Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
104 results about "Marker vaccine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A marker vaccine allows for immunological differentiation (or segregation) of infected from vaccinated animals, and is also referred to as a DIVA (or SIVA) vaccine [Differentiation (or Segregation) of infected from vaccinated animals] in veterinary medicine. In practical terms, this is most often achieved by omitting an immunogenic antigen present in the pathogen being vaccinated against, thus creating a negative marker of vaccination. In contrast, vaccination with traditional vaccines containing the complete pathogen, either attenuated or inactivated, precludes the use of serology (e.g. analysis of specific antibodies in body fluids) in epidemiological surveys in vaccinated populations.
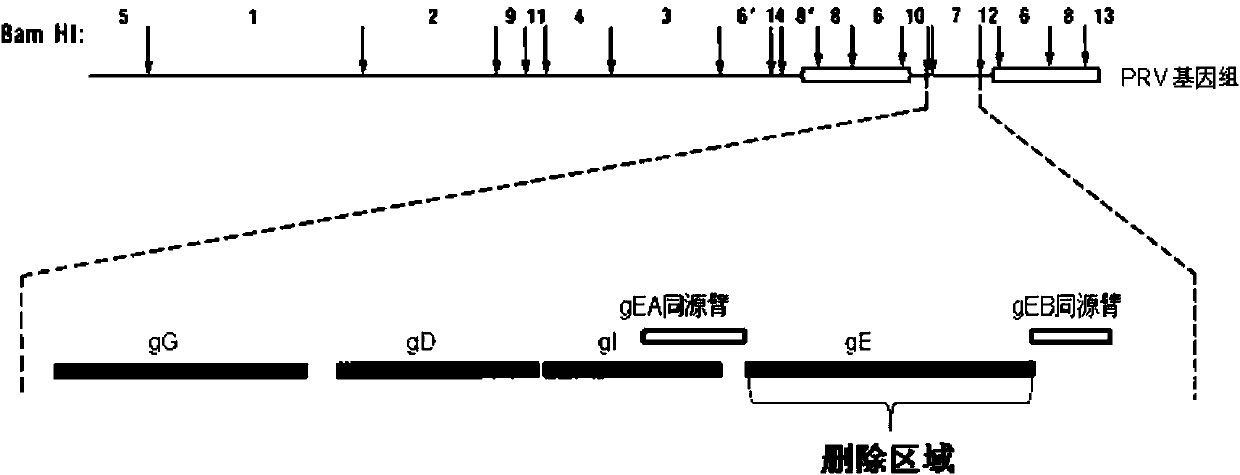
Porcine pseudorabies virus gene deletion strain, vaccine composition, and preparation method and application of vaccine composition
ActiveCN103923884ASymptoms relieved or improvedMicroorganism based processesAntiviralsVirus antigenTGE VACCINE
The invention provides a porcine pseudorabies virus gene deletion strain, a vaccine composition, and a preparation method and an application of the vaccine composition. The vaccine composition comprises an immunizing dose of an attenuated livetotivirus antigen and an inactivated totivirus antigen of the porcine pseudorabies virus gene deletion strain or its culture. The vaccine composition can effectively induce the antibody production, can effectively protect pigs, and can be used as a marking vaccine to effectively differentiate wild strains and vaccine strains.
Owner:PU LIKE BIO ENG
Avian influenza virus marking vaccine, preparation process and application thereof
The invention discloses a vaccine strain H5N1 / PR8-5B19 marked by H5N1 hypotype poultry influenza virus, which also provides the application to prevent and monitor poultry influenza.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Establishing method of bacterial artificial chromosome recombinant duck plague virus rescue system platform and application
InactiveCN105802922ALower titerDoes not affect the replication cycleVirus peptidesNucleic acid vectorBacteroidesRecombinant vaccines
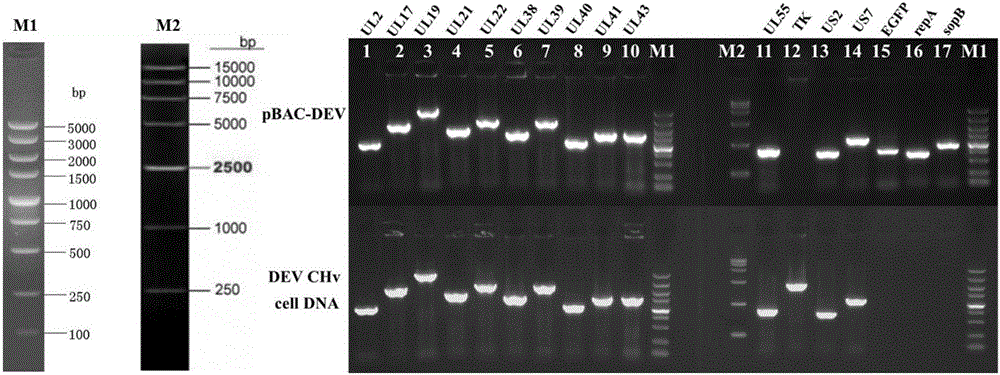
The invention discloses an establishing method of a bacterial artificial chromosome recombinant duck plague virus rescue system platform and application of the platform. A bacterial artificial chromosome recombinant duck plague virus is obtained by inserting a recombinant duck plague virus transfer vector pUC18 / EGFP-TKAB-BAC11 in a TK domain, wherein the recombinant duck plague virus transfer vector contains a TK gene left-right homologous arm, a reporter gene EGFP and a bacterial artificial chromosome core function component. By means of the platform, the in-vitro biologics characteristics of a UL55 gene-deleted strain established through an inside-bacterium two-step RED recombination method and a back mutation strain and parent strain of the UL55 gene-deleted strain are quite close; the functions are not related to positioning of a UL26.5 gene in a cell. The method is beneficial to development of pathogenic mechanism and gene function research of DPV CHv and is beneficial to the duck plague virus prevention and the research and application of recombinant duck plague virus vaccines of other poultry infectious diseases based on the platform; in addition, due to the fact that the recombinant virus carries a TK deletion mark and an EGFP gene, a mark vaccine can be developed to clinically distinguish a wild virus and a recombinant vaccine virus.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Genotype VII Newcastle disease virus marker vaccine strain and application thereof
ActiveCN104988124AHigh growth titerHigh biological propertiesViral antigen ingredientsMicroorganism based processesViral MarkersChick embryos
