Method for separating microorganisms on surface of tobacco leaf at high temperature by utilizing pure tobacco leaf leach liquor solid plate
A solid plate and extraction liquid technology, applied in the field of applied microorganisms, can solve the problems of single action point, poor temperature tolerance, uneconomical economy, etc., and achieve the effect of improving physiological activity, reliable safety, and high biological activity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Example 1: Fermentation process parameters of bacterial strain YN91 and bacterial strains YN114, YN113, YN104 of the present invention. The fermentation medium of strain YN91 is: wheat bran 1.5%, urea 0.5%, NaCl 0.5%. Fermentation process parameters: temperature 50°C, time 18h, stirring speed 125rpm. The enzyme activity level is around 6960U / mL. The fermentation medium of strain YN114 is: soluble starch 0.5%, beef extract 1.0%, CaCO 3 0.3%. Fermentation process parameters: temperature 43°C, time 36h, stirring speed 125rpm. The enzyme activity level is around 28(U / mL). The fermentation parameters of strains YN113 and YN104 were the same as those of YN114.
[0033] The specific method is as follows: culture medium preparation, take 5-15mL of the waste tobacco leaf extraction stock solution soaked for 2-3 days in a 500mL triangular flask, add 95-85mL of tap water, add 2.5g of agar powder, the pH is natural, after shaking well, use 15 lb. Autoclave for 30 minutes. Af...
Embodiment 2
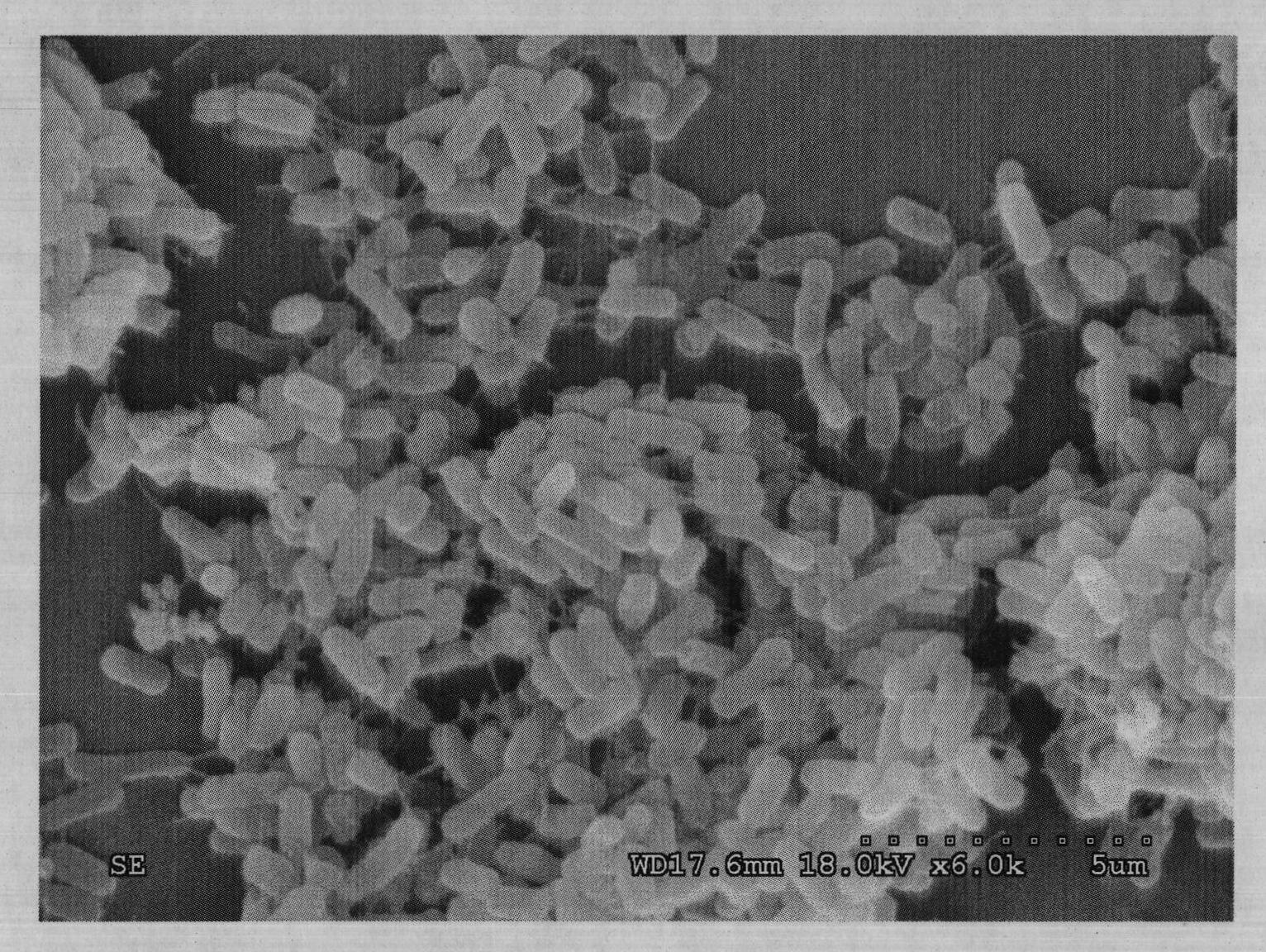
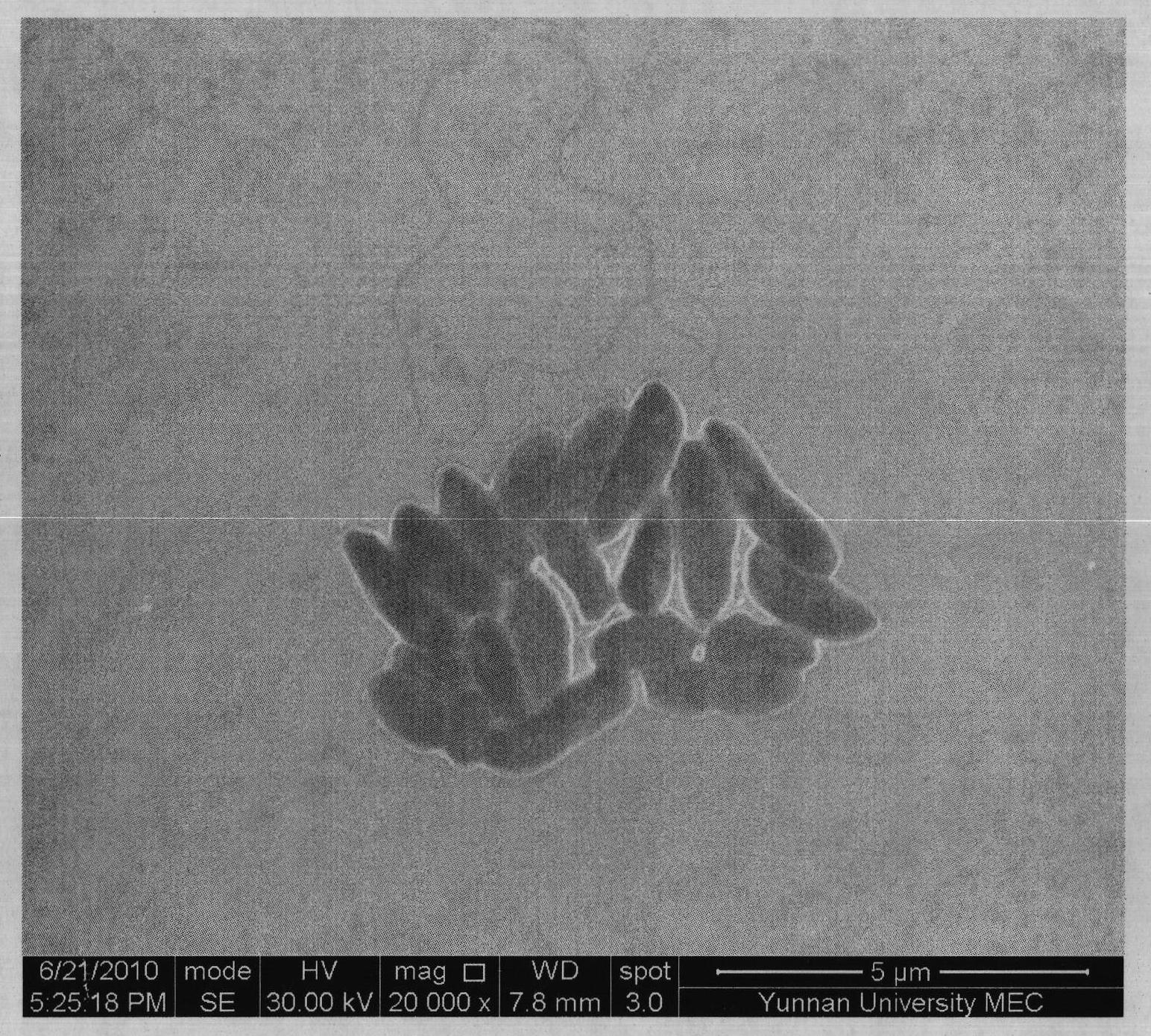
[0037] Example 2: The high-temperature bacteria strain YN114 isolated by the method of the present invention forms milky white colonies on the solid medium, which are opaque, with irregular edges, slightly raised center, wrinkled texture, and are usually relatively dry. The average length of the bacteria is about 3.3 μm, and the average width is about 1.4 μm. The electron microscope photos are as follows: figure 1 . The optimum growth temperature is 50°C, protease is produced, and the protease activity of the fermentation broth reaches 28.25U / mL.
