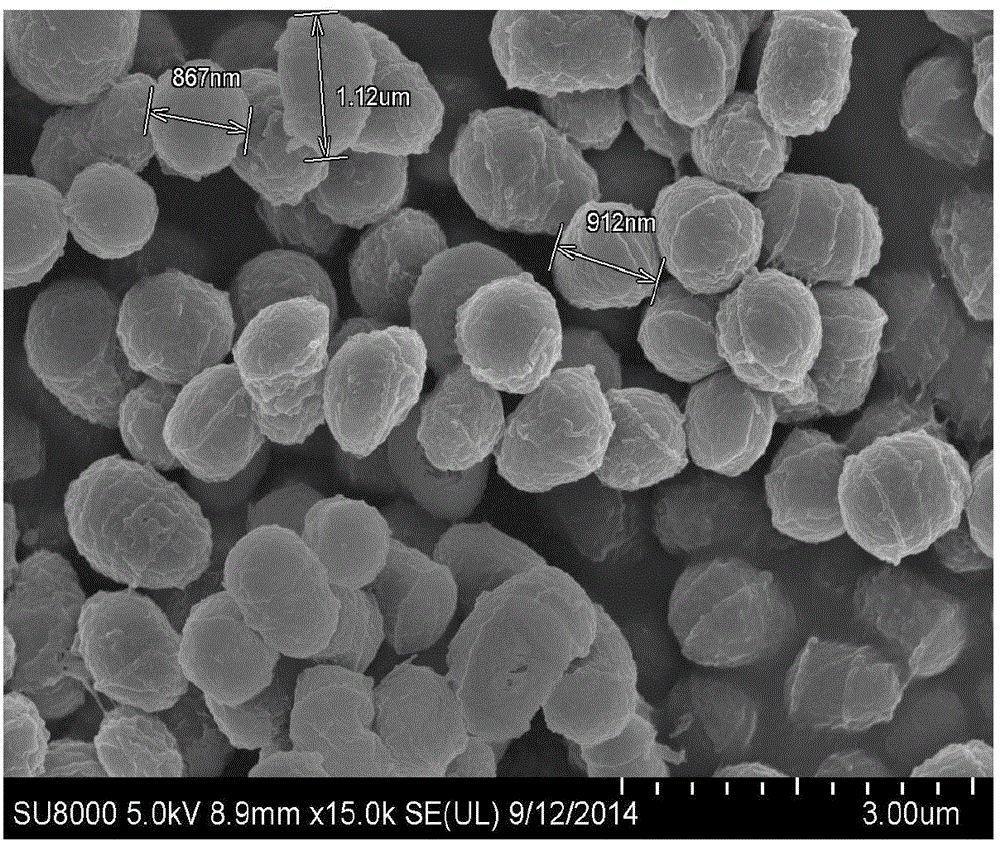
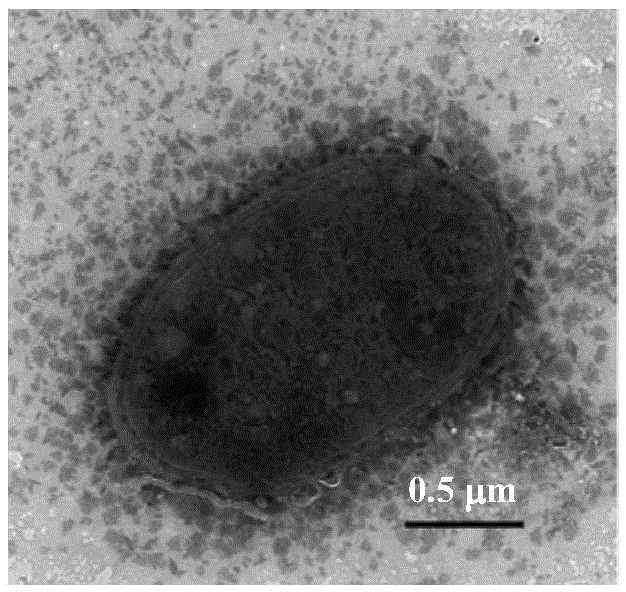
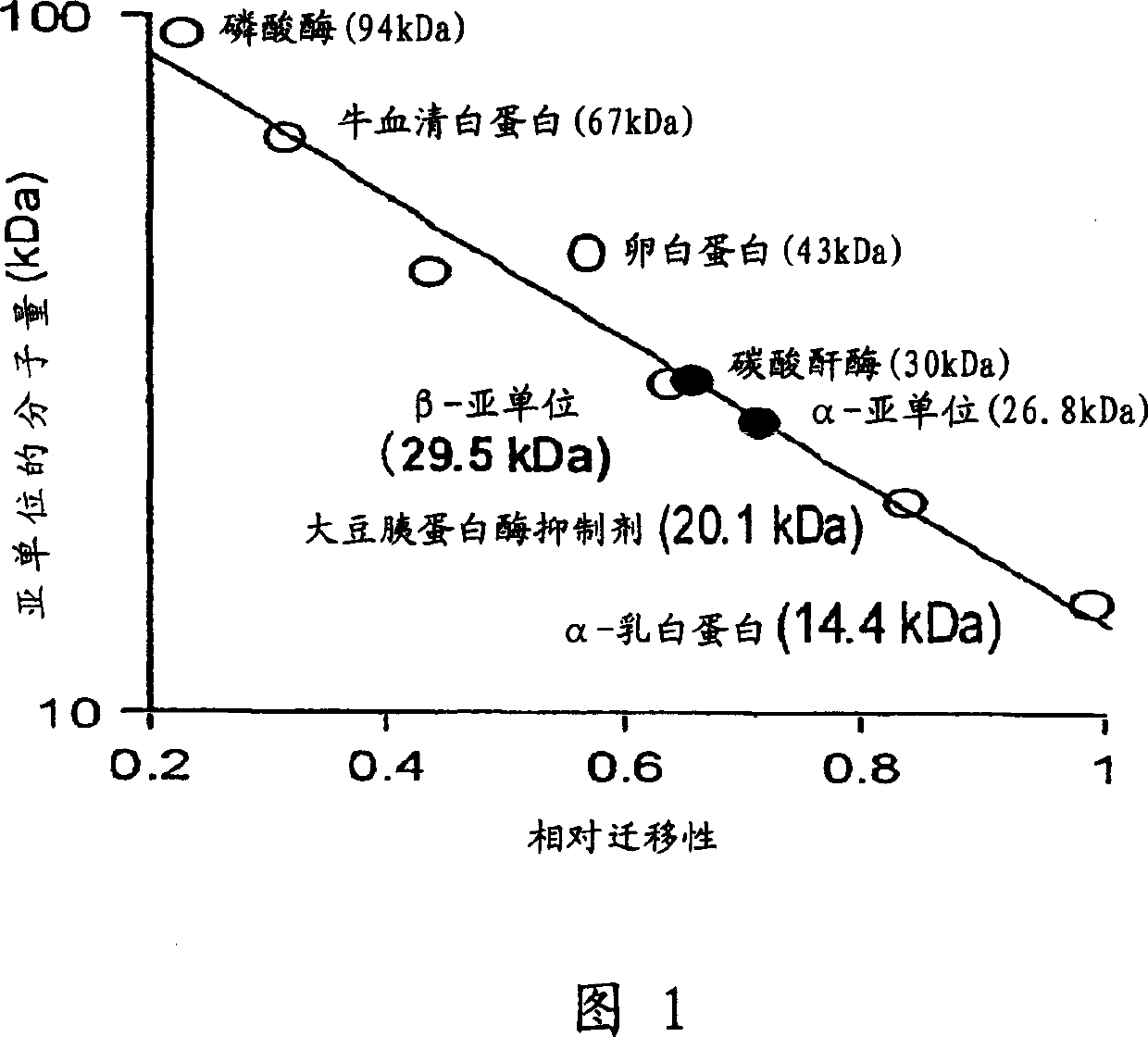
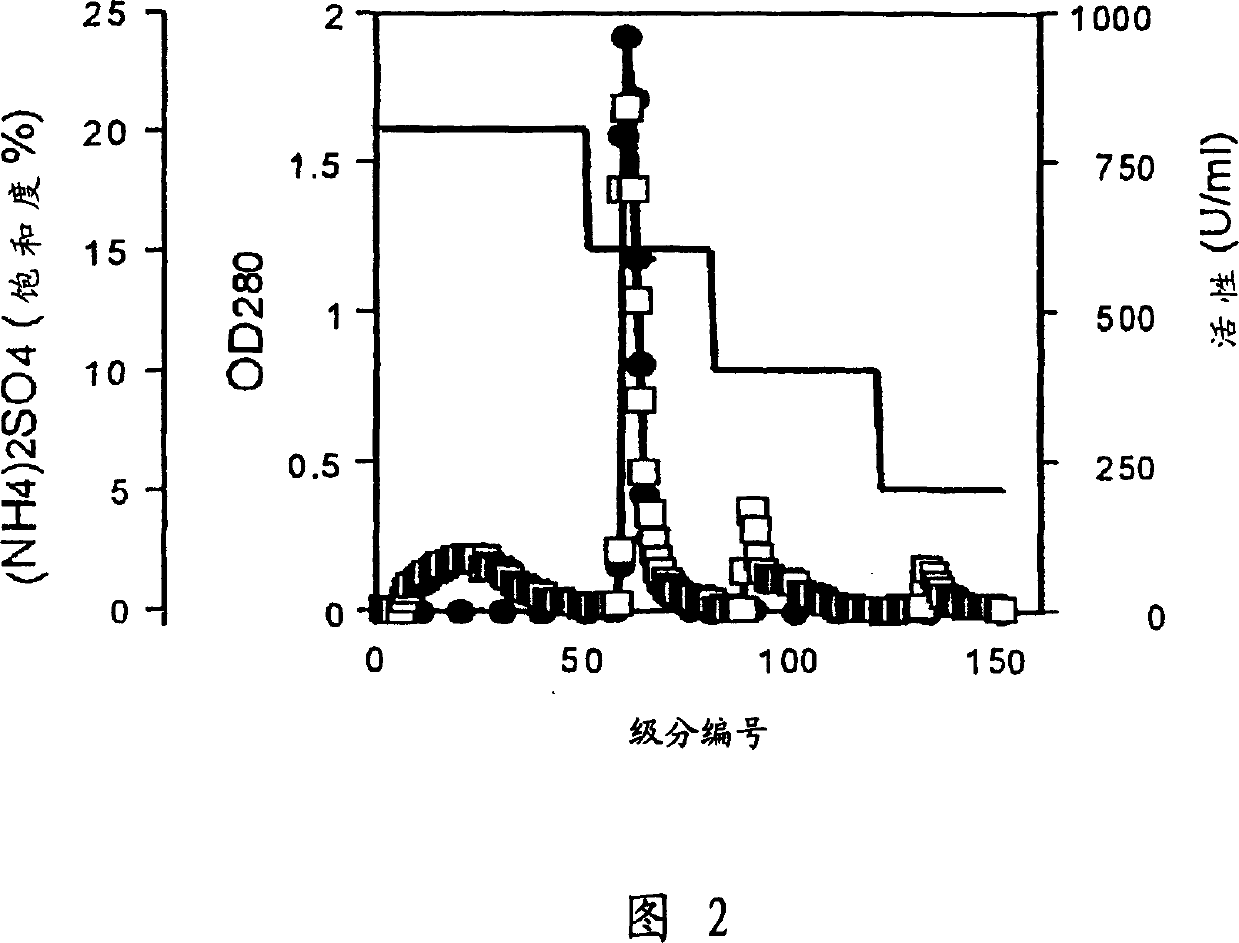
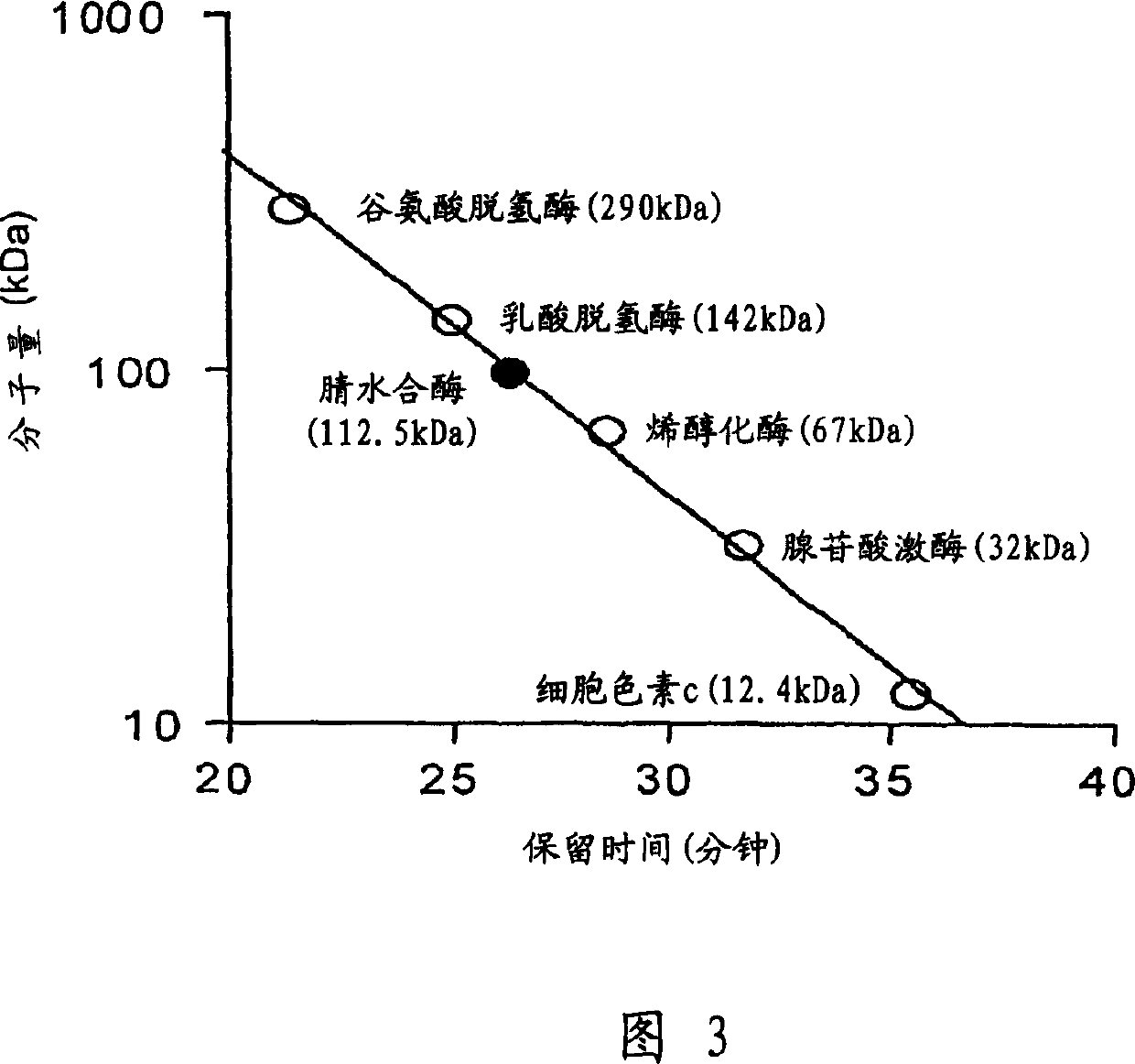
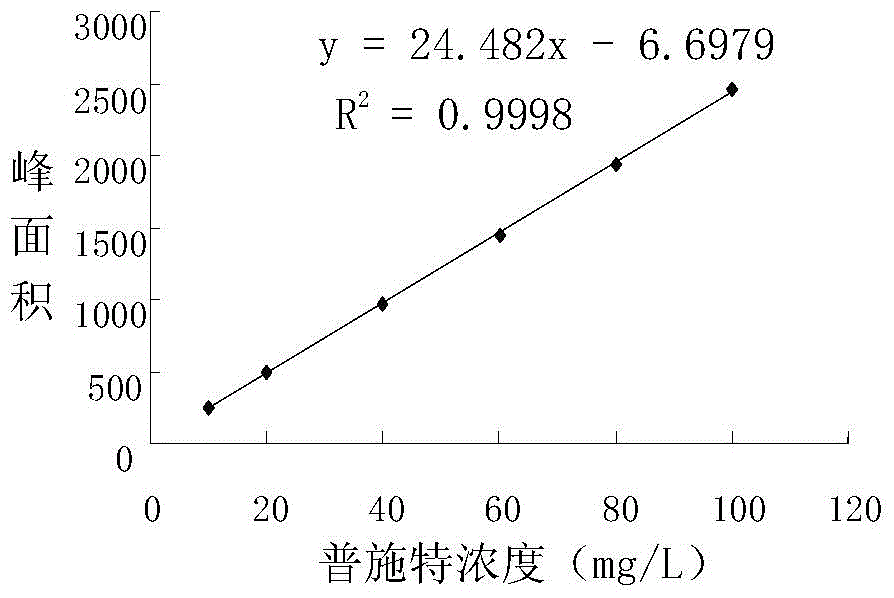
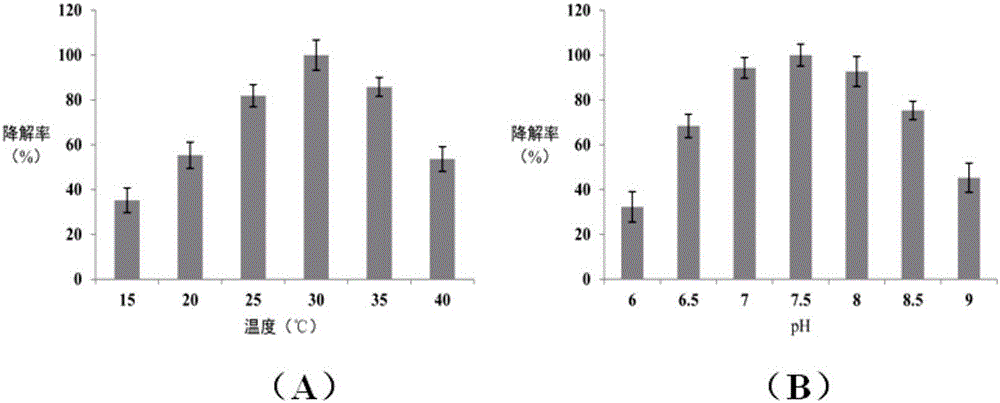
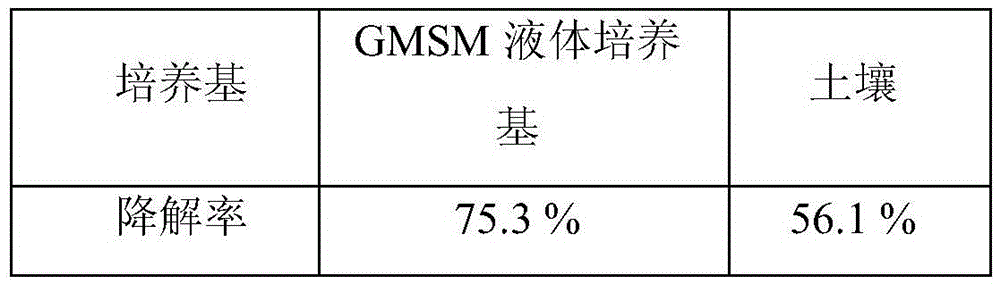
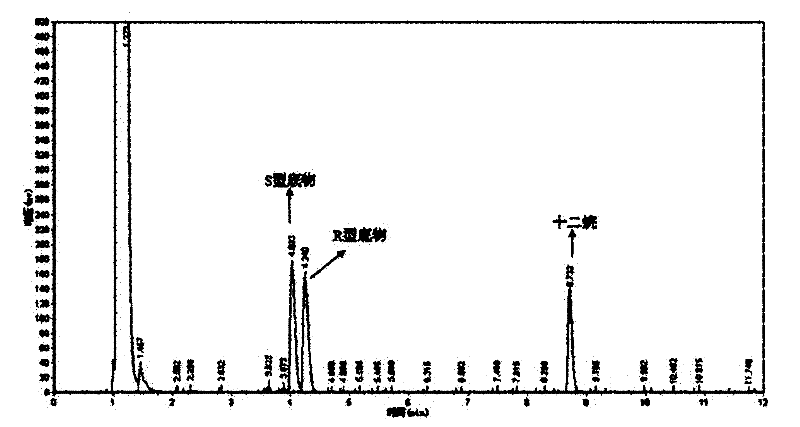
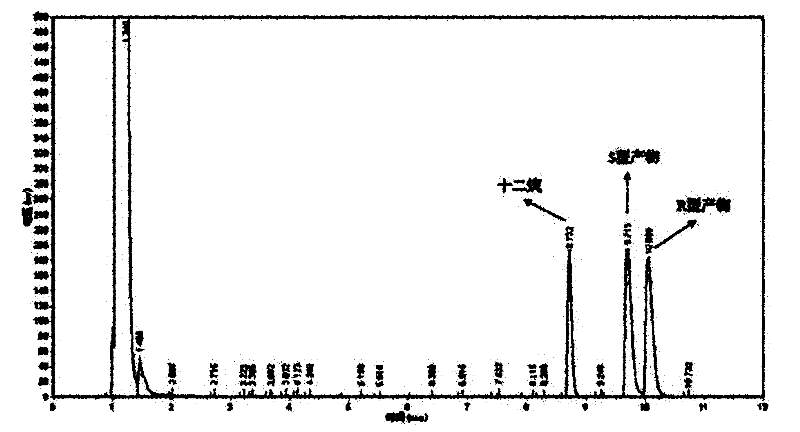
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
95 results about "Rhodococcus sp." patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Rhodococcus erythropolis and microbial inoculum and application thereof
ActiveCN101857846AReduce production and use costsStrong resistanceBacteriaWater contaminantsPetrochemicalCoking wastewater
The invention discloses a rhodococcus erythropolis (rhodococcus sp.) BZ-9 which is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center with the accession number of CGMCC No.3695. The invention also discloses a microbial inoculum, the active component of which is the rhodococcus erythropolis BZ-9. The rhodococcus erythropolis BZ-9 and the microbial inoculum thereof have high-efficient degradation performance on various toxic organic substances as well as high degradation ability even under the condition of chromium (VI), and are applicable to treatment on coking wastewater, tanning wastewater, printing and dying wastewater and other organic wastewater containing phenol, pyridine and other toxic organic substances produced in the process of the production of the petrochemical industry.
