Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
59 results about "Cycle threshold" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
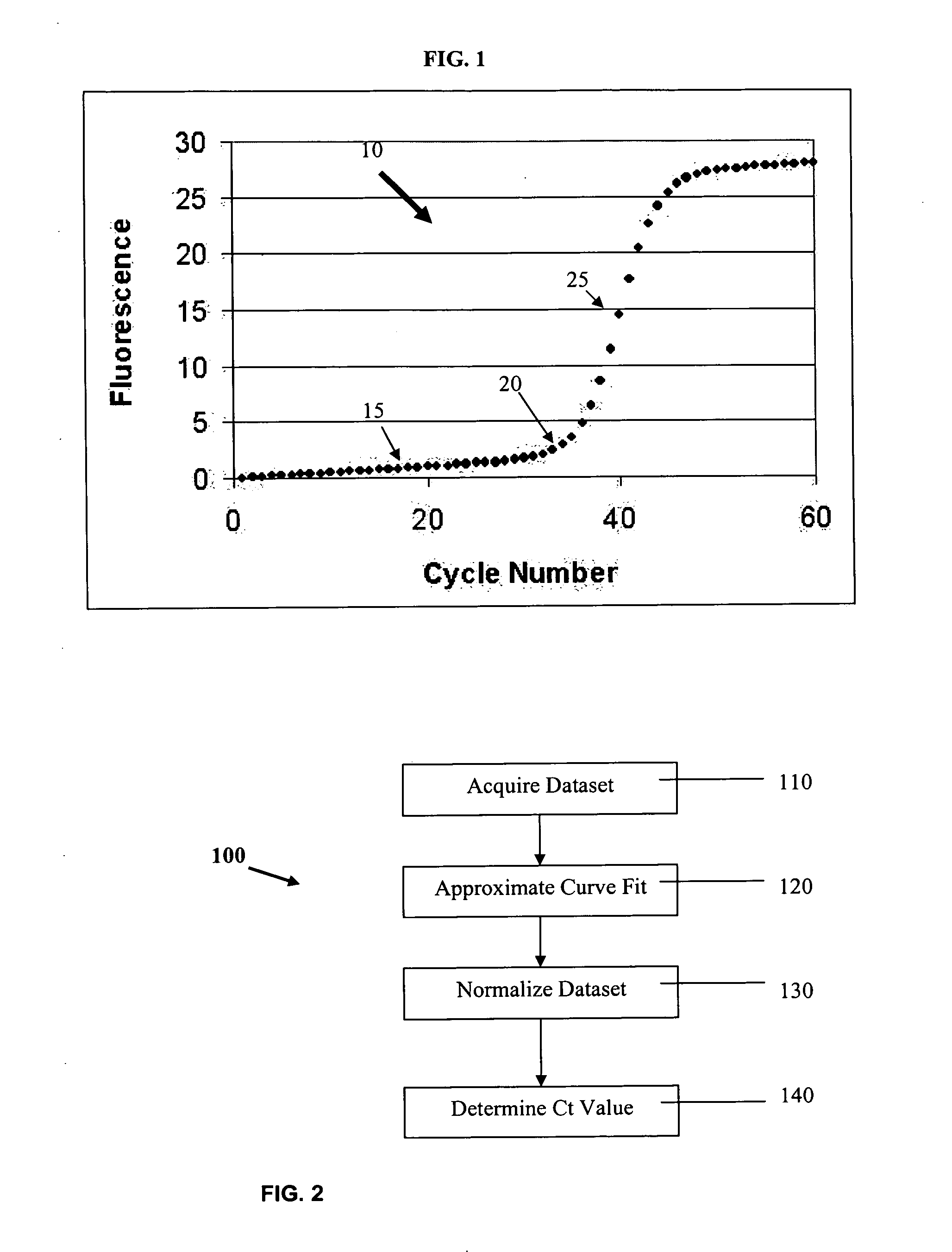
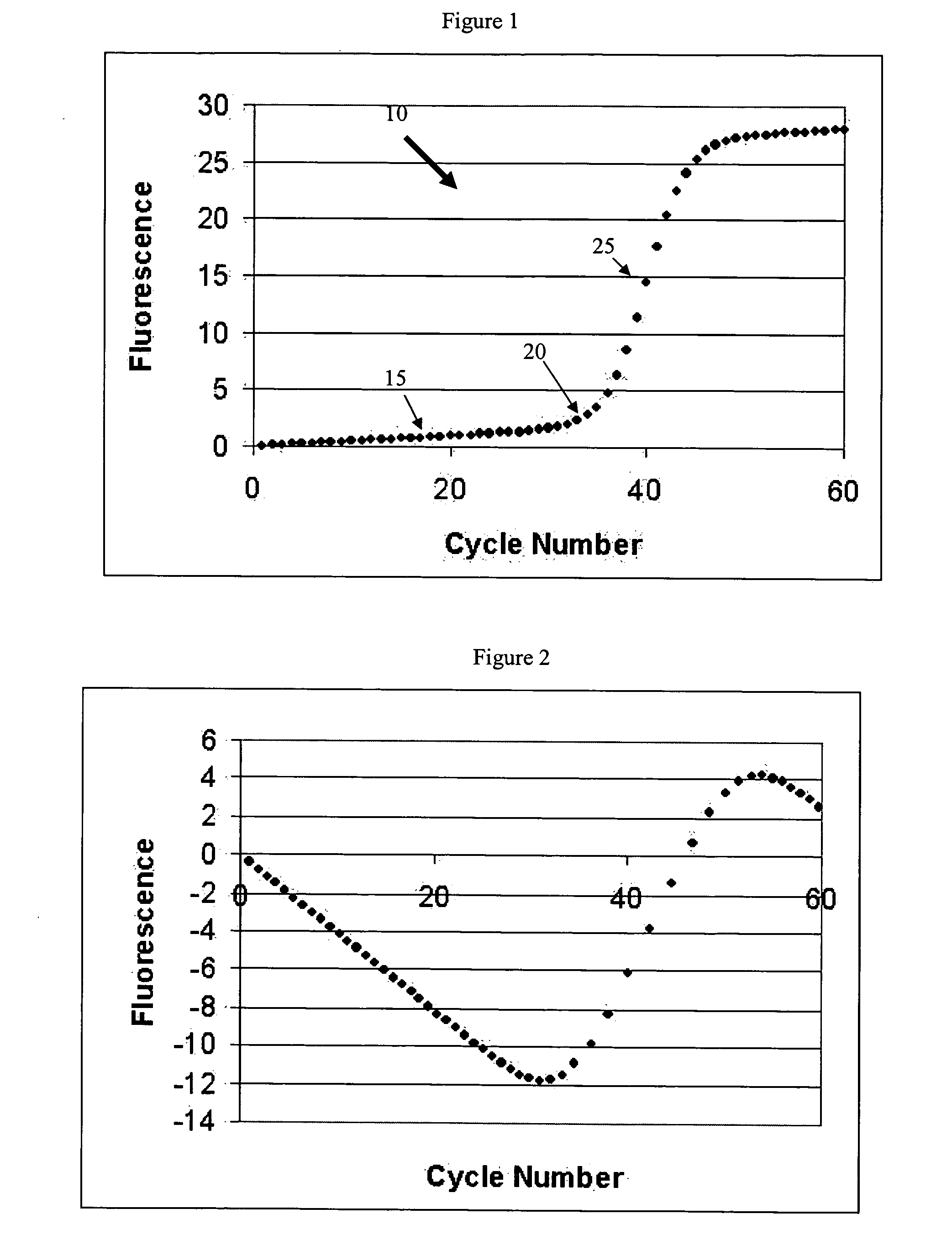
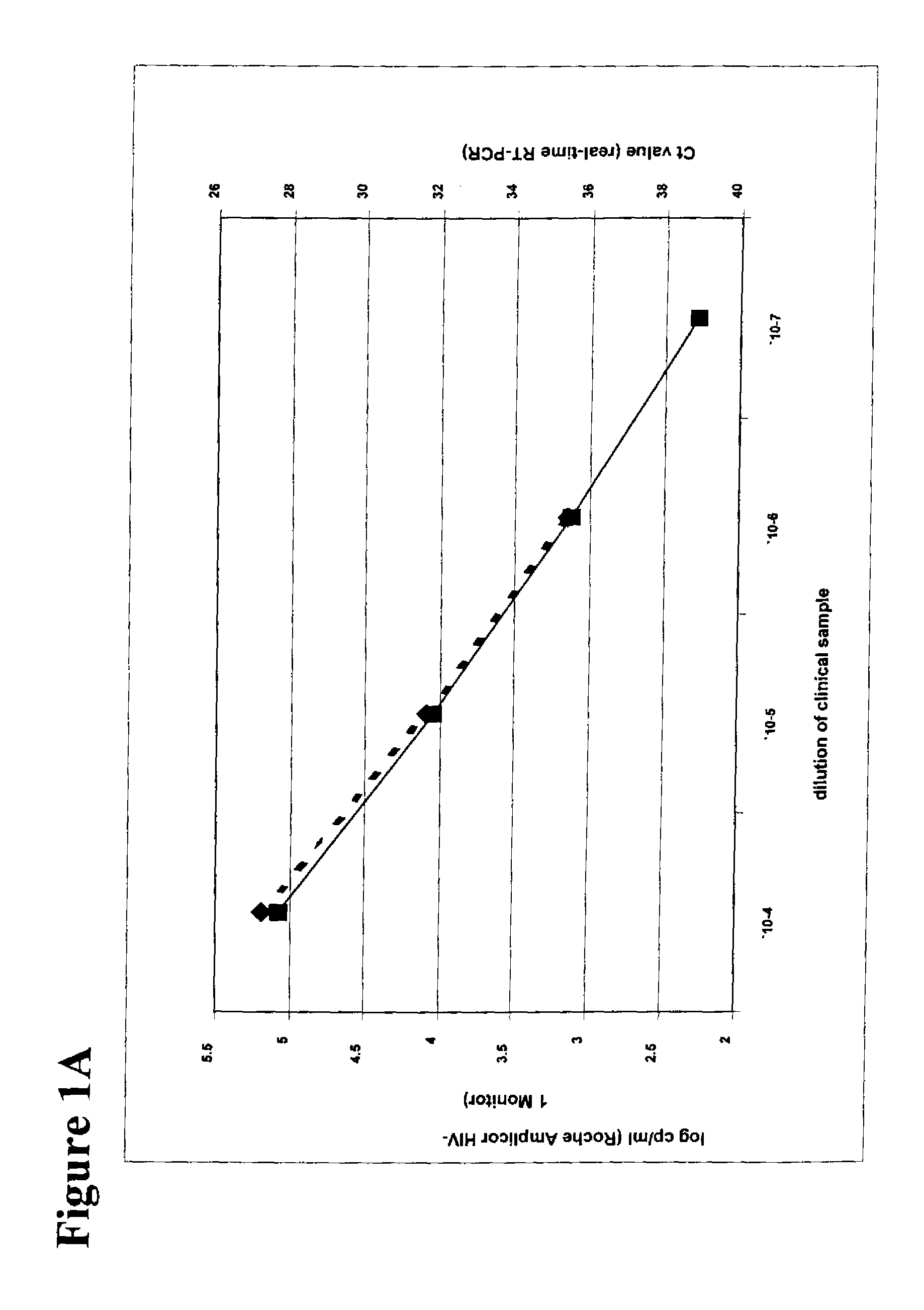
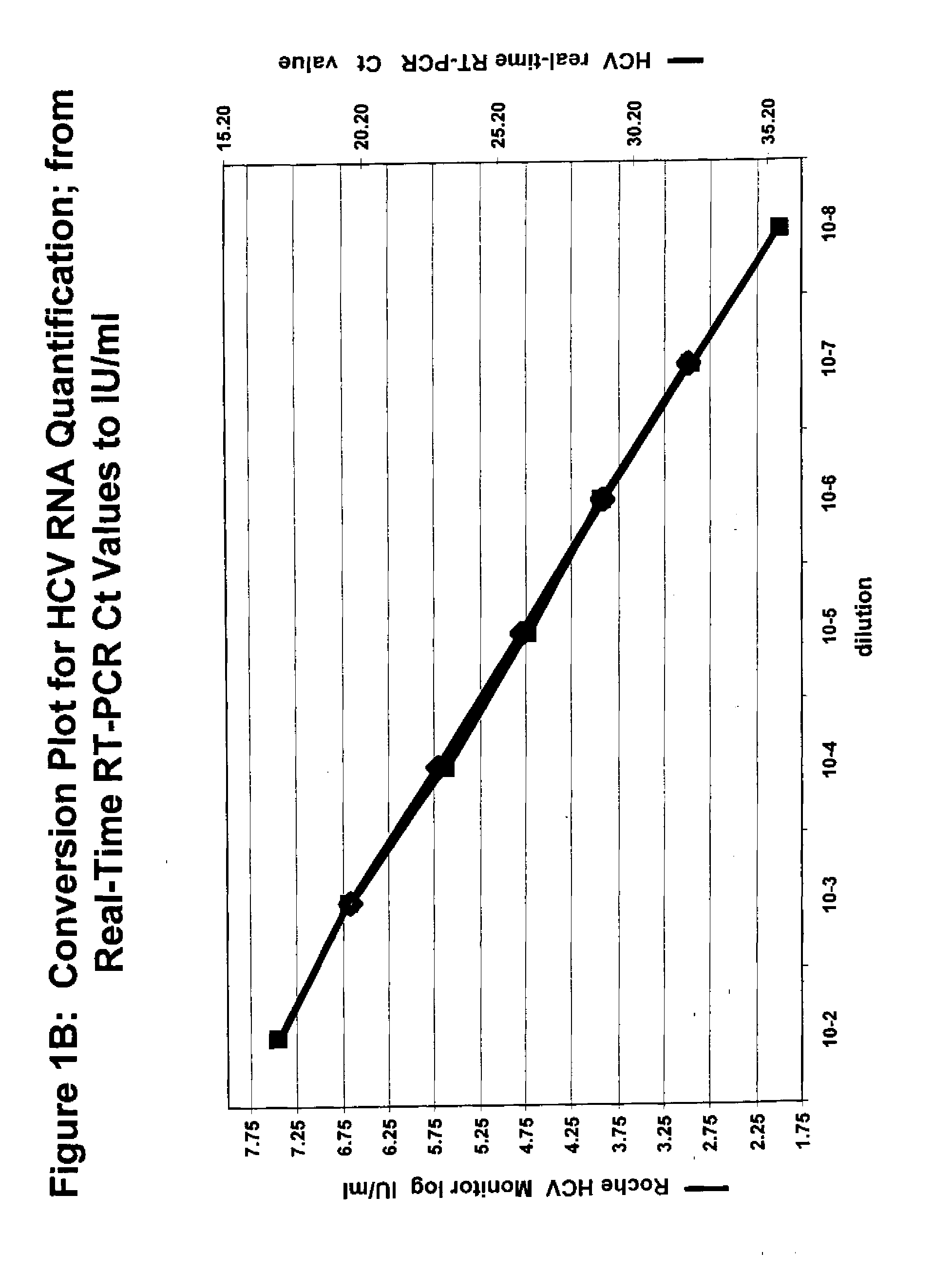
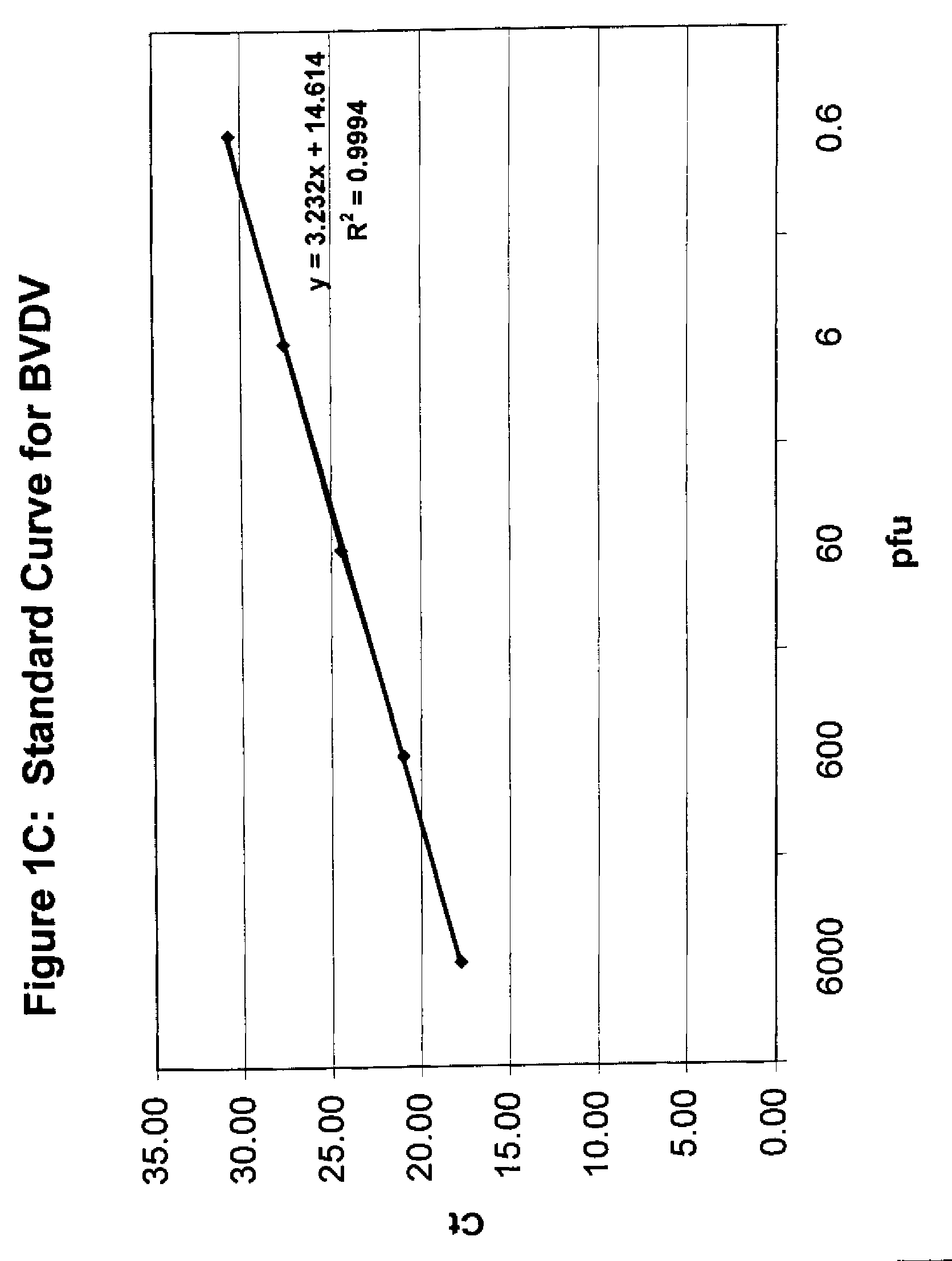
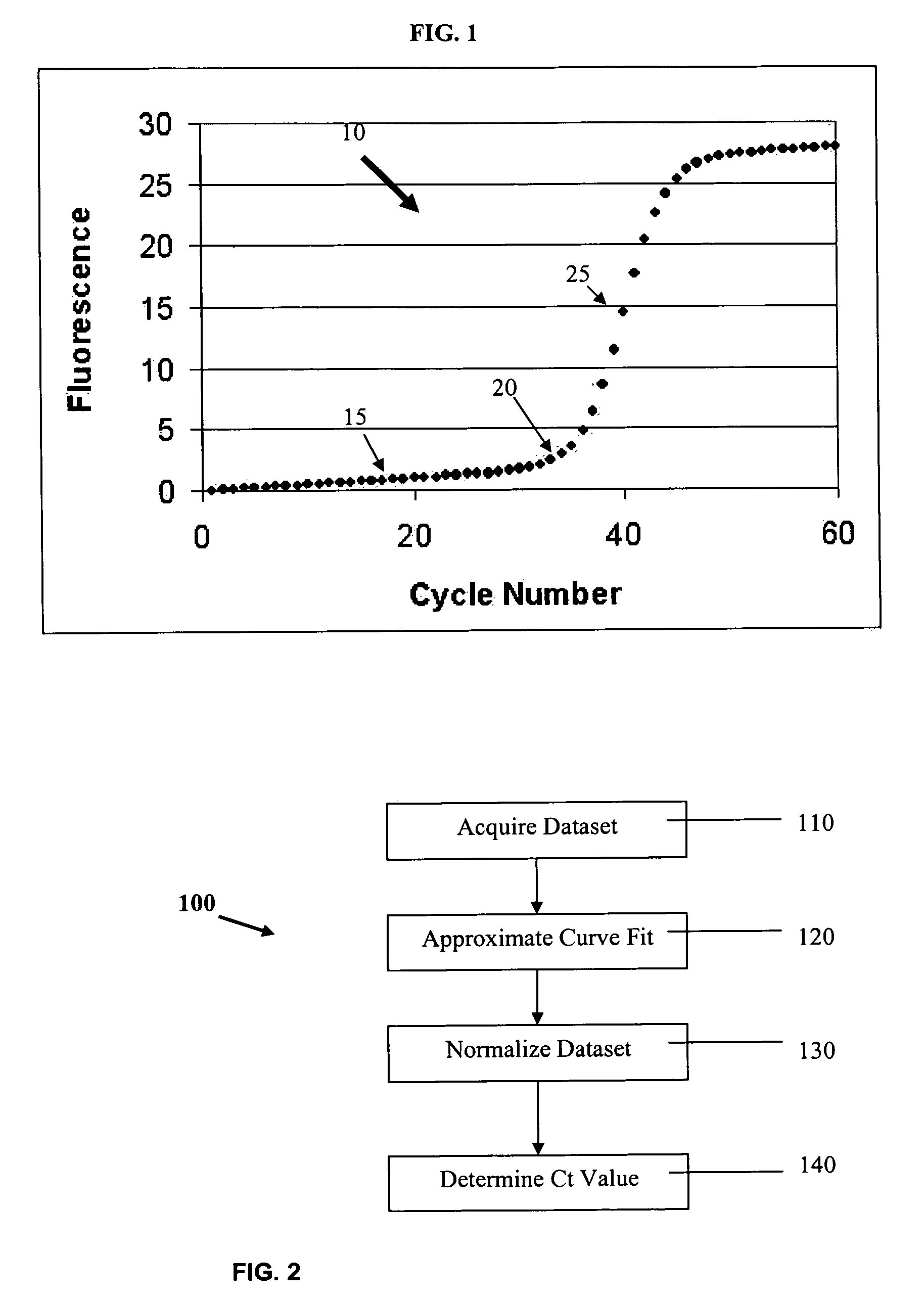
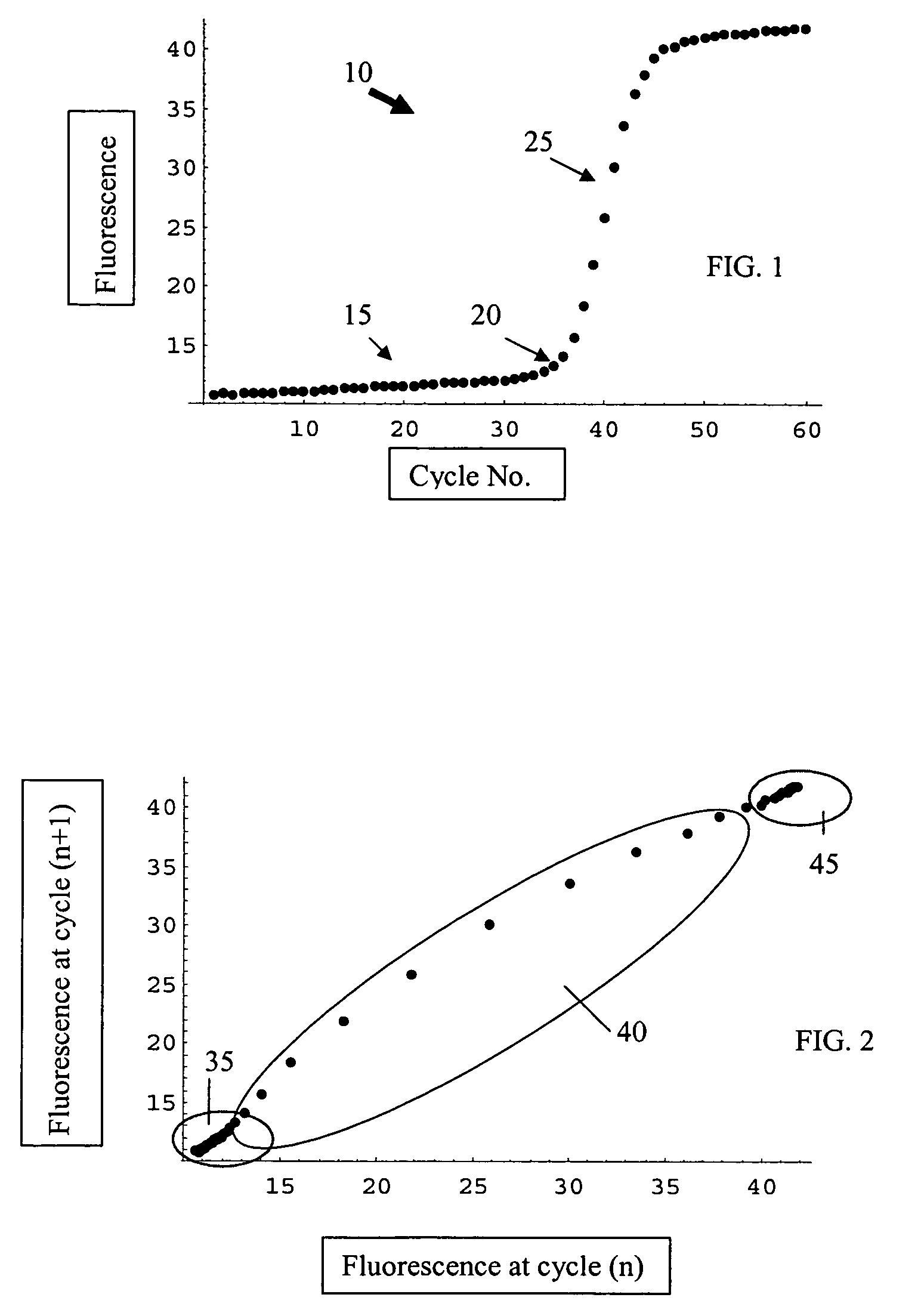
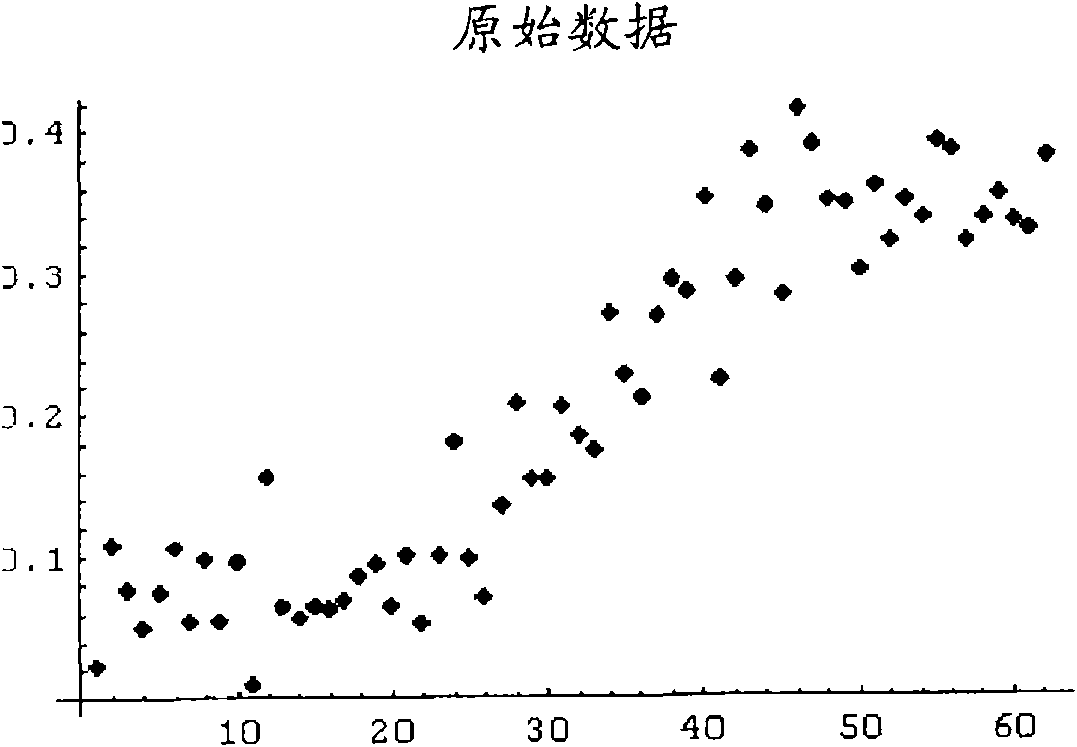
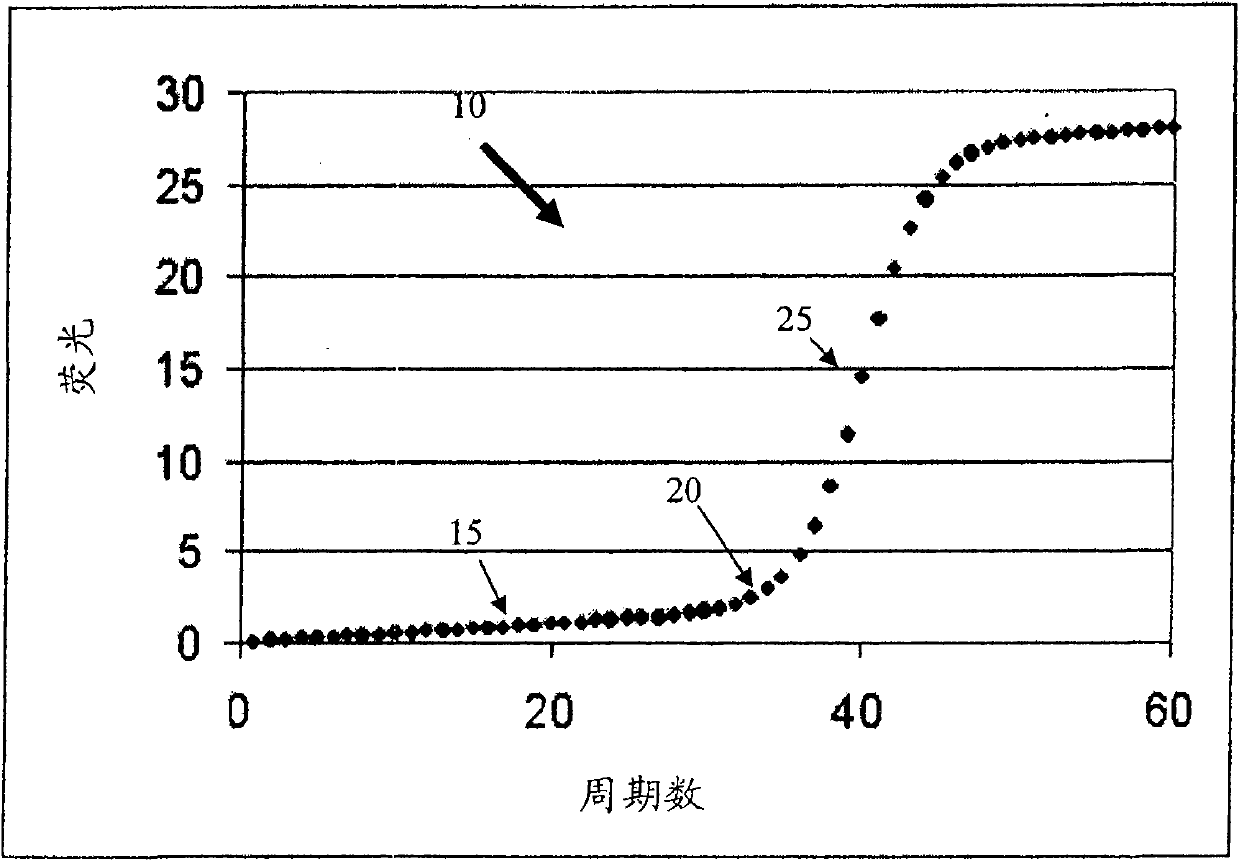
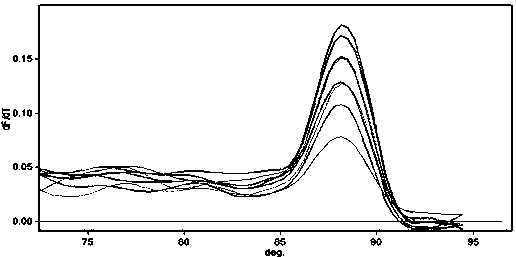
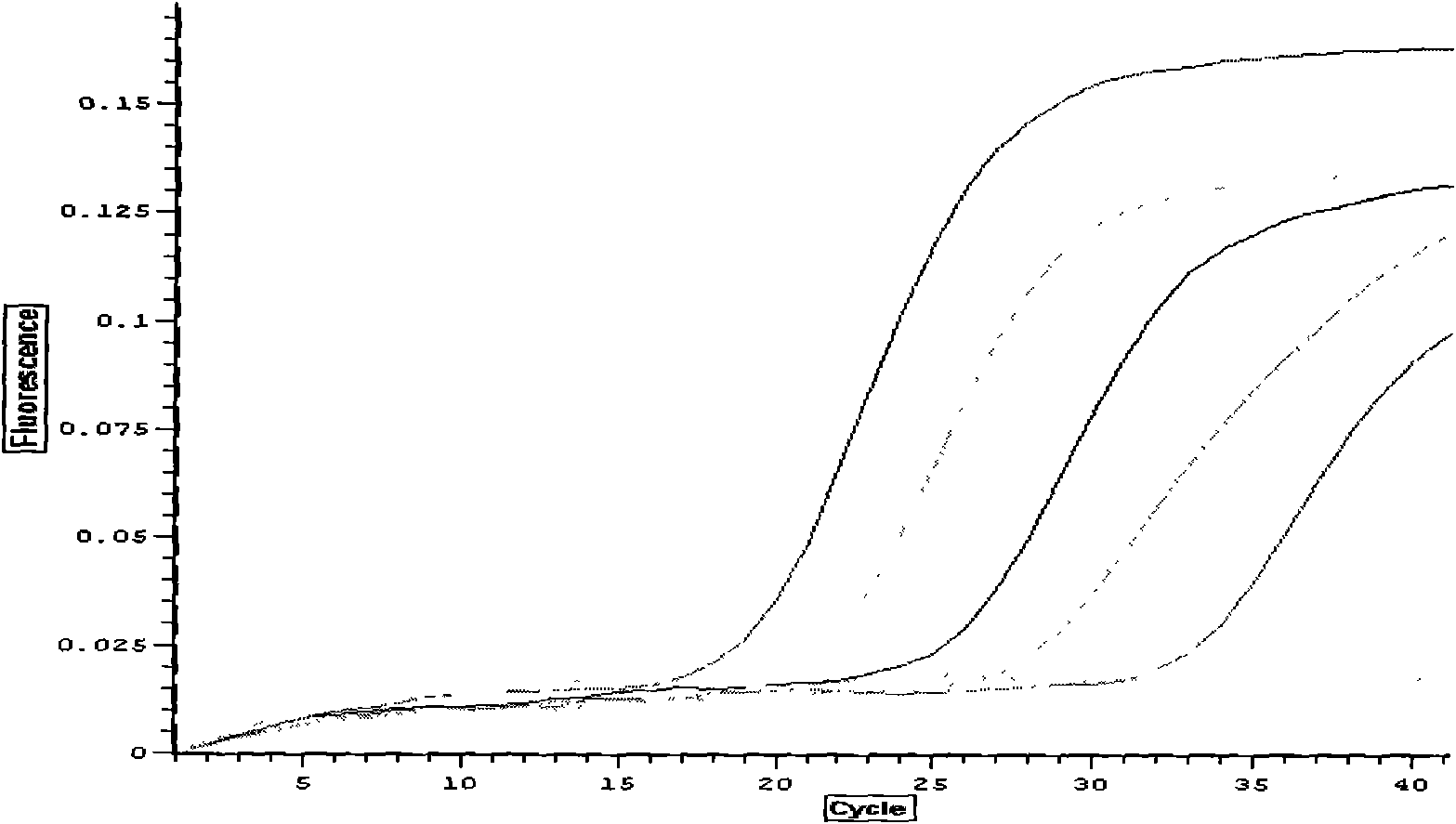
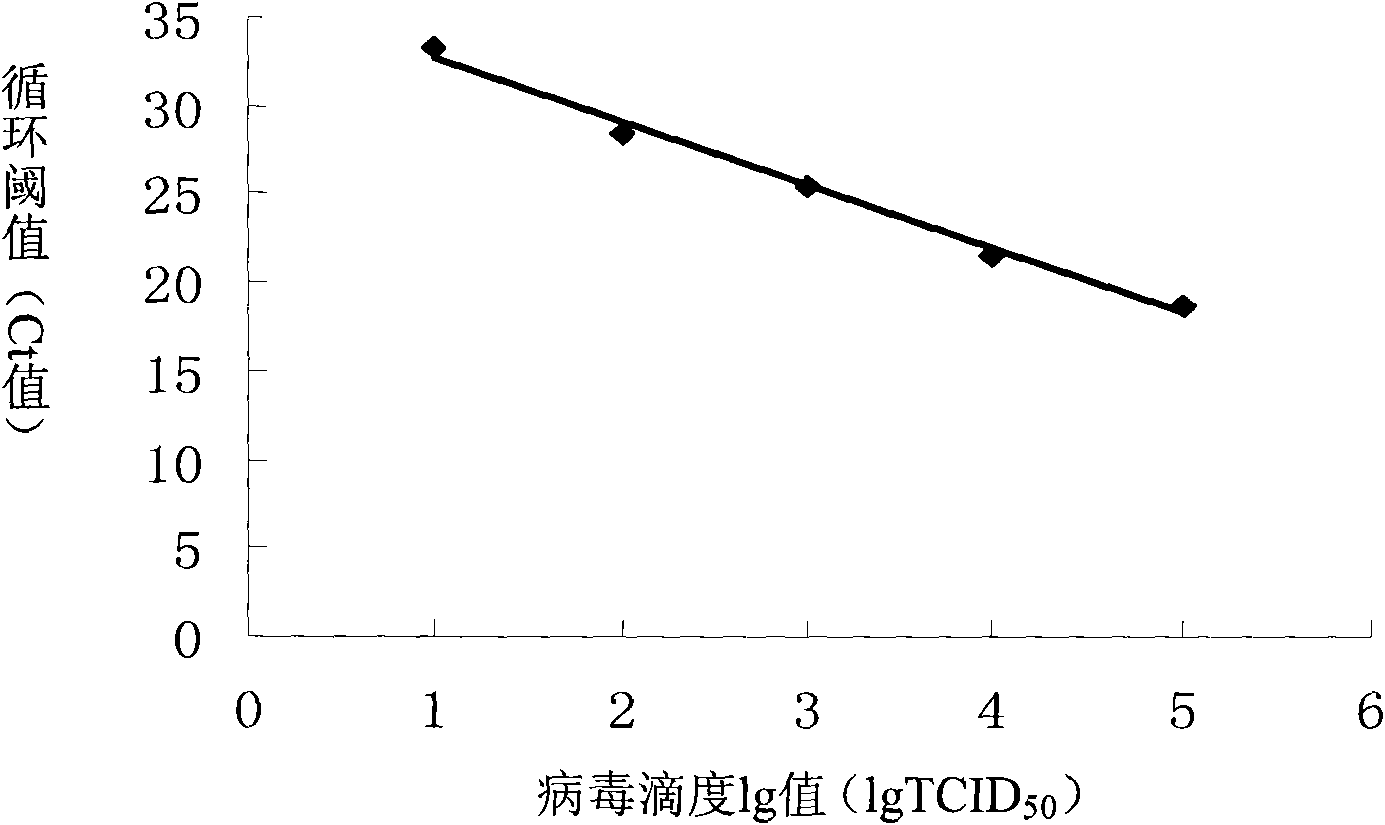
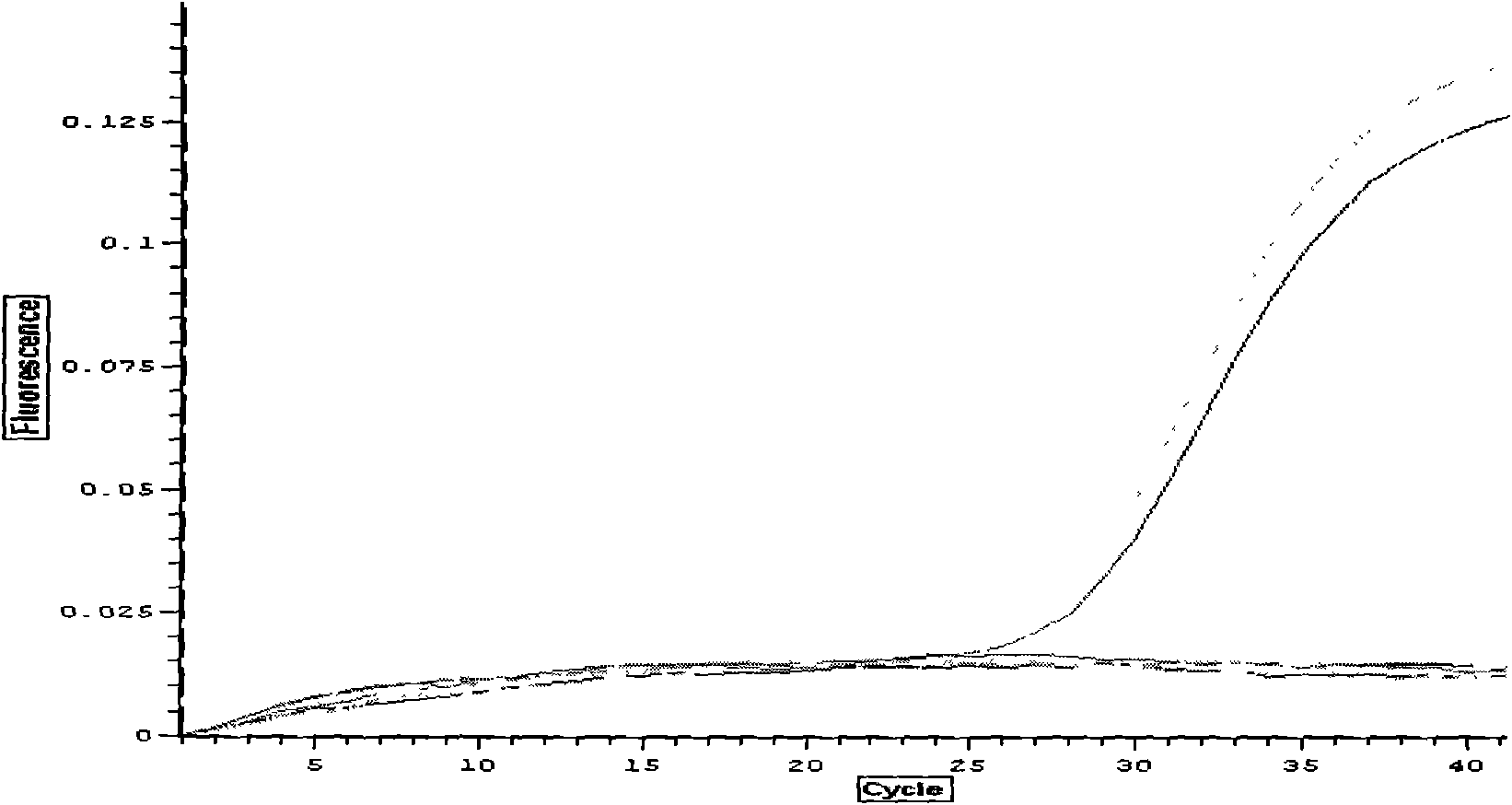
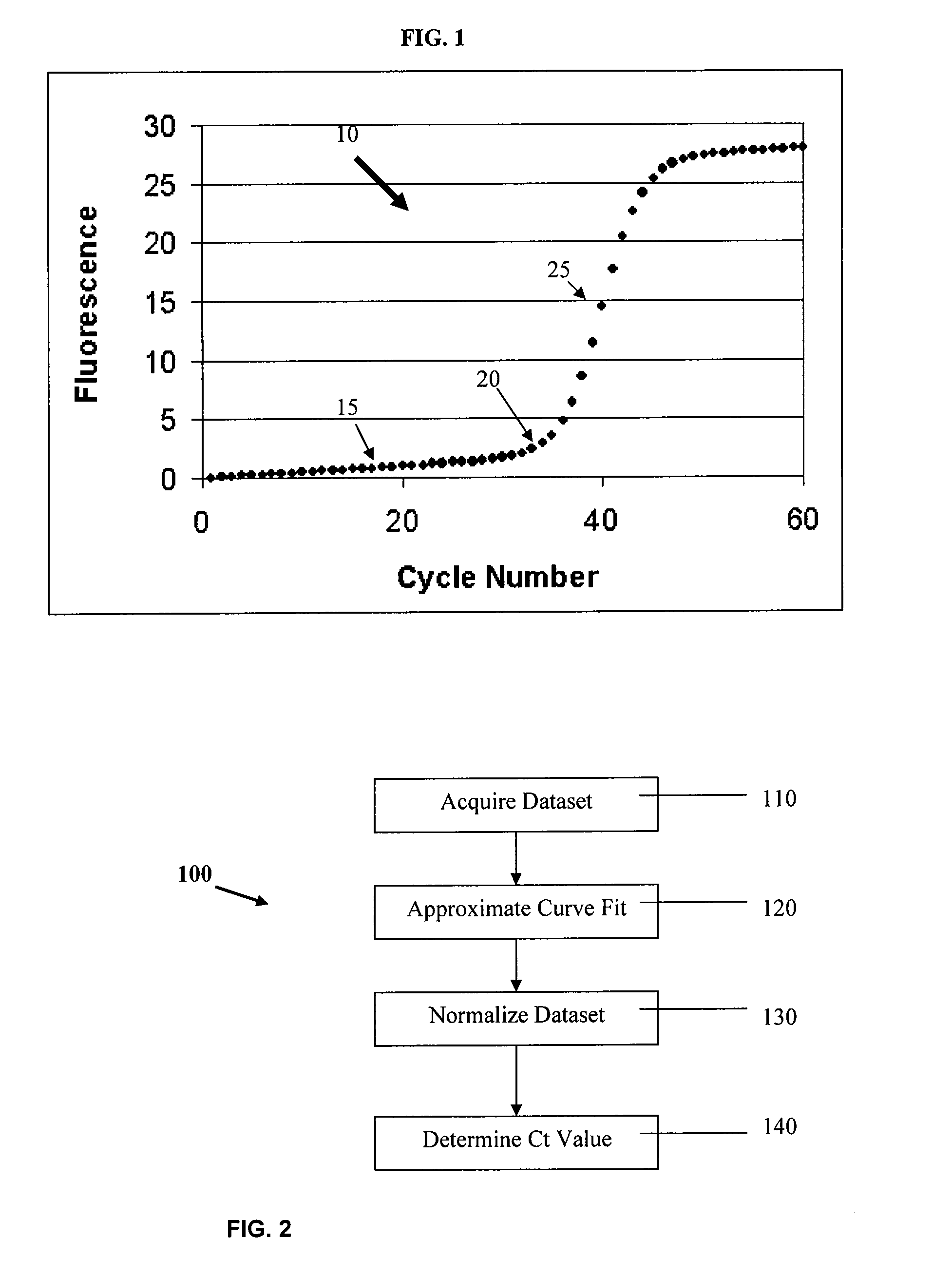
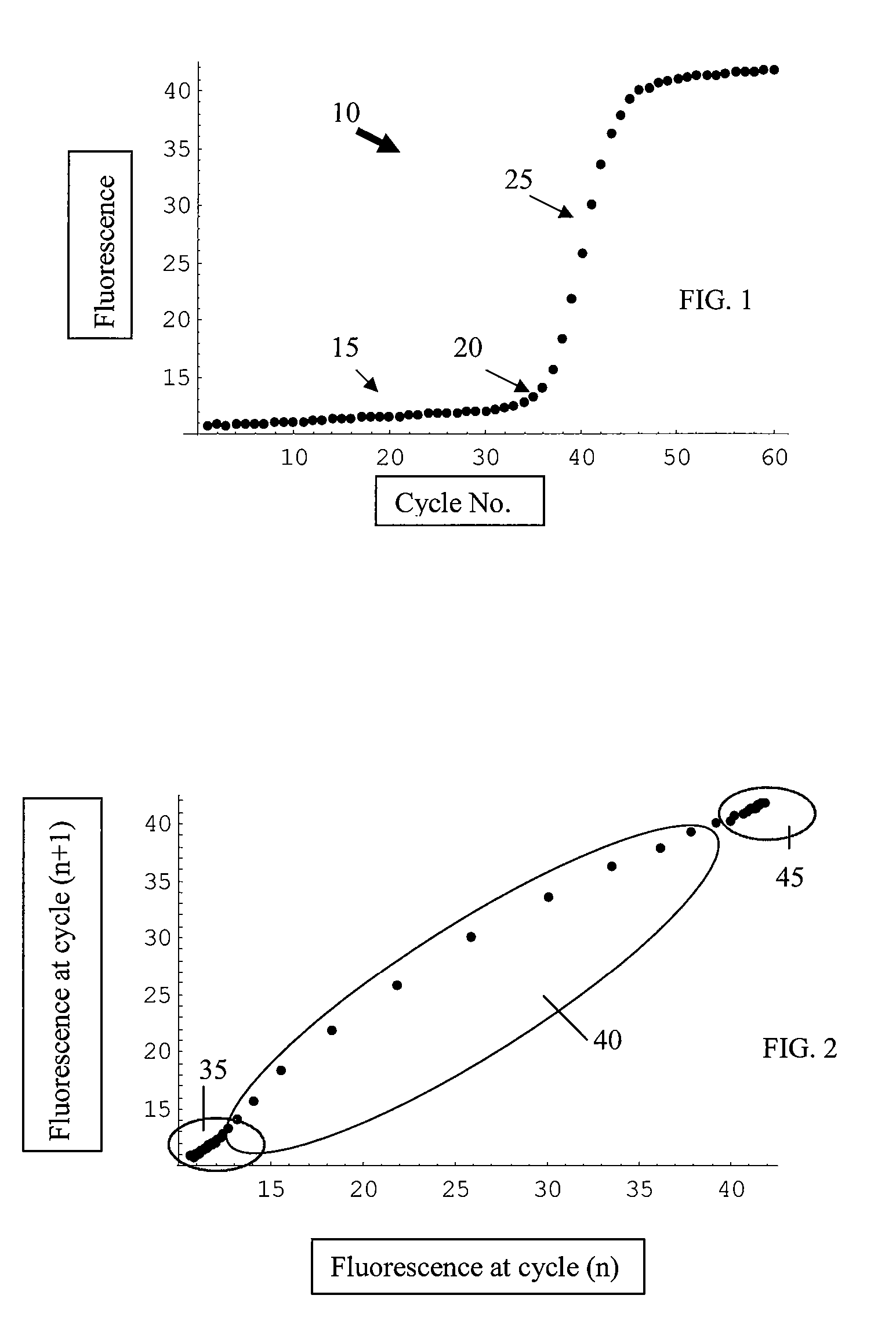
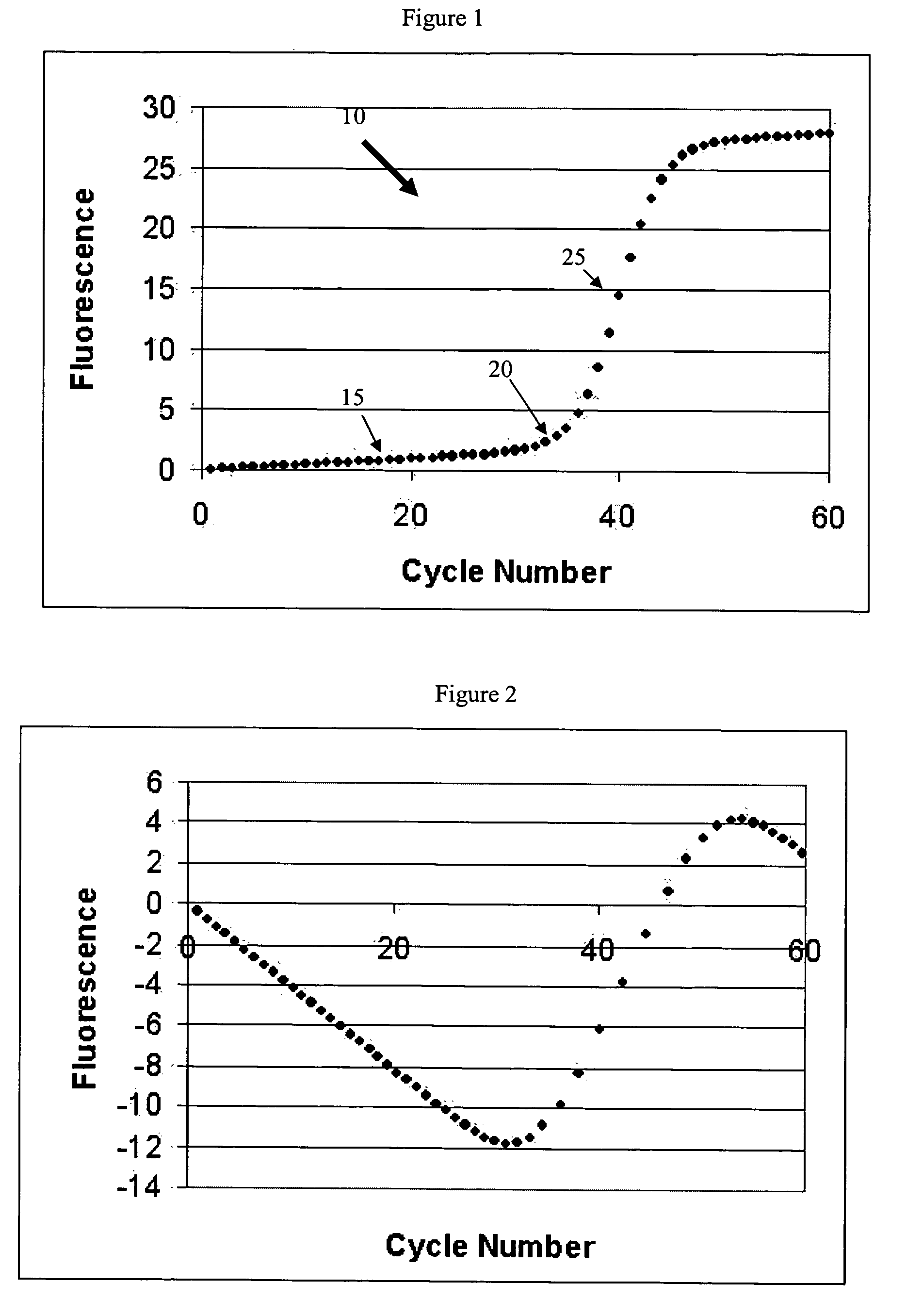
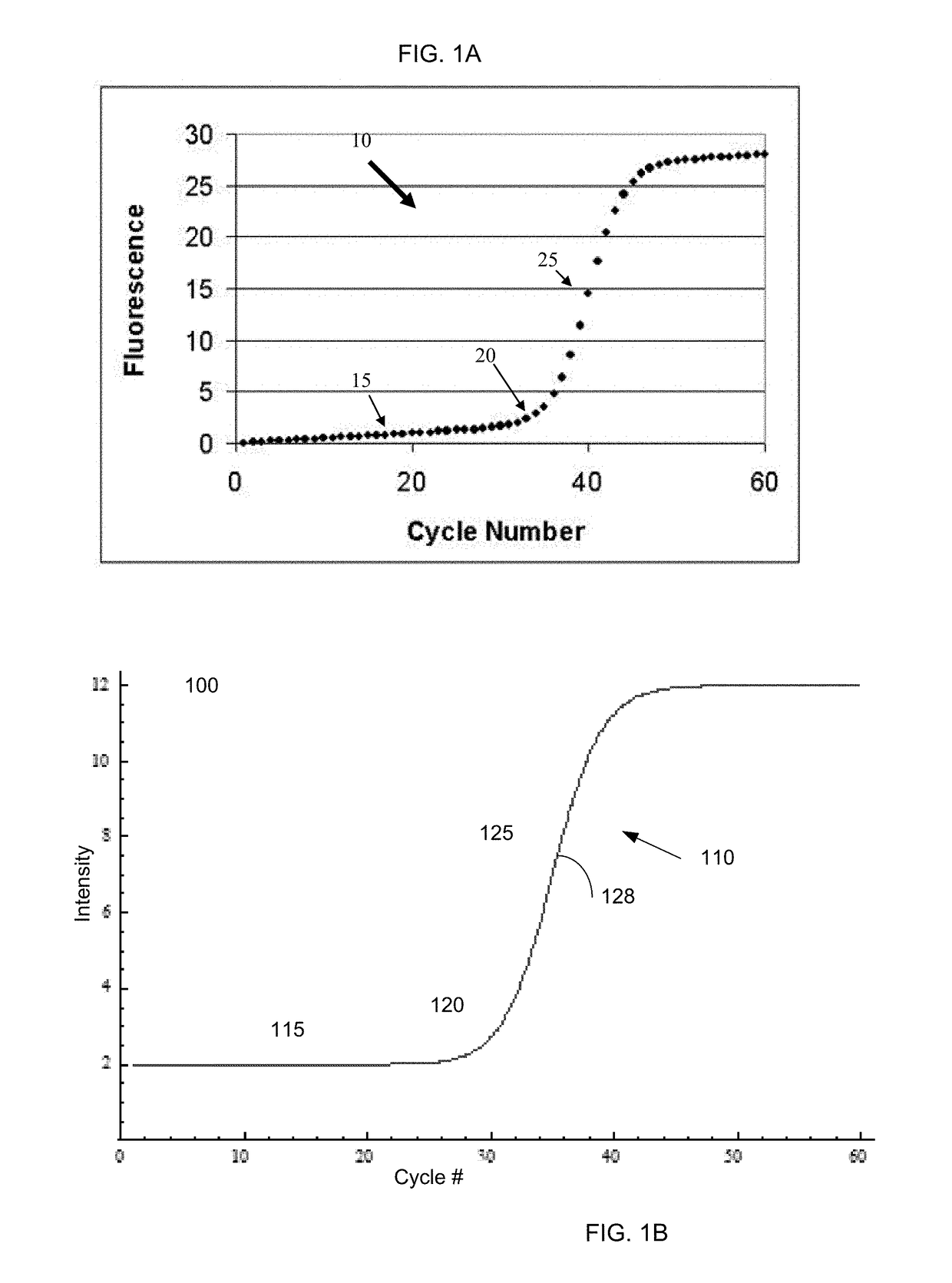
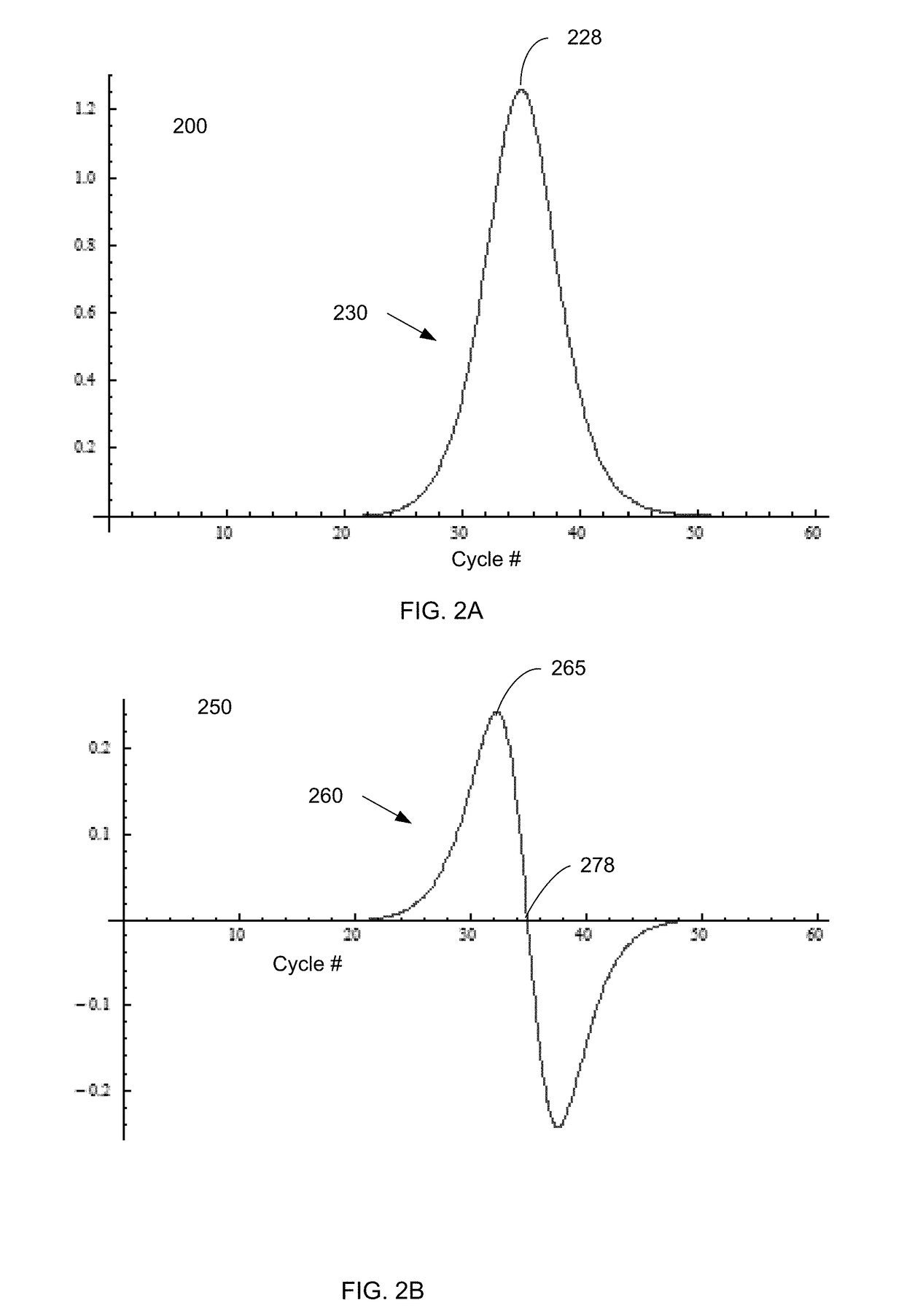
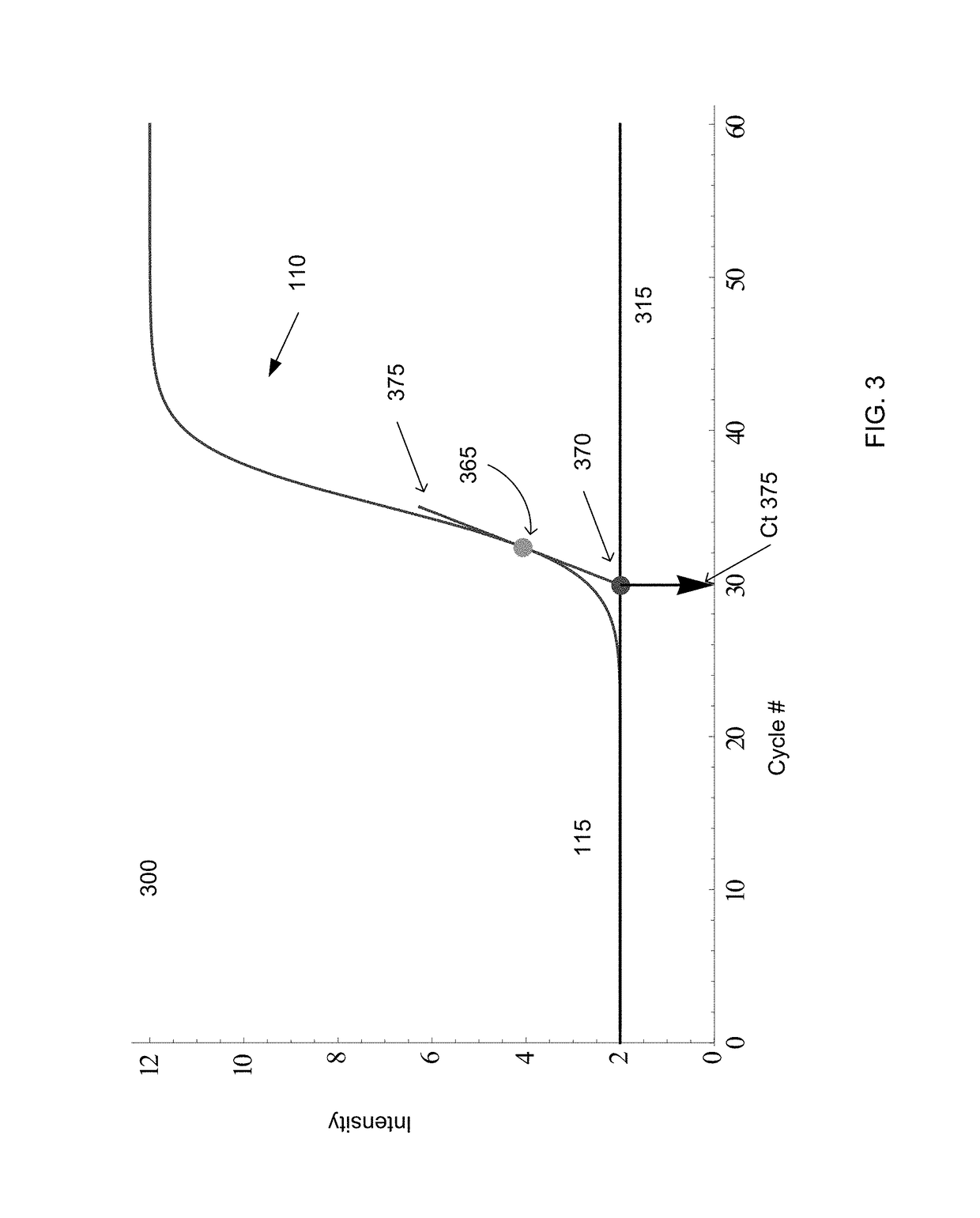
The cycle threshold (Ct) value of a reaction is defined as the cycle number when the fluorescence of a PCR product can be detected above the background signal. In order to calculate the Ct value, it is necessary to draw a horizontal line (threshold) on the amplification plot.
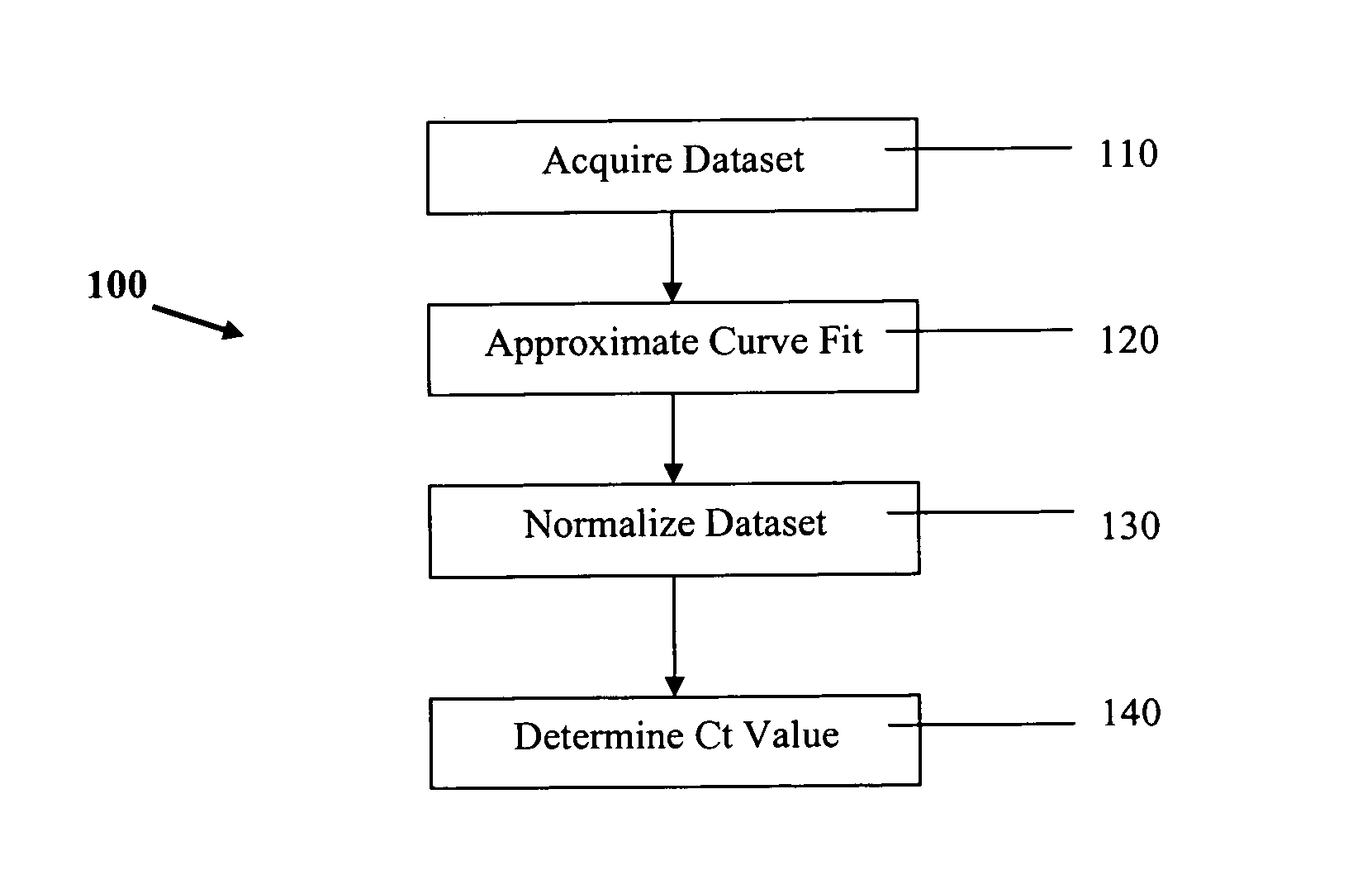
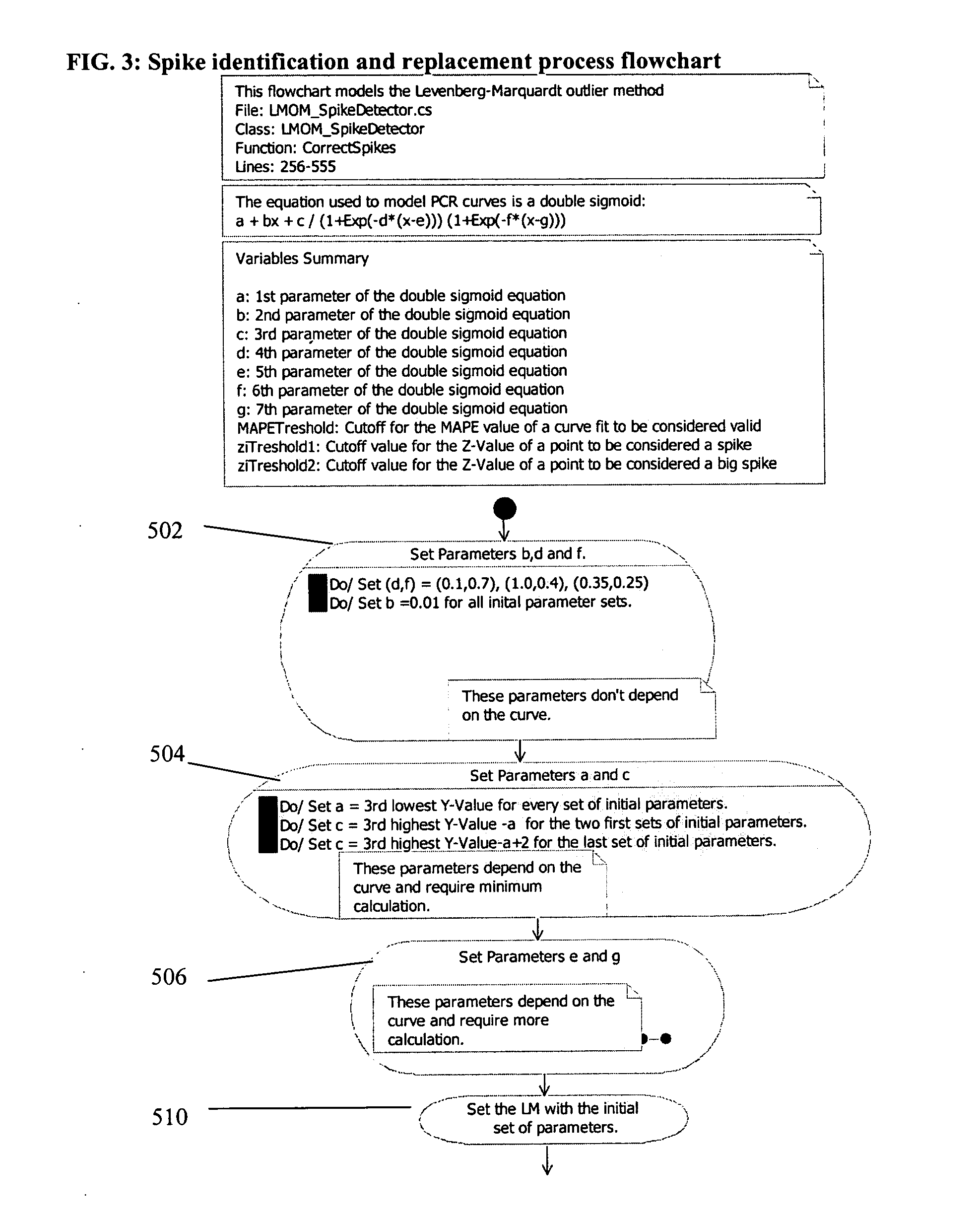
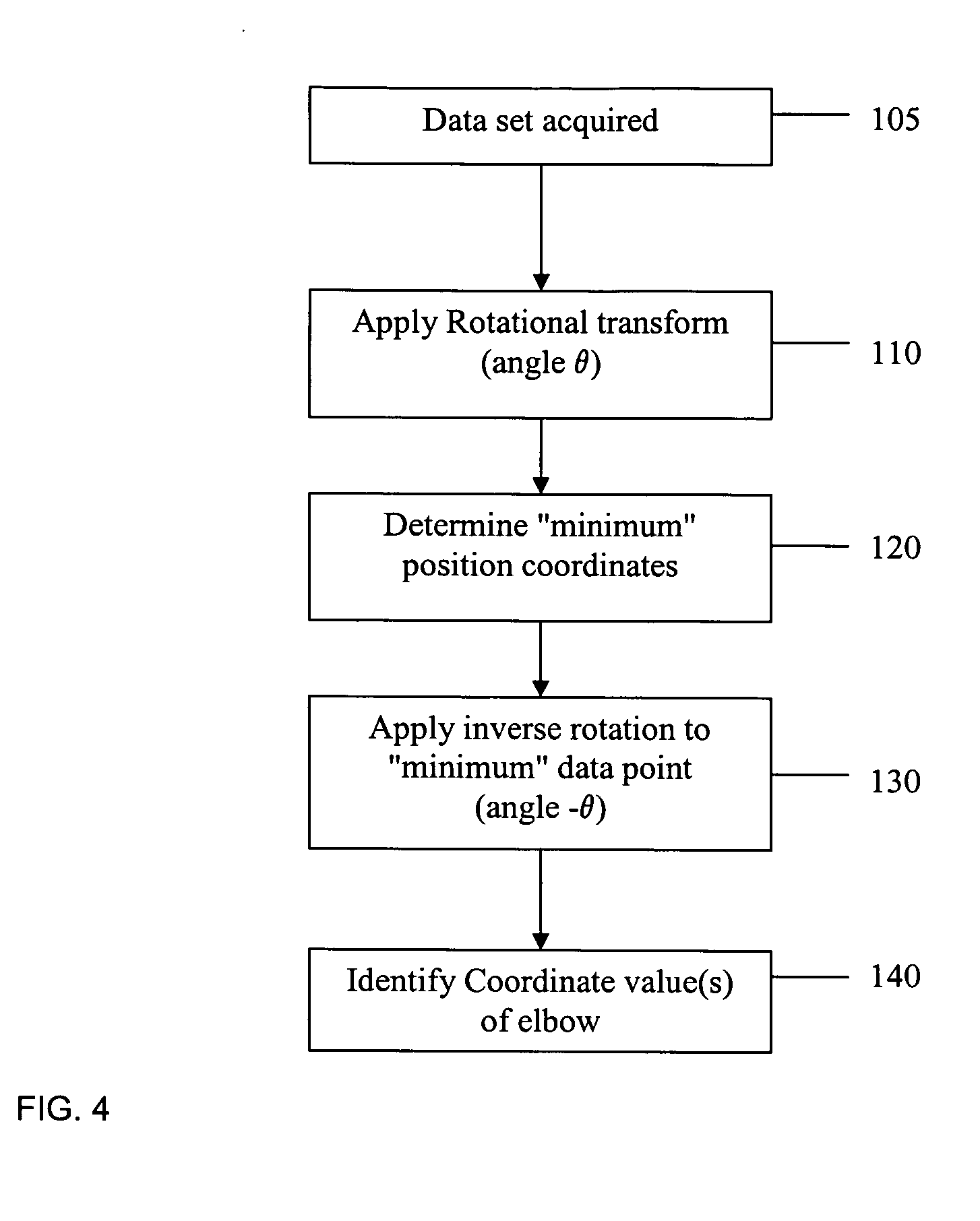
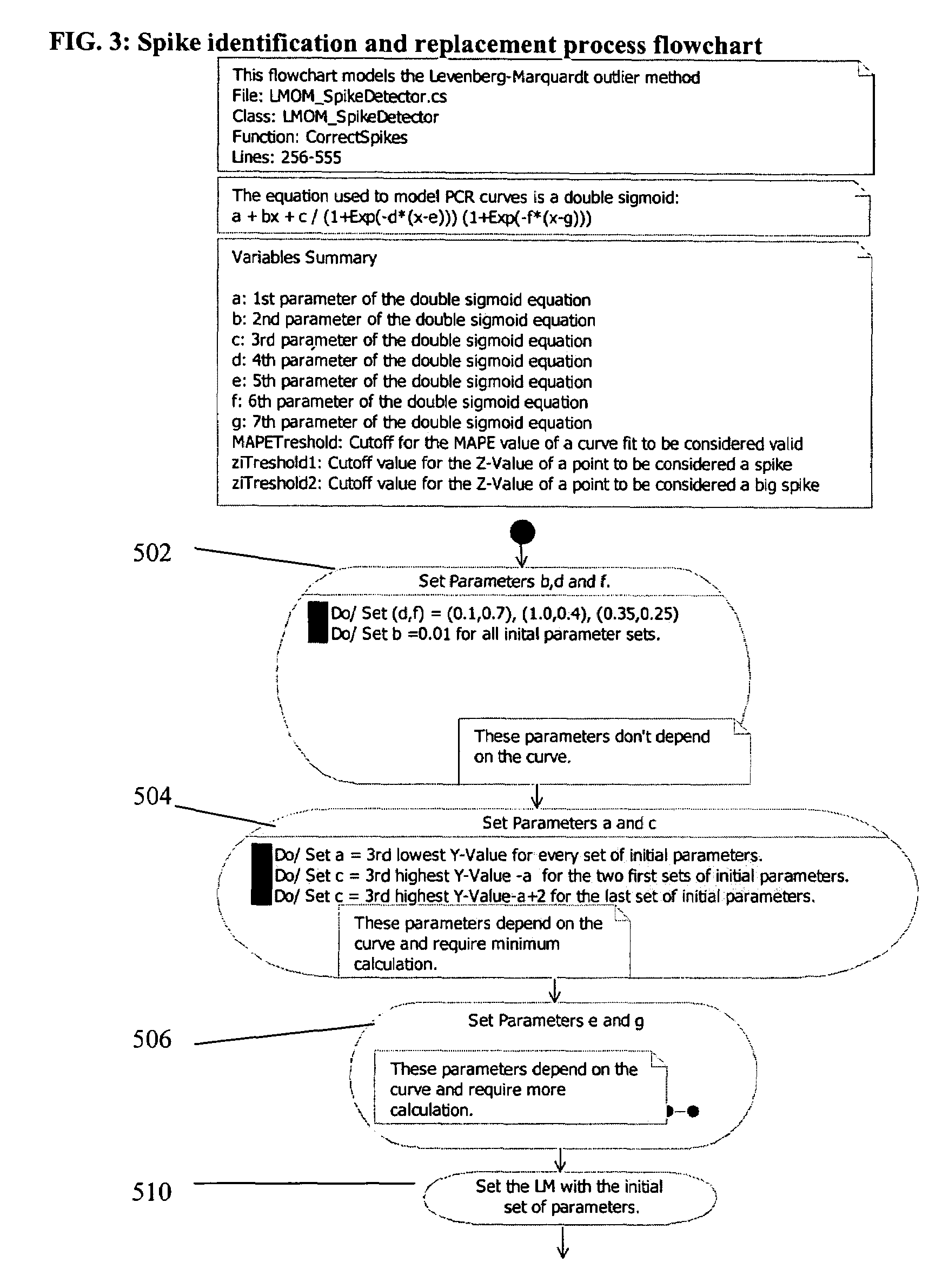
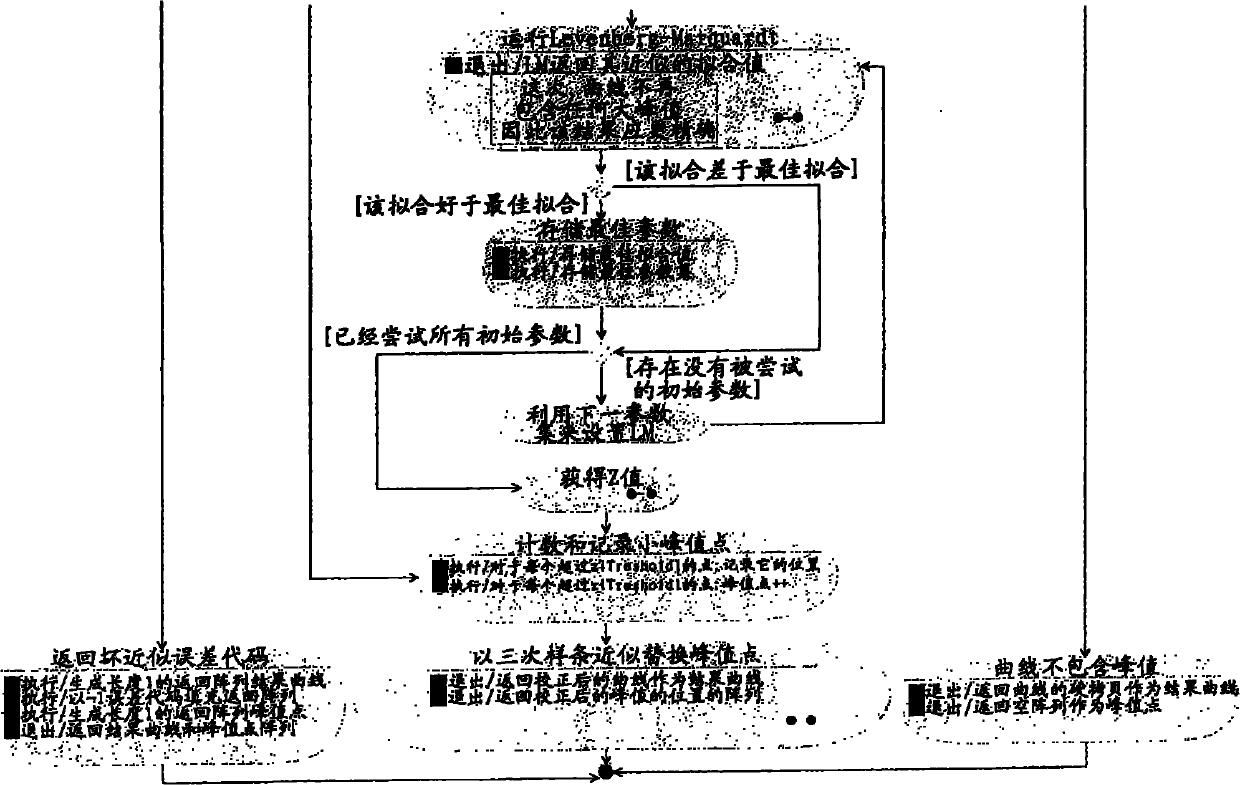
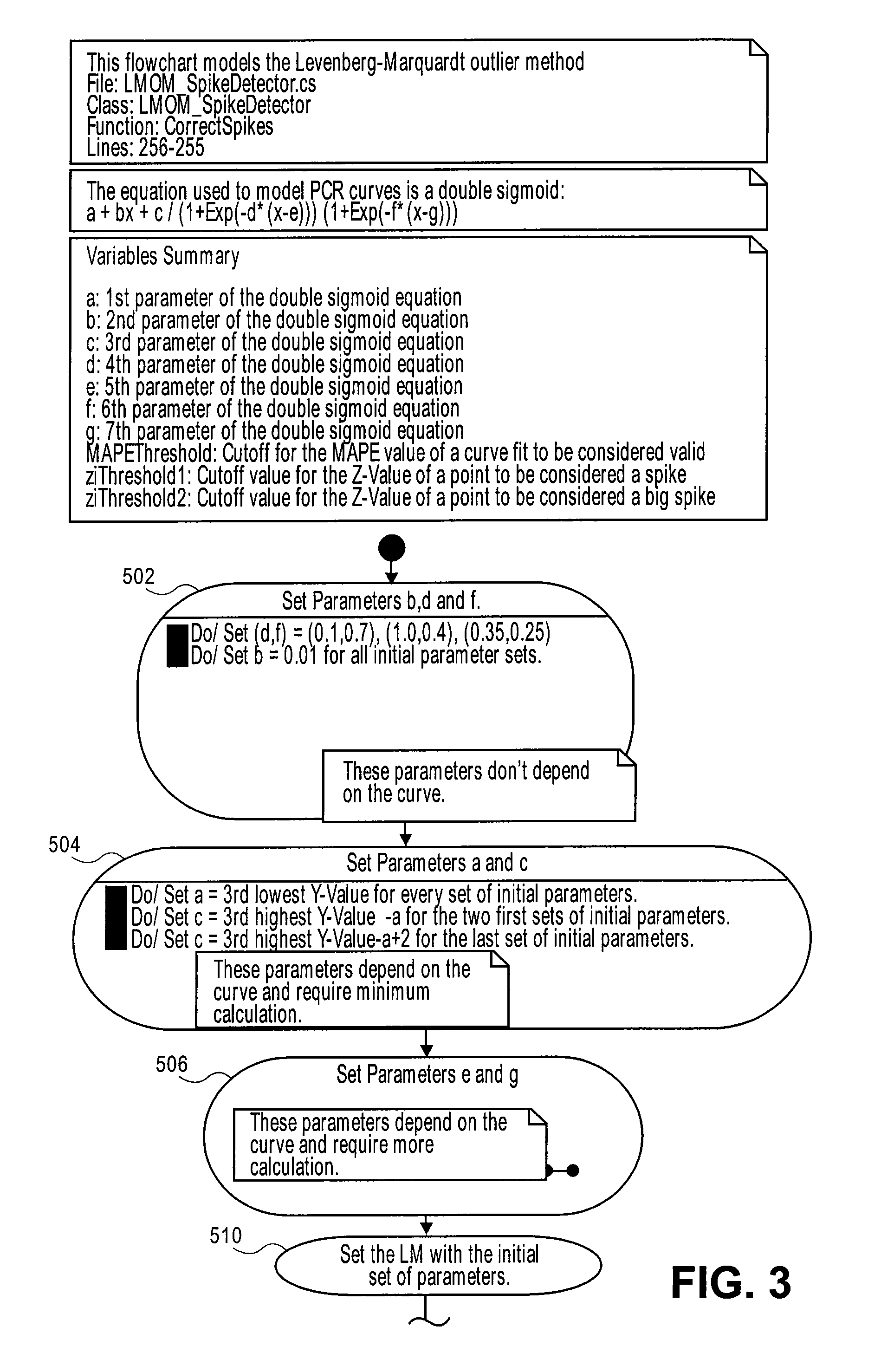
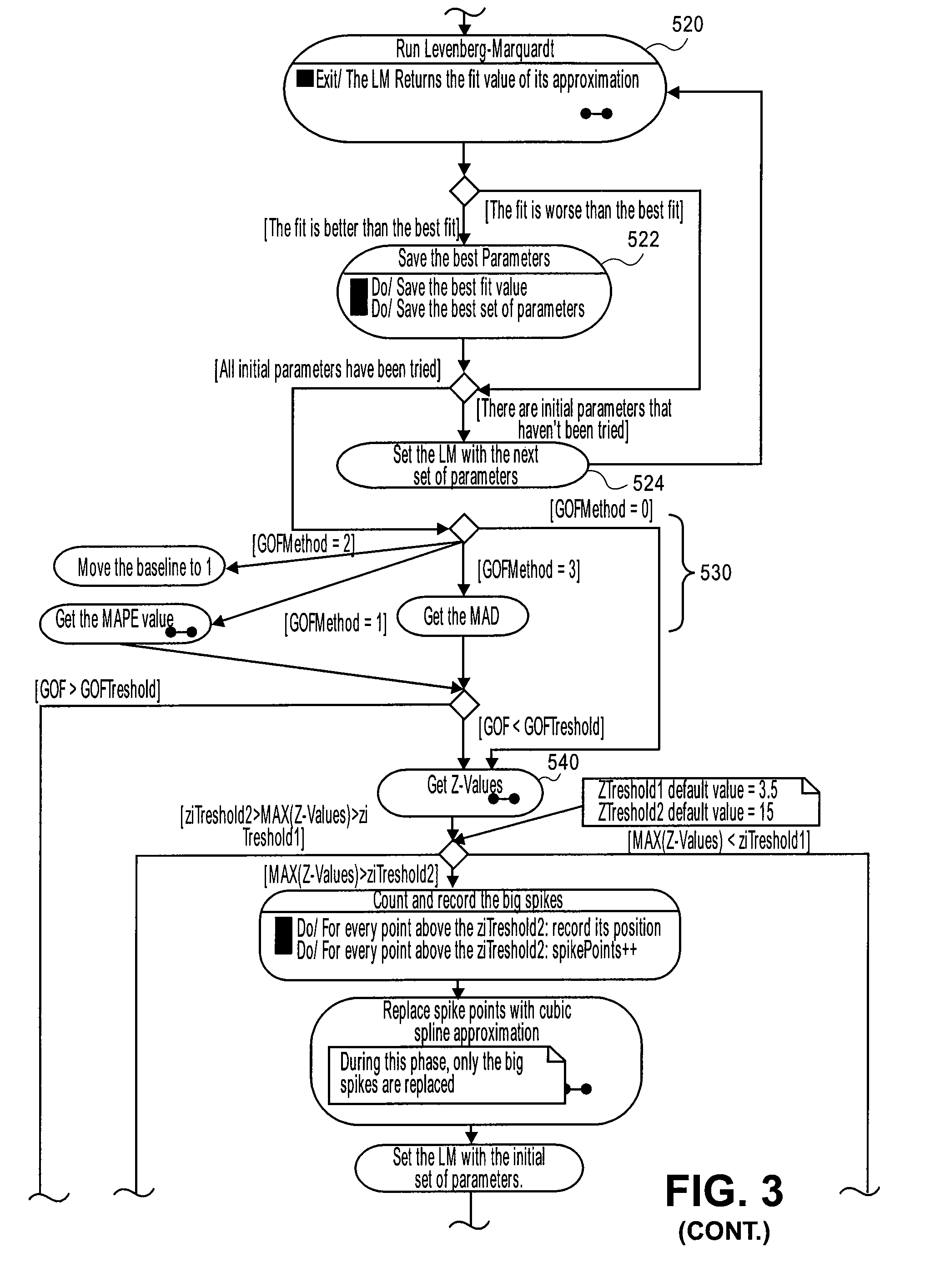
PCR elbow determination by use of a double sigmoid function curve fit with the Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm and normalization
ActiveUS20070143385A1Microbiological testing/measurementDigital function generatorsLevenberg–Marquardt algorithmData set
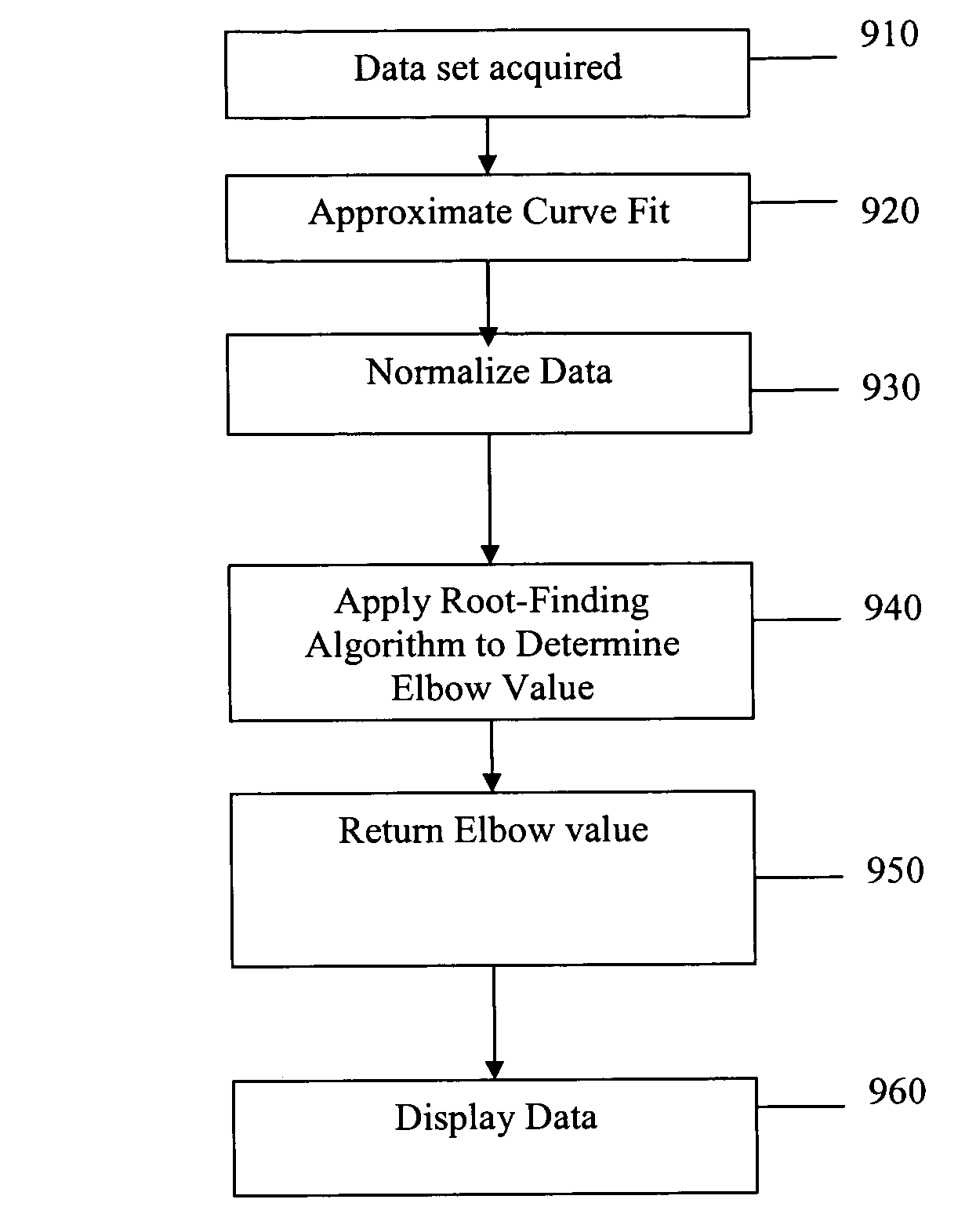
