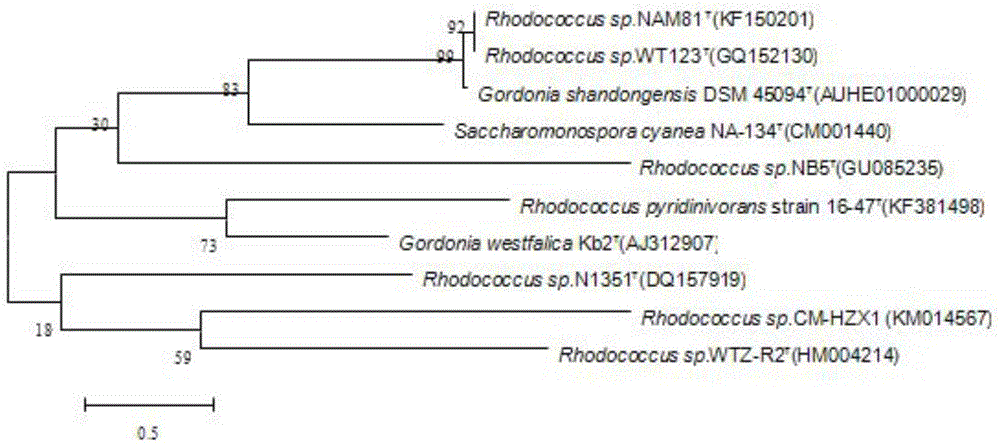
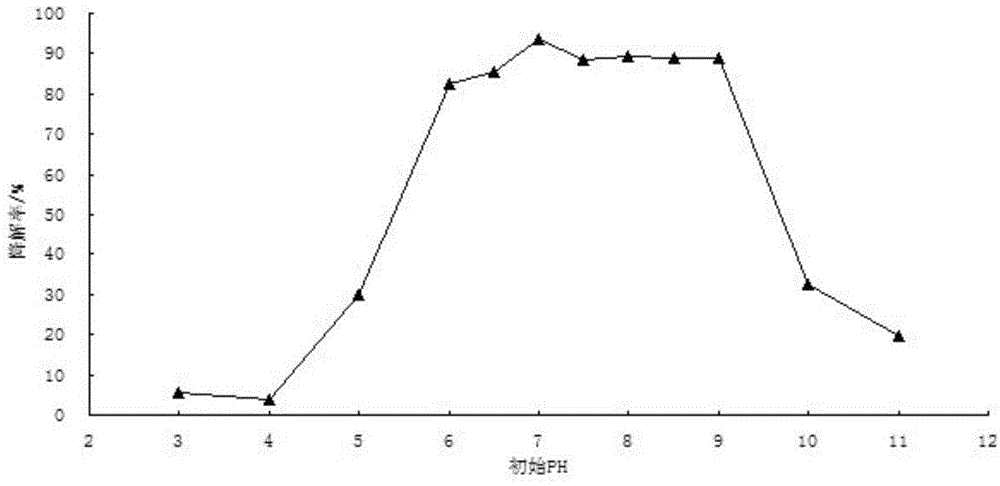
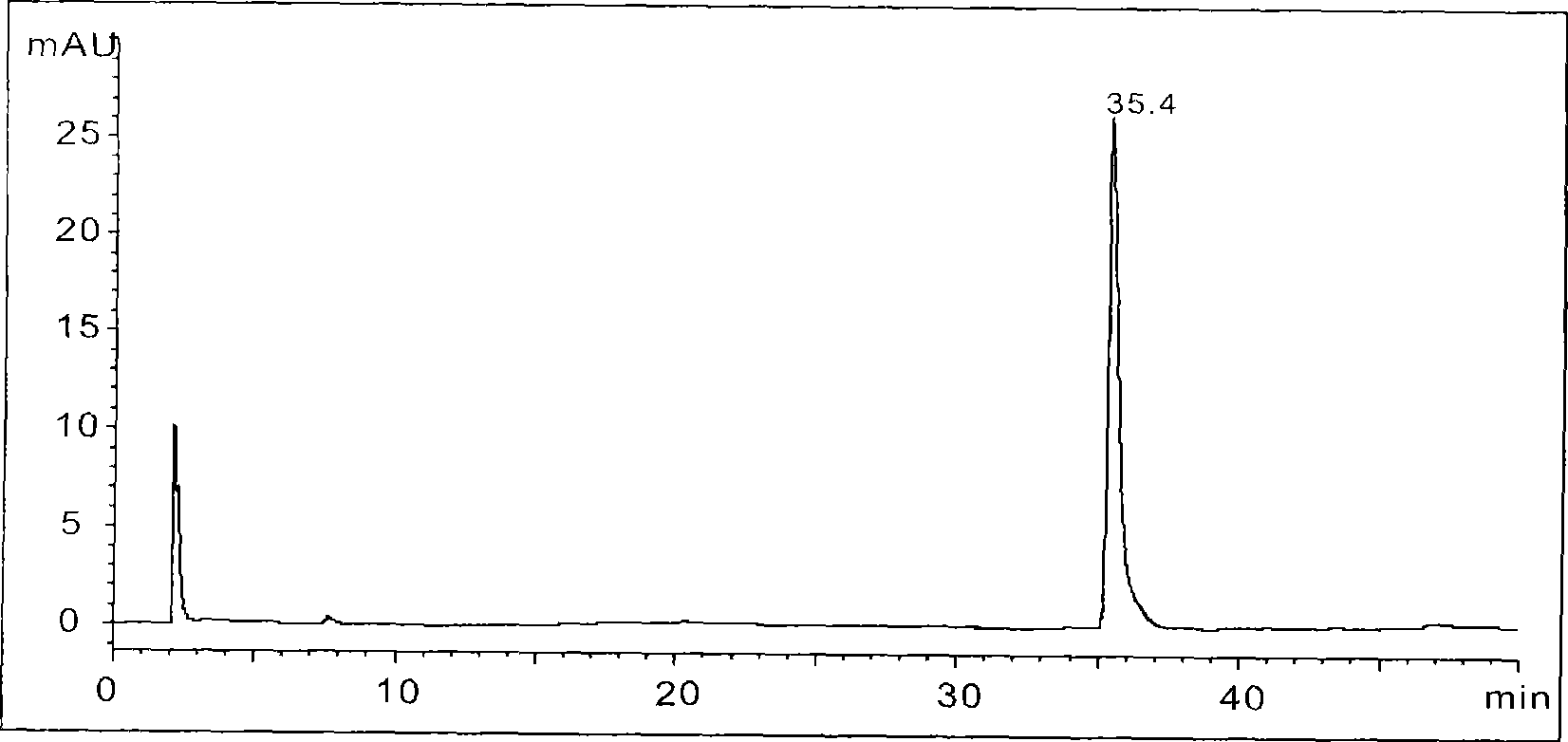
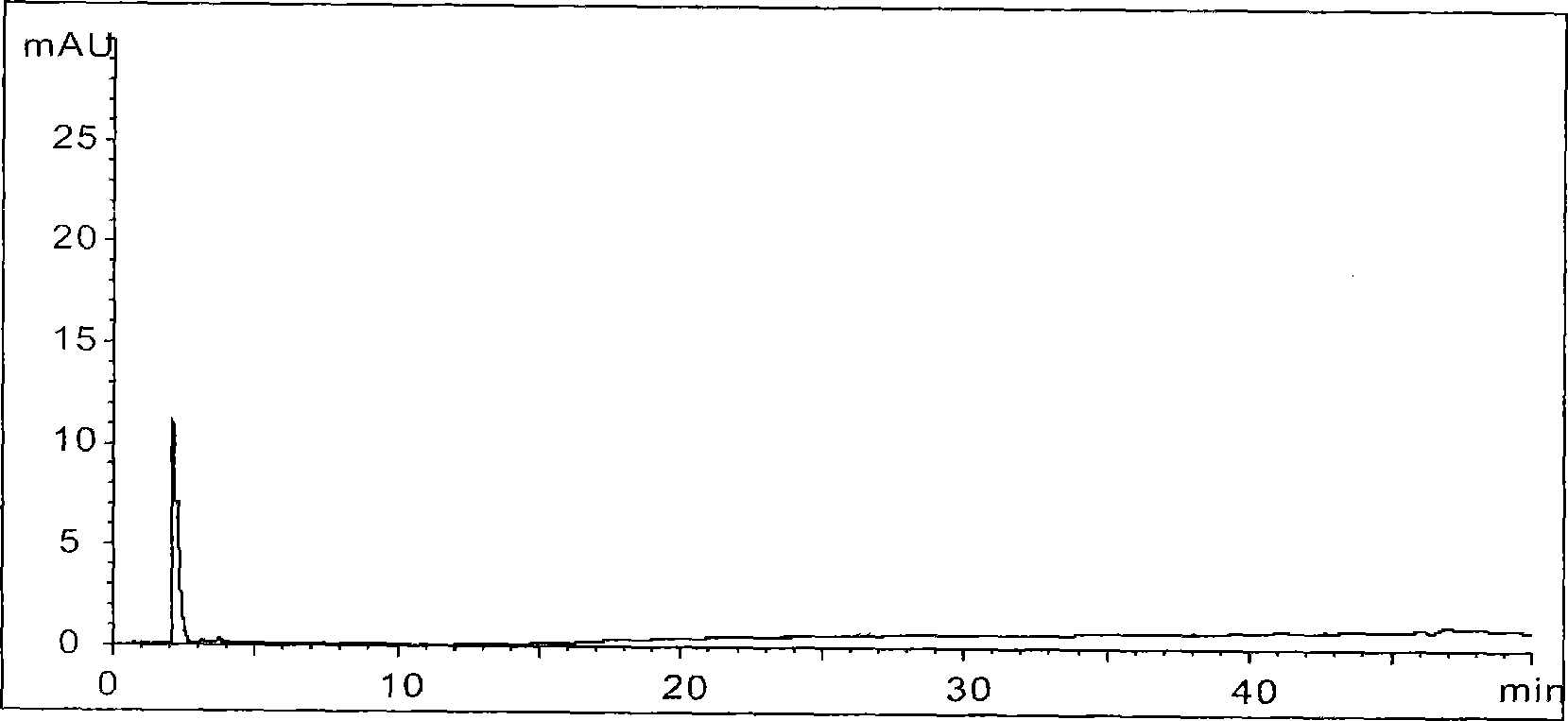
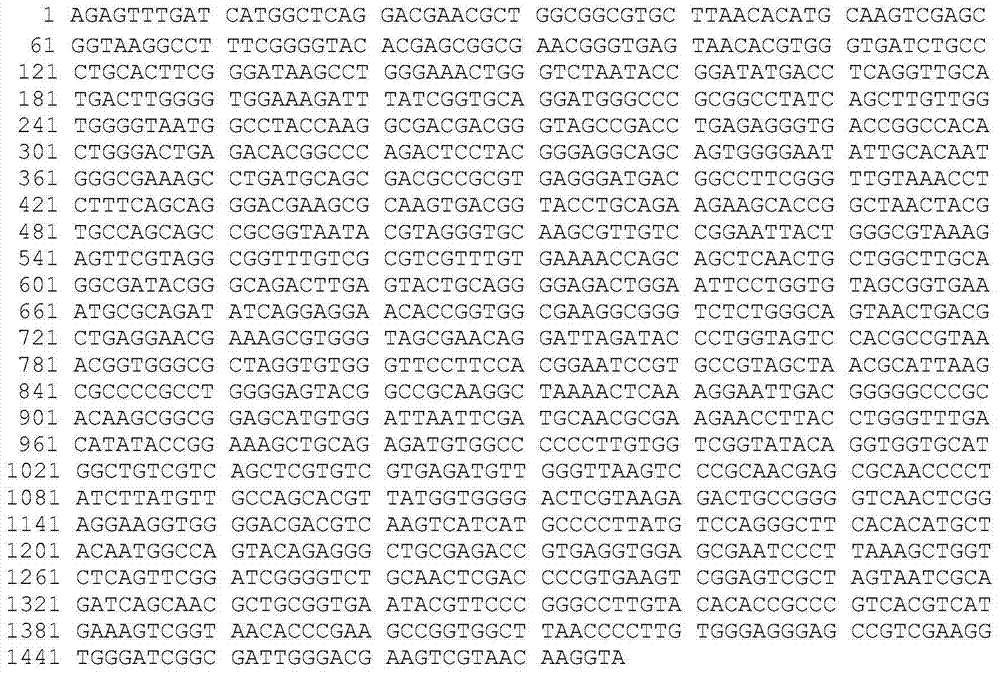Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
33 results about "Rhodococcus strain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
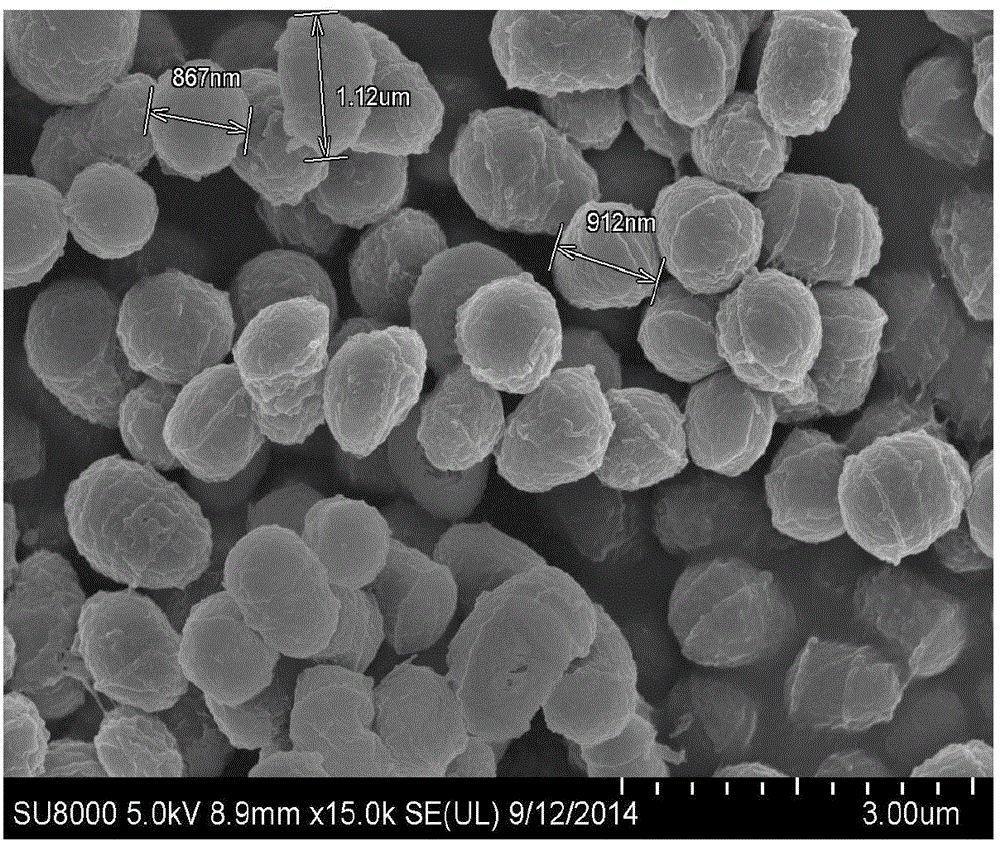
Rhodococcus sp. strain and application thereof
ActiveCN104673710AStrong ability to degrade phenolAdaptableBacteriaWater contaminantsMicroorganismRhodococcus strain
The invention discloses a rhodococcus sp. strain and application thereof, belonging to the field of environmental microbiological application. The strain is named as (Rhodococcus sp.) CM-HZX1 and is now collected with the serial number of CCTCC (China Center For Type Culture Collection) NO:M 2014329 in CCTCC on July 9th, 2014. The rhodococcus sp.CM-HZX1 has relatively strong phenol degrading capacity, namely that the degradation rate is up to 93.6% after 0.5g / L of phenol is degraded for 24 hours, and the degradation rate is up to more than 90% after 1.5g / L of phenol is degraded for 48 hours. The strain is capable of tolerating the salinity of 4% and strong in adaptability; and the strain is efficient when being used for biological treatment of phenol wastewater so as to be wide in application prospect.
