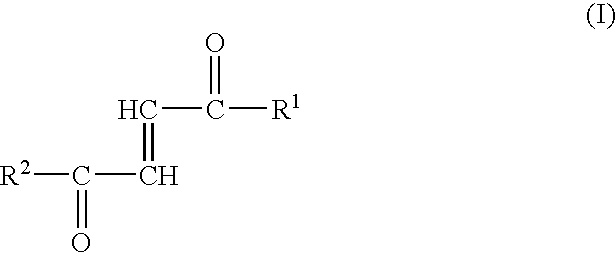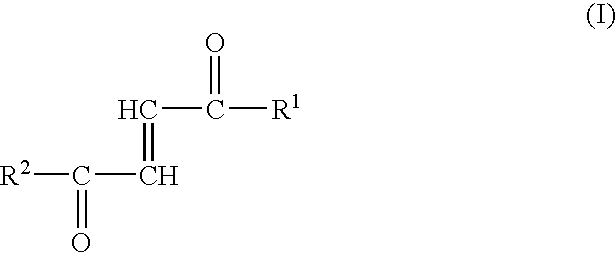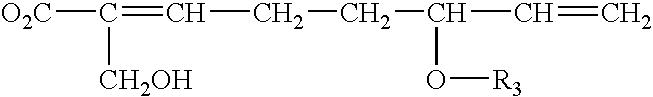Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
108 results about "Nf kappab" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
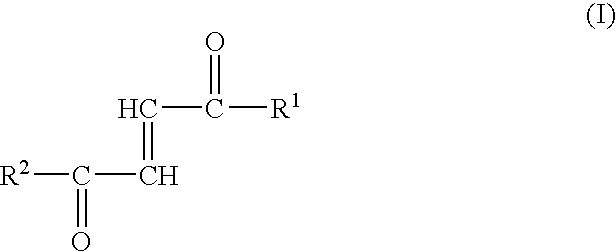
Fumaric acid amides
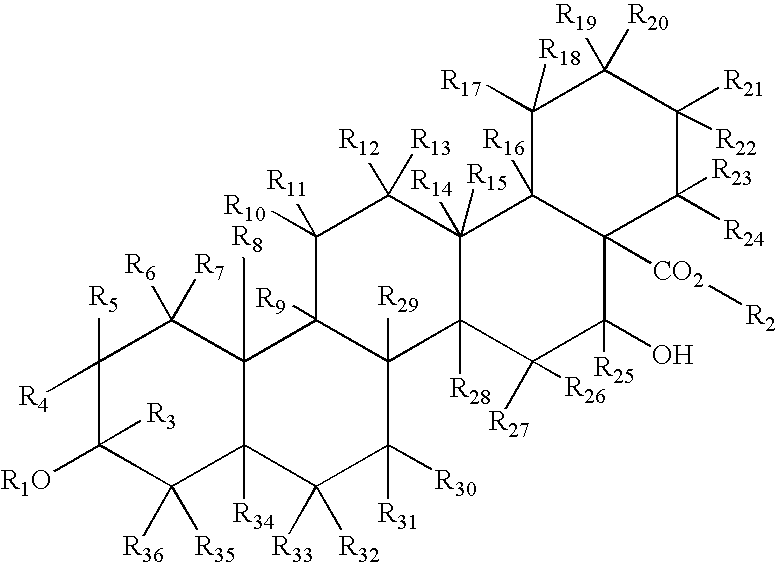
InactiveUS7157423B2More resistant to hydrolysisEasy to handleAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderDiseaseSide chain
Fumaric acid amides of the general formula (I)wherein R1 represents OR3 or a D- or L-amino acid radical —NH—CHR4—COOH bonded via an amide bond, wherein R3 is hydrogen, a straight-chained or branched, optionally substituted C1-24 alkyl radical, a phenyl radical or C6-10 aralkyl radical and R4 is a side chain of a natural or synthetic amino acid and R2 represents a D- or L-amino acid radical —NH—CHR5—COOH bonded via an amide bond or a peptide radical comprising 2 to 100 amino acids bonded via an amide bond, wherein R5 is a side chain of a natural or synthetic amino acid, are used for preparing a drug (1) for the therapy of an autoimmune disease; (2) for use in transplantation medicine; (3) for the therapy of mitochondrial diseases; or (4) for the therapy of NF-kappaB mediated diseases.
Owner:BIOGEN INT
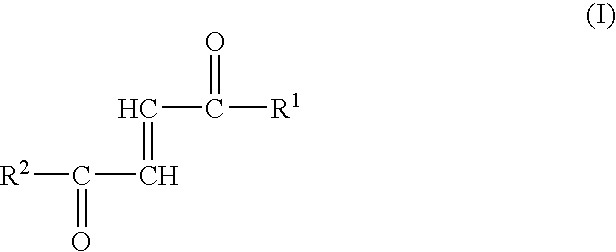
Fumaric Acid Amides
InactiveUS20060205659A1Easy to handleMore resistant to hydrolysisAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsAutoimmune conditionHydrogen
Fumaric acid amides of the general formula (I) wherein R1 represents OR3 or a D- or L-amino acid radical —NH—CHR4—COOH bonded via an amide bond, wherein R3 is hydrogen, a straight-chained or branched, optionally substituted C1-24 alkyl radical, a phenyl radical or C6-10 aralkyl radical and R4 is a side chain of a natural or synthetic amino acid and R2 represents a D- or L-amino acid radical —NH—CHR5—COOH bonded via an amide bond or a peptide radical comprising 2 to 100 amino acids bonded via an amide bond, wherein R5 is a side chain of a natural or synthetic amino acid, are used for preparing a drug (1) for the therapy of an autoimmune disease; (2) for use in transplantation medicine; (3) for the therapy of mitochondrial diseases; or (4) for the therapy of NF-kappaB mediated diseases.
Owner:BIOGEN INT
Compositions and methods for detecting and treating prostate disorders
InactiveUS7598028B2Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisDiseaseEccentric hypertrophy
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for the detecting, treating, and empirically investigating cellular proliferation disorders and cellular motility disorders. In particular, the present invention provides compositions and methods for using CXCL chemokines (e.g., CXCL1, CXCL5, CXCL6, CXCL12), CXCL receptors (e.g., CXCR1, CXCR2, CXCR4, CXCR7), and / or pathway related compounds (e.g., NF-kappaB, ERK ½, ELK-1) in the diagnosis, treatment, and empirical investigation of prostate disorders (e.g., prostate cancer, benign prostatic hypertrophy, prostatitis).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Medical devices to treat or inhibit restenosis
Implantable medical devices having anti-restenotic coatings are disclosed. Specifically, implantable medical devices having coatings of certain NF-kappaB inhibitors, particularly certain dialkyl fumarates, are disclosed. Dimethyl fumarate is a particularly preferred dialkyl fumarate. The anti-restenotic medical devices include stents, catheters, micro-particles, probes and vascular grafts. Intravascular stents are preferred medical devices. The medical devices can be coated using any method known in the art including compounding the dialkyl fumarate with a biocompatible polymer prior to applying the coating. Moreover, medical devices composed entirely of biocompatible polymer-dialkyl fumarate blends are disclosed. Additionally, medical devices having a coating comprising at least one dialkyl fumarate in combination with at least one additional therapeutic agent are also disclosed. Furthermore, related methods of using and making the anti-restenotic implantable devices are also disclosed.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Treatment of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases
InactiveUS20010051654A1Low rate and severityEffective treatmentBiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsDiseaseGlucocorticoid
This invention is directed to the treatment of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases by administering proteasome inhibitors, ubiquitin pathway inhibitors, agents that interfere with the activation of NF-kappaB via the ubiquitin proteasome pathway, or mixtures thereof. The invention is further directed to the treatment of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases by administering an effective combination of a glucocorticoid and a proteasome inhibitor, ubiquitin pathway inhibitor, agent that interferes with the activation of NF-kappaB via the ubiquitin proteasome pathway, or mixture thereof. Pharmaceutical compositions comprising a combination of a glucocorticoid and a proteasome inhibitor, ubiquitin pathway inhibitor, agent that interferes with the activation of NF-kappaB via the ubiquitin proteasome pathway, or mixture thereof are also contemplated within the scope of the invention.
Owner:ELLIOTT PETER J +2
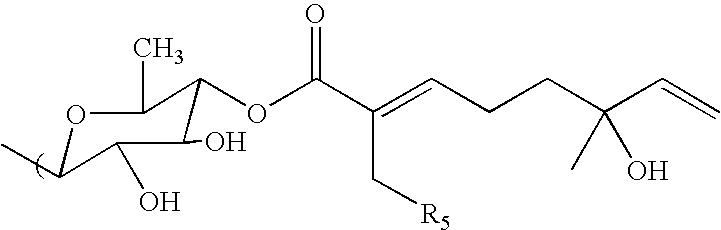
Inhibition of NF-kappaB by triterpene compositions
The invention provides methods for the inhibition of inflammation by providing, to a cell, in need thereof, monoterpene compositions that inhibit NF-κB. These compositions may also contain a carrier moiety that renders the monoterpene composition membrane permeable. The carrier may include triterpenoid moieties, sugars, lipids, or even additional monoterpenoid moieties. The composition can also contain additional chemical functionalities. Methods for using these compounds to prevent and treat a wide range of inflammatory conditions, especially, premalignant inflammatory conditions are described.
