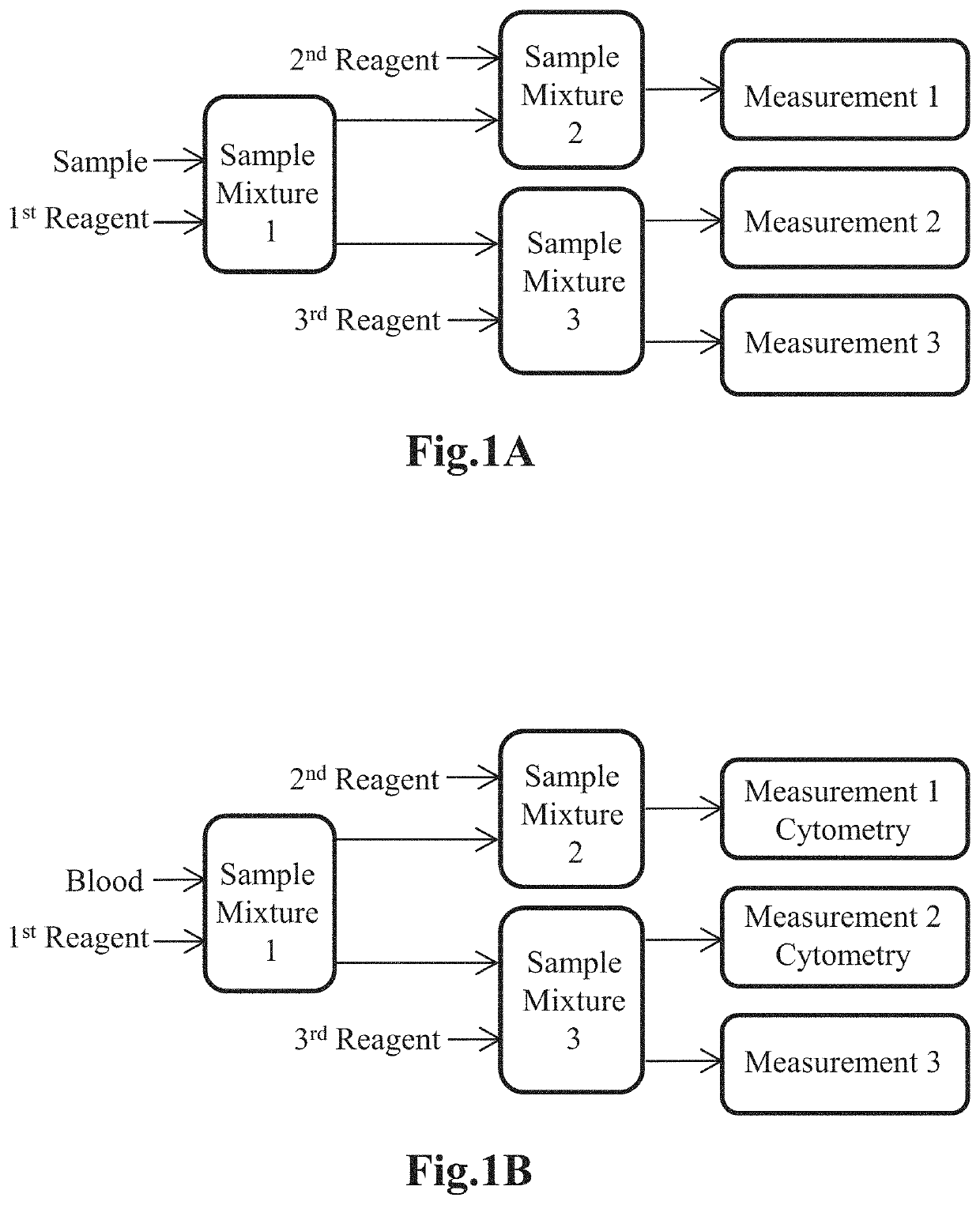
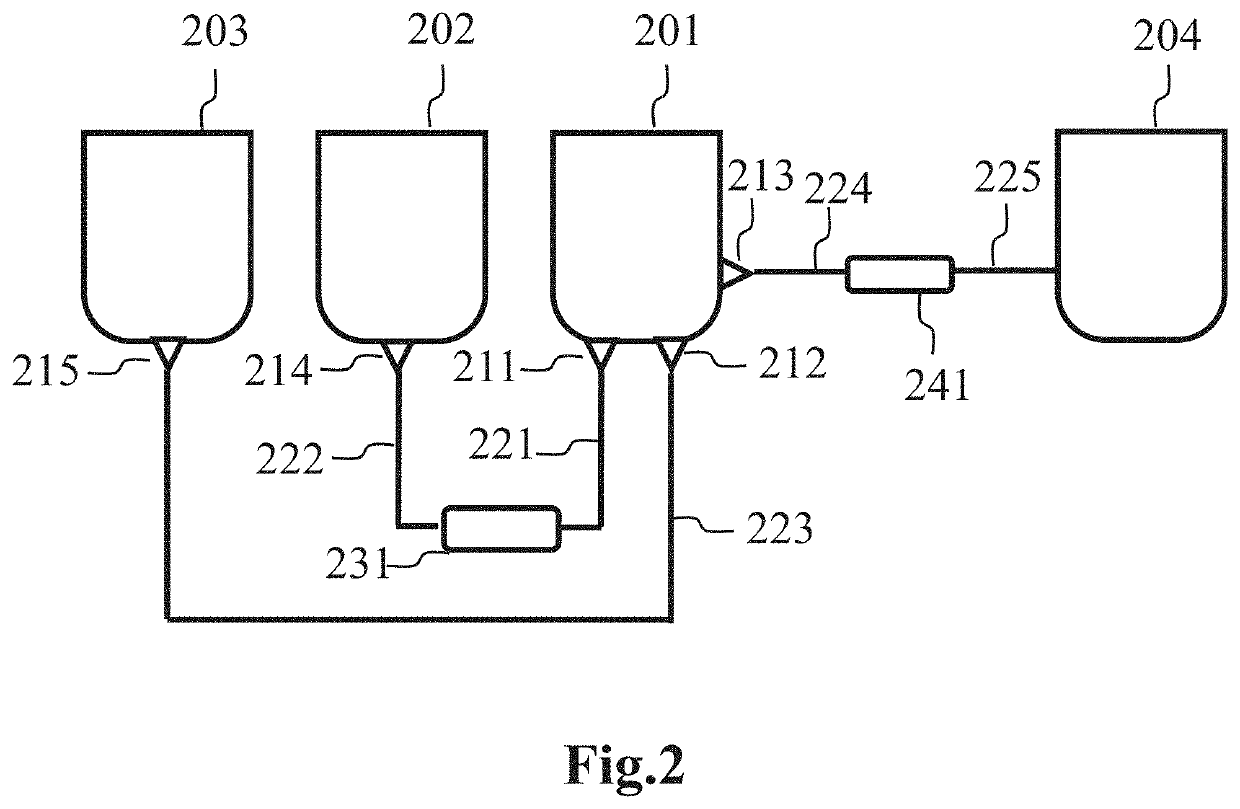
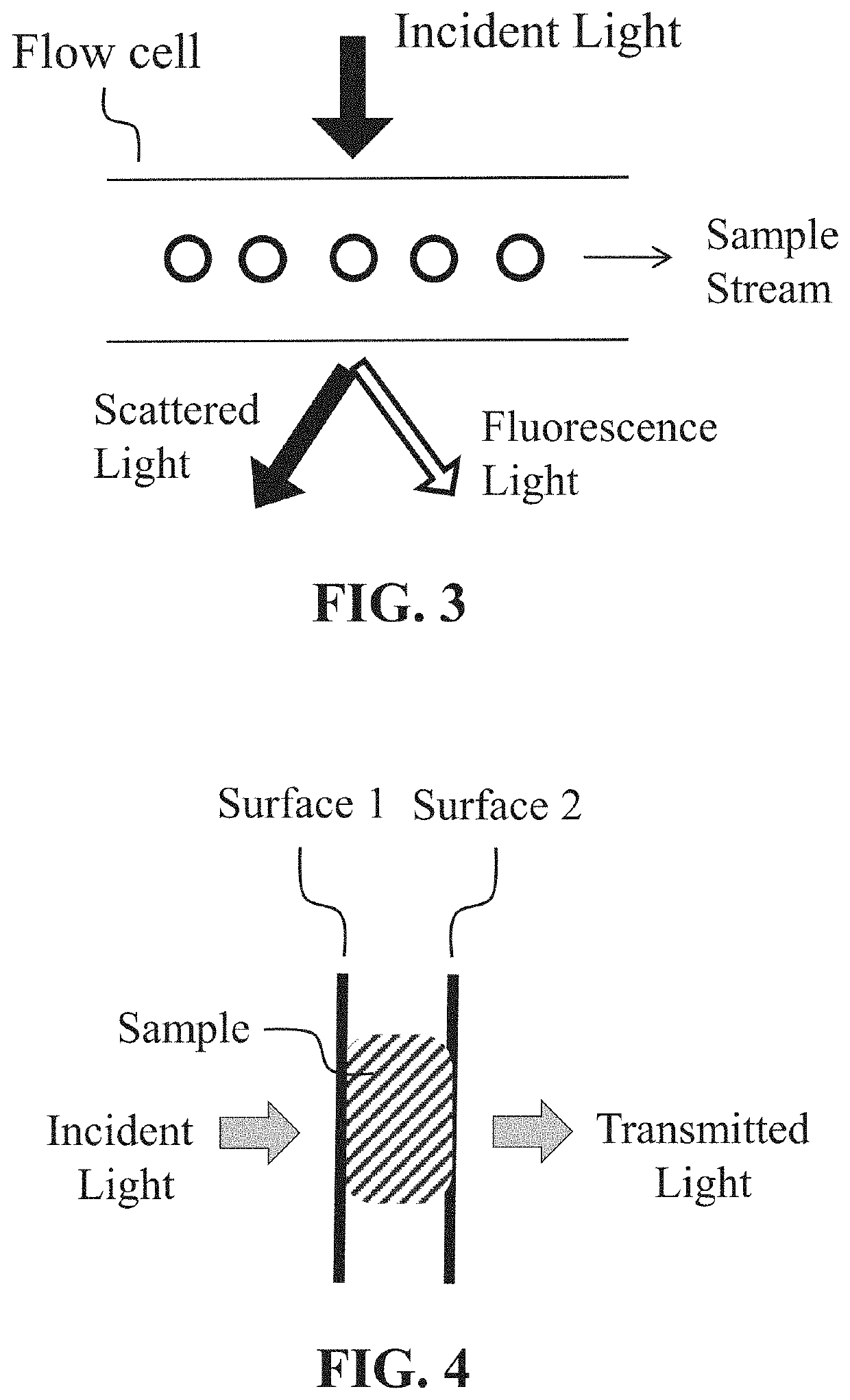
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
40 results about "Serial dilution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
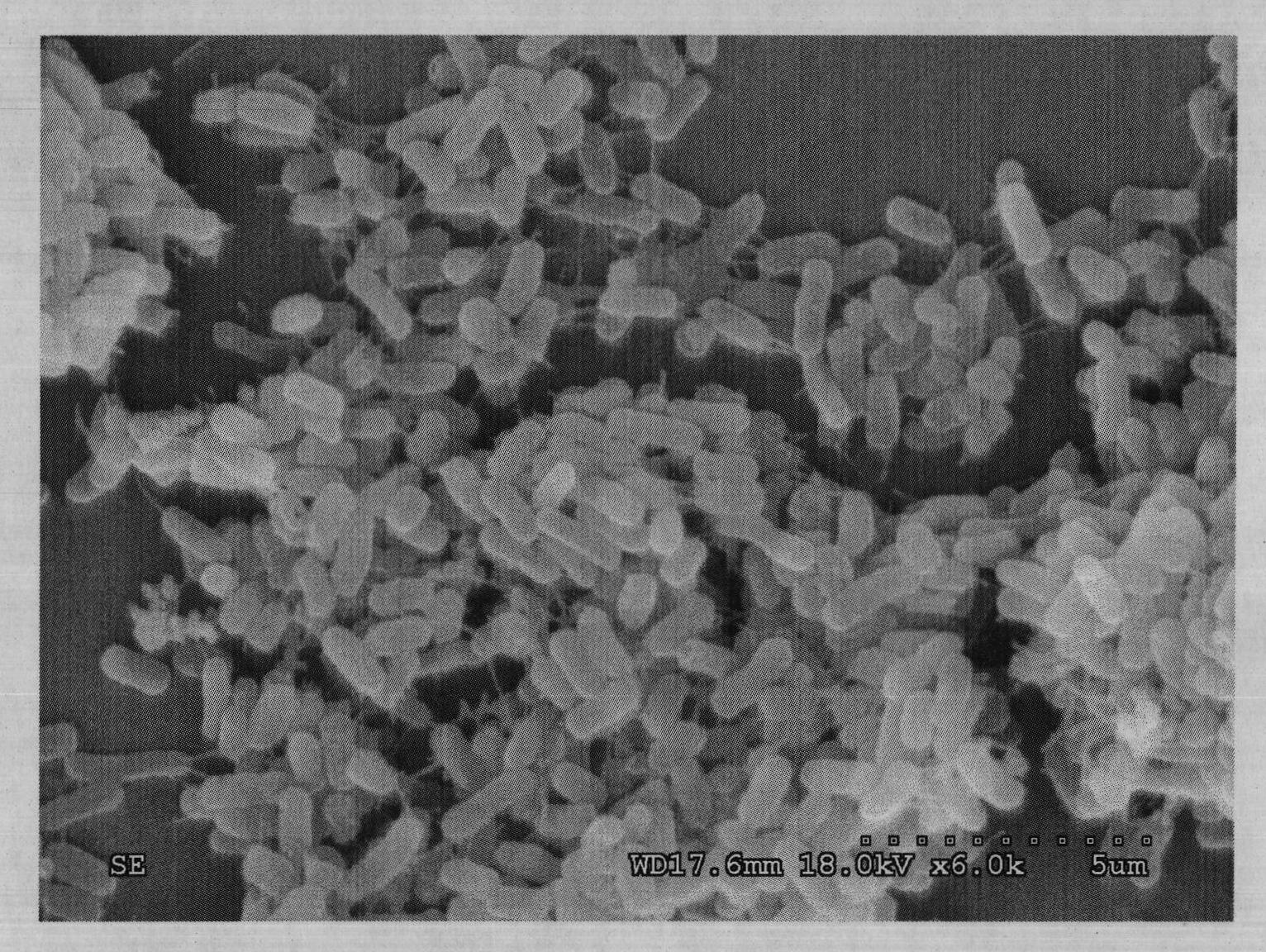
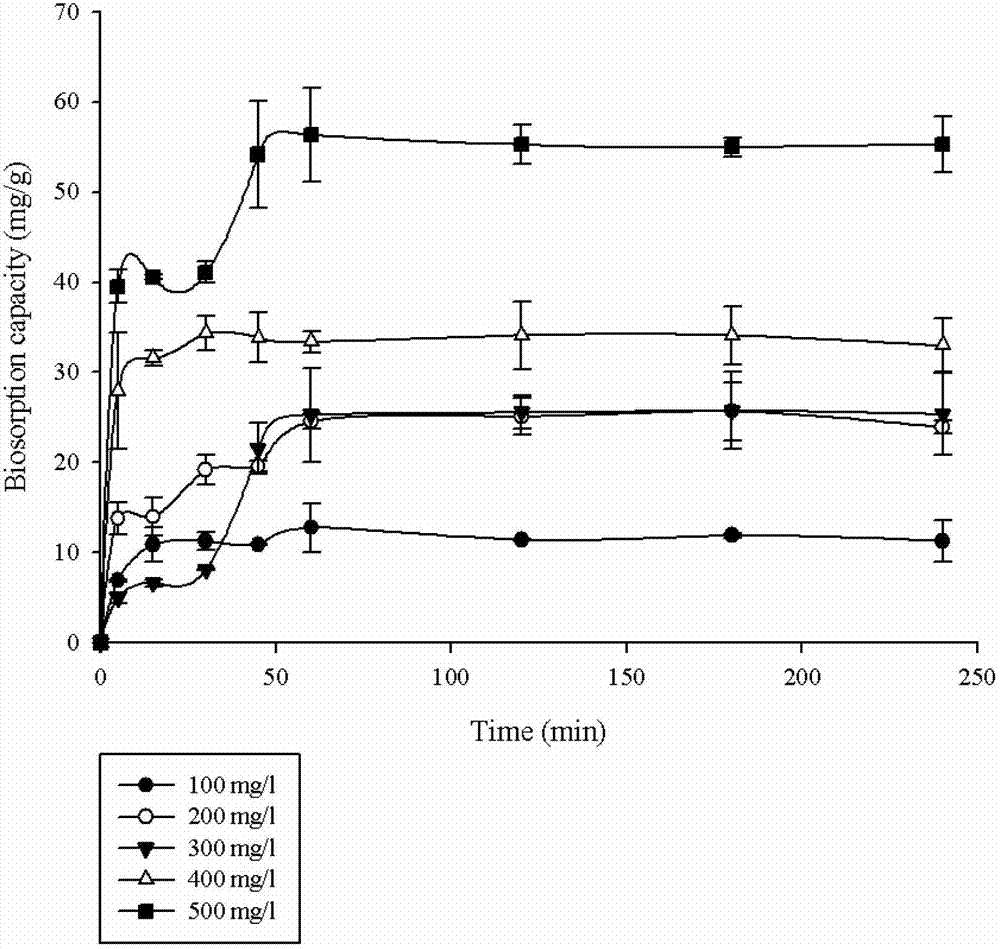
A serial dilution is the stepwise dilution of a substance in solution. Usually the dilution factor at each step is constant, resulting in a geometric progression of the concentration in a logarithmic fashion. A ten-fold serial dilution could be 1 M, 0.1 M, 0.01 M, 0.001 M ... Serial dilutions are used to accurately create highly diluted solutions as well as solutions for experiments resulting in concentration curves with a logarithmic scale. A tenfold dilution for each step is called a logarithmic dilution or log-dilution, a 3.16-fold (10⁰·⁵-fold) dilution is called a half-logarithmic dilution or half-log dilution, and a 1.78-fold (10⁰·²⁵-fold) dilution is called a quarter-logarithmic dilution or quarter-log dilution. Serial dilutions are widely used in experimental sciences, including biochemistry, pharmacology, microbiology, and physics.