The invention discloses a genotype VII Newcastle disease virus marker vaccine strain and an application thereof, and belongs to the field of genotype VII Newcastle disease virus marker vaccine strain rescue and application. A built Newcastle disease virus reverse genetic operating platform is utilized for enabling NP protein of a G7 strain to miss 18 amino acids and conducting mutation on F-protein cleavage loci, and the highly-weak virulence and high-virus titer genotype VII Newcastle disease virus marker vaccine strain MG7-NPdelta18+Fmut is rescued through screening. The microbial preservation serial number is CCTCC NO: V201505. The marker vaccine strain has the biological characteristics of high growth titer and low virulence in chick embryos and is genetically stable. The immune protection test result shows that the marker vaccine strain is good in immunogenicity, capable of inducing high-level protective antibodies, and capable of completely protecting immunized chicken, can be used for preventing and controlling a currently-popular genotype VII Newcastle disease virus and lays the foundation of identifying vaccine immunity and wild virus infection.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF VETERINARY SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for constructing hog-cholera virus infectious cDNA carrier having molecule mark
ActiveCN101864445AFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionTotal rnaTechnological system
The invention relates to a virus antibody research and provides a method for constructing a hog-cholera virus infectious cDNA carrier having a molecule mark. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) diluting a hog-cholera live vaccine to 1 portion per milliliter as the experimental material, after extracting the head RNA, amplifying 6 corresponding cDNA fragments through RT-PCR section according to designed 6 pairs of primers, (2) leading in the corresponding molecule marks from F1 and F5 of cDNA fragments, (3) reforming plasmids required by overall length cDNA cloning, and (4) constructing the overall length cDNA carrier. A hog-cholera virus lapinized vaccine C stem infectious cDNA carrier pA-FL22 having a molecule mark can be acquired through the method of the invention. The permissive cells of RNA electro transferred hog-cholera virus acquired by the carrier can save the infectious progeny virus which can stably inherit the molecule mark led in the construction. By using the saving technique system of the infectious cDNA carrier and the progeny virus, the copy stem and the pathopoiesia reason of the virus can be deeply researched and the foundation for developing new marked vaccines can be settled.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Application of brucellosis A19 molecular marking vaccine and immunological identification thereof
InactiveCN102772794ASolve difficult to identifyGood immune protectionAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsMarker vaccineVirus
The invention relates to an application of brucellosis A19 molecular marking vaccine and immunological identification of the brucellosis A19 molecular marking vaccine. The brucellosis vaccine can be applied to an enzyme-linked immunosordent assay (iELISA) method to distinguish an animal inoculated with the vaccine from a wild virus infected animal. According to the invention, a cattle is used as a test target animal antiepidemic to the brucellosis, the cattle is immune to brucellosis A19-detlaVirB12 marking vaccine so as to evaluate the immunological protection of the molecular marking vaccine. An iELISA method for distinguishing the brucellosis A19-detlaVirB12 immune animal from the wild virus infected animal is created. The brucellosis A19-detlaVirB12 marking vaccine provided by the invention not only has good immunological protection against the cattle brucellosis, and the iELISA method provided by the invention solves the problem that the immune animal is difficult to be distinguished from the clinic diseased animal, and the brucellosis A19 molecular marking vaccine has an actual application value in prevention and control, elimination and purification of the cattle brucellosis.