Owner:RES DEVMENT FOUND
Treatment of iatrogenic disease
InactiveUS20080194489A1Maintain securityTetrapeptide ingredientsTripeptide ingredientsGeneMedical treatment
The invention relates to the field of human or veterinary medicine and to the treatment of subjects (be it man or animal) that suffer from iatrogenic disease, i.e., experience problems or complications resulting from a medical treatment. Provided is a method for modulating an iatrogenic event in a subject, the method comprising: providing the subject with a gene-regulatory peptide or functional analogue thereof. Furthermore, provided is the use of an NF-kappaB down-regulating peptide or functional analogue thereof for the production of a pharmaceutical composition for the treatment of an additional pro-inflammatory cytokine response occurring after an iatrogenic event in a subject.
Owner:BIOTEMPT
Thiomolybdate analogues and uses thereof
The current invention provides novel thiomolybdate derivatives, methods of making novel thiomolybdate derivatives, pharmaceutical compositions of novel thiomolybdate derivatives, methods of using novel thiomolybdate derivatives to treat diseases associated with aberrant vascularization, copper metabolism disorders, neurodegenerative disorders, obesity or NF-kappaB dysregulation and methods of using pharmaceutical compositions of thiomolybdate derivatives to treat diseases associated with aberrant vascularization, copper metabolism disorders, neurodegenerative disorders, obesity or NF-kappaB dysregulation.
Owner:ALEXION PHARMA INC +1
Thiosuccinic Acid Derivatives and the Use Thereof
ActiveUS20090011986A1Similar effectEasy to prepareOrganic active ingredientsBiocideThio-Autoimmune disease
The present invention relates to compounds of the Formula (I), wherein X1 and X2 independently represent O, NH or S; R1 and R2 are independently selected from the group consisting of a C1-C30 hydrocarbyl group, an amino acid bonded via an amide bond or a peptide bonded via an amide bond each having up to 200 amino acids, the conjugated residue X1 or X2 in this case being NH, and hydrogen, both radicals R1 and R2 preferably not being H; and R3 is a residue selected from group consisting of —S—R6, wherein R6 is a C1-C30 hydrocarbyl group, at least one of R1 and R2 not being H when X1 and X2 are oxygen, —S—CH2—CH(NH2)(COOH) (cysteine-S-yl), a homologue or derivative (e.g. N-acetyl cysteine-S-yl) thereof, a peptide having up to 200 amino acids which contains at least one amino acid radical with a thiol group, preferably a cysteine radical, and is bonded via the thio sulfur, preferably via the cysteine sulfur (peptide-S-yl), coenzyme A which is bonded via a thiol group or fragments thereof, acyl carrier protein bonded via a thiol group, and dihydrolipoic acid bonded via a thiol group; and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof. The present invention also relates to the use of these compounds for preparing a drug, drugs containing the same and their use for the therapy of diseases such as autoimmune disease, NF-kappaB mediated diseases, psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, neurodermitis, enteris regionalis Crohn, cardiac insufficiency, chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases and asthma and in transplantation medicine.
Owner:BIOGEN INT
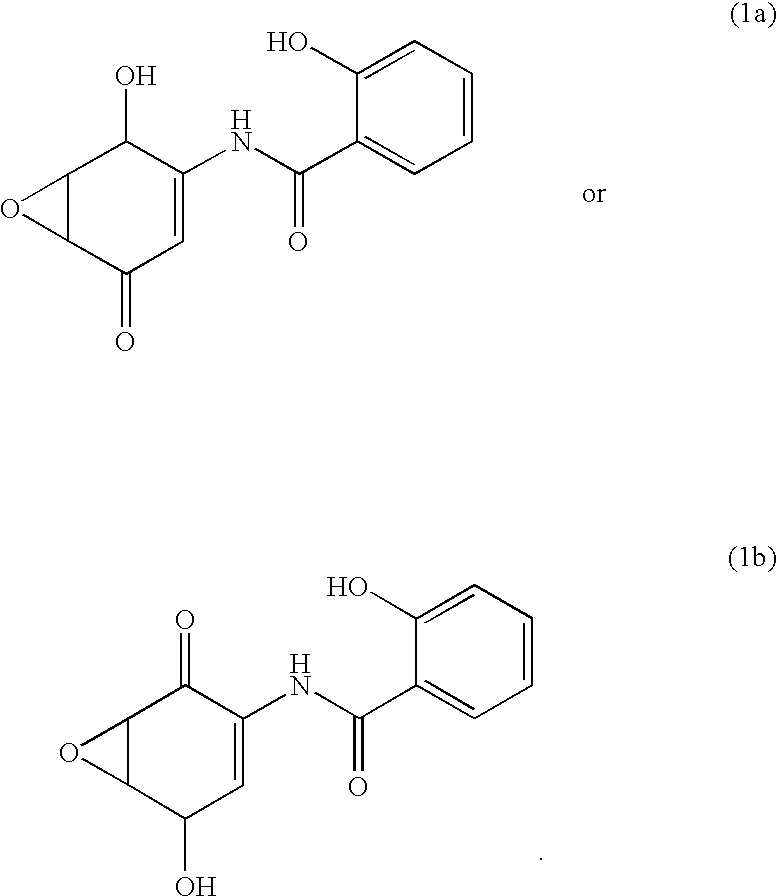
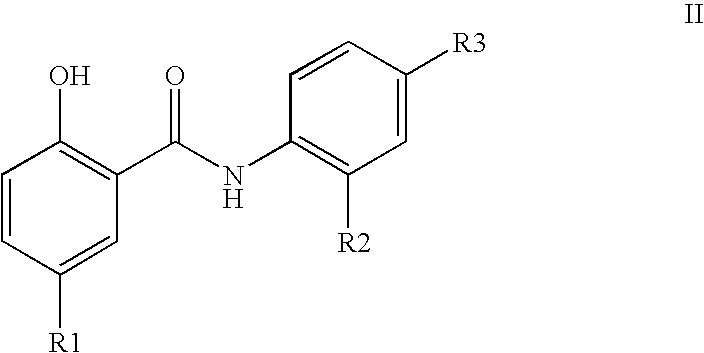
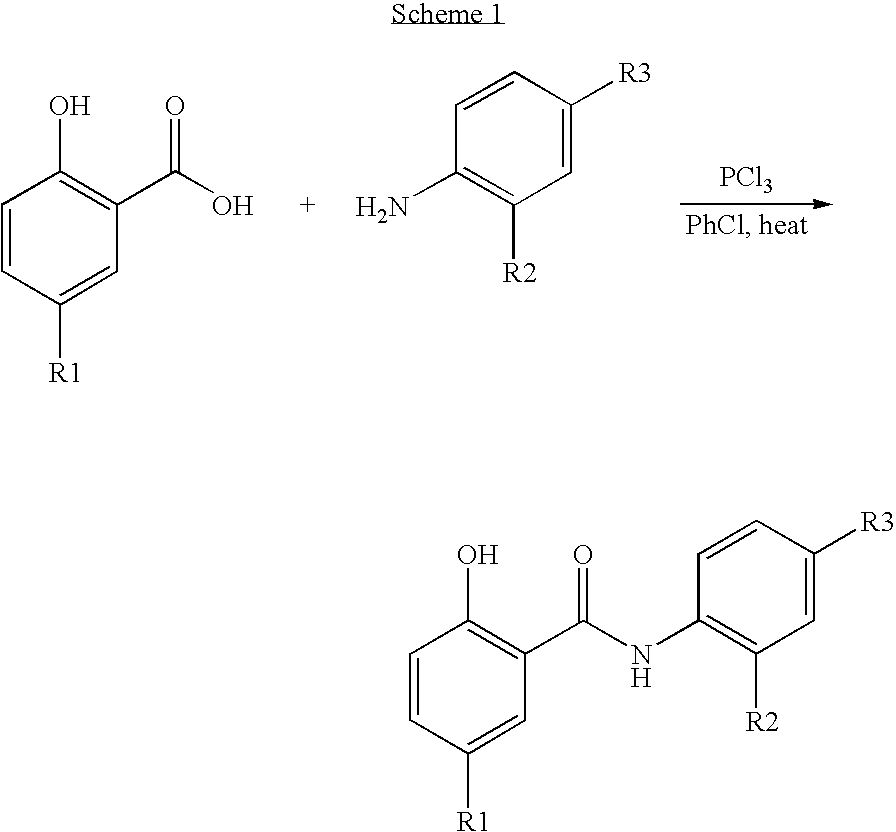
Salicylamide derivatives
Salicylamide derivatives represented by formulae (1a) and (1b); intermediates in the production thereof; a process for producing the same; and drugs containing the same as the active ingredient. The salicylamide derivatives represented by formulae (1a) and (1b) are useful as anti-inflammatory agents and immunosuppressive agents which exert an effect of inhibiting the activation of NF-kappaB with little side effects.
Owner:SIGNAL CREATION +2
Inhibitors against activation of NF-kappaB
A method of inhibiting NF-κB activation in a mammal including a human, which comprises the step of administering an effective dose of a substance selected from the group consisting of a compound represented by the following general formula (I) and a pharmacologically acceptable salt thereof, and a hydrate thereof and a solvate thereof:
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL MOLECULAR DESIGN
Novel regulatory mechanisms of NF-kappaB
InactiveUS20050147608A1Inhibiting degredation of NF-kBIncreasing nuclear accumulation and protein stabilityHydrolasesAntipyreticIsomerizationProteolysis
The instant invention pertains to the discovery of two novel regulatory mechanisms of NF-kB. The instant invention demonstrates that NF-kB is regulated by Pin1-catalyzed prolyl isomerization and ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis of p65. Accordingly, the instant invention provides methods for regulating NF-kB, and diseases and disorders associated with NF-kB. Further, the invention provides compositions capable of modulating the activity or expression of NF-kB, Pin1, and / or the proteolysis of p65.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
NF-kappaB oligonucleotide decoy molecules
InactiveUS20050182012A1Level of negativePotent of activitySenses disorderNervous disorderDecoyBiochemistry
The present invention concerns double-stranded NF-κB decoy oligodeoxynucleotide (NF-κB dsODN) molecules that contain a core sequence capable of specific binding to an NF-κB transcription factor. In a particular aspect, the invention concerns NF-κB decoy molecules that preferentially bind p50 / p65 and / or cRel / p50 heterodimers over p50 / p50 homodimers. In another aspect, the invention concerns NF-κB decoy molecules with improved binding affinity to p65.