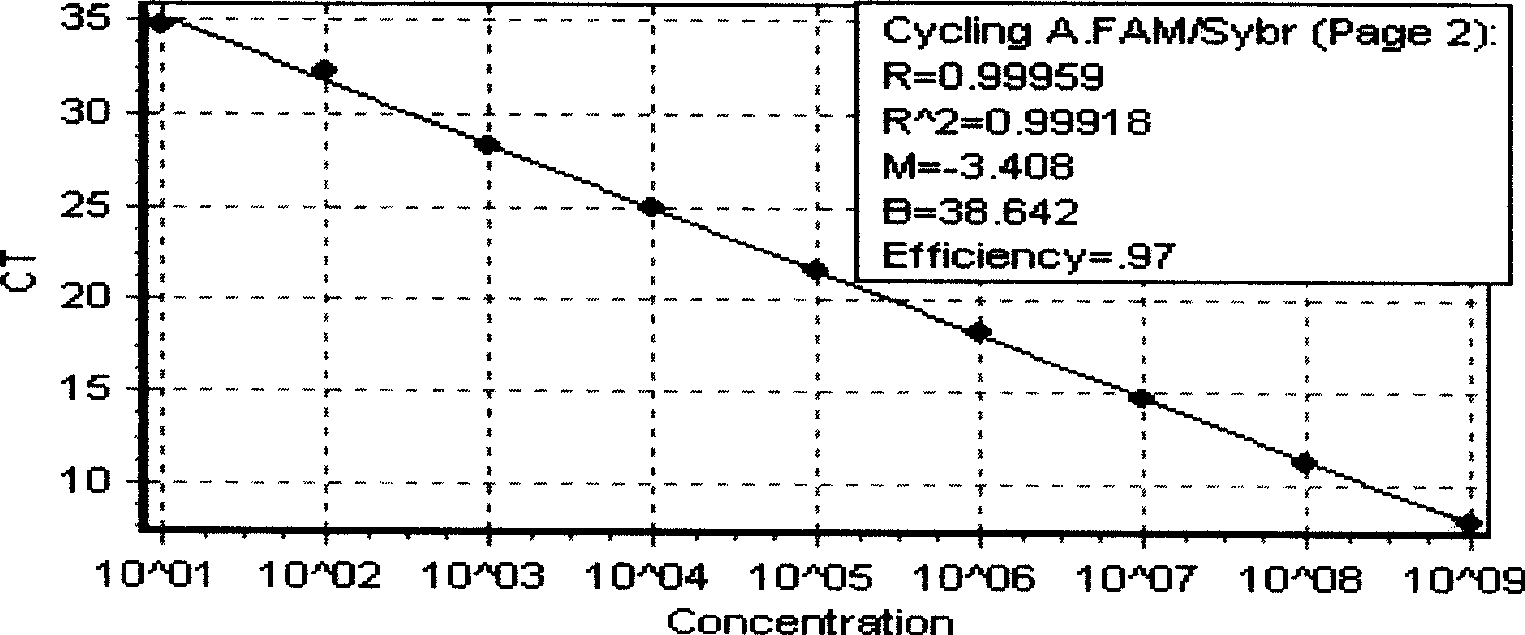
Multiple real time fluorescence quantifying PCR method for detecting porcine circovirus, porcine parvovirus, porcine pseudorabies virus and classical swine fever virus
InactiveCN101260442ALow costImprove application stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementClassical swine fever virus CSFVRegression analysis
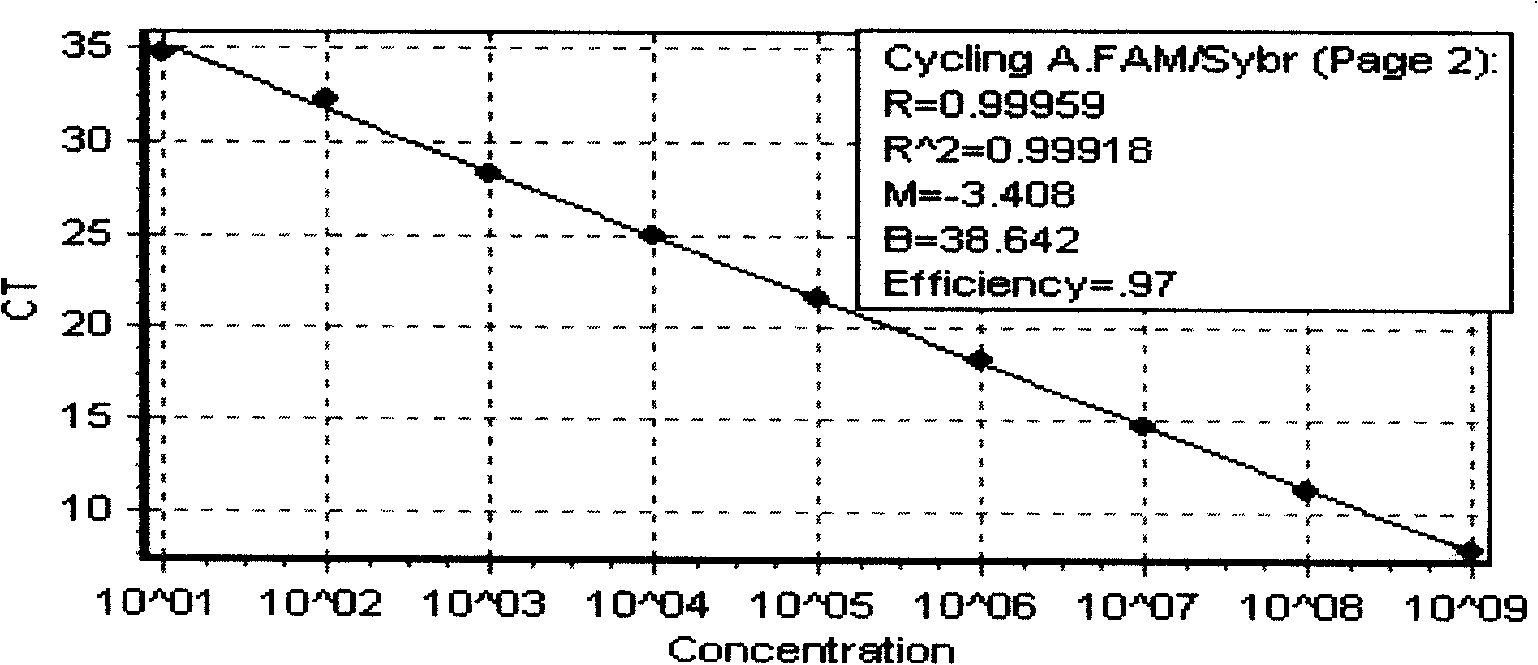
The invention discloses a multiplex real-time fluorescent quantitation PCR method capable of detecting porcine circovirus, porcine parvovirus, porcine pseudorabies virus and hog cholera virus at the same time. The method of the invention detects that the four virus are all in good linear relations at the same time, all ten times serial dilution points of constructed normal plasmid are all in one straight line, CT value and copy number are in good linear relation, and regression analysis shows that the related coefficient of the CT value and the copy number is R<2> more than 0.99.The multiplex real-time fluorescent quantitation PCR method has the advantages of excellent specificity, sensibility and stability, which can rapidly, sensitively and differentially detect the four virus with serious harm to the economy and can be used for early diagnosis of virus infection.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Medicinal agent for treating fatness, diabetes, and diseases associated with impaired glucose tolerance
InactiveUS20110008452A1Specific pharmacologicalImprove efficacyPowder deliveryEnergy modified materialsDiseaseIGT - Impaired glucose tolerance
The inventive medicinal agent comprises antibodies against beta-subunit of insulin receptor in an activated form produced by means of repeated serial dilution and an external action performed according to homeopathic technology. The inventive method for producing a solid medicinal formulation for perorally treating fatness, diabetes, and other diseases associated with impaired glucose tolerance, consists in mixing the effective amount of carrier, which is showered in a fluidised layer by a water-alcohol dilution of antibodies in the form active against the beta-subunit of the insulin receptor produced by combining the repeated serial dilution, thereby reducing the concentration of antibodies, and an external action according to homeopathic technology, and is dried at a temperature equal to or less than 35° C., with pharmaceutically acceptable additives and in subsequently pelleting the mixture thus obtained by means of direct dry compression.
Owner:EPSHTEIN OLEG ILIICH
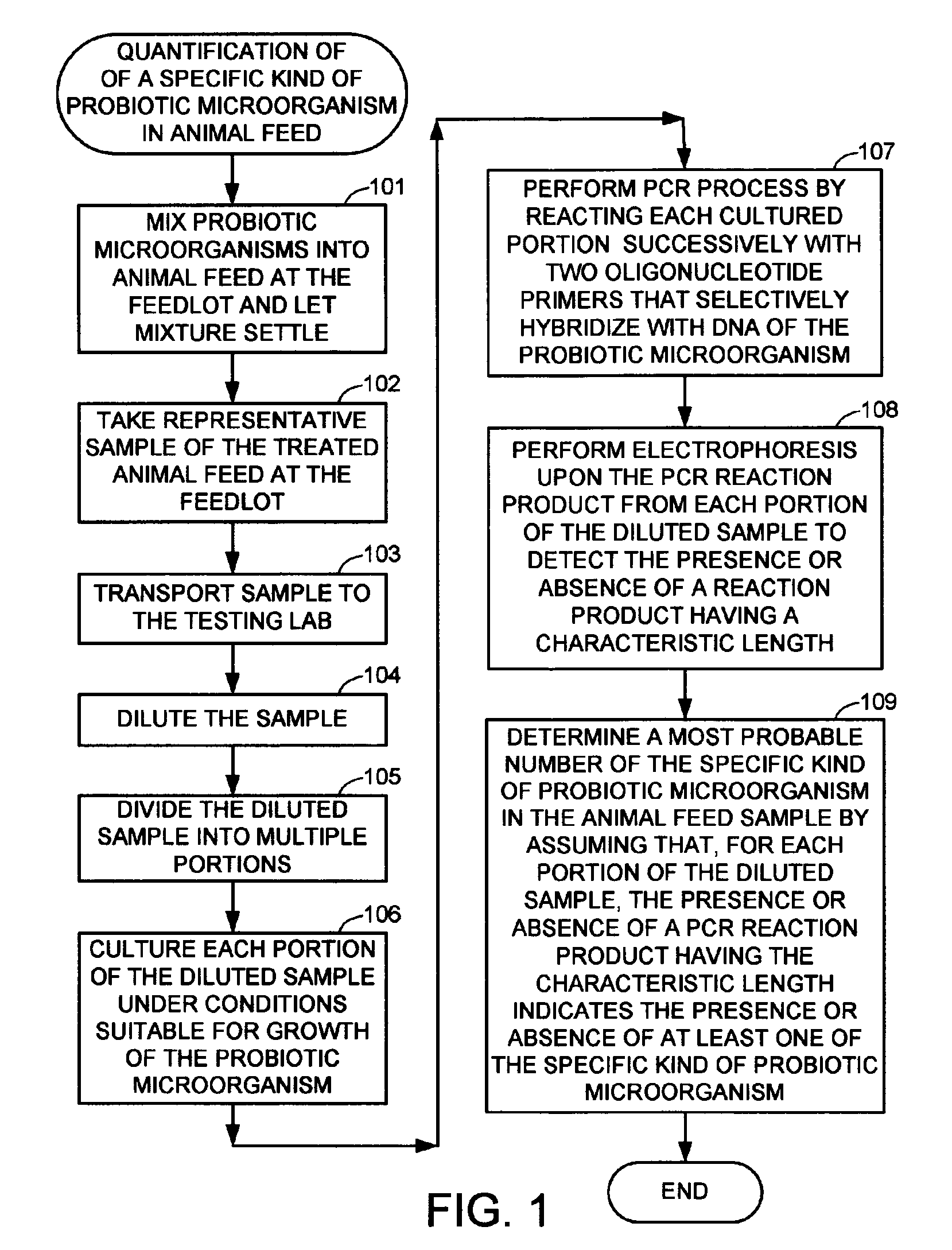
Methods for detecting and quantifying specific probiotic microorganisms in animal feed
Methods and compositions are disclosed for confirming and quantifying the presence of a specific probiotic microorganism in a sample of animal feed. Hybridization and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) techniques are applied to identify the presence of the specific probiotic microorganism in cultures grown in most probable number and serial dilution methods, after calibration of the techniques using blank and control samples.
