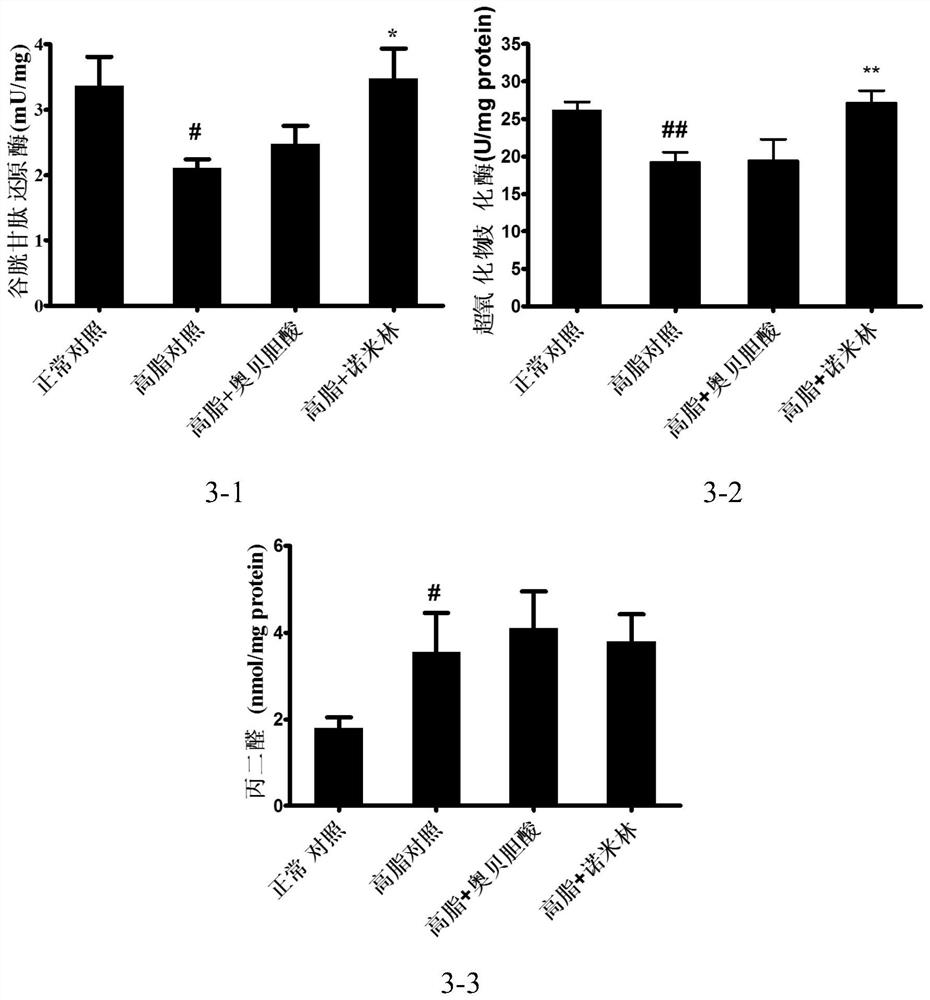
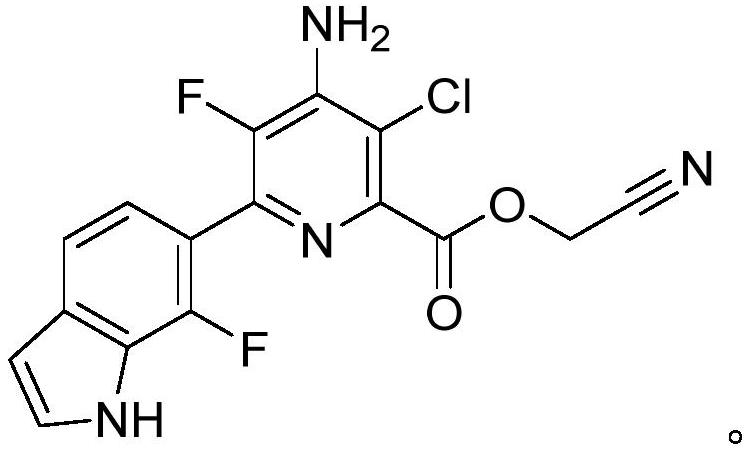
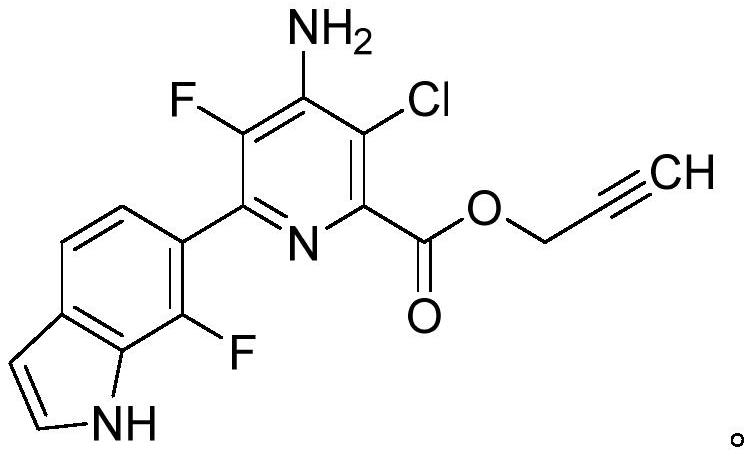
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
33 results about "Lipid A synthesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Paclitaxel lipid composite
ActiveCN101396346AImprove solubilityGood dispersionOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsEmulsionDrug loading dose
The invention discloses a paclitaxel lipid complex. The paclitaxel lipid complex consists of paclitaxel and lipid material. The weight proportion of the paclitaxel and the lipid material is 1 to 1 - 19, the preferential proportion is 1 to 2 - 10, and the more preferential proportion is 1 to 3 - 6. The lipid material is selected from natural lipid and synthetic lipid or the mixture thereof. The paclitaxel lipid complex can also contain antioxidation stabilizer. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the paclitaxel lipid complex and the application in the preparation of injection submicron emulsion and dry emulsion. The paclitaxel lipid complex has high solubility in oil, and the prepared submicron emulsion has the advantages of high drug loading quantity, high stability, high safety and low irritability.
Owner:BEIJING WEHAND BIO PHARMA CO LTD
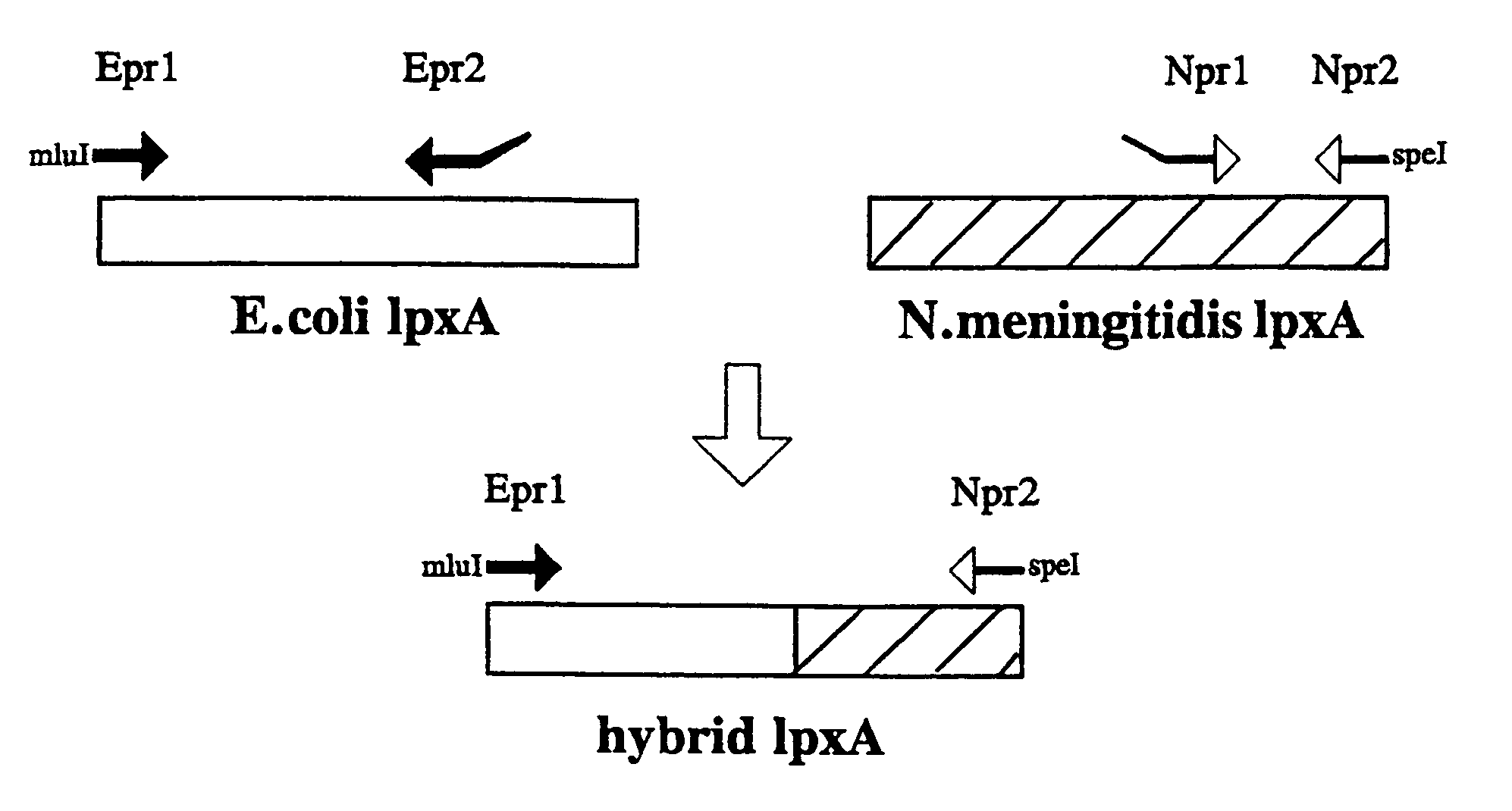
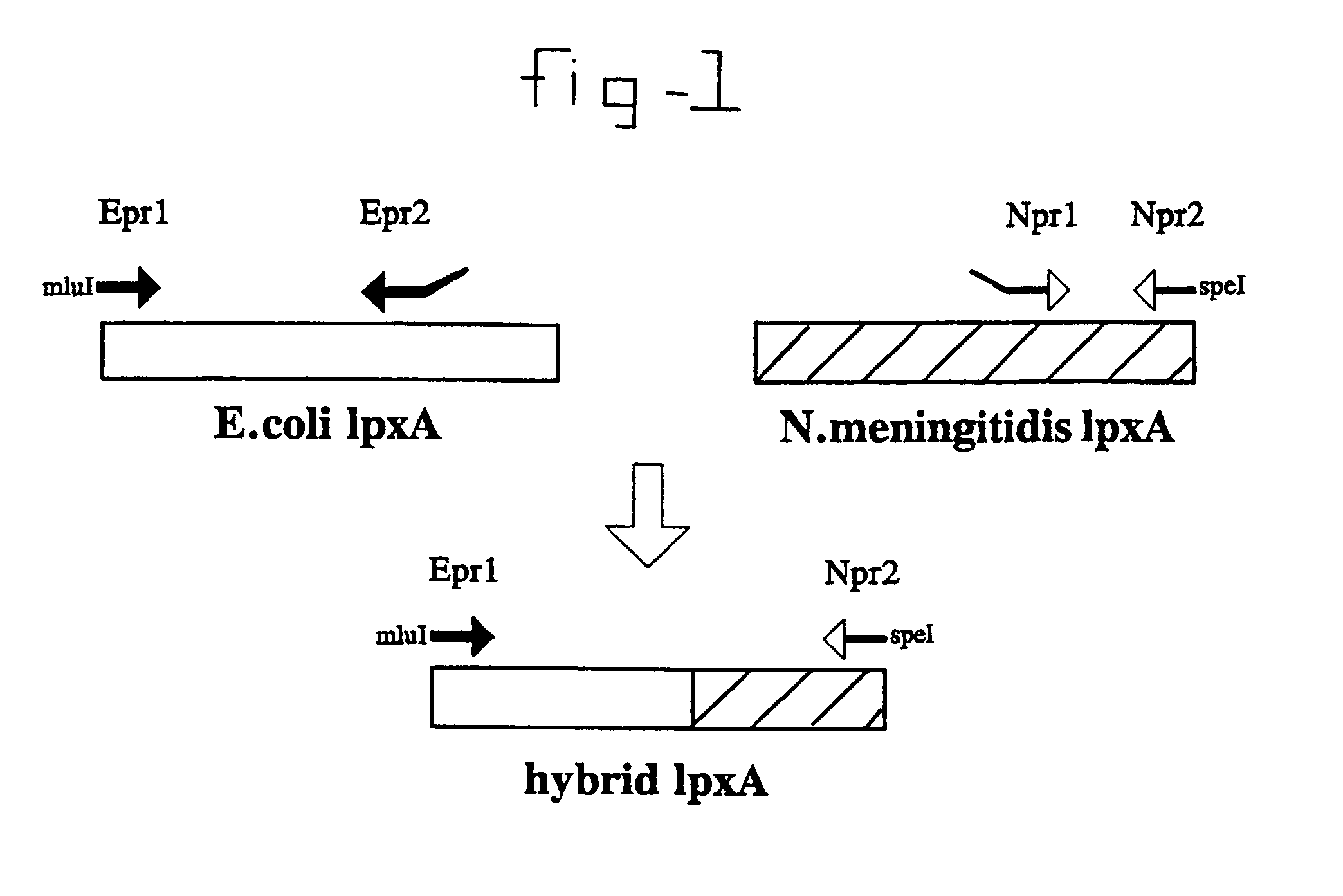
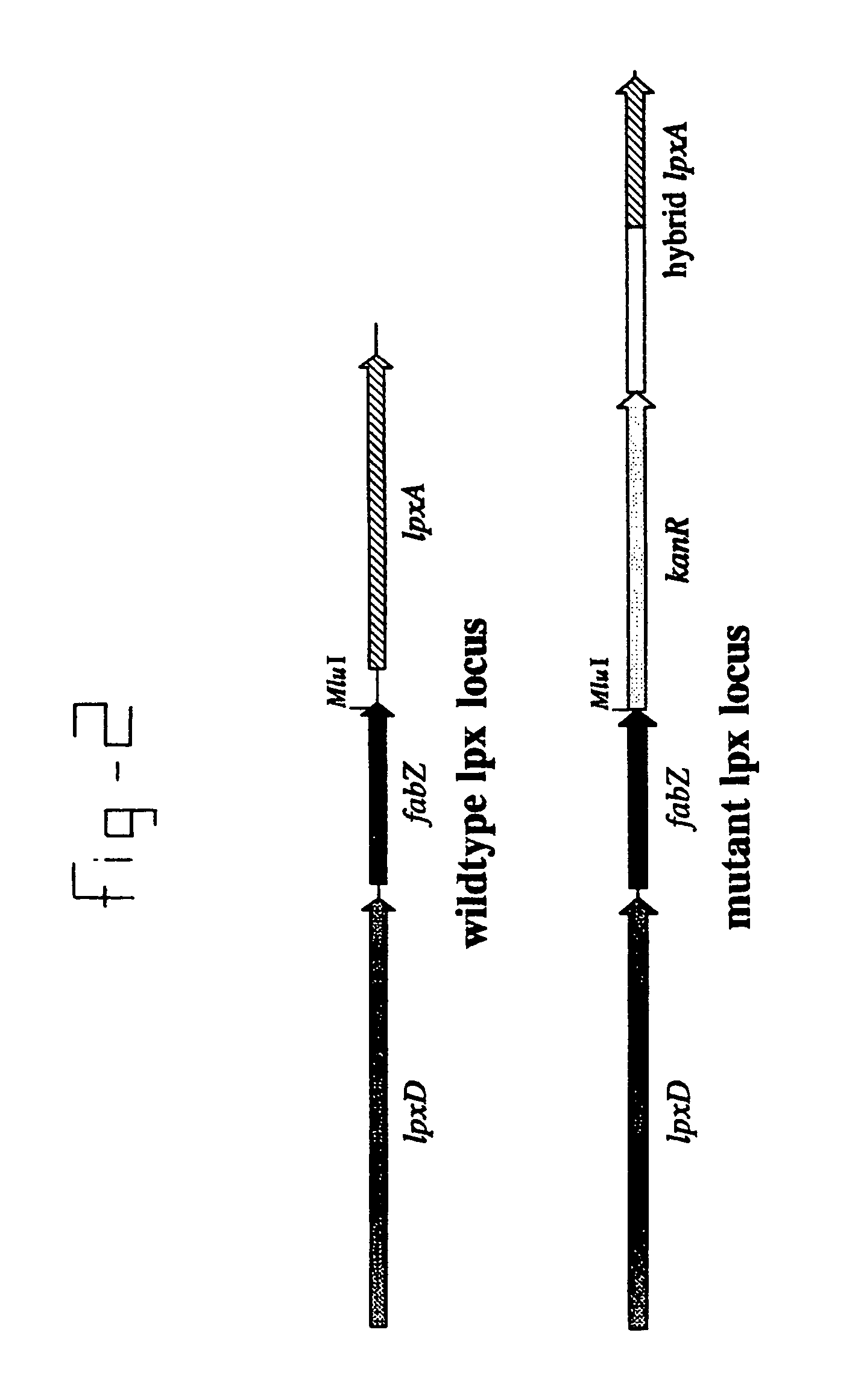
Mutants of gram negative mucosal bacteria and application thereof in vaccines
