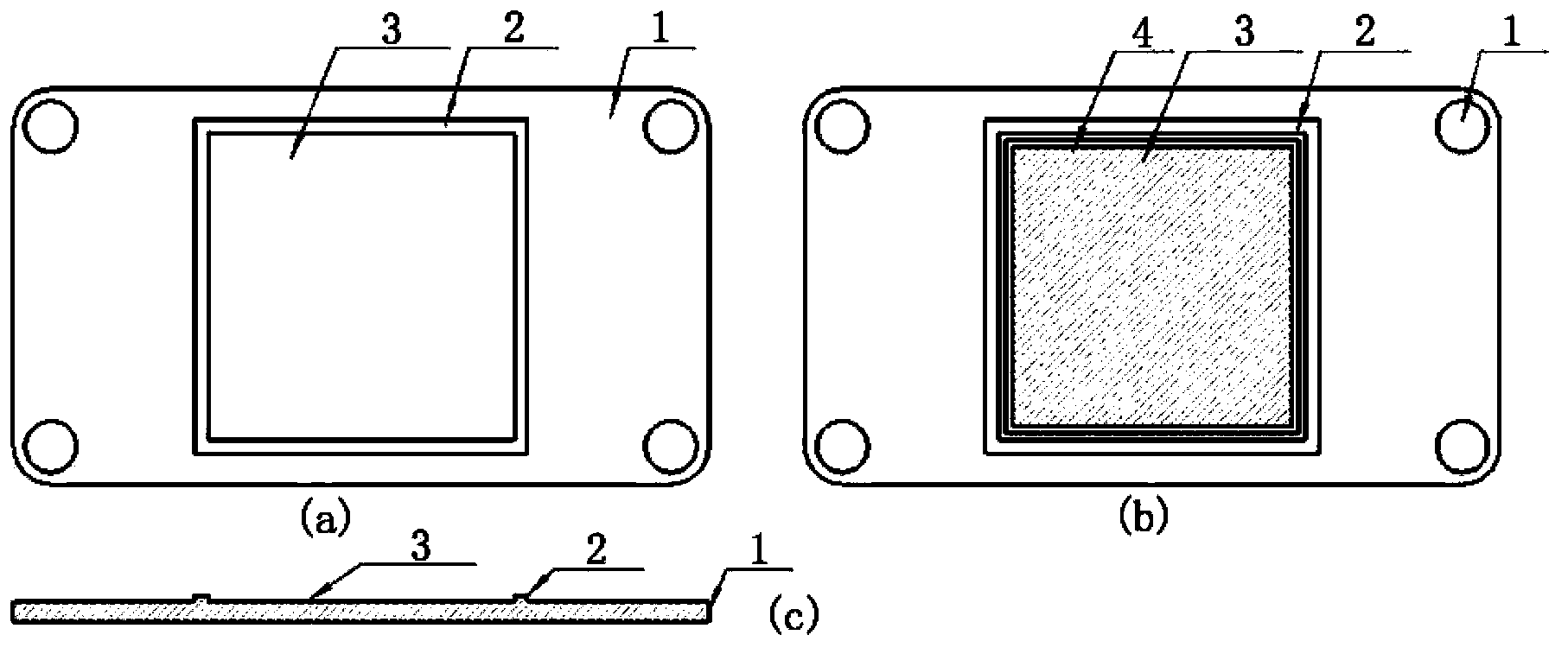
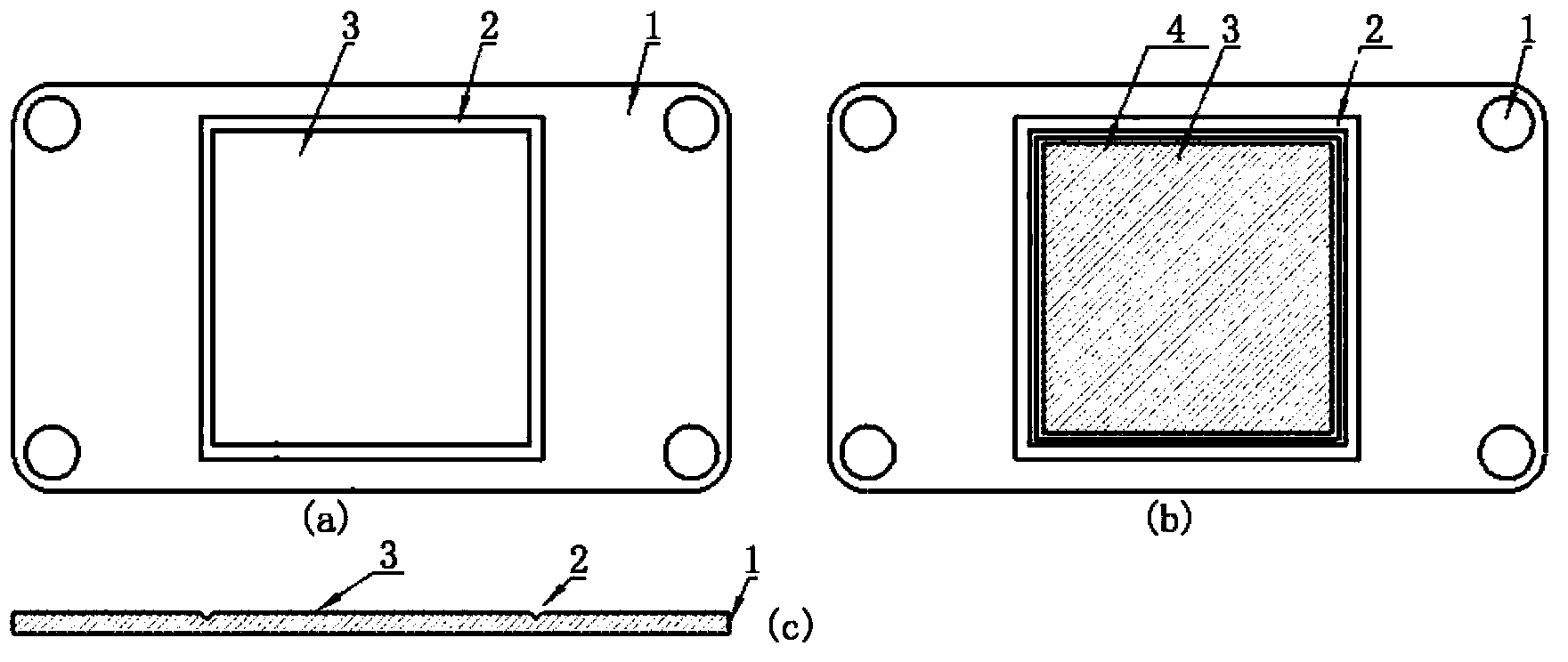
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
118 results about "Power cycling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Power cycling is the act of turning a piece of equipment, usually a computer, off and then on again. Reasons for power cycling include having an electronic device reinitialize its set of configuration parameters or recover from an unresponsive state of its mission critical functionality, such as in a crash or hang situation. Power cycling can also be used to reset network activity inside a modem. It can also be among the first steps for troubleshooting an issue.
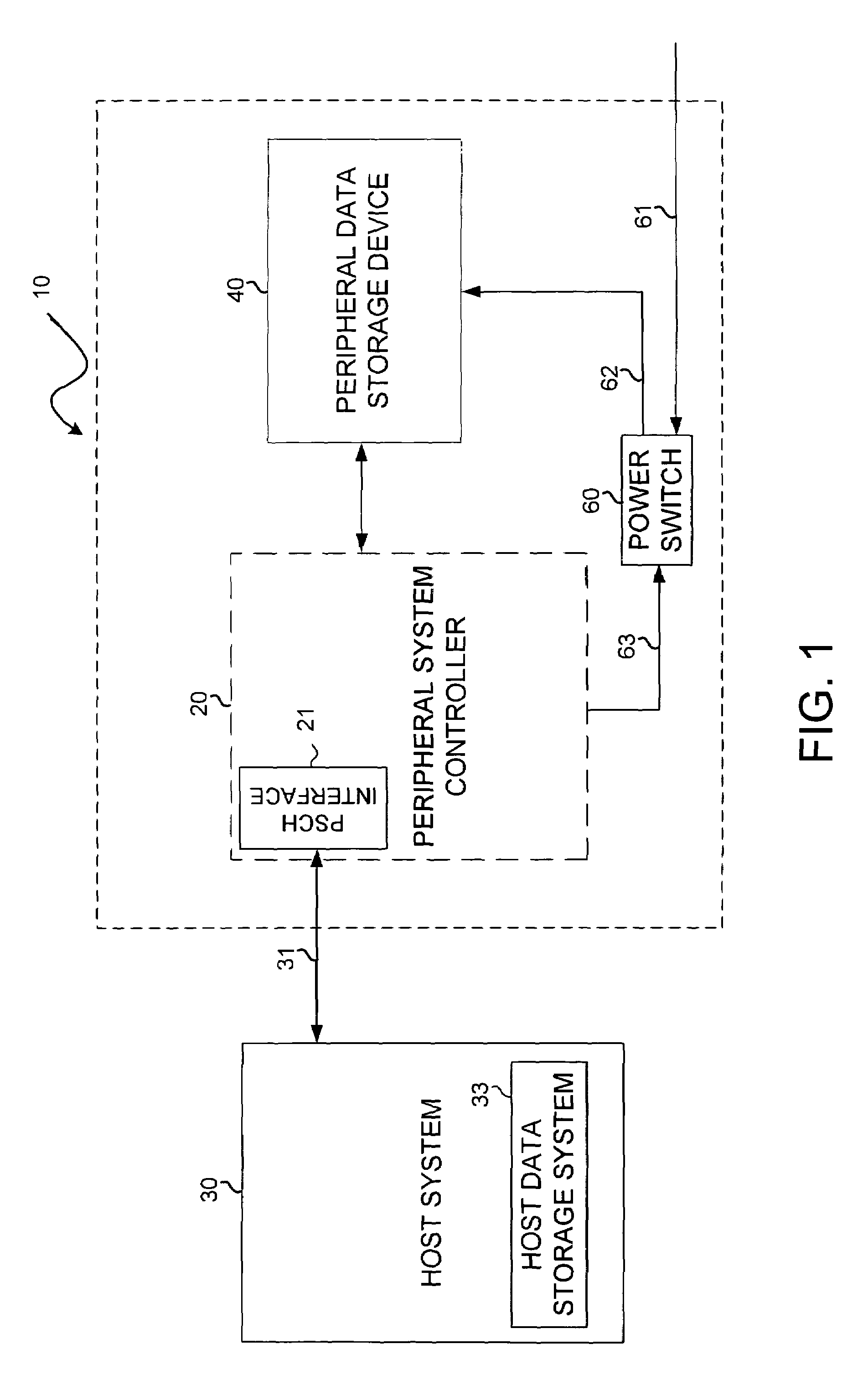
Remote power cycling of peripheral data storage system
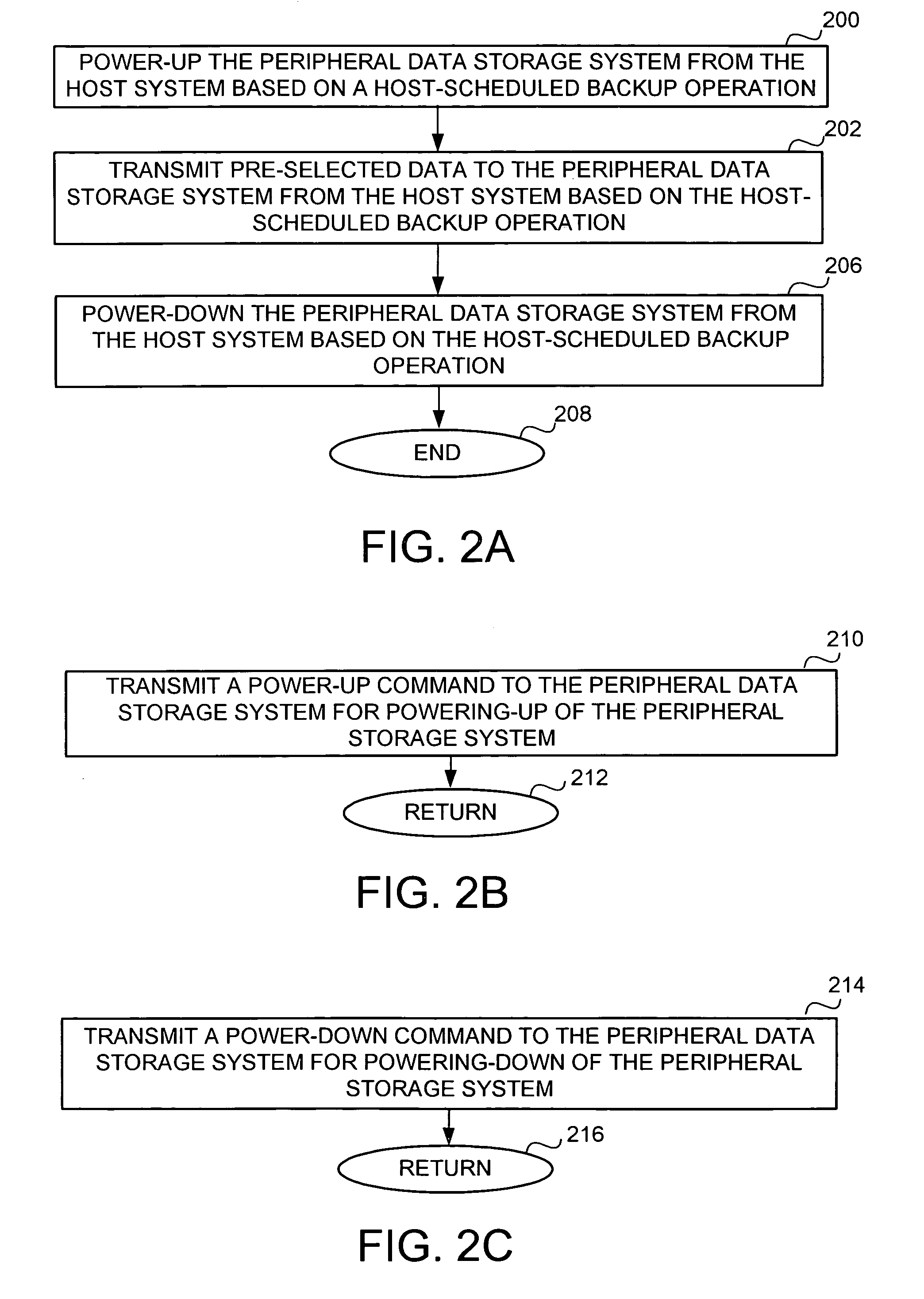
A method for remotely power cycling a peripheral data storage system (PDSS) from a host system. The method comprises powering-up the PDSS from the host system based on a host-scheduled backup operation; transmitting pre-selected data to the PDSS from the host system based on the host-scheduled backup operation; and powering-down the PDSS from the host system based on the host-scheduled backup operation. Another method is for operating a PDSS for use with a host system configured to perform scheduled backup operations to the PDSS, the PDSS comprising a peripheral data storage device, a PDSS controller, and a peripheral data storage controller host interface adapted for communication with the host system. The method comprises powering-up the PDSS based on a host-scheduled backup operation; receiving data from the host system for storing in the peripheral data storage device; and powering-down the PDSS based on the host-scheduled backup operation.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
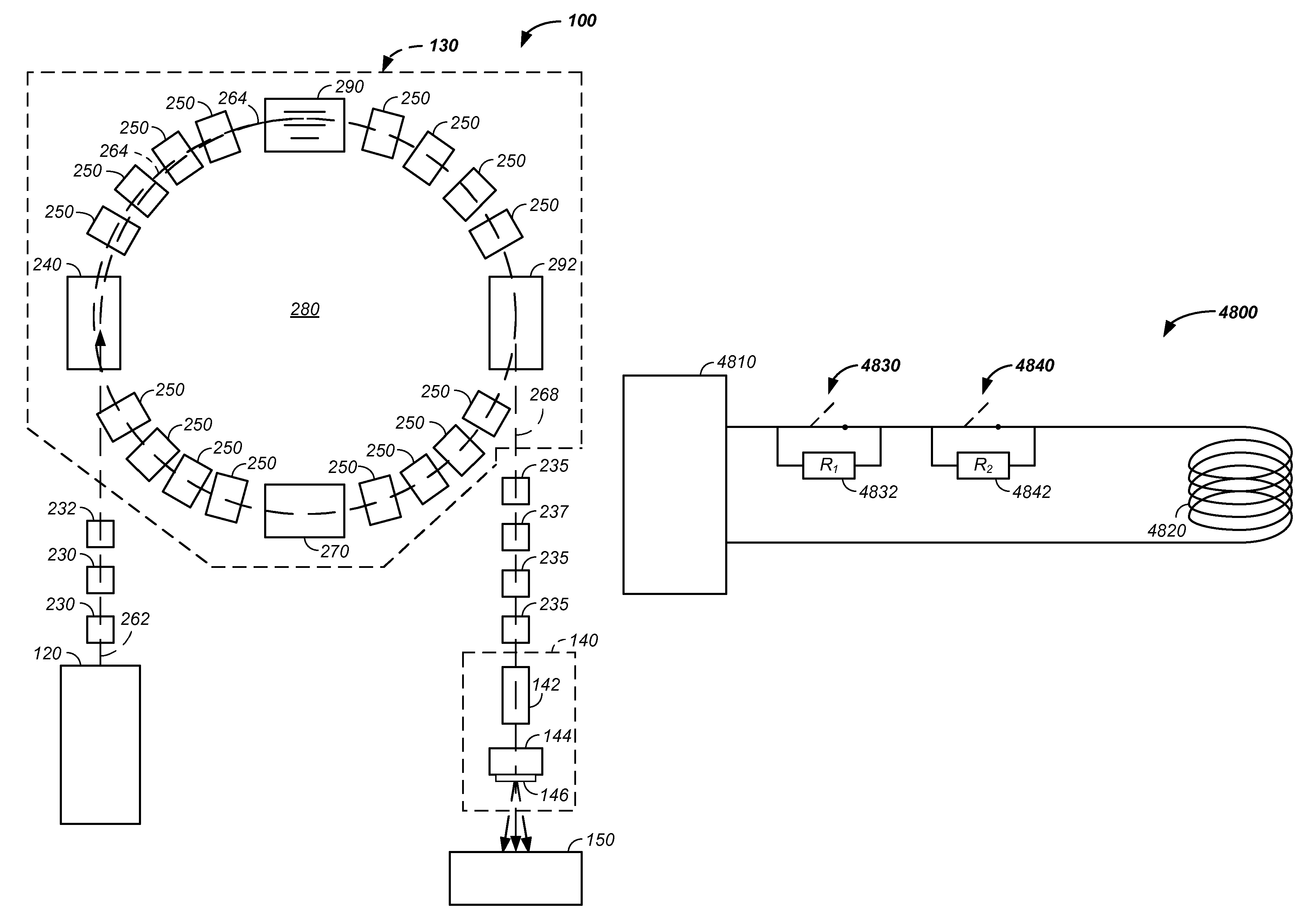
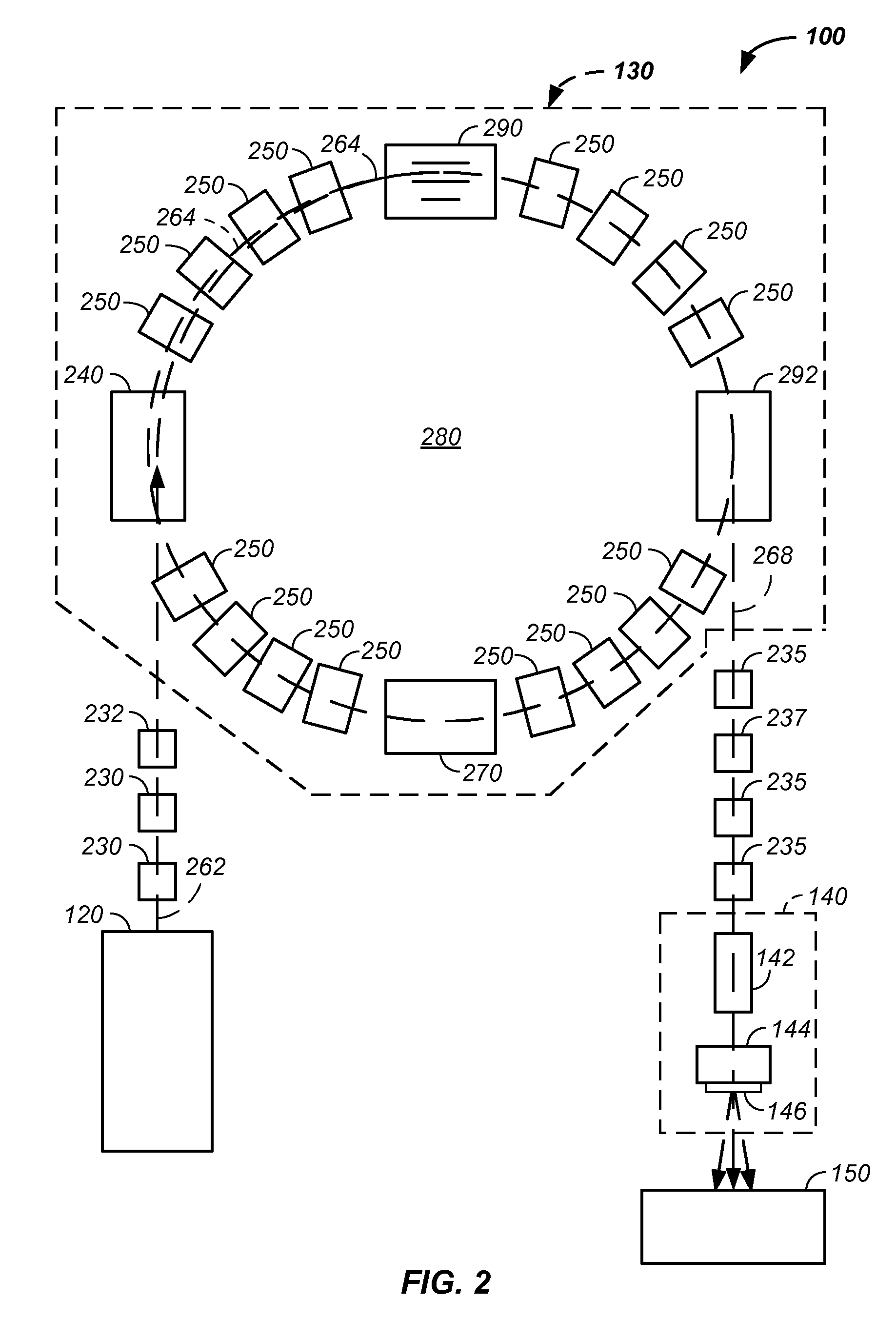
Synchrotron power cycling apparatus and method of use thereof
InactiveUS20110284760A1Stability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsInductorSynchrotron
The invention comprises a charged particle cancer therapy system or synchrotron system using one or more switches to introduce a corresponding one or more resistors into a circuit linking a power supply to a magnet or an inductor during an applied power recovery phase between acceleration cycles of the synchrotron, which reduces time of reduction in power from an active applied power to a power suitable for use with a subsequent injection of charged particles into the synchrotron.