Owner:浙江至美环境科技有限公司
Rhodococcus strain for degrading 3-nitrotoluene, as well as preparation method and use
The invention discloses a Rhodococcus strain ZWL3NT CCTCC NO: M 208206. The preparation method of the strain includes formulation of an inorganic salt substrate, strain concentration, separation and degradation of bacteria, wherein, the inorganic salt substrate contains Na2HPO4*12H2O, KH2PO4, MnSO4*H2O, FeSO4*7H2O and other components; the bacterial concentration includes: formulating the soil sample and inorganic salt substrate into a suspending liquid, inoculating the suspending liquid in a certain volume of inoculating amount onto a fresh inorganic salt medium containing 3-nitrotoluene, shaking table culturing at constant temperature until obtaining the accumulation culture object with significant degradation performance; the separation adopts a plating technique to separate and purify the culture in the LB medium. The bacterial strain provided by the invention can be used to degrade the 3-nitrotoluene with the degradation rate of 99 percent, and the preparation method is simple and easy to operate.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
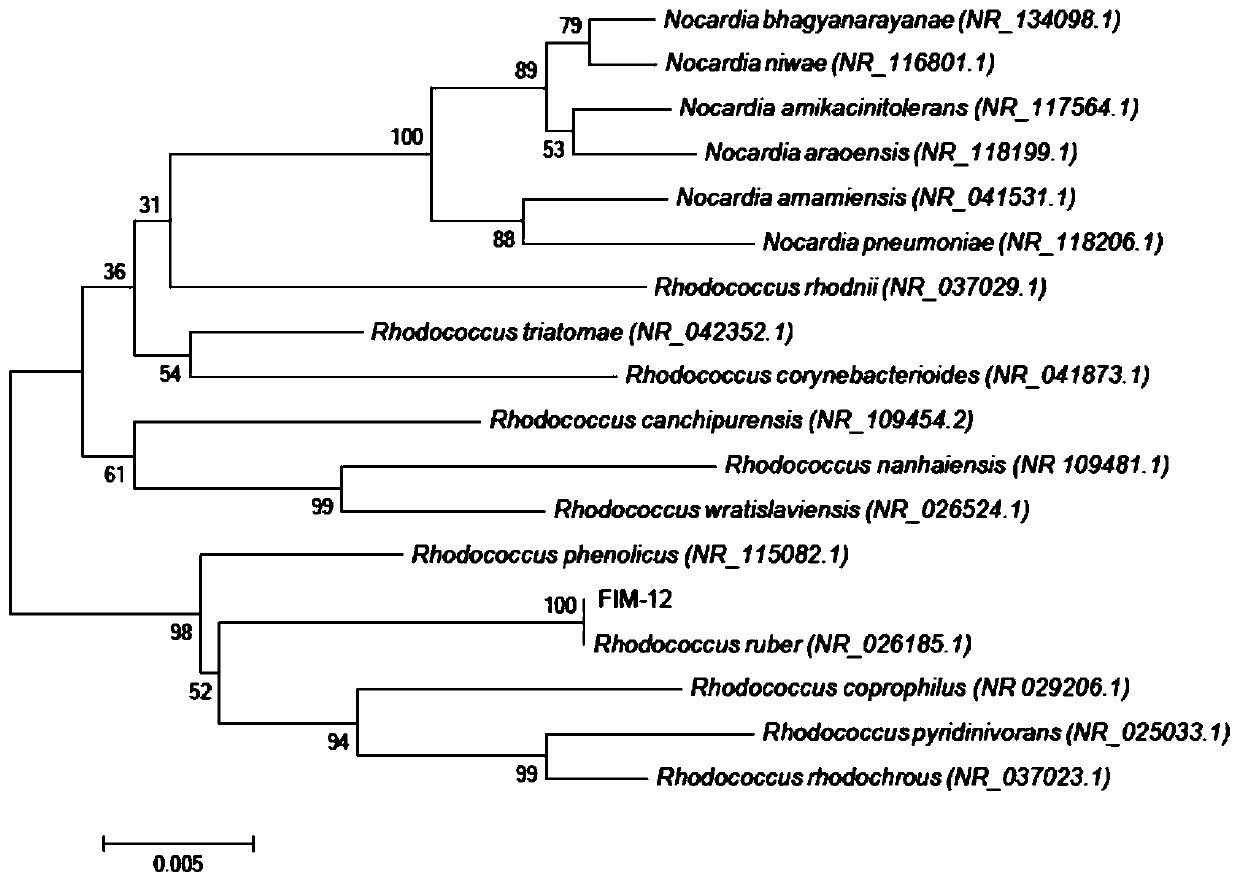
Rhodococcus ruber strain, rhodococcus ruber bacterium preparation and application of thalli cells and extracts of rhodococcus ruber
ActiveCN110184215AEnhanced immune functionEnhance anti-tumorBacteriaBacteria material medical ingredientsFreeze thawingMicroorganism
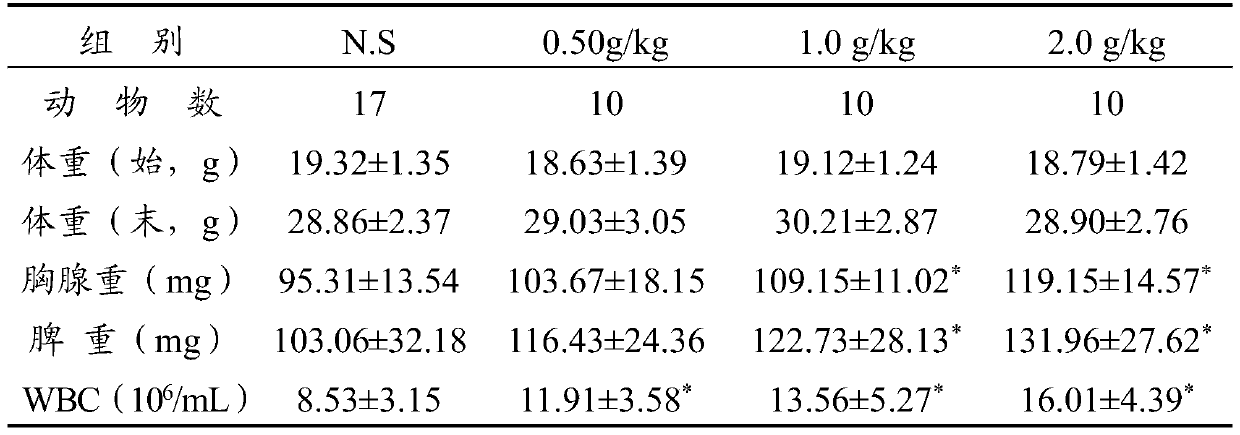
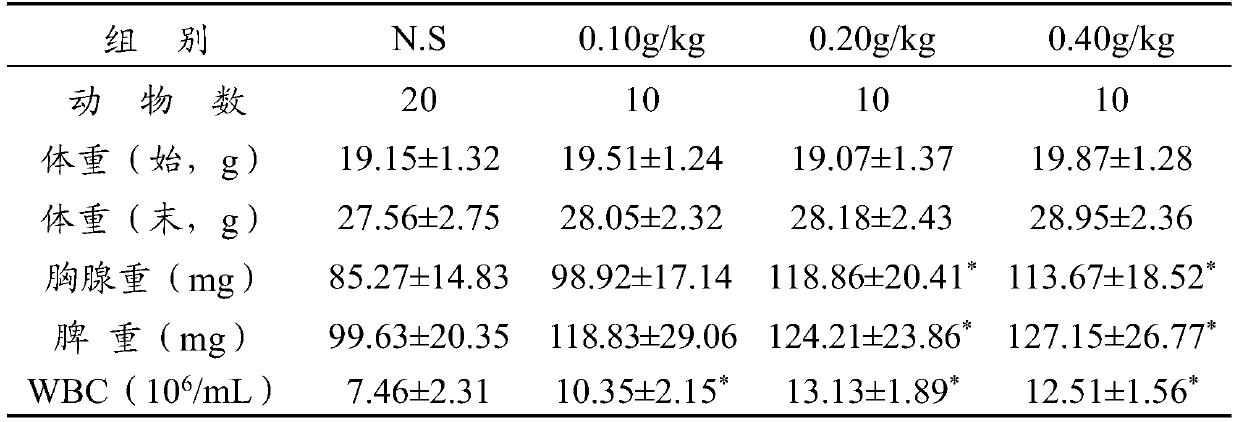
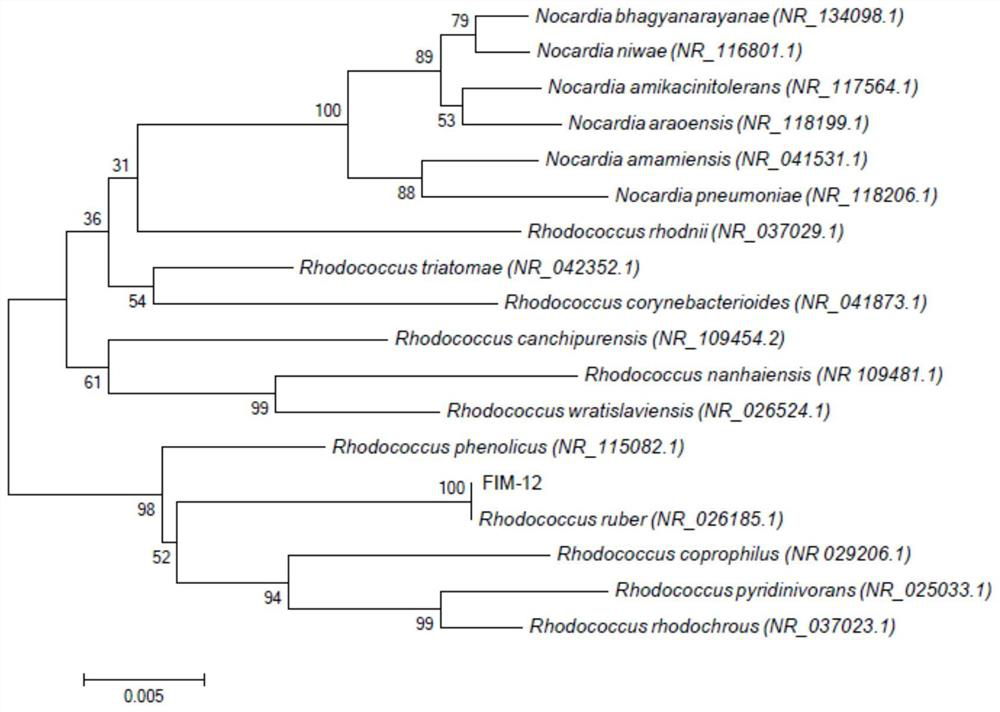
The invention provides a rhodococcus ruber strain, a rhodococcus ruber bacterium preparation and an application of thalli cells and extracts of rhodococcus ruber. The strain is rhodococcus ruber (Rhodococcus ruber) FIM-12 which is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on April 3, 2019, with the preservation number being CGMCC No.17525. The strain can be used forpreparing rhodococcus ruber cells and extracts of the rhodococcus ruber through microorganism fermentation: after the rhodococcus ruber (Rhodococcus ruber) FIM-12 is subjected to fermentation and culture, thalli cells are collected, the thalli cells are washed with purified water so that wet cells are obtained, the wet cells are subjected to repeated freeze-thawing combined with ultrasonic wall breaking, then extraction with anhydrous alcohol is performed, and the rhodococcus ruber extracts are obtained. The rhodococcus ruber strain can be applied to industrialized fermentation and production,the rhodococcus ruber thalli cells and the rhodococcus ruber extracts are prepared, the prepared products have the functions of increasing immunity activity and restraining effects, and the rhodococcus ruber strain can be used as a production strain for further research and development.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF MICROBIOLOGY
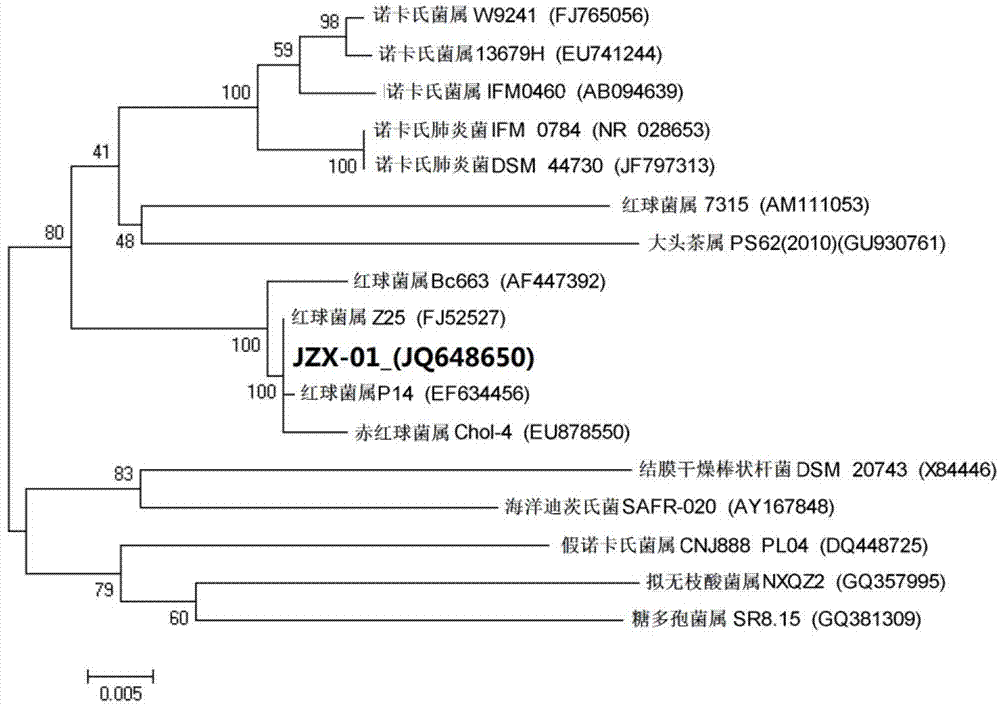
Rhodococcus JZX-01 used for degrading petroleum pollutants, and culturing method thereof
InactiveCN102851234APromote degradationImprove degradation rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismRhodococcus strain
The invention relates to a rhodococcus JZX-01 used for degrading petroleum pollutants, and a culturing method thereof. The identification of the rhodococcus is achieved through 16S rDNA sequencing and comparison on NCBI. An adopted 16S rDNA upstream primer is a universal primer 27F with a specific sequence of 5'-AGA GTT TGA TCC TGGCTCAG-3'. A downstream universal primer is 1492R with a specific sequence of 5'-GGT TAC CTT GTT ACG ACTT-3'. According to the invention, an inducing agent is added into a culture medium or culture solution, and soil is added into the culture solution or culture medium; culturing is carried out in a shaking table under a culturing temperature of 10-40 DED C and a culturing rotation speed of 100-300rpm; when culturing is carried out for 1-4days, a product is transferred into a fresh culture medium or culture solution, and screening is carried out. The rhodococcus strain is collected by China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, and has a collection register number of CGMCC No. 5958. The collection date is April 9th, 2012. With a surfactant-producing capacity of rhodococcus JZX-01, petroleum degradation efficiency is further enhanced. The rhodococcus JZX-01 can be used in biological treatments of petroleum pollutants.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Rhodococcus corynebacterioides strain and application thereof in printing and dyeing wastewater treatment
ActiveCN103667108ABroad degradation spectrumGood removal effectBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismRhodococcus strain
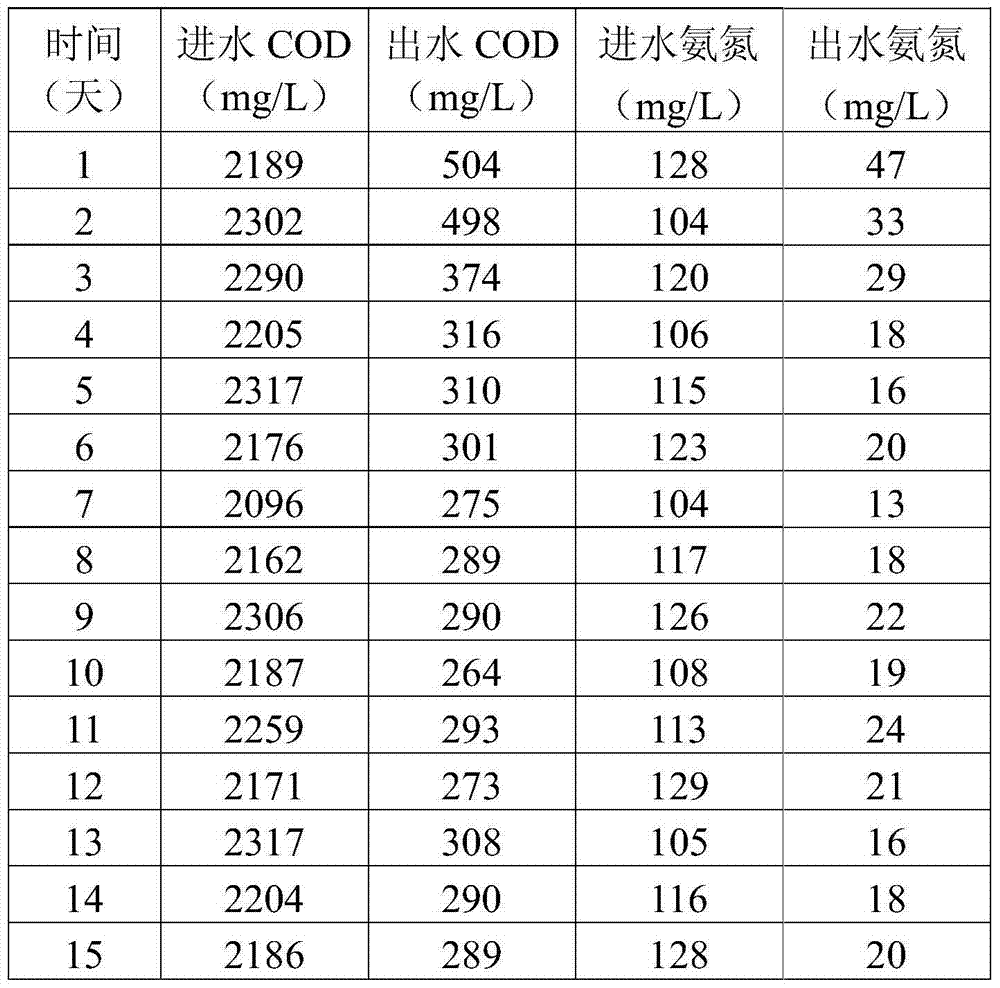
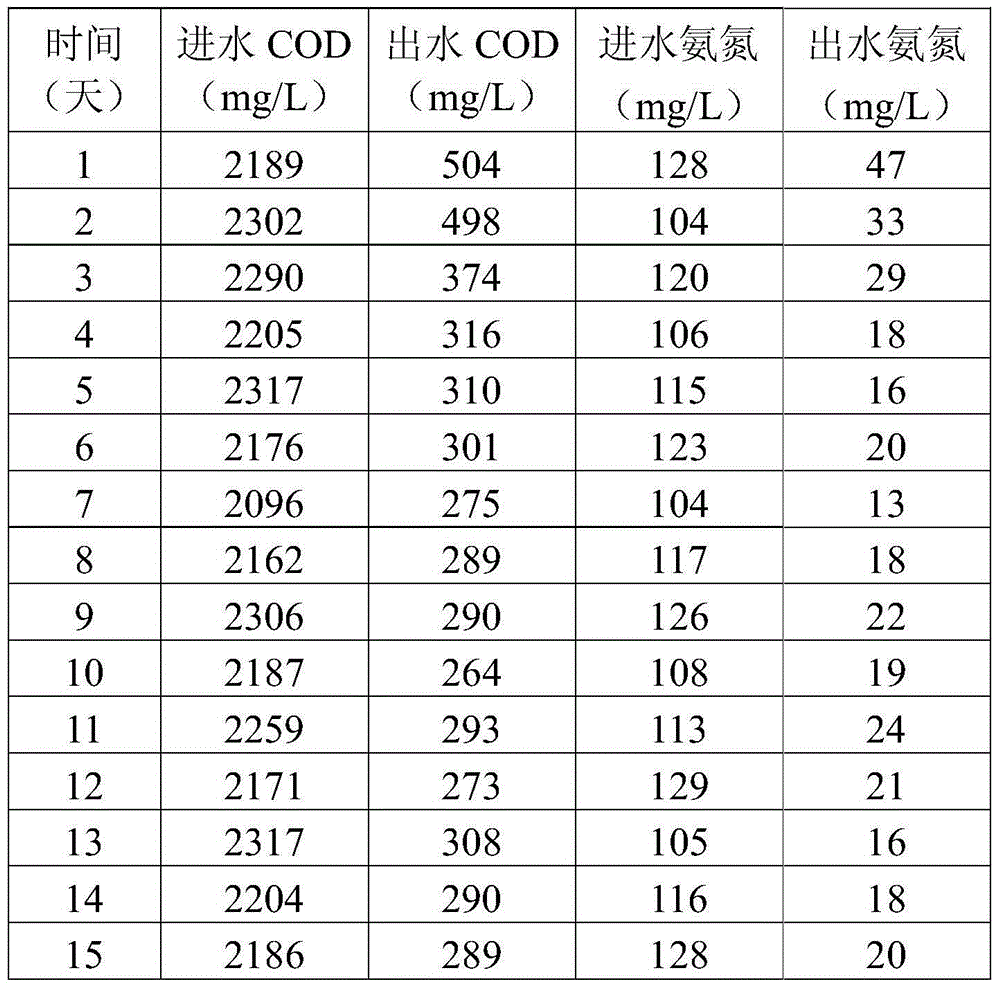
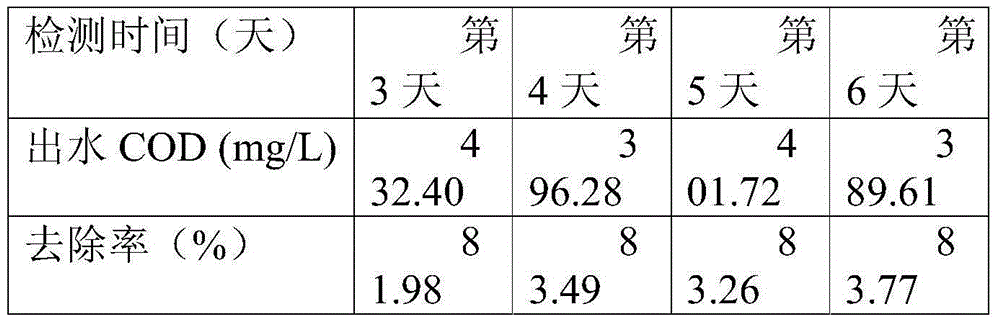
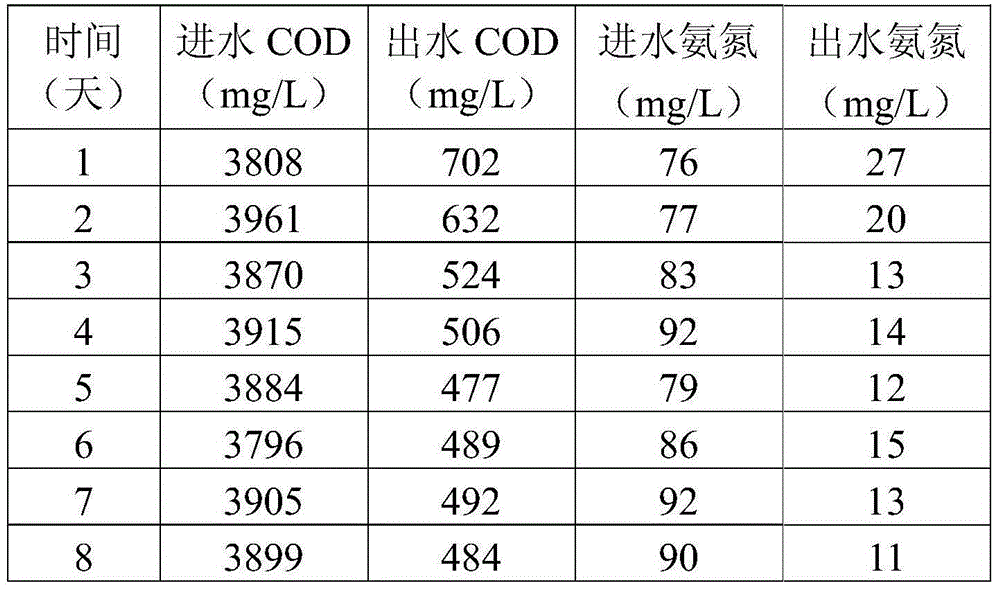
The invention discloses a rhodococcus corynebacterioides strain and an application thereof in printing and dyeing wastewater treatment. The rhodococcus corynebacterioides strain is named as Rhodococcus corynebacterioides ZHY1-4, and the preservation number is CGMCC No. 8172. The rhodococcus corynebacterioides strain is prepared as microbial agent; the rhodococcus corynebacterioides ZHY1-4 and the microbial agent prepared from the strain are used for treating high-salt printing and dyeing wastewater or deeply treating the printing and dyeing wastewater, the deep treatment effects on a plurality of high-salt printing and dyeing wastewater and the printing and dyeing wastewater are good, and COD (chemical oxygen demand) and ammonia nitrogen can be well removed.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL SCI RES & DESIGN INST OF ZHEJIANG PROVINCE