It is possible to inactivate the early stage of lipid A synthesis of mucosal gram negative bacteria without compromising cell viability. In particular the lpxA gene in N. meningitidis was mutated and resulting lpxA knockout mutants were found to be completely lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-deficient. The major outer membrane proteins (OMPs) were detected in normal amounts. The finding provides important implications for understanding of structure and biogenesis of the outer membrane. On a practical level, the availability of LPS-deficient mutants of pathogenic mucosal bacteria such as N. meningitidis opens up new avenues to vaccine development. It enables easy isolation of endotoxin-free purified proteins, outer membranes or even whole-cell preparations for use in immunisation.
Owner:INTRAVACC BV +1
Health products with hypolipemic function, preparation method and usage thereof
ActiveCN101524422AClear blood lipid depositsInhibit endogenous cholesterol synthesis and low-density lipoprotein productionOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderToxicityAdemetionine
The invention relates to health products with hypolipemic function and also relates to a preparation method for the health products and the usage thereof. The health products comprise active constituents of hongqu powder, hawthorn extract, ginkgo biloba leaf extract, obtuseleaf senna seed extract and radix salviae miltiorrhizae extract. The active constituents have very obvious synergistic effect, thus playing a positive role in hypolipemic in many aspects such as reducing endogenous lipid synthesis, promoting the transfer and excretion of lipid, regulating lipid metabolism and the like, having obvious hypolipemic effect; safety toxicity test proves that the active constituents are safe, innoxious and harmless.
