Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
31 results about "Most probable number" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
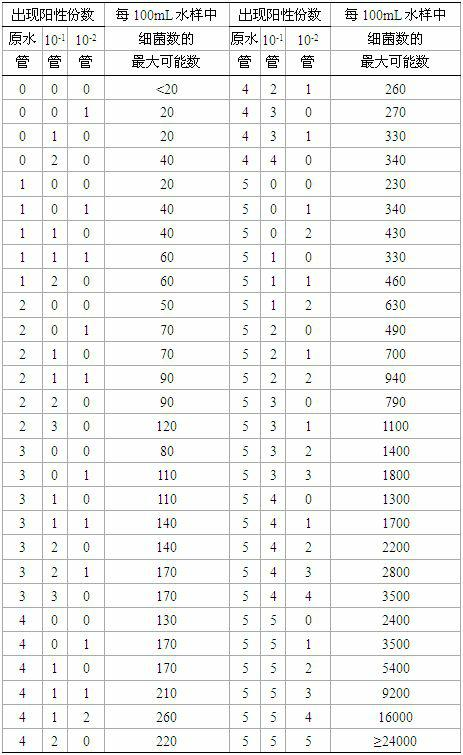
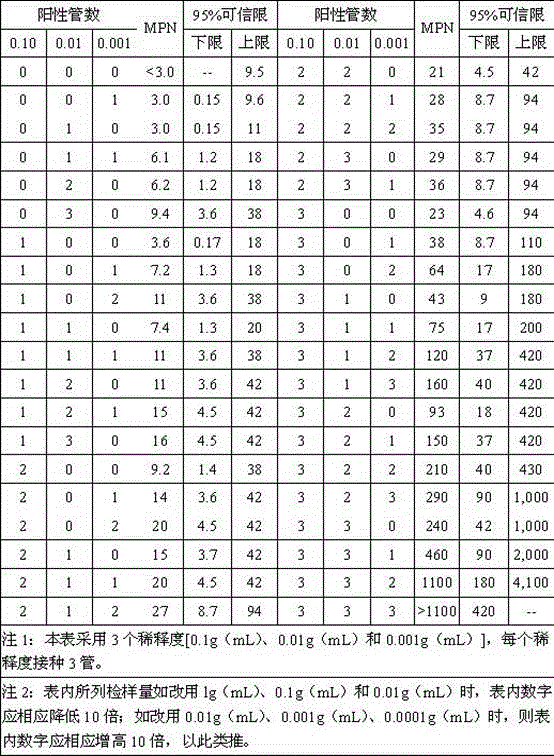
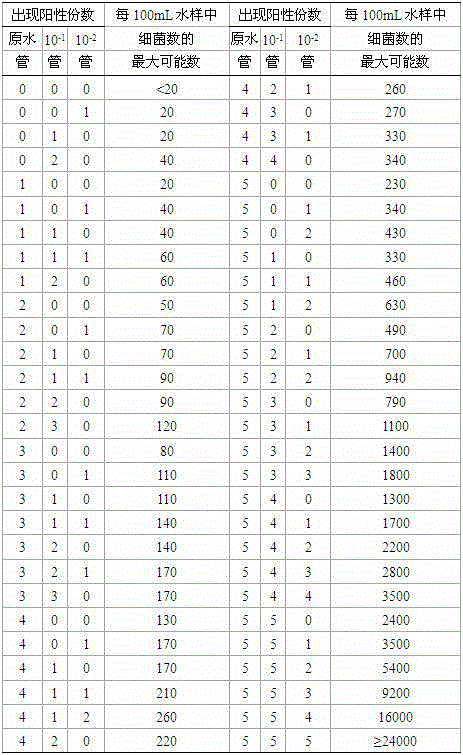
The most probable number method, otherwise known as the method of Poisson zeroes, is a method of getting quantitative data on concentrations of discrete items from positive/negative (incidence) data. There are many discrete entities that are easily detected but difficult to count. Any sort of amplification reaction or catalysis reaction obliterates easy quantification but allows presence to be detected very sensitively. Common examples include microorganism growth, enzyme action, or catalytic chemistry. The MPN method involves taking the original solution or sample, and subdividing it by orders of magnitude (frequently 10× or 2×), and assessing presence/absence in multiple subdivisions.
Precise quantization method for nitrogen cycle of lake ecosystem
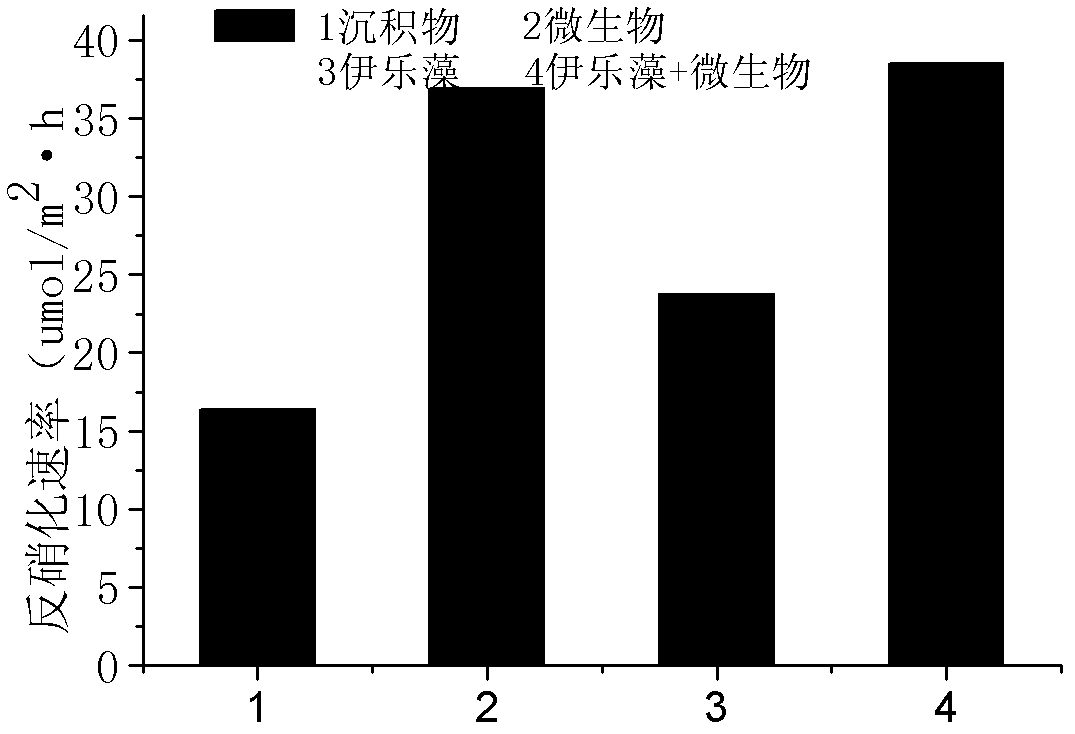
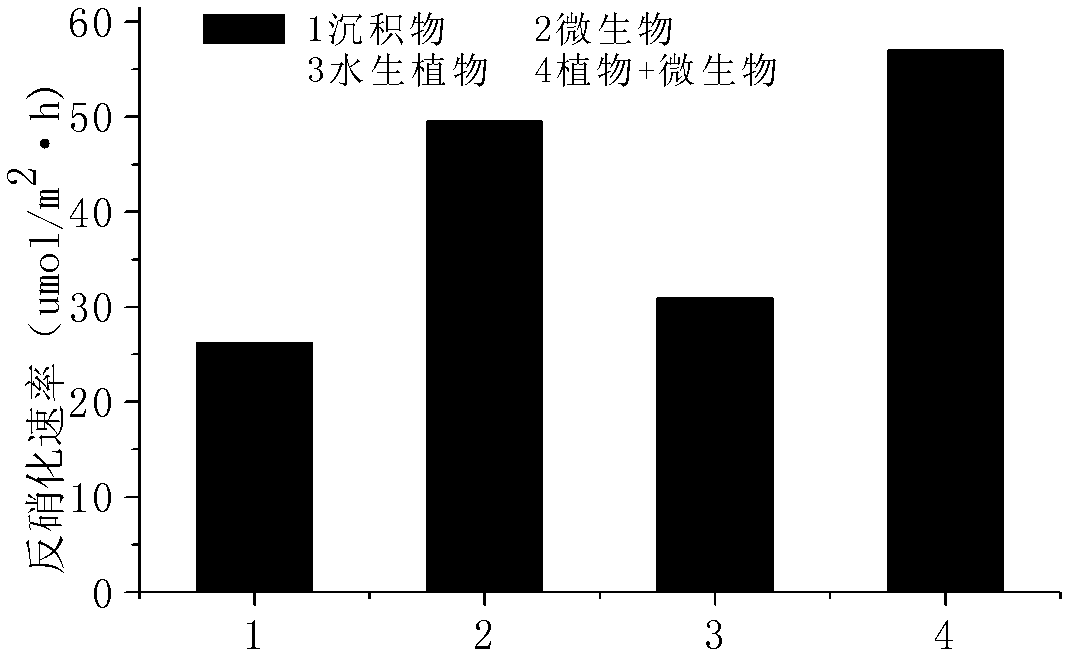
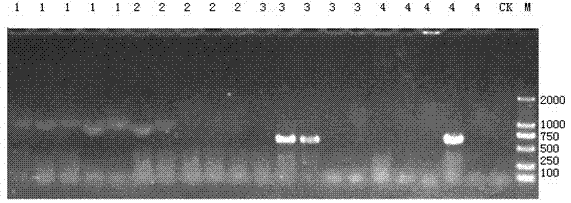
A precise quantization method for nitrogen cycle of a lake ecosystem includes 1), applying an isotope pairing method to quantitatively research nitrogen migration and conversion of a sediment-water interface of the lake ecosystem; 2), determining release of nitrogen of a water-gas interface by measuring N2O yield by the aid of a closed chamber-gas chromatograph method; 3), measuring biomass of aquatic plants and nitrogen content in bodies of the aquatic plants by the aid of a Dumas method and determining nitrogen absorbed quantity of the aquatic plants; 4), measuring biomass of microorganisms in the ecosystem by the aid of an MPN (most probable number) method, and measuring the effect of the microorganisms in a nitrogen conversion process and conversion quantity of the microorganisms to the nitrogen; and 5), applying the stable isotope