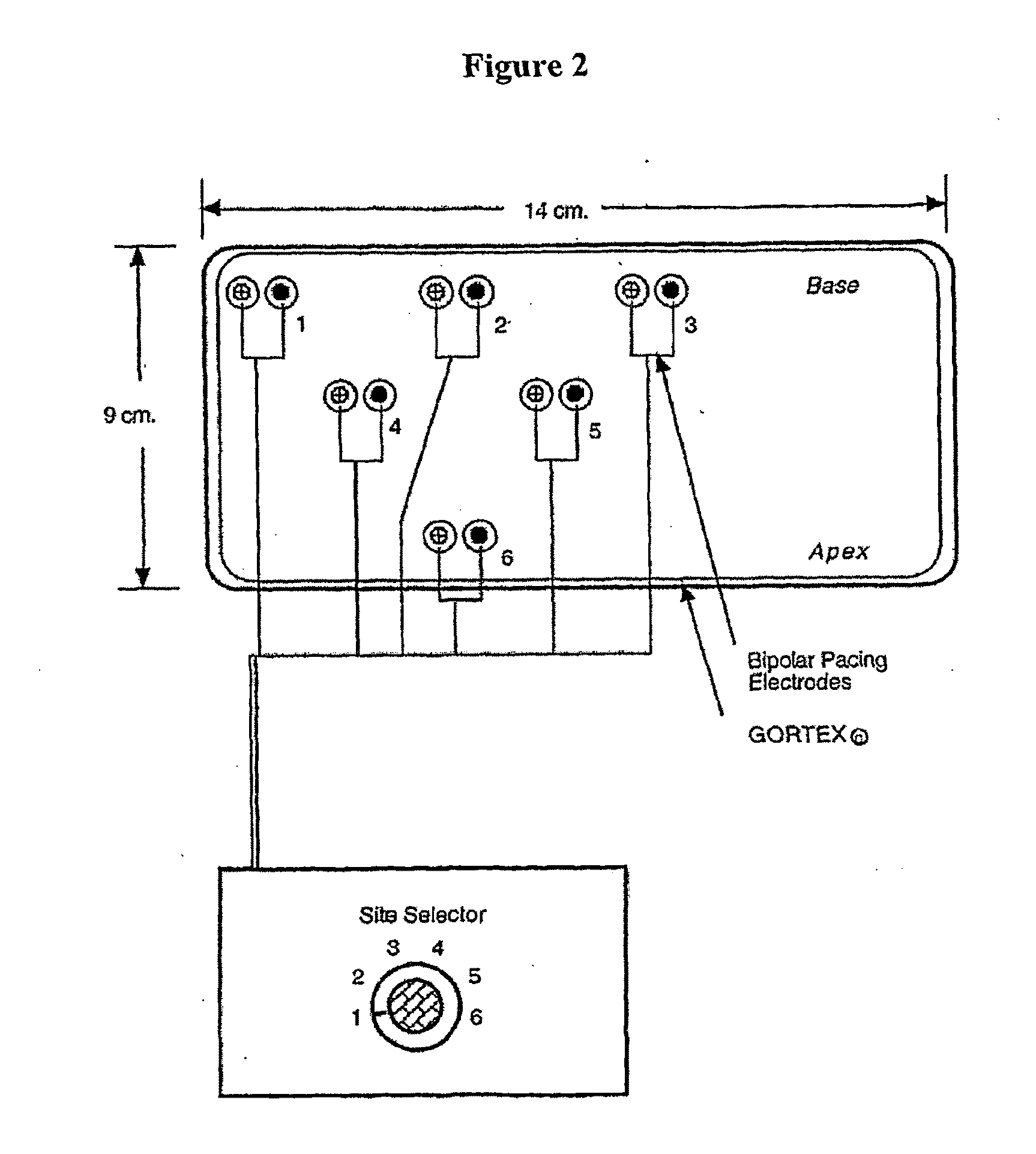
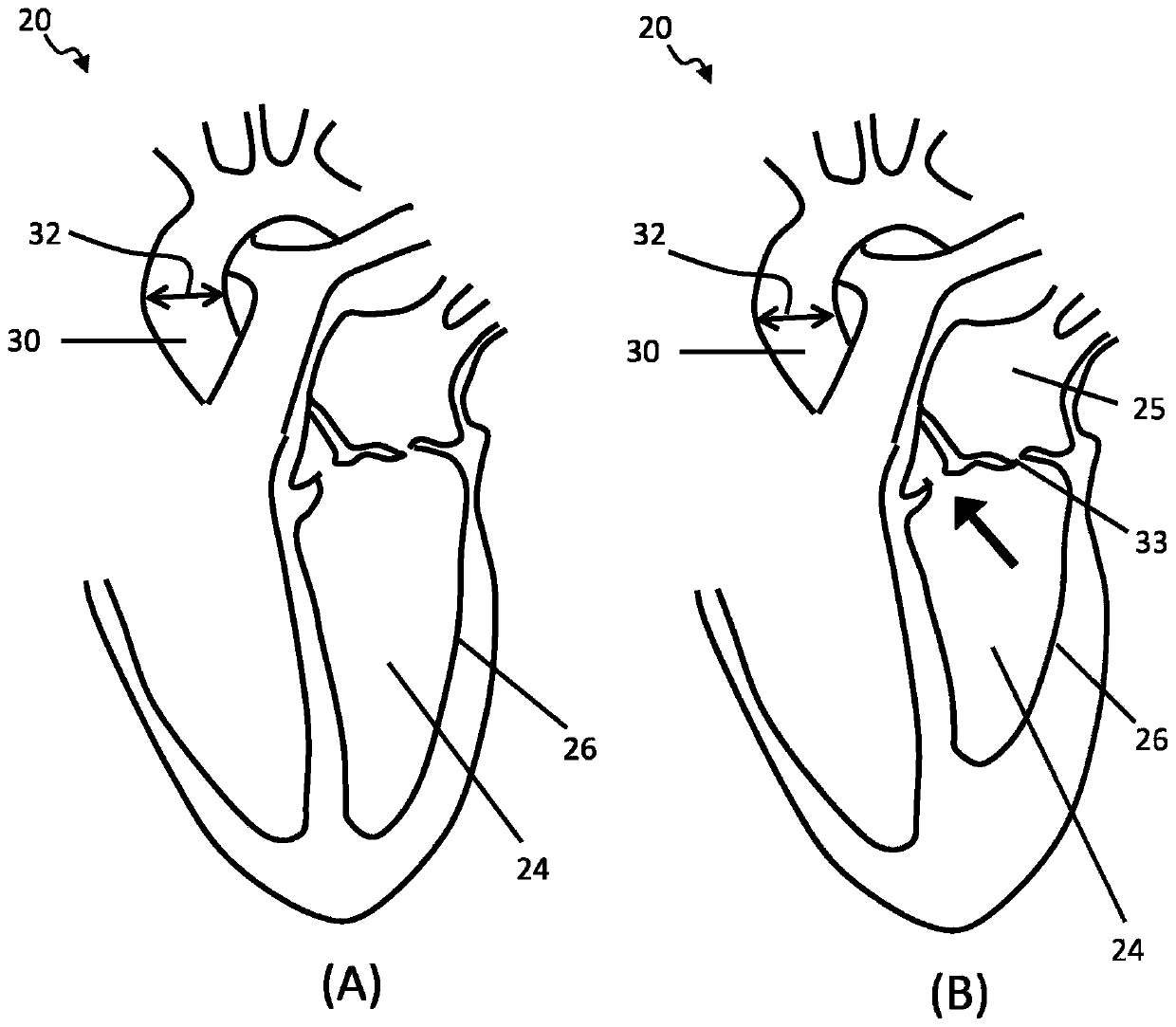
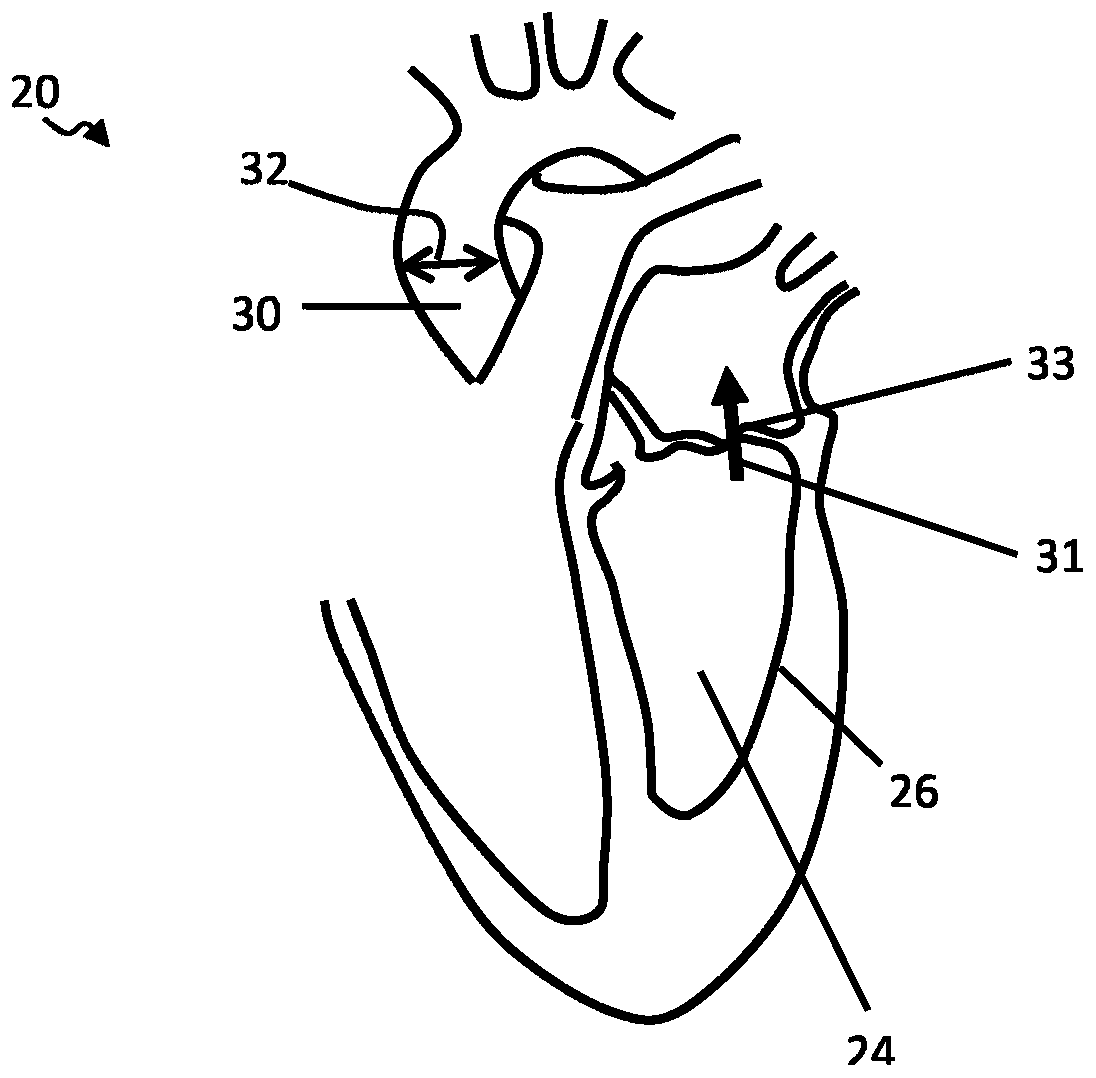
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
90 results about "Right heart ventricle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
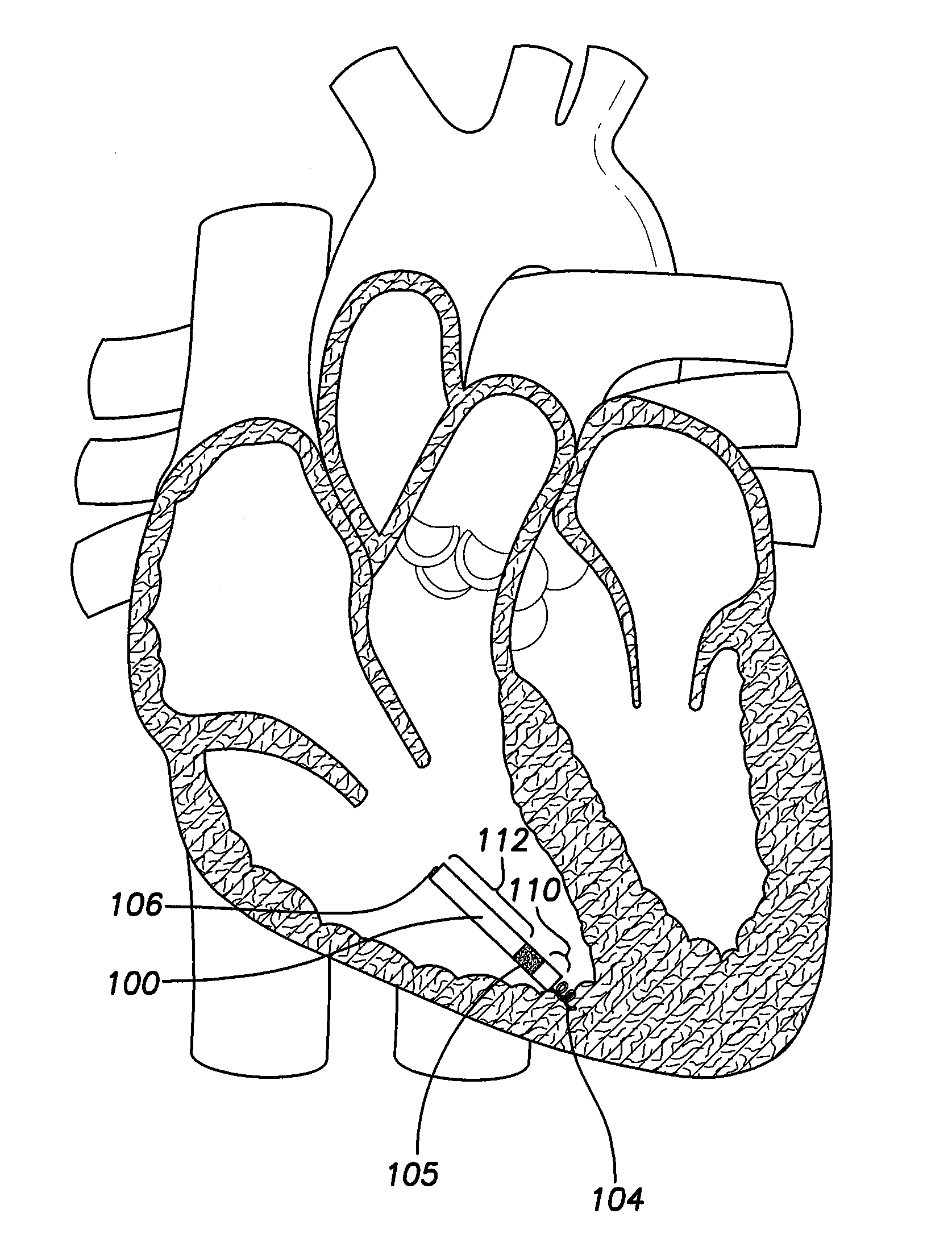
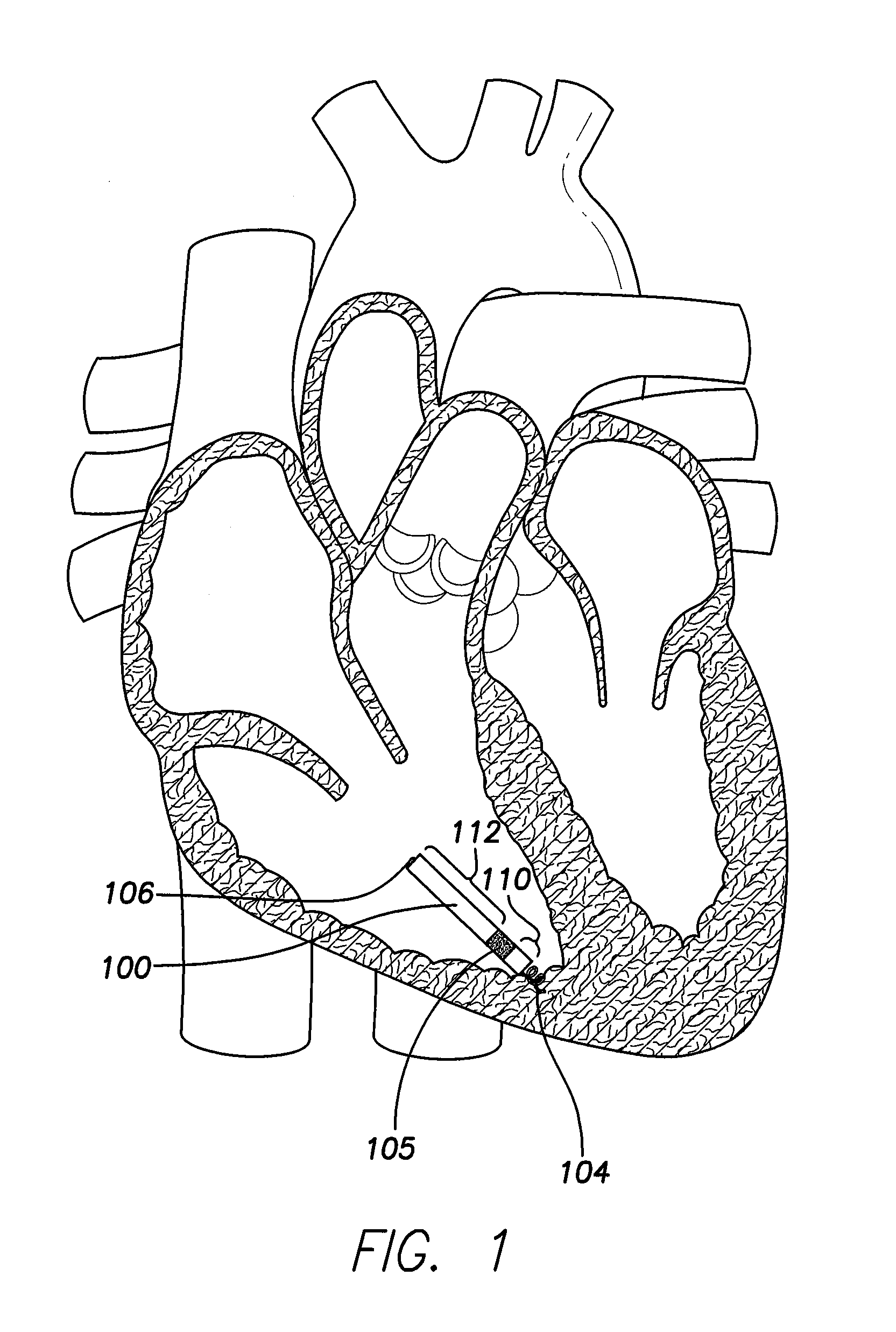
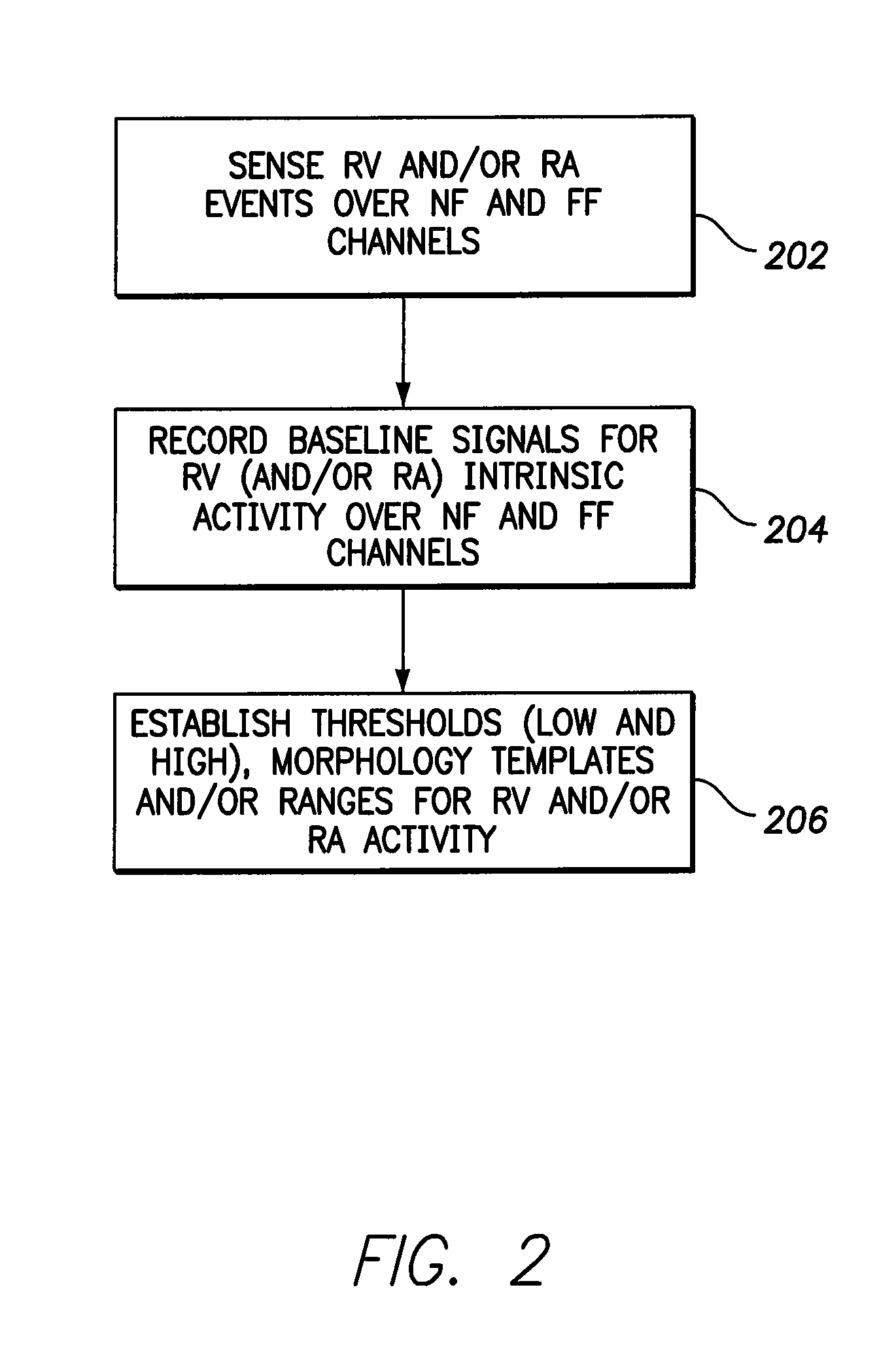
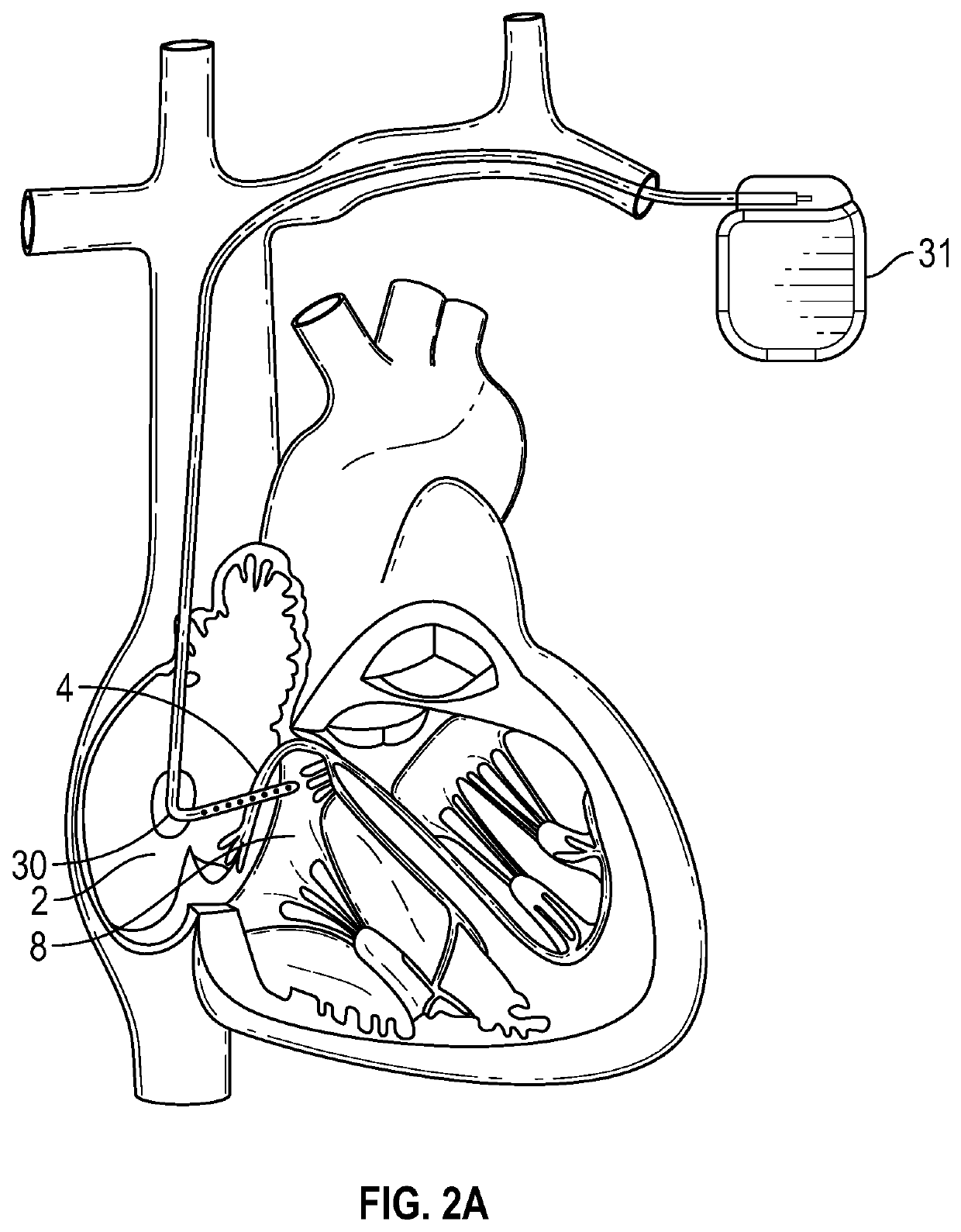
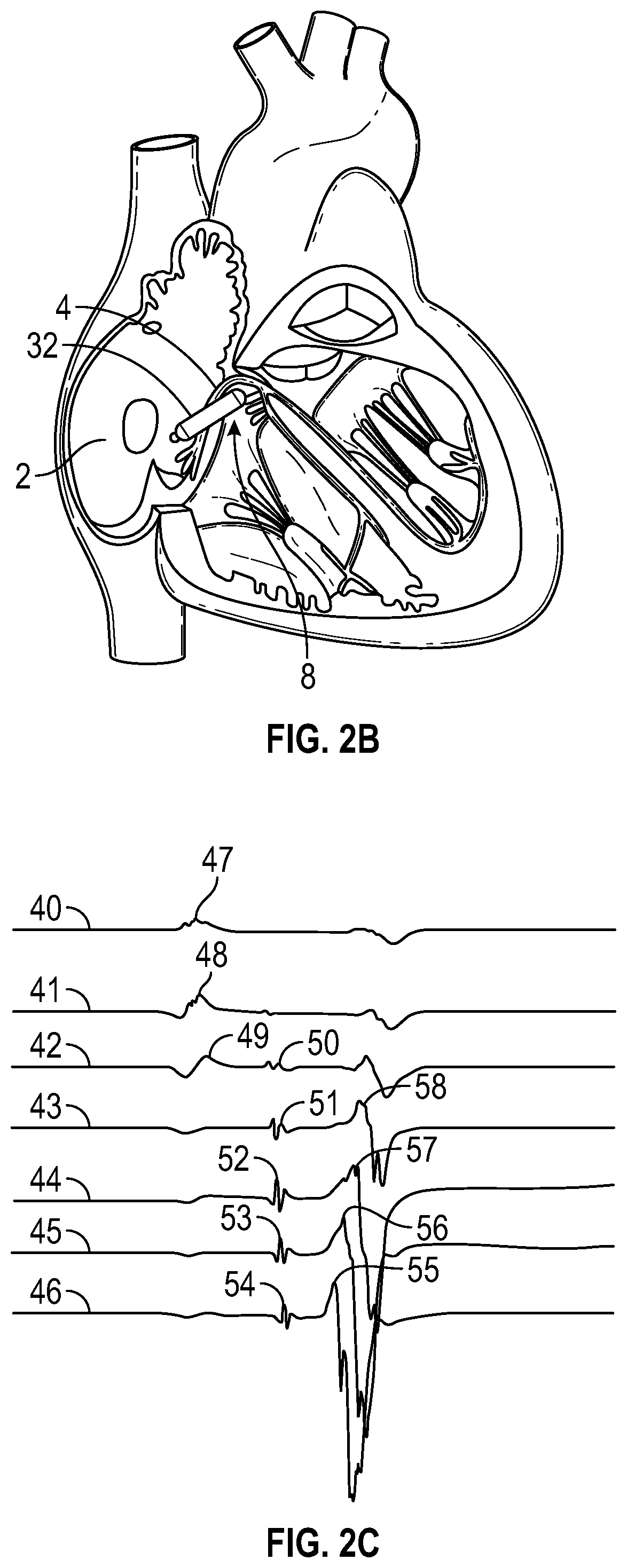
Single chamber leadless intra-cardiac medical device having dual chamber sensing with signal discrimination
A leadless intra-cardiac medical device (LIMD) includes multiple electrodes that allow for stimulation and sensing of the right ventricle (RV) and sensing of the right atrium (RA), even though it is entirely located in the RV. The LIMD includes a housing having a proximal end configured to engage local tissue in the local chamber and electrodes located at multiple locations along the housing. Sensing circuitry is configured to define a far field (FF) channel between a first combination of the electrodes to sense FF signals occurring in the adjacent chamber. The sensing circuitry is configured to define a near field (NF) channel between a second combination of the electrodes to sense NF signals occurring in the local chamber. A controller is configured to analyze the NF and FF signals to determine whether the NF and FF signals collectively indicate that a validated event of interest occurred in the adjacent chamber.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
