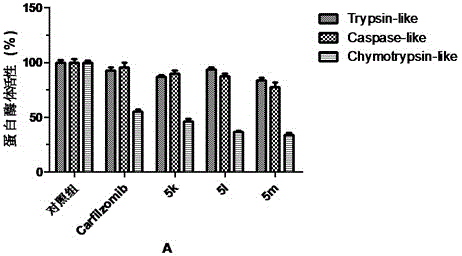
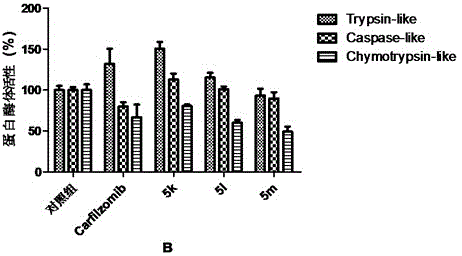
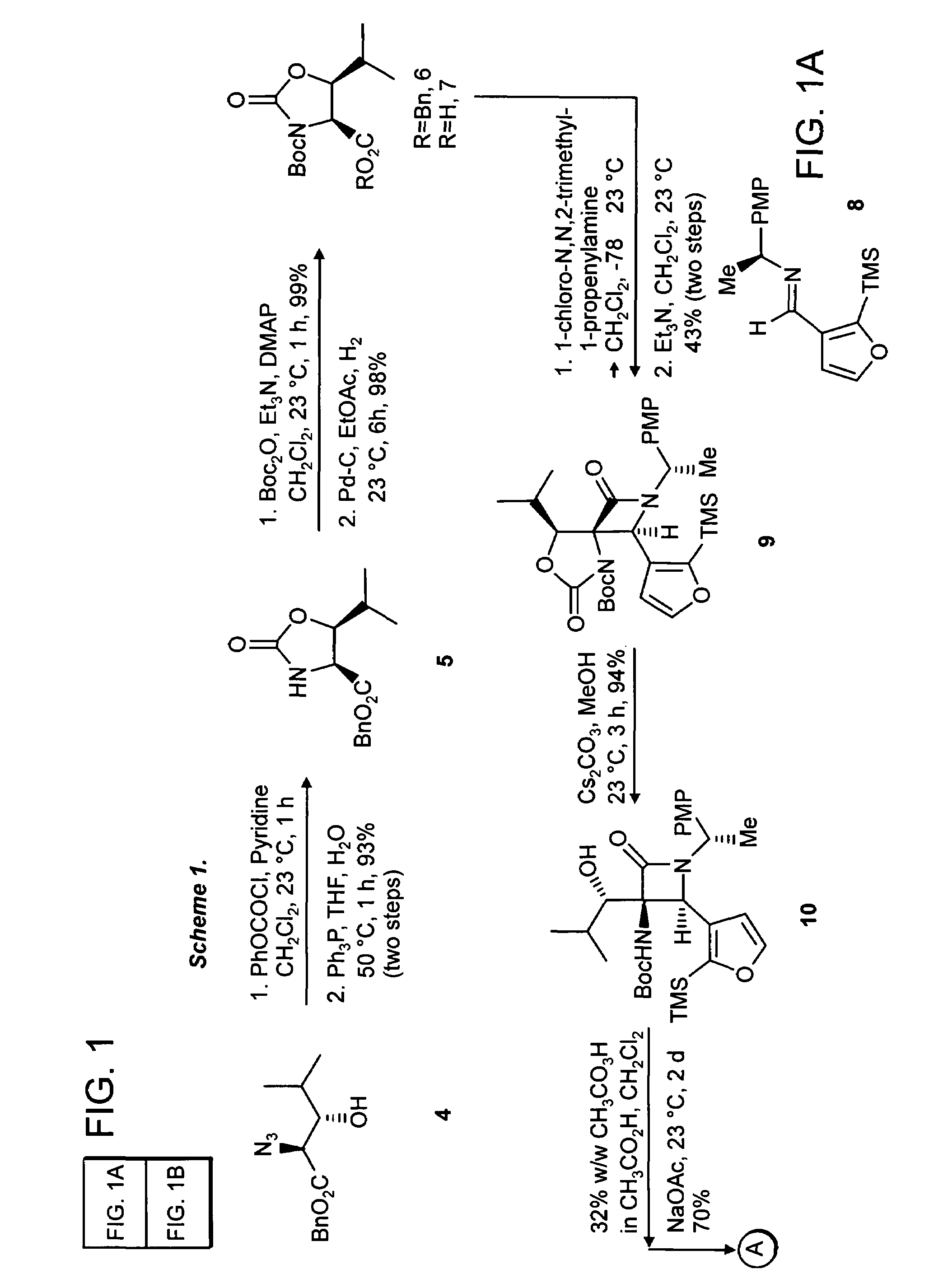
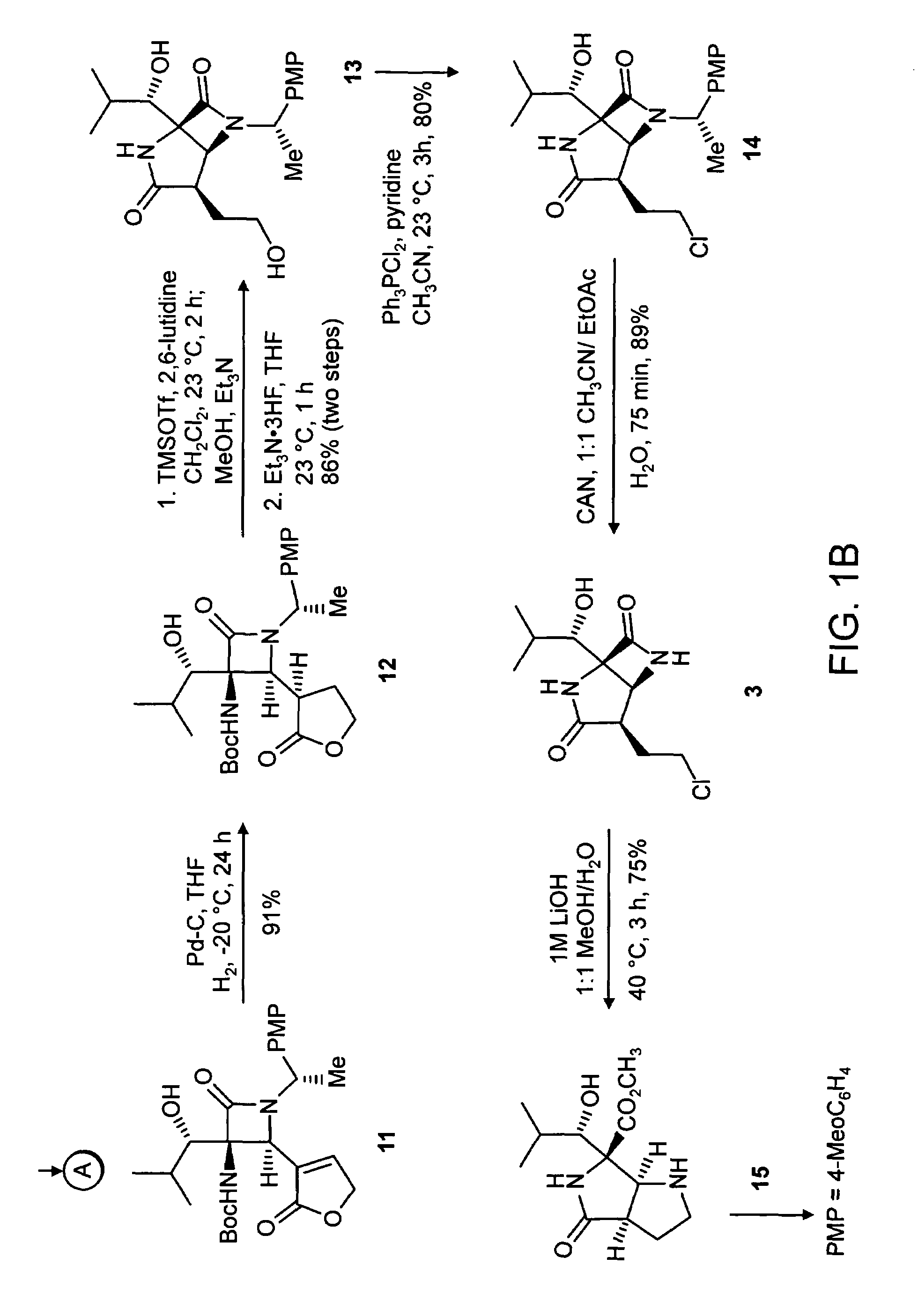
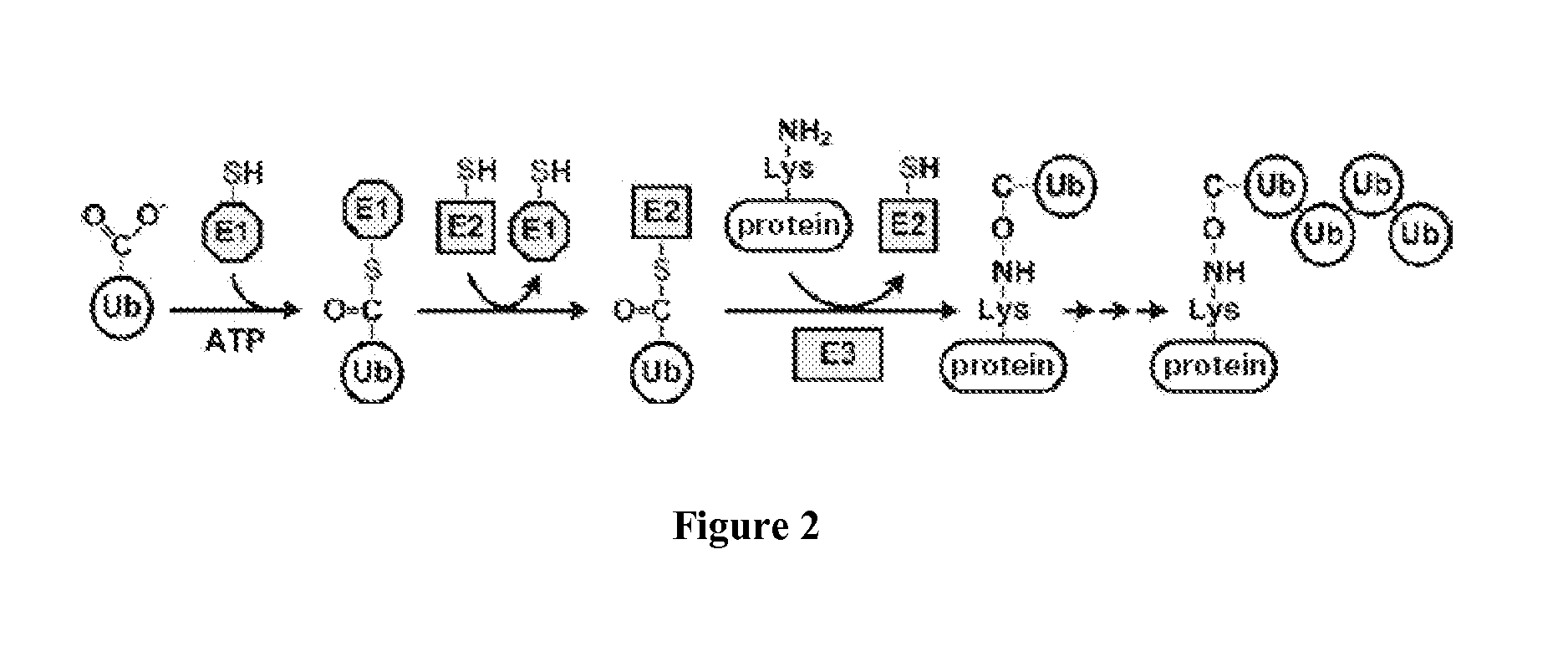
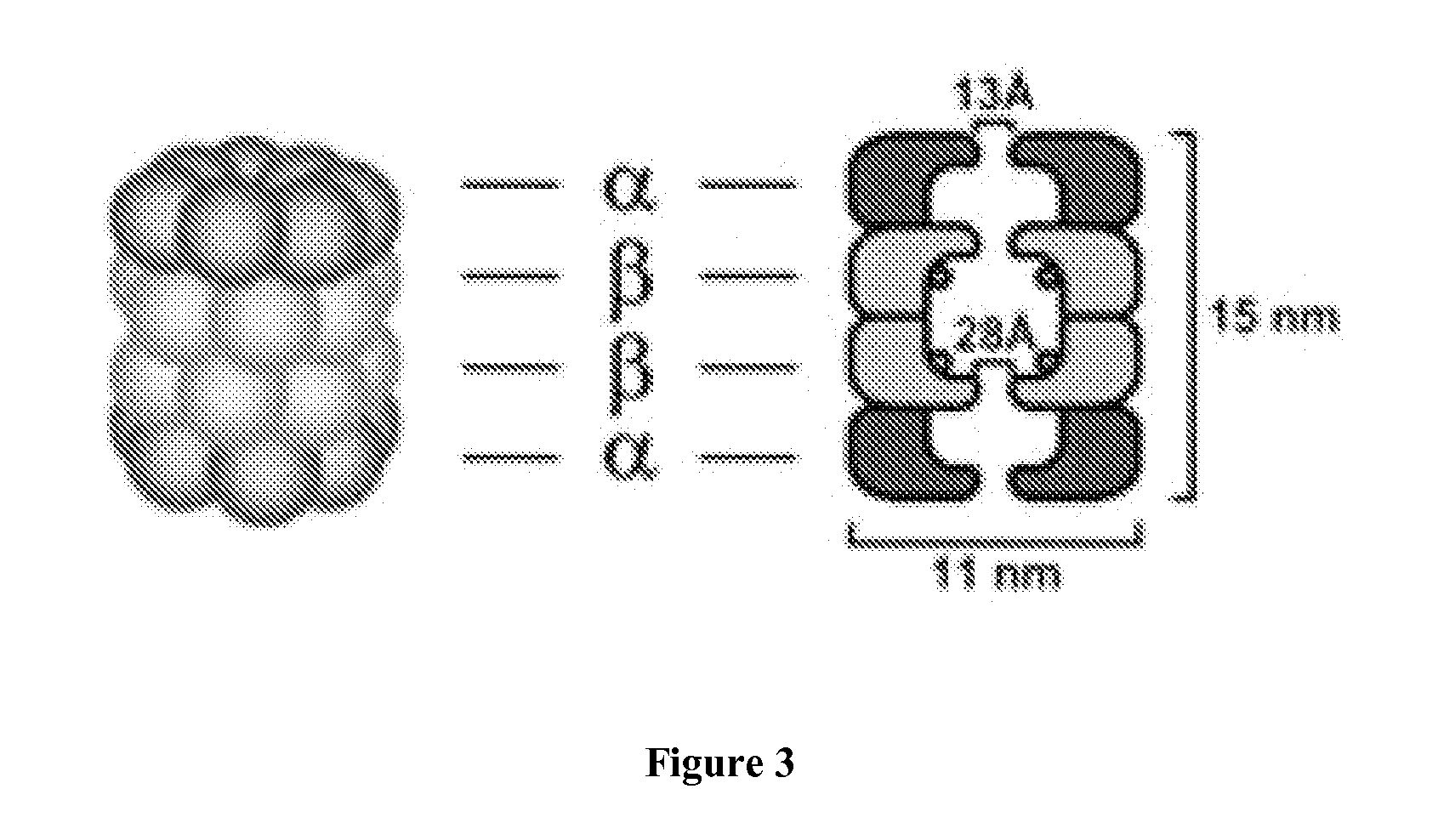
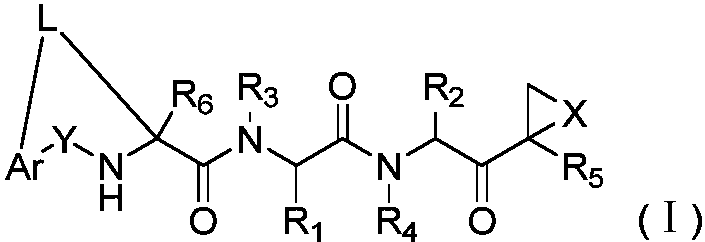
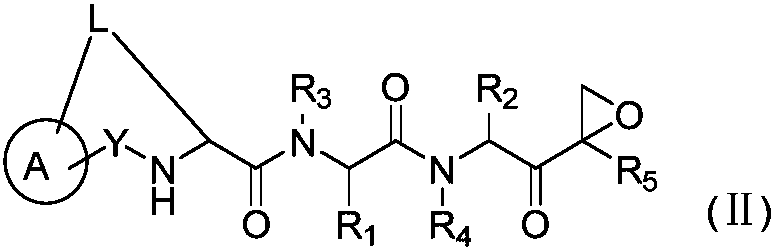
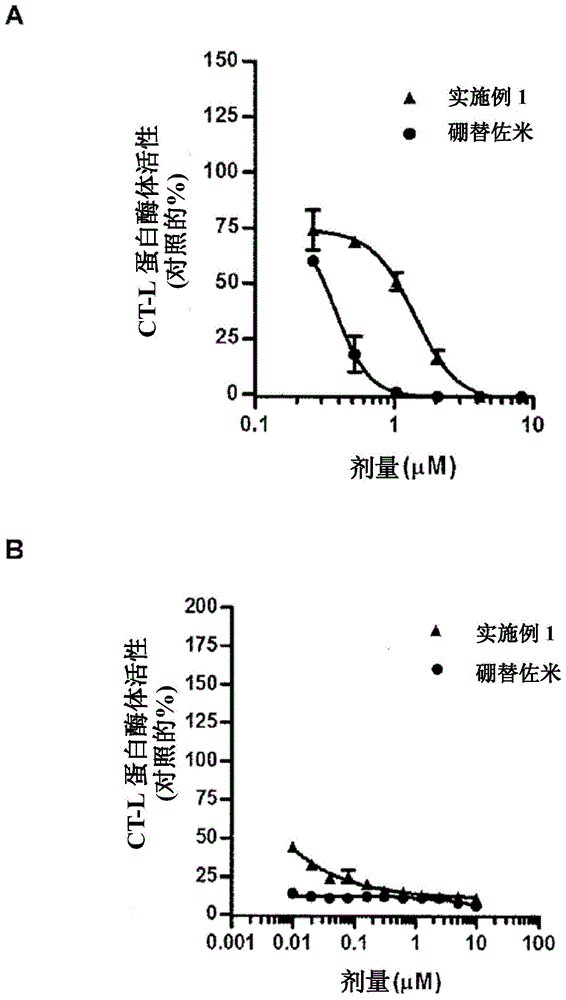
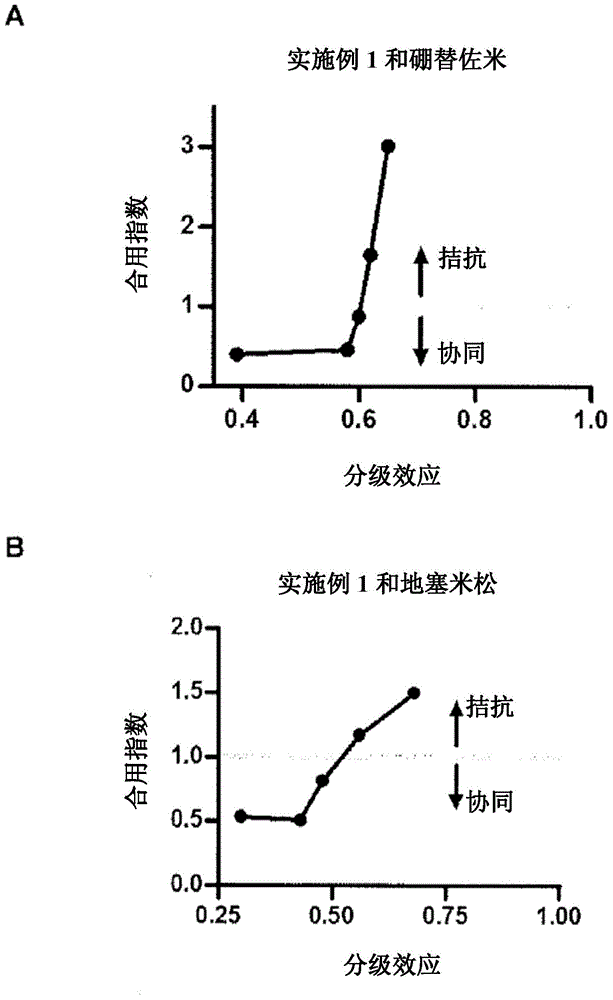
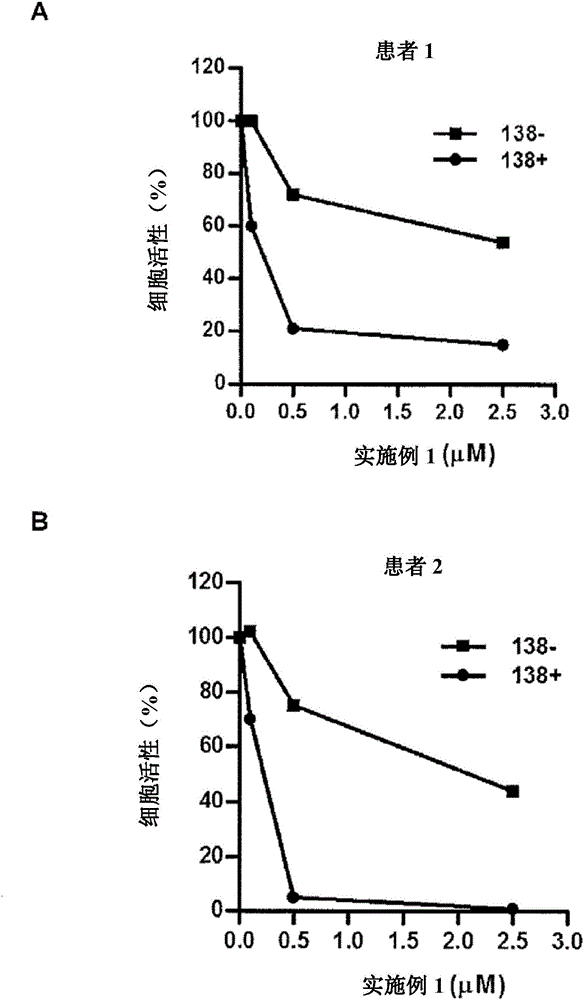
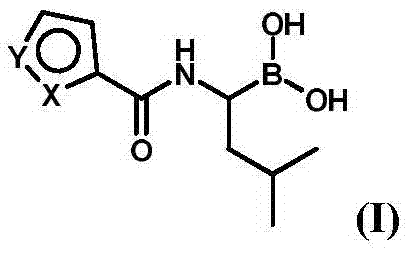
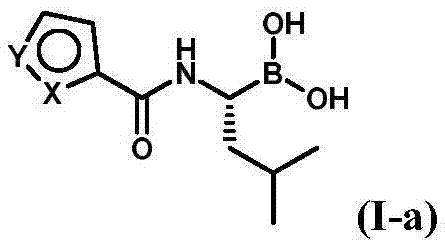
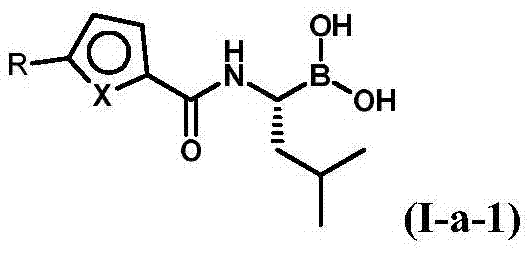
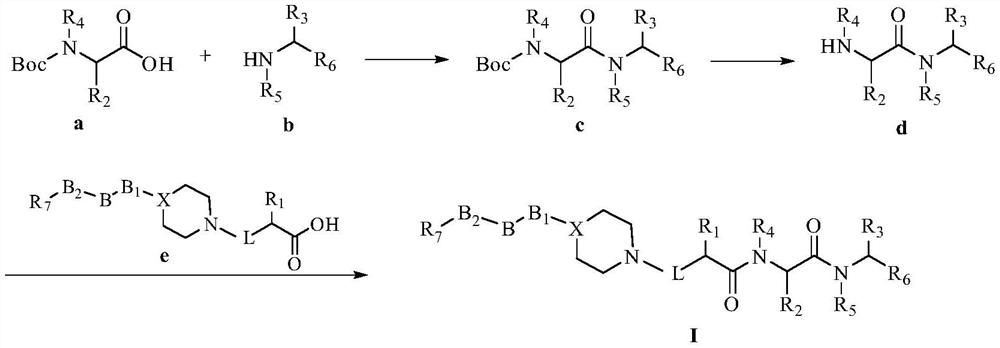
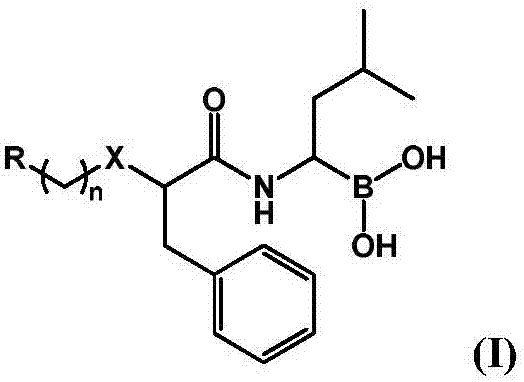
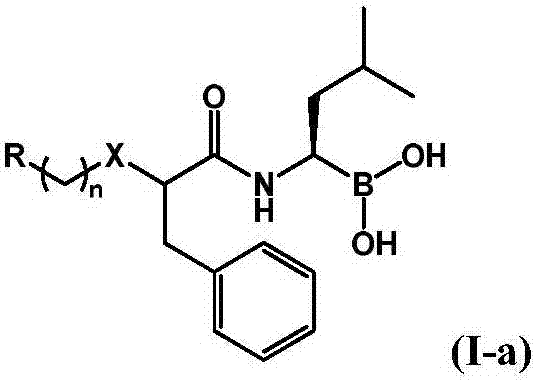
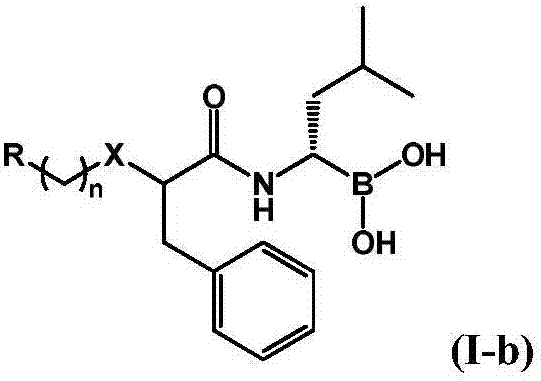
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34 results about "Proteasome Inhibition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Compounds acting at the centrosome