Microorganism
ActiveUS20090269822A1Easy to produceHigh activityBacteriaHybrid cell preparationUrea derivativesHydration reaction
A microorganism which is Rhodococcus rhodochrous strain NCIMB 41164 or a mutant thereof. A method of culturing the microorganism in a culture medium comprising urea or urea derivative is claimed. A nitrile hydratase obtainable from the microorganism is claimed. Also claimed is a process of preparing an amide from the corresponding nitrile wherein the nitrile is subjected to a hydration reaction in an aqueous medium in the presence of a biocatalyst selected from the group consisting of a microorganism which is a Rhodococcus rhodochrous strain NCIMB 41164, a mutant thereof and a nitrile hydratase obtainable from Rhodococcus rhodochrous strain NCIMB 41164 or a mutant thereof. Also claimed is a method of storing the Rhodococcus rhodochrous NCIMB 41164.
Owner:SOLENIS TECH CAYMAN
Pseudomonas strain and identification and application methods thereof
ActiveCN109423459AIncrease abundanceSolve the lack of high purity requirementsBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementConserved sequenceRhodococcus strain
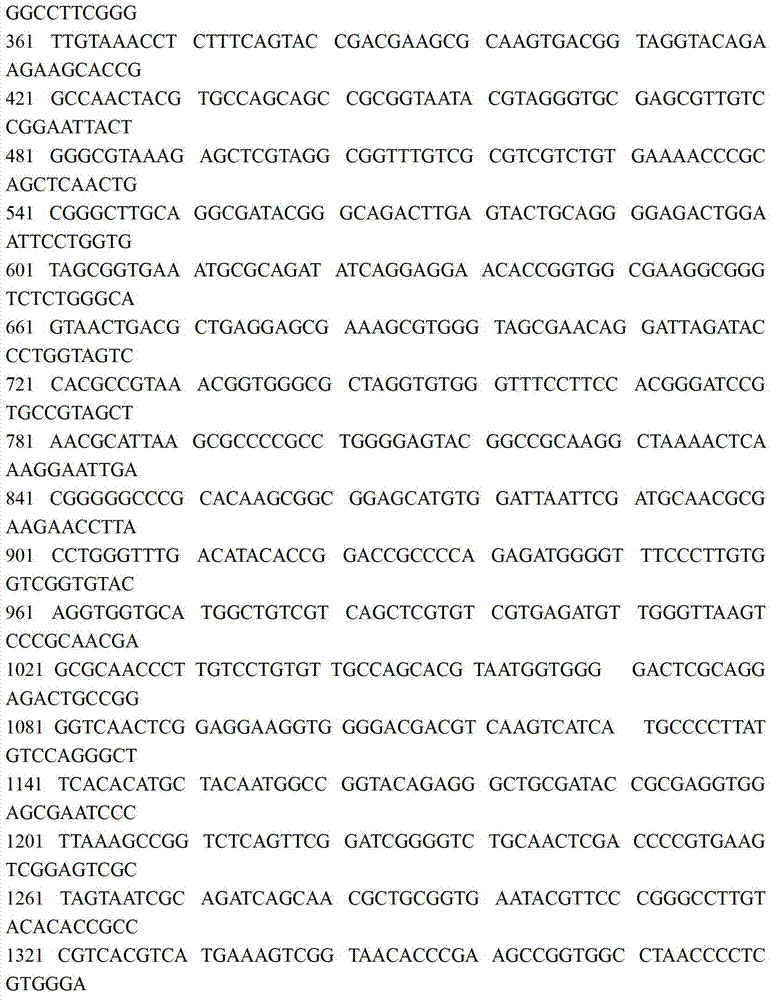
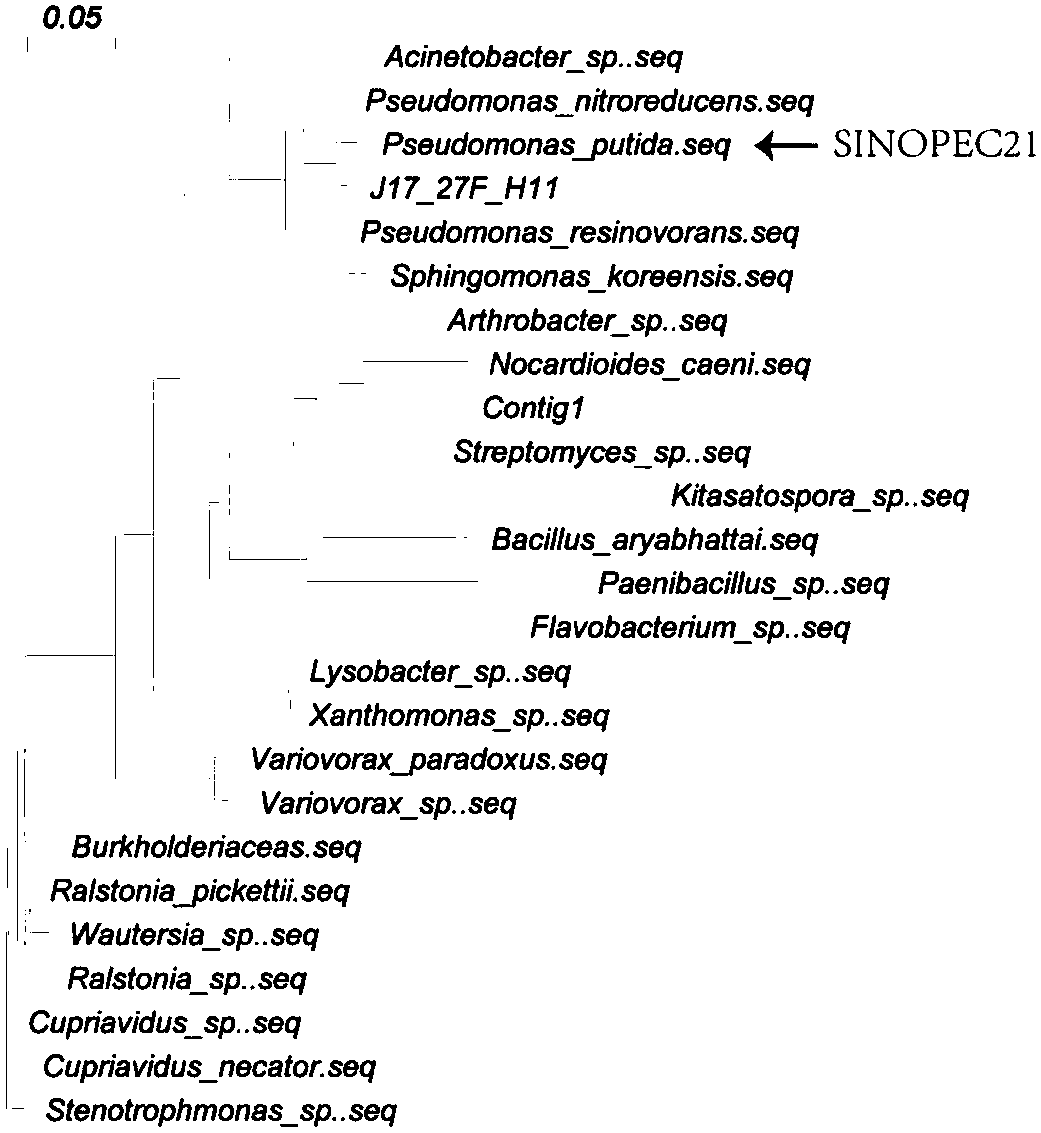
The invention relates to a pseudomonas strain and identification and application methods thereof in the technical field of microorganisms. The rhodococcus strain has a 16S rDNA (16S ribosome deoxyribonucleic acid) gene sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.1, a strain name of SINOPEC21 and a preservation number of CCTCC NO: M2016111 in China Center for Type Culture Collection. The abundance of the pseudomonas strain in soil above an oil reservoir is positively related to the concentration of floating gaseous hydrocarbons of the oil reservoir, so that the pseudomonas strain can serve as an oil exploitation microorganism to mark areas with high hydrocarbon leakage above the oil reservoir; meanwhile, the pseudomonas strain is high in abundance in soil above the oil reservoir and saves amplification culture, the 16S rDNA conserved sequence of the pseudomonas strain SINOPEC21 in soil through improved primers, so that the concentration of floating gaseous hydrocarbons of the oil reservoir can be determined accurately and efficiently, and the deficiency of long detecting cycle and high requirements on purity of sample culture in traditional physiological and biochemical detection can be solved.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Rhodococcus strain capable of degrading metamitron and application of rhodococcus strain
InactiveCN104862246APromote degradationEfficient degradationBacteriaWater contaminantsRhodococcus strainMicrobiology
The invention discloses a rhodococcus strain capable of degrading metamitron and an application of the rhodococcus strain. The strain is named as (Rhodococcus sp.) MET to be preserved at China Center For Type Culture Collection (for short, CCTCC) of Wuhan University, Wuhan, China on April 7th, 2014 with the preservation number being CCTCC No.M2014116. By means of the strain, metamitron can be degraded rapidly and efficiently, and pollution of metamitron to soil and water can be prevented and treated effectively.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Rhodococcus strain and identification and application methods thereof
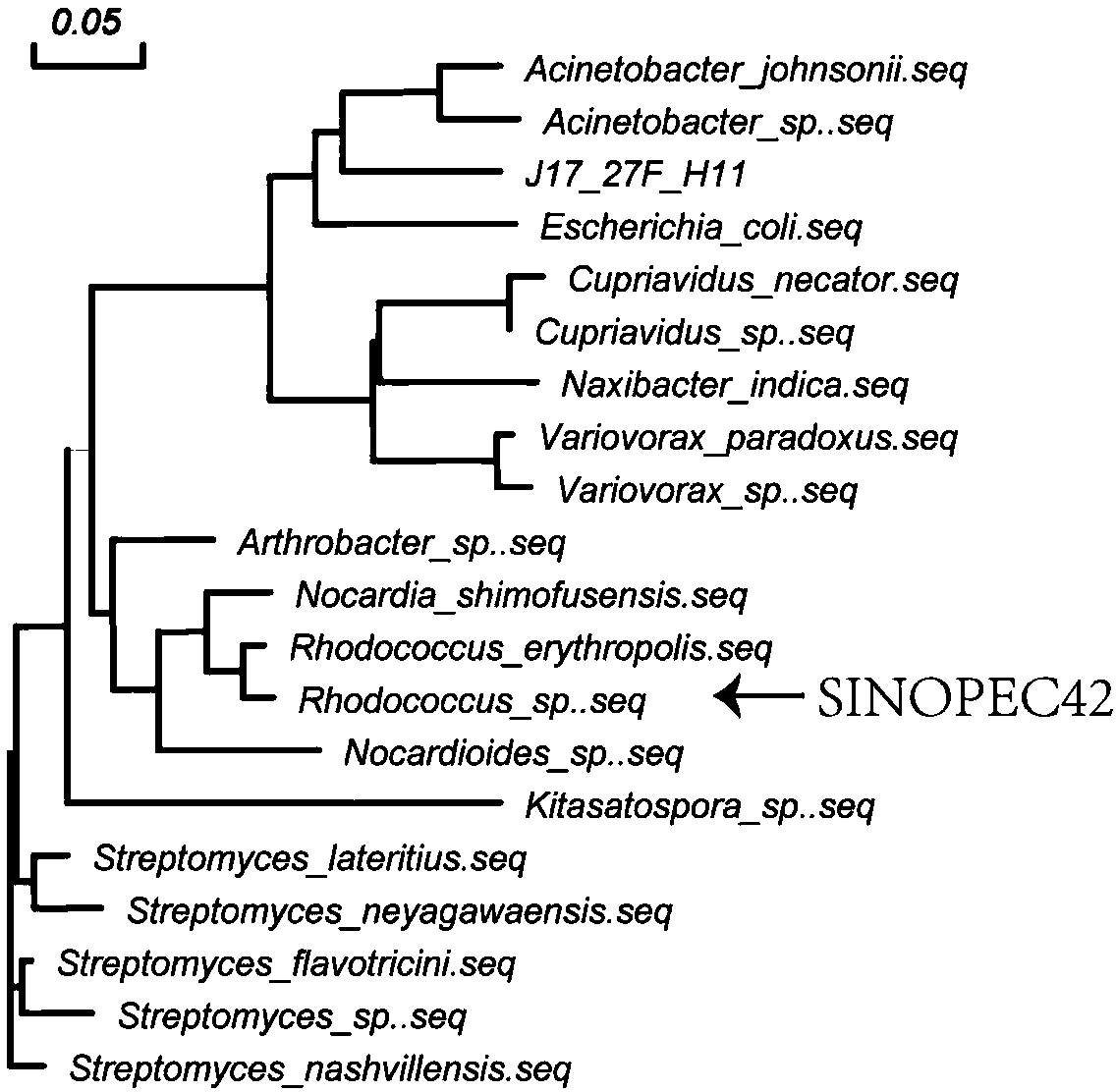
ActiveCN109423458ASolve the lack of high purity requirementsBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismConserved sequence
The invention relates to a rhodococcus strain and identification and application methods thereof in the technical field of microorganisms. The rhodococcus strain has a 16S rDNA (16S ribosome deoxyribonucleic acid) gene sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.1, a strain name of SINOPEC42 and a preservation number of CCTCC NO: M2016112 in China Center for Type Culture Collection. The abundance of the rhodococcus strain in soil above an oil reservoir is positively related to the concentration of floating gaseous hydrocarbons of the oil reservoir, so that the rhodococcus strain can serve as an oil exploitation microorganism to mark areas with high hydrocarbon leakage above the oil reservoir; meanwhile, the rhodococcus strain is high in abundance in soil above the oil reservoir and saves amplification culture, the 16S rDNA conserved sequence of the rhodococcus strain SINOPEC42 in soil through improved primers, so that the concentration of floating gaseous hydrocarbons of the oil reservoir can be determined accurately and efficiently, and the deficiency of long detecting cycle and high requirements on purity of sample culture in traditional physiological and biochemical detection can be solved.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Rhodococcus strain for degrading 3-nitrotoluene, as well as preparation method and use
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
A Rhodococcus strain and its application in printing and dyeing wastewater treatment