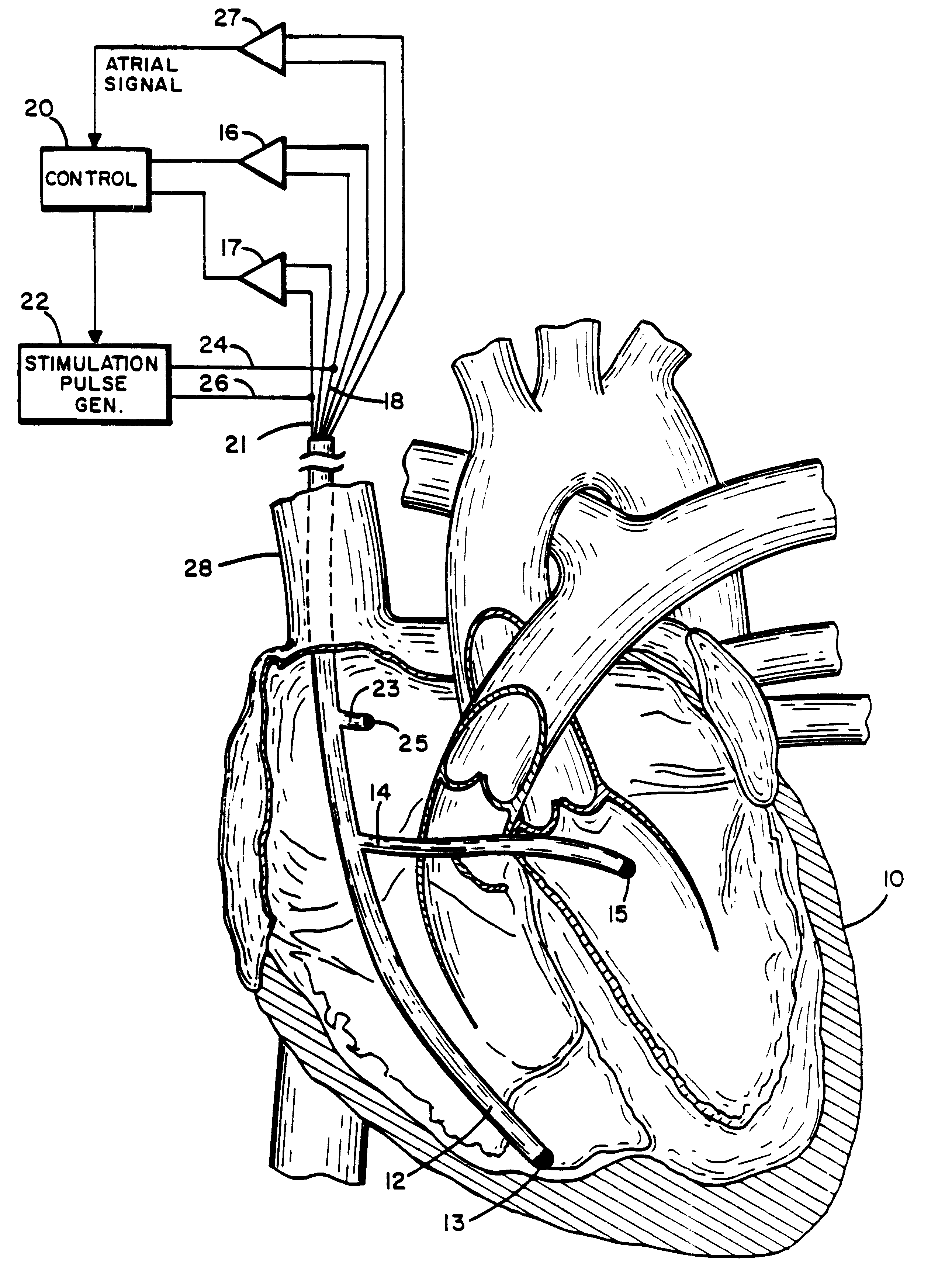
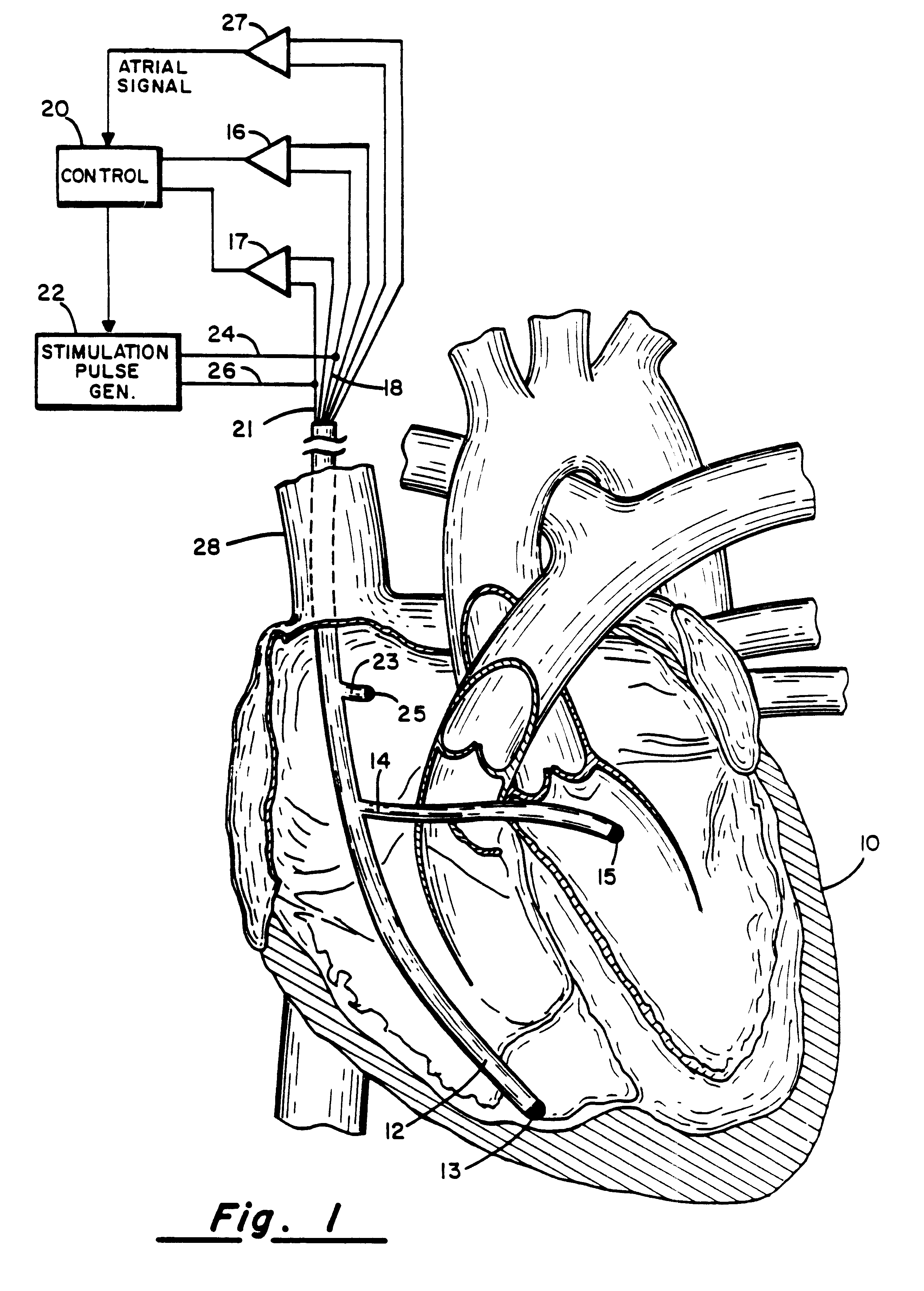
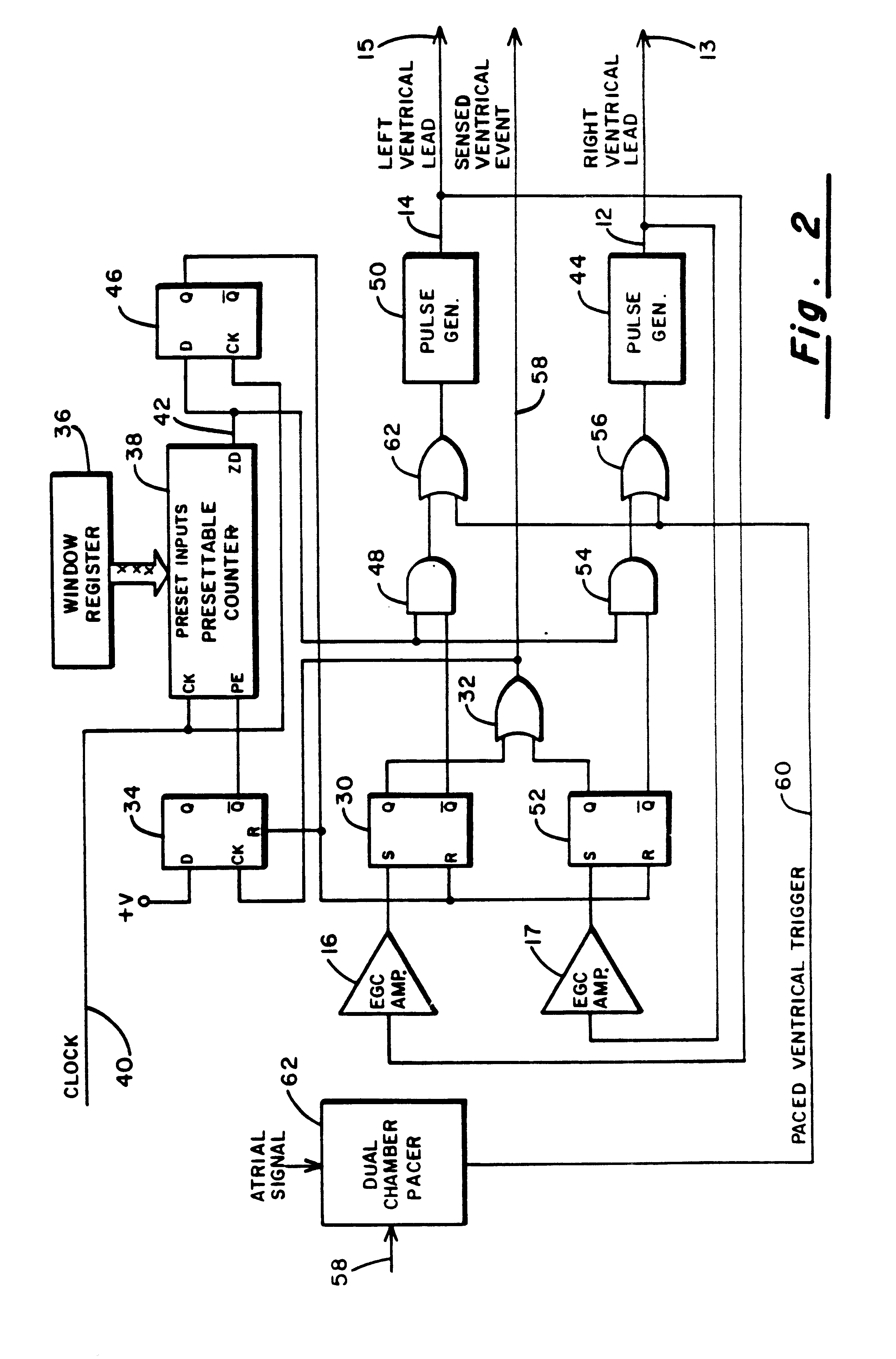
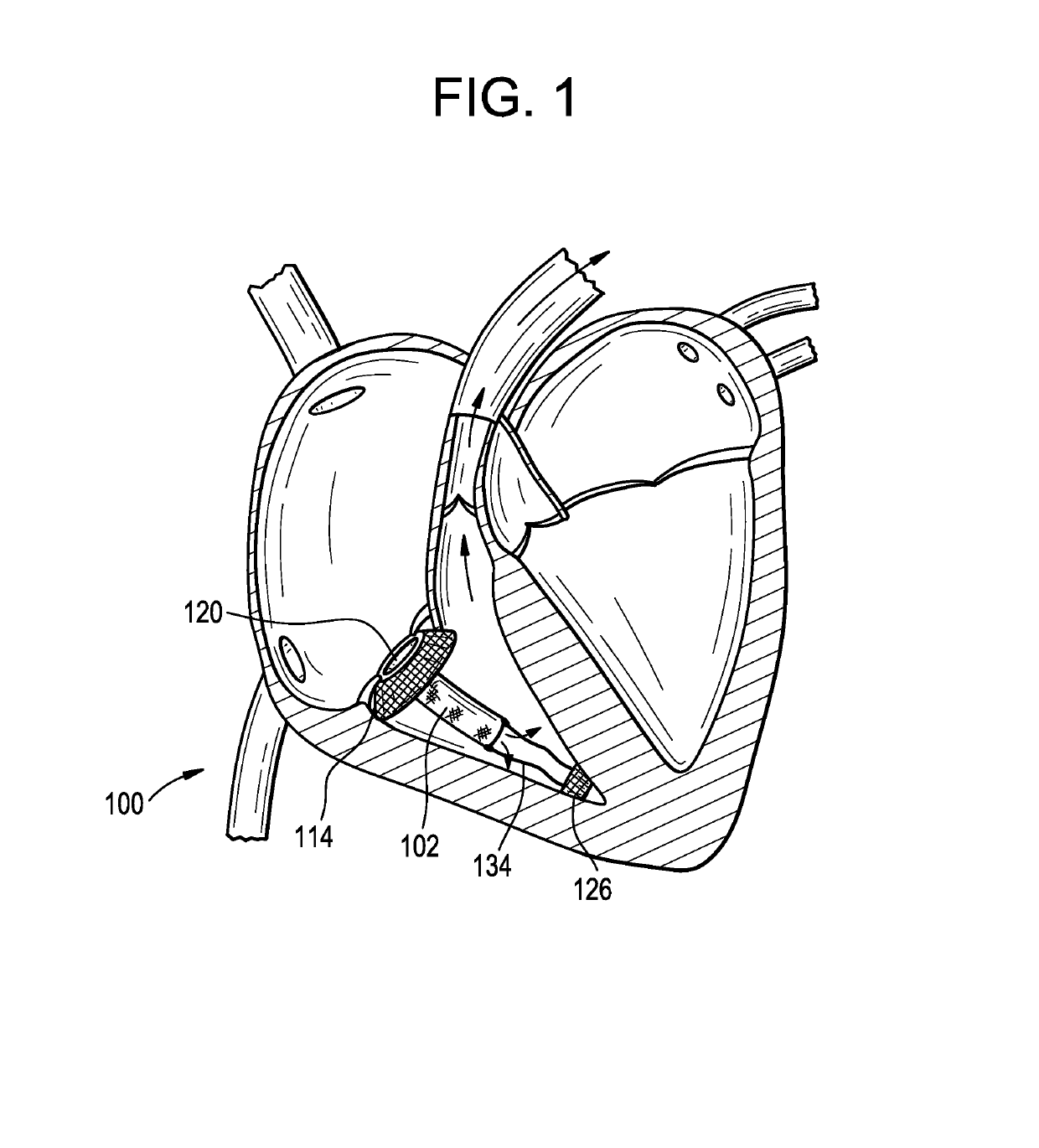
Method and apparatus for treating hemodynamic disfunction
A method of treating hemodynamic disfunction by simultaneously pacing both ventricles of a heart. At least one ECG amplifier is arranged to separately detect contraction of each ventricle and a stimulator is then activated for issuing stimulating pulses to both ventricles in a manner to assure simultaneous contraction of both ventricles, thereby to assure hemodynamic efficiency. A first ventricle is stimulated simultaneously with contraction of a second ventricle when the first fails to properly contract. Further, both ventricles are stimulated after lapse of a predetermined A-V escape interval. One of a pair of electrodes, connected in series, is placed through the superior vena cava into the right ventricle and a second is placed in the coronary sinus about the left ventricle. Each electrode performs both pacing and sensing functions. The pacer is particularly suitable for treating bundle branch blocks or slow conduction in a portion of the ventricles.