Owner:BALAKIN ANDREY VLADIMIROVICH +1
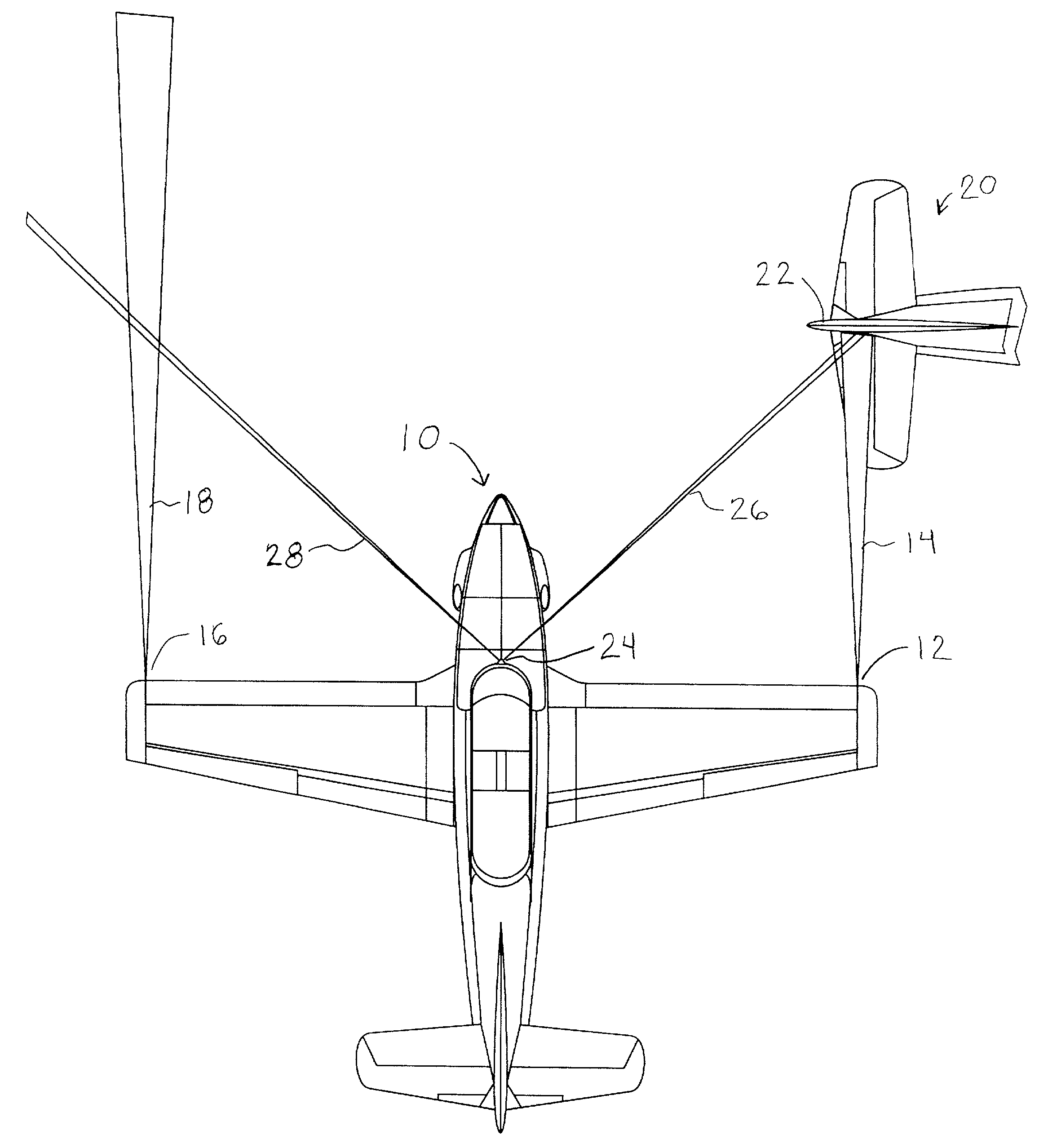
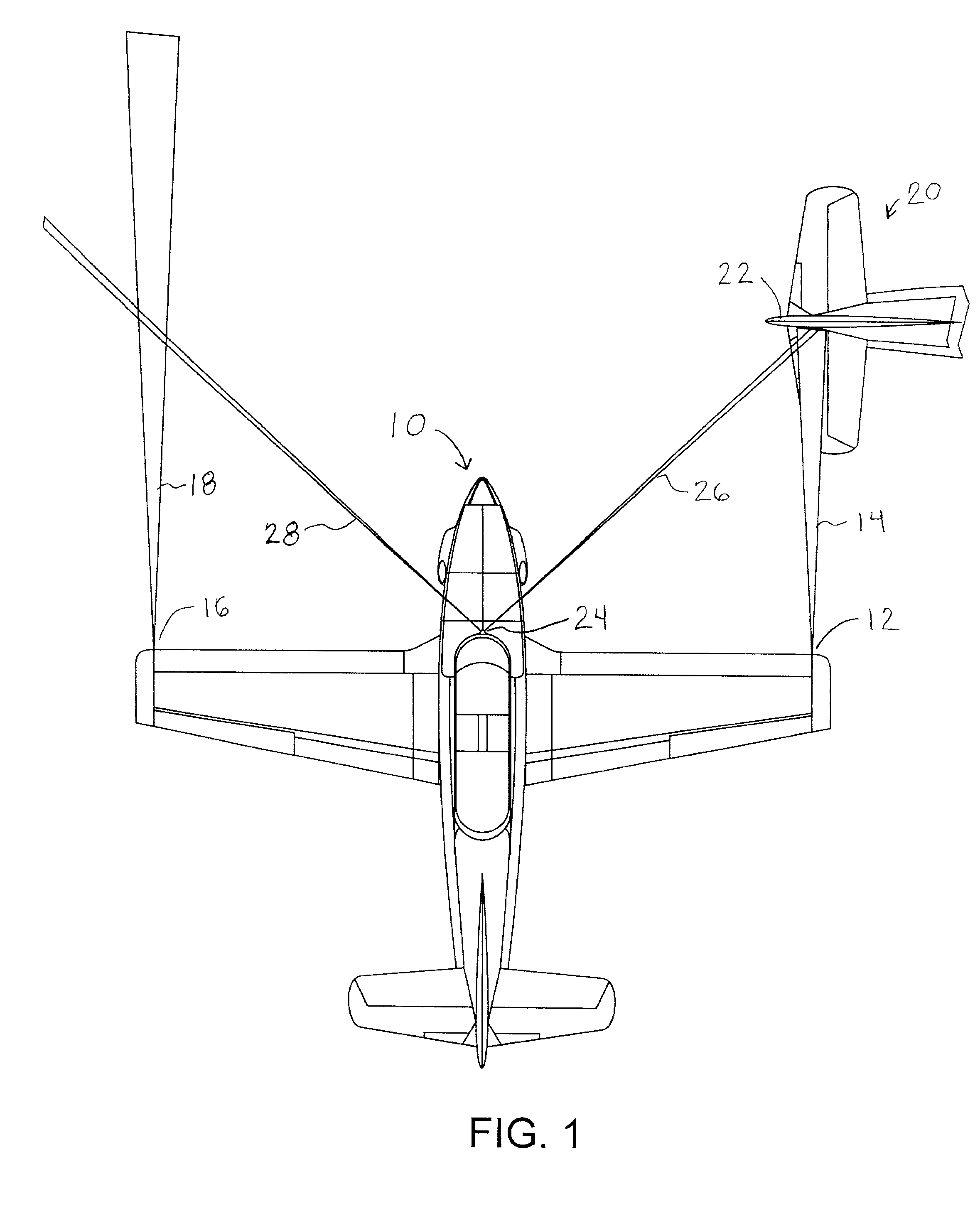
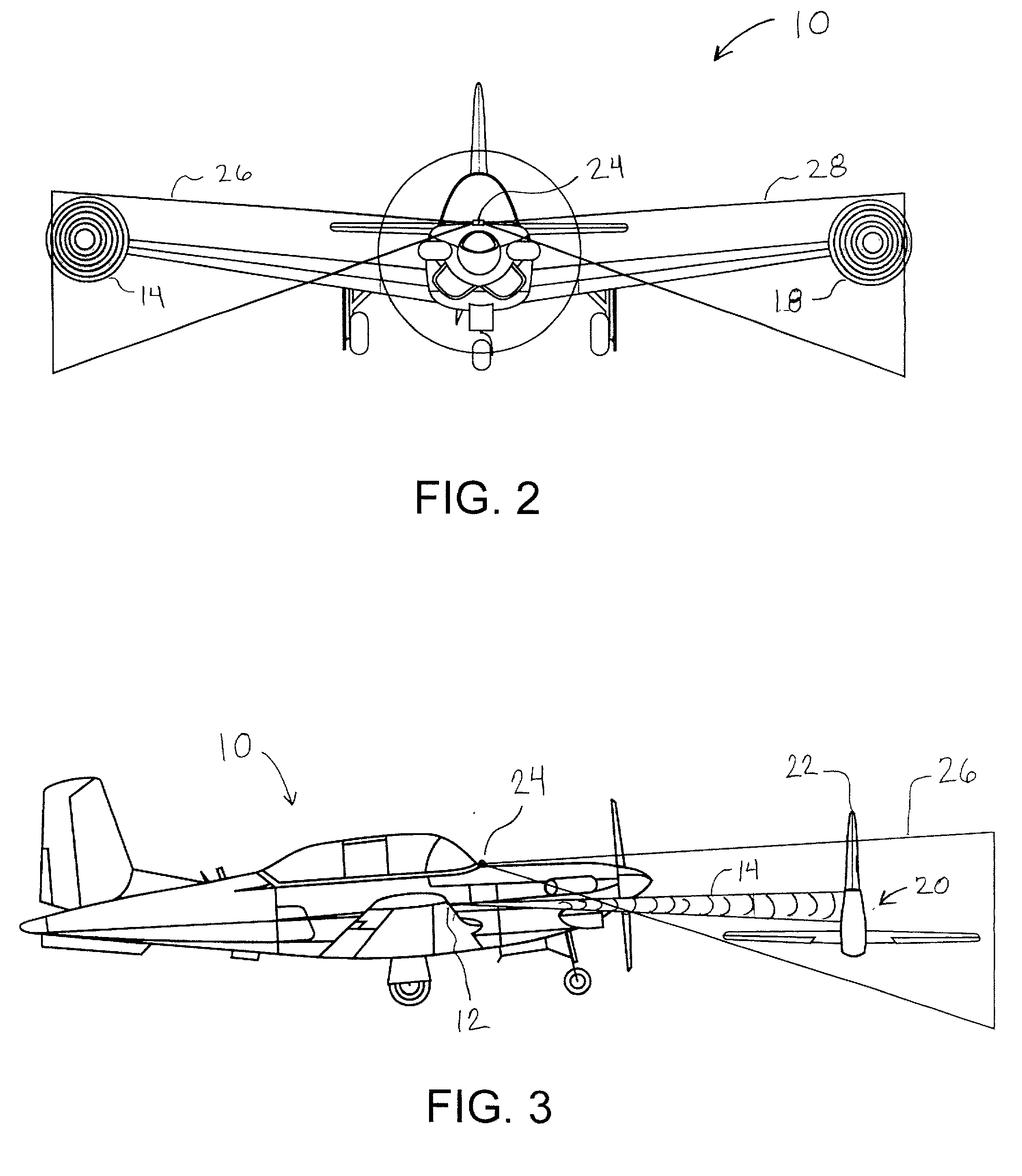
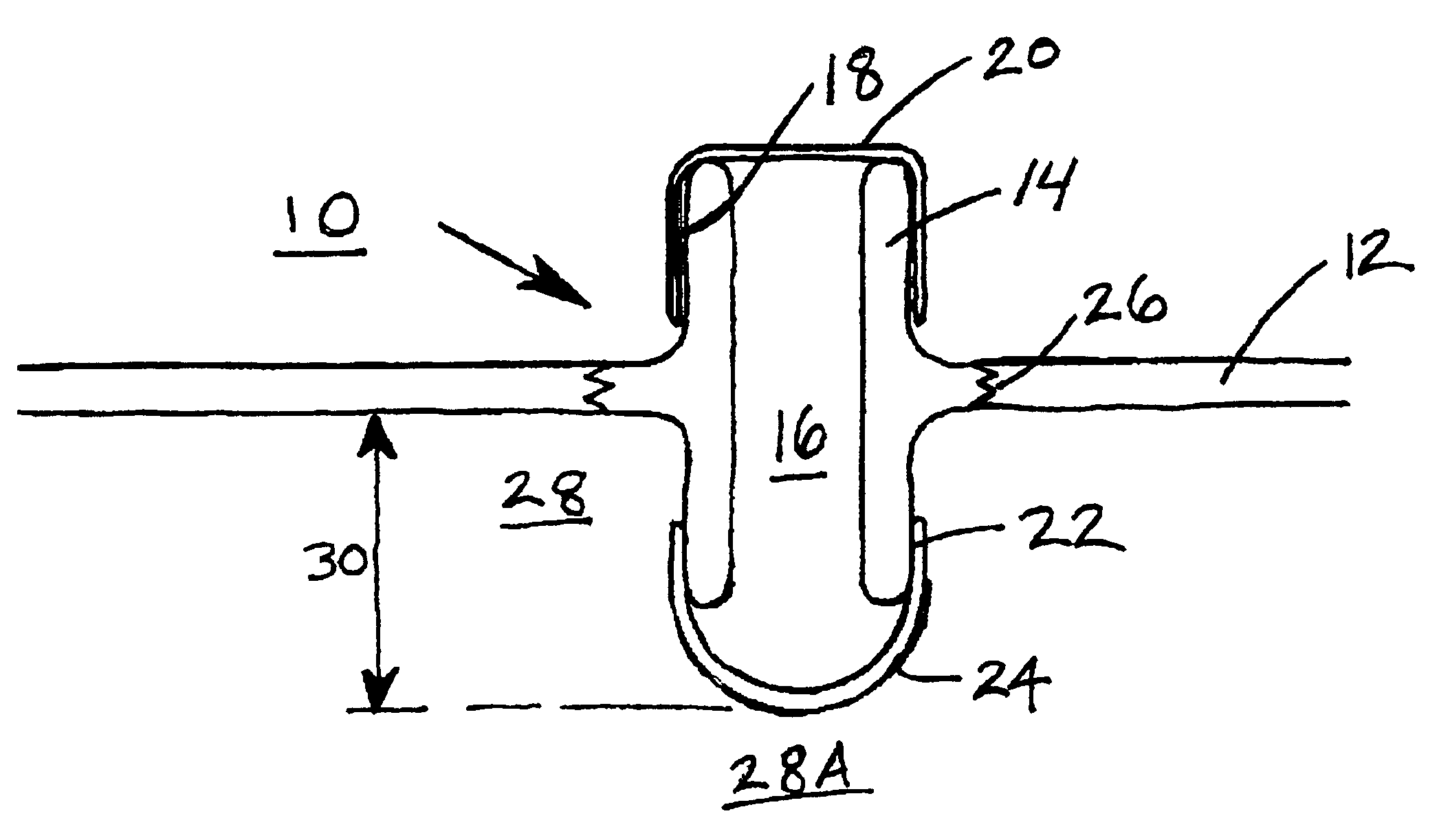
System and method of preventing aircraft wingtip ground incursion
InactiveUS20050007257A1Input/output for user-computer interactionAircraft componentsEffect lightBiological activation
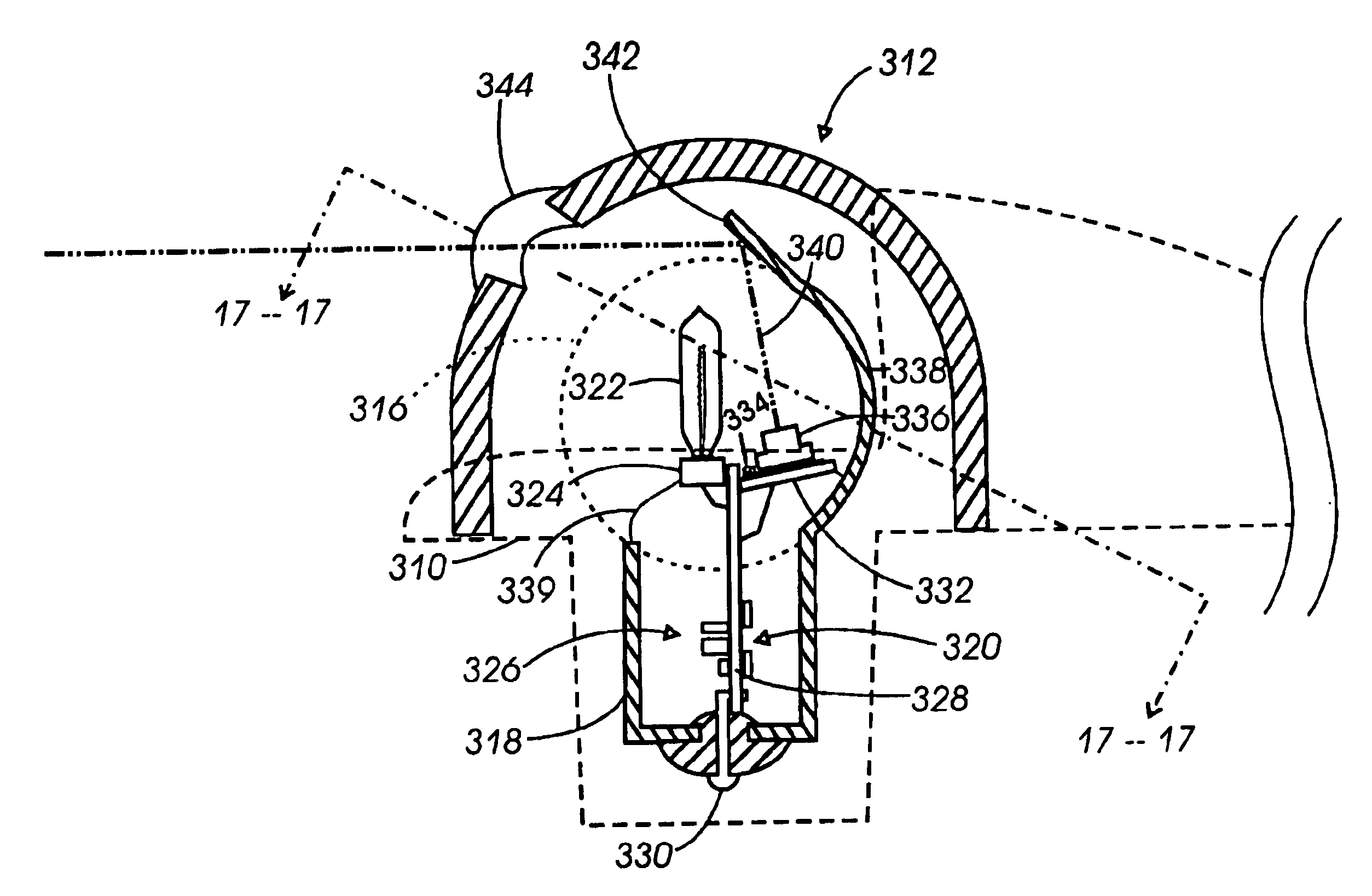
An apparatus and method for tracking aircraft wingtip position during taxi operations to prevent wingtip ground incursion. A patterned illumination source is attached proximal the wingtips to project a readily discernable target pattern in the direction of taxi travel. At least a portion of the target pattern is reflected off of any obstructions that lie in the straight-line direction of travel, such that the pilot can maneuver to avoid striking the obstruction. By way of example, the patterned illumination source comprises a laser module positioned with the navigation and / or strobe light of the aircraft. The device may be retrofitted to existing aircraft without additional wiring with the control of activation being selectable via power cycling of existing aircraft lighting controls. One aspect of the invention provides a tip tracking module bulb that may be retrofitted into existing light sockets to simplify system installation.
Owner:RAST RODGER H
Phase control in the capillary evaporators
InactiveUS6889754B2Guaranteed uptimeIndirect heat exchangersRefrigeration machinesTransport systemEngineering
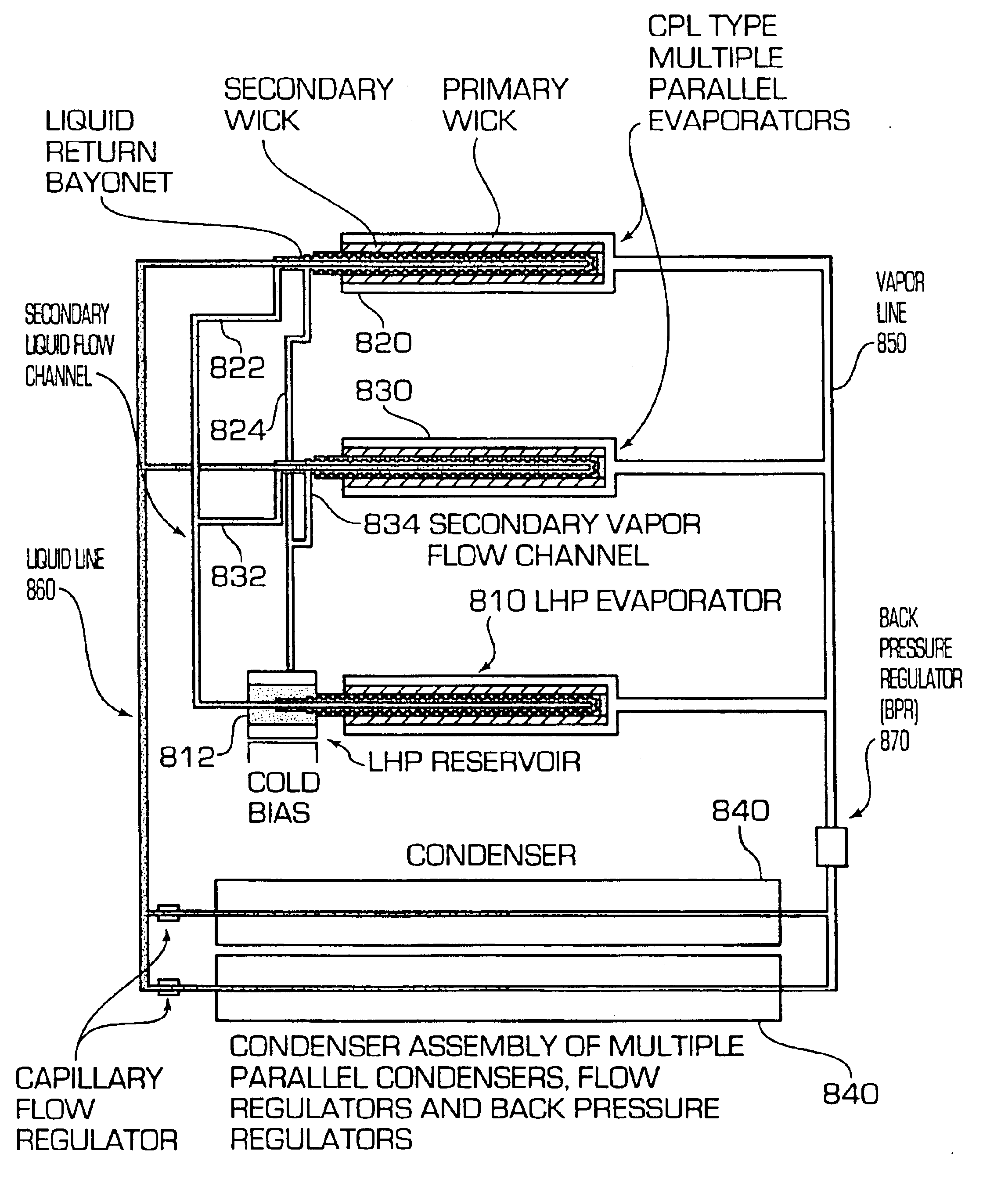
A capillary pump two phase heat transport system that combines the most favorable characteristics of a capillary pump loop (CPL) with the robustness and reliability of a loop heat pipe (LHP). Like a CPL, the hybrid loop has plural parallel evaporators, plural parallel condensers, and a back pressure flow regulator. Unlike CPLs, however, the hybrid system incorporates elements that form a secondary loop, which is essentially a LHP that is co-joined with a CPL to form an inseparable whole. Although secondary to the basic thermal management of the system thermal bus, the LHP secondary loop portion of the system provides for important operational functions that maintain healthy, robust and reliable operation. The LHP secondary loop portion provides a function of fluid management during start-up, steady state operation, and heat sink / heat source temperature and power cycling.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
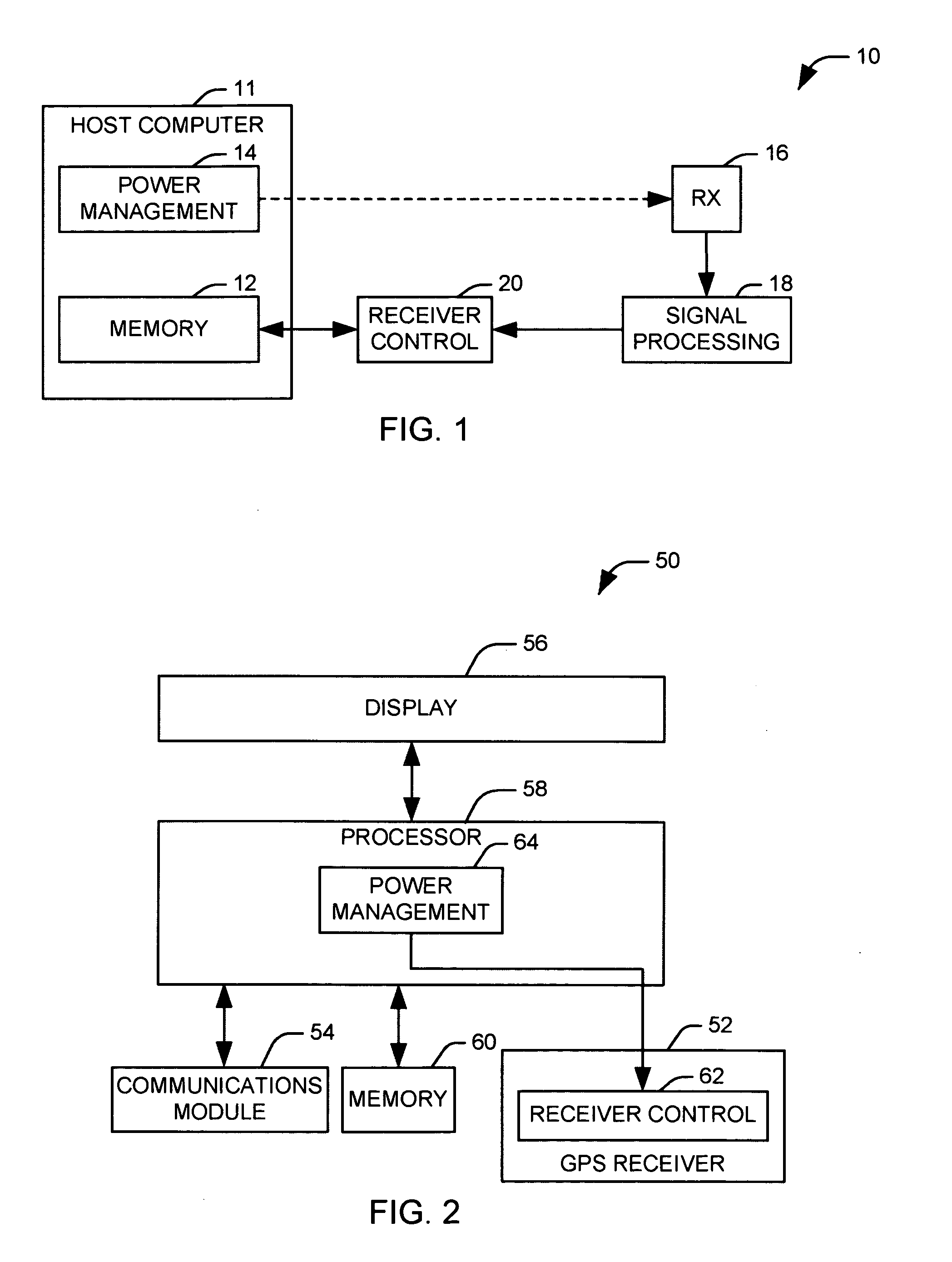
Power cycling for a global positioning system
ActiveUS20050275587A1Extend battery lifeSave powerPower managementPosition fixationControl powerGps receiver
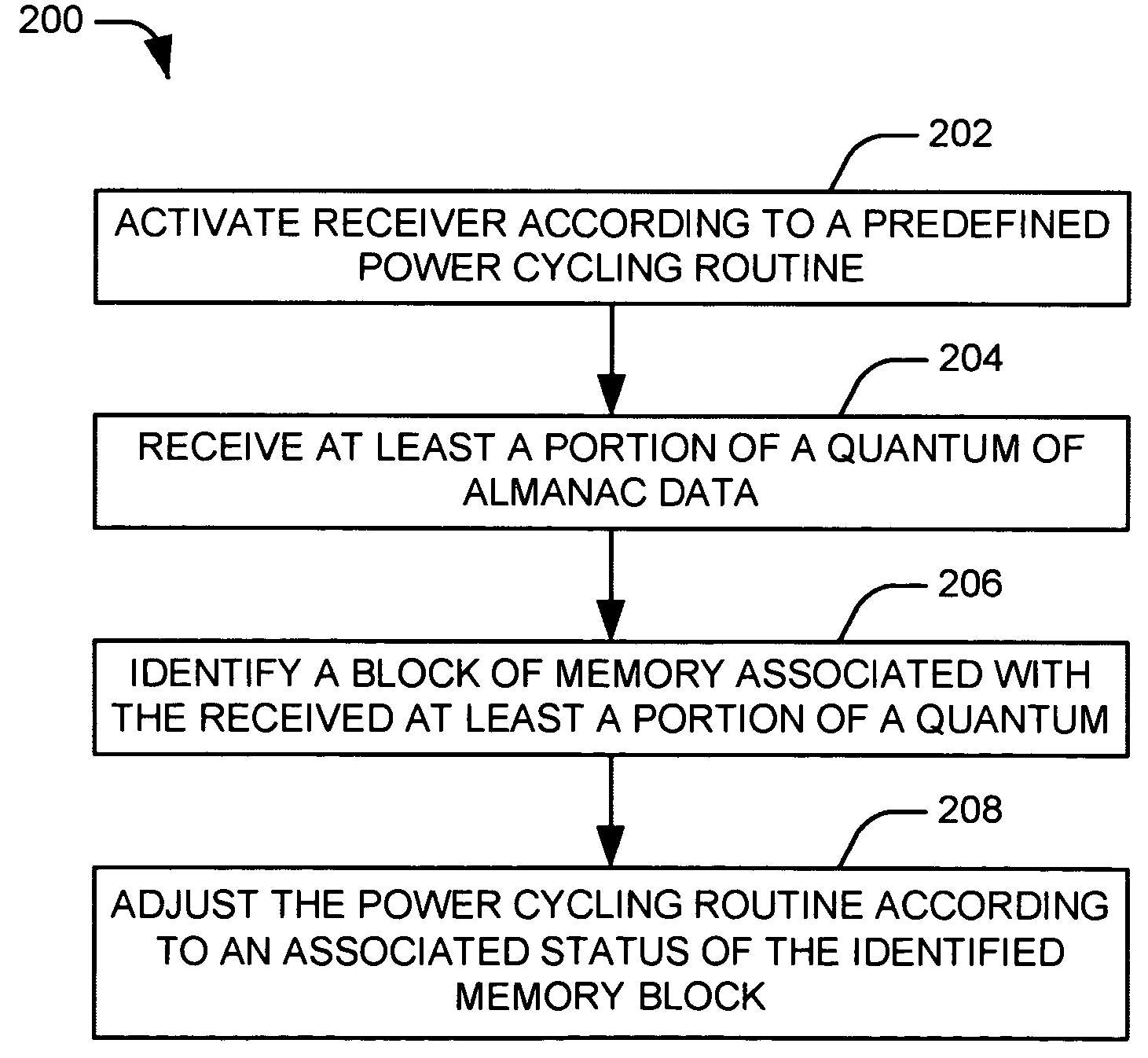
Methods and systems are presented for controlling power cycling in a global positioning system (GPS) assembly. The assembly comprises a power management component that operates to switch a GPS receiver between at least a first mode, in which the receiver is actively receiving almanac and positioning data, and a second mode, in which the receiver does not actively receive data according to a power cycling routine of the receiver. A memory stores a plurality of quanta of almanac data as associated memory blocks, each memory block having an associated status indicating the length of time for which the associated almanac data is expected to be useful. A signal processing component processes a received signal containing at least a portion of a quantum of almanac data and identifies the quantum of almanac data within the received signal. A receiver control adjusts the power cycling routine of the GPS receiver according to the associated status of a memory block associated with the identified quantum of almanac data.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