Owner:新疆维吾尔自治区畜牧科学院兽医研究所
Construction and application of recombinant peste des petits ruminants virus expressing fused exogenous epitope N protein
The invention relates to the field of immune marking vaccines and in particular relates to construction and an application of recombinant peste des petits ruminants virus expressing fused exogenous epitope N protein.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Reverse genetic system for Rift Valley fever virus and uses thereof
ActiveUS20070122431A1SsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsAntiviral drugRna expression
The present invention describes a reverse genetic system for Phlebovirus such as Rift Valley fever virus. This system comprised of RNA expression plasmids and protein expression plasmids. Additionally, the present invention also discloses the modification of this system to generate a recombinant virus that expresses a non-viral foreign gene. Furthermore, the present invention discloses the use of this system in the development of anti-Rift Valley fever virus vaccines, screening of antivirals testing for anti RVF immune response and developing marker vaccines for Rift Valley fever virus. We also claim the utility of this approach to other phleboviruses.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Newcastle disease virus infectious clones, vaccines and new diagnostic assays
InactiveUS7332169B2Immune responseImprove propertiesSsRNA viruses negative-senseGenetic material ingredientsAntigenVirulent characteristics
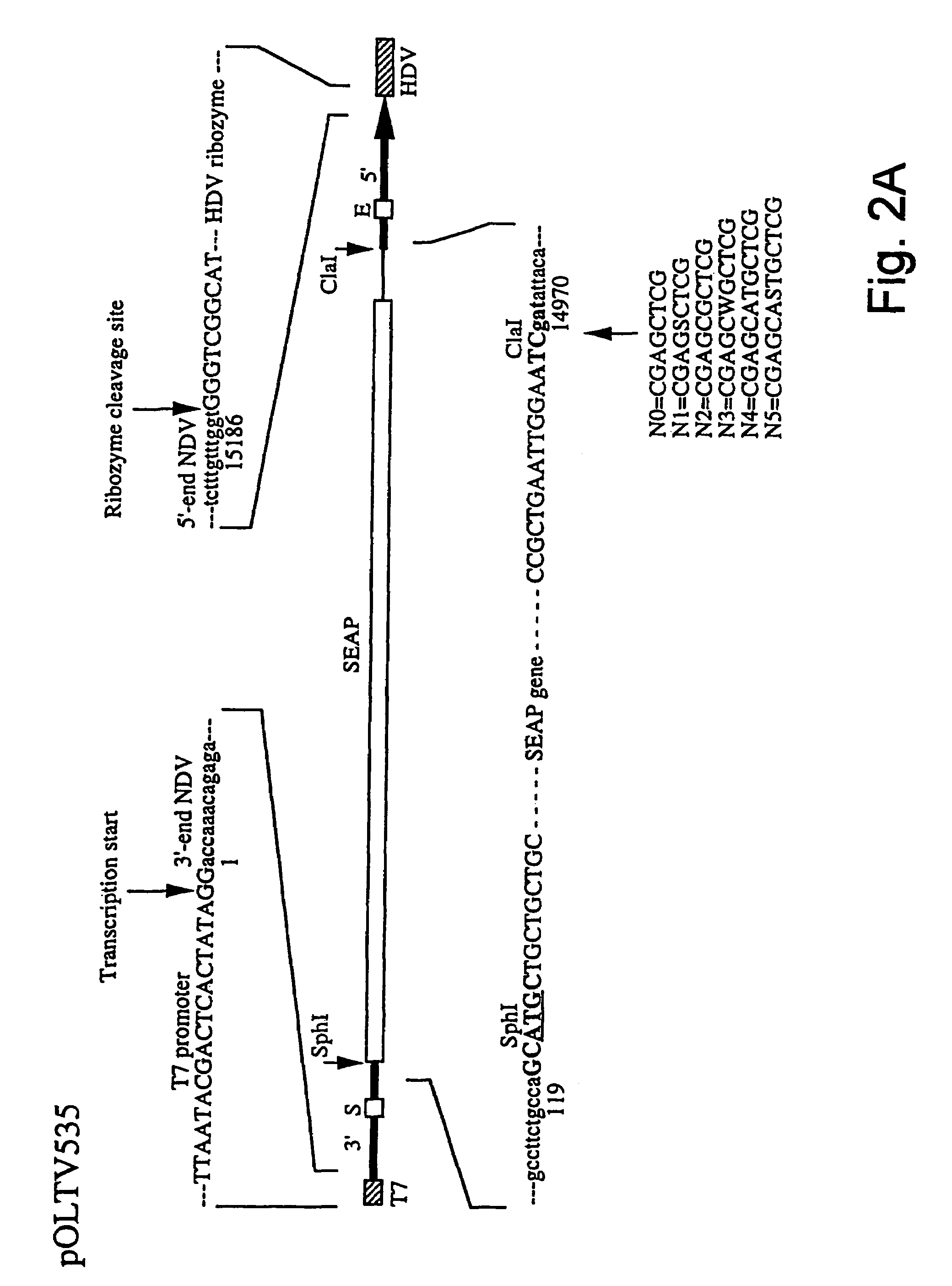
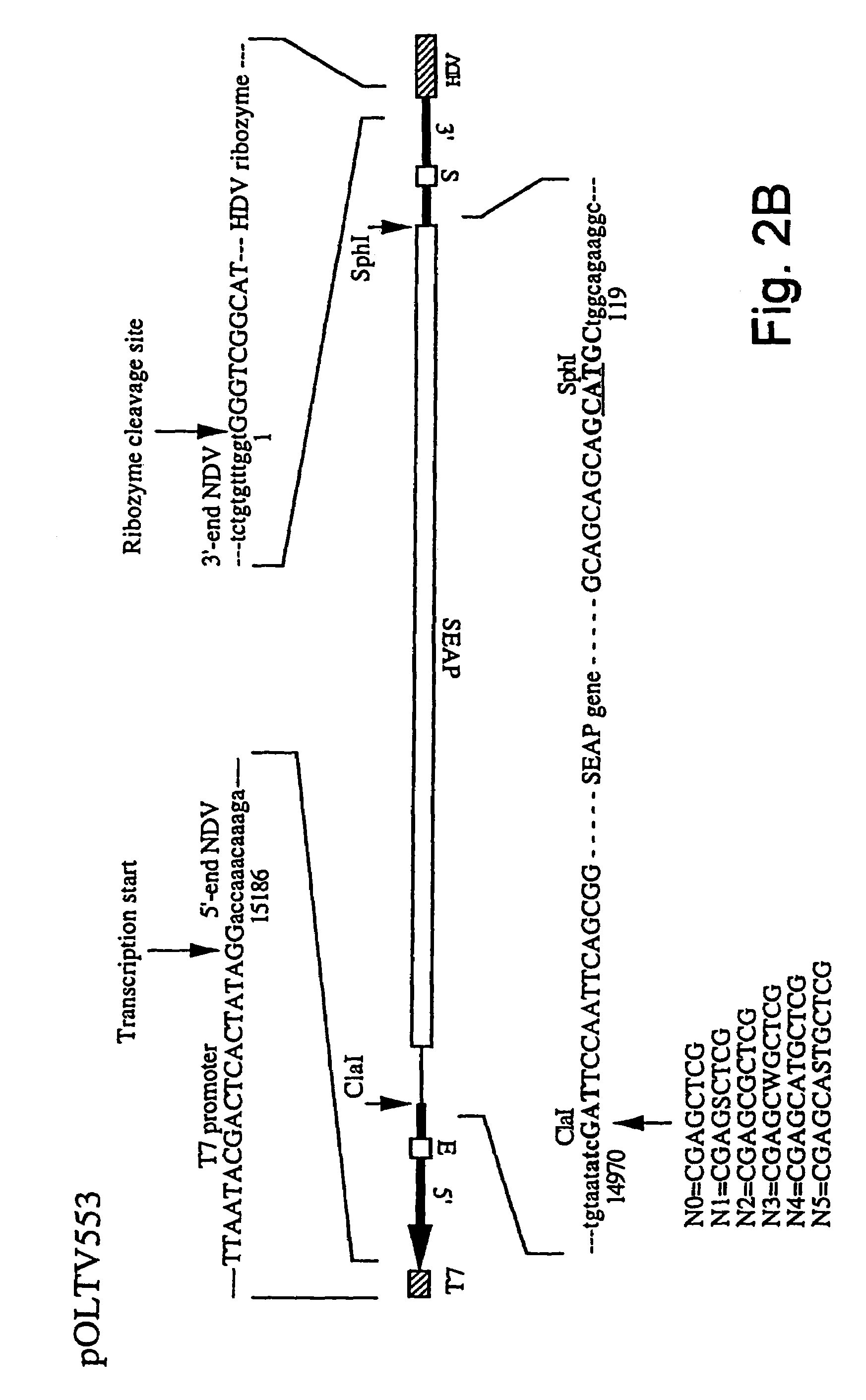
The invention relates to a process for generating infectious Newcastle disease virus (NDV) entirely from cloned full-length cDNA and to the use of vaccines and diagnostic assays generated with and derived from the process. The process offers the possibility to modify the NDV genome by means of genetic modification and allows for the introduction of