ActiveCN103667108BBroad degradation spectrumGood removal effectBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismRhodococcus strain
The invention discloses a rhodococcus corynebacterioides strain and an application thereof in printing and dyeing wastewater treatment. The rhodococcus corynebacterioides strain is named as Rhodococcus corynebacterioides ZHY1-4, and the preservation number is CGMCC No. 8172. The rhodococcus corynebacterioides strain is prepared as microbial agent; the rhodococcus corynebacterioides ZHY1-4 and the microbial agent prepared from the strain are used for treating high-salt printing and dyeing wastewater or deeply treating the printing and dyeing wastewater, the deep treatment effects on a plurality of high-salt printing and dyeing wastewater and the printing and dyeing wastewater are good, and COD (chemical oxygen demand) and ammonia nitrogen can be well removed.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL SCI RES & DESIGN INST OF ZHEJIANG PROVINCE
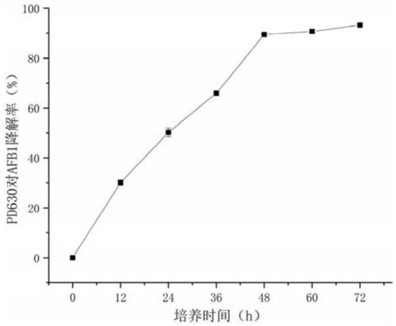
Method and device for degrading aflatoxin in spina date seeds
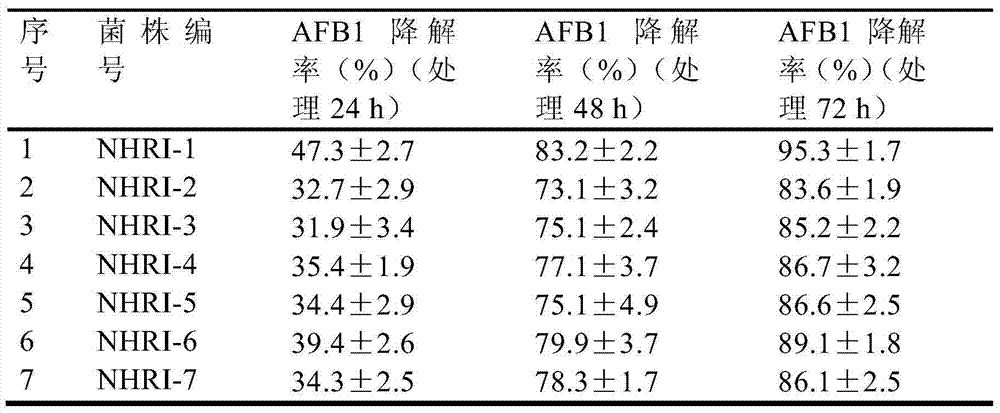
PendingCN113558175AImprove degradation efficiencyOptimal degradation conditionFood scienceMicroorganismRhodococcus strain
The invention belongs to the field of aflatoxin degradation, and discloses a method and device for degrading aflatoxin in spina date seed. A method for detecting aflatoxin by using an immunosensor is used for detecting the spina date seed treated by chlorine dioxide by using a solution containing aflatoxin to obtain the initial concentration of aflatoxin; adding a rhodococcus PD630 strain activating solution and an aflatoxin solution into a centrifugal tube, performing uniform shaking, and performing water bath reaction at 20-60 DEG C; performing fermentation treatment at room temperature; performing microfiltration treatment on the reacted sample, and detecting the concentration of residual aflatoxin in the reacted sample; and performing single factor treatment and orthogonal experiment treatment to obtain optimal conditions for degrading an aflatoxin initial concentration solution through concentration pretreatment of the rhodococcus PD630 strain activating solution. A chemical detoxification agent is combined with microorganisms, so that the operation is simple, no harm is caused to a human body, and the degradation efficiency is high.
Owner:赞皇县光森中药材有限公司
Rhodococcus ruber and application of preparation thereof in pyrethroid pesticide pollution remediation
ActiveCN114107095AEfficient bioremediationPromote bioremediationBacteriaWater contaminantsRhodococcus strainGermplasm
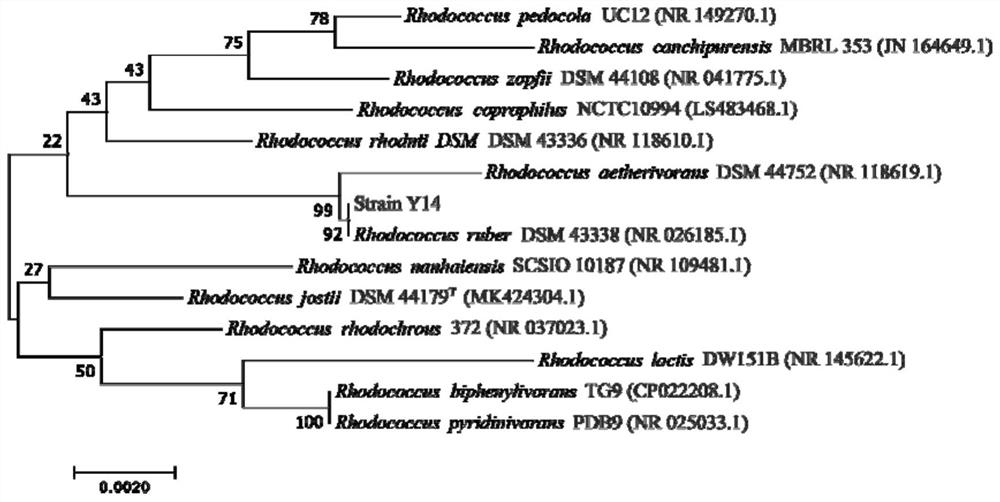
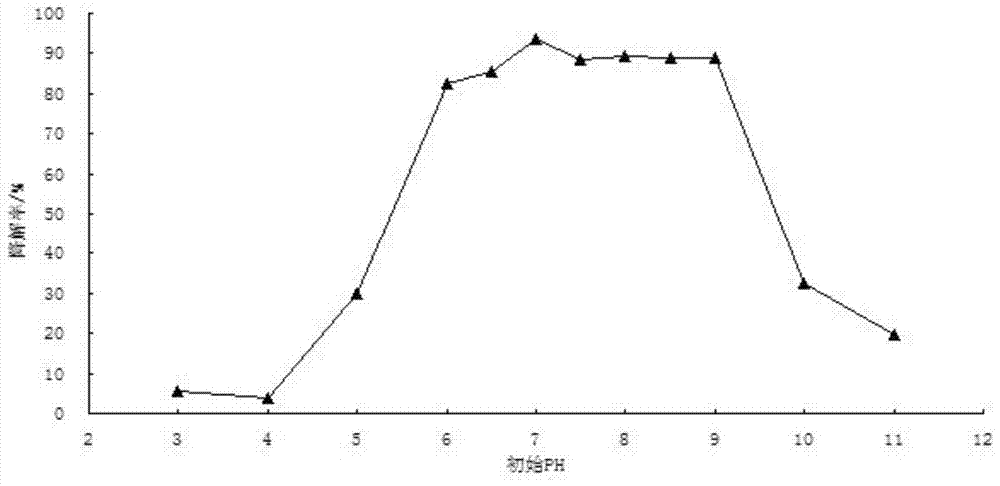
The invention discloses application of rhodococcus ruber and a preparation thereof in pyrethroid pesticide pollution remediation. The bacterial strain is a gram positive bacterium Rhodococcus ruber bacterial strain Y14, and is preserved in Guangdong Microbial Culture Collection Center on July 21, 2021, and the preservation number is GDMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) NO: 61813. The strain has remarkable pyrethroid insecticide biodegradation capacity, especially has the highest activity on D-cyhalothrin, is prepared into a suspension with the thallus number of not less than 1.0 * 10 < 6 > CFU.mL <-1 >, can completely remove 50 mg.L <-1 > D-cyhalothrin in a water body after being treated for 6 days, and also has an efficient bioremediation effect on polluted soil. The invention provides a new thought for solving the problems of excessive pyrethroid pesticide residue and environmental pollution in agricultural production, enriches the germplasm resource library of pesticide degrading bacteria, and has important practical application value for producing non-toxic and pollution-free green agricultural products.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
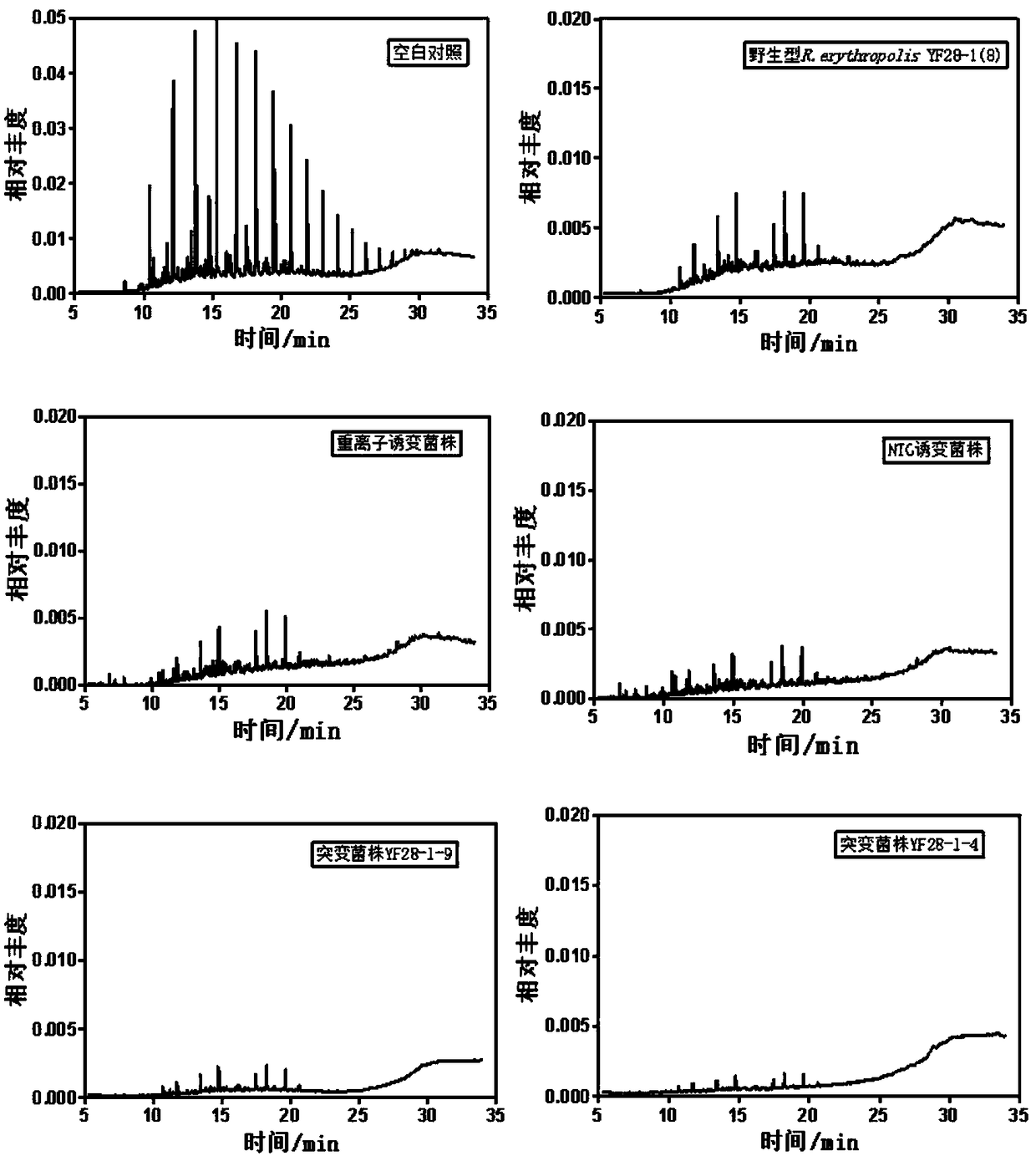
Induced mutation screening method and applications of Rhodococcus erythropolis bacterial strain YF28-1-4
InactiveCN108251412AImprove efficiencyEasy to operateMutant preparationMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismInduced mutation
The invention discloses an induced mutation screening method and applications of Rhodococcus erythropolis bacterial strain YF28-1-4. The induced mutation screening method comprises following steps: firstly, heavy ion irradiation is adopted for primary induced mutation of the genome of Rhodococcus erythropolis YF28-1(8) so as to obtain a bacterial strain with excellent degrading effect; then superpower mutagen NTG is adopted for a second time of induced mutation so as to obtain a Rhodococcus erythropolis mutant library, and then crude oil flat and GC-MS screening are adopted so as to obtain the Rhodococcus erythropolis bacterial strain YF28-1-4 with transcription system mutation and translation system mutation. The Rhodococcus erythropolis bacterial strain YF28-1-4 possesses high efficiency crude oil degradation capacity; operation of the induced mutation screening method is simple; period is short; efficiency is high; the induced mutation screening method is suitable for Rhodococcus erythropolis and other microorganisms with certain crude oil degrading capacity; and the popularization and application value is high.