Owner:MIROWSKI FAMILY VENTURES LLC
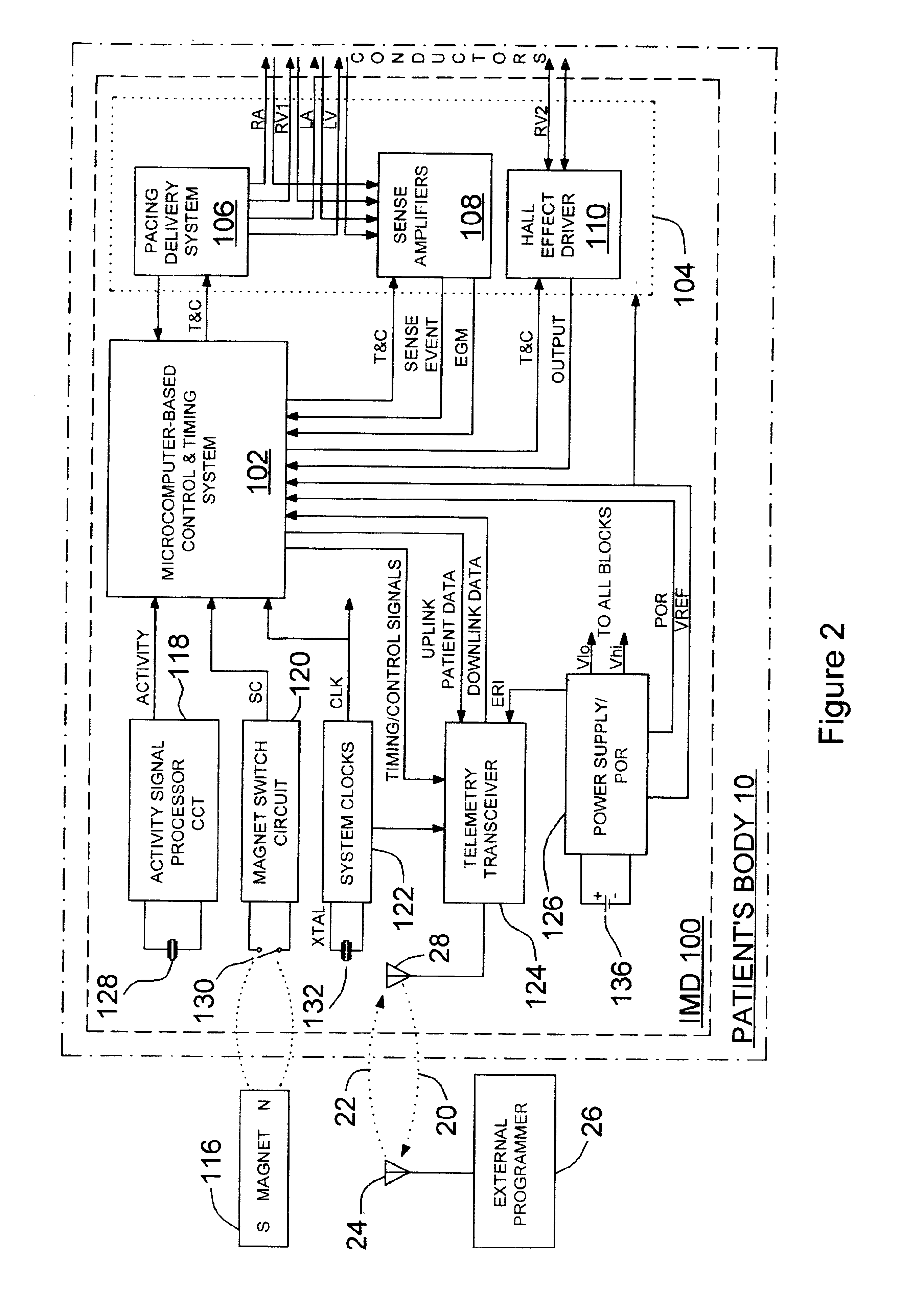
Implantable medical device for measuring mechanical heart function
InactiveUS6959214B2Output maximizationPrecise positioningHeart stimulatorsProper treatmentHeart chamber
An implantable device for measuring mechanical heart function of selected heart chambers using a heart contraction detection system that includes a magnetic field sensor. The system may be used for monitoring signs of acute or chronic cardiac heart failure, to enable diagnosis of the condition of the heart, to prescribe appropriate therapies, and to assess delivered pacing therapies. Distance measurements within the heart are made using the magnetic field sensor which is implanted at a sensor site in or on one of the right or left ventricle. A magnet implanted at a site relative to the other of the left or right heart ventricle is sufficiently spaced at a distance that fluctuates with expansion and contraction of the ventricles. The magnetic field sensor provides a sensor output signal having a signal magnitude proportional to the magnetic field strength of the magnet, and which is indicative of changing cardiac dimensions.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
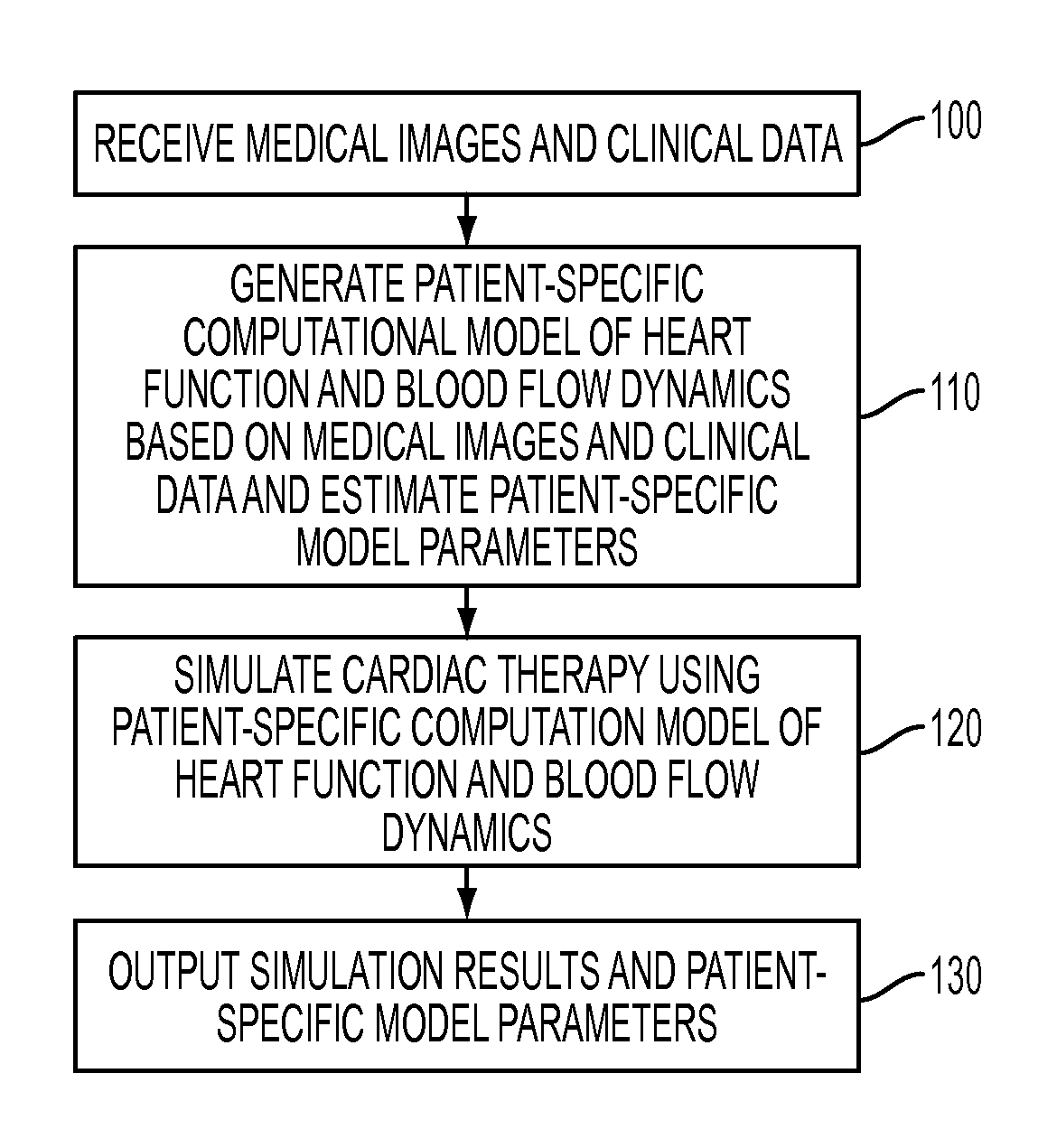
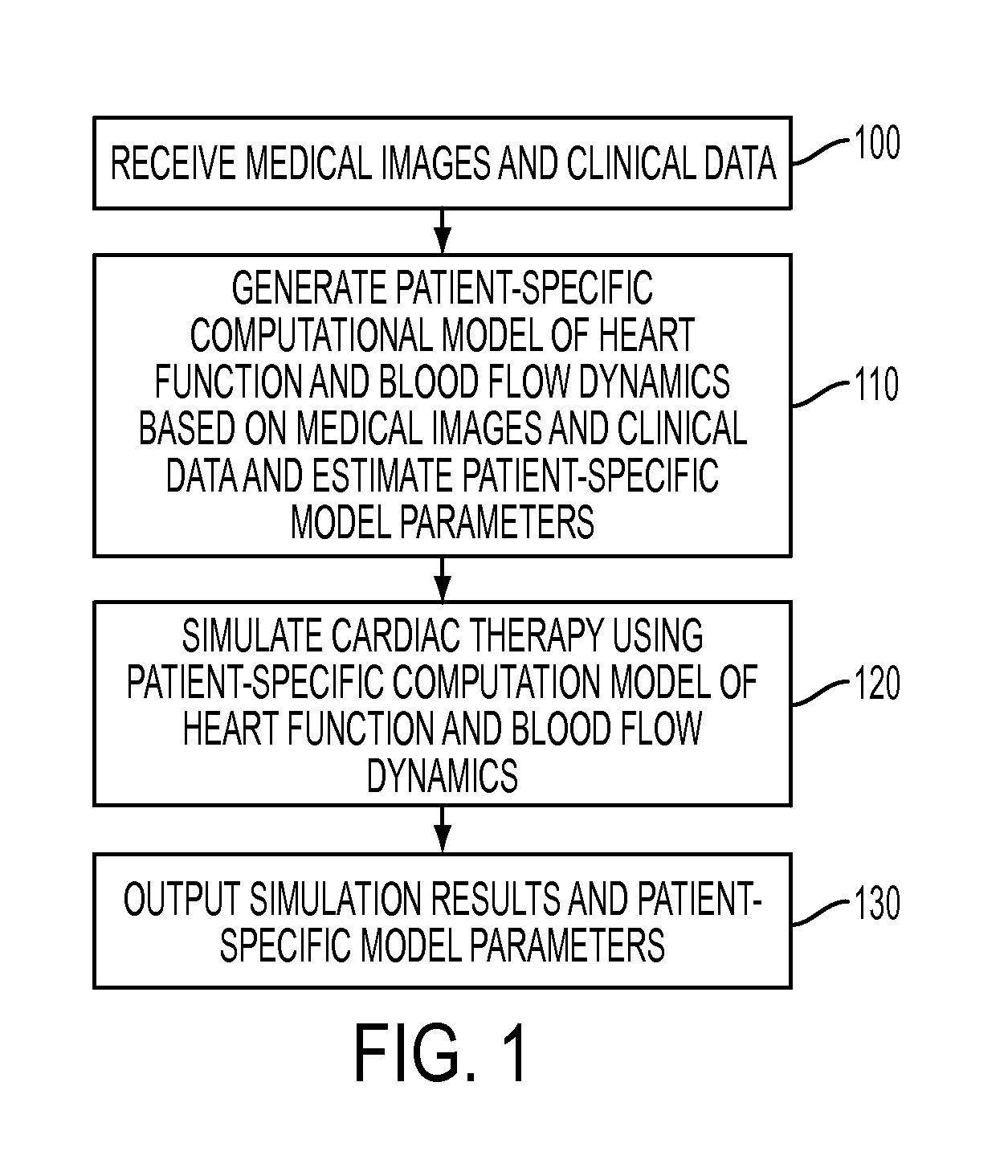
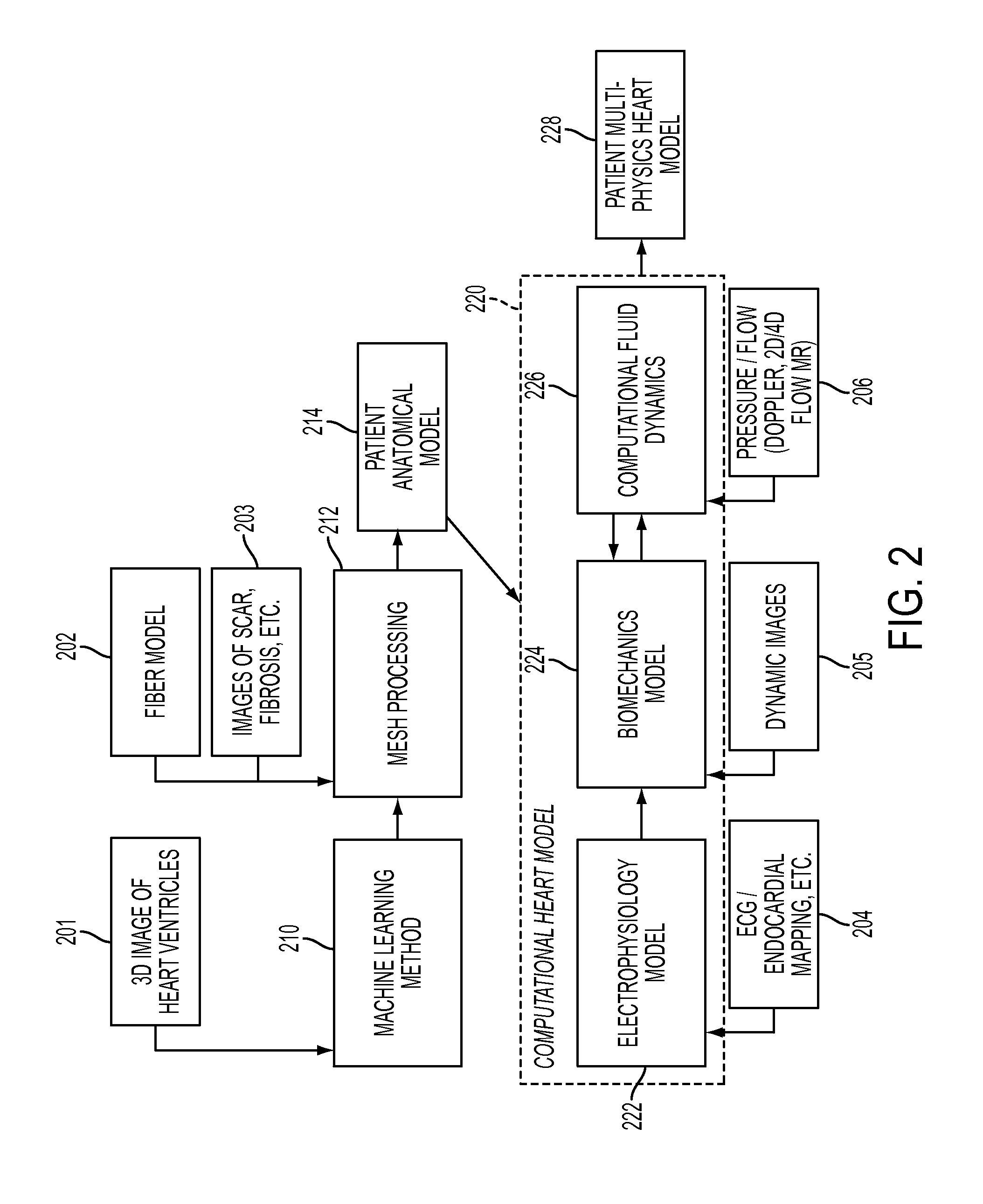
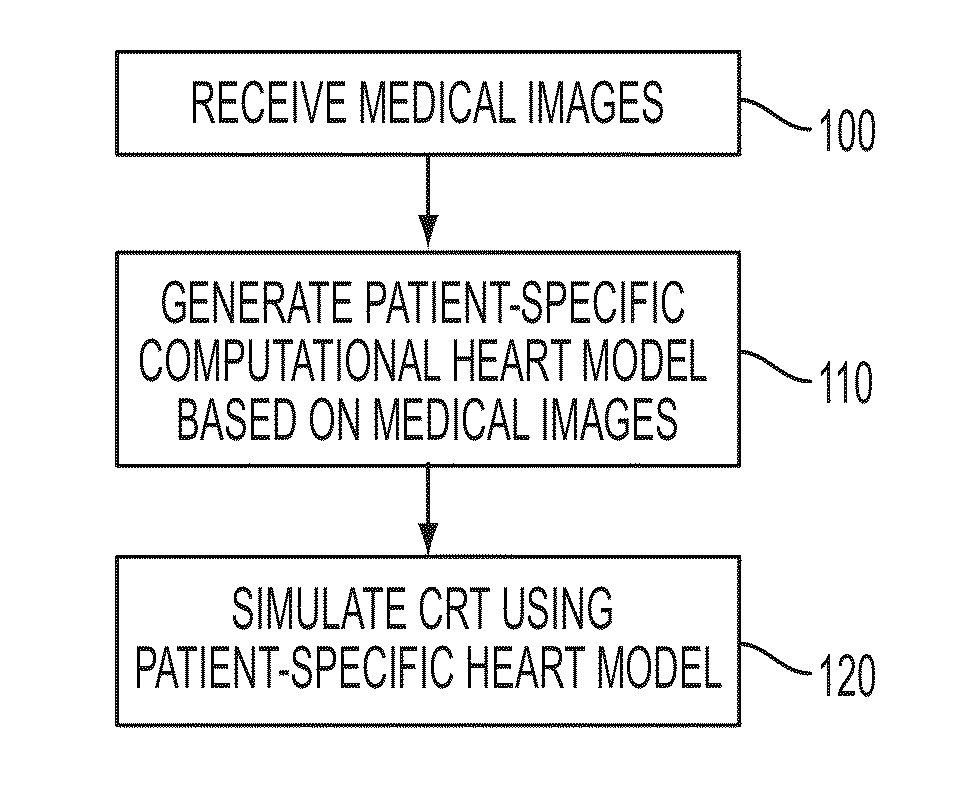
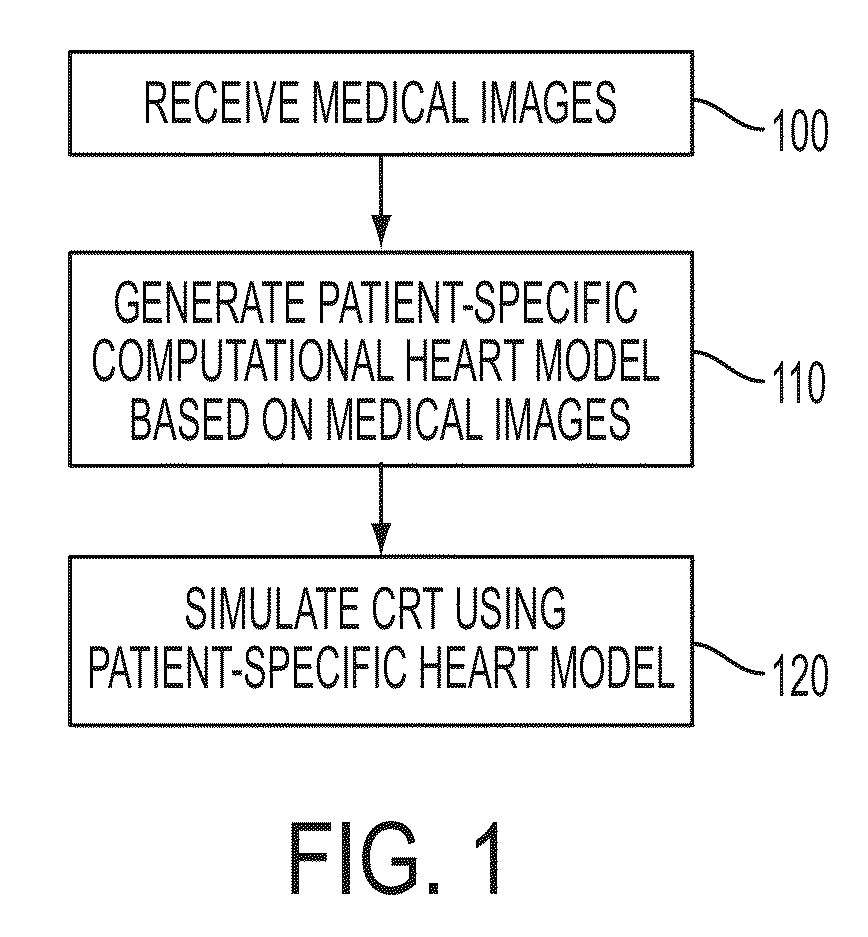
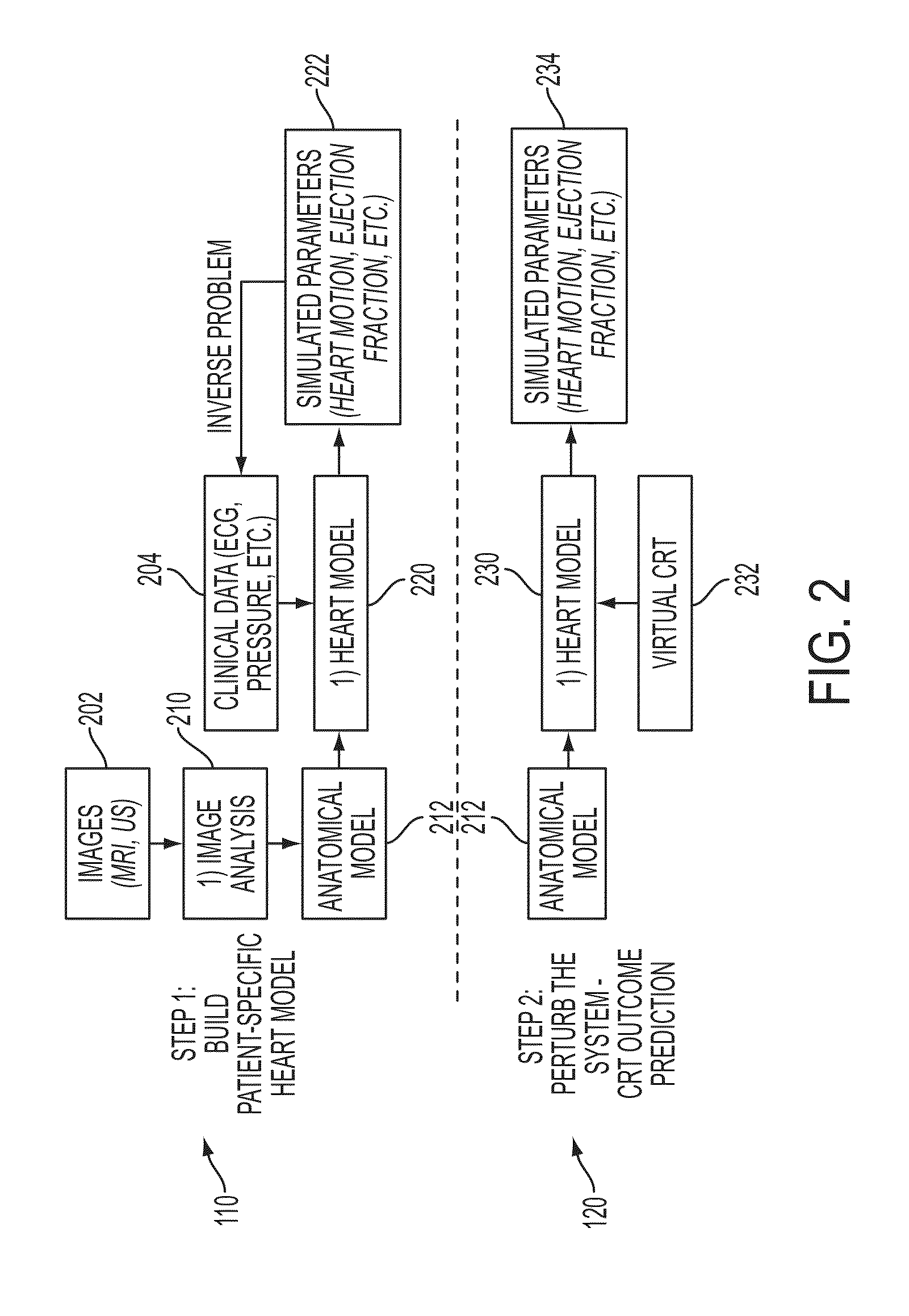
Method and System for Advanced Measurements Computation and Therapy Planning from Medical Data and Images Using a Multi-Physics Fluid-Solid Heart Model
ActiveUS20130197884A1Exact reproductionMedical simulationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsComputational modelPatient data
Method and system for computation of advanced heart measurements from medical images and data; and therapy planning using a patient-specific multi-physics fluid-solid heart model is disclosed. A patient-specific anatomical model of the left and right ventricles is generated from medical image patient data. A patient-specific computational heart model is generated based on the patient-specific anatomical model of the left and right ventricles and patient-specific clinical data. The computational model includes biomechanics, electrophysiology and hemodynamics. To generate the patient-specific computational heart model, initial patient-specific parameters of an electrophysiology model, initial patient-specific parameters of a biomechanics model, and initial patient-specific computational fluid dynamics (CFD) boundary conditions are marginally estimated. A coupled fluid-structure interaction (FSI) simulation is performed using the initial patient-specific parameters, and the initial patient-specific parameters are refined based on the coupled FSI simulation. The estimated model parameters then constitute new advanced measurements that can be used for decision making.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and System for Patient Specific Planning of Cardiac Therapies on Preoperative Clinical Data and Medical Images
ActiveUS20130197881A1Increase the number ofEasy to placeUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMedical imagingSonificationBiomechanics
A method and system for patient-specific planning of cardiac therapy, such as cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT), based on preoperative clinical data and medical images, such as ECG data, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data, and ultrasound data, is disclosed. A patient-specific anatomical model of the left and right ventricles is generated from medical image data of a patient. A patient-specific computational heart model, which comprises cardiac electrophysiology, biomechanics and hemodynamics, is generated based on the patient-specific anatomical model of the left and right ventricles and clinical data. Simulations of cardiac therapies, such as CRT at one or more anatomical locations are performed using the patient-specific computational heart model. Changes in clinical cardiac parameters are then computed from the patient-specific model, constituting predictors of therapy outcome useful for therapy planning and optimization.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH
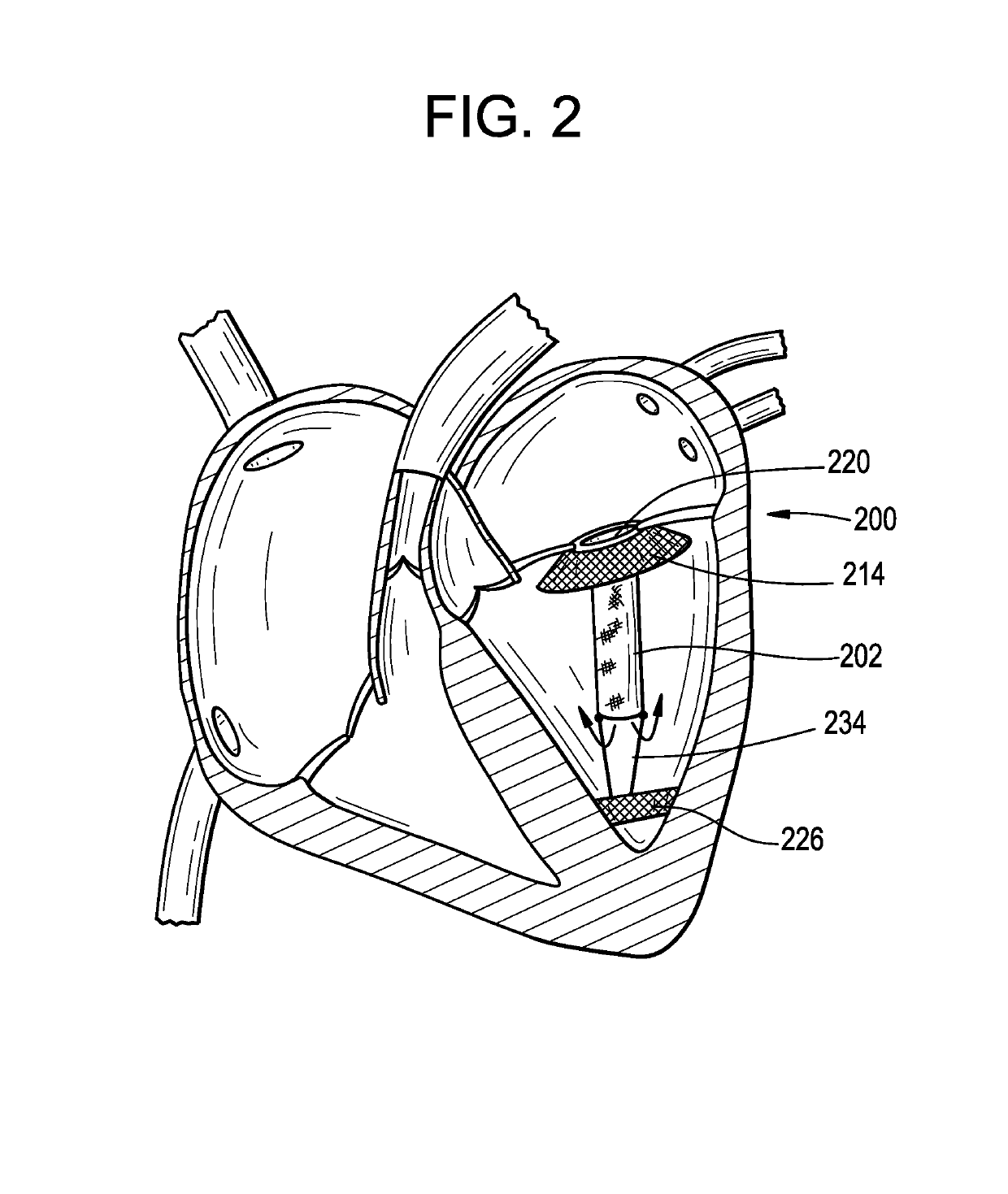
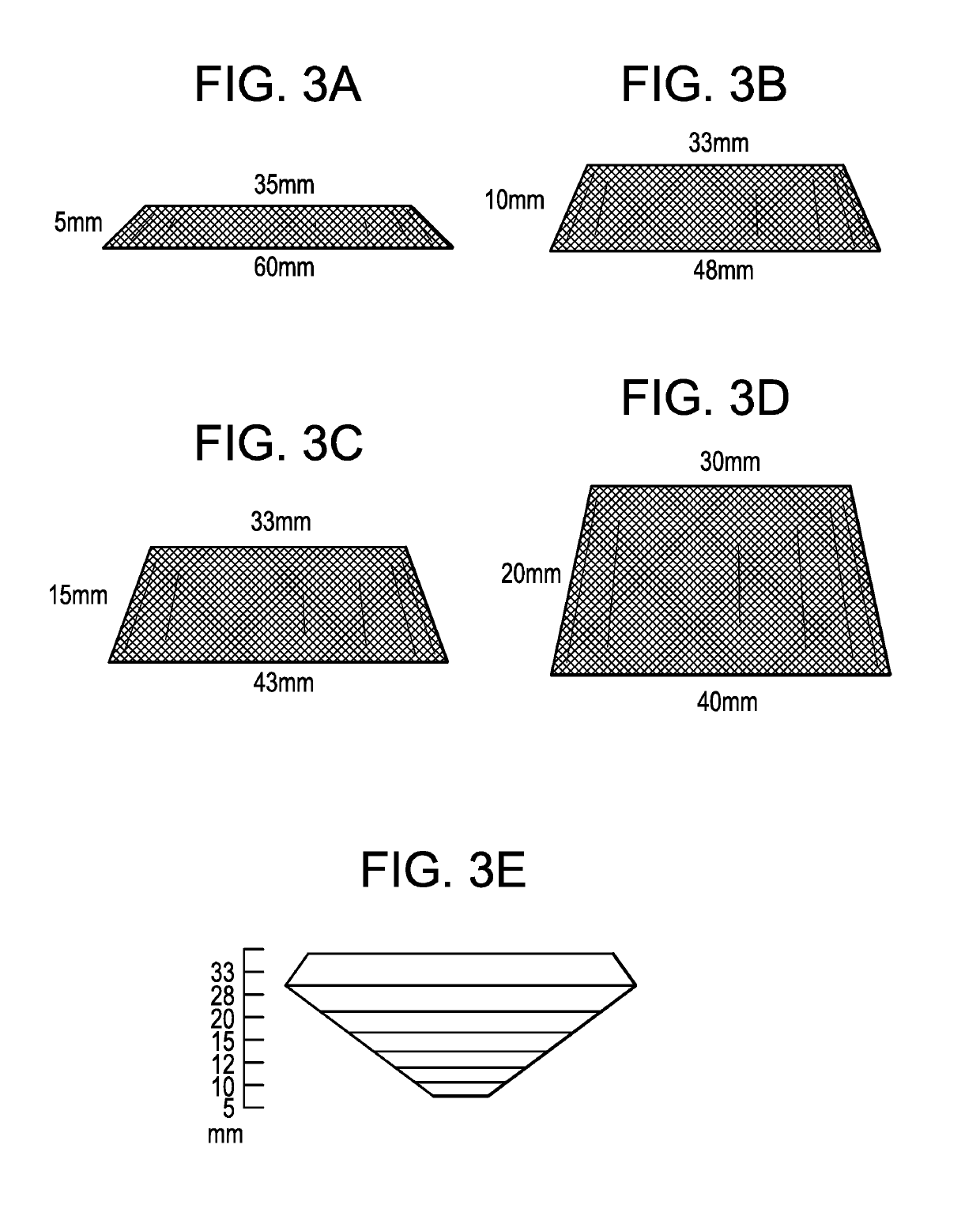
Pressure differential actuated prosthetic medical device
The invention relates to a medical prosthesis, and in particular a heart valve substitute comprising a pliant tubular conduit mounted on a resilient annular frame and tethered to a non-perforating anchor within the right or left ventricle of the heart, wherein the pliant tubular conduit is a reciprocating mechanical member that is compressed by pressurized working fluid within the ventricle during systole.
