The invention relates to an ubiquitin E1 inhibitor and a preparation method thereof. Series compound Y-1-benzene pyrazole silane-3,5-diketone and relevant derivative (such as 4-(4-ethyoxyl-3-methoxybenzylidene)-1-benzene pyrazole silane-3,5-diketone, and the like) with different alternative groups are prepared by a liquid-phase organic synthesis method according to the structure of PRY-41(4(4-(5-nitro-furan group-methylene]-3,5-dioxo-pyrazolidine-1-radical)-ethyl benzoate). The ubiquitin E1 inhibitor can be used for inhibiting protein degradation mediated by ubiquitination and nondegradation of ubiquitination, and can kill transformed cells containing p53 in the process of blocking up the NFkB activity by the inhibitor, that is to say, the inhibitor possibly has the potential property of treating tumor and can be used as an important tool for researching ubiquitin proteinase system mechanism.
Owner:西安杰诺瓦生物科技有限公司
Cereblon binders for the degradation of ikaros
PendingUS20210009559A1Potent binderEnhanced interactionOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryCereblonUbiquitin proteasome
The present invention provides cereblon binders for the degradation of Ikaros or Aiolos by the ubiquitin proteasome pathway along with their use in therapeutic applications as described herein.
Owner:C4 THERAPEUTICS INC
Derivative of multi-target antitumor inhibitor 2-aminopyrrole-triazine and synthesis method thereof
InactiveCN102153558AHigh activityThe synthesis process is matureOrganic chemistryAntineoplastic agentsChemical synthesisSide effect
The invention discloses a derivative of a multi-target antitumor inhibitor, namely 2-aminopyrrole-triazine and a synthesis method thereof, and relates to the technical field of the treatment of abnormal cells in mammals. The derivative is synthesized by taking ethyl isocyanoacetate as a starting point through a chemical synthesis method, and has the advantages of mature process, short production period, environment