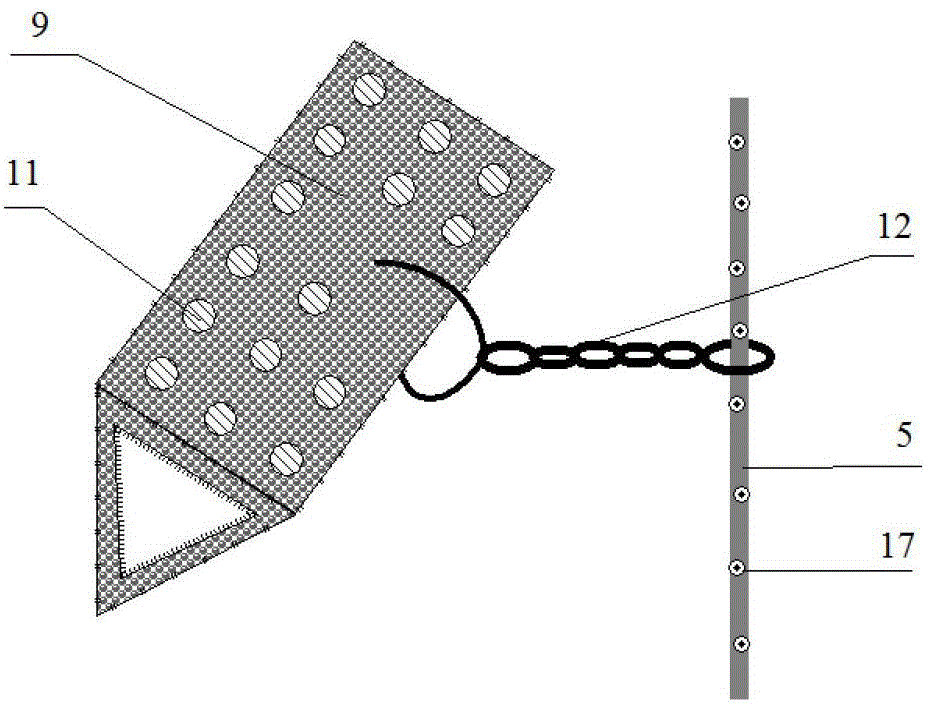
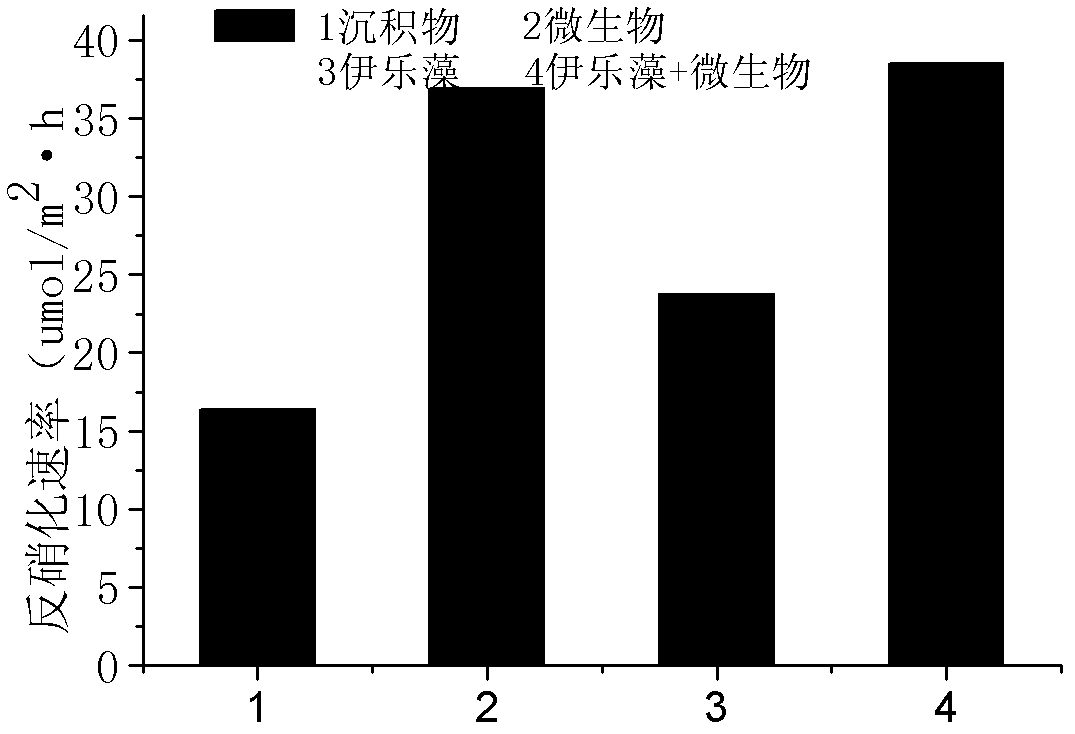
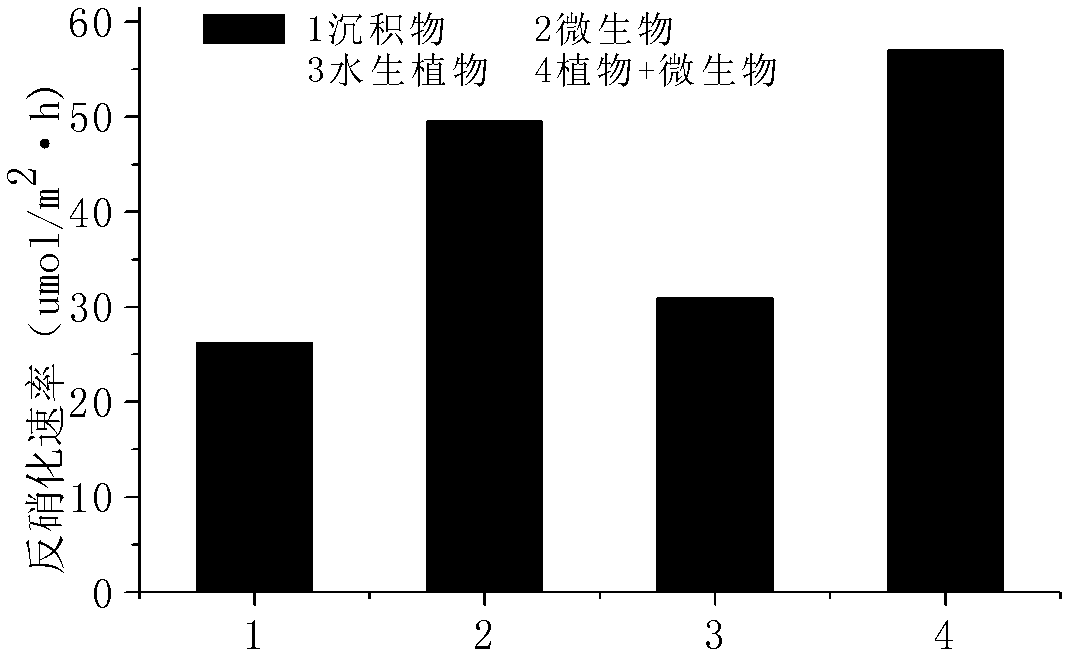
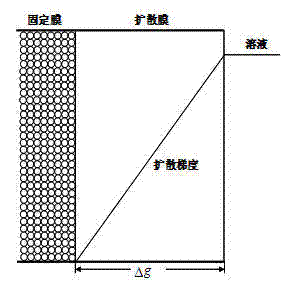
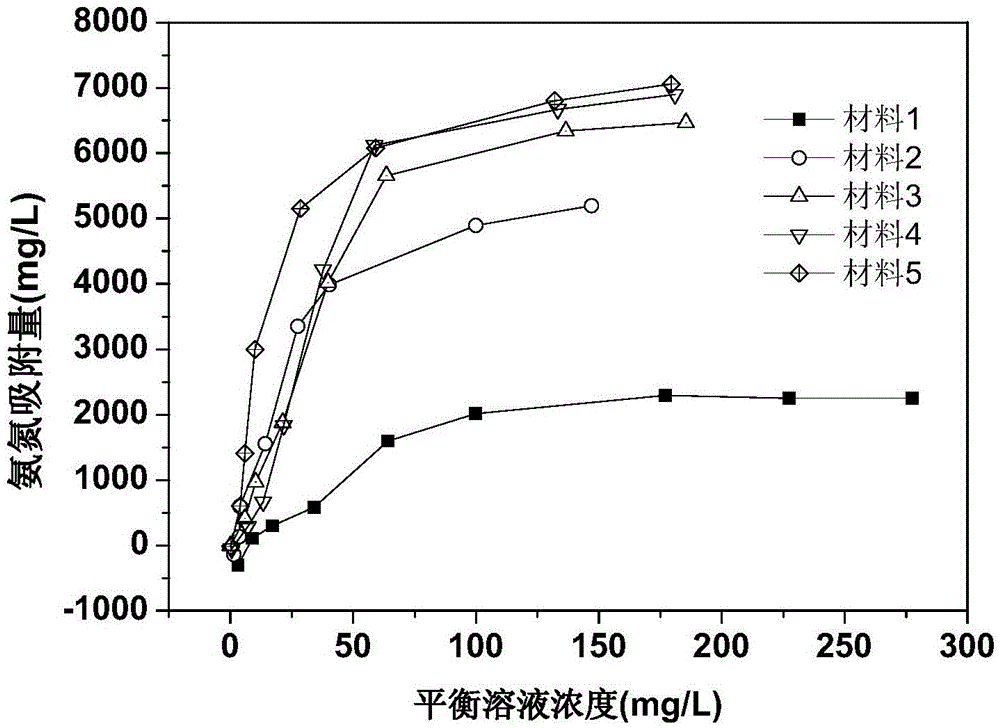
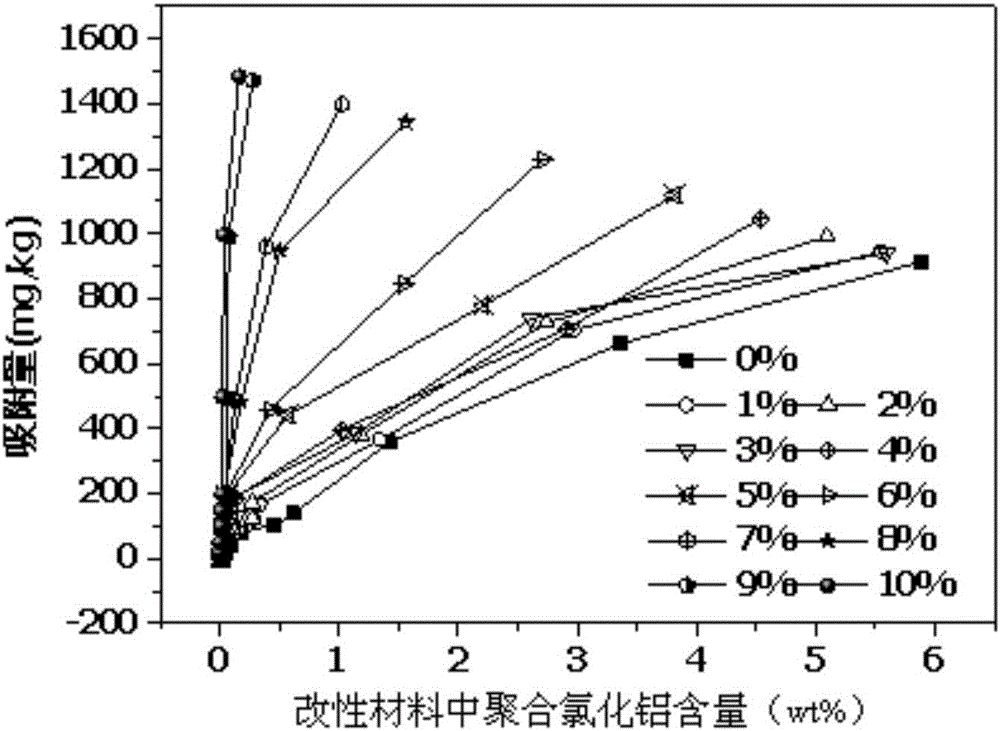
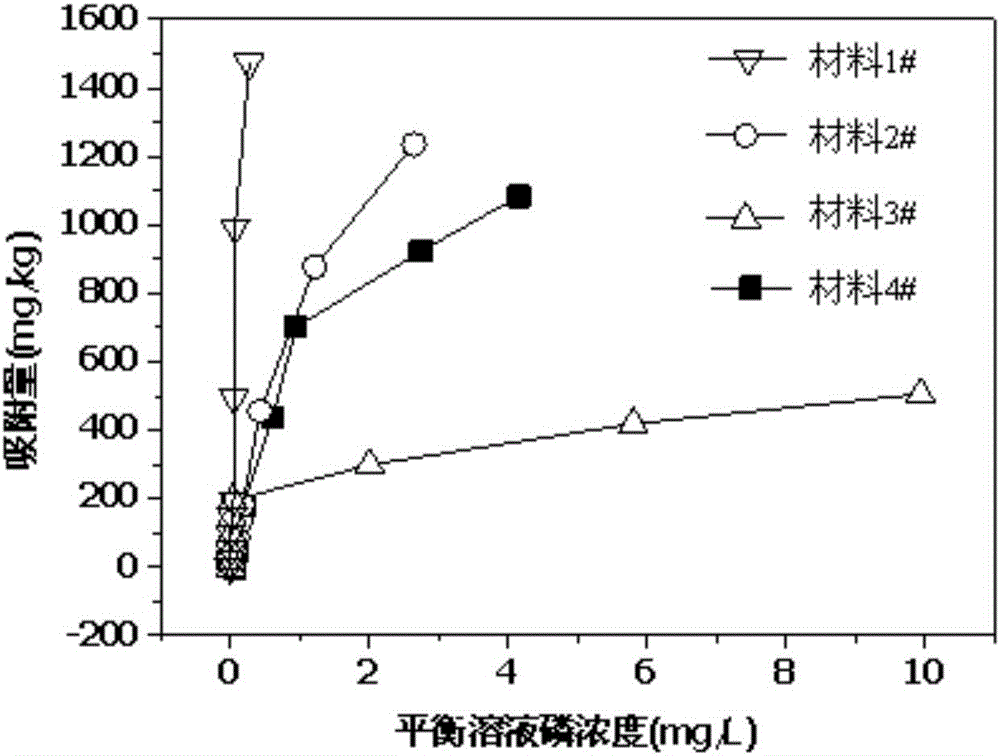
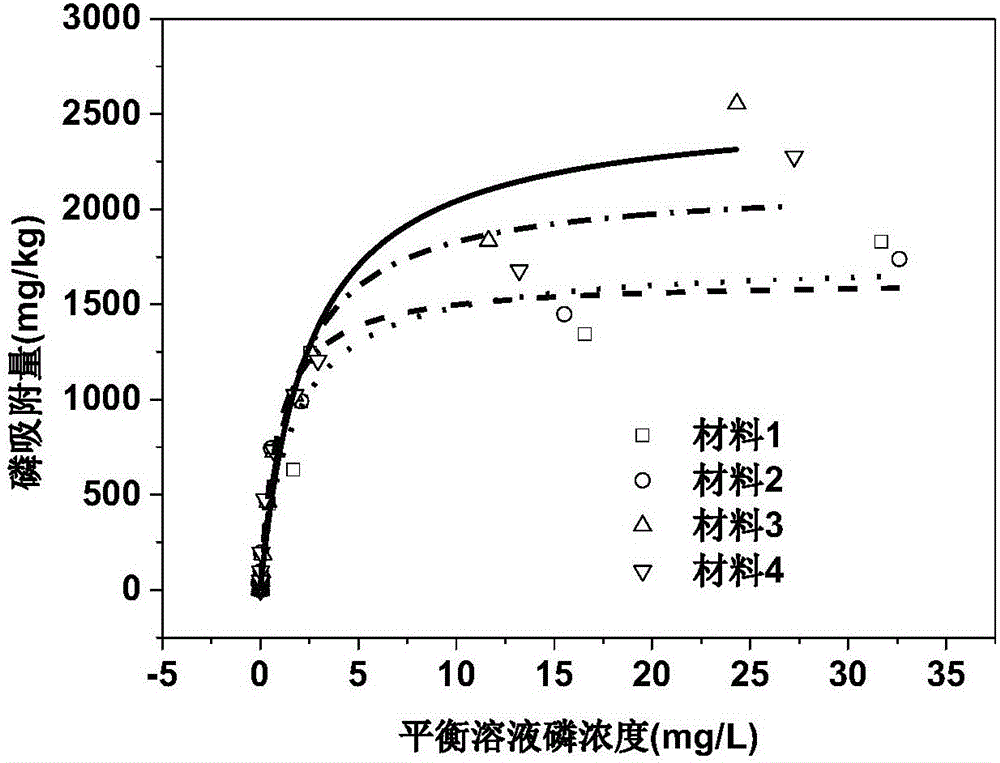
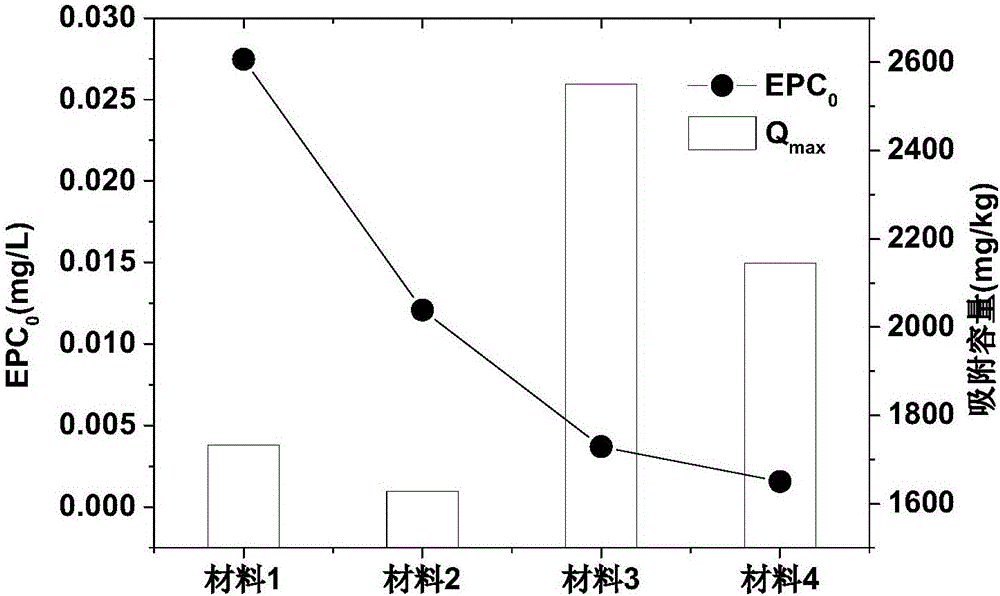
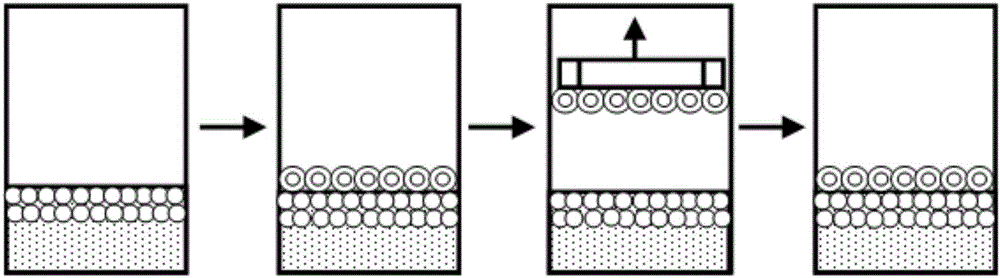
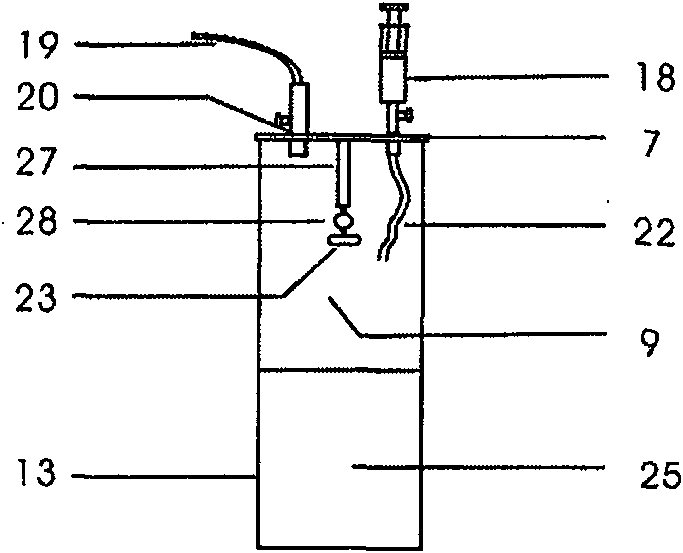
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
50 results about "Sediment–water interface" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In oceanography and limnology, the sediment–water interface is the boundary between bed sediment and the overlying water column. The term usually refers to a thin layer (approximately 1 cm deep, though variable) of water at the very surface of sediments on the seafloor. In the ocean, estuaries, and lakes, this layer interacts with the water above it through physical flow and chemical reactions mediated by the micro-organisms, animals, and plants living at the bottom of the water body. The topography of this interface is often dynamic, as it is affected by physical processes (e.g. currents causing rippling or resuspension) and biological processes (e.g. bioturbation generating mounds or trenches).
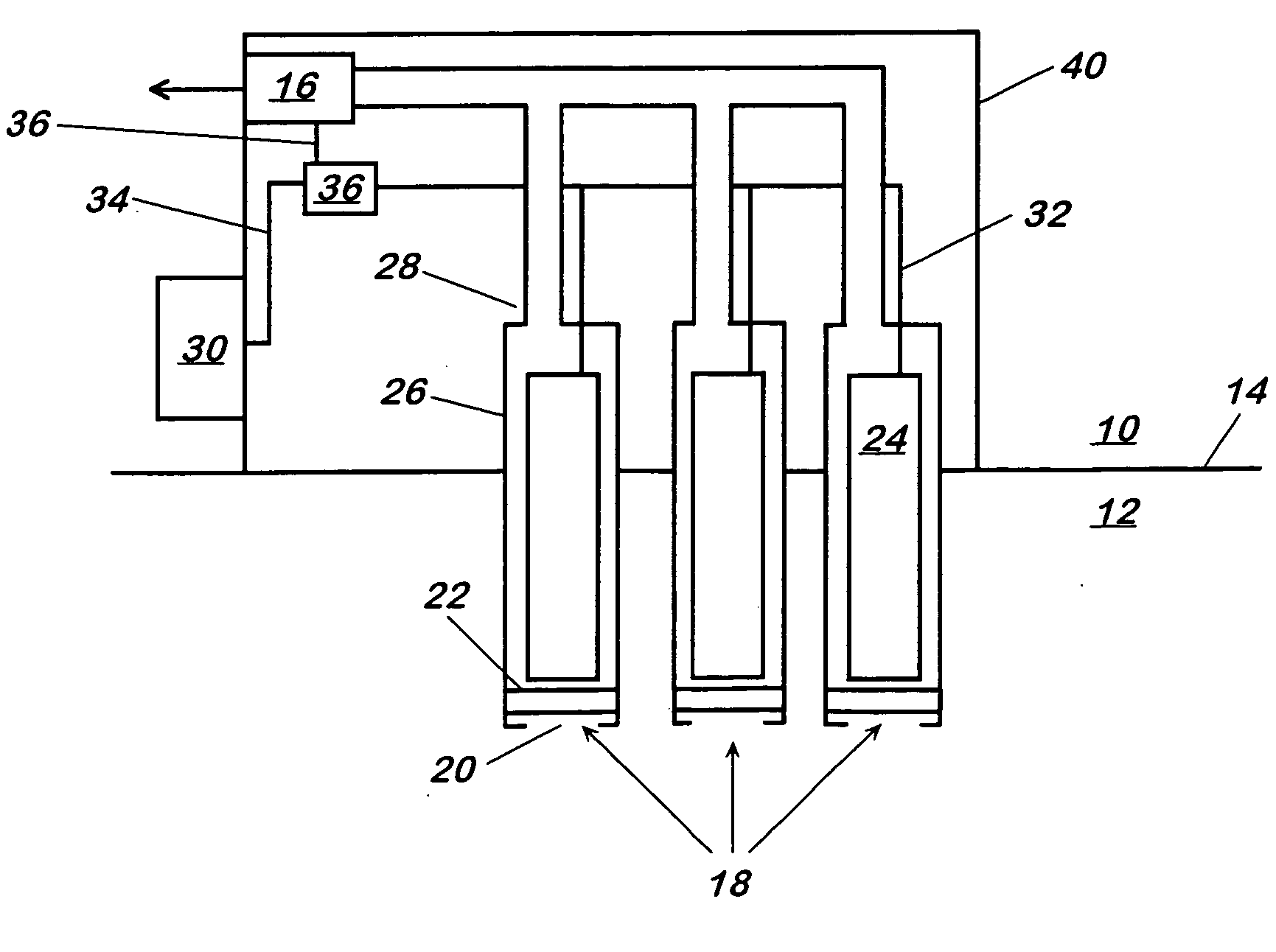
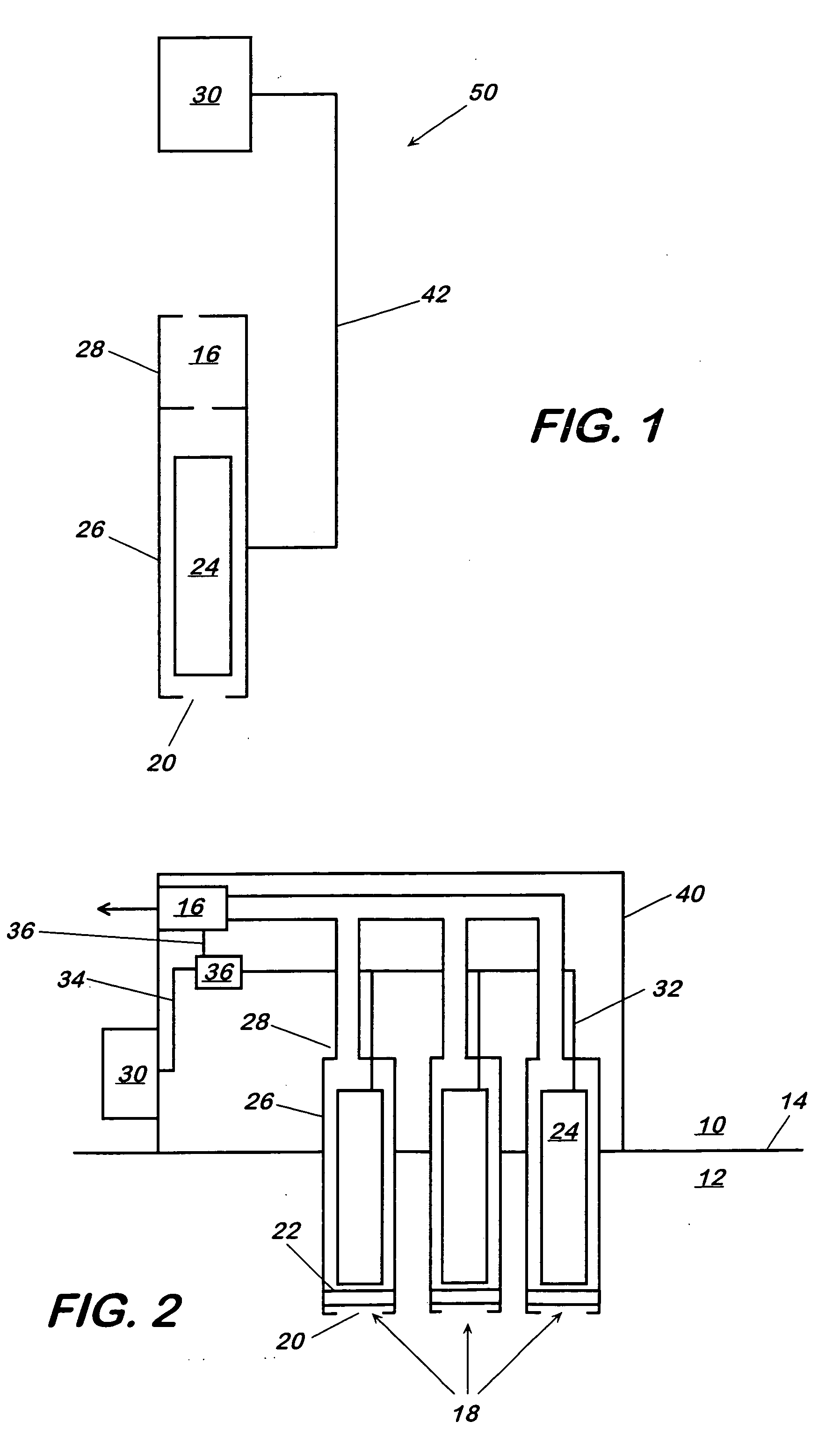
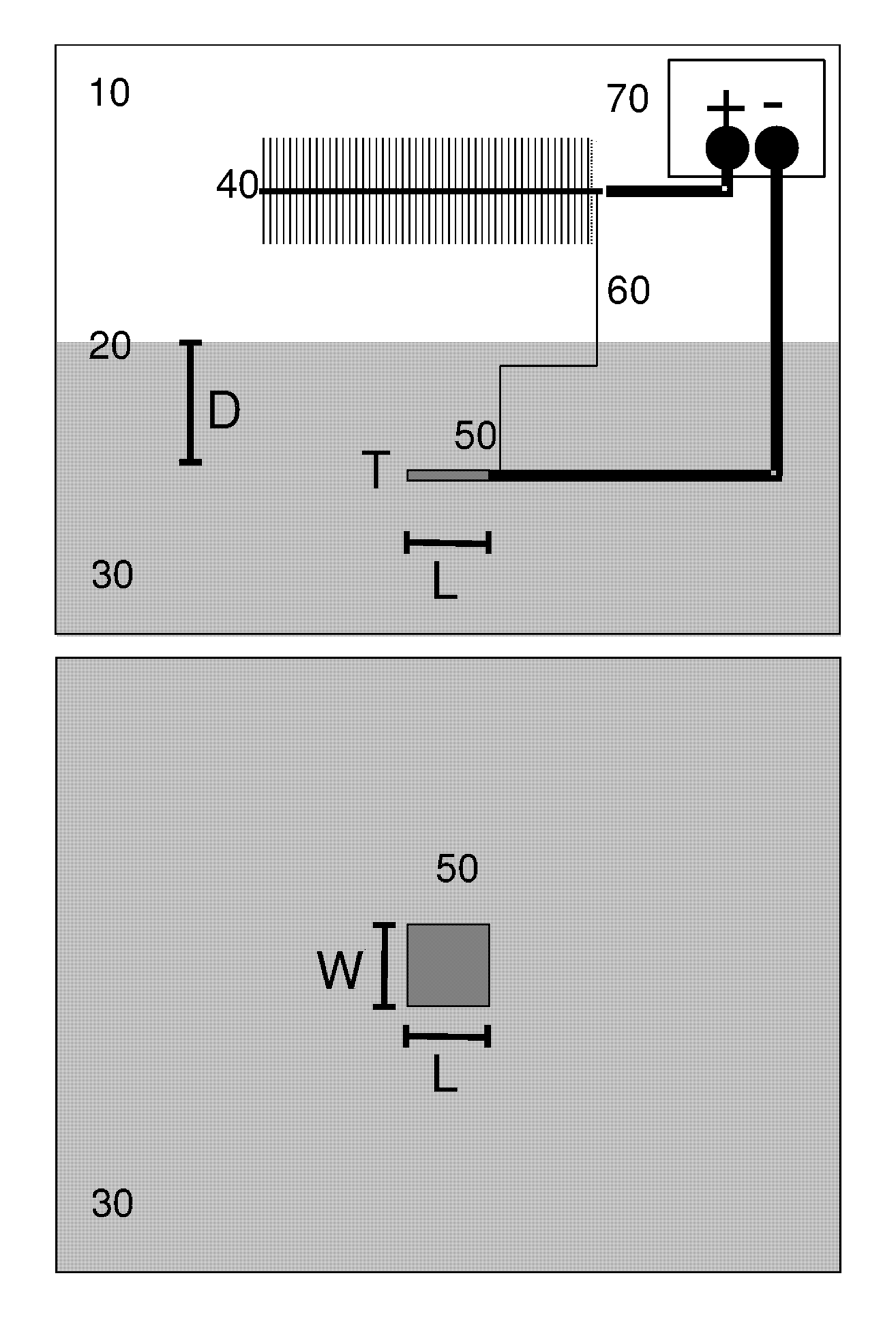
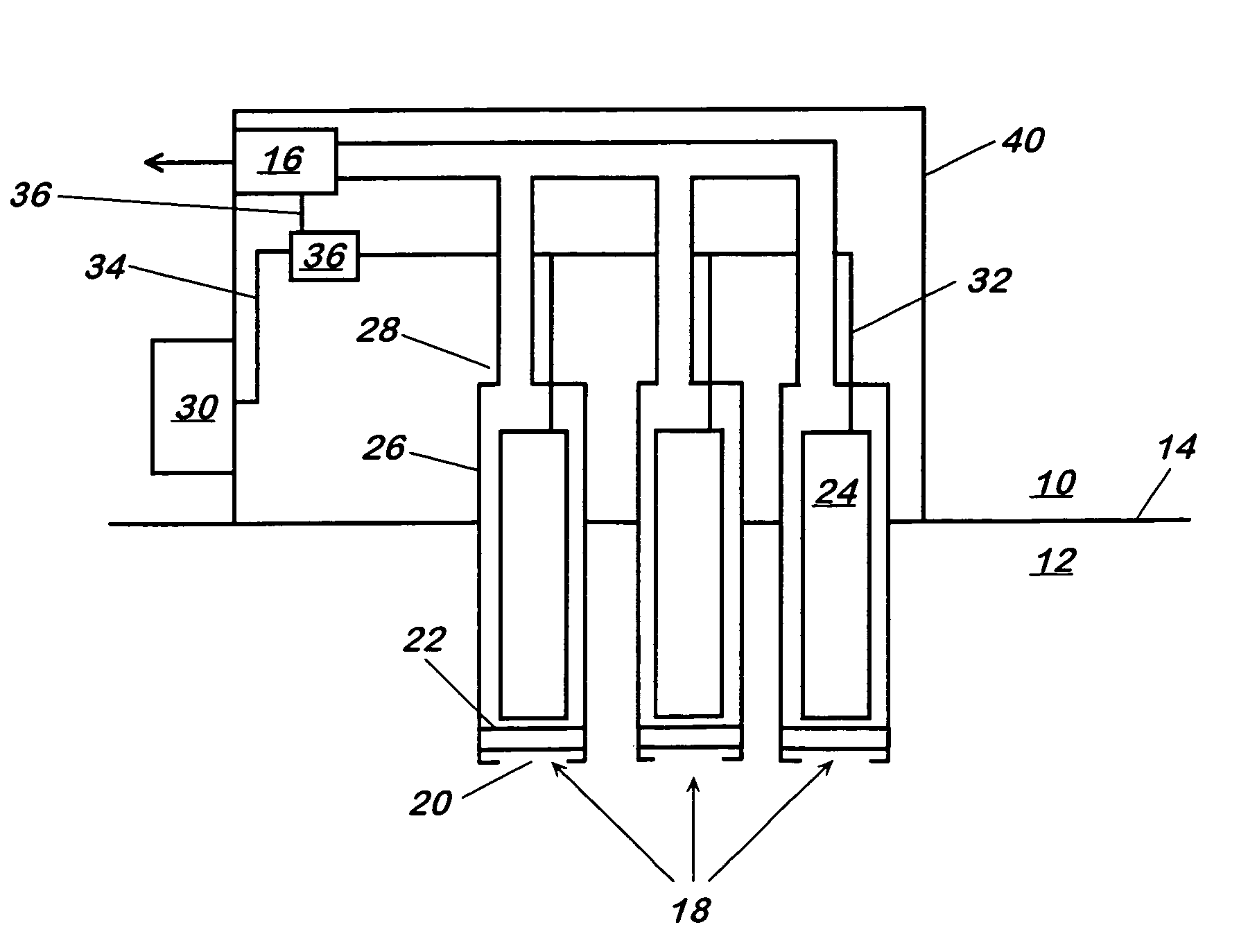
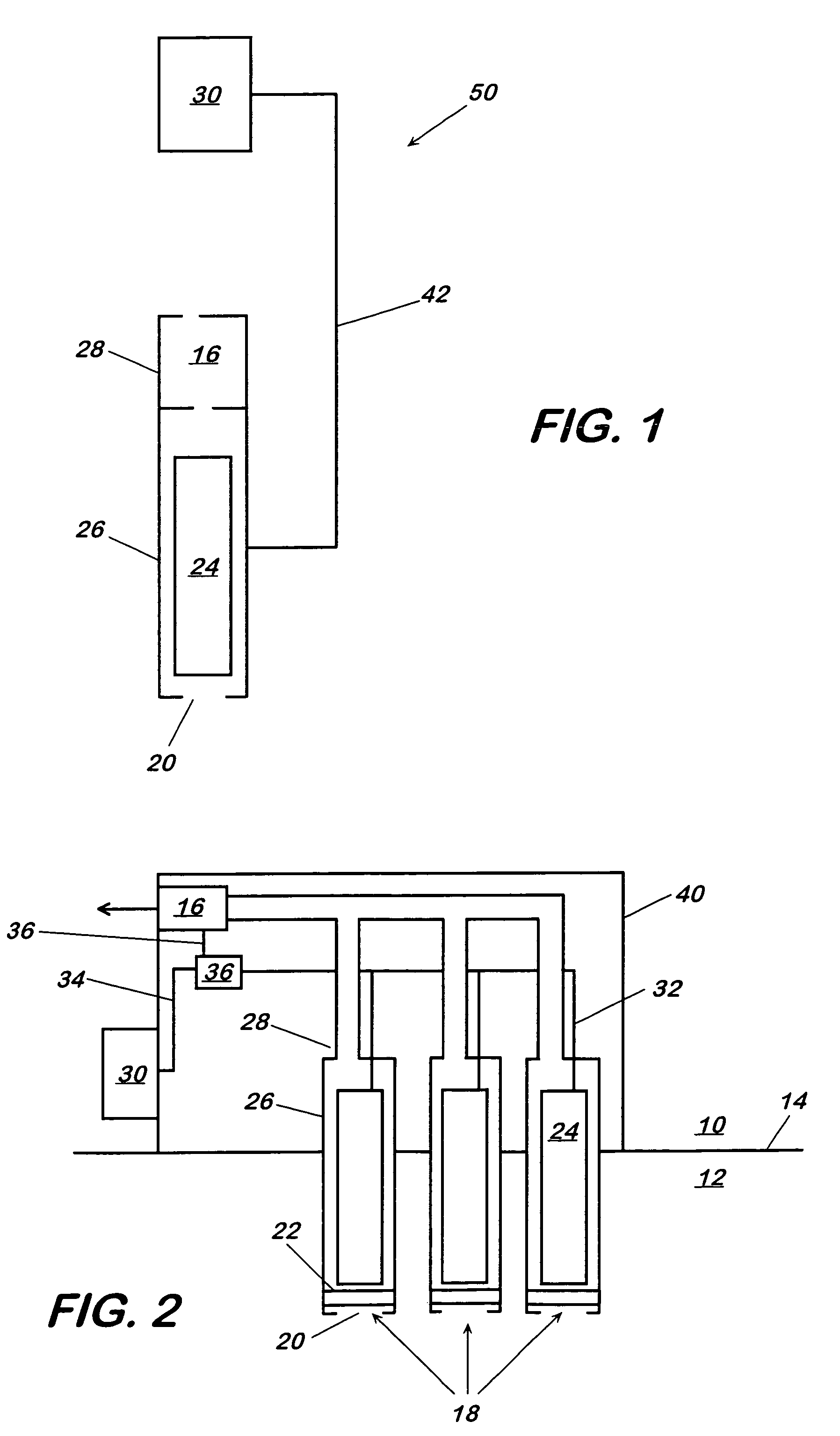
Method and apparatus for generating power from voltage gradients at sediment-water interfaces
A method and apparatus for generating power from voltage gradients at sediment-water interfaces or within stratified euxinic water-columns is provided. Natural voltage gradients typically exist at and about sediment-water interfaces or in isolated water bodies. One electrode (anode) is positioned in the sediment or water just below the redox boundary and the other electrode (cathode) is positioned in the water above the redox boundary over the first electrode. The anode is lower in voltage than the cathode. Current will flow when the electrodes are connected through a load, and near-perpetual generating of worthwhile power may be sustained by the net oxidation of organic matter catalyzed by microorganisms.