Owner:ANESIVA
Modulators of the glucocorticoid receptor, AP-1, and/or NF-kappaB activity and use thereof
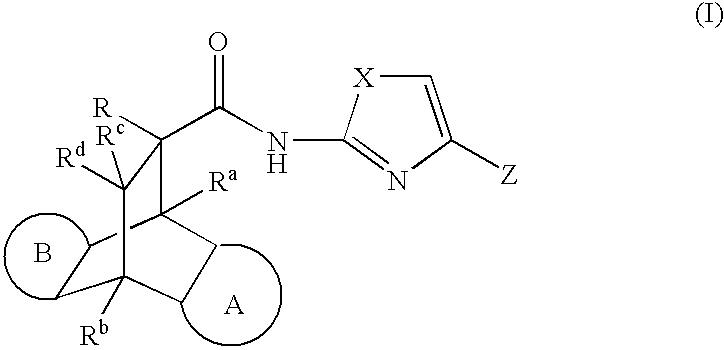
A class of novel non-steroidal compounds are provided which are useful in treating diseases associated with modulation of the glucocorticoid receptor, AP-1, and / or NF-κB activity including obesity, diabetes, inflammatory and immune diseases, and have the structure of formula (I) its stereoisomers thereof, or a solvate thereof, or a prodrug thereof, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, where Z is CONR1R2 or CH2NR1R2 and where at least two of X1-X4 and / or X5-X8 is N or NR18, and R, Ra, Rb, Rc, Rd, R1, R2 and R18 are defined herein. Also provided are pharmaceutical compositions and methods of treating obesity, diabetes and inflammatory or immune associated diseases comprising said compounds.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
NF-kappaB activating gene
Provided are proteins having NF-κB activity, which are used for diagnosing, treating or preventing diseases associated with the excessive activation or inhibition of NF-κB. Using plasmid pNFκB-Luc, cDNA encoding a protein capable of activating NF-κB has been cloned from a cDNA library constructed from human lung fibroblasts, and the DNA sequence and the deduced amino acid sequence determined. The protein, the DNA encoding the protein, a recombinant vector containing the DNA, and a transformant containing the recombinant vector are useful for screening a substance inhibiting or promoting NF-κB activation.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI PHARMA
Nucleotide sequence encoding a modulator of NF-kappaB
InactiveUS20030059911A1Effective activityAlter adverse consequenceCompound screeningApoptosis detectionNucleotideNF-kappaB activation
The present invention relates to nucleotide sequences encoding a modulator of NF-kappaB, and to the polypeptides encoded by the nucleotide sequences. In particular, the invention relates to nucleotide sequences and the polypeptides encoded thereby, wherein the polypeptides are involved in the response to NF-kappaB-activating stimuli, including HTLV-1 Tax, LPS, PMA and IL-1. The invention also relates to antibodies to the modulator of NF-kappaB, methods of detecting modulator of NF-kappaB using the antibodies, methods of treatment associated with NF-kappaB activation and to methods of identifying compounds which modulate the activity of the modulator of NF-kappaB.