friendliness, low cost and the like. The product can be used as a heat shock protein (Hsp) 90 multi-target antitumor inhibitor, can inhibit Hsp90, and promote the degradation of Hsp90 effect proteins which play an important role in tumor growth signal pathways through ubiquitination, so that multiple targets of the tumor growth signal pathways are blocked and the growth of tumor is effectively prevented. The derivative has higher affinity with tumor cells, can selectively kill the tumor cells, and promote the degradation of primer proteins thereof through ubiquitin-proteasome pathways, so that the effects of tumor treatment and resistance of the targets are achieved, and the derivative has strong action and small side effect.
Owner:青岛佳诺华医药科技有限公司
Mutated HOXB4 proteins with improved stability, and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS8039436B2Rapid and sustained hematopoietic reconstitutionReduce sensitivityPeptide/protein ingredientsTissue cultureUbiquitin proteasomeBiology
A polypeptide, the amino acid sequence of which comprises a sequence as set forth in SEQ ID NO:2, including at least one mutation within the degron domain of the polypeptide encompassed between positions 1 and 35 of the sequence, wherein said at least one mutation reduces the susceptibility of the polypeptide to ubiquitin-proteasome degradation.
Owner:VALORISATION RECH LLP +3
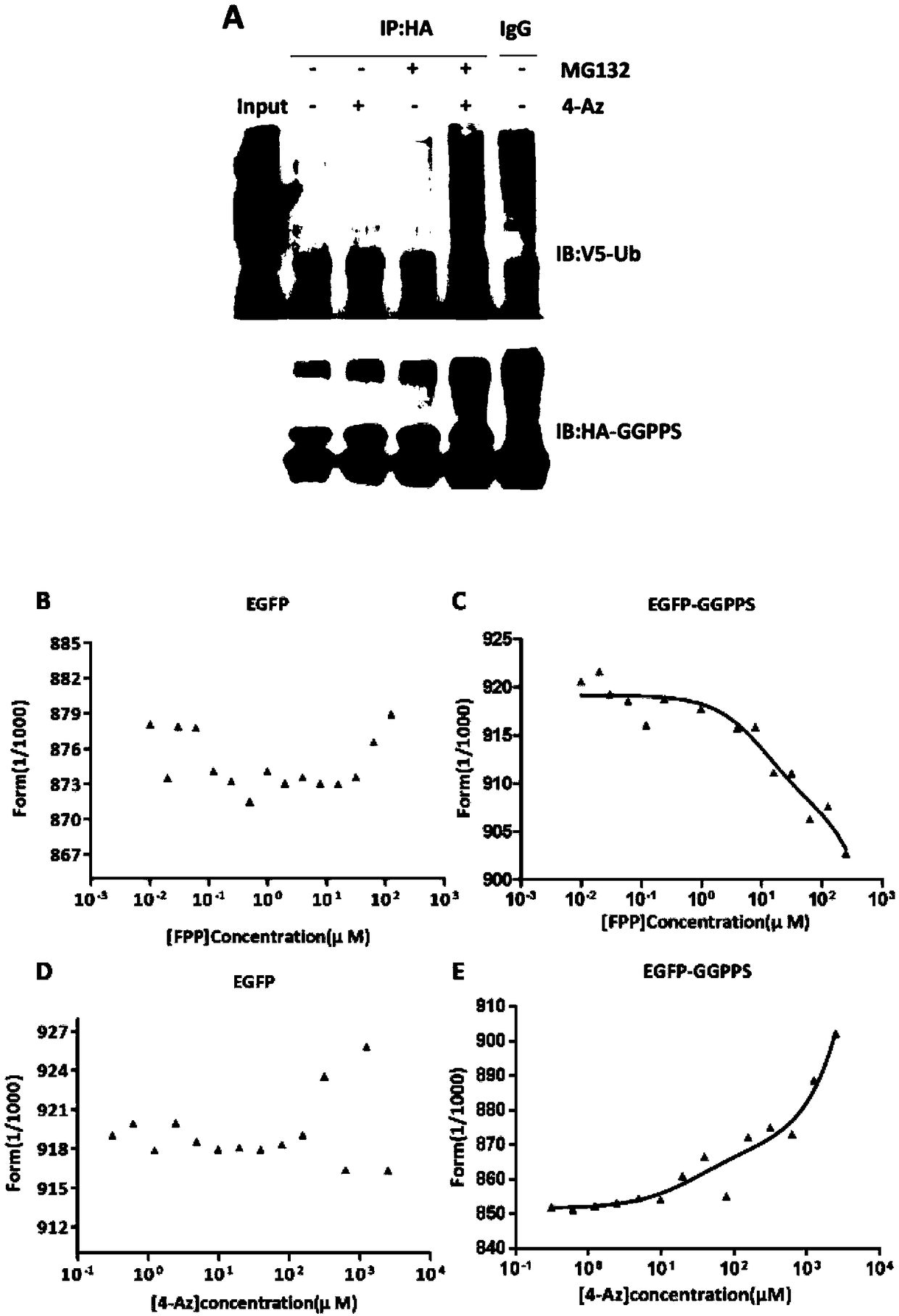
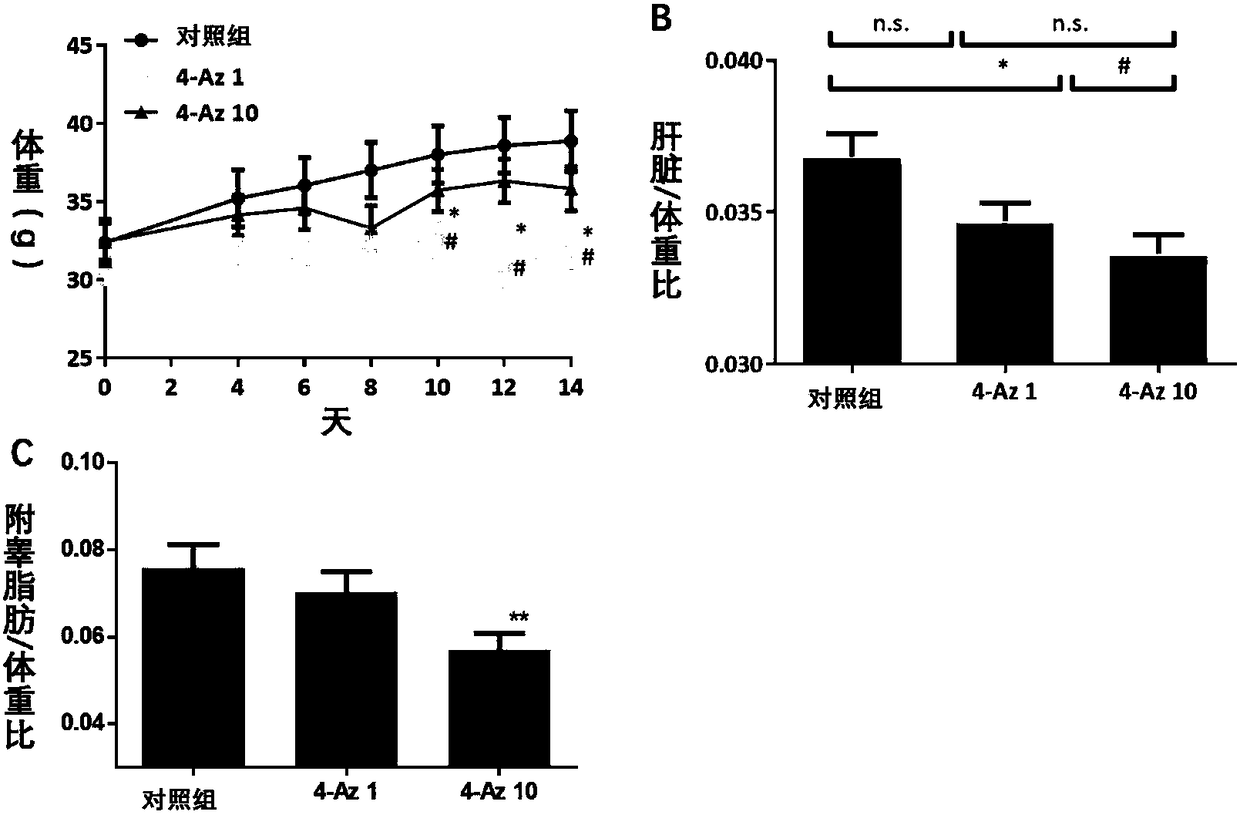
Use of nitrine phlorizin in preparing drug for treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
InactiveCN108721308AReduce lipid accumulationReduce fatty degenerationOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemIsrapafantMevalonate pathway
