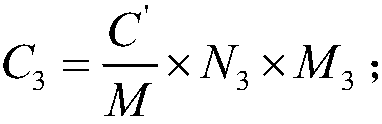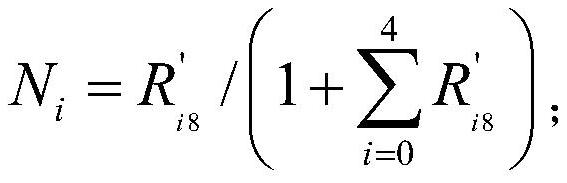Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
31 results about "Liquid scintillation counting" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Liquid scintillation counting is the measurement of radioactive activity of a sample material which uses the technique of mixing the active material with a liquid scintillator (e.g. Zinc sulfide) , and counting the resultant photon emissions. The purpose is to allow more efficient counting due to the intimate contact of the activity with the scintillator. It is generally used for alpha and beta particle detection.
Nanoscintillation systems for aqueous-based liquid scintillation counting
The present invention relates to the use of nanoscintillation systems, or nanoparticles containing fluor molecules, that can be used to detect an electron-emitting or alpha-particle-emitting radioisotope in the absence of organic-solvents commonly used in organic-based liquid scintillation cocktails. The invention also relates to compositions and use of three oil-in-water microemulsion precursors that can be engineered rapidly, reproducibly, and cost-effectively to produce useful nanoparticles less than 100 nanometers.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
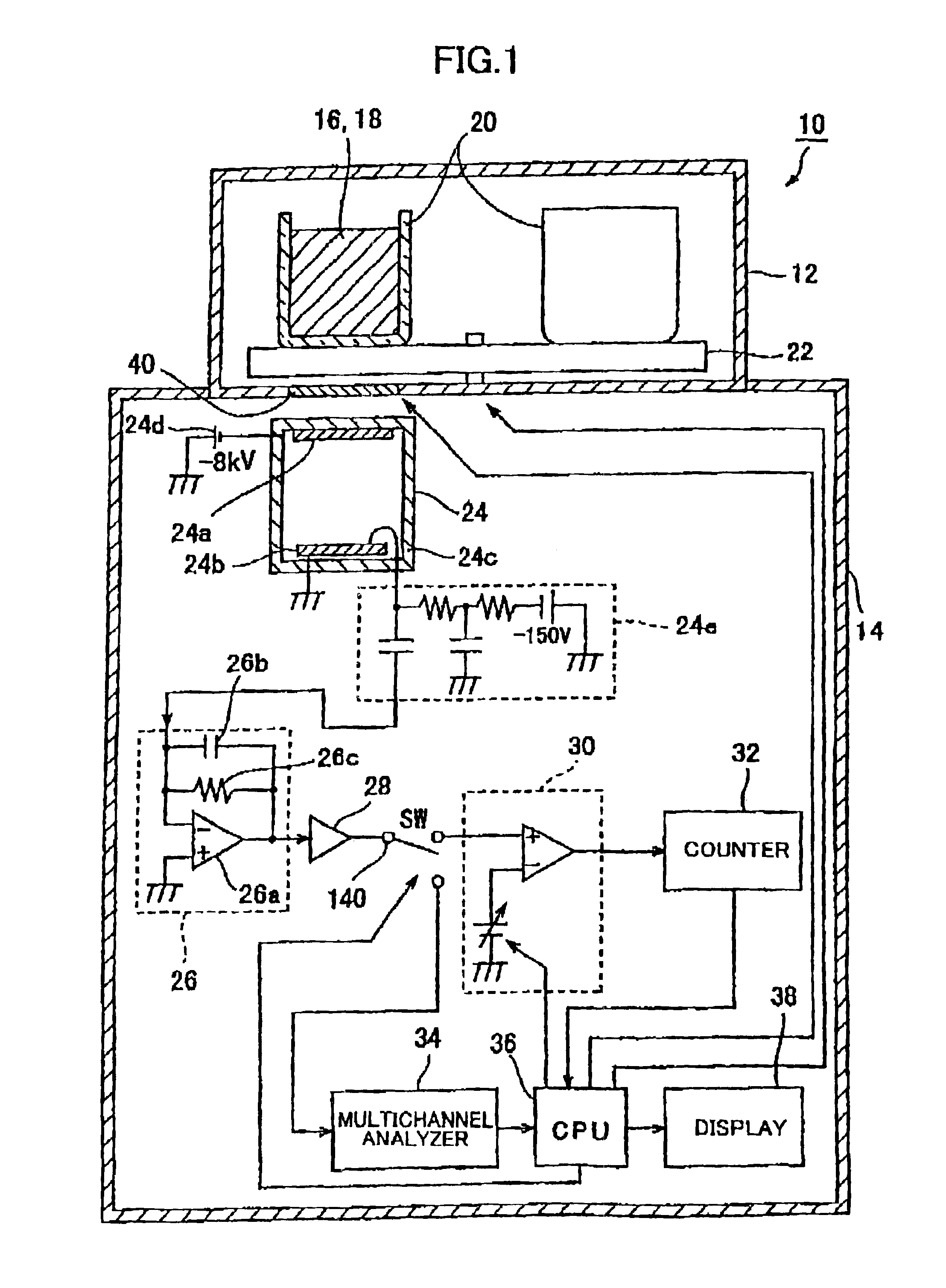
Optical measurement apparatus and method for optical measurement
InactiveUS6960771B1Effectively eliminate dark current pulseEfficiently signaledPhotometry using reference valueIndividual particle analysisPhotocathodeDisplay device
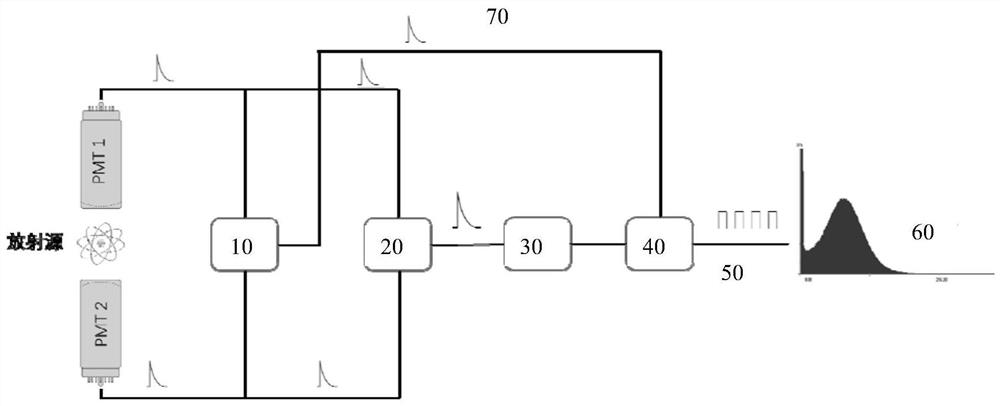
