Separating, culturing and application methods for Rhodococcus erythropolis strain used for degrading aflatoxin B1
A technology of Rhodococcus rhodochrous and aflatoxin is applied in the field of culturing Rhodococcus erythropolis, which can solve the problems of low toxin removal efficiency, low toxin degradation efficiency, complicated degradation operation process, etc., and achieves high detoxification activity. , the effect of solving the source of raw materials and simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0060] Example 1 Preliminary screening and preliminary identification of Rhodococcus strains that degrade AFB1
[0061] Using moldy grains (a mixture of moldy peanuts, corn, rice and sorghum) as materials, the PBS gradient dilution separation method was used for primary screening using the primary screening medium with AFB1 as the only carbon source. The specific operation is:
[0062] Use PBS (0.01mol / L) to prepare AFB1 solution with a concentration of 3.00% as component B of the primary screening medium, filter and sterilize; Sodium dihydrogen 0.25%, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 0.20%, magnesium sulfate 0.05%, sodium nitrate 0.30%, agar 1.50%; pH7.2; 121 ℃ autoclave for 20min) uniformly mixed according to the volume ratio of 1:9 to prepare the primary screening The medium was poured onto the plate, and the final concentration of AFB1 in the primary screening medium was 0.3%.
[0063] Use PBS (0.01mol / L) to prepare PBS moldy grain sample dilutions with different concentra...
Embodiment 2
[0066] Example 2 Re-screening and identification of Rhodococcus strains that degrade AFB1
[0067] Use PBS (0.01mol / L) to prepare AFB1 solution with a concentration of 3.00% as component B of the re-screening medium, filter and sterilize; , sodium chloride 0.50%; pH7.2; 121°C autoclave for 20 minutes) were uniformly mixed according to the volume ratio of 1:9 to prepare a re-screening liquid medium, and the final concentration of AFB1 in the medium was 0.3%.
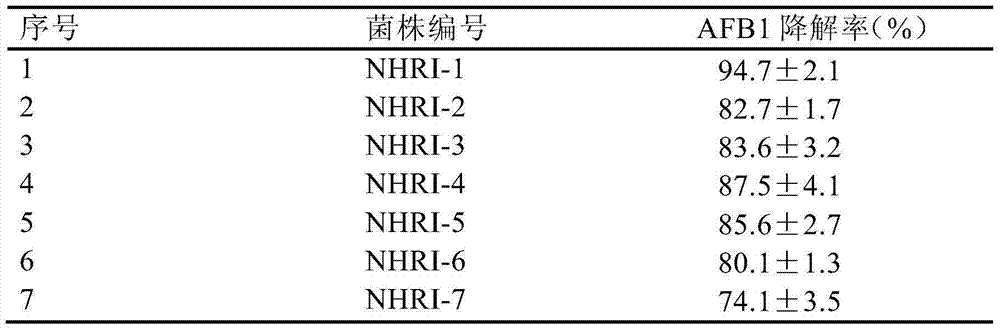
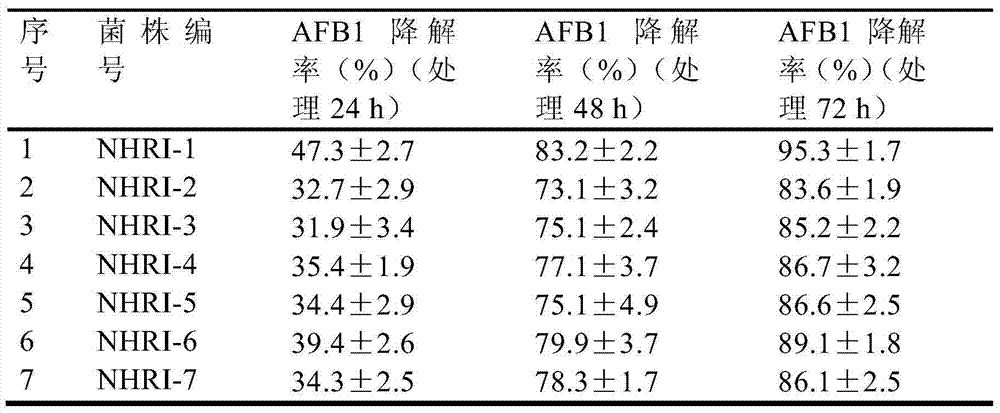
[0068] The refrigerated colonies of 7 strains of Rhodococcus erythropolis strains NHRI-1, NHRI-2, NHRI-3, NHRI-4, NHRI-5, NHRI-6 and NHRI-7 obtained in Example 1 were respectively inoculated in 5.0 In mL of re-screened liquid medium, the re-screened liquid medium without adding bacteria was used as a blank control, placed in a constant temperature shaker, and cultured at 30°C and 100r / min for 72h.
[0069] After the cultivation, the concentration of AFB1 in the re-screening medium was detected by HPLC-MS, and the degrada...
Embodiment 3
[0081] Example 3 Preservation and Preservation of Rhodococcus Rhodococcus Strains Degrading AFB1
[0082] Inoculate the pure colonies of seven identified strains of Rhodococcus erythropolis into solid medium (composition: 1.00% peptone, 0.50% beef extract, 0.50% glucose, 0.50% sodium chloride, 1.50% agar; pH7.2- 7.4) Incubate on a plate for 72 hours in a 30°C incubator, and verify its purity by microscopy. Pick a single colony with a purity ≥ 99.5% and transfer it to a test tube for slant culture, then refrigerate for use, and store a backup copy of the strain in a glycerol tube, and store it at -80°C for low temperature storage.
[0083] In addition, the seven identified Rhodococcus strains NHRI-1, NHRI-2, NHRI-3, NHRI-4, NHRI-5, NHRI-6 and NHRI-7 were deposited on December 17, 2013 at General Microbiology Center (CGMCC), China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms, the preservation numbers are CGMCC No.8590, CGMCC No.8591, CGMCC No.8592, CGMCC No.8593, CGMCC No...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com