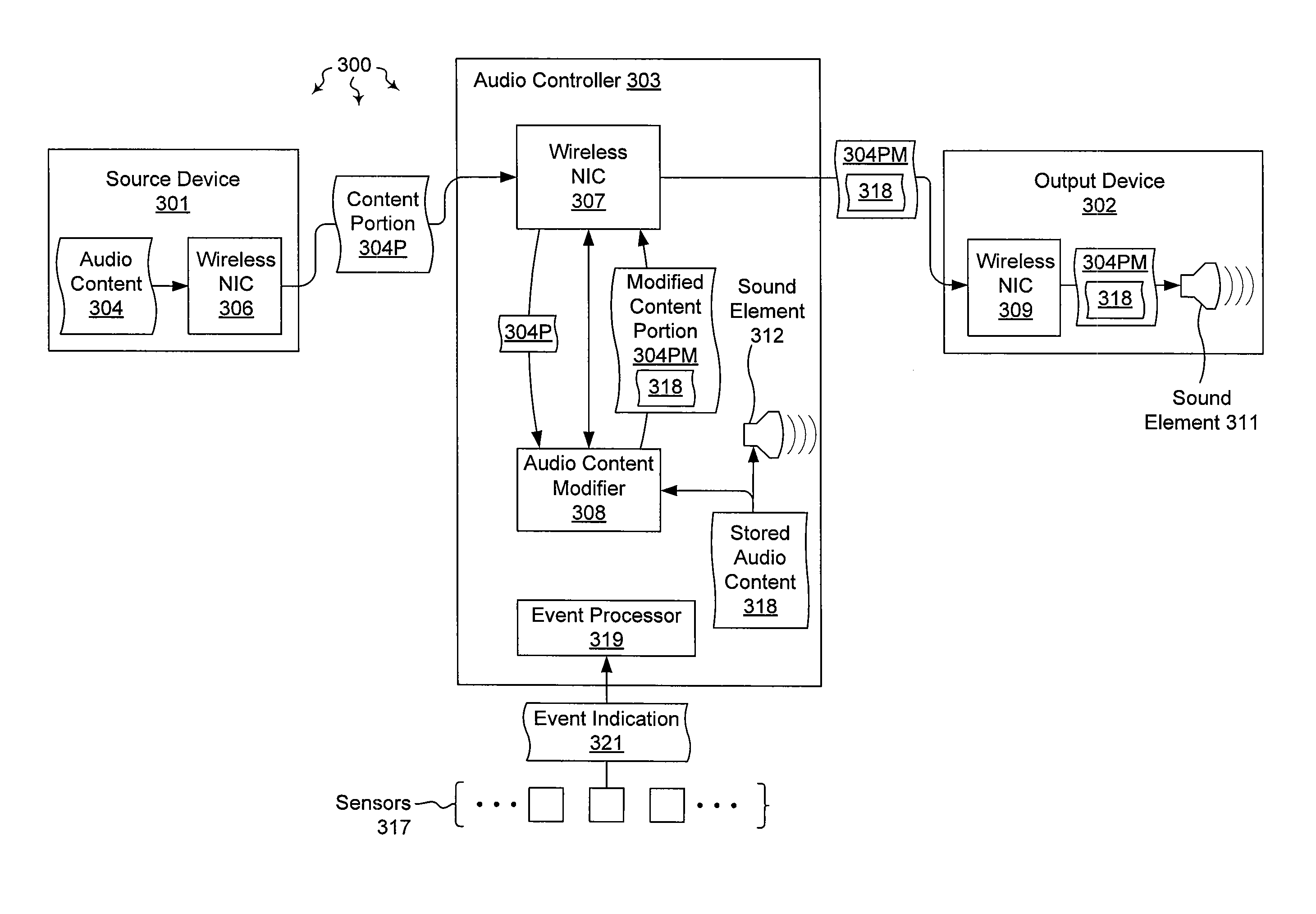
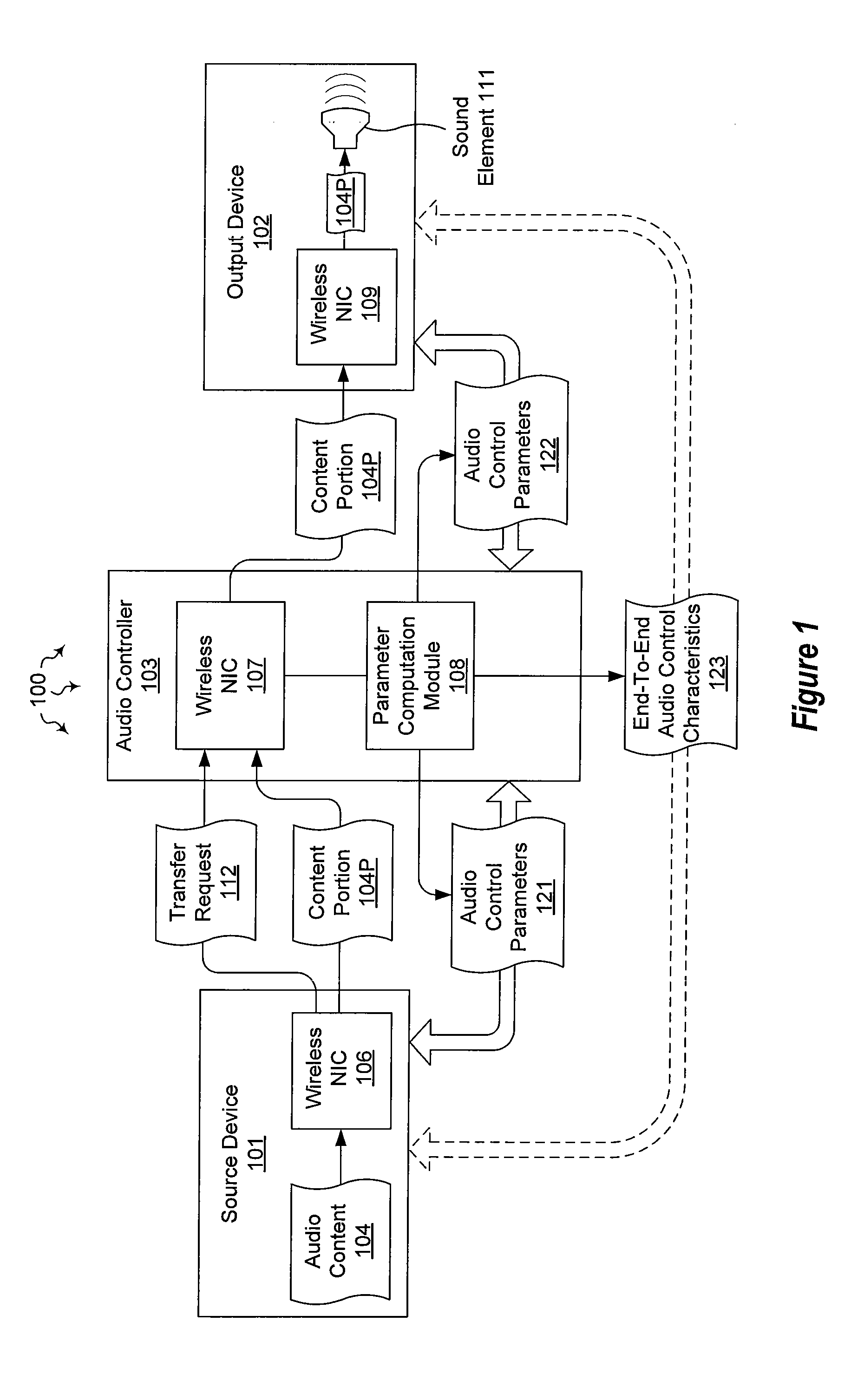
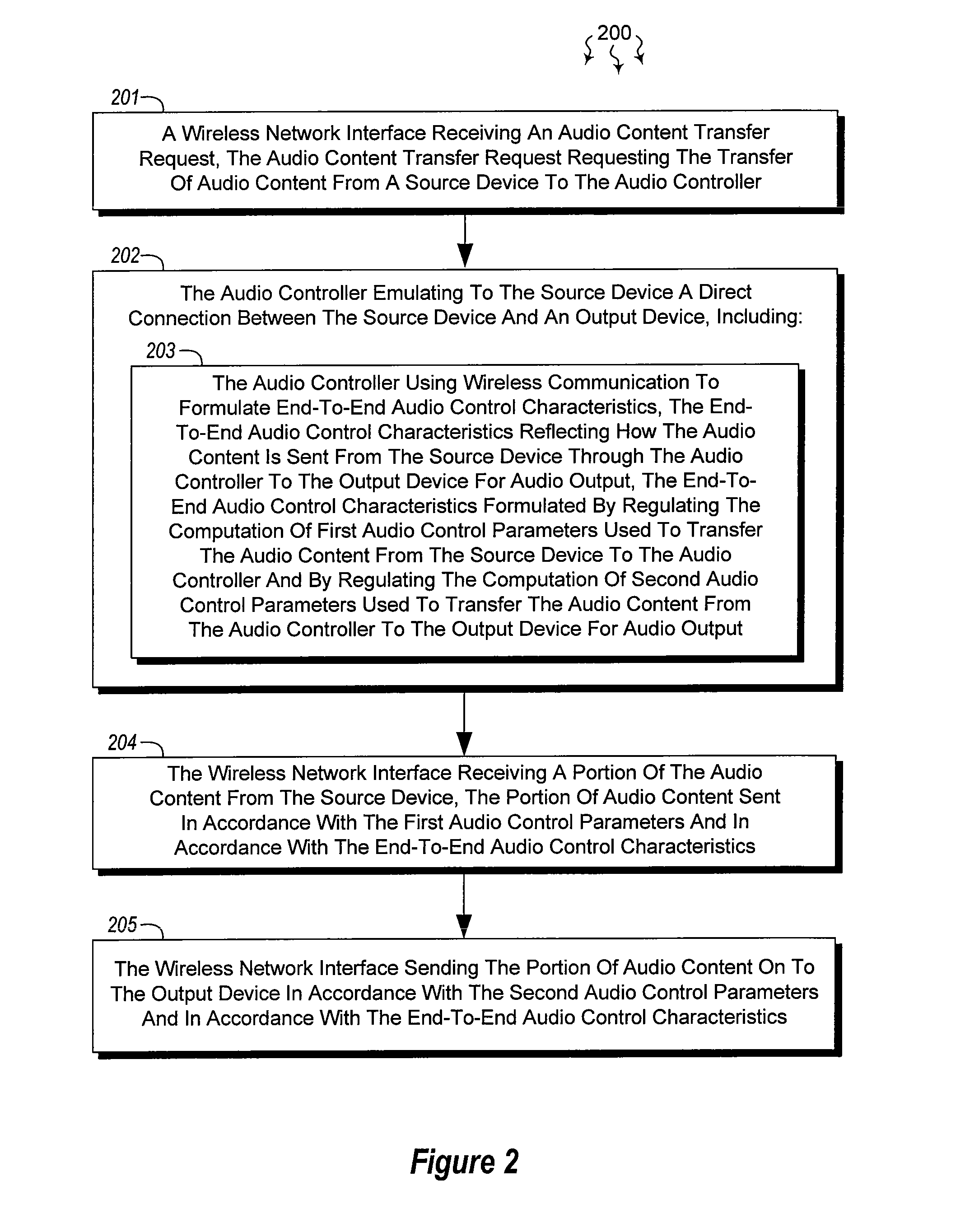
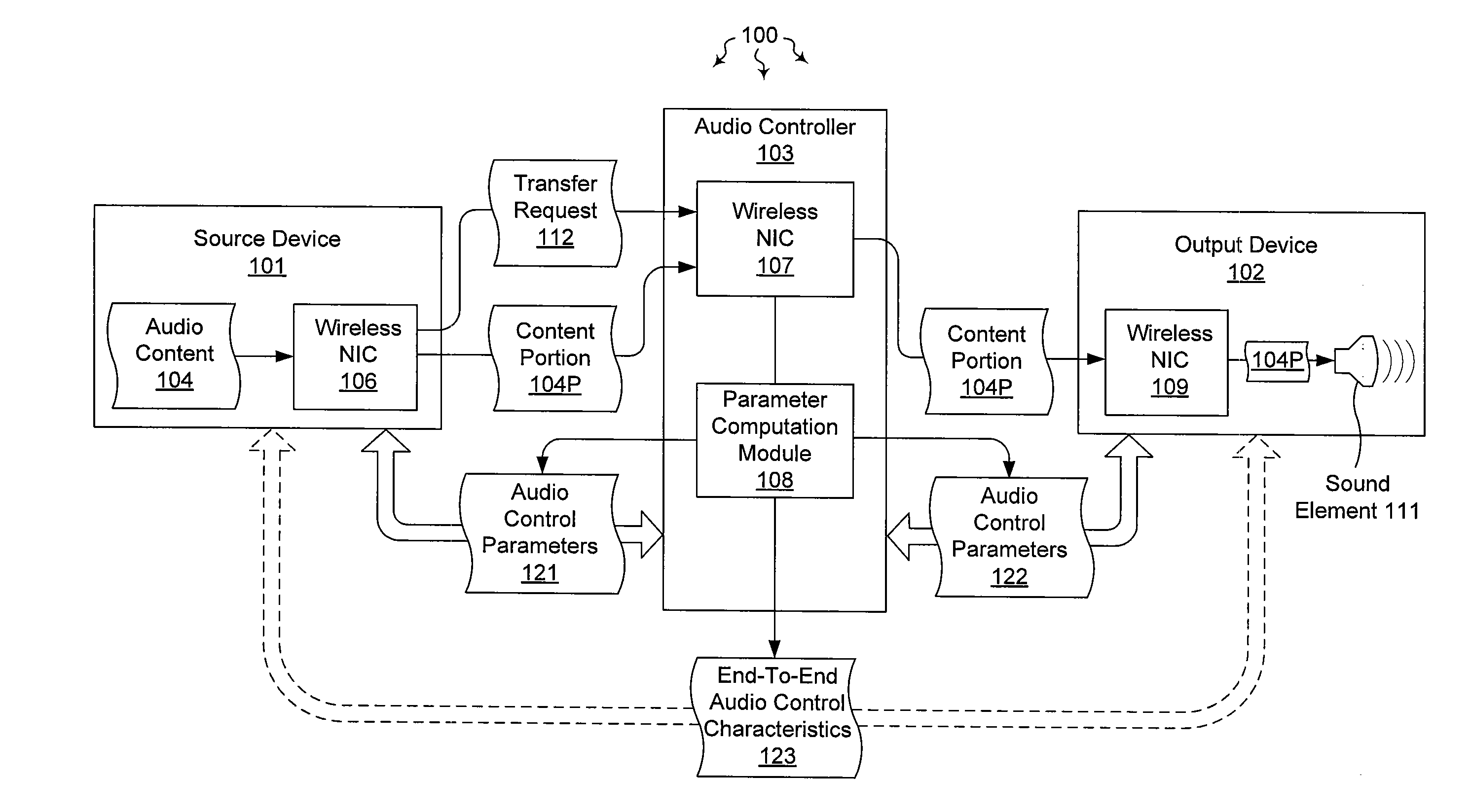
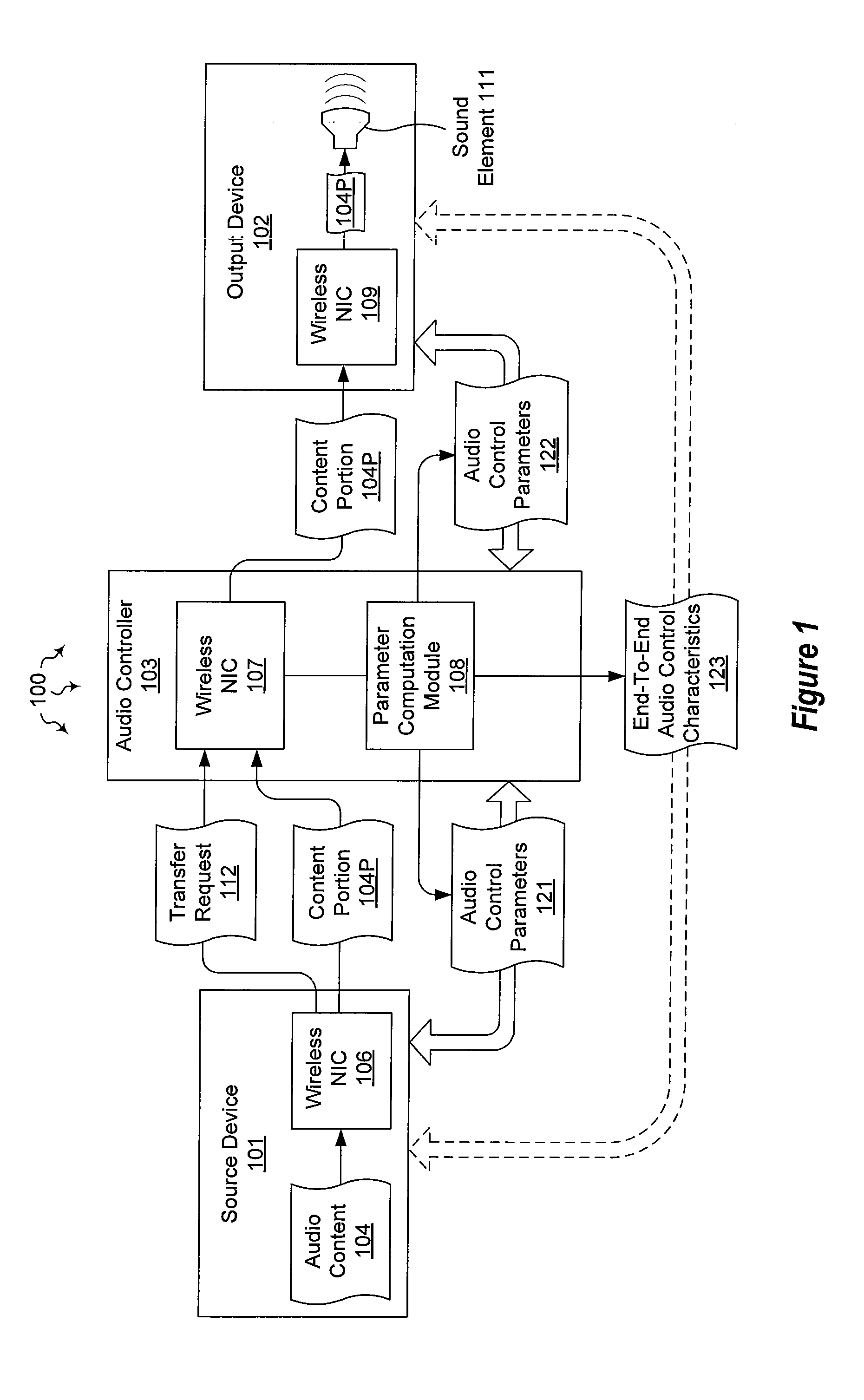
Managing audio output through an intermediary
The present invention extends to methods, systems, and computer program products for managing audio output through an intermediary. In some embodiments, an audio controller emulates a direct connection between an audio source device and an audio output device. In other embodiments, audio content local to an audio controller is combined with other audio content passing through the audio controller on its way from an audio source device to an audio output device. In additional embodiments, an audio output device is locked to an audio controller. The lock survives power cycling and soft resets of the audio output device. A special hard reset can be used to release the audio output device.
Owner:VIVINT INC
Customer facing interface power cycling of wireless terminals
ActiveUS20130094346A1Good serviceMinimizing disconnectionError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsComputer terminalCustomer-premises equipment
Systems and methods are described for configuring customer premises equipment in a wireless network in response to reconnection of subscriber station to a base station. A set of rules is provided that governs configuration of a network interface based in part on whether the interface connects to a different base station after reconnection. Reconfiguration may include cycling power of the network interface and the decision to cycle power may be based on network configuration determined after the loss of communication. This decision can be made after the loss of communication and after the network interface is reconnected to the wireless network through the same or a different base station. The rules may be processed by a combination of subscriber equipment, network interface and base station. Power may be cycled responsive to a message transmitted by the one base station to the network interface.
Owner:TELSIMA
System and method of preventing aircraft wingtip ground incursion
InactiveUS6963293B1Input/output for user-computer interactionLighting support devicesFlight vehicleEffect light
An apparatus and method for tracking aircraft wingtip position during taxi operations to prevent wingtip ground incursion. A patterned illumination source is attached proximal the wingtips to project a readily discernable target pattern in the direction of taxi travel. At least a portion of the target pattern is reflected off of any obstructions that lie in the straight-line direction of travel, such that the pilot can maneuver to avoid striking the obstruction. By way of example, the patterned illumination source comprises a laser module positioned with the navigation and / or strobe light of the aircraft. The device may be retrofitted to existing aircraft without additional wiring with the control of activation being selectable via power cycling of existing aircraft lighting controls. One aspect of the invention provides a tip tracking module bulb that may be retrofitted into existing light sockets to simplify system installation.