InactiveUS20060167106A1Network disruptionBiocideBacterial antigen ingredientsActin cytoskeletonProteasome degradation
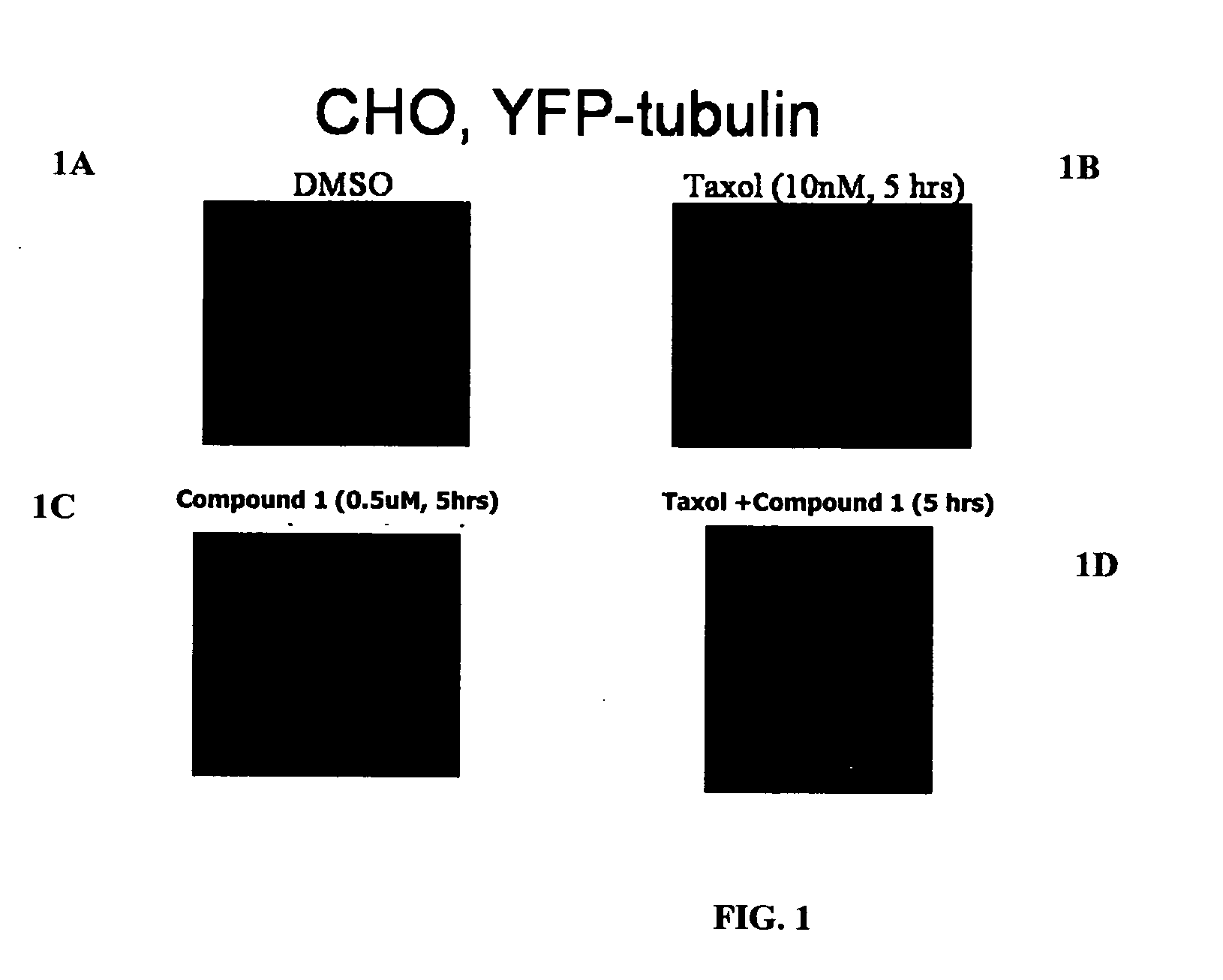
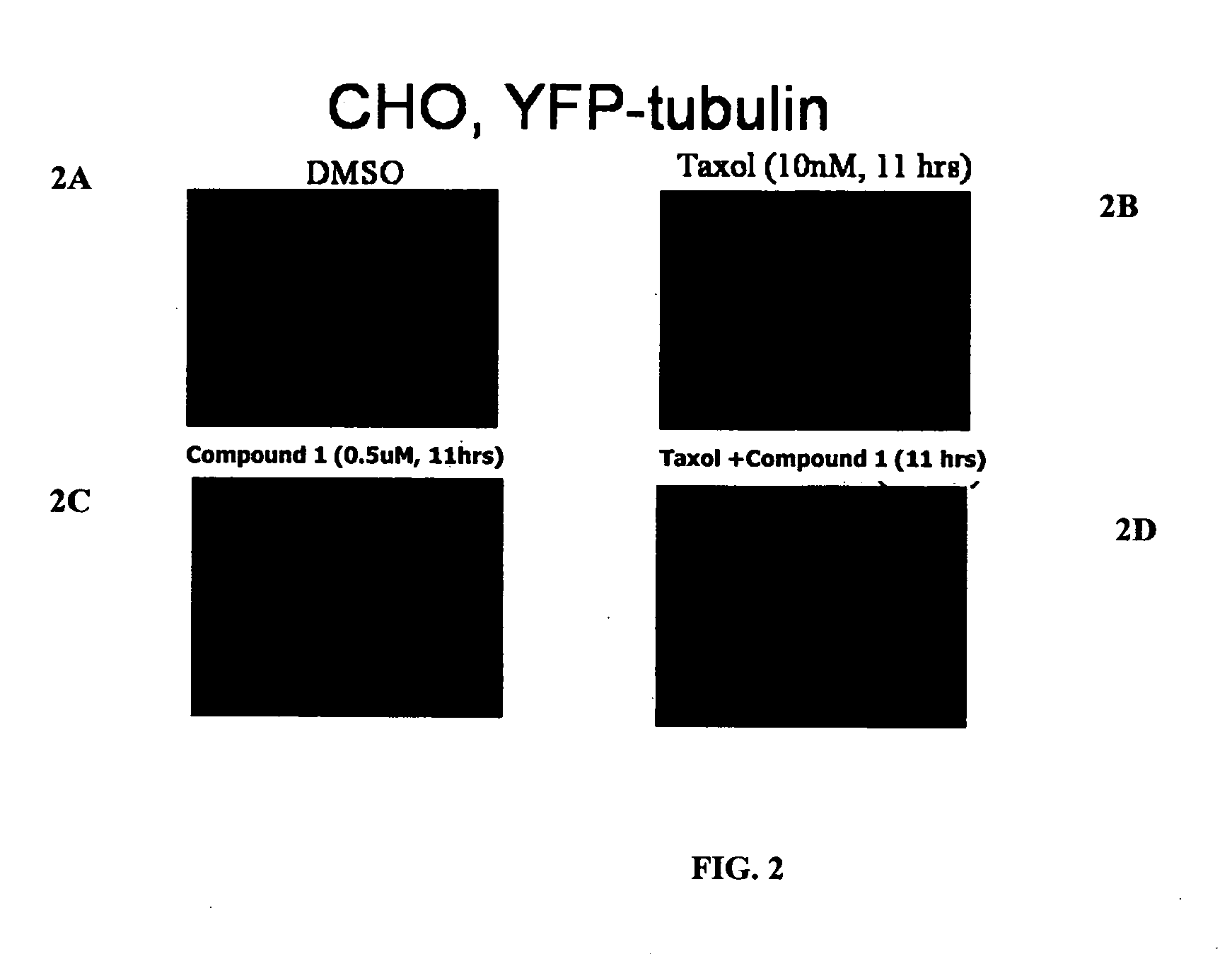
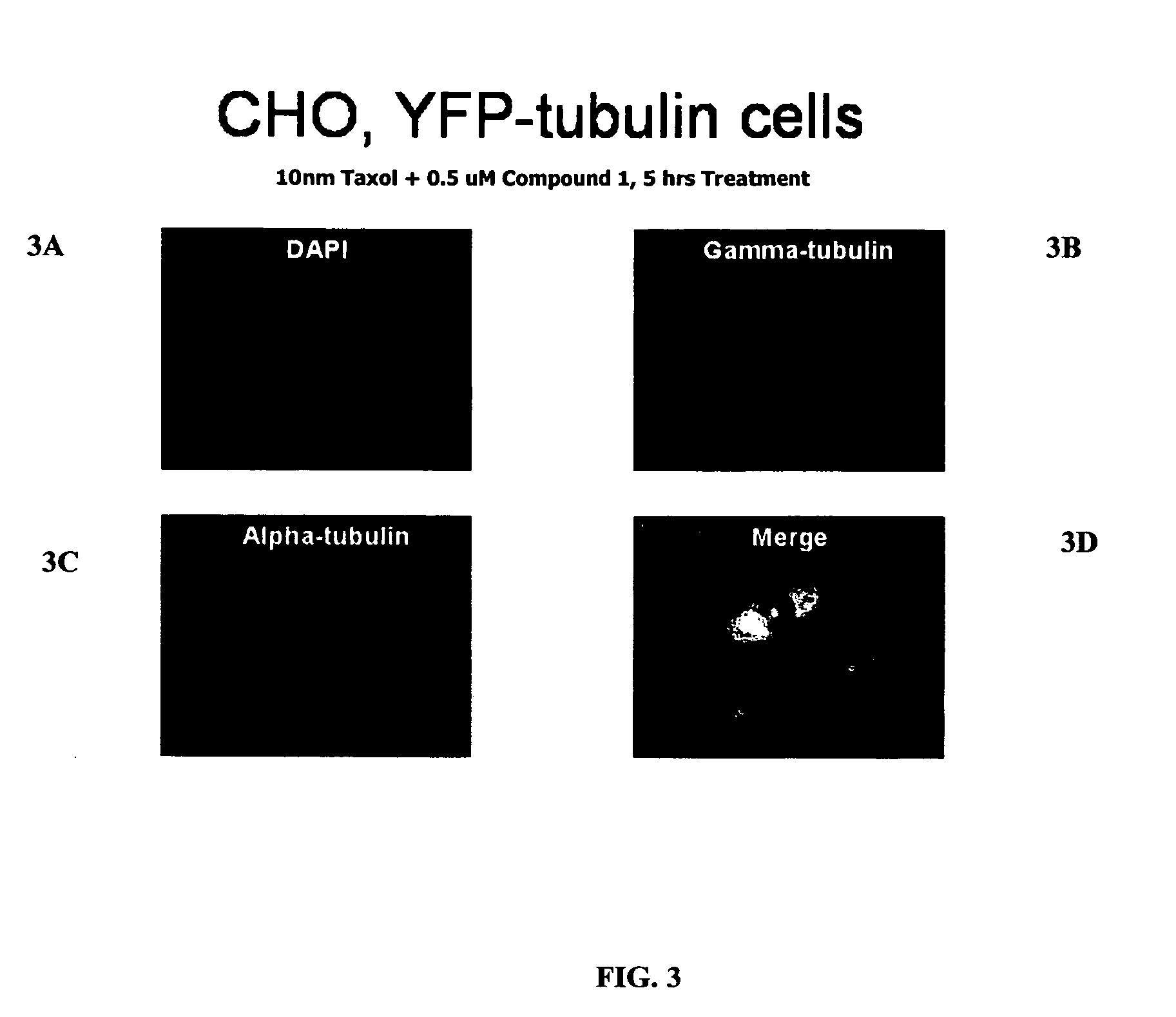
The present invention relates to compounds, and methods utilizing compounds, which exhibit one or more of the following properties: i) disrupts organization of an actin cytoskeleton of a cell; ii) disrupts organization of a microtubule network of a cell; iii) induces accumulation of tubulin at centrosomes but does not induce accumulation of tubulin in a nucleus of a cell; iv) induces accumulation of tubulin at centrosomes at a concentration of 500 nM or less within four hours; v) induces accumulation of Hsp70 and has weak-to-moderate proteasome inhibitory activity; and vi) does not have proteasome inhibitory activity when assayed on purified proteasomes.