Owner:WUXI JIANTE PHARM CO LTD +1
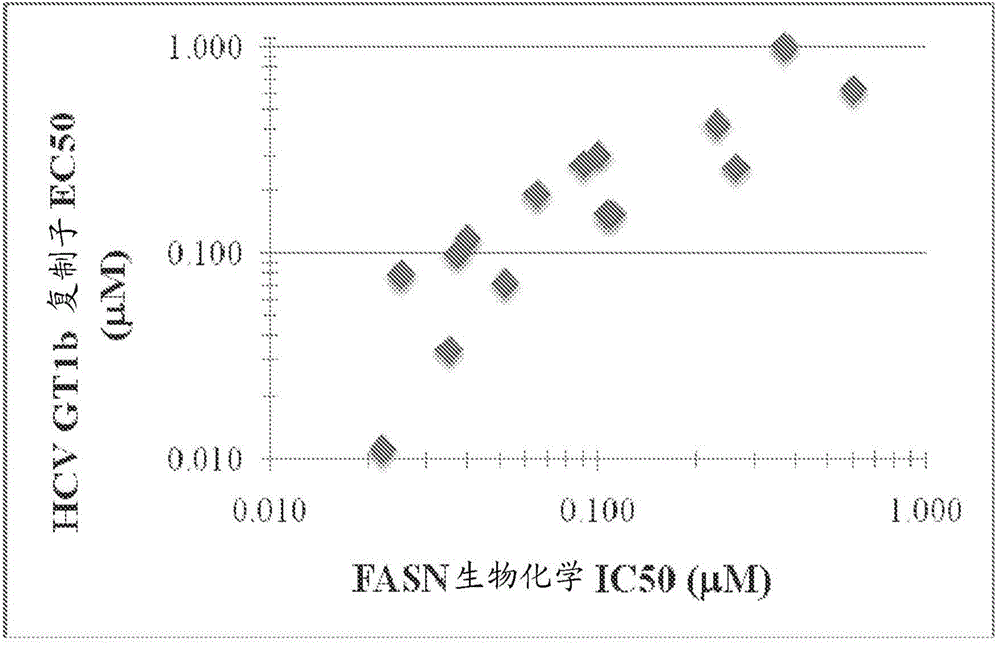
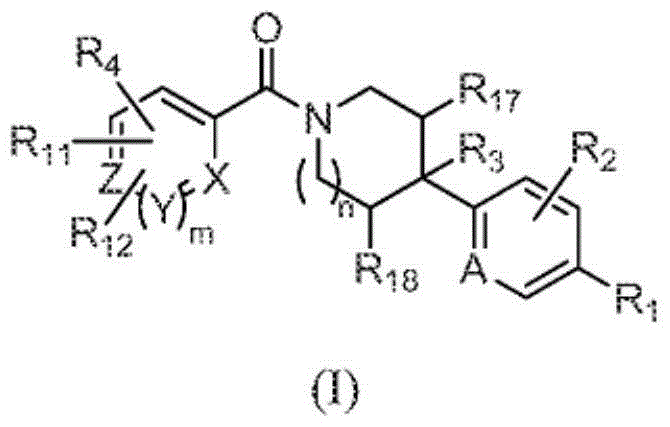
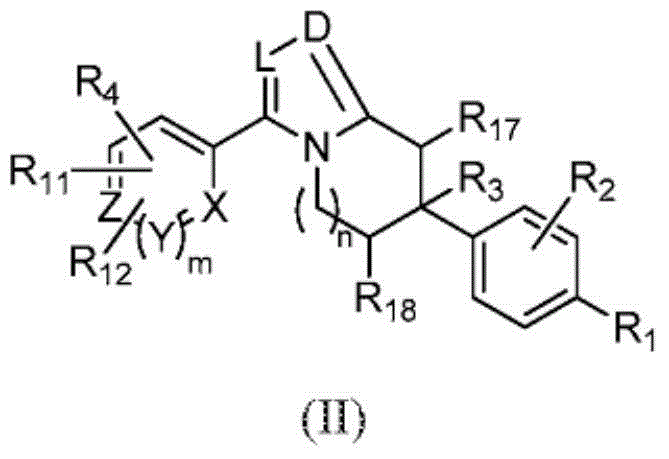
Heterocyclic modulators of lipid synthesis
ActiveCN103561576AImproved antiviral activityHigh anticancer activityBiocideSenses disorderFatty acid biosynthesisMembrane lipid metabolism
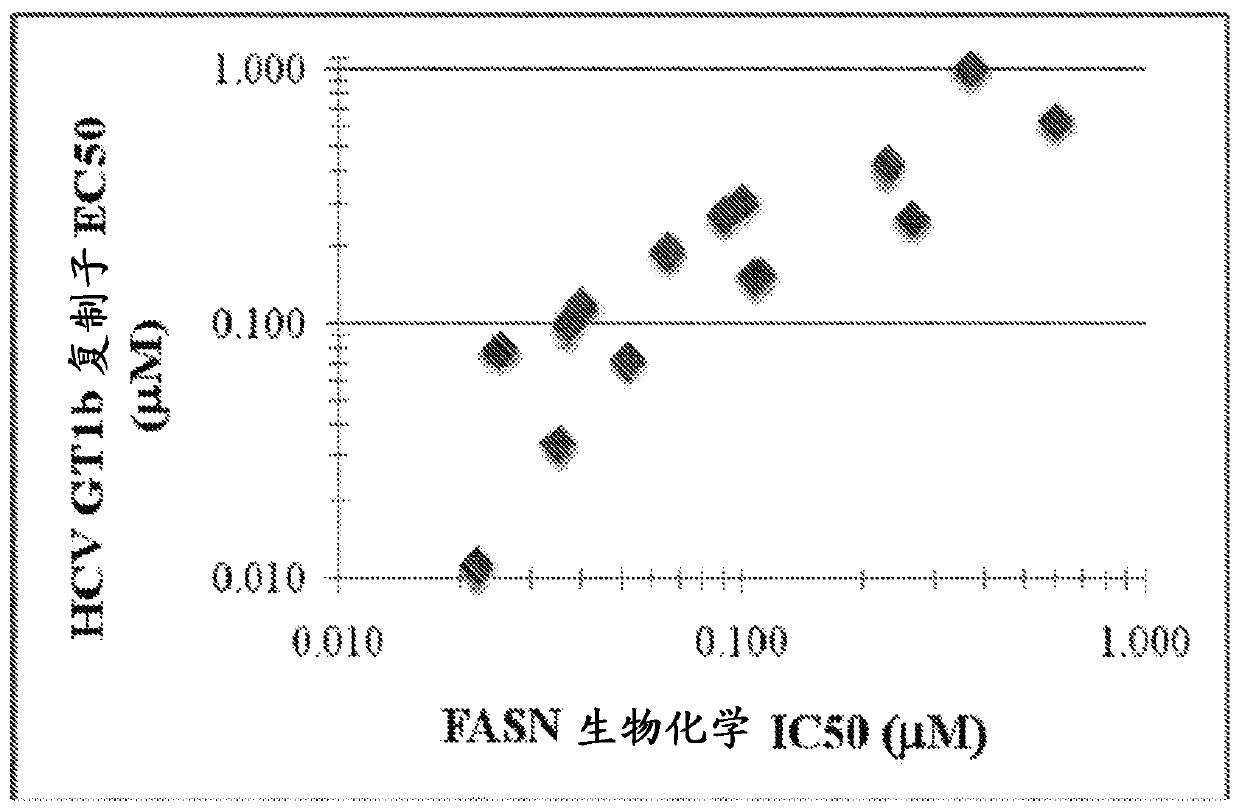
Compounds that are fatty acid synthesis modulators are provided. The compounds may be used to treat disorders characterized by disregulation of the fatty acid synthase function by modulating the function and / or the fatty acid synthase pathway. Methods are provided for treating such disorders including viral infections, such as hepatits C infection, cancer and metabolic disorders.
Owner:GANNEX PHARM CO LTD
Application of soluble dietary fibers in kelp in preparation of lipid-lowering and weight-losing medicines and functional foods
InactiveCN110787191AImprove securityLow priceMetabolism disorderAlgae medical ingredientsInflammatory factorsFat mouse
The invention discloses an application of soluble dietary fibers in kelp in preparation of lipid-lowering and weight-losing medicines and functional foods. The soluble dietary fibers are extracted from the waste kelp residues, after feeding for 3 weeks, the weight of obese mice is remarkably reduced compared with that of a negative control group; after 6 weeks of experiment period, the lipid-lowering effect is obvious; the epididymis fat and the liver of a mouse are subjected to histopathological section, the soluble dietary fibers in the section dyed by HE can obviously reduce the size of thefat, and the fat lesion of the liver of the mouse is relieved. By detecting mRNA expression of related factors related to lipid metabolism in fat and liver and mRNA expression of common inflammatoryfactors in obesity, the soluble dietary fibers can down-regulate expression of lipid synthesis genes and pro-inflammatory factors and up-regulate expression of lipid metabolism genes. The soluble dietary fiber disclosed by the invention is high in safety and low in price, and has a remarkable effect in the aspects of reducing fat and losing weight of OB obese mice.
Owner:THE FIRST INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY SOA
Heterocyclic modulators of lipid synthesis for use against cancer and viral infections
The invention discloses heterocyclic modulators of lipid synthesis for use against cancer and viral infections. According to the invention, also provided are heterocyclic modulators of lipid synthesis are provided as well as pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, pharmaceutical compositions comprising such compounds, and methods of treating conditions characterized by disregulation of a fatly acid synthase pathway by the administration of such compounds.