Owner:VDYNE INC
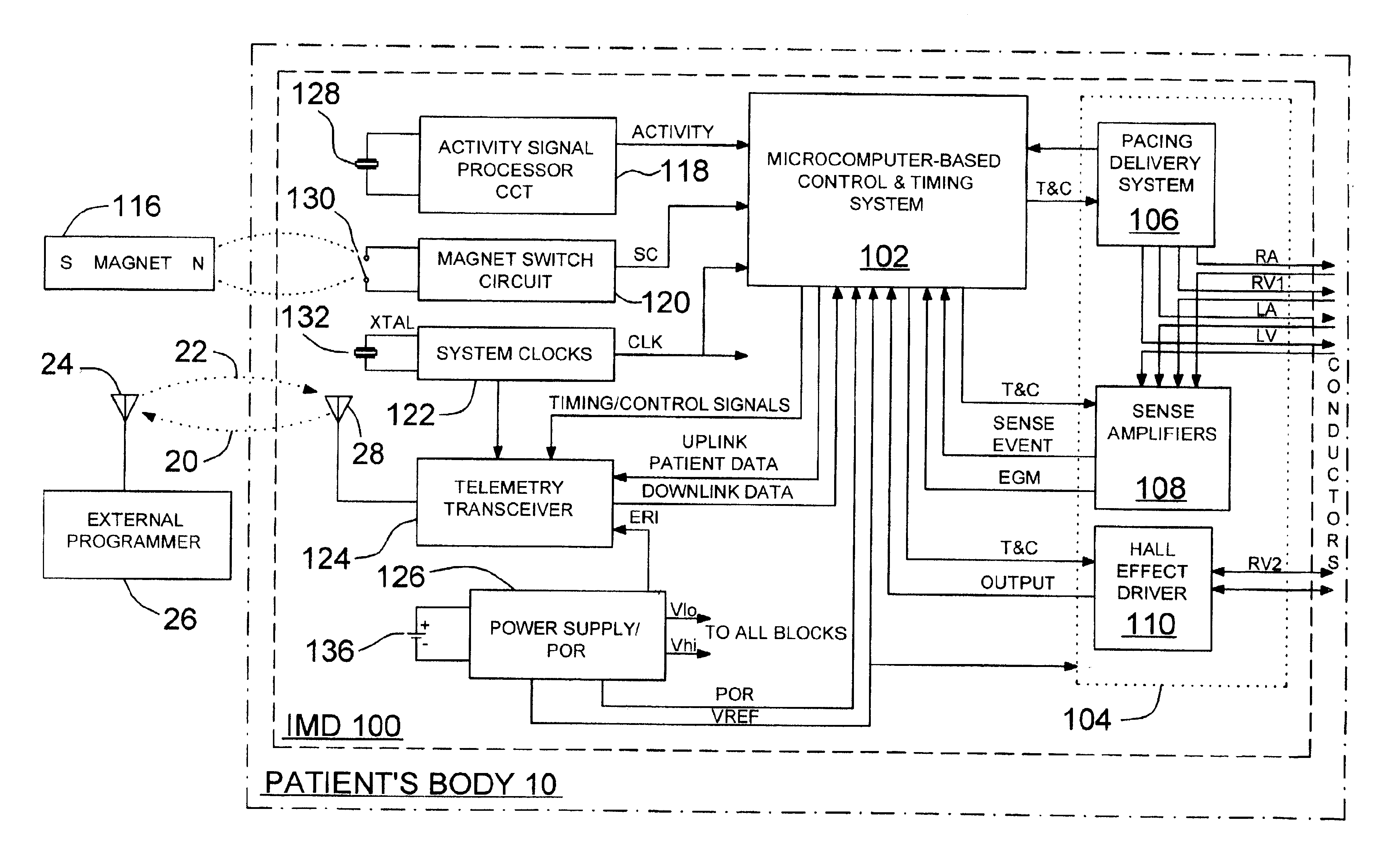
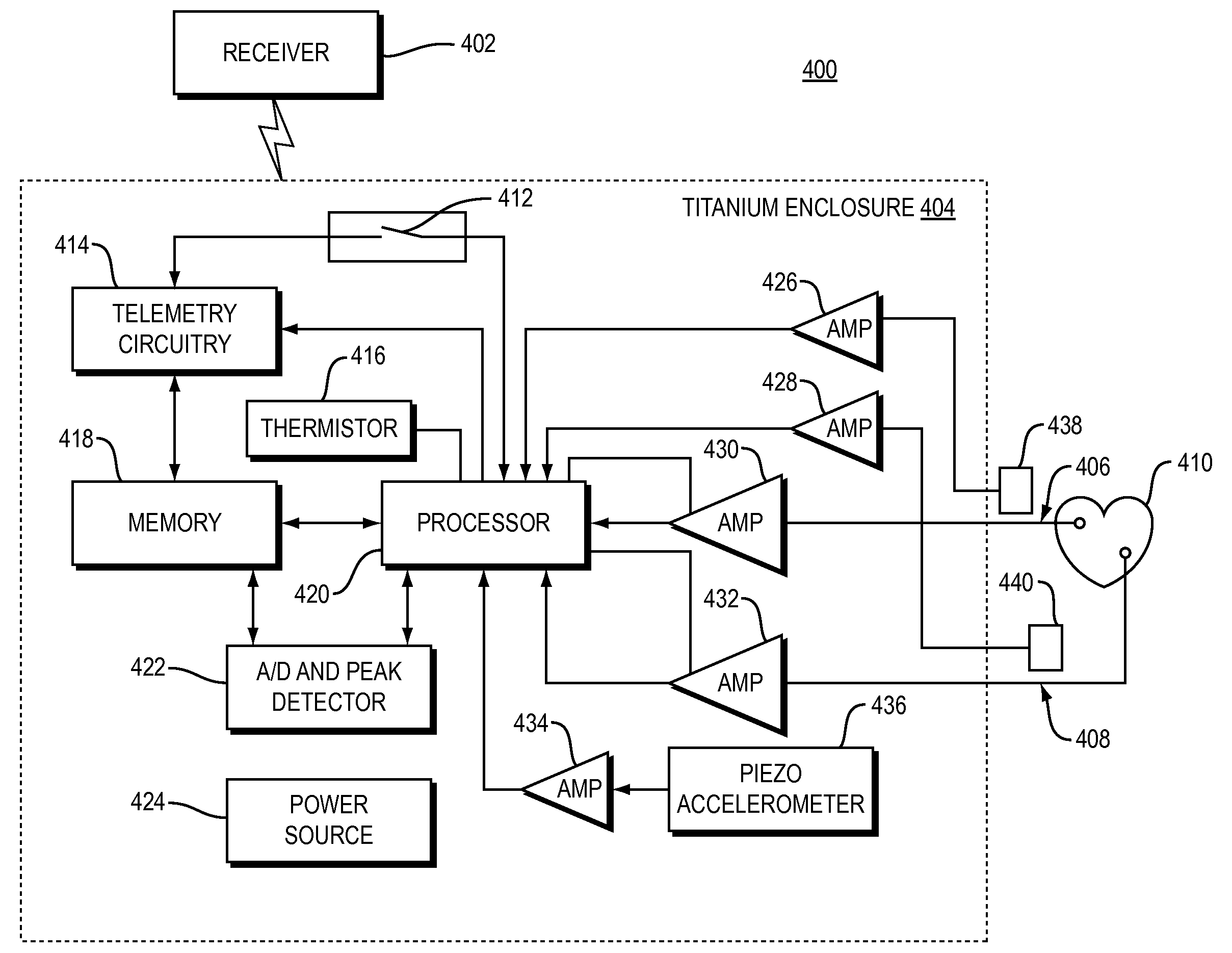
Systems and Methods for Heart and Activity Monitoring
InactiveUS20120165684A1ElectrocardiographyLocal control/monitoringTransplant rejectionCardiac muscle
Methods and systems for monitoring a heart failure or transplant rejection status of a patient including use of a device or system to collect intramyocardial electrogram (IMEG) signals from the patient at different times automatically when a detected activity level of the patient is below a preset threshold level for a predetermined amount of time, and use of a device or system to generate a status indicator value proportional to a combination of parameters extracted from at least a portion of the collected IMEG signals. Methods and systems can also include measuring time delay values between IMEG signals collected from different locations in the patient. The IMEG signals can be collected from the right ventricular septum and the right ventricular apex of the patient or from the right and left ventricular myocardium of the patient.
Owner:QRS HEART
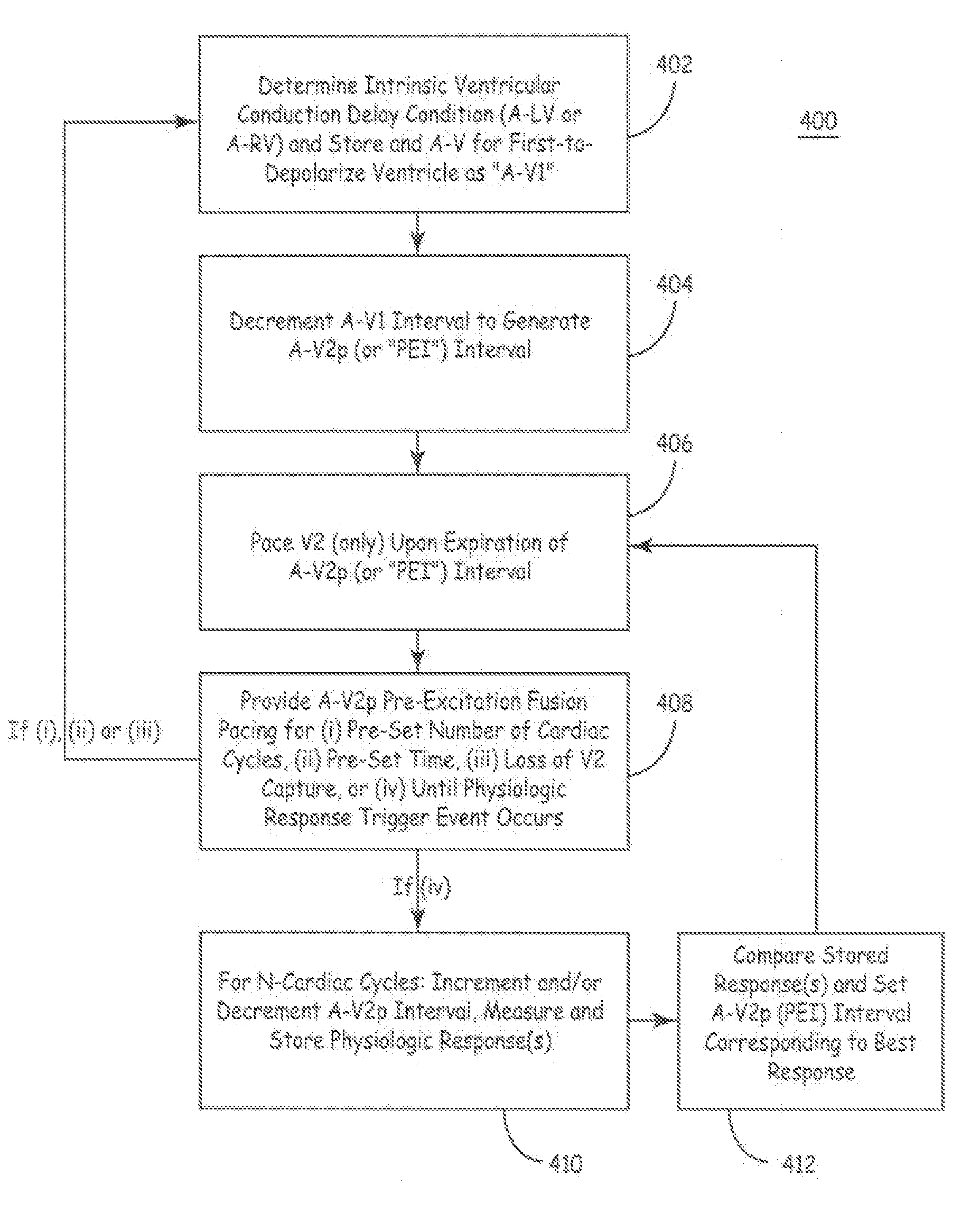
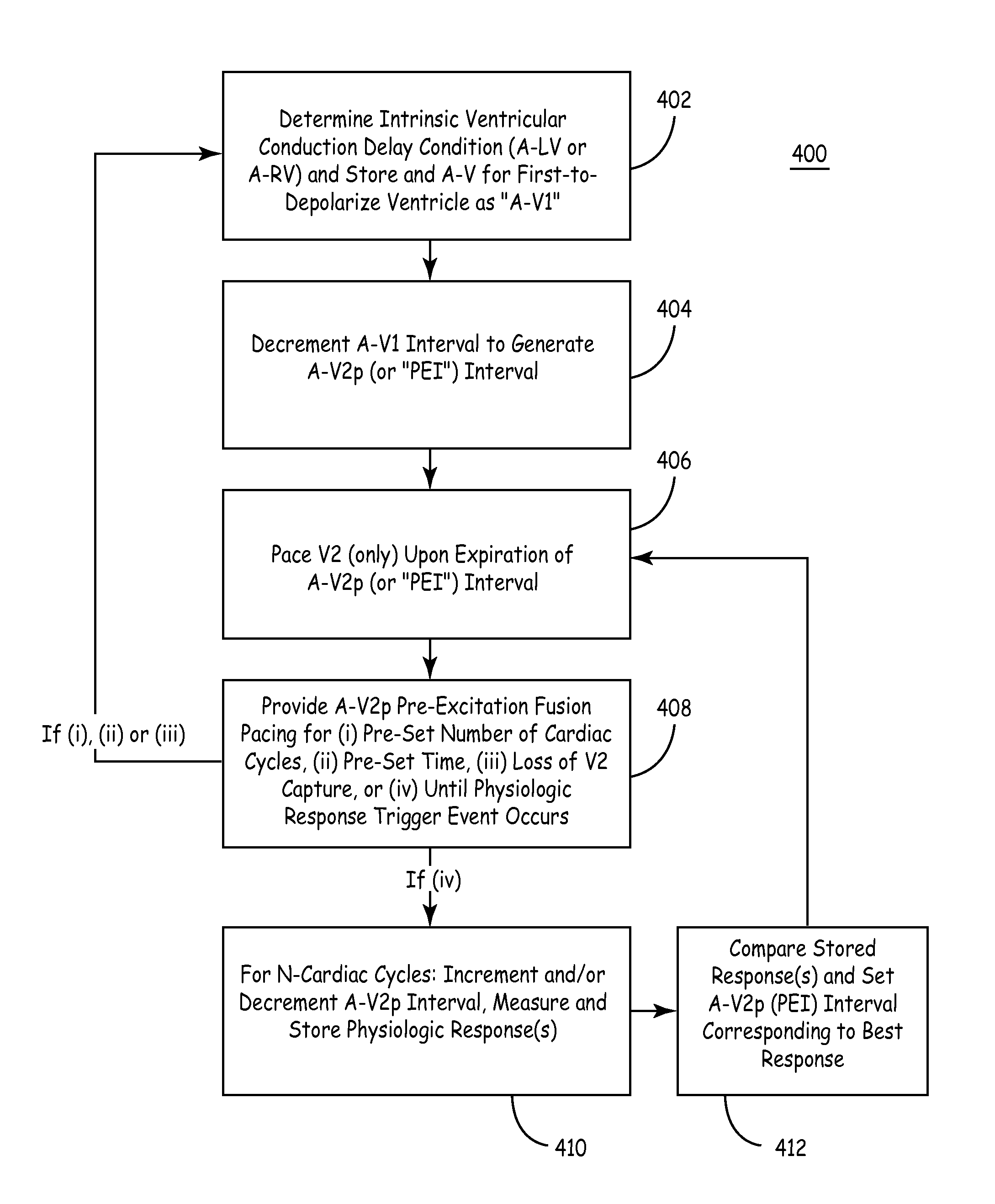
Fusion Pacing Enhancements
The disclosure provides methods and apparatus of left ventricular pacing including automated adjustment of a atrio-ventricular (AV) pacing delay interval and intrinsic AV nodal conduction testing. It includes—upon expiration or reset of a programmable AV Evaluation Interval (AVEI)—performing the following: temporarily increasing a paced AV interval and a sensed AV interval and testing for adequate AV conduction and measuring an intrinsic atrio-ventricular (PR) interval for a right ventricular (RV) chamber. Thus, in the event that the AV conduction test reveals a physiologically acceptable intrinsic PR interval then storing the physiologically acceptable PR interval in a memory structure (e.g., a median P-R from one or more cardiac cycles). In the event that the AV conduction test reveals an AV conduction block condition or if unacceptably long PR intervals are revealed then a pacing mode-switch to a bi-ventricular (Bi-V) pacing mode occurs and the magnitude of the AVEI is increased.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
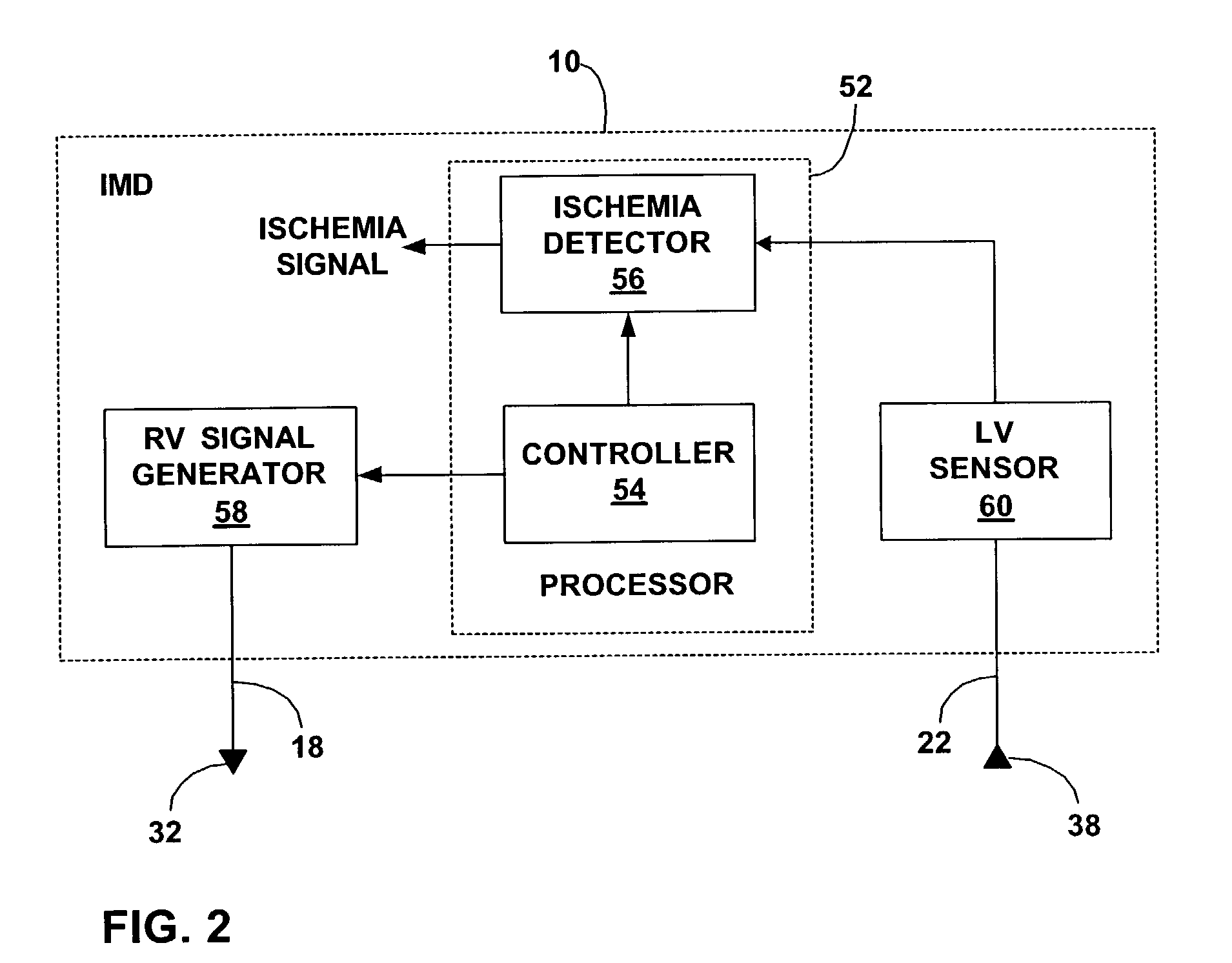
Ischemia detection based on cardiac conduction time
ActiveUS7415307B2Reliable indicationStrong specificityHeart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringElectricityCardiac muscle
Methods and process for detection of myocardial ischemia involve detection and analysis of changes in electrical conduction velocity within the heart to monitor changes in the condition of the cardiac muscle and indicate possible ischemia. Conduction velocity slows considerably when oxygen supply to the heart is reduced. Analysis of electrical conduction velocity can be used to verify the occurrence of myocardial ischemia in a more reliable manner. Changes in conduction velocity may be monitored based on conduction time between electrodes positioned in the left and right ventricles of the heart. The electrodes may be endocardial or epicardial electrodes. In general, the techniques may involve launching a stimulation waveform at one electrode and sensing a local cardiac depolarization at another electrode to assess conduction time.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
High resolution multi-function and conformal electronics device for diagnosis and treatment of cardiac arrhythmias
PendingUS20180235692A1Accurate locationRestore normal heart functionEpicardial electrodesTransvascular endocardial electrodesCardiac arrhythmiaElectrode array
The present invention is a high resolution, multi-function, conformal electronics device generally having a flexible and stretchable, high-density electrode array, integrated with a catheter (e.g., balloon catheter) for mapping, ablating, pacing and sensing of cardia tissue associated with heart arrhythmias. The active sensing electrode array can acquire diagnostic information including electrical (e.g., electrograms), mechanical (e.g., strain measurements), impedance (e.g., resistance), metabolic (e.g., pH or NADH measurement) from the underlying heart tissue surface with which it is in contact. The electrode array may be designed to be of various sizes and shapes to conform to the targeted cardiac tissue architecture (e.g. atrial, ventricle, right ventricular outflow tract, coronary sinus, pulmonary veins, etc.) corresponding to the specific type of cardiac arrhythmia. The present invention can precisely locate the source of arrhythmia as described above and deliver therapy from the same electrode array. This is achieved using a capacitive sensing electrode array that can not only monitor but also deliver electrical stimulation.
Owner:GEORGE WASHINGTON UNIVERSITY
Sleeved type permanent magnetic impeller axial flow type blood pump for assisting heart and assisting method
InactiveCN101121045AImprove efficiencyImprove accessibilitySuction devicesProsthesisThrombusIliac artery bypass
A bushing-type permanent magnetic impeller shaft bleeding pump, which is used for heart boosting and the boosting method of the bleeding pump are provided. A rotor of the bleeding pump is a whole magnetic impeller or an impeller with magnetic vanes, which greatly improves a magnetic field intensity of a bleeding pump air gap. A defending, a packing and a biochemical treatment are taken on the surface of the impeller. A tube cavity of the bleeding pump is made from a material with good blood compatibleness. A pre-diversion system structure is simplified, and a pre-diversion wimble is supported by a single cantilever, which are all in favor of preventing a thrombosis. The boosting method adopts a serial-type connection of an axial bleeding pump and ventricles of heart (left ventricle, right ventricle or double ventricles) and requests that an appearance of the bleeding pump is a geometrical shape of as ascending aorta or a main pulmonary artery which is fit for implantation, and the tube cavity and an artificial blood vessel caliber match with a natural blood vessel. In order to prevent a pumping action of the bleeding pump reduces a perfusion pressure of a coronary artery, a coronary artery and aorta bypass transplantation can be performed.