Owner:SYNTA PHARMA CORP
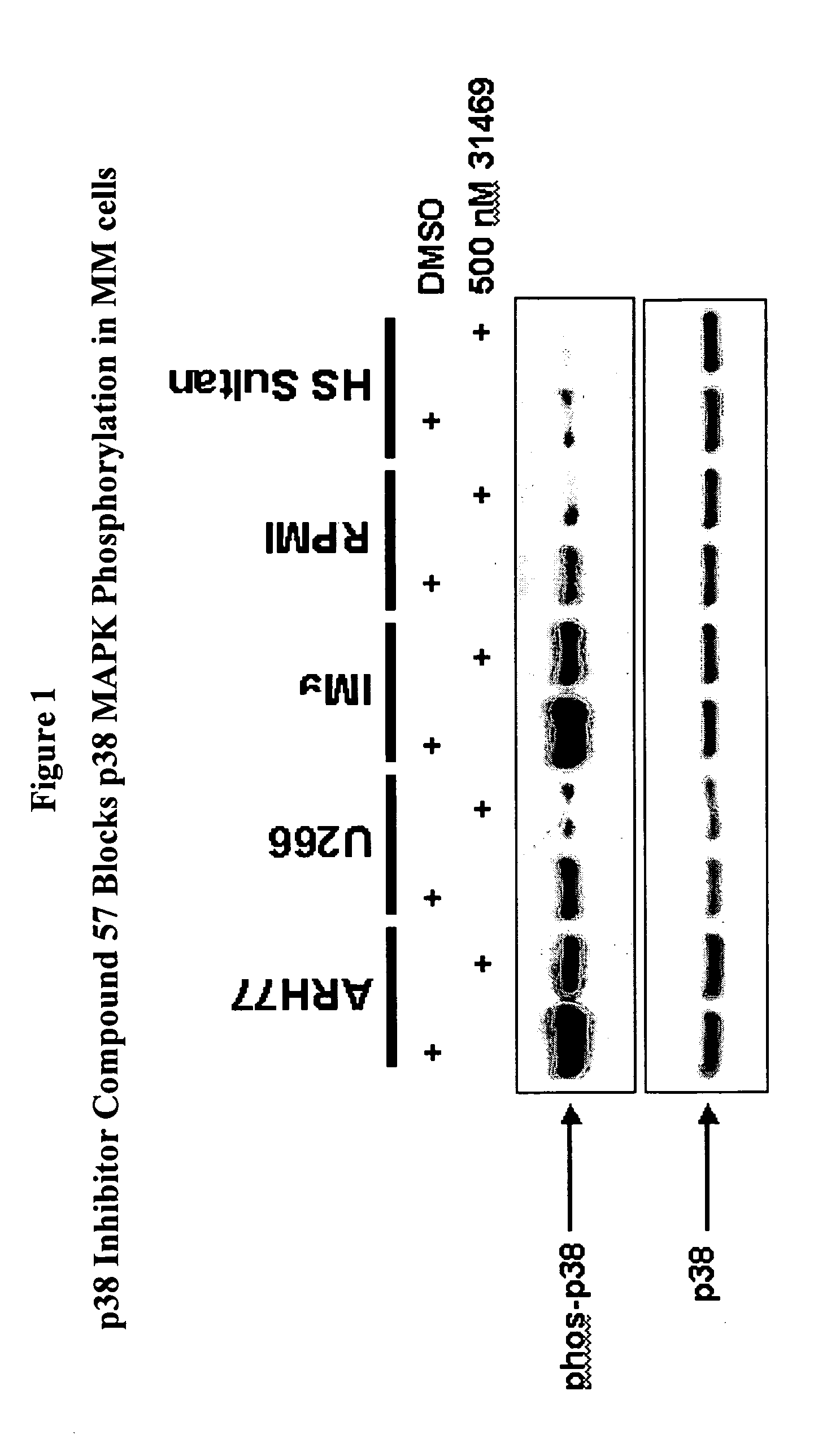
Treatment of multiple myeloma by p38 MAP kinase and proteasome inhibition
The present invention provides a method to treat multiple myeloma by the co-administration of one or more p38 MAP kinase inhibitors with one or more proteosome inhibitors.
Owner:SCIOS
Methods for the identification, assessment, and treatment of patients with proteasome inhibition therapy
InactiveUS20090181393A1Good choiceFacilitate uptake and implementationCompound screeningApoptosis detectionClinical settingsMedicine
The present invention is directed to the identification of markers that can be used to determine whether patients with cancer are clinically responsive or non-responsive to a therapeutic regimen prior to treatment. In particular, the present invention is directed to the use of certain combinations of markers, wherein the expression of the markers correlates with responsiveness or non-responsiveness to a therapeutic regimen comprising proteasome inhibition. Thus, by examining the expression levels of individual markers and those comprising a marker set, it is possible to determine whether a therapeutic agent, or combination of agents, will be most likely to reduce the growth rate of tumors in a clinical setting.
Owner:MILLENNIUM PHARMA INC
Synthetic method of proteasome inhibitor MLN9708
InactiveCN106608883AReduce usageEasy to operateGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsBulk chemical productionBenzoic acidProteasome Inhibition
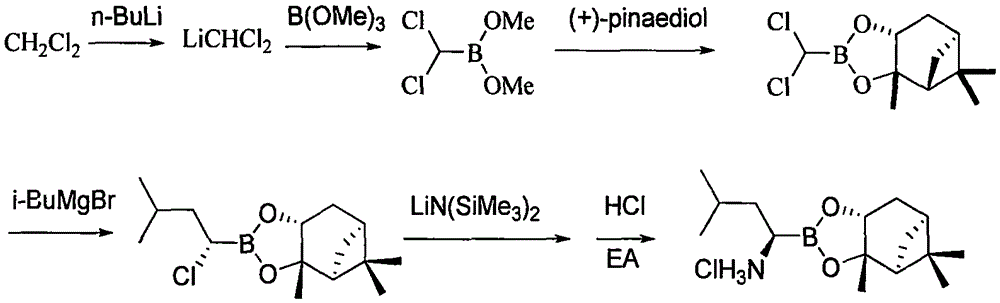
The invention provides a synthetic method of a proteasome inhibitor MLN9708. The method comprises: taking 2,5-dichloro benzoic acid as an initial raw material, and performing condensation and saponification to prepare N-(2,5-dichlorobenzoyl) glycine; joining N-(2,5-dichlorobenzoyl) glycine to L-leucine boronic acid pinacol ester hydrochloride; purifying the obtained product through forming a complex with diethanolamine and performing hydrolysis for deprotection to obtain corresponding free boric acid; and reacting the obtained product with citric acid to obtain MLN9708. The method is cheap and available in raw materials, simple and convenient to operate, mild in reaction conditions and easy for industrial production.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Tripeptide epoxy ketone compound constructed by heterocycle as well as preparation method and application thereof
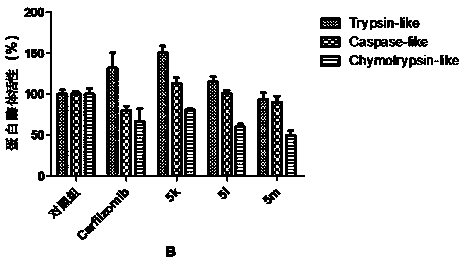
ActiveCN104945470AReasonable designRaw materials are easy to getNervous disorderDigestive systemEpoxyProteasome Inhibition
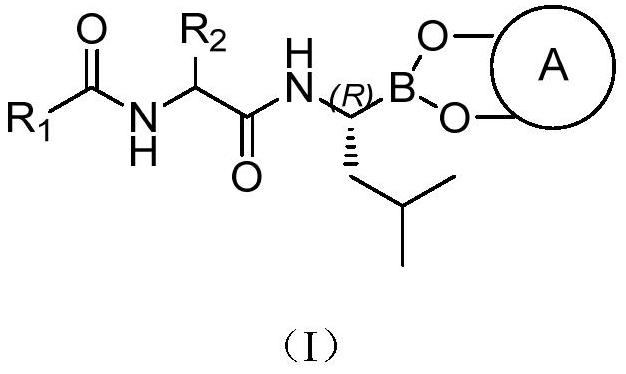
The invention provides a tripeptide epoxy ketone compound constructed by heterocycles. Carfilzomib is taken a pilot compound, a Boc protecting group is removed under condensation and acid conditions, reaction is carried out under alkaline condition to obtain amino acid methyl ester isocyanate, and hydrolysis is carried out under the action of a condensation agent, so that the tripeptide epoxy ketone compound is obtained. The tripeptide epoxy ketone compound is a micromolecule short-peptide proteasome inhibitor; the tripeptide epoxy ketone compound has extremely strong proteasome inhibitory activity and cell prolifation inhibitory activity and has a prospect, and a new way is provided for study of a cancer treatment medicine; raw materials for synthesizing the tripeptide epoxy ketone compound are available, route design is reasonable, reaction conditions are mild, yield of each step is high, operation is easy, and the tripeptide epoxy ketone compound is applicable to industrial production; and the tripeptide epoxy ketone compound has a general structural formula shown in a formula I (described in the specification).