The invention discloses use of nitrine phlorizin (4-Az) as a key branching enzyme GGPPS inhibitor in an MVA pathway (mevalonate pathway), especially use in preparing a drug for treating non-alcoholicfatty liver disease. According to a series of experiments, the 4-Az can cause GGPPS protein to generate ubiquitin-proteasome pathway dependent degradation, has an inhibiting effect on GGPPS protein expression, and can be used as the inhibitor of GGPPS protein expression. More specifically, the nitrine phlorizin can reduce lipid accumulation and fatty degeneration of the livers, can reduce level ofglutamic-pyruvic transaminase and glutamic oxalacetic transaminase in blood, has the activity of protecting the liver function, and can be used for preparing the drug for treating the non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Reducing axon degeneration with proteasome inhibitors
Reduced degeneration of an axon predetermined to be subject to degenerative neuropathy in a term patient is effected by contacting the axon in situ with an effective amount of a ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) inhibitor sufficient to reduce degeneration of the axon; and detecting a resultant reduction in the degeneration of the axon in situ.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
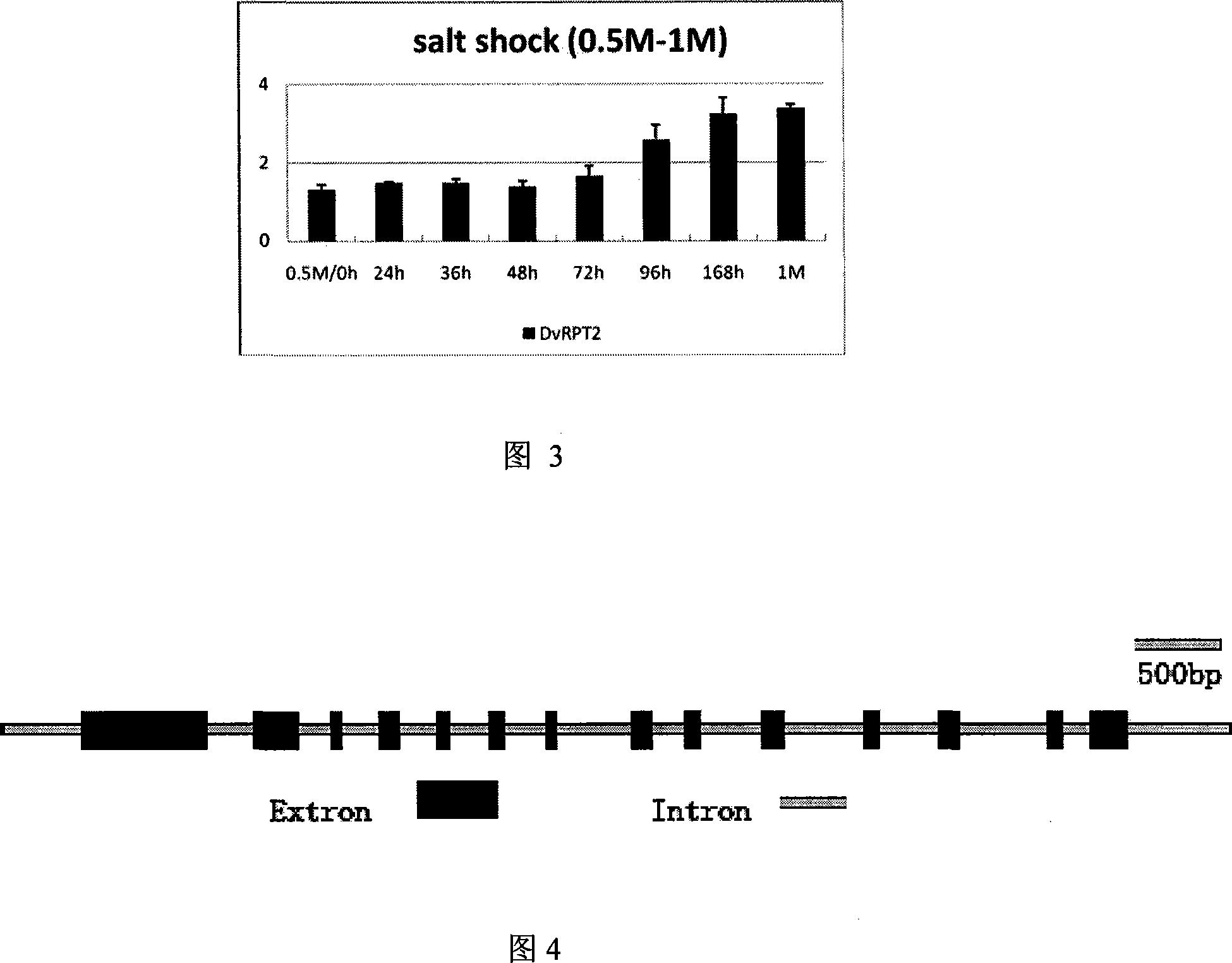
cDNA order of salt algae 26s proteasome subunit RPT2 gene, its coding protein and full-length gene order and clone method
InactiveCN101096678AStrong salt toleranceImprove salt resistanceHydrolasesAlgae/lichens peptidesGene ordersUbiquitin proteasome
The invention relates to a cDNA sequence, a coding protein, a full-length gene sequence and the clone method of a 26S proteinase body subunit RPT2 gene (DvRPT2)in Dunaliella viridis. The uplift expression of 26S proteinase body subunit RPT2 gene in Dunaliella viridis enhances the hydrolytic efficient of TP, accelerates that the substrate protein enters the active position of the proteinase body, reduces the abnormal protein content in the cell, and improves the salt resistance of Dunaliella viridis, so the research about Dunaliella viridis RPT2 subunit indicates the protein degradation pathway of 26S proteinase body, the salt endurance mechanism and the salt-resistance plant improvement, which has the finite theoretical and actual application value.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