Systems and methods for determining characteristic transition values such as elbow values in sigmoid or growth-type curves, such as the cycle threshold (Ct) value in PCR amplification curves. A double sigmoid function with parameters determined by a Levenberg-Marquardt (LM) regression process is used to find an approximation to a curve that fits a PCR dataset. Once the parameters have been determined, the curve can be normalized using one or more of the determined parameters. Normalization is advantageous for determining the Ct value if one chooses the arbitrary fluorescence level (AFL) approach to calculating Ct values for amplification curves. After normalization, the normalized curve is processed by applying a root-finding algorithm to determine the root of the function representing the normalized curve, which root corresponds to the Ct value. The Ct value is then returned and may be displayed or otherwise used for further processing.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
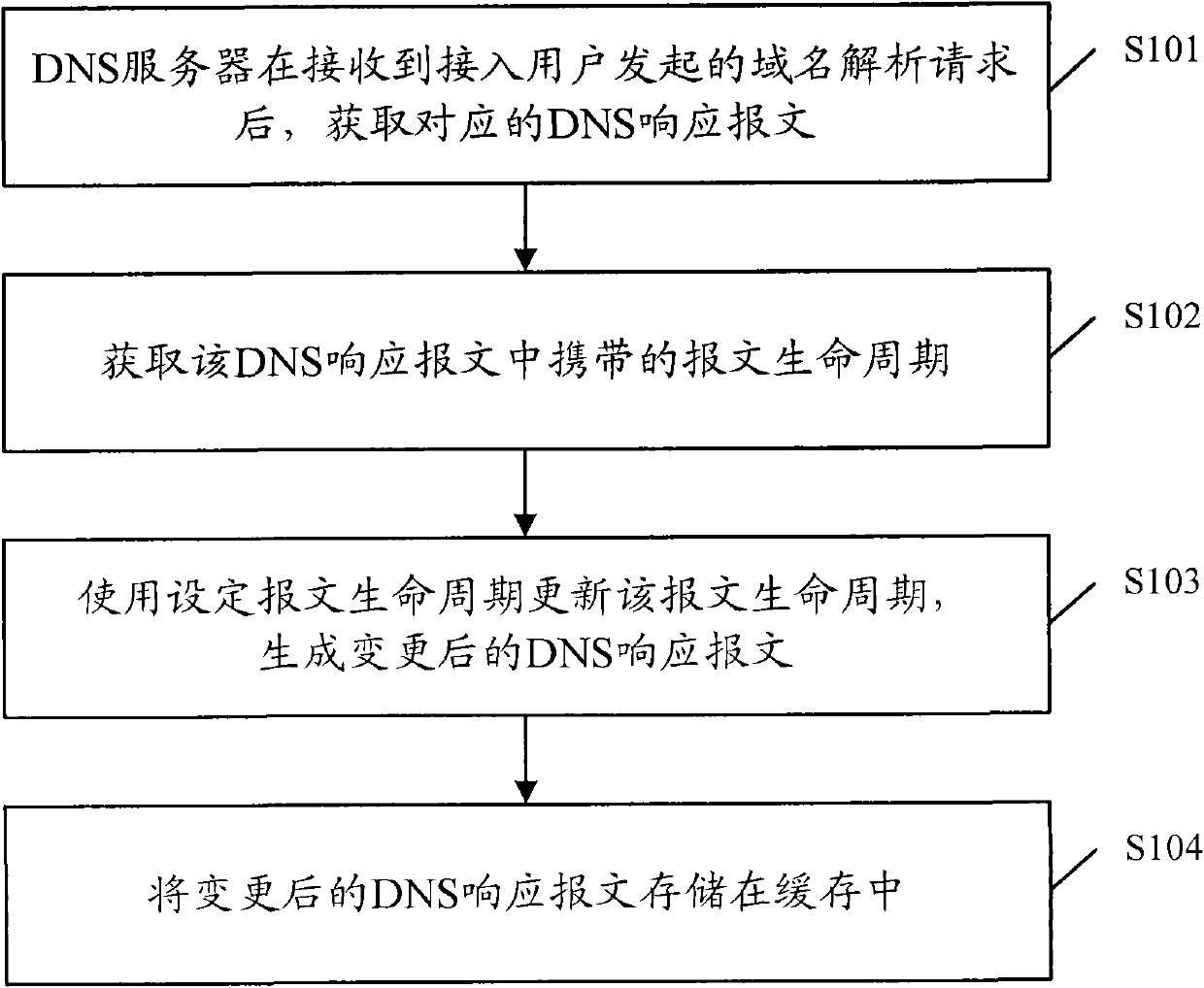
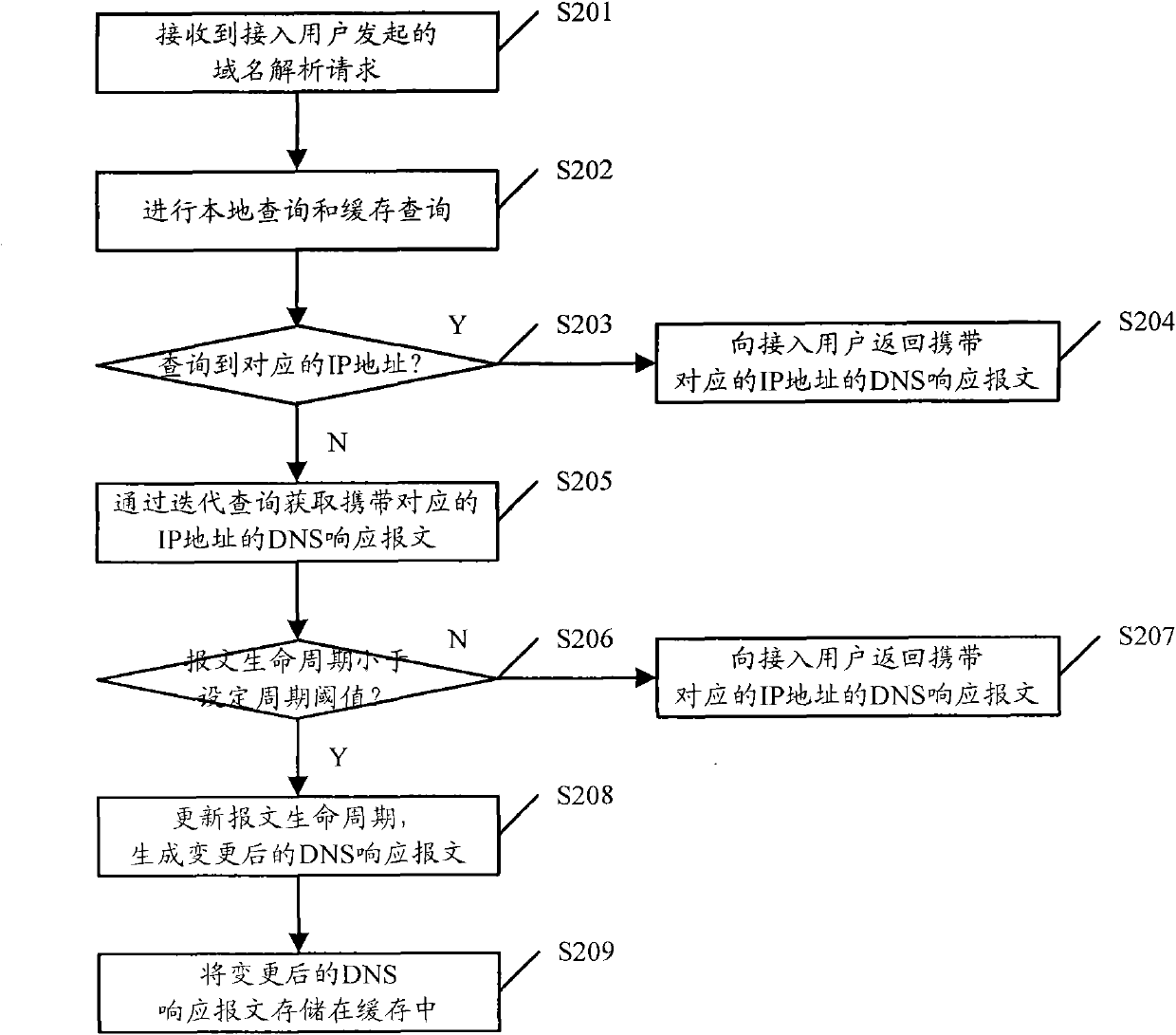
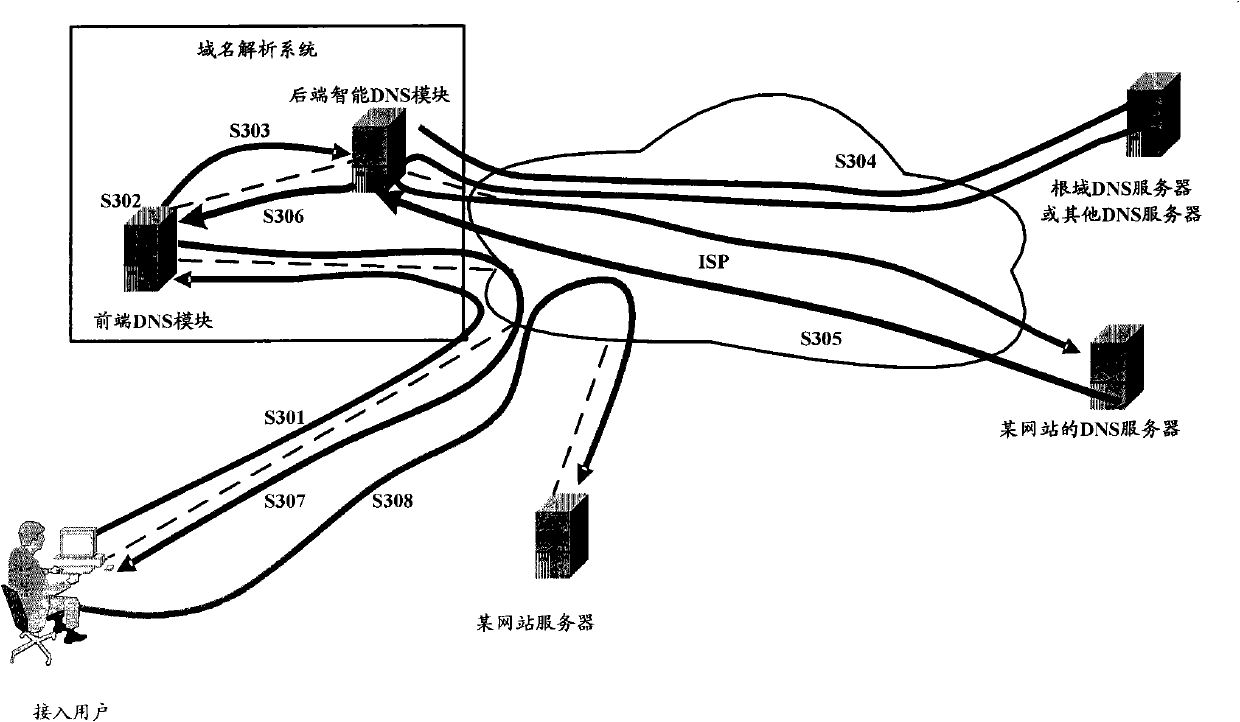
DNS response message processing method, DNS server and system
ActiveCN102025795AExtended storage timeImprove analysis efficiencyData switching networksIp addressCycle threshold
The invention discloses a domain name system (DNS) response message processing method, a DNS server and a system. The method comprises: when the DNS server receives a website-domain-name-carrying domain name analysis request initiated by an access user, acquiring a DNS response message carrying an internet protocol (IP) address corresponding to the website domain name by iterative query; acquiring a message life cycle carried by the DNS response message; when the acquired message life cycle is smaller than a cycle threshold, updating the message life cycle by using a set message life cycle, and generating an updated DNS response message, wherein the set message life cycle is longer than the message life cycle; and storing the updated DNS response message in a cache. When the method, the device and the system, which are disclosed by the invention, are used, the times of requested iterative query of a website domain name in a short period are reduced, and the analysis efficiency of the system is improved, compared with the prior art.