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Proteasome inhibiting beta-lactam compounds
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Structures of proteasome inhibitors and methods for synthesizing and use thereof
InactiveUS20150336915A1Good treatment effectMonitor progressOrganic chemistryAntineoplastic agentsProteasome InhibitionChemistry
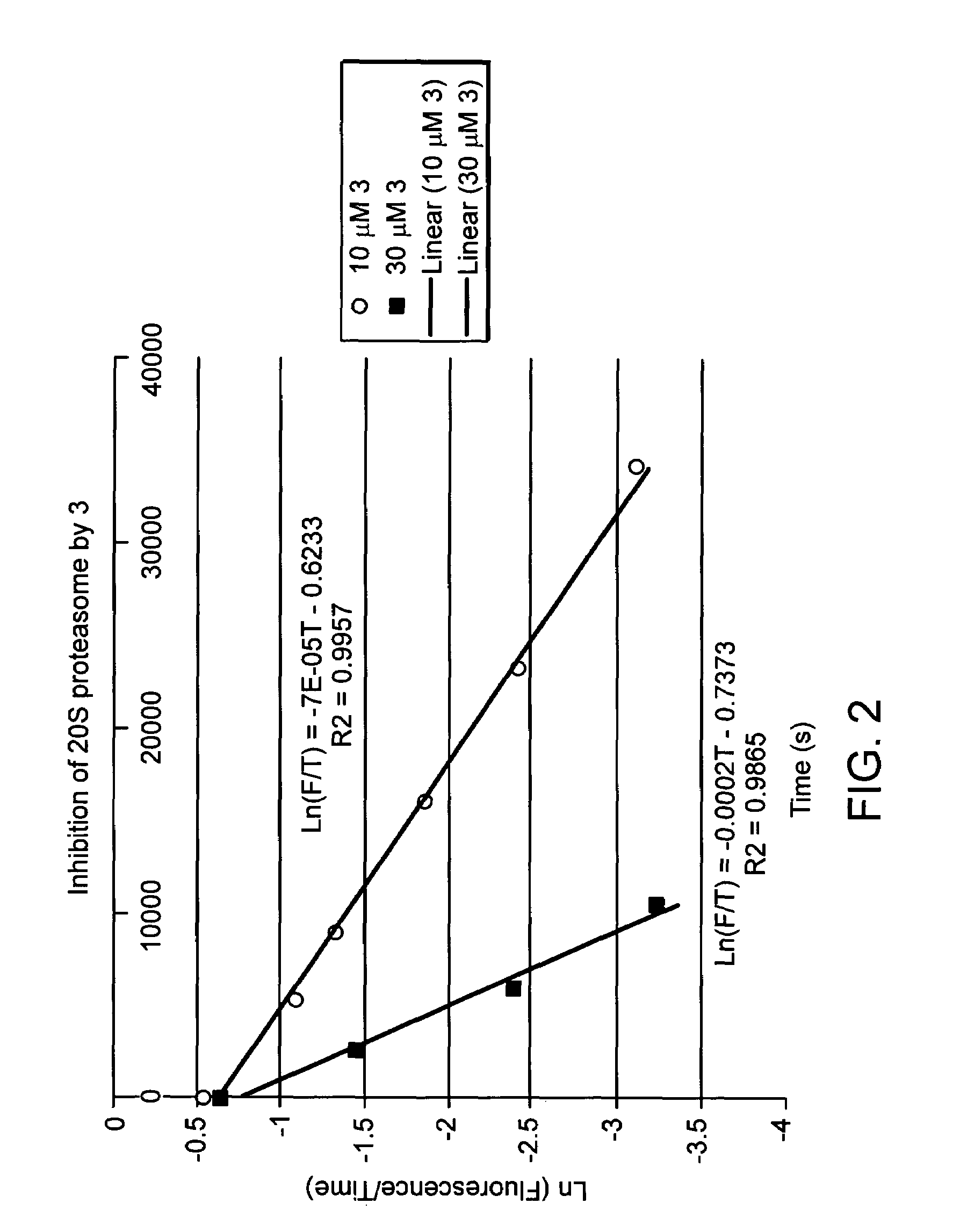
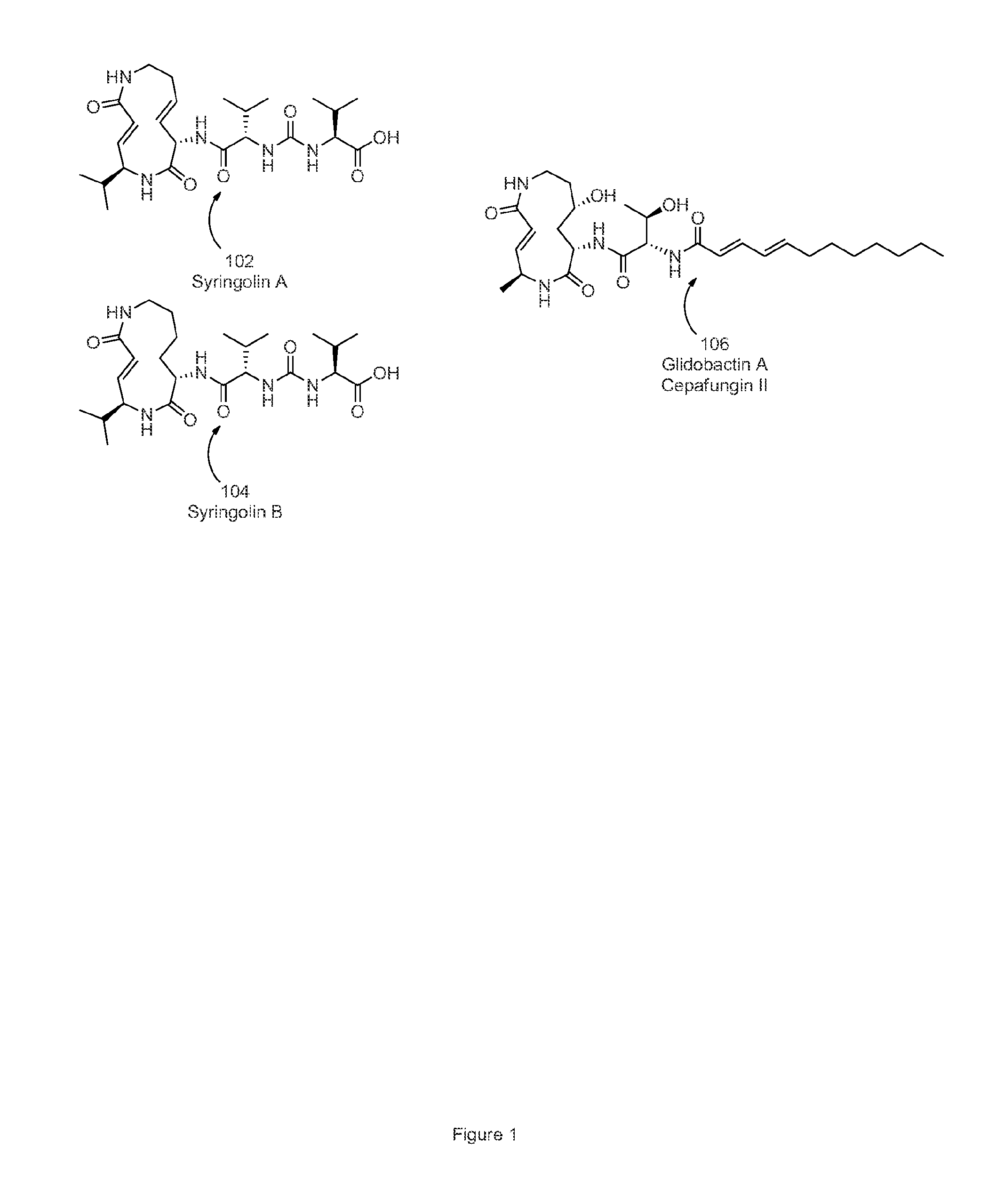
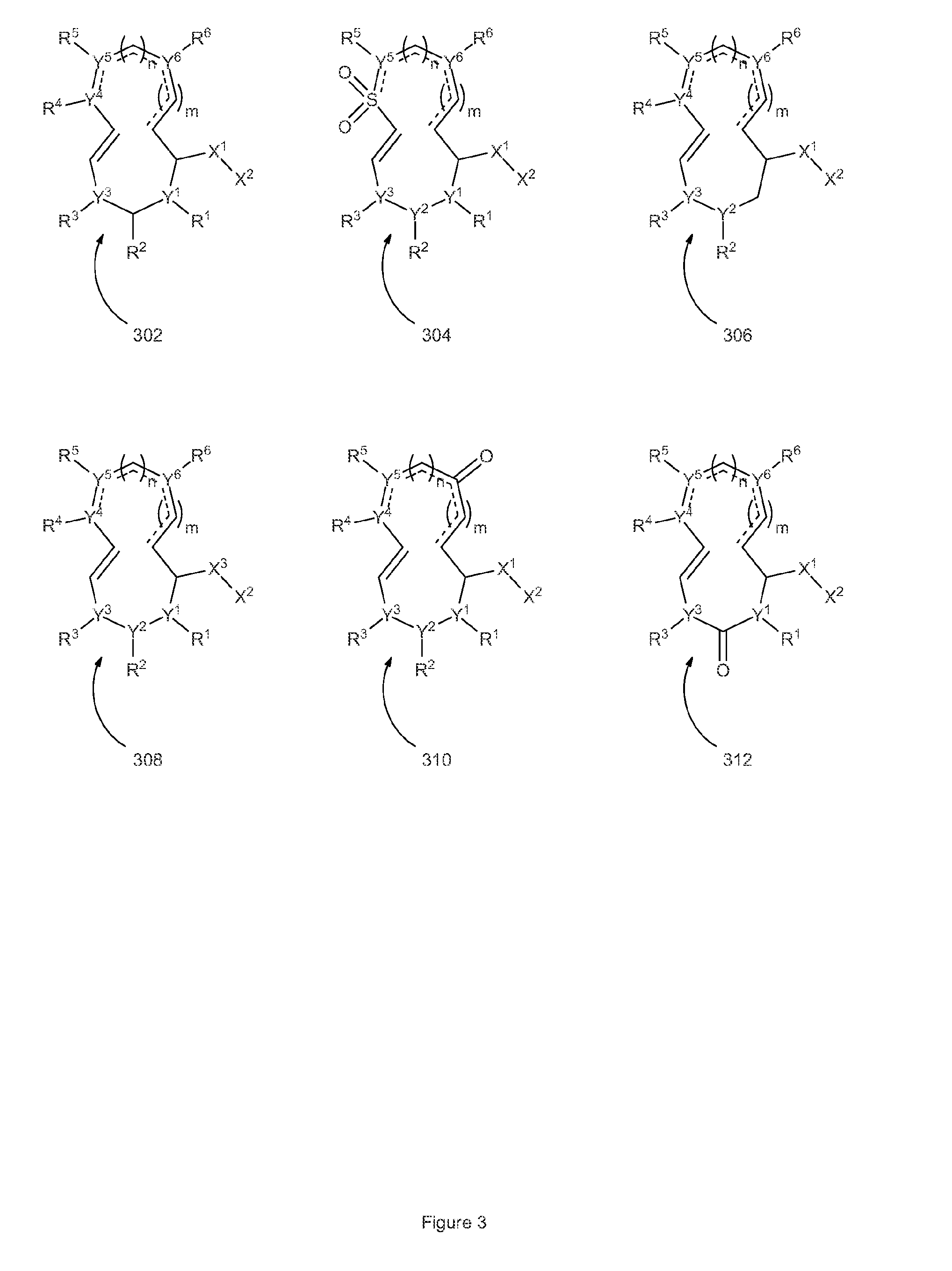
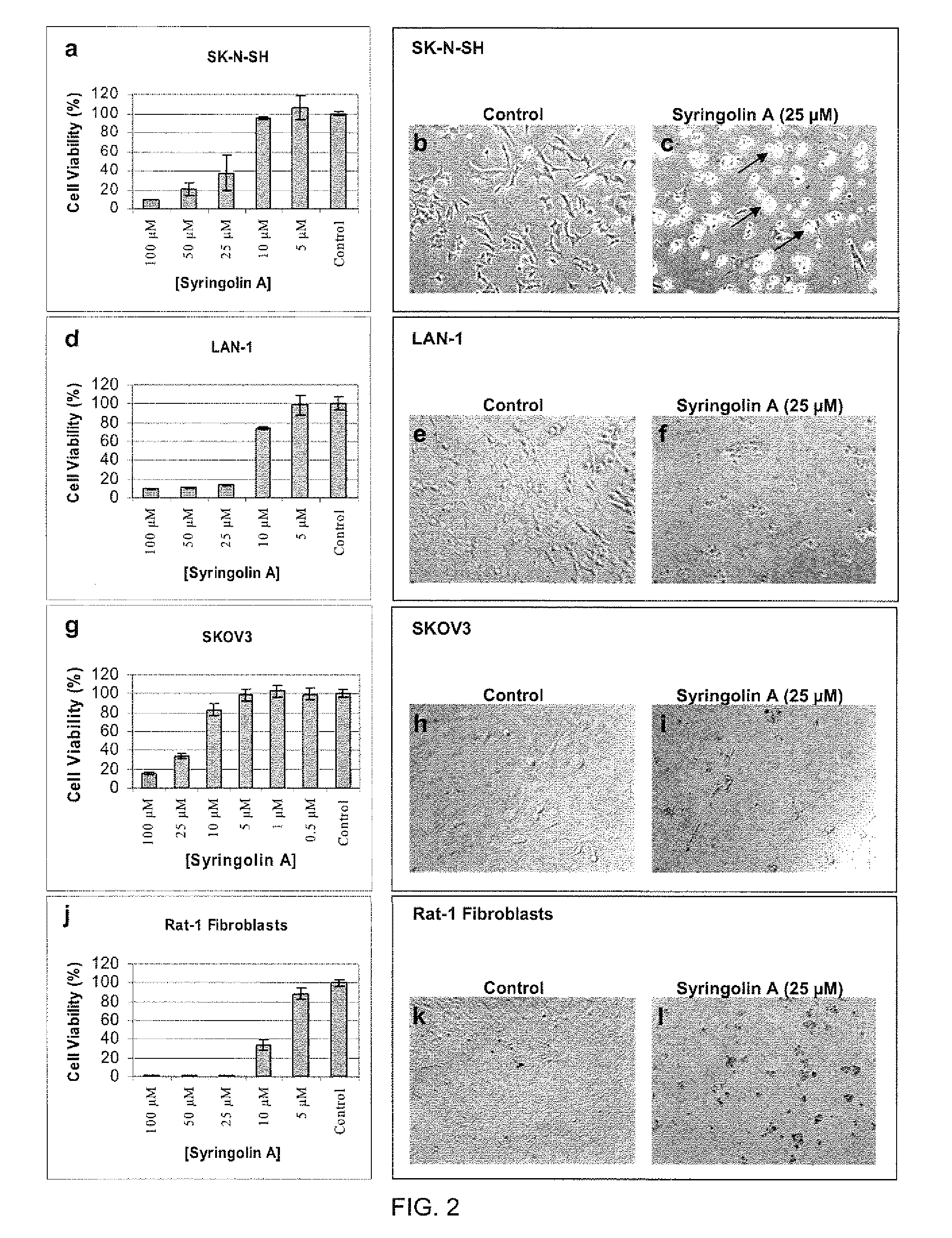
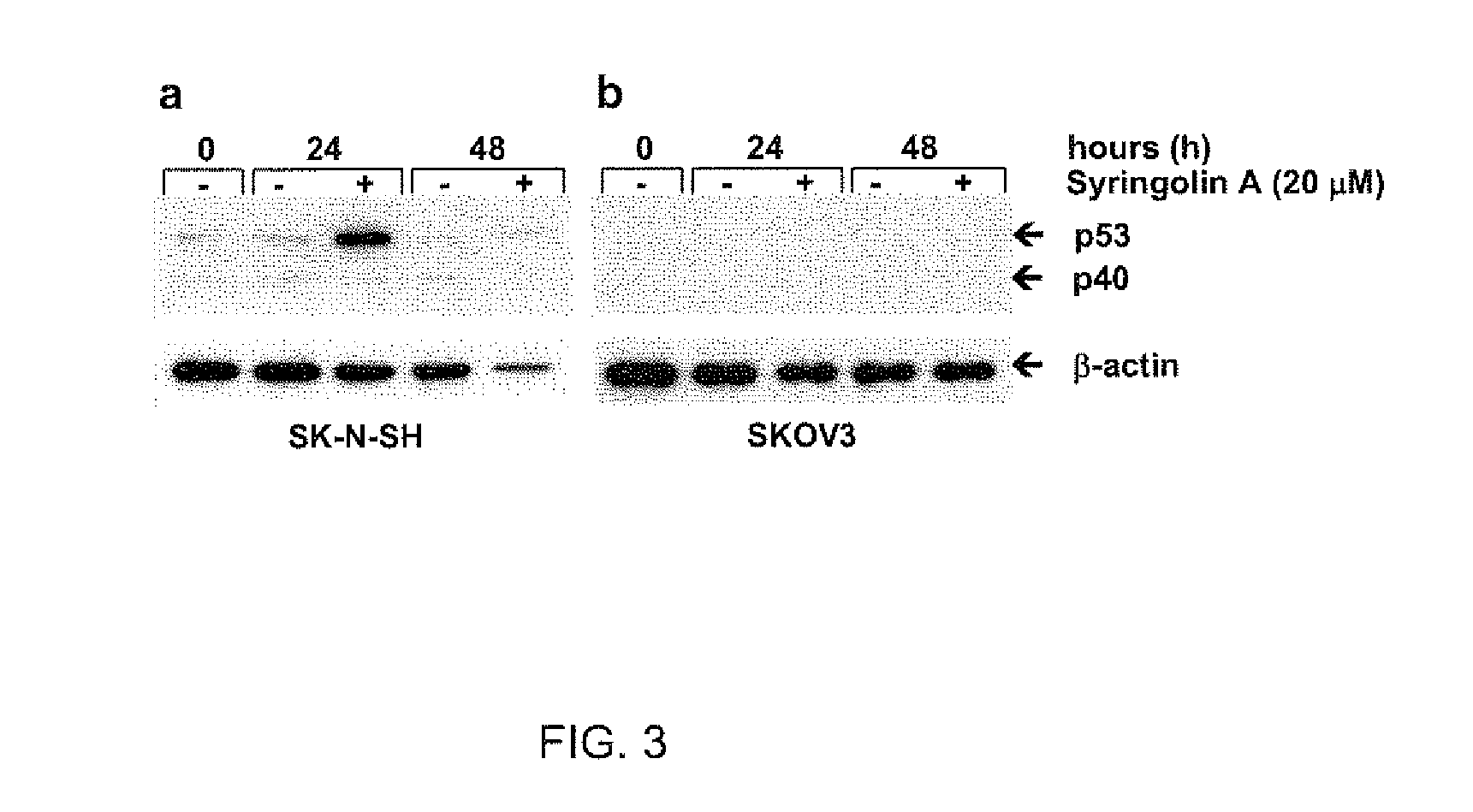
Disclosed herein are novel structures of proteasome inhibitors and methods for synthesizing and use thereof, including novel structures of proteasome inhibitors, such as syrbactins and its analogs, and methods for synthesizing them and using them for effective proteasome inhibition.
Owner:PONO
Proteasome inhibitors having chymotrypsin-like activity
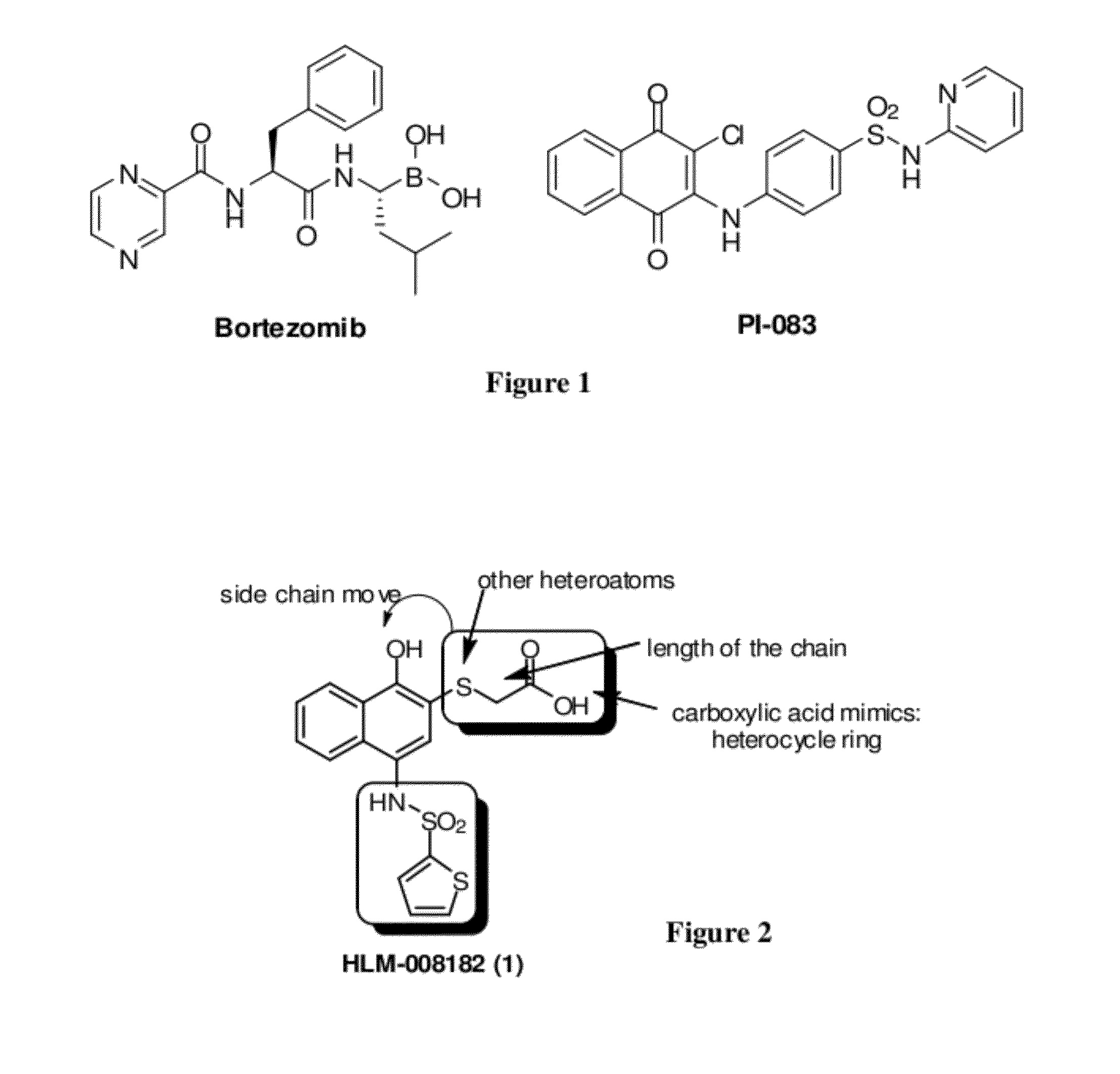
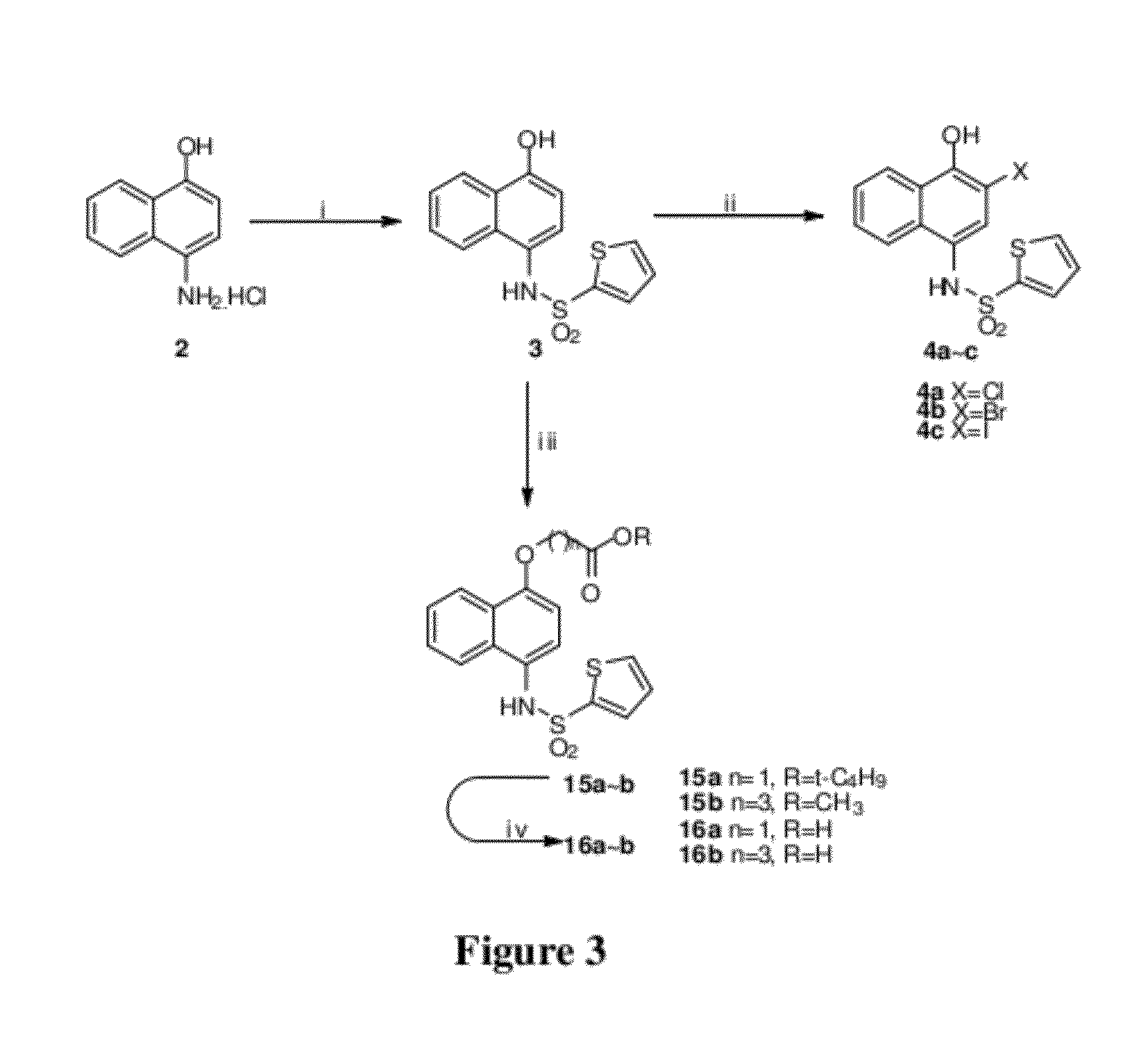
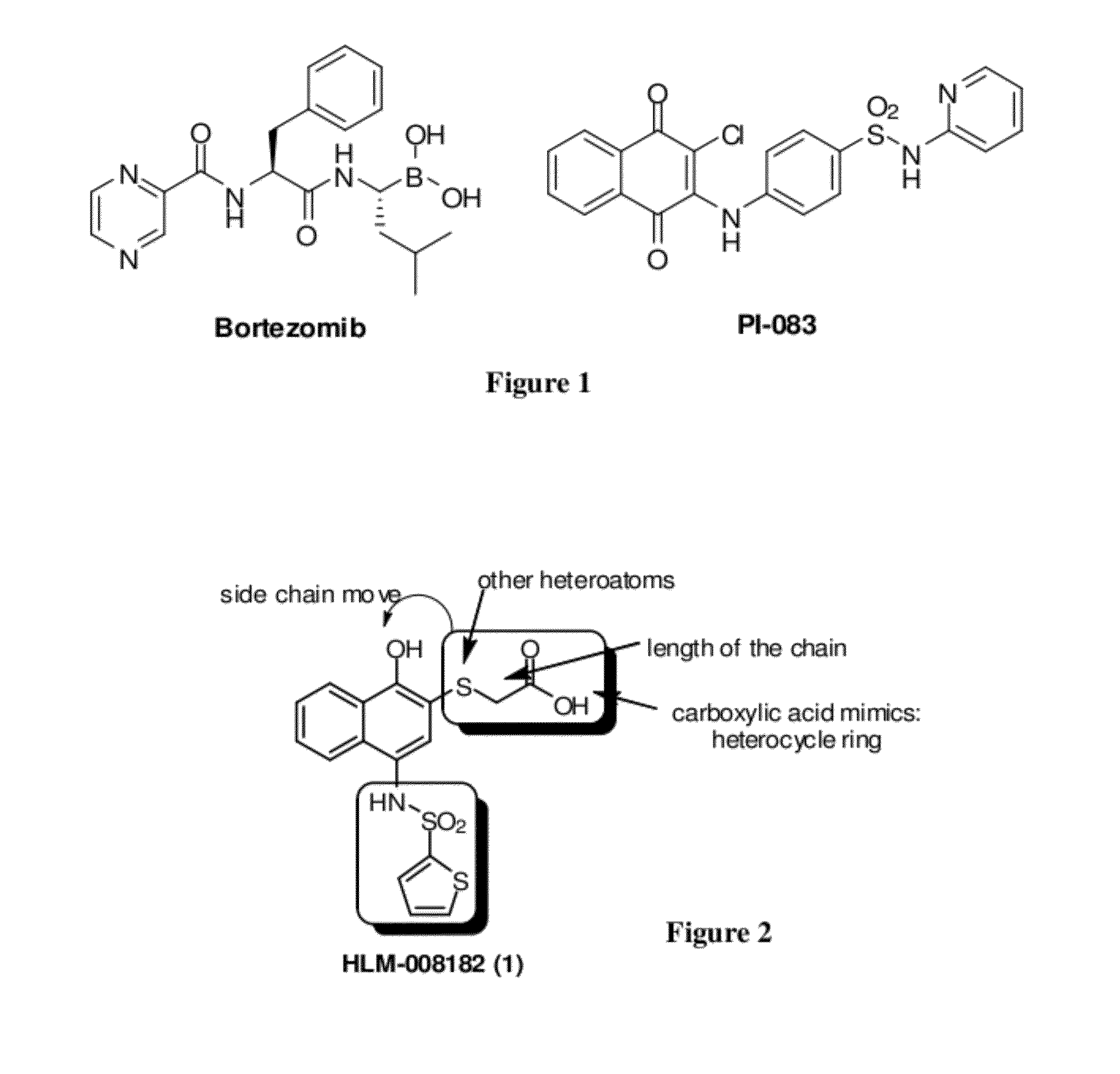
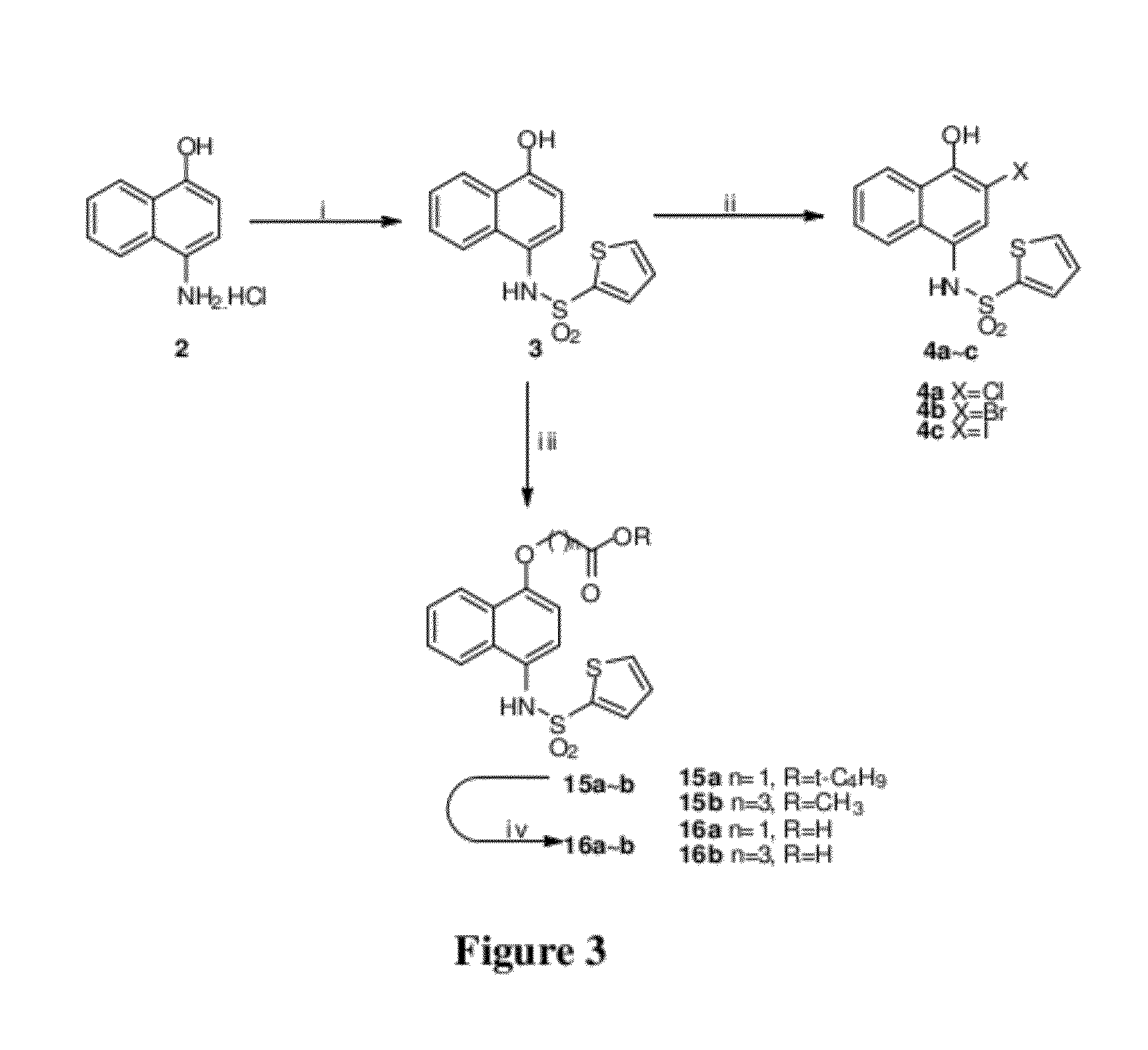
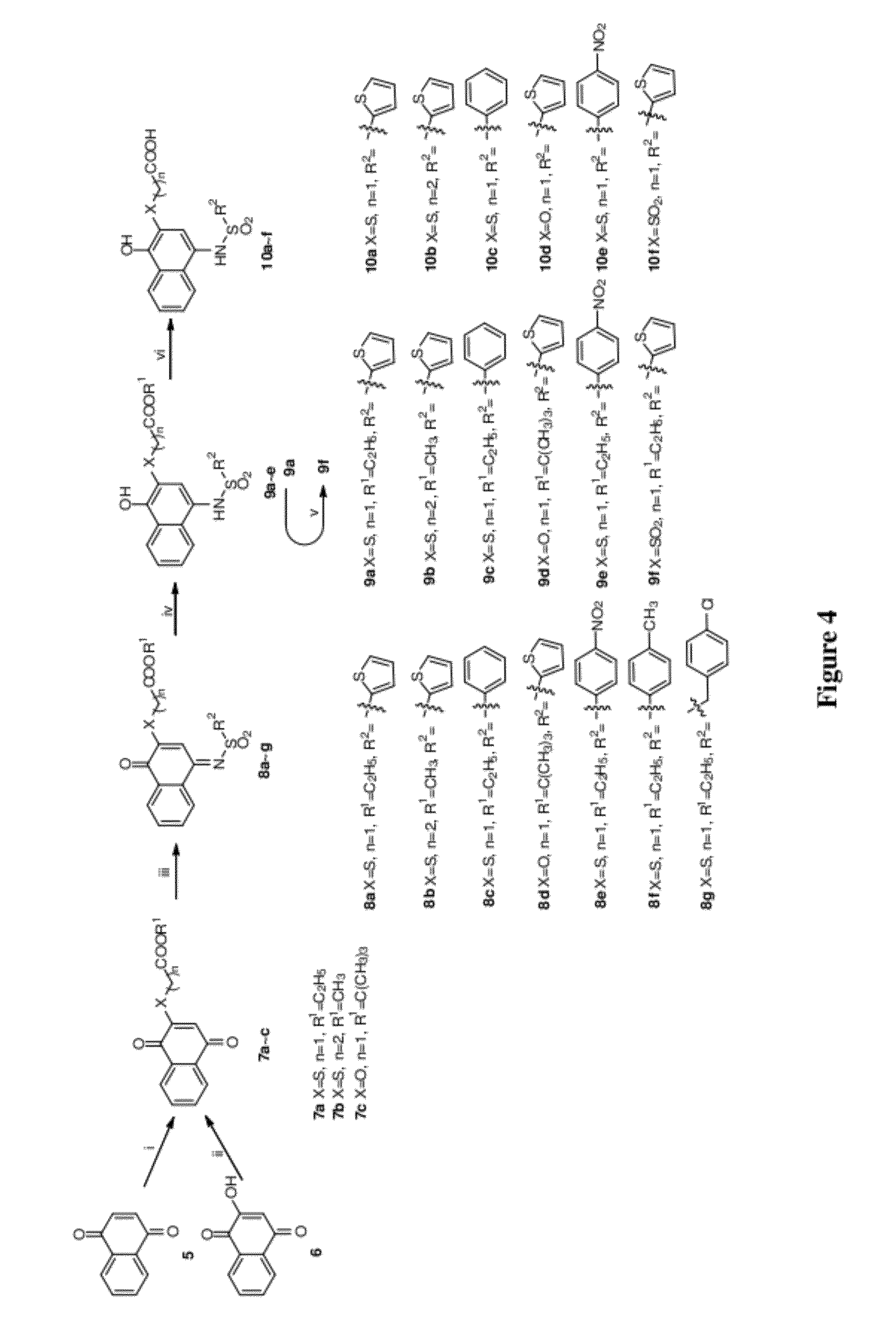
Disclosed herein is the use of HLM-008182, as well as its analogues formed via in-house synthesis, as a potent proteasome inhibitors. A new method was developed for HLM-008182 through a four-step protocol and the method was further optimized to a two step protocol. The synthesis in both protocols was regioselective with TiCl4. The reaction was highly efficient with microwave assisted heating and THF as solvent. The modification around the molecule HLM-008182 established primary SAR, indicating that the proteasome inhibition activity was a function of the 2-side chain.
Owner:H LEE MOFFITT CANCER CENT & RES INST INC +1
Proteasome inhibitors having chymotrypsin-like activity
Disclosed herein is the use of HLM-008182, as well as its analogues formed via in-house synthesis, as a potent proteasome inhibitors. A new method was developed for HLM-008182 through a four-step protocol and the method was further optimized to a two step protocol. The synthesis in both protocols was regioselective with TiCl4. The reaction was highly efficient with microwave assisted heating and THF as solvent. The modification around the molecule HLM-008182 established primary SAR, indicating that the proteasome inhibition activity was a function of the 2-side chain.
Owner:H LEE MOFFITT CANCER CENT & RES INST INC +1
Pharmaceutical compositions for the treatment of conditions responsive to proteasome inhibition
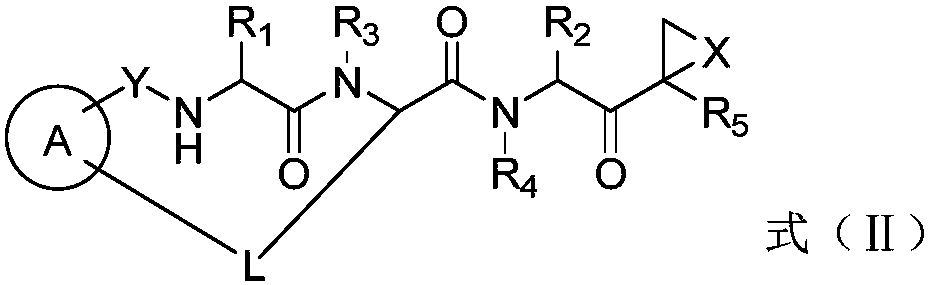
The invention disclosed herein generally relates to methods and compositions for inhibiting proteasome activity comprising a syrbactin compound have the structure of Formula (I) or (II).
Owner:PONO
Method for preparing proteasome inhibitor Oprozomib and analogs thereof
InactiveCN105949279AAvoid racemizationEliminate the purification processPeptide preparation methodsBulk chemical productionDipeptideProteasome Inhibition
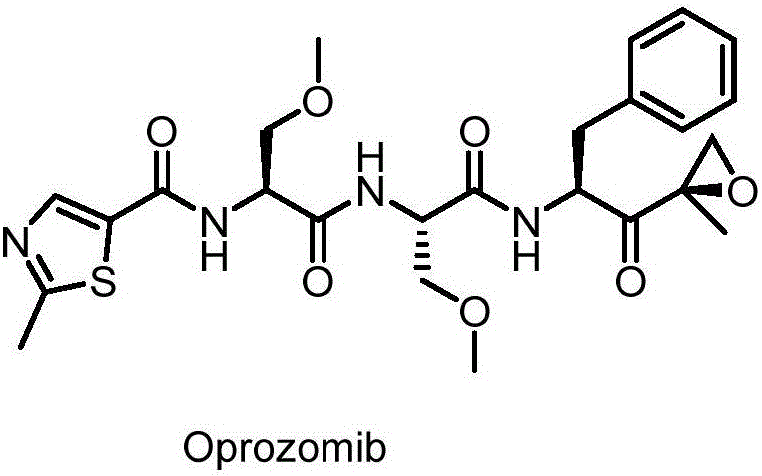
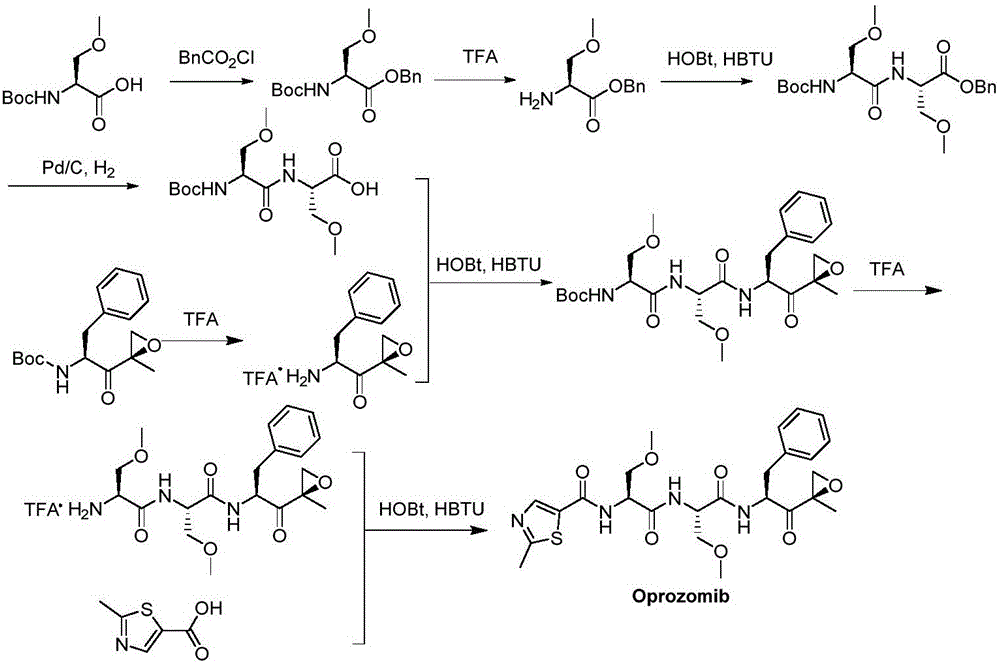