technology to measure assimilation of aquatic animals to the nitrogen, and realizing precise quantization of the nitrogen, namely, measuring a food web of the aquatic animals and a trophic-level structure to determine migration and conversion of the nitrogen in the food web. Procedures of the precise quantization method are realized in the same simulation ecosystem.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
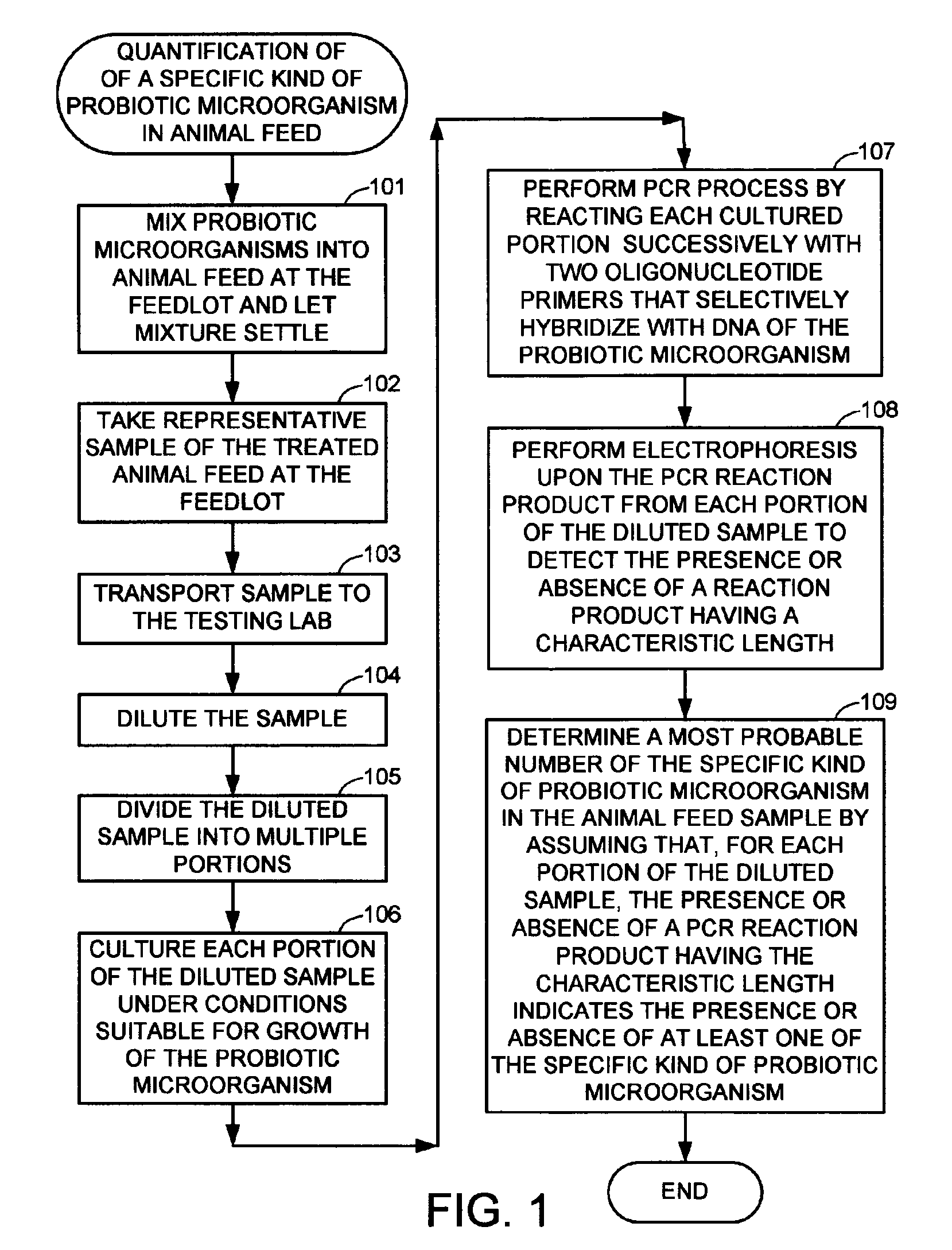
Methods for detecting and quantifying specific probiotic microorganisms in animal feed
Methods and compositions are disclosed for confirming and quantifying the presence of a specific probiotic microorganism in a sample of animal feed. Hybridization and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) techniques are applied to identify the presence of the specific probiotic microorganism in cultures grown in most probable number and serial dilution methods, after calibration of the techniques using blank and control samples.
Owner:NUTRITION PHYSIOLOGY
Low Mean Cell Residence Time Anaerobic Digestion Process
InactiveUS20130105390A1Increase capacityShorten the timeWater treatment parameter controlWater contaminantsDry weightGram
A Class B biosolids sludge digestion process whereby feed sludge is introduced to a completely-mixed, continuously- or intermittently fed and drawn, sealed, anaerobic digester, and sludge is drawn off at a rate such that the average mean cell residence time for the sludge in the digester is greater than or equal to 10 days, and less than 15 days. The temperature of the sludge is maintained in the thermophilic range to produce treated sludge having: a volatile solids content that is at least 38% less than the volatile solids content of the feed sludge, a reduced fecal coliform content that is at least a 2 log (base 10) reduction from the feed sludge, and where there is no more than 2,000,000 most probable number / gram total solids (dry weight basis) of fecal coliform in the treated sludge.