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE GRP BEIJING
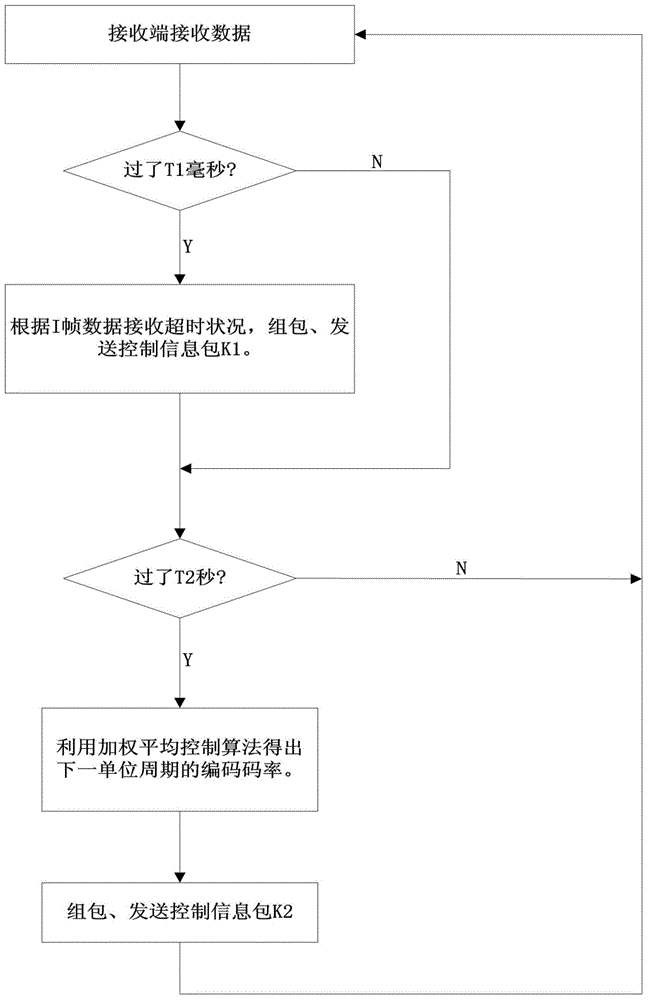
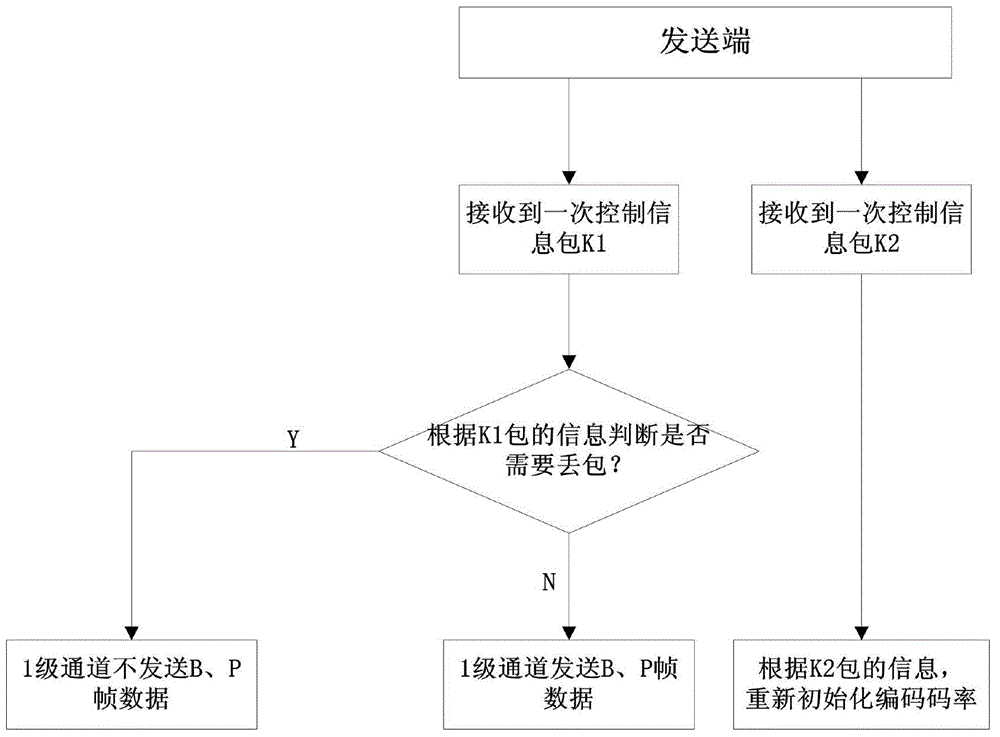
TCP/UDP (Transmission Control Protocol and User Datagram Protocol) mixed protocol based streaming media wireless self-adaptive transmission method
ActiveCN104618337AReliable transmissionReduce transmissionError prevention/detection by using return channelReliable transmissionCycle threshold
The invention discloses a TCP / UDP (Transmission Control Protocol and User Datagram Protocol) mixed protocol based streaming media wireless self-adaptive transmission method. The reliable transmission of a TCP is combined with the small transmission overhead, the high speed and the high efficiency of the UDP, the encapsulation is performed on video and audio data through a fixed length of data packet header, and the hierarchical transmission is performed through different channels according to different data frame types. A receiver is provided with a data packet life cycle threshold vale and a feedback information packet is sent to a sender if the timeout of the data receiving is produced. The sender starts to discard non-critical frame data of the unreliable transmission channels and accordingly the channel congestion is alleviated, the audio and video delay is reduced, and the real-time performance of the streaming media playing is ensured. In addition, the dynamic adjustment on the coding rate of the sender is implemented by an average code rate weighed control algorithm according to the channel transmission data received by the receiver and accordingly the good self-adaption to the changes of the wireless channel bandwidth can be achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Non-invasive type household load intelligent detection method and system