The invention provides a method for synthesizing a proteasome inhibitor Oprozomib and analogs thereof. The proteasome inhibitor Oprozomib is prepared through subjecting a dipeptide intermediate represented by a formula IV shown in the description to deprotection, and then, subjecting the de-protected dipeptide intermediate to a reaction with a peptide-terminated epoxy ketone fragment represented by a formula VIII shown in the description. The proteasome inhibitor Oprozomib synthesized by the method provided by the invention, i.e., an object compound is obtained through separately preparing the dipeptide intermediate and the peptide-terminated epoxy ketone fragment and finally carrying out condensation, the yield of synthesis is 42%, the racemization of amino acids is avoided, and meanwhile, HPLC purification for the end product is avoided, so that the reaction cycle is greatly shortened, the production cost is reduced, and the yield and purity of the product are improved. The proteasome inhibitor Oprozomib has a structural general formula shown in the description.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Proteasome inhibiting beta-lactam compounds
Disclosed is a total synthesis of a biologically active β-Lactam—Compound 3, which is related to Salinosporamide A and Omuralide, both structurally and by its activity as a proteasome inhibitor. Also disclosed are proteasome inhibiting compounds having the formula: wherein: R1 is a cyclolower alkyl group; or R1 is a lower alkyl group; and R2 is either hydrogen or a lower alkyl group; R3 is either hydrogen or a lower alkyl group; R4 a halo-lower alkyl group; and R5 is either hydrogen or a lower alkyl group.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Macrocyclic ketone peptide compound as well as preparation method and medical purpose thereof
InactiveCN108117582AGood proteasome inhibitory activityOral effect is goodTetrapeptide ingredientsTripeptide ingredientsDiseaseKetone
The invention provides a novel macrocyclic ketone peptide derivative, an optical isomer or pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvolyte thereof. Carboxyl protection compounds are used as starting rawmaterials to be subjected to condensation with amino protection amino acid, deamination protection, olefin ring closing double decomposition and decarboxylizing protection, and condensation with epoxy ketone fragment. The macrocyclic ketone peptide compound with a fire-new framework has high protease body inhibition activity; the high in vitro proliferation inhibition effect is achieved on multiple myeloma such as RPMI 8226, MM.1S and NCI-H929 and various other solid tumor cell strains; meanwhile, the compound has good oral administration effects, and can also be applied to preparation of anti-tumor and immune disease medicine. The compound has the advantages that raw materials required for synthesis can be easily obtained; the route design is reasonable; the reaction conditions are mild;the yield in each step is high; the operation is simple and convenient; the compound is suitable for industrial production. The compound has a structure shown by a formula (I) shown in the description.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Methods for enzyme inhibition
InactiveUS20060193844A1Inhibiting and reducing HIV infectionAffecting levelBiocideAntiviralsRegimenEnzyme inhibition
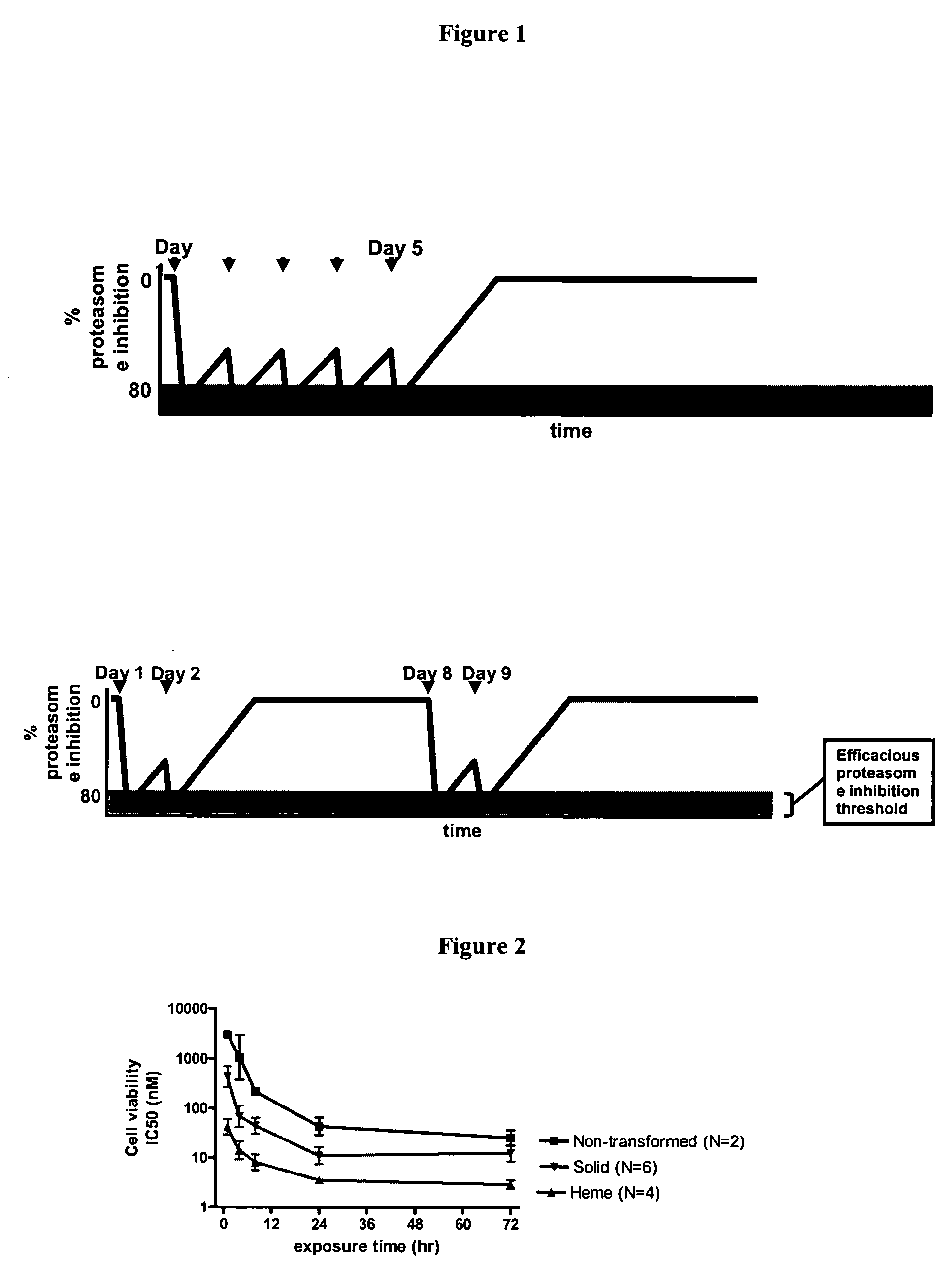
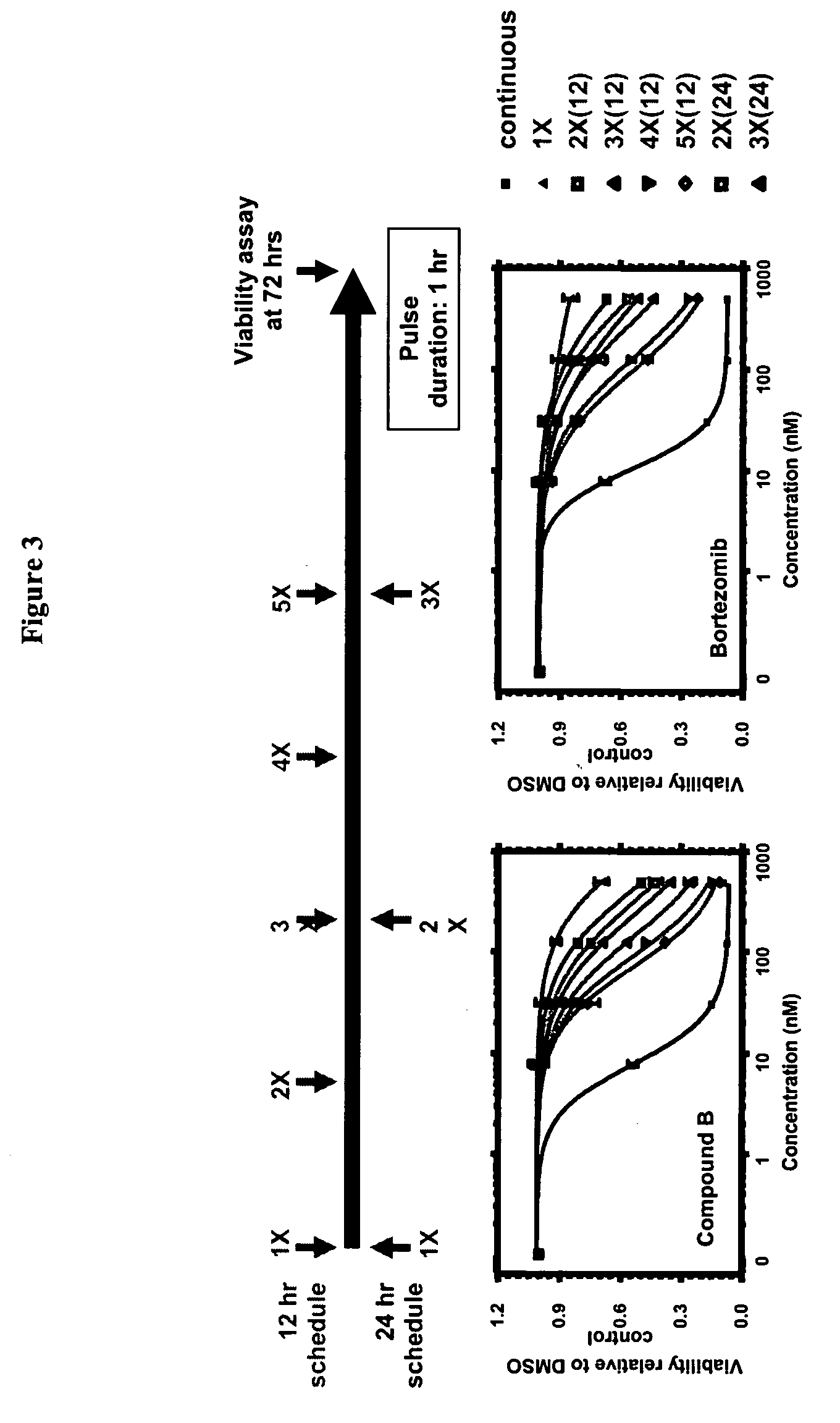
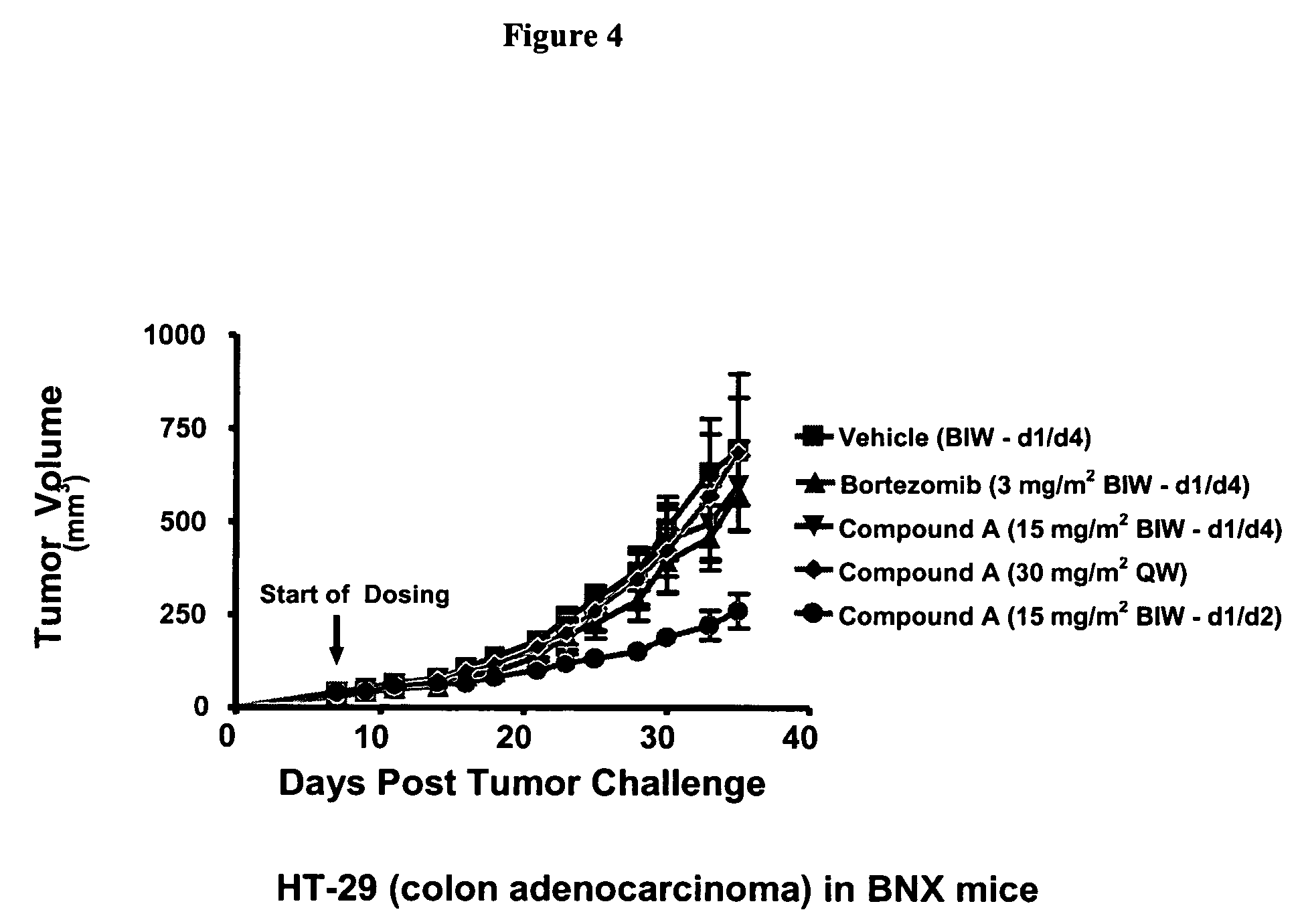
Improved regimens for administering proteasome inhibitors are described, wherein proteasome inhibition is more sustained relative to certain current regimens which permit substantial recovery of proteasome activity between doses of inhibitor.
Owner:PROTEOLIX INC
Bortezomib pharmaceutical composition and applications thereof
InactiveCN108201622AAvoid fluctuations in blood levelsLower blood levelsDipeptide ingredientsAerosol deliveryControlled drugsSide effect