Owner:NUTRITION PHYSIOLOGY
High-cadmium-adsorption filamentous fungus Paecilomyces lilacinus XLA, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103451103AEasy accessLow costFungiContaminated soil reclamationCadmium adsorptionPaecilomyces lilacinus
The invention relates to a high-cadmium-adsorption filamentous fungus Paecilomyces lilacinus XLA, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1, weighing a pot experiment soil sample used for heavy metal restoration and having a content of heavy metal cadmium of 50mg / Kg, adding to sterile water with glass beads, oscillating on a constant temperature shaking table, allowing an obtained solution to stand, taking an obtained supernatant, and carrying out serial dilution; 2, coating a Martin flat containing 60mM of cadmium with different dilution rates of dilutions, allowing the obtained flat to stand for a moment, inverting on a constant temperature culturing box, and culturing; 3, carrying out streaking purification of single colonies growing on the flat, coating the Martin flat with the obtained single colonies, and culturing; 4, carrying out separating screening to obtain the Paecilomyces lilacinus XLA stably resisting cadmium, and preserving on a PDA inclined plane for later use. The Paecilomyces lilacinus XLA is preserved and has a preservation number of CCTCC NO:M2012135. Viable and non-viable organism of the XLA can efficiently adsorb and remove the heavy metal cadmium in heavy metal sewage, so the XLA has the advantages of low cost and simple technology, and has an efficient restoration potential of heavy metal polluted soil and water.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Intestinal bacteria culture method and culture medium thereof
The invention discloses a method for culturing intestinal bacteria. The method comprises the steps of putting fresh feces into a test tube of diluent A added with glass beads, blending the materials for more than 3 minutes on a blending device, diluting the materials to the dilution degree between 10<-> and 10<-8> according to a serial dilution method, partitioning a culture medium plate according to different spreading concentration, adding the same amount of diluted mixed solution to subareas respectively, uniformly spreading the mixed solution and putting the plate in a thermostat at 37 DEG C for incubation and culture. The method has the advantages of intuitively reflecting the species and quantity of bacteria in specimens, further researching and analyzing the biochemical characteristics, metabolic characteristics, genetic characteristics and the like of cultured bacteria.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Ewod device with calibrated serial dilution function
ActiveUS20160375437A1Minimize sample lossEasy to controlElectrolysis componentsTransportation and packagingEngineeringElectrode array
In a method of performing dilution of a droplet in an EWOD device, a parent droplet is provided on an electrode array of the EWOD device, wherein the parent droplet has a first concentration of a species. A diluent droplet also is provided on the electrode array of the EWOD device. The method includes controlling actuation voltages applied to the electrode array of the EWOD device to join the parent droplet and the diluent droplet into a product droplet having a diluted second concentration of the species different from the first concentration in the parent droplet. The actuation voltages then are controlled to split the product droplet into one or more daughter droplets having the second concentration of the species. A dilution ratio may be calibrated based on the volumes of the droplets. Serial dilution steps may be performed to generate daughter droplets of different species concentrations at each step.
Owner:SHARP LIFE SCI EU LTD
Low Density Microarrays for Vaccine Related Protein Quanitification, Potency Determination and Efficacy Evaluation
Methods for the quantification of influenza HA proteins and anti-influenza antibodies for the fields of vaccine-related protein quantification, potency determination, and efficacy evaluation are provided. According to the technology, quantification is achieved by providing capture agents attached to an array in a series of decreasing concentrations. Serial dilutions of a reference material also may be introduced. The reference material within each solution binds to the capture agents on the array and is labeled with a label agent capable of producing a detectable signal used to construct a calibration curve. A target material of unknown concentration is introduced to a separate identical array, and the target material binds to the capture agents and also is labeled by a label agent to produce a detectable signal. The calibration curve based on the reference material is then utilized to determine the concentration of the target material without the need to perform replicate experiments.
Owner:INDEVR
Method for rapidly determining drug tolerance of strain
InactiveCN101760502ADetermining Antibiotic SpectrumEfficient determinationMicrobiological testing/measurementMethyl thiazolyl tetrazoliumCulture fluid
The invention discloses a method for rapidly determining drug tolerance of a strain. The method comprises the following steps: A, preparing nutrient fluid containing methyl thiazolyl tetrazolium; B, preparing bacterial suspension; C, preparing antibiotic solution; D, adding the nutrient fluid containing the methyl thiazolyl tetrazolium, the antibiotic solution and the bacterial suspension into holes of a culture plate, and performing serial dilution on the antibiotic solution; and E, scanning and determining the diluent in real time, and determining the drug tolerance of the strain to antibiotic according to the scanning result. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of simply, rapidly, economically and high-efficiently determining the drug tolerance of the strain.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF INSPECTION & QUARANTINE +1
High-throughput micro-droplet serial dilution device and high-throughput micro-droplet serial dilution method
PendingCN108837718AConditions needed to control multiple dilutionsUnderstand the purposeTransportation and packagingLaboratory glasswaresRelative displacementComputer science
The invention discloses a high-throughput micro-droplet serial dilution device and a high-throughput micro-droplet serial dilution method and relates to the field of serial dilution. The high-throughput micro-droplet serial dilution device comprises an upper subchip and a lower subchip, wherein relative displacement of the upper subchip and the lower subchip reaches a second position; micropores of series 1 are superposed with those of a first-row series 2; the concentration of a solution 1 in the micropores of the series 1 is changed by a solution 2 in the micropores in the first-row series 2; after the solutions are sufficiently mixed, the upper subchip is displaced to the third position relative to the lower subchip, and the micropores of the series 1 are enabled to be superposed with micropores in a second-row series 2; and the concentration of the solution 1 in the morepores of the series 1 is changed by the solution 2 in the micropores of the series 2 for the second time. Multiple relative displacement of the upper subchip and the lower subchip can be realized, and thereby the aim of performing gradient change of the solution 1 in the micropores of the series 1 is achieved. The high-throughput micro-droplet serial dilution device and the high-throughput micro-droplet serial dilution method disclosed by the invention can perform accurate serial dilution for nano-liter level or smaller volume and multi-proportion parallel operation at the same time; and complex workers or expensive liquid transfer robots do not be needed and environmental conditions of serial dilution are conveniently controlled.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Medicinal agent for treating fatness, diabetes, and diseases associated with impaired glucose tolerance
InactiveUS9308259B2Specific pharmacologicalImprove efficacyMetabolism disorderEnergy modified materialsIGT - Impaired glucose toleranceAlcohol
The inventive medicinal agent comprises antibodies against beta-subunit of insulin receptor in an activated form produced by means of repeated serial dilution and an external action performed according to homeopathic technology. The inventive method for producing a solid medicinal formulation for perorally treating fatness, diabetes, and other diseases associated with impaired glucose tolerance, consists in mixing the effective amount of carrier, which is showered in a fluidized layer by a water-alcohol dilution of antibodies in the form active against the beta-subunit of the insulin receptor produced by combining the repeated serial dilution, thereby reducing the concentration of antibodies, and an external action according to homeopathic technology, and is dried at a temperature equal to or less than 35° C., with pharmaceutically acceptable additives and in subsequently pelleting the mixture thus obtained by means of direct dry compression.
Owner:EPSHTEIN OLEG ILIICH
EWOD device with calibrated serial dilution function
ActiveUS9539573B1Minimize sample lossEasy to controlTransportation and packagingMixersEngineeringElectrode array
Owner:SHARP LIFE SCI EU LTD
Method for separating microorganisms on surface of tobacco leaf at high temperature by utilizing pure tobacco leaf leach liquor solid plate
InactiveCN102078027AImprove biological activitySimple production processTobacco treatmentBacteriaMicroorganismMicrobiological Techniques
The invention provides a method for separating microorganisms on a surface of a tobacco leaf at a high temperature by utilizing a pure tobacco leaf leach liquor solid plate, belonging to the technical field of applied microbiology. The technical scheme of the method comprises the following steps: mixing a waste tobacco leaf liquid which is fully soaked (for 3-5 days) with agar (2.5g / 100ml) based on the volume ratio of 5-15% (V / V), autoclaving at the pressure of 0.11-0.13MPa for 25-35 minutes (sterilizing for 230 minutes according to the ratio of 15 pounds per inch) under the conditions that no additional component is added and the pH value is not regulated, and pouring the mixture into a double layer plate to prepare the pure tobacco leaf leach liquor solid plate; and carrying out serial dilution on a tobacco leaf sample according to the conventional process, adding the diluted tobacco leaf sample into the pure tobacco leaf leach liquor solid plate, uniformly coating, and cultivating the pure tobacco leaf leach liquor solid plate in an incubator at the temperature of 50-60 DEG C until a bacterial colony is produced. The quantity and type of microorganisms grown on the surface of the tobacco leaf at a high temperature can be really reflected, and the microorganisms separated by the method are applicable to improving the quality of the tobacco leaf when the tobacco leaf is cured by flue.
Owner:KUNMING GUIXUN TECH
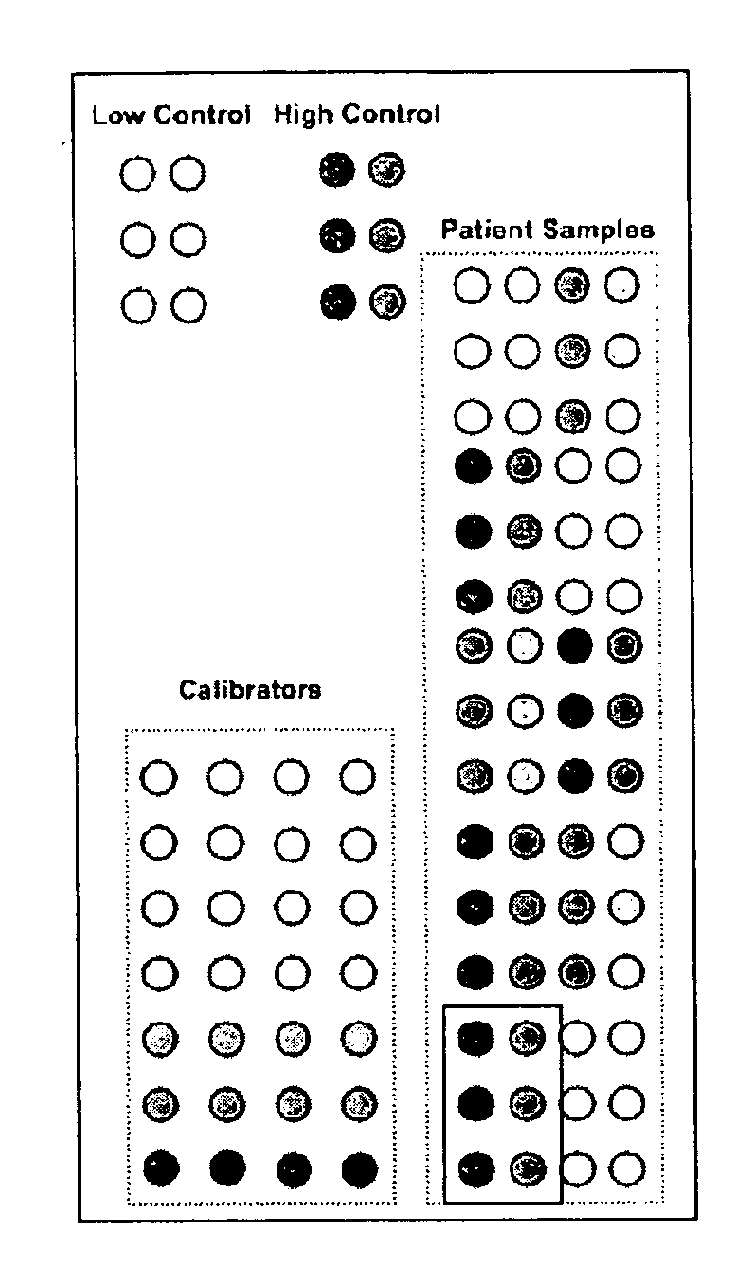
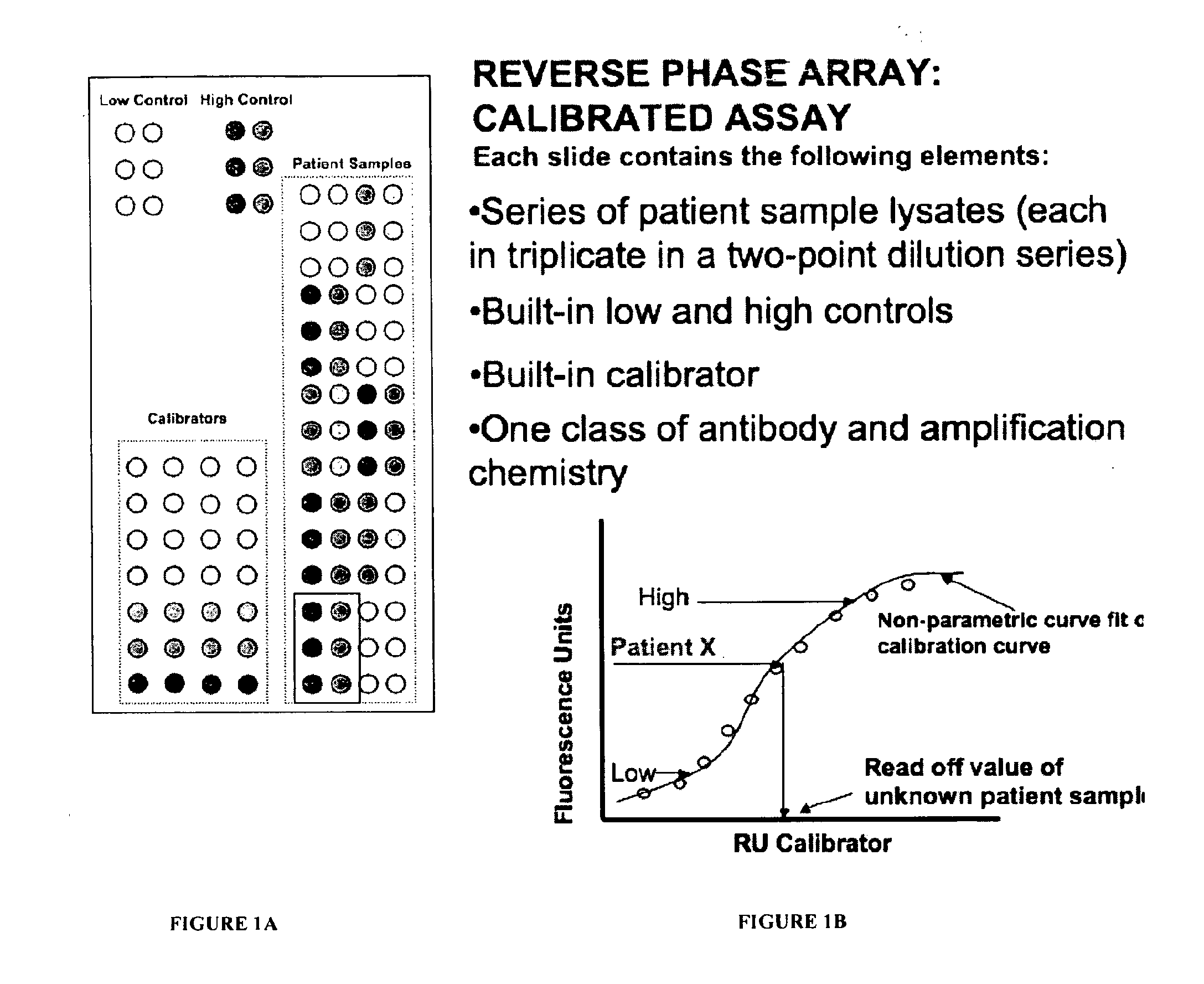
Calibrated rpma assay
This invention relates, e.g., to a set of calibrants for determining the amount in a sample of an analyte (e.g., a protein, such as a protein that has been post-translationally modified), comprising a plurality of calibrants, which contain a range of amounts (e.g., defined amounts and / or serial dilutions) of the analyte, spanning the expected amount of the analyte in the sample. In each of the calibrants, a defined amount of the analyte is present in the same suitable, biological diluent (e.g., a cell or tissue lysate, or a bodily fluid). In one embodiment of the invention, the diluent reflects the same or a similar biological milieu (proteins, lipids, serum proteins, serum matrix proteins, etc.) as that in the sample in which the analyte to be measured is present. In embodiments of the invention, a single calibrant (e.g., a cell lysate) may comprise as many as hundreds of analytes, and can be used for the quantification of those hundreds of analytes in a sample. Methods are described for performing an assay (e.g. RPMA analysis), in which the calibrants of a set of calibrants of the invention are immobilized on each of the surfaces to which samples to be analyzed are immobilized, thereby providing an internal calibration curve for quantifying an RPMA assay.