Owner:RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF TSINGHUA UNIVERSITY IN SHENZHEN
Fungicide for removing and/ or degrading polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and application thereof
InactiveCN101851582AHigh removal rateBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationFungicidePolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon
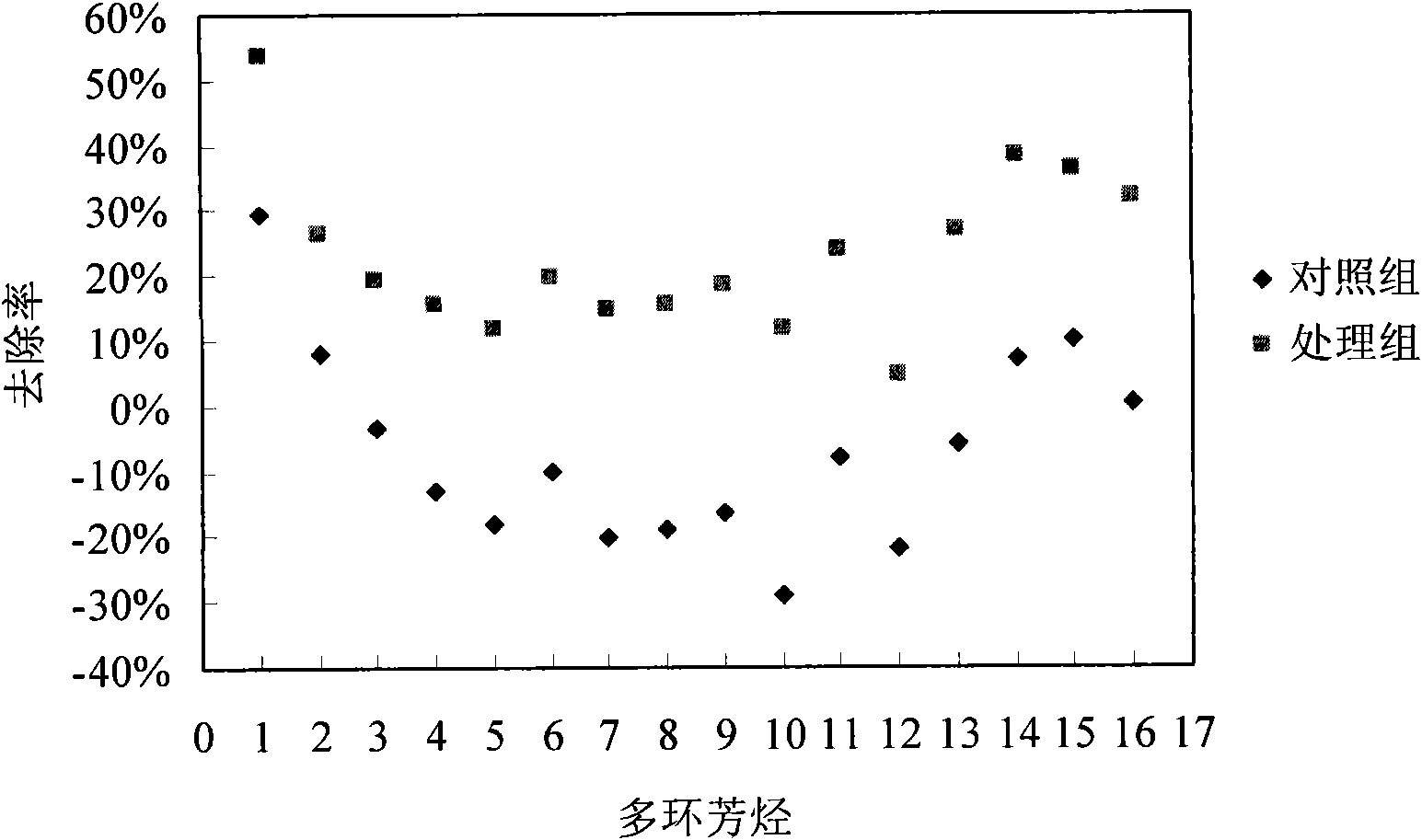
The invention discloses a fungicide for removing and / or degrading polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and application thereof. The invention provides a fungicide of which the active ingredients are (Rhodococcus sp.) LU3 CGMCC No.3610, (Microbacterium sp.) LU1 CGMCC No.3581, (Ochrobacterium sp.) LU2CGMCC NO.3582 and (Bordetella sp.) LU4 CGMCC No.3611. The experiment of the invention shows: after four weeks, the strainaway rate of 16 types of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon in soil added with the fungicide is averagely improved by 30% if being compared with that of soil which is not added with the fungicide, wherein the strainaway rate of six types of low-cyclic (two / three cyclic) polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon is averagely improved by 26%, and the stainaway rate of ten types of middle and high cyclic (more than four cycle) polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon is averagely improved by 32%.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Microbe bacteria agent for treatment of refinery waste water, its preparation method and application
InactiveCN1789406AImprove preservation methodExtended service lifeFungiBacteriaWater in oilPollutant
The invention discloses a microbiological bacterium for processing waste water in oil refining, its preparing process and use. The bacterium comprises Rhodococcus, Microbacterium spp, bacillus, Candida and Brachybacterium by the ratio of 0-10:0-10:0-10:0-10:0-10:0-10. The bacterium can be activated for treating waste water.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
Denitrification rhodococcus and rhodococcus microbial agent production method and application
The invention relates to rhodococcus with the function of removal of ammonia nitrogen and nitrite in water and a low cost rhodococcus microbial agent production method and an application method, and belongs to the technical field of environmental microorganisms. The adopted strain is an efficient denitrification bacteria-(Rhodococcus sp.) YY12 strain separated and screened from activated sludge of sewage treatment plants, and the strain is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) with the preservation number of CGMCC No. 6924. According to the method, monosodium glutamate wastewater is used as a fermentation medium for large-scale culture of the Rhodococcus, the microbial agent for efficient removal of ammonia nitrogen and nitrite in water is prepared, and the process has the advantages of low production cost, simple operation, resource utilization of the monosodium glutamate wastewater, and reduction of pollution emissions. The microbial agent used for aquaculture not only can improve the water quality of aquaculture water, but also can significantly improve the aquatic products output, and shows a wide application prospect.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Biological-Based Catalyst to Delay Plant Development Processes
ActiveUS20080236038A1Extended shelf lifeFacilitating longer-distance transportationBiocideBacteriaBacteroidesBrevibacterium ketoglutamicum
The present invention is directed to methods for delaying a plant development process comprising exposing a plant or plant part to one or more bacteria or enzymes. In specific embodiments, the one or more bacteria are selected from the group consisting of Rhodococcus spp., Pseudomonas chloroaphis, Brevibacterium ketoglutamicum, and a mixture comprising any combination of these bacteria. Apparatuses for delaying a plant development process comprising a catalyst that comprises one or more of the above bacteria.
Owner:CROWPIERCE TECH LLC
Heterotrophic nitrification aerobic denitrifying bacteria and culture method and application thereof
ActiveCN101875909AEfficient removalWide range of substratesTreatment using aerobic processesBacteriaHigh concentrationBacteroides
The invention belongs to the technical field of environmental microbiology, and relates to high-efficiency heterotrophic nitrification aerobic denitrifying bacteria and a culture method and application thereof. The bacteria are Rhodococcus sp. DN2.3 with the preservation registration number of CCTCC M209300, can effectively remove ammonia nitrogen, nitrite nitrogen, nitric nitrogen and the mixture thereof from a water body, also can remove CODCr from organic wastewater, are suitable for treating high-concentration organic nitrogen-containing wastewater; the accumulation of nitrite and nitrate is avoided in the denitrifying process; and the process for treating wastewater by using the strain is simple and the denitrifying effect is stable.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
Rhodococcus sp. strain and application thereof
ActiveCN104673710AStrong ability to degrade phenolAdaptableBacteriaWater contaminantsMicroorganismRhodococcus strain
The invention discloses a rhodococcus sp. strain and application thereof, belonging to the field of environmental microbiological application. The strain is named as (Rhodococcus sp.) CM-HZX1 and is now collected with the serial number of CCTCC (China Center For Type Culture Collection) NO:M 2014329 in CCTCC on July 9th, 2014. The rhodococcus sp.CM-HZX1 has relatively strong phenol degrading capacity, namely that the degradation rate is up to 93.6% after 0.5g / L of phenol is degraded for 24 hours, and the degradation rate is up to more than 90% after 1.5g / L of phenol is degraded for 48 hours. The strain is capable of tolerating the salinity of 4% and strong in adaptability; and the strain is efficient when being used for biological treatment of phenol wastewater so as to be wide in application prospect.