Owner:李国荣 +2
Method and system for advanced measurements computation and therapy planning from medical data and images using a multi-physics fluid-solid heart model
ActiveUS9129053B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMedical simulationComputational modelModel parameters
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Fusion pacing enhancements
The disclosure provides methods and apparatus of left ventricular pacing including automated adjustment of a atrio-ventricular (AV) pacing delay interval and intrinsic AV nodal conduction testing. It includes—upon expiration or reset of a programmable AV Evaluation Interval (AVEI)—performing the following: temporarily increasing a paced AV interval and a sensed AV interval and testing for adequate AV conduction and measuring an intrinsic atrio-ventricular (PR) interval for a right ventricular (RV) chamber. Thus, in the event that the AV conduction test reveals a physiologically acceptable intrinsic PR interval then storing the physiologically acceptable PR interval in a memory structure (e.g., a median P-R from one or more cardiac cycles). In the event that the AV conduction test reveals an AV conduction block condition or if unacceptably long PR intervals are revealed then a pacing mode-switch to a bi-ventricular (Bi-V) pacing mode occurs and the magnitude of the AVEI is increased.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
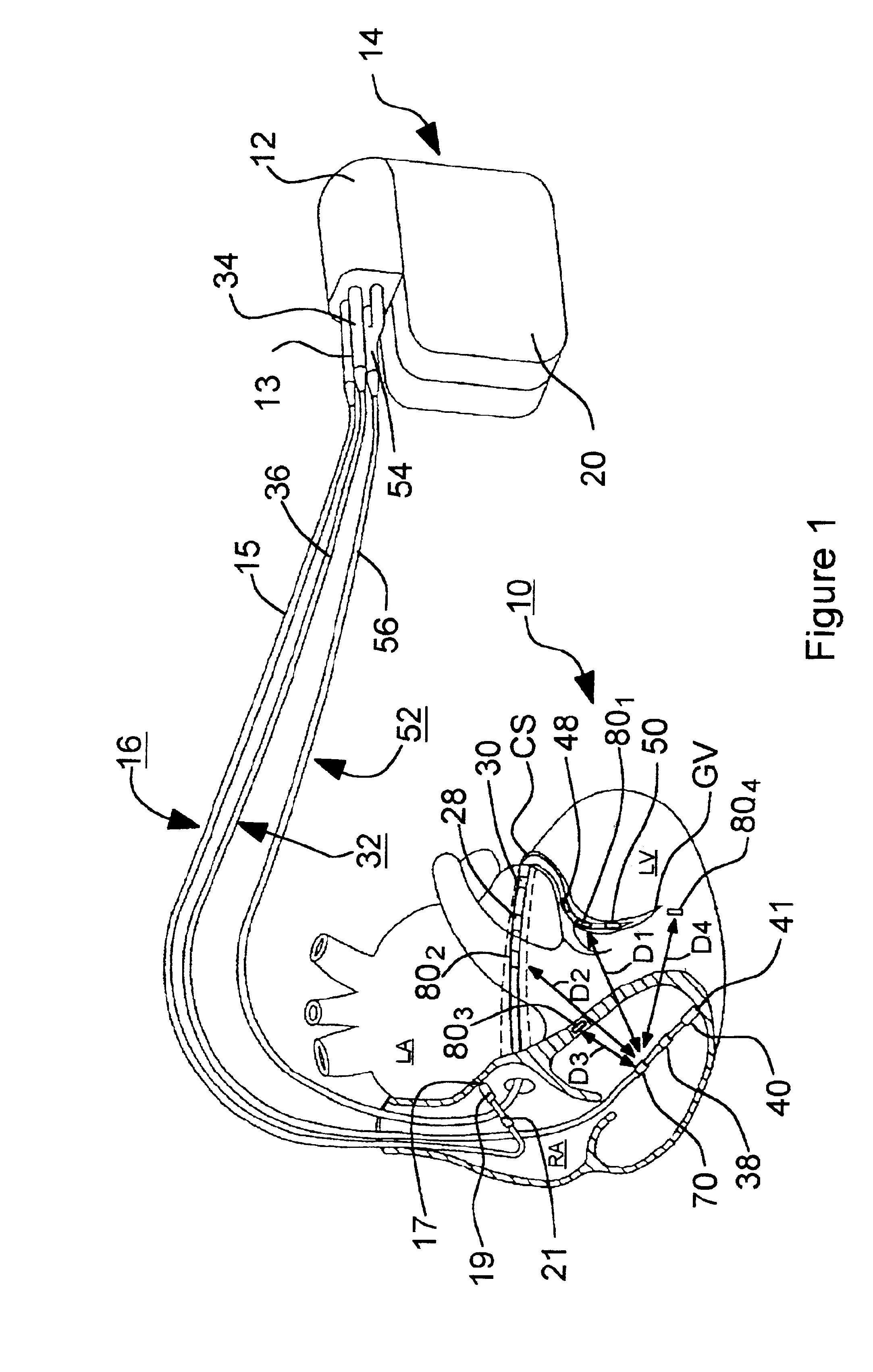
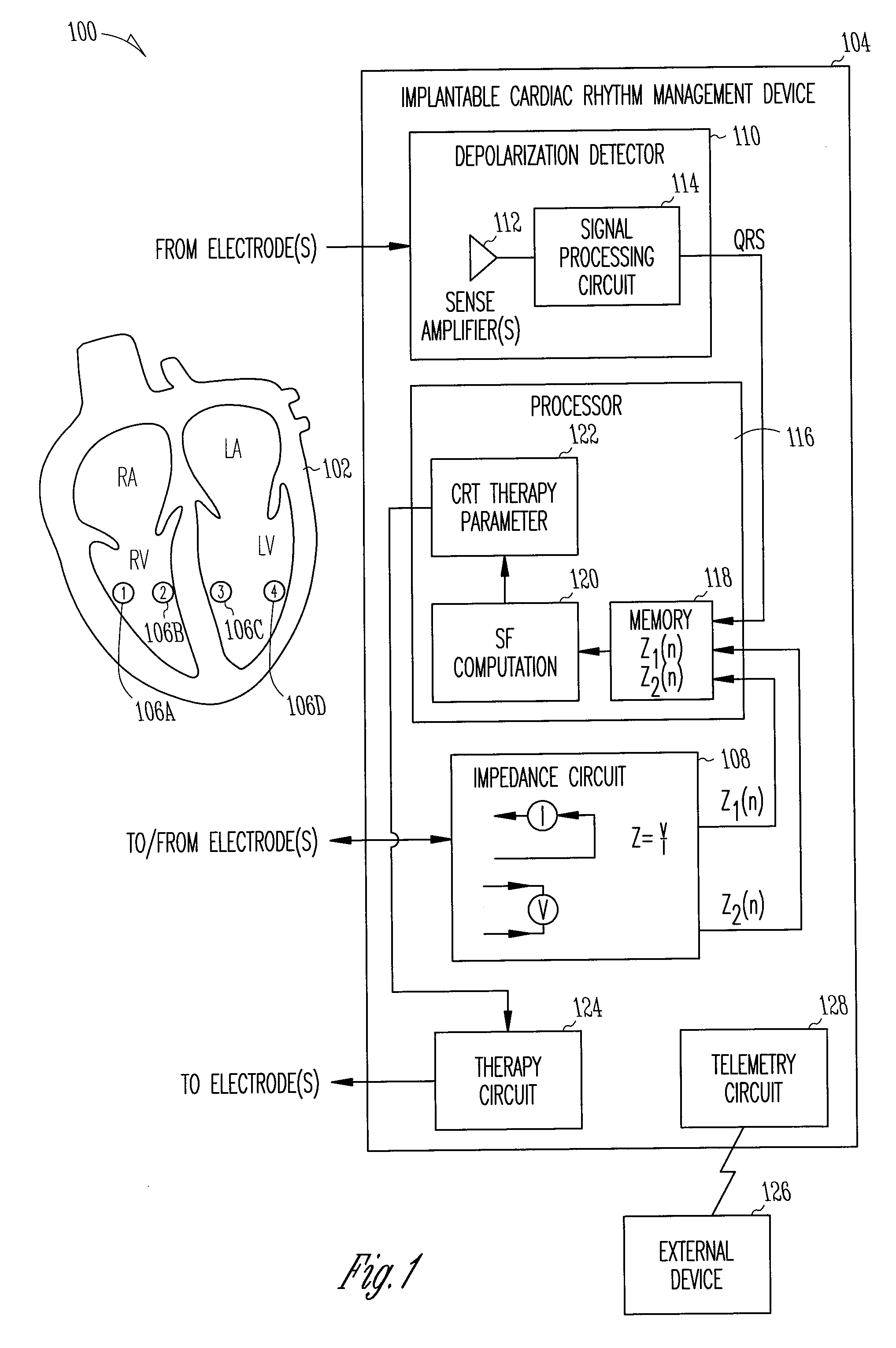
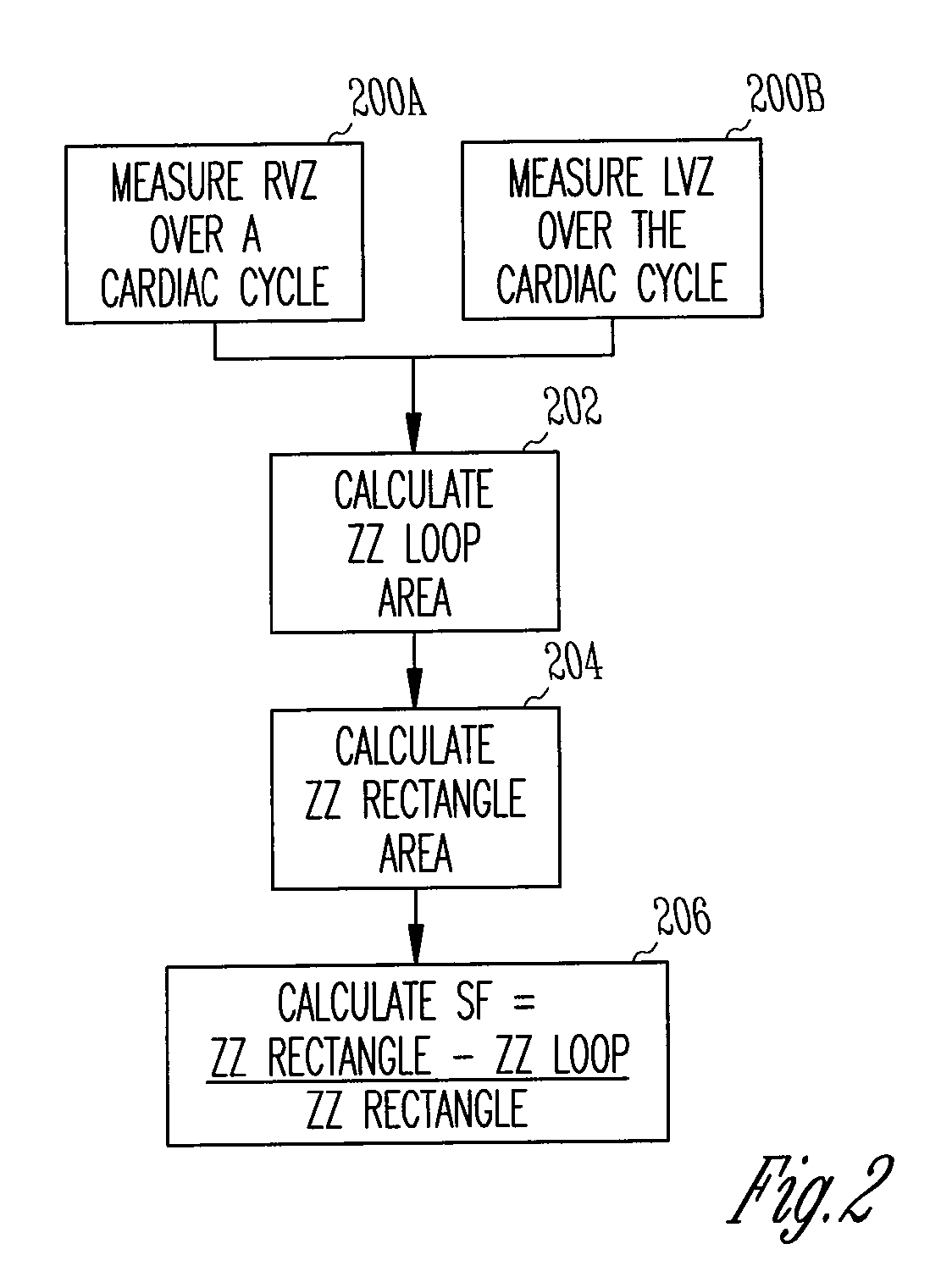
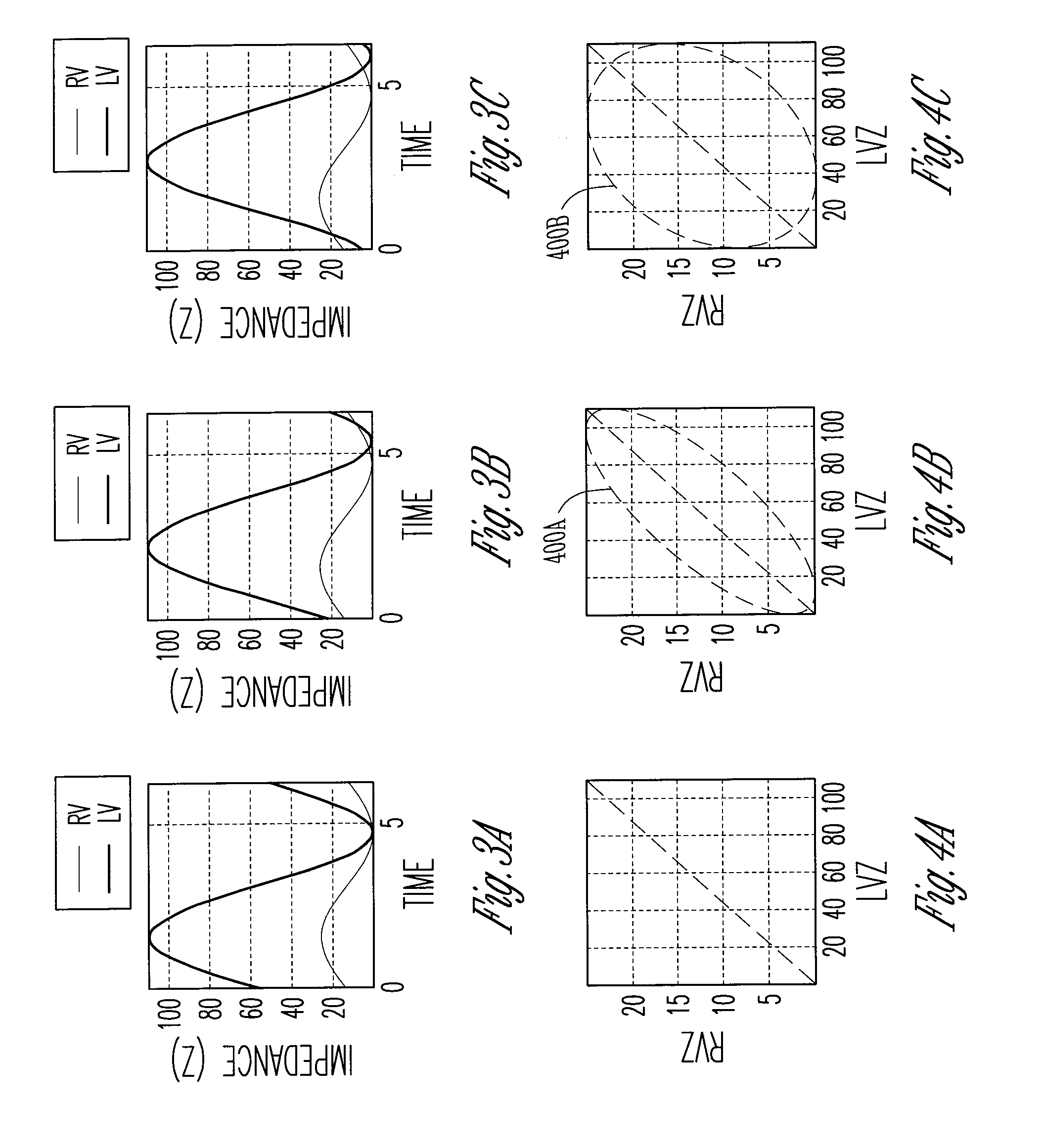
Closed loop impedance-based cardiac resynchronization therapy systems, devices, and methods
ActiveUS20080114410A1Heart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringLeft cardiac chamberVentricular volume
This document discusses, among other things, systems, devices, and methods measure an impedance and, in response, adjust an atrioventricular (AV) delay or other cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) parameter that synchronizes left and right ventricular contractions. A first example uses parameterizes a first ventricular volume against a second ventricular volume during a cardiac cycle, using a loop area to create a synchronization fraction (SF). The CRT parameter is adjusted in closed-loop fashion to increase the SF. A second example measures a septal-freewall phase difference (PD), and adjusts a CRT parameter to decrease the PD. A third example measures a peak-to-peak volume or maximum rate of change in ventricular volume, and adjusts a CRT parameter to increase the peak-to-peak volume or maximum rate of change in the ventricular volume.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Pressure differential actuated prosthetic medical device
The invention relates to a medical prosthesis, and in particular a heart valve substitute comprising a pliant tubular conduit mounted on a resilient annular frame and tethered to a non-perforating anchor within the right or left ventricle of the heart, wherein the pliant tubular conduit is a reciprocating mechanical member that is compressed by pressurized working fluid within the ventricle during systole.