Owner:COLD & ARID REGIONS ENVIRONMENTAL & ENG RES INST CHINESE
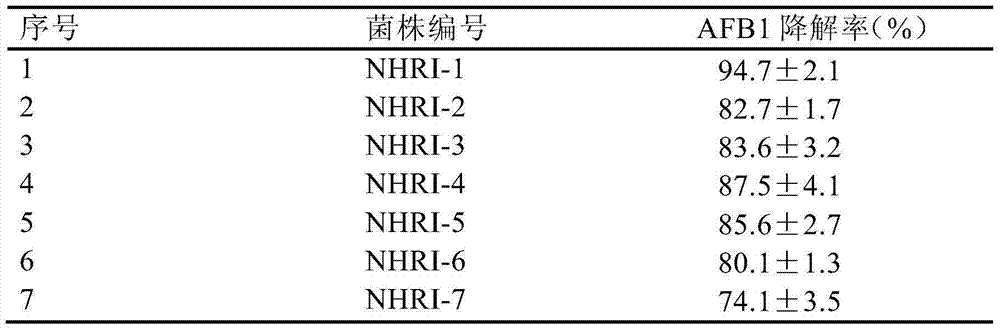
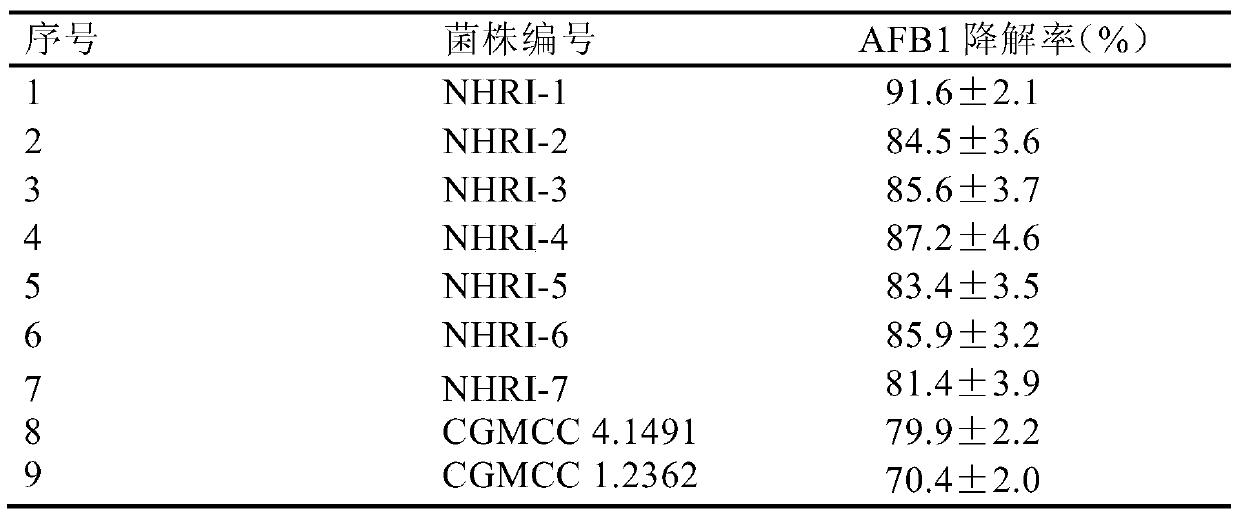
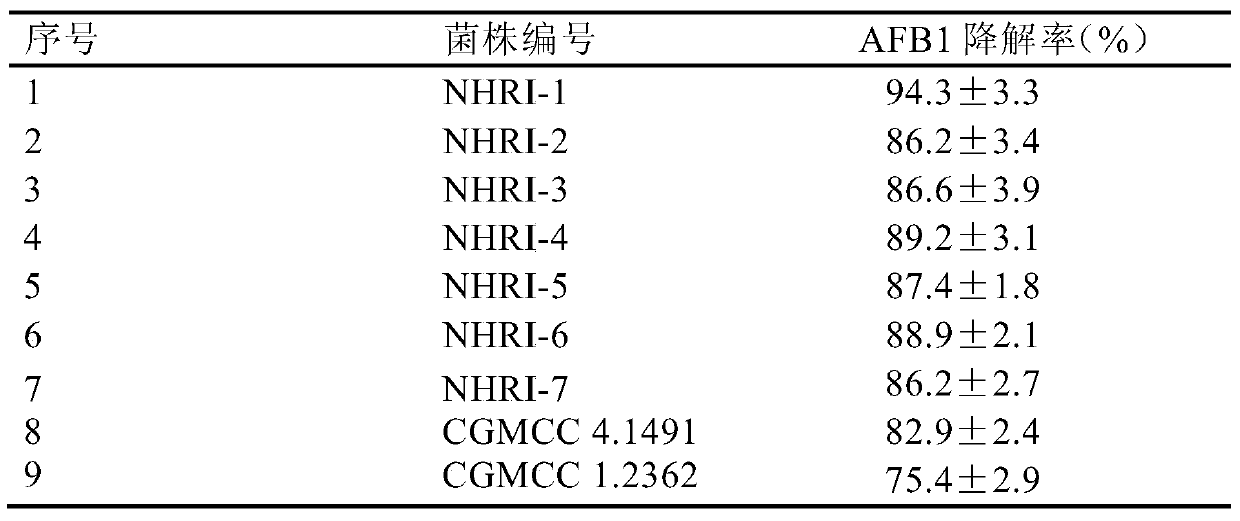
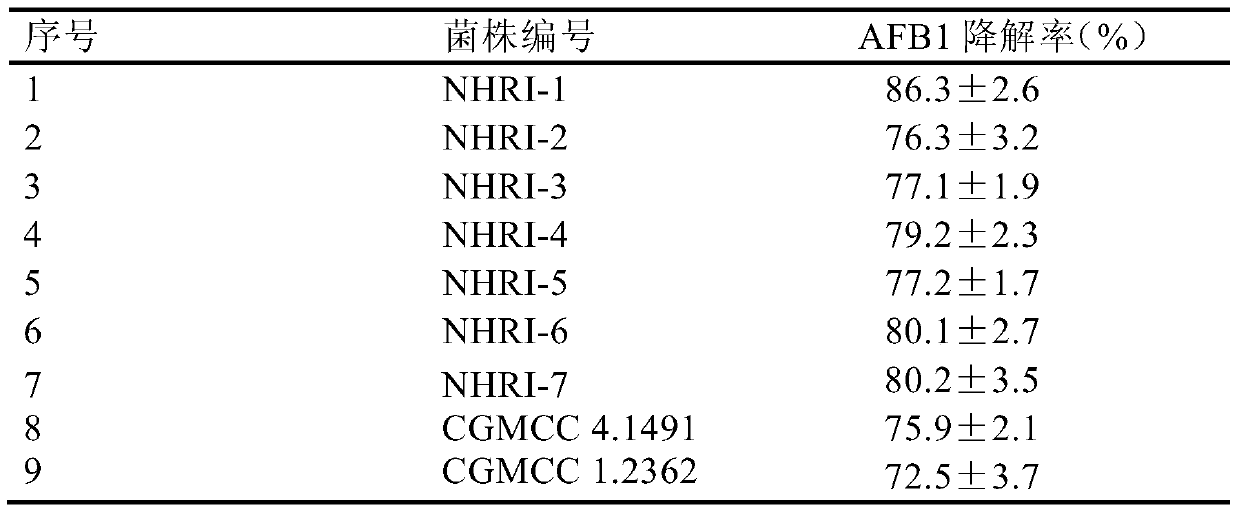
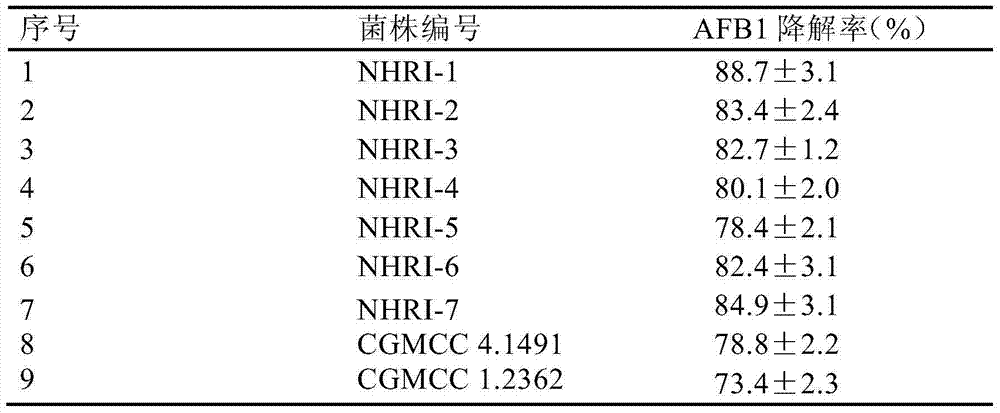
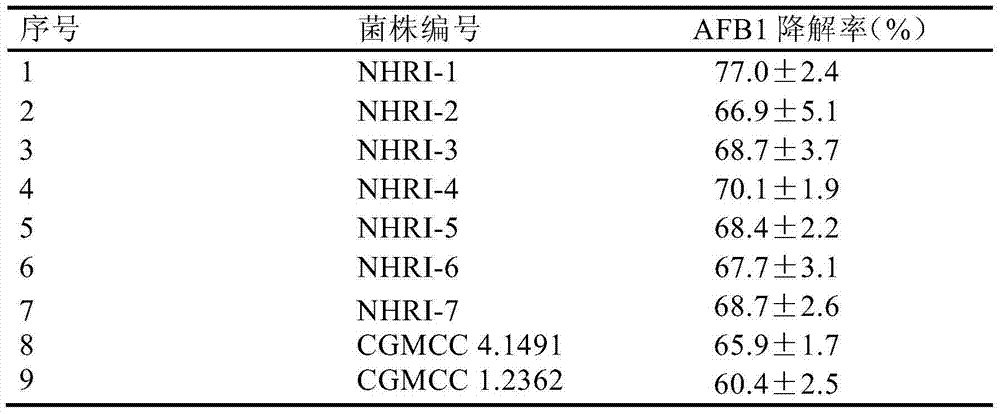
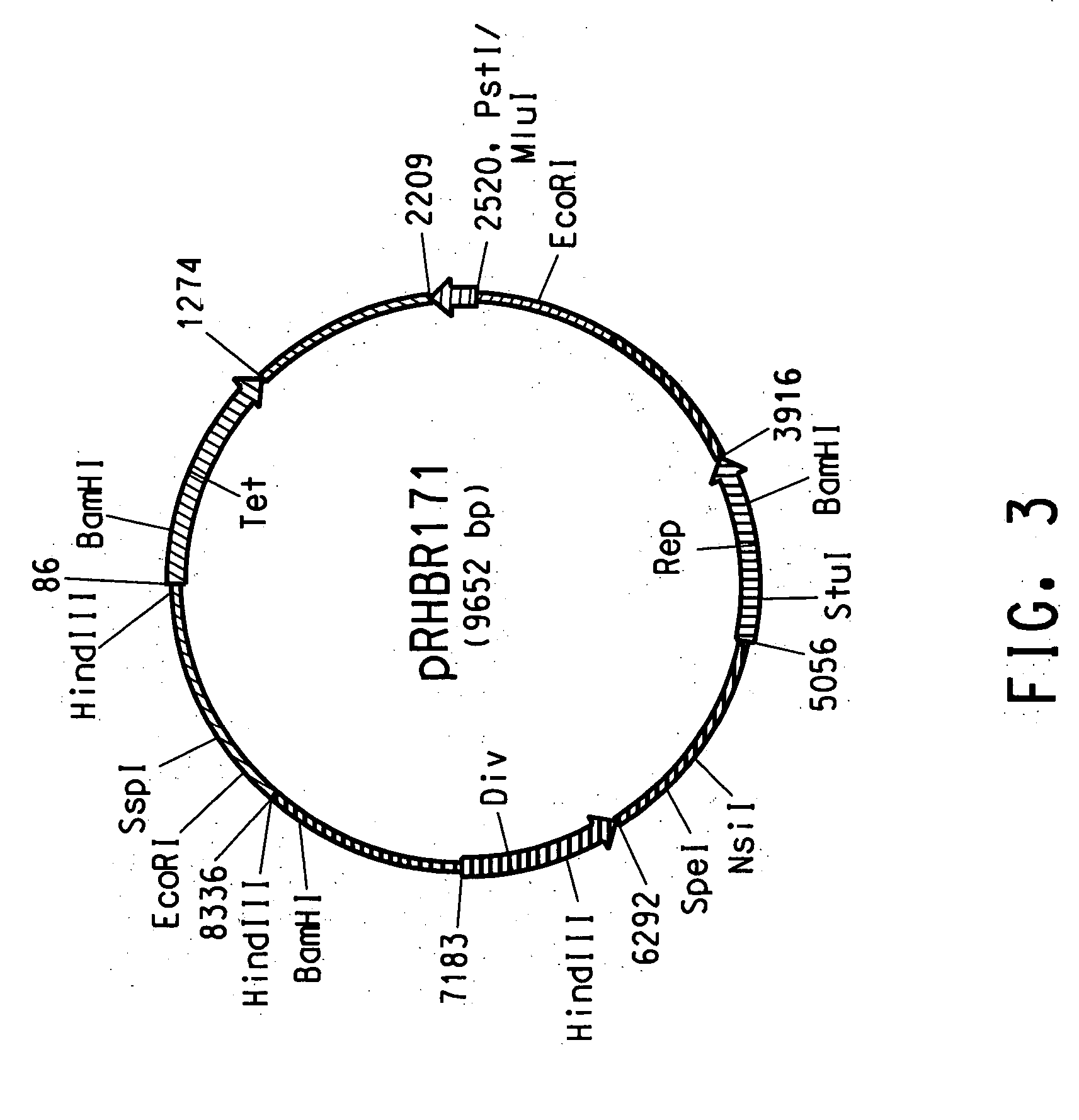
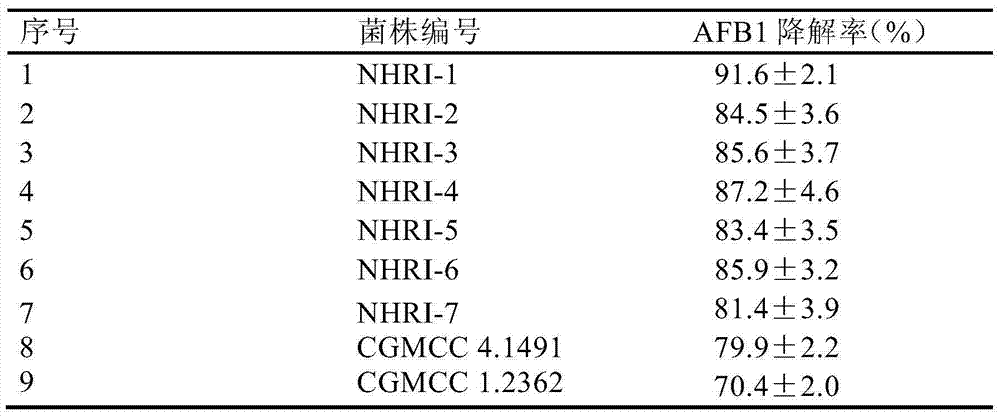
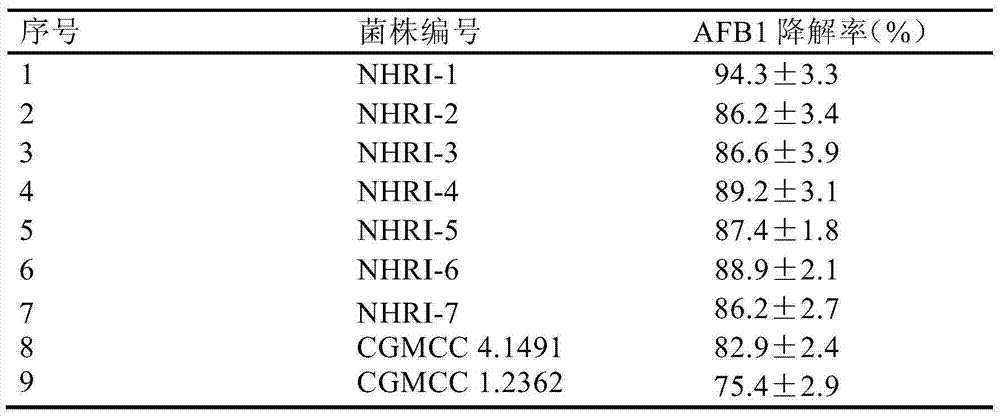
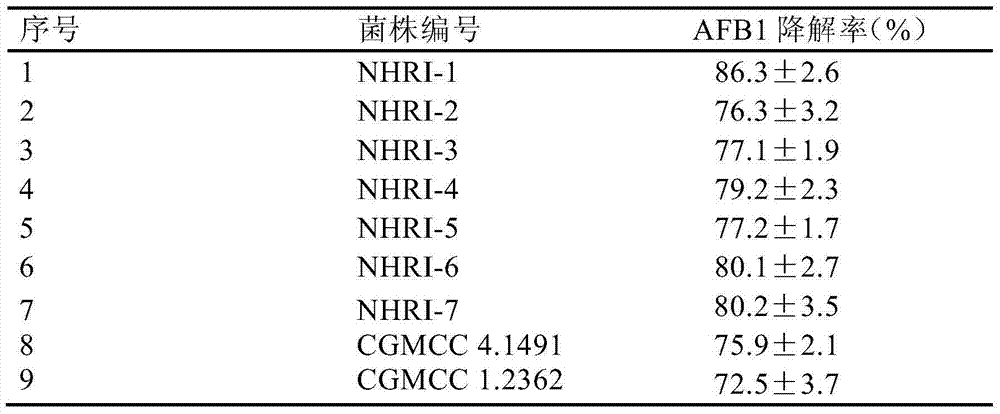
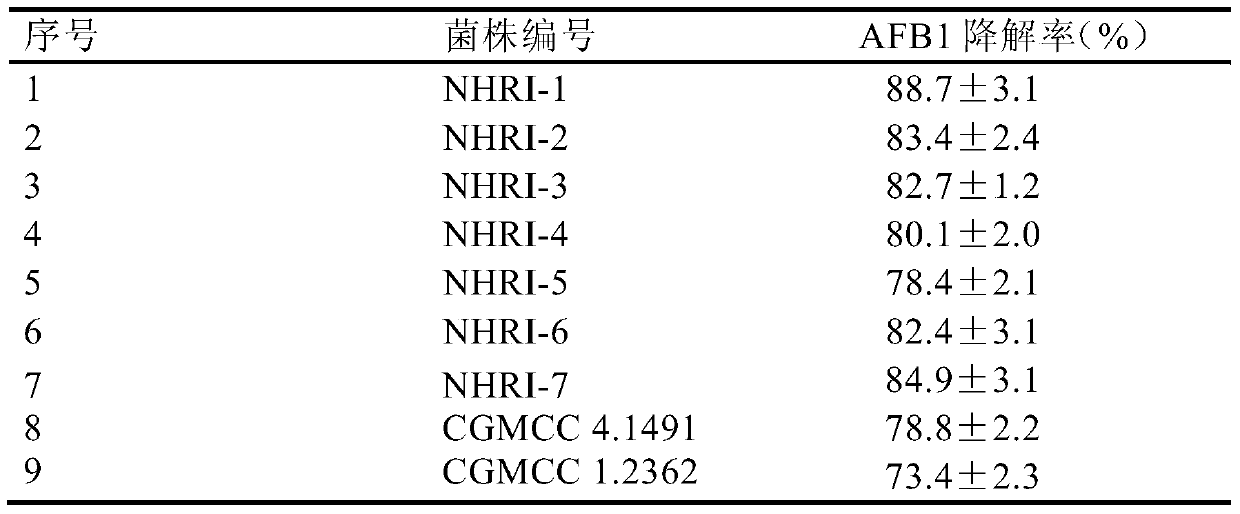
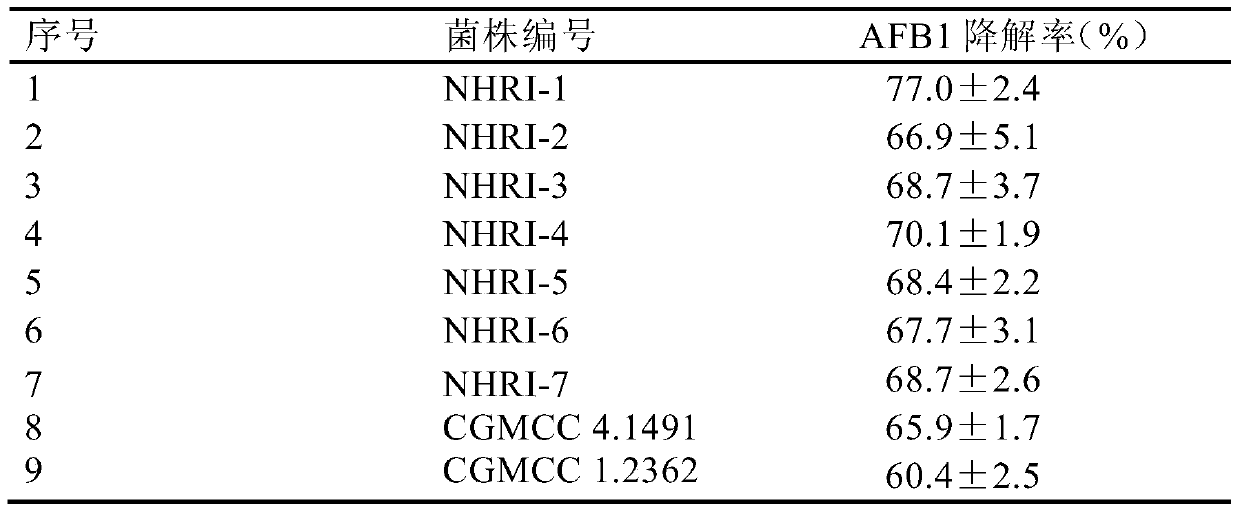
Separating, culturing and application methods for Rhodococcus erythropolis strain used for degrading aflatoxin B1
InactiveCN104745493ASolve the problems in the detoxification methodSimple processBacteriaMicroorganism based processesRhodococcus strainAflatoxin B
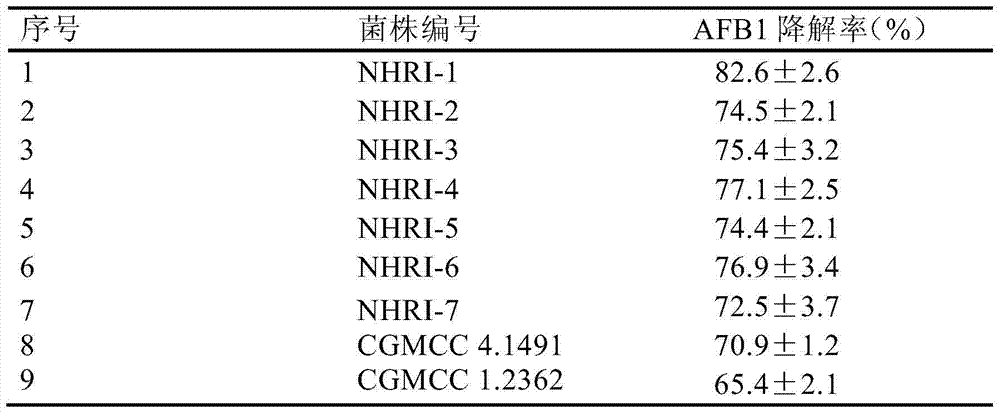
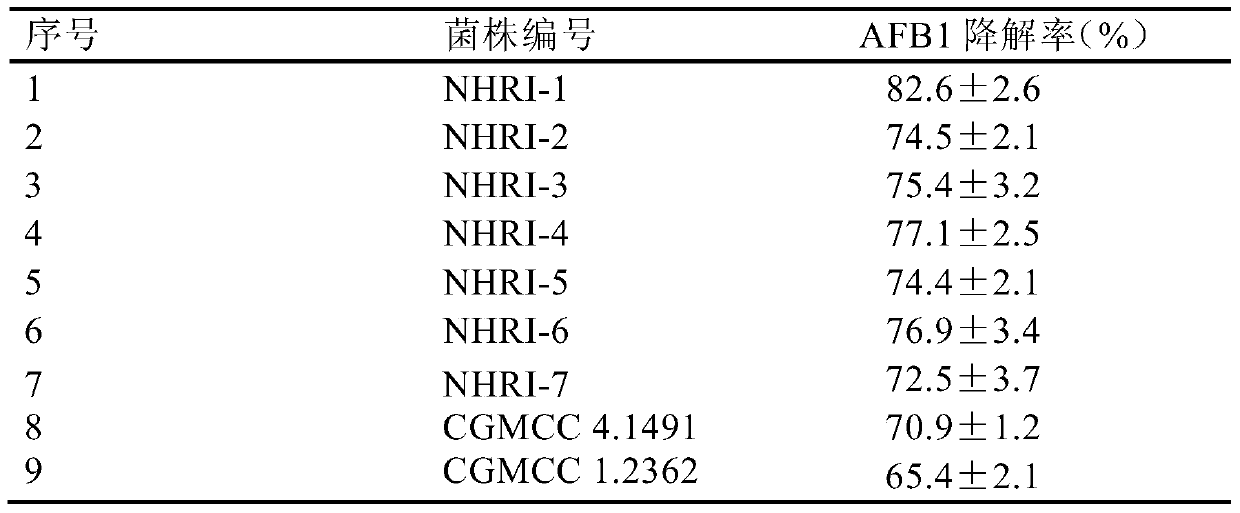
The invention relates to separating, culturing and application methods for a Rhodococcus erythropolis strain used for degrading aflatoxin B1 (AFB1), specifically to a separating method for the Rhodococcus erythropolis strain used for degrading AFB1, a culturing method for the Rhodococcus erythropolis strain obtained by using the separating method and a method for applying the Rhodococcus erythropolis strain in degradation of AFB1. The separating method for the strain has high specificity and high efficiency and is simple to operate; and the obtained Rhodococcus erythropolis strain has the advantages of a wide source, simple preparation, mild reaction conditions, high detoxification activity, etc.