The invention discloses a bortezomib pharmaceutical composition and applications thereof, wherein the bortezomib pharmaceutical composition comprises, by weight, 0.1-200 parts of bortezomib, 0.1-500 parts of an auxiliary material for adjusting release rate, 0-10 parts of a small molecule adjusting agent, and 0-2000 parts of a pharmaceutically acceptable injectable solvent. According to the presentinvention, the bortezomib pharmaceutical composition has the controlled drug release behavior, and can maintain the effective blood concentration and the proteasome inhibition level in the body; through the long-acting injection of the bortezomib pharmaceutical composition, the in vivo blood concentration and the efficacy providing of bortezomib can be controlled, the treatment effect of the drugcan e improved, the acting time can be prolonged, and the toxic-side effect of the drug can be reduced; the in vivo proteasome inhibition pharmaceutical composition with characteristics of high efficiency, long acting and low toxic-side effect is provided; and the invention further discloses uses of the bortezomib pharmaceutical composition in treatment of refractory / recurrent multiple myeloma.
Owner:NINGBO NINGRONG BIOPHARMA CO LTD
Modulation of the ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS)
The invention relates to the field of 26S proteasome inhibition, activation and modulation and to identify compounds which activate 26S proteasome in live cells and a method of treating autoimmune diseases, cancer, inflammation and neurogenerative disorders by inhibition, activation and modulation of the 26S proteasome.
Owner:STICHTING HET NEDERLANDS KANKER INST ANTONI VAN LEEUWENHOEK ZIEKENHUIS
Tripeptide macrocyclic derivative as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108191957AEasy route designReasonable route designTripeptide ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsRing-closing metathesisProteasome Inhibition
The invention provides a tripeptide macrocyclic derivative as well as an optical isomer, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or a solvent compound thereof. A preparation method comprises the followingsteps: by taking a carboxyl protected compound as an initial raw material, condensation with an acid, performing olefin ring closing metathesis, removing carboxyl, condensing Boc protected amino acidwith an epoxy ketone segment, removing an amino protection group, and further condensing with an intermediate of which the carboxyl is removed, so as to obtain a target product. Experiments show thatthe derivative which has a completely novel framework and relatively good proteasome inhibition activity has a very good propagation inhibition function on multiple myeloma such as RPMI 8226, and MM.1S. The compound provided by the invention is easy in raw material obtaining, reasonable in route design, gentle in reaction condition, simple and convenient to operate and applicable to industrial production. The derivative is of a structure of formula (I) as shown in the specification.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Fluorinated epoxyketone-based compounds and uses thereof as proteasome inhibitors
The present application relates to novel fluorinated epoxyketone-based compounds, compositions comprising these compounds and their use, in particular for the treatment of diseases, disorders or conditions mediated by proteasome inhibition, in particular, the present application includes compounds of Formula I, and compositions and uses thereof:
Owner:特里乌姆治疗公司