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
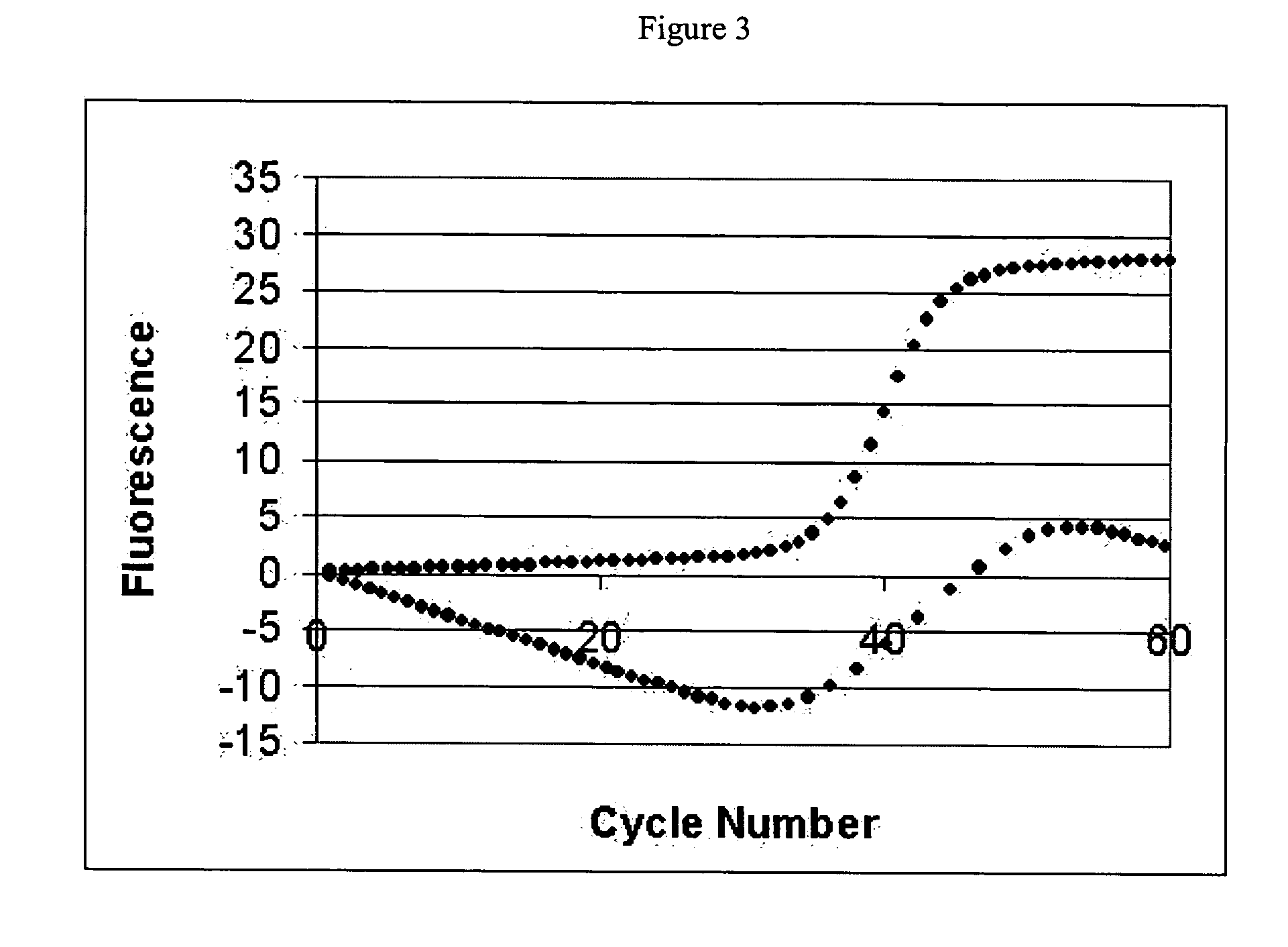
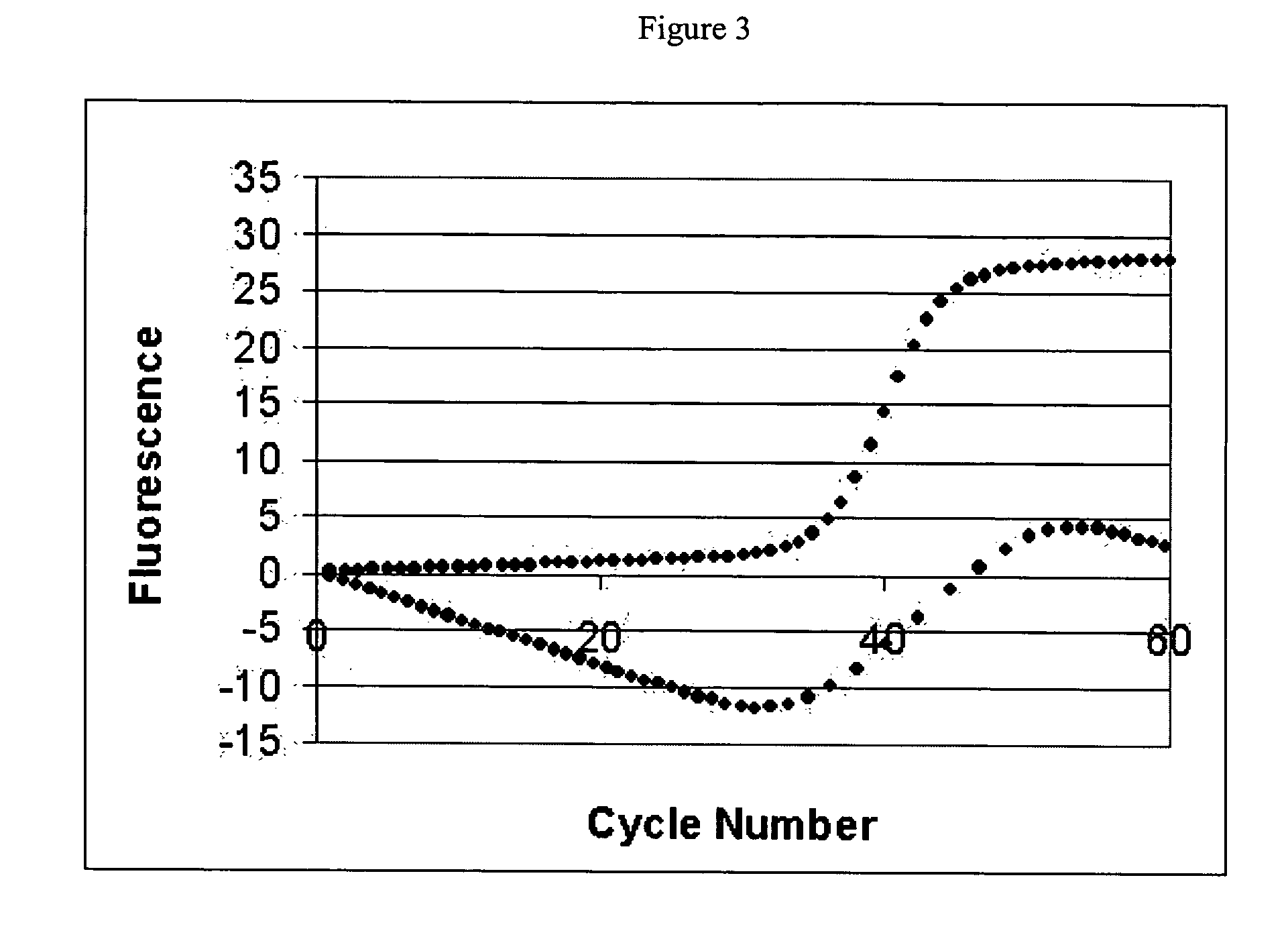
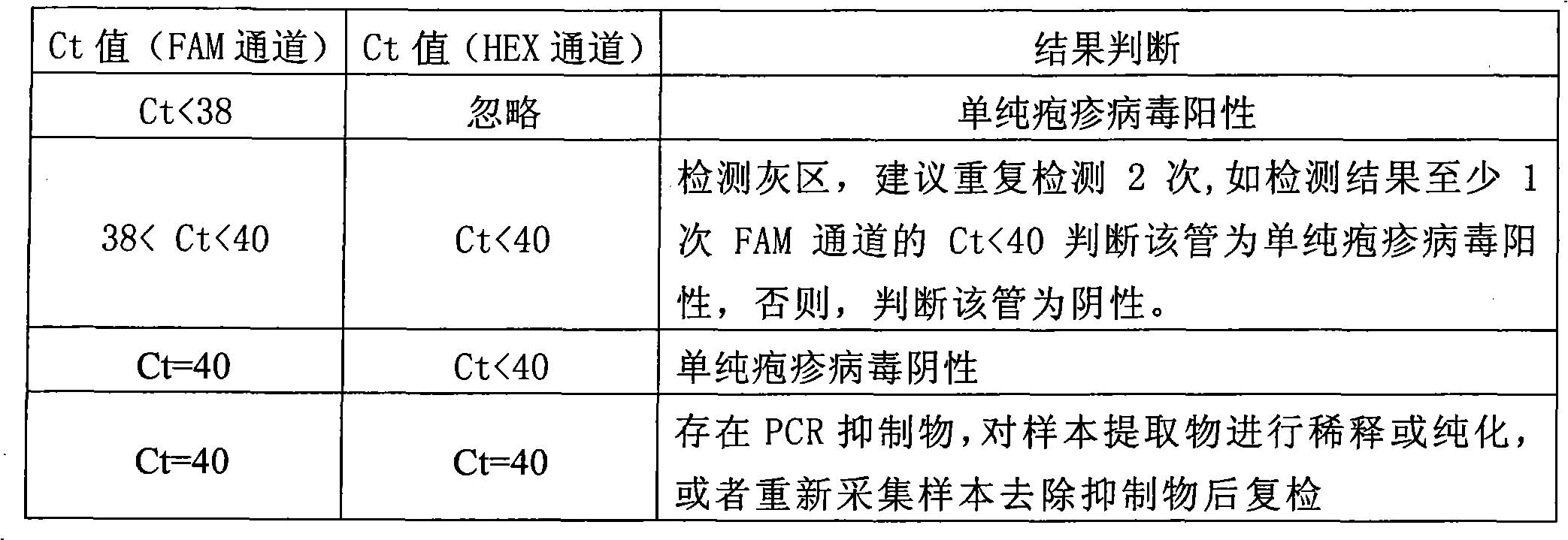
Systems and methods for determining real-time PCR cycle thresholds using a rotation transformation
Systems and methods for determining the elbow or Ct value in a real-time, or kinetic, PCR amplification curve data set. The PCR data set may be visualized in a two-dimensional plot of fluorescence intensity vs. cycle number. A rotation transform is applied to the data set to rotate the data about a defined coordinate such as the origin so that the data point representing the Ct value becomes a minimum or a maximum along the intensity axis. The data point representing the elbow or Ct value of the PCR curve is identified, and this data point is then rotated back and the cycle number of the data point is returned or displayed.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Method for detecting lncRNA (long noncoding RNA) in plasma
InactiveCN103966311AReduce degradationQuality improvementMicrobiological testing/measurementTotal rnaFluorescence
The invention discloses a method for detecting lncRNA in plasma. Through steps of TrizolLS pretreatment of theplasma, chloroform and isoamyl alcohol mixed liquid extraction, isopropanol precipitation, ethanol washing, RNA RT (reverse transcription), PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection and the like, a TrizolLSreagentcan well remove impurities such as polysaccharide, mucoprotein and the like in blood, RNA degradation is less, the phenomenon thattrichloromethane is easy to emulsify under the TrizolLS strong acid condition is effectively eliminated by a chloroform and isoamyl alcohol mixed liquid, high-quality and high-content extraction of RNA in the plasma is realized, fluorescence quantitative RT-PCR detection is performed on the quality of lncRNA, and meanwhile, a reference Ct (cycle threshold) value of the total RNA (that is, cDNA) mass can be detected.