Owner:INST PASTEUR
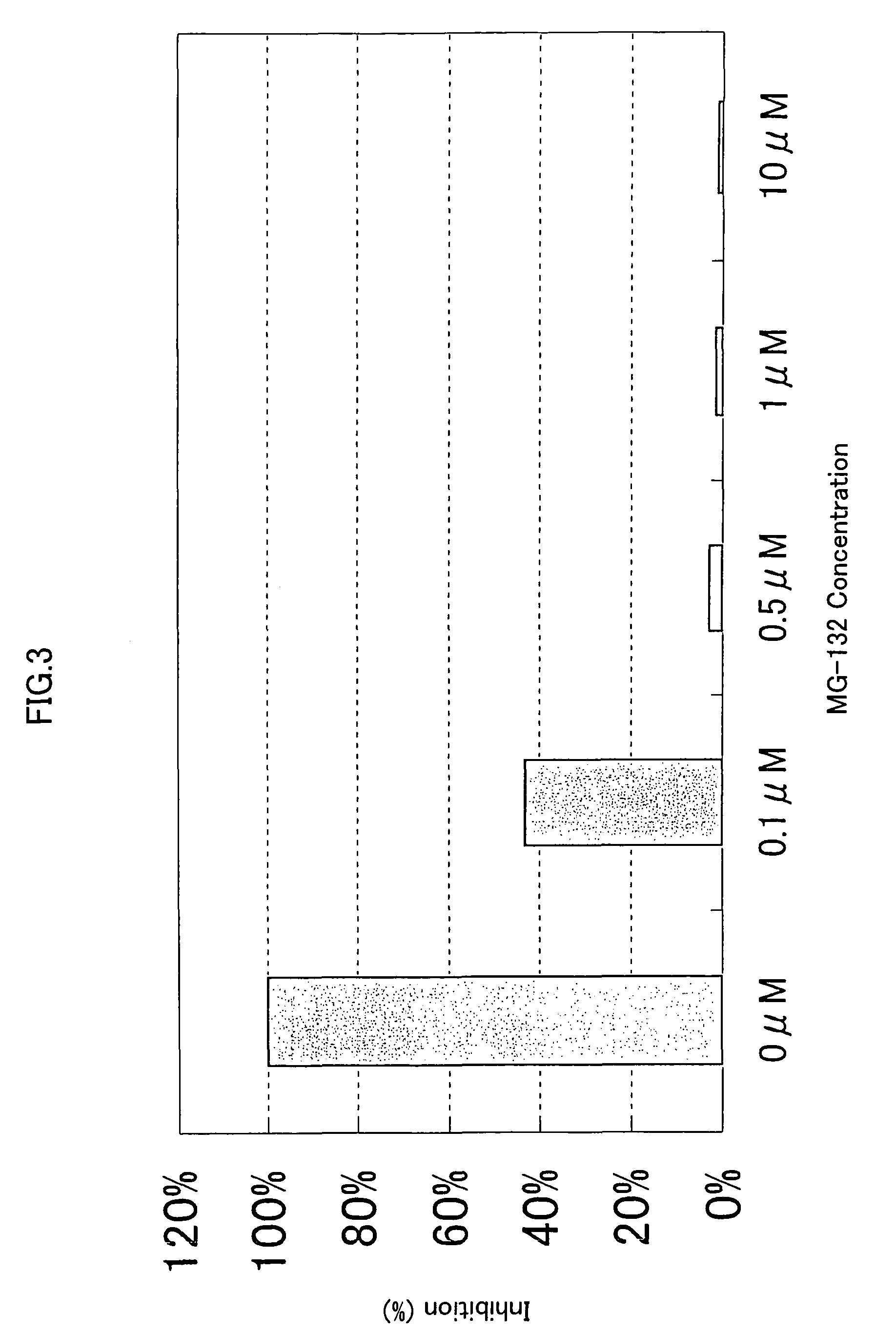
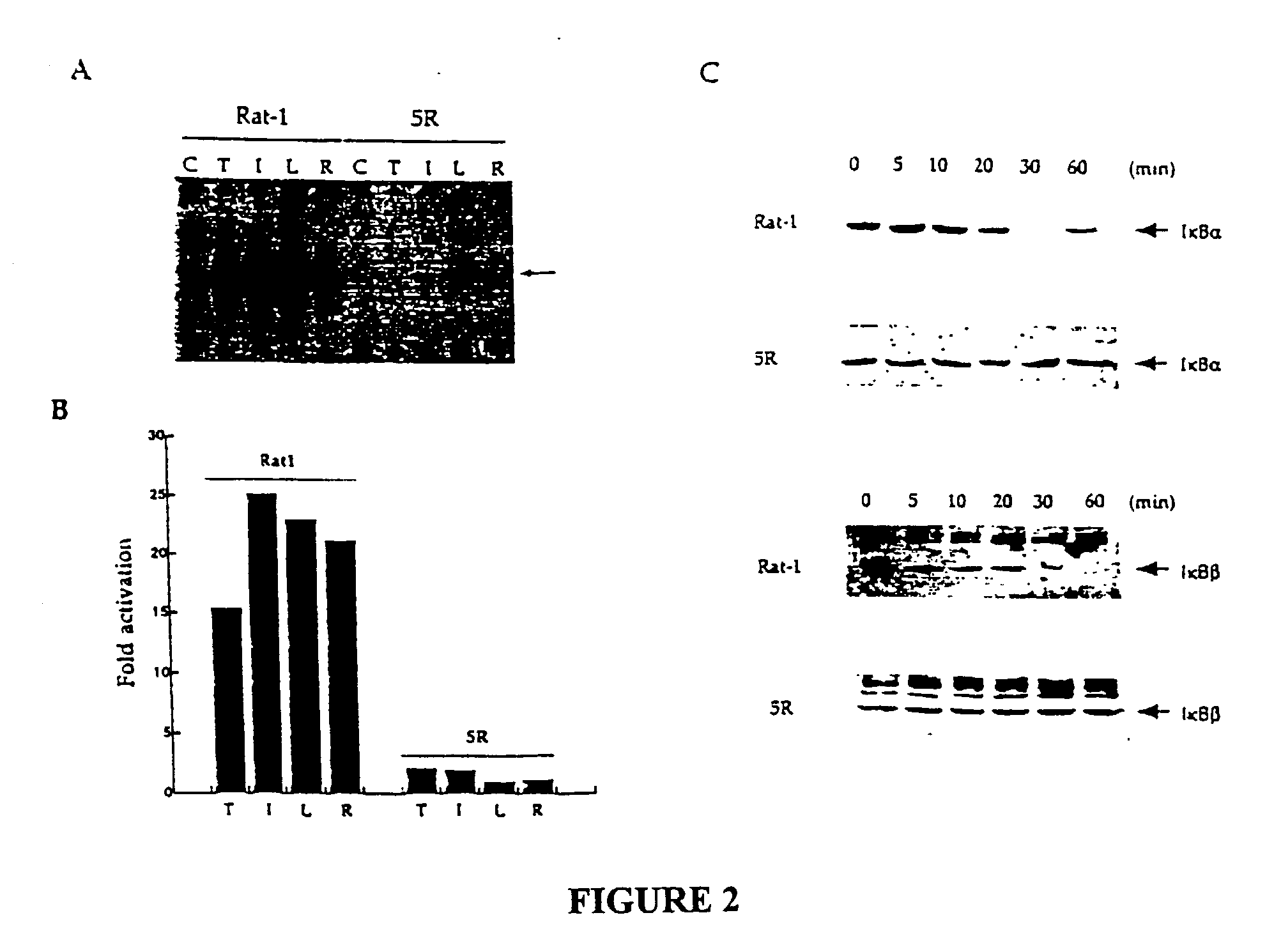
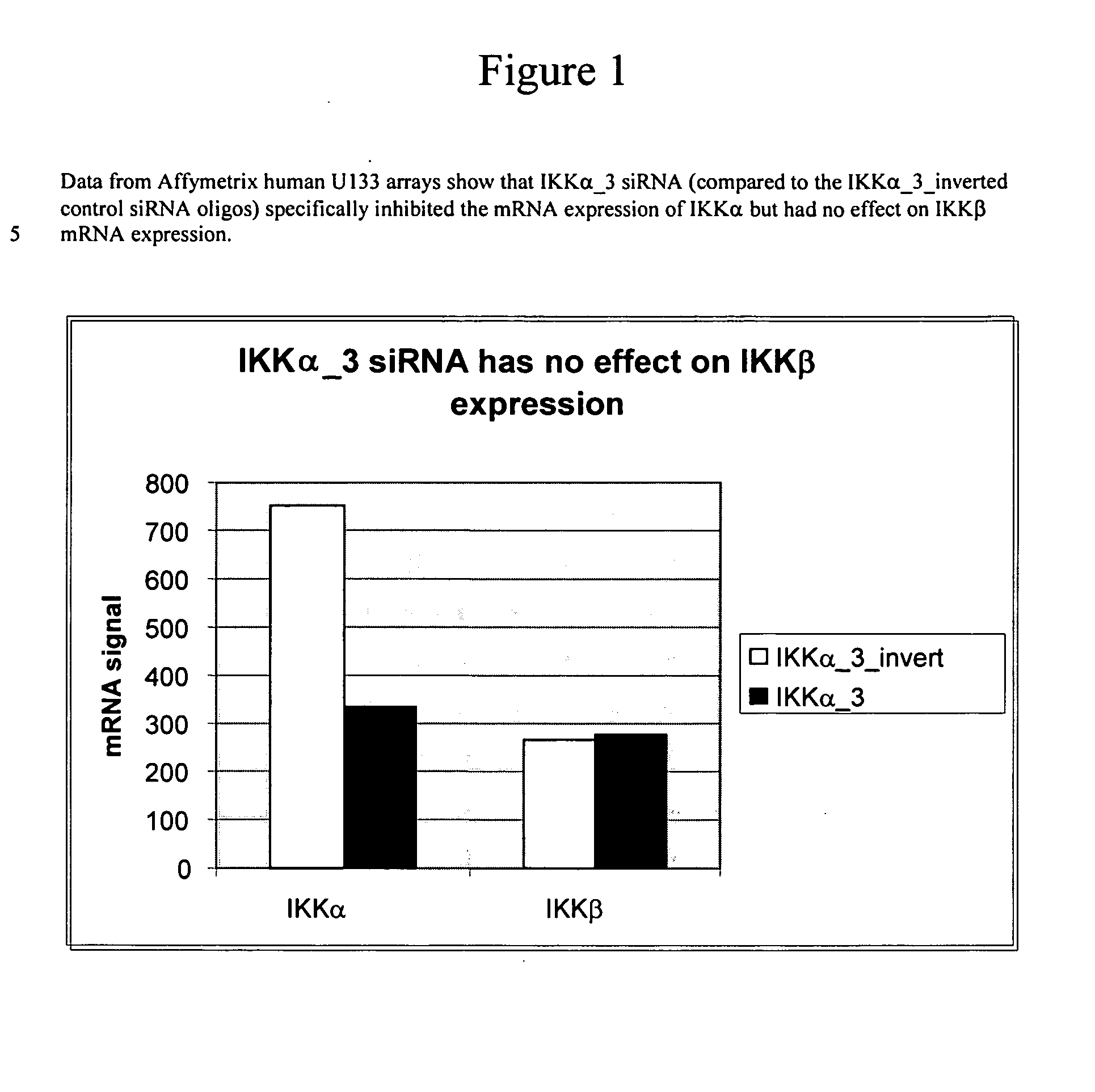
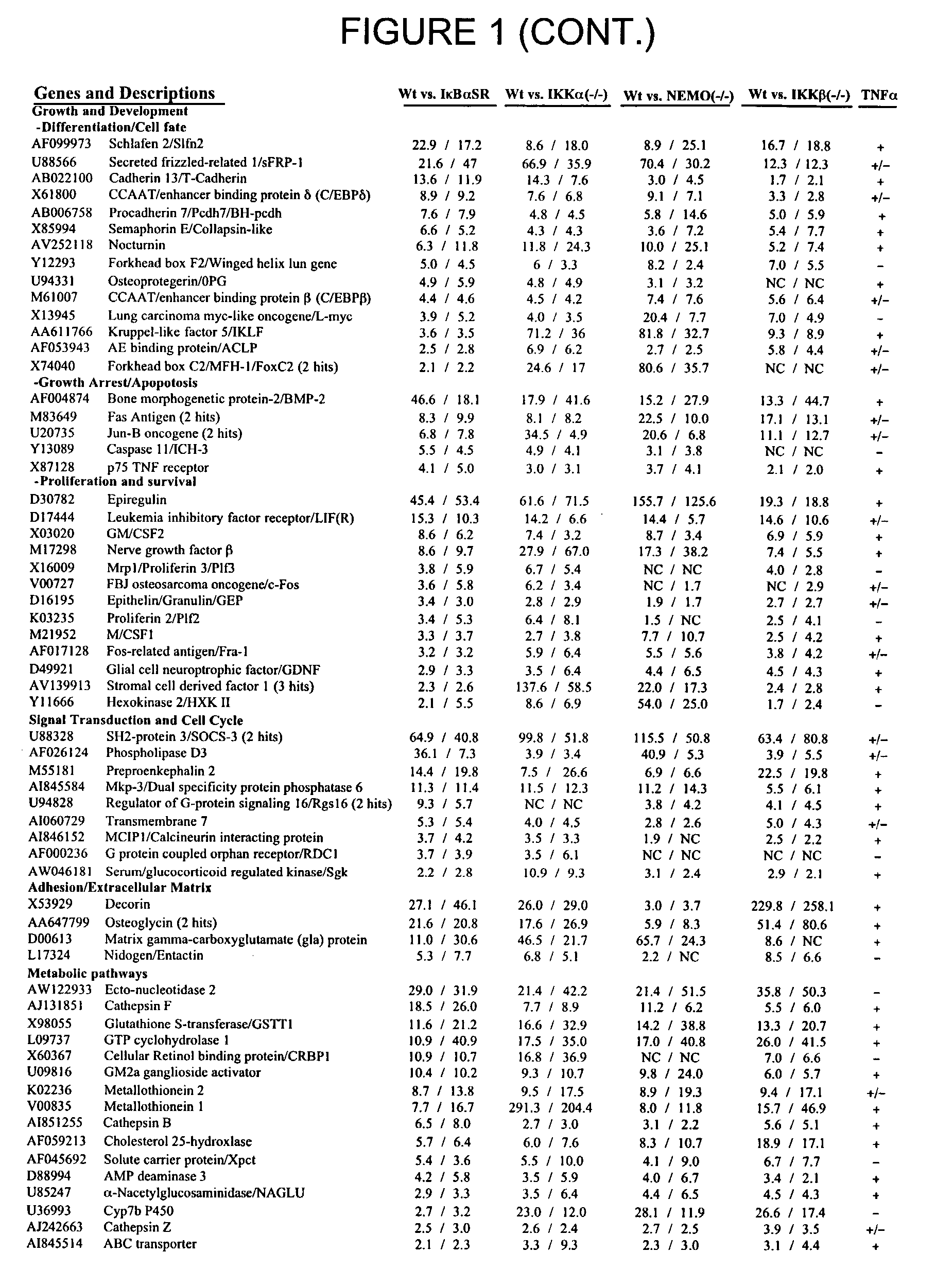
Methods for the identification of IKKalpha function and other genes useful for treatment of imflammatory diseases
The invention provides a method for identifying genes involved in the NF-kappaB pathway comprised of the steps of determining the level of expression of a gene in an experimental sample obtained from the cells having deficient levels of a component of the NF-kappaB pathway; determining the level of expression of said gene in a control sample obtained from wild type cells having levels of a component of a biological pathway; selecting genes having a level of expression that are modulated in said experimental sample relative to said wild type sample. The invention also provides a method of treating inflammatory related diseases by modulating the activity of IKKalpha.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM PHARMA INC
Inhibitors of transcription factor NF-kappaB
The present invention provides pharmaceutical compositions of salicylanilide inhibitors of transcription factor NF-κB, and methods for treating diseases in which activation of NF-κB is implicated. More specifically, the present invention provides methods of treatment of a variety of diseases associated with NF-κB activation including inflammatory disorders; particularly rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and asthma; dermatosis, including psoriasis and atopic dermatitis; autoimmune diseases; tissue and organ rejection; Alzheimer's disease; stroke; atherosclerosis; restenosis; cancer, including Hodgkin's disease; certain viral infections, including AIDS; osteoarthritis; osteoporosis; and Ataxia Telangiestasia by administering to a patient in need thereof a compound of the present invention.