Owner:COFCO NUTRITION & HEALTH RES INST +1
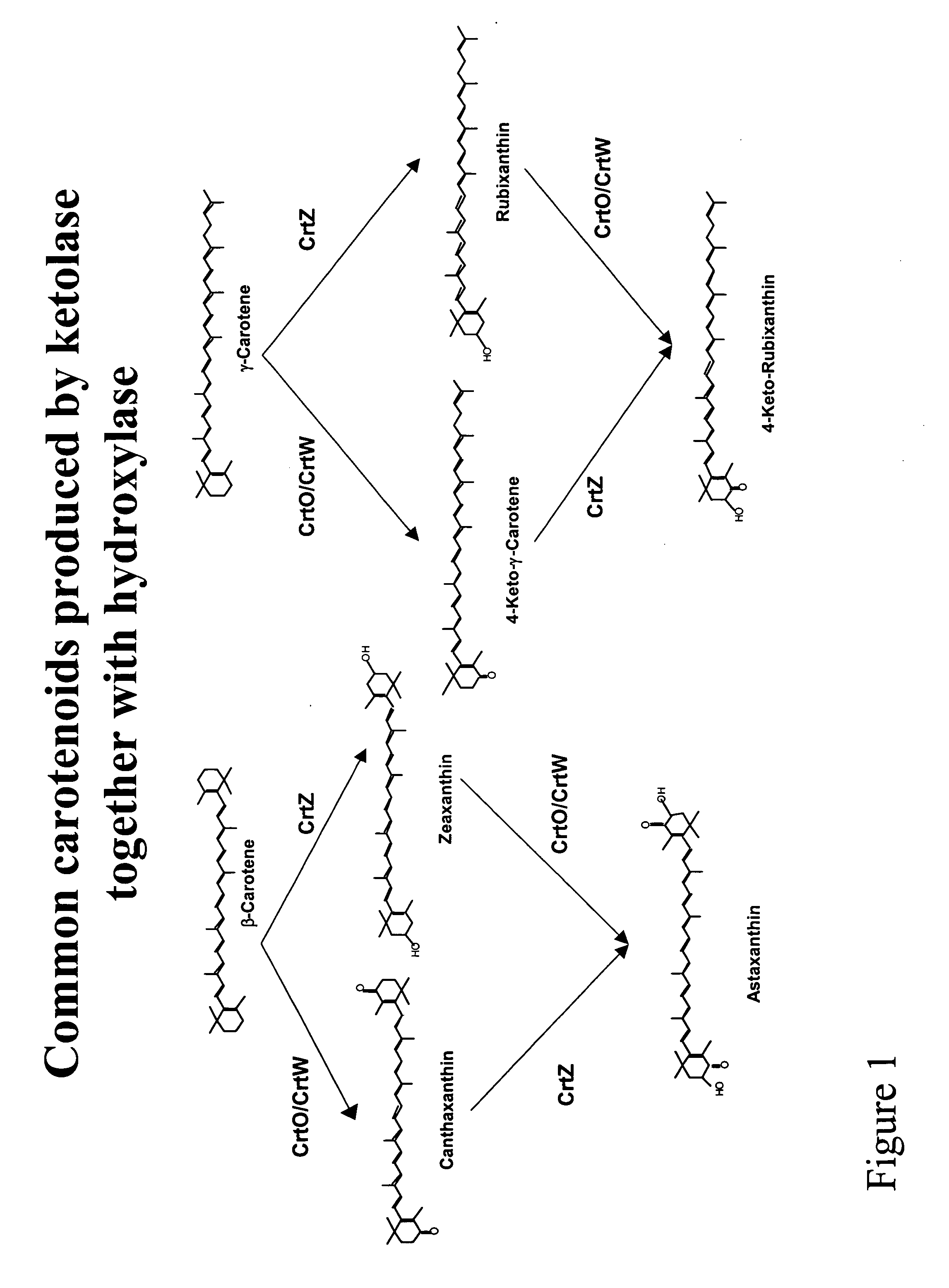
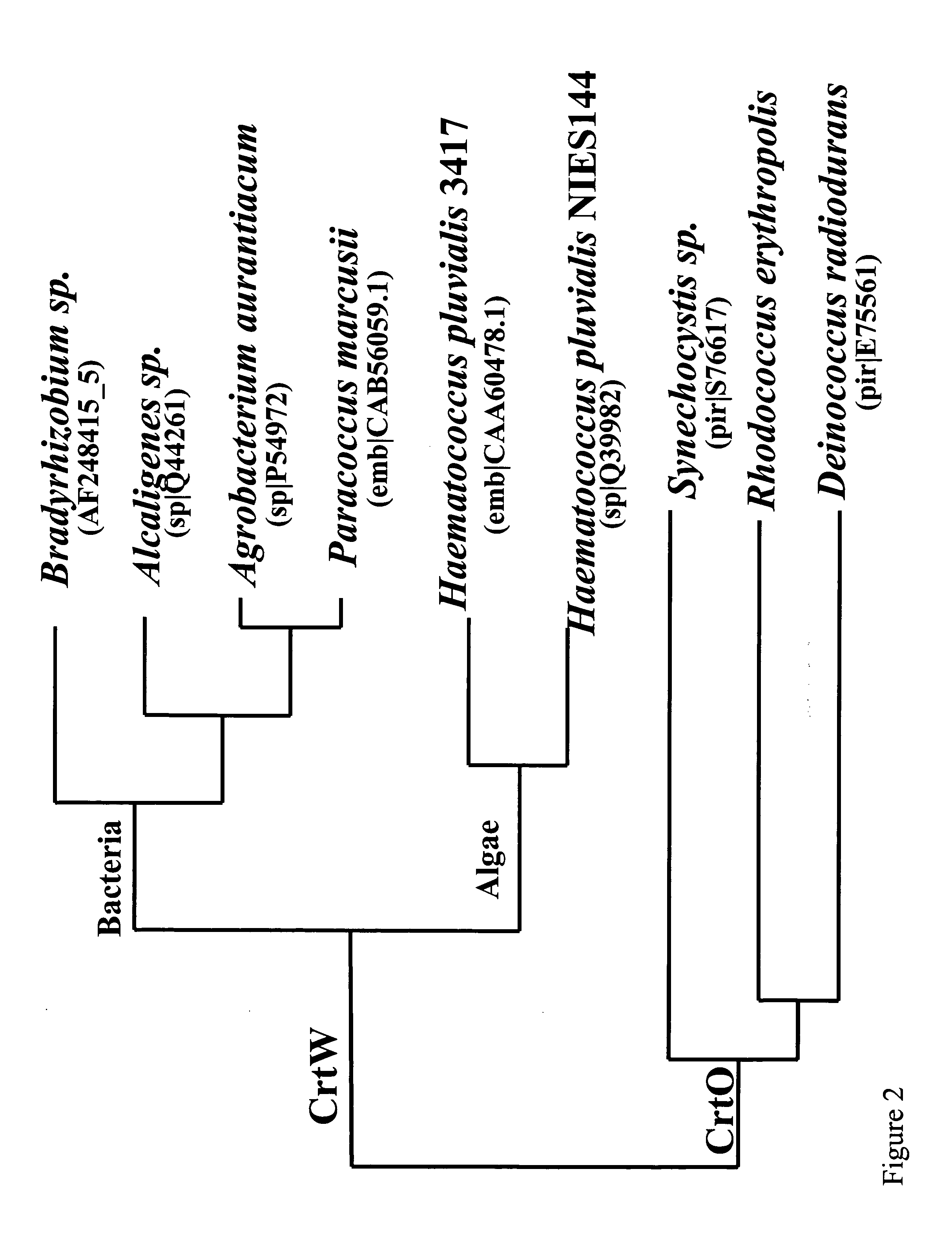
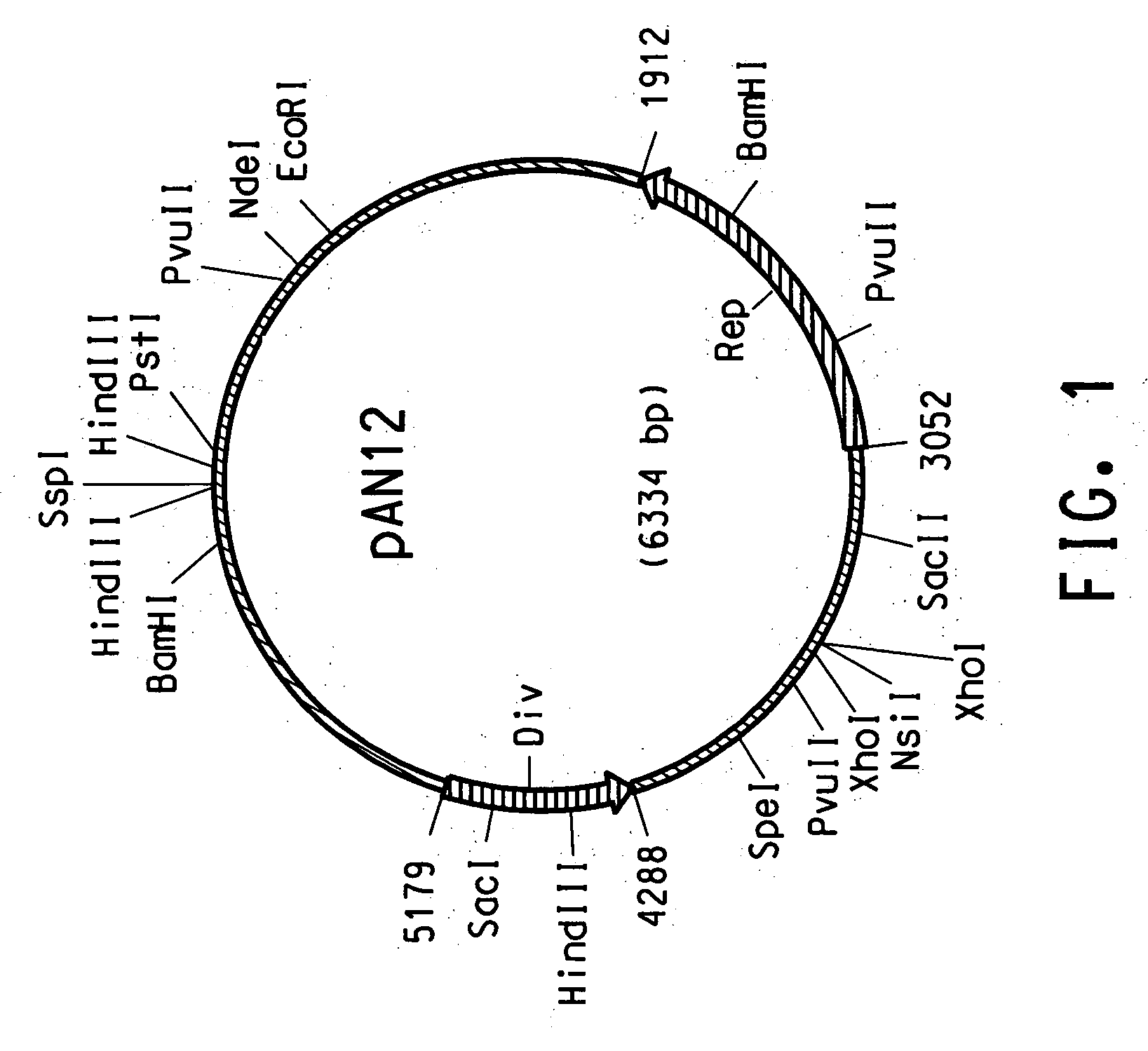
Carotenoid ketolase gene
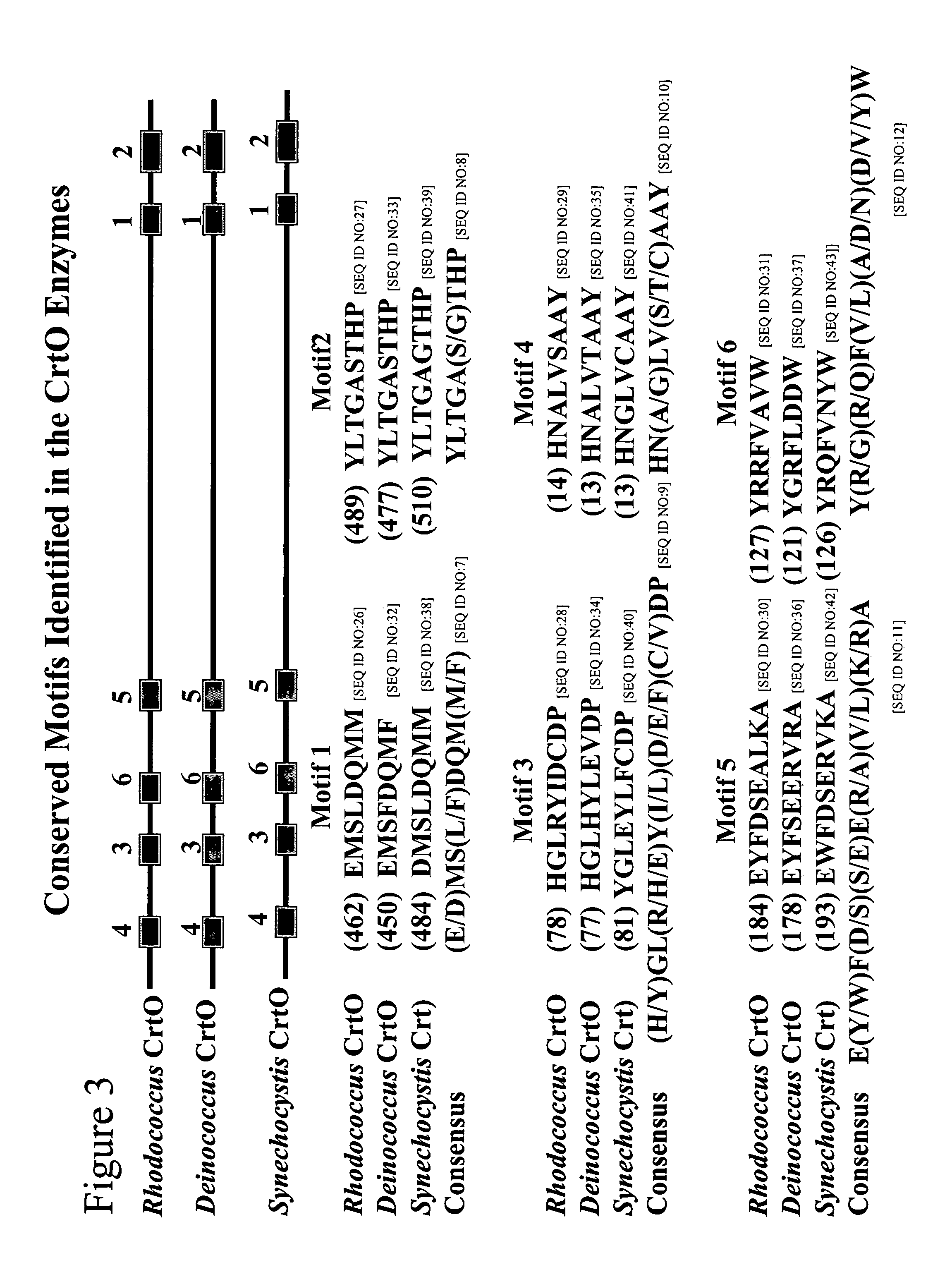
A ketolase gene has been isolated from Rhodococcus erythropolis AN12 strain encoding a carotenoid modification enzyme of the carotenoid biosynthetic pathway. The gene and gene product are the first isolated from a Rhodococcus strain. Six conserved amino acid motifs have been identified as the characteristic of this type of ketolase enzymes. The gene and gene product of the present invention may be used in a variety of ways for the production of keto-carotenoid compounds in a variety of organisms.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Application of a kind of Rhodococcus rhodochrous and its preparation in the remediation of pyrethroid pesticide pollution
ActiveCN114107095BEfficient bioremediationPromote bioremediationBacteriaWater contaminantsRhodococcus strainGermplasm
The invention discloses the application of Rhodococcus rhodochrous and its preparation in the remediation of pyrethroid pesticide pollution. The strain is the gram-positive bacterium Rhodococcus ruber strain Y14, and was deposited in the Guangdong Provincial Microbial Culture Collection Center on July 21, 2021, and the deposit number is GDMCC NO: 61813. The strain has significant biodegradation ability of pyrethroid insecticides, especially the highest activity to dextrofenothrin, and the number of bacterial cells is not less than 1.0×10. 6 CFU·mL ‑1 The suspension of 50mg·L in water after 6 days of treatment ‑1 D-Cyphenothrin is completely removed, and it also has a high-efficiency bioremediation effect on polluted soil. It provides a new idea to solve the problems of excessive pyrethroid pesticide residues and environmental pollution in agricultural production, and also enriches the germplasm resource bank of pesticide-degrading bacteria, which is of great practical importance for the production of non-toxic and pollution-free green agricultural products. Value.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
A strain of Rhodococcus spp. and its screening method and application
InactiveCN103966127BEasy to operatePromote degradationBacteriaWater contaminantsBiotechnologyRhodococcus strain
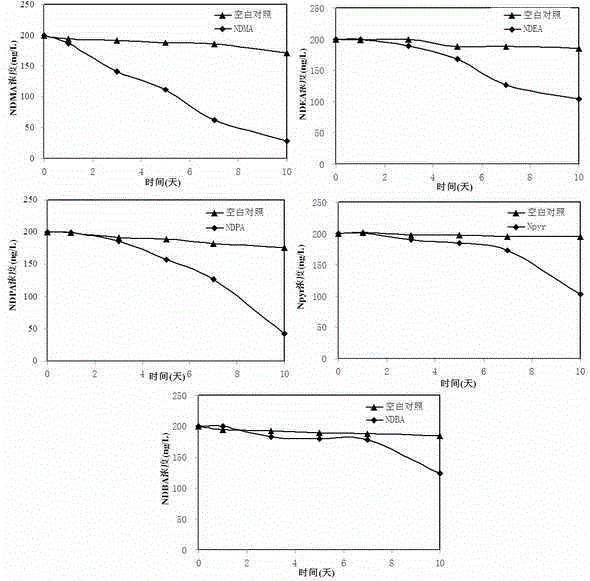
The invention discloses a rhodococcus strain and its screening method and application. The key points of the technical scheme of the present invention are: a strain of Rhodococcus Rhodococcus? cercidiphylli, preserved in the General Microorganism Center of China Microbiological Culture Collection Management Committee, the preservation number is: CGMCC? No. 9067. The invention also discloses the screening method of the Rhodococcus syringae and its application in degrading nitrosamines. The screening method of the rhodococcus strains of the present invention is simple and fast, and can be used in drinking water polluted by nitrosamines to degrade and remove nitrosamines, and carry out screening on drinking water polluted by nitrosamines. Biological treatment to reduce its health and safety risk level.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
Deep-sea actinomycete rhodococcus erythropolis and application thereof in inhibition of aflatoxin
The invention provides a deep-sea actinomycete strain capable of inhibiting synthesis of aflatoxin. The actinomycete strain is a rhodococcus erythropolis BC14-M2AF-1 strain, is separated from sediments at water depth of 6105 meters in West Pacific Ocean, is preserved in Guangdong Microbial Culture Collection Center, and has a preservation number of GDMCC No.61239. The BC14-M2AF-1 strain is fermented in a freshwater M2 culture medium, and the obtained fermented cell-free supernate can completely inhibit aflatoxin from the source of an aflatoxin synthesis route; and the fermentation cell-free supernate is treated at 121 DEG C and 103 kPa for 30 minutes at high temperature and high pressure, and synthesis of aflatoxin can still be inhibited by 100%. The rhodococcus erythropolis BC14-M2AF-1 strain and the fermentation product thereof can be used for effectively preventing and controlling aflatoxin pollution in field crop cultivation, grain storage, food and beverage processing, feed production and the like.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH AT WEIHAI +1
Application of Rhodococcus erythrococcus in degrading aflatoxin b1 in feed or its raw materials
ActiveCN104738363BSolve the problems in the detoxification methodSolve the real problemBacteriaMicroorganism based processesLiquid wasteRhodococcus strain
The invention relates to a method of microbial detoxication for aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) in feed or raw materials of the feed and uses, and particularly relates to a method of using rhodococcus erythropolis for detoxication of AFB1 in feed or raw materials of the feed and uses thereof. Efficient degradation detoxication of the AFB1 in the feed or the raw materials of the feed can be achieved by uniformly mixing target AFB1-containing feed or raw materials thereof with a rhodococcus erythropolis strain fermentation broth or a liquid supernatant of the fermentation broth and reacting. The method can reduce the content of the AFB1 in the feed or the raw materials of the feed in an efficient, mild and safe manner, and is low in energy consumption, low in equipment requirement, low in environment cleanliness requirement, free of need of continuous ventilation, low in waste liquid (dreg) yield, low in environment pollution, and particularly suitable for AFB1 detoxication in the field of feed processing.