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Apparatus, system, and method for migrating wear spots
ActiveUS20090319743A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory systemsComputer architectureSolid-state drive
An apparatus, system, and method are disclosed for migrating wear spots in solid-state drives. A count module counts lifetime write cycles for logical units of a plurality of solid-state memories. Each logical unit has a logical address. An identification module identifies a wear spot on a first logical unit of a first solid-state memory if a count for the first logical unit exceeds a cycle threshold. A migration module dynamically migrates data of the first logical unit to a second solid-state memory, wherein the data is continuously available at an original logical address.
Owner:IBM CORP
Simultaneous quantification of nucleic acids in diseased cells
InactiveUS20070196824A1Assess potential side-effectsLow variabilitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementReal-Time PCRsAntiviral drug
Processes and methods for the simultaneous quantification of nucleic acids in diseased cells that are based on real-time PCR are provided. The real-time PCR protocol is an excellent tool for reliable quantification of in vitro drug screening and evaluation protocols to determine the efficacy of potential anti-viral agents. Quantification using these simultaneous PCR cycle threshold (Ct) detection techniques during one-step real-time RT-PCR (Applied Biosystems, CA) eliminates the variability resulting from quantification of end-point RT-PCR products. In addition, the mitochondrial toxicity assay is an added tool to assess potential side-effects for these chemotherapeutic agents.