Boric acid compounds, and preparation method and use thereof
InactiveCN107151255AStrong inhibitory activityOrganic chemistry methodsGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsBenzeneChemical compound
The invention relates to the fields of pharmaceutical chemistry and medicine therapeutics, concretely relates to a new boric acid compounds, and a preparation method and a use thereof, and especially relates to new substituted five-membered heterocyclic boric acid and substituted benzo five-membered boric acid compounds, and a preparation method thereof. A result of bioactive screening test of the substituted five-membered heterocyclic boric acid and substituted benzo five-membered boric acid compounds having a structure represented by a formula shown in the description shows that the compounds have a proteasome inhibition effect, and can be further used for preparing medicines for treating proteasome correlated diseases.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Dipeptide compound constructed from piperidine or piperazine, its preparation method and application
ActiveCN107417767BGood proteasome inhibitory activityReasonable designNervous disorderDipeptide ingredientsDipeptideProteasome Inhibition
Owner:杭州市西溪医院
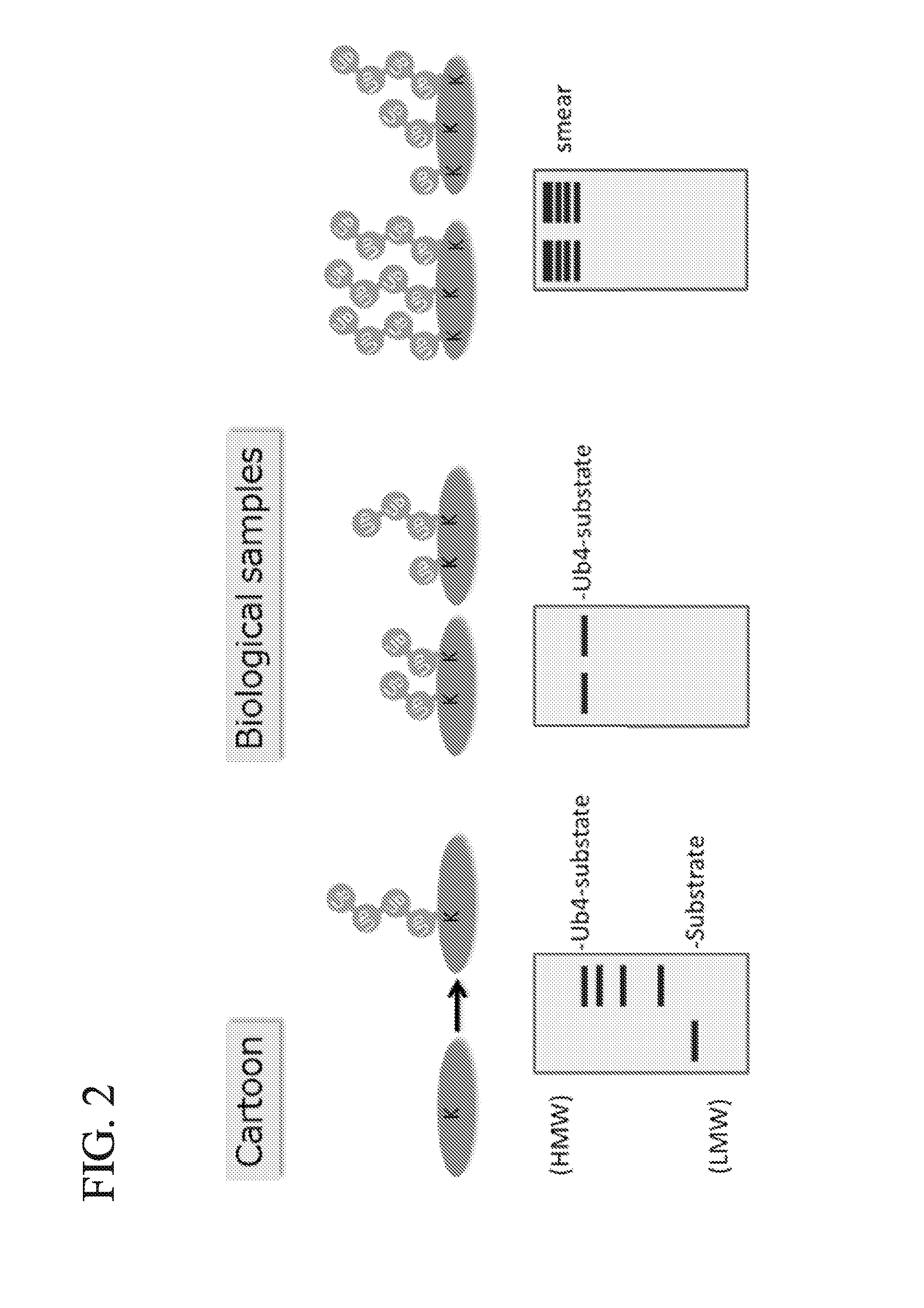
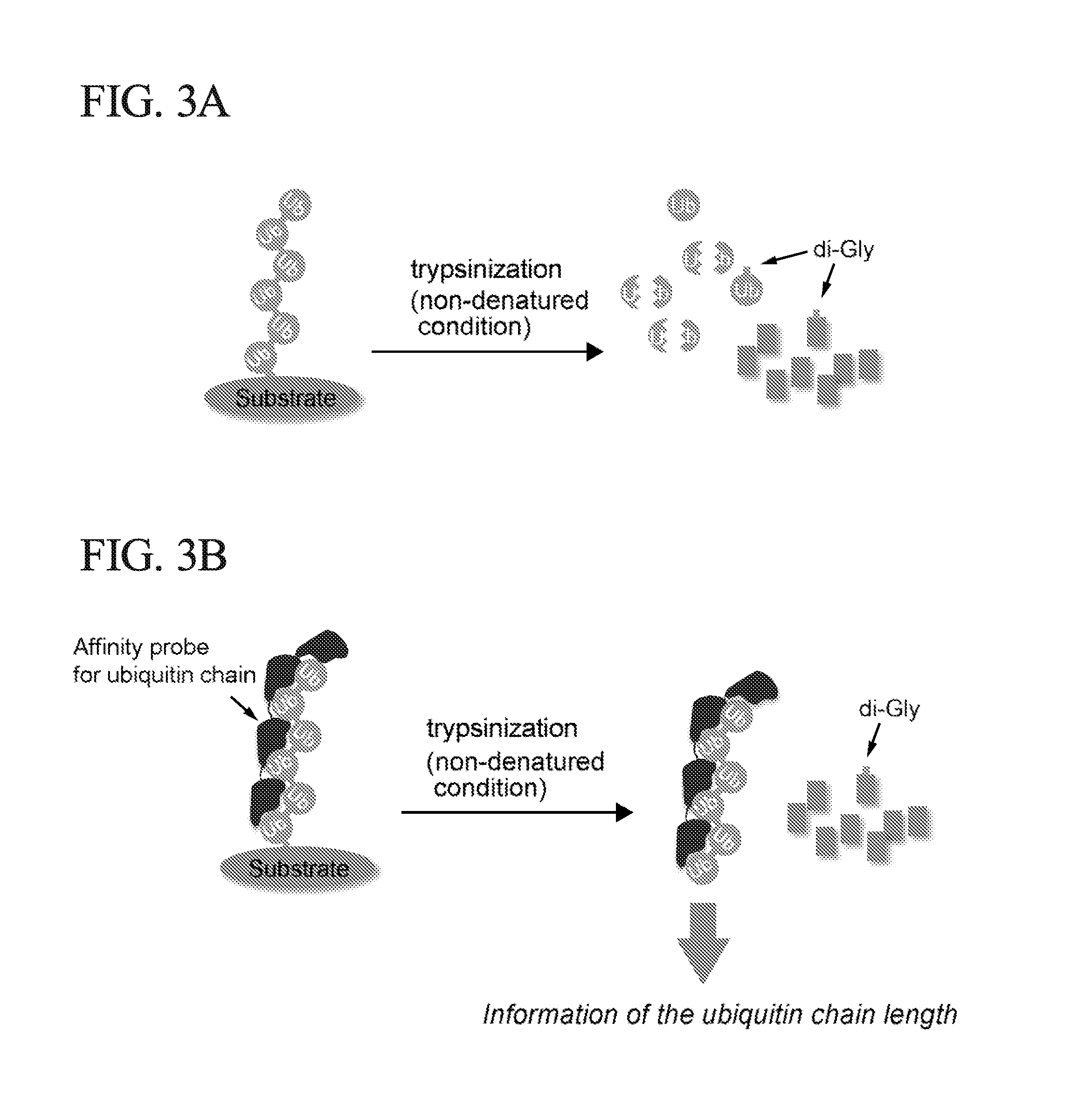
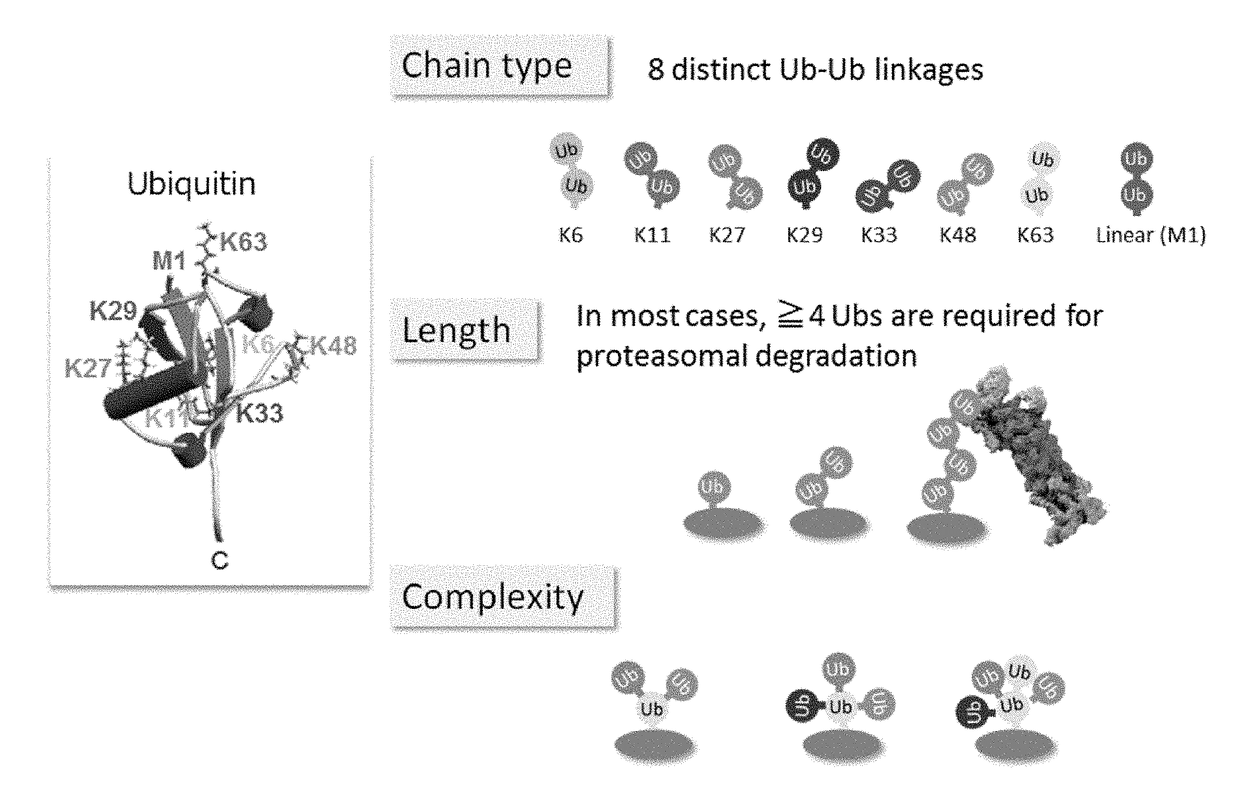
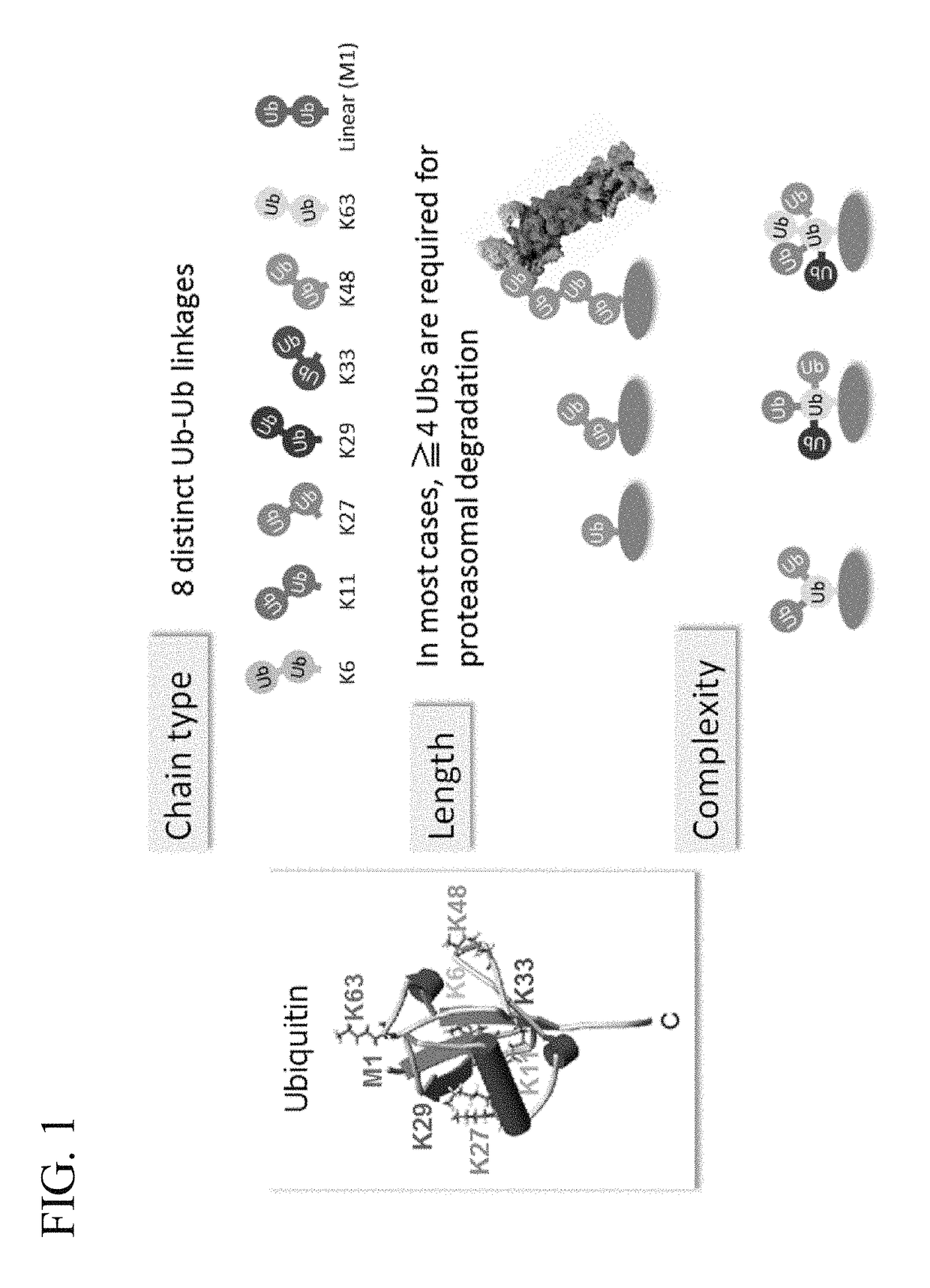
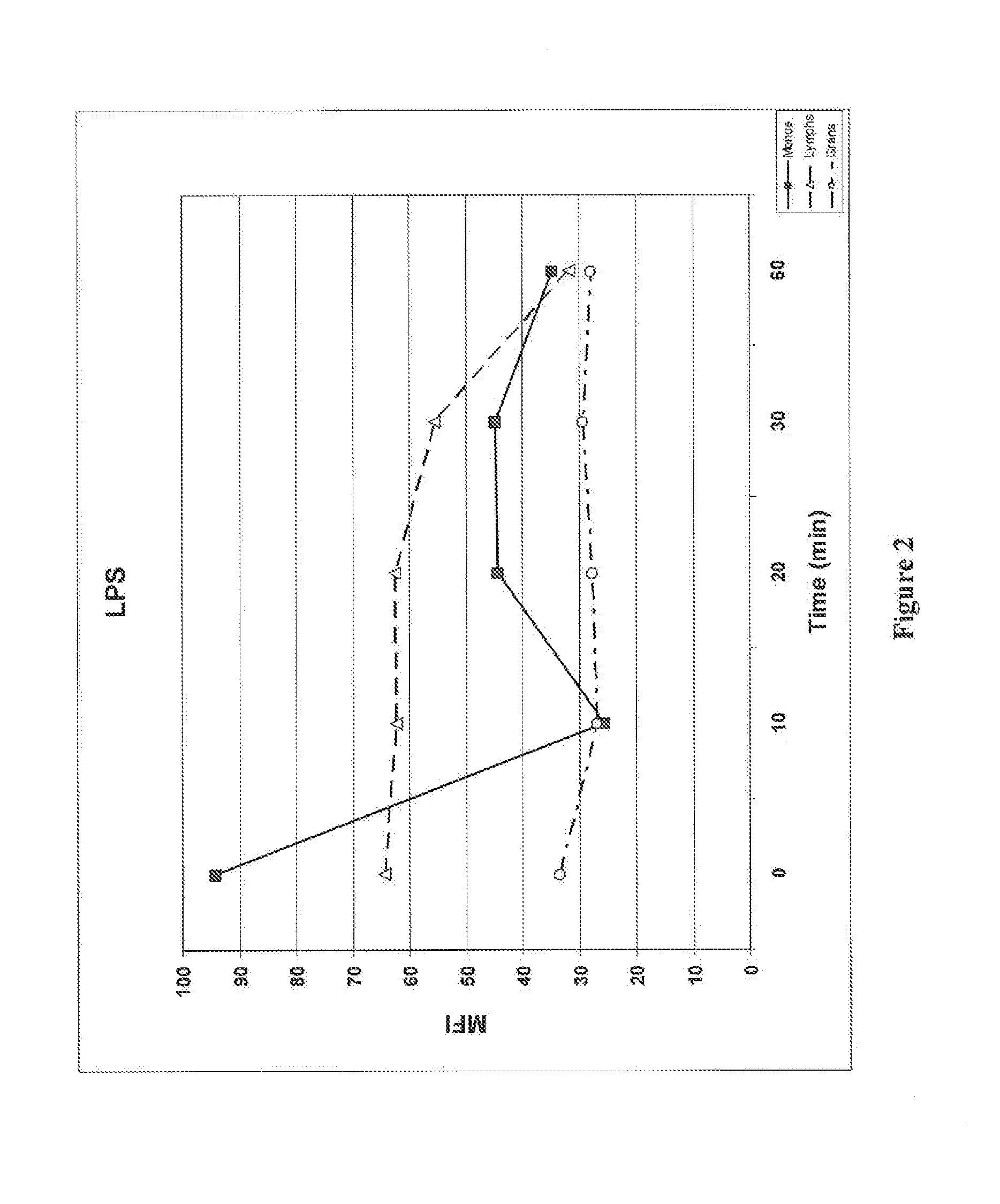
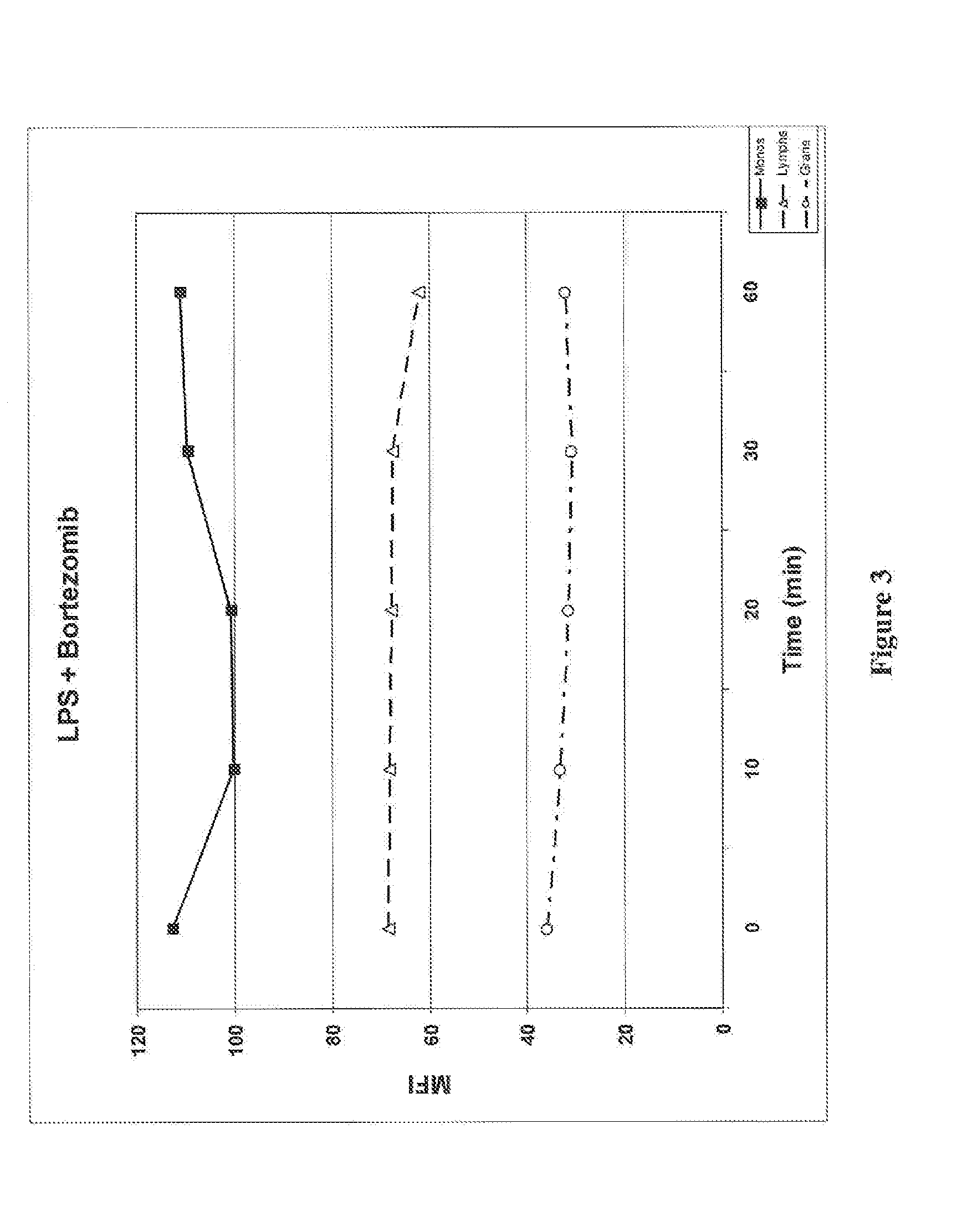
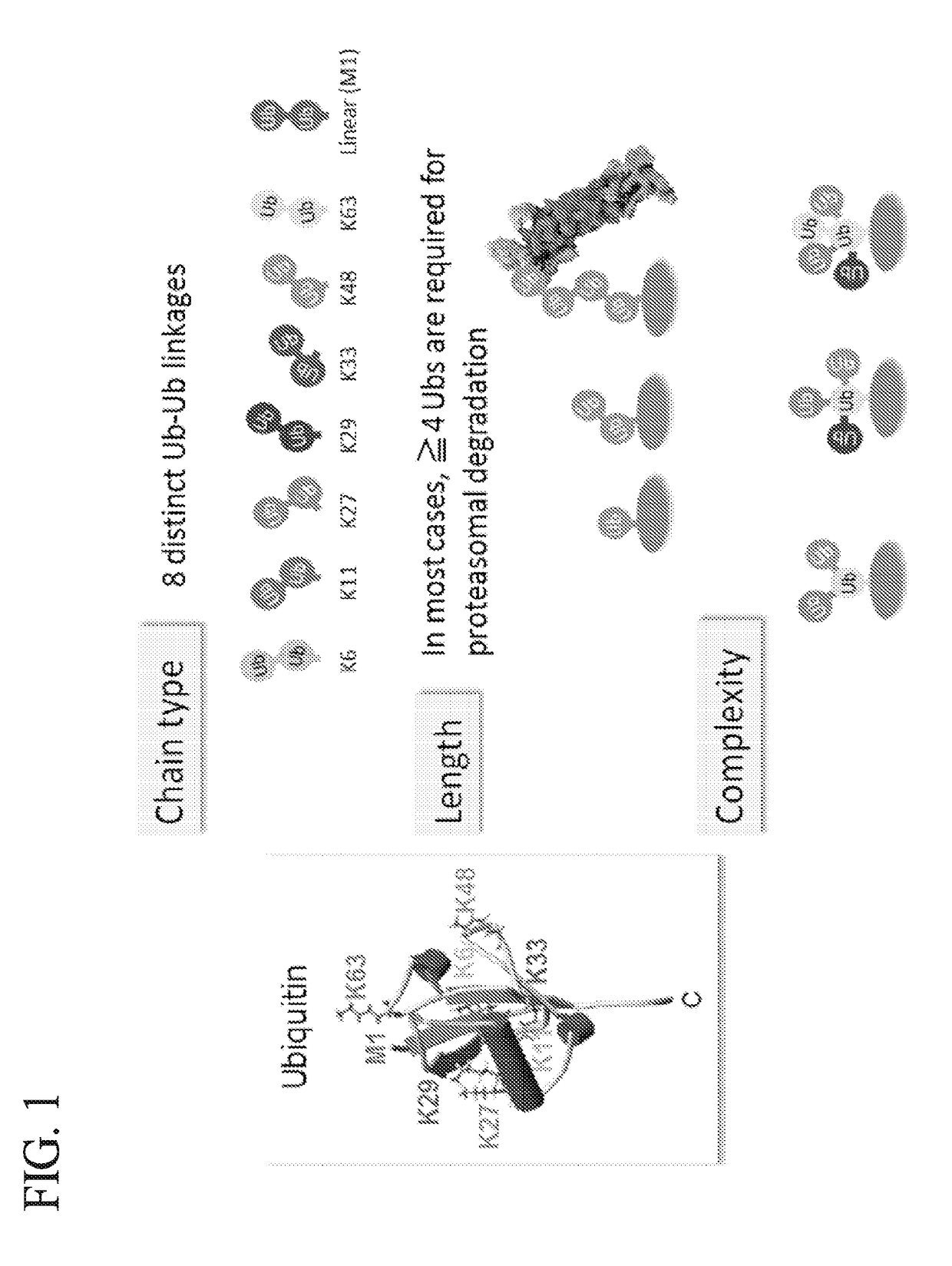
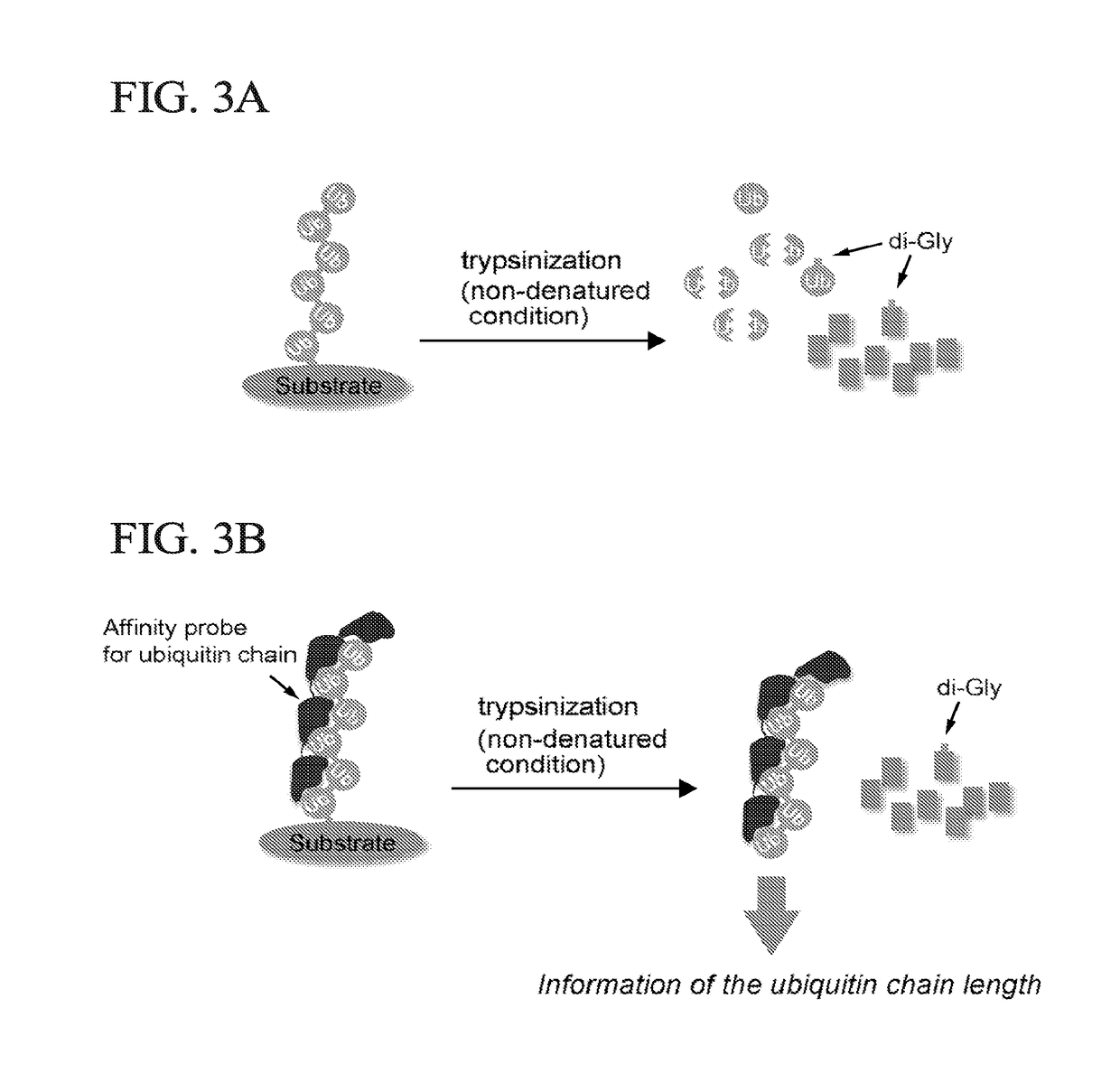
Method for Determining Ubiqutin Chain Length
ActiveUS20150132779A1Used to determineDepsipeptidesPeptide preparation methodsProtein DegradationsProteasome Inhibition
Protein ubiquitylation, an essential post-translational modification, regulates almost every cellular process including protein degradation, protein trafficking, signal transduction, and DNA damage response in eukaryotic cells. The diverse functions of ubiquitylation are thought to be mediated by distinct chain topologies resulting from eight different ubiquitin linkages, chain lengths, and complexities. Currently, ubiquitin linkages are generally thought to be a critical determinant of ubiquitin signaling. However, ubiquitin chain lengths, another key element of ubiquitin signaling, have not been well documented especially in vivo situation during past three decades from the discovery of ubiquitin. The reason of this was simply because no method has been available for determination of ubiquitin chain length in endogenous ubiquitylated substrates. In the present invention, a practical technique for determining the actual length of substrate-attached polyubiquitin chains from biological samples is established. Using the method, the mean length of substrate-attached polyubiquitin chains was determined and the robustness of ubiquitin chain length regulation in cells is investigated. The following is a summary of findings in this invention: 1. A method for determining ubiquitin chain length was developed and this method was named ‘ubiquitin protection from trypsinization’ (Ub-ProT). 2. Using Ub-ProT, it was determined that the mean length of substrate-attached ubiquitin chains is in the dimer to decamer range. 3. By quantitative proteomics, it was found that the mean lengths of five major types of ubiquitin chains can be divided into two groups. 4. Proteasome-inhibition did not alter the mean length of substrate-attached polyubiquitin chains, indicating that cells have a robust system for regulating ubiquitin chain length.