Owner:EAST BAY MUNICIPAL UTILITY DISTRICT
Quantitative detection method of escherichia coli in soil and assay kit thereof
InactiveCN102337344AReduce cumbersome stepsImprove detection efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliPathogenic microorganism
The invention discloses a quantiative detection method of escherichia coli in soil and an assay kit thereof. On the basis of taking related researches as reference, the method performs quantitative detection on pathogenic microorganism in the soil by adopting a method of combining MPN (most probable number) with PCR (polymerase chain reaction). By utilizing advantages of quickness and accuracy ofthe PCR method, biochemical identification, serological identification and other steps of positive results in the traditional MPN method are substituted, so that complex steps in a national standard method are reduced, the detection efficiency is improved, and a pre-enrichment step in the national standard method is adopted at the same time to improve the accuracy of detection targeting pathogenic bacteria; and due to the complexity of soil, the soil contains massive microorganisms, as well as various pathogenic microorganisms of different items, so that the targeting pathogenic bacteria is selectively cultured to improve the detection efficiency in order to quantitatively detect the targeting pathogenic bacteria better and more accurately. By virtue of creative effort of the inventor andscientific test verification, the sensitivity of the escherichia coli quantitative detection method in an experiment of adding pure bacteria in the soil is 25 per gram of soil.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Quantitative detection method of salmonella living body in water
InactiveCN102154472AStrong specificityEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesSewageSurface water
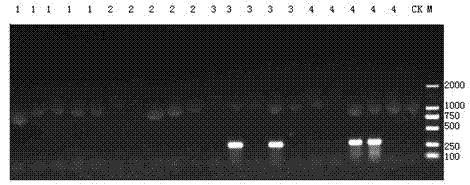
The invention discloses a quantitative detection method of salmonella living body in water, which adopts a multiple-tube fermentation method to preliminarily screen living bacteria taking salmonella as the principal component from water sample according to the growth characteristics of the salmonella and the conservative property of invA gene. By utilizing universal primers 139 and 141 of the salmonella, the quantitative detection method can be used for distinguishing the positive colony of the salmonella by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification. The quantitative detection method can be used for detecting the salmonella living body in water in a quantitative way by a most probable number (MPN) counting method. The method can accurately detect the content of the salmonella living body in water, is high in specificity as well as simple and convenient to operate, and is suitable for detecting multiple water samples such as surface water, sewage and the like.
Owner:XI'AN UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE AND TECHNOLOGY
Aflatoxin detection reagent kit based on loop-mediated isothermal gene amplification method
InactiveCN102586455AStrong specificityAvoid pollutionMicrobiological testing/measurementWater bathsLoop-mediated isothermal amplification
An aflatoxin detection reagent kit based on a loop-mediated isothermal gene amplification method is based on the basic principle of loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP). The loop-mediated isothermal gene amplification method includes particular steps: preparing a culture medium of PDA (potato dextrose agar); cultivating strains; designing a loop-mediated isothermal gene amplification (LAMP) primer; extracting a fungus DNA (deoxyribose nucleic acid) template; and proportionally preparing, adding a PCR (polymerase chain reaction) tube and realizing water bath heat-insulation reaction, agarose gel electrophoresis and the like. The aflatoxin detection reagent kit is combined with a method (GB\T13092-2006) for detecting the total number of mold in feed, the concentration of selected fungus liquid is detected by an MPN (most probable number) method, and the aflatoxin detection reagent kit is prepared according to the method. When used for detecting aflatoxin fungi in the feed and food, the reagent kit is high in specificity and sensitivity, quick in detection and low in cost, can be used for detecting a plurality of samples at the same time, and is applicable to sanitation examination for primary-level feed and worthy of being widely popularized.
Owner:万俊松
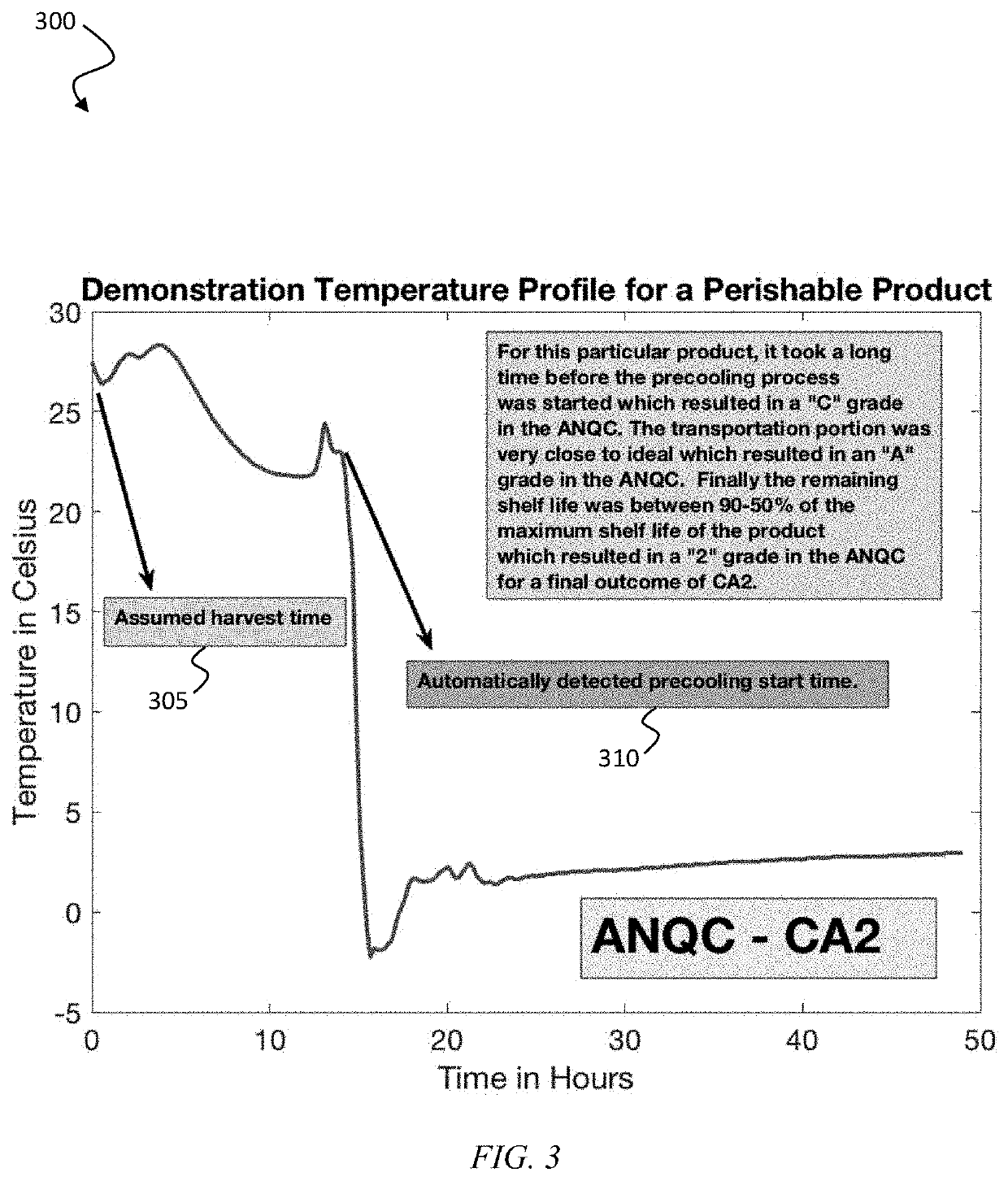
System and method for robust, modular, product sensitive monitoring and encoding of quality and safety along the perishable supply chain
ActiveUS20190370817A1Improve postharvest monitoring and modelingIncrease supplyLogisticsCommerceCold chainFood safety
A system and method for assessing a supply chain for a perishable product. In various embodiments, the present invention provides a quality code for a perishable product which encodes a plurality of the most important performance metrics of the cold chain for the perishable product, including food quality oriented measures such as cut-to-cool time, transportation quality and accumulated shelf-life loss, and food safety oriented measures such as most probable number range for microorganism growth into a compact, modular and simple to read format.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA +1
Detection and counting method for relative content of microorganism
ActiveCN106755287AImprove comparabilityDetection is precise and accurateAnalysis using chemical indicatorsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicroorganismRedox indicator
The invention relates to the technical field of microorganism detection, and particularly relates to a detection and counting method for the relative content of a microorganism. The method comprises the following steps: adding an oxidation-reduction indicator into a culture medium to obtain an indicator culture medium, wherein the color change interval of the oxidation-reduction indicator comprises three or more colors which can be easily recognized by naked eyes; diluting a sample to be detected, and culturing the diluted sample to be detected through the indicator culture medium, wherein multiple dilutions are used for the diluting operation, and multiple parallel samples are used for each dilution; reading the color or absorbency of the indicator culture medium during and / or the culturing operation; and obtaining the relative content of a microorganism in the sample to be detected according to the color change degree or absorbency change value of the indicator culture medium. Compared with the conventional MPN (most probable number) method, the method provided by the invention detects the relative contents of microorganisms in different samples more precisely and accurately; the comparability of the relative contents of microorganisms in different samples is higher; and the obtained data have favorable continuity. Thus, the method is wide in application range.