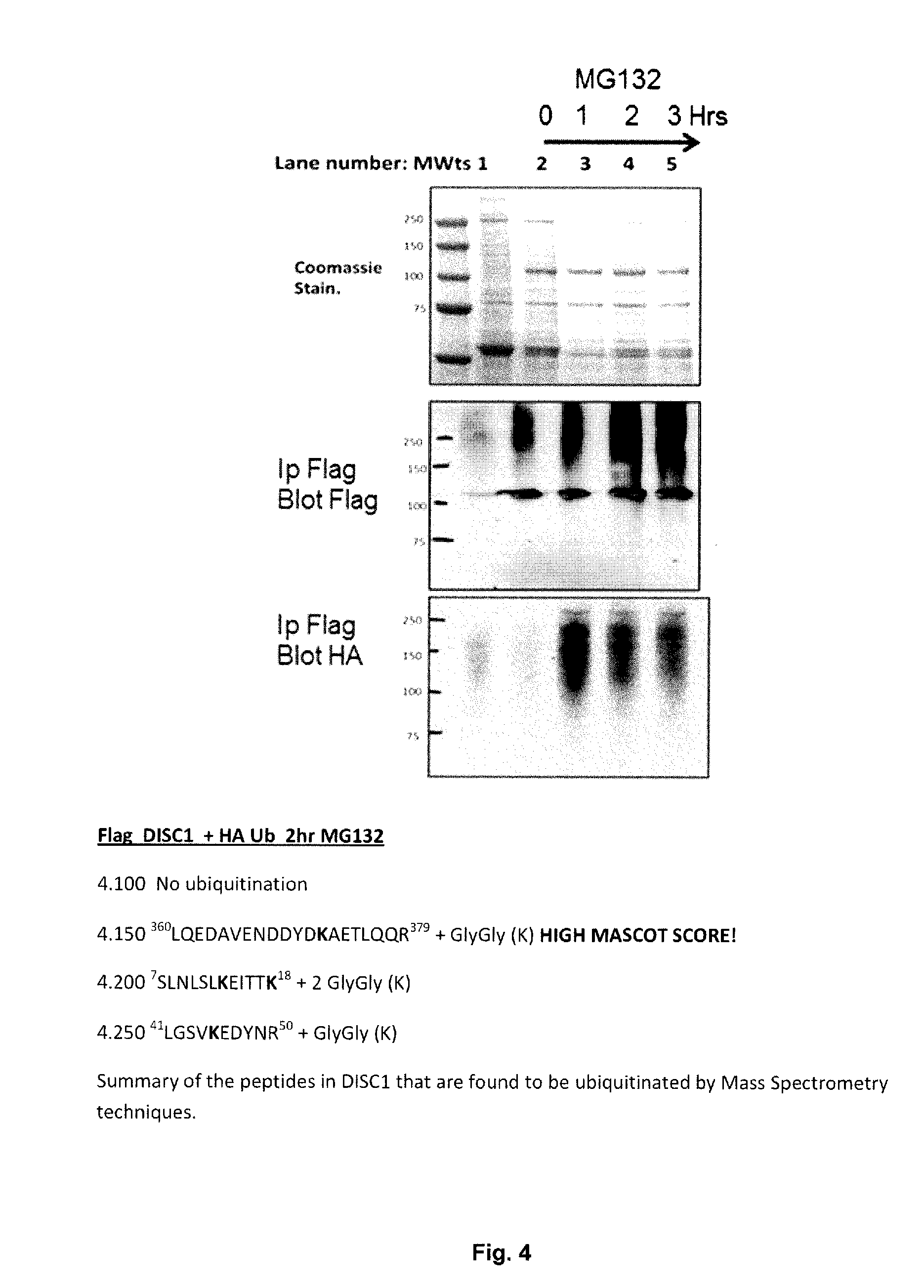
Materials and Methods for Modulating DISC1 Turnover
ActiveUS20160206679A1Modifies its propertyGood membrane permeabilityCompound screeningNervous disorderUbiquitin proteasomeWd repeat
The invention relates to the finding that turnover of DISC1 (Disrupted in schizophrenia 1) is mediated by the F-box-containing protein FBXW7 (F-box / WD repeat-containing protein 7). The sequence within DISC1 that binds to FBXW7 and targets DISC1 for turnover by the ubiquitin-proteasome system is identified. The invention provides antagonists that inhibit this interaction and methods of using these antagonists to decrease DISC1 turnover, for example in treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders, as well as methods of identifying new antagonists.
Owner:THE UNIV COURT OF THE UNIV OF GLASGOW
Agents for the treatment of viral infections
InactiveUS20070265194A1High selectivityLong metabolic half-lifeBiocideNervous disorderUbiquitin proteasomeUbiquitin-Proteasomal Pathway
Owner:SCHUBERT ULRICH +7
Medicine that cures muscle atrophy after spinal cord injury and its application method
InactiveCN106474119ARelieve atrophyPrevent atrophyOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderSkeletal muscle atrophyPharmacon
The invention discloses a medicine that cures muscle atrophy after spinal cord injury and its application method: the medicine that cures muscle atrophy after spinal cord injury is losartan. The application method is that losartan activates a signal pathway of IGF1 / Akt / mTOR and inhibits an expression of MuRF-1; A receptor blocking pharmacon of angiotensin II takes effect through activating the pathway of IGF-1 / Art / mTOR and inhibiting a ubiquotin-proteasomes system. The receptor blocking pharmacon