Owner:GEORGE MASON INTPROP INC
Cytokines as prognostic markers of respiratory-tract infection following major surgery
InactiveUS20120129176A1Reduces and excludes variationHigh riskHealth-index calculationMicrobiological testing/measurementFactor iiPre operative
The invention relates to the use of a certain subset of cytokine markers as prognostic variables of infection status in an individual, and especially as prognostic markers of a patients developing severe infection such as pneumonia, and respiratory tract infection following surgery. The subset of cytokine markers consists of the interleukin cytokines IL-2, IL-7, IL-23, IL-27, and IL-IO, and Interferon-γ (INFγ) and Tissue Necrosis Factor-α (TNFα). The markers may be employed as individual prognostic variables of infection status, or they may be used in pairs or other combinations. Generally, the abundance of the markers is correlated with infection status by means of an absolute pre-operative value of biomarker abundance, ratio's of pre-operative to post-operative biomarker abundance, or ratio values for pairs of certain biomarkers within the subset. Typically, cytokine abundance is expressed in terms of mRNA copy number wherein the copy numbers are ideally normalised to a house keeping gene and quantification of mRNA copy number is determined by RT-PCR containing reference serial dilutions of cytokine specific cDNA.
Owner:THE PROVOST FELLOWS & SCHOLARS OF THE COLLEGE
Cytokines as prognostic markers of respiratory-tract infection following major surgery
InactiveUS20150197808A1Reduce riskHigh riskHealth-index calculationMicrobiological testing/measurementInterferon alphaPre operative
The invention relates to the use of a certain subset of cytokine markers as prognostic variables of infection status in an individual, and especially as prognostic markers of a patients developing severe infection such as pneumonia, and respiratory tract infection following surgery. The subset of cytokine markers consists of the interleukin cytokines IL-2, IL-7, IL-23, IL-27, and IL-10, and Interferon-γ (INFγ) and Tissue Necrosis Factor-α (TNFα). The markers may be employed as individual prognostic variables of infection status, or they may be used in pairs or other combinations. Generally, the abundance of the markers is correlated with infection status by means of an absolute pre-operative value of biomarker abundance, ratio's of pre-operative to post-operative biomarker abundance, or ratio values for pairs of certain biomarkers within the subset. Typically, cytokine abundance is expressed in terms of mRNA copy number wherein the copy numbers are ideally normalised to a house keeping gene and quantification of mRNA copy number is determined by RT-PCR containing reference serial dilutions of cytokine specific cDNA.
Owner:TRINITY COLLEGE DUBLIN
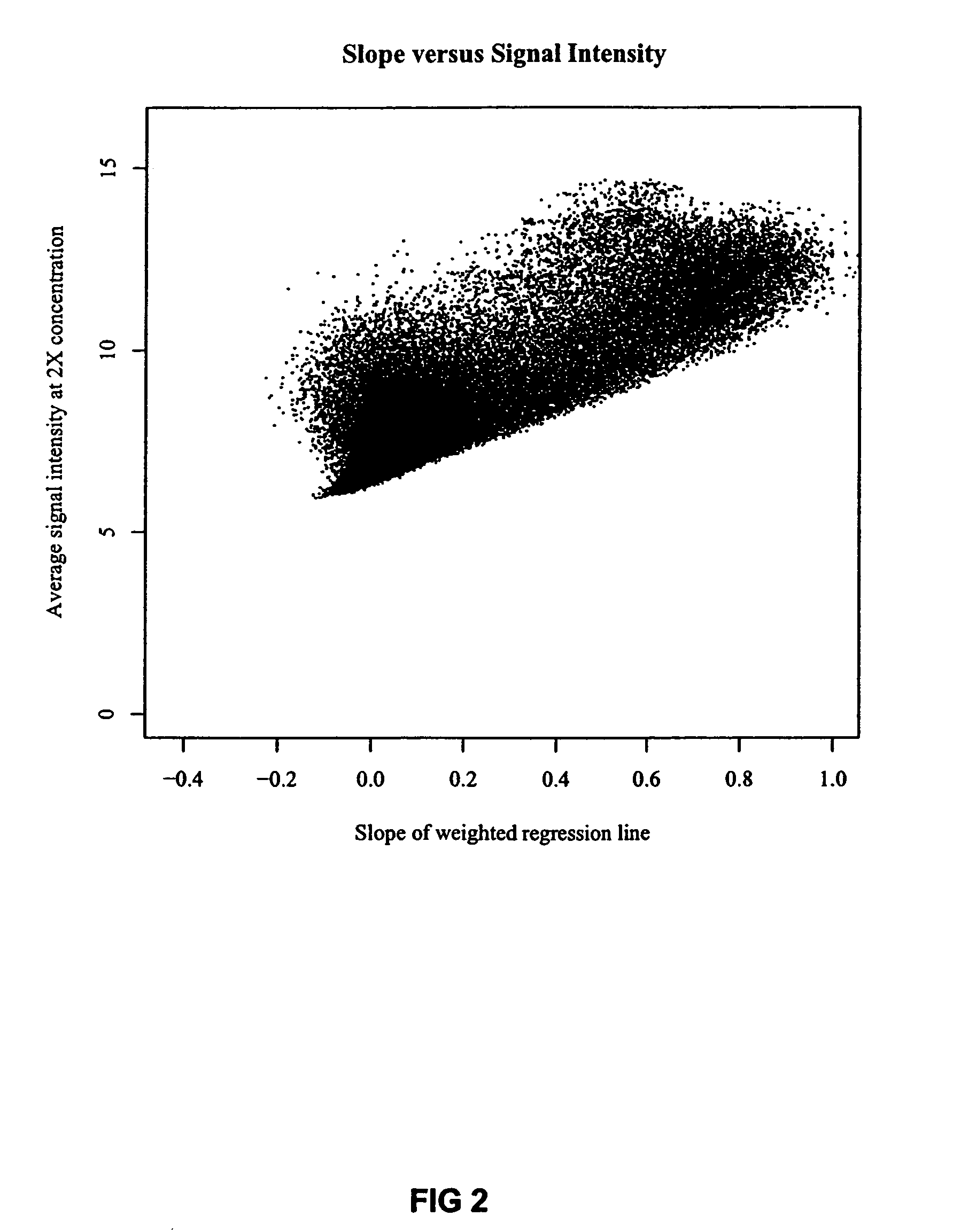
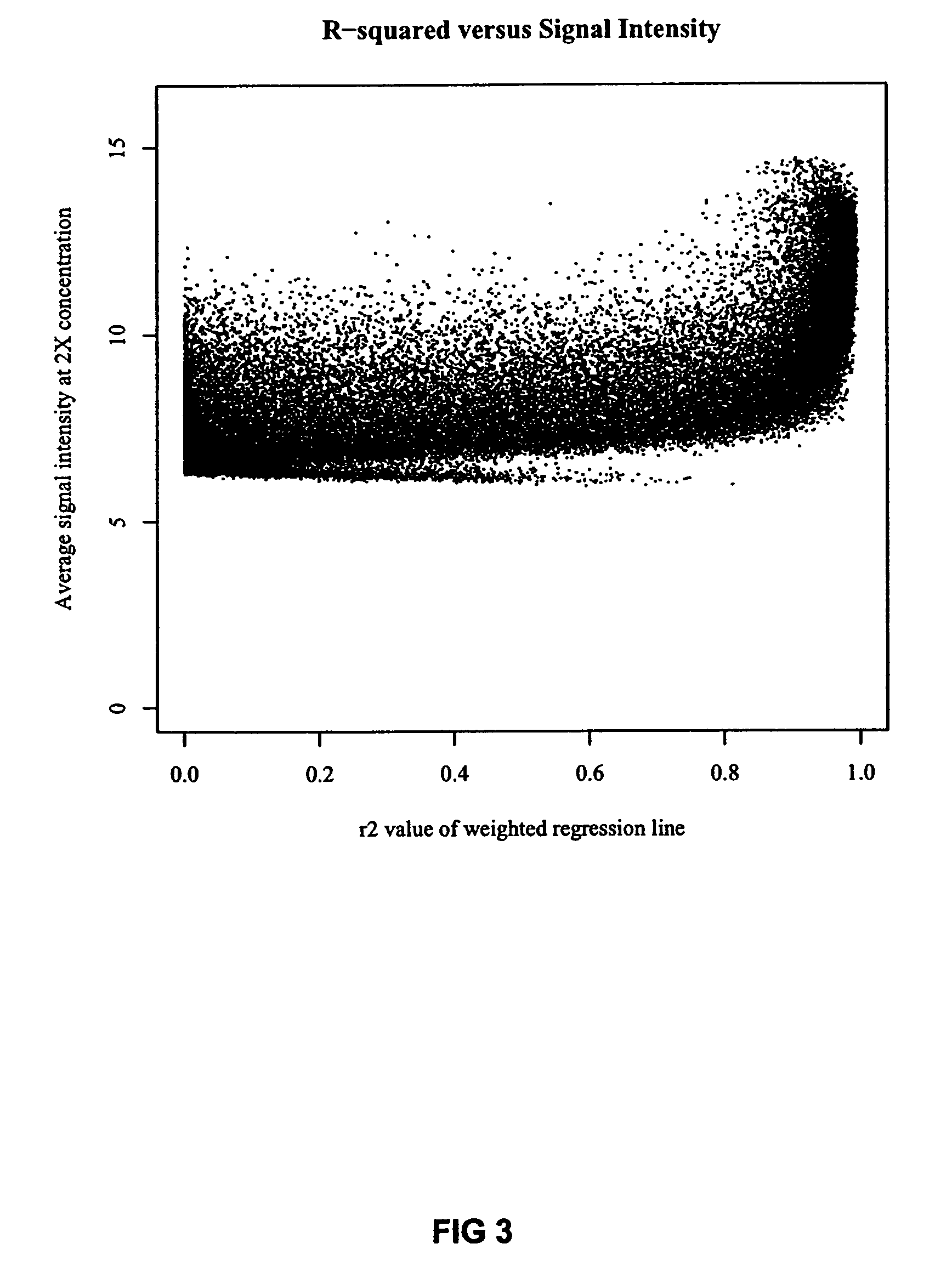
Optimized probe selection method
InactiveUS7869959B2Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingClinical researchBioinformatics
The present invention provides methods for optimizing oligonucleotide hybridization probes for use in basic and clinical research. Specifically, the invention involves hybridizing serially diluted genomic sample to the oligonucleotide probes on the array, such that a signal intensity is produced for each of the probes; computationally identifying optimized probes which exhibit signal intensities that correspond to the serial dilutions of genomic sample and are reproducibly strong relative to non-optimized probes.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Multiple real time fluorescence quantifying PCR method for detecting porcine circovirus, porcine parvovirus, porcine pseudorabies virus and classical swine fever virus
InactiveCN101260442BSimple and fast operationHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementClassical swine fever virus CSFVFluorescence
The invention discloses a multiplex real-time fluorescent quantitation PCR method capable of detecting porcine circovirus, porcine parvovirus, porcine pseudorabies virus and hog cholera virus at the same time. The method of the invention detects that the four virus are all in good linear relations at the same time, all ten times serial dilution points of constructed normal plasmid are all in one straight line, CT value and copy number are in good linear relation, and regression analysis shows that the related coefficient of the CT value and the copy number is R<2> more than 0.99.The multiplexreal-time fluorescent quantitation PCR method has the advantages of excellent specificity, sensibility and stability, which can rapidly, sensitively and differentially detect the four virus with serious harm to the economy and can be used for early diagnosis of virus infection.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Apparatus for the simultaneous transfer of liquid analytes
InactiveUS20020081629A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteLiquid medium
A method for the rapid screening of analytes, such as potential drug candidates, comprises the steps of applying a plurality of analytes to be screened onto one or more, solid support(s) (61) such that the analytes remain isolated from one another; contacting said analyte-carrying solid support(s) (61) with targets provided in a semi-solid or liquid medium, whereby said analytes are released from the solid support(s) (61) to the targets; and measuring analyte-target interactions. This method allows for the manipulation of thousands of different analytes simultaneously. When the analyte is applied to the solid support (61) it can diffuse thereon so as to produce a concentration gradient and serial dilution of analyte if a dose response curve for a candidate drug is required. The method described can be readily automated.