Owner:ADVANCED ENERGY & ENVIRONMENTAL TECH INC
Coliform single-tube quantitative rapid detection method
InactiveCN101613738AReduce incubation timeFast test resultsMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesSpecific detectionAbsorbance
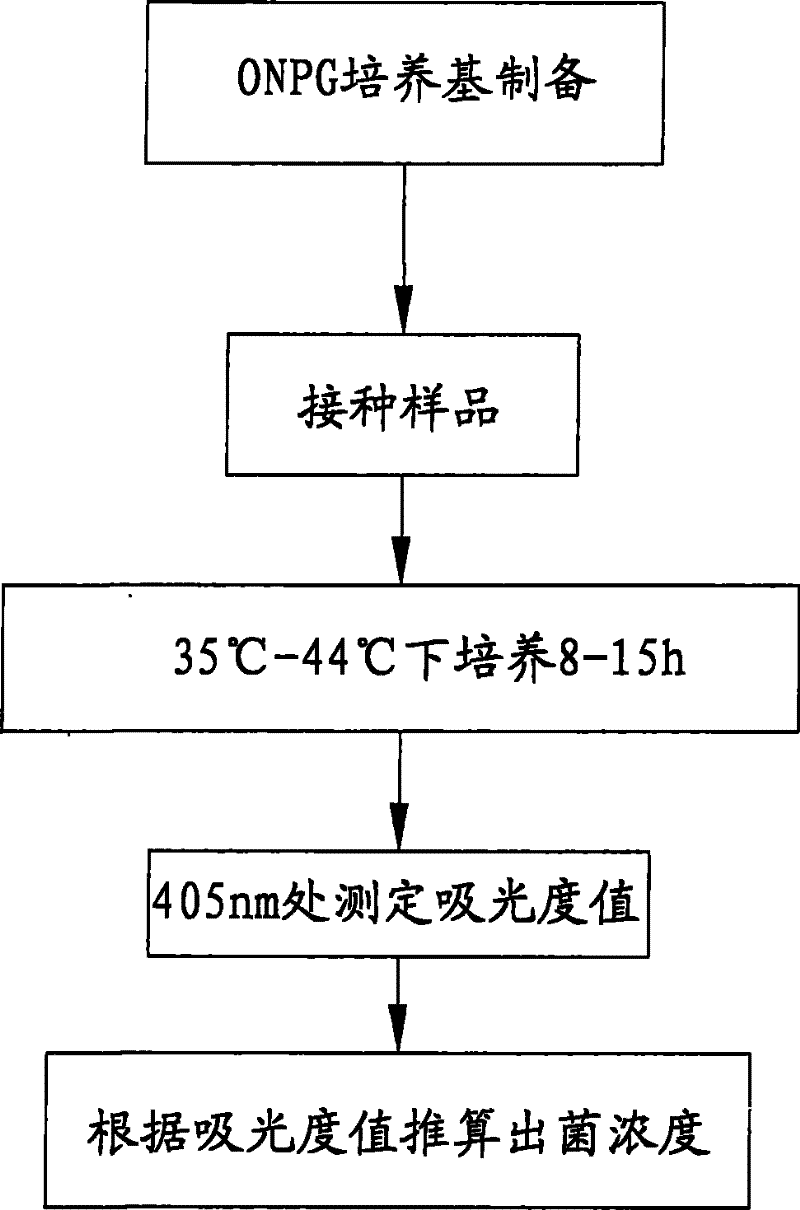
The invention discloses a coliform single-tube quantitative rapid detection method which comprises the steps: preparing specific detection culture medium; inoculating sample; culturing the inoculated sample for 8-15h at the temperature of 35-44DEG C; centrifugating for 5-10min at the speed of 8000-12000rpm; measuring absorbance value at the part of 405nm of supernate by a spectrophotometer; and calculating bacteria concentration according to formula. The method utilizes the spectrophotometer to measure the absorbance value of culture solution, and is more sensitive than visual evaluation, thus greatly shortening the culturing time. By adopting the single-tube quantitative detecting technique, one simple needs a tube of culture solution, so that a great deal of reagent and consumable materials can be saved compared with most probable number method; furthermore, the detection method is more rapid and stabler, and has high sensitivity.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
Ready-to-use culture apparatus for most probable number detection of flora
PendingCN109628294AEasy to collect and observeEasy dischargeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsReady to useEngineering
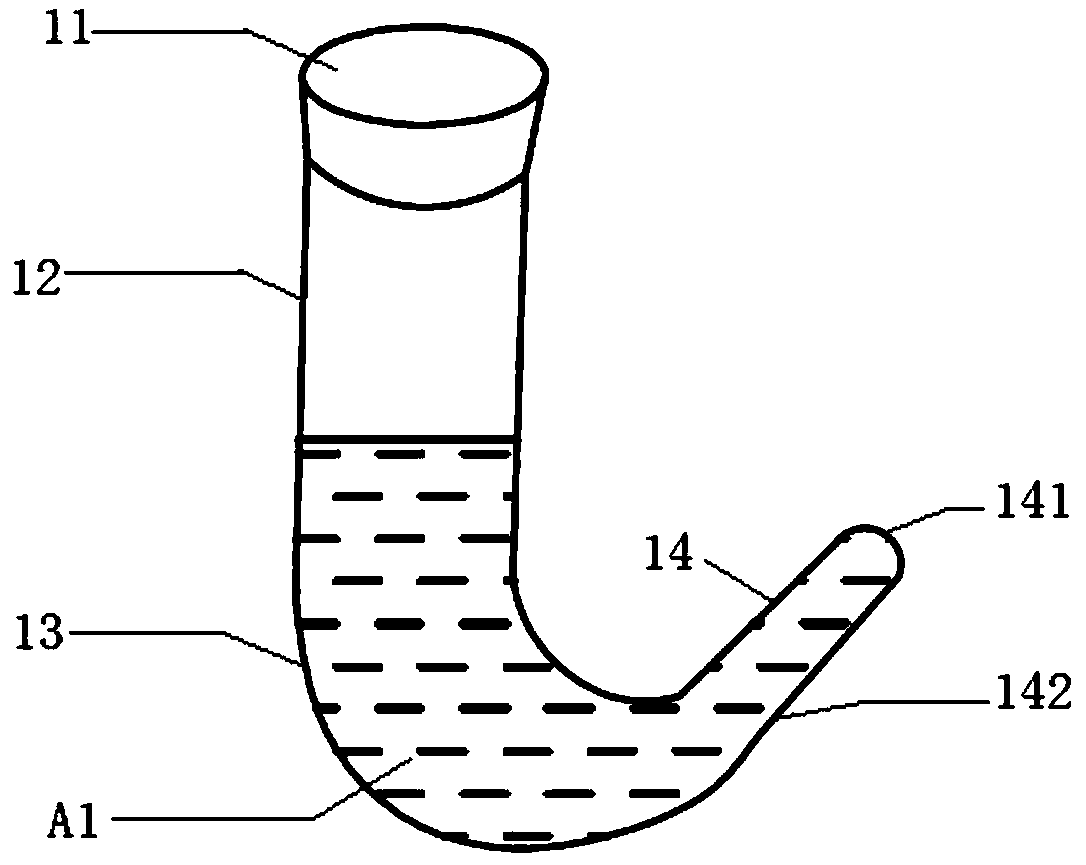
The invention relates to a ready-to-use culture apparatus for the most probable number detection of a flora. A culture detection tube comprises a main pipe, a gas collection pipe and a pipe cap for sealing the main pipe. The main pipe is of a curved hose structure and is connected with the gas collection pipe. The main pipe, the gas collection pipe and the pipe cap form a sealed chamber, the length of the main pipe is greater than that of the gas collection pipe, and the inner diameter of the main pipe is greater than that of the gas collection pipe. The culture detection tube is the externalgas collection pipe. Compared with a built-in small inverted pipe which is disposed 180 degrees upside down in the prior art, the angle between the gas collection pipe and the main pipe can be flexibly set, which greatly reduces exhausting difficulty.