Owner:NAVY SEC OF THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES +1
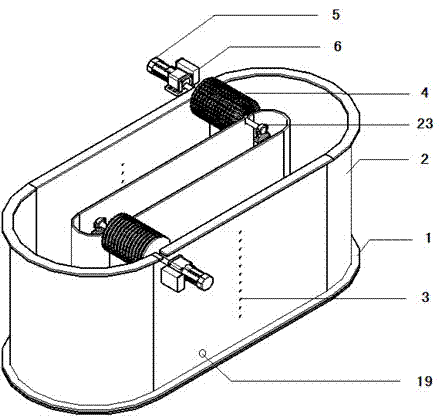
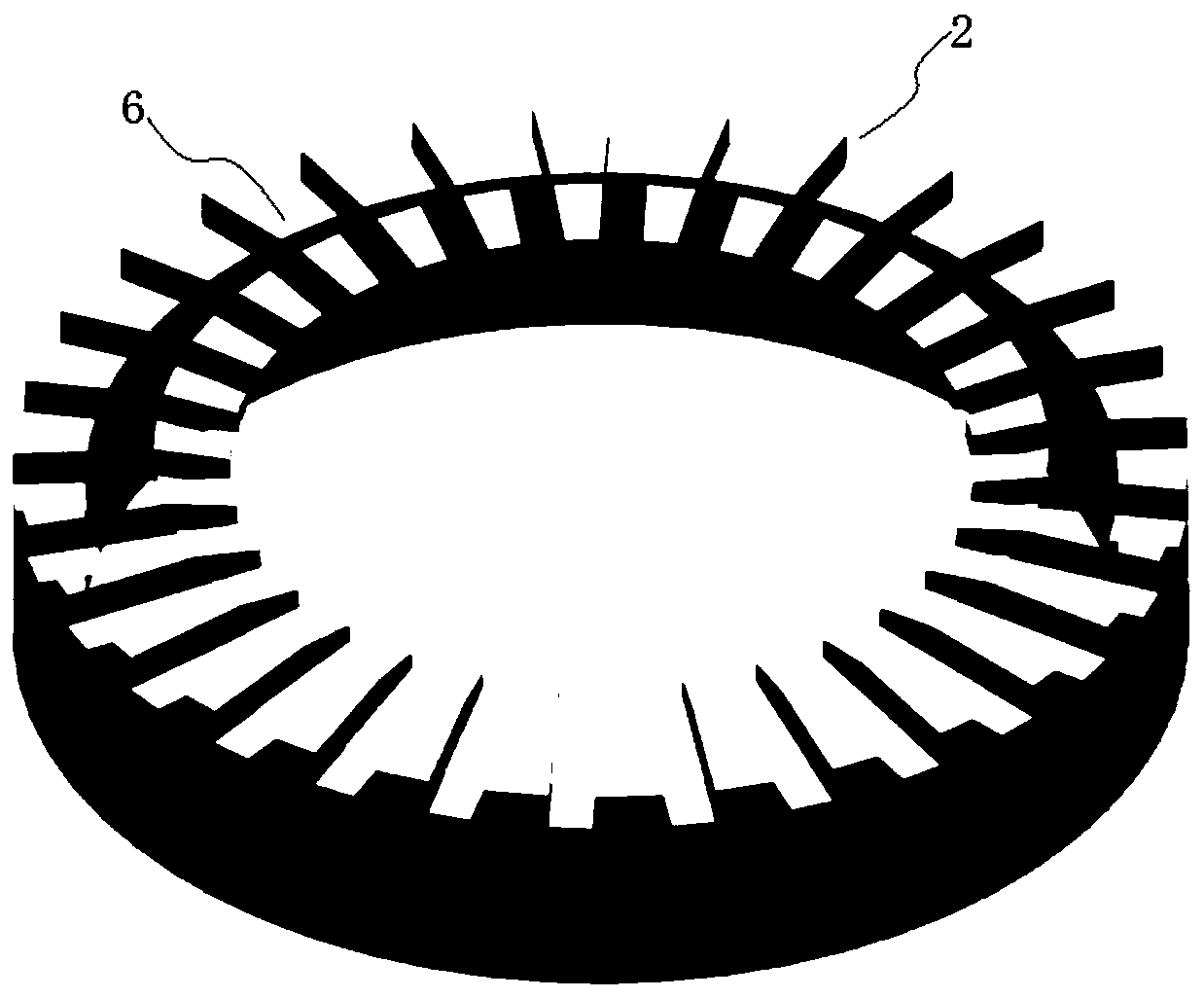
Undisturbed box type sampler for sediment on water surface layers
InactiveCN102607887AKeep intactClear water-soil interfaceWithdrawing sample devicesSurface layerEngineering
An undisturbed box type sampler for sediment on water surface layers comprises a mud acquiring bucket, a mud acquiring bucket carrying handle, an expansion bracket, a counterweight and a traction rope. The mud acquiring bucket carrying handle consists of a carrying handle upright column and a carrying handle crossbeam, the carrying handle upright column is fixedly connected with the mud acquiring bucket, small holes are arranged on the carrying handle crossbeam, the expansion bracket comprises an expansion bracket upper plate and an expansion bracket lower plate, expansion bracket upright columns are fixedly connected with the expansion bracket upper plate and the expansion bracket lower plate and fixed onto the expansion bracket lower plate, an expansion bracket strut and the expansion bracket upright columns penetrate through the small holes on the carrying handle crossbeam, a compression spring is sleeved on the expansion bracket strut, the mud acquiring bucket is provided with a square box and two symmetric mud acquiring claws, shaft heads are disposed on two sides of the box, the mud acquiring claws are rotationally connected with the shaft heads, a tension spring is connected between the mud acquiring claws, the mud acquiring claws are connected with suspension plates, the traction rope penetrates through the expansion bracket upper plate to be connected with the carrying handle crossbeam, and the other end of the traction rope penetrates out from a hole on the counterweight. The sampler has the advantages that a sediment-water interface of acquired sediment on a surface layer is clear, layers of the sediment keep well, a sampling process is undisturbed, and the volume of the acquired sediment can be accurately computed.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
Light enhancing oxygen-enriched organism structural system for synchronously repairing eutrophicated water bodies in rivers and lakes and sediments in situ
InactiveCN103332790ALow densityLarge specific surface areaBiological water/sewage treatmentTreatment effectEutrophication
The invention relates to an ecological repairing method of eutrophicated water bodies in rivers and lakes and sediments, and provides a construction method of an organism structural system for synchronously repairing eutrophicated water bodies in rivers and lakes and sediments in situ by means of emergent aquatic plants, submerged plants, benthonic animals, fishes and microorganisms. The light enhancing oxygen-enriched organism structural system for synchronously repairing eutrophicated water bodies in rivers and lakes and sediments in situ has the double effects of synchronously and ecologically repairing polluted water bodies and sediments and providing habitats for aquatic organisms and microorganisms. The system comprises a lens reflective light enhancing surface water emergent aquatic plant survival area, a hollow prismoid free sliding middle water purifying area, a sediment-water interface submerged plant, a benthonic animal and fish survival area, a microorganism enriched intensified sediment purifying area and an oxygen-enriching fixed rod. The system provided by the invention can synchronously and ecologically repair the water bodies and the surface sediments, has the characteristics of good pollutant removing effect, stable and lasting treatment effect and the like, and is suitable for synchronously repairing water bodies in rivers and lakes and sediments in situ.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Precise quantization method for nitrogen cycle of lake ecosystem
A precise quantization method for nitrogen cycle of a lake ecosystem includes 1), applying an isotope pairing method to quantitatively research nitrogen migration and conversion of a sediment-water interface of the lake ecosystem; 2), determining release of nitrogen of a water-gas interface by measuring N2O yield by the aid of a closed chamber-gas chromatograph method; 3), measuring biomass of aquatic plants and nitrogen content in bodies of the aquatic plants by the aid of a Dumas method and determining nitrogen absorbed quantity of the aquatic plants; 4), measuring biomass of microorganisms in the ecosystem by the aid of an MPN (most probable number) method, and measuring the effect of the microorganisms in a nitrogen conversion process and conversion quantity of the microorganisms to the nitrogen; and 5), applying the stable isotope technology to measure assimilation of aquatic animals to the nitrogen, and realizing precise quantization of the nitrogen, namely, measuring a food web of the aquatic animals and a trophic-level structure to determine migration and conversion of the nitrogen in the food web. Procedures of the precise quantization method are realized in the same simulation ecosystem.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Large deep lake water ecosystem restoration method
ActiveCN105152346AEfficient degradationEffective absorptionSustainable biological treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentRestoration methodSelf purification
The invention discloses a large deep lake water ecosystem restoration method. The large deep lake water ecosystem restoration method adopts basic condition improvement, a lake reservoir fencing net separation and partition technology, a transitional zone wash-preventing technology system, an inflow water front-arranged reservoir pre-treatment system, an ecological plant floating island construction, planting of submerged plants and floating-leaf vegetations in a planting area, spreading and planting of submerged vegetations in a deep-water area, a food network chain establishment, repair and management technology system, a sediment-water interface nutrient salt control system, a microbial membrane strengthening system, a species diversity habitat system and a lake water ecosystem protection technology. By the adoption of the large deep lake water ecosystem restoration method, the water body pollution load is effectively reduced, the water self-purification ability is improved, and a water body can be clear and be free of color and smell and accordingly is suitable for human to use.