Owner:TIBOTEC NV
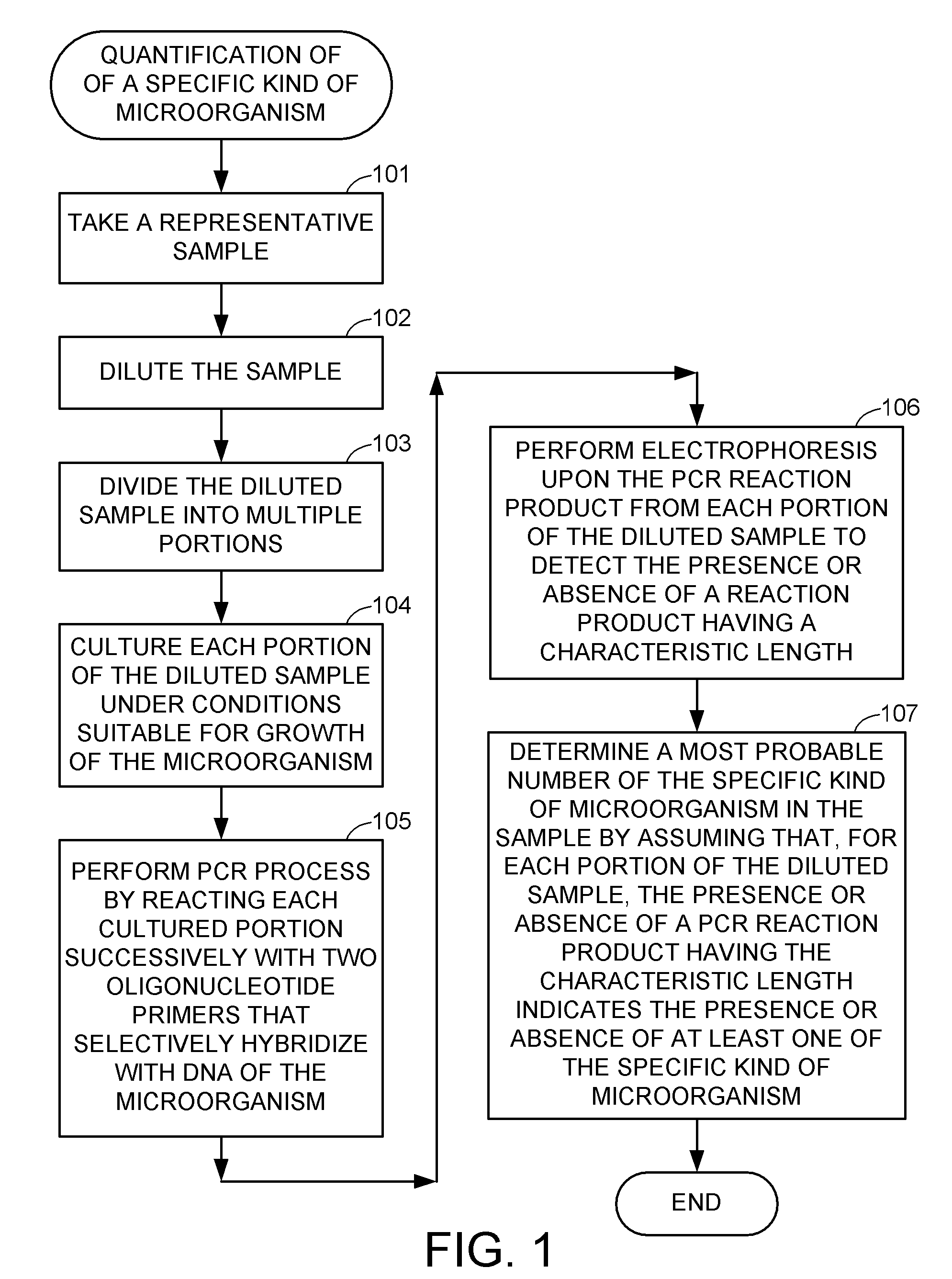
Methods for detecting and quantifying specific microorganisms
InactiveUS20050048516A1Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisMicroorganismMicrobiology
Methods and compositions are disclosed for confirming and quantifying the presence of a specific kind of microorganism in a sample of material. Hybridization and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) techniques are applied to identify the presence of the specific microorganism in cultures grown in most probable number and serial dilution methods, after calibration of the techniques using blank and control samples. For example, samples of animal feed can be cultured and analyzed to determine the quantity of specific probiotic microorganisms present in the feed.
Owner:NUTRITION PHYSIOLOGY
Methods for Detecting and Quantifying Specific Probiotic Microorganisms in Animal Feed
Methods and compositions are disclosed for confirming and quantifying the presence of a specific probiotic microorganism in a sample of animal feed. Hybridization and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) techniques are applied to identify the presence of the specific probiotic microorganism in cultures grown in most probable number and serial dilution methods, after calibration of the techniques using blank and control samples.
Owner:GARNER BRYAN E +2
Devices and methods for sample analysis with serial dilution
ActiveUS20200400534A1Extended shelf lifeWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationEngineeringInstruments apparatus
Devices and methods for analyzing a sample are disclosed. In various embodiments, the present disclosure provides devices and methods for preparing a serial dilution of a sample. In various embodiments, the present disclosure provides devices and methods for preparing a serial dilution of a sample and conducting sample analysis. In various embodiments, the present disclosure provides a cartridge device and a reader instrument device. The reader instrument device receives, operates, and / or actuates the cartridge device to prepare a serial dilution of a sample and conduct sample analysis.
Owner:CYTOCHIP INC
Method for screening virus strain
InactiveCN104109654AHigh titerImproving immunogenicityMicroorganism based processesViruses/bacteriophagesCulture cellVirus strain
The invention provides a method for screening a virus strain for preparing vaccines, which comprises the following steps: (a) providing a culture cell; (b) contacting the virus strain to be screened with the culture cell for some time; (c) separating out different virus clones from the culture cell, which has contacted the virus strain to be screened in the step (b), by a plaque cloning process, and screening out a first round virus strain for preparing vaccines; (d) repeating the steps (a)-(c) by using the first round virus strain collected in the step (c), screening out a second round virus strain for preparing vaccines; (e) carrying out serial dilution on the second round virus strain collected in the step (d) to obtain a series of diluted substances with degressive virus concentrations; (f) contacting every diluted substance in the step (e) with the culture cell for some time; and (g) cloning the pathological change virus with the maximum times of diluted substance in the step (f), continuing culture, and screening out a third round virus strain for preparing vaccines.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF BIOLOGICAL PROD
Simulated moving bed chromatographic focusing
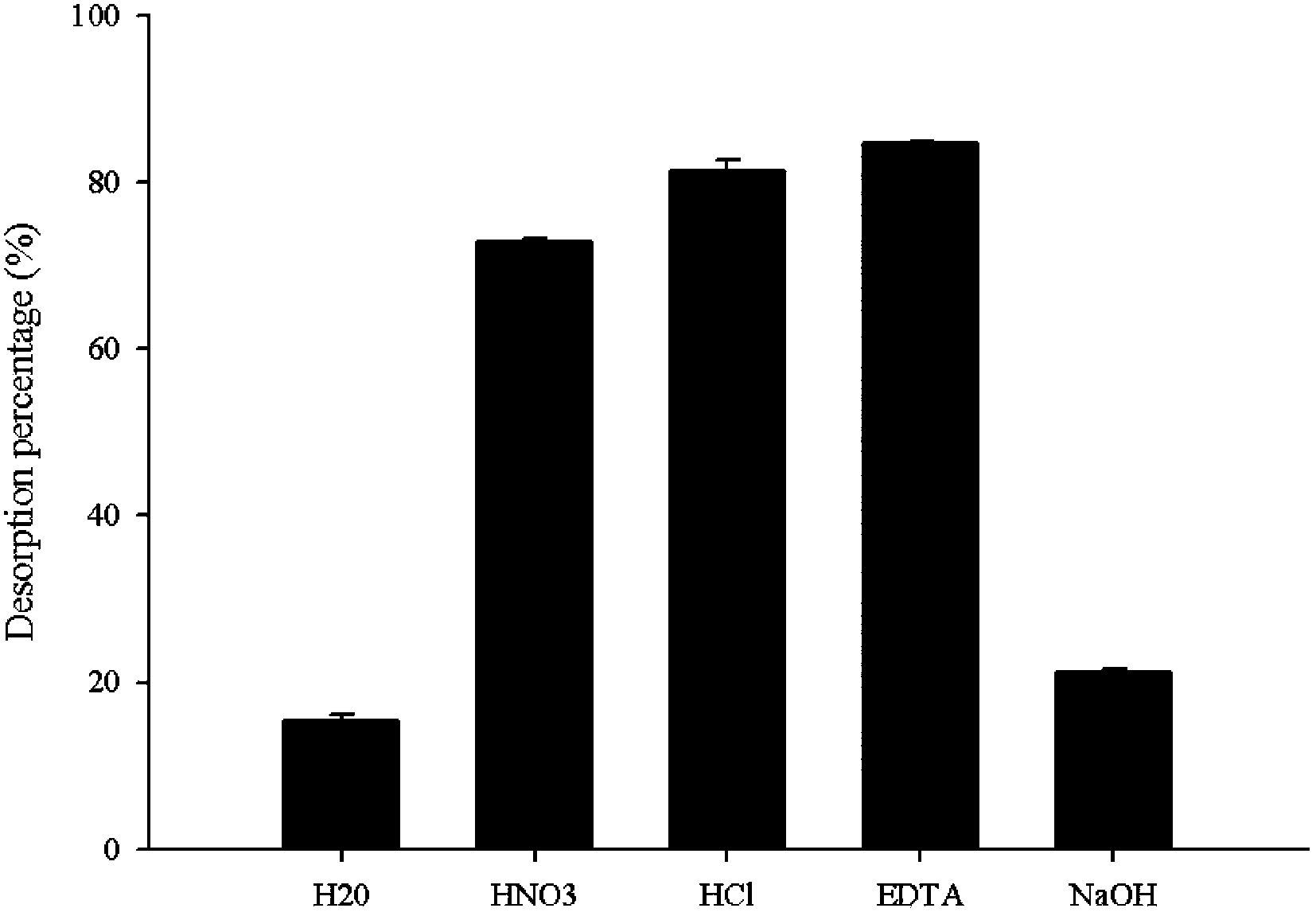
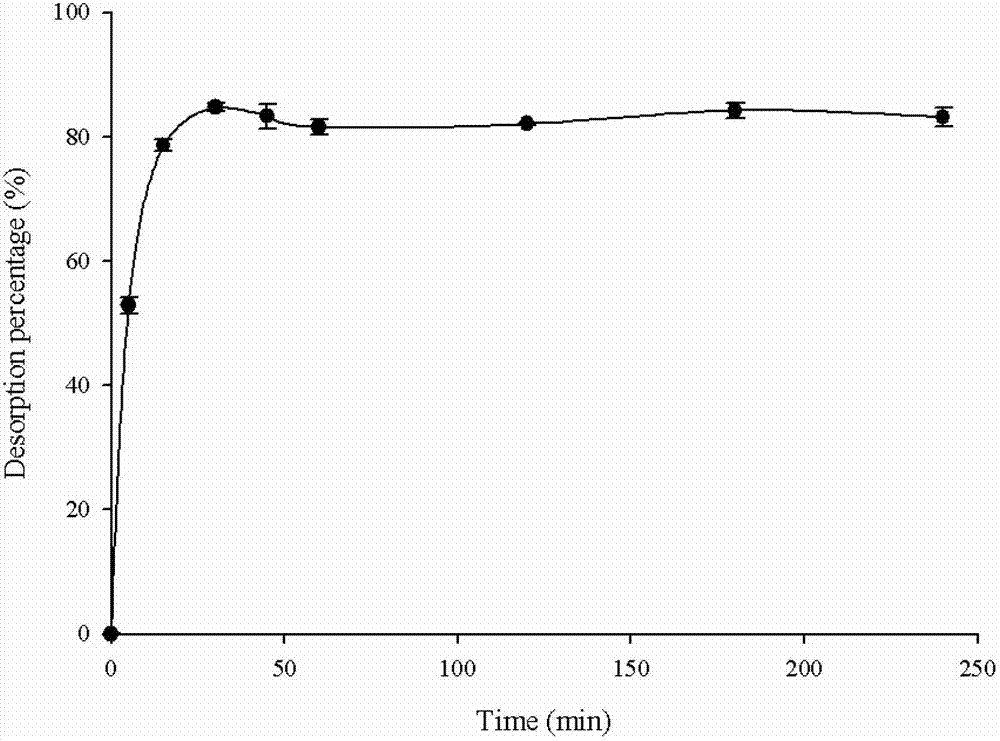
InactiveCN100444920CIncrease production capacityReduce production consumptionIon-exchange process apparatusIon-exchanger regenerationDesorptionSimulated moving bed
A continuous simulated moving bed focusing chromatography method disclosing the separation and concentration of multiple components from a complex compound. This method consists of several zones connected together in a certain order, and the eluent is eluted unidirectionally along these zones, and is serially diluted one zone after another to reduce its desorption strength; each zone is equipped with A detachable column that periodically resets upstream one zone. The sample containing multiple components is injected into the downstream zone and adsorbed in the chromatography column in this zone, and is brought upstream zone by zone with the reset of the chromatography column, and is selectively desorbed from different zones And be separated. A certain component desorbed from one zone is re-adsorbed in the chromatography column in the adjacent downstream zone, and is brought back to the previous zone as the chromatography column is reset. The sample is thus maintained between the preceding zone and its adjacent downstream zone, and is accumulated by successive loadings and repeated resetting of the column.