Owner:GANNEX PHARM CO LTD
Heterocyclic modulators of lipid synthesis
Compounds that are fatty acid synthesis modulators are provided. The compounds may be used to treat disorders characterized by disregulation of the fatty acid synthase function by modulating the function and / or the fatty acid synthase pathway. Methods are provided for treating such disorders including viral infections, such as hepatitis C infection, cancer and metabolic disorders, such as non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
Owner:3 V BIOSCI INC
Applications of 18beta-glycyrrhetinic acid in preparation drugs for diseases related to abnormal lipid metabolism
PendingCN110960535AReduce formationReduce secretionOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderVery low-density lipoproteinLiver functions
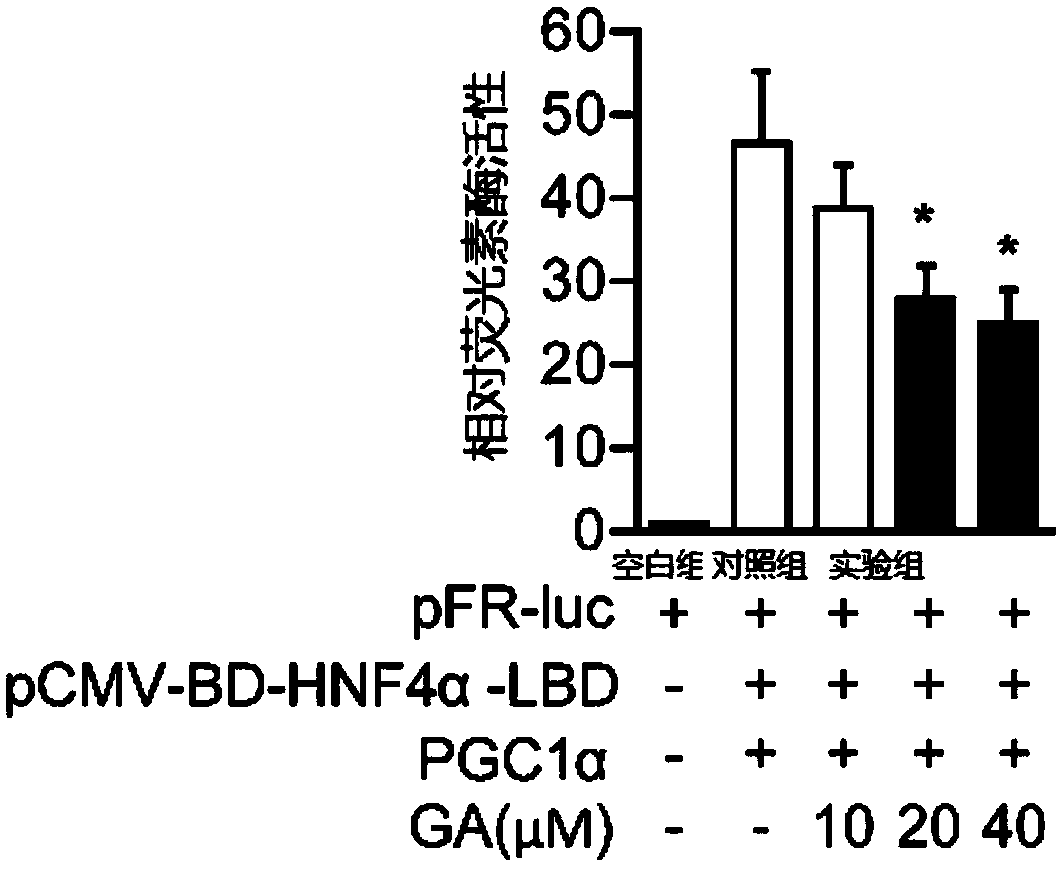
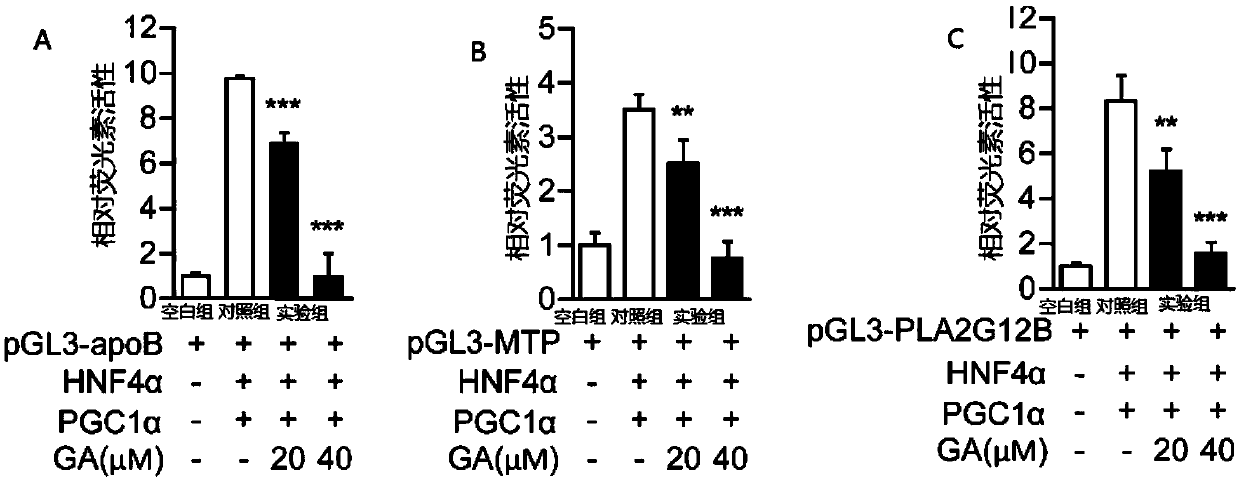
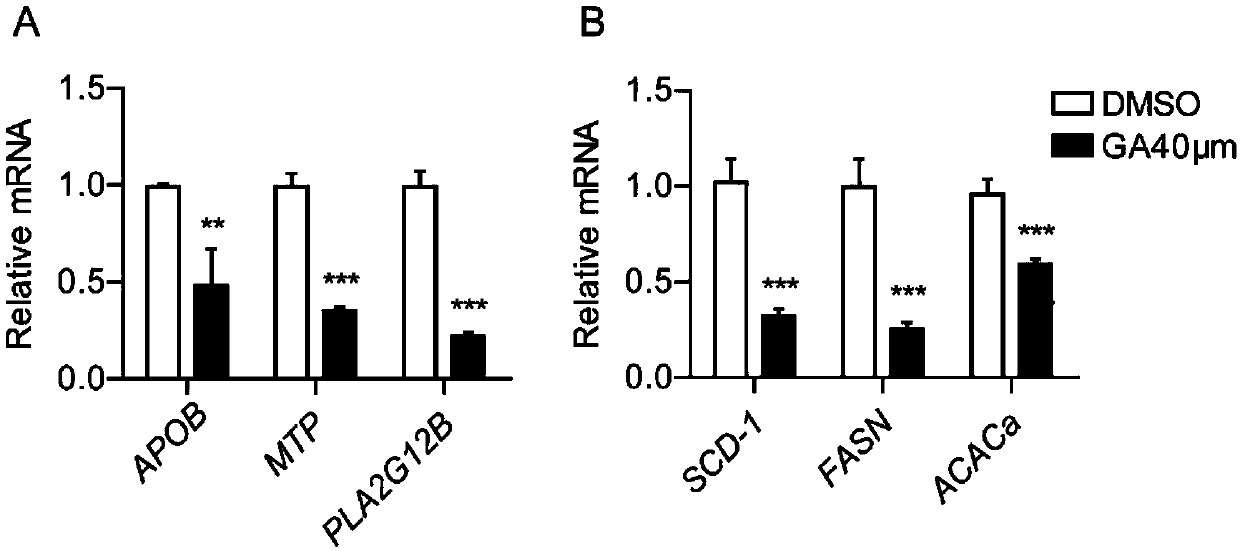
The invention discloses applications of 18beta-glycyrrhetinic acid taken as a conditioning agent for reduce lipid synthesis and / or the conditioning agent for reducing very low density lipoprotein formation and secretion in drugs. A drug containing the 18beta-glycyrrhetinic acid with effective doses is disclosed; the 18beta-glycyrrhetinic acid can be taken as a conditioning agent of HNF4alpha and can lower the expression of APOB, MTP and PLA2G12B; and a method for inhibiting the expression of FASN, SCD-1 and ACAC[alpha] is also disclosed. The 18beta-glycyrrhetinic acid can inhibit the expression of lipid metabolism related genes, so that lipid synthesis and the formation and secretion of very low density lipoprotein can be inhibited, lipid content in the liver can be lowered, the fatty degree of the liver can be reduced, liver functions can be obviously improved, blood fat can be reduced, and the effects of preventing and / or treating diseases related to abnormal lipid metabolism can befinally achieved. In addition, as the 18beta-glycyrrhetinic acid is a natural substance, the 18beta-glycyrrhetinic acid is good in curative effect and small in toxic and side effect.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Application of rosustat in medicine for inhibiting acute alcoholic fatty liver
InactiveCN112274512AAvoid damageInhibit lipid accumulationOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemPharmaceutical drugMembrane lipid metabolism