Owner:SMITHKLINE BECKMAN CORP
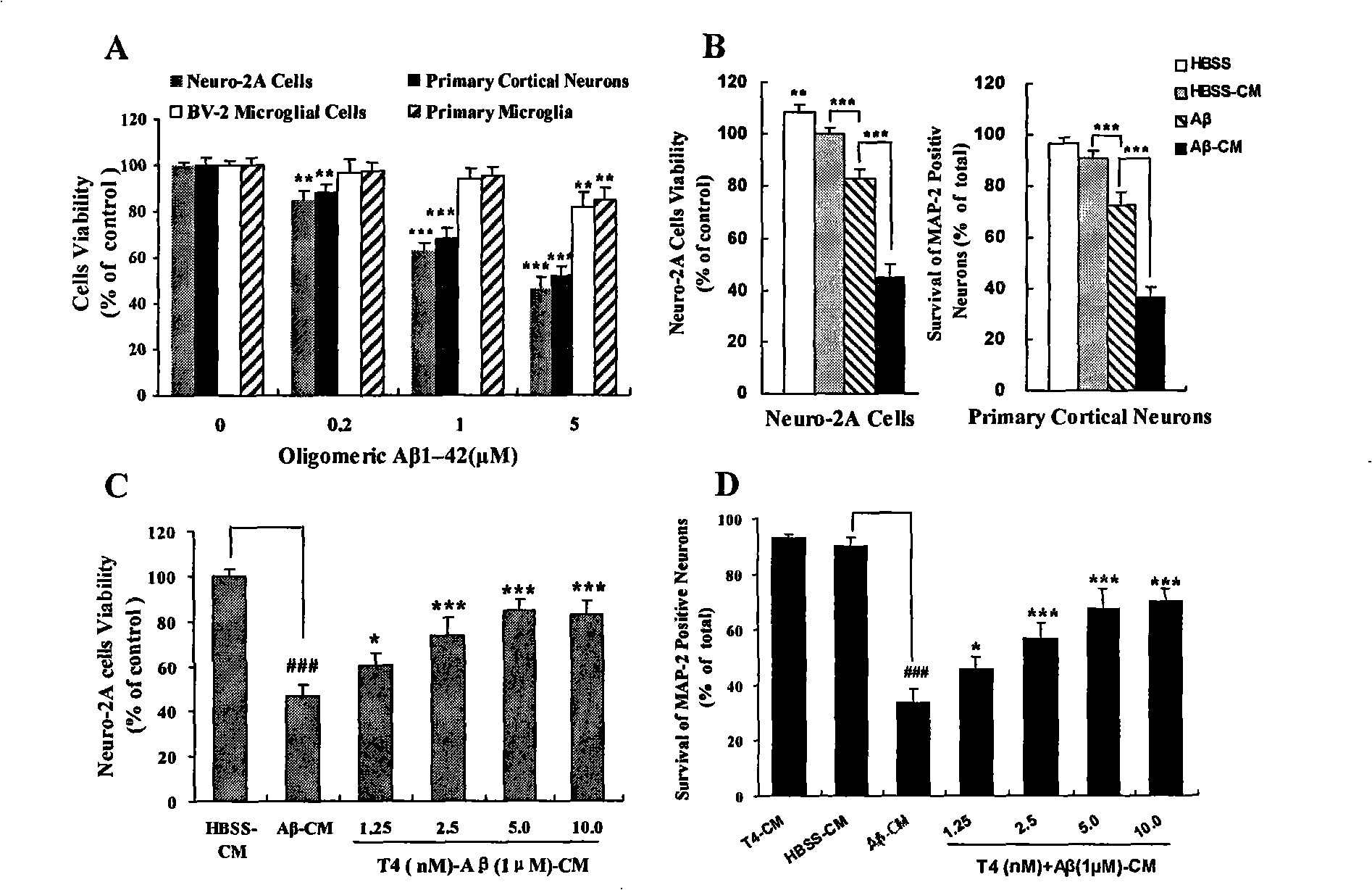
New use of tripchlorolide,T4
InactiveCN101332200AReduce early damageAvoid damageOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDiseaseTripchlorolide
The present invention relates to the usage of wilfordii chlorine lactonic alcohol T4 for curing neural immune inflammatory diseases and provides a new usage of the wilfordii chlorine lactonic alcohol T4 for curing neural immune inflammatory diseases caused by the neural toxicity of microglia-mediated ABeta1-42 and LPS. The traditional medicine monomer of the wilfordii chlorine lactonic alcohol T4 has the following functions: obviously reducing the toxic damages of the oligmeric ABeta1-42 and LPS-induced gel-inflammation reaction on nerve cells, so as to protect the survival of nerve cells; inhibiting the level of inflammation medium produced by the oligmeric ABeta1-42 and the LPS-induced microglia cells; inhibiting the increase of iNOS and COX-2 expression of the oligmeric ABeta1-42 and the LPS-induced microglia cells; inhibiting the activation of NF-KappaB and JNK signal access of the oligmeric ABeta1-42 and the LPS-induced microglia cells. Therefore, the present invention provides direct powerful experimental evidence and theoretical basis for the application of the wilfordii chlorine lactonic alcohol T4 in neural immune inflammatory diseases, especially prevention and treatment of Alzheimer disease, thus having strong scientificity and creativity, as well as high development and application value.
Owner:FUJIAN MEDICAL UNIV UNION HOSPITAL
Heterocyclic modulators of the glucocorticoid receptor, AP-1, and/or NF-kappaB activity and use thereof
The invention relates to a class of novel non-steroidal compounds which are useful in treating diseases associated with modulation of the glucocorticoid receptor, AP-1, and / or NF-κB activity including obesity, diabetes, inflammatory and immune diseases, and have the structure of formula (I)or stereoisomers or prodrugs or solvates or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, wherein Z, R, R4, R5, Ra, Rb, Rc, and Rd, are defined herein. Also provided are pharmaceutical compositions and methods of treating obesity, diabetes and inflammatory or immune associated diseases comprising said compounds.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