Owner:GILEAD PHARMASSET LLC
Universal method to determine real-time PCR cycle threshold values
ActiveUS20140095080A1Accuracy in determiningAchieve accuracyAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceMicrobiological testing/measurementIntersection of a polyhedron with a lineCycle threshold
A single technique for determining Ct is provided that can be used for standard sigmoidal growth curves and for problematic growth curves, such as parabolic curves. The Ct value can be determined as the intersection of a line tangent to the growth curve at the maximum of the second derivative with a baseline of the growth curve. Such a Ct value is usable for sigmoidal curves and parabolic curves, and can provide linear calibration curves to achieve accuracy in determining initial concentrations of a sample.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
PCR elbow determination by use of a double sigmoid function curve fit with the Levenburg-Marquardt algorithm and normalization
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
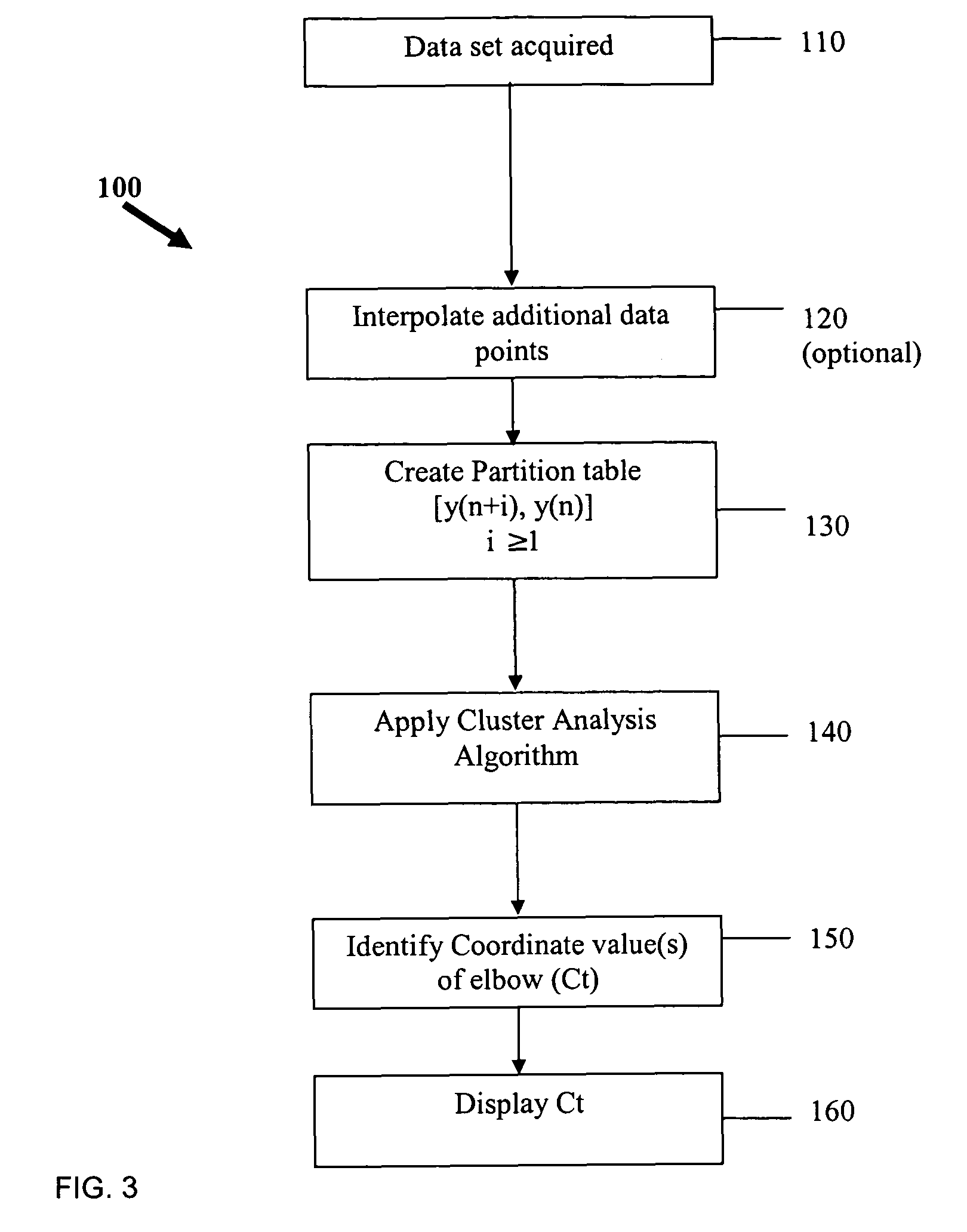
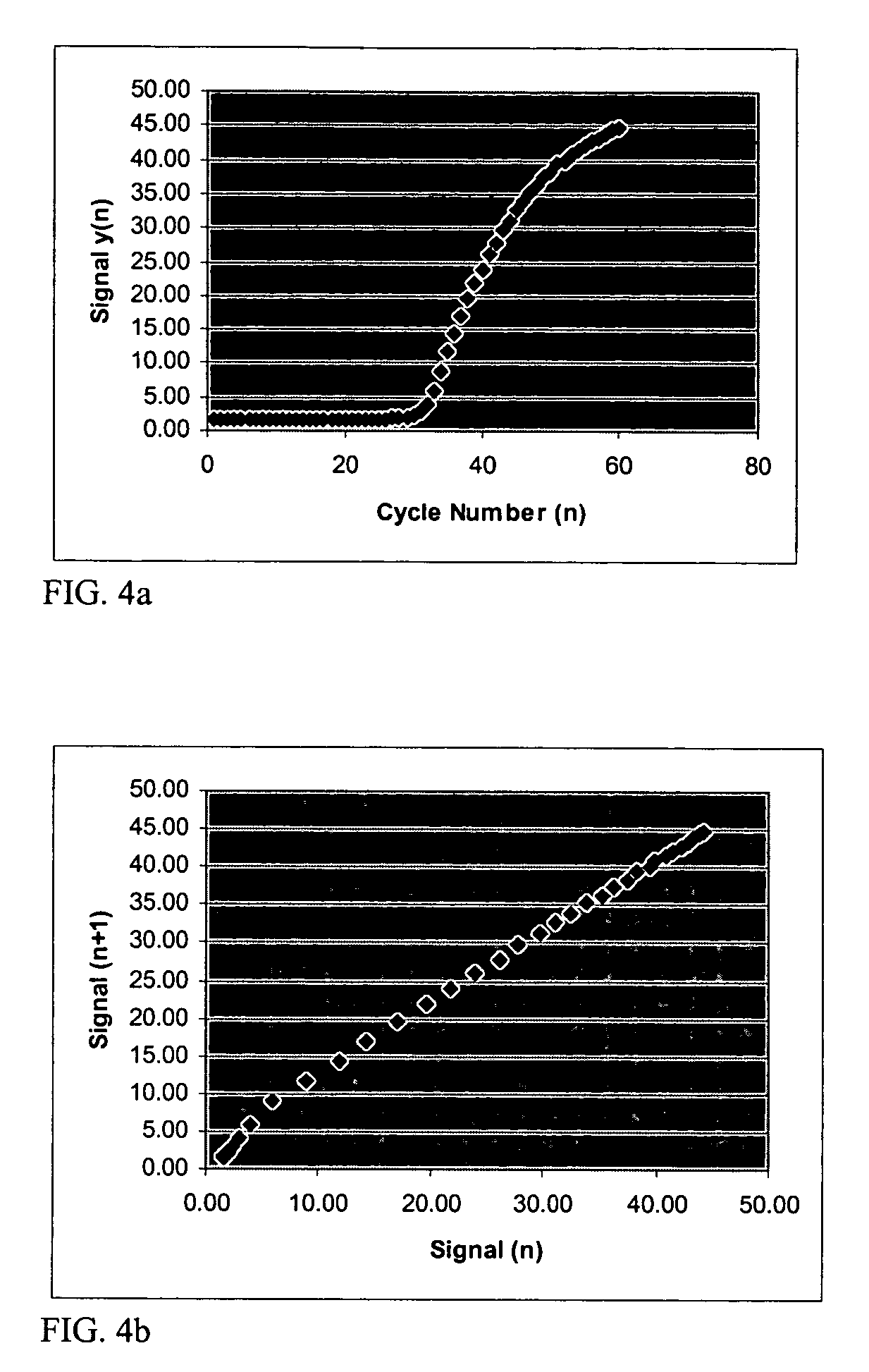
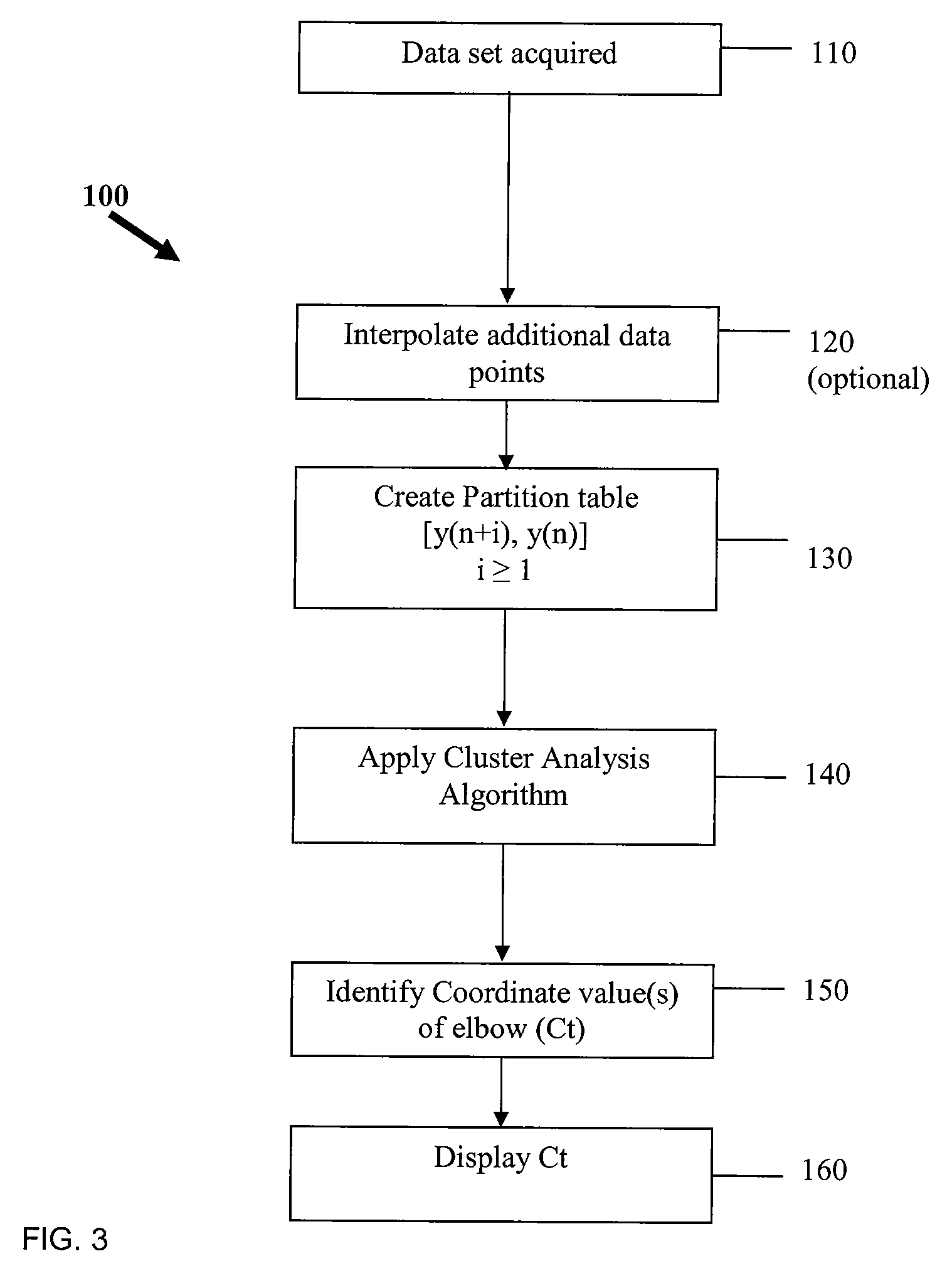
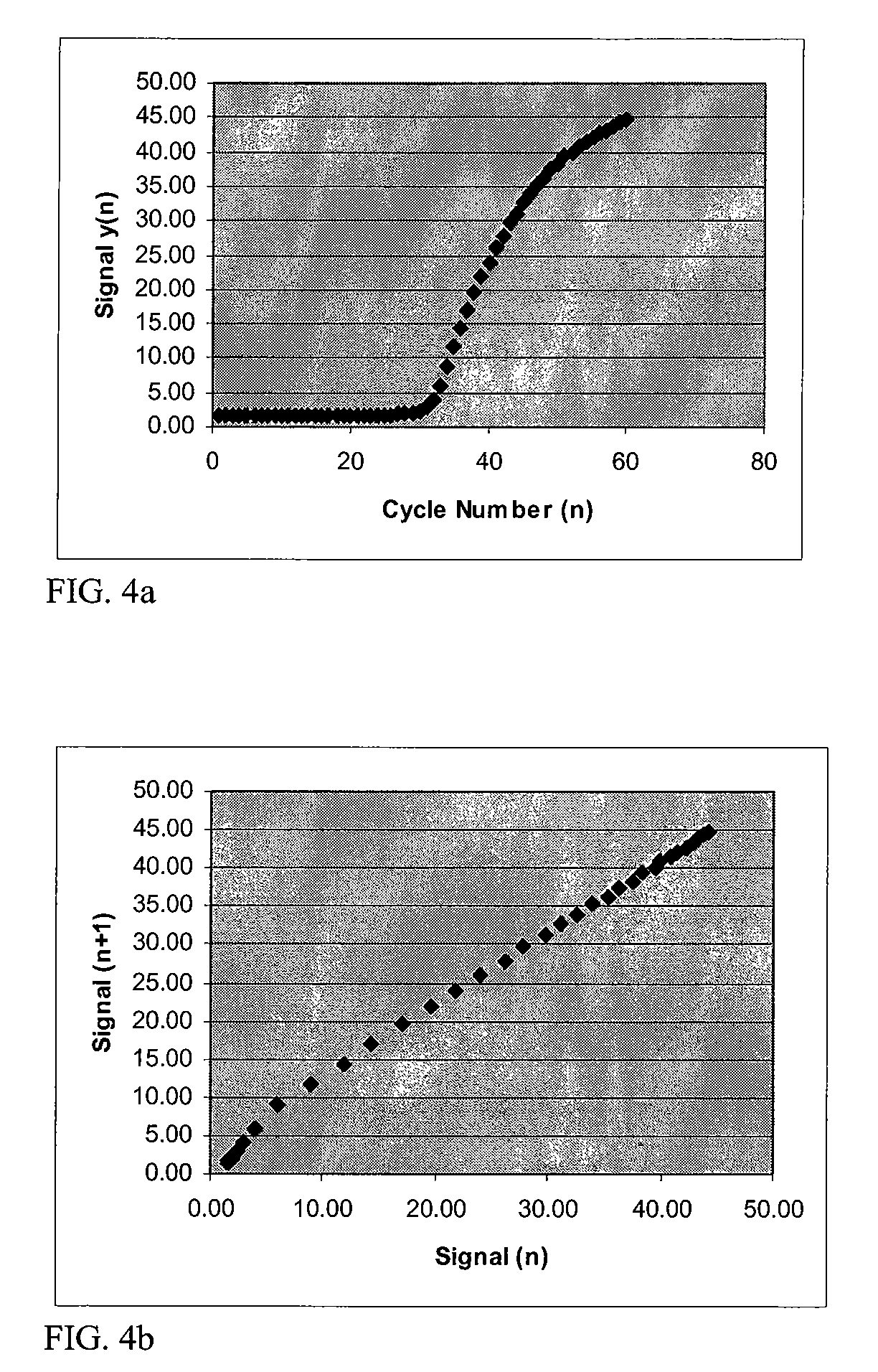
Systems and methods for determining real-time PCR cycle thresholds using cluster analysis
ActiveUS7991558B2Eliminate needNoisy dataMicrobiological testing/measurementData visualisationData setCycle threshold
Systems and methods for determining the elbow or Ct value in a real-time, or kinetic, PCR amplification curve data set. The PCR data set may be visualized in a two-dimensional plot of fluorescence intensity (y-axis) vs. cycle number (x-axis). The data set is transformed to produce a partition table of data points with one column including the fluorescence at cycle (n) and a second column including the fluorescence at cycle (n+i), where i is typically 1 or greater. A cluster analysis process is applied to the partition table data set to determine a plurality of clusters in the partition table data set. In one aspect, the clustering process used includes a k-means clustering algorithm, where k≧3. The data point representing the elbow or Ct value of the PCR curve is identified as an end point of one of the identified clusters, and the cycle number corresponding to this data point is returned or displayed.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
PCR elbow determination using curvature analysis of a double sigmoid
ActiveCN101908037AMicrobiological testing/measurementRecognisation of pattern in signalsData setSigmoid function
Systems and methods for determining characteristic transition values such as elbow values in sigmoid or growth-type curves, such as the cycle threshold (Ct) value in PCR amplification curves. A double sigmoid function with parameters determined by a Levenberg-Marquardt (LM) regression process is used to find an approximation to a curve that fits a PCR dataset. Once the parameters have been determined, the curve can be normalized using one or more of the determined parameters. After normalization, the normalized curve is processed to determine the curvature of the curve at some or all points along the curve, e.g., to produce a dataset or plot representing the curvature v. the cycle number. The cycle number at which the maximum curvature occurs corresponds to the Ct value. The Ct value is then returned and may be displayed or otherwise used for further processing.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
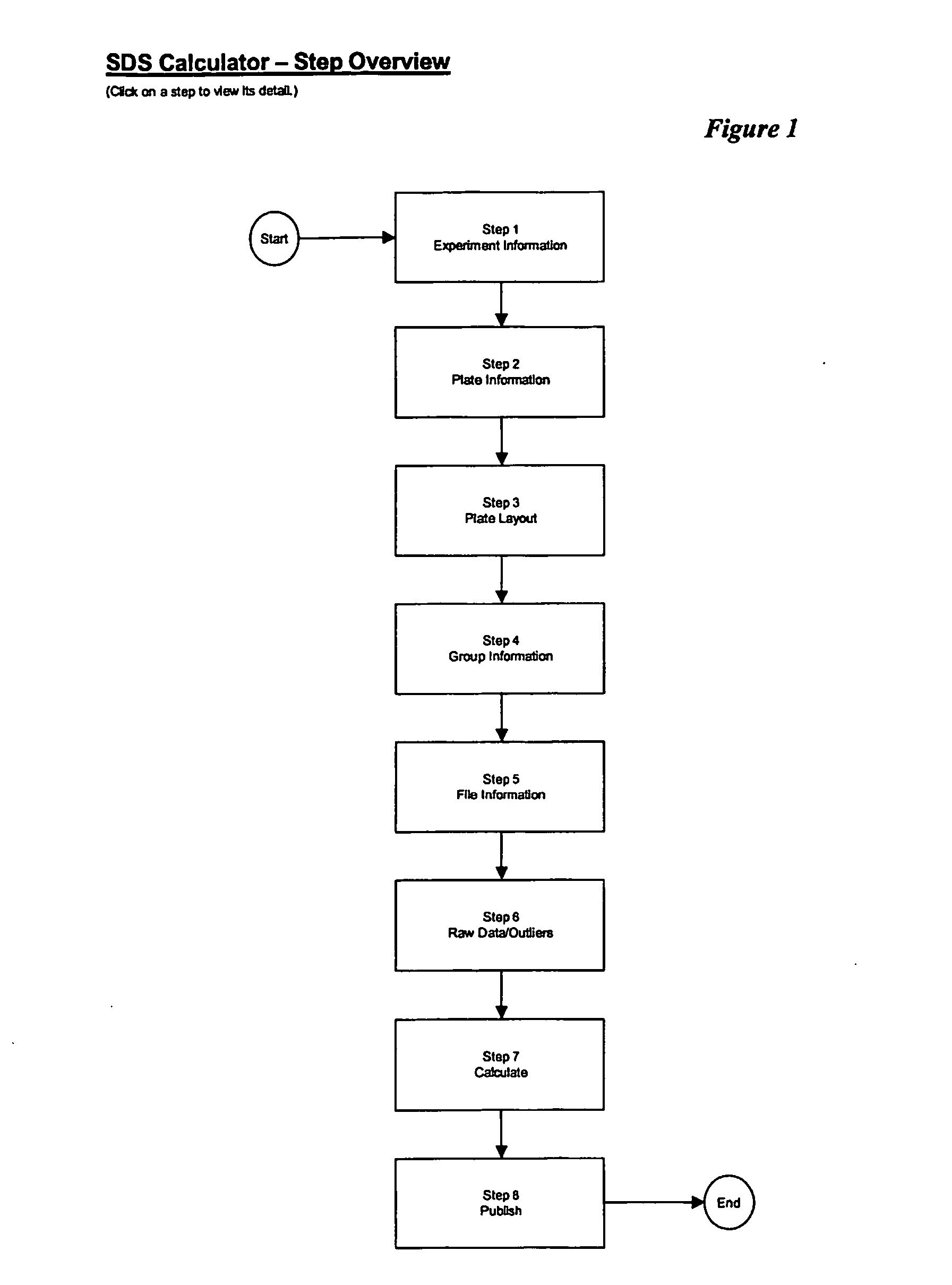
Sequence detection system calculator
InactiveUS20050165558A1Shorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingBiologyCycle threshold
A computer-readable medium contains instructions for controlling a computer system in the analysis of an experiment to detect RNA or DNA in a sample by receiving exported cycle threshold values (exported CT values) for a plate of wells from a polymerase chain reaction system and then calculates the delta CT, the delta delta CT and the relative transcriptional change for the sample. The results including the cycle threshold values inputted from the polymerase chain reaction system are then displayed.
Owner:BECKER ROBERT G +3
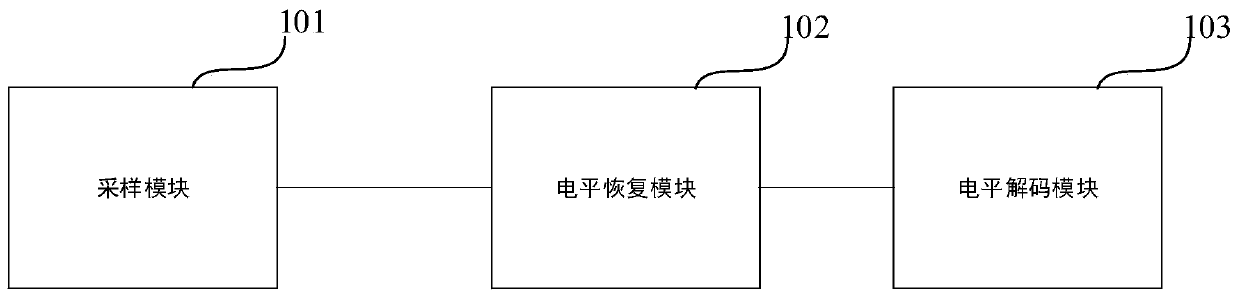
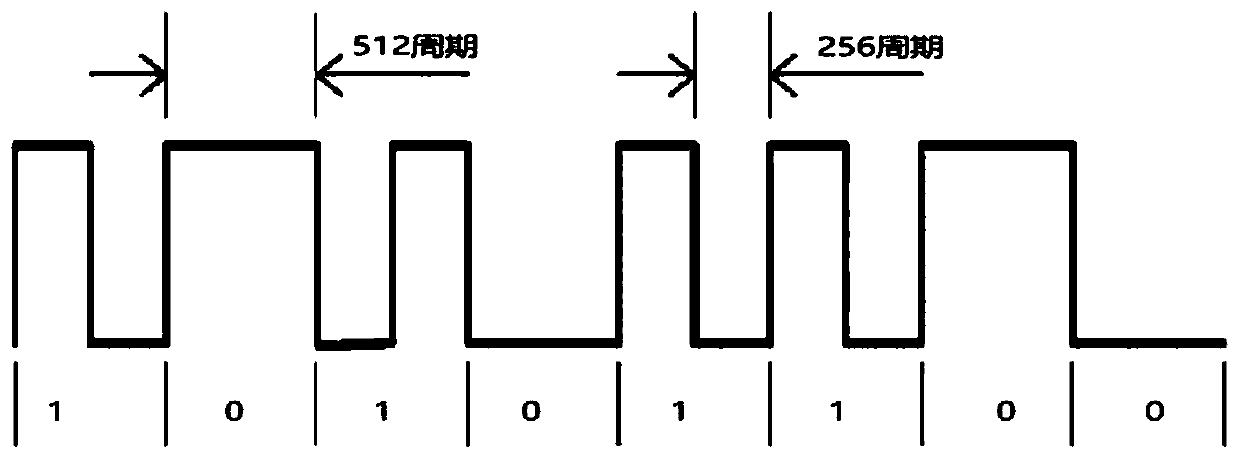
FSK demodulator, related equipment and method
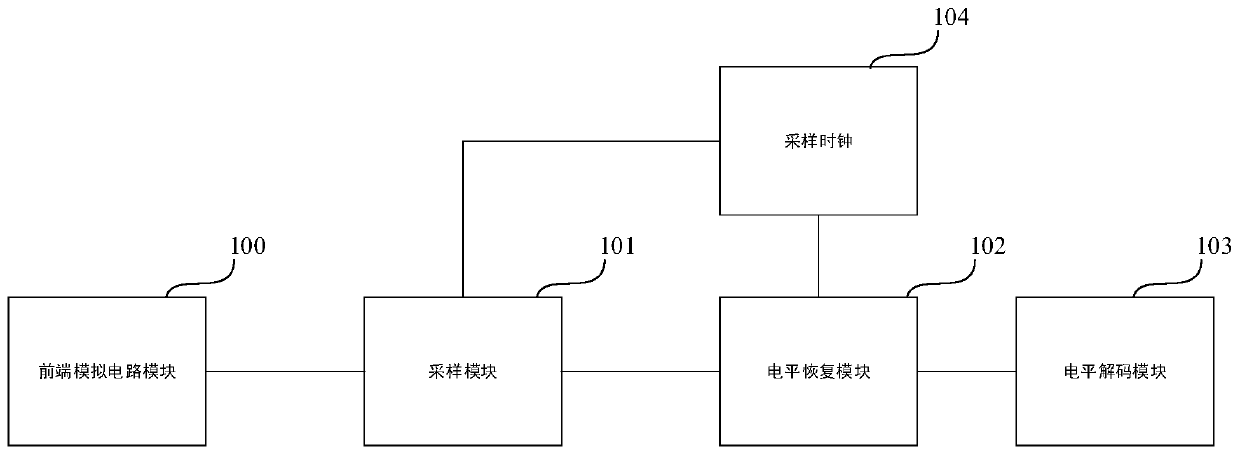
ActiveCN110445736AEliminate single-cycle errorsSimple structureCircuit arrangementsFrequency-modulated carrier systemsCycle thresholdComputer science
The invention discloses an FSK decoder, equipment and a decoding method, and the FSK decoder comprises a sampling module which is used for employing a preset sampling frequency at an FSK starting stage, carrying out the frequency sampling of an FSK modulation signal for many times according to a preset sampling period number, and determining a working frequency average sampling value correspondingto the frequency sampling for many times; a level recovery module which is used in an FSK communication stage and used for performing frequency sampling on the FSK modulation signal in real time according to a preset sampling period number by adopting the preset sampling frequency to obtain a signal frequency dynamic statistical value of each time of frequency sampling, and obtaining a level signal according to an absolute value of a difference value between the signal frequency dynamic statistical value and the working frequency average sampling value; and a level decoding module which is used for counting the number of cycles from each time of level edge change to the next time of level edge change in the level signal, matching the number of cycles with a preset cycle threshold range, and determining a corresponding bit value. The FSK decoder is accurate in processing result and easy to implement.
Owner:MAXIC TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION
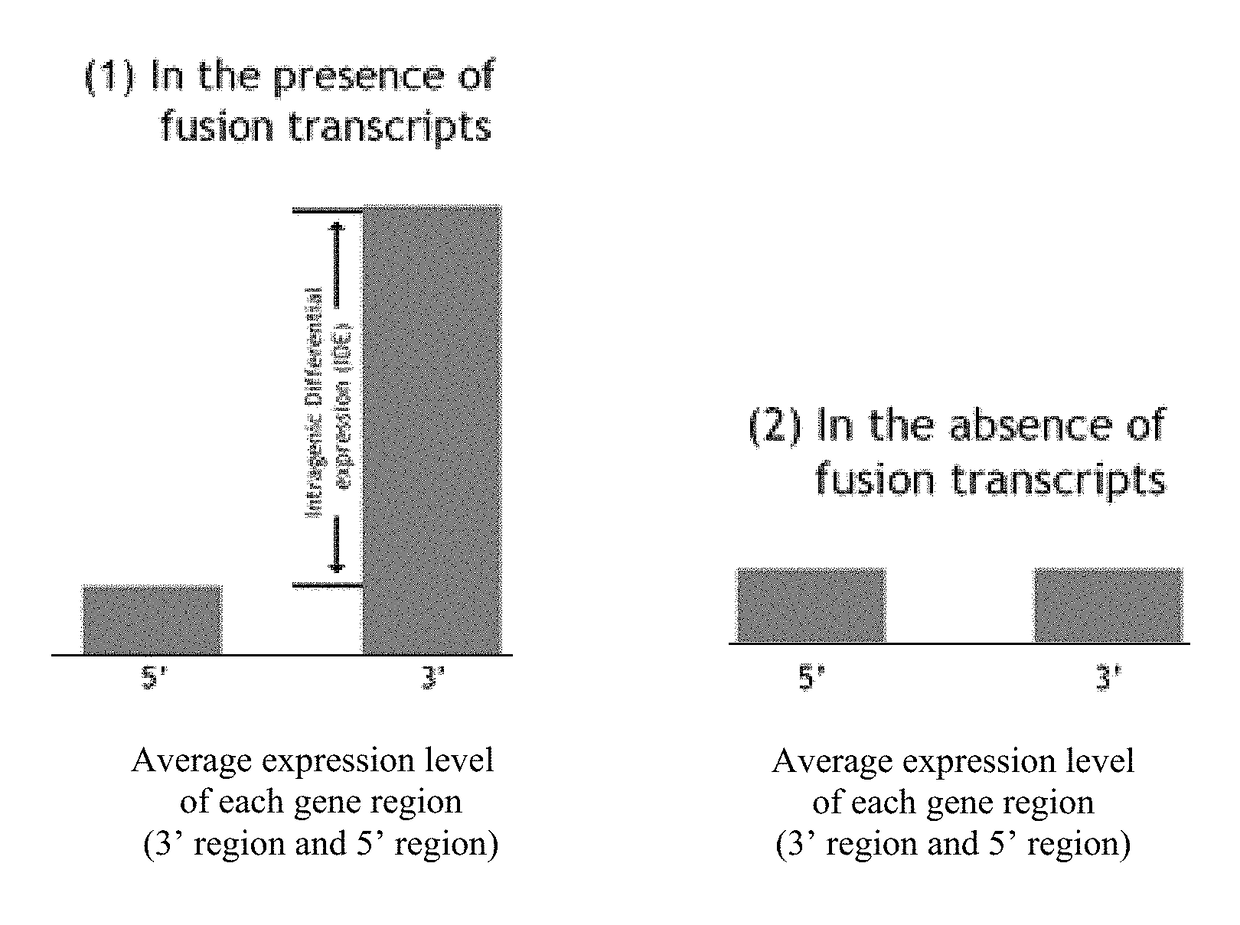
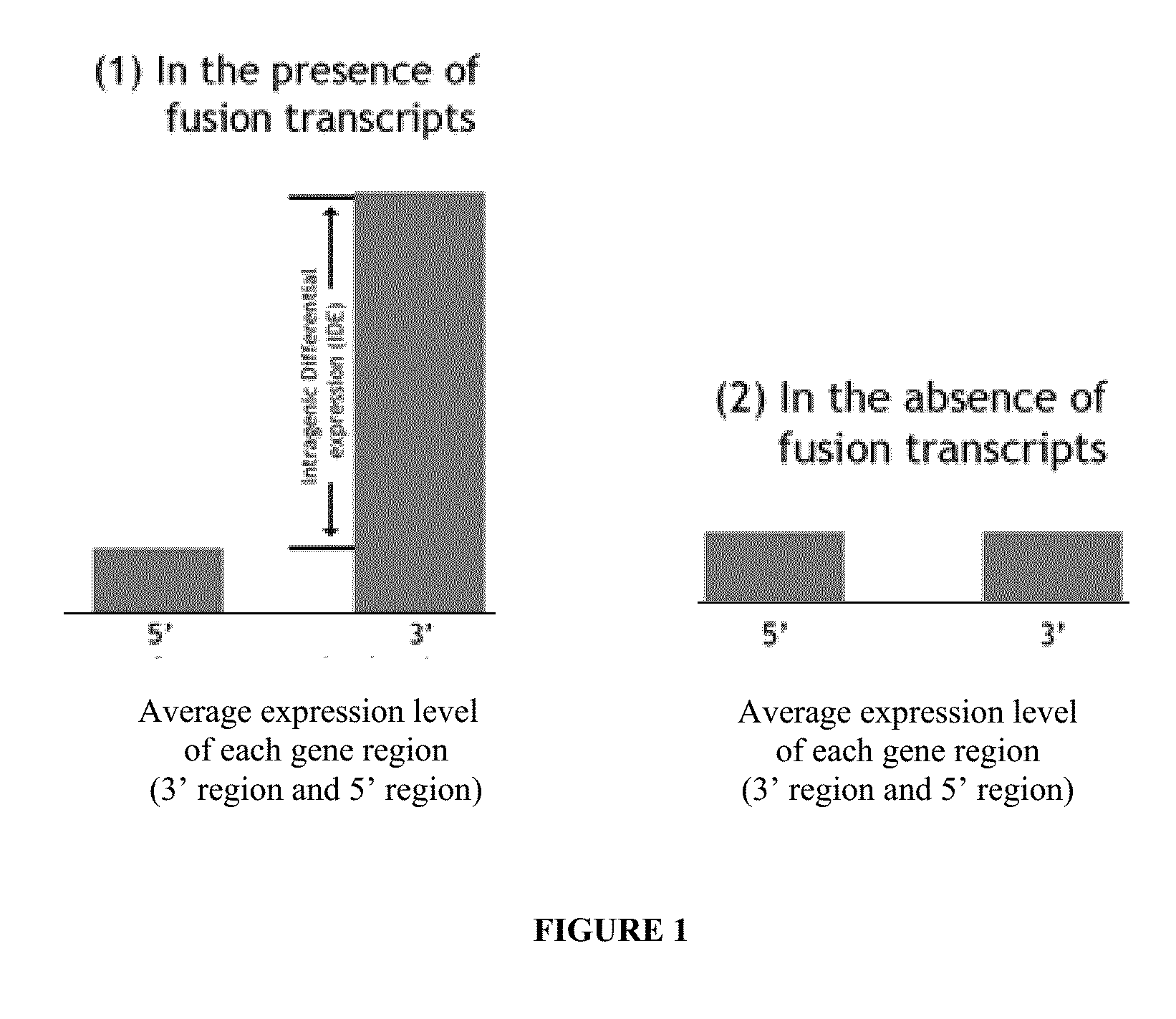
Detection of gene fusions by intragenic differential expression (IDE) using average cycle thresholds
ActiveUS9914973B2Microbiological testing/measurementFermentationCycle thresholdProtein translocation
Described herein are methods and kits for detecting the presence or absence of gene dysregulations such as those arising from gene fusions and / or chromosomal abnormalities, e.g. translocations, insertions, inversions and deletions. The methods, compositions and kits are useful for detecting mutations that cause the differential expression of a 5′ portion of a target gene relative to the 3′ region of the target gene. The average expression of the 5′ portion of the target gene is compared with the average expression of the 3′ portion of the target gene to determine an intragenic differential expression (IDE). The IDE can then be used to determine if a dysregulation or a particular disease (or susceptibility to a disease) is present or absent in a subject or sample.