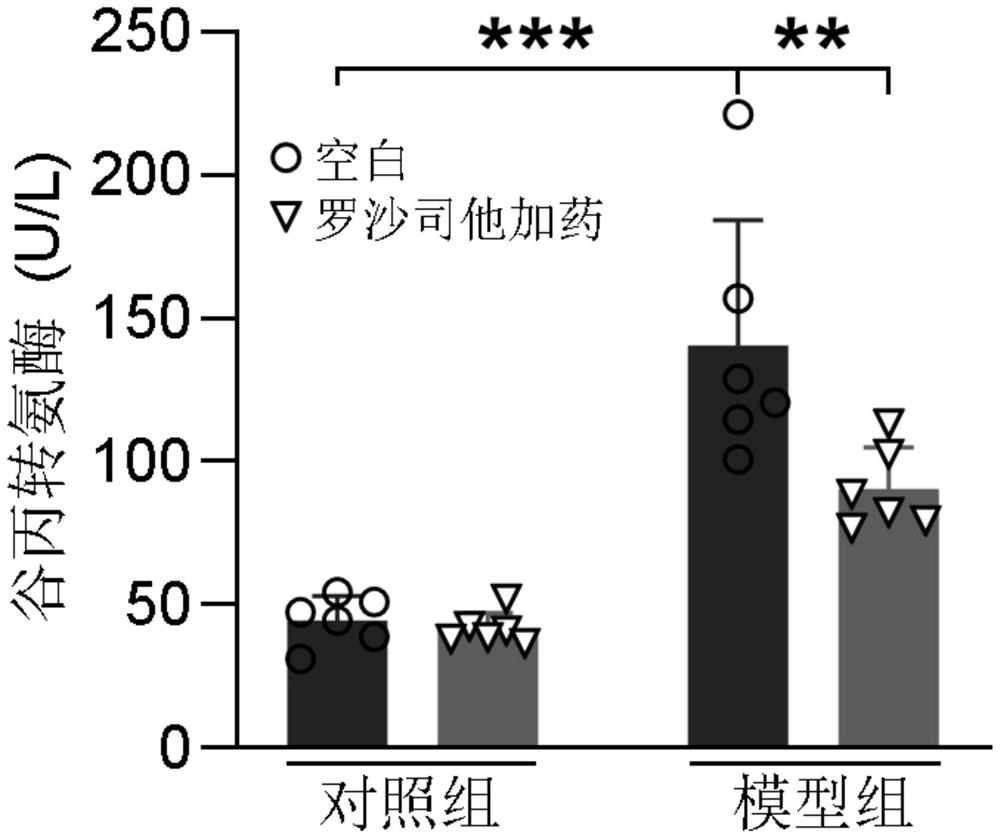
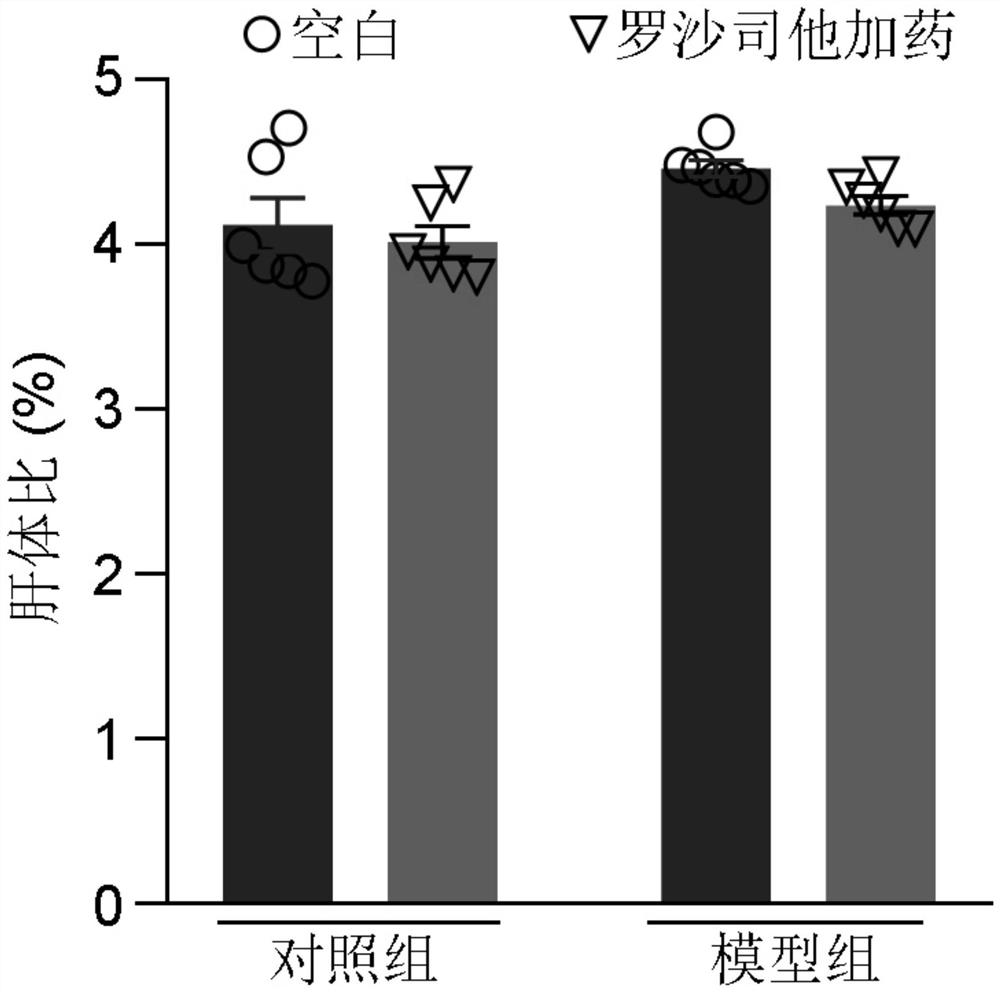
The invention provides an application of rosustat in a medicine for inhibiting acute alcoholic fatty liver. Roxasstat can significantly inhibit liver injury and lipid accumulation caused by acute alcohol. According to the mechanism, rosustat plays a role in inhibiting mouse liver lipid accumulation mainly by regulating and controlling the expression of lipid synthesis key genes. The medicine is expected to become an effective medicine for clinically treating the alcoholic fatty liver.
Owner:ZHEJIANG JIANFENG PHARM CO LTD
Heterocyclic modulators of lipid synthesis
PendingCN107428728AImproves antiviral activityHigh anticancer activityOrganic chemistryDigestive systemFatty acid biosynthesisMembrane lipid metabolism
Compounds that are fatty acid synthesis modulators are provided. The compounds may be used to treat disorders characterized by disregulation of the fatty acid synthase function by modulating the function and / or the fatty acid synthase pathway. Methods are provided for treating such disorders including viral infections, such as hepatits C infection, cancer and metabolic disorders.
Owner:3 V BIOSCI INC
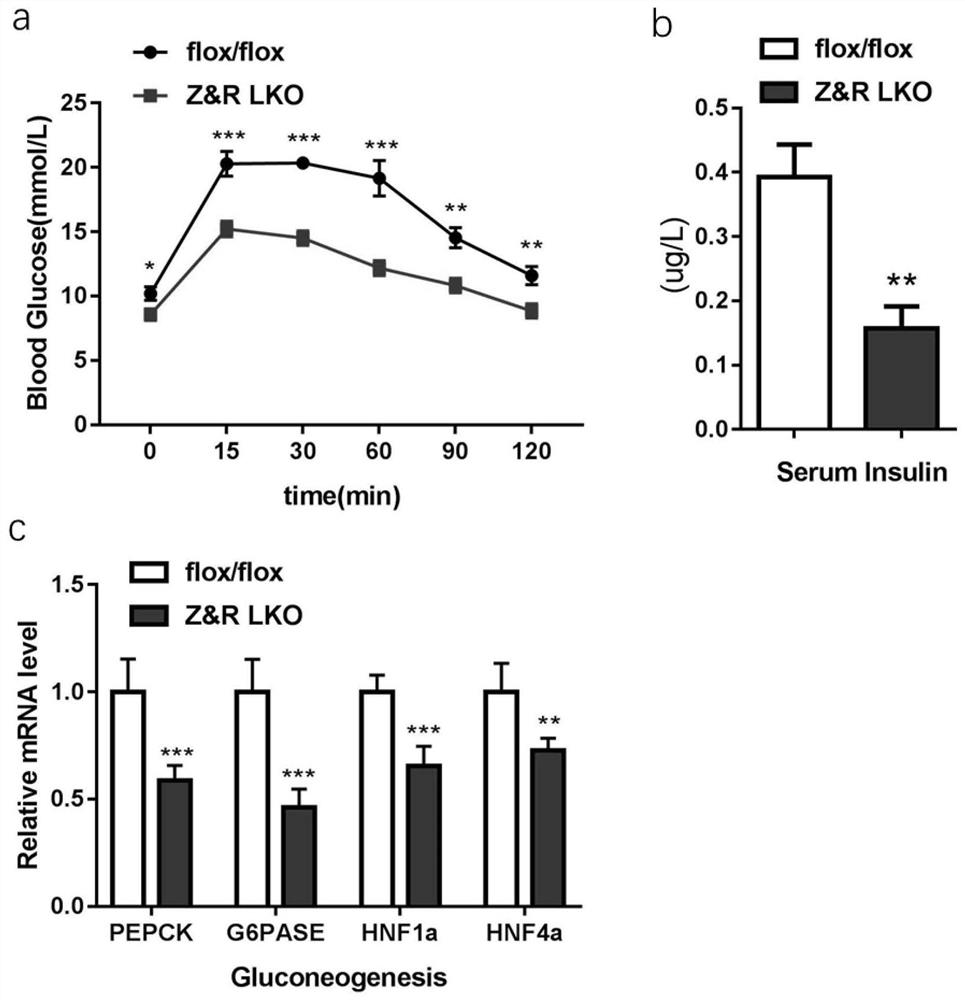
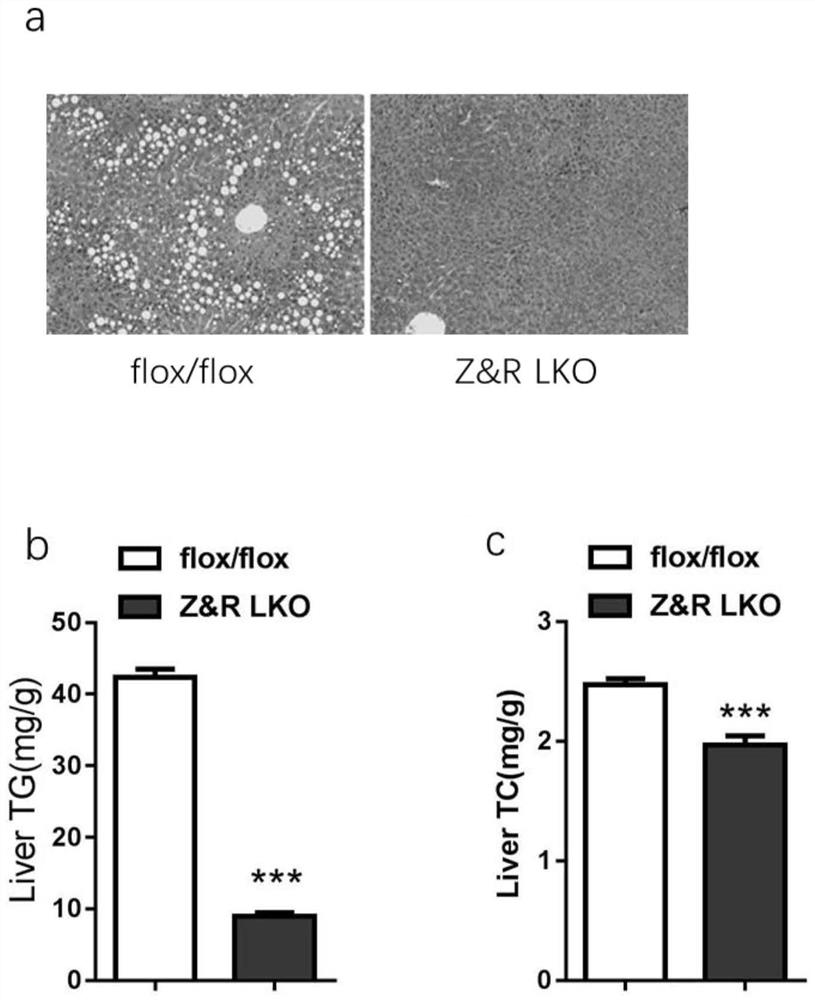
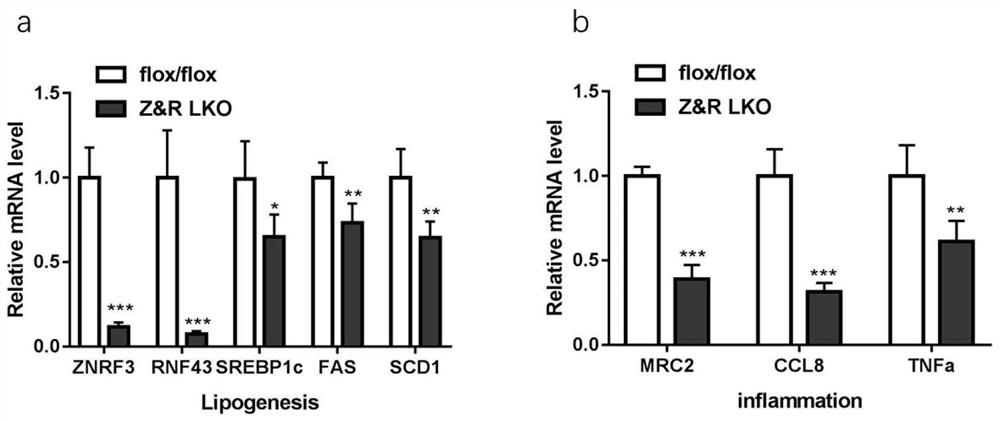
Application of ZNRF3/RNF43 in preparation of medicine for regulating energy metabolism
ActiveCN111920951AReduce depositionLower blood sugar levelsMetabolism disorderPharmaceutical active ingredientsGlucose sensitivityPancreatic hormone
The invention relates to application of ZNRF3 / RNF43 in preparation of a medicine for regulating energy metabolism. It proves that the ZNRF3 / RNF43 double knockout can reduce the blood sugar content andserum insulin level, increase the sensitivity of the body to glucose and down-regulate the expression of glucose allogeneic related genes; meanwhile, liver lipid deposition is reduced, lipid synthesis and expression of inflammation-related genes are reduced, it is shown that the ZNRF3 / RNF43 double knockout can improve liver insulin resistance possibly through the ways of influencing glycoxenesis,lipid synthesis and the like, and then a theoretical basis is provided for preparing energy metabolism regulating medicine.