of angiotensin II can improve the skeletal muscle atrophy after spinal cord injury of rats and may take effect through activating the pathway of IGF-1 / Akt / mTOR and inhibiting the ubiquitin-proteasomes system, which provides a part of basis for later clinical application and combined therapy.
Owner:天津运三泽生物医药科技有限公司 +1
3-substituted piperidine compounds for Cbl-b inhibition, and use thereof
Compounds, compositions, and methods for use in inhibiting the E3 enzyme Cbl-b in the ubiquitin proteasome pathway are disclosed. The compounds, compositions, and methods can be used to modulate the immune system, to treat diseases amenable to immune system modulation, and for treatment of cells in vivo, in vitro, or ex vivo. Also disclosed are pharmaceutical compositions comprising a Cbl-b inhibitor and a cancer vaccine, as well as methods for treating cancer using a Cbl-b inhibitor and a cancer vaccine; and pharmaceutical compositions comprising a Cbl-b inhibitor and an oncolytic virus, as well as methods for treating cancer using a Cbl-b inhibitor and an oncolytic virus.
Owner:NURIX THERAPEUTICS INC
Reducing axon degeneration with proteasome inhibitors
Reduced degeneration of an axon predetermined to be subject to degenerative neuropathy in a term patient is effected by contacting the axon in situ with an effective amount of a ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) inhibitor sufficient to reduce degeneration of the axon; and detecting a resultant reduction in the degeneration of the axon in situ.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Modulation of the ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS)
The invention relates to the field of 26S proteasome inhibition, activation and modulation and to identify compounds which activate 26S proteasome in live cells and a method of treating autoimmune diseases, cancer, inflammation and neurogenerative disorders by inhibition, activation and modulation of the 26S proteasome.