Owner:ODEKO INC
High-cadmium-adsorption filamentous fungus Paecilomyces lilacinus XLA, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103451103BEasy accessLow costFungiContaminated soil reclamationCadmium adsorptionPaecilomyces lilacinus
The invention relates to a high-cadmium-adsorption filamentous fungus Paecilomyces lilacinus XLA, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1, weighing a pot experiment soil sample used for heavy metal restoration and having a content of heavy metal cadmium of 50mg / Kg, adding to sterile water with glass beads, oscillating on a constant temperature shaking table, allowing an obtained solution to stand, taking an obtained supernatant, and carrying out serial dilution; 2, coating a Martin flat containing 60mM of cadmium with different dilution rates of dilutions, allowing the obtained flat to stand for a moment, inverting on a constant temperature culturing box, and culturing; 3, carrying out streaking purification of single colonies growing on the flat, coating the Martin flat with the obtained single colonies, and culturing; 4, carrying out separating screening to obtain the Paecilomyces lilacinus XLA stably resisting cadmium, and preserving on a PDA inclined plane for later use. The Paecilomyces lilacinus XLA is preserved and has a preservation number of CCTCC NO:M2012135. Viable and non-viable organism of the XLA can efficiently adsorb and remove the heavy metal cadmium in heavy metal sewage, so the XLA has the advantages of low cost and simple technology, and has an efficient restoration potential of heavy metal polluted soil and water.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Methods for Detecting and Quantifying Specific Microorganisms
InactiveUS20090203031A1Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisMicroorganismMicrobiology
Owner:GARNER BRYAN E +2
Method for rapidly determining drug tolerance of strain
InactiveCN101760502BJudgment SensitivityLow inhibitory concentrationMicrobiological testing/measurementMethyl thiazolyl tetrazoliumCulture fluid
The invention discloses a method for rapidly determining drug tolerance of a strain. The method comprises the following steps: A, preparing nutrient fluid containing methyl thiazolyl tetrazolium; B, preparing bacterial suspension; C, preparing antibiotic solution; D, adding the nutrient fluid containing the methyl thiazolyl tetrazolium, the antibiotic solution and the bacterial suspension into holes of a culture plate, and performing serial dilution on the antibiotic solution; and E, scanning and determining the diluent in real time, and determining the drug tolerance of the strain to antibiotic according to the scanning result. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of simply, rapidly, economically and high-efficiently determining the drug tolerance of the strain.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF INSPECTION & QUARANTINE +1
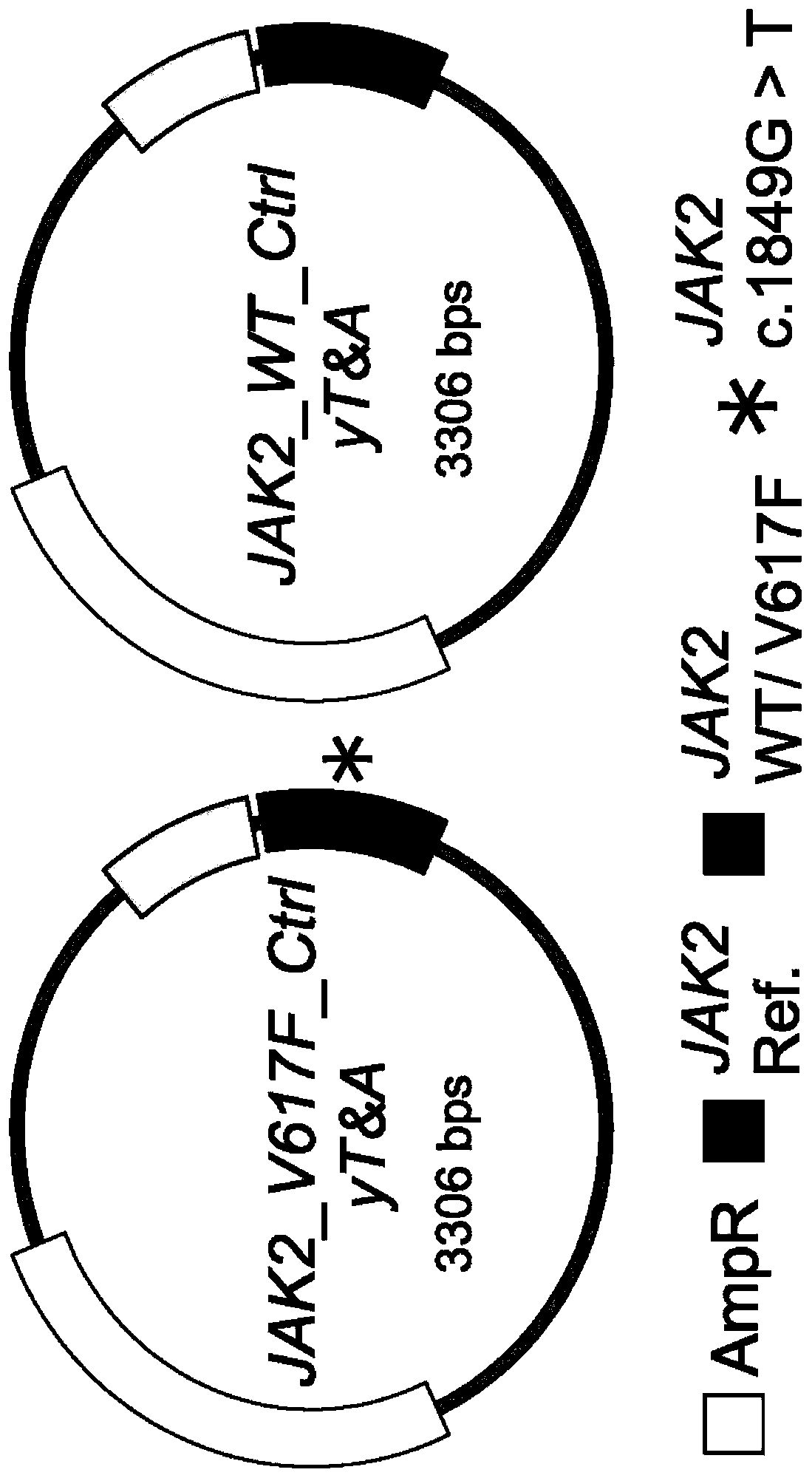