Owner:RUIJIN HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
miRNA markers of lipid synthesis capacity under whole grain diet
ActiveCN112111578BHigh lipid synthesis capacityLow lipid synthesisMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologySequence analysis
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
A kind of β-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase and its application in lipid synthesis
ActiveCN110499300BImprove biosynthetic abilityOxidoreductasesFermentationIsopropylmalic acidMembrane lipid metabolism
The invention discloses beta-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase and application of the beta-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase in lipid synthesis, and belongs to the technical fields of gene engineering and microbial engineering. An amino acid sequence of the beta-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase is shown in SEQ ID No. 1, and the beta-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase has a function of promoting microorganism to produce fatty acids. Recombinant mortierella alpina containing the beta-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase is subjected to shake cultivation for 7 d, so that the fatty acid content in the mortierella alpinacontaining the beta-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase can reach 46.4% of dry cell weight, and is 20.2% higher than that of mortierella alpina without the beta-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase. According tothe beta-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase, through gene engineering, the fatty acid production ability of the mortierella alpine and other oil producing microorganisms is further improved, and solid theoretical support for improving the fatty acid biosynthesis ability is provided.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
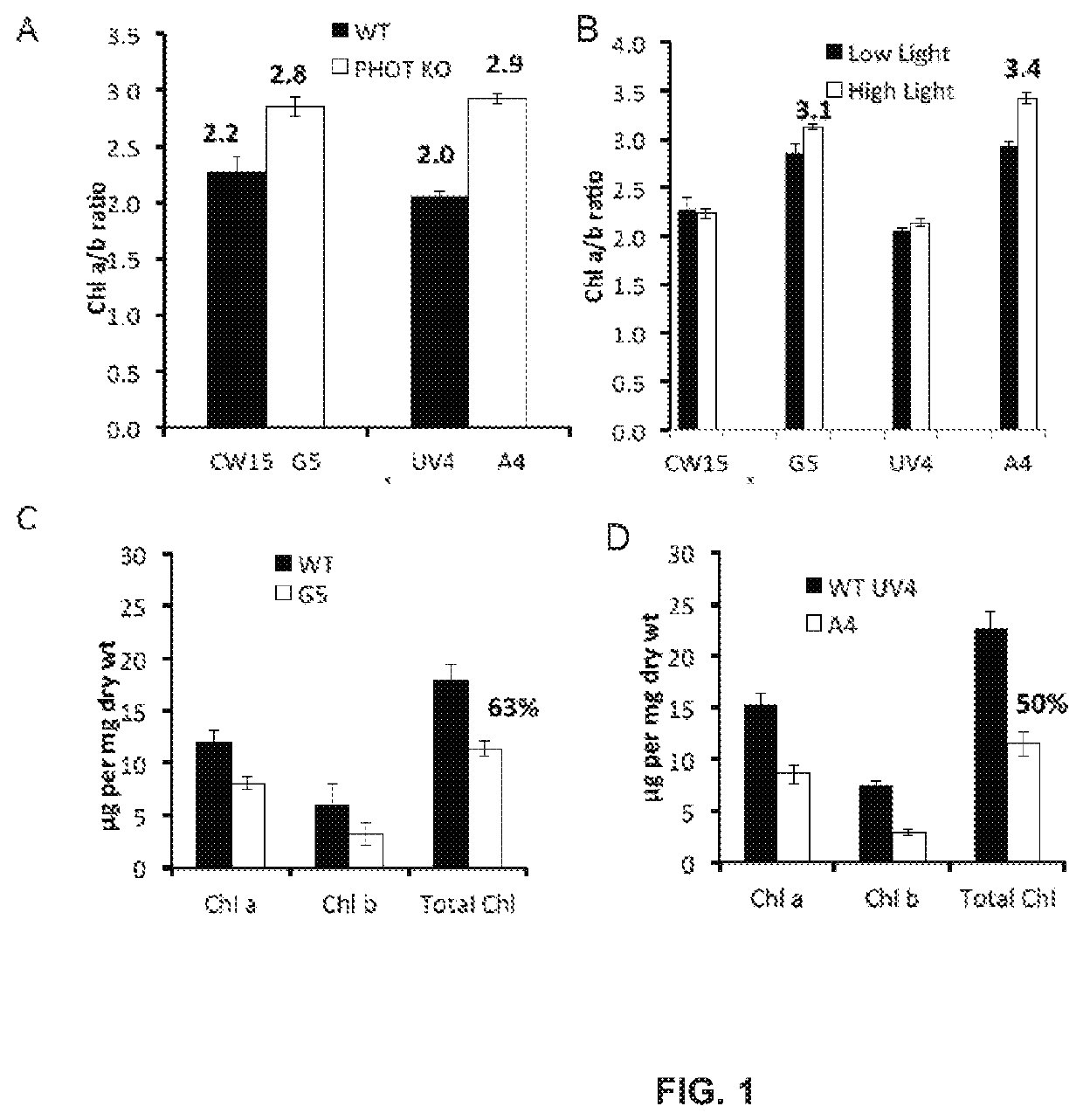
Productivity and Bioproduct Formation in Phototropin Knock/Out Mutants in Microalgae
InactiveUS20200208125A1Reduced PHOT expressionHigh genetic stabilityUnicellular algaeTransferasesElectron micrographsChlamydomonas reinhardtii
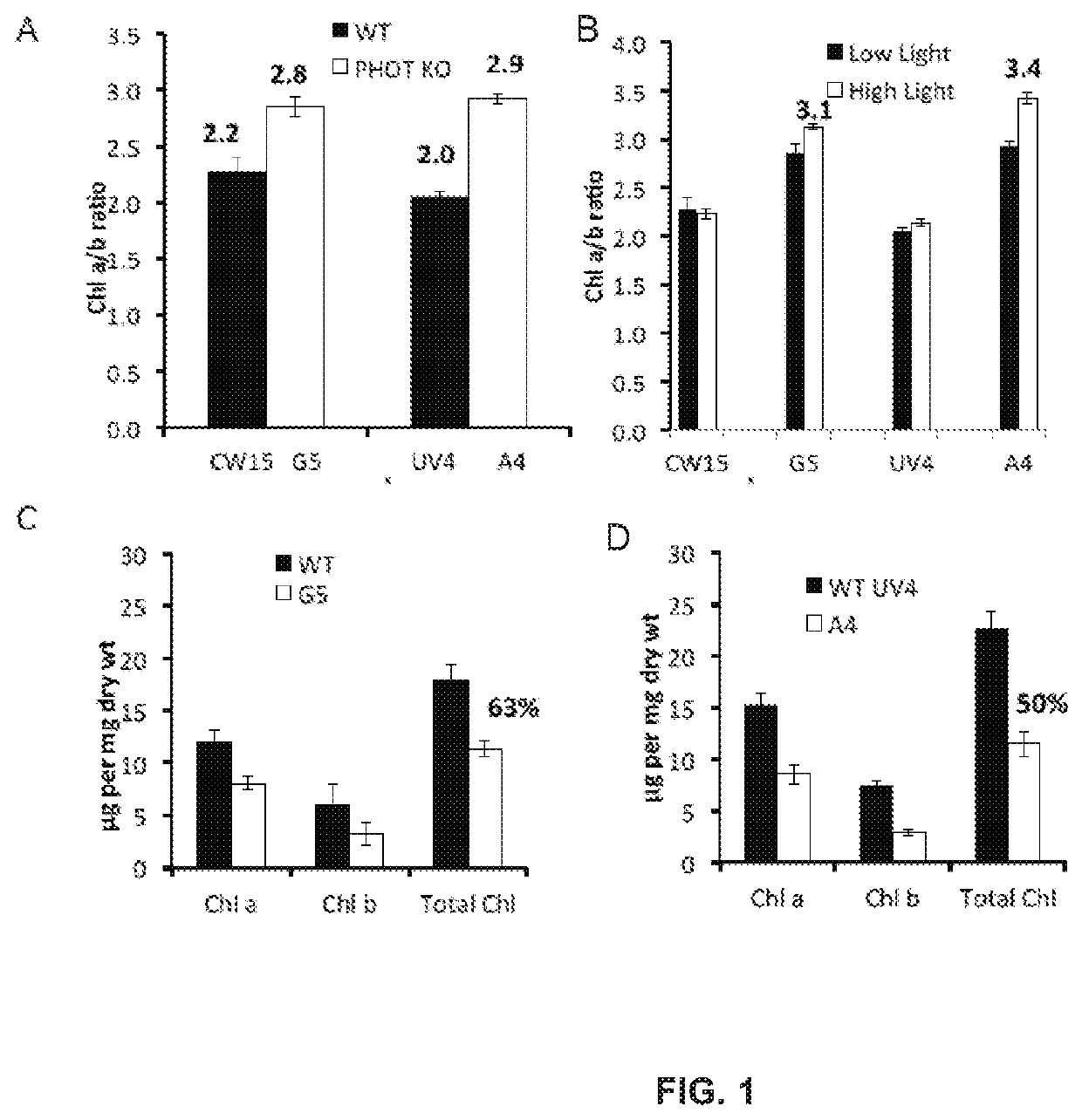
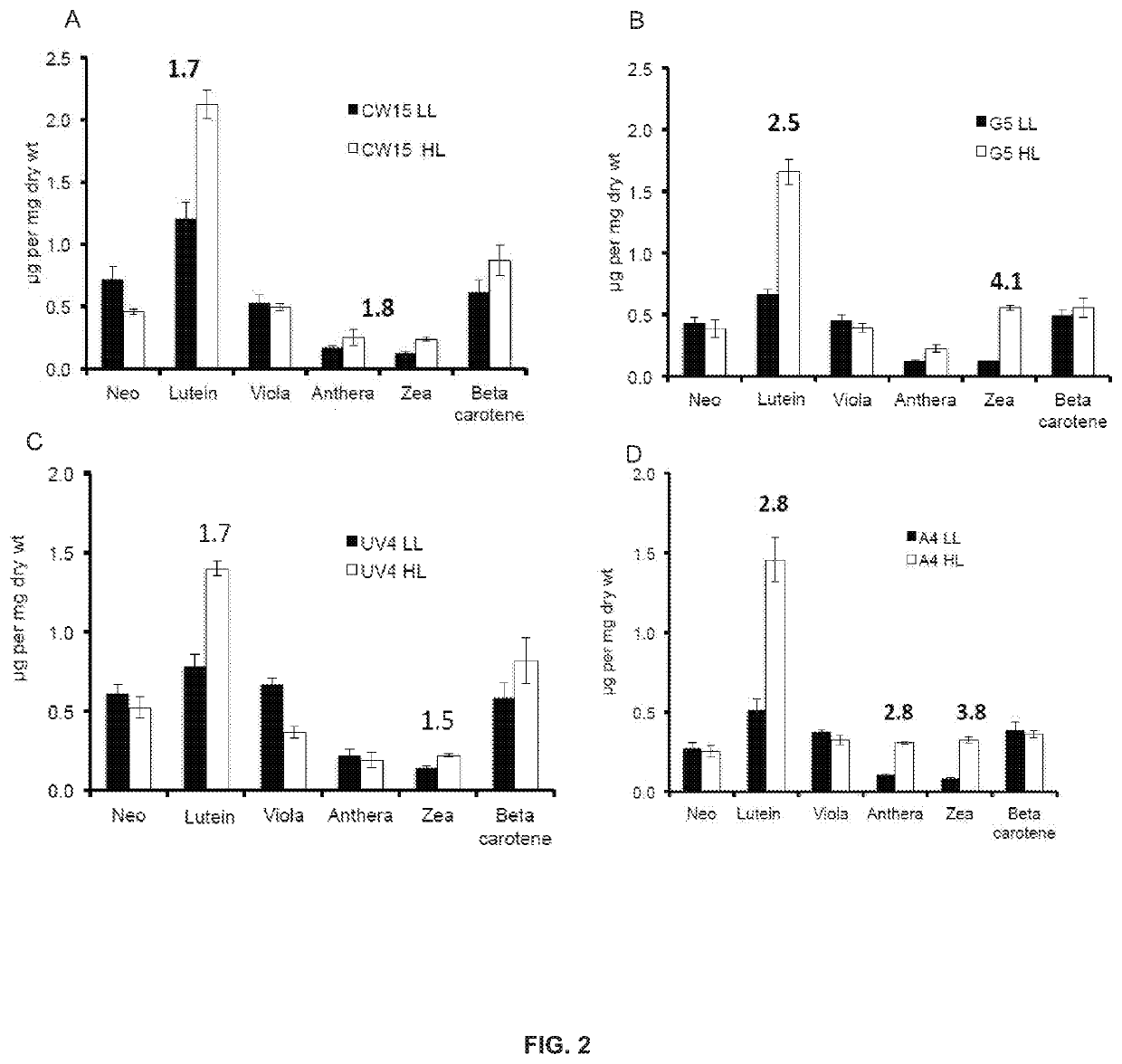
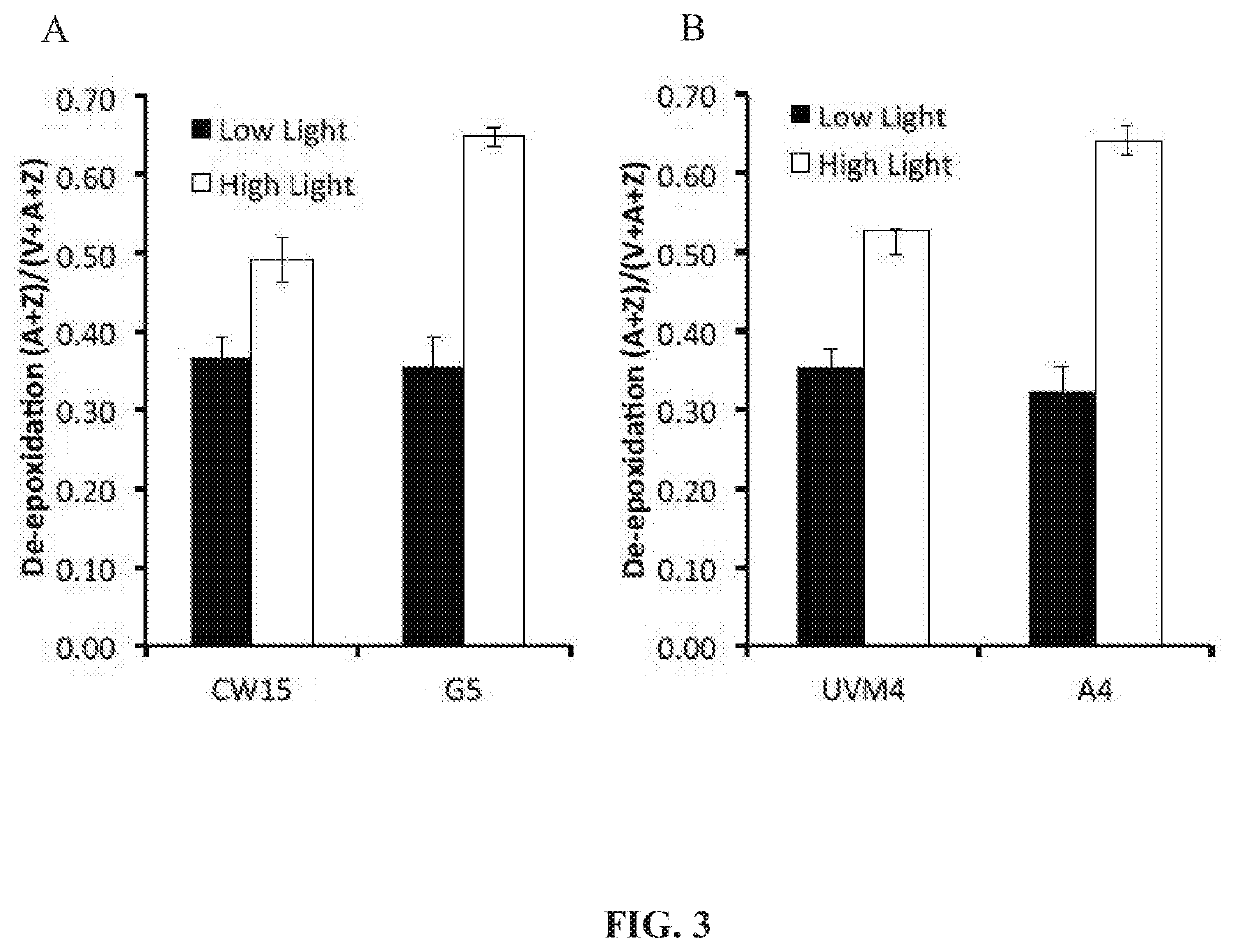