Owner:VDYNE INC
Methods and apparatuses for cardiac resynchronization therapy mode selection based on intrinsic conduction
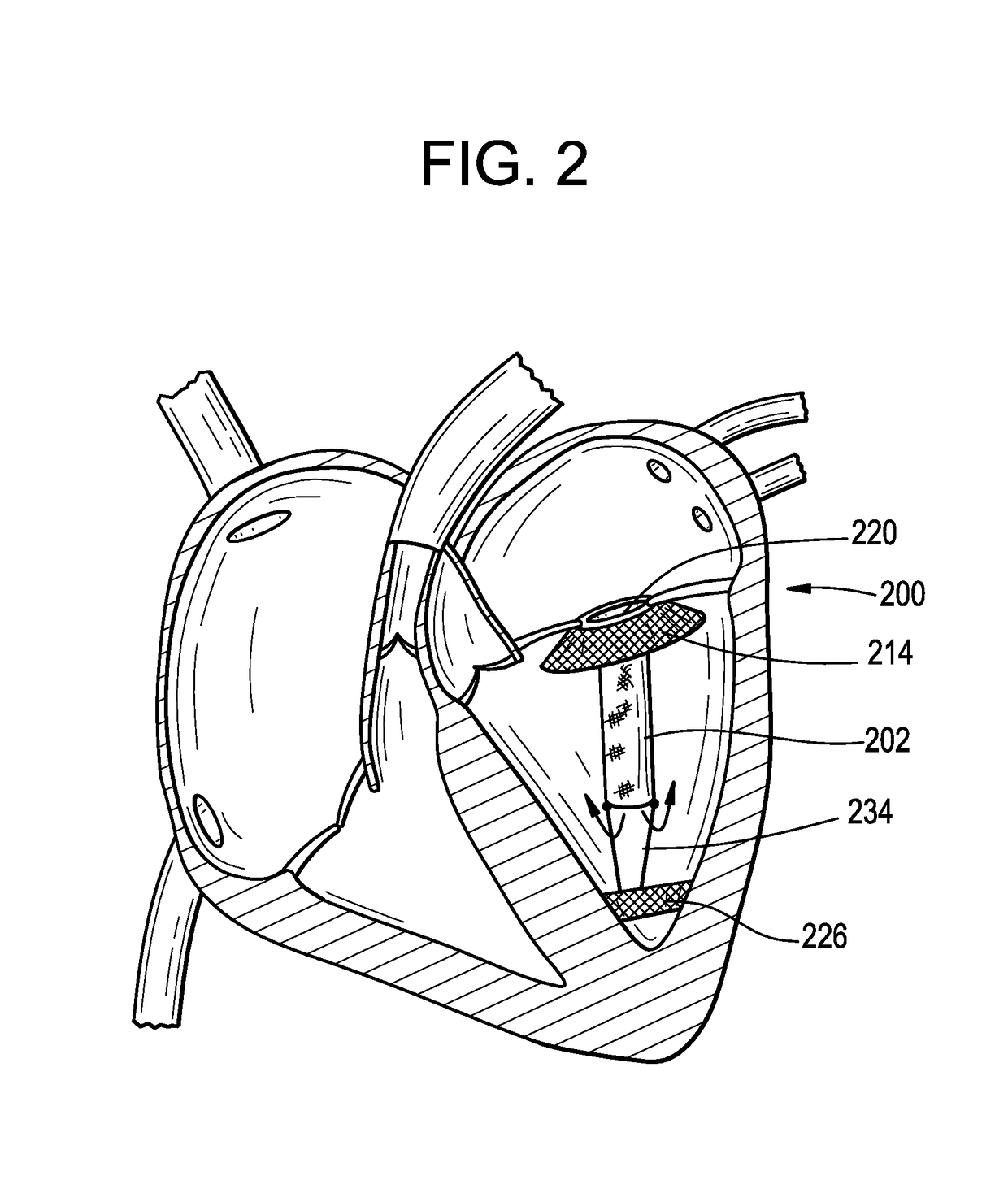
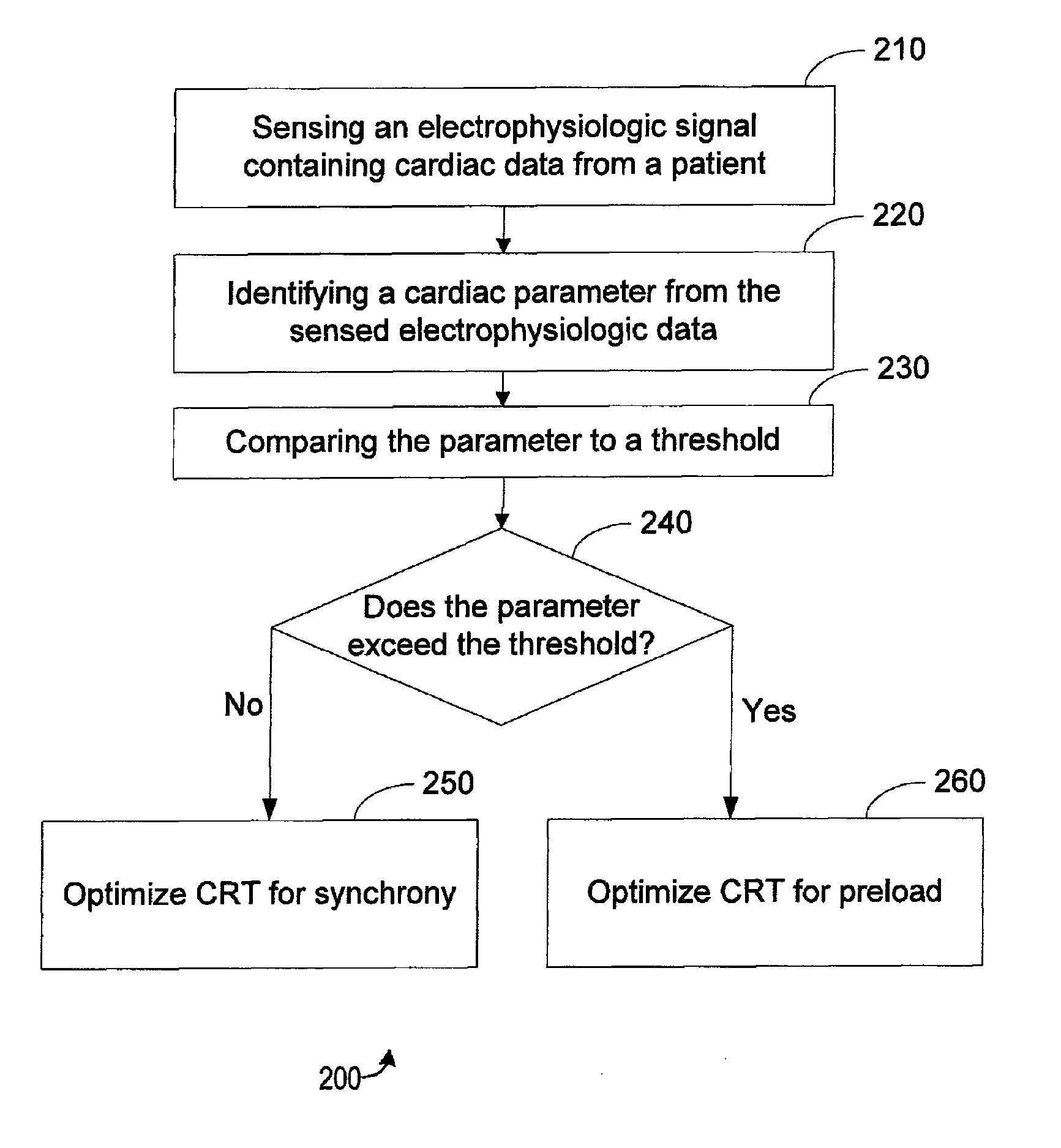
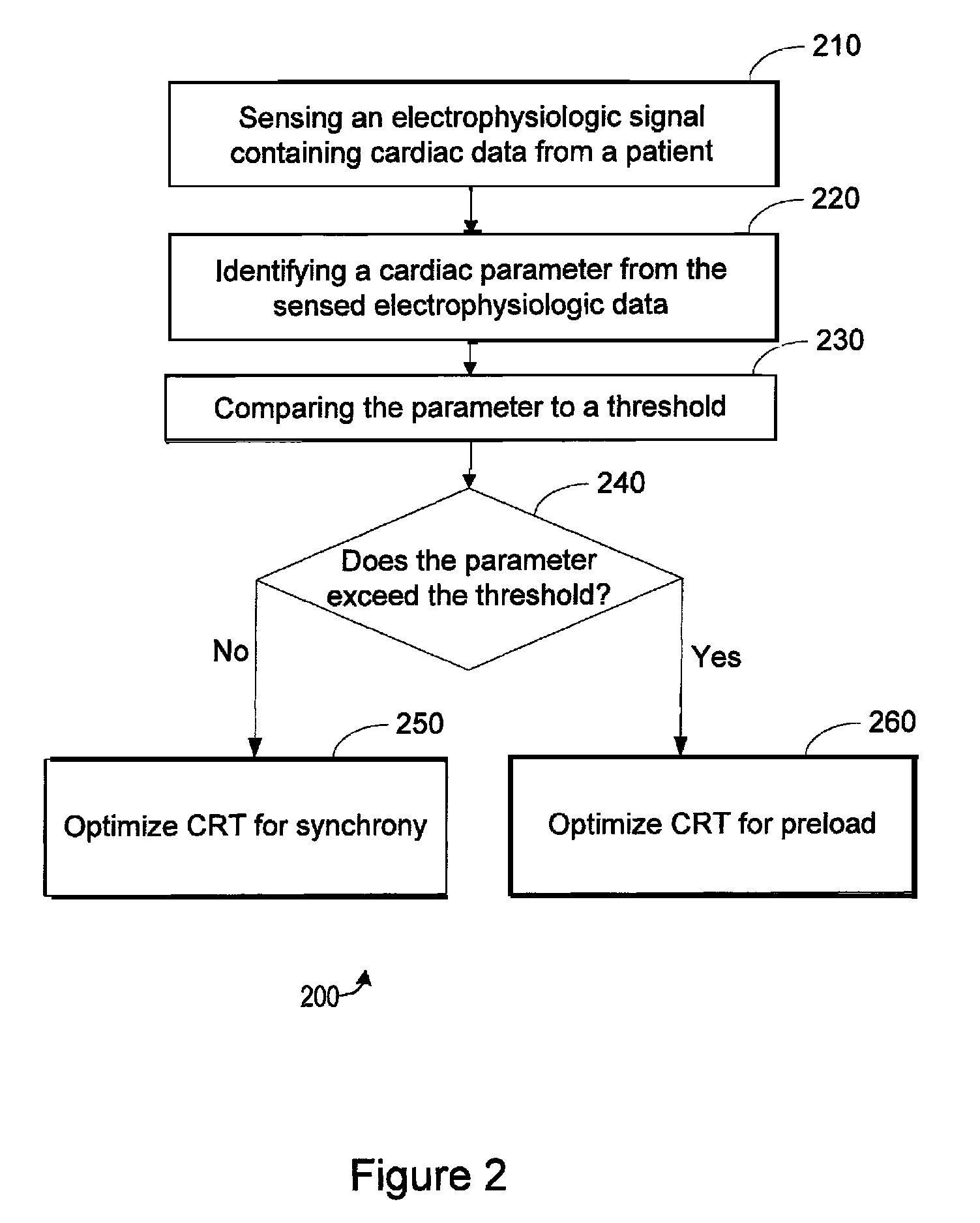
Systems and methods for selecting a cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) mode involve sensing electrocardiogram (ECG) data for a patient, identifying a PR interval from the sensed ECG data, comparing the PR interval to a threshold, and selecting a CRT mode by selecting between a synchrony optimization mode and a preload optimization mode, the selection based on the comparison of the PR interval to the threshold. A synchrony optimization mode may be selected if the parameter is less than the threshold, and may optimize CRT for fusion between a left ventricular pulse and an intrinsic wavefront. The preload optimization mode may be selected if the parameter is greater than the threshold, and may optimize CRT for fusion between respective wavefronts of the left ventricular pace and a right ventricular pace.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Systems and devices for setting anchor
An anchoring system and related methods are provided for treatment of dilated hearts and of functional valve regurgitation, the system comprising one or more self- expandable or manually expandable anchors and associated devices for fixating a valve splint within the heart. For example, a spade-shaped assembly may be configured to be deployed in a right ventricle of the heart and to stabilize a puncturing instrument to puncture the septum. Various puncturing instruments may also be part of the anchoring system, including one or more of a flexible needle having a multiplicity of slits disposedalong the length of the needle, a trocar catheter with a retractable head, and a catheter needle having a blunt introducer to protect nearby tissue within the heart during advancing a guidewire. A cutter catheter and puncture location catheter may also be part of the system and be used during treatment.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Optimizing and monitoring adaptive cardiac resynchronization therapy devices
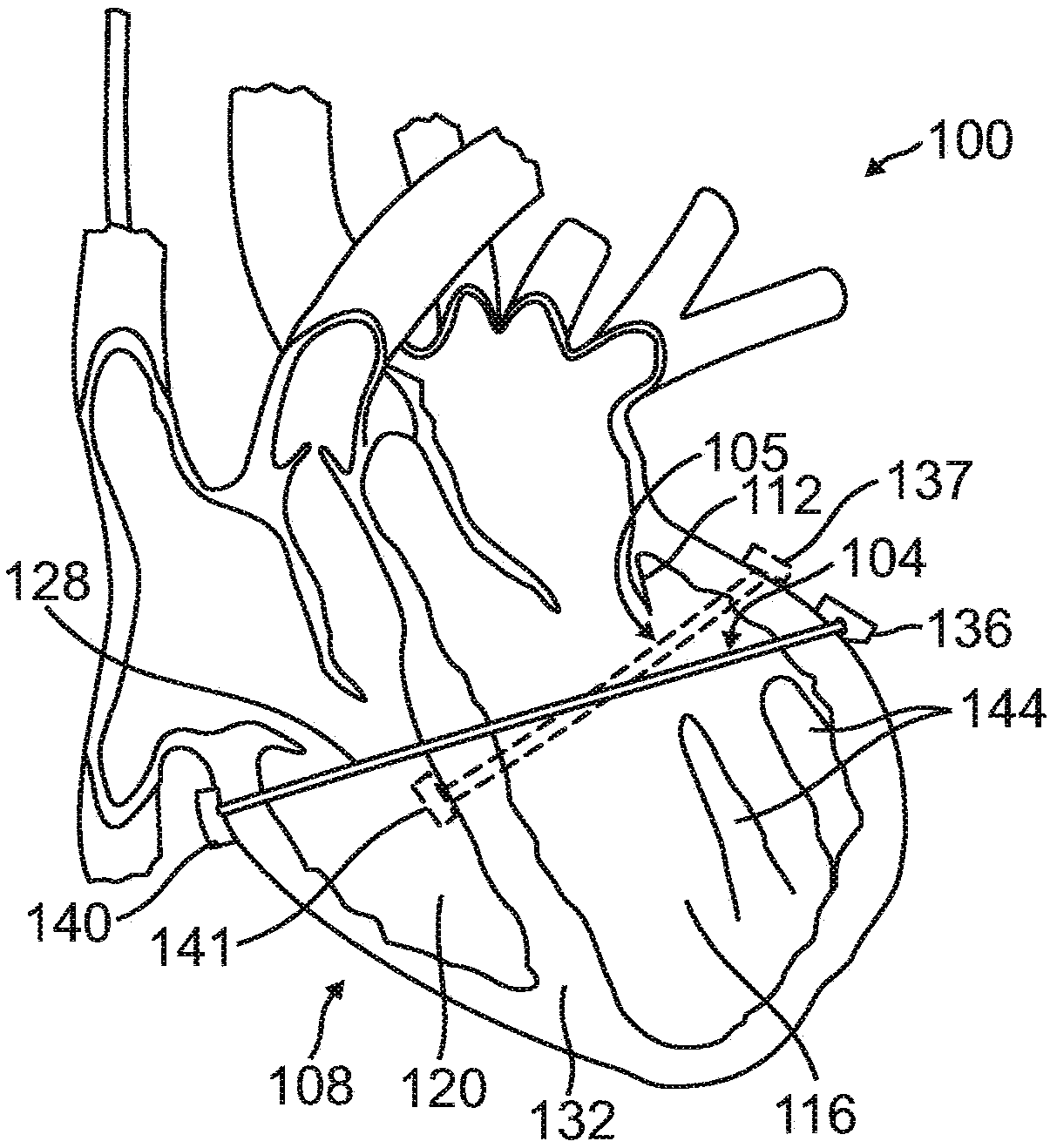
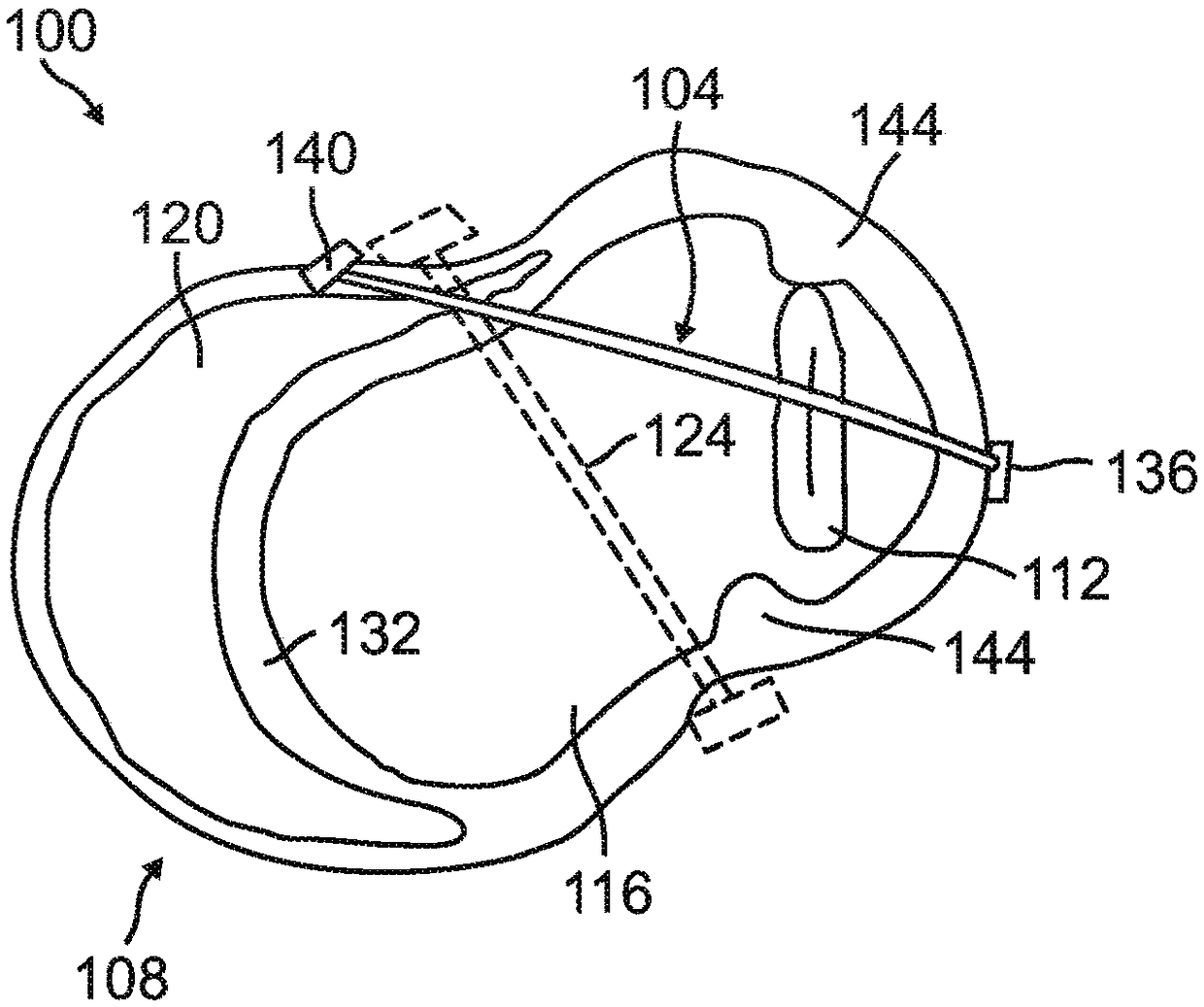
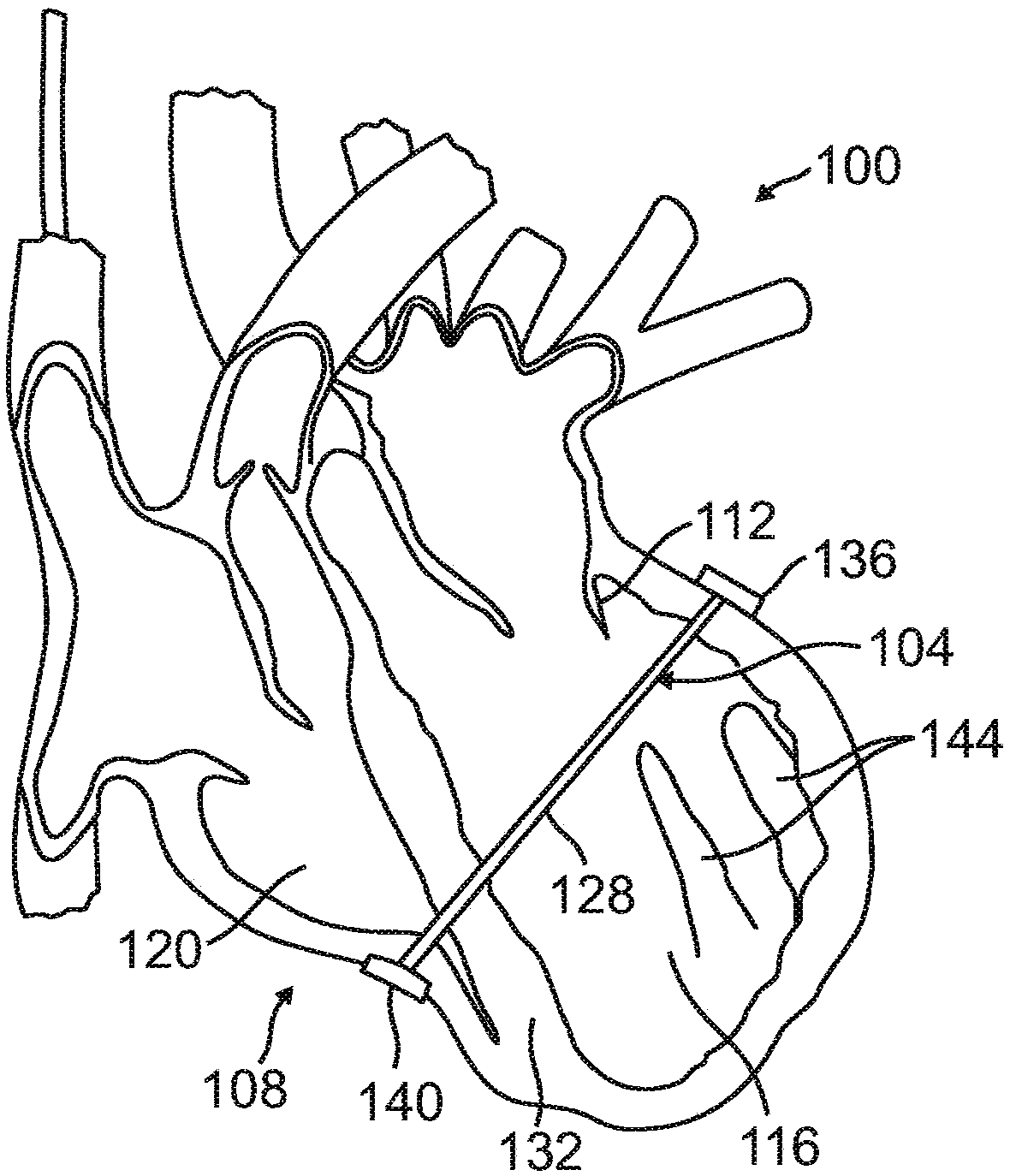
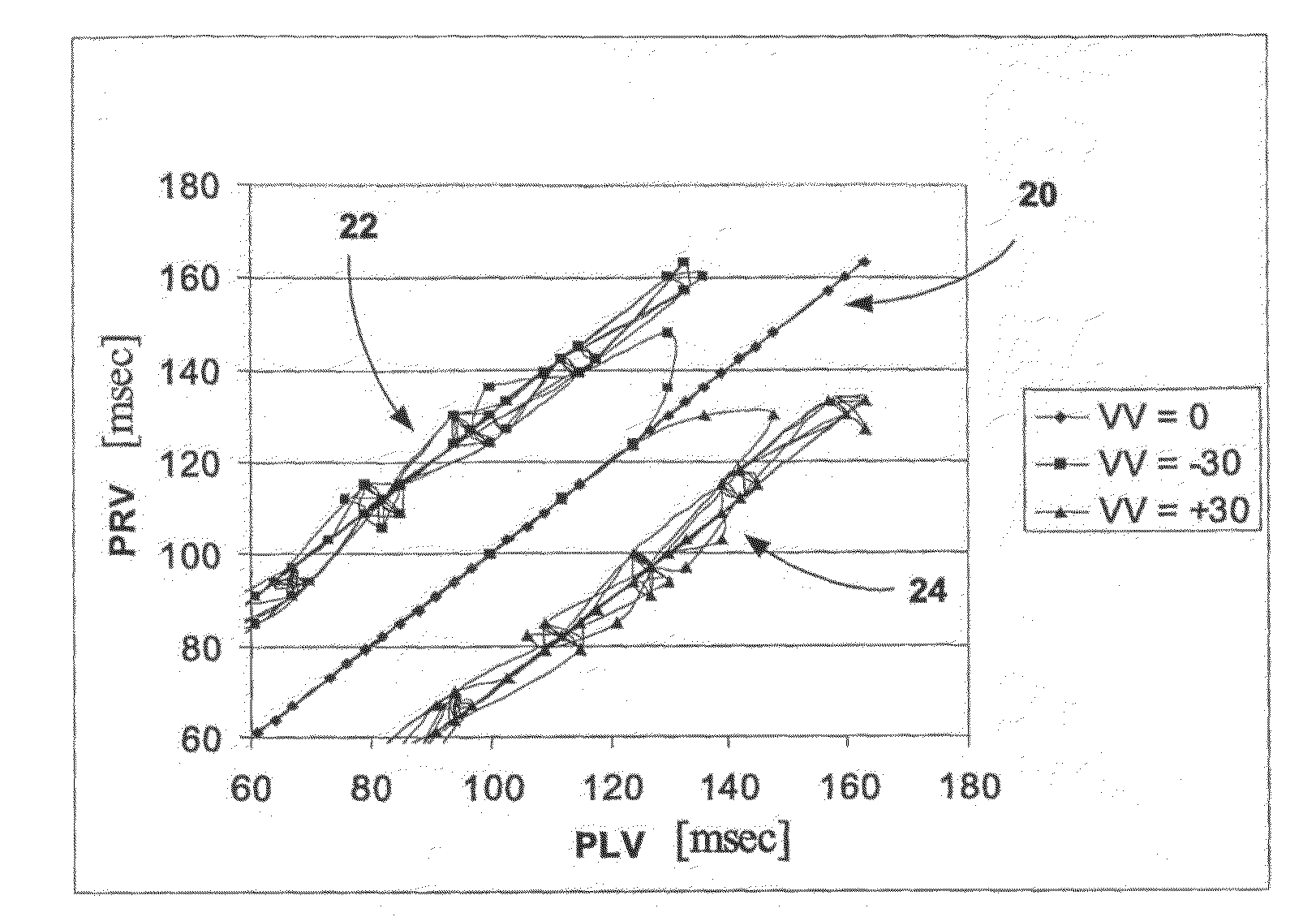
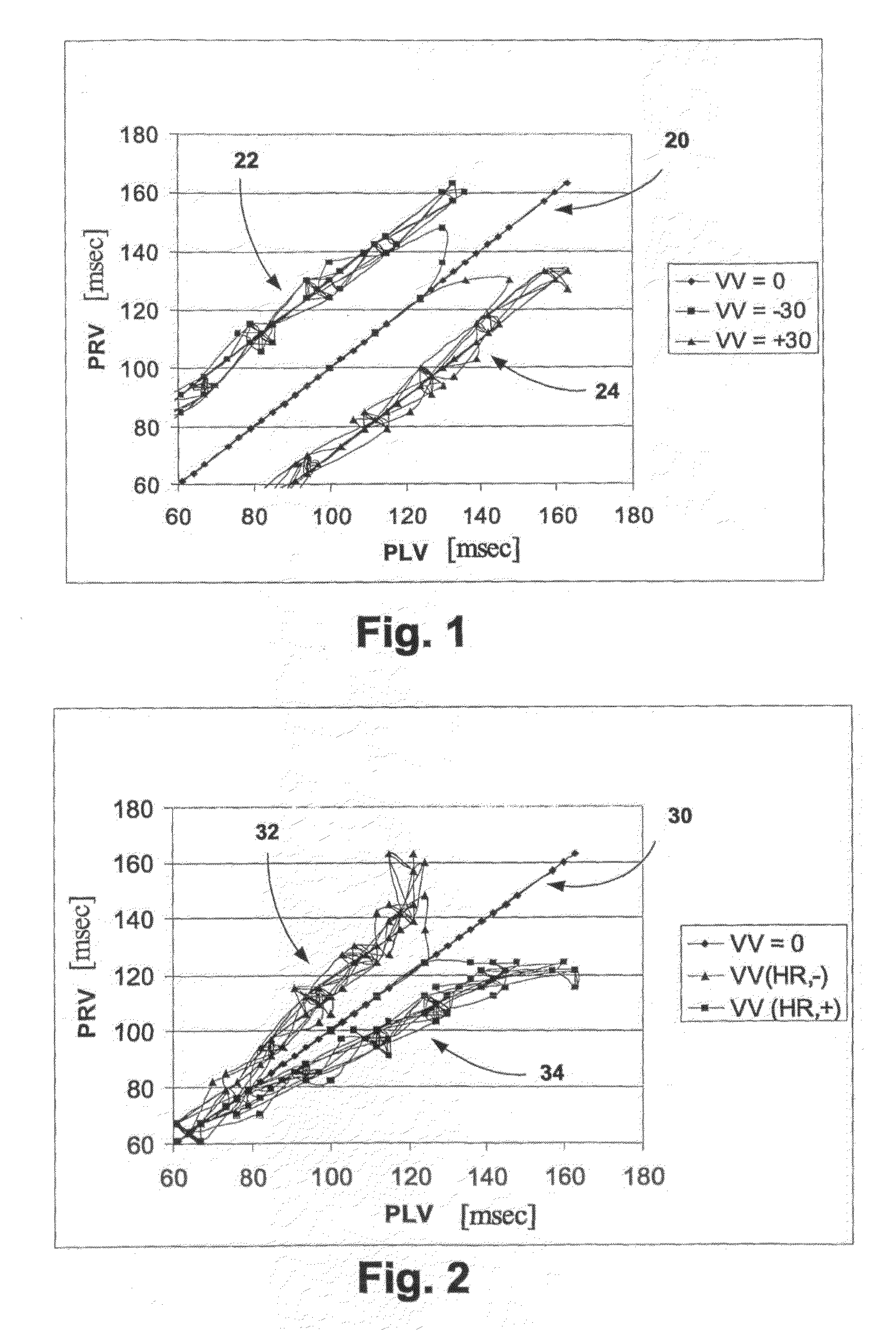
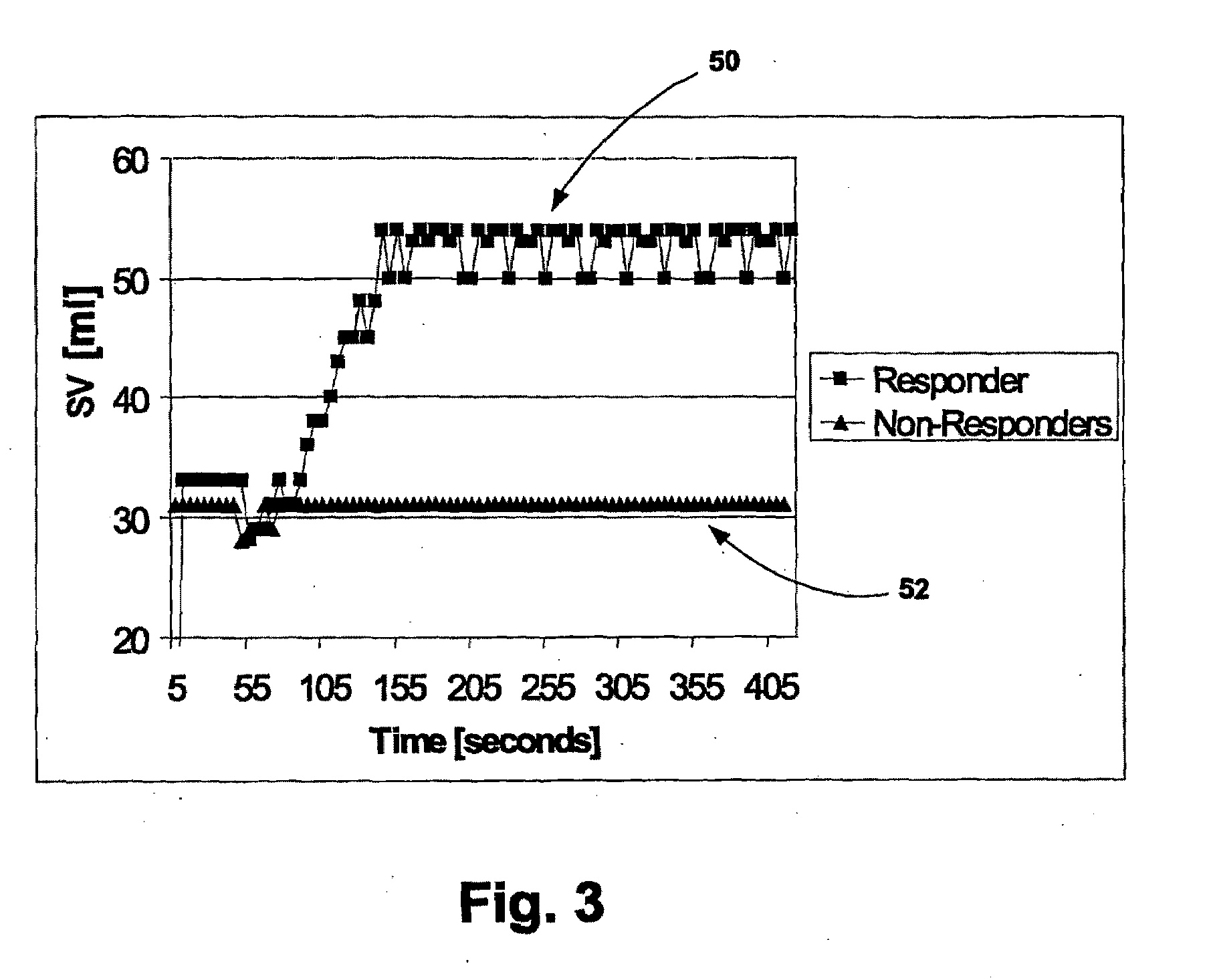
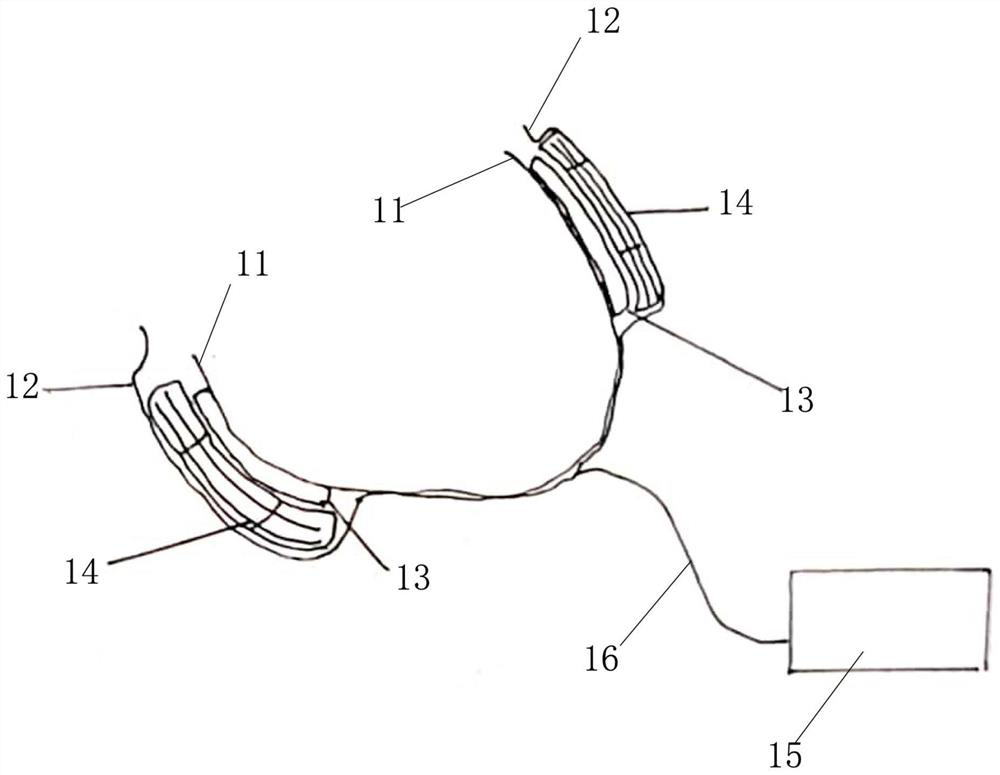
A system for remotely monitoring cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) devices and for optimizing location of implanted leads. The system displays a graph of the right ventricle pacing interval (PRV) vs. left ventricle pacing interval (PLV) diagram at maximal stroke volume and or a graph of a responder curve that demonstrates the stroke volume obtained beat after beat by the implanted hemodynamic sensor with dynamically optimized AV and VV parameters. The system lends itself easily to be used as a remote monitoring means for active and resting patients.