Owner:COFCO NUTRITION & HEALTH RES INST +2
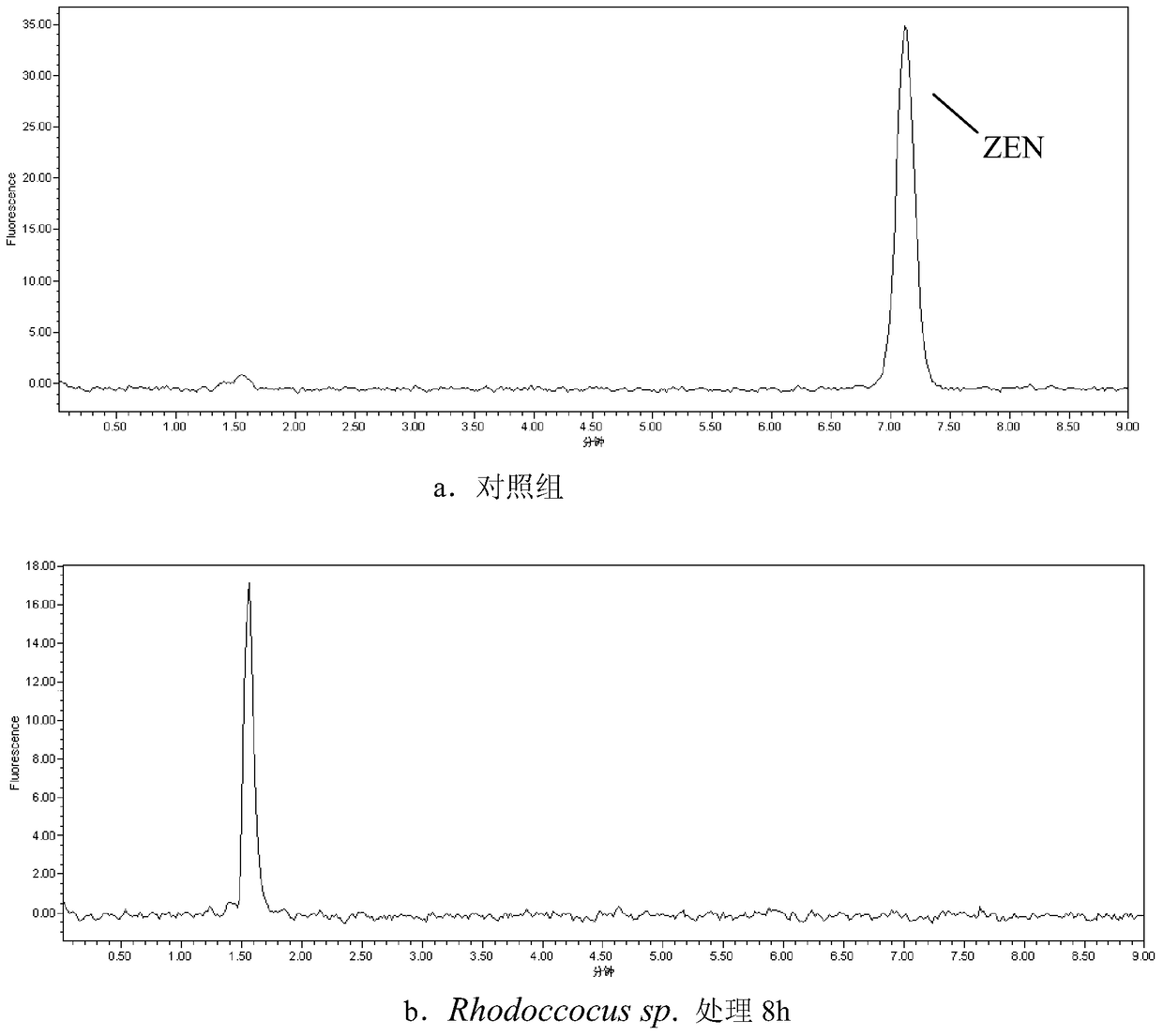
A strain of Rhodococcus and its application in degrading zearalenone
ActiveCN105154351BFast and efficient detoxification abilitySolve pollutionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesRhodococcus strainMicrobiology
Owner:ACAD OF NAT FOOD & STRATEGIC RESERVES ADMINISTRATION
Application of a kind of rhodococcus erythrococcus strain, bacterial preparation and its bacterial cell and extract
ActiveCN110184215BEnhanced immune functionEnhance anti-tumorBacteriaBacteria material medical ingredientsBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The present invention provides a strain of Rhodococcus ruber, a bacterial preparation and the application of its cells and extracts. The strain is Rhodococcus ruber FIM-12, which was preserved in China Microorganism Culture Collection on April 03, 2019 General Microbiology Center of the Management Committee, the preservation number is CGMCC No.17525; it can be used for microbial fermentation to prepare Rhodococcus cells and their extracts: Rhodococcus ruber (Rhodococcus ruber) FIM‑12 is fermented and cultured to collect bacterial cells and wash with purified water Wet cells are obtained; the wet cells are repeatedly frozen and thawed combined with ultrasonic breaking, and then extracted with absolute ethanol to obtain the Rhodococcus erythrococcus extract. The rhodococcus erythrococcus strain of the invention can be applied to industrial fermentation production to prepare rhodococcus erythrococcus cells and extracts of the rhodococcus erythrococcus. The prepared product has the functions of improving immune activity and tumor inhibition, and can be used as a production strain for further research and development.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF MICROBIOLOGY
Application of rhodococcus erythropolis in degrading aflatoxin B1 in brewing seasoning or raw materials
ActiveCN104738362ASolve the problems in the detoxification methodReduce outputFood preparationMicroorganismRhodococcus strain
The invention relates to a method for microorganism detoxifying of aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) in brewing seasoning or its raw materials and an application thereof. Specifically, the invention relates to a method for detoxifying AFB1 in brewing seasoning or its raw materials and an application thereof. By uniformly mixing the target AFB1-containing brewing seasoning or its raw materials with a rhodococcus erythropolis strain fermentation broth or its fermentation broth supernatant, ventilating and fully reacting, AFB1 in the brewing seasoning or its raw materials can be efficiently degraded and detoxified. By the method of degrading AFB1 in the brewing seasoning or its raw materials, content of AFB1 in the brewing seasoning or its raw materials can be efficiently, mildly and safely reduced. In addition, energy consumption is low, requirements for equipment are low, output of wastewater (waste residue) is low, and environmental pollution is low. The method provided by the invention is especially suitable for detoxification of AFB1 in brewing seasoning or its raw materials.
Owner:COFCO NUTRITION & HEALTH RES INST +2
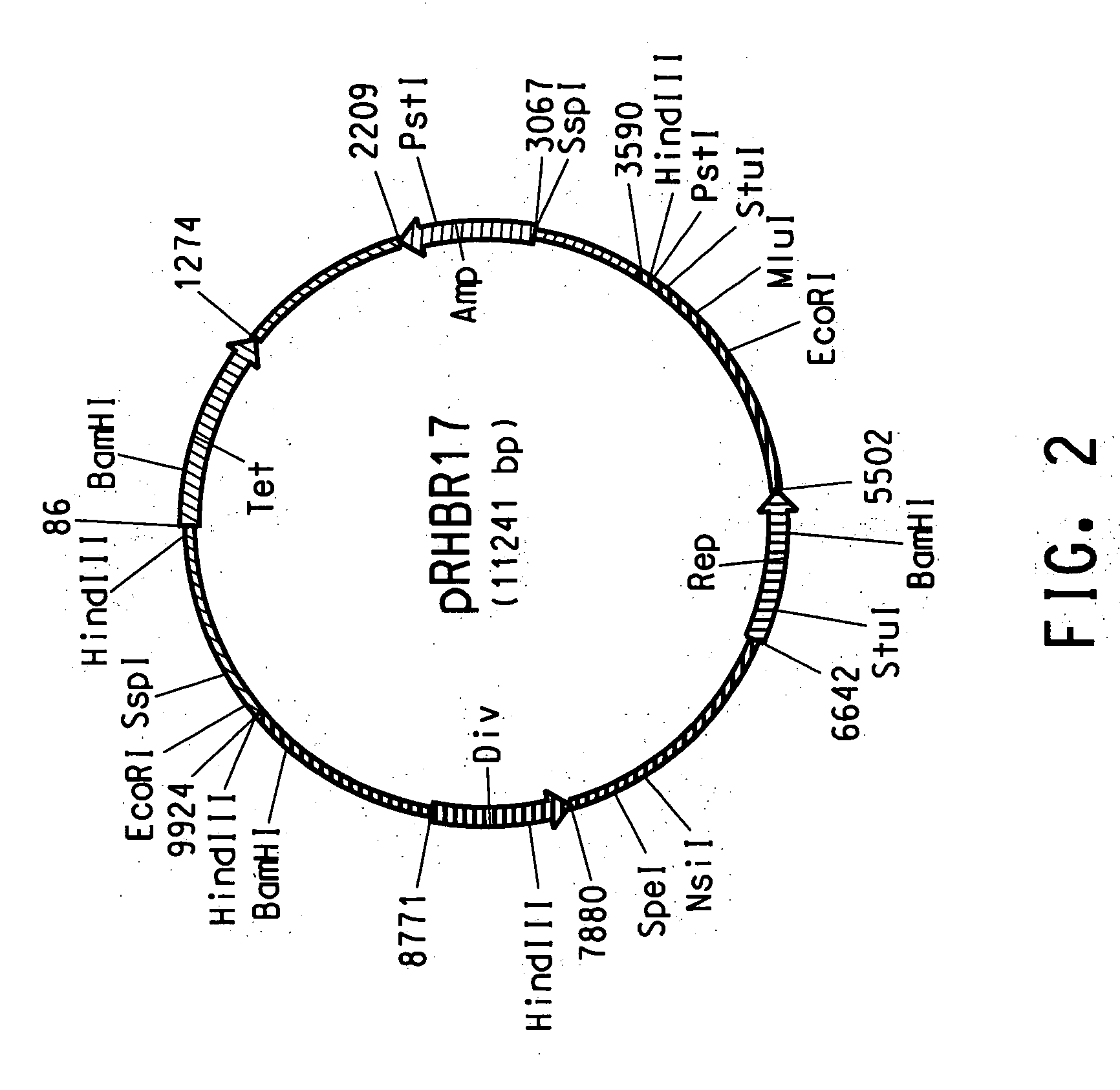
Rhodococcus cloning and expression vectors
InactiveUS20050170420A1Maintain relatively stableBacteriaSugar derivativesHeterologousRhodococcus strain
A plasmid has been isolated from Rhodococcus erythropolis strain AN12 comprising a unique replication protein. The replication protein may be used in a variety of cloning and expression vectors and particularly in shuttle vectors for the expression of heterologous genes in Rhodococcus sp.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Uses of rhodococcus erythropolis in degradation of aflatoxin B1 in feed or raw materials of the feed
ActiveCN104738363ASolve the problems in the detoxification methodSolve the real problemBacteriaAnimal feeding stuffLiquid wasteRhodococcus strain
The invention relates to a method of microbial detoxication for aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) in feed or raw materials of the feed and uses, and particularly relates to a method of using rhodococcus erythropolis for detoxication of AFB1 in feed or raw materials of the feed and uses thereof. Efficient degradation detoxication of the AFB1 in the feed or the raw materials of the feed can be achieved by uniformly mixing target AFB1-containing feed or raw materials thereof with a rhodococcus erythropolis strain fermentation broth or a liquid supernatant of the fermentation broth and reacting. The method can reduce the content of the AFB1 in the feed or the raw materials of the feed in an efficient, mild and safe manner, and is low in energy consumption, low in equipment requirement, low in environment cleanliness requirement, free of need of continuous ventilation, low in waste liquid (dreg) yield, low in environment pollution, and particularly suitable for AFB1 detoxication in the field of feed processing.