Owner:浙江至美环境科技有限公司
Novel rhodococcus, rhodococcus-origin nitrilase gene, nitrilehydratase gene and amidase gene and process for producing carboxylic acids by using the same
InactiveCN1340101AHigh puritySuitable for industrial productionBacteriaHydrolasesChemical compoundCarboxylic acid
The present invention relates to a novel Rhodococcus bacterium and to a process of hydrolyzing a cyano group of a nitrile compound using a novel Rhodococcus bacterium to produce the corresponding carboxylic acid. The present invention also relates to a process of producing carboxylic acids, in particular cyano carboxylic acids using a transformant transformed with a plasmid containing a nitrilase gene, a nitrile hydratase gene and an amidase gene derived from Rhodococcus bacteria capable of exhibiting particularly excellent position selectivity for the cyano group of aromatic polynitrile compounds, to such a transformant, such a plasmid, to such genes, to a process of producing an enzyme using the transformant, and to enzymes obtained by the process. The carboxylic acids, in particular cyano carboxylic acids obtained by the present invention are useful as starting materials for the synthesis of drugs, agrochemicals, dyestuffand other chemicals.
Owner:RESONAC HOLDINGS CORPORATION
Degradation bacteria for carbendazim pesticide residue and bacterial agent produced thereby
InactiveCN1827764AEasy to useReduce production and use costsBacteriaPesticide residueBacterial strain
The invention provides a carbendazim pesticide residue degrading bacteria and a prodegradant, which belongs to biological high-tech domain. The used bacterial strain DJL-6 is judged as Rhodococcus sp. The main biological feature is: G+, the thallus is of ball rod and atrichosis; the reaction between catalase and V-P is positive; the oxidase reaction is negative; the barley sugar, carubinose, citrate, acetamide and agedoite can be used as unique carbon source or nitrogen source to carry out its growth, but the lactin and bitter almond acid can not be used as unique carbon source to carry out its growth; and the bacterial colony is orange when cultivated on LB culture medium. The pesticide residual quantity of the crop can be reduced by more than 95 % by directly applying the degrading bacteria product, which solves the overproof pesticide residue problem, and can produce non-toxic and nuisanceless environmental farm product.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
A strain of Rhodococcus and use thereof for preparing optical pure chiral sulphoxide
InactiveCN101372676AEasy to manufactureMild reaction conditionsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiological oxidationCatalytic oxidation
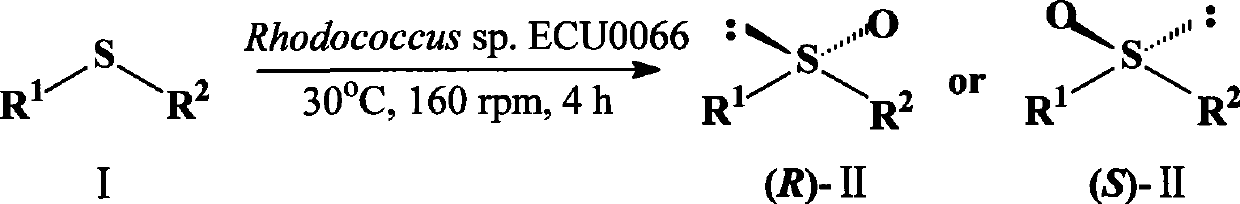
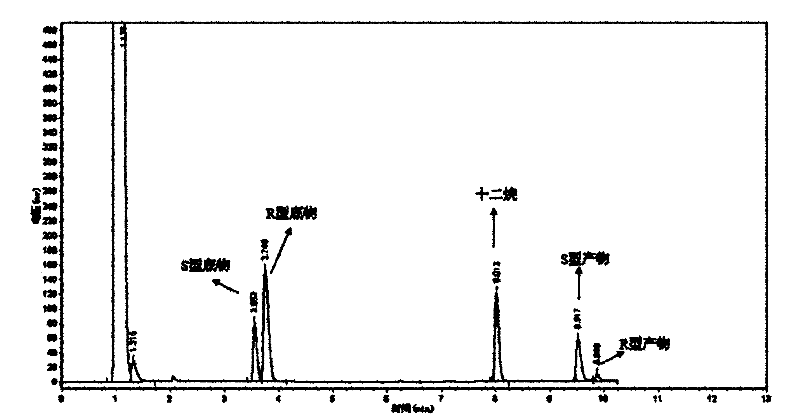
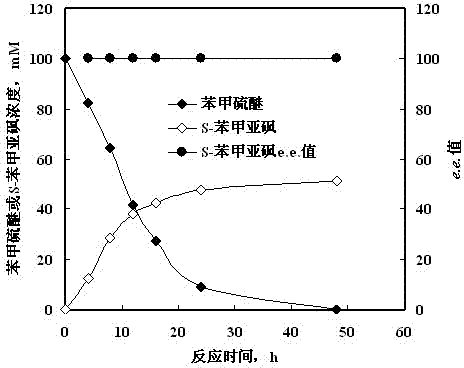
The invention discloses a Rhodococcus (Rhodococcus sp.ECU0066) and the use thereof, and the culture collection number of the strain is CGMCC No.2547. The resting cells of the strain is taken as a biological catalyst, and prochiral phenyl alkyl sulfide and a derivative thereof are carried out catalytic oxidation asymmetrically to obtain benzoylate sulfoxide and a derivative thereof with optical activity. The strain and the stereoselective biological oxidation process have the advantages of better catalysis effect, simple and safe operation and low cost, the product is easily purified and is friendly to environment.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Novel compositions and methods for genetic manipulation of Rhodococcus bacteria