A liquid scintillation counter 10 serving as an optical measurement apparatus includes: an HPD 24, a charge amplifier 26, a voltage amplifier 28, a comparator 30, a counter 32, a multi-channel analyzer 34, a display 38, and the like. The HPD 24 has a photocathode 24a and an APD 24b for outputting a signal that corresponds to the number of incident photons. The comparator 30 outputs a logic pulse signal, serving as a comparison result signal, only when the signal outputted from the HPD 24 and amplified by the charge amplifier 26 and voltage amplifier 28 is larger than a prescribed threshold value. This threshold value is set larger than an output signal that is outputted when a single photoelectron is emitted from the photocathode 24a and smaller than another output signal that is outputted when two or more photoelectrons are emitted.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
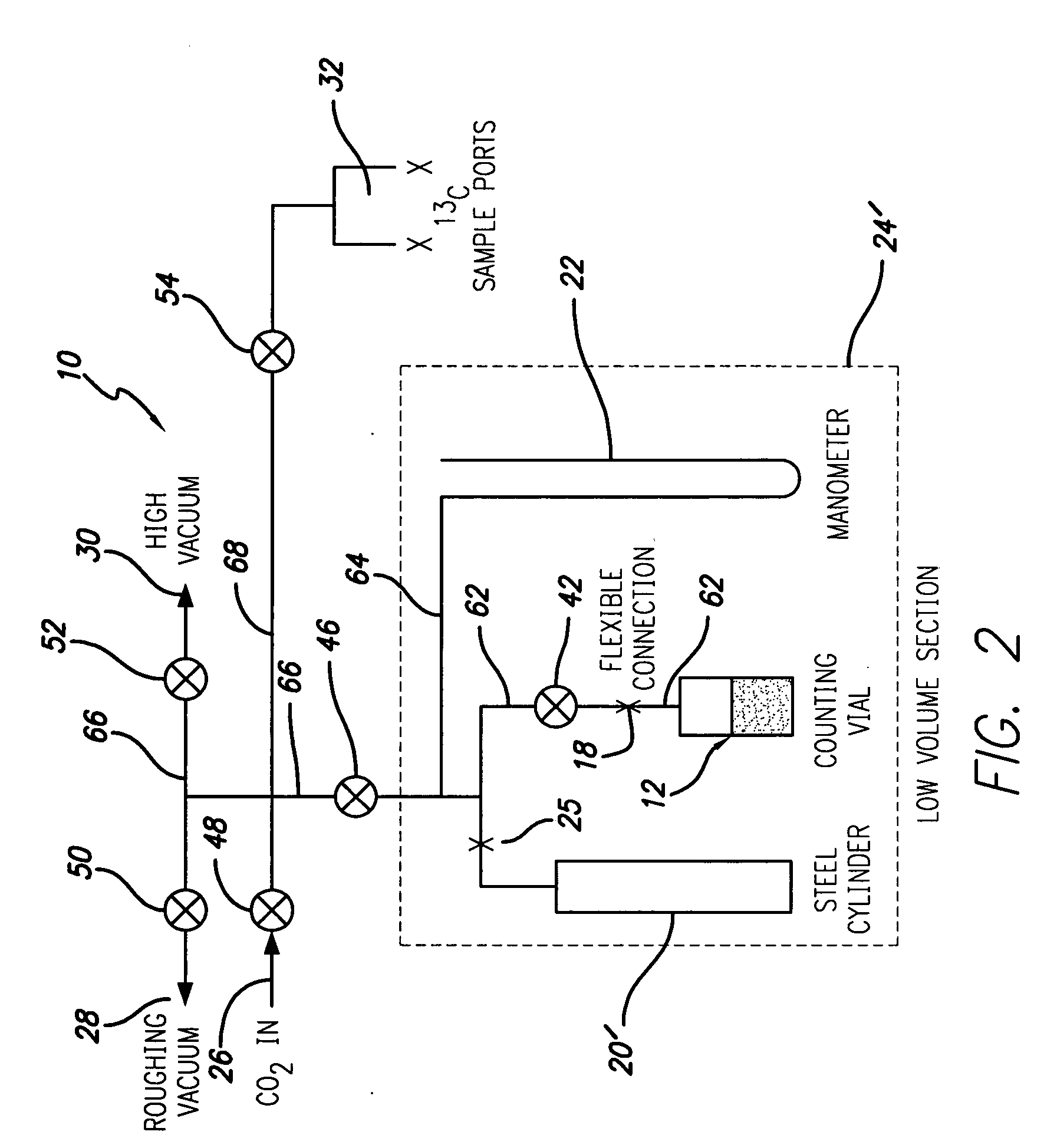
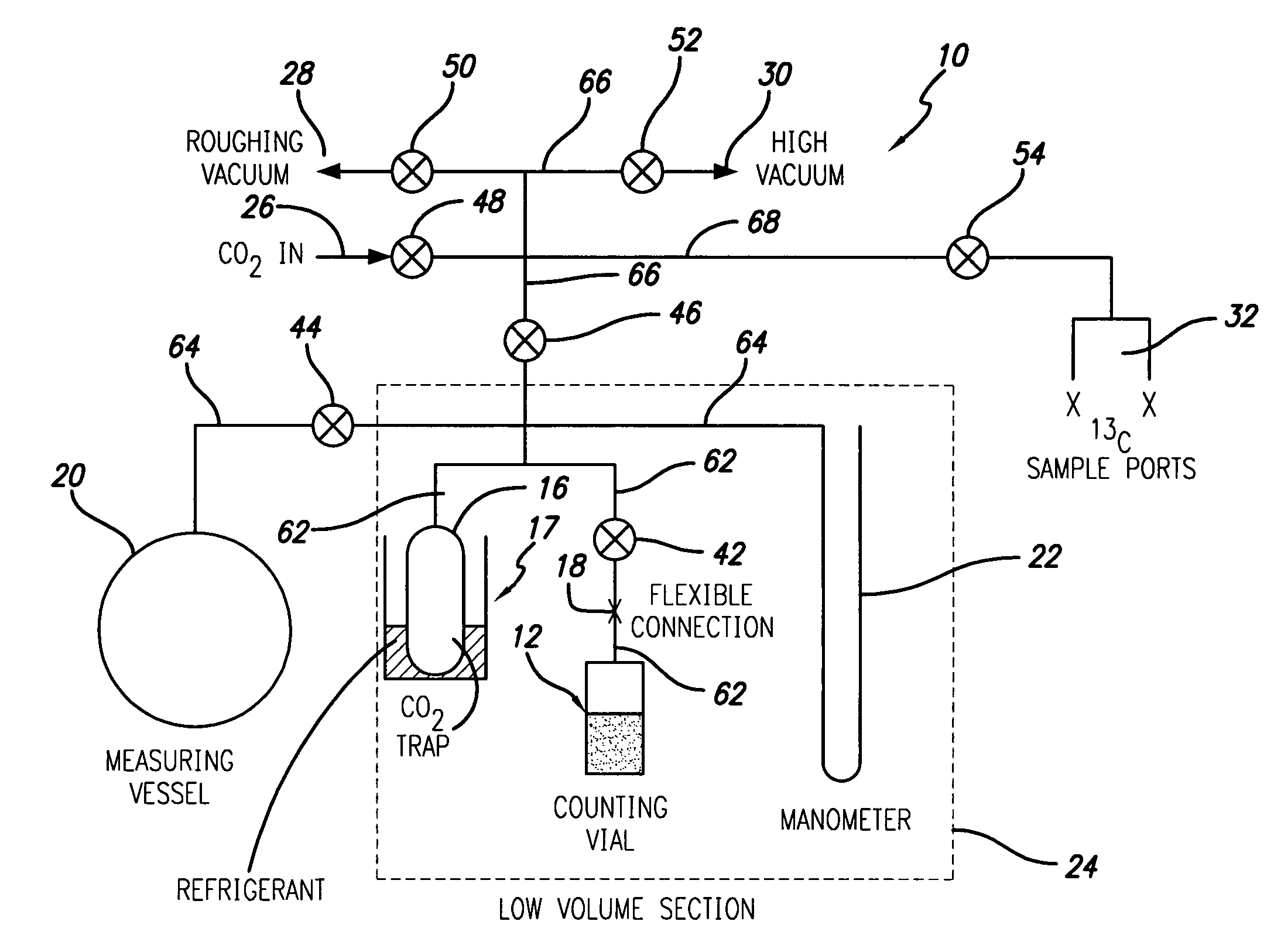
Apparatus and method for preparing samples for radiocarbon dating
InactiveUS20060038124A1Simple and fast and reliable and accurate methodPromote absorptionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationWithdrawing sample devicesRadiocarbon datingLiquid scintillation counting
The invention provides a method and apparatus for preparing samples of carbon dioxide with a 14C content for analysis in liquid scintillation counting equipment, the sample being of a known mass and being introduced into and substantially wholly absorbed into an absorption “cocktail”, absorption being completed at a stage before saturation of the absorbent occurs. The absorbent is contained in a vial which, when absorption has been completed, is transferred into the scintillation counting equipment without intermediate transfer of the contents.