Phototropin is a blue light receptor, which mediates a variety of blue-light elicited physiological processes in plants and algae. In higher plants these processes include phototropism, chloroplast movement and stomatal opening. In the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, phototropin plays a vital role in progression of the sexual life cycle and in the control of the eye spot size and light sensitivity Phototropin is also involved in blue-light mediated changes in the synthesis of chlorophylls, carotenoids, chlorophyll binding proteins. We compared the transcriptome of phototropin knock out (PHOT KO) mutant and wild-type parent to analyze differences in gene expression in high light grown cultures (500 μmol photons m−2s−1). Our results indicate the up-regulation of genes involved in photosynthetic electron transport chain, carbon fixation pathway, starch, lipid, and cell cycle control genes. With respect to photosynthetic electron transport genes, genes encoding proteins of the cytochrome b6f and ATP synthase complex were up regulated potentially facilitating proton-coupled electron transfer. In addition genes involved in limiting steps in the Calvin cycle Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase / oxygenase (RuBisCO), Sidoheptulose 1,7 bisphosphatase (SBPase), Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (3PGDH) and that mediate cell-cycle control (CDK) were also up regulated along with starch synthase and fatty acid biosynthesis genes involved in starch and lipid synthesis. In addition, transmission electron micrographs show increased accumulation of starch granules in PHOT mutant compared to wild type, which is consistent with the higher expression of starch synthase genes. Collectively, the altered patterns of gene expression in the PHOT mutants were associated with a two-fold increase in growth and biomass accumulation compared to wild type when grown in environmental photobioreactors (Phenometrics) that simulate a pond environment. In conclusion, our studies suggest that phototropin may be a master gene regulator that suppresses rapid cell growth and promotes gametogenesis and sexual recombination in wild type strains.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC +1
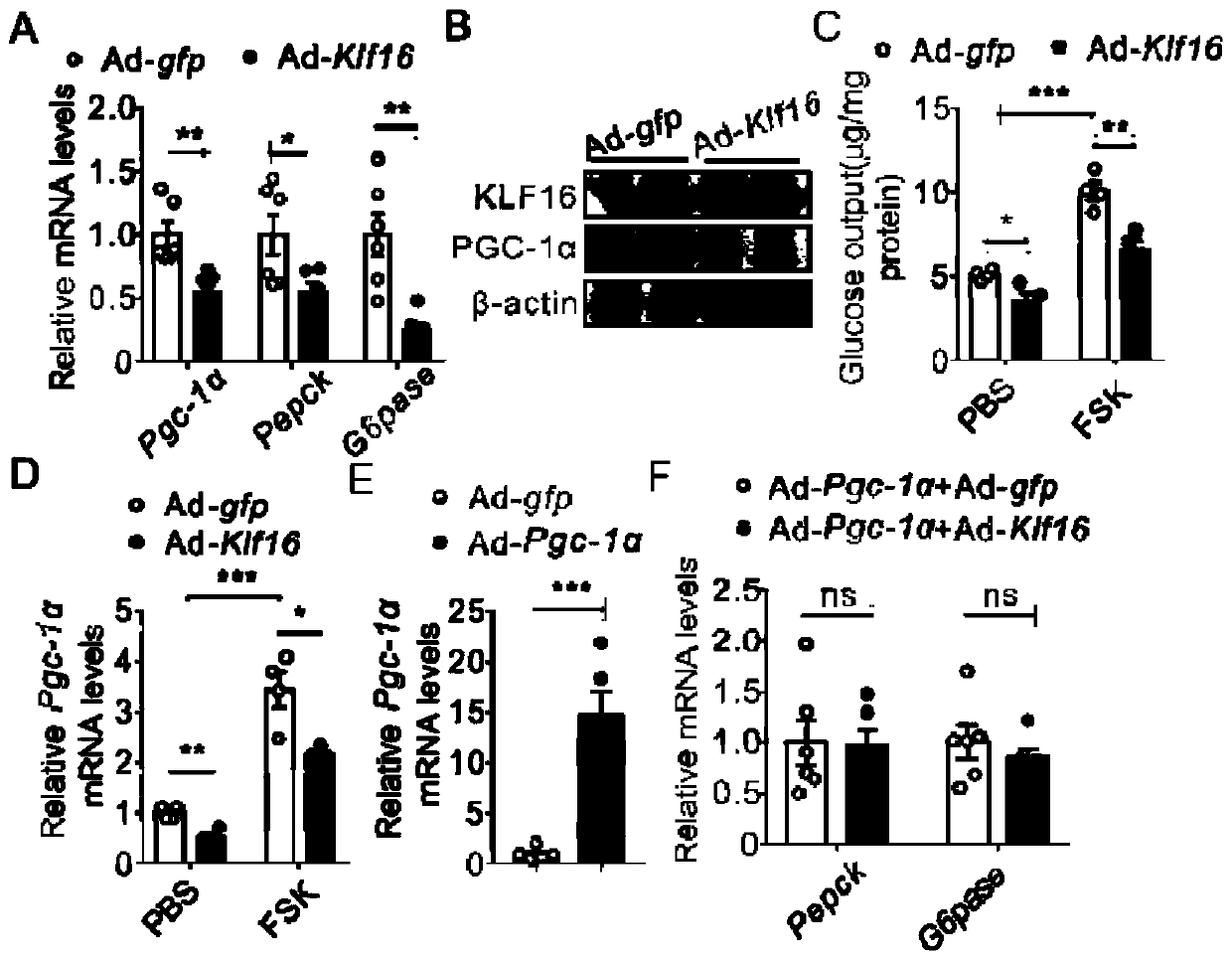