InactiveUS20050227356A1Reduced activityBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesMicrobiology
The present invention provides novel compostions and methods of using the same for genetic manipulation of a variety of bacterial strains such as Rhodococcus.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Effective phenylamine degrading strain as well as use and use method thereof
InactiveCN101831391AStrong toleranceFast degradationBacteriaWater contaminantsHigh concentrationMicroorganism
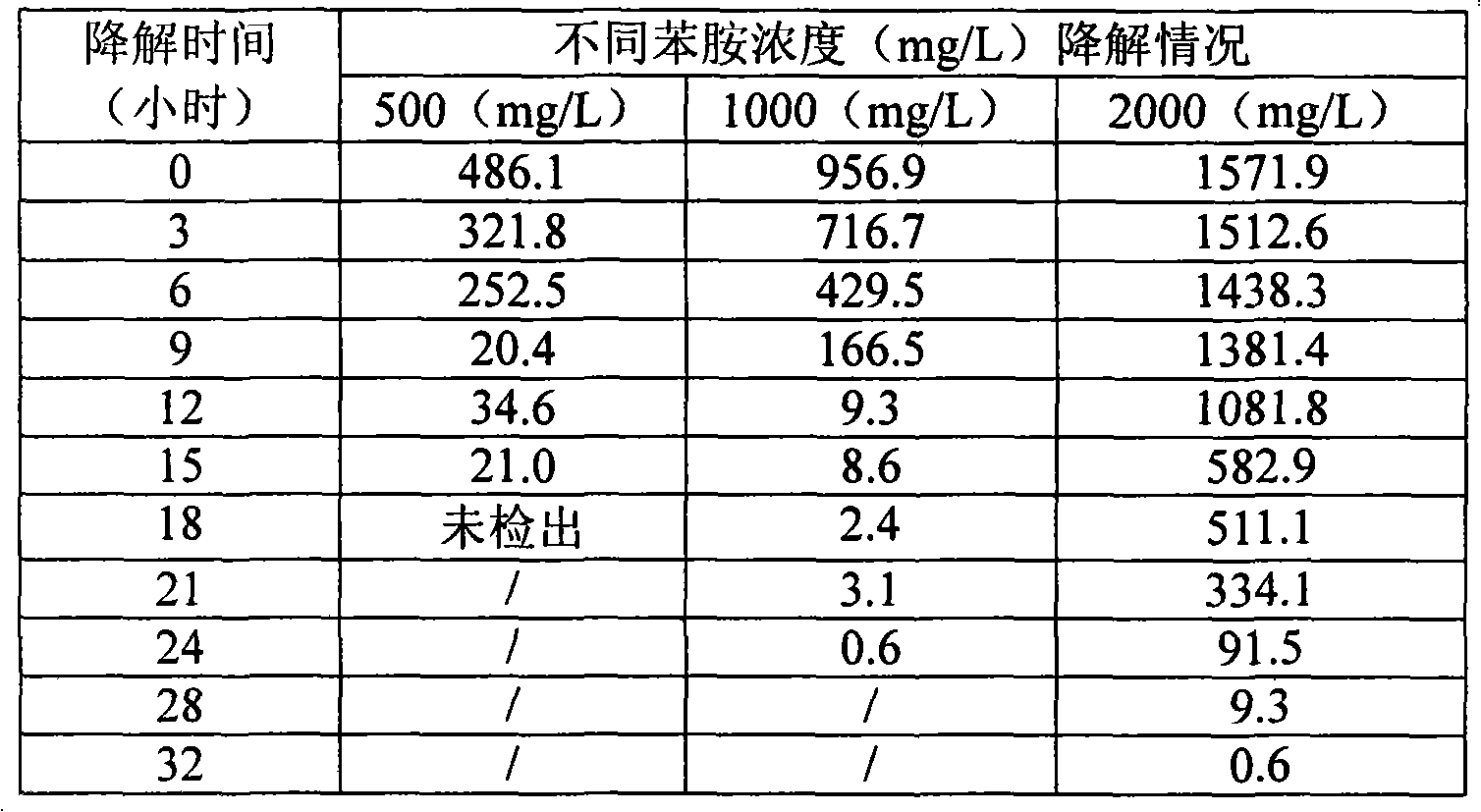
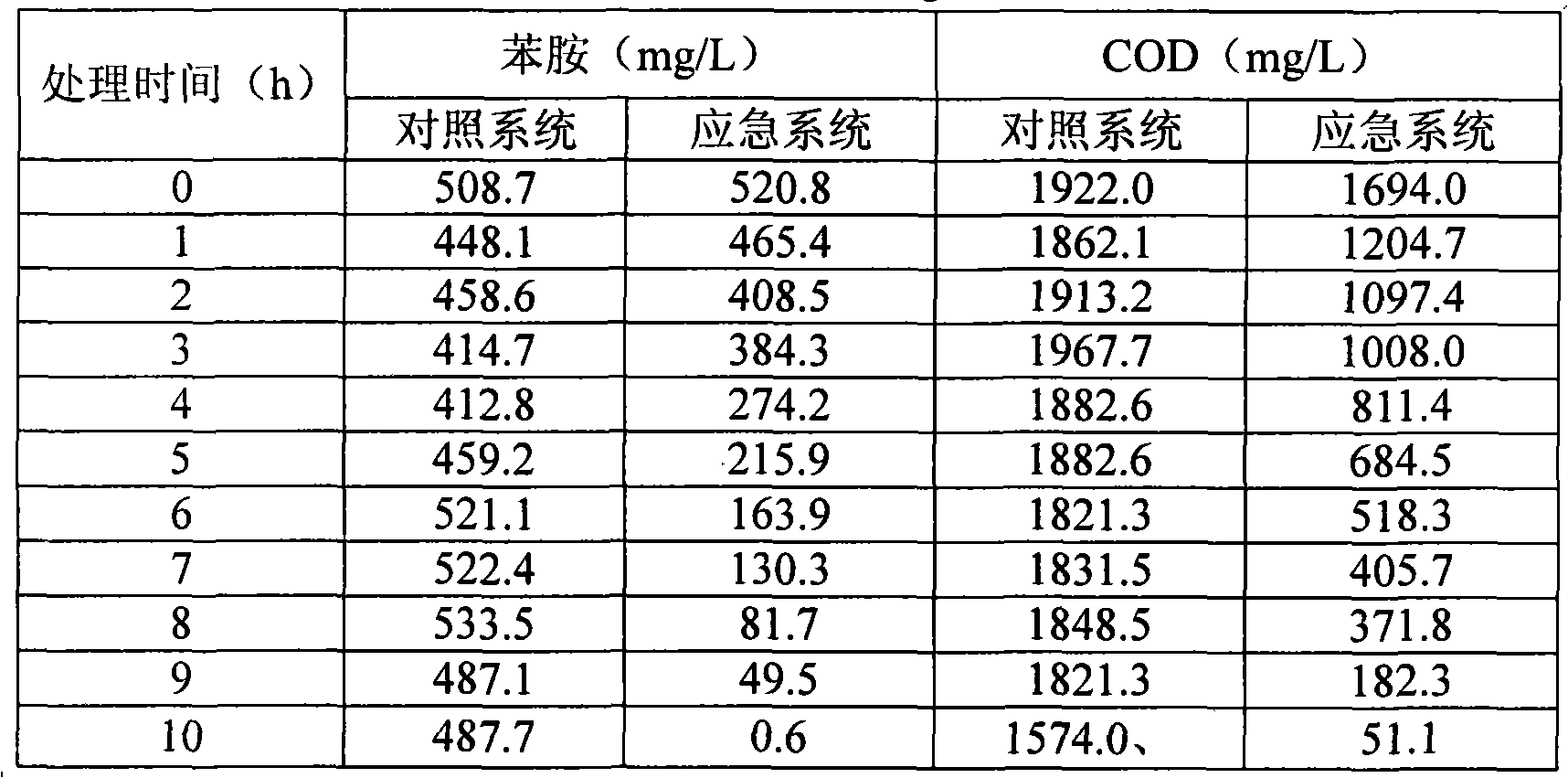
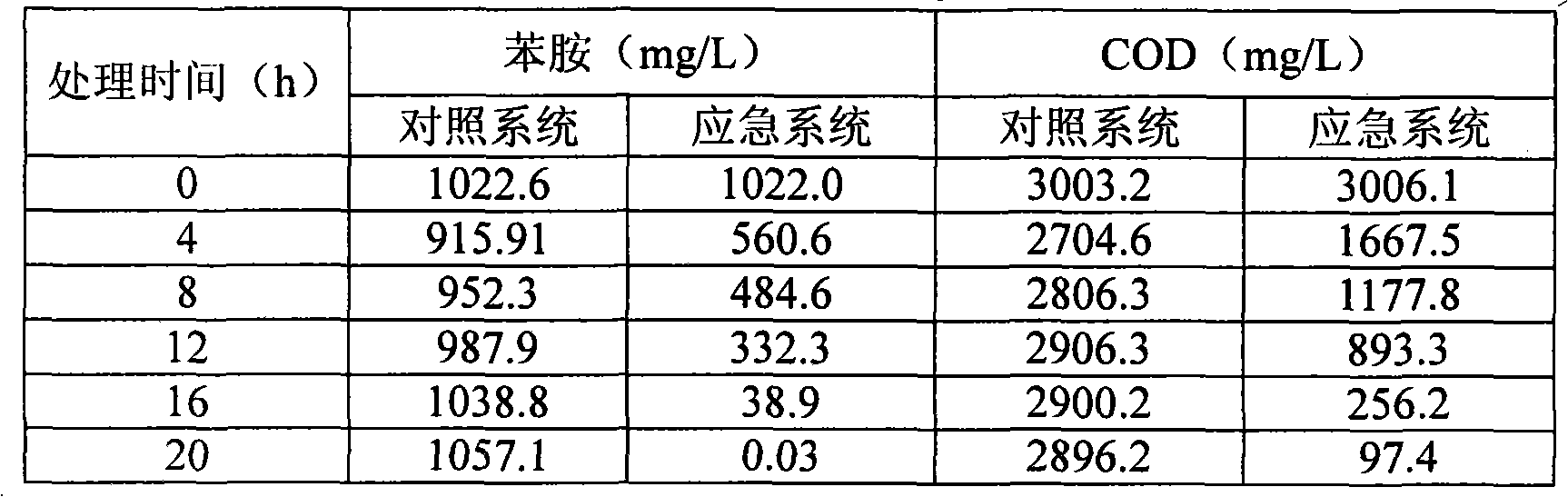
The invention belongs to the technical field of environment protection, in particular an effective phenylamine degrading strain as well as use and use method thereof. In the invention, a code number of the effective phenylamine degrading bacteria is AN-P1; and the effective phenylamine degrading bacteria is authenticated to be rhodococcus sp, which is preserved in China committee for culture preservation of general microorganism centre with the preservation number of CGMCC No.2783 in DEC.4th, 2008. The effective phenylamine degrading strain is applied to high-concentration phenylamine waste water treatment or phenylamine pollution incident emergency treatment. The effective phenylamine degrading strain has the characteristics of strong endurance capability of high-concentration phenylamine, high degradation speed, no secondary pollution, safe use, no bad influence on microorganism in an original processing system and the like.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degrading bacterium and applications thereof
ActiveCN106434470AImprove developmentEfficient use ofBacteriaWater contaminantsPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbonHigh concentration
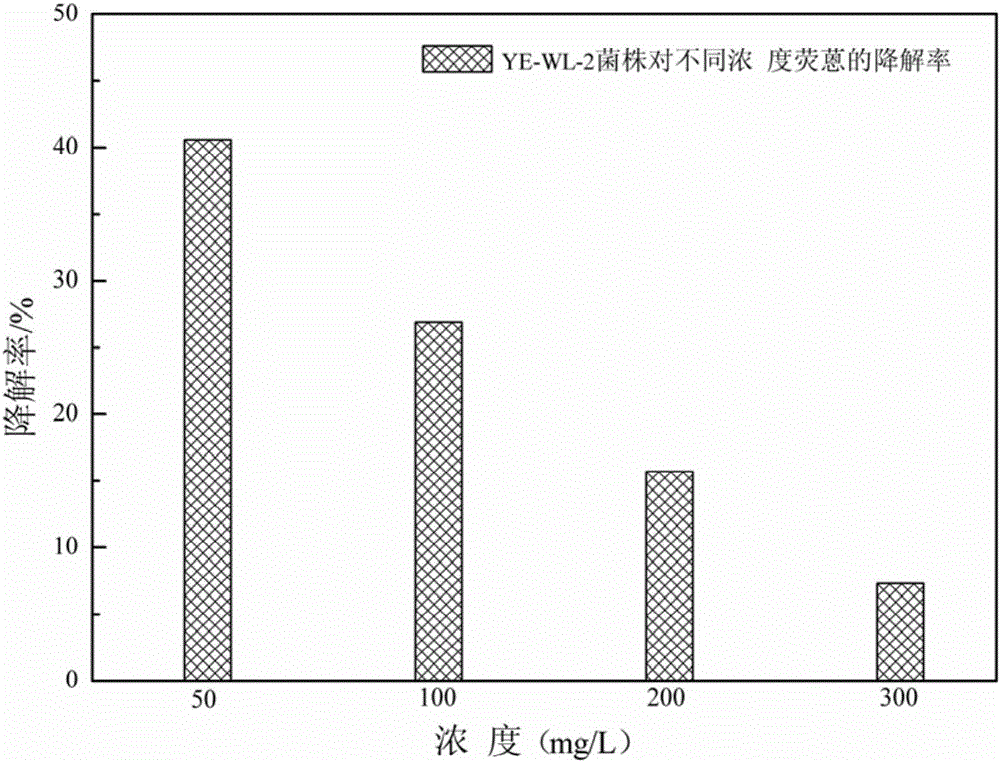
The invention relates to the technical field of microbes, and in particular relates to a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degrading bacterium and applications of the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degrading bacterium in polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degradation, wherein the degrading bacterium is Rhodococcus sp., belongs to the gram-positive bacterium, and is assigned with the accession number of CCTCC M 2016517. The polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degrading bacterium can efficiently degrade polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, especially fluoranthene in fluoranthene-containing solutions. The polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degrading bacterium has strong tolerance to the fluoranthene solution with high concentration, is tolerant to the fluoranthene concentration of 300mg / L, and is especially suitable for the biological treatment for fluoranthene-containing waste water.