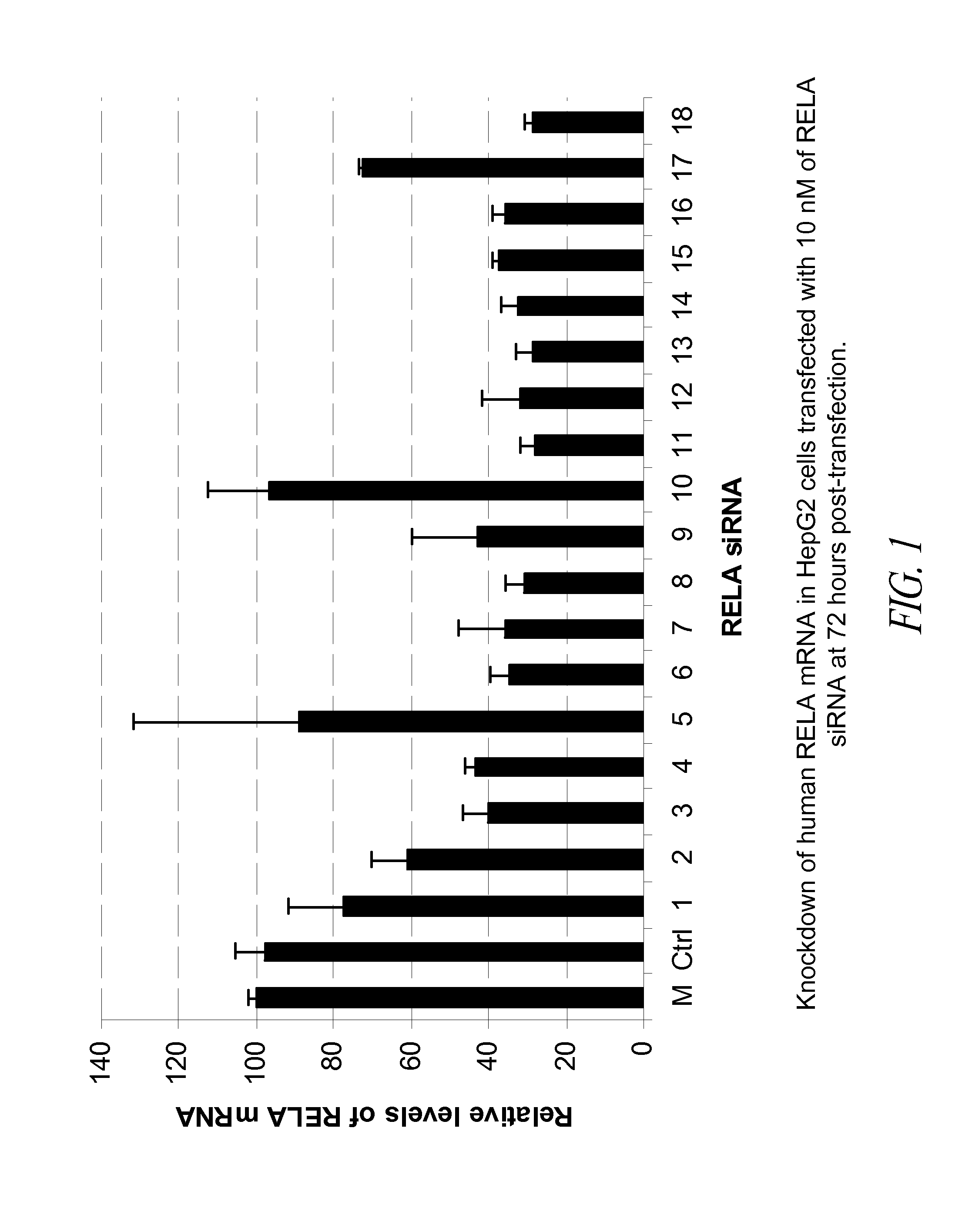
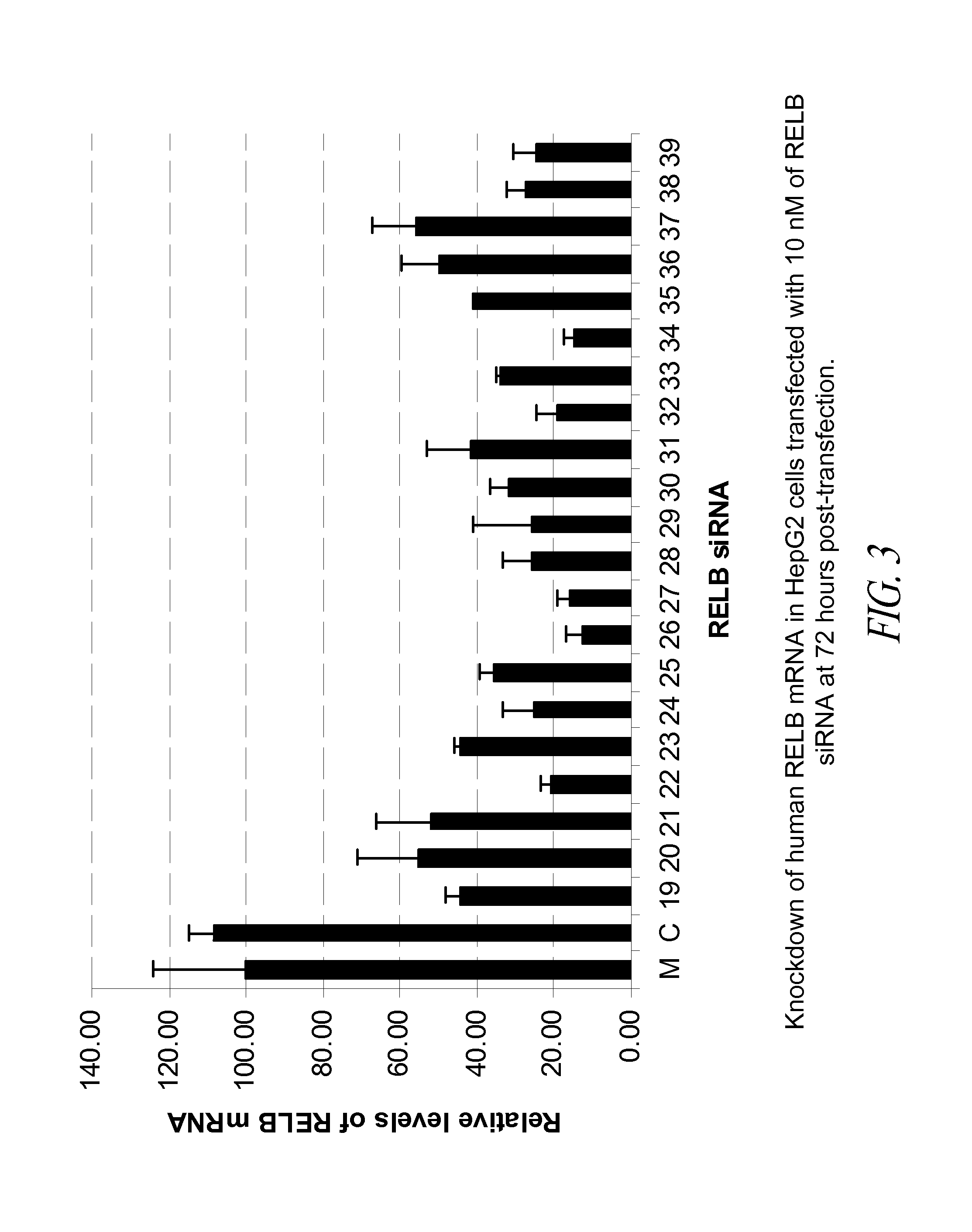
Compositions comprising nuclear factor-kappa b (nf-kb) sirna and methods of use
InactiveUS20110053861A1Improve stabilityReduce severityOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesNf kappabNucleic acid molecule
The present invention provides siRNA nucleic acid molecules that inhibit NF-kappaB expression. Methods of using the nucleic acid molecules are also provided.
Owner:INTRADIGM CORP
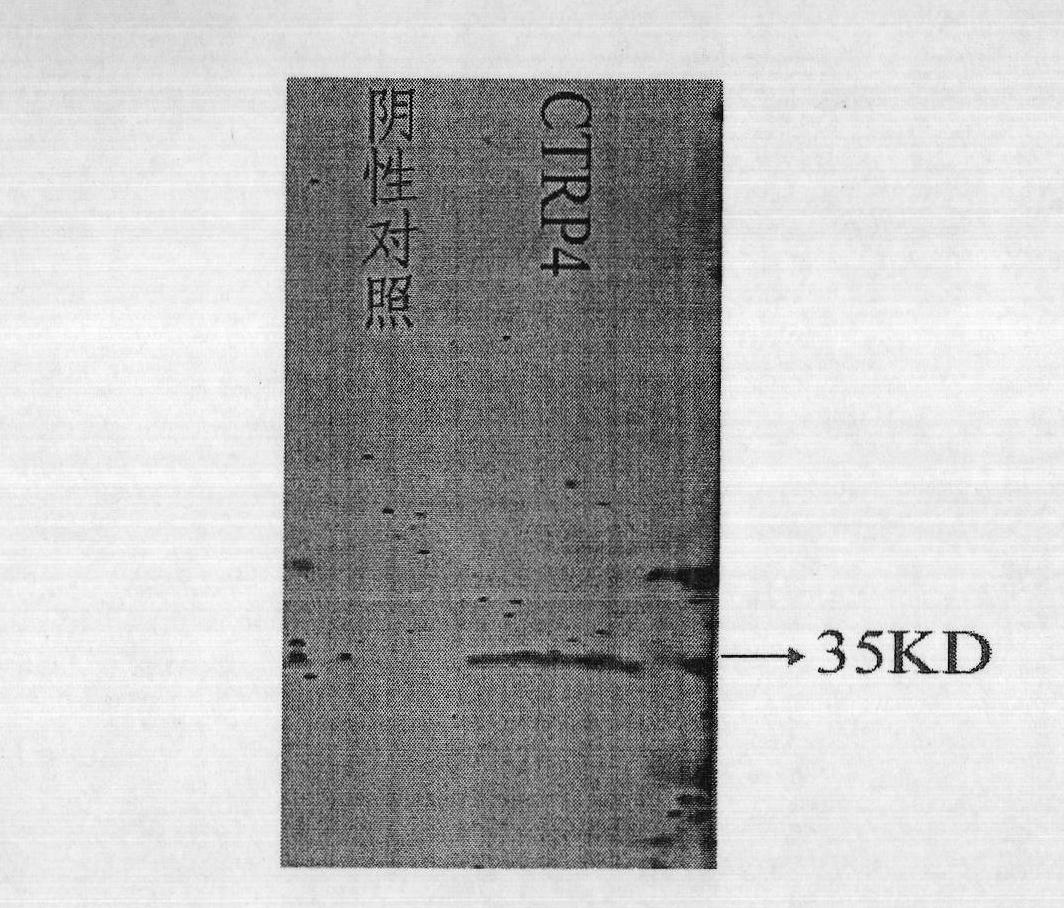
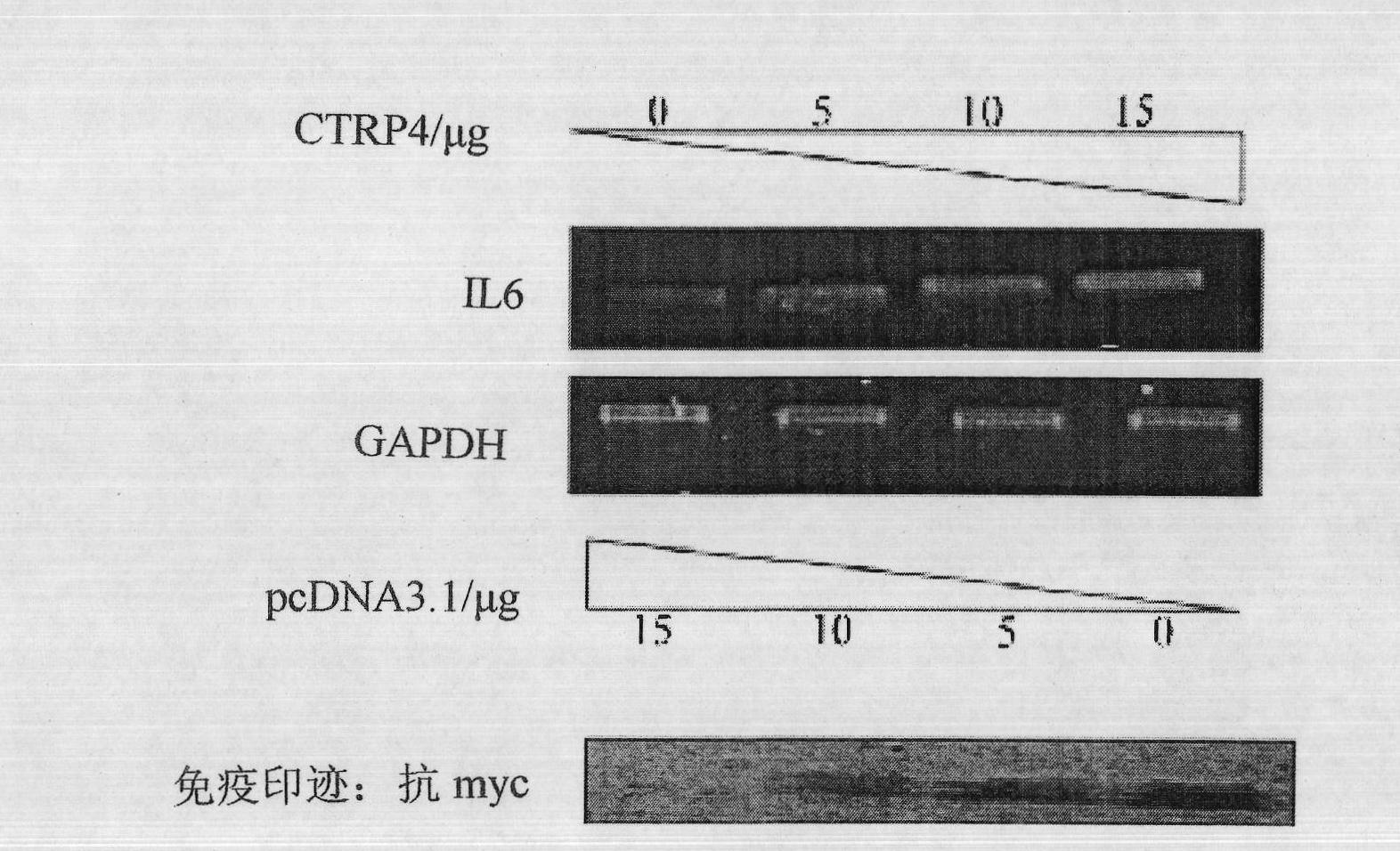
Human CTRP4 gene, its coding protein and their application
The invention discloses a kind of human gene CTRP4 and its coding CTRP4 protein. The invention also relates to the application of an antagonist of the gene and protein in the preparation of NF-kappaB and / or IL6-STAT3 pathway activity inhibiting drug, and relates to the application of an agonist of the gene and the protein in the preparation of hematopoiesis promoting drug and GP130 molecule up-regulating drug.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
NF-kB inhibitors and uses threreof
A new class of imidazolines as 4-position acids or esters with very potent anti-inflammatory as well as antimicrobial activity is described. The synthesis of these imidazolines includes a multicomponent reaction applicable to a combinatorial synthetic approach. The combination of these two key characteristics provides an effective therapeutic drug in the treatment of septic shock as well as many other inflammatory (arthritis and asthma) and infectious disorders. The use of this novel class of non-steroidal agents as anti-inflammatory agents (for the treatment of asthma, etc.), antibacterial agents, and antiseptic agents is described. The compounds are also useful in the treatment of tumors (such as cancers). The imidazolines are potent inhibitors of the transcription factor NF-kappaB as well as potent activity against the Gram (+) bacterium. The compositions are also useful for treating autoimmune diseases and for inhibiting rejection of organ and tissue transplants.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Modulators of glucocorticoid receptor, AP-1, and/or NF-kappaB activity and use thereof
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Brain-protective agent