Owner:STICHTING HET NEDERLANDS KANKER INST ANTONI VAN LEEUWENHOEK ZIEKENHUIS
Methods to identify compounds useful for tumor sensitization to DNA damage
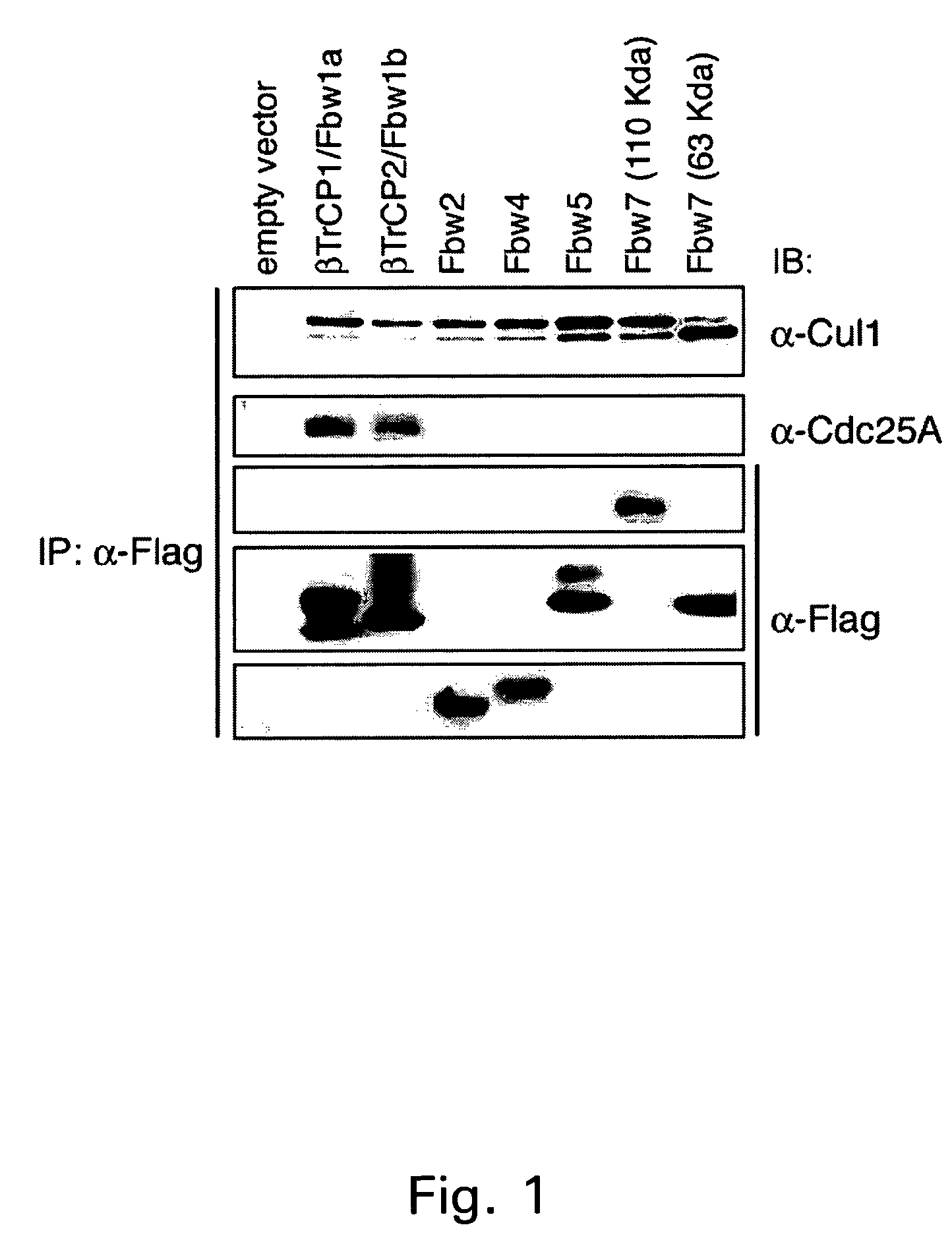
Cdc25A is herein identified as a substrate for β-TrCP1- or β-TrCP2-mediated ubiquitination and subsequent degradation via the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. In particular, it has been found that interfering with β-TrCP expression or function, or increasing β-TrCP degradation, leads to accumulation of Cdc25A in a cell. Since degradation of Cdc25A is a key feature of the response to DNA damage, leading to a stall in the cell cycle during which the cell can repair the damage, Cdc25A accumulation can abolish this response, thereby sensitizing the cell to DNA damage. Described herein are assays for identifying β-TrCP inhibitors, and method of using such inhibitors for modulating Cdc25A degradation, sensitization of tumor cells, and as adjuvants in cancer therapy based on DNA damaging agents.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Proteasom or ups inhibitor for treating infections with influenza viruses
InactiveCN101384301AAvoid spreadingInhibition releaseBoron compound active ingredientsAntiviralsUbiquitin proteasomeBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The invention relates to compositions for the prophylaxis and / or treatment of viral infections, in particular of infections with influenza viruses which cause influenzal infections. The invention relates to compositions which comprise inhibitors of the ubiquitin-proteasome system, in particular proteasome inhibitors, as active ingredients. The present invention further relates to the systemic and topical, preferably the aerogenic administration of proteasome inhibitors. The active substance employed according to the invention as proteasome inhibitor can be employed with at least one further substance having antiviral activity for the prophylaxis and / or therapy of influenzavirus infections.