Owner:RASTAR CORP
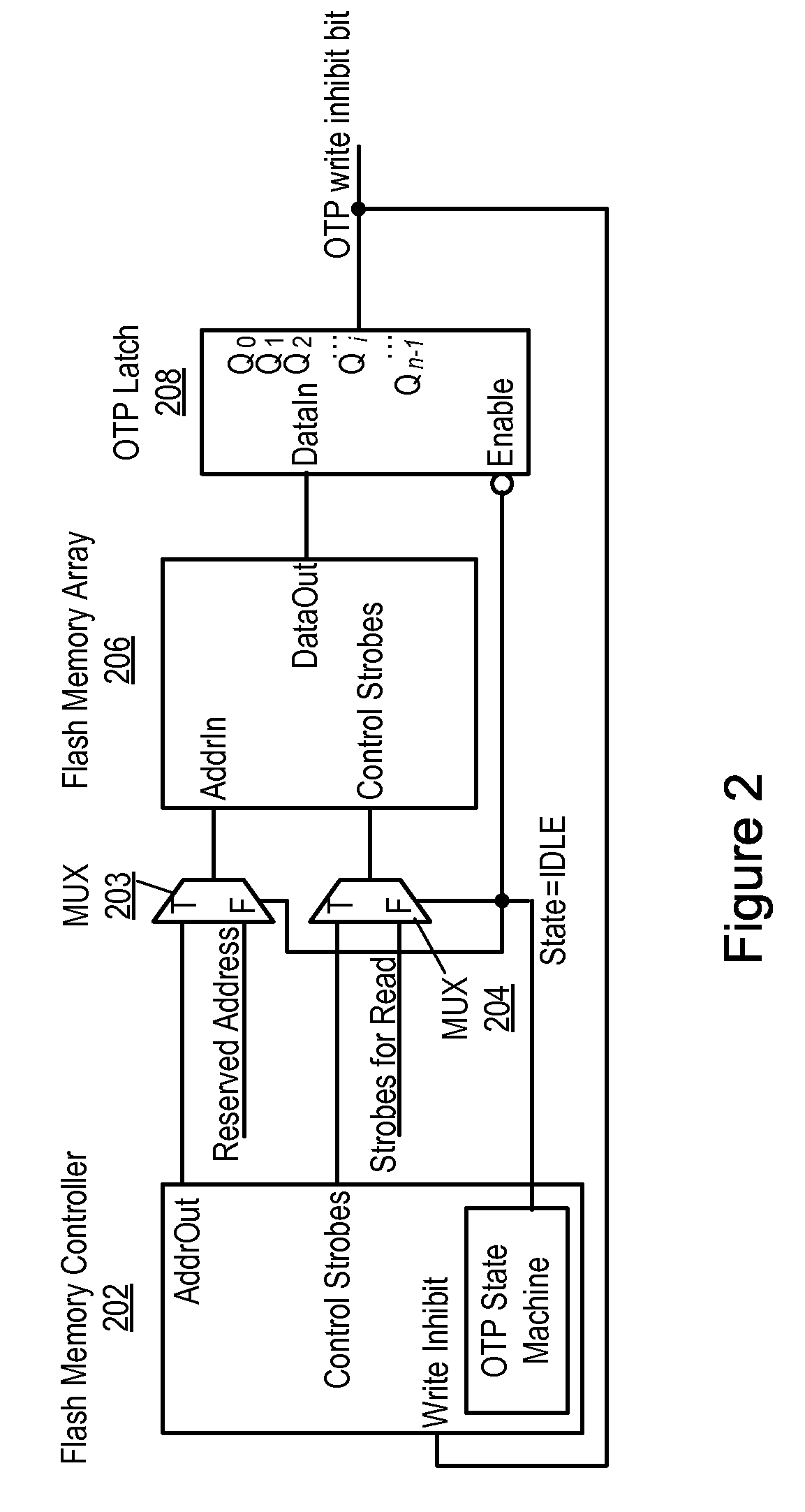
Implementation of One Time Programmable Memory with Embedded Flash Memory in a System-on-Chip
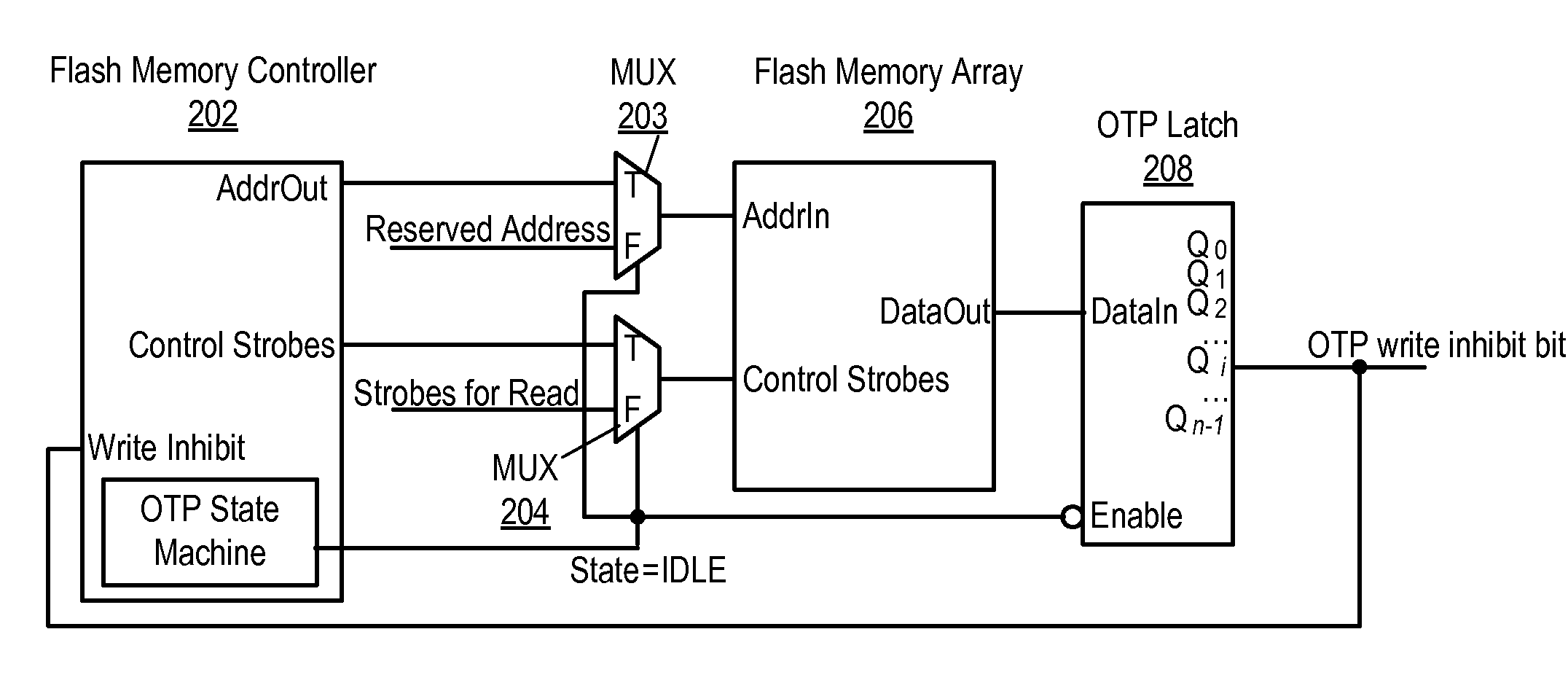
ActiveUS20090113114A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationPower cycleFlash memory controller
System and method for implementing one time programmable (OTP) memory using embedded flash memory. A system-on-chip (SoC) includes a cleared flash memory array that includes an OTP block, including an OTP write inhibit field that is initially deasserted, a flash memory controller, and a controller. Data are written to the OTP block, including setting the OTP write inhibit field to signify prohibition of subsequent writes to the OTP block. The SoC is power cycled, and, in response, at least a portion of the OTP block is latched in a volatile memory, including asserting an OTP write inhibit bit based on the OTP write inhibit field, after which the OTP block is not writeable. In response to each subsequent power cycling, the controller is held in reset, the latching is performed, the controller is released from reset, and the flash array, now write protected, is configured to be controlled by the controller.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
Synchrotron power cycling apparatus and method of use thereof
InactiveUS8378311B2Stability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsEngineeringInductor
The invention comprises a charged particle cancer therapy system or synchrotron system using one or more switches to introduce a corresponding one or more resistors into a circuit linking a power supply to a magnet or an inductor during an applied power recovery phase between acceleration cycles of the synchrotron, which reduces time of reduction in power from an active applied power to a power suitable for use with a subsequent injection of charged particles into the synchrotron.
Owner:BALAKIN ANDREY VLADIMIROVICH +1
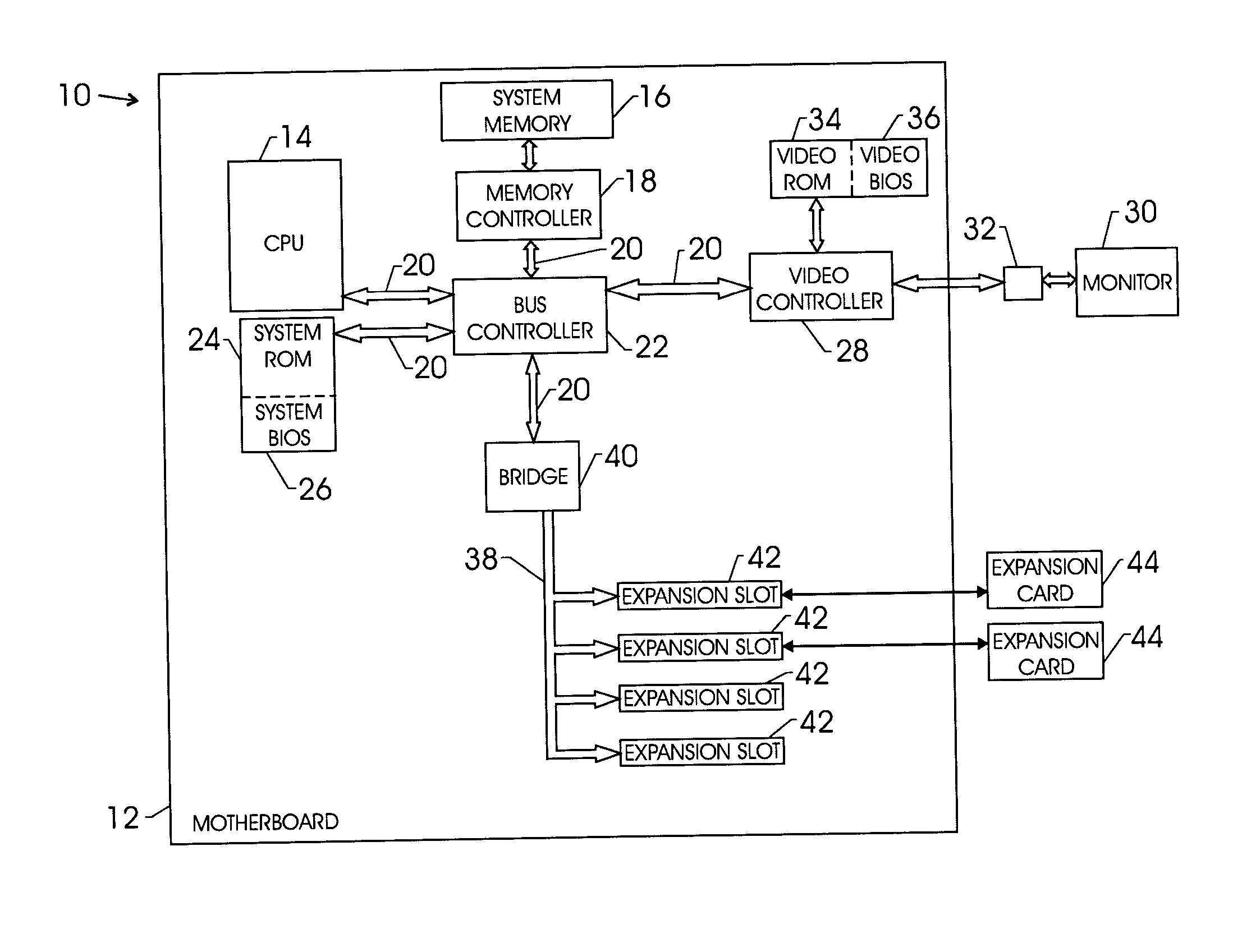
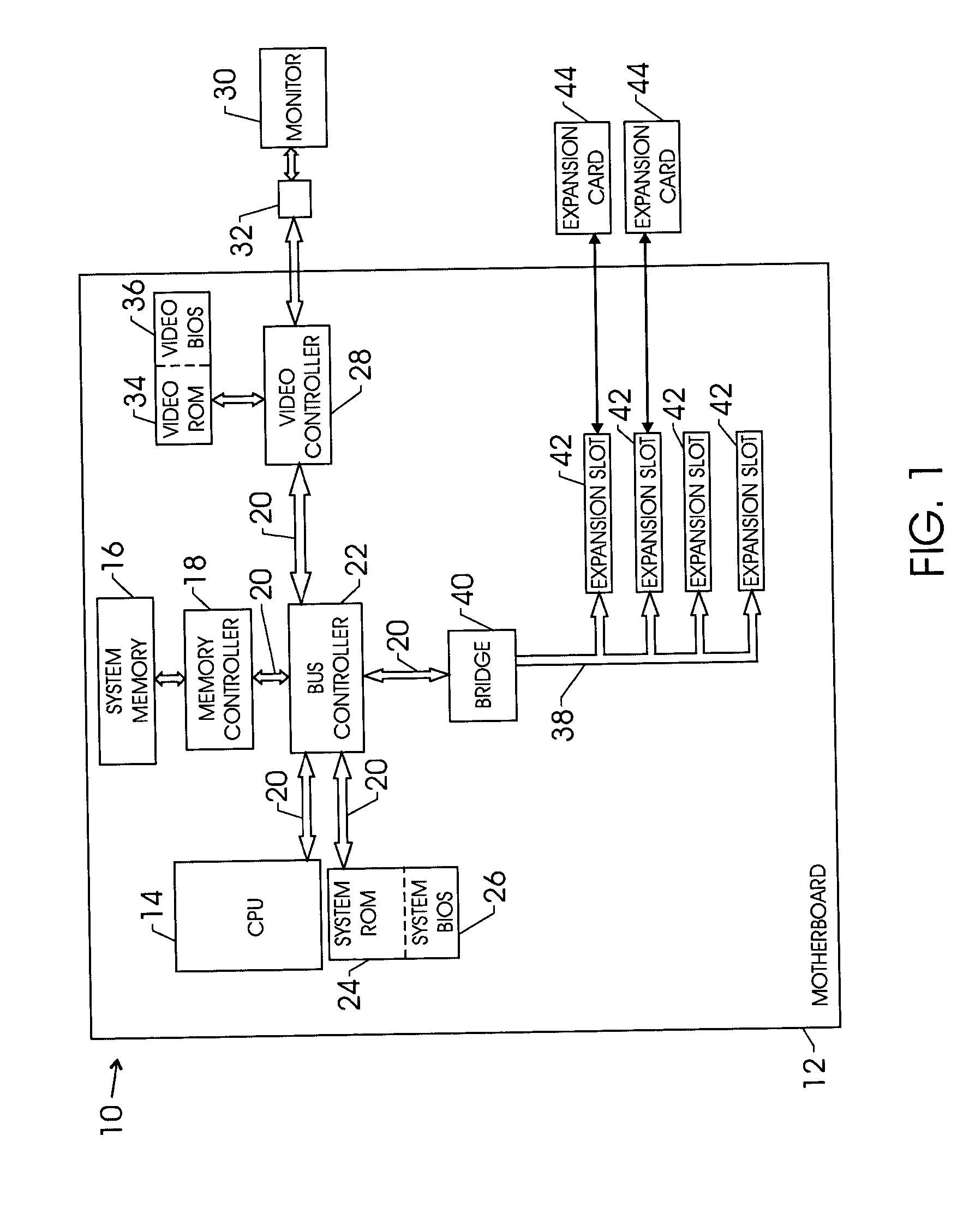
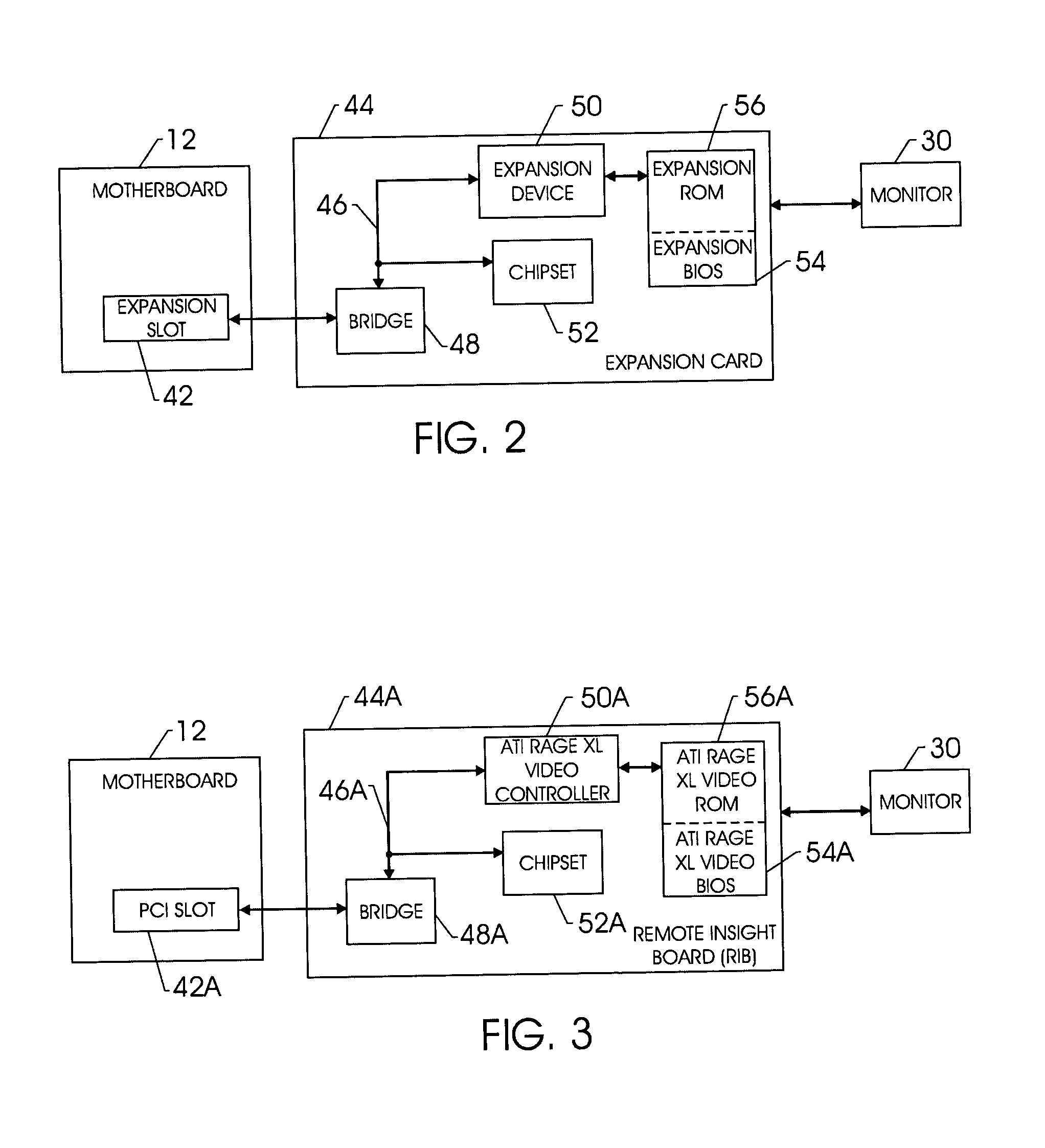
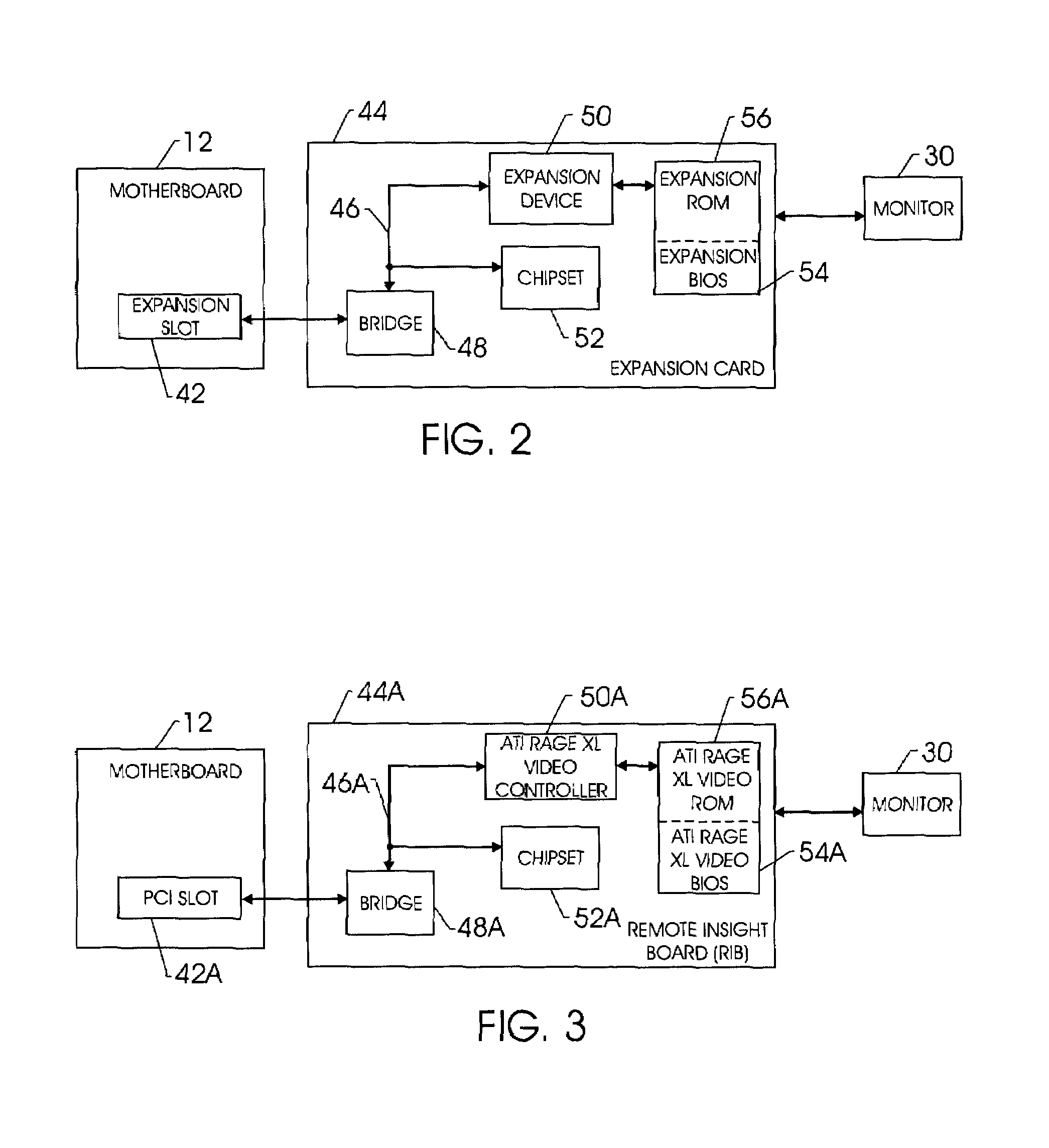
Techniques for initializing a device on an expansion card
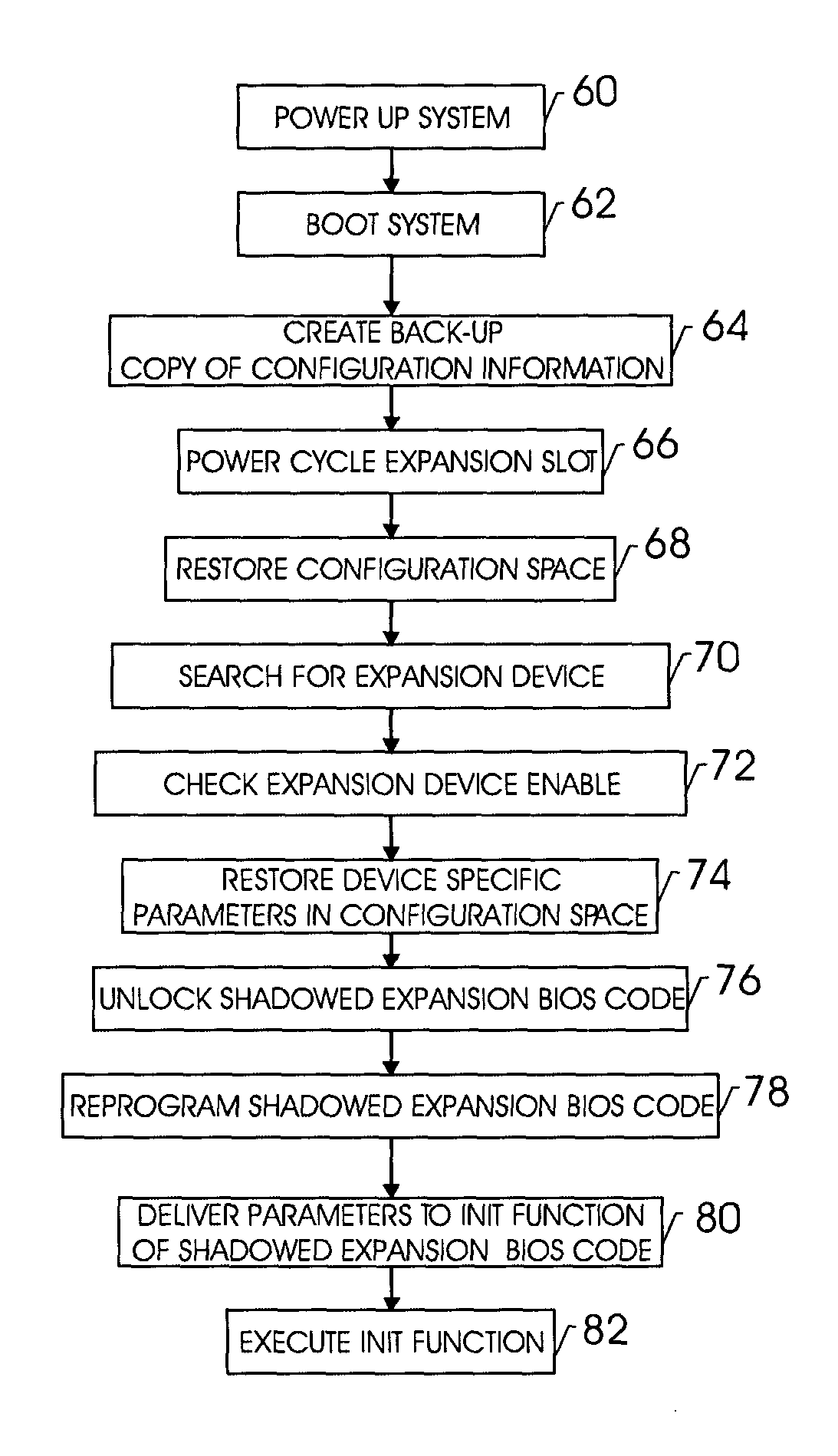
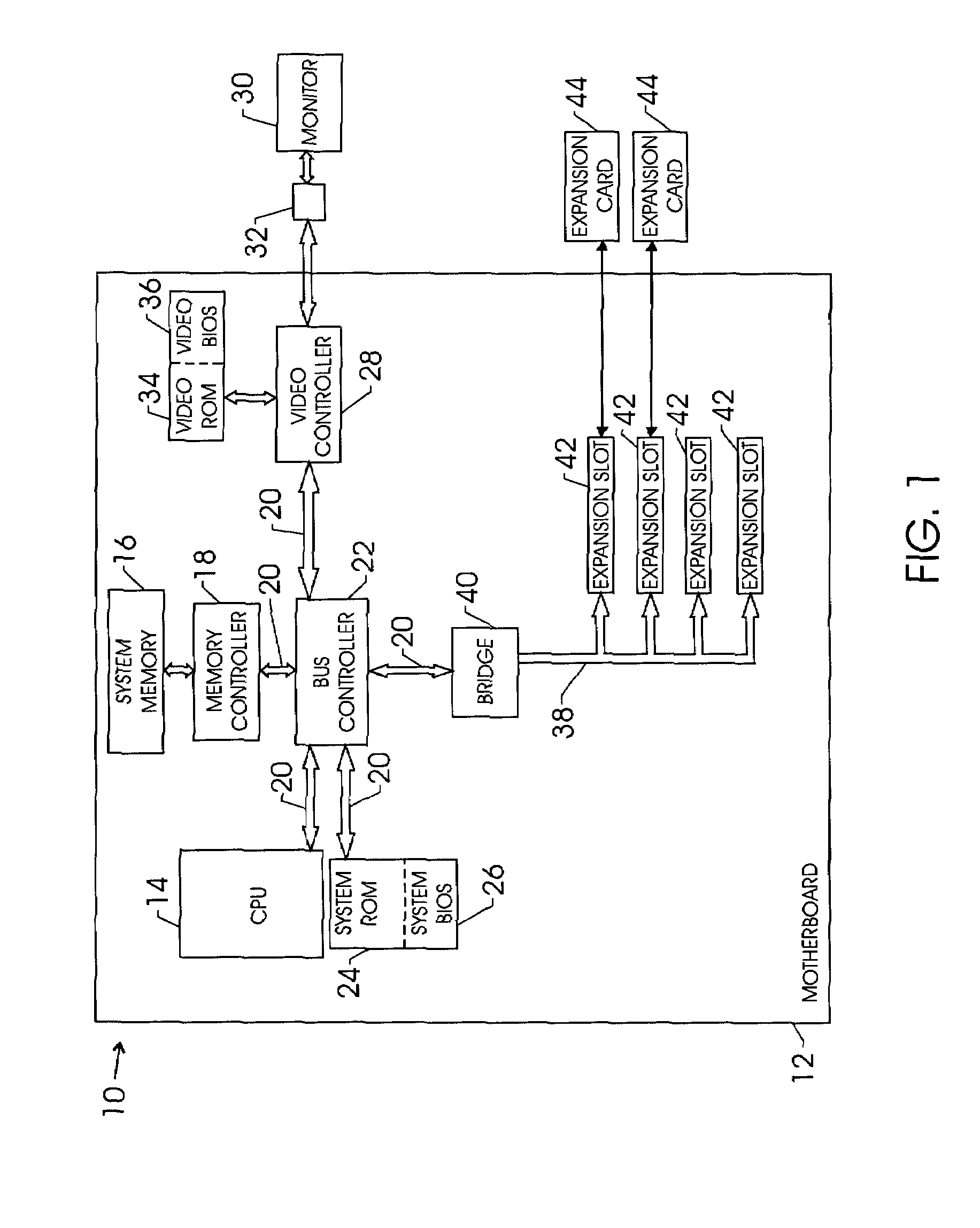
InactiveUS20050038986A1Digital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsExpansion cardPower cycle
Techniques for initializing / reinitializing a device on an expansion card without power cycling the system. More specifically, an instruction set is provided such that a device on an expansion card can be reinitialized without power cycling the system. Further, the instruction set may be implemented to initialize a device on a replacement expansion card. During the system boot, an expansion basic input / output system (BIOS) is copied into the system memory. After the system boot, a copy of the configuration information for the device on the expansion card is saved in a backup file in the system memory. The expansion card can be removed and replaced and the configuration information stored in the backup file in the system memory can be used to configure the replacement device. The copy of the expansion BIOS in the system memory can be reprogrammed such that it can be implemented to initialize the device on the replacement expansion card without power cycling the system.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
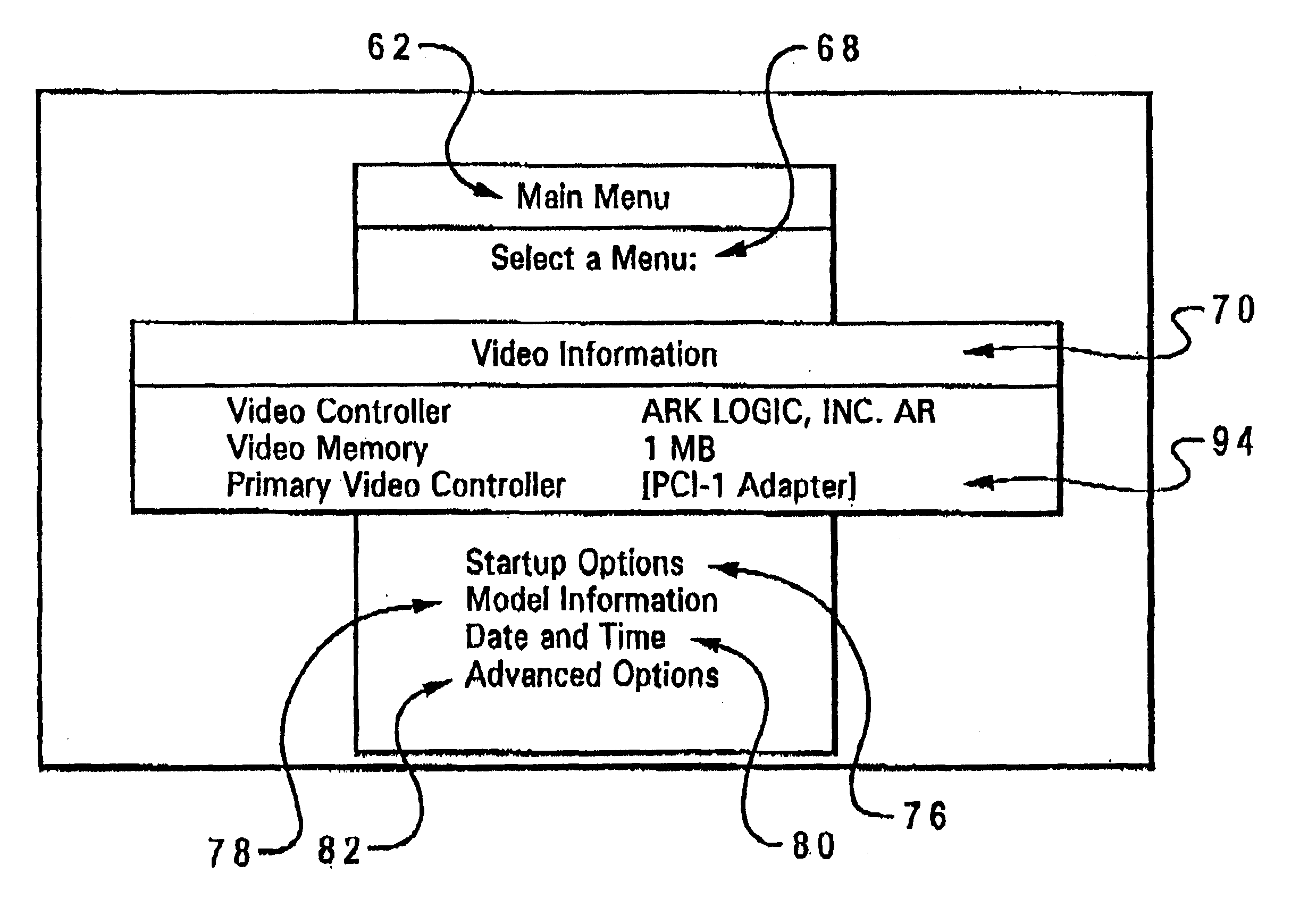
Method and system for dynamically selecting video controllers present within a computer system
InactiveUS6304244B1Improved video controller supportCathode-ray tube indicatorsMultiple digital computer combinationsPower cycleOn board
A method and system in a computer having a primary video controller for dynamically selecting an alternative video controller present within the computer. Initially, a diagnostic is performed to determine if alternative video controllers are connected to the computer system. A user is thereafter prompted to select an alternative video controller, if at least one alternative video controller is detected. The primary video controller is then temporarily disabled, in response to a selection of an alternative video controller. The alternative video controller is then automatically designated as the primary video controller, in response to the disabling of the primary video controller, such that the alternative video controller may be temporarily utilized as a primary video controller without altering internal computer system hardware settings or power cycling the computer system. The primary video controller may be implemented initially as an on-board video controller, while the alternative video controllers may be connected to the computer via adapter peripheral cards and slots.