Owner:SHENYANG RES INST OF CHEM IND
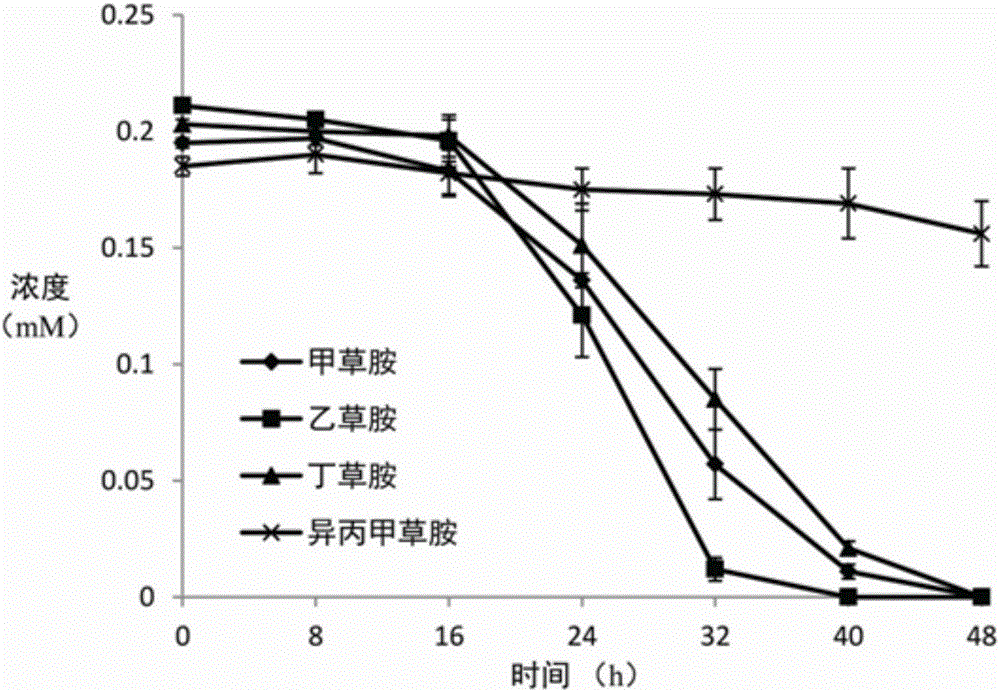
Microorganism composition for degrading acetochlor and/or butachlor and application of microorganism composition
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological treatment and discloses a microorganism composition for degrading acetochlor and / or butachlor and an application of the microorganism composition. The microorganism composition comprises Rhodococcus sp. T3-1, Delftia sp. T3-6 and / or Sphingobium sp. MEA3-1 which are all preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection on December 15, 2012, wherein preservation numbers of the microorganism strains are respectively CCTCC NO: M2012525, CCTCC NO: M2012526 and CCTCC NO: M2015527. The microorganism composition can be applied in combined degradation of acetochlor and / or butachlor.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Rhodococcus sp., lipopeptid extra-cellular bio-demulsifier, preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to Rhodococcus sp., lipopeptid extra-cellular bio-demulsifier produced by culturing the Rhodococcus sp. and an application thereof. The dosage of the bio-demulsifier is 100-200mg / L, and the demulsification rate of the W / O type kerosene model emulsion can be 72.7-89.1% within 24h when the demulsification test temperature is 35 DEG C. When the bio-demulsifier is used in thin oil extraction liquid in ocean extraction plants of Shengli Oil Field (SLOF) and the dosage is 90-140mg / L, the demulsification rate can achieve 60.0-62.5% within 6.5h which is further superior to the chemical demulsifier used on site. The extra-cellular bio-demulsifier has the advantages of convenient extraction, low production cost, easy storage and transportation, and can solve the problems of influenced oil product quality and high extraction cost of cell wall combined products when full culture liquid is added.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Nitrile hydratase and a method for producing amides
An objective of the present invention is to provide a nitrile hydratase capable of producing 2-hydroxy-4-methylthiobutyroamide. The present invention provides a novel nitrile hydratase producing alpha-hydroxyamide using, alpha-hydroxnitrile as the substrate, and the encoding DNA thereof. The enzyme can be obtained from Rhodococcus sp. Further, the enzymatic activity of the enzyme can he maintained stably during the reaction. The present invention provides a method for producing amide compounds, the method comprising the step of reacting this enzyme to nitrile compounds. According to the present invention, from hydroxy nitrile compounds, corresponding amide compounds can be produced biochemically without reducing the enzyme activity of nitrile hydratase.
Owner:DAICEL CHEM IND LTD
Rhodococcus sp. capable of degrading four herbicides and application thereof
The invention discloses a bacterium capable of degrading herbicides and an application thereof. The bacterium capable of degrading herbicides is rhodococcus sp. 198-R-56, and the collection number of the bacterium in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Centre is CGMCC No. 9868. With regard to the rhodococcus sp. 198-R-56 CGMCC No. 9868 provided by the invention, in an inorganic salt culture medium for 7 days, the degradation rate for 100mg / L of imazethapyr achieves 84.63%, the degradation rate for 50mg / L of acetochlor achieves 69.15%, the degradation rate for 100mg / L of chlorimuron-ethyl achieves 52.20%, and the degradation rate for 100mg / L of acifluorfen sodium achieves 20.16%, which indicates that the strain is capable of degrading the herbicides imazethapyr, acetochlor, chlorimuron-ethyl and acifluorfen sodium; meanwhile, the strain has a capacity of producing plant hormone heteroauxin and has a yield of 62.35+ / -3.76mu g / ml, which indicates that the strain has a capacity of promoting plant growth.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
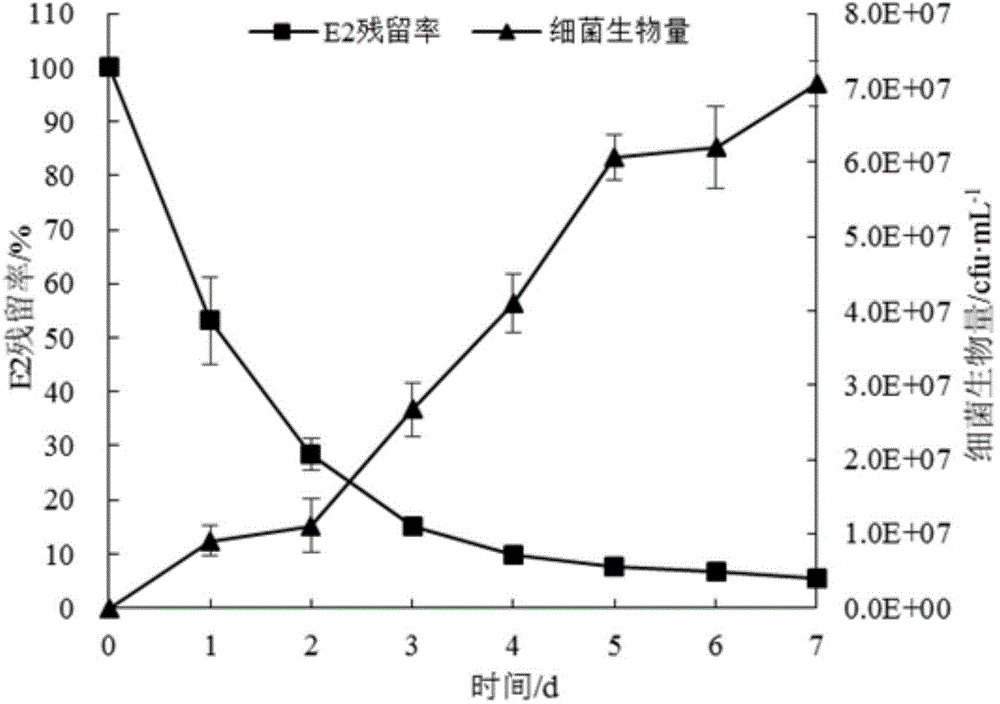
17 beta-estradiol degrading strain and application thereof
InactiveCN104894012ASolve the hazardResidue reductionBacteriaBiological water/sewage treatmentBiotechnologyFeces
The invention discloses a 17 beta-estradiol degrading strain and an application thereof. A rhodococcus sp. JX-2 is preserved in China general microbiological culture collection center at September 4, 2014, and the strain preservation number is CGMCC NO.9636. An immobilized 17 beta-estradiol degrading bacterial agent produced by the rhodococcus sp. JX-2 is provided, a JX-2 bacterial suspension is mixed evenly with a sodium alginate solution, a CaCl2 solution is used as a crosslinking agent, crosslinking is carried out for 5.5-6.5 h, and immobilized small balls with a diameter of about 3-5 mm are obtained. The rhodococcus sp. JX-2 obtained from screening enables the 17 beta-estradiol degradation rate to reach 90% or more under laboratory shake flask culture conditions. The immobilized bacterial agent is applied directly in 17 beta-estradiol polluted water bodies and livestock and poultry manure, and can allow 17 beta-estradiol residues to be reduced by 60% or more in a short period of time.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Chloroacetamide herbicide degrading strain, bacterium produced thereby and application thereof
ActiveCN105062917ABroad degradation spectrumEasy to useBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationMicroorganismMicrobiology
The invention discloses a chloroacetamide herbicide degrading strain, a bacterium produced thereby and application thereof. The chloroacetamide herbicide degrading strain, rhodococcus sp. AC-1, is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center under CGMCC No.10778 on 30th April, 2015. The chloroacetamide herbicide degrading strain AC-1 is suitable for use in degrading chloroacetamide herbicides, preferably in degrading chloroacetamide herbicides in soil; by directly applying a degrading strain product, residue of the chloroacetamide herbicides (specifically alachlor, acetochlor and butachlor) in the soil can be decreased by above 85%, the problem that the residue of the alachlor, acetochlor and butachlor in agricultural production is out of limits is solved, and chemical damage caused by herbicide residue to crops is prevented.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY +1
Metribuzin pesticide residue degrading bacteria, microbial agent produced through same and application of metribuzin pesticide residue degrading bacteria
InactiveCN105420172AEasy to useReduce production and use costsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicrobial agentPesticide residue
The invention provides metribuzin pesticide residue degrading bacteria and a microbial agent produced through the same. The bacterial strain is gram-positive bacteria, and is authenticated as Rhodococcus sp. and preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection on June 29, 2015, and the preservation number of the bacterial strain is CCTCC NO: M2015392. A culture solution obtained after QCT10 bacterial strain fermentation is the microbial agent. According to the QCT10 bacterial strain and the microbial agent produced through the same, the quantity of metribuzin pesticide residues in soil can be reduced by 50% or above, and the problem that the metribuzin pesticide residues exceed the standard in agricultural production can be solved.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Biochemical preparation for treating threonine fermentation sewage
ActiveCN105921099AReduce dosageShorten the timeOther chemical processesSilicon compoundsBiotechnologyMicrobial agent
The invention relates to a biochemical preparation for treating threonine fermentation sewage. The biochemical preparation is characterized by comprising a physical adsorbent and a composite microbial agent, wherein the composite microbial agent is prepared from the following raw materials by a volume ratio: 6 to 7 parts of arthrobacter sp., 5 to 7 parts of pseudomonas stutzeri, 5 to 7 parts of rhodococcus sp., 4 to 5 parts of bacillus amyloliquefaciens, 4 to 5 parts of clostridium papyrosolvens and 3 to 4 parts of scenedesmus obliquus. The biochemical preparation contains multiple microorganisms having good degrading capability to recalcitrant pollutants; various strains are reasonably matched to realize a good degrading effect; the biochemical preparation has a broad application prospect.