mutations, deletions and / or insertions. The process can be used to modify the virulence of NDV, thus generating new attenuated live vaccines with enhanced properties. The process can be used to modify the antigenic make-up of NDV, to allow the generation of live NDV marker vaccines that can be serologically distinguished from NDV field strains.
Owner:STICHTING DIENST LANBOUWKUNDIG ONDERZOEK
Live attenuated antigenically marked classical swine fever virus
ActiveUS20080292653A1Effective protectionSsRNA viruses positive-senseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsEpitopeStructural glycoprotein
Classical swine fever virus is a world-wide distributed highly-contagious disease affecting swine. The two main strategies for diseases control are prophylactic vaccination and non-vaccination stamping out policies. Marker vaccines are a promising strategy. Here we report the rational development of a doubly antigenic marker CSFV experimental live attenuated candidate strain vaccine (Flag / T4 virus). Flag / T virus (Flag / T4v) is based in the combination of two Brescia derived recombinant attenuated viruses: RB-C22 and T4. RB-C22v contains a 19mer insertion in the structural glycoprotein E1, while T4v posses mutated CSFV amino acid residues 830 to 834 in the structural glycoprotein E2, deleting the highly conserved epitope recognized by monoclonal antibody (mAb) WH303. Flag / T4 virus contains a positive foreign antigenic marker, due to the insertion of the highly antigenic epitope Flag in the 19mer insertion of E1, as well as a negative antigenic marker, the lack of reactivity with mAb WH303. Immunized with Flag / T4v induced a complete protection against the challenge with virulent strain Brescia both at 3 and 28 days post infection when nasally administered and since the second day post infection when intramuscularly administered. These results constitute an example of rational design of a CSFV antigenically marked LAV.