Owner:绵阳市靓固建设工程有限公司
Method for acquiring two-dimensional distribution of sediment dissolved reactive phosphorus (DRP)
ActiveCN102507471AHigh-resolutionUniform and dense distributionColor/spectral properties measurementsDiffusionSolid content
The invention discloses a method for acquiring two-dimensional distribution of sediment dissolved reactive phosphorus (DRP), which comprises: vertically placing a diffusion gradient in thin-films (DGT) device containing a modified phosphorus immobilizing film in a sediment to extract the DRP in the section of the sediment by using modified ZrO2 polyacrylamide gel thin film, in which the particle size of zirconium dioxide is less than or equal to 5mu m, as a phosphorus immobilizing film based on a DGT principle, and keeping 3 to 5 centimeters of overlying water; marking a sediment-water interface, taking out the immobilizing film, and performing two-dimensional and submillimeter slicing on the part below the interface; and extracting the DRP in the slices by using NaOH, measuring the DRP content in the extract by using microcolorimetry, converting the DRP content into the DRP solid content in the slices, calculating the DRP concentration at the corresponding position in the section of the sediment based on Fick's first law of diffusion, and drawing a two-dimensional distribution map.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
Device and method for study on release of heavy metals and/or phosphate in sediments
InactiveCN103364473AImprove applicabilityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPeristaltic pumpPhosphate
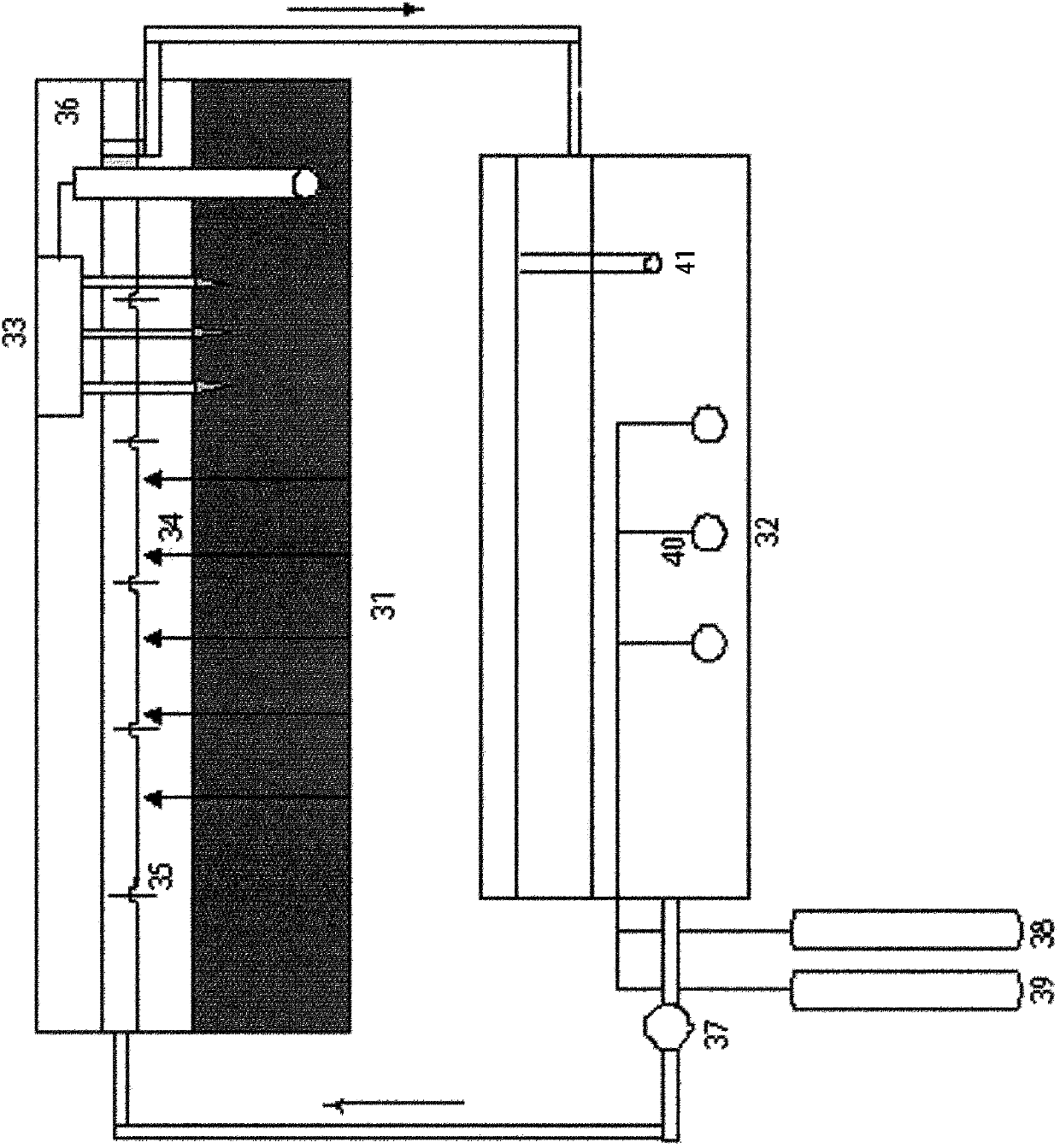
Provided is a device for study on release of heavy metals and / or phosphate in sediments. The main body of the device is a sediment-water interface system and a dissolved oxygen control device. The sediment-water interface system is composed of a tank. The bottom of the water tank is parallelly inserted with a plurality of sets of plate-type DGTs along the length direction of the central line. A microelectrode control system is arranged at the top of the water tank. The microelectrode control system is composed of a four-channel host, a motor controller, and pH, DO, ORP probes. Both sides of the tank are engraved with grooves. Staggered baffle plates are arranged in the grooves. A joint is arranged at one end of the water tank and connected with the dissolved oxygen control device through a peristaltic pump. A joint of the other end of the water tank is close to the upper liquid surface and connected with the dissolved oxygen control device directly. The dissolved oxygen control device is a water tank. The water tank contains a filtered water sample inside. Two joints are arranged at the top of the tank. One ends of the joints are respectively connected with a N2 steel cylinder and an O2 steel cylinder. The other ends of the joints are connected with aeration heads. The aeration heads extend into water for aeration. The invention also discloses a method for study on release of heavy metals and phosphate in sediments.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Method and apparatus for generating power from voltage gradients at sediment-water interfaces using active transport of sediment porewater
ActiveUS20060172186A1Reduced specieElectrolyte moving arrangementsFuel cells groupingEngineeringVoltage gradient
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Generator for simulating pollution release process of aquatic plants to sediments and use method
InactiveCN102539644AImprove sampling accuracyStable Pollution Release ConditionsTesting waterMeasuring instrumentOrganic glass
The invention relates to a generator for simulating the pollution release process of aquatic plants to sediments and a preparation method of the generator, and belongs to the field of environment protection. The generator comprises an organic glass annular water tank, a water flow pushing motive power system and a flow speed measuring fixing device. The dimension of the water tank is determined according to the test requirements, the cross section is in a triangular shape, the height is 50 to 100cm, the radio of the length to the width of the straight passage part is not smaller than 4, and the bent passage inner diameter is not smaller than 10cm. Sediments with the thickness being 15cm are paved at the bottom of the water tank, the aquatic plants are planted on the sediments for simulating the natural water body for growing the aquatic plants, a rotating disc arranged on the water body surface is driven through an adjustable motor, the water body in the tank is driven to flow to simulate the disturbance effect of the wind-driven flow formed by the natural water body under different wind fields on the bottom sediments, a flow speed measuring instrument is precisely positioned through the flow speed measuring fixing device, and the water flow movement condition of the water tank cross section, particularly the sediment-water interface is observed. The generator can be used for perfectly simulating the pollution release influence process on the sediments, caused by the lake aquatic plants under the different-intensity wind field effects.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
In-situ combination method used for surface water black odorous sediment remediation
InactiveCN105668965AAchieve fixAchieve release controlSludge treatmentWater contaminantsSediment remediationSorbent
The invention belongs to the technical field of environment protection and particularly relates to an in-situ combination method used for surface water black odorous sediment remediation. The method includes: adding zeolite modified by zirconium to a position above a sediment-water interface, and stirring or hydraulically disturbing to mix sediment with the zeolite modified by the zirconium; injecting nitrate into the sediment; adding the zeolite modified by the zirconium and zeolite to the position above the sediment-water interface to form a first covering system; covering the first covering system with a second covering system built by geotechnical cloth wrapping special absorbent materials; continuously remedying for a certain period of time, then removing the second covering system, and allowing the first covering system to be still placed at the position above the sediment-water interface. The method has the advantages that the method combines nitrate injection, adding of the zeolite modified by the zirconium, covering by the zeolite / zeolite modified by the zirconium mixture and covering by the geotechnical cloth wrapping the special absorbent materials to remedy the black odorous sediment and control the release of sediment ammonia, nitrogen and total phosphorus, and the method can effectively prevent the nitrate from leaking into overlying water.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
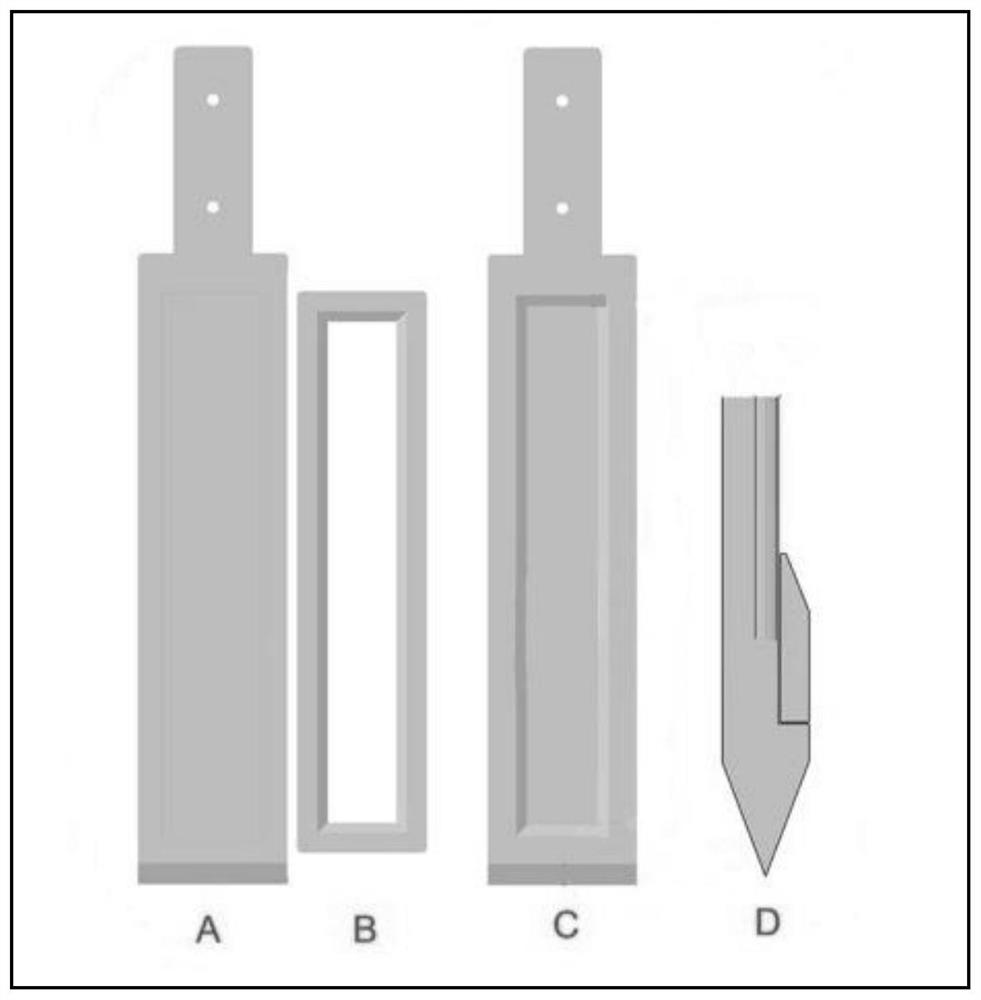
Passive sampler for high-resolution determination of freely dissolved pollutant concentration of pore water
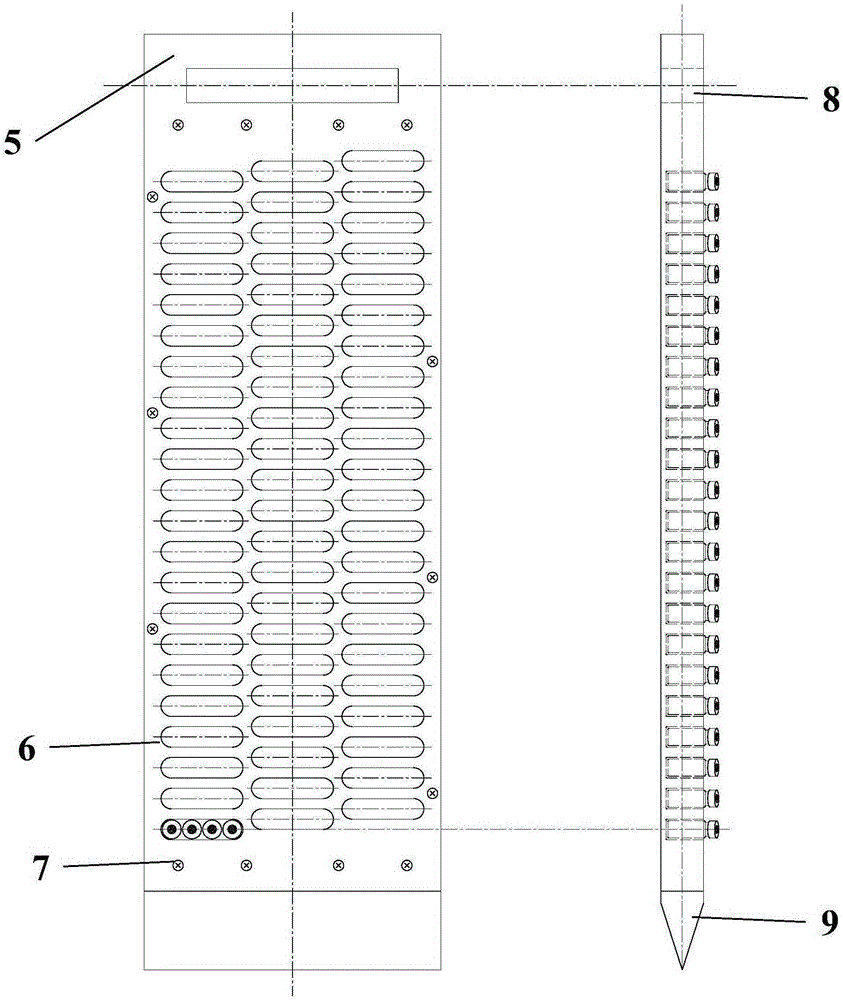
InactiveCN105784415AIncrease vertical resolutionEasy to disassembleWithdrawing sample devicesLow-density polyethyleneEngineering
The invention discloses a passive sampler for high-resolution determination of the freely dissolved pollutant concentration of pore water and belongs to the field of environmental research.The device includes a supporting frame, an inorganic pollutant passive unit and an organic pollutant sampling unit.The supporting frame of the passive sampler is I-shaped, and grooves are formed in stainless steel plates of two fixing faces on both sides.A whole system is kept in a vertical state and is inserted into a water body sediment by utilizing the self gravity of the system and combining with a bottom wedge-shaped tip.After balance is performed for a period of time, the determination of the typical inorganic pollutant and organic pollutant concentrations of the sediment pore water is achieved through dialysis balancing and low-density polyethylene film enrichment respectively.A small inorganic passive sampling bottle and an organic passive sampling film are taken in a layered mode, the typical inorganic pollutant and organic pollutant concentrations are respectively determined according to corresponding treatment methods, and accordingly a high-resolution freely dissolved pollutant concentration profile in the vertical direction of a sediment-water interface is obtained.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
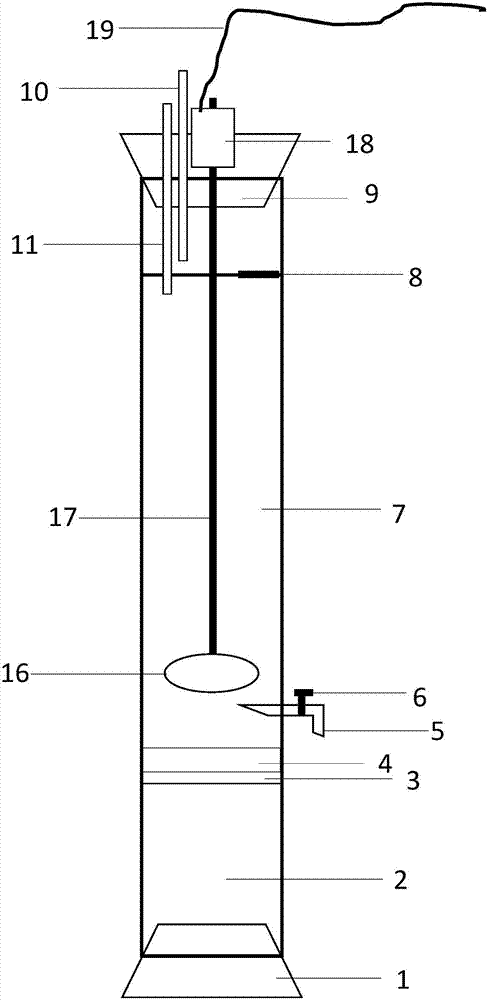
Indoor simulated system applied in lake sediment-water interface process research
InactiveCN101172668ATemperature controlReduce work intensityWater/sewage treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentWater bathsSea surface temperature