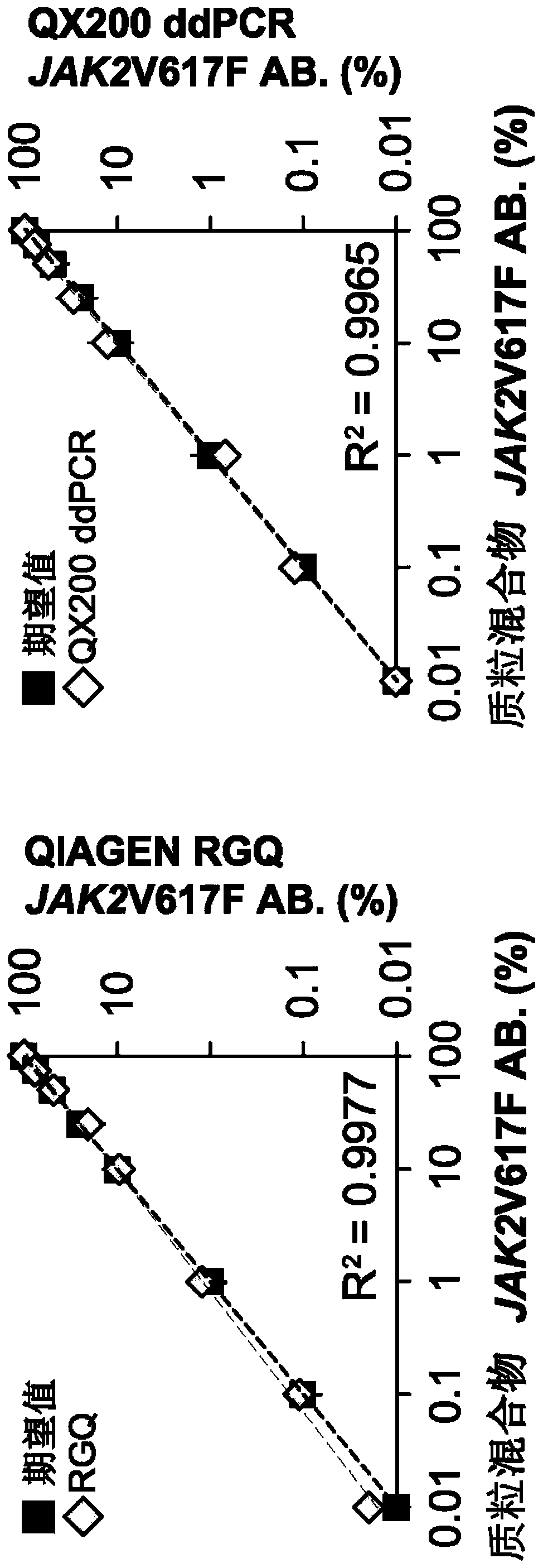
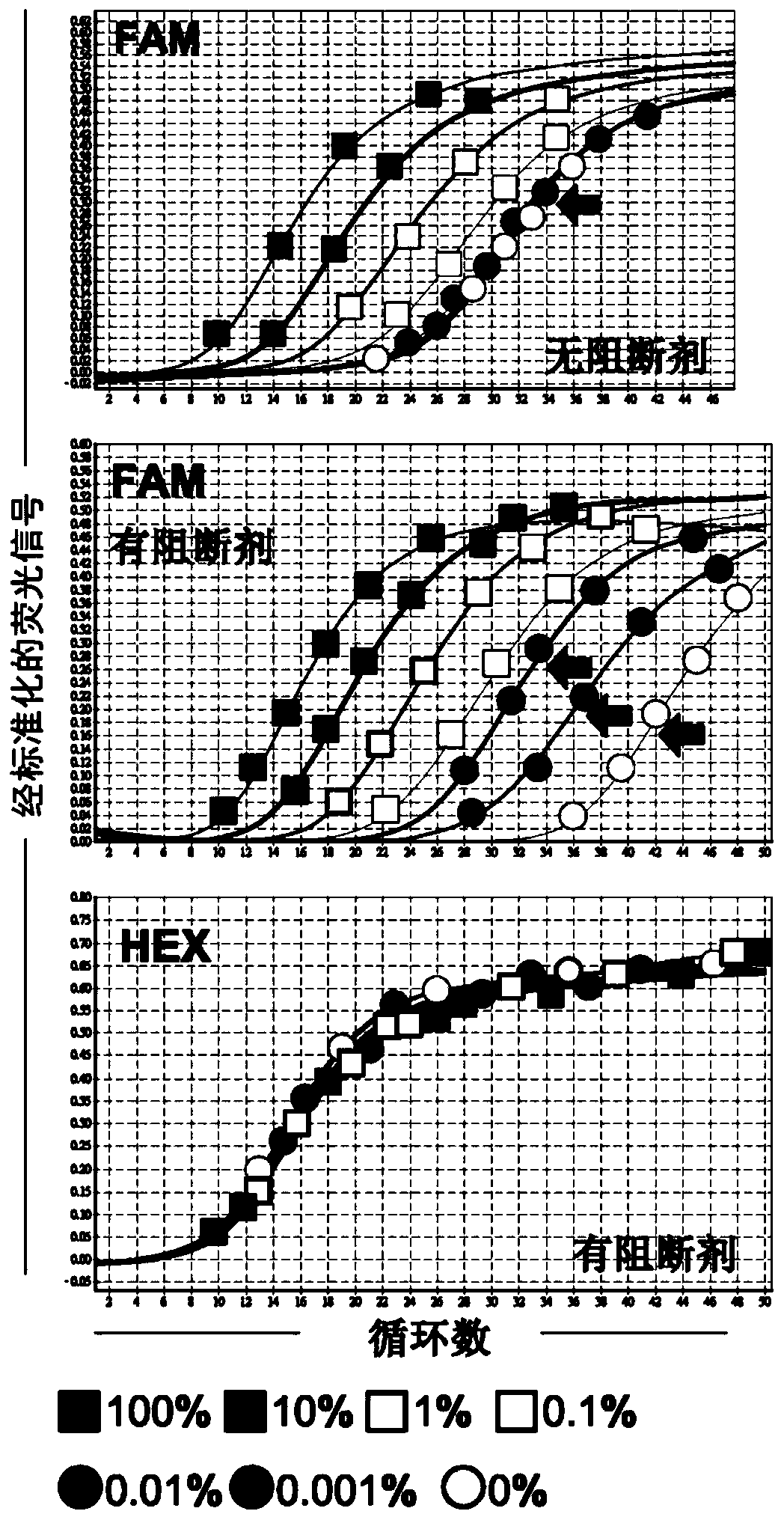
Method of quantifying mutant allele burden of target gene
The invention relates to a method and kit for quantifying a mutant allele burden of a target gene in a subject. The invention also discloses use of a nucleic acid agent for preparing the kit for quantifying a mutant allele burden of a target gene in a subject. The nucleic acid agent includes a first plasmid, a second plasmid and a reaction mixture, wherein steps for quantifying a mutant allele burden of a target gene by utilizing the kit include providing the first plasmid that includes a mutant allele sequence and an internal control sequence, and the second plasmid that includes a wild-typeallele sequence and the internal control sequence; and subjecting DNA of the subject to quantitative polymerase chain reaction to measure a mutant allele expression level of the target gene, so as todetermine the mutant allele burden of the target gene in the subject based on a standard curve of the mutant allele burden of the target gene created by serial dilution of the first and second plasmids.
Owner:CHANG GUNG MEDICAL FOUND CHANG GUNG MEMORIAL HOSPITAL CHIAYI
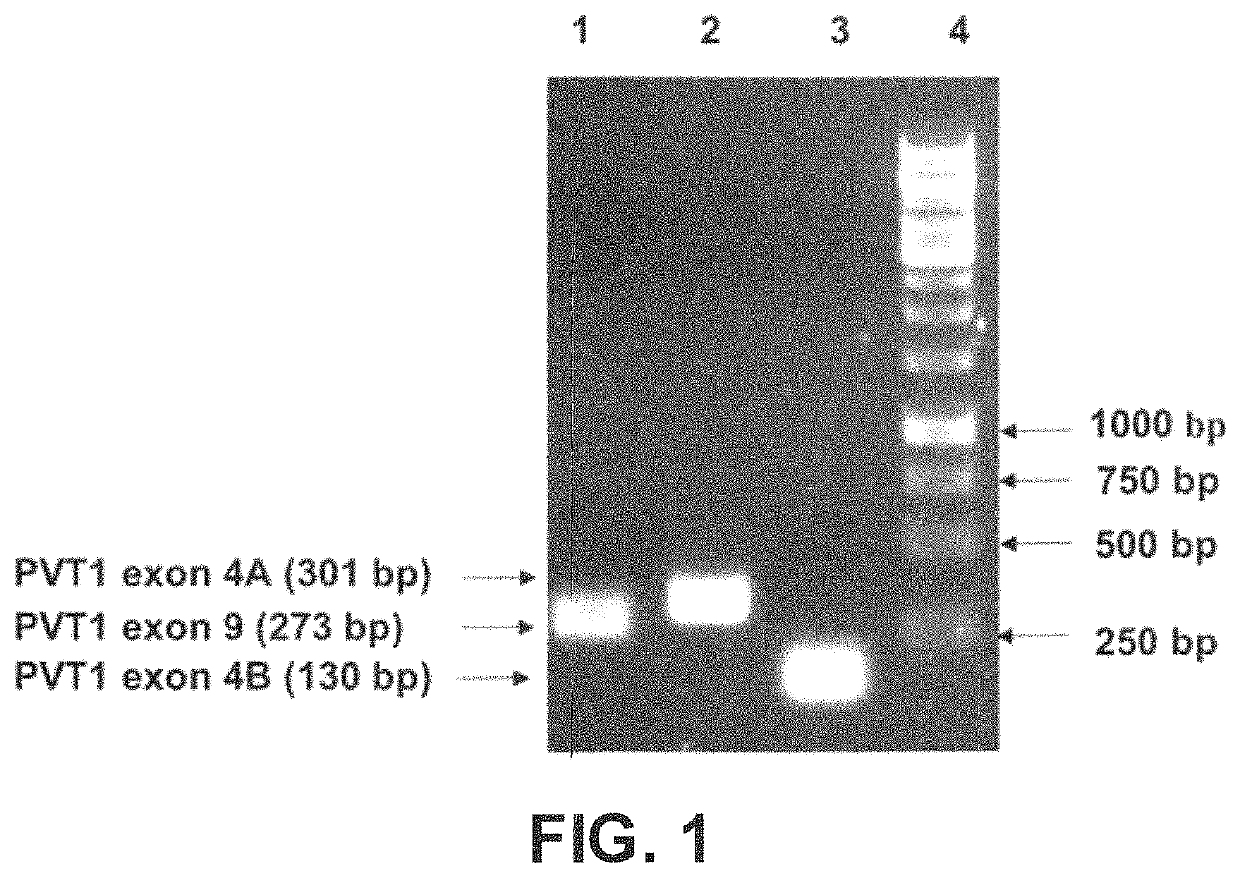
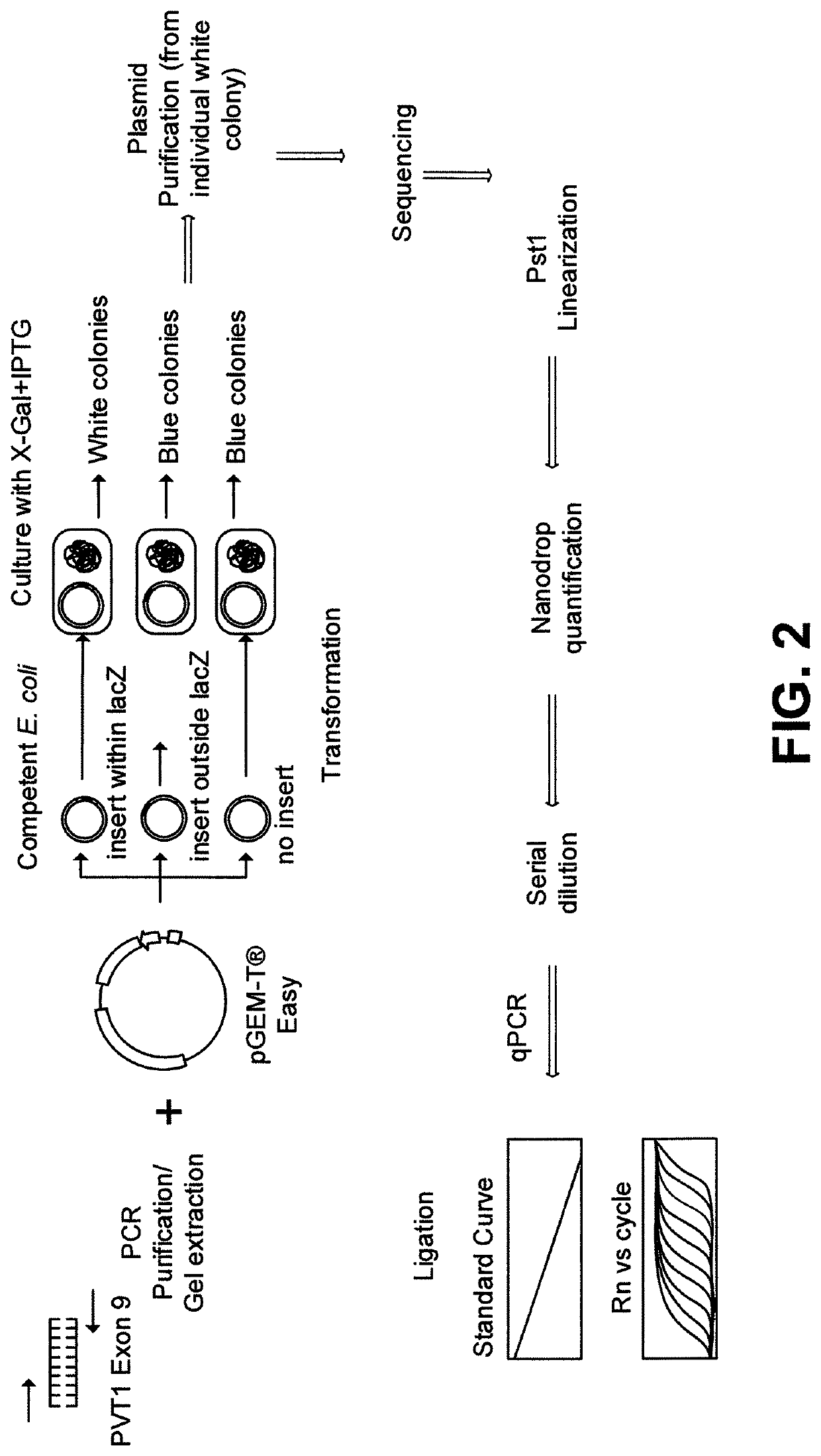
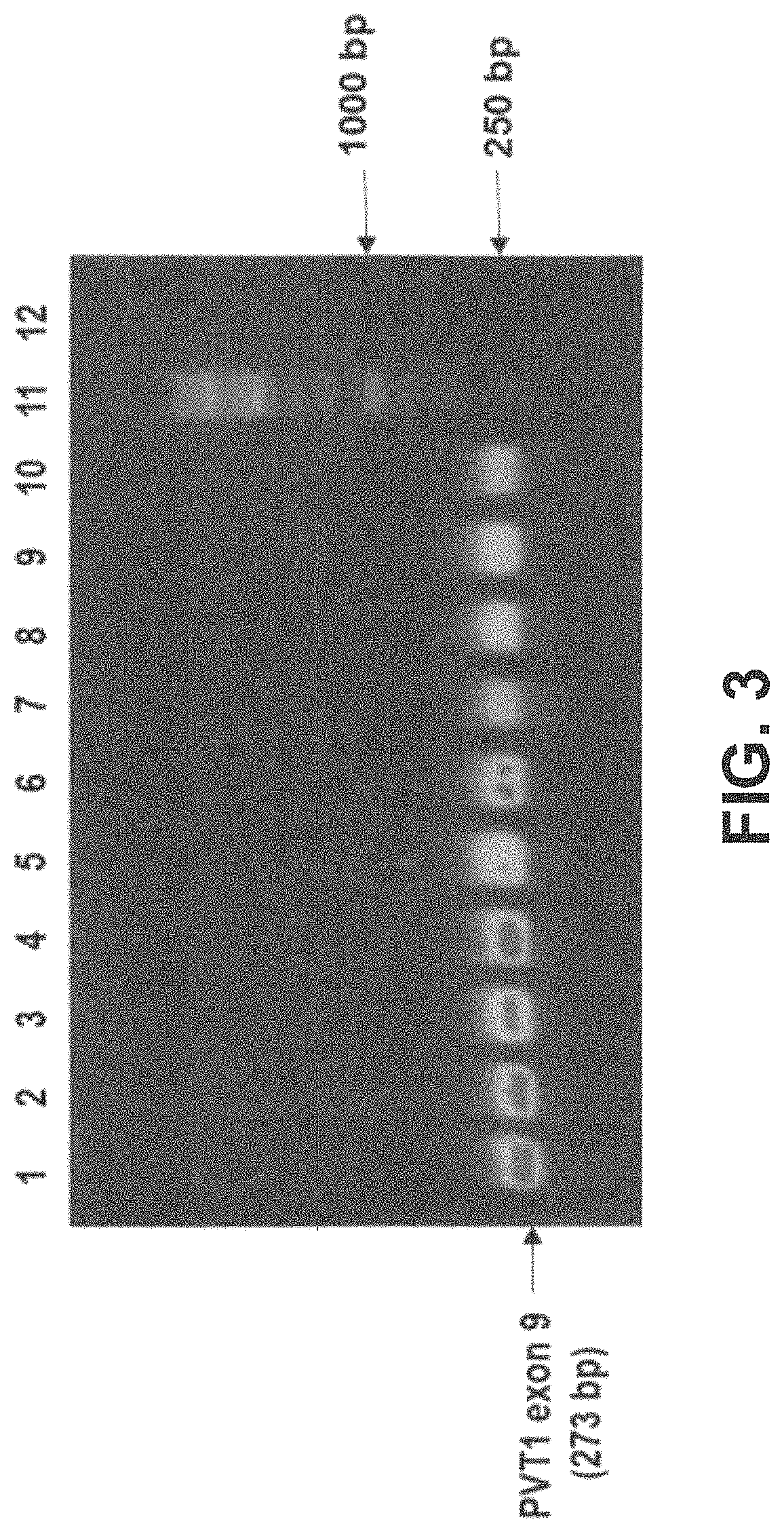
Plasmid vector for expressing a PVT1 exon and method for constructing standard curve therefor
ActiveUS11225666B2Nucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionMedicinePlasmid Vector
A method for cloning an exon into a plasmid vector. Exons related to prostate cancer (PVT1 exon 9, PVT1 exon 4A or PVT1 exon 4B) and miRNAs (miR-1205 or miR-1207-3p) are transformed into the plasmid vector. The cloned exons or miRNAs are linearized and their concentrations quantified. Serial dilutions in conjunction with spectroscopy permit the construction of a standard curve that permits absolute quantification of the exons or miRNAs in a biological sample from a patient.
Owner:RES FOUND THE CITY UNIV OF NEW YORK
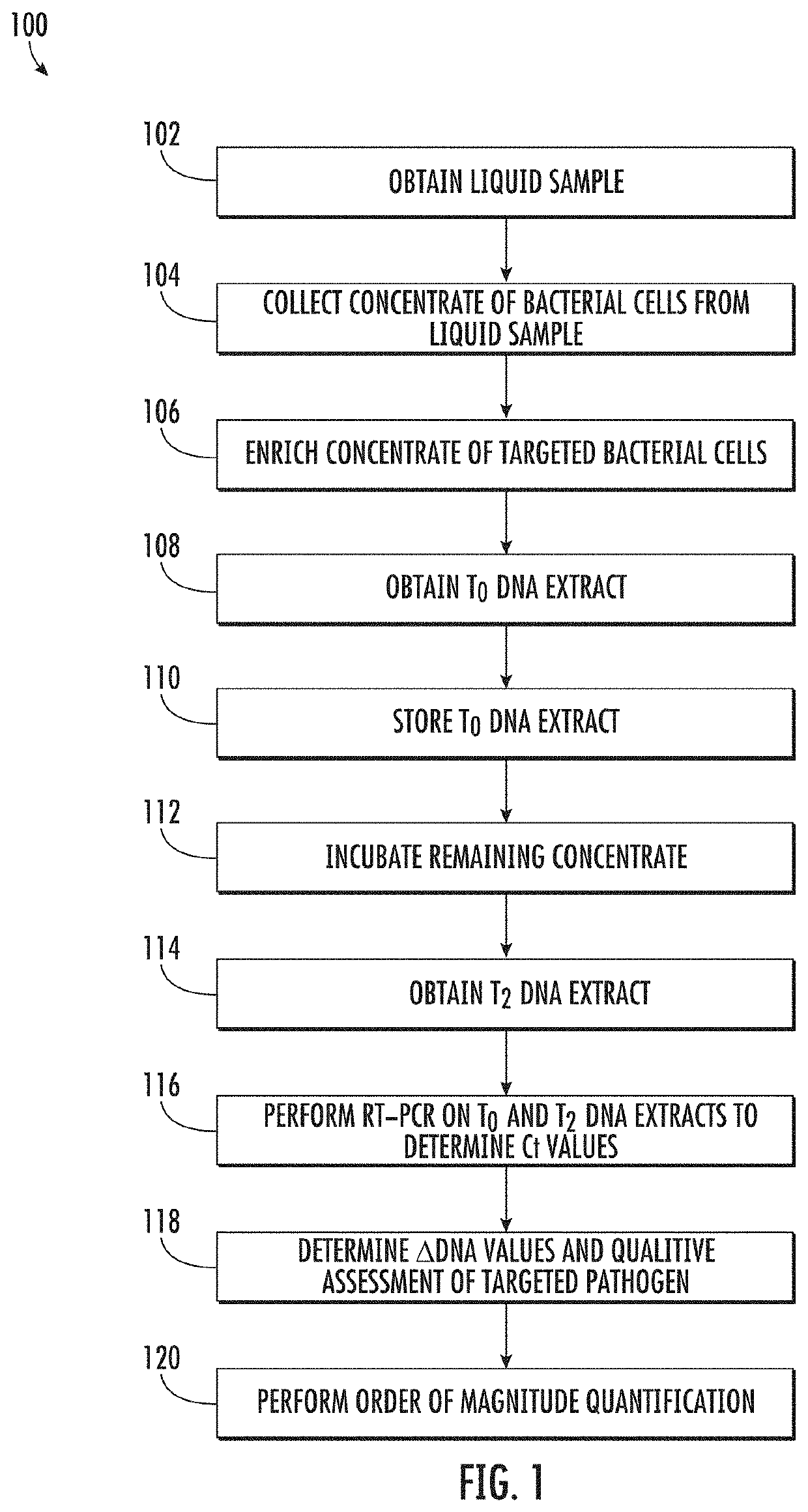
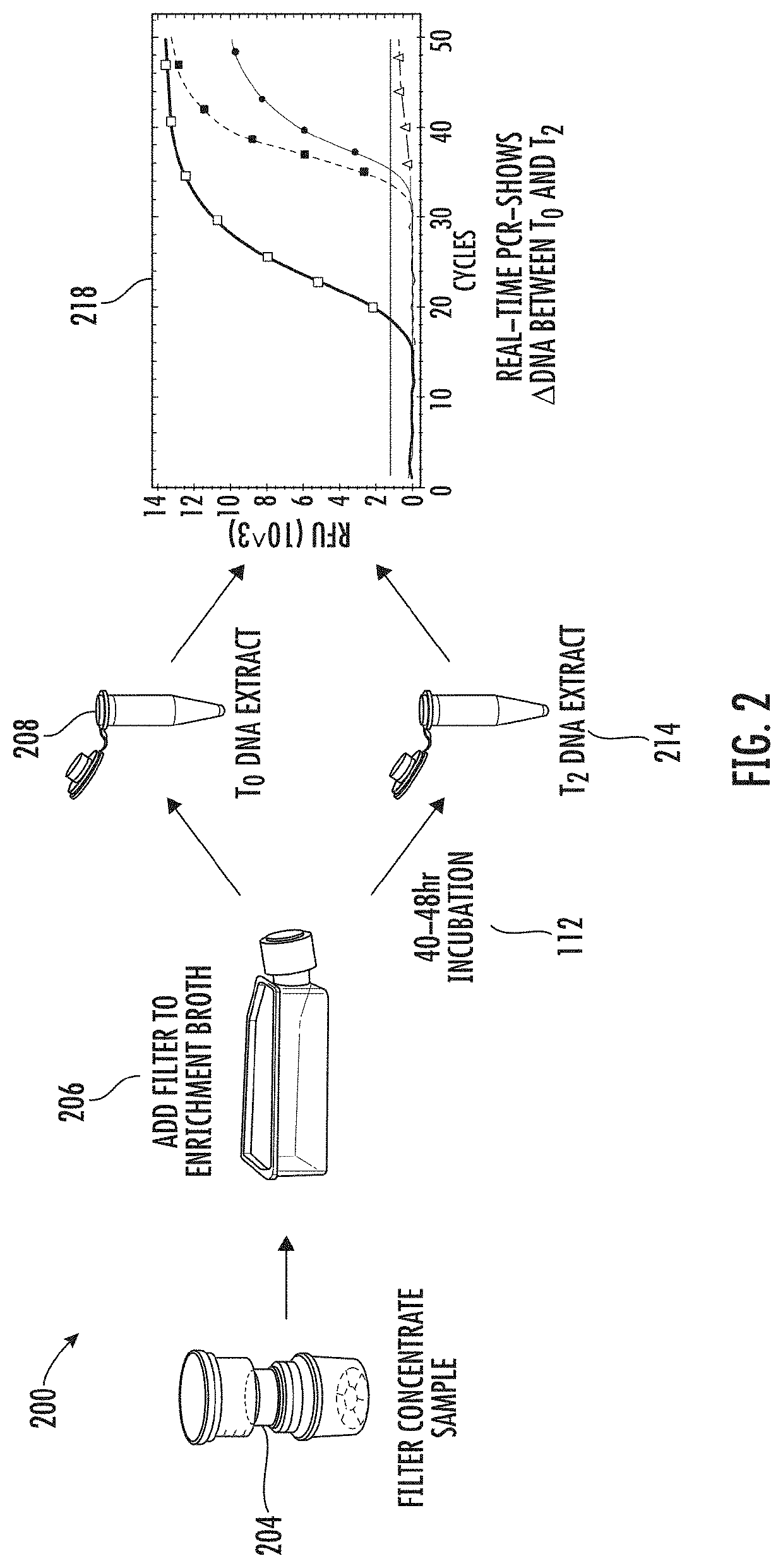
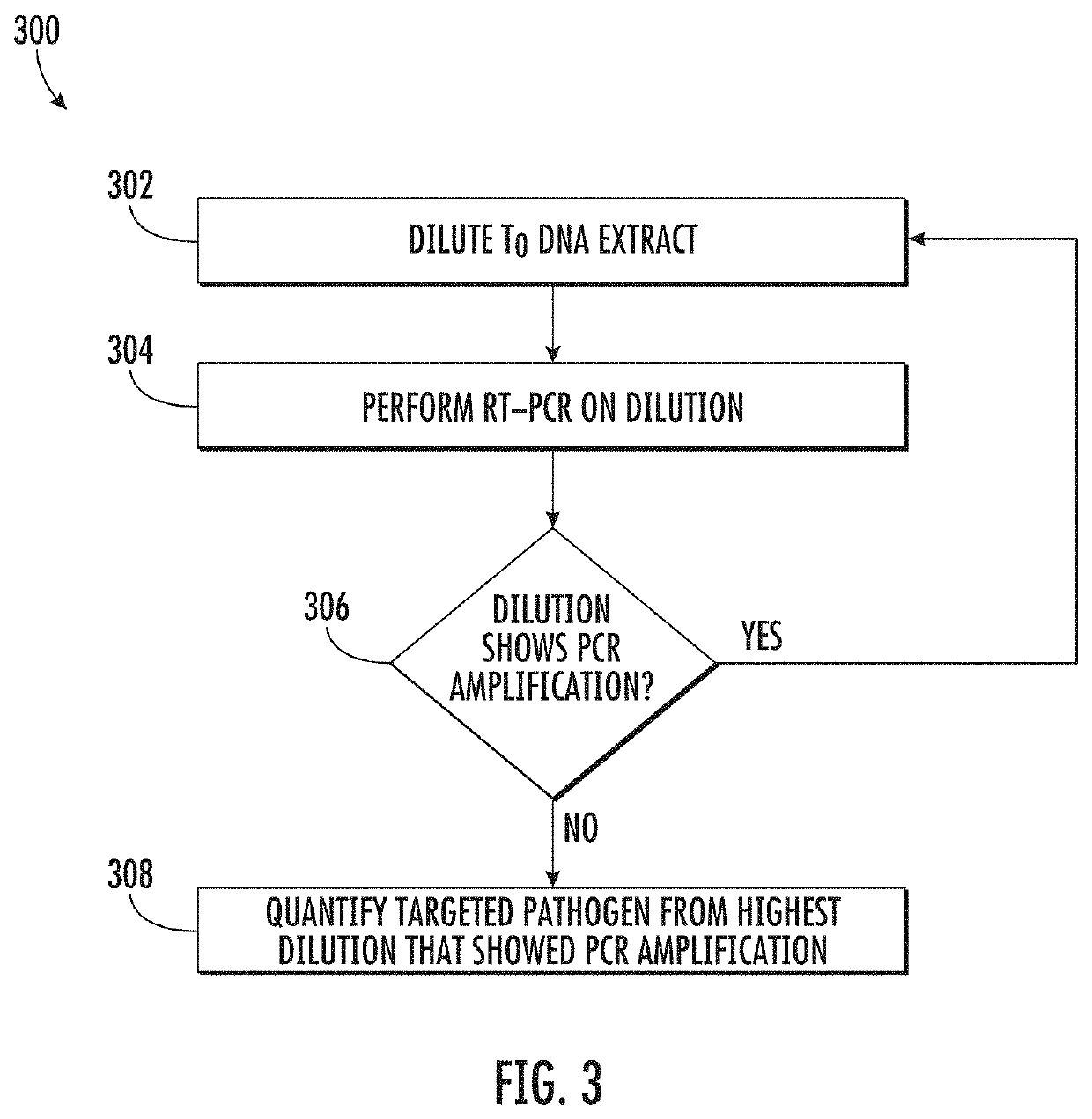
Viability detection and quantification assay of waterborne pathogens by enrichment
A process for detecting viable waterborne pathogens in a water sample, includes enriching at least a portion of the sample with an enrichment broth and taking a first DNA extract at time T0 and a second DNA extract at time T2 after an incubation period. Real-time polymerase chain reaction performed on the DNA extracts yields respective cycle threshold values Ct. The change in Ct provides an indication of viability of the targeted pathogen in the sample. An order of magnitude quantification of the sample can also be performed using a serial dilution technique on the T0 DNA extract. The process has particular application for detecting Legionella, including viable but not culturable cells.