Owner:VERHAGEN BALTHAZAR T
Method for measuring 14C in biological sample
InactiveCN104062674AHigh measurement accuracyHigh measurement sensitivityX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentMicrobiologyLiquid scintillation counting
The invention discloses a method for measuring 14C in a biological sample. The method includes the following steps that (1) the biological sample is pretreated, wherein the biological sample is frozen to be in the dry state and burned and absorbs a NaOH solution and finally the biological sample is converted into CaCO3 sediment; (2) a CO2 direct absorption method is used for preparing the sample, wherein CaCO3 powder obtained in the step (1) is dissolved in HCl and a measurement bottle cooled through an ice bath and containing liquid scintillation absorption mixed liquid is used for absorbing generated CO2; (3) a low-background liquid scintillation counter is used for measurement, wherein the sample is measured, so that the counting rate is obtained, and meanwhile the value of the SQP(E) is measured; quenching correction is conducted through an SQP(E) method and the specific activity of 14C in the biological sample is calculated. The method is rapid and accurate in operation and the lower detection limit of 14C specific activity in the biological sample can reach 0.0084 Bq / gC.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
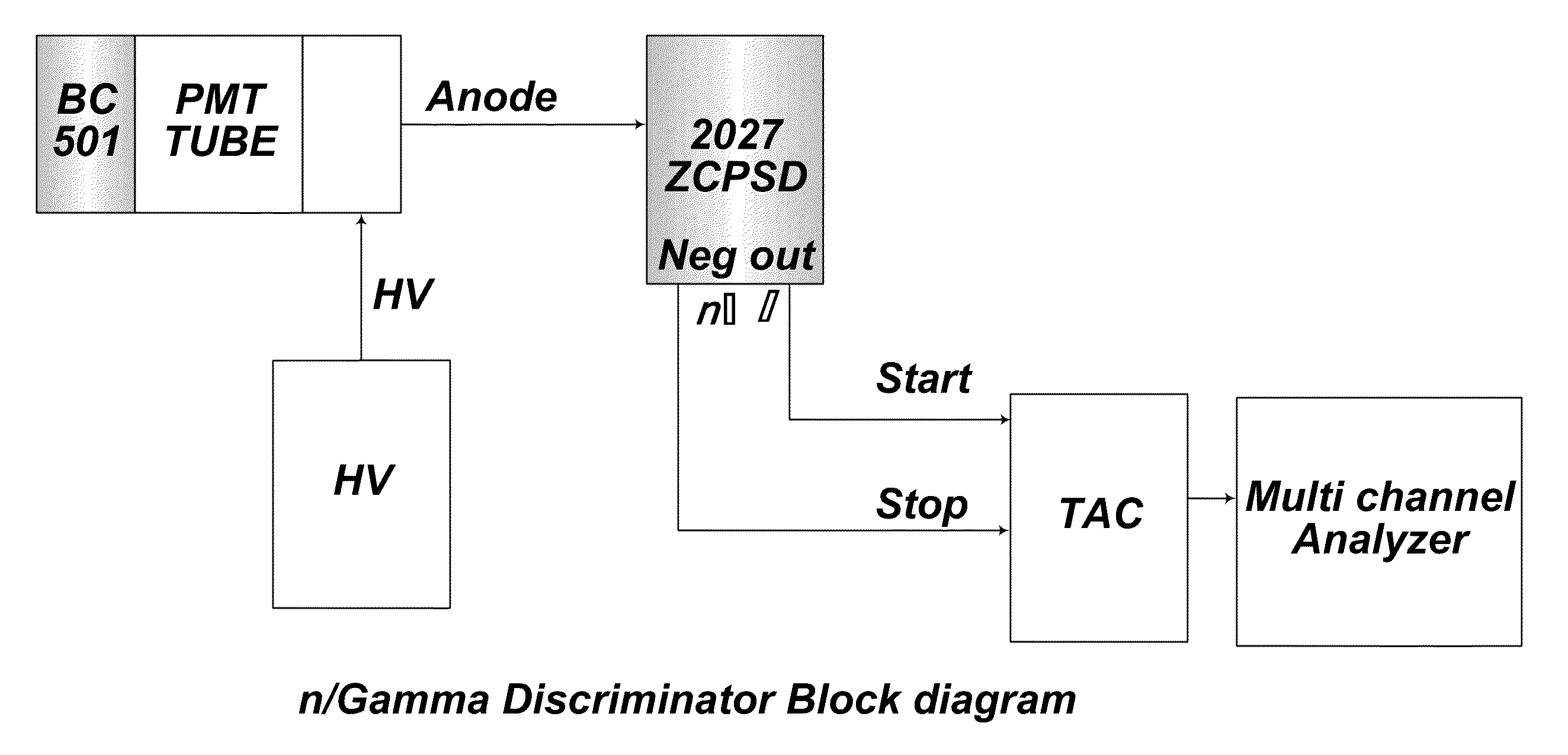
Method and system for discrimination pulse shape
InactiveUS20100308231A1Large dynamic rangeQuickly checking system capabilityMeasurement with scintillation detectorsMaterial analysis by optical meansScintillation counterElectron
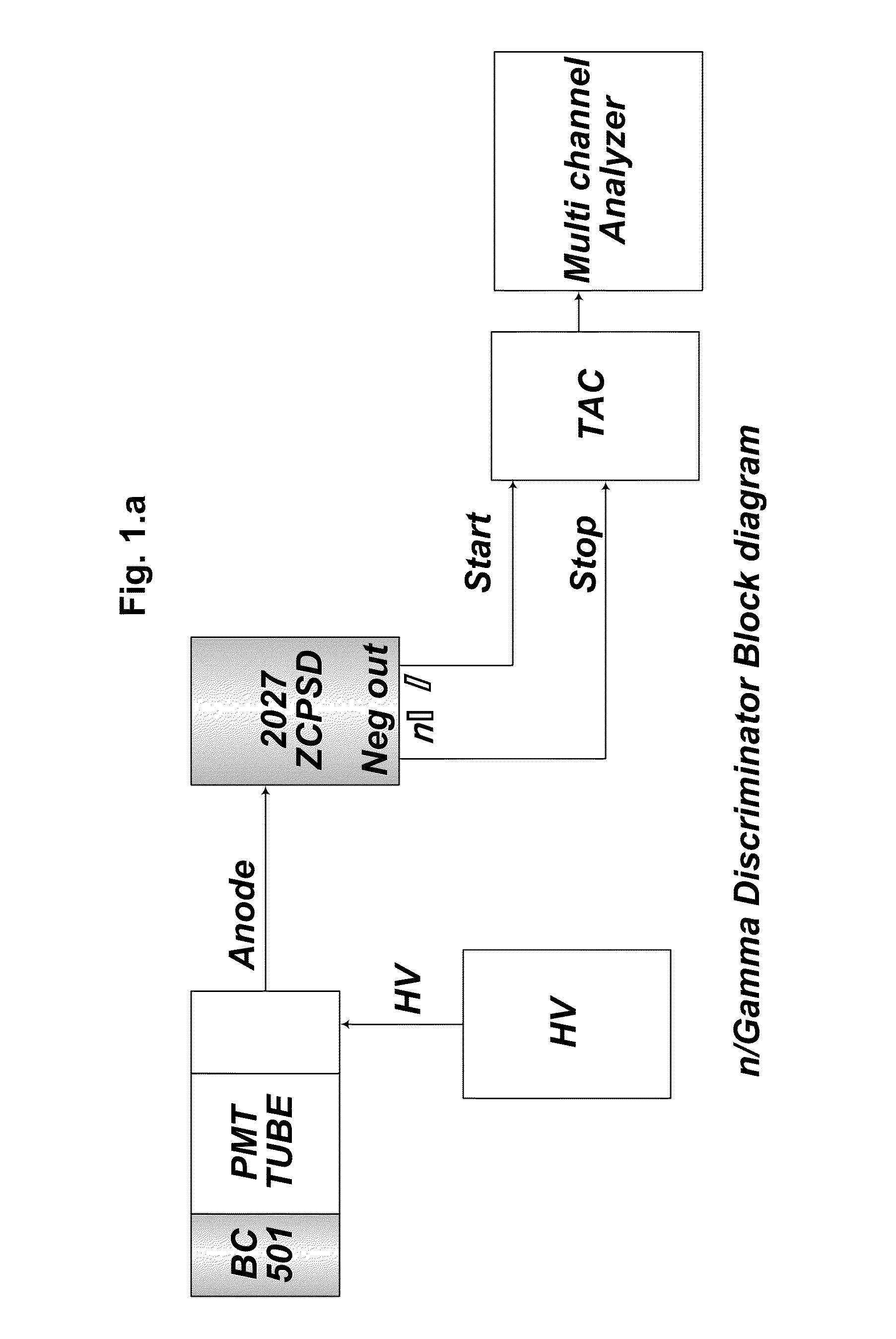
This ZCPSD Module can be used to separate neutron and gamma particles, alphas and protons, electrons and alphas etc depending on the detector used. ZCPSD provides optimum pulse shape separation for liquid scintillation counters. However the applications are not limited to n / γ separation. The ZCPSD can also be used for particle separation with inorganic scintillators, phoswitches, thick SBdetectors and proportional counters. The dc coupling allows high statistical count rate without affecting resolution, a major problem of conventional designs. The Single width NIM conforming to International Standards is easy to use, since only the anode signal is required from PM tubes. The ZCPSD can be used to generate identification spectra with a TAC and MCA or an identification signal for one species of particle.