Owner:AGRI UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS RESPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE +1
Newcastle disease chimeric virus marker vaccine strain as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN111575247AImprove growth characteristicsImproving immunogenicitySsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsF proteinChick embryos
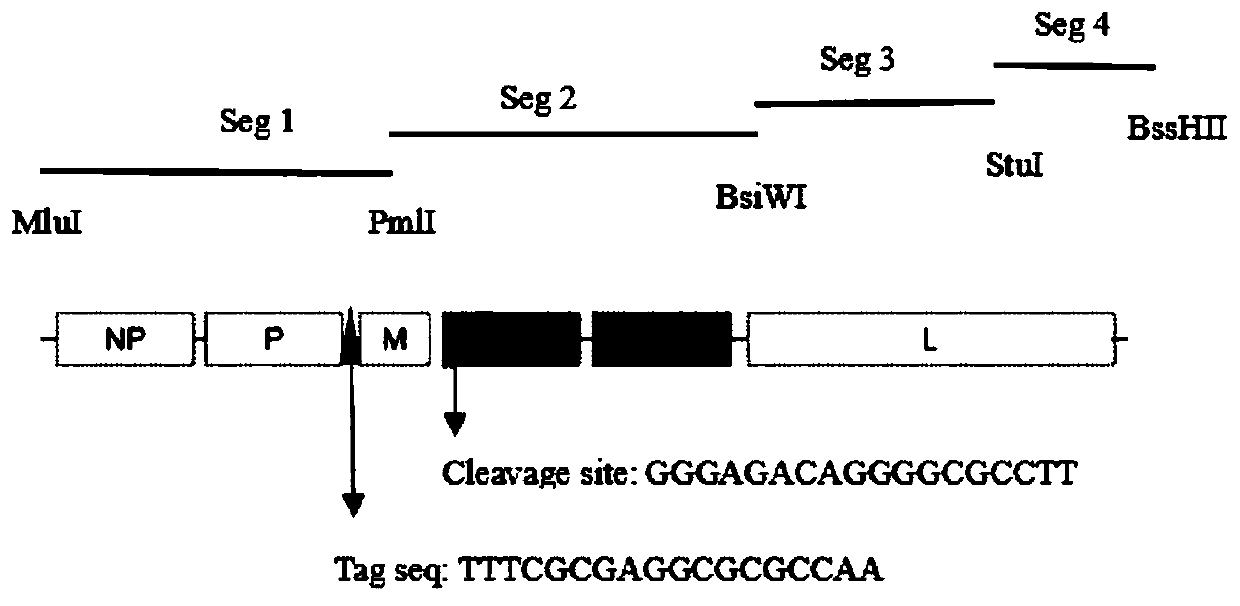
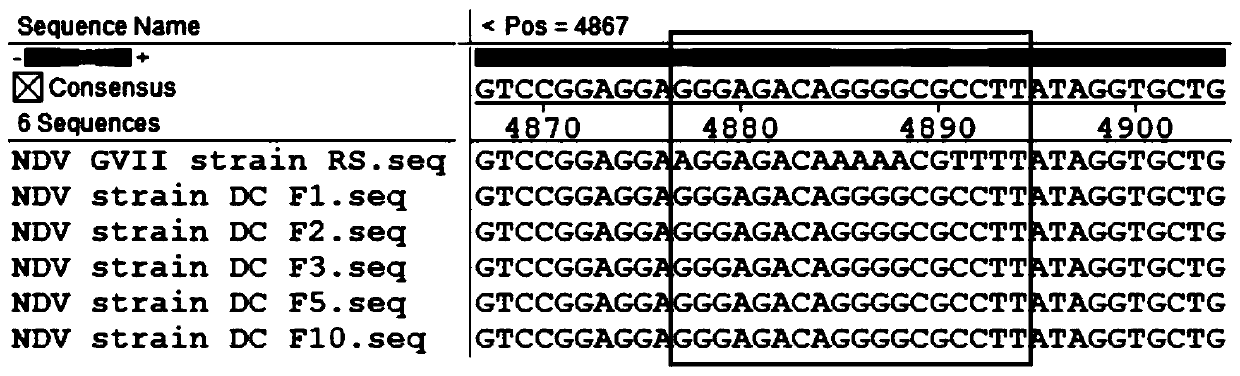
The invention relates to a Newcastle disease chimeric virus marker vaccine strain as well as a construction method and application thereof, and belongs to the field of rescue and application of Newcastle disease chimeric vaccine strains. A Newcastle disease virus reverse genetic operation platform is utilized to mutate an F protein cleavage site of a Newcastle disease gene GVII type strain into acleavage site of an attenuated strain, F and HN genes of a mutated gene VII type Newcastle disease strain and NP, P, M and L of a gene II type NDV La Sota strain construct a full-length chimeric cDNAsequence, and a 18bp nucleotide marker sequence is inserted into a non-coding region between P and M. A Newcastle disease chimeric virus NDV DC strain is obtained through transfection cell rescue. Theconstructed chimeric virus can reach relatively high culture titer in chick embryos and cells. The chimeric strain contains envelope surface glycoprotein of the gene VII type Newcastle disease strain, contains a skeleton of the gene II type strain, and has immunogenicity of the Newcastle disease gene VII type strain and high reproduction and high safety characteristics of the gene II type La Sotastrain.
Owner:ZHEJIANG VBIOSCI INC +1
Reverse genetic system for rift valley fever virus and uses thereof
The present invention describes a reverse genetic system for Phlebovirus such as Rift Valley fever virus. This system comprised of RNA expression plasmids and protein expression plasmids. Additionally, the present invention also discloses the modification of this system to generate a recombinant virus that expresses a non-viral foreign gene. Furthermore, the present invention discloses the use of this system in the development of anti-Rift Valley fever virus vaccines, screening of antivirals testing for anti RVF immune response and developing marker vaccines for Rift Valley fever virus. We also claim the utility of this approach to other phleboviruses.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Indirect ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immuno Sorbent Assay) method established based on classical swine fever virus NS3
The invention relates to an indirect ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immuno Sorbent Assay) method established based on classical swine fever virus (CSFV). The swine fever virus recombination protein NS3 is obtained by a gene clone expression technique and the indirect ELISA method is established by using the recombination protein NS3 as the envelope antigen. The method comprises the steps of preparing the antigen recombination protein NS3, establishing indirect ELIS, establishing a judging standard and carrying out clinical serology detection. The invention can be used for detecting specific antibody of CSFV NS3 in the swinery so as to judge the antibody level of CSFV NS3 in the swinery and the condition of natural infection of CSFV in the swinery, and provides a detection method for identifying ELISA in the marker vaccine in the CSFV E2 gene engineering. At present, the method firstly adopts CSFV NS3 to establish the ELISA for detecting the CSFV antibody in the swinery worldwide. The sensitivity and the specificity are obviously higher than the ELISA established based on Ems.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Synthetic peptide-based marker vaccine and diagnostic system for effective control of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS)
ActiveUS20140335118A1Enhance their respective immunogenicityRisk minimizationAntibacterial agentsSsRNA viruses positive-senseHelper epitopeMonitoring and control
A peptide-based marker vaccine against Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome (PRRS) and a set of immunodiagnostic tests for the prevention, monitoring and control of Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus (PRRSV) are disclosed. Vaccine formulations according to various embodiments of the invention contain a mixture of peptides derived from PRRSV GP2, GP3, GP4, or GP5 proteins; each peptide individually contains a B cell PRRSV neutralizing / receptor binding epitope which is individually linked to an artificial T helper epitope for enhancement of the respective peptide's immunogenicity; and which can be supplemented with a mixture of peptides representing the T helper epitopes derived from the PRRSV GP4, GP5, M and Nucleocapsid proteins to provide cell mediated immunity. Such viral peptide compositions are prepared in an acceptable delivery system as vaccine formulations and can provide cross protection of PRRSV antibody free pigs from infection upon PRRSV challenge.