Owner:内蒙古阜丰生物科技有限公司
Rhodococcus ZJPH1003 and application thereof in preparing S-(+)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropane carboxylic acid
ActiveCN102161978AEasy to trainReduce manufacturing costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismCarboxylic acid
The invention provides a new strain-Rhodococcus sp. ZJPH1003 and an application thereof in preparing S-(+)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropane carboxylic acid through microbial catalytic asymmetric hydrolysis of 2,2-dimethylcyclopropane ethyl formate. The strain is conserved at China Center for Type Culture Collection, the conservation address is Wuhan University, Wuhan, China, postcode 430072, the conservation number is CCTCC M 2010371, and the conservation date is December 29, 2010. In the invention, the adopted method for preparing the S-(+)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropane carboxylic acid through microbial catalytic asymmetric hydrolysis of the 2,2-dimethylcyclopropane ethyl formate by utilizing the new microbial strain has the advantages of novel route, high yield, environmental friendliness and the like; and by utilizing a chiral biocatalysis method which takes a Rhodococcus ZJPH1003 cell as a catalyst, for the target product-S-(+)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropane carboxylic acid, the e.e can reach 82.5% and the yield can reach 41.3% when the substrate concentration is 30mmol / L.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Rhodococcus sp. and application of rhodococcus sp. to zearalenone degradation
ActiveCN105154351ASolve pollutionIncrease profitBacteriaMicroorganism based processesRhodococcus sp. WB1Microbiology
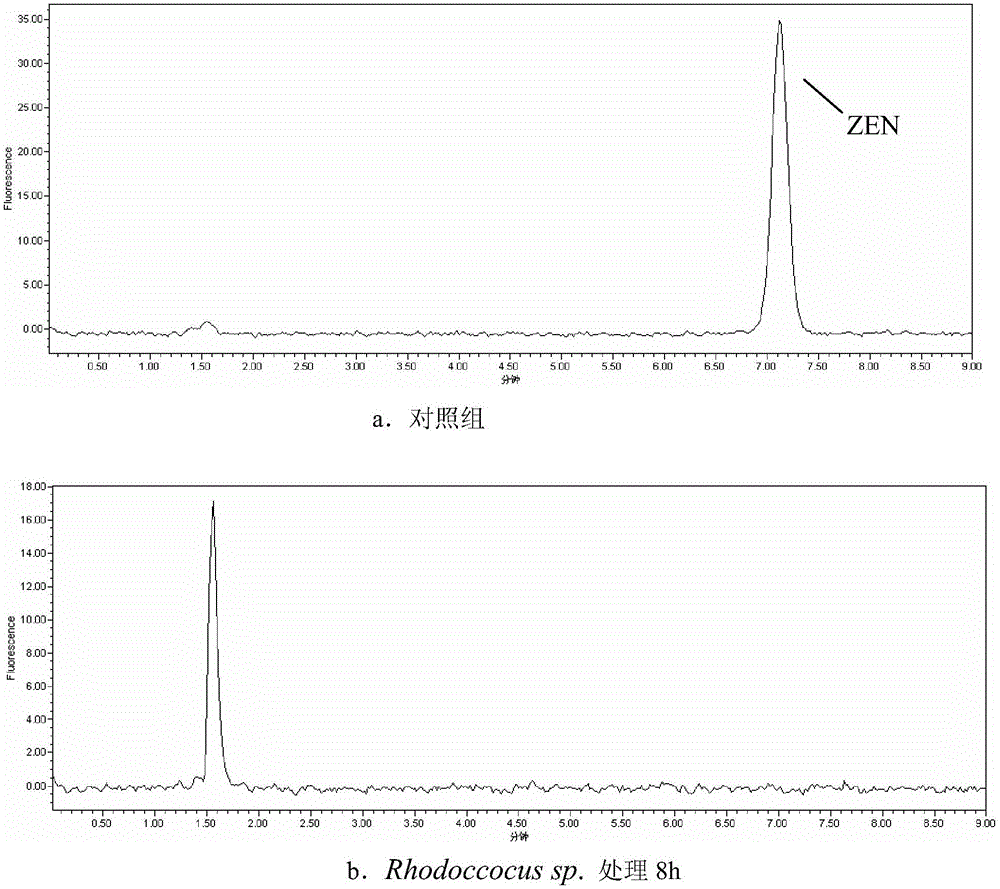
The invention discloses rhodococcus sp. and application of the rhodococcus sp. to zearalenone degradation. The preservation number of the rhodococcus sp. is CGMCC No.7186. The invention also provides a biological detoxication agent containing the preserved bacterial strain of the rhodococcus sp. and a preparing method of the biological detoxication agent. In addition, the invention also provides application of the bacterial strain or the biological detoxication agent to the zearalenone degradation.
Owner:ACAD OF NAT FOOD & STRATEGIC RESERVES ADMINISTRATION
Rhodococcus DSH capable of degrading environmental hormone bisphenol A, and applications thereof
InactiveCN107227266AStrong degradabilityPromote degradationBacteriaWater contaminantsLaboratory cultureHormone
The invention discloses Rhodococcus DSH capable of degrading environmental hormone bisphenol A, and applications thereof, wherein the Rhodococcus DSH belongs to Rhodococcus sp, is named as Rhodococcus DSH, has the preservation number of CGMCC NO. 12392, and is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, wherein the address is Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 3# Court No.1, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, and the sequence of the 16S rDNA fragment of the Rhodococcus DSH is represented by SEQ ID NO:1 in the sequence table. According to the present invention, the active sludge of the bisphenol A production drug factory is subjected to enrichment acclimation, purification separation and re-screening to obtain the Rhodococcus DSH, wherein the Rhodococcus DSH can stably and efficiently degrade bisphenol A, and can be used for the bisphenol A biodegradation in the environment, and the environmental remediation.
Owner:NORTHEAST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
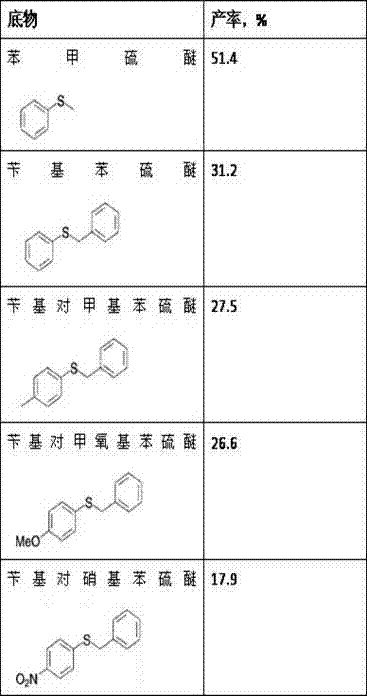
Method for synthesizing chiral sulfoxide from thioether under catalytic action of Rhodococcus
InactiveCN103114109ASimple process routeMild reaction conditionsMicroorganism based processesFermentationPtru catalystCatalytic effect
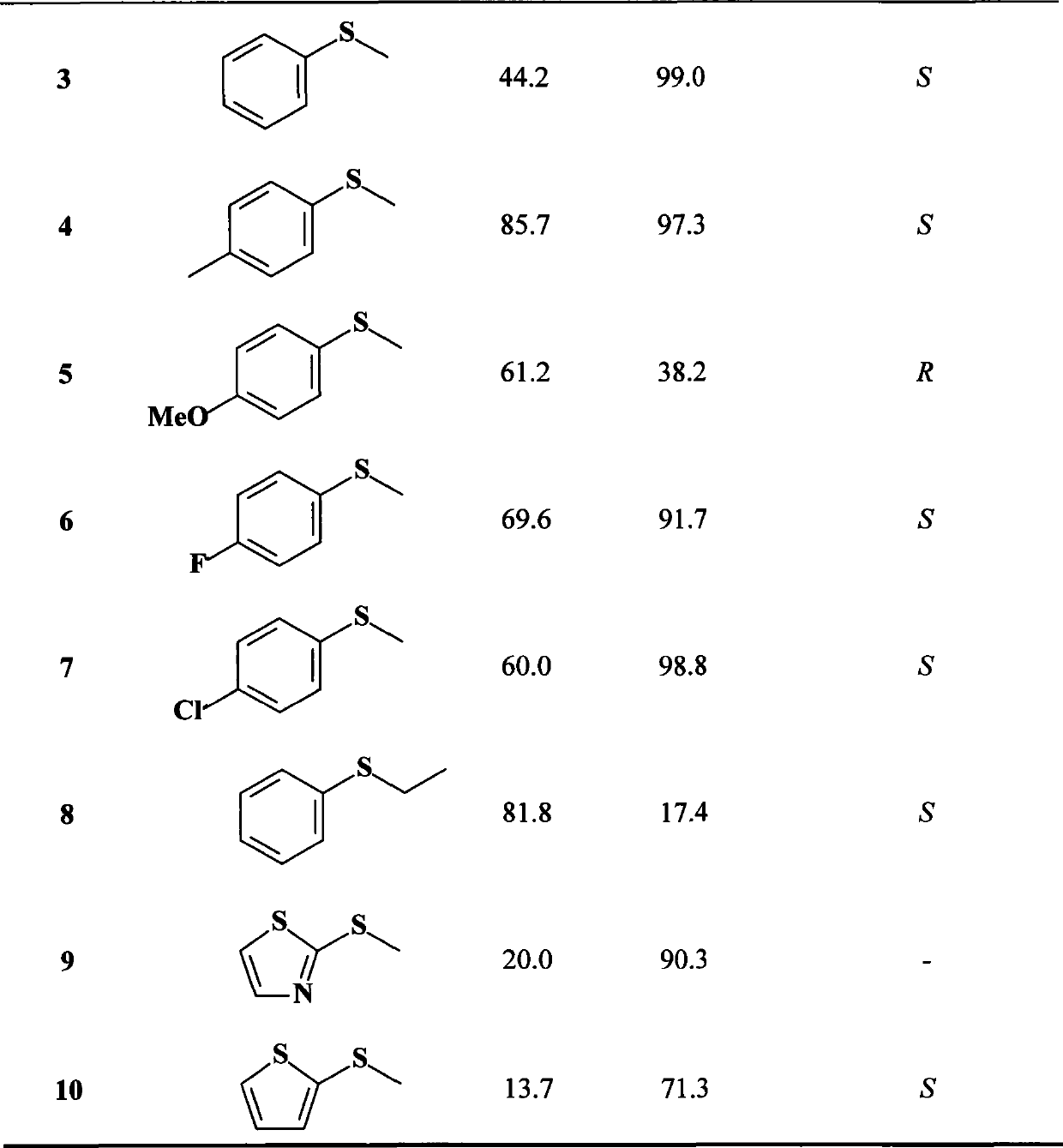
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing chiral sulfoxide from thioether under the catalytic action of Rhodococcus, belonging to the technical field of microorganisms. By using a resting cell of Rhodococcus sp. CCZU10-1 of which the collection number is CGMCC NO.4911 as a biocatalyst, asymmetric catalytic oxidation is performed on prochiral thioanisole and derivatives thereof, thus synthesizing chiral S-methyl phenyl sulfoxide (e.e.>99.9%) and derivatives thereof. The strain disclosed by the invention and the stereoselective biological oxidation method using the same have the characteristics of favorable catalytic effect, simple operating process route, mild reaction conditions, no pollution and the like.