Owner:SHARGHI IDO AMIN +1
Guard efficiency compensation system and method
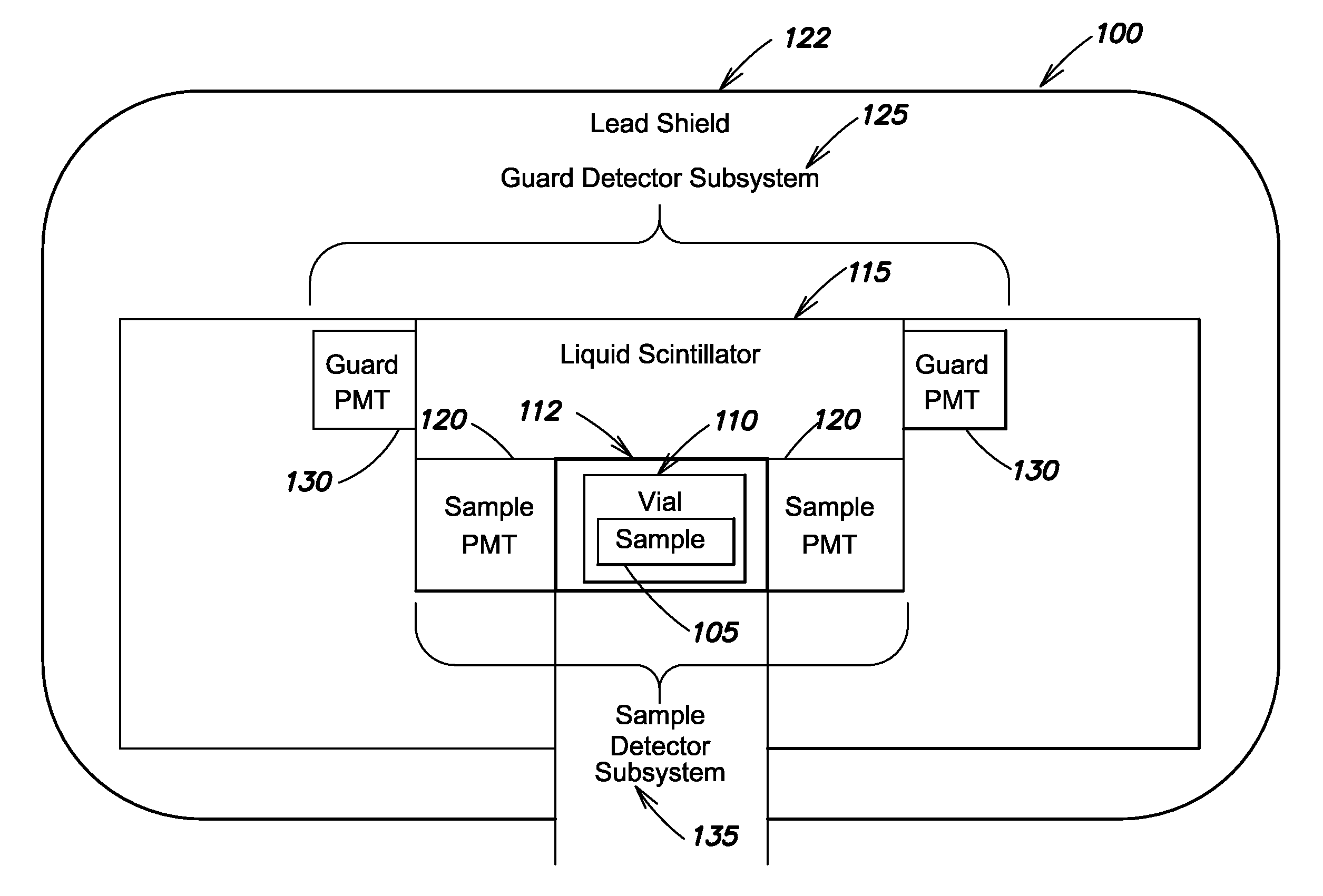
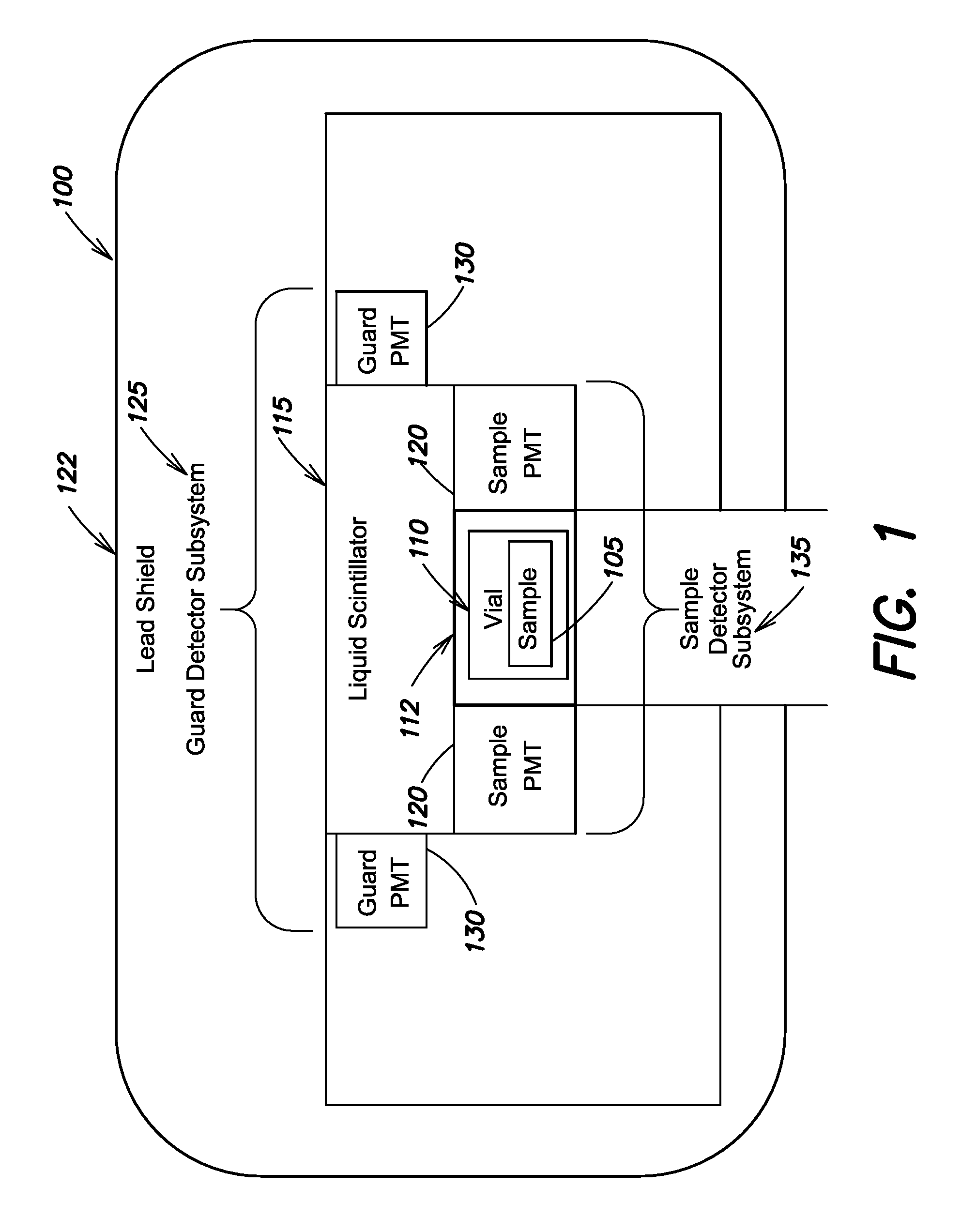
A liquid scintillation counting system employs a guard detector efficiency compensation system to adjust sample event counts to compensate for a non-ideal guard which may not detect all cosmic and environmental gamma background noise events. The system and method determines counts of events detected coincidently by a guard detector subsystem and a sample detector subsystem in one or more energy regions as well as counts of events that are detected by the sample detector subsystem and not coincidently detected by the guard detector subsystem for the respective energy regions. The system and method calculates correction values for the respective energy regions based on the counts of coincident and non-coincident events and the guard efficiency values associated with the respective energy regions, using, for example, a quenched or unquenched sample. The system then applies the calculated correction values to counts for the respective energy regions, to produce corrected sample event counts.