InactiveUS20040063614A1Efficient managementNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseApoptosis
A brain-protective agent containing an NF-kappaB decoy. In brain diseases, the brain can be particularly effectively protected against brain disorders (for example, cerebral vasospasm following a subrachnoidal hemorrhage and apoptosis of the nerve cells following a cerebrovasucular accident or serious head injury) caused by the undesired activation of cytokines or cell adhesion factors which are regulated by NF-kappaB by administering the brain-protective agent containing an NF-kappaB decoy, i.e., a compound antadonistic specifically to a nucleic acid to which NF-kappaB binds.
Owner:ANGES MG INC
Modulators of the glucocorticoid receptor, AP-1, and/or NF-kappaB activity and use thereof
A class of novel non-steroidal compounds are provided which are useful in treating diseases associated with modulation of the glucocorticoid receptor, AP-1, and / or NF-κB activity including obesity, diabetes, inflammatory and immune diseases, and have the structure of formula (I):where X is S, O or N; Z is —T—COOR1 or —T—COR1; and T, R, R1, Ra, Rb, Rc, Rd, Z, A and B are defined herein. Also provided are pharmaceutical compositions and methods of treating obesity, diabetes and inflammatory or immune associated diseases comprising said compounds.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Preparation and immune-enhancement use of lucid ganoderma liquid fermentation extracellular active polysaccharides
ActiveCN110438180AHigh activityOrganic active ingredientsMicroorganism based processesLiquid mediumEmbryo
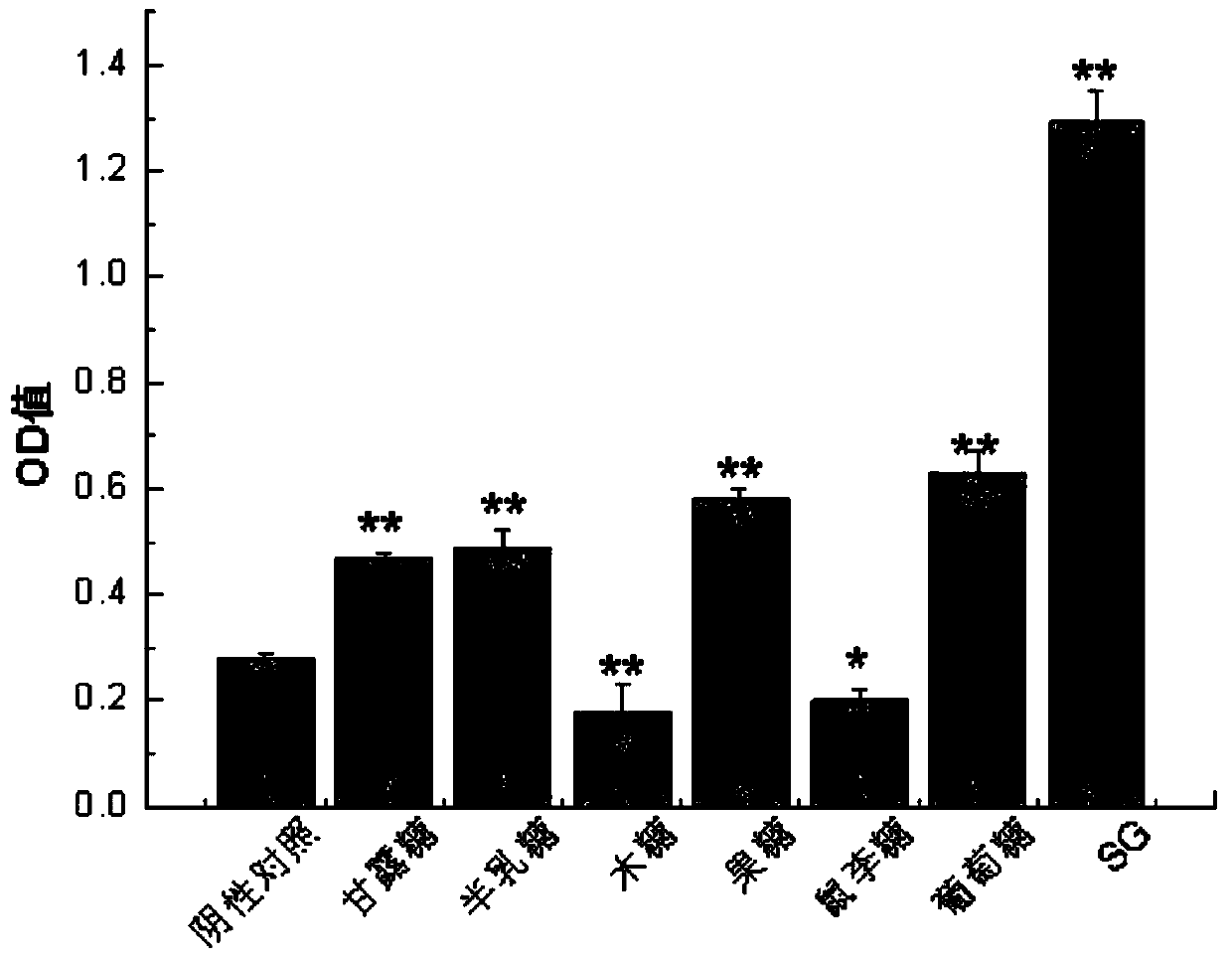
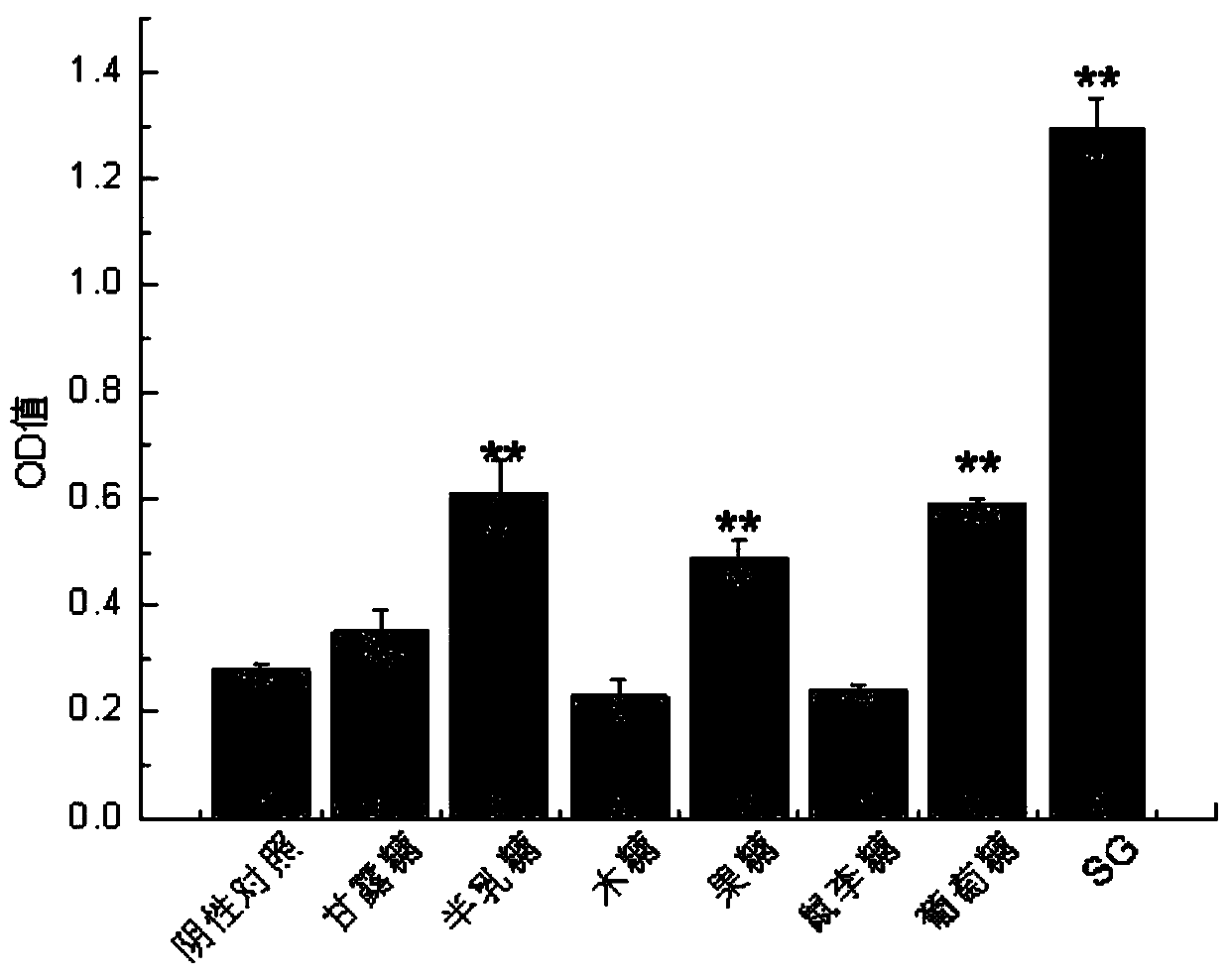
The invention discloses preparation and immune-enhancement use of lucid ganoderma liquid fermentation extracellular active polysaccharides. Lucid ganoderma strains are transferred into a flat PDA medium, then is inoculated to a liquid medium with inoculums size of 10%, and is correspondingly inoculated to a liquid medium with glucose, galactose, mannose, fructose and the like as carbon sources andyeast powder or yeast extracts as nitrogen sources for culturing, ethyl alcohol is added to make the final concentration is 20%-30%, collecting and precipitating are conducted, and drying is conducted after washing by 20%-30% of the ethyl alcohol for 2-3 