Owner:UNITED BIOMEDICAL INC
Method for establishing hog cholera lapinized virus labeled vaccine strain and preparing vaccine
ActiveCN102221618AImprove welfareReduce economic lossAntiviralsViruses/bacteriophagesHigh cellVaccine virus
The invention relates to a method for establishing a hog cholera lapinized virus labeled vaccine strain and preparing a vaccine. The method comprises the following steps: (1) establishing the overall-length infectious clone of the hog cholera lapinized virus strain (the C strain or the Chinese strain); (2) introducing labeled protein genes; (3) rescuing the hog cholera lapinized labeled vaccine virus; (4) breeding the virus; (5) inspecting a virus solution; (6) preparing a vaccine; and (7) inspecting the finished product of the vaccine, comprising safety inspection and efficacy inspection. The hog cholera lapinized virus labeled vaccine established by the invention maintains the characteristics of good safety, excellent immunogenicity and the like of the hog cholera lapinized virus strain; the virus strain has the advantages of good stability and high cell production virus content, can be used for industrial mass production and can generate a labeled protein specificity antibody aftera hog is immunized to distinguish immunization and natural infection and has important significances on hog cholera prevention, control and purification and emergent immunization.
Owner:CHINA INST OF VETERINARY DRUG CONTROL
Recombinant bacterium of brucella abortus with immunity labeling and use thereof
InactiveCN101386831ALow toxicityImprove purification effectAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsBrucella abortusAnimal use
The invention discloses a recombinant strain for Brucella abortus provided with an immune label. The recombinant strain for the Brucella melitensis provided with the immune label is a strain obtained by killing encoding genes of perosamine synthetase in the Brucella abortus. Compared with an original strain, the obtained strain has lower virulence, and can be used as a vaccine to immunize animals without killing the genes. By utilization of the strain to immunize a mouse, immunoreaction states different from those of the standard strain and the prior vaccine strain can be generated in the body of the mouse, and sicken animals can be identified from immune animal groups by immunological detection of serum of the animals. The modification of the brucelliasis vaccine and the research of a diagnosis and identification agent have important significance in developing a brucelliasis gene deletion marker vaccine and a matched diagnosis and identification agent and promoting the elimination and purification of brucelliasis of the animals all over the world.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for constructing PRRSV gene deletion vaccine toxin strain by using Nsp2 gene deletion and uses thereof
InactiveCN101220351AIncreased neutralizing antibody levelsOvercome inhibitory factorsGenetic material ingredientsInactivation/attenuationNucleotideVaccine virus
The invention discloses a method for utilizing Nsp2 gene deletion for constructing a PRRSV gene deletion vaccine virus strain and the application thereof. The method for lowering the toxicity of the PRRSV BJ-4 strain of the invention is that a nucleotide segment with the length of 69nt in a Nsp2 coding region of the PRRSV BJ-4 strain genome is continuously deleted to obtain the virus strain with reduced toxicity; the nucleotide sequence of the 69nt nucleotide segment is shown as the 2795 to 2863 sites from the 5' tail end of GenBank Accession Number AF331831. The Nsp2 of the virus rV63 which is prepared by the method for lowering the toxicity of the PRRSV BJ-4 strain deletes 21 amino acids, which has the potential to develop a marker vaccine and can identify the diagnosis method of the deleted polypeptide. When in the development process of vaccine, the invention can utilizes a reverse genetic technical platform which is already established for carrying out the transformation of GP5 glycosylation sites, thus overcoming the suppression factors which affect the neutralizing epitope and further improving the level of the vaccine-induced neutralizing antibody.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Foot-and-mouth disease marker vaccine strain with 3B protein dominant epitope deficiency and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN107201346ASsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsStructural proteinMarker vaccine
The invention provides a foot-and-mouth disease marker vaccine strain with 3B protein dominant epitope deficiency and a construction method and application thereof; 3B1 and 3B2 non-structural protein encoded amino acid sequences of the marker vaccine strain are shown as in SEQ ID No. 8. The vaccine strain constructed herein has mutation modifications (4AGP6-4TAA6) of 3B1 and 3B2 non-structural protein amino acids, wherein the mutations of the 3B1 and 3B2 protein amino acids enable a recombinant virus to be completely deprived of the ability to bind with monoclonal antibody 3B4B1 recognizing 3B1and 3B2 dominant epitopes, and the marked virus has the similar replicating ability as parent viruses. Therefore, the foot-and-mouth disease marker vaccine strain constructed herein is suitable for developing foot-and-mouth disease marker vaccines for distinguishing natural infections and vaccine immunity, and reliable technical support is provided for the construction of control, purification and infection-free zones in China.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF VETERINARY SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Gene VII type Newcastle disease virus (NDV) marker vaccine strain and application thereof
ActiveCN107630008AGenetic stabilityGood immune protectionViral antigen ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementViral MarkersNucleotide