Owner:PERKINELMER HEALTH SCIENCES INC
Method for measuring activity of beta-glucan synthase
InactiveCN102443621AImprove securityReduce experiment costMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsBeta-glucan synthesisSalicylic acid
The invention discloses a method for measuring the activity of beta-glucan synthase. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantage that the activity of the beta-glucan synthase is determined by detecting the amount of glucan consumed by synthesizing the beta-glucan synthase into beta-glucan with the glucan as an enzymatic reaction substrate and 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid as a color developing agent under visible light. Compared with a traditional method for measuring the activity of the beta-glucan synthase by measuring the change of radioactive activity of UDP (Uridine Diphosphate)-[14C] glucan through a liquid scintillation counting instrument by using the UDP-[14C] glucan as a substrate, and the experiment cost is greatly reduced. In addition, no radioactive glucan is used as the substrate in the method, thus the safety of the experiment is high. The method has the advantages of high sensitivity, simpleness and safety in operation, convenience, quickness and convenience for large-scale popularization and application. The method disclosed by the invention can be widely used for researching and developing saccharide and enzyme products.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY +1
Method for testing activity concentrations of strontium-89 and strontium-90 in liquid effluent of nuclear power plant
ActiveCN106405617AReduce radiation effectsGet quicklyX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentActivity concentrationNuclear power
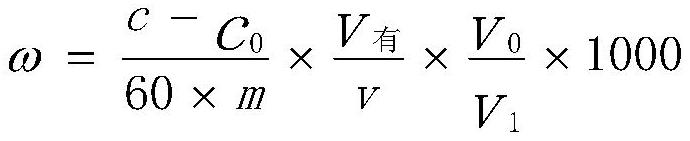
The present invention relates to a method for testing the activity concentrations of strontium-89 and strontium-90 in a liquid effluent of a nuclear power plant. The method includes the following steps that: (a) a strontium carrier is added into the liquid effluent, the strontium carrier and the liquid effluent are mixed, an obtained mixture is made to pass through a cationic resin column, so that a first eluent can be collected; (b) the first eluent is evaporated until the first eluent is dried, an obtained product is dissolved by a first nitric acid solution, an obtained mixture is made to pass through a strontium specific resin column, the first nitric acid solution is used to elute the strontium specific resin column, so that a second eluent can be collected; (c) the second eluent is arranged in a constant-weight liquid scintillation counting vial, and the second eluent is weighed after being dried, and the recovery rate Y of strontium is calculated; (d) the total radioactivity activity concentration A of the strontium-89 and strontium-90 in the liquid effluent is calculated; and (e) the strontium-89 and strontium-90 are generated based on fission in a nuclear facility and are released for testing time, the proportions of the strontium-89 and strontium-90 in the liquid effluent are calculated according to a formula (2), and the activity concentrations of the strontium-89 and strontium-90 in the liquid effluent are calculated. With the method adopted, work efficiency can be greatly improved, and radiation impact on workers caused by the liquid effluent can be reduced.
Owner:SUZHOU NUCLEAR POWER RES INST +2
Rapid joint analysis method for Pu-239, Sr-90 and Cs-137 in waste liquid
PendingCN112285226AMeet quantitative analysis requirementsEasy to separateComponent separationStrontiumWastewater
The invention discloses a rapid joint analysis method for Pu-239, Sr-90 and Cs-137 in waste liquid. The rapid joint analysis method comprises the following steps of: precipitating plutonium and strontium by controlling a pH value of wastewater, and separating then from cesium; dissolving plutonium and strontium precipitates, meanwhile, adjusting a valence state of Pu to Pu(IV), separating 239Pu and 90Sr through using a TEVA resin and Sr resin double-column series connection method, and measuring 239Pu and 90Sr through using ICP-MS and a liquid scintillation counter respectively; and collectingall liquid in the plutonium and strontium precipitation process, directly enriching 137Cs through using KNiF-PAN resin, naturally airing the resin, and measuring 137Cs by using a gamma spectrometer.The rapid joint analysis method has the advantages of small sample size, simple process, short experiment period, high separation efficiency and the like, and a feasible and efficient technical meanscan be provided for rapid analysis of nuclide in nuclear emergency monitoring and nuclear safety supervision.
Owner:63653 FORCES PLA
63Ni activity concentration measuring method
ActiveCN108918646AReduce distractionsImprove measurement accuracyMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAnalysis by material excitationActivity concentrationMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
The invention discloses a 63Ni activity concentration measuring method. The method comprises the following steps: step 1), preparing a sample to be tested Y1 into a sample Y2 and a sample Y3 respectively; step (2), measuring the mass concentration of nickel in the sample Y2 by adopting an atomic emission spectrometry; step 3), measuring the nickel isotopic abundance ratio of the sample Y3 by adopting an inductive coupling plasma mass spectrometry; and step 4), calculating the mass concentration of nickel C', the nickel isotopic abundance ratio R'i8, the nickel isotopic abundance ratio Ni, N8,the 63Ni mass concentration C3, and the 63Ni activity concentration A3 of the sample to be tested Y1. The 63Ni activity concentration measuring method provided by the invention solves the problem thatan existing liquid scintillation counter method leads to low measurement accuracy, environmentally unfriendly, and incomplete measurement indexes.
Owner:NUCLEAR POWER INSTITUTE OF CHINA
Sampling method for tritiated water in air
InactiveCN106840766AEasy to sampleSimple samplingWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationInsulation layerWater vapor
The invention provides a sampling method for tritiated water in air. A system used by the sampling method comprises a cooling fan, a semiconductor refrigeration sheet, a heat insulation layer, a collection container, a movable cover plate, a hose I, a hose II, a hose III, a power air pump, a power supply, an AC plug, a temperature display, a temperature sensor and a flow display controller. The sampling method comprises the steps of adjusting an intake flow rate equivalent to short-term respiratory volume of a person through the power air pump; pumping tritiated water vapor in air by using a peltier effect of the semiconductor refrigeration sheet; quickly condensing the tritiated water vapor into tritiated water through a coil of the collection container; carrying out volume measurement and liquid scintillation counting on the collected tritiated water; and obtaining the inhalation dose of tritium in air near a respiratory zone of a worker of a tritium-related place according to a calculation formula. The sampling method is suitable for fast sampling of the tritiated water of the air near the worker of the tritium-related place, and is a practical and simple sampling method; and a support can be provided for radiation protection of the worker of the tritium-related place.
Owner:INST OF NUCLEAR PHYSICS & CHEM CHINA ACADEMY OF
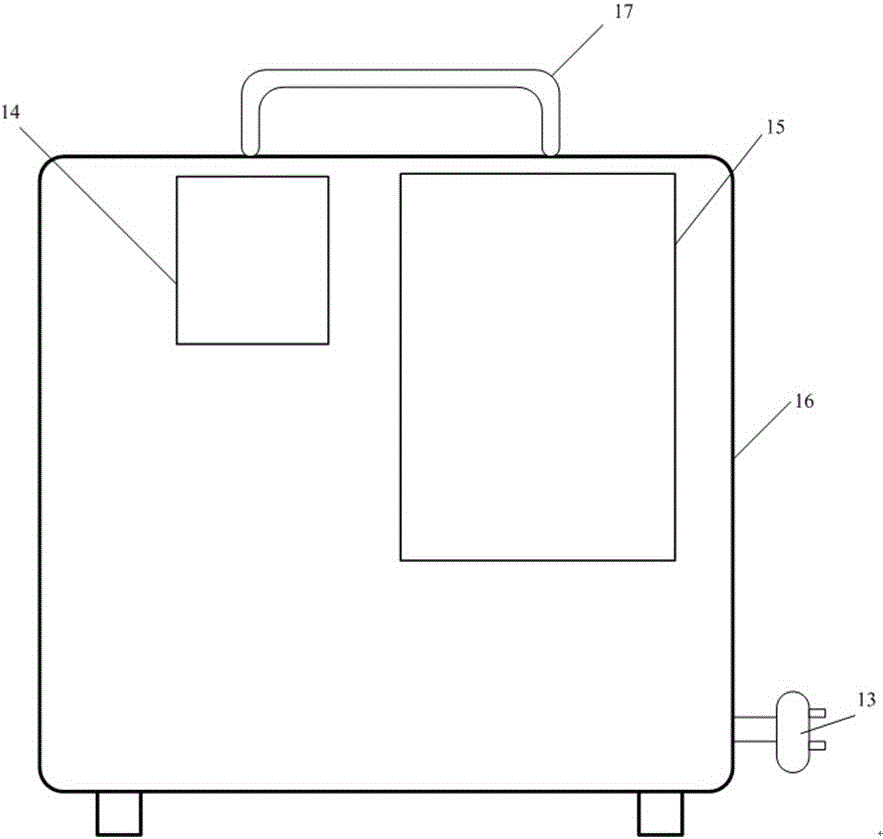
Liquid scintillation counter
The invention discloses a liquid scintillation counter which comprises a casing, wherein a functional area is arranged on the casing; an operation panel, a display screen and a miniprinter are arranged in the functional area; a control system, a power module, a photomultiplier tube and a sample moving device are arranged in the casing; a mounting groove is formed in the sample moving device and used for accommodating a sample bottle; the sample bottle is moved by the sample moving device to the middle of the photomultiplier tube for detection; the control system is used for power control as well as signal analysis and output; the power module is used for supplying power. The liquid scintillation counter is simple and skillful in structure, a sample is moved by the sample moving device to the photomultiplier tube for detection, a detection environment is guaranteed by means of an added sealing cover, the control system outputs a detection result to the internet or a printer, and convenience and fastness are realized.