Owner:济南市疾病预防控制中心
Method for quick combinative monitoring of total coliform and escherichia coli
InactiveCN105907874ASimple application productionSimple methodMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliDuplex pcr
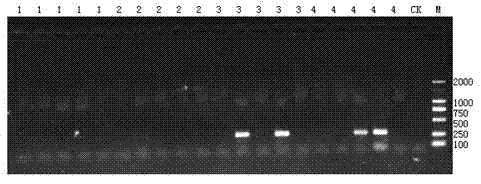
The invention provides a method for quick combinative monitoring of total coliform and escherichia coli. Water fecal pollution indicator bacteria including total coliform and escherichia coli are defected through the most probable number duplex PCR (MPN-dulpex PCR) method. The method is simple and quick, only four steps of experiments are needed, and the detection rate is higher than that of the national standard multi-tube fermentation method; specificity is high, repeatability is good, and two alive indicator bacteria including total coliform and escherichia coli in water can be monitored at the same time in a combinative and quantitative mode. A new method is provided for quick combinative monitoring of the water fecal pollution indicator bacteria including total coliform and escherichia coli.
Owner:CHONGQING THREE GORGES UNIV
Quantitative detection method for salmonellas in municipal surplus sludge
InactiveCN101993909AThe need for quantitative detectionQuantitatively accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesBiotechnologySludge
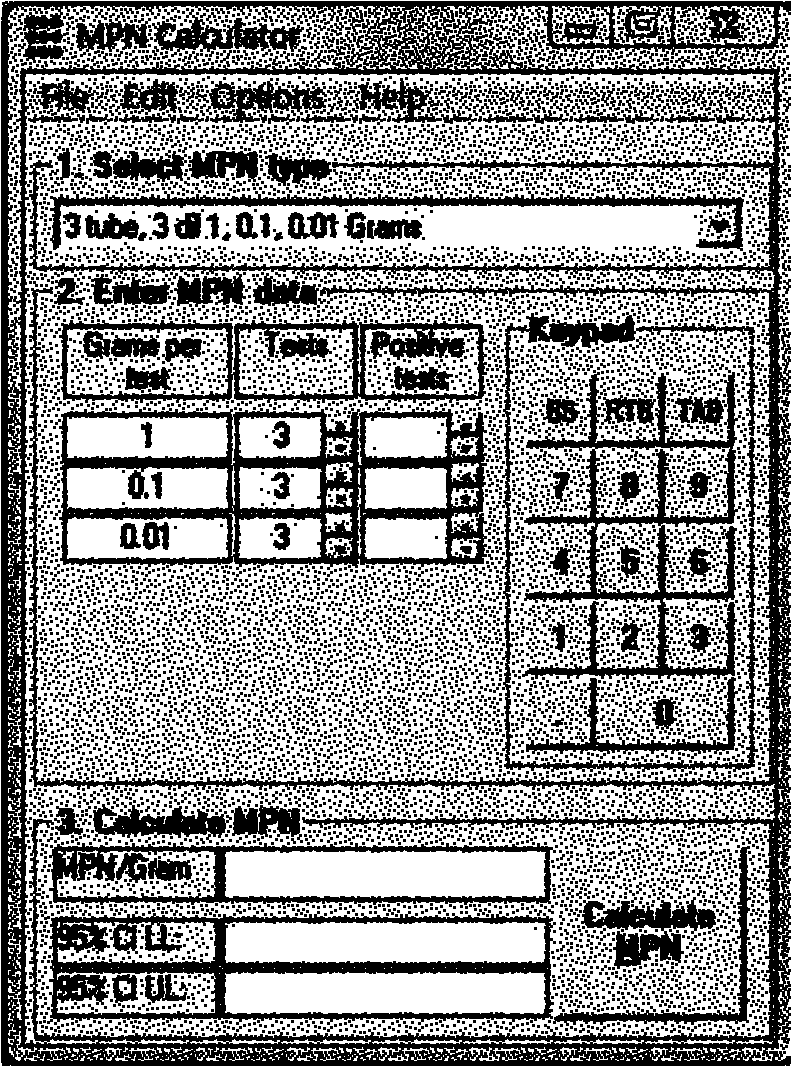
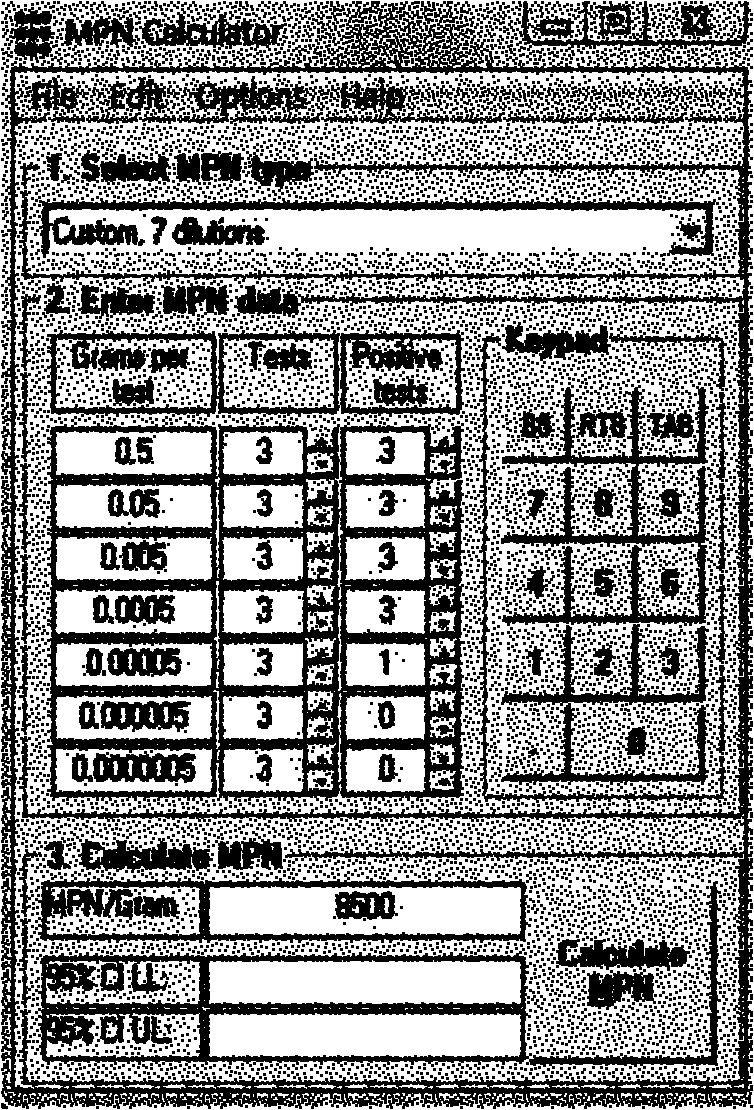
The invention relates to a quantitative detection method for salmonellas in municipal surplus sludge, belonging to the technical field of pathogenic bacterium detection of municipal surplus sludge in the biotechnology. The detection method comprises the following steps of: (1) carrying out gradient dilution of a sludge sample and bacterial enrichment cultivation; (2) carrying out selective enrichment cultivation; (3) separating and identifying a color developing culture medium; and (4) calculating by using MPN (Most Probable Number) counting software to obtain a result. The invention combines the MPN method and a salmonella detection method in the national standard of food safety, not only meets the requirement on the detection of salmonellas in the municipal surplus sludge, but also avoids interference of a large quantity of mixed bacteria in the sludge on the basis of obvious selectivity effect and is beneficial to the quick quantifying of the salmonellas. The invention has important theoretical values and actual guide meanings in the aspects of formulating and improving municipal surplus sludge treatment and application standards, and the like.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
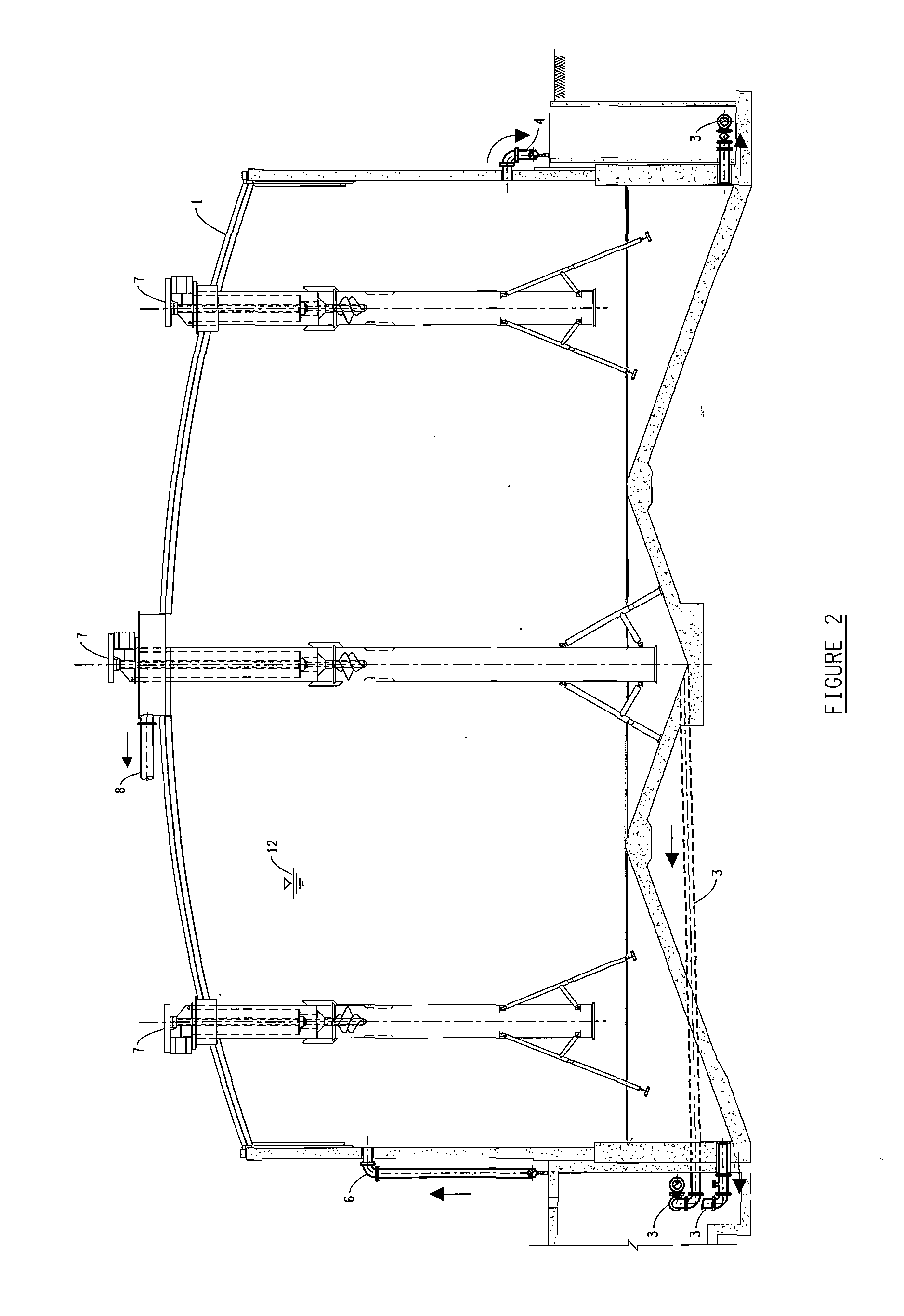
Sample holding device
InactiveCN103215182ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPhysicsMost probable number
A sample holding device having a plurality of sample wells. A gutter surrounds the sample wells and is in fluidic communication with an overflow sample well. An upper surface of the device is sealed with a sealing film that fluidically isolates each sample well from each other and from the gutter and overflow well. The device is used to perform a most probable number (MPN) procedure.
Owner:安泰凯生物技术有限公司
Method for counting bacteria in liquid
InactiveCN105671123AEasy to detectQuick analysisMicrobiological testing/measurementProjection imageFood safety