The invention provides an indoor simulation system used for the process study between the sediments and the water surface of a lake. The indoor simulation system mainly comprises a water power disturbance system, an illuminating system, a constant-temperature water bathing system and an automatic sampling system. The invention has the advantages that the lake sediments are collected and directly put into a heat reserving box, the surface water power disturbance, the surface illumination, the surface temperature and the overlying water chemical features can be manually controlled, and long-time operation and multi-sampling are also available, without influencing the sediments and the surface process; the invention can, in fairly large scope, satisfy the requirements of the scheduled experimental conditions, so as to achieve the basic requirements of the researchers on studying the surface chemical or biological process. The system, being reliable and cheap, has advantages of compact structure, stable operation, long-time continuous running and long service life as well as convenient component disassembly-assembly and low cost.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
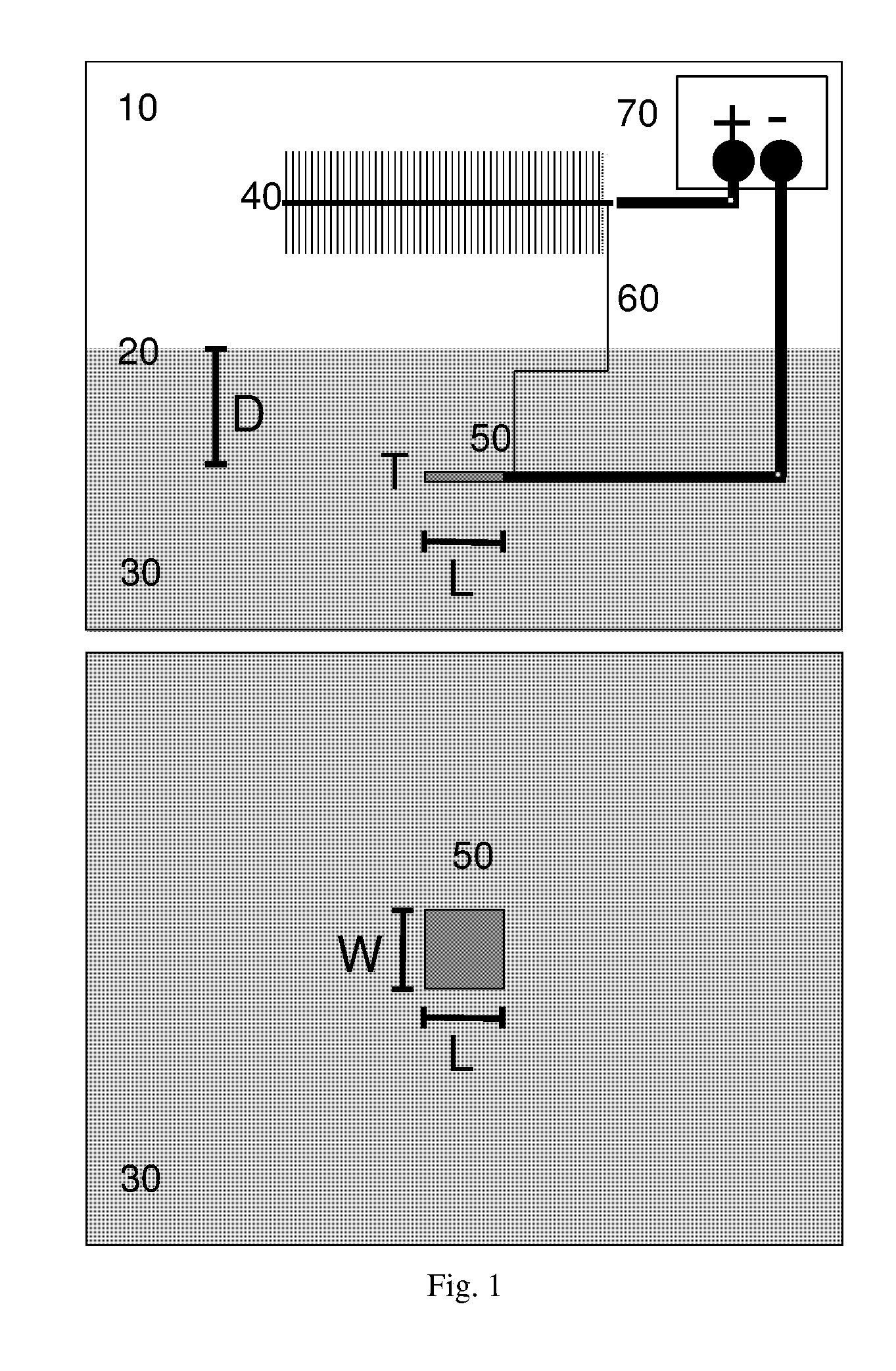
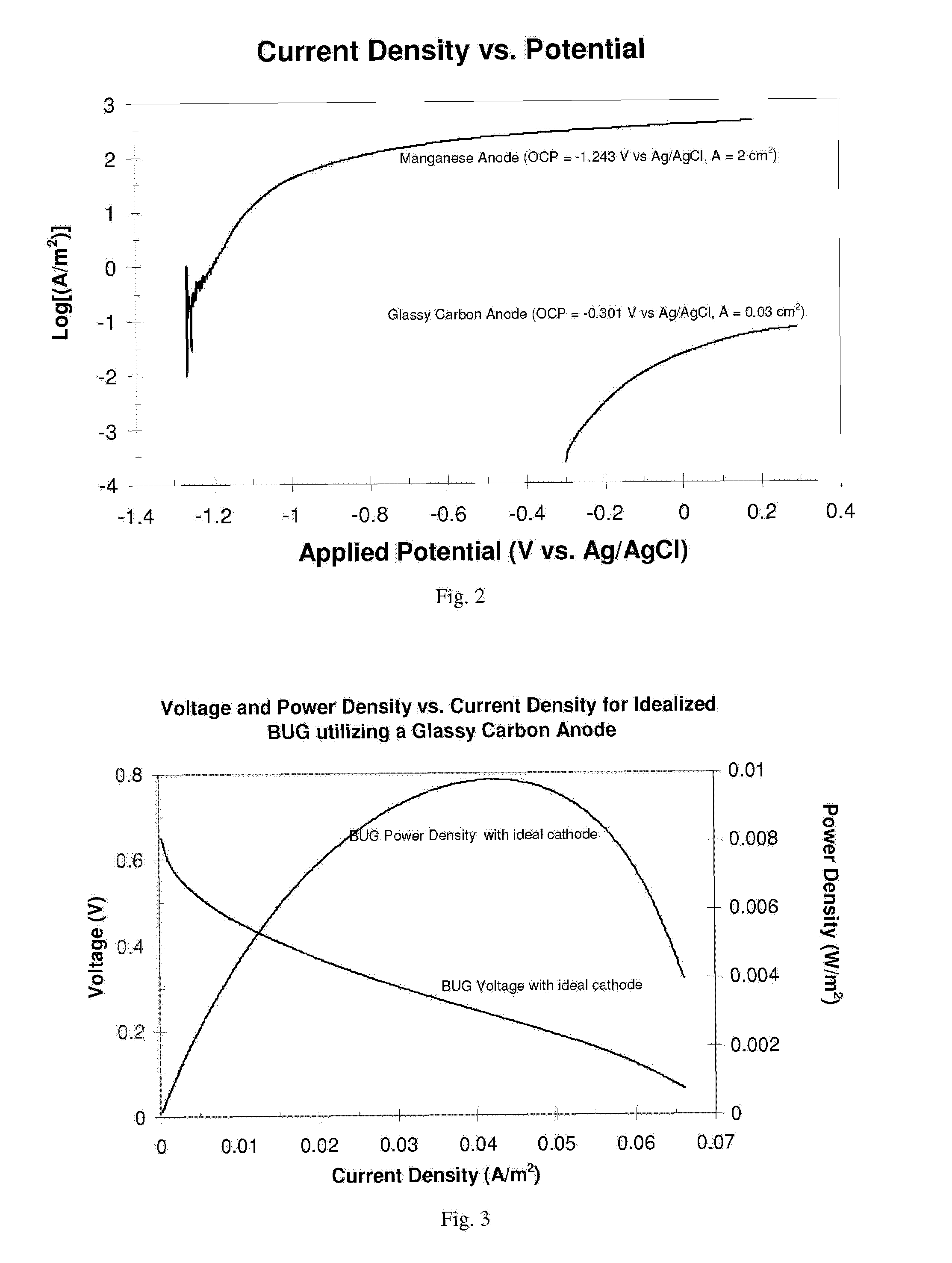
Apparatus equipped with metallic manganese anode for generating power from voltage gradients at the sediment-water interface
An apparatus having a metallic manganese anode; a cathode capable of reducing at least one species found in marine water; and a rig coupled to the anode and the cathode capable of maintaining the anode below a marine sediment surface and maintaining the cathode above marine the sediment surface. A method of generating power by: positioning in marine sediment a metallic manganese anode; positioning in marine water a cathode capable of reducing at least one species found in marine water; and connecting electrical leads between the anode, the cathode, and an electrical load.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Synchronous measuring sediment pore-water inorganic and organic matter concentration passive sampler
InactiveCN106546448ASimultaneous determination of free dissolved concentrationIncrease vertical resolutionWithdrawing sample devicesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansUltrapure waterChemical substance
The invention discloses a synchronous measuring sediment pore-water inorganic and organic matter concentration passive sampler, and belongs to the field of environmental research. The synchronous measuring sediment pore-water inorganic and organic matter concentration passive sampler comprises a passive sampling system and a supporting framework. In applications, sampling small bottles are filled with ultrapure water, are preloaded with different chemicals or articles based on the difference of pollutants, are covered with 0.45<mu>m microfiltration membrane, and are sealed with bottle caps provided with middle holes; the sampling small bottles are placed in grooves in the supporting framework; the whole synchronous measuring sediment pore-water inorganic and organic matter concentration passive sampler is immersed into water body sediment vertically under the action of self weight, and is allowed to stand; when balance is achieved, the synchronous measuring sediment pore-water inorganic and organic matter concentration passive sampler and the passive sampling small bottles are taken out from the water body sediment; and the concentrations of nutritive salts, heavy metals, and organic pollutants in wate samples in the passive sampling small bottles are measured via corresponding methods, so that synchronous measuring of high resolution ratio sediment-water interface inorganic and organic pollutant concentration is realized.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Lake endogenesis control brick and use method thereof
ActiveCN104445627AReduce disturbanceImprove adsorption capacityWater contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesIron saltsBrick
The invention provides a lake endogenesis control brick and a use method thereof. The brick is prepared by steps as follows: (1), bottom sediment of a lake is taken, and content of iron and phosphorus in the bottom sediment is measured; (2), iron salt is added to the bottom sediment and mixed; (3), a mixture obtained from step (2) is air-dried, and a green brick is prepared from the mixture when the moisture content is 50 wt%-60 wt% after air-drying; (4), the green brick is dried in the shade for 2-3 days and then sintered; (5), a plurality of planting holes are punched in the sintered brick; and (6), submerged plants are planted in the planting holes, and the lake endogenesis control brick is obtained. After the lake endogenesis control brick is placed in the lake, the shearing force of bottom water and disturbance of water flowing to sediment can be reduced, so that release of nutrient salt suspended on the sediment is reduced, the chemical property of the sediment-water interface can be effectively improved by adjusting iron-phosphorus ratio of the sediment water interface, stability of phosphorus in the sediment is improved, and the planting and amplification capability of the submerged plants is enhanced.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
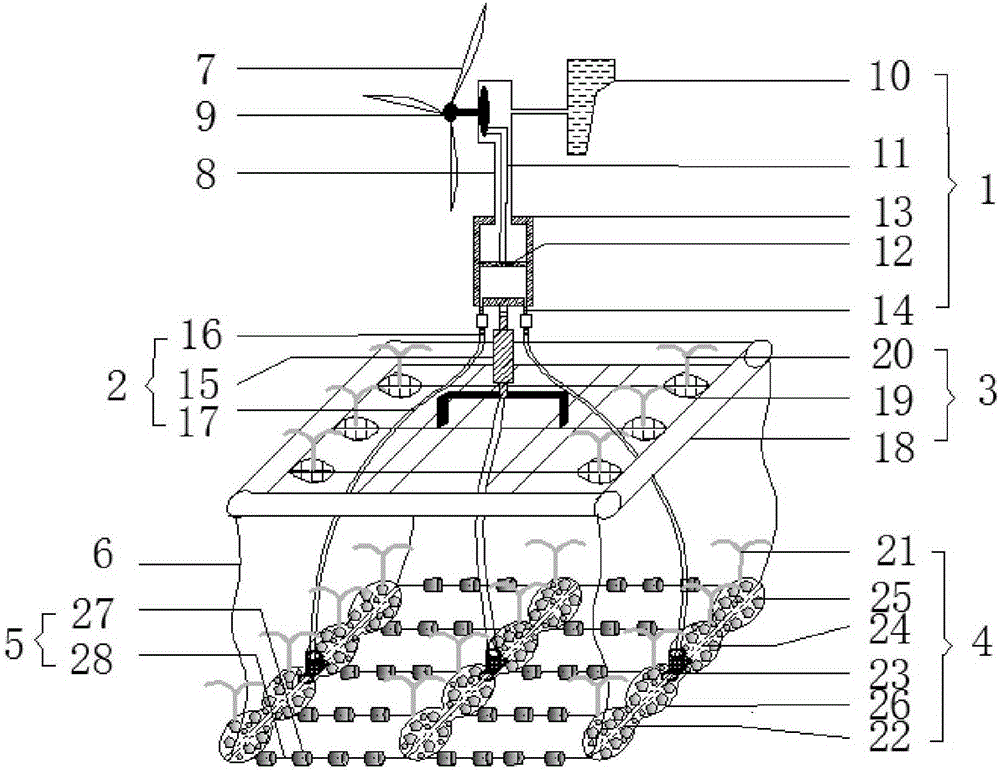
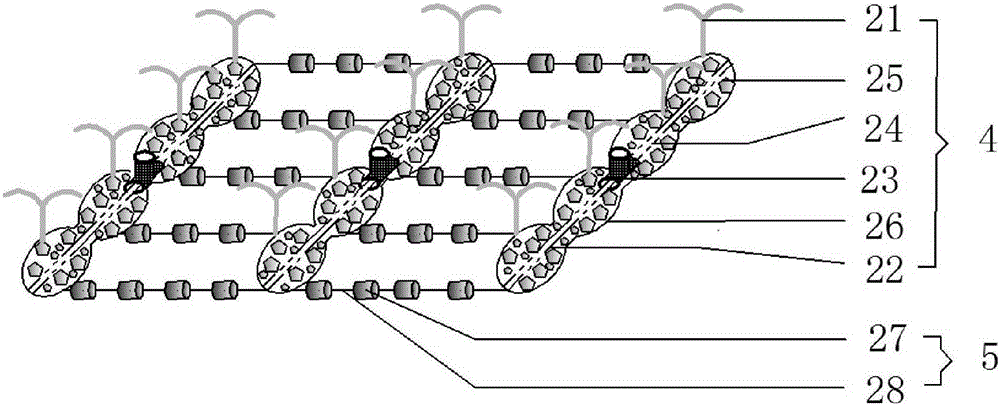
Lotus-root-shaped eutrophic sediment remediation system capable of aeration
InactiveCN105236583APrevent resuspensionGood water permeabilitySustainable biological treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentEutrophicationSediment remediation
Owner:HOHAI UNIV +1
Modified nitrogen control material prepared from lake sediments, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106000283AGood effectIncrease cation exchange capacityOther chemical processesWater contaminantsFreeze-dryingRaw material
The invention relates to a modified nitrogen control material prepared from lake sediments, a preparation method and application thereof. The method includes: collecting lake sediments, conducting freeze drying, grinding and sieving for standby use; then subjecting the treated lake sediments to constant temperature heating treatment, then performing cooling, and adding zeolite into the sediments in proportion, mixing the materials evenly, then adding a mixed solution of a salt solution and an alkaline solution, carrying out oscillation impregnation modification, then conducting filtering and cooling to obtain residue, i.e. the sediment modified nitrogen control material. The method provided by the invention adopts lake sediments as the raw materials, the prepared modified nitrogen control material has significantly enhanced ammonia nitrogen adsorption performance, especially has good ammonia nitrogen removal effect on lake sediment interstitial water, the materials are cheap, the safety is high, the social and economical benefits are good, also the material has no ecological risk to lake water, is energy saving and environment-friendly, and can be applied to the lake sediment-water interface nitrogen pollution control field.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Preparation method and application of sediment endogenous phosphorus load control bottom sediment modified material
ActiveCN106277673ADesorption does not occur easilyIncrease the adsorption-desorption equilibrium concentrationSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningSludge treatment by thermal conditioningPhosphateWater quality
The invention provides a preparation method and application of a sediment endogenous phosphorus load control bottom sediment modified material. With creatively lake sediments being basic materials, by the utilization of the processes of modifying, granulating, calcining and others of zeolite and aluminum polychlorid, the adsorption-desorption balance concentration of the material for phosphate is obviously reduced, and the maximum adsorbing quantity of the material is increased. By in-situ simulation of a sediment-water interface phosphate release process, it is proved that the material can effectively restrain release of sediment-water interface phosphate; because the desorption capacity of the material for the phosphate is low, and the adsorption capacity is large, the material can really achieve sediment endogenous phosphorus load control, and the purpose of improving the water quality of a lake / reservoir is achieved. Taken materials are cheap, and the material has good economic benefits and high safety and has no ecological risks for a water body of the lake, saves energy, is environmentally-friendly and achieves an obvious control effect on sediment-water interface phosphorus release at different lake regions of the Dian lake during application.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Preparation method and application of sediment-water interface phosphorus release control material
ActiveCN106277672ADecrease the adsorption-desorption equilibrium concentrationLess materialFixation/solidifcation sludge treatmentContaminated waterways/lakes/ponds/rivers treatmentIron saltsPhosphate