Owner:IBM CORP
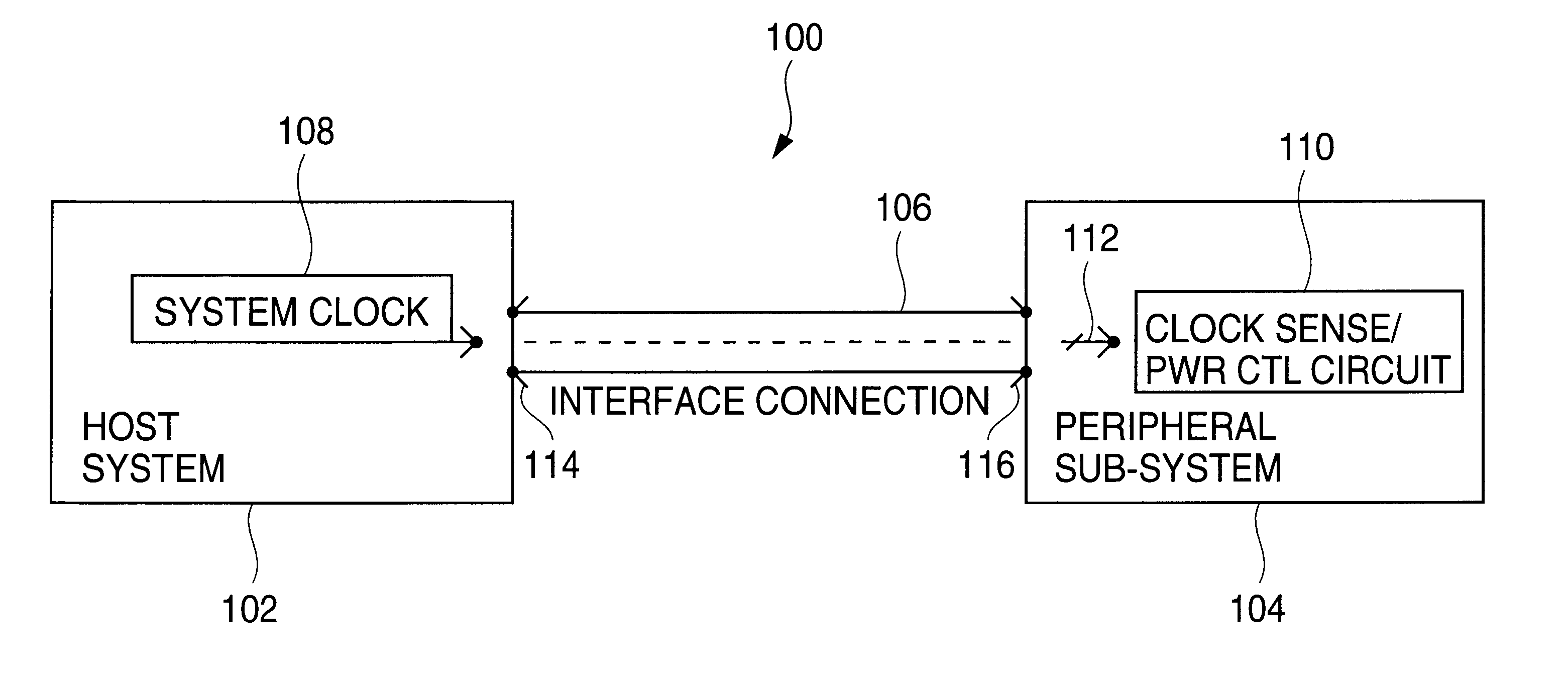
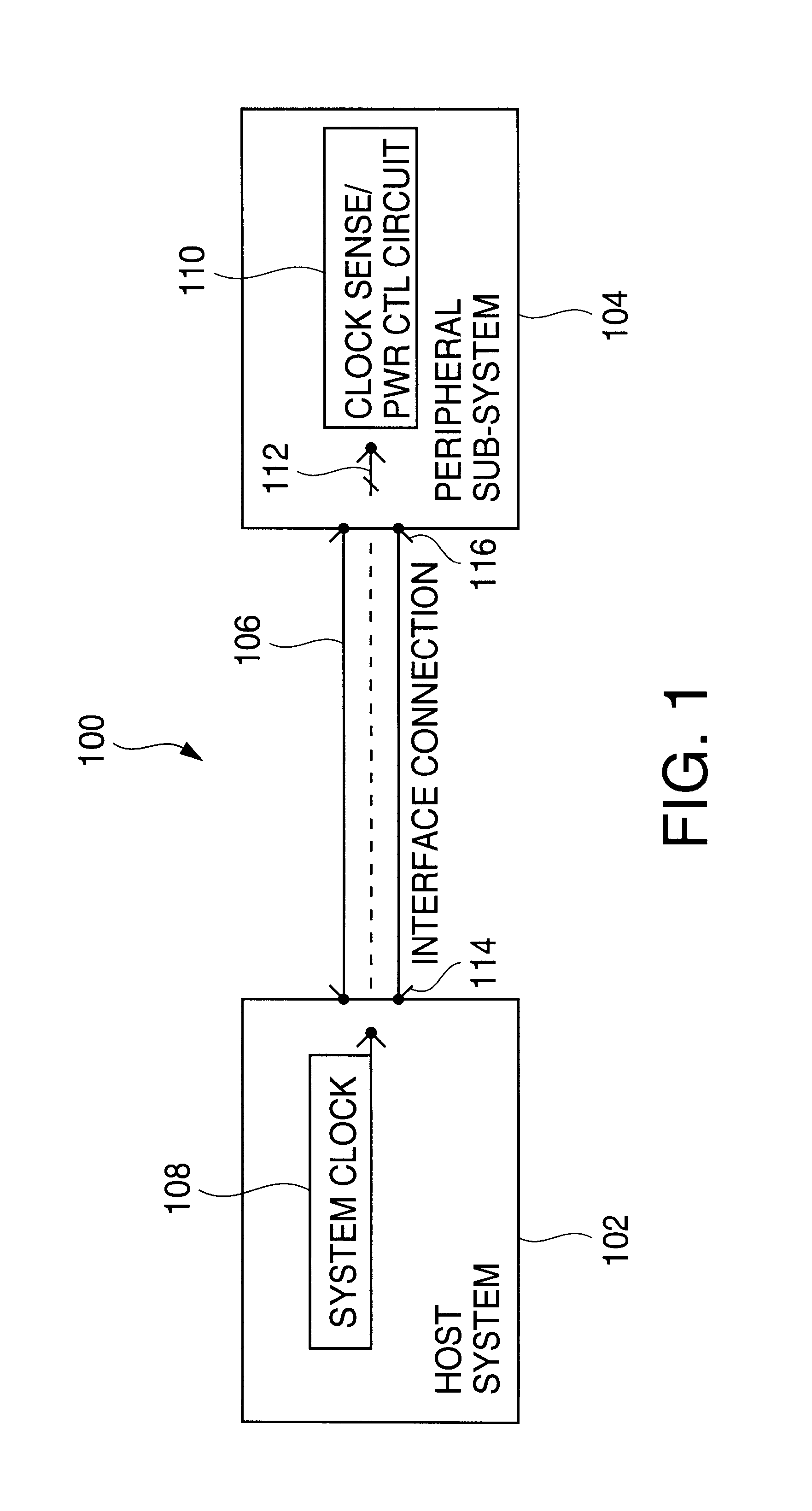
System for remotely controlling power cycling of a peripheral expansion subsystem by a host
A system and method for remotely power cycling a peripheral subsystem. A host system to remotely control the power cycling of a peripheral subsystem, without the need to include or add any dedicated or special signals beyond those needed for the normal interface between the host system and peripheral subsystem. A peripheral subsystem according to the present invention includes circuitry that senses the presence of a downstream, running switching signal such as a clock line or any “heart beat” type signal such as a clock pulse and initiates the power up event of the peripheral system. Conversely, the same circuitry also senses the absence of a downstream signal and initiates a power down event of the peripheral subsystem.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
System and method of preventing aircraft wing damage
InactiveUS6486798B2Easy to implementGuaranteed uptimeNon-electric lightingPoint-like light sourceFlight vehicleComputer module
An apparatus and method for tracking aircraft wingtip position during taxi operations to prevent collisions with nearby obstructions. A patterned illumination source is attached proximal the wingtips to project a readily discernable target pattern in the direction of taxi travel. At least a portion of the target pattern is reflected off of any obstructions that lie in the straight-line direction of travel, such that the pilot can maneuver to avoid striking the obstruction. By way of example, the patterned illumination source comprises a laser module positioned with the navigation and / or strobe light of the aircraft that is configured to project a circular pattern in front of the wingtip. The device may be retrofitted to existing aircraft without additional wiring with the control of activation being selectable via power cycling of existing aircraft lighting controls.
Owner:RASTAR CORP
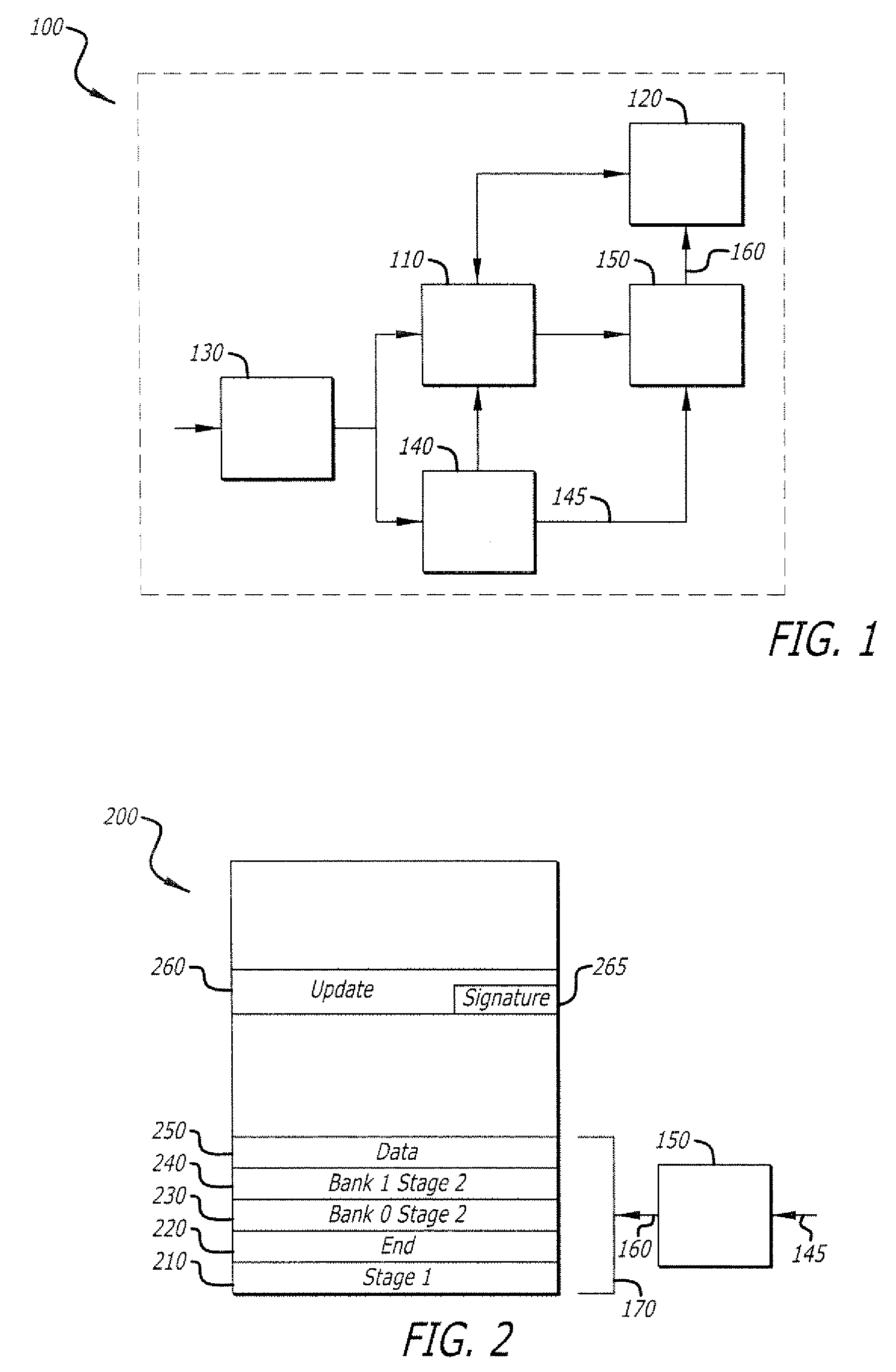
Secure Boot ROM Emulation
Secure boot ROM emulation with locking storage device. A locking storage device is provided by combining a nonvolatile memory device such as flash or EEPROM with one-shot locking logic which write enables at least a portion of the nonvolatile memory device upon power cycling of the overall digital device. This write enable is cleared during the stage 1 bootloader process, thus providing a protected update interval for updating a stage 2 bootloader once per power cycle.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
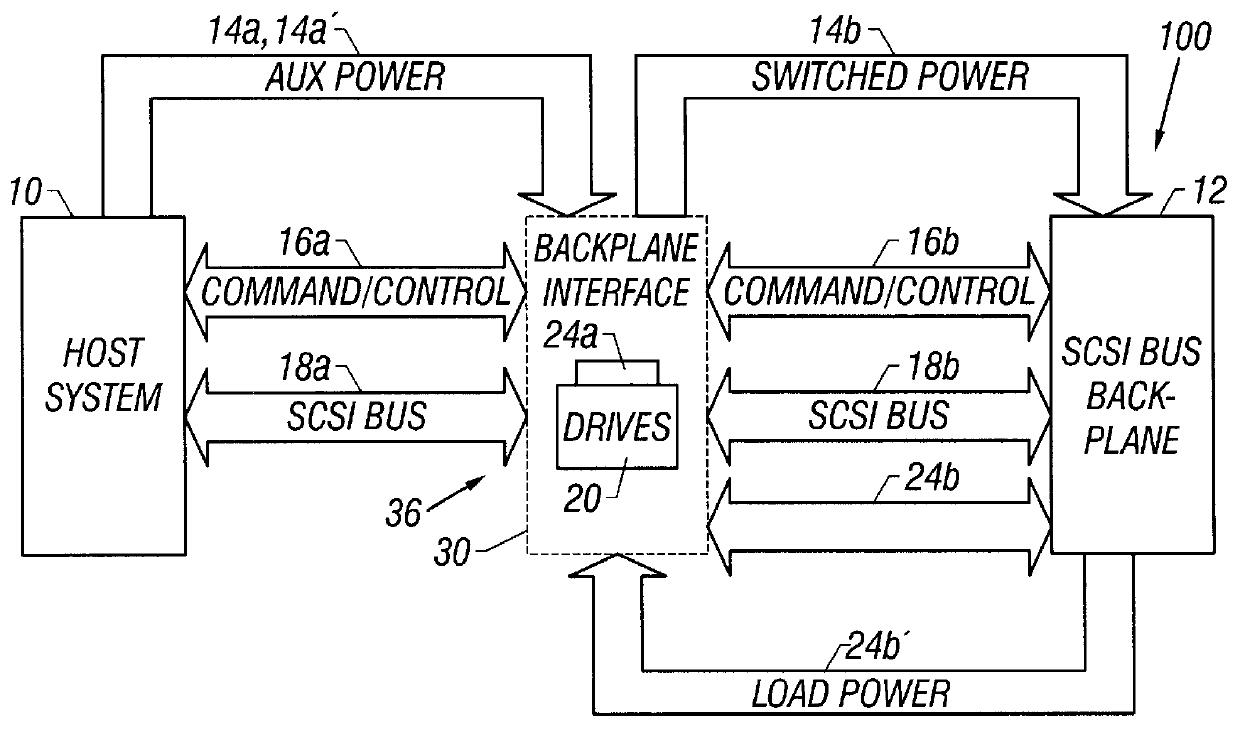
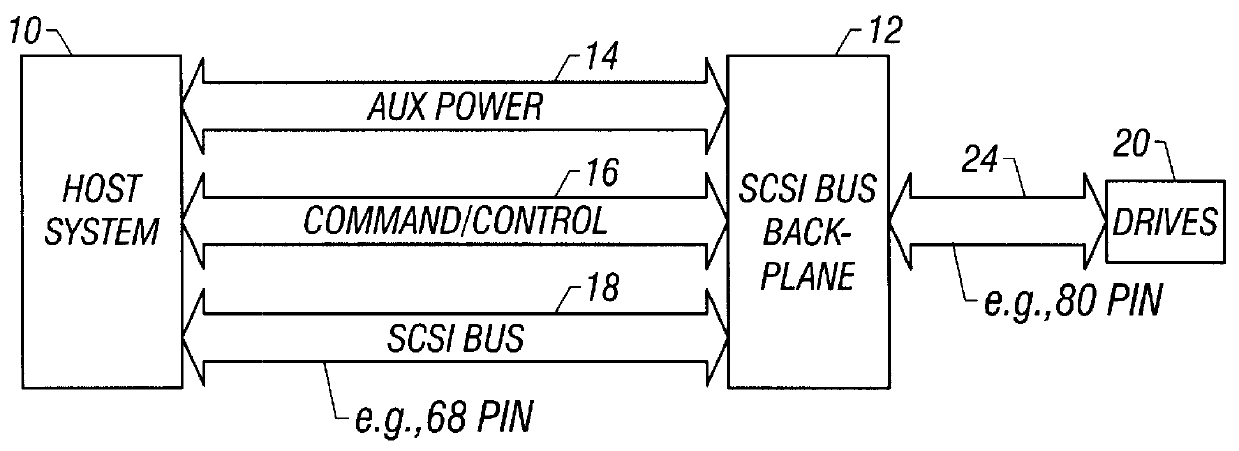
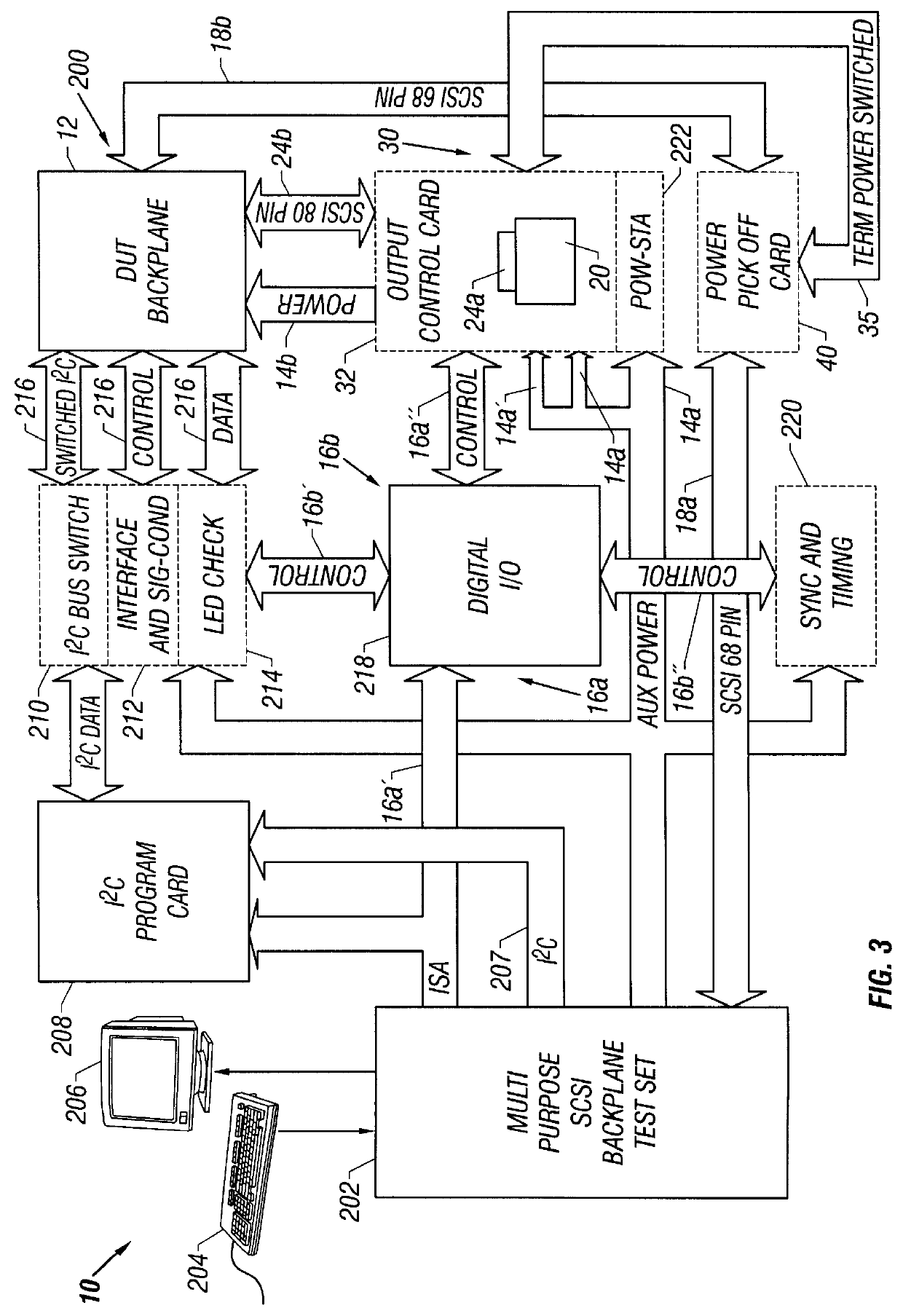
Small computer system interface (SCSI) bus backplane interface
A SCSI bus backplane interface coupled between a host system and a SCSI bus backplane is used to functionally test the backplane. The interface allows the backplane to be disconnected and exchanged for another backplane while avoiding interruption of the operation of the host system and avoiding powering down a cluster of drives present at the interface. The interface intercepts the SCSI bus termination signal during backplane exchange and re-establishes it to the drives (the SCSI bus) after the exchange is made. Complete isolation between the host system, the backplane, and the drives during power cycling permits the backplane to be exchanged without damage. Host system BIOS reboot recognition of the drives is not required each time the backplane is replaced, or to establish the number of active drives to functionally test each backplane after replacement. Test time is therefore reduced.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method and system for managing peripheral connection wakeup in a processing system supporting multiple virtual machines