Owner:ROM RAMI
Electromagnetic cardiac pulse assisting device
PendingCN112933396AEasy to shrinkEasy to relaxBlood pumpsMedical devicesSurgical operationCardiac surface
The invention relates to the technical field of medical instruments, in particular to an electromagnetic cardiac pulse assisting device. The electromagnetic cardiac pulse assisting device comprises an inner membrane, an outer membrane supporting body, two permanent magnets, electromagnets, a power source and a controller. The inner membrane covers the surface of the heart, and the outer membrane supporting body covers the outer side of the inner membrane. The two permanent magnets are fixed to the outer side of the inner membrane and correspond to the left ventricle and the right ventricle respectively. The two electromagnets are fixed to the inner side of the outer membrane supporting body and are opposite to the permanent magnets. The power source and the controller are used for supplying power to the electromagnets and adjusting the magnitude and the direction of current, so that the electromagnets can apply repulsive force or attractive force to the permanent magnets, and then the heart is driven to contract or relax. The device has the advantages of being capable of assisting the heart of the human body to beat, high in controllability, capable of improving the heart failure symptom and prolonging the service life of a patient, simple in structure, small and exquisite in size, capable of being implanted only through surgical operation, convenient to replace, low in manufacturing and using cost, long in service life and easy to accept by doctors and patients.
Owner:深圳脉腾医学技术有限公司 +1
Perfusion phantom device
ActiveUS20160027340A1Eliminate riskAchieve trafficMagnetic measurementsSurgeryRight atriumThoracic cavity
The invention relates to a phantom device for reproducing the fluid perfusion in a body, said device comprising a phantom organ that may be introduced into a scanner, said phantom organ comprising a housing in which are defined a plurality of fluid channels, suitably of differing cross-sectional areas; a feed tube arranged to supply liquid to a first end of all of said channels and means for collecting liquid from the other end of the channels. Alternatively or additionally, the device may comprise an element comprising a phantom heart through which fluid can flow, wherein the phantom heart comprises a first chamber representing a right atrium which is arranged to receive fluid from a fluid supply, a second chamber representing a right ventricle which receives fluid leaving said first chamber, a third chamber representing a left atrium which receives fluid leaving the second chamber and a fourth chamber representing left ventricle which receives fluid leaving the third chamber; and wherein a phantom thoracic system is interposed between the second chamber and the third chamber.Uses of the device in quality control, validation or calibration of monitoring devices such as magnetic resonance (MR) or computerised tomography (CT) scanners, in teaching or training of machine operatives or for research purposes including for research into scanners, scanning techniques or reagents such as contrast agents used in such processes, form further aspects of the invention.
Owner:KING'S COLLEGE LONDON
Heart nuclear magnetic resonance image key point detection method based on convolutional neural network
ActiveCN111144486AGuaranteed accuracyReduce false positive rateImage enhancementImage analysisLeft ventricle wallNeural network nn
The invention discloses a heart nuclear magnetic resonance image key point detection method based on a convolutional neural network, and the method comprises the steps of constructing the convolutional neural network, efficiently detecting the regions of a plurality of key points through a pixel-by-pixel classifier, predicting the distances from pixels to the centers of the key points, and guaranteeing the precise prediction of the key points. The false positive rate of detection is reduced and the accuracy of key point detection is ensured by removing false detection key points, removing leftand right ventricular intersection points, which are not between the left ventricle and the right ventricle, in the fusion information graph and obtaining the local maximum value in the fusion information graph according to the local maximum value search method.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
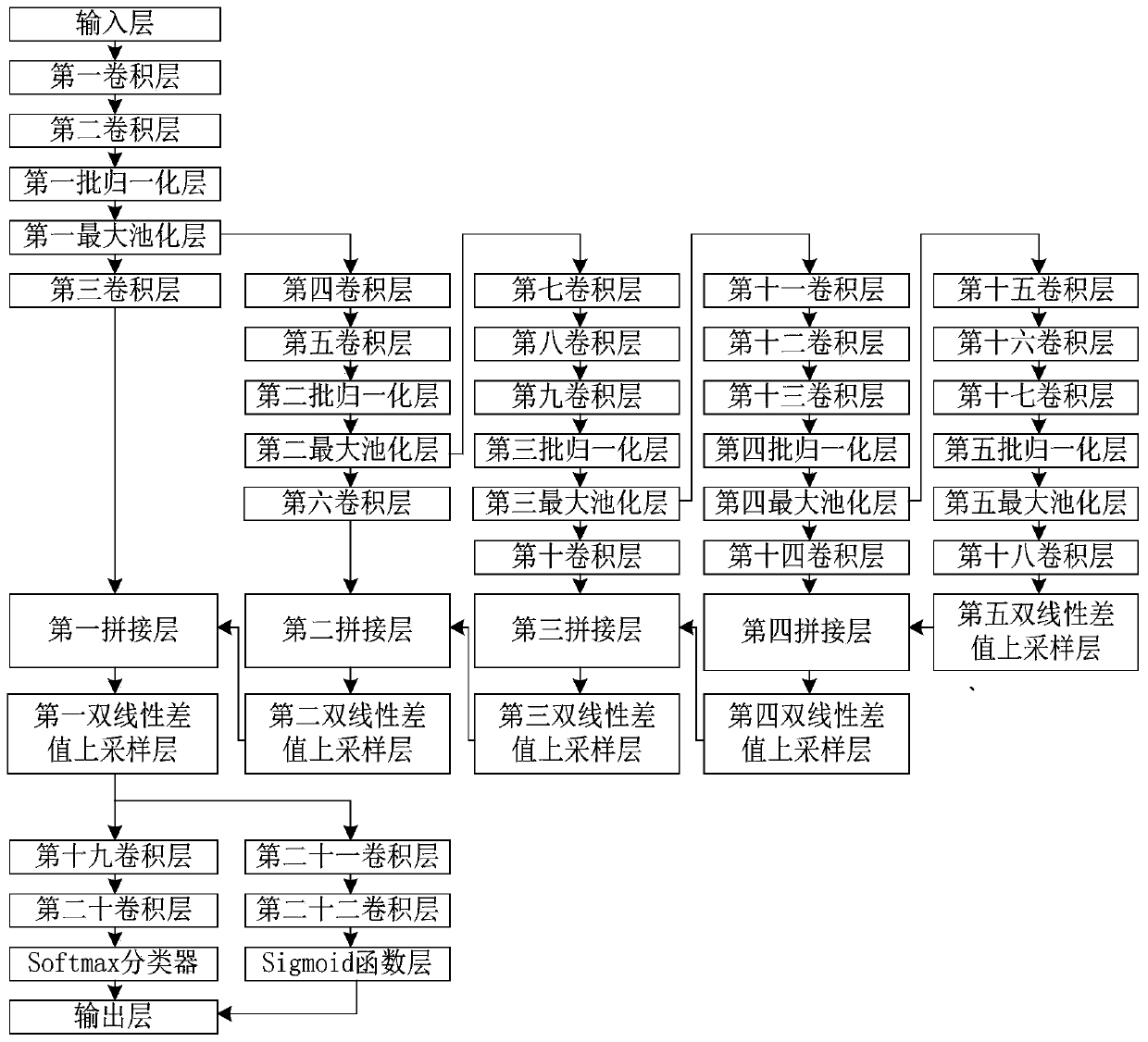
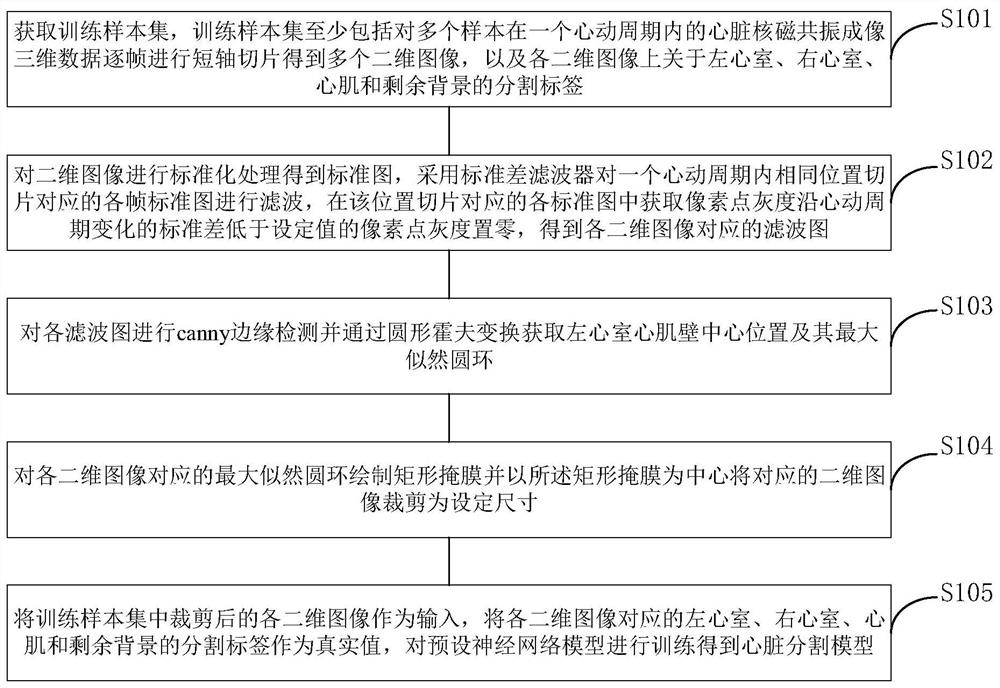
Heart segmentation model and pathological classification model training, heart segmentation and pathological classification method and device based on heart MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
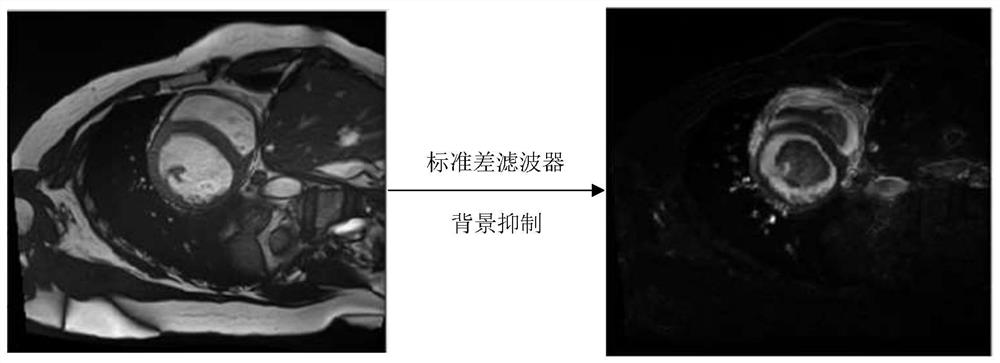
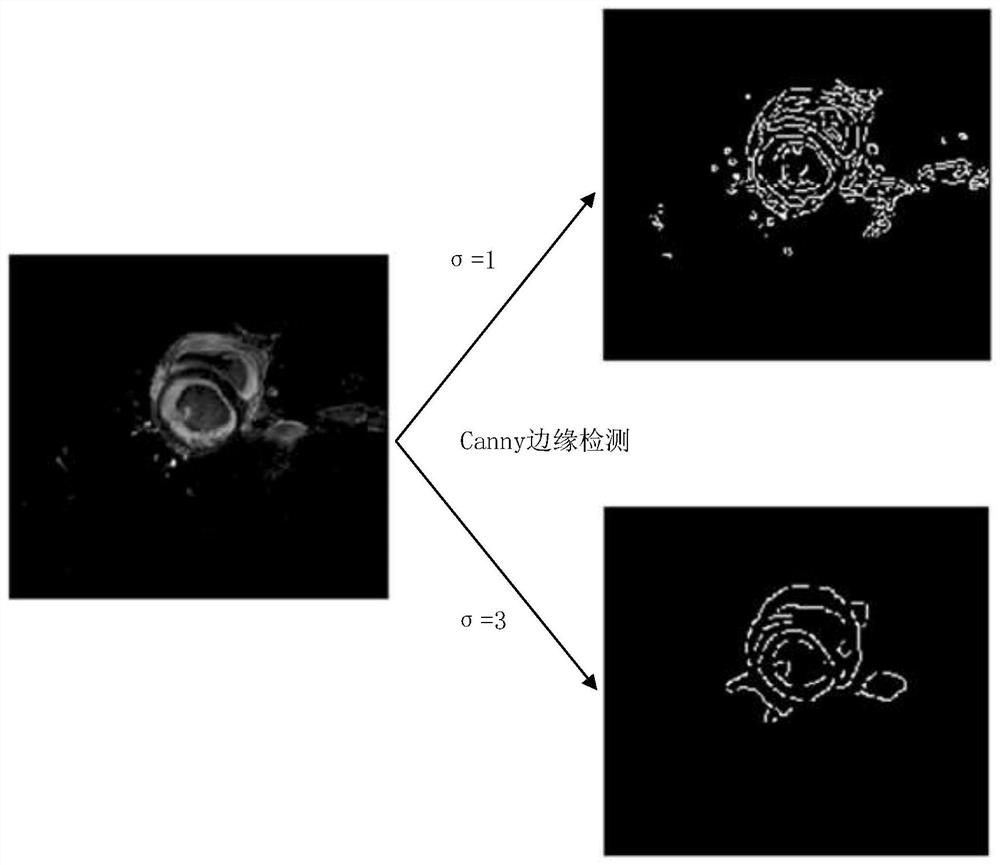
PendingCN113012173AFast convergenceSuppress background distractionsImage enhancementImage analysisLeft ventricular sizeCardiac cycle
The invention provides a heart segmentation model and pathology classification model training, heart segmentation and pathology classification method and device based on heart MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging), and the method comprises the steps: suppressing a residual background part with a small pixel gray level change through a standard deviation filter, highlighting a left ventricle, a right ventricle and a myocardial ,the central position of the left ventricular myocardial wall being further obtained through canny edge detection and circular Hough transform, drawing a rectangular mask, the two-dimensional image being cut based on the rectangular mask to serve as input for training a preset neural network model for training. Background interference can be greatly inhibited, and fast convergence of neural network training is promoted. The pathology classification model training method comprises the following steps: segmenting a two-dimensional image obtained by segmenting each frame of cardiac magnetic resonance imaging short axis in a cardiac cycle based on a cardiac segmentation model, calculating classification feature values, and constructing a random forest based on the classification feature values of a plurality of samples and pathology classification to obtain a cardiac pathology classification model; and realizing automatic pathological classification.
Owner:PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
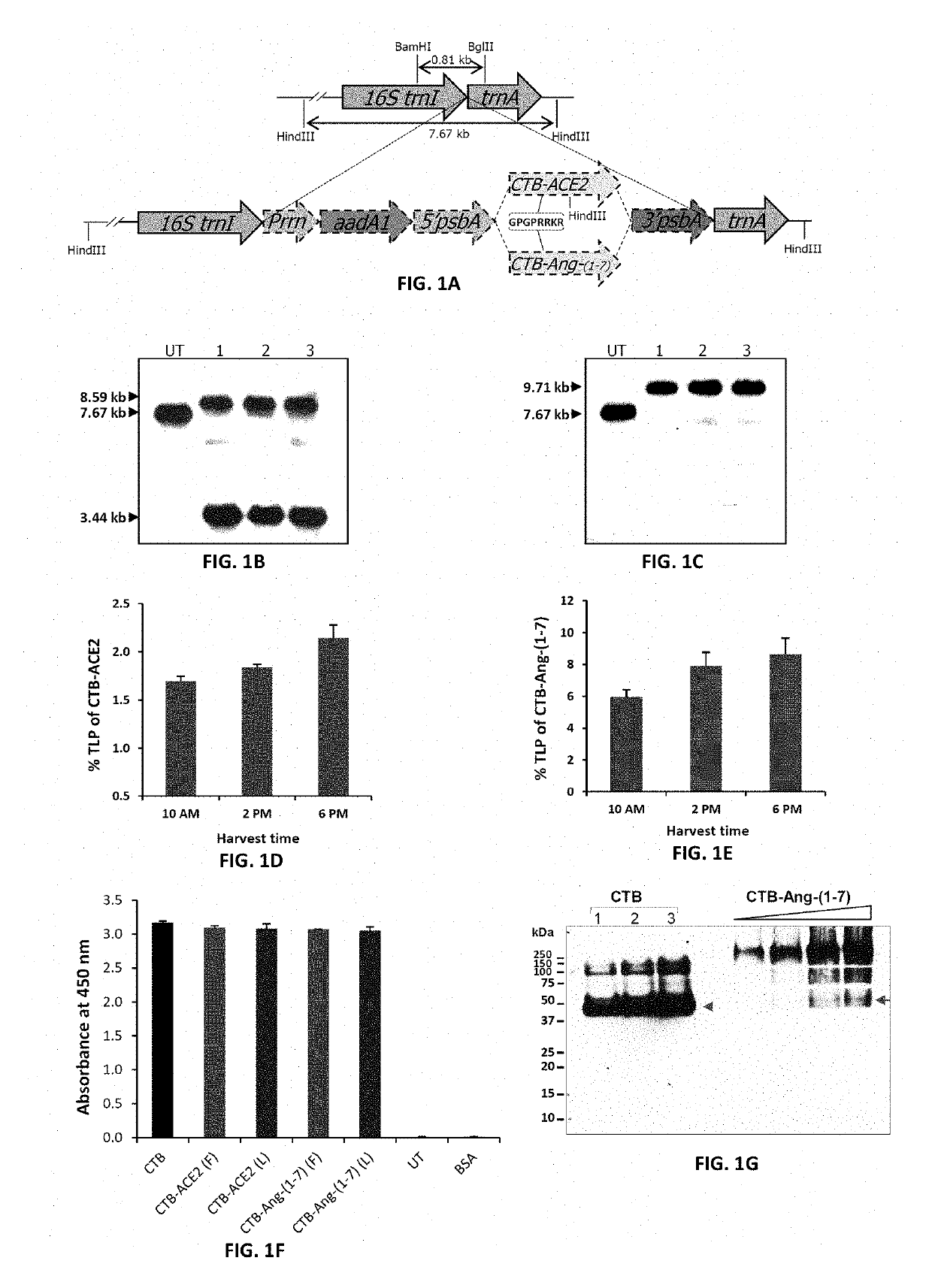
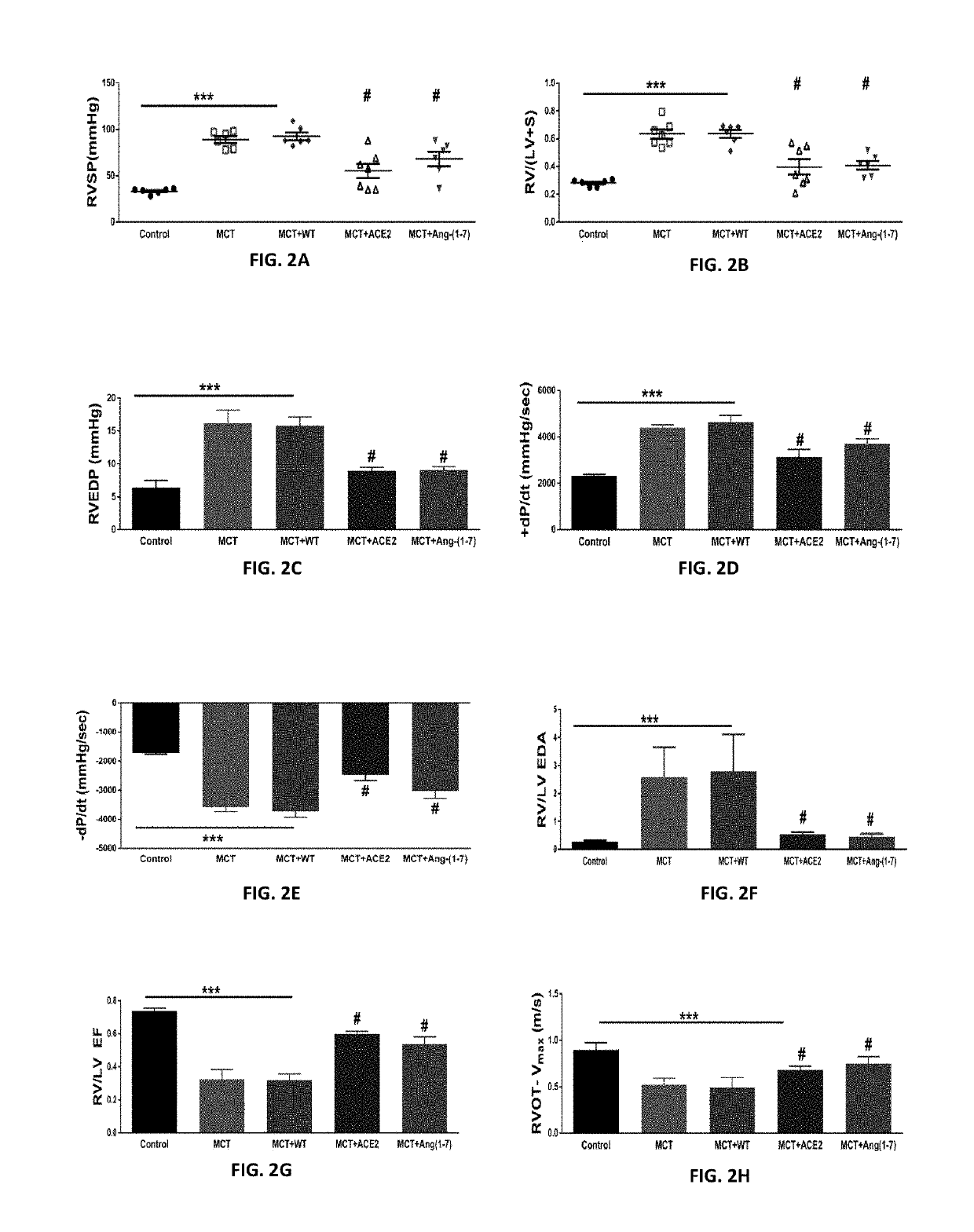
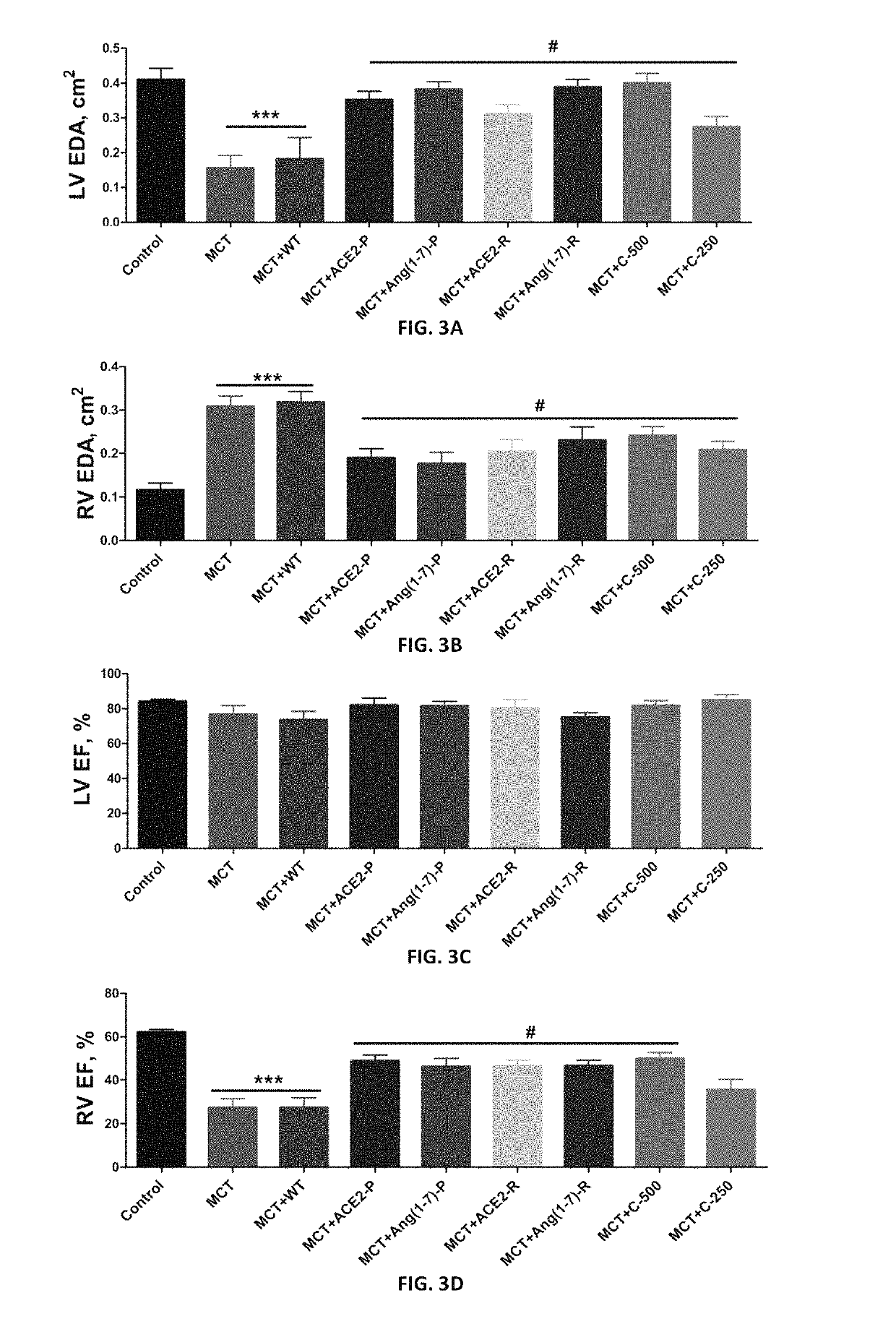
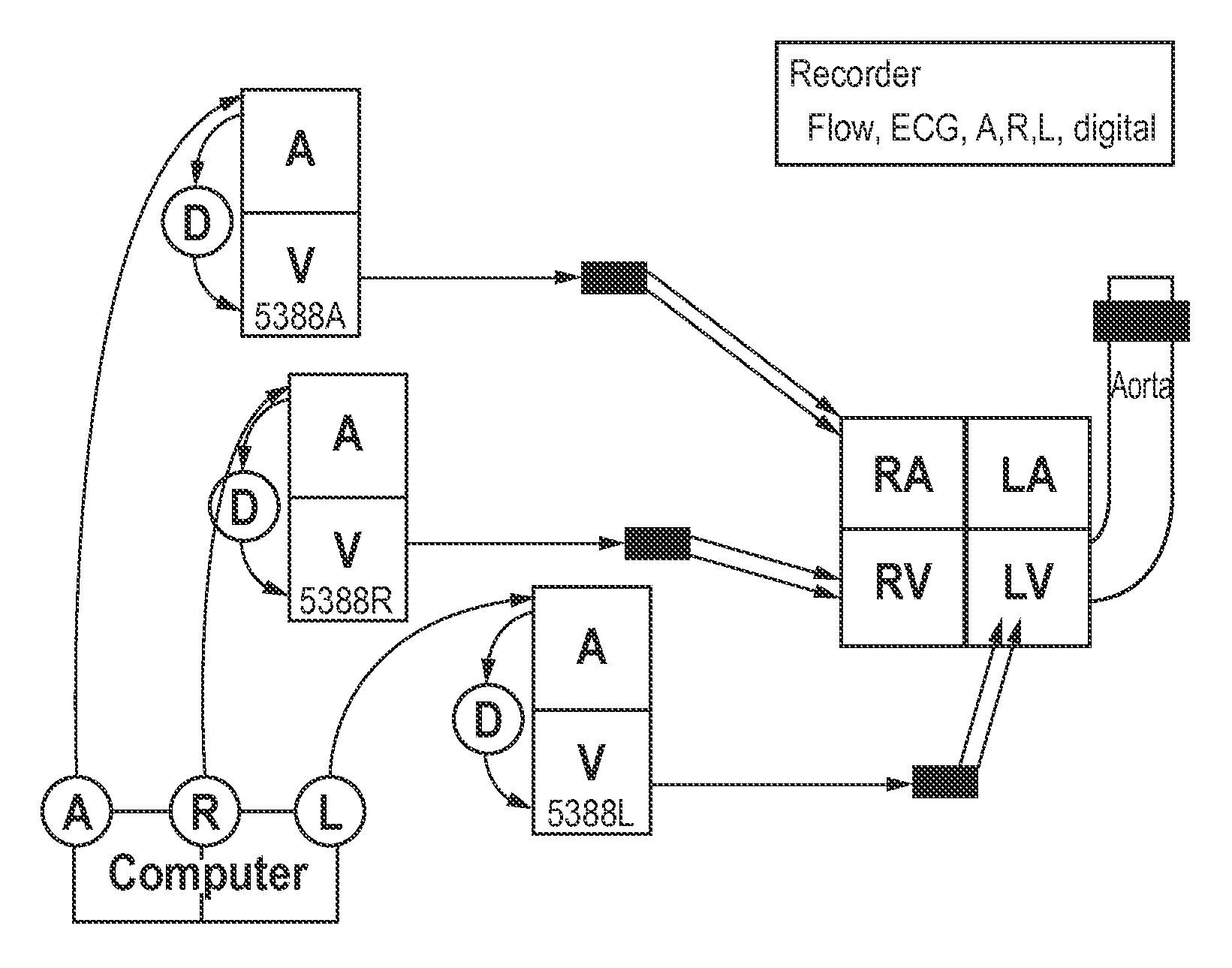
Oral delivery of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) or angiotensin-(1-7) bioencapsulated in plant cells attenuates pulmonary hypertension, cardiac dysfunction and development of autoimmune and experimental induced ocular disorders
ActiveUS10314893B2Good effectAvoid poor resultsPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseUveitis
Emerging evidence indicates that diminished activity of the vasoprotective axis of the renin-angiotensin system, constituting angiotensin converting enzyme2 (ACE2) and its enzymatic product, angiotensin-(1-7) [Ang-(1-7)] contribute to pulmonary hypertension (PH). However, clinical success for long-term delivery of ACE2 or Ang-(1-7) would require stability and ease of administration to increase patient compliance. Chloroplast expression of therapeutic proteins enables their bioencapsulation within plant cells to protect from acids and gastric enzymes; fusion to a transmucosal carrier facilitates effective systemic absorption. Oral feeding of rats with bioencapsulated ACE2 or Ang-(1-7) attenuated monocrotaline (MCT)-induced increase in right ventricular systolic pressure, decreased pulmonary vessel wall thickness and improved right heart function in both prevention and reversal protocols. Furthermore, combination of ACE2 and Ang-(1-7) augmented the beneficial effects against cardio-pulmonary pathophysiology induced by MCT administration.Experiments have also been performed which indicate that this approach is also suitable for the treatment or inhibition of experimental uveitis and autoimmune uveoretinitis These studies provide proof-of-concept for a novel low-cost oral ACE2 or Ang-(1-7) delivery system using transplastomic technology for pulmonary and ocular disease therapeutics.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA +1