Embodiment 3
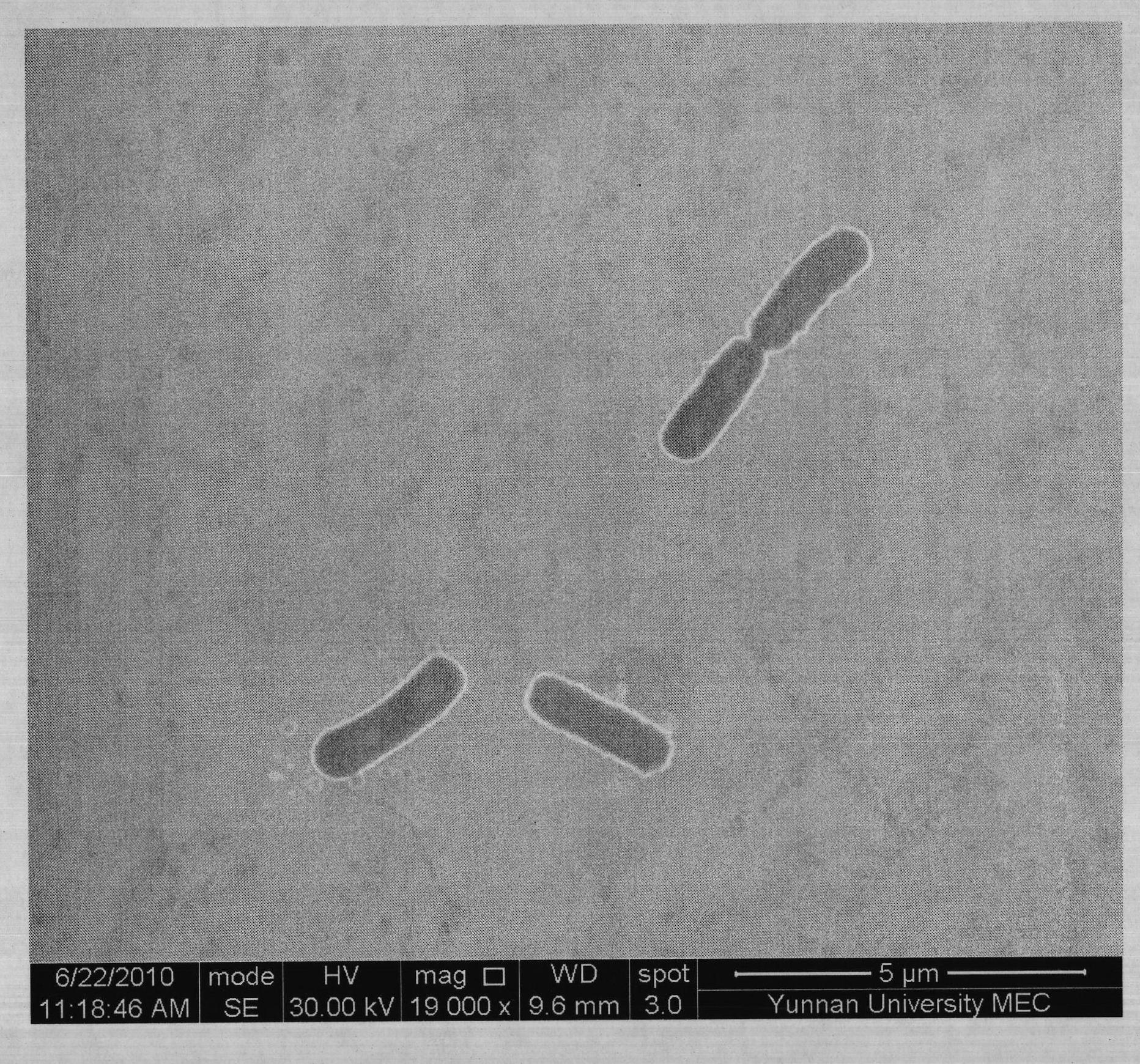
[0038] Example 3: The bacterial strain YN91 isolated by the method of the present invention forms a milky white colony on a solid medium, which is irregular, opaque, wrinkled in texture, and wavy at the edge. The shape of the colony changes greatly with the dryness and humidity of the medium. When it is wet, the colony is easy to spread and becomes slimy, and the surface is creamy. However, in most cases, the colony is rough and wrinkled, with a prominent center and irregular edges. The bacteria grow rapidly. Observed under the oil microscope, YN91 is transparent and shiny, short rod-shaped, does not produce spores, 2.6μm-1.1μm, see the electron microscope photo figure 2 . Strain YN91 belongs to Pseudomonas pridus. Produce amylase, the optimum growth temperature is 55°C for 30 hours, and the enzyme activity of the fermentation broth is 7840U / mL.
[0039] The present invention adds 0.1%-0.5% MnSO to the fermentation liquid before the end of fermentation 4 After stirring for...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Vitality | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com