Owner:PHIGENICS
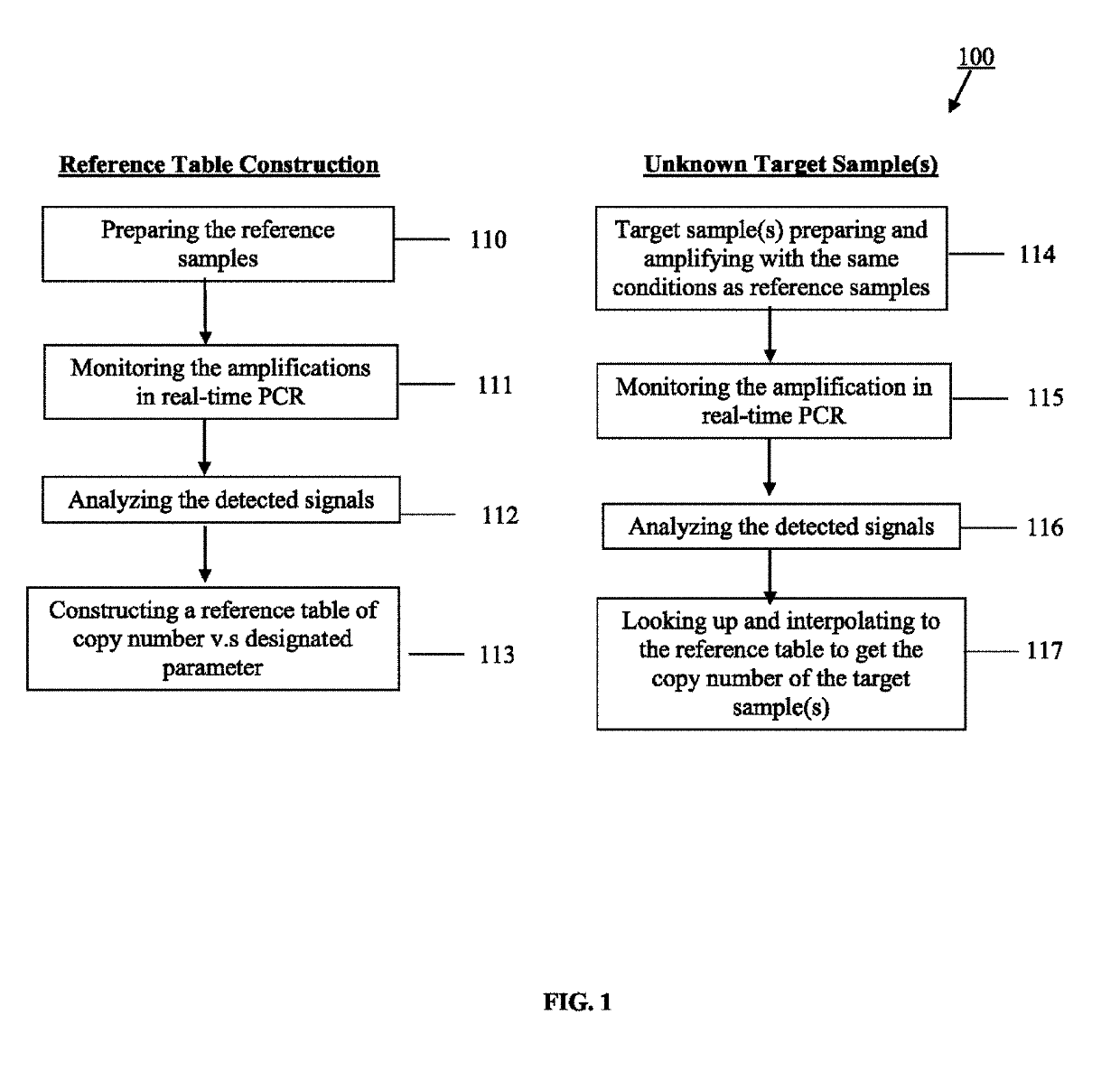
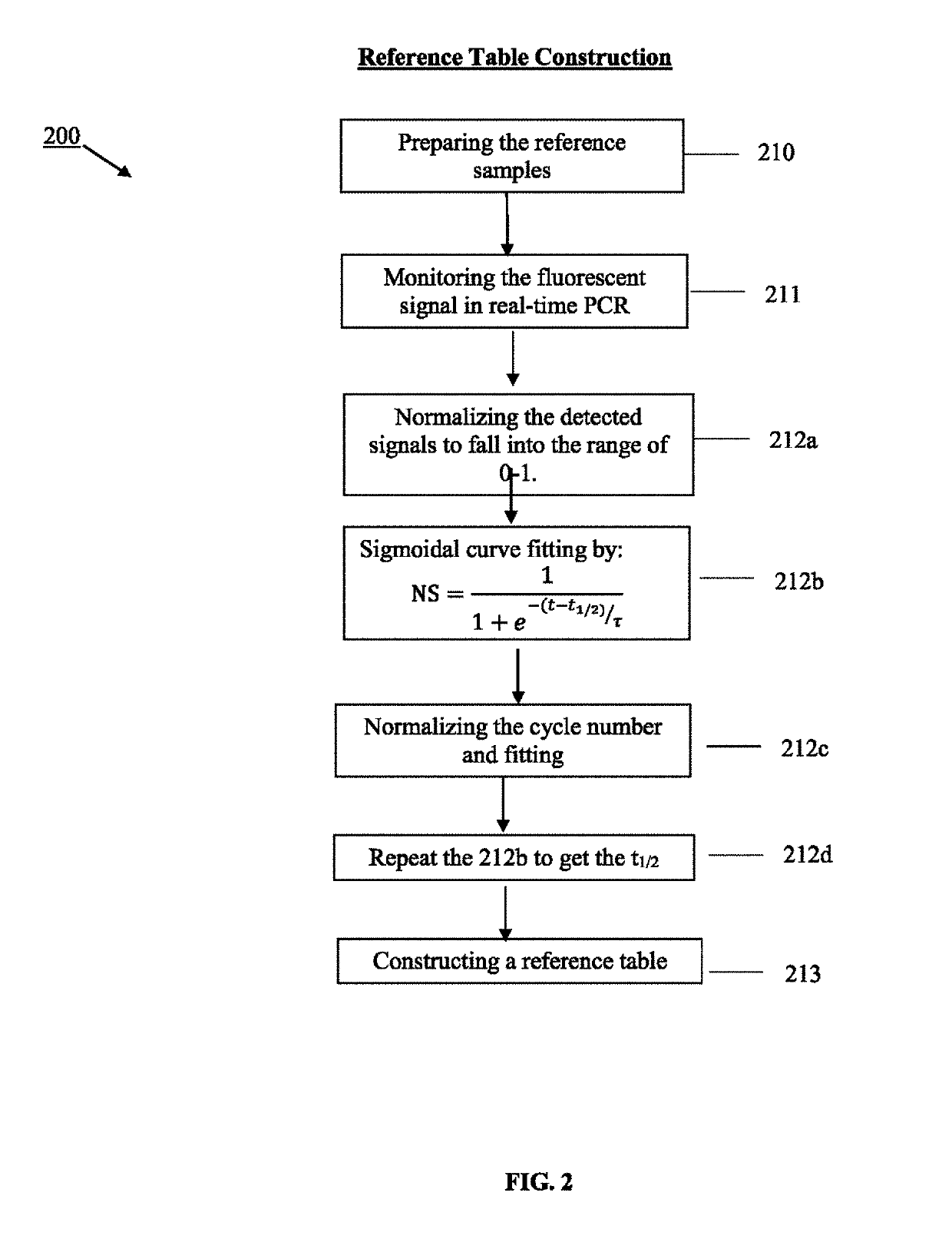
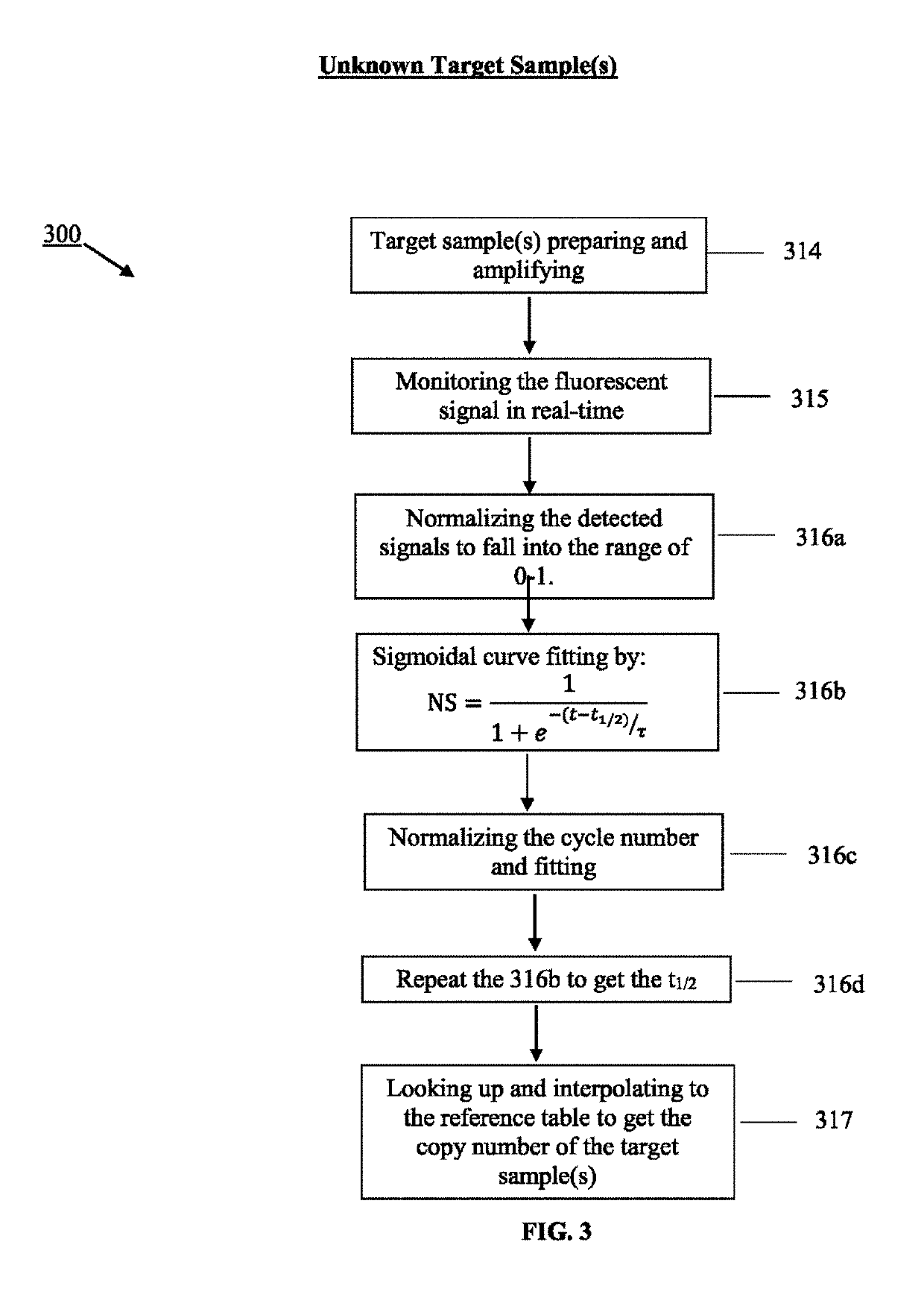
Using serial dilutions of reference samples to construct a reference table for sigmoidal fitting in real-time PCR copy number analysis
ActiveUS10510436B2Overcome disadvantagesMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisReference sampleCopy number analysis
Owner:CREDO BIOMEDICAL PTE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com