The invention discloses a method for counting bacteria in liquid.The method includes steps: taking a to-be-detected solution, selecting three continuous ten-time dilution gradients to obtain solutions of three dilutions; respectively taking three samples from the solution of each dilution to obtain A1, A2 and A3, and dripping drop by drop after forming of drops; emitting a laser beam to penetrate through the drops from one side of each drop to form projections, acquiring a projection image of each drop, subjecting the projection images to pattern recognition to judge whether bacteria exist or not, and counting the bacteria according to an MPN (most probable number) counting method.The method for counting the bacteria in liquid is short in time consumption, convenient and simple in operation, easy to implement and widely applicable to detection of the bacteria in liquid in the fields of environment monitoring, food safety, medical treatment and health care and the like.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Quantitative detection method of salmonella in soil and assay kit thereof
InactiveCN102337343AReduce cumbersome stepsImprove detection efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesPre enrichmentPathogenic microorganism
The invention discloses a quantiative detection method of salmonella in soil and an assay kit thereof. On the basis of taking related researches as reference, the method performs quantitative detection on pathogenic microorganism in the soil by adopting a method of combining MPN (most probable number) with PCR (polymerase chain reaction). By utilizing advantages of quickness and accuracy of the PCR method, biochemical identification, serological identification and other steps of positive results in the traditional MPN method are substituted, so that complex steps in a national standard methodare reduced, the detection efficiency is improved, and a pre-enrichment step in the national standard method is adopted at the same time to improve the accuracy of detection targeting pathogenic bacteria; and due to the complexity of soil, the soil contains massive microorganisms, as well as various pathogenic microorganisms of different items, so that the targeting pathogenic bacteria is selectively cultured to improve the detection efficiency in order to quantitatively detect the targeting pathogenic bacteria better and more accurately. By virtue of creative effort of the inventor and scientific test verification, the sensitivity of the salmonella quantitative detection method in an experiment of adding pure bacteria in the soil is 250 per gram of soil.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY +1
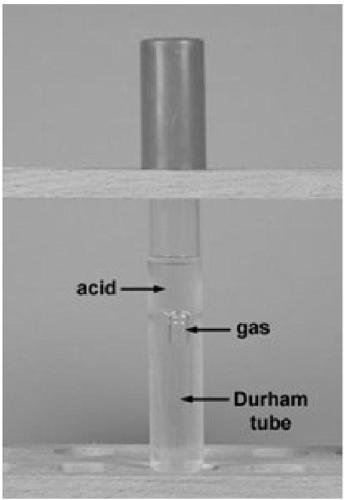
Instant culture device for detecting flora by most probable number method
PendingCN109679835AEasy accessEliminate errorsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFloraProduct gas
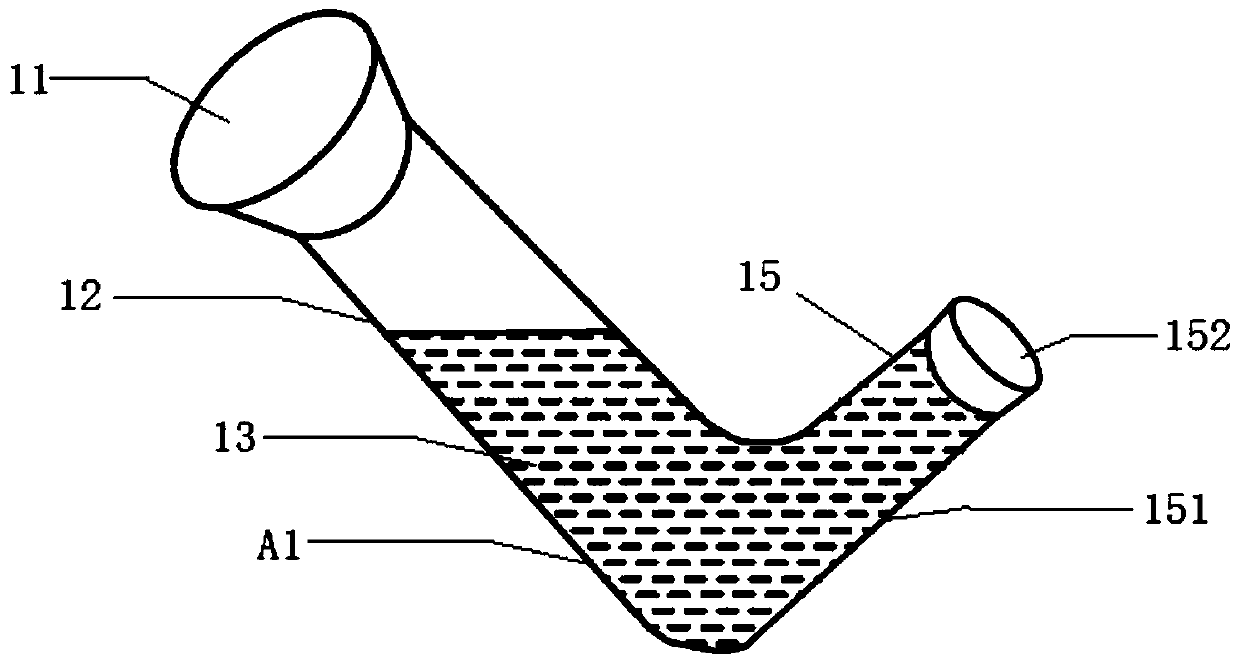
The invention relates to the field of flora detection, in particular to an instant culture device for detecting flora by a most probable number method. In the prior art, a reverse Durham tube is usedas a culture tube of an MPN method; the fermentation condition is judged by observing the gas generation in a small reverse tube, but the space of the culture tube is narrow and small; before use, theair in the small reverse tube is difficult to be completely eliminated. In order to solve the technical problems, the invention provides an instant fermentation culture tube for MPN. The culture tubecomprises a hard main tube and a hard gas generating tube which are connected through a bent connector; the sealed hard gas generating tube is used for replacing the built-in small reverse tube in the prior art and is not put into the fermentation tube, so that the limitation by the built-in tube diameter and the limitation by the reverse position are avoided; therefore the inner diameter of thehard gas generating collecting tube and the reverse angle selection freedom are increased; the tube line connection of the hard main tube and the hard gas generating collecting tube is more smooth; the gas exhaust is convenient; the advantages of high speed, high efficiency, time saving, labor saving and the like are realized.