ActiveUS20060036877A1Volume/mass flow measurementMultiple digital computer combinationsHandling systemEmbedded system
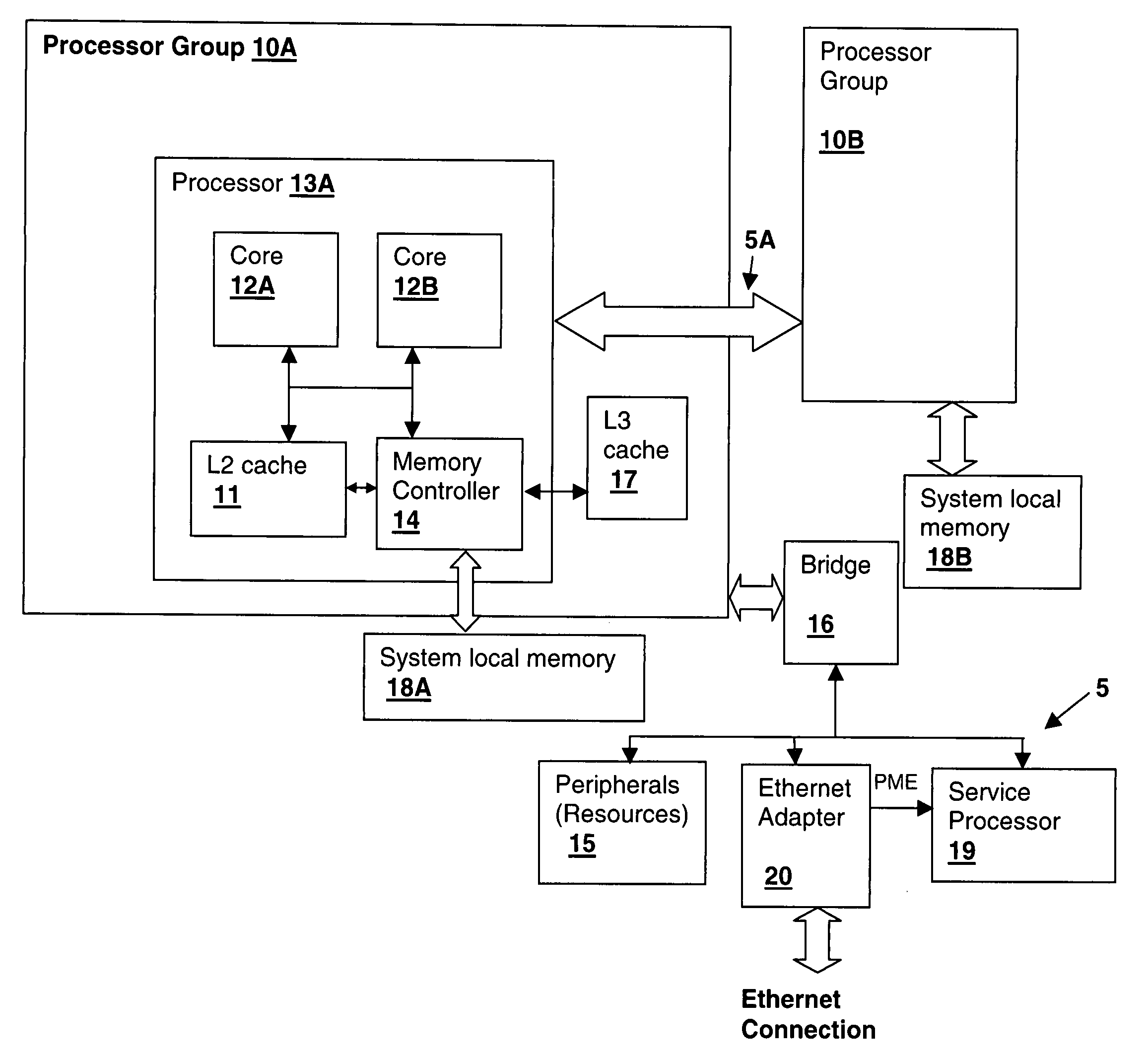
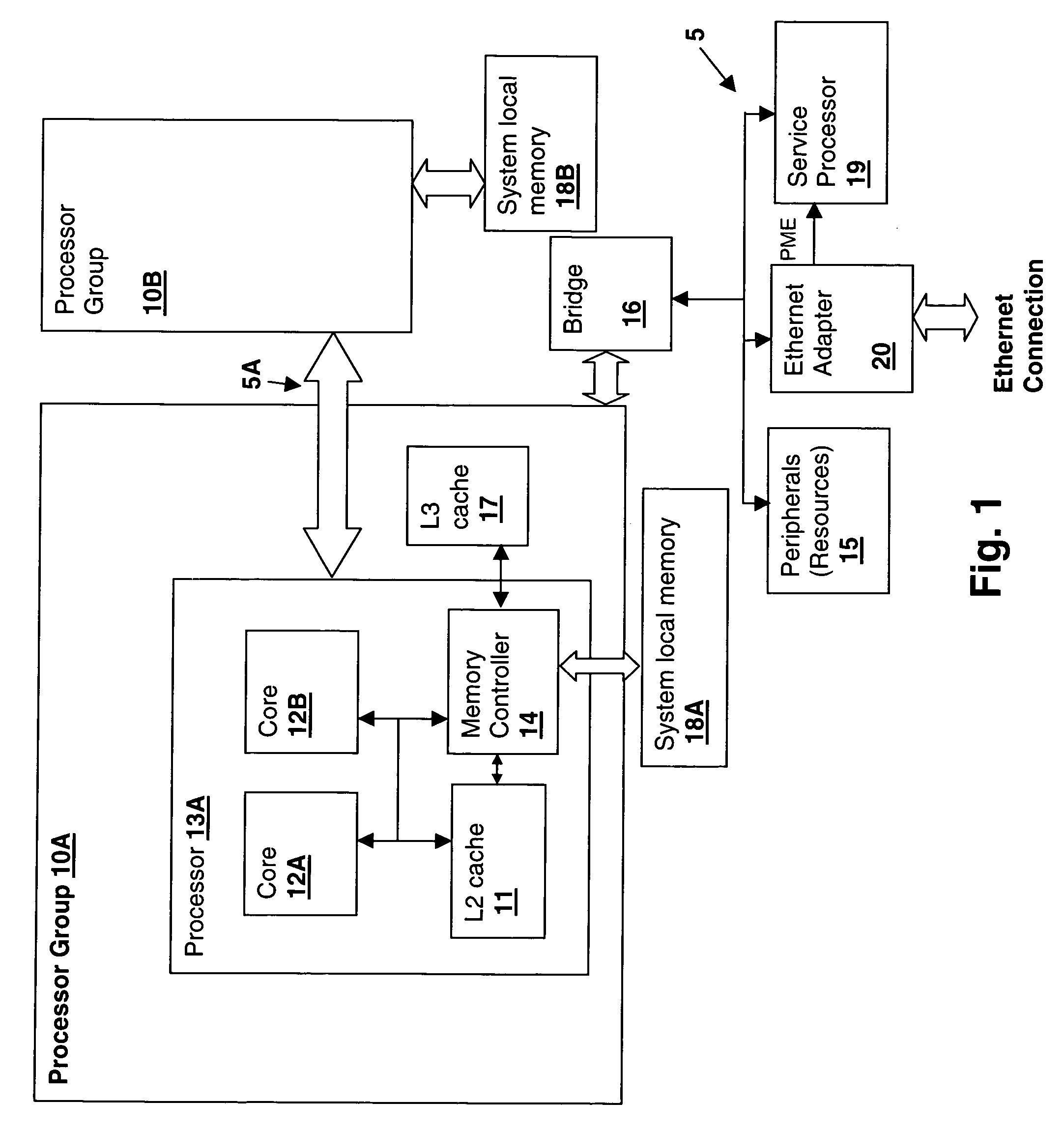
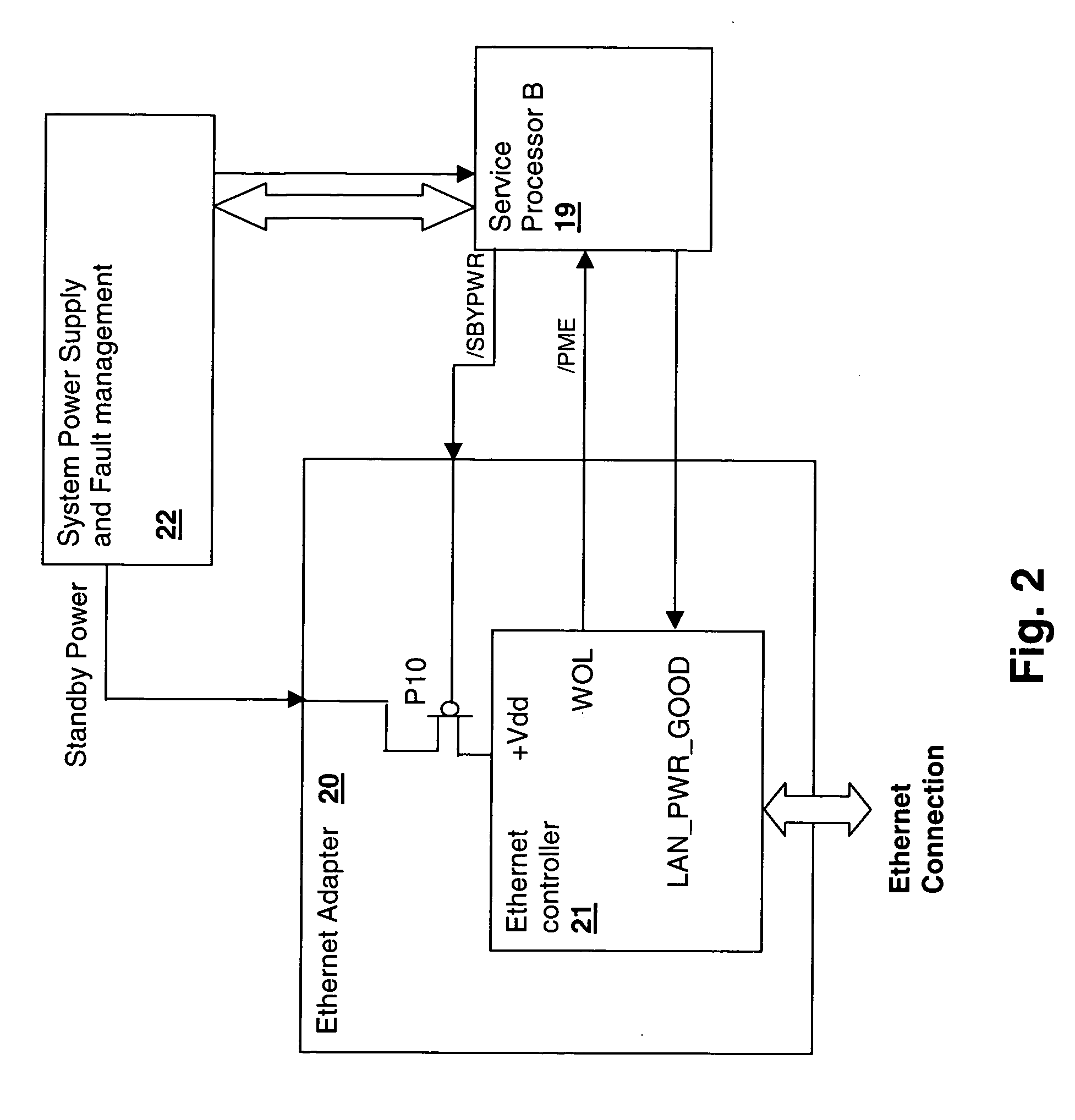
A method and system for managing peripheral connection wakeup signaling in a processing system supporting multiple virtual machines provides a mechanism by which ownership of a peripheral having system wakeup capability is transferred between virtual machines. The power management event signal is connected to a service processor input that in turn signals a hypervisor to direct the wakeup activity to a particular logical partition in which the virtual machine was last executing. The hypervisor can then determine whether or not to wake up the entire system, or portions thereof and can direct the power management event to the appropriate virtual machine. In particular the peripheral may be an Ethernet adapter supporting Wake-On-LAN capability. State initialization, which is typically ensured by system power cycling is provided instead by controlling power to the standby power source or in some instances by forcing an indication of a disconnect / reconnect of the wakeup signaling connection.
Owner:META PLATFORMS INC
System and method of preventing aircraft wing damage
InactiveUS20020018009A1Easy to implementGuaranteed uptimeNon-electric lightingLighting support devicesComputer moduleBiological activation
An apparatus and method for tracking aircraft wingtip position during taxi operations to prevent collisions with nearby obstructions. A patterned illumination source is attached proximal the wingtips to project a readily discernable target pattern in the direction of taxi travel. At least a portion of the target pattern is reflected off of any obstructions that lie in the straight-line direction of travel, such that the pilot can maneuver to avoid striking the obstruction. By way of example, the patterned illumination source comprises a laser module positioned with the navigation and / or strobe light of the aircraft that is configured to project a circular pattern in front of the wingtip. The device may be retrofitted to existing aircraft without additional wiring with the control of activation being selectable via power cycling of existing aircraft lighting controls.
Owner:RASTAR CORP
Leak proof pressure relief valve for secondary batteries
Secondary batteries are subjected to power cycling, and those which have a liquid electrolyte within the interior volume are equipped with a pressure relief valve. A void space over the liquid electrolyte may be subjected to gas pressure variations with respect to the ambient. The pressure relief valve structure comprises a vertically oriented gas flow chamber, and an outer relief vent adapted to open only when gas pressure within the battery and the gas flow chamber exceeds a predetermined pressure with respect to the ambient pressure. The gas flow chamber extends below the top surface of the battery, and has a dome-like cap which extends downwardly and has a plurality of openings so as to permit unimpeded gas flow between the interior of the battery and the gas flow chamber. There is a porous membrane covering the dome which permits gas flow between the interior of the battery and the gas flow chamber, but precludes flow of liquid electrolyte from the interior volume of the battery to the gas flow chamber.
Owner:ZINCFIVE POWER INC
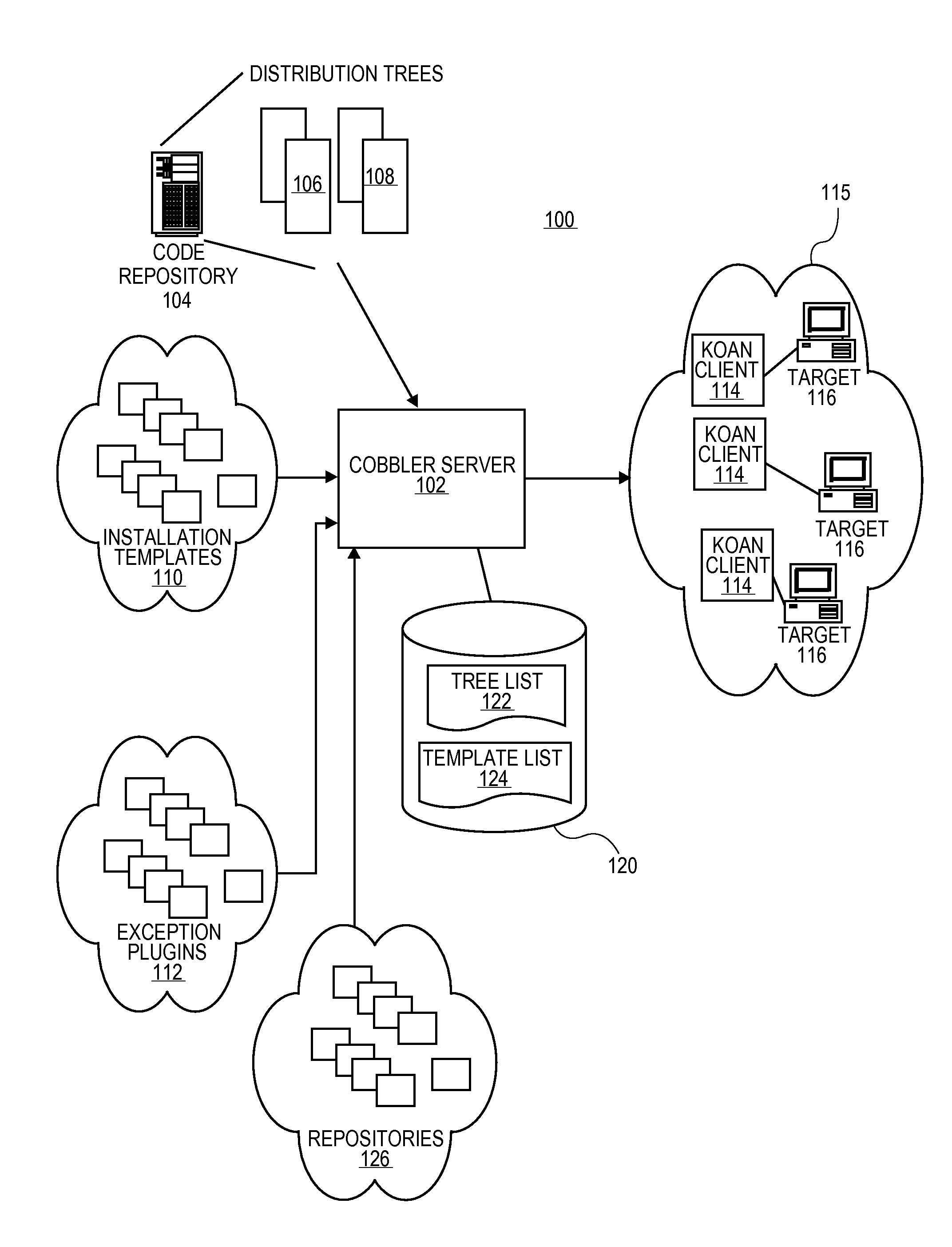
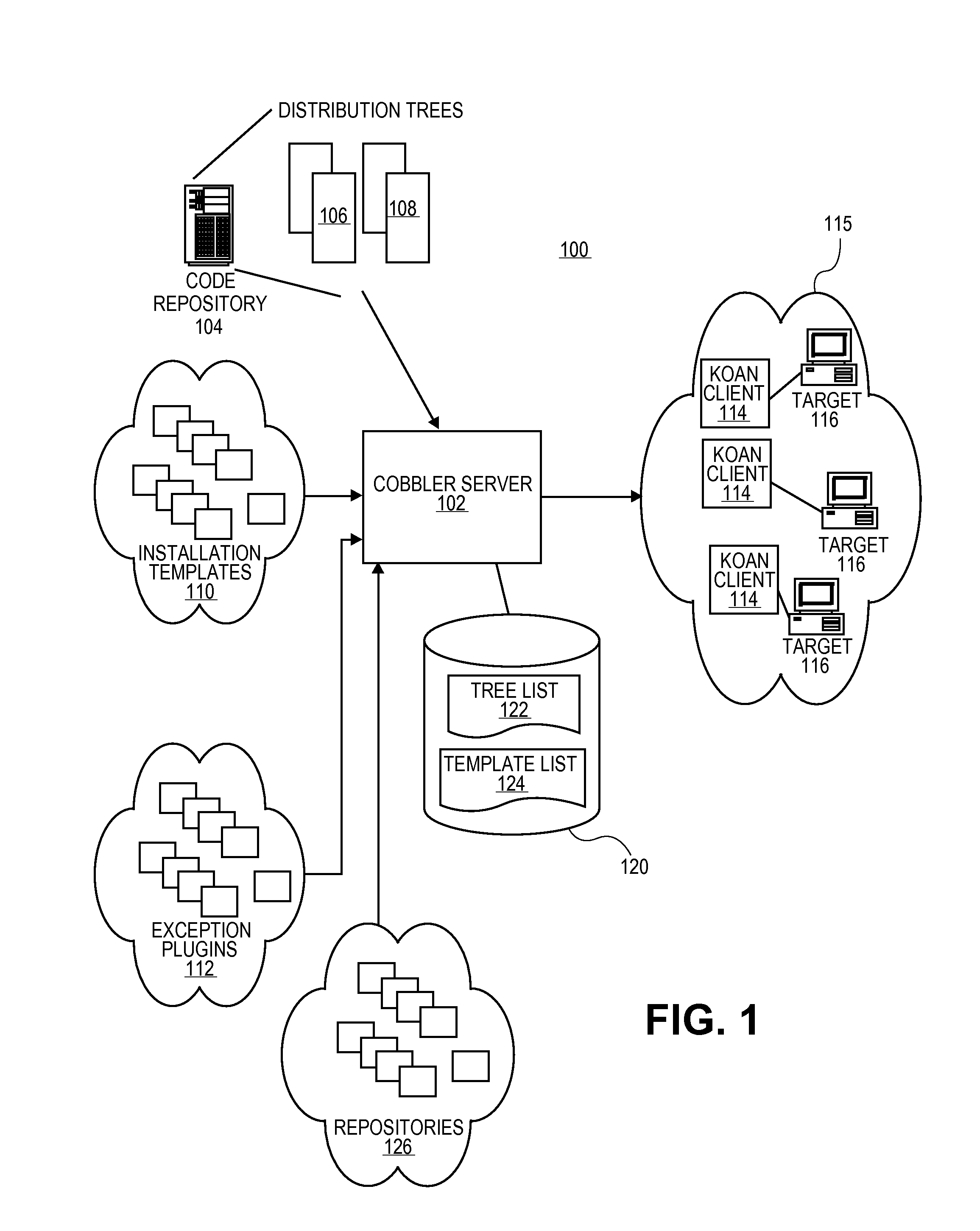
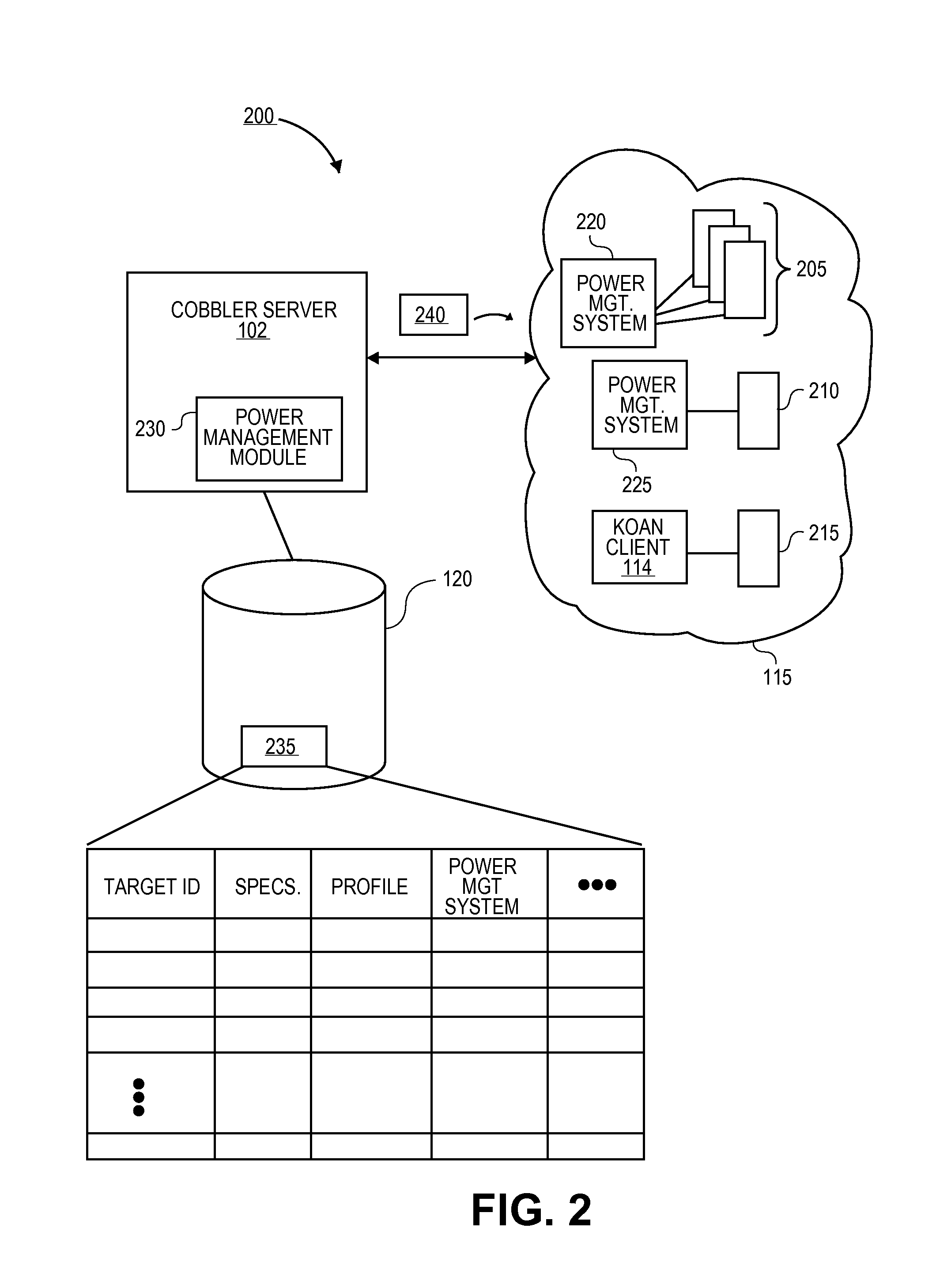
Methods and systems for providing power management services in a software provisioning environment
ActiveUS20100131648A1Digital computer detailsPower supply for data processingPower cycleElectric power
A software provisioning server can be configured to communicate with a power management system of the target machines to alter the power state of the target machines during actions requiring a change in the power states such as power cycling the target machines during a software installation. The software provisioning server can communicate with the power management system of the target machines and instruct the power management systems to alter the power state of the target machines during the actions.