Owner:ANHUI YOUNG HEARTY MEDICAL APPLIANCE & EQUIP
Method for determining subcellular distribution of graphene in rice
ActiveCN109187401AAccurate measurementSimple methodMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationColor/spectral properties measurementsRice plantsSlurry
The invention discloses a method for determining subcellular distribution of graphene in rice, and belongs to the application development of nanotechnology in the agricultural field. The method comprises the following steps: performing germination treatment on rice seeds, exposing graphene to germinated rice; respectively collecting stem and leaf parts of rice plants for fully grinding after beingcrushed and liquid nitrogen frozen; adding a pre-cooled homogenizing medium into the ground tissue to prepare a homogenate; separating the homogenate into five parts by differential centrifugation: cell wall, chloroplast, nucleus, mitochondria and soluble fraction; fully burning each component by a bio-oxidation instrument to collect carbon dioxide generated; and determining the grapheme contentin each component by a liquid scintillation counter. In order to evaluate the possible interaction between organelles and graphene during centrifugation, three control experiments are designed to accomplish this goal. The method achieves accurate quantification of graphene in subcellular of rice plants.
Owner:NANJING UNIV +1
Guard efficiency compensation system and method
ActiveUS20150301194A1Material analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementLiquid scintillation countingBackground noise
A liquid scintillation counting system employs a guard detector efficiency compensation system to adjust sample event counts to compensate for a non-ideal guard which may not detect all cosmic and environmental gamma background noise events. The system and method determines counts of events detected coincidently by a guard detector subsystem and a sample detector subsystem in one or more energy regions as well as counts of events that are detected by the sample detector subsystem and not coincidently detected by the guard detector subsystem for the respective energy regions. The system and method calculates correction values for the respective energy regions based on the counts of coincident and non-coincident events and the guard efficiency values associated with the respective energy regions, using, for example, a quenched or unquenched sample. The system then applies the calculated correction values to counts for the respective energy regions, to produce corrected sample event counts.
Owner:PERKINELMER HEALTH SCIENCES INC
Liquid scintillation counting method for measuring 231 Pa nuclide activity
The invention relates to a liquid scintillation counting method for measuring 231 Pa nuclide activity. The liquid scintillation counting method is characterized by at least comprising the following steps of calculating a kinetic equation of a 231 Pa decay chain; establishing a relationship between the atomic concentration of daughter nuclides in the 231 Pa decay chain and the 231 Pa atomic concentration; establishing a measurement equation based on the measured relationship among total count data, the atomic concentration of the daughter nuclides in the 231 Pa decay chain and the radionuclidedetection efficiency; and calculating the 231 Pa nuclide activity based on the measured sample count and the radionuclide detection efficiency. According to the liquid scintillation counting method for measuring the 231 Pa nuclide activity, the relation between the atomic concentration of the daughter nuclides in the 231 Pa decay chain and the 231 Pa atomic concentration is established by calculating the solution of the kinetic equation of the 231 Pa decay chain, the problems of 231 Pa radioactive imbalance and branch decay measurement can be solved, and the accuracy of a result is further improved.
Owner:NAT INST OF METROLOGY CHINA
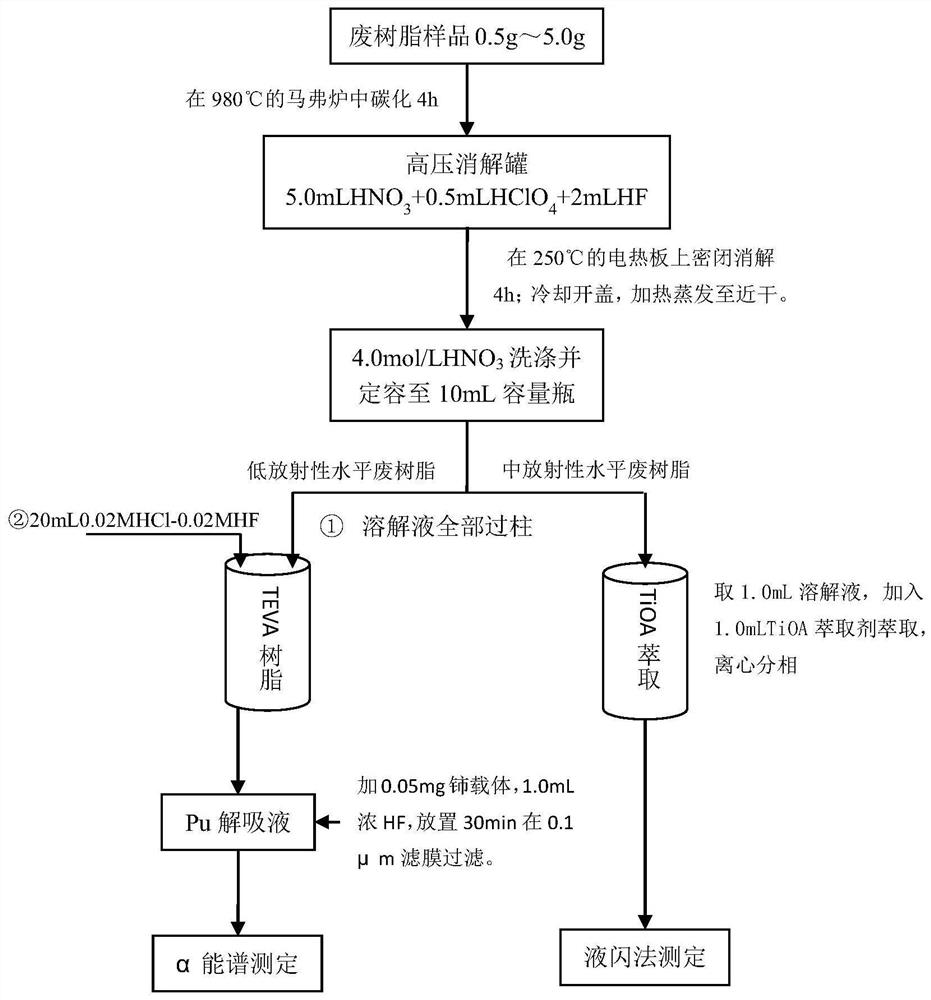
Method for analyzing plutonium in waste ion exchange resin sample
The invention belongs to the technical field of nuclear facility decommissioning and three-waste treatment, and particularly relates to a method for analyzing plutonium in a waste ion exchange resin sample. The method comprises the following steps of carrying out sample pretreatment: weighing a waste resin sample, carrying out high-temperature carbonization and high-pressure digestion, and dissolving with a nitric acid solution; carrying out Pu separation and enrichment: separating and purifying Pu from the waste resin dissolving solution with a low radioactivity level by adopting a TEVA extraction chromatography resin; extracting, separating and purifying Pu of the waste resin dissolving solution with a medium radioactive level by adopting TiOA; carrying out Pu determination: preparing analpha source from a Pu leacheate subjected to TEVA separation and purification by using a cerium fluoride micro-deposition method, and determining the energy of 238-240 Pu by using an alpha energy spectrum, and selecting 5.11 MeV- 5.50 MeV; and measuring Pu for the Pu extracted, separated and purified by TiOA by using a liquid scintillation counter. The method realizes analysis and determinationof Pu in the waste resin sample.
Owner:THE 404 COMPANY LIMITED CHINA NAT NUCLEAR
Multifunction measuring instrument
InactiveUS20060127279A1Analysis by electrical excitationFluorescence/phosphorescenceMeasuring instrumentFluorescence
The object of the invention is a multifunction instrument (10 ) for measuring biochemical and medical samples, which are preferably placed into the wells (13) of the sample plates (12) and measured by a detector (20). The detector is movable with slide (26, 27) and guide (22, 23) elements so that a rotating device (14) can turn the detector into vertical position for liquid scintillation counting and / or luminescence counting. The second horizontal position and light path (30) is provided for fluorescence measuring with a light source (40) for excitation. Also an absorbance detector (50) is included.
Owner:HIDEX
Systems and methods for emulating scintillation events using an electronic test source
ActiveUS11275188B2Improve calibration resultsFacilitate calibration and testingX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentNuclear engineeringRadioactive agent
Presented herein are systems and methods that provide for calibration and / or testing of liquid scintillation counters (LSCs) using an electronic test source. In certain embodiments, the electronic test source described herein provides for emission of emulated radioactive event test pulses that emulate light pulses produced by a scintillator as a result of radioactive decay of a variety of different kinds of radioactive emitters (e.g., beta, alpha, and gamma emitters). Additionally, in certain embodiments, the systems and methods described herein provide for the emission of emulated background light (e.g., luminescence and after-pulses) from the electronic test source. The emulated radioactive event test pulses and, optionally, emulated background light can be used for the calibration and / or testing of LSCs, in place of hazardous radioactive material and / or volatile chemicals. Accordingly, the systems and methods described herein dramatically improve the calibration and / or testing of liquid scintillation counters.