Owner:临泉县嘉鸿装饰工程有限公司
Biochemical preparation for treating glutamic acid fermentation sewage
ActiveCN105833832APromote degradationHigh activityOther chemical processesSilicon compoundsBiotechnologyAzotobacter chroococcum
The invention relates to a biochemical preparation for treating glutamic acid fermentation sewage. The biochemical preparation contains a physical adsorbent and a composite microbial preparation, wherein the composite microbial preparation is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 6-8 parts of azotobacter chroococcum, 4-6 parts of Rhodococcus sp., 4-6 parts of bacillus amyloliquefaciens, 3-5 parts of clostridium papyrosolvens, 3-5 parts of penicillium ochrochlorron, 3-4 parts of Pseudomonas stutzeri and 2-3 parts of bacillus cereus. The biochemical preparation contains a variety of microbes which have excellent degradation capability to refractory contaminants, and all strains are reasonably combined, so that the biochemical preparation has a good degradation effect and has a broad application prospect.
Owner:内蒙古阜丰生物科技有限公司
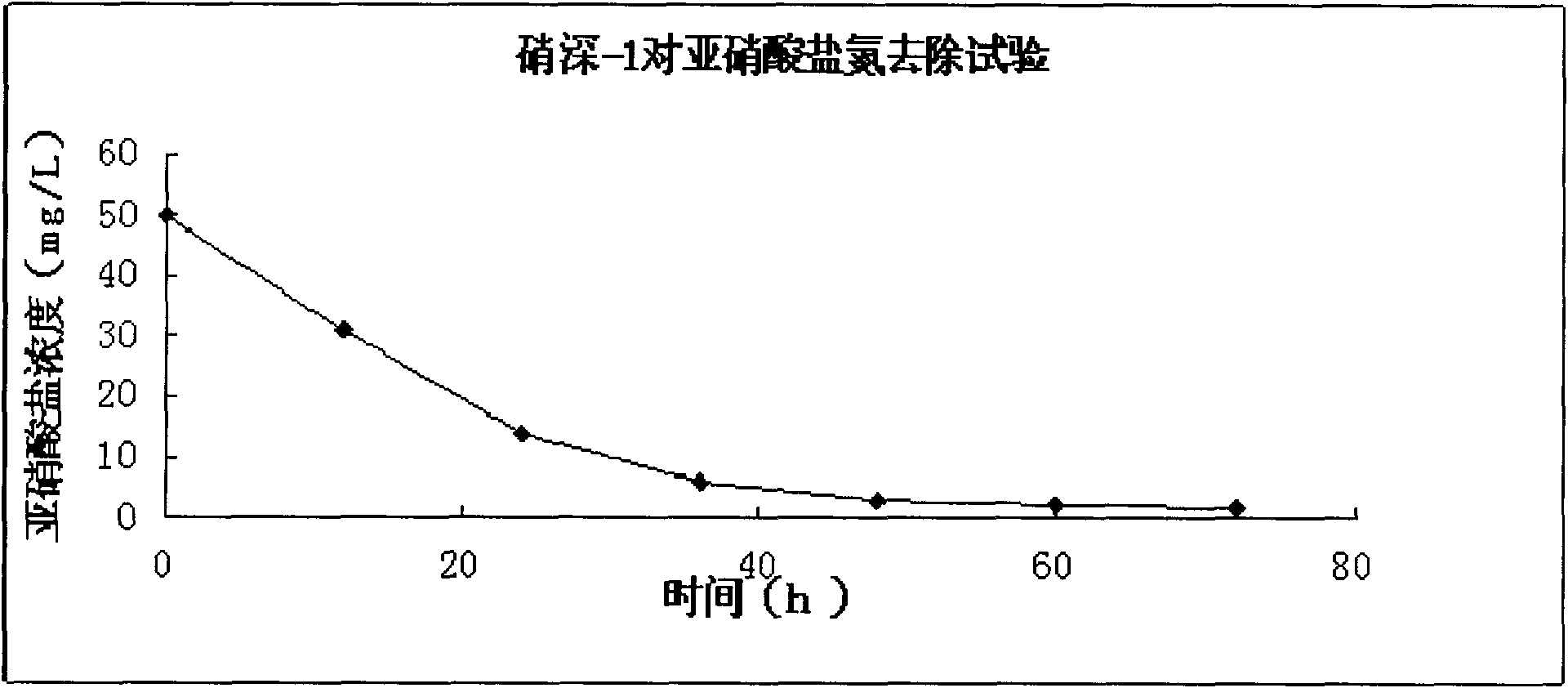
Rhodococcus sp. for removing nitrite nitrogen from sewage at low temperature condition, and separation and culture method thereof
The present invention discloses Rhodococcus sp. for removing nitrite nitrogen from sewage at a low temperature condition, and a separation and culture method thereof. The Rhodococcus sp. xiaoshen-1 CGMCC No.5277 for removing the nitrite nitrogen from the sewage at the low temperature condition has the function of removal of the nitrite nitrogen from the sewage at the low temperature and aerobic condition. The experimental results show that: the significant reinforcement effect of removal of the nitrite nitrogen in the sewage at the low temperature and especially at the temperature of 8-12 DEGC is provided despite the significant inhibition of the low temperature environment after the Rhodococcus sp. xiaoshen-1 CGMCC No.5277 of the present invention is added to the sewage, wherein the nitrite nitrogen removal rate in the sewage inoculated with the Rhodococcus sp. of the present invention is increased by about 10% compared to the nitrite nitrogen removal rate in the sewage without inoculation with the Rhodococcus sp. of the present invention.
Owner:GUOZHONG AIHUA TIANJIN MUNICIPAL ENCIRONMENT ENG
Rhodococcus and application of rhodococcus in degradation of lignin
ActiveCN104726364ALow costNo secondary pollutionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyCatalase
The invention relates to a rhodococcus and application of the rhodococcus in degradation of lignin, belonging to the technical field of microorganism. The rhodococcus is obtained from China South Sea mud through separation and purification, is a variety of rhodococcus, and is named (Rhodococcus sp.) L17, the rhodococcus is Gram-positive according to authentication, no conidium is formed, and the rhodococcus is aerobic, is catalase positive, and is aryl-sulfatidase negative; besides, the 16SrDNA sequence of the rhodococcus is submitted to the NCBI database, the accession number is KM215139, and is preserved in the general microorganism center of CCCCM (China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms) on March 20th in 2014 with the preservation number CGMCC8943; according to verification of experiments, the rhodococcus has the capacity of degrading the lignin, and the degradation rate can reach 90%-100%, so that the rhodococcus can be applied to the field of environment protection, and can be particularly applied to biodegradation of the lignin.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
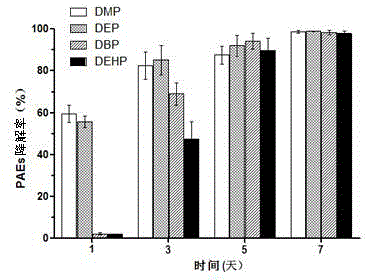
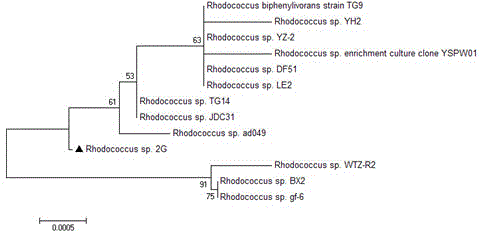
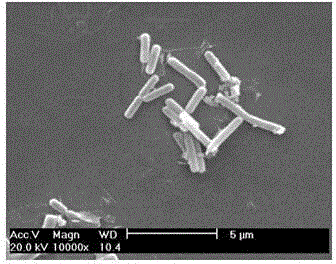
Rhodococcus sp. 2G used for simultaneous degradation of plurality of phthalic acid esters
InactiveCN104805035AIncrease vitalityWidely distributedBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyPure culture
The invention belongs to the technical field of environmental pollutant biological treatment, and specifically discloses rhodococcus sp. 2G used for simultaneous degradation of a plurality of phthalic acid esters (PAEs). The rhodococcus sp. 2G is preserved at China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) on 22th, Jan., 2015, and preservation number is CCTCC No.M 2015056. The rhodococcus sp. 2G is high in activity, and is capable of realizing growth and breeding by taking a plurality of PAEs as the only carbon source and energy; complete degradation of PAEs mixed with a inorganic salt culture medium at a ratio of 200mg / kg can be almost realized in 7 days by the rhodococcus sp. 2G under pure culture conditions; the rhodococcus sp. 2G is widely distributed in the natural world; adaptability is high; culture collection is enlarged greatly, and the rhodococcus sp. 2G possesses a promising application prospect in biological treatment of environmental pollutants.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Bioremediation preparation for industrial waste water produced by using concentration isoelectric point technology to prepare sodium glutamate
ActiveCN105132326APromote degradationGood removal effectFungiBacteriaMonosodium glutamateIndustrial waste water
The invention relates to bioremediation preparation for industrial waste water produced by using the concentration isoelectric point technology to prepare sodium glutamate. The bioremediation preparation is mixed and prepared by nitrosomonas europaea, paracoccus pantotrophus, acinetobacter baumannii, aspergillus niger, rhodococcus sp., alcaligenes faecalis, streptomyces lateritius, candida albicans, paenibacillus polymyxa and an absorbent carrier. The bioremediation preparation has the advantages that the preparation contains various microorganisms with good degrading ability to degradation-resistant pollutants, various strains are reasonably combined, and the preparation is good in degrading effect and promising in application prospect.
Owner:HULUNBEIER NORTHEAST FUFENG BIOTECHNOLOGIES CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com