Owner:济南市疾病预防控制中心
Fast quantitative detection method of shigella contained in sludge
InactiveCN101993954AOvercome the cycleOvercoming cumbersome stepsMicrobiological testing/measurementSludgeTrue positive rate
The invention relates to a fast quantitative detection method of shigella contained in sludge, belonging to the technical field of pathogenicbacteria detection in biotechnologies. The fast quantitative detection method of the shigella contained in the sludge comprises the following steps of: (1) carrying out gradient dilution and front enriched culture on a sludge sample; (2) carrying out selectively enriched culture; (3) carrying out DNA extraction; (4) carrying out PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification and amplified product detection; and (5) calculating to obtain a result by utilizing MPN (Most Probable Number) counting software. The invention realizes the fast quantitative detection of the shigella contained in the sludge by adopting a method combining an MPN method with specific PCR detection and can prevent the disturbance of other microbes through selective enrichment and specific PCR, thereby enhancing the sensitivity and the specificity of detection; and in addition, the invention also has the advantages of shortening the detection time, enhancing the detection efficiency and increasing the quantity of detection samples.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
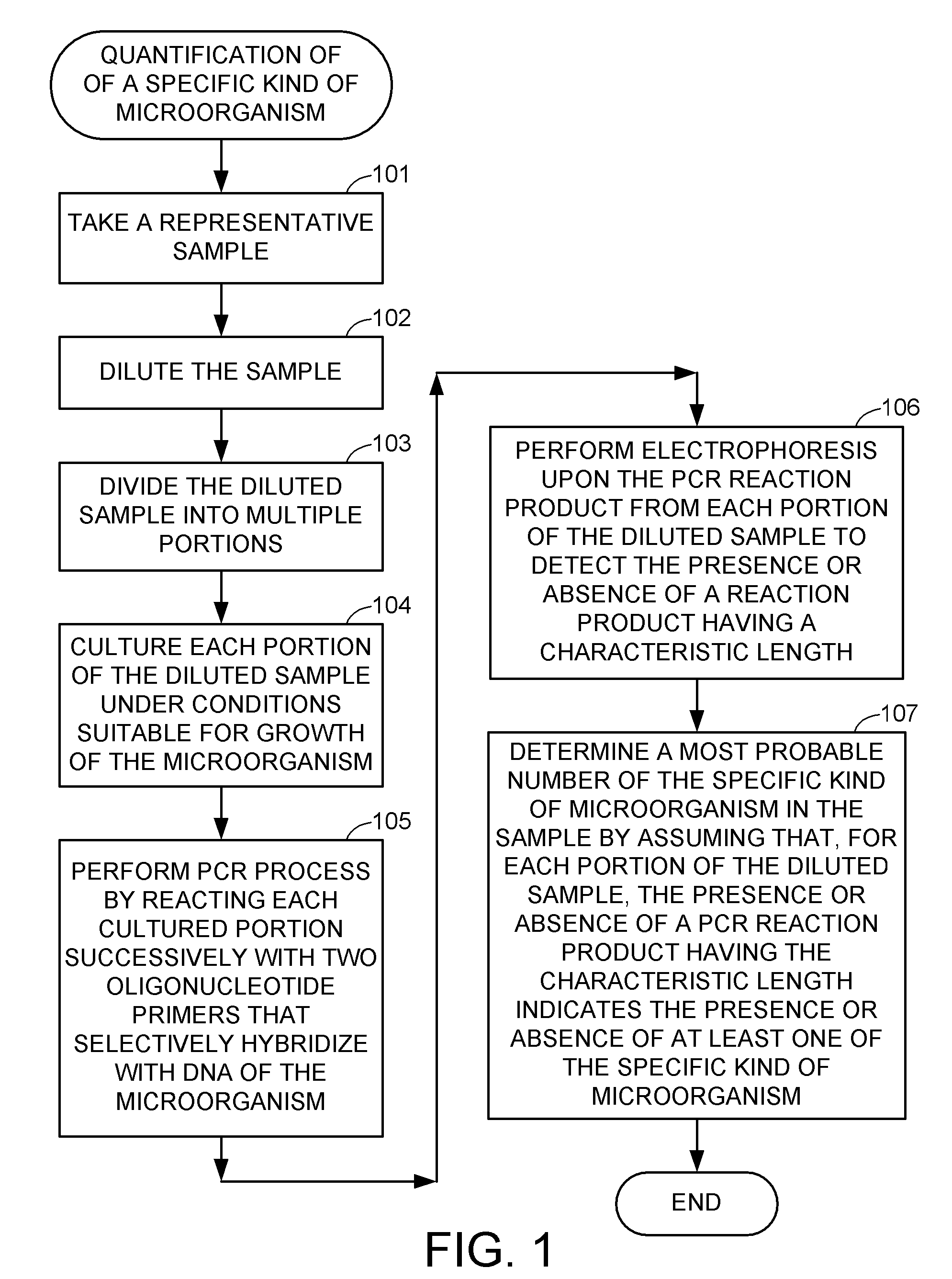
Methods for detecting and quantifying specific microorganisms
InactiveUS20050048516A1Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisMicroorganismMicrobiology
Methods and compositions are disclosed for confirming and quantifying the presence of a specific kind of microorganism in a sample of material. Hybridization and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) techniques are applied to identify the presence of the specific microorganism in cultures grown in most probable number and serial dilution methods, after calibration of the techniques using blank and control samples. For example, samples of animal feed can be cultured and analyzed to determine the quantity of specific probiotic microorganisms present in the feed.
Owner:NUTRITION PHYSIOLOGY
Methods for Detecting and Quantifying Specific Probiotic Microorganisms in Animal Feed
Methods and compositions are disclosed for confirming and quantifying the presence of a specific probiotic microorganism in a sample of animal feed. Hybridization and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) techniques are applied to identify the presence of the specific probiotic microorganism in cultures grown in most probable number and serial dilution methods, after calibration of the techniques using blank and control samples.