The invention provides a gene VII type NDV marker vaccine strain aSG10-mHN. The marker vaccine strain is an attenuated strain aSG10 in the noncoding region of the 5' terminal of a HN gene and with a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID No. 1. The marker vaccine strain constructed in the invention has obviously reduced virulence and is genetically stable. Results of immunoprotection tests show that the marker vaccine strain has good immunoprotection effect on NDVs, can effectively inhibit and eliminate viruses and is applicable to prevention of currently epidemic gene VII type NDVs. Through aPCR method, animals infected by wild viruses and vaccinated animals can be discriminated; so the marker vaccine strain is of important significance to monitoring, diagnosis, control and purificationof ND and has good application value.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
General foot-and-mouth disease virus structural protein antibody and blocking ELISA detection reagent kit thereof
ActiveCN110642945ASimple compositionConducive to specific bindingBiological material analysisImmunoglobulins against virusesDiseaseFoot mouth disease virus
The invention provides a general foot-and-mouth disease virus structural protein antibody and a blocking ELISA detection reagent kit thereof, and belongs to the technical field of virus detection. Thegeneral foot-and-mouth disease virus structural protein antibody and the blocking ELISA detection reagent kit thereof comprise the following composition of an antigen coating elisa plate and a biotinmarker concentrating monoclonal antibody, wherein a monoclonal antibody in the biotin marker concentrating monoclonal antibody is a monoclonal antibody E32, and the antigen coating elisa plate is anFMDV antigen indirectly coated through a monoclonal antibody F104. The E32 antibody and the F104 antibody are specifically combined to between-genotype conservative epitope in FMDV structural proteinVP2 protein, the sensitivity and the specificity are high, the general foot-and-mouth disease virus structural protein antibody and the blocking ELISA detection reagent kit thereof are suitable for detection of structural protein antibodies after O, A and Asia1 type FMDV infected or inactivated vaccine immunity, and are a new method for monitoring FMD non-immune animal community infection conditions, and a complete set of identifying and diagnosing method is provided for a marker vaccine having FMDV structural protein VP2 epitope deletion.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF VETERINARY SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Marking vaccine and serological identification method for porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome high in pathogenicity
ActiveCN105749267AHigh production virus contentHigh virus contentSsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsHighly pathogenicPathogenicity
The invention relates to a marking vaccine for the porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome high in pathogenicity and a preparation method thereof.A virus seed produced through the vaccine is a constructed JXA1-RM strain, safety and immunogenicity of the JXA1-RM strain are maintained, in addition, the strain is good in stability, and the content of viruses produced by cells is high; after a pig is immunized through the vaccine, no sequence antibody against the M protein linear list position peptide amino acid sequence of the PRRS virus of an American strain is generated, and the vaccine can be used for differentiating an immunized animal from a naturally-infected animal.By means of a method for identifying and diagnosing the strain, antibodies generated by a field strain and a vaccine strain can be diagnosed, a conventional ELISA detection method is combined, an animal immunized through the vaccine and a naturally-infected animal can be differentiated, and it is beneficial to purification of the porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome high in pathogenicity.
Owner:CHINA ANIMAL DISEASE CONTROL CENT
Newcastle disease virus infectious clones, vaccines and new diagnostic assays
InactiveUS7547442B2Easy cDNA transfection and replicationSsRNA viruses negative-senseGenetic material ingredientsAntigenVirulent characteristics
The invention relates to the process for generating infectious Newcastle disease virus (NDV) entirely from cloned full-length cDNA and to the use of vaccines and diagnostic assays generated with and derived from said process. The process offers the possibility to modify the NDV genome by means of genetic modification and allows the introduction of mutations, deletions and / or insertions. The process can be used to modify the virulence of NDV, thereby generating new attenuated live vaccines with enhanced properties. The process can be used to modify the antigenic make-up of NDV, thus allowing the generation of live NDV marker vaccines which can be serologically distinguished from NDV field strains.
Owner:STICHTING DIENST LANBOUWKUNDIG ONDERZOEK
Aftosa totivirus particle vaccine composition as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104548085AGood effectKeep aliveAntiviralsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsAlcoholVaccine antigen
The invention discloses an aftosa totivirus particle vaccine composition as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The aftosa totivirus particle vaccine composition disclosed by the invention contains totivirus particles of aftosa virus and a stable cryoprotectant, wherein the stable cryoprotectant is composed of the following matters: polyhydric alcohol, a buffer solution and a nonionic surfactant. The stable cryoprotectant provided by the invention stabilizes the vaccine antigen, protects the titer and the effect of the marker vaccine, protects the antigen stability of the marker vaccine or the antigen stability of the marker antigen library in a production process and a cold chain process, and can maintain the titer or the activity of the marker vaccine for a longer time under liquid and refrigeration conditions.