Owner:QUEST DIAGNOSTICS INVESTMENTS INC
Method for detecting quantity of pseudomonas fluorescens in rhizospheric soil during growth period of transgenic wheat by virtue of fluorescent quantitative PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction)
ActiveCN103397099AConsistent repetitive responseEasy to distinguishMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescencePseudomonas fluorescensPseudomonas
The influence of transgenic crops on rhizospheric microorganisms in soil is an important aspect in environmental biosafety research. The invention establishes a detection system of Real-Time QPCR (Real-Time Fluorescent Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction)) by carrying out absolute quantification on the quantity of pseudomonas fluorescens in rhizospheric soil during the growth period of transgenic disease-resistant wheat. By virtue of application of the reaction system, the absolute quantification is carried out on the copy number of the pseudomonas fluorescens in the rhizospheric soil during the whole growth period of the transgenic wheat. A result shows that the designed primer has better specificity; the intervals of cycle thresholds (Ct values) of plasmids with various gradient standards in an amplification curve of Real-Time QPCR are uniform, the peak value of a melting curve is more obvious, and for the standard curve, the correlation coefficient R2 is equal to 0.99905, the slope is minus 3.203, and the amplification efficiency E is equal to 100%. In the seeding stage, seedling establishment stage, watery stage and mature stage of the transgenic wheat, the quantity of the pseudomonas fluorescens in the rhizospheric soil takes on a trend of gradually rising.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Target sequence for detecting RNA of influenza A H1N1 viruses and kit
InactiveCN102071260AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesNegative controlReaction tube
The invention provides a target sequence for detecting the RNA of influenza A H1N1 viruses (2009) and a kit. The invention is characterized in that: specific primer probes designed on the basis of the two nucleotide target sequences of influenza A H1N1 viruses are adopted to detect the RNA of the influenza A H1N1 viruses (2009) by a one-step fluorescent reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) in a single reaction tube, and detect the existence of the RNA of the influenza A H1N1 viruses in a sample by the fluorescent signal intensity and circulating threshold of an amplification template. The kit comprises the following components: PCR buffer solution, RT / Taq mixed enzymes, a negative reference and a positive reference. The kit is used by two steps, namely, a sample processing step and an amplification detection step. The operation of the kit is simple, convenient and quick, and the sensitivity of the kit is high. The kit can be widely used disease control and quick detection of influenza A H1N1 viruses (2009) in clinic.
Owner:SHANGHAI XINGYAO MED TECH DEV CO LTD +1
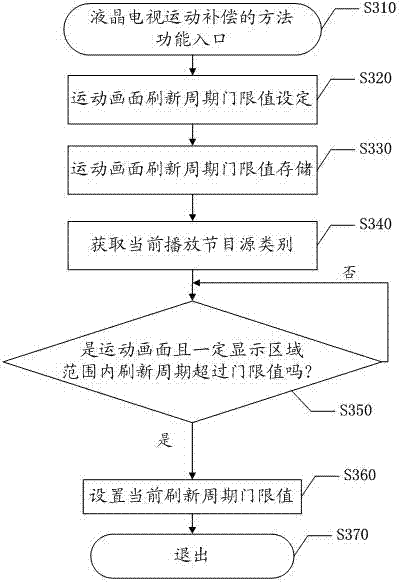
Method and system for processing motion graphic compensation of LCD TV (liquid crystal display television)
ActiveCN103051856AAvoid displaying frameratesReduce display frame rateStatic indicating devicesStandards conversionRefresh cycleComputer graphics (images)
The invention relates to the technical field of televisions and discloses a method and a system for processing motion graphic compensation of an LCD TV (liquid crystal display television). The method specifically comprises the following steps of: pre-configuring a motion graphic refreshing cycle threshold, and storing the threshold; when receiving an operation instruction of a user to open a motion graphic compensation function of the LCD TV, controlling to obtain the category of a currently playing film source and judging whether a motion graphic exists in an existing frame and the on-off frequency of a lamp in a certain display area is higher than the preset motion frame refreshing cycle threshold or not; and when judging that the on-off frequency of the lamp in the certain display area is higher than the preset motion frame refreshing cycle threshold, identifying to start a motion graphic compensation mode. According to the method and system for processing the motion graphic compensation of the LCD TV, disclosed by the invention, the resolution is improved by intelligently identifying a motion mode of the system and reducing display frames of the motion graphic, so that the motion graphic is clearer and more smooth.
Owner:KONKA GROUP
Hepatitis a virus detecting method in food
InactiveCN101550458ATime-consuming to solveResolve SensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesRNA extractionHepatitis A viruses
The present invention discloses an hepatitis a virus detecting method in food, the detecting method including following steps : 1) processing of sample under test; 2) RNA extraction of sample under test; 3) RNA reverse transcription; 4) SYBR Green I Real-time PCR reaction; 5) judgement of detected results: when cyclic threshold value of the sample under test is less than 33, judging as hepatitis a virus positive; when cyclic threshold value of the sample under test is more than 35, judging as hepatitis a virus negative; when cyclic threshold value of the sample under test is less than 35 and more than 33, treating as suspicious sample, if the renewed detected results is still in the range, then judging as hepatitis a virus negative. The detecting method of the invention is provided with advantages of rapid, high sensitivity and specificity and quantitative. judging as hepatitis a virus positive.
Owner:INSPECTION & QUARANTINE TECH CENT OF GUANGDONG ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU
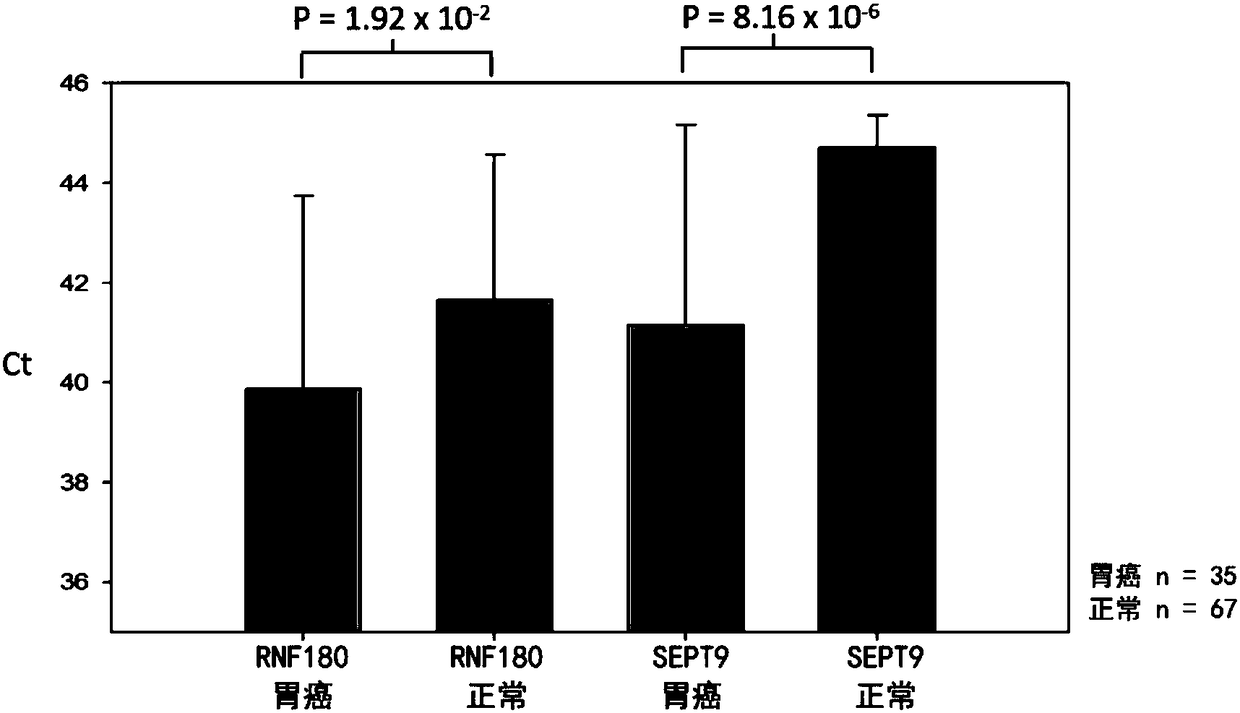
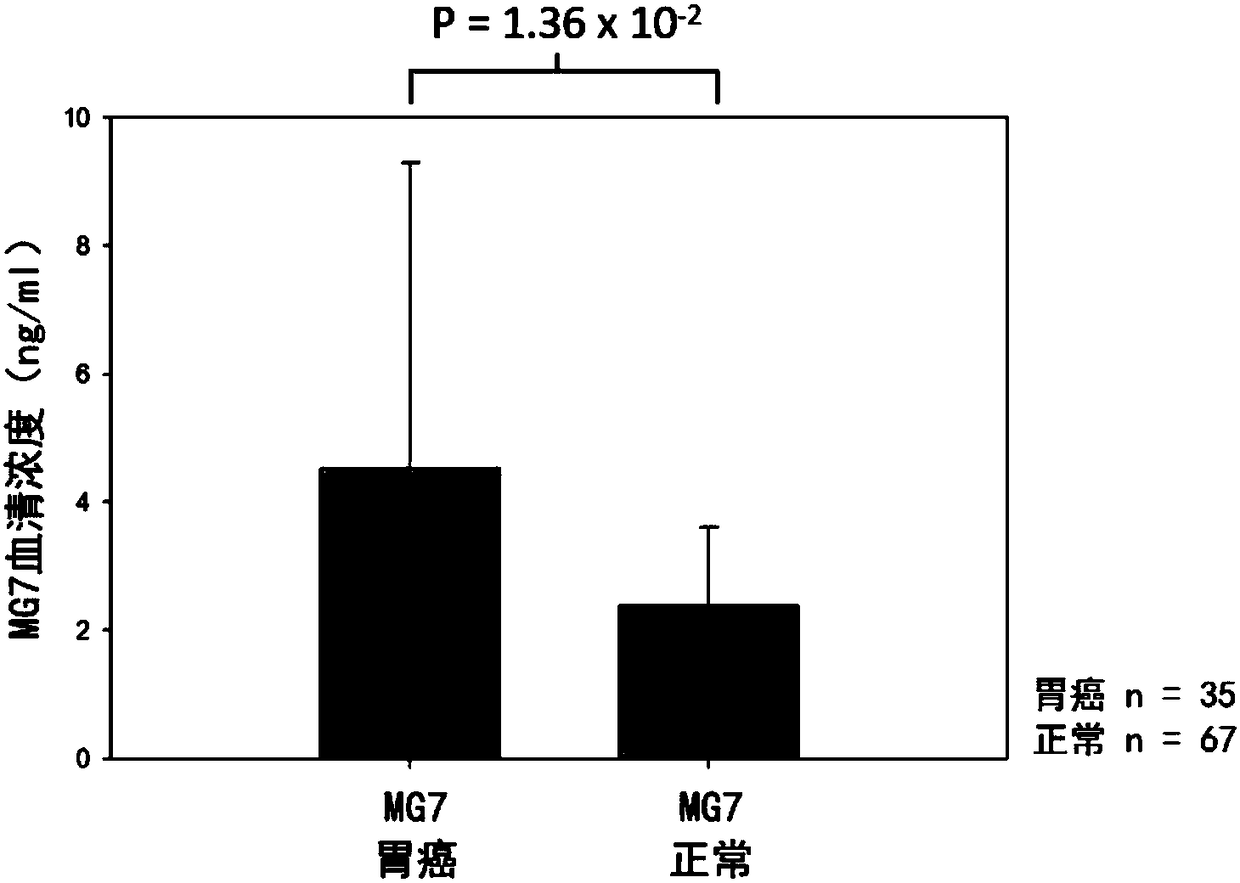
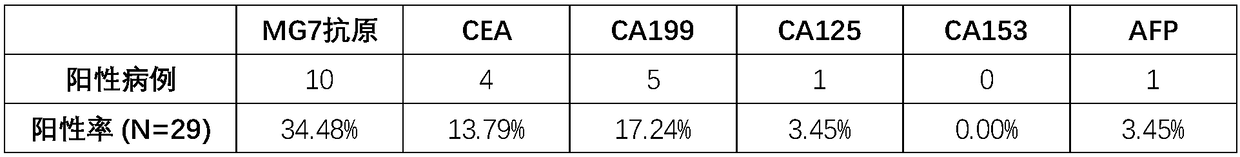
Composition for detecting gastric cancer as well as kit and use thereof
The invention provides a composition for detecting gastric cancer, wherein the composition comprises: 1) a nucleic acid for detecting a methylation state in at least one region of a target gene, wherein the target gene is selected from an SEPT9 gene or fragments thereof and / or an RNF180 gene or fragments thereof; 2) an agent for detecting a concentration of an MG7 antigen in serum / plasma; the gastric cancer is detected by the methylation state of the target gene and a protein expression level of the target gene. The invention further provides a kit comprising the composition and a method for detecting the gastric cancer in vitro. Therefore, a method for analyzing DNA in a plasma sample by real-time PCR in the invention can conveniently detect the SEPT9 gene or the fragments thereof and / orthe RNF180 gene or the fragments thereof, and can rapidly and conveniently judge whether the sample is positive or not according to a cycle threshold (Ct) of the real-time PCR; further, the inventionprovides an accurate in-vitro detection method for detecting the concentration of the MG7 antigen in the serum / plasma of the sample to be detected.
Owner:BIOCHAIN BEIJING SCI & TECH +1
PCR elbow determination using curvature analysis of a double sigmoid
ActiveUS7991562B2Feeler-pin gaugesUsing subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic vibration meansData setSigmoid function
Systems and methods for determining characteristic transition values such as elbow values in sigmoid or growth-type curves, such as the cycle threshold (Ct) value in PCR amplification curves. A double sigmoid function with parameters determined by a Levenberg-Marquardt (LM) regression process is used to find an approximation to a curve that fits a PCR dataset. Once the parameters have been determined, the curve can be normalized using one or more of the determined parameters. After normalization, the normalized curve is processed to determine the curvature of the curve at some or all points along the curve, e.g., to produce a dataset or plot representing the curvature v. the cycle number. The cycle number at which the maximum curvature occurs corresponds to the Ct value. The Ct value is then returned and may be displayed or otherwise used for further processing.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Method and kit for detecting DNA polymerase activity
ActiveCN107034280ASimple and fast operationGood reproducibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementForward primerPolymerase L
The invention relates to a method and kit for detecting DNA polymerase activity; the method comprises: mixing DNA polymerase under detection and a sufficient template to be filled in, and using, in the presence of dNTP, the DNA polymerase under detection to induce a first DNA fragment in the template to be filled in so as to form a filling-in fragment complementary with a base of a projecting fragment, thereby acquiring a filled-in template; digesting to remove the base U of the filled-in template through sufficient UDG (uracil DNA glycosylase) to obtain a template suitable for PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification, designing a forward primer for the projecting fragment and a reverse primer for 5' end of the first DNA fragment, and inducing first template chain amplification, wherein a template which is not filled in and has the base U removed via a digestive enzyme is unable to pair with the forward primer, and PCR amplification cannot be performed; CT (cycle threshold) value of DNA polymerase under detection can be brought to a standard curve established via a DNA polymerase standard, and activity of the DNA polymerase under detection can be acquired just by calculating.
Owner:FAPON BIOTECH INC +1
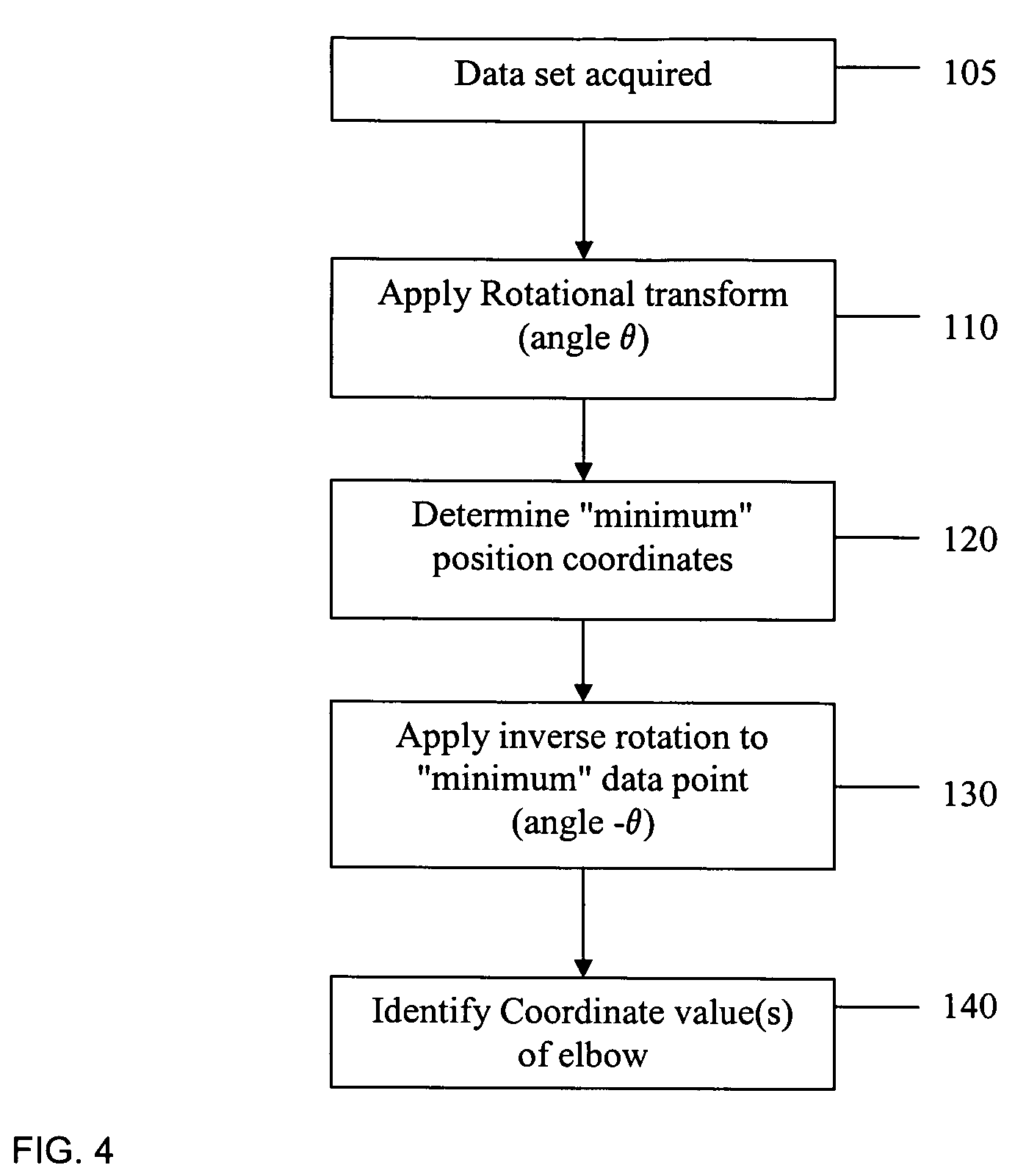
Ct determination by cluster analysis with variable cluster endpoint
Systems and methods for determining the cycle threshold (Ct) value in a kinetic PCR amplification curve. The PCR data set may be visualized in a two-dimensional plot of fluorescence intensity (y-axis) vs. cycle number (x-axis). The data set is transformed to produce a partition table of data points with one column including the fluorescence at cycle (n) and a second column including the fluorescence at cycle (n+i), where i is typically 1 or greater. A cluster analysis process is applied to the partition table data set to determine a plurality of clusters in the partition table data set. In one aspect, the clustering process used includes a k-means clustering algorithm, where the number of identified clusters, k, is greater than or equal to three. In another aspect, a Partitioning Around Medoids (PAM) algorithm is used to identify three or more clusters. Using the identified clusters, a linear slope of each of the clusters is determined based on y(n+1) vs. n, and for each cluster, a ratio of the slope of that cluster with the slope of an adjacent cluster is determined. The ratios are then compared. An end point of a cluster having the largest or smallest ratio represents a specific point of interest in the data curve. The data point representing the elbow or Ct value of the PCR curve is identified as an end point of one of the identified clusters, and the cycle number corresponding to this data point is returned or displayed.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
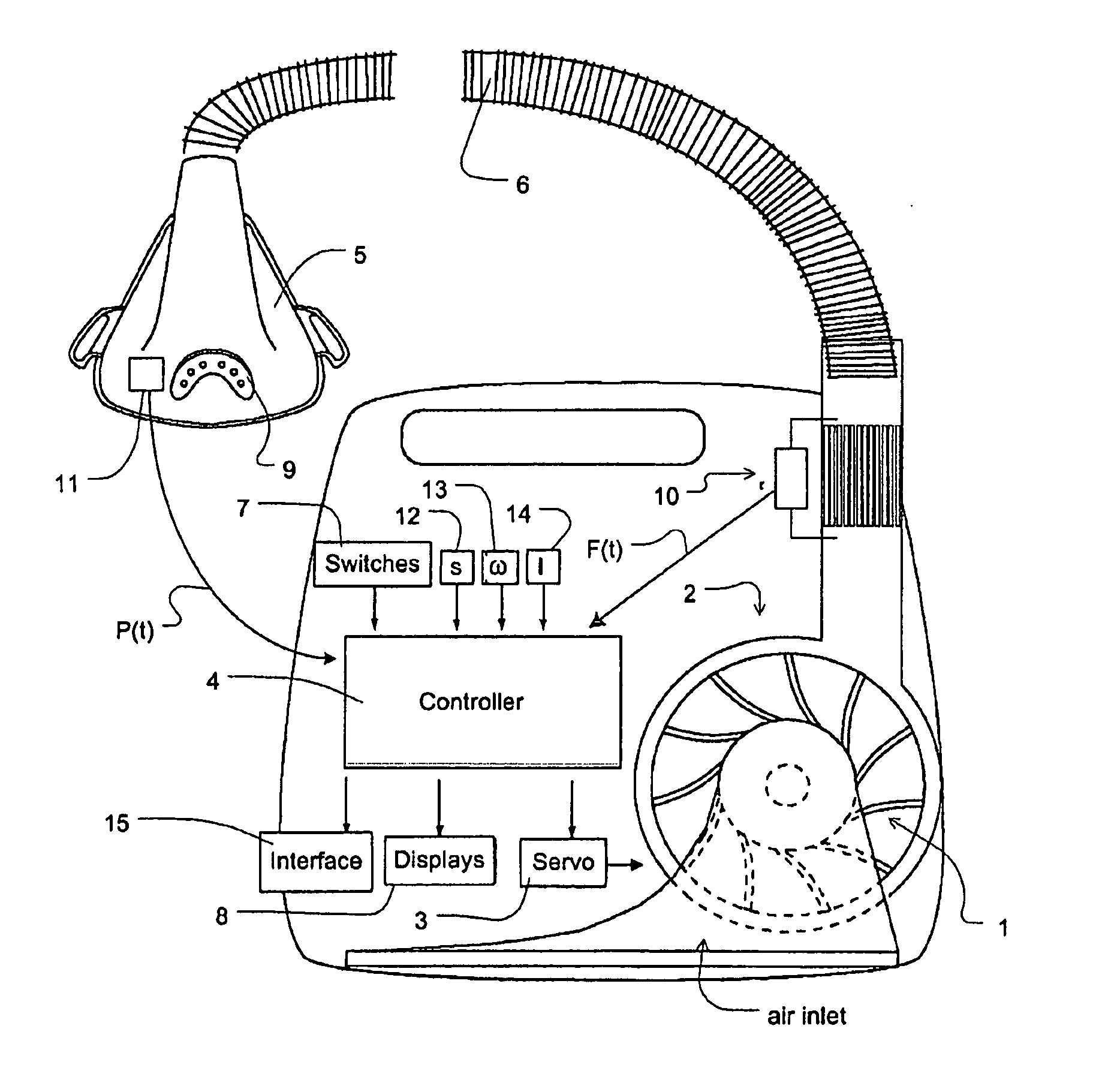
Methods, systems and apparatus for paced breathing
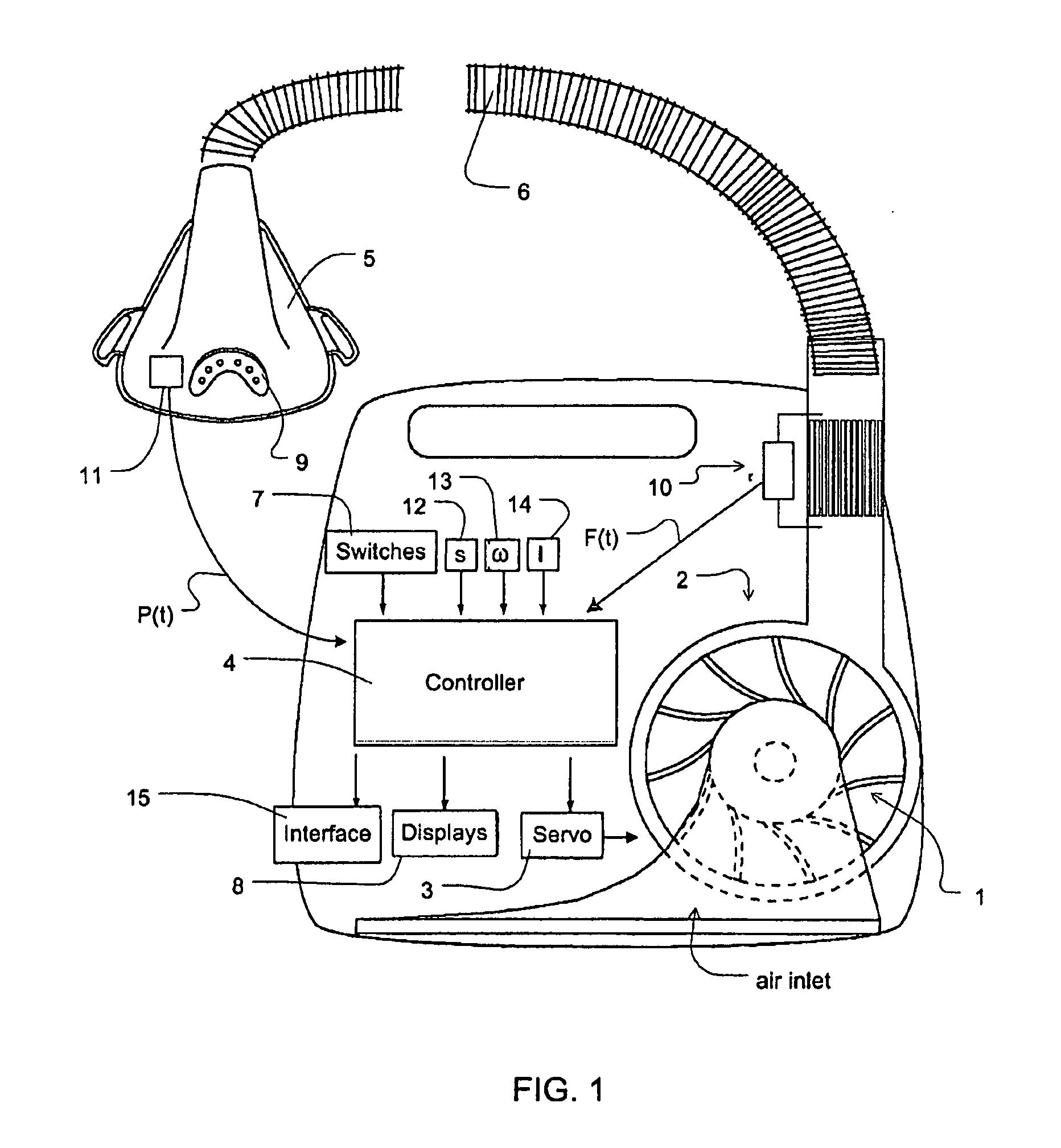
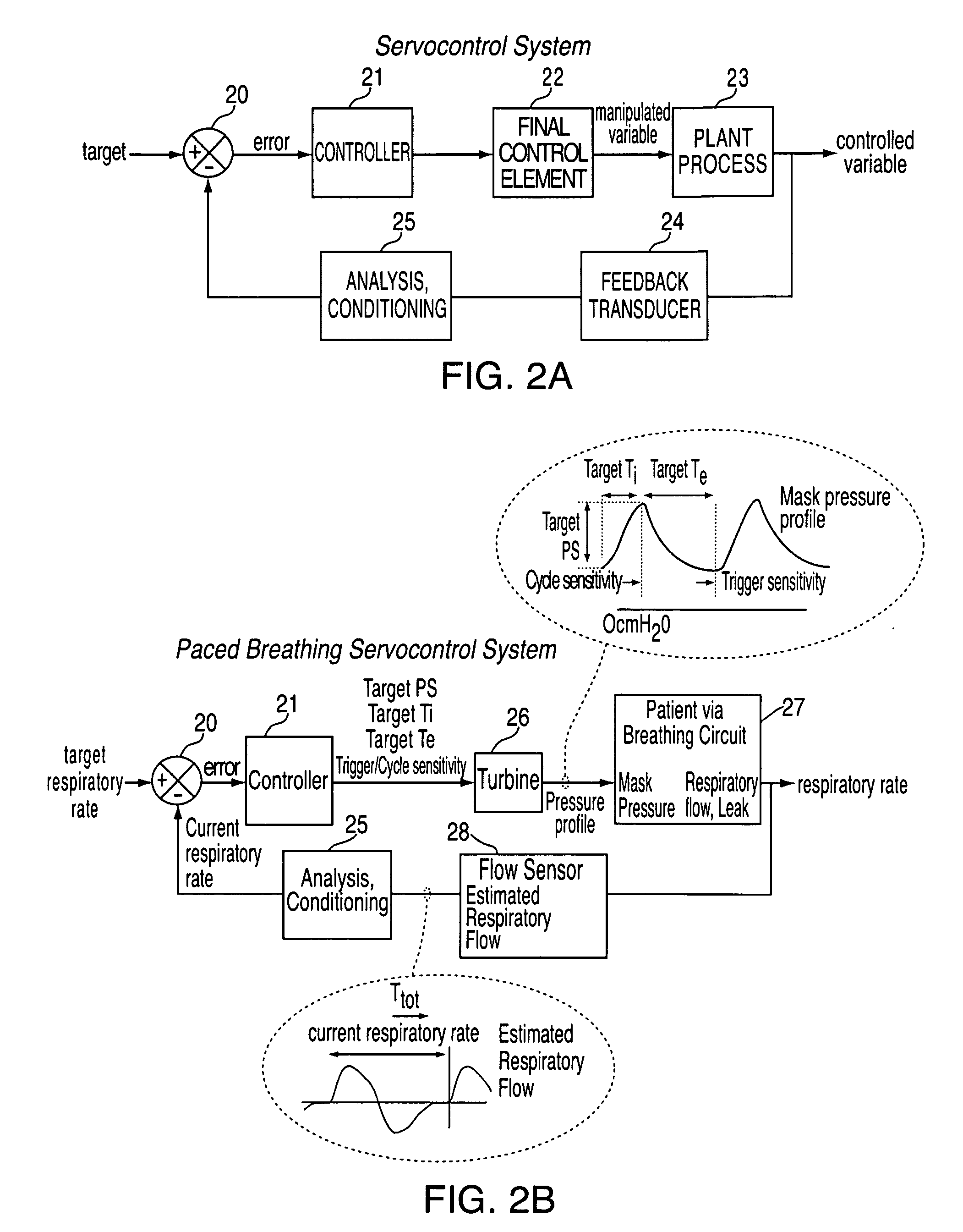
ActiveUS8844527B2Promote circulationEasy to triggerRespiratorsElectrocardiographyCycle thresholdPaced breathing
Methods, systems and / or apparatus for slowing a patient's breathing by using positive pressure therapy. In certain embodiments, a current interim breathing rate target is set, and periodically the magnitude of a variable pressure waveform that is scaled to the current interim breathing rate target is increased if the patient's breathing rate is greater than the interim breathing rate target in order to lengthen the patient's breath duration. The magnitude of the pressure increase may be a function of the difference between the interim breathing rate target and the patient's breathing rate. The interim breathing rate target may be periodically reduced in response to the patient's breathing rate slowing down toward the current interim breathing rate target. The variable pressure waveform cycles from an inhalation phase to an exhalation phase when the patient airflow decreases to a cycle threshold, the cycle threshold being a function of flow versus time within a breath and generally increasing with time. Different interim breathing rate targets have different cycle threshold functions, and the cycle threshold functions allow easier cycling as the interim breathing rate targets decrease. Similarly, the variable pressure waveform triggers from an exhalation phase to an inhalation phase when the patient airflow increases to a trigger threshold, the trigger threshold being a function of flow versus time within a breath and generally decreasing with time. Different interim breathing rate targets have different trigger threshold functions, and the trigger threshold functions allow easier triggering as the interim breathing rate targets decrease.