Owner:PERKINELMER HEALTH SCIENCES INC
Method for leaching plutonium in waste resin
PendingCN112596093AExtended half-lifeHarmfulPreparing sample for investigationX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentEnvironmental engineeringPerchloric acid
The invention belongs to the technical field of nuclear facility decommisioning treatment, and particularly relates to a method for leaching plutonium in waste resin. The method comprises the steps ofweighing a waste resin sample, putting into a porcelain crucible, covering with a crucible cover, ashing in a muffle furnace, taking out, and placing to room temperature; adding HNO3+HF into a waterbath kettle for leaching, taking out, and placing to room temperature; filtering the leaching solution, fixing the volume to 10mL, accurately transferring the supernatant, adding a scintillation solution, fully shaking up, and measuring on a liquid scintillation counter; respectively weighing three groups of plutonium-containing waste resin samples in a porcelain crucible, requiring that upper-layer resin is weighed for first group, middle-layer resin is weighed for the second group and lower-layer resin is weighed for the third group, and covering a crucible cover; after ashing in a muffle furnace, transferring ash into a high-pressure digestion tank by using a nitric acid solution; and adding hydrofluoric acid and perchloric acid into the high-pressure digestion tank for high-pressure digestion. According to the invention, 90% or above of plutonium in the waste resin is transferred to an aqueous phase.
Owner:THE 404 COMPANY LIMITED CHINA NAT NUCLEAR
Apparatus and method for preparing samples for radiocarbon dating
InactiveUS7291837B2Promote absorptionPreventing vapor lossMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationWithdrawing sample devicesRadiocarbon datingLiquid scintillation counting
The invention provides a method and apparatus for preparing samples of carbon dioxide with a 14C content for analysis in liquid scintillation counting equipment, the sample being of a known mass and being introduced into and substantially wholly absorbed into an absorption “cocktail”, absorption being completed at a stage before saturation of the absorbent occurs. The absorbent is contained in a vial which, when absorption has been completed, is transferred into the scintillation counting equipment without intermediate transfer of the contents.
Owner:VERHAGEN BALTHAZAR T
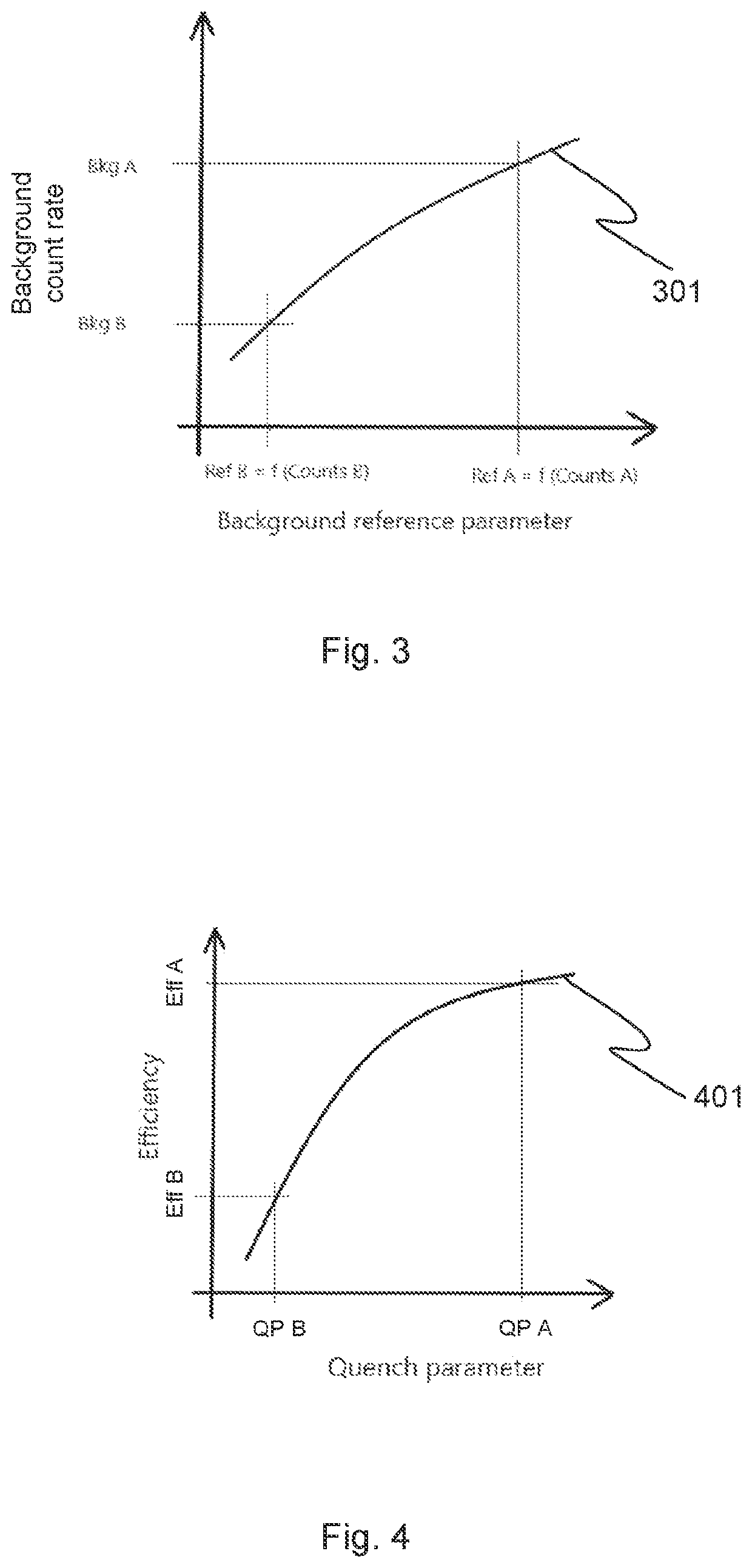
Method for determining a background count rate in liquid scintillation counting
PendingUS20220326401A1Inhibition of energy transferReduce outputRadiation intensity measurementCounting rateComputational physics
The present invention provides a method for determining a background count rate in liquid scintillation counting. The method comprises measuring external standard spectra of a sample, determining, from the external standard spectra, a triple to double coincidence ratio and a quench parameter, determining, based on the triple to double coincidence ratio and the quench parameter, a background reference parameter, and determining, based on the background reference parameter, the background count rate from a background reference curve.
Owner:HIDEX
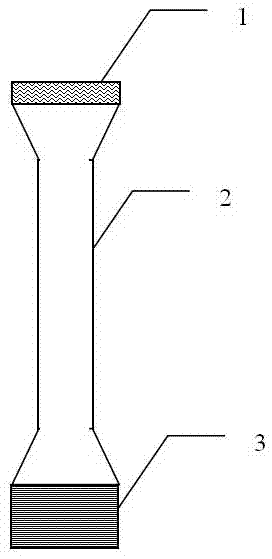
Method for determining living plant unidirectional ion absorption speed by liquid scintillation counting method and special sample pipe of method
InactiveCN104749195AReduce volumeSimple structureMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationEngineeringStructural engineering
The invention discloses a special sample pipe for a method for determining a living plant unidirectional ion absorption speed by using a liquid scintillation counting method. The special sample pipe comprises a top cover, a pipe body and a base, wherein the top cover, the pipe body and the base are circular; the top cover is covered on the upper end of the pipe body; and the base is fixedly connected with the lower end of the pipe body. According to the method for determining the living plant unidirectional ion absorption speed by using the liquid scintillation counting method, the measurement of the living plant unidirectional ion absorption speed can be solved by the simple and efficient liquid scintillation counting method and the instant speed determination which cannot be finished by a common determination method can be effectively solved. The volume of the special sample pipe is smaller than that of a common sample pipe so that the use amount of a radioactive solution is reduced; a sealing gasket cushion is designed so that the safety of operators and the uniformity of uniformly shaking the sample are guaranteed; a flexible model can be put into a common sample bottle to be determined, and is made of a polypropylene material so that the special sample pipe is not easy to break and radioactive leakage is not caused; and the special sample pipe has a simple structure and is convenient to operate, and a testing result can accurately represent the actual condition of ion transportation.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY PHARMA OF CAAS
Quantitative detection method for <14>C in urine
PendingCN113188863AEffectively remove interferenceEliminate distractionsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPreparing sample for investigationPotassium persulfateChloride
The invention discloses a quantitative detection method for <14>C in urine, which belongs to the technical field of radiohygiene. The method comprises the following steps of (1) measuring a certain volume of urine sample, adding potassium persulfate, heating, stirring, converting organic carbon and inorganic carbon in the urine sample into carbon dioxide, purging the generated carbon dioxide through carrier gas, and absorbing with alkali liquor, and (2) adjusting the pH value of the absorption liquid with ammonium chloride, adding a saturated calcium chloride solution to generate calcium carbonate precipitate, standing, carrying out suction filtration, and drying, and (3) grinding the prepared calcium carbonate precipitate powder into powder by using a mortar, weighing a proper amount of powder, and carrying out <14>C activity measurement by using a liquid scintillation counter. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of high accuracy, high recovery rate and stable detection result, and can meet the analysis of the activity concentration of <14>C in the urine sample.