times, the level of fetal alkaline phosphatase (SEAP) is determined by a QUANTI-Blue method, and the activity of NF-kappaB is activated by an evaluation sample through a Dectin-1 pathway. The results show that the lucid ganoderma fermentation extracellular polysaccharides obtained by the method all have the activity of activating NF-kappaB, and the obtainedpolysaccharides have very good immune activity.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Medical composition containing nf-kb decoy for treating and preventing respir atory diseases and method of using the same
A pharmaceutical composition for treating and preventing diseases, disorders and / or conditions of airway inflammation, airway stenosis or nasal cavity inflammation caused by the expression of a gene regulated by NF-kappaB which contains an NF-kappaB decoy and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The above diseases may be asthma, COPD or rhinitis. Moreover, the above diseases may be diseases caused by an eosinophil abnormality (for example, asthma, rhinitis and COPD). The pharmaceutically acceptable carrier may be a hydrophilic polymer, a liposome and so on.
Owner:ANGES MG INC
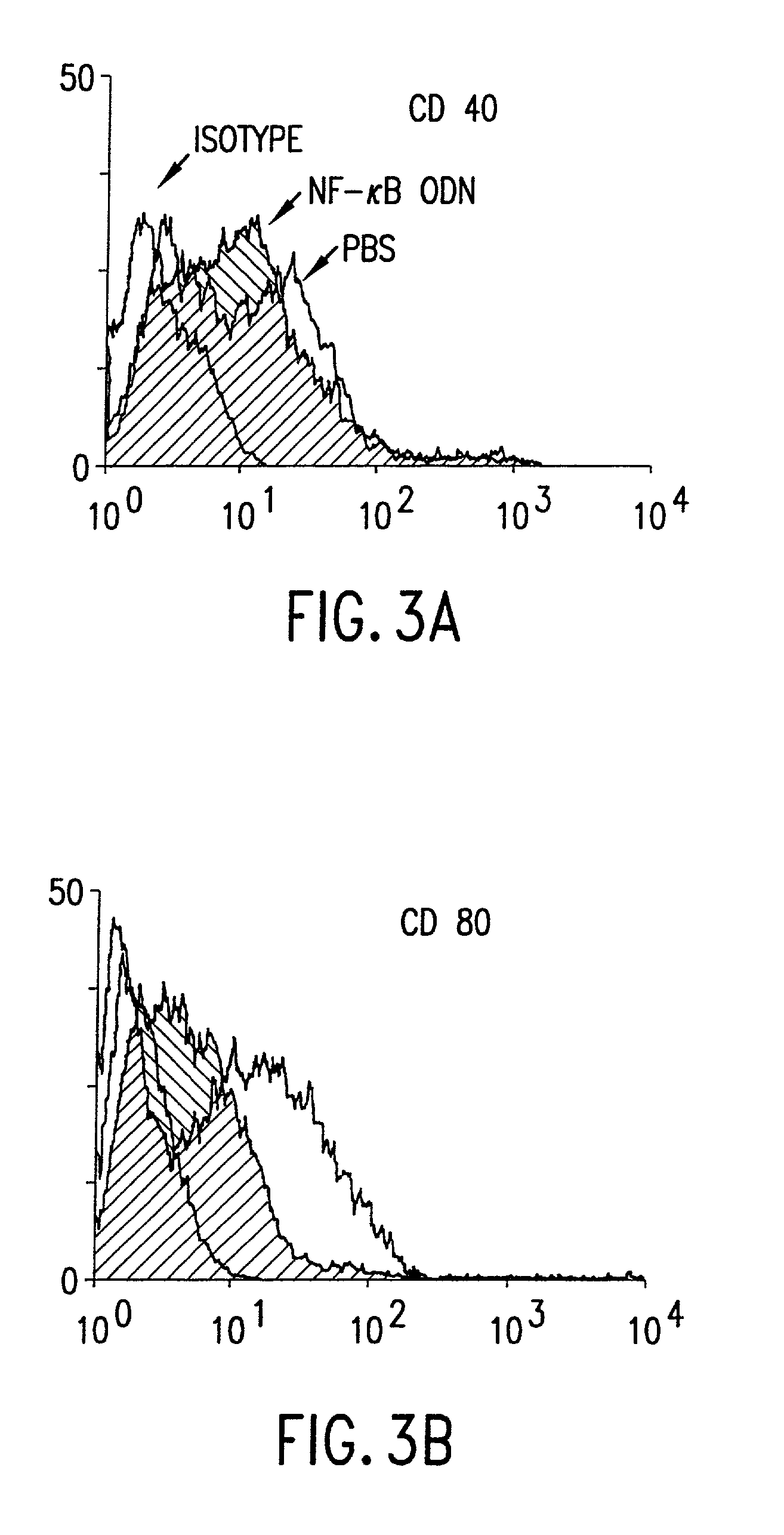
Use of tolerogenic dendritic cells for enhancing tolerogenicity in a host and methods for making the same
InactiveUS20020048564A1Improve graft survivalImprove toleranceVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseDendritic cell
The present invention relates to tolerogenic mammalian dendritic cells (DCs) and methods for the production of the tolerogenic DCs. In addition, the present invention provides a method for enhancing tolerogenicity in a host comprising administering the tolerogenic mammalian DCs of the present invention to the host. The tolerogenic DCs of the present invention comprise an oligodeoxyribonucleotide (ODN) which has one or more NF-kappaB binding sites. The tolerogenic DCs of the present invention may further comprise a viral vector, and preferably an adenoviral vector, which does not affect the tolerogenicity of the tolerogenic DCs when present therein. Enhanced tolerogenicity in a host is useful for prolonging foreign graft survival and for treating inflammatory related diseases, such as autoimmune diseases.
Owner:PITTSBURGH UNIV OF
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com