Owner:COFCO NUTRITION & HEALTH RES INST +2
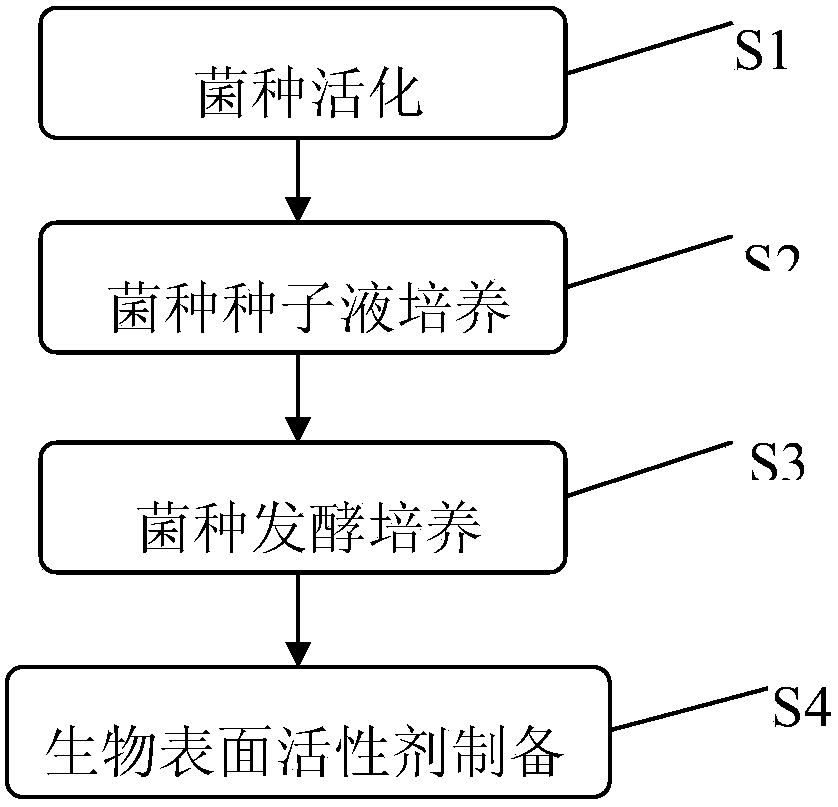
A kind of preparation method of rhodococcus producing surfactant
ActiveCN104988182BGood emulsificationSimple processMicroorganism based processesFermentationOrganic solventRhodococcus strain
The invention discloses a preparation method for a surfactant produced from rhodococcus; the rhodococcus isolated and screened from the mud of the coastal beach is utilized, and is fermented to produce the surfactant; the technical steps comprise strain activation, strain seed liquid culture, strain fermentation culture and biosurfactant preparation; rhodococcus strain is firstly inoculated into solid fermentation medium for activating, and then is inoculated into liquid fermentation medium to obtain seed liquor; the seed liquor is inoculated into the liquid fermentation medium to obtain fermentation culture liquid, and then acid precipitation, centrifugal separation, organic solvent extraction and rotary evaporation are performed on the fermentation culture liquid; a biosurfactant finished product with high surface activity is prepared. The preparation method for the surfactant produced from the rhodococcus has a simple preparation technology, good emulsification on petroleum, good market application potential, and is convenient for popularization and application.
Owner:TIANJIN SEA WATER DESALINATION & COMPLEX UTILIZATION INST STATE OCEANOGRAPHI
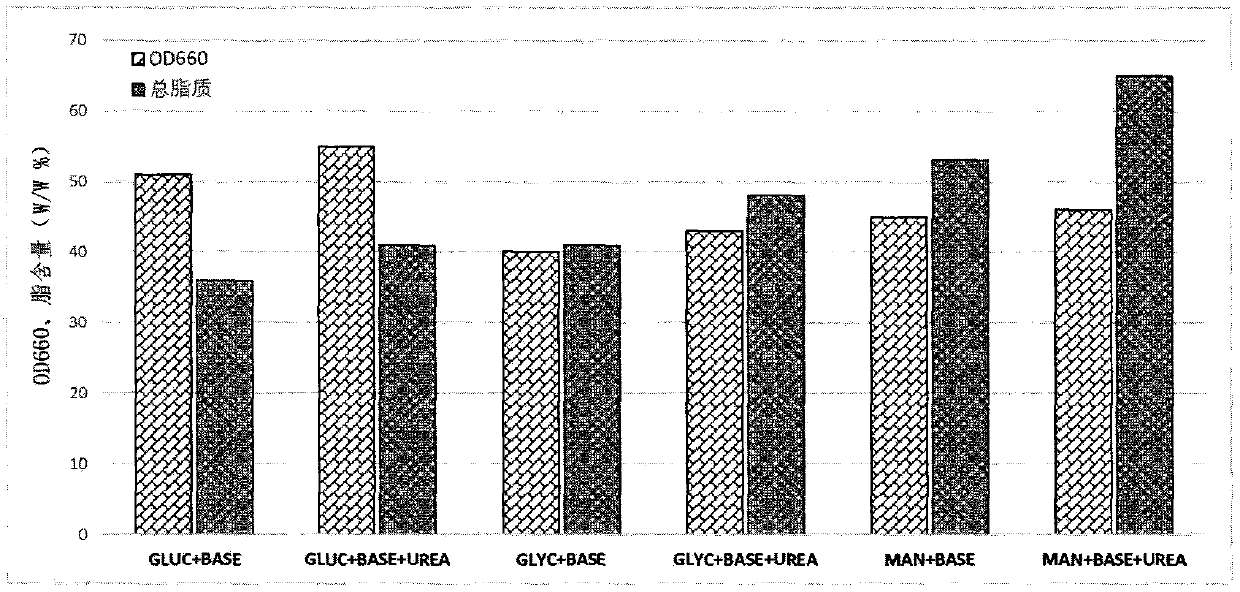
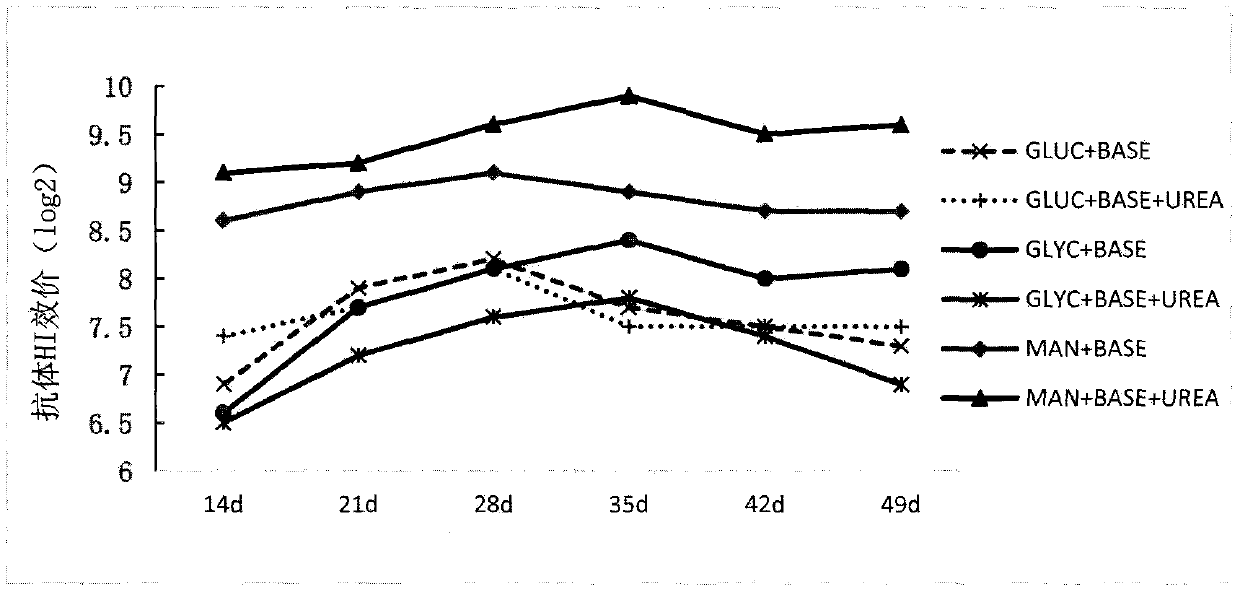
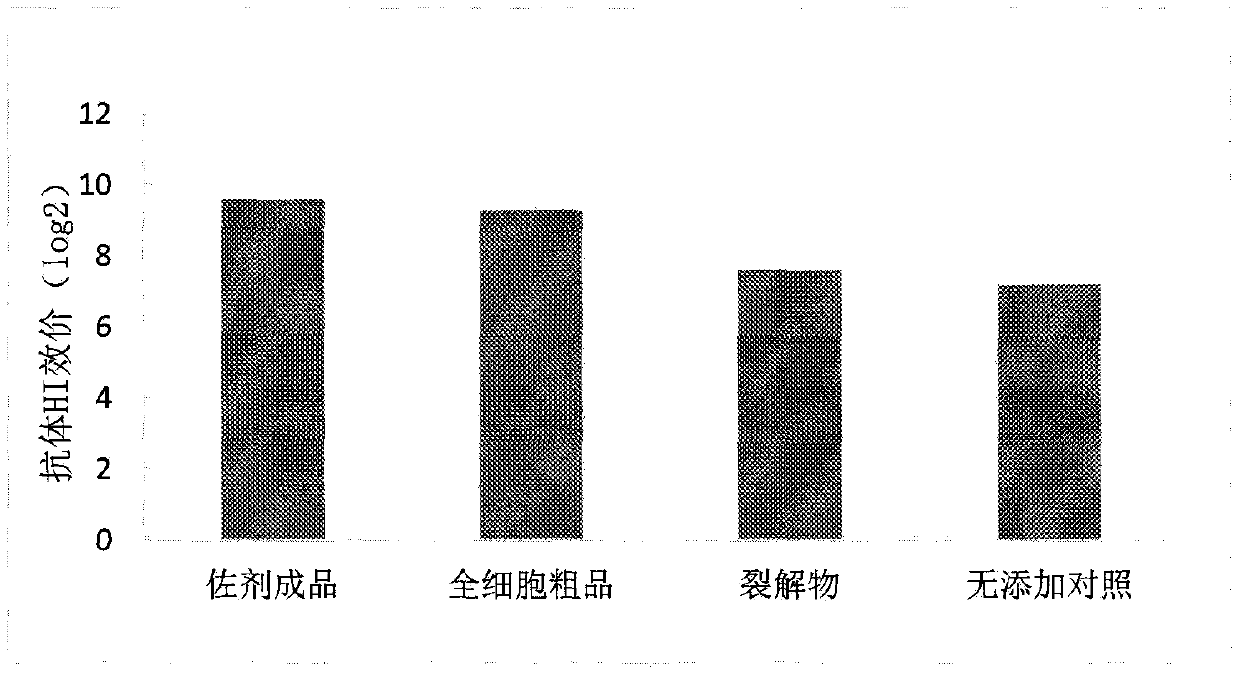
A kind of fermentation method of rhodococcus and its application as adjuvant in animal vaccine
ActiveCN109666609BUnusual humoral immunomodulatory effectsImprove securityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyRhodococcus strain
The present invention relates to a unique fermentation process of Rhodococcus ruber (CGMCC NO.17012 Rhodococcus ruber.GD0704A) and its preparation process of different formulation adjuvants and its use as an adjuvant in animal vaccines. The Rhodococcus strain is isolated from a farm and passed through The single bacterium colony is purified and identified, and the invention provides a special fermentation process when the inactivated product of the strain is used as an animal vaccine adjuvant, and provides a preparation process for adjuvants in different dosage forms containing the strain and its products. Animal experiments have confirmed that when the adjuvant products prepared by the above process are used in monovalent or multivalent animal vaccines, especially inactivated Newcastle disease vaccines, inactivated avian influenza vaccines, and live swine fever vaccines, they have clear non-specific immune enhancement The specific performance is that the peak level of antibodies induced by animal vaccines is significantly increased, the time to produce protective antibody levels is advanced, the maintenance period of antibodies is prolonged, and the immune effect of animal vaccines is enhanced.
Owner:刘春郁
A strain of Rhodococcus erythrococcus and its application in wastewater treatment containing organic pollutants
ActiveCN103627653BGood removal effectBroad degradation spectrumBacteriaWater contaminantsRhodococcus strainEcological environment
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL SCI RES & DESIGN INST OF ZHEJIANG PROVINCE
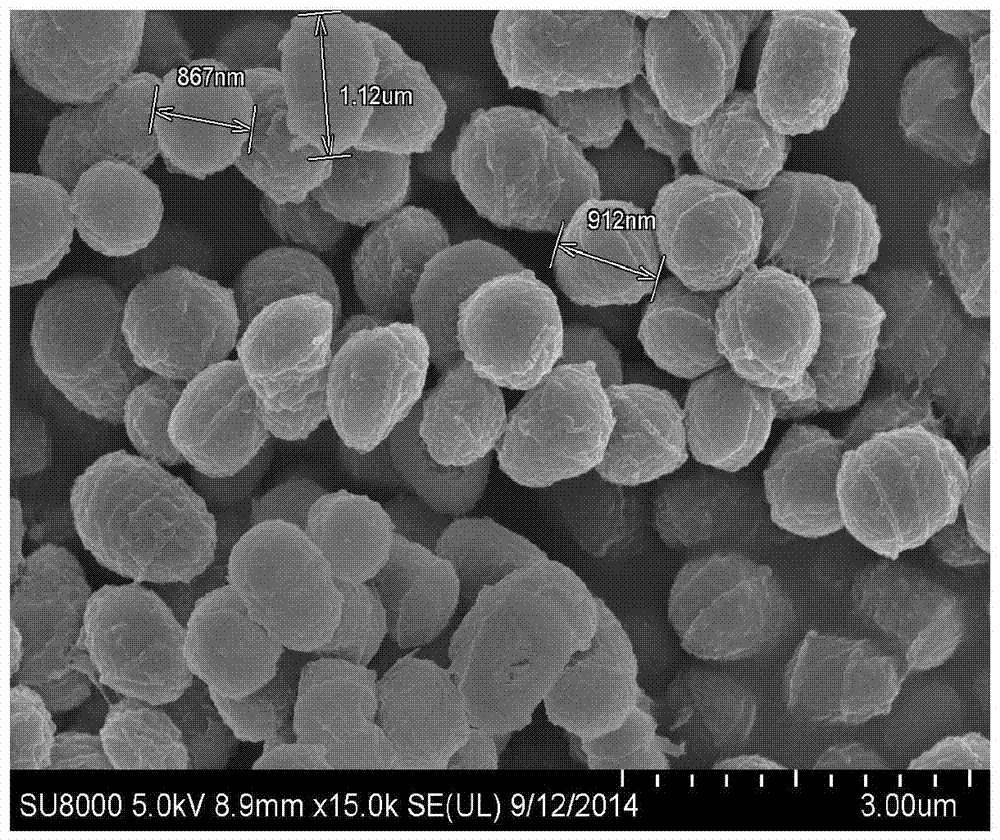
Rhodococcus strains and their applications
ActiveCN104673710BStrong ability to degrade phenolAdaptableBacteriaWater contaminantsMicroorganismRhodococcus strain
The invention discloses a Rhodococcus strain and its application, which belongs to the field of environmental microorganism application. The strain is named as Rhodococcus sp. C M‑H Z X 1 and is now preserved in the China Center for Typical Culture Collection (C C T C C for short). The number is C C T C C N O: M 2014329, and the deposit date is July 9, 2014. Rhodococcus C M-H Z X 1 provided by the invention has a strong ability to degrade phenol, and the degradation rate reaches 93.6% after 24 hours of 0.5g / L phenol degradation, and more than 90% after 48 hours of 1.5g / L phenol degradation; the bacterial strain The invention can tolerate 4% salinity and has strong adaptability; the invention has high efficiency in the biological treatment of phenolic waste water and has broad application prospects.
Owner:浙江至美环境科技有限公司
Application of Rhodococcus erythrococcus in degrading aflatoxin b1 in brewing seasoning or its raw materials
ActiveCN104738362BSolve the problems in the detoxification methodReduce outputBacteriaFood scienceMicroorganismRhodococcus strain
Owner:COFCO NUTRITION & HEALTH RES INST +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com