The invention provides a preparation method and application of a sediment-water interface phosphorus release control material. For the first time, a lake sediment and kaolin mixture is used as a basic raw material, and processes like oxidation, iron salt modification, granulation and calcination are adopted, so that adsorption-desorption balance concentration EPC0 value of the material to phosphate is remarkably lowered, linear distribution coefficient Kd value of the material is increased, and the material can effectively reduce sediment interstitial water phosphate concentration and can inhibit sediment-water interface phosphate release. The material itself has weak phosphate desorption capability and high adsorption and buffering capability, so that the material can truly realize effective obstruction and control on sediment-water interface phosphorus release. The material is low in material cost, high in social and economic benefit and safety, free of ecological risk to lake water, energy-saving and environment-friendly and has remarkable effect on controlling sediment-water interface phosphorus release in different lake areas of the Dian Lake in the process of application.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Method and apparatus for generating power from voltage gradients at sediment-water interfaces using active transport of sediment porewater
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Method for restoring existing lake water ecosystem
ActiveCN105152345AImprove the living environmentControl the trend of continued deterioration of eutrophication levelsSustainable biological treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentSelf purificationWater quality
The invention discloses a method for restoring an existing lake water ecosystem. According to the method, basic condition improvement (water level maintenance, water quality improvement and bottom mud improvement), a filamentous alga (spirogyra) preventing technology, a transitional zone flushing preventing technology system, a water inlet front reservoir treatment system, shallow water zone sinking and floating leaf vegetation planting, deep water zone sinking vegetation planting, food net chain rebuilding, a sediment-water interface biological system, a microbial film reinforcing system, a species diversity habitat system and an ecological water purification system long-acting management are included. Through the method, water pollution loads are effectively lowered, the water self-purification capacity is improved, water is clear and free of heterochrome and peculiar smells, and therefore the water is suitable for being touched by people.
Owner:绵阳市靓固建设工程有限公司
Preparation method and application of efficient removing materials for interstitial water phosphate of sediments
ActiveCN106311129ALess materialHigh porositySludge treatmentOther chemical processesPhosphateDesorption
The invention provides preparation method and application of efficient removing materials for interstitial water phosphate of sediments. Lake sediments are initiatively taken as basic materials of the materials and are subjected to calcination and alkaline washing, then the obtained material is mixed with kaolin, and mixed powder obtained is modified via ferric salt and then pore-forming agents are added for granulation and calcination shaping is peformed, and the low EPCo value and high Qmax value efficient removing materials for the interstitial water phosphate of the sediments are obtained. Concentration of the interstitial water phosphate of the sediments can be effectively cut down through the materials, and release of the phosphate of the sediments-water interfaces is restrained; desorption capacity of phosphate of the materials is weak and adsorption capacity is large, so that effective resistance and control of the materials on the sediments-water interfaces can be truly realized; the materials are low in cost, good in social and economic benefits, high in security, free of ecological risk on lake water, energy saving and environment friendly and remarkable in control effect on the sediments-water interfaces of different lakes of the Dian Lake during application.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
In-situ combination method used for sediment nitrogen and phosphorus release control
InactiveCN105668964AControl releaseProtection from dissolved oxygen oxidationSludge treatmentOther chemical processesSorbentEarth surface
The invention belongs to the technical field of environment protection and particularly relates to an in-situ combination method used for sediment nitrogen and phosphorus release control. The method includes: adding zeolite or zeolite modified by calcium to a position above a sediment-water interface, and mechanically stirring or hydraulically disturbing to mix sediment with the zeolite; adding magnetic absorbent containing zirconium to the position above the sediment-water interface, and using the applied magnetic field effect to remove the used magnetic absorbent containing the zirconium from water; preferably adding the magnetic absorbent containing the zirconium to the position above the sediment-water interface again. The method is low in destruction on a surface water demersal ecological system, can effectively control the release of sediment nitrogen and phosphorus, and is simple and convenient to operate.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Indoor simulated system applied in lake sediment-water interface process research
InactiveCN100548894CTemperature controlReduce work intensityWater/sewage treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentWater bathsEngineering
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
Evaluation method and device of control effect of lake sediment covering material
ActiveCN107121527AReduce environmental risksAvoid blindnessTesting waterWater qualityEnvironmental factor
The invention provides an evaluation method and a device of a control effect of a lake sediment covering material. The evaluation method initiatively considers the different physical and chemical properties, nitrogen and phosphorus forms and release characteristics of sediments in different lakes or different lake districts of the same lake, and evaluates the control effect of the covering material on the different types of the sediments by means of a real-time water quality monitoring system, a micro-interface measurement system, an environmental factor regulation system, system program control, data transmission and the like according to a sediment-water surface diffusion flux model on a basis of an in-situ sediment sampling technology, a sediment-water interface nitrogen-phosphorus release covering control technology, and evaluates an environmental risk of the covering material by regulating an environmental factor. According to the method and the device, a corresponding material covering project technology measure can be provided specifically to the different types of the sediments, so that project implementation blindness is avoided; the social economy cost is reduced; the environmental risk of material implementation is reduced.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
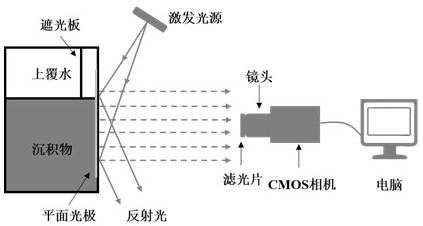
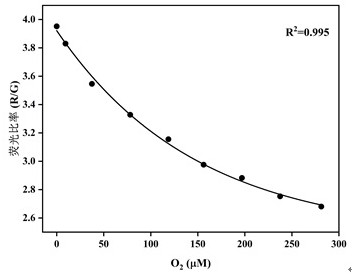
Preparation method of dissolved oxygen fluorescence sensing film and sediment-water interface dissolved oxygen two-dimensional dynamic distribution detection method
ActiveCN112098386AIncreased sensitivityShort reaction timePolyurea/polyurethane coatingsFluorescence/phosphorescenceSoil scienceFluorescence sensing
The invention discloses a preparation method of a dissolved oxygen fluorescence sensing film and a sediment-water interface dissolved oxygen two-dimensional dynamic distribution detection method, canaccurately obtain concentration dynamic change information of sediment-water interface two-dimensional and high-resolution (micrometre level) dissolved oxygen, and is suitable for the technical fieldof detection of sediment-water interface dissolved oxygen.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
A method applied to the restoration of large deep-water lake ecosystems
ActiveCN105152346BEfficient degradationEffective absorptionSustainable biological treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentRestoration methodWater quality
The invention discloses a large deep lake water ecosystem restoration method. The large deep lake water ecosystem restoration method adopts basic condition improvement, a lake reservoir fencing net separation and partition technology, a transitional zone wash-preventing technology system, an inflow water front-arranged reservoir pre-treatment system, an ecological plant floating island construction, planting of submerged plants and floating-leaf vegetations in a planting area, spreading and planting of submerged vegetations in a deep-water area, a food network chain establishment, repair and management technology system, a sediment-water interface nutrient salt control system, a microbial membrane strengthening system, a species diversity habitat system and a lake water ecosystem protection technology. By the adoption of the large deep lake water ecosystem restoration method, the water body pollution load is effectively reduced, the water self-purification ability is improved, and a water body can be clear and be free of color and smell and accordingly is suitable for human to use.