Owner:RED HAT
Managing audio output through an intermediary
The present invention extends to methods, systems, and computer program products for managing audio output through an intermediary. In some embodiments, an audio controller emulates a direct connection between an audio source device and an audio output device. In other embodiments, audio content local to an audio controller is combined with other audio content passing through the audio controller on its way from an audio source device to an audio output device. In additional embodiments, an audio output device is locked to an audio controller. The lock survives power cycling and soft resets of the audio output device. A special hard reset can be used to release the audio output device.
Owner:VIVINT INC
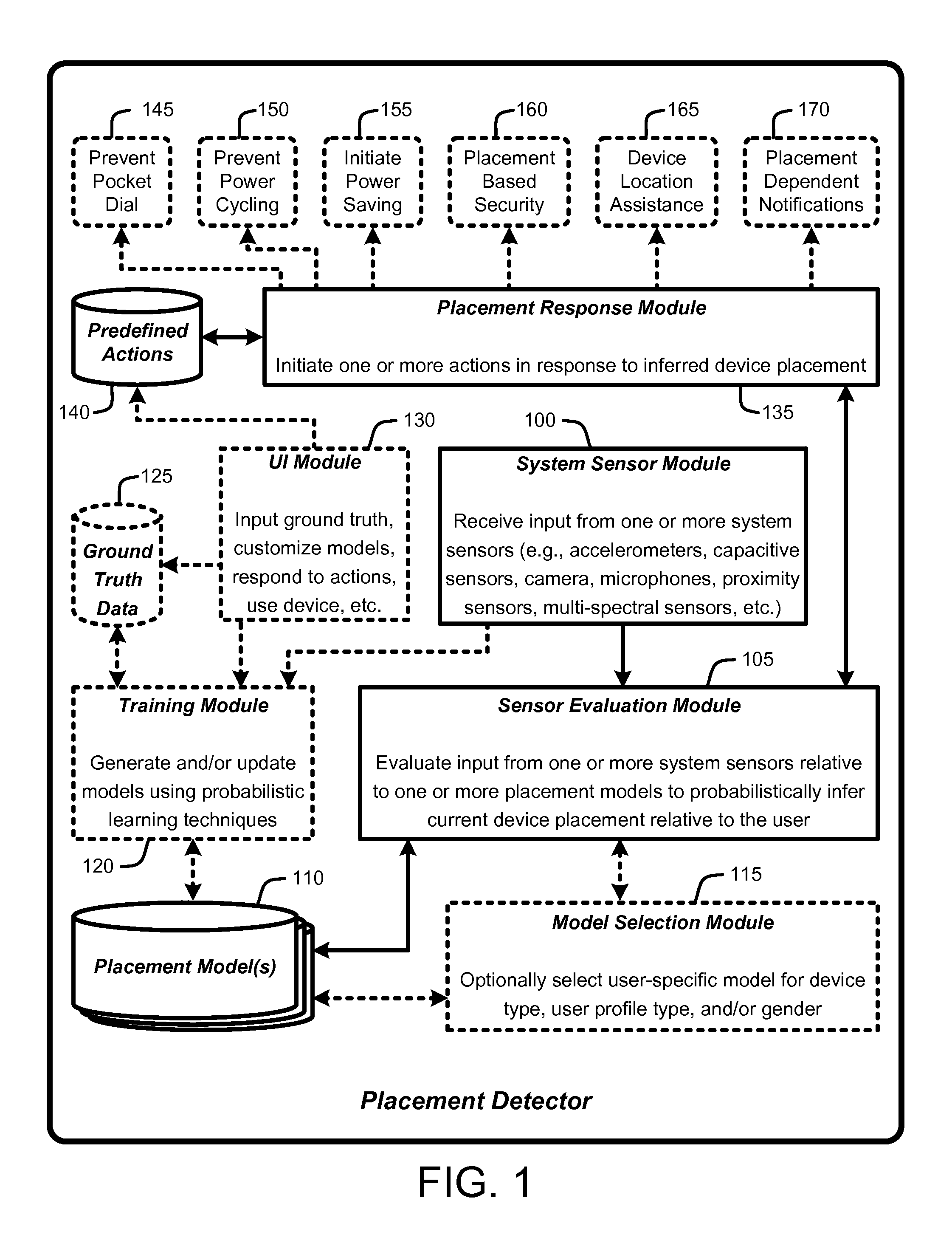
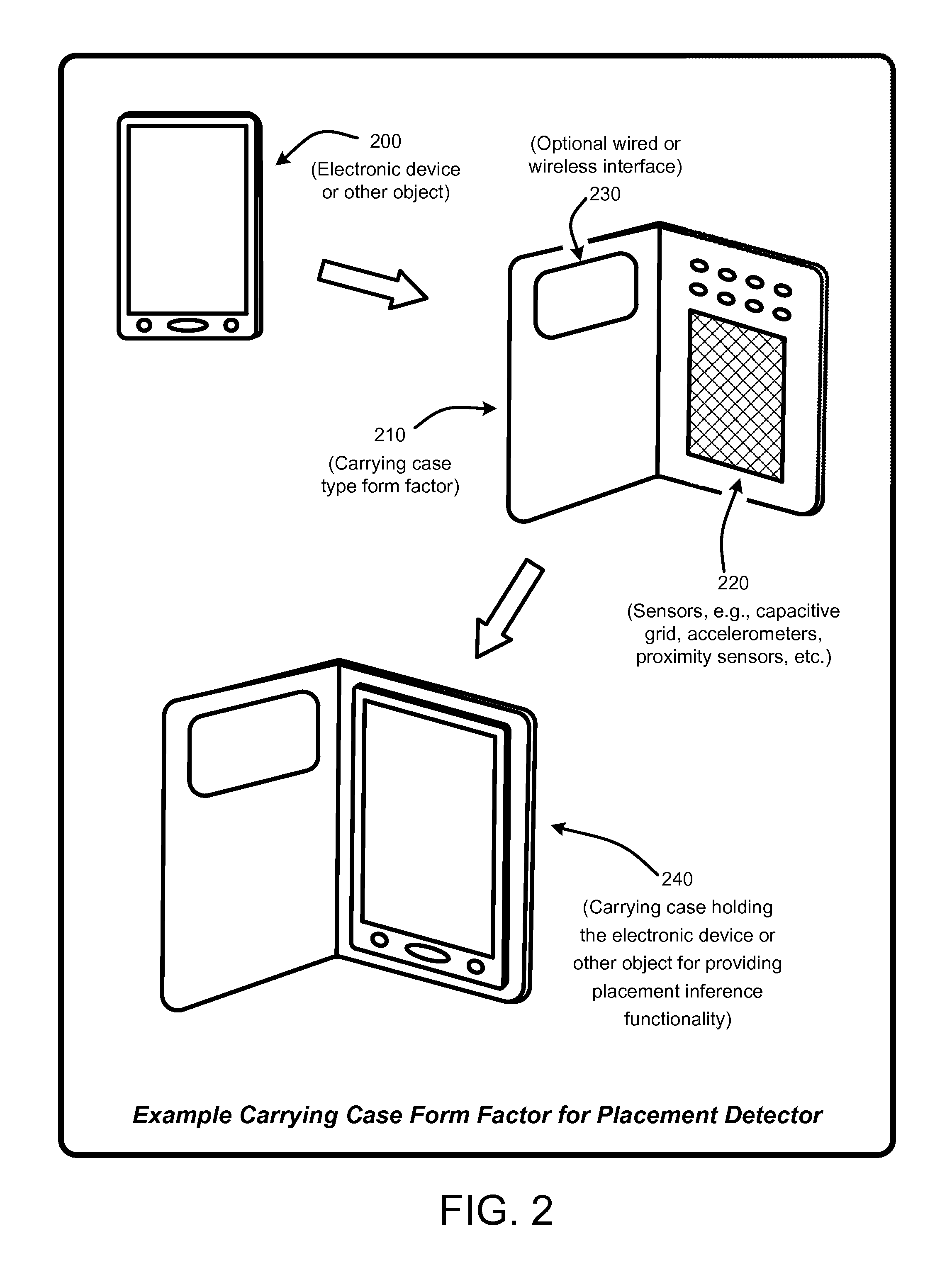
Inferring placement of mobile electronic devices
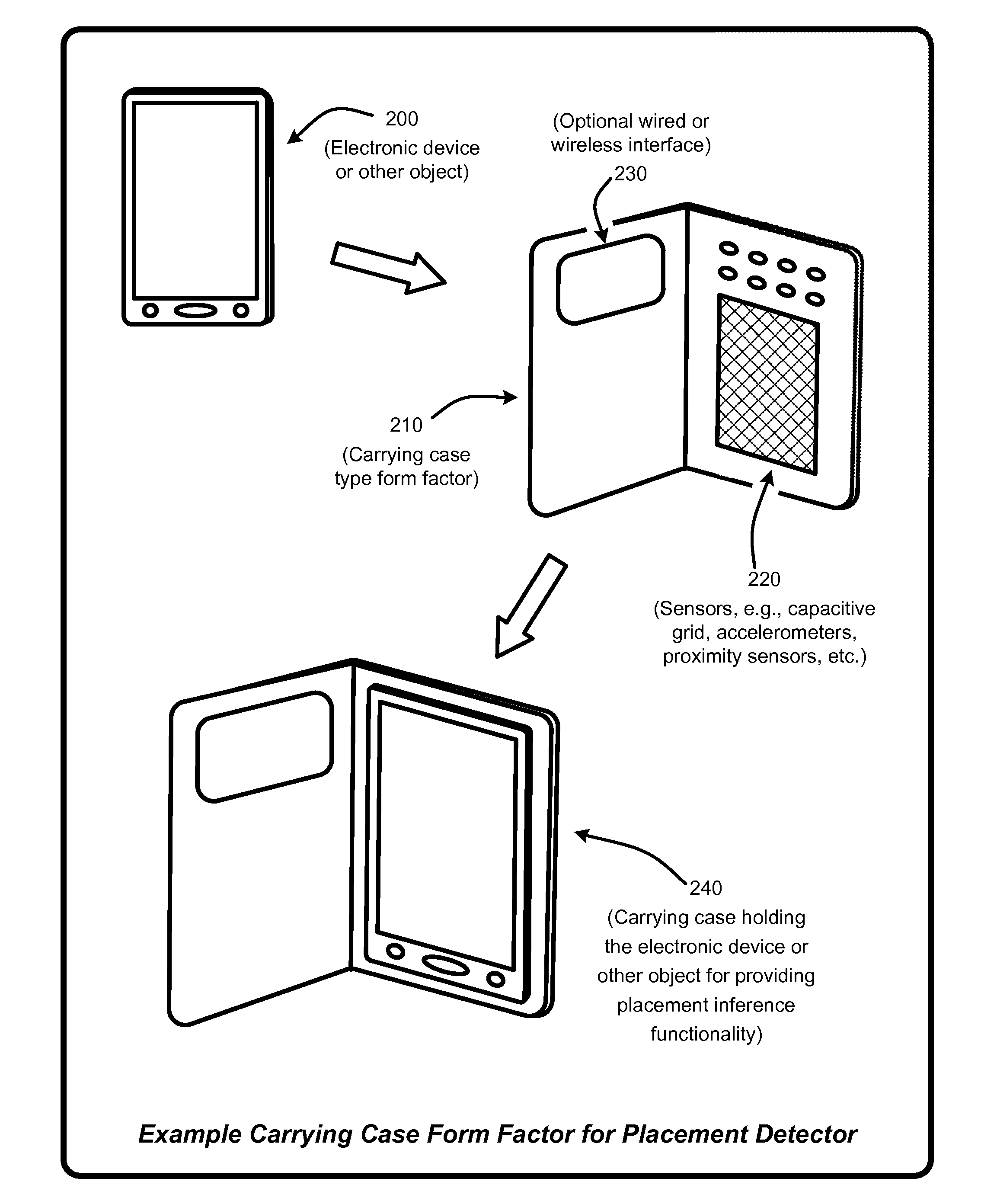
ActiveUS20140274159A1Wide rangeAvoid problemsDigital computer detailsDevices with sensorProbit modelUser device
A “Placement Detector” enables handheld or mobile electronic devices such as phones, media players, tablets, etc., to infer their current position or placement. Placement inference is performed by evaluating one or more sensors associated with the device relative to one or more trained probabilistic models to infer device relative to a user. Example placement inferences include, but are not limited to, inferring whether the device is currently in a user's pocket, in a user's purse (or other carrying bag or backpack), in a closed area such as a drawer or box, in an open area such as on a table, indoors, outdoors, etc. These types of placement inferences facilitate a wide range of automated user-device interactions, including, but not limited to, placement-dependent notifications, placement-dependent responses to various inputs, prevention of inadvertent “pocket dialing,” prevention of inadvertent power cycling of devices, lost or misplaced device location assistance, etc.
Owner:ZHIGU HLDG
Techniques for initializing a device on an expansion card
Techniques for initializing / reinitializing a device on an expansion card without power cycling the system. More specifically, an instruction set is provided such that a device on an expansion card can be reinitialized without power cycling the system. Further, the instruction set may be implemented to initialize a device on a replacement expansion card. During the system boot, an expansion basic input / output system (BIOS) is copied into the system memory. After the system boot, a copy of the configuration information for the device on the expansion card is saved in a backup file in the system memory. The expansion card can be removed and replaced and the configuration information stored in the backup file in the system memory can be used to configure the replacement device. The copy of the expansion BIOS in the system memory can be reprogrammed such that it can be implemented to initialize the device on the replacement expansion card without power cycling the system.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
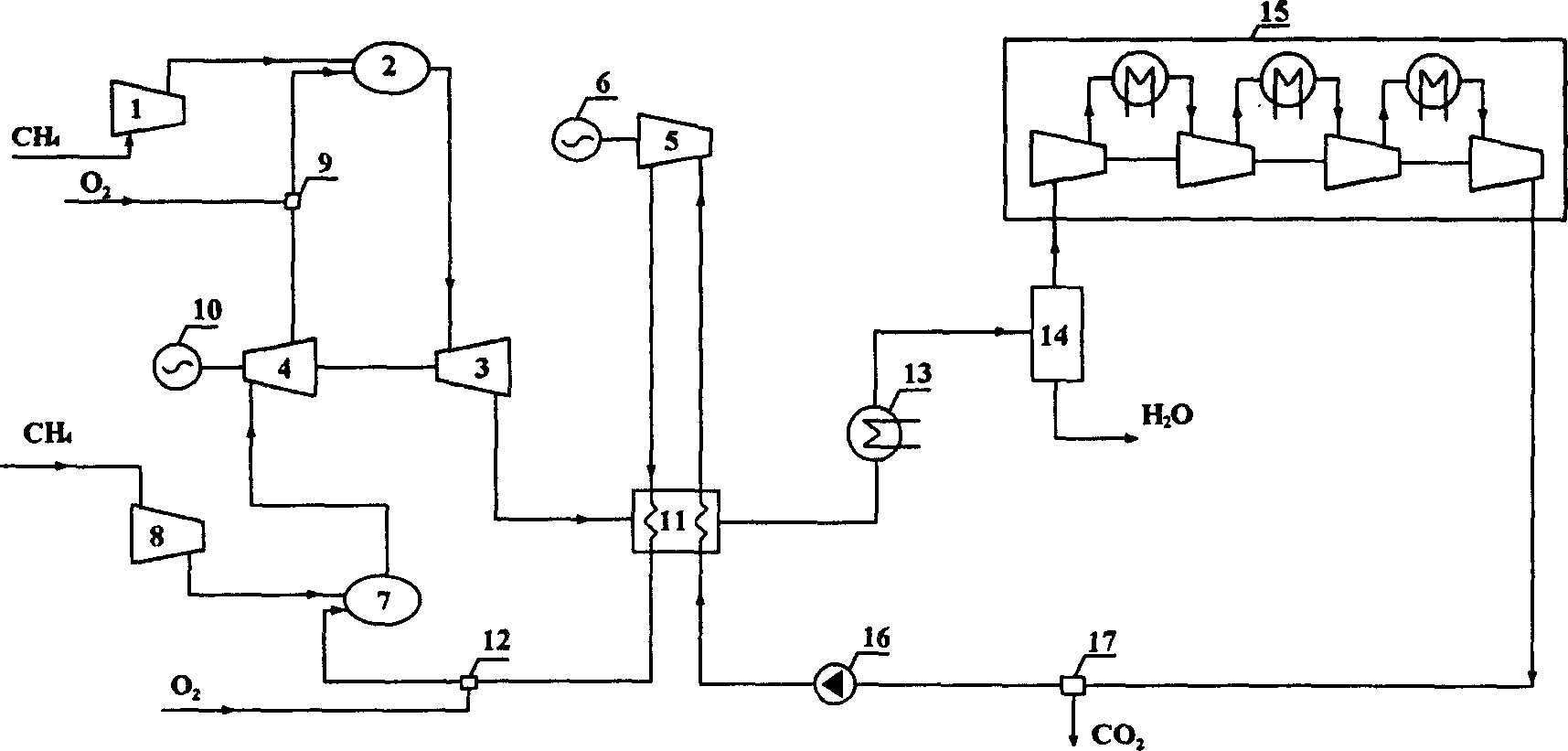
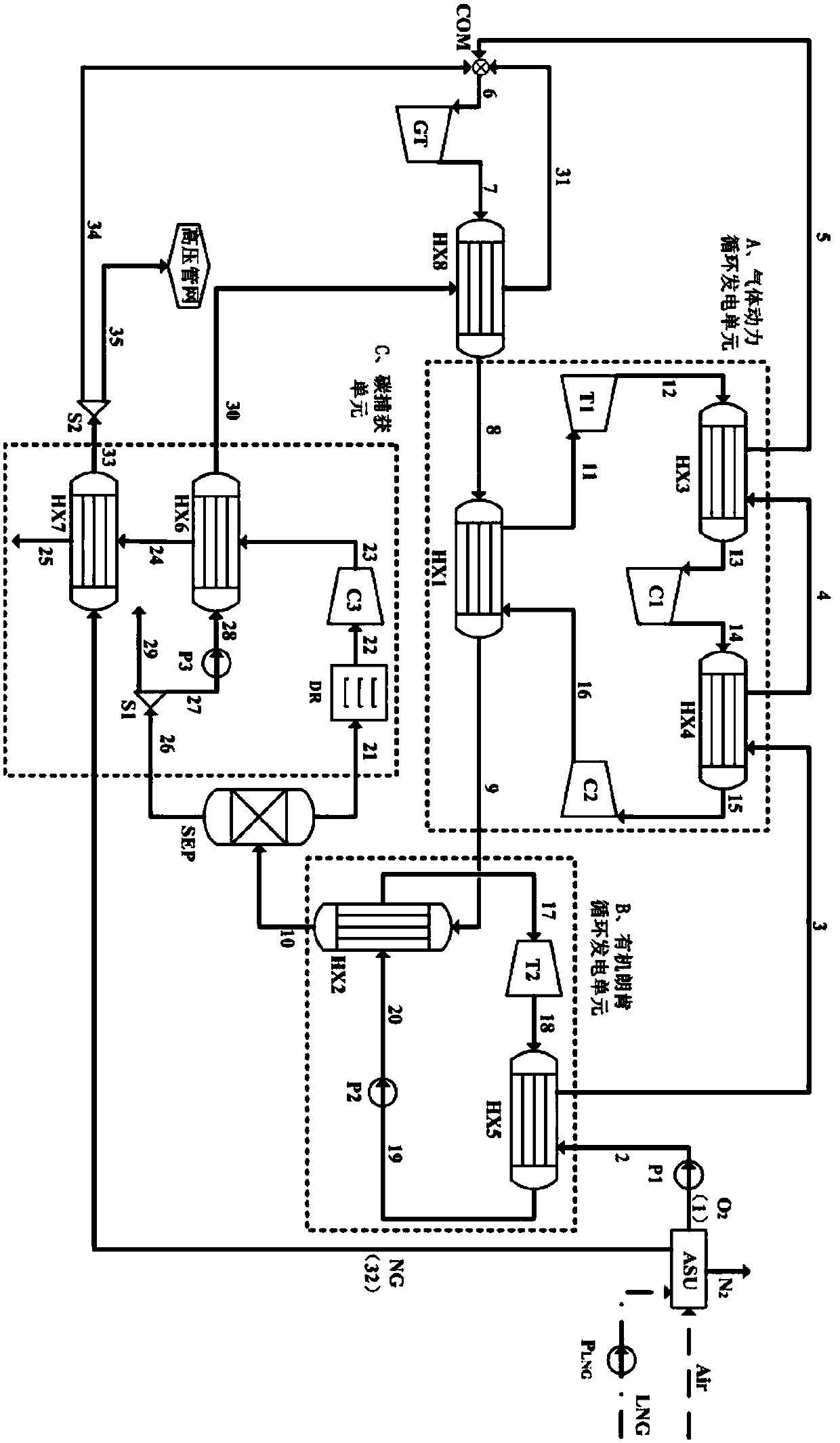
Gas power circulation system and circulation method
InactiveCN1869418AFunctionalWith water saving functionInternal combustion piston enginesClimate change adaptationCombustion chamberMethane
The invention supplies a fuel gas power cycling system and the cycling method. It includes the following steps: it combines O2 / CO2 chemical heat backing power cycling and ammonia absorbing refrigeration system, the compressed CO2 gas taking reforming reaction with natural gas in reforming reactor, and the gas after reforming taking burning reaction with pure oxygen in burning room; the high temperature would coming into turbine and expanding to apply; the turbine exhausting and supplying heat to reforming reactor and supplying heat to ammonia absorbing refrigerating cycling system; the cold quantity would be used to cool CO2 and output; the condenser would separate water and CO2, and outputting the water; part of CO2 would be used to take driving cycling, and the other part would be transformed to liquid state and output from system. The invention could generate electric and cold, and has CO2 trapping function and water saving function.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
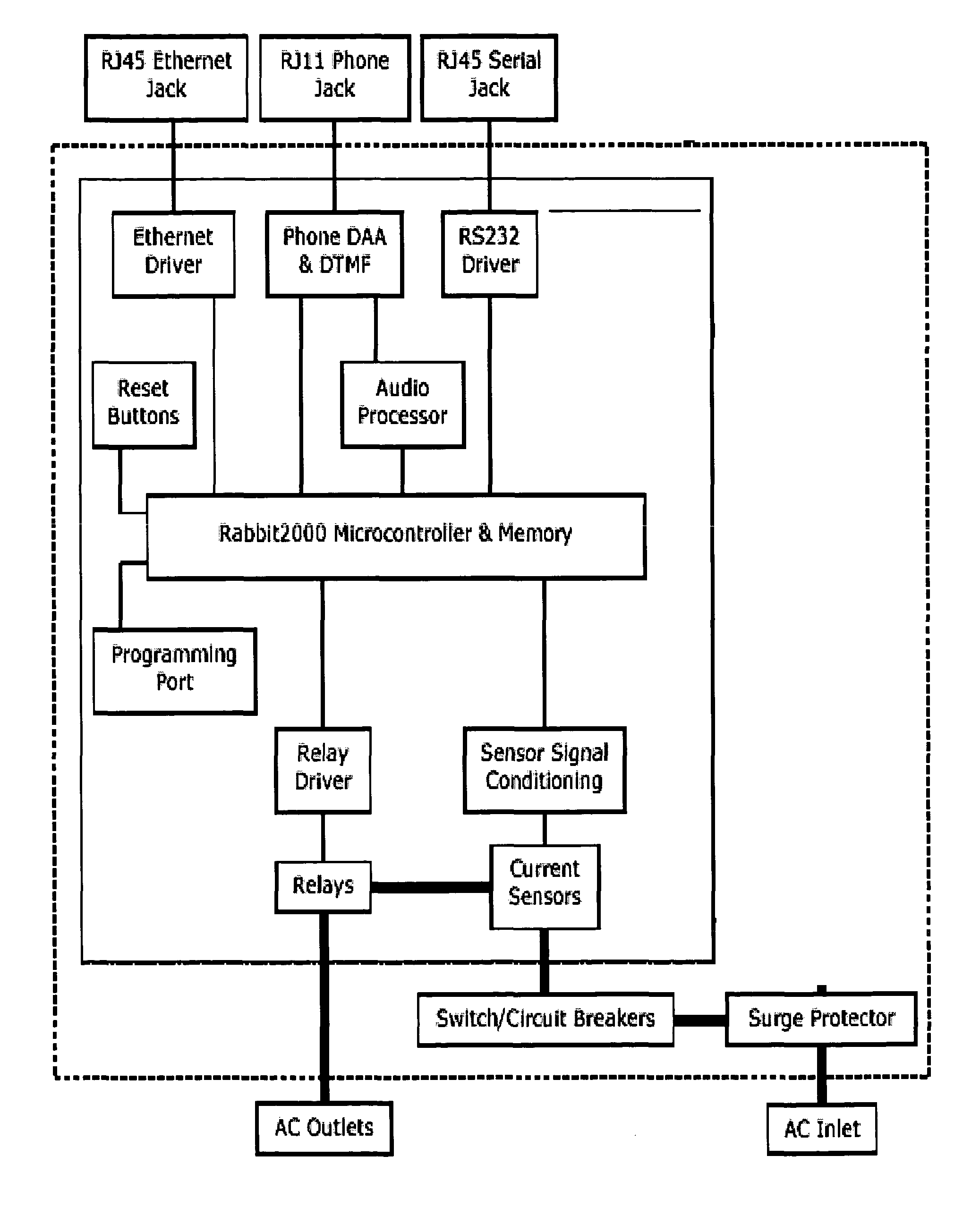
Method and apparatus for remote power management and monitoring
ActiveUS7550870B2New capabilityMechanical power/torque controlDc network circuit arrangementsEngineeringElectric power
Methods and / or systems for power monitoring and / or power cycling management provide a variety of different remote interfacing and provide individual current monitoring for each output in a power supply strip. In various implementations, the invention can be incorporated into a power supply strip for a network device rack thereby providing compact controllable and monitorable power for multiple network devices.