Owner:国家卫生健康委职业安全卫生研究中心
Systems and methods for emulating scintillation events using an electronic test source
ActiveUS20200284927A1Improve calibration resultsFacilitate calibration and testingX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentNuclear engineeringRadioactive agent
Presented herein are systems and methods that provide for calibration and / or testing of liquid scintillation counters (LSCs) using an electronic test source. In certain embodiments, the electronic test source described herein provides for emission of emulated radioactive event test pulses that emulate light pulses produced by a scintillator as a result of radioactive decay of a variety of different kinds of radioactive emitters (e.g., beta, alpha, and gamma emitters). Additionally, in certain embodiments, the systems and methods described herein provide for the emission of emulated background light (e.g., luminescence and after-pulses) from the electronic test source. The emulated radioactive event test pulses and, optionally, emulated background light can be used for the calibration and / or testing of LSCs, in place of hazardous radioactive material and / or volatile chemicals. Accordingly, the systems and methods described herein dramatically improve the calibration and / or testing of liquid scintillation counters.
Owner:PERKINELMER HEALTH SCIENCES INC
a measurement 231 Liquid scintillation counting method for pa nuclide activity
The invention relates to a measurement 231 The liquid scintillation counting method of Pa nuclide activity is characterized in that, described method step comprises at least: calculating 231 The kinetic equation of the Pa decay chain; establishing the 231 The atomic concentration of neutron nuclides in the Pa decay chain and 231 The relationship of Pa atomic concentration; based on the measured total count data and the described 231 The relationship between the atomic concentration of the neutron nuclide in the Pa decay chain and the detection efficiency of the radionuclide establishes a measurement equation; based on the measured sample count and the detection efficiency calculation of the radionuclide 231 Pa nuclide activity. Measurements of the invention 231 The liquid scintillation counting method of Pa nuclide activity is calculated by 231 The solution of the kinetic equation for the Pa decay chain to establish 231 The atomic concentration of neutron nuclides in the Pa decay chain and 231 The relationship between Pa atomic concentration can be solved 231 Pa radioactivity imbalance, and the difficulty of measuring branch decay, also further improved the accuracy of the results.
Owner:NAT INST OF METROLOGY CHINA
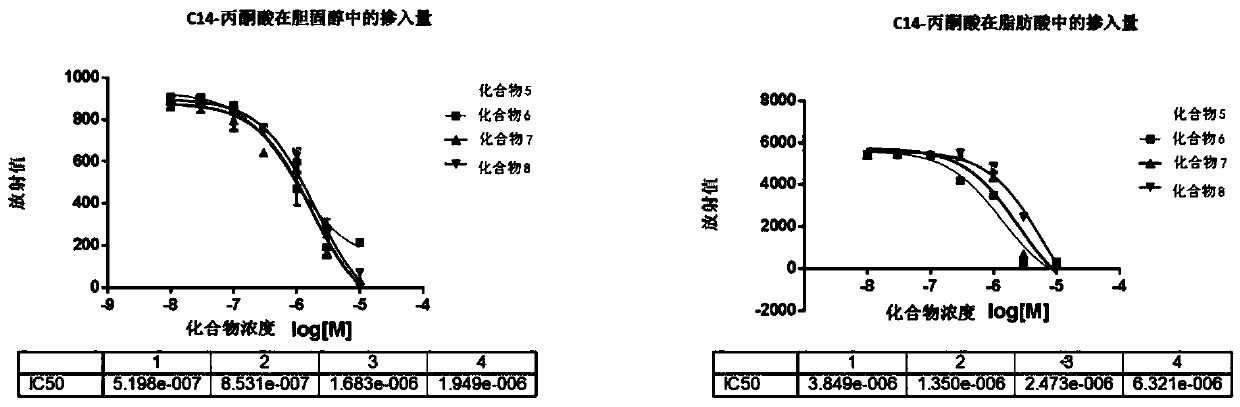
High-flux evaluation method for cholesterol and aliphatic acid metabolism inhibition medicament
ActiveCN109633141AImprove extraction efficiencyLow costBiological testingHigh fluxCholesterol metabolism
The invention relates to a high-flux evaluation method for a cholesterol and aliphatic acid metabolism inhibition medicament. The method comprises the following steps that (1) cells are cultured and marked; (2) cholesterol is extracted in the alkaline environment via petroleum ether, a Microbeta liquid scintillation counting instrument is used for counting, and an cholesterol metabolism inhibitioneffect of the inhibition medicament to be evaluated is obtained; and (3) aliphatic acid is extracted in the acidic environment via the petroleum ether, the Microbeta liquid scintillation counting instrument is used for counting, and an aliphatic acid metabolism inhibition effect of the inhibition medicament to be evaluated is obtained. Compared with the prior art, a simple, rapid, high-efficiencyand high-flux cholesterol and aliphatic acid extraction technology is established, the cost of instrument is reduced, convenience is provided for operation, the product extraction efficiency is higher, and the method is much more competitive in the market.
Owner:辉源生物科技(上海)有限公司
Method for measuring activity of beta-glucan synthase
InactiveCN102443621BImprove securityReduce experiment costMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsBeta-glucan synthesisSalicylic acid
The invention discloses a method for measuring the activity of beta-glucan synthase. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantage that the activity of the beta-glucan synthase is determined by detecting the amount of glucan consumed by synthesizing the beta-glucan synthase into beta-glucan with the glucan as an enzymatic reaction substrate and 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid as a color developing agent under visible light. Compared with a traditional method for measuring the activity of the beta-glucan synthase by measuring the change of radioactive activity of UDP (Uridine Diphosphate)-[14C] glucan through a liquid scintillation counting instrument by using the UDP-[14C] glucan as a substrate, and the experiment cost is greatly reduced. In addition, no radioactive glucan is used as the substrate in the method, thus the safety of the experiment is high. The method has the advantages of high sensitivity, simpleness and safety in operation, convenience, quickness and convenience for large-scale popularization and application. The method disclosed by the invention can be widely used for researching and developing saccharide and enzyme products.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY +1
Systems and methods for emulating scintillation events using an electronic test source
ActiveUS20220229197A1Improve calibration resultsFacilitate calibration and testingX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentNuclear engineeringRadioactive agent
Presented herein are systems and methods that provide for calibration and / or testing of liquid scintillation counters (LSCs) using an electronic test source. In certain embodiments, the electronic test source described herein provides for emission of emulated radioactive event test pulses that emulate light pulses produced by a scintillator as a result of radioactive decay of a variety of different kinds of radioactive emitters (e.g., beta, alpha, and gamma emitters). Additionally, in certain embodiments, the systems and methods described herein provide for the emission of emulated background light (e.g., luminescence and after-pulses) from the electronic test source. The emulated radioactive event test pulses and, optionally, emulated background light can be used for the calibration and / or testing of LSCs, in place of hazardous radioactive material and / or volatile chemicals. Accordingly, the systems and methods described herein dramatically improve the calibration and / or testing of liquid scintillation counters.
Owner:REVVITY HEALTH SCI INC
A sort of 63 Ni activity concentration measurement method
ActiveCN108918646BReduce distractionsImprove measurement accuracyMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAnalysis by material excitationActivity concentrationPhysical chemistry
Owner:NUCLEAR POWER INSTITUTE OF CHINA
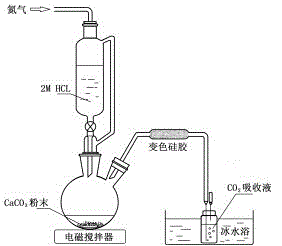
Method and apparatus for measuring radioactive strength of plant and soil
InactiveCN1255672CNo lossHigh recovery rateChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceEarth material testingRadioactive wasteScintillation counter
A method for determinating radioactive intensity of plant and soil includes adding oxidant in a closed system, heating and digesting sample of plant and soil, leading oxygen in to oxidate sample thoroughly, absorbing generated CO2 with sodium hydroxide after it being purified and using liquid scintillation counter to analyse C-14 radioactive intensity of absorption liquid.
Owner:INST OF SUBTROPICAL AGRI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com