Owner:绵阳市靓固建设工程有限公司
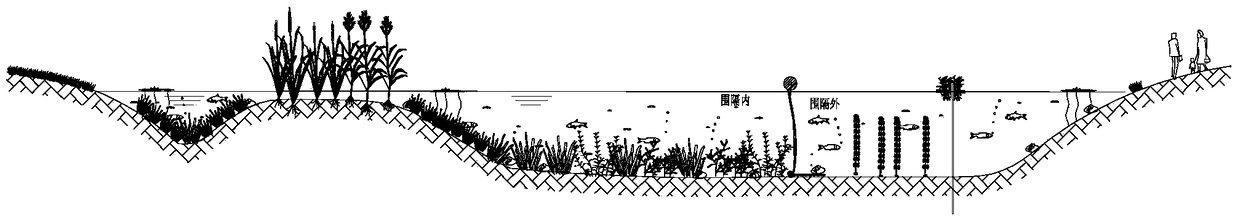
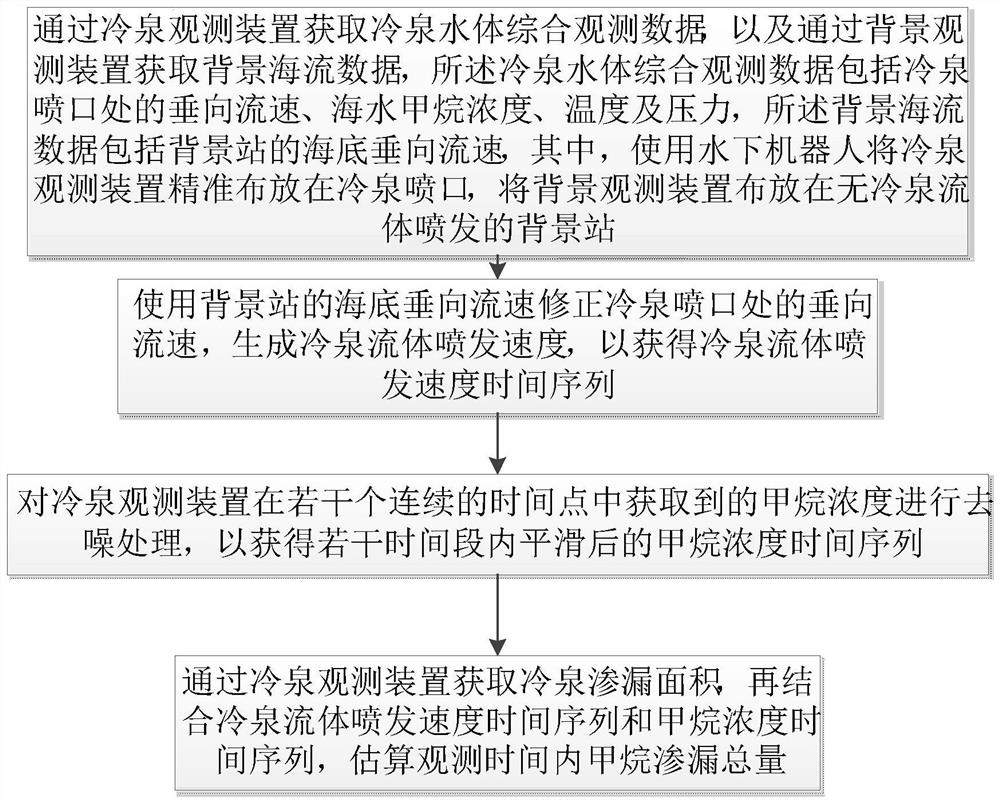
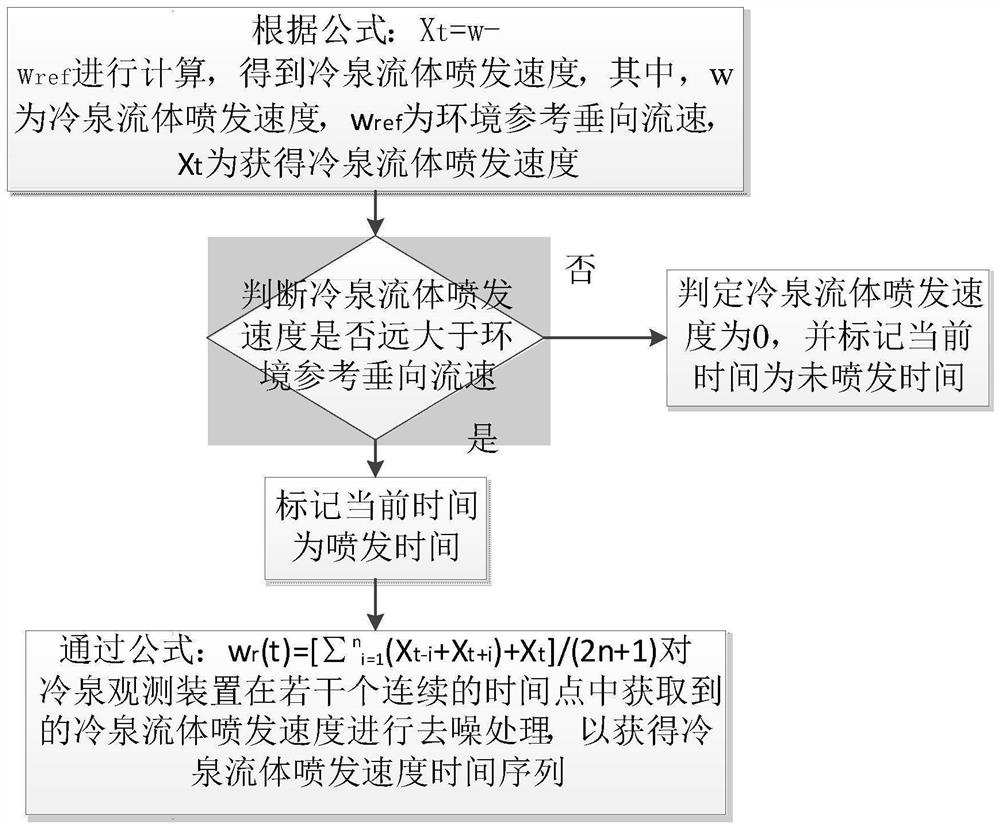
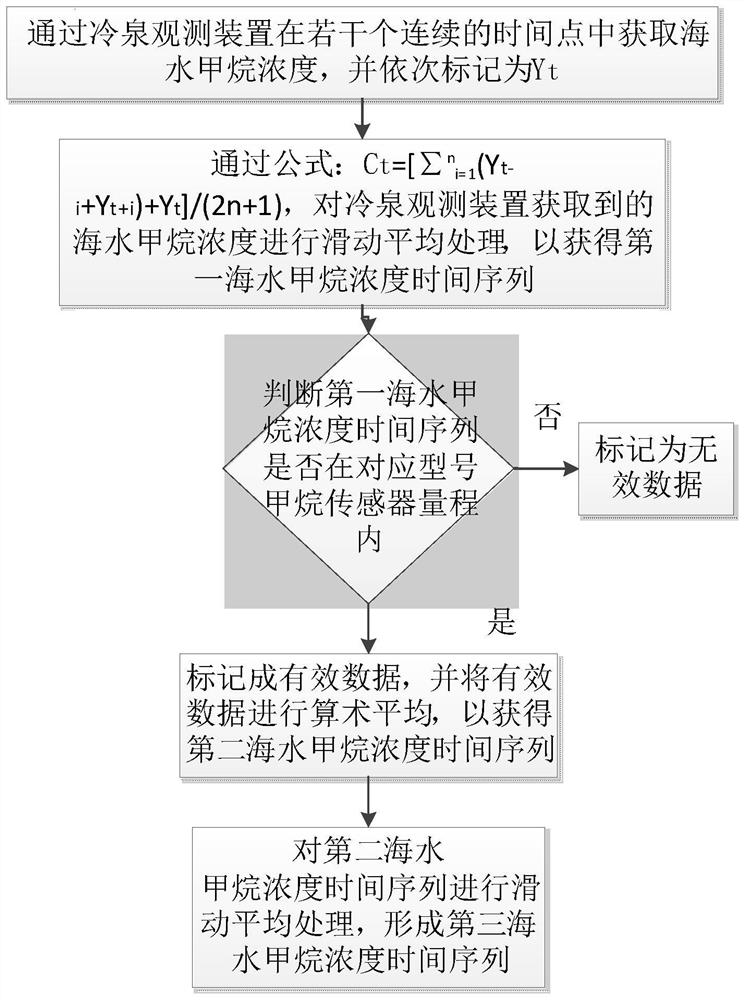
In-situ observation method for methane macro leakage strength of sediment-water interface in cold spring area
ActiveCN113932854ARealize synchronous observationMeasurement devicesWater resource assessmentObservational methodOcean observations
The invention discloses an in-situ observation method for the methane macro leakage strength of a sediment-water interface in a cold spring area. The in-situ observation method comprises the following steps that: comprehensive observation data of a cold spring water body are obtained through a cold spring observation device; a background vertical flow velocity is obtained through a background observation device, the cold spring fluid eruption velocity is corrected, and a cold spring fluid eruption velocity time sequence is obtained; the methane concentration obtained by a multi-range sensor in the cold spring observation device is smoothed, and a smoothed methane concentration time sequence within the time is obtained; the area of a cold spring nozzle is estimated through the cold spring observation device, and the methane leakage flux is calculated in combination with the cold spring fluid eruption velocity time sequence and the methane concentration time sequence. According to the invention, the simple combination of common ocean observation equipment is utilized to synchronously observe the seabed methane concentration and ocean dynamic environment elements in the cold spring region, so as to achieve the purpose of exploring the time evolution rule of the sediment-water interface methane macro leakage flux in the cold spring region.
Owner:GUANGDONG LAB OF SOUTHERN OCEAN SCI & ENG GUANGZHOU +1
In-situ sampling device, detection device and detection method for maximum diffusion flux of sediment-water interface pollutants
ActiveCN109781588AEarly warning release riskOvercome the disadvantages of forming an anaerobic stateWithdrawing sample devicesSurface/boundary effectEngineeringUltimate tensile strength
The invention discloses an in-situ sampling device, a detection device and a detection method for maximum diffusion flux of sediment-water interface pollutants. The sampling device comprises an annular upper shell, a fixed film and a lower shell, a groove used for containing the fixed film is formed in the top of the lower shell, the fixed film is arranged in the groove of the lower shell, a plurality of fins are arranged at the upper end edge of the annular upper shell at intervals, the annular upper shell sleeves the upper end of the lower shell and fixes the fixed film, and the average densities of the sampling device is larger than water densities. According to the invention, the maximum diffusion flux of sediments can be measured, the operation is convenient, and the experimental strength is relatively low; The applicability is high, and the types of target objects capable of being measured are wide; the size is small, and the release flux of the whole lake can be estimated through large-scale arrangement in the lake.
Owner:中科智感(南京)环境科技有限公司
Method for dividing sediment-water interface in water ecosystem
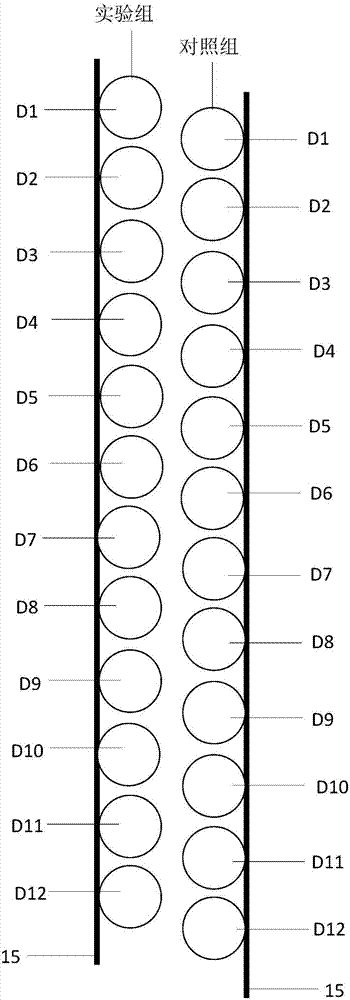
PendingCN114739870AAccurate divisionSurface/boundary effectSustainable biological treatmentAdsorptive membraneEnvironmental engineering
The invention relates to a method for dividing a sediment-water interface in a water ecosystem. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, collecting a sediment columnar core sample at a preset sampling point by utilizing a gravity type sediment sampler; step 2, placing the collected sediment columnar core sample in a constant-temperature water tank, and performing simulated culture under the condition that the temperature is close to that of a sampling point; step 3, acquiring vertical distribution characteristics of the concentration of a target object in the columnar core sample of the sediment by adopting a flat plate type DGT device; step 4, enabling the concentration of the target object on the adsorption film to correspond to the one-dimensional section of the columnar core sample of the sediment to obtain the concentration distribution of the one-dimensional section of the target object of the environmental medium or the micro-interface; and 5, dividing the concentration of the target object into intervals according to the gradient limit value, and marking different colors to finish division. According to the method, the sediment-water interface in the water ecosystem can be accurately divided, and a scientific basis is provided for in-depth research on migration and transformation rules and environmental behaviors of various pollutants on the sediment-water interface.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com