Owner:VIROLOGIK GMBH
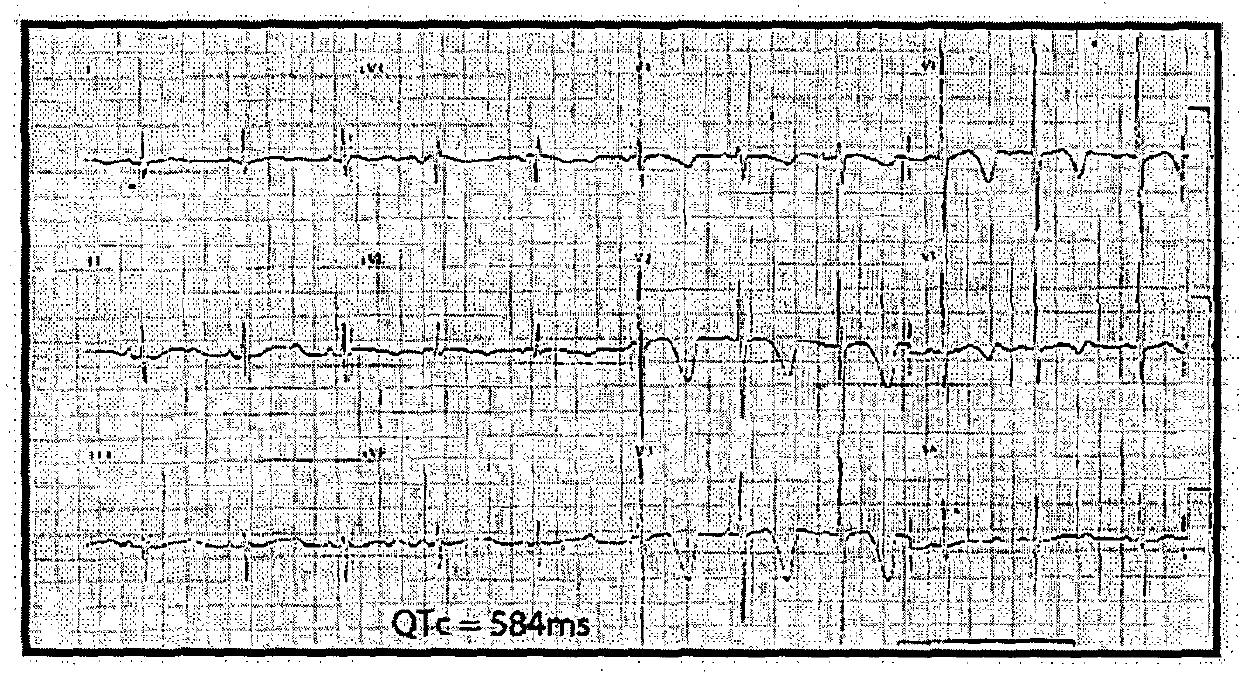
Re-trafficking of HERG reverses long QT syndrome 2 phenotype in human ips-derived cardiomyocytes
InactiveUS20160033481A1Suppress expressionEliminate the effects ofBiocideMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansDisease phenotypeDisease
The present invention relates to generating hiPSC-derived cardiomyocytes and embryoid bodies that recapitulate the disease phenotype of Long QT Syndrome and their use in developing pharmacological treatments thereof. The present invention also includes the use of a compound which inhibits the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway for the preparation of a medicament for the prophylaxis or treatment of a disease associated with prolonged ventricular repolarization (cardiac arrhythmia) caused by one or more mutations in the amino acid sequence of the hERG potassium channel.
Owner:SINGAPORE HEALTH SERVICES PTE
Compositions and treatments for dystrophies
InactiveUS20140213559A1Prevent relapseBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsDuchenne muscular dystrophyUbiquitin proteasome
The present invention provides an inhibitor of intracellular protein degradation for use in the treatment and prevention of muscular dystrophy in a mammal. In particular, the invention provides an autophagy inhibitor and / or an inhibitor of the ubiquitin-proteasome system (such as a proteasome inhibitor) for use in the treatment and prevention of muscular dystrophy (such as congenital muscular dystrophy [e.g. MDC1A) and Duchenne muscular dystrophy [DMD]). The invention further provides corresponding methods of treatment and prevention of muscular dystrophy.