Owner:CYBERSWITCHINGPATENTS
Oriented connections for leadless and leaded packages
InactiveUS20040178250A1Increase surface tensionStrong capillary characteristicFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsFixation pointThermal deformation
The invention discloses design concepts and means and methods that can be used for enhancing the reliability and extending the operating life of electronic devices, and assemblies incorporating such devices, and substrates and / or PCBs, especially if such assemblies are exposed to severe environments such as thermal cycling or power cycling. The main thrust of the invention is to provide flexible joints, such as columns, between the attached components, and preferably to orient such joints, so that they would present their softest bending direction towards the thermal center or fixation point of the assemblies. Joints with rectangular or elongated cross-section are preferred, and they should be oriented so that the wide face of each joint would be facing the thermal center, perpendicular to the thermal deformation ray emanating from the thermal center towards the center of each respective joint. The concepts apply equally to leadless packages as well as to leaded packages.
Owner:CHERIAN GABE
Method, system and equipment for restarting remote control equipment
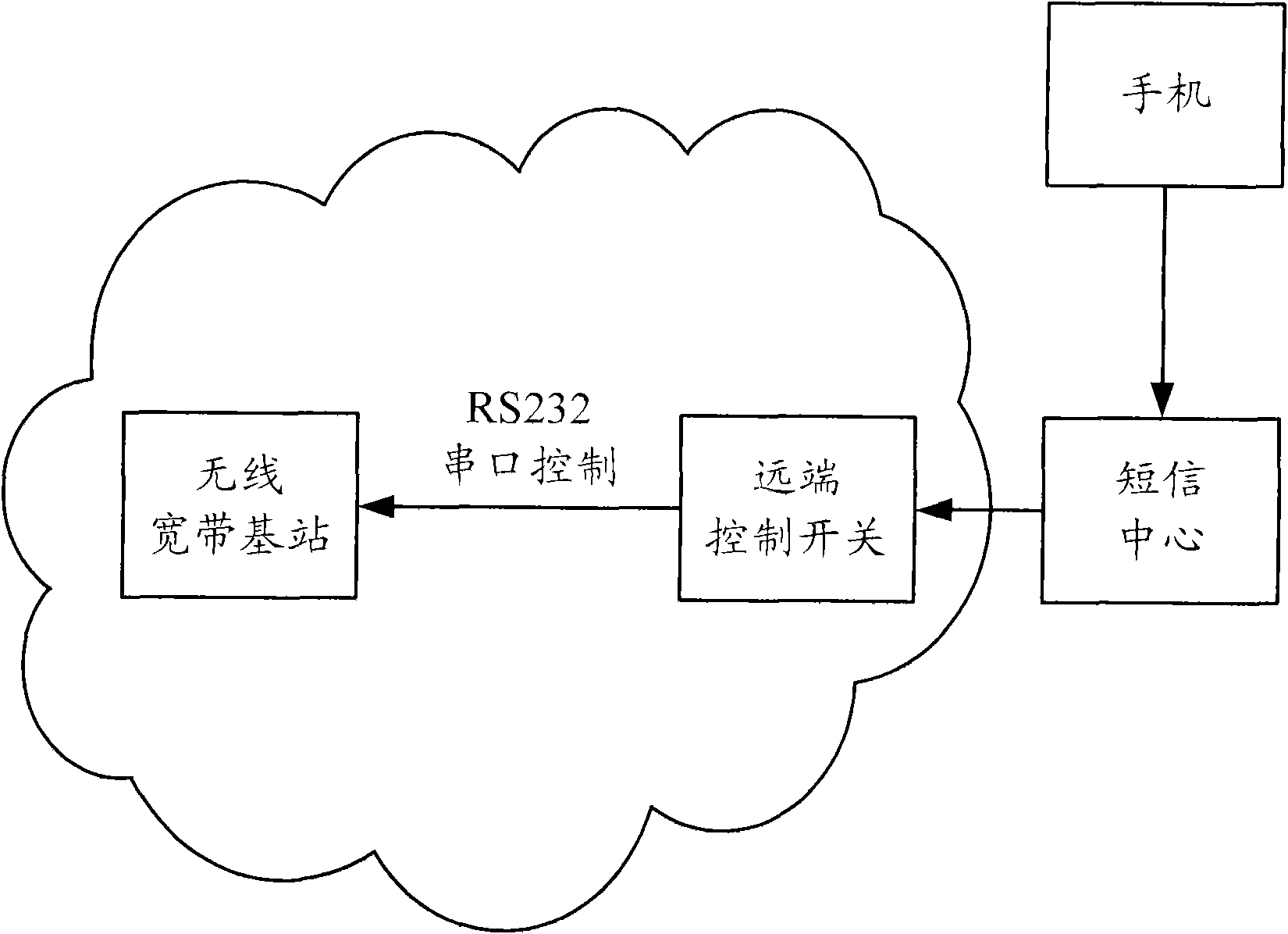
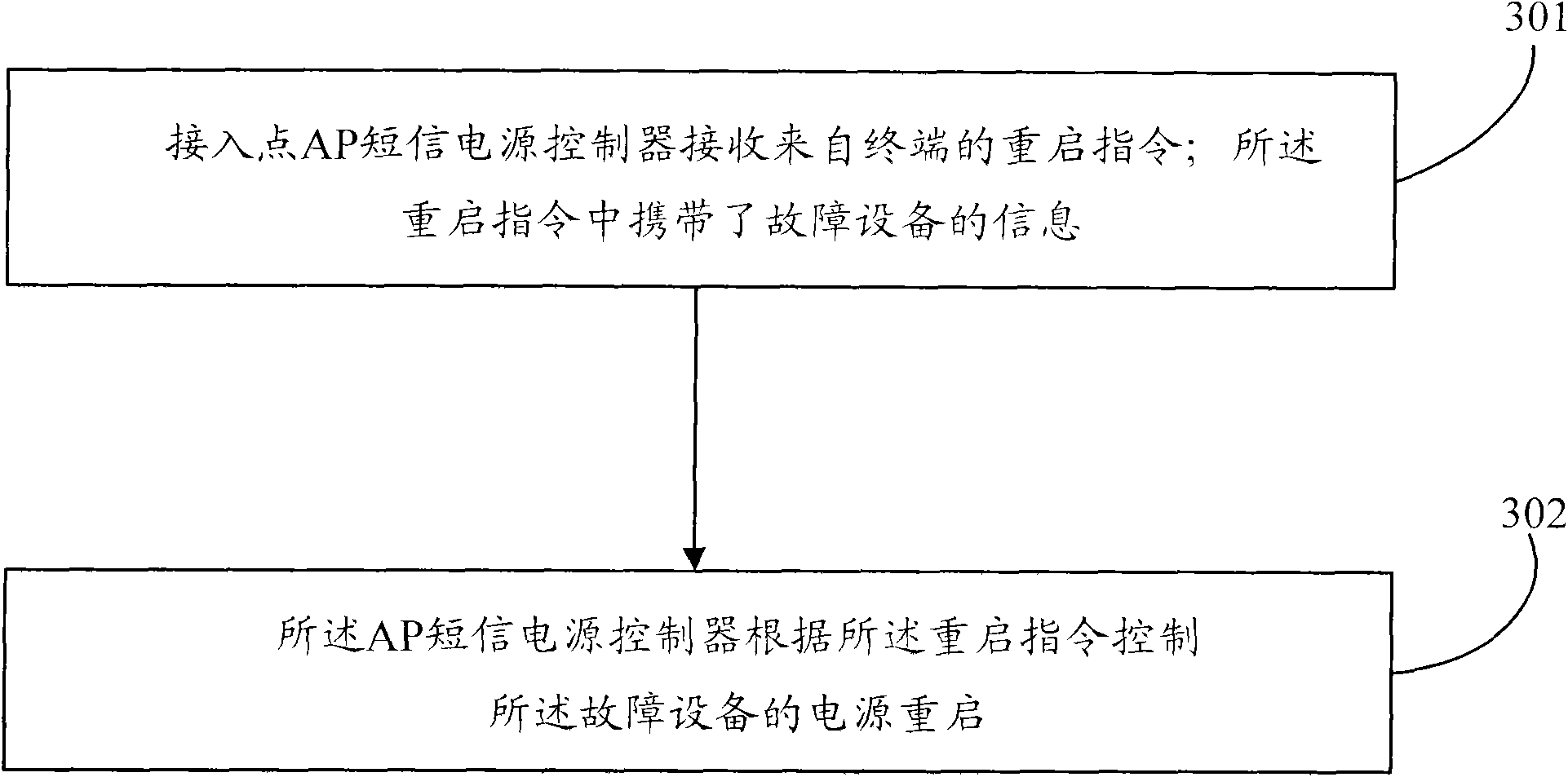
ActiveCN102083023ARealize "zero" time response maintenanceRealize automatic monitoringNetwork topologiesMessaging/mailboxes/announcementsPower controllerRemote control
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method, system and equipment for restarting remote control equipment. The method comprises the following steps of: receiving a restarting instruction from a terminal by using an access point (AP) short message power supply controller, wherein the restarting instruction carries information of fault equipment; and controlling the power supply starting of the fault equipment by using the AP short message power supply controller according to the restarting instruction. In the embodiment of the invention, maintainers can carry out management without the need of arriving at scenes and send short messages to a network card or SIM (Subscriber Identity Module) card of the AP short message power supply controller in a remote short message sending mode so that faults appearing in an AP are solved; and an interface of the AP short message power supply controller provided in the embodiment of the invention is open so that the equipment can be used together with any third network management systems and realizes the automatic monitoring and restarting of network management system sides for the AP faults.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE GROUP JIANGSU
Trenching resistance welding type IGBT module base plate
InactiveCN104347553AImprove insulation performanceIncrease powerSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDBcSolder mask
A grooved solder mask insulated-gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) module base plate (1). A groove (2) is provided at the edge of a soldering region of the grooved solder mask IGBT module base plate (1). The inner-edge dimension of the groove (2) matches with the contour dimension of a solder substrate (4) and constitutes one closed ring. By designing a ring of grooved structure at the edge of the soldering region (3) of the module base plate to divert a molten solder that spilled over, the molten solder is evenly distributed within the defined soldering region, thus implementing the goal of preventing spillover of the molten solder, preventing deposition of the solder at the edge of a copper-plated ceramic substrate (a DBC substrate), ensuring the thickness of a solder layer, facilitating increased insulating capability and increased power cycling capability of the module, and preventing occurrences of module insulation failure and of cracking between the DBC substrate and the base plate.
Owner:XIAN YONGDIAN ELECTRIC
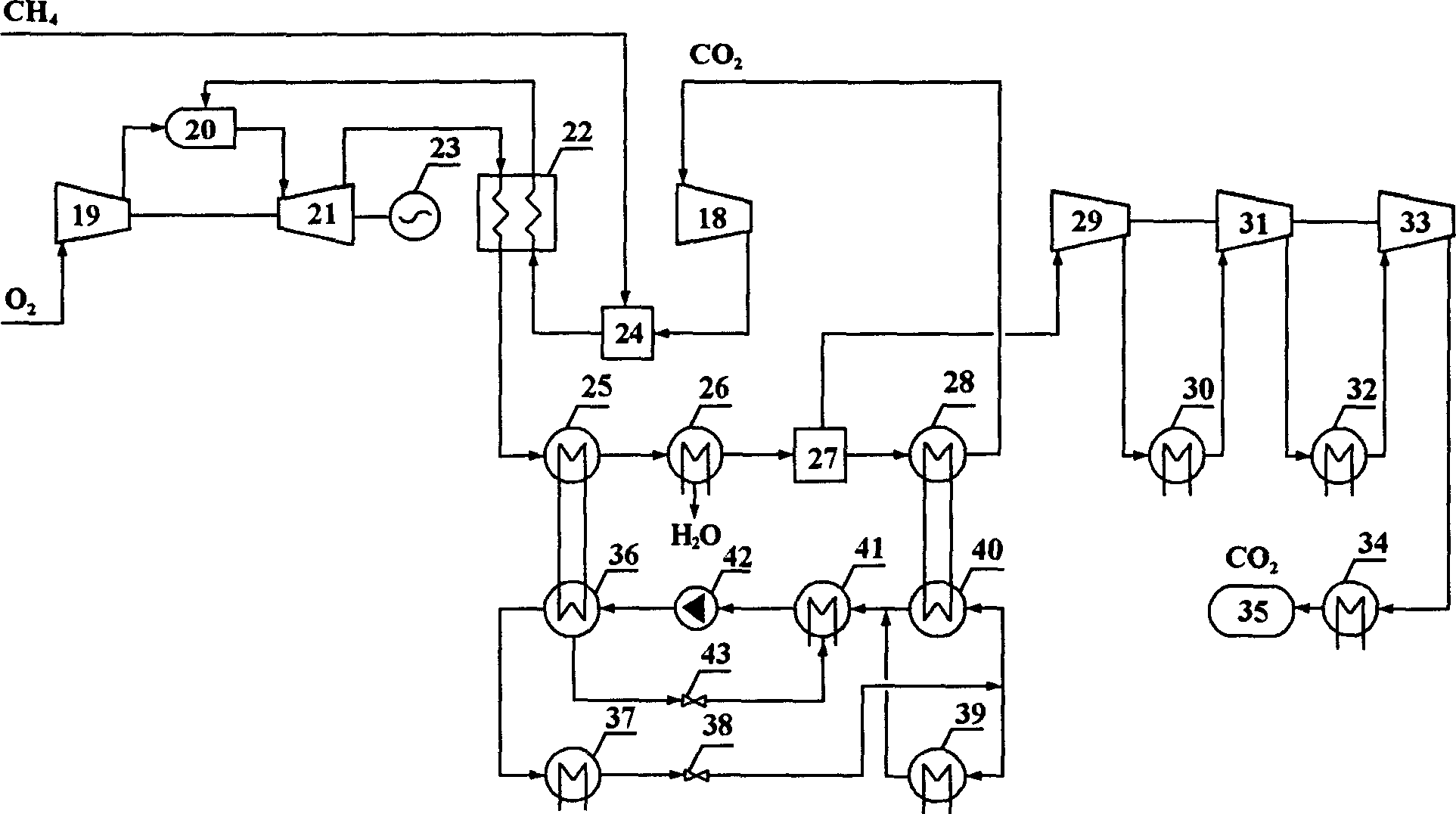
Power generating system utilizing vaporization latent heat of exhaust fume of natural gas power plant
ActiveCN108331625ASolve the problem of general waste of latent heat of vaporizationImprove power generation efficiencySolidificationLiquefactionOrganic Rankine cycleNatural gas
The invention discloses a power generating system utilizing vaporization latent heat of exhaust fume of a natural gas power plant. According to the power generating system, aiming at the oxygen enriched combustion natural gas power plant, a composite-type combined cycling power generating unit is put forward, fume generated after oxygen enriched combustion sequentially passes through a combustiongas turbine GT, a gas power cycling power generating unit A and an organic Rankine cycle power generating unit B, the vaporization latent heat in the fume can be sufficiently recycled, the temperatureof the exhaust fume is decreased to below the normal temperature, CO2 and water in the fume are separated accordingly, and carbon capture is achieved. In the power generating system, gas power cycling is adopted, thus phase change of heat exchange media is avoided, and the heat exchange effect is improved; through organic Rankine cycle, the vaporization latent heat in the fume is sufficiently recovered, and the power generating efficiency of the system is greatly improved; and according to the integrated power generating system, the problems that the steam vaporization latent heat in the low-temperature fume is generally wasted, carbon capture energy consumption is high, and LNG cold energy waste is serious can be effectively solved, meanwhile the power generating efficiency of the systemis improved, and energy saving, environmental friendliness and high efficiency are achieved truly.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
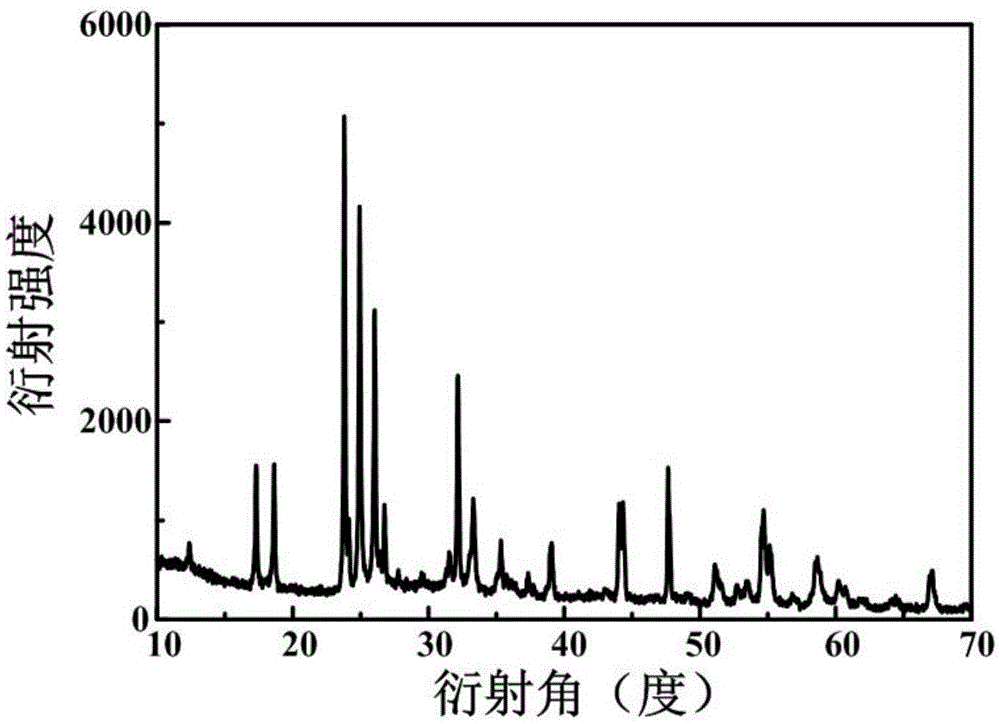
Preparation method of lithium ion battery negative material titanium niobate
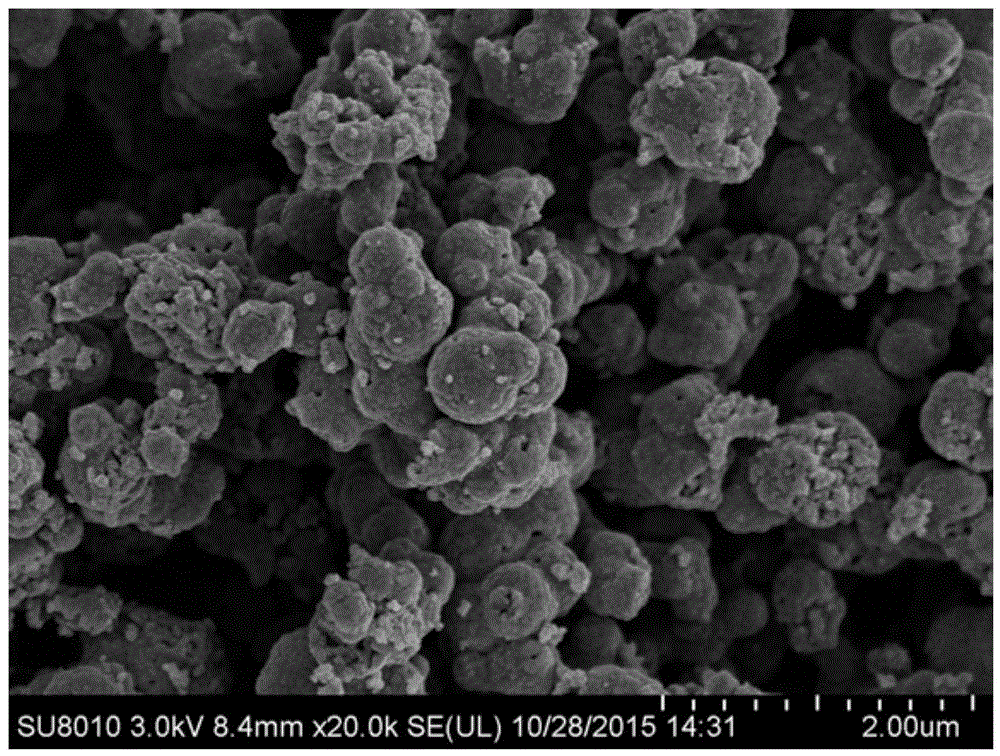
InactiveCN105633456ASmall sizeIncreased diffusion rateCell electrodesSecondary cellsNiobiumSpherical shaped
The invention discloses a preparation method of lithium ion battery negative material titanium niobate. The preparation method comprises the following steps: separately dissolving a niobium source and a titanium source into acetic acid, and slowly mixing the niobium source and the titanium source; loading a mixed solution obtained in the previous step into a reaction kettle, and heating to facilitate the reaction; after the reaction kettle is naturally cooled to the room temperature, washing obtained precipitates for multiple times by separately utilizing deionized water and ethanol, and drying in a vacuum drying oven to obtain powder; and roasting the obtained powder to obtain titanium niobate. The preparation method is moderate in conditions, simple in procedures, easy to operate and convenient in industrialized production. The prepared titanium niobate material is in a spherical shape and is relatively small in size, so that the diffusion speed of lithium ions in the material is increased; and when the prepared titanium niobate material is used as a lithium ion battery negative electrode, the charging-discharging specific capacity is relatively high, and the multiplying power cycling performance is excellent.
Owner:NANYANG NORMAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com