Owner:RESMED LTD
Method and kit for detecting genotypes of herpes simplex virus
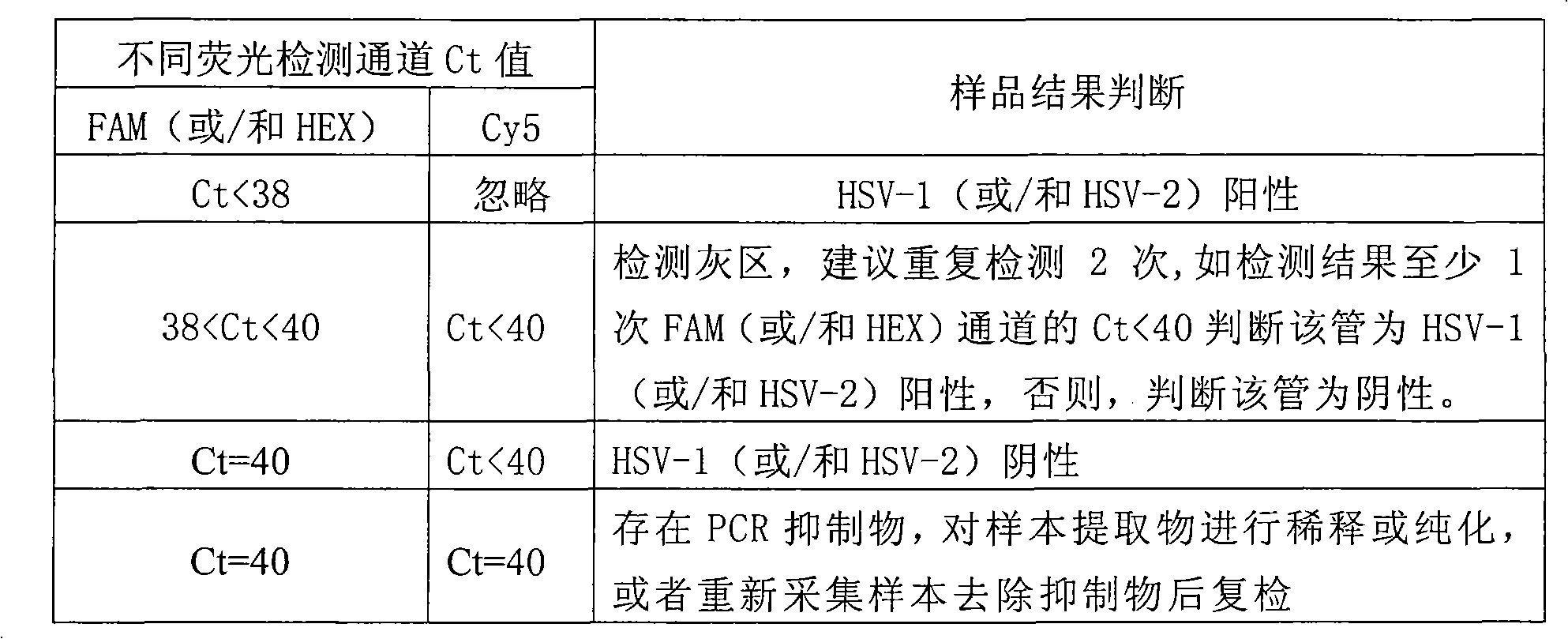
InactiveCN102071262AReliable resultsAvoid misdiagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesFluoProbesCycle threshold
The invention discloses a method and a kit for detecting genotypes of a herpes simplex virus (HSV). Primer probes designed on the basis of HSV DNA polymerase gene are adopted, type 1 and type 2 of the HSV are detected simultaneously in a single tube by TaqMan probe dual-wavelength fluorescent PCR technology, and the existence and the type of the HSV in a sample are judged through fluorescent signals and circulating threshold values of amplification templates with different wavelengths. In the kit, a manually constructed internal reference system is used for avoiding false negative of a detection result. The kit comprises nucleic acid extracting solution, PCR buffer solution, Taq enzyme, an internal reference, negative control and positive control; and two steps of sample treatment and amplification detection are adopted. The kit is easy and convenient to operate and high in sensitivity, can avoid false positive caused by PCR product nucleic acid pollution, can solve the problem of false negative caused by a PCR inhibitor in the sample, and can be widely applied to quick detection of the genotypes of the pathogen clinically.
Owner:SHANGHAI XINGYAO MED TECH DEV CO LTD +1
Detection of gene fusions by intragenic differential expression (IDE) using average cycle thresholds
ActiveUS20150275277A1Sensitive and accurate and cost-effective assayMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningCycle thresholdProtein translocation
Described herein are methods and kits for detecting the presence or absence of gene dysregulations such as those arising from gene fusions and / or chromosomal abnormalities, e.g. translocations, insertions, inversions and deletions. The methods, compositions and kits are useful for detecting mutations that cause the differential expression of a 5′ portion of a target gene relative to the 3′ region of the target gene. The average expression of the 5′ portion of the target gene is compared with the average expression of the 3′ portion of the target gene to determine an intragenic differential expression (IDE). The IDE can then be used to determine if a dysregulation or a particular disease (or susceptibility to a disease) is present or absent in a subject or sample.
Owner:QUEST DIAGNOSTICS INVESTMENTS LLC
Systems and methods for determining real-time PCR cycle thresholds using a rotation transformation
Systems and methods for determining the elbow or Ct value in a real-time, or kinetic, PCR amplification curve data set. The PCR data set may be visualized in a two-dimensional plot of fluorescence intensity vs. cycle number. A rotation transform is applied to the data set to rotate the data about a defined coordinate such as the origin so that the data point representing the Ct value becomes a minimum or a maximum along the intensity axis. The data point representing the elbow or Ct value of the PCR curve is identified, and this data point is then rotated back and the cycle number of the data point is returned or displayed.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Method and kit for detecting nucleic acid with herpes simplex virus
InactiveCN102071261AAvoid misdiagnosisWill not interfere with each otherMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesPositive controlFluorescence
The invention discloses a method and a kit for identifying a herpes simplex virus (HSV) by utilizing fluorescent PCR. Primer probes designed on the basis of HSV DNA polymerase gene and a manually constructed internal reference system are adopted, the herpes simplex virus and internal reference DNA are detected in a single tube by TaqMan probe dual-wavelength fluorescent PCR technology, and the existence of the HSV in a sample is judged through fluorescent signal intensity and a circulating threshold value of an amplification template. The kit comprises nucleic acid extracting solution, PCR buffer solution, Taq enzyme, an internal reference, negative control and positive control; and two steps of sample treatment and amplification detection are adopted. The kit is easy and convenient to operate and high in sensitivity, can avoid false positive caused by PCR product nucleic acid pollution, can solve the problem of false negative caused by a PCR inhibitor in the sample, and can be widely applied to quick detection of the pathogen clinically.
Owner:SHANGHAI XINGYAO MED TECH DEV CO LTD +1
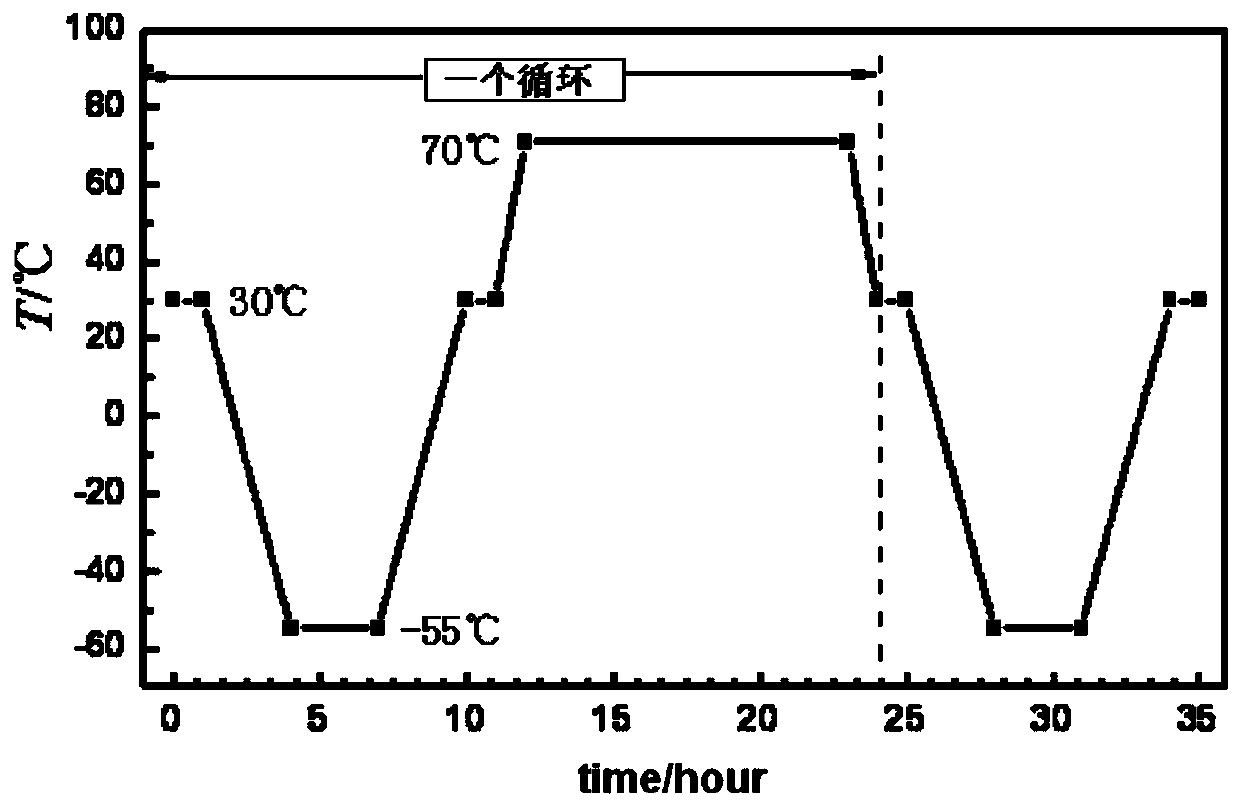
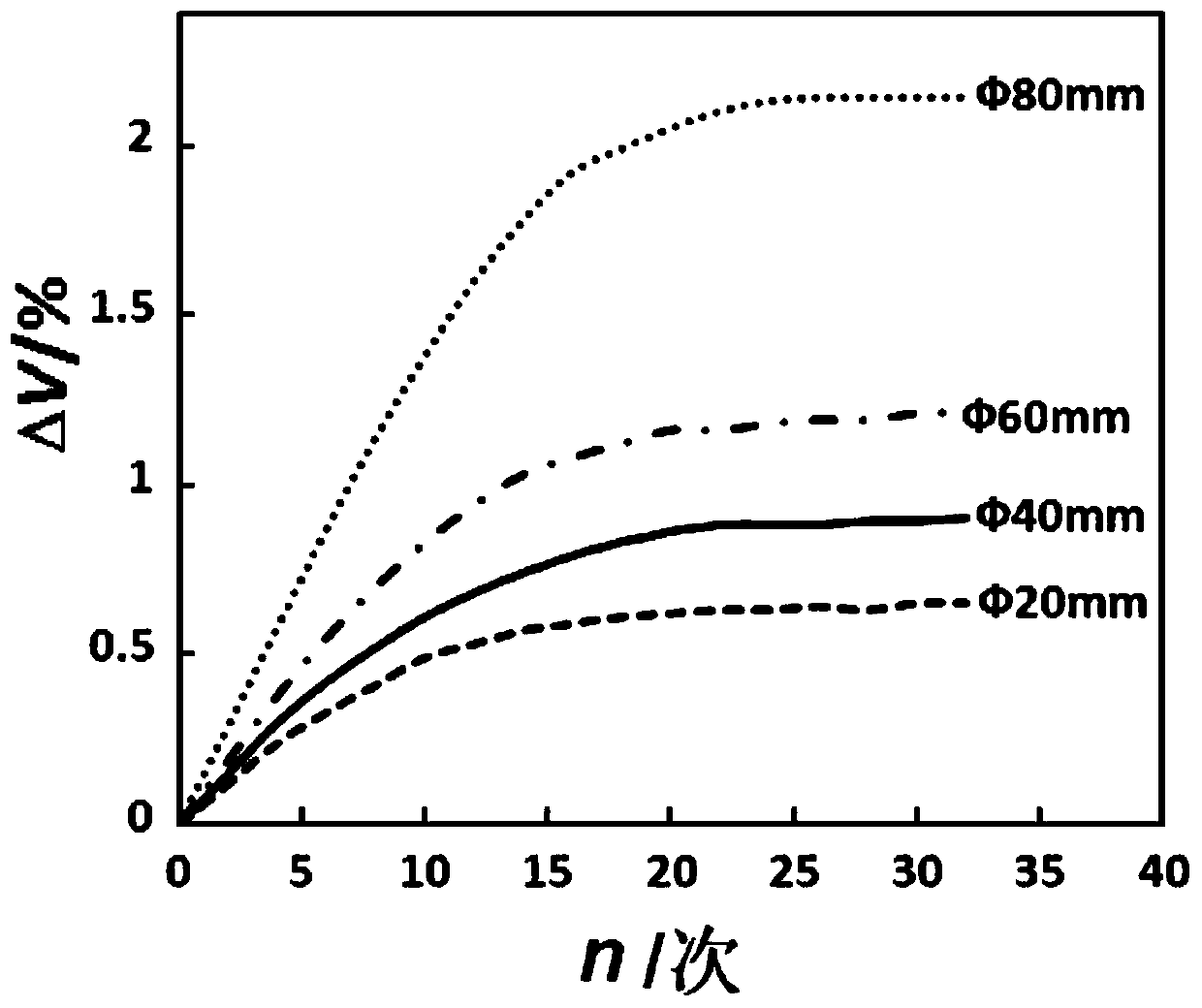
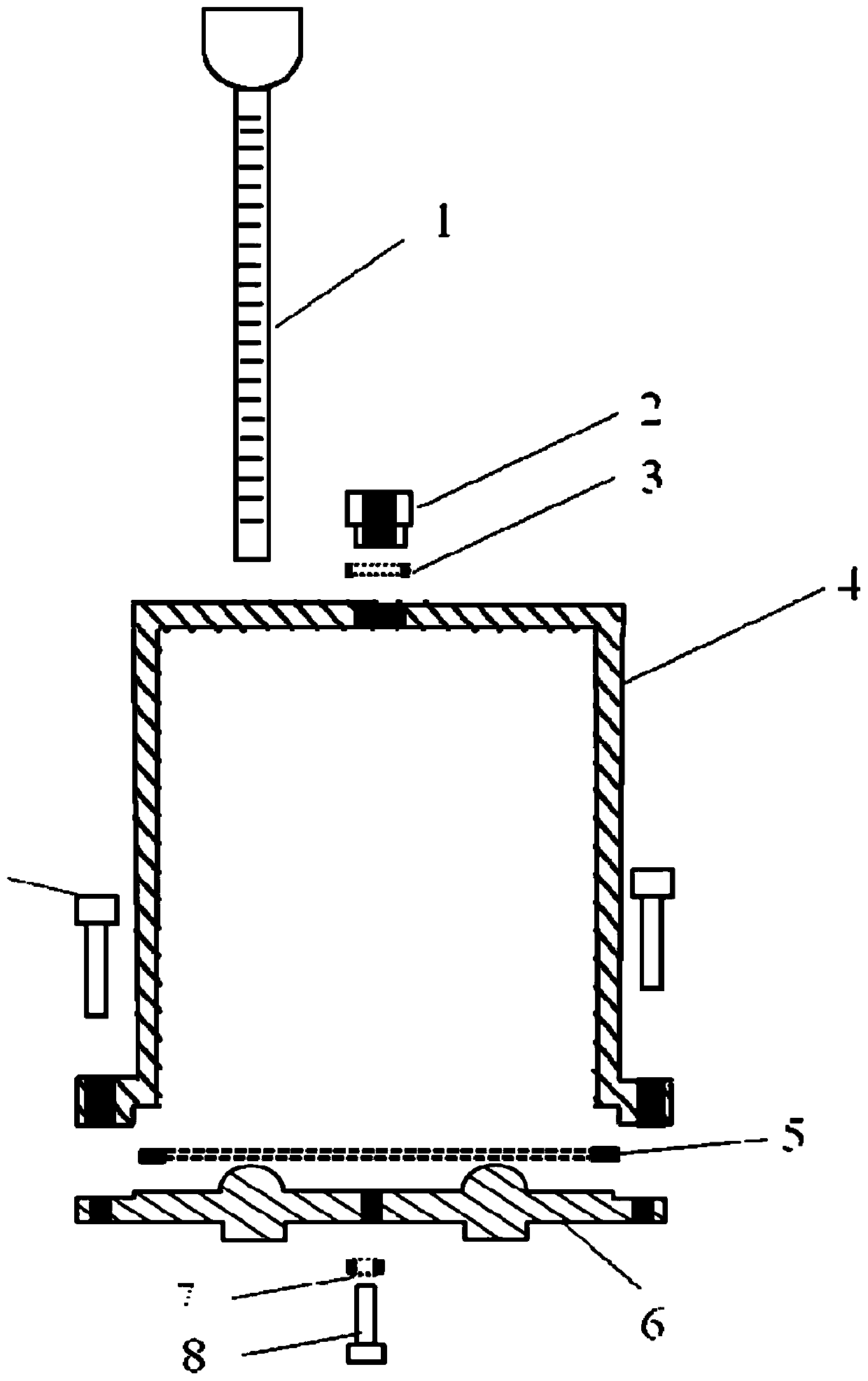
Large-scale press-fit explosive column temperature cycle threshold detecting device and method
ActiveCN110095494AAccurate volumeAccurate Internal CrackMaterial thermal analysisSurvivabilityColumn temperature
The invention discloses a large-scale press-fit explosive column temperature cycle threshold detecting device and method. The detecting device comprises sample cages and a temperature cycling environment test box. Each sample cage consists of a glass tube, a connecting button, a sample cover, a base, and the like. One sample cage loaded with an explosive column with the size of phi 60nm to 84nm and silicone oil is placed in the temperature cycling test box; and the sample cage is taken out after one cycling and then detection is performed. The explosive column irreversible volume expansivity is larger than or equal to 1% or the cycling number of the crack occurrence in the explosive column is reduced by one to obtain a temperature cycle threshold of the explosive column. According to the invention, the explosive column is in a restrained state being consistent with the actual charge state; and the test result can reflect the actual survivability of the charge.
Owner:XIAN MODERN CHEM RES INST
Universal method to determine real-time PCR cycle threshold values
ActiveUS10176293B2Accuracy in determiningAchieve accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsCycle thresholdCalibration curve
A single technique for determining Ct is provided that can be used for standard sigmoidal growth curves and for problematic growth curves, such as parabolic curves. The Ct value can be determined as the intersection of a line tangent to the growth curve at the maximum of the second derivative with a baseline of the growth curve. Such a Ct value is usable for sigmoidal curves and parabolic curves, and can provide linear calibration curves to achieve accuracy in determining initial concentrations of a sample.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com