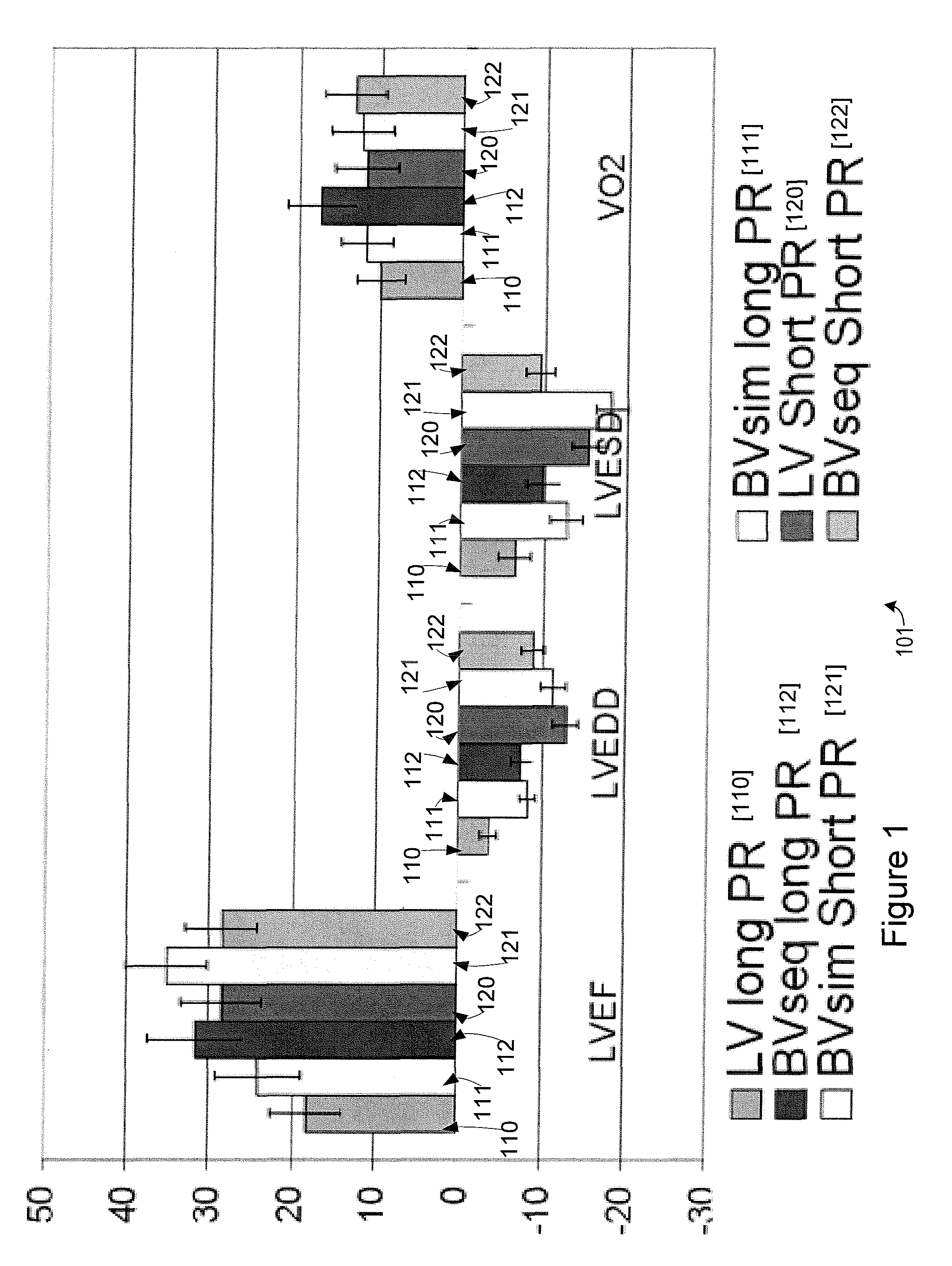
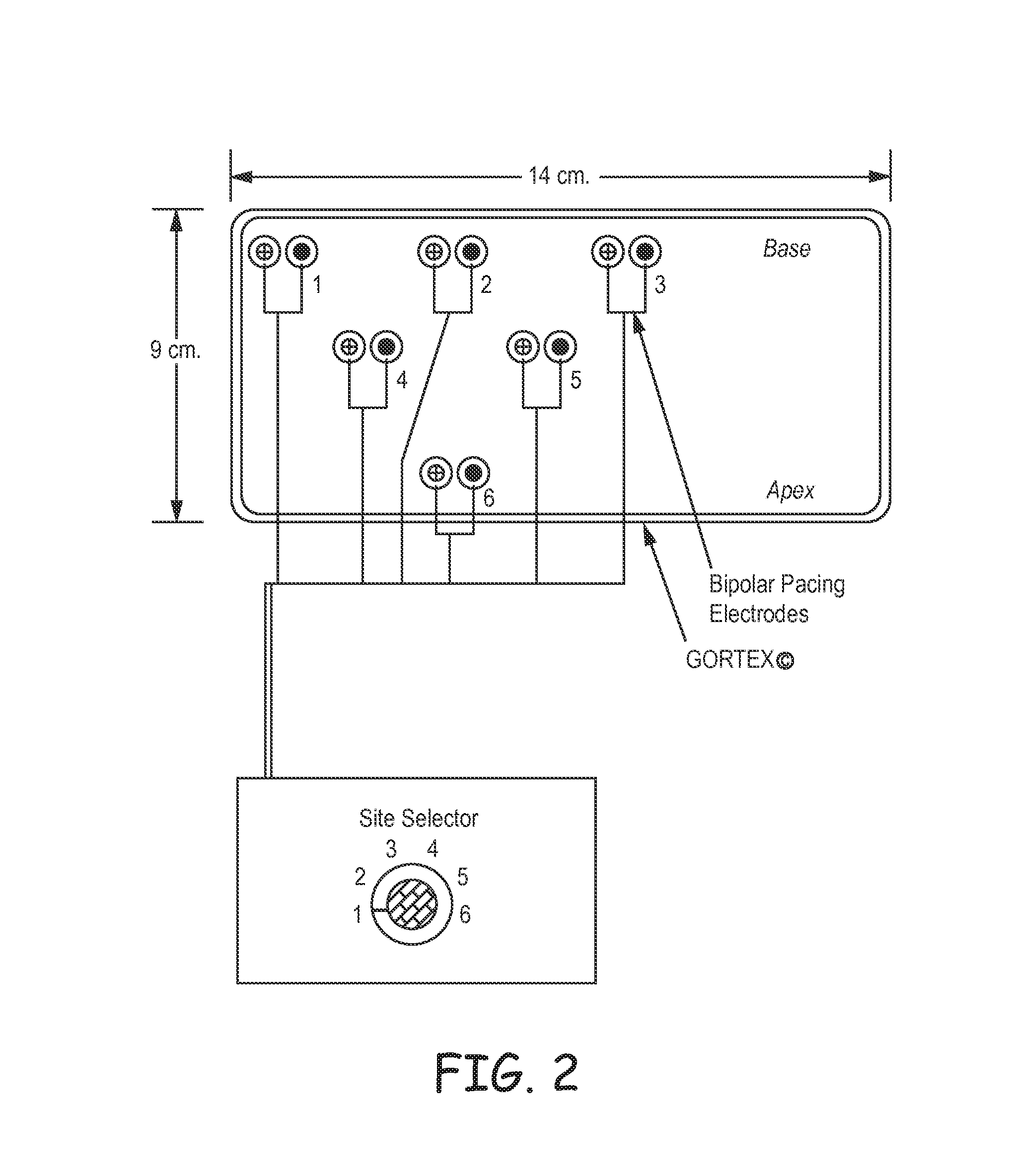
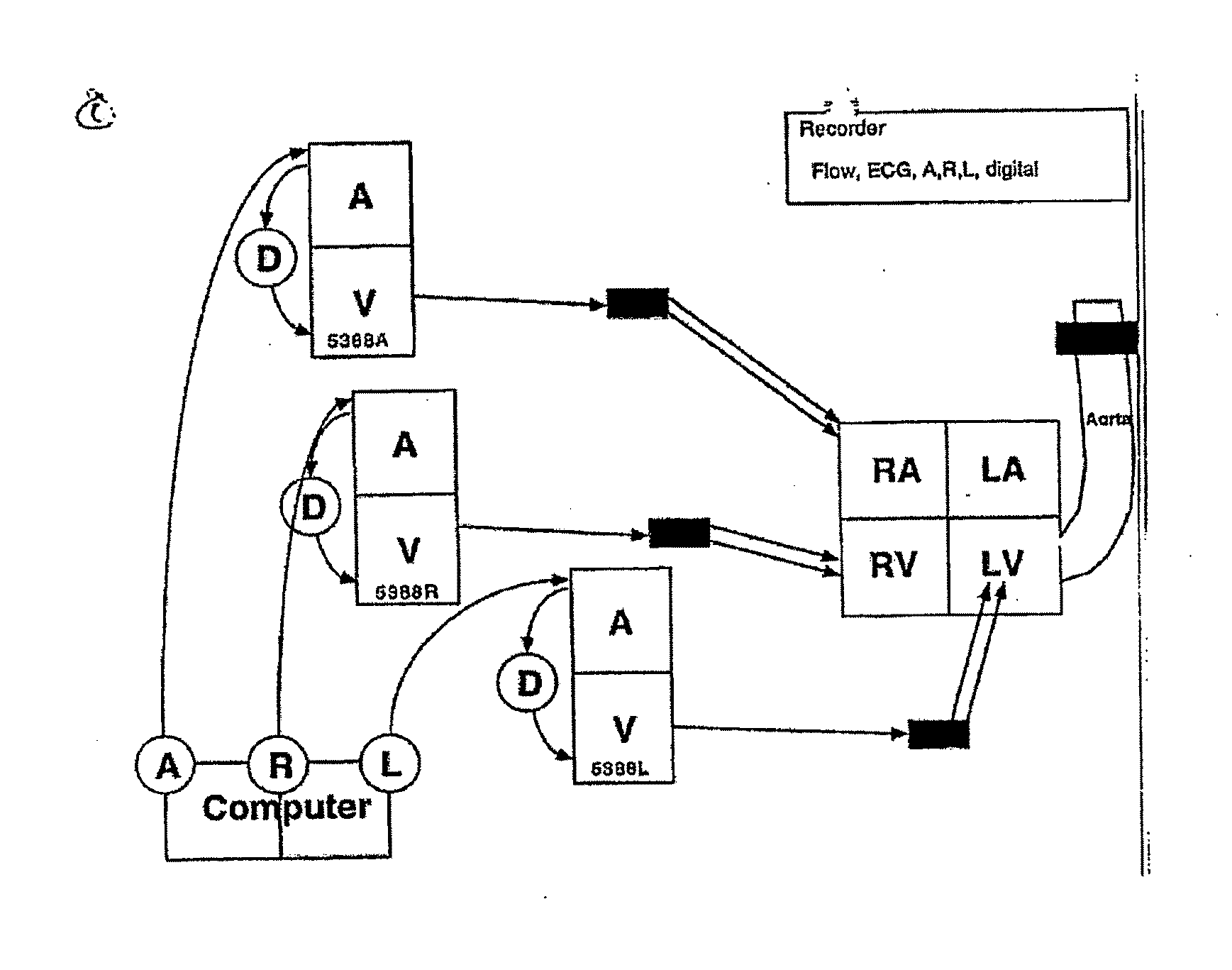
Methods for optimization of biventricular pacing devices and systems useful therefor
The invention is directed to methods and devices for optimization of biventricular pacing in subjects suffering from heart failure. The invention provides for a method for selection of optimal parameters for permanent pacing, the method comprising: positioning one or more arrays of lead wires in the posterior pericardium of a subject, wherein the arrays are connected to a multiplexing switch, wherein the switch is connected to a computer processor and a biventricular pacemaker; from the computer processor, generating a randomized sequence of: (i) pacing sites (VPS), (ii) right ventricular-left ventricular delays (RLDs), (iii) heart rates (HR); (iv) atrioventricular delays (AVDs), (v) or any combination or permutation thereof; and determining cardiac output in real time, using aortic flow velocity, thereby allowing selection of optimal parameters for permanent pacing.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
NO (nitric oxide) donor type polydatin (PD) derivative as well as preparation method and medical application thereof
InactiveCN102336790AIncrease contentReduce contentOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesDiseaseChemical reaction
The invention relates to the field of pharmaceutical chemistry and particularly provides a polydatin (PD) derivative containing a NO (nitric oxide) donor. A PD (3,4',5-trihydroxystilbene-3-beta-D-glucoside)4' hydroxyl group and a corresponding nitrate ester are subjected to chemical reaction so as to generate the NO donor type PD derivative which is in ester bond connection. After being absorbed into a lung tissue, the compound is subjected to biological transformation and ester bond breakage so that a bulk pharmaceutical chemical PD and the NO donor are dissociated, the NO donor can release NO slowly, and NO and PD can play roles of reducing pulmonary hypertension, relieving right ventricular hypertrophy, improving the pulmonary vascular endothelium function and resisting lipid peroxide cooperatively. The NO donor type PD derivative has an application in the aspect of preparing medicaments for preventing or treating pulmonary hypertension and high altitude pulmonary edema diseases caused by oxygen deficiency.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
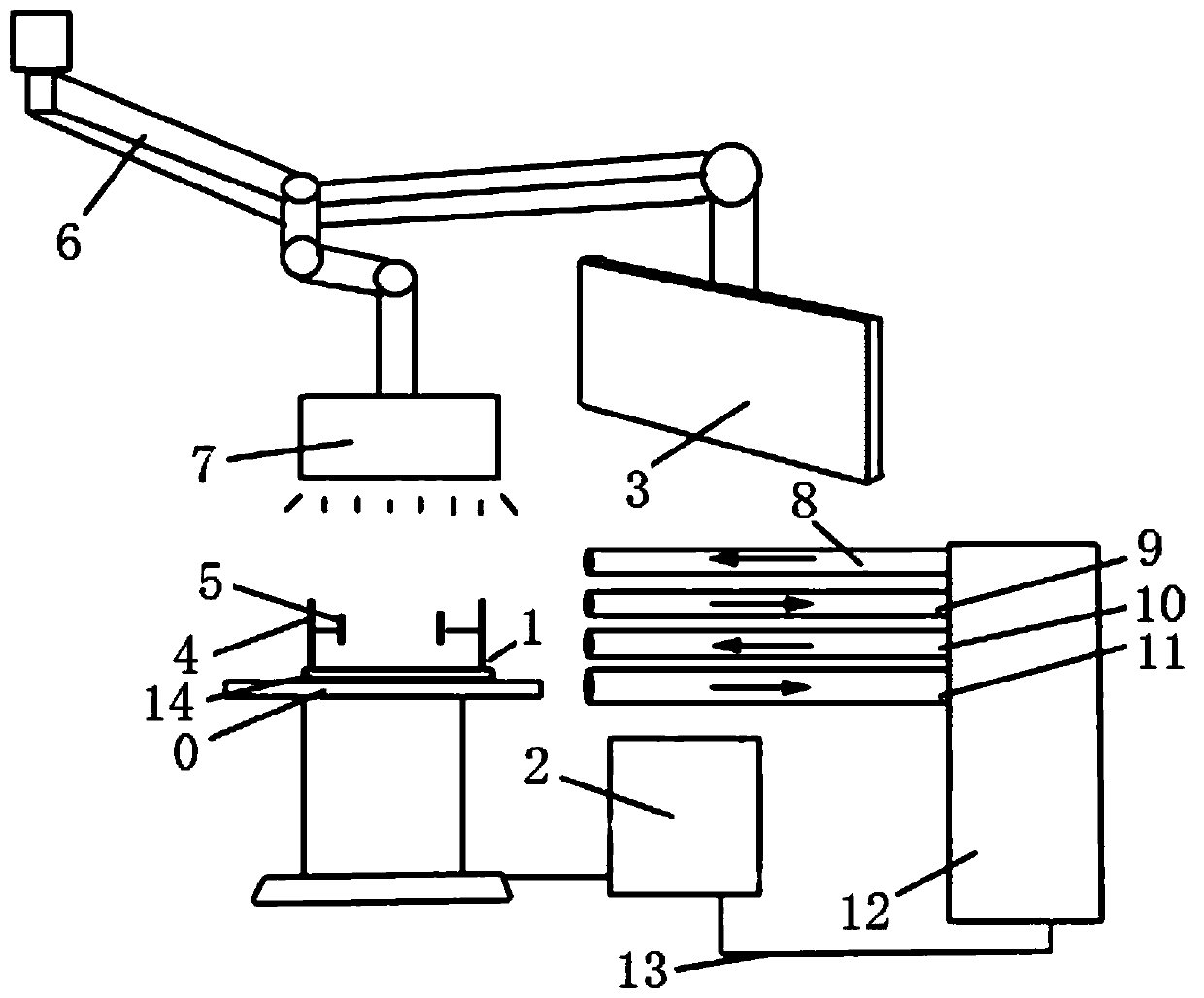
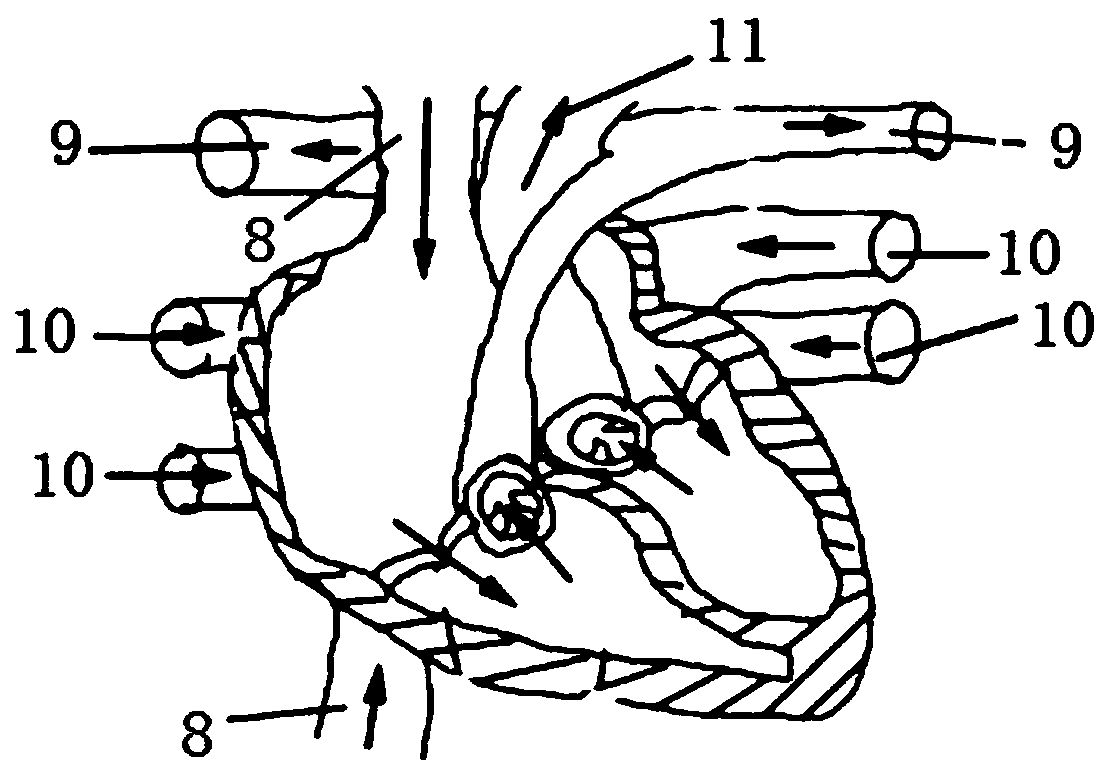
Assisted teaching device for cardiac interventional operation
InactiveCN110827642AAvoid radiation damageRealistic surgical practiceCosmonautic condition simulationsEducational modelsExtracorporeal circulationLeft cardiac chamber
The invention discloses an assisted teaching device for a cardiac interventional operation. The device comprises a fixed device, a near infrared scanning device, an information processing device, a display device and an extracorporeal circulation device; the fixed device comprises a fixed bracket and a distance adjusting device; the near infrared scanning device comprises a tower crane, a near infrared laser emitter and a near infrared laser receiver, and a motor is arranged in the tower crane; the information processing device is used for processing and converting scanning information into aDSA image; the display device is used for displaying and simulating the DSA image; and the extracorporeal circulation device comprises an atrium dextrum catheter, a ventriculus dexter catheter, an atrium sinistrum catheter, a ventriculus sinister and a pump. By utilizing the imaging of the near infrared light, the DSA imaging can be simulated through computer software synthesis, thereby avoiding unnecessary radiation damage of an exerciser in the operation exercise process; and the human body cardiac blood flow process can be simulated by utilizing the extracorporeal circulation device, so that the operation exercise becomes more realistic, and the teaching quality and level are improved.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV
Systems, devices, and methods for his bundle cardiac pacing
The present disclosure relates to devices and methods for cardiac pacing therapy. Disclosed herein are methods for His bundle cardiac pacing; cardiac leads and leadless cardiac pacemakers that enables pacing and sensing of the His bundle as well as the right atrium and right ventricle; and delivery sheaths for placing the cardiac lead or leadless cardiac pacemaker in the heart. The devices and methods disclosed increase the success at which His bundle pacing can be implemented.
Owner:EPQUANT LLC
Use of urokinase inhibitors for the treatment and/or prevention of pulmonary hypertension and/or cardiac remodelling
InactiveUS20030125233A1Improve stabilityImpairs myocyte hypertrophyOrganic active ingredientsBiocideSelective inhibitionCardiac dysfunction
The present invention relates to methods of treatment and / or prevention of pulmonary hypertension and to methods of treatment and / or prevention of cardiac remodelling and more specifically to cardiac remodelling induced by systemic hypertension in a mammal, particularly a human being. In particular, the invention shows a novel, negative role for urokinase-type plasminogen activator in the pathogenesis of cardiac remodelling, leading to subsequent cardiac dysfunction, and in the pathogenesis of pulmonary hypertension usually complicated by subsequent right ventricular hypertrophy. Consequently, the use of selective inhibitors of u-PA activity can be of benefit for treatment of patients suffering from pulmonary hypertension and / or cardiac remodelling.
Owner:VLAAMS INTERUNLVERSLTAIR INST VOOR BIOTECH
Methods for optimization of biventricular pacing devices and systems useful therefor
ActiveUS20110264159A1Increase cardiac outputGood effectHeart stimulatorsLeft cardiac chamberLeft ventricular size
The invention is directed to methods and devices for optimization of biventricular pacing in subjects suffering from heart failure. The invention provides for a method for selection of optimal parameters for permanent pacing, the method comprising: positioning one or more arrays of lead wires in the posterior pericardium of a subject, wherein the arrays are connected to a multiplexing switch, wherein the switch is connected to a computer processor and a biventricular pacemaker, from the computer processor, generating a randomized sequence of: (i) pacing sites (VPS), (ii) right ventricular-left ventricular delays (RLDs), (iii) heart rates (HR); (iv) atrioventricular delays (AVDs), (v) or any combination or permutation thereof; and determining cardiac output in real time, using aortic flow velocity, thereby allowing selection of optimal parameters for permanent pacing.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Ultrasound imaging system and method
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com