Owner:GARNER BRYAN E +2
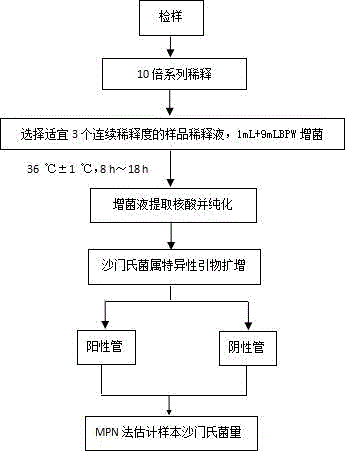
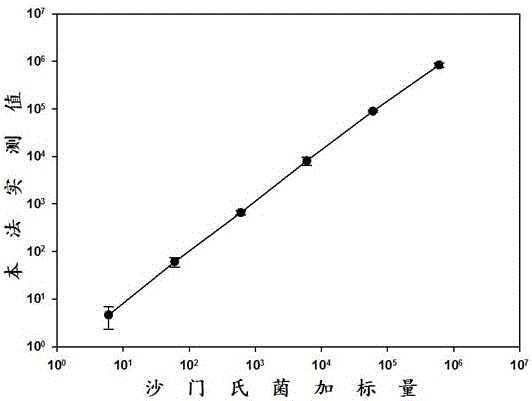
Rapid quantitative method for salmonellas in food based on MPN (most probable number) and PCR (polymerase chain reaction)
InactiveCN106636437AShorten the detection processReduce workloadMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesFood safetyDiluent
The invention discloses a novel and rapid quantitative method for salmonellas in food and related food samples. Based on the technical principle of MPN (most probable number) and PCR (polymerase chain reaction), the method includes the steps: firstly, performing gradient dilution for the food samples; taking multi-tube diluents from each dilution degree; performing non-selective increasing bacteria for the diluents; extracting DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of total bacteria of increasing bacteria samples; performing amplification for the DNA by the aid of specific salmonella primers; estimating pollution load of salmonellas in original samples according to the number of amplified positive tubes under different dilution degrees. The whole detecting process can be finished within two working days, the detection process can be effectively shortened, and workload is saved as compared with a traditional MPN (most probable number) method based on plate separation and biochemical confirmation. The method is simple and convenient, easy to operate, accurate in result and particularly applicable to rapid estimation of pollution dose or bacterium carrying level of the salmonellas in samples of fresh and cold food and the like in operations such as food safety risk assessment.
Owner:江西省疾病预防控制中心
Methods for Detecting and Quantifying Specific Microorganisms
InactiveUS20090203031A1Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisMicroorganismMicrobiology
Owner:GARNER BRYAN E +2
Precise quantization method for nitrogen cycle of lake ecosystem
A precise quantization method for nitrogen cycle of a lake ecosystem includes 1), applying an isotope pairing method to quantitatively research nitrogen migration and conversion of a sediment-water interface of the lake ecosystem; 2), determining release of nitrogen of a water-gas interface by measuring N2O yield by the aid of a closed chamber-gas chromatograph method; 3), measuring biomass of aquatic plants and nitrogen content in bodies of the aquatic plants by the aid of a Dumas method and determining nitrogen absorbed quantity of the aquatic plants; 4), measuring biomass of microorganisms in the ecosystem by the aid of an MPN (most probable number) method, and measuring the effect of the microorganisms in a nitrogen conversion process and conversion quantity of the microorganisms to the nitrogen; and 5), applying the stable isotope technology to measure assimilation of aquatic animals to the nitrogen, and realizing precise quantization of the nitrogen, namely, measuring a food web of the aquatic animals and a trophic-level structure to determine migration and conversion of the nitrogen in the food web. Procedures of the precise quantization method are realized in the same simulation ecosystem.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Coliform single-tube quantitative rapid detection method
InactiveCN101613738BReduce incubation timeFast test resultsMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesSpecific detectionAbsorbance
The invention discloses a coliform single-tube quantitative rapid detection method which comprises the steps: preparing specific detection culture medium; inoculating sample; culturing the inoculated sample for 8-15h at the temperature of 35-44DEG C; centrifugating for 5-10min at the speed of 8000-12000rpm; measuring absorbance value at the part of 405nm of supernate by a spectrophotometer; and calculating bacteria concentration according to formula. The method utilizes the spectrophotometer to measure the absorbance value of culture solution, and is more sensitive than visual evaluation, thus greatly shortening the culturing time. By adopting the single-tube quantitative detecting technique, one simple needs a tube of culture solution, so that a great deal of reagent and consumable materials can be saved compared with most probable number method; furthermore, the detection method is more rapid and stabler, and has high sensitivity.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
Methods and compositions for rapidly detecting and quantifying viable legionella
ActiveUS20090087902A1Quicker procedureEarly detectionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicrobiologyMost probable number
Methods and compositions detect and quantify viable Legionella. Dip-slides that include an absorbent medium, growth promoting, and growth selective substances are useful in rapid detection and quantification of microcolonies of Legionella. Most probable number method of detection and quantification of Legionella are disclosed.
Owner:PHIGENICS
Methods and compositions for rapidly detecting and quantifying viable Legionella
ActiveUS7939314B2Early detectionMinimize contaminationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGrowth promotingMicrobiology
Owner:PHIGENICS
Preparation method and application of persimmon syrup
InactiveCN110419709ASolve the problem of unmanned harvestingAvoid churnFood scienceFlavorBacteria coliforms
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of persimmon syrup. By adopting a series of unique preparation processes of harvesting and sorting, washing and crushing, softening and astringency removal, ultra-micro refining, syrup residue separation, low-temperature concentration and the like, the preparation method suitable for mopan persimmons is provided, the persimmon syrup prepared through the preparation method does not contain any additives such as a preservative, a sterilizing agent and a color retention agent, not only are the original flavor characteristics of the mopan persimmons retained, but also the efficacy functions in traditional medicine are maintained, the color of the persimmon syrup is brown orange, the persimmon syrup has the rich persimmon fragrance and is sweet but not oily in taste and free of astringent taste, the total acidity is 54.02 degree T, the viscosity is 542.73 mPa.s, the total number of bacterial colonies (cfu / mL) is less than or equalto 100, and the most probable number of coliform bacteria (MPN / 100mL) is less than or equal to 3; and no pathogenic bacterium is detected, and the persimmon syrup has the wide application value in the processing field of beverages, desserts, ice creams and heal care products.
Owner:王永旺
Quantitative detection method of salmonella in soil and assay kit thereof
InactiveCN102337343BReduce cumbersome stepsImprove detection efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesPre enrichmentPathogenic microorganism
The invention discloses a quantiative detection method of salmonella in soil and an assay kit thereof. On the basis of taking related researches as reference, the method performs quantitative detection on pathogenic microorganism in the soil by adopting a method of combining MPN (most probable number) with PCR (polymerase chain reaction). By utilizing advantages of quickness and accuracy of the PCR method, biochemical identification, serological identification and other steps of positive results in the traditional MPN method are substituted, so that complex steps in a national standard methodare reduced, the detection efficiency is improved, and a pre-enrichment step in the national standard method is adopted at the same time to improve the accuracy of detection targeting pathogenic bacteria; and due to the complexity of soil, the soil contains massive microorganisms, as well as various pathogenic microorganisms of different items, so that the targeting pathogenic bacteria is selectively cultured to improve the detection efficiency in order to quantitatively detect the targeting pathogenic bacteria better and more accurately. By virtue of creative effort of the inventor and scientific test verification, the sensitivity of the salmonella quantitative detection method in an experiment of adding pure bacteria in the soil is 250 per gram of soil.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY +1
Key technology of agricultural product safe fresh keeping
InactiveCN107279680AMake sure the circulation temperatureEffective preservationFood freezingMeat/fish preservation by heatingFood additiveUnit/Kilogram
The invention relates to the technical field of food production and processing, and particularly relates to a key technology of agricultural product safe fresh keeping. The technology comprises the following technological processes: material selecting, proportioning, rolling, subpackaging, boiling, sterilization, cooling, quick-freezing, packaging, and storage in warehouses. The technical indexes of the key technology are as below: a nutrient index: protein is 15 grams per 100 grams or above; microbe indexes: a total number of bacterial colonies is 70000 cfu (colony forming unit) per gram or less, and coliform groups is 110 MPN (most probable number) per 100 grams or less; physical and chemical indexes: lead is 0.45 milligram per kilogram or less, total mercury is 0.04 milligram per kilogram or less, and nitrite is 25 milligrams per kilogram or less; and safety: no preservative, no food additive, and shelf life of 60 days or above at the temperature of 0-4 DEG C. The technology of cooking at a proper temperature is stricter on the control of selected material quality, time and temperature so as to maintain the original taste and flavor of products. The products prepared by the technology are safe and nutritive, and the technology has excellent application prospects, social benefits and economic benefits.
Owner:苏州市妙意煮食品有限公司
Quantitative detection method of salmonella living body in water
InactiveCN102154472BStrong specificityEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesSewageSurface water
Owner:XI'AN UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE AND TECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com