Owner:吕宏亮 +2
Brucella molecular marker vaccine strain for bovine species and application thereof
ActiveCN105039233ASolve the problem of not being able to distinguish between artificial immunization and wild bacterial infectionReduced toxicityAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsBrucellosisMarker vaccine
The invention discloses a brucella molecular marker vaccine strain for bovine species and an application thereof. The brucella molecular marker vaccine strain for bovine species, which is provided by the invention, is obtained by replacing the coding gene of a protein bp26 of brucella BH1 with the coding gene of a BLS protein and the coding gene of a protein L7 / L12 and inactivating the coding gene of a wboA protein of brucella. Experiments prove that the molecular marker vaccine strain BH1deltabp26deltawboA-BL has good immunoprotection effects on brucellosis, has lower toxicity and obviously improved safety, can be used for immunoprophylaxis of brucellosis of cattle and sheep, can distinguish wild strain infected animals from immune animals by adopting the immunological technique, has great significance in monitoring, diagnosing, purifying and controlling brucellosis and has extensive application value.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA HUAXI BIOTECH
Porcine pseudorabies virus gene-deleted strain, vaccine composition and their preparation method and application
InactiveCN105368791ASymptoms relieved or improvedMicroorganism based processesAntiviralsRabiesMarker vaccine
The invention provides a vaccine composition, comprising porcine pseudorabies virus gE gene-deleted strain of immunizing dose, or an attenuated live totivirus antigen or inactivated totivirus antigen of the culture thereof. The vaccine composition is effective in inducing generation of antibodies to provide effective protection for swine and can be used as a marker vaccine to effectively distinguish wild strains and vaccine strains.
Owner:PULIKE BIOLOGICAL ENG INC
Immunology identification method for Brucella A19-delta VirB12 molecular marker vaccine
InactiveCN105628937AGood immune protectionSolve difficult to identifyBiological material analysisBiological testingAntigenAgricultural science
The invention discloses an immunology identification method for Brucella A19-delta VirB12 molecular marker vaccine. The method comprises the following steps: a, carrying out bioinformatics software analysis according to the VirB12 gene characteristics of Brucella A19, so as to obtain an active sequence, wherein the corresponding DNA sequence is a polypeptide 074 DNA sequence: GGCCTGACGGACAACAACTGCCCTCCTCCCGGTGATACGTACGCAA; b, conducting artificial synthesis on the sequence obtained in the step a by taking the DNA sequence as a template, so as to obtain polypeptide, wherein the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide is a polypeptide 074 amino acid sequence: GLTDNNCPPPGDTQ; c, taking the active polypeptide ingredient obtained in the step b as an envelope antigen. According to the method, the problem that an immune animal and a clinic sick animal are difficult to identify is solved, and the practical application value in preventing, controlling, eliminating and purifying cattle brucellosis is high.
Owner:VETERINARY INST XINJINAG ACADEMY OF ANIMAL SCI CLINIC MEDICAL SCI RES CENT XINJIANG ACADEMY OF ANIMAL HUSBANDRY SCI
Recombinant h7n9 subtype avian influenza virus, inactivated marked vaccine and preparation method thereof
ActiveUS20210244810A1Accurate distinctionEffective preventionSsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsPeptide sequenceMarker vaccine
Provided is a recombinant H7N9 subtype avian influenza virus, a marked vaccine and a preparation method thereof. For the recombinant H7N9 subtype avian influenza virus, a strain JD / 17 of H7N9 subtype avian influenza virus is used as parent virus and a peptide sequence in HA protein of the strain JD / 17 is replaced with a peptide sequence in HA protein of H3 subtype; the strain JD / 17 of H7N9 subtype avian influenza virus has a preservation number of CCTCC No. V201862. The results of HA titers, EID50, TCID50 show that the rescued virus maintains similar biological characteristics of parent virus, such as high HA titers and EID50, and chickens immunized with the marked inactivated and emulsified vaccine produce a high level of antibody, and this antibody can be distinguished from antibodies produced by chickens naturally infected with H7N9 subtype avian influenza virus.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Escape mutants of newcastle disease virus as marker vaccines
InactiveCN1744915AViral antigen ingredientsInactivation/attenuationBinding siteNewcastle disease virus NDV
A vaccine against Newcastle Disease contains one or more mutant immunogens of the NDW strain. The mutant immunogen lacks the antigenic binding site on the F glycoprotein which is recognized by the monoclonal antibody mAb 54. Reagent kits and assay methods help to distinguish vaccinated members of a poultry flock from those that may have been infected with wild-type Newcastle Disease virus.
Owner:ZOETIS W LLC
Methods of improving vaccine immunogenicity
InactiveUS20120195926A1Useful in treatmentSsRNA viruses negative-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsVaccine efficacyMarker vaccine
The present invention provides a process called “Immune Banking” that enhances vaccine efficacy by exploiting existing humoral responses. The process involves tagging new antigens with molecular markers recognized by an existing anti-body response. This recognition of the tagged vaccine components enhances adaptive immune responses to the new vaccine.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND
Recombinant bacterium of brucella melitensis and use thereof
ActiveCN101386832ALow toxicityReduced toxicityAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsVirulent characteristicsPcr method
The invention discloses a recombinant strain for Brucella melitensis. The recombinant strain for the Brucella melitensis is a bacterial strain obtained by killing encoding genes of cold shock protein in the Brucella melitensis. Compared with an original strain, the obtained strain has virulence lower than that of the prior vaccine M5, and can be used as a vaccine to immunize animals without killing the genes. By utilization of the strain to immunize a mouse, whether a strain separated from the body of a sicken animal is a vaccine strain or a wild strain can be identified by the PCR method. The modification of the brucelliasis vaccine and the research of a diagnosis and identification agent have important significance in developing a brucelliasis gene deletion marker vaccine and a matched diagnosis and identification agent and promoting the elimination and purification of brucelliasis of the animals all over the world.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com