Owner:TOKYO METROPOLITAN INST OF MEDICAL SCI
Borate compound and pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, and preparation method and application of boric acid ester compound and pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof
PendingCN113105486ANovel structureImprove stabilityBoron compound active ingredientsGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsDiseaseAntigen
The invention relates to a borate compound as shown in a formula (1), a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, a preparation method and application thereof. The borate compound is novel in structure and has a proteasome inhibition function. The stability of the borate compound disclosed by the invention in a solution is far higher than that of Ixazomib. Especially when the pH is 1.2 and the pH is 6.8, the stability of the compound provided by the invention is more advantageous. Besides, microsome stability results show that the compound has good stability in five different liver microsomes, the half-life period of the microsomes of Ixazomib in cynomolgus monkeys is too long, the medicine is basically not metabolized, and serious toxicity can be caused. The compound can be used for preparing medicines for treating inflammation, immune-related diseases, cancers or hyperproliferative diseases and changing antigen peptides generated by proteasomes in organisms.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Tripeptide epoxy ketone compound constructed by heterocycle and its preparation and application
ActiveCN104945470BReasonable designRaw materials are easy to getNervous disorderDigestive systemEpoxyProteasome Inhibition
The invention provides a tripeptide epoxy ketone compound constructed by a heterocyclic ring. Carfilzomib is used as a lead compound. After condensation and removal of the Boc protecting group under acidic conditions, amino acid methyl ester isocyanate is obtained by reaction under alkaline conditions, hydrolyzed, and condensed. Obtained under the effect of mixture. The invention is a small molecular short peptide proteasome inhibitor. The compound of the invention has extremely strong proteasome inhibitory activity and cell proliferation inhibitory activity, is a promising proteasome inhibitor, and provides a new idea for the research of cancer treatment drugs. The raw materials required for the synthesis of the compound of the invention are easily available, the route design is reasonable, the reaction conditions are mild, the yield of each step is high, the operation is simple and convenient, and the method is suitable for industrial production. It has the general structural formula of the following formula I:.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Method for determining ubiquitin chain length
Protein ubiquitylation, an essential post-translational modification, regulates almost every cellular process including protein degradation, protein trafficking, signal transduction, and DNA damage response in eukaryotic cells. The diverse functions of ubiquitylation are thought to be mediated by distinct chain topologies resulting from eight different ubiquitin linkages, chain lengths, and complexities. Currently, ubiquitin linkages are generally thought to be a critical determinant of ubiquitin signaling. However, ubiquitin chain lengths, another key element of ubiquitin signaling, have not been well documented especially in vivo situation during past three decades from the discovery of ubiquitin. The reason of this was simply because no method has been available for determination of ubiquitin chain length in endogenous ubiquitylated substrates. In the present invention, a practical technique for determining the actual length of substrate-attached polyubiquitin chains from biological samples is established. Using the method, the mean length of substrate-attached polyubiquitin chains was determined and the robustness of ubiquitin chain length regulation in cells is investigated. The following is a summary of findings in this invention: 1. A method for determining ubiquitin chain length was developed and this method was named ‘ubiquitin protection from trypsinization’ (Ub-ProT). 2. Using Ub-ProT, it was determined that the mean length of substrate-attached ubiquitin chains is in the dimer to decamer range. 3. By quantitative proteomics, it was found that the mean lengths of five major types of ubiquitin chains can be divided into two groups. 4. Proteasome-inhibition did not alter the mean length of substrate-attached polyubiquitin chains, indicating that cells have a robust system for regulating ubiquitin chain length.
Owner:TOKYO METROPOLITAN INST OF MEDICAL SCI
Proteasome inhibition assay and methods of use
ActiveUS20160258934A1Useful in treatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against animals/humansProteasome InhibitionProtease
Assays that can measure the effect of proteasome inhibitors on target cells in a biological sample are provided. The assays include evaluation of the effects of proteasome inhibitors on proteasome activity in cells in a biological sample.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC +1
Method for determining ubiquitin chain length
ActiveUS20180017571A1Biological testingAnimals/human peptidesProtein DegradationsProteasome Inhibition
Protein ubiquitylation, an essential post-translational modification, regulates almost every cellular process including protein degradation, protein trafficking, signal transduction, and DNA damage response in eukaryotic cells. The diverse functions of ubiquitylation are thought to be mediated by distinct chain topologies resulting from eight different ubiquitin linkages, chain lengths, and complexities. Currently, ubiquitin linkages are generally thought to be a critical determinant of ubiquitin signaling. However, ubiquitin chain lengths, another key element of ubiquitin signaling, have not been well documented especially in vivo situation during past three decades from the discovery of ubiquitin. The reason of this was simply because no method has been available for determination of ubiquitin chain length in endogenous ubiquitylated substrates. In the present invention, a practical technique for determining the actual length of substrate-attached polyubiquitin chains from biological samples is established. Using the method, the mean length of substrate-attached polyubiquitin chains was determined and the robustness of ubiquitin chain length regulation in cells is investigated. The following is a summary of findings in this invention: 1. A method for determining ubiquitin chain length was developed and this method was named ‘ubiquitin protection from trypsinization’ (Ub-ProT). 2. Using Ub-ProT, it was determined that the mean length of substrate-attached ubiquitin chains is in the dimer to decamer range. 3. By quantitative proteomics, it was found that the mean lengths of five major types of ubiquitin chains can be divided into two groups. 4. Proteasome-inhibition did not alter the mean length of substrate-attached polyubiquitin chains, indicating that cells have a robust system for regulating ubiquitin chain length.
Owner:TOKYO METROPOLITAN INST OF MEDICAL SCI
Proteasome inhibition assay and methods of use
ActiveUS10073082B2Microbiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against animals/humansProteasome InhibitionProtease
Assays that can measure the effect of proteasome inhibitors on target cells in a biological sample are provided. The assays include evaluation of the effects of proteasome inhibitors on proteasome activity in cells in a biological sample.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC +1
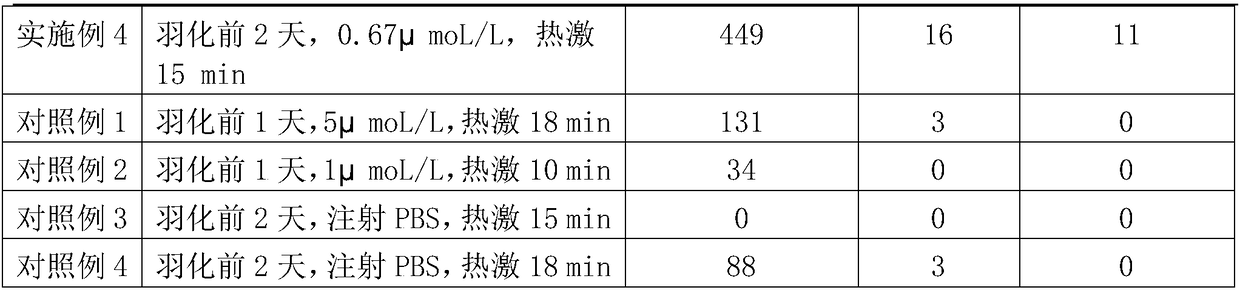
Method for improving silkworm parthenogenesis early generation hatching rate
ActiveCN108235971AImprove hatchabilityImprove breeding efficiencyAnimal husbandryEarly generationWater baths
The invention relates to the technical field of insect genetic breeding, and particularly relates to a method for improving silkworm parthenogenesis early generation hatching rate. The method is characterized in that old mature female pupas are injected with a proteasome inhibitor MG132 with a concentration of 0.5-2 [mu]mol / L 1-2 days before emergence; after emergence, abdomens of virgin moths aretaken to obtain unfertilized silkworm eggs; the unfertilized silkworm eggs are immersed in a water bath of 46 DEG C, and are heat shock induced for 15-18 min; and after the induction, the unfertilized eggs are protected at 16 DEG C for 3 days, then the bivoltine breed is hastened for hatching after immediate acid immersion, and the polyvoltine breed is directly hastened for hatching. According tothe method, the silkworm parthenogenesis induction method is improved, while induction of the unfertilized eggs to remove fission block and restore mitosis is maintained, the side effect that the hatching rate of silkworm eggs is decreased is relieved, thereby improving the parthenogenesis early generation hatching rate, and shortening a parthenogenesis breed breeding cycle.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Boric acid compound used as 20S proteasome inhibitor, and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107151254AStrong inhibitory activityNervous disorderBoron compound active ingredientsProteasome InhibitionCombinatorial chemistry
The invention relates to the fields of pharmaceutical chemistry and medicine therapeutics, concretely relates to new boric acid compounds, and a preparation method and a use thereof, and especially relates to a boric acid compound used as a 20S proteasome inhibitor, and a preparation method thereof. The invention also discloses a boric acid compound represented by formula I, and a preparation method thereof. A result of bioactive screening test shows that the compound prepared in the invention has a proteasome inhibition function, and can be further used for preparing medicines for treating proteasome correlated diseases.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
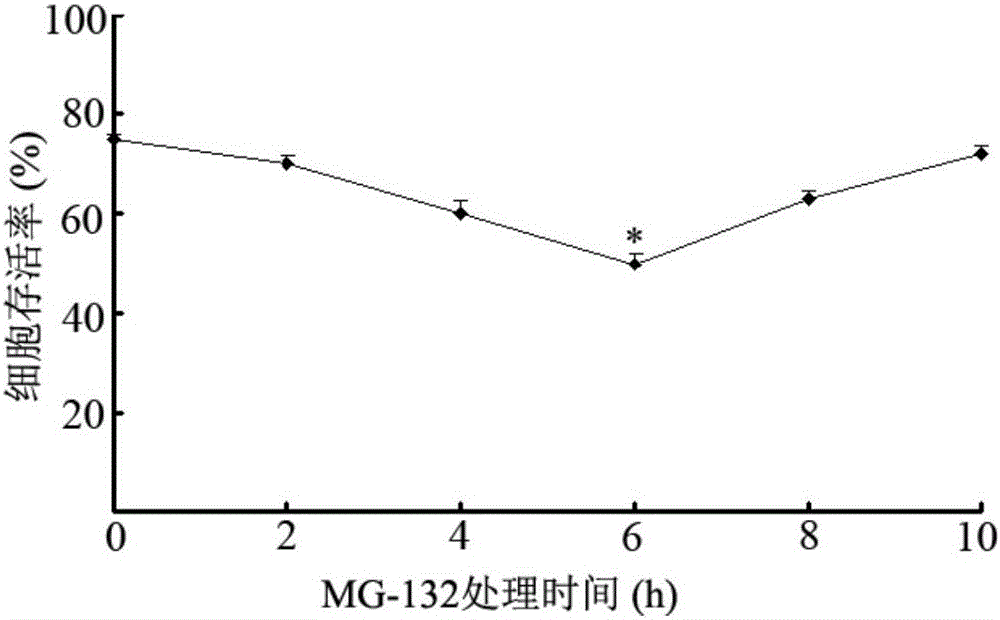
Application of proteasome inhibitor MG-132 to synergist of pyrethroid insecticides
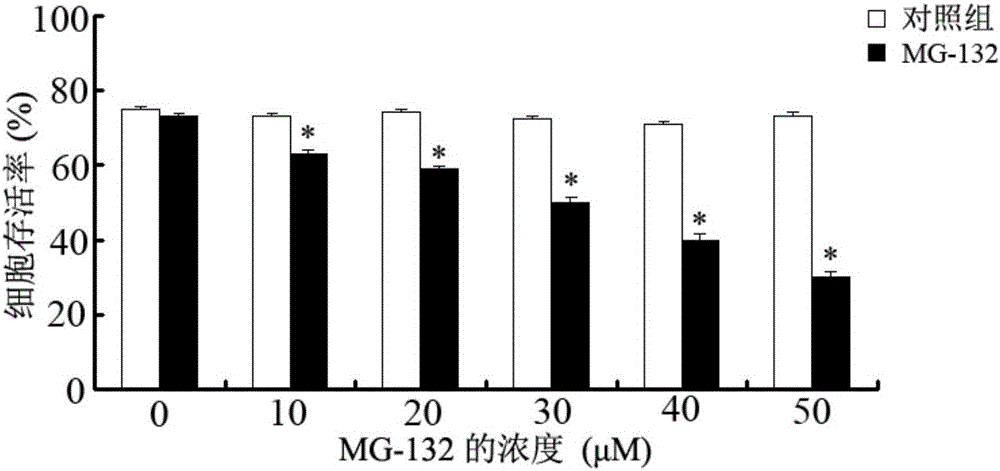
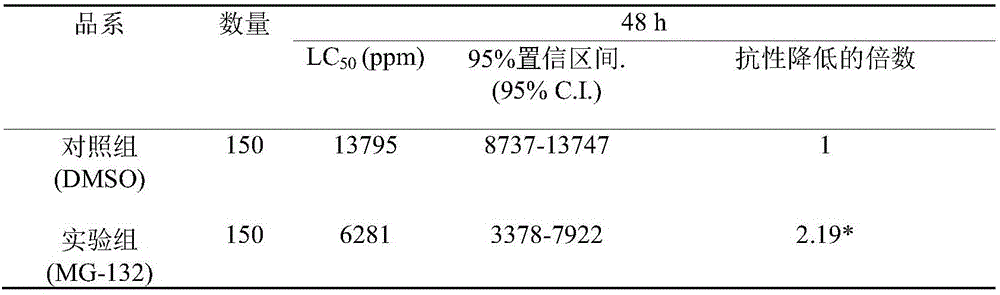
InactiveCN105961426AImprove efficiencyBiocideDead animal preservationProteasome InhibitionDiamondback moth
The invention belongs to the field of control of pest resistance to insecticides, and more specifically relates to an application of a proteasome inhibitor MG-132 to a synergist of pyrethroid insecticides. The proteasome inhibitor MG-132 is used as the synergist of pyrethroid insecticides, dimethyl sulfoxide is used as a solvent in order to prepare the proteasome inhibitor MG-132 whose concentration is 30[mu]M, the proteasome inhibitor MG-132 is sprinkled on eggs and larvae of diamondback moth in fields as well as feed for pretreatment, and after 24 hours of pretreatment, pyrethroid insecticides can be applied. That MG-132 can substantially improve protection effects of deltamethrin is separately proved in individual and cell levels.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com