Owner:MD PHARMA
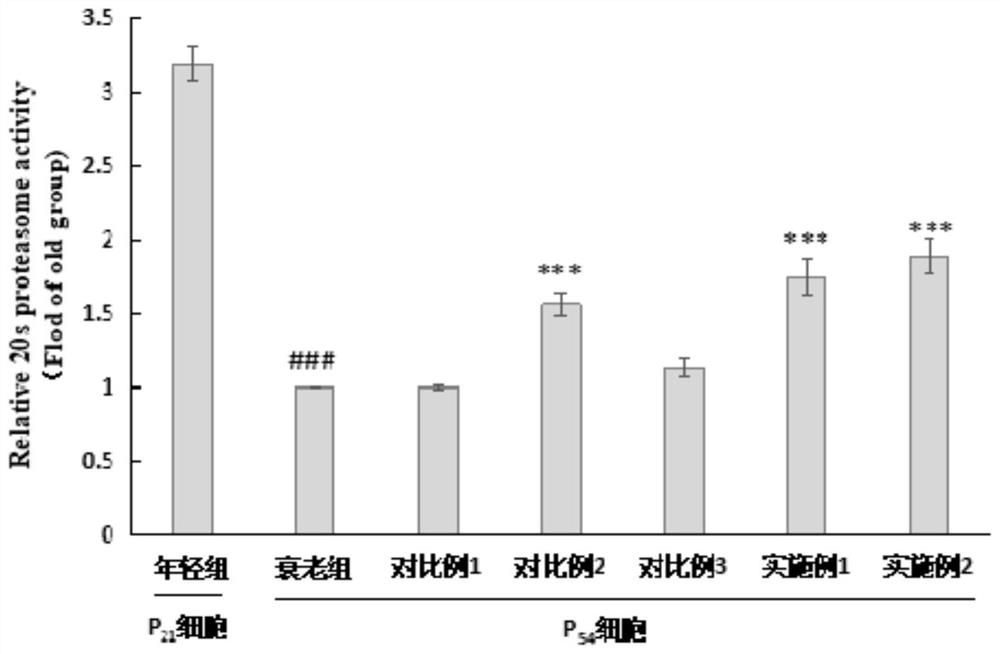
Composition with aging delaying effect and skin care product thereof
ActiveCN112999123AActivate your vitalityAnti agingCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsBiotechnologyApoptosis
The invention relates to a composition with an aging delaying effect and a skin care product thereof. The composition comprises the following components: a pumpkin seed extract and an olive leaf extract. The composition provided by the invention achieves the purpose of delaying senescence by activating mitochondrial autophagy and ubiquitin-proteasome activity and through the synergistic effect of the mitochondrial autophagy and ubiquitin-proteasome activity. When the composition is added to a skin care product and applied to skin, cell waste such as aged and damaged mitochondria and damaged protein can be timely removed from the skin, cell renewal is accelerated, cell apoptosis is reduced, and thus skin aging caused by endogenous and exogenous factors is delayed.
Owner:山东福瑞达生物股份有限公司
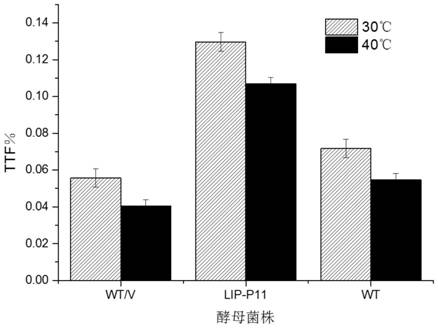
A kind of method and application of improving cell viability and multiple stress resistance of Saccharomyces cerevisiae
ActiveCN107974453BIncrease the amount of bacteriaImprove multiple stress resistanceFungiHydrolasesIndustrial fermentationUbiquitin proteasome
The invention discloses a gene expression cassette composed of a promoter, a nucleic acid sequence of SEQ ID NO.1, and a terminator connected in sequence, inserting the expression vector of the gene expression cassette and using the gene expression cassette to prepare two strains with high cell viability multiple stress-resistant yeast strains. Through the above technical scheme, the gene expression cassette of the present invention is used to transform Saccharomyces cerevisiae to realize the fine transformation of ubiquitin proteasome, and to invent a method and application that can simultaneously improve the cell viability and multiple stress resistance of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The obtained The engineering strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae has stable genetic performance and has wide application and application prospects in industrial fermentation.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com