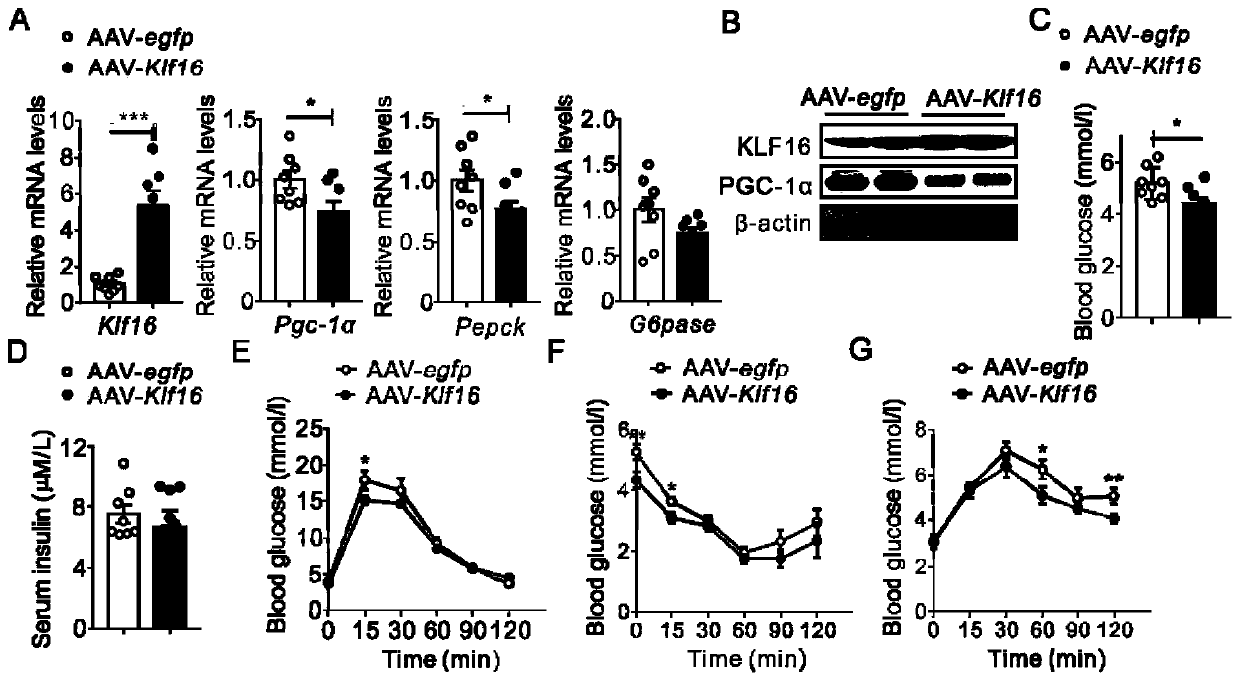
Application of transcription factor KLF16 protein in preparing drugs for preventing and treating diseases related to abnormal lipid and glucose metabolism
InactiveCN111529689ANo side effectsImprove securityPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderDiabetic complicationMembrane lipid metabolism
The invention provides an application of a transcription factor KLF16 protein in the preparation of drugs for preventing and treating diseases related to abnormal lipid and glucose metabolism. The transcription factor KLF16 protein provided by the invention significantly reduces the blood sugar and blood lipid level in disease model animals by mediating and regulating the expression of gluconeogenesis-related genes, and has effects of inhibiting gluconeogenesis and inhibiting lipid synthesis and deposition, and thereby inhibits the progress of hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia. Therefore, the transcription factor KLF16 protein has the potential of preventing and treating diseases caused by hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia such as diabetes, diabetic complications, obesity, hyperinsulinemia,hyperlipidemia, hypercholesterolemia, hypertriglyceridemia, and arteriosclerosis, and a new target for the prevention and treatment of the above-mentioned diseases, especially type II diabetes and obesity is provided. The KLF16 protein has no toxic side effects, has good safety, can adapt to the industrial application of new drugs, and has good clinical application prospect.
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF CHINESE MEDICINE
Compositions and methods for treating obesity and hyperphagia
ActiveUS10548951B2Peptide/protein ingredientsVertebrate antigen ingredientsDiseaseMembrane lipid metabolism
The present disclosure is directed to the treatment of diseases or conditions characterized by the buildup of fatty tissue, or hyperphagia, such as Prader-Willi syndrome, obesity, metabolic syndrome, type II diabetes, etc. A composition containing a monoclonal antibody directed against gastric inhibitory polypeptide is administered. This results in a reduced rate of weight gain, weight loss, and / or reduction in fatty tissue, and a marked decrease in lipid synthesis and accumulation.
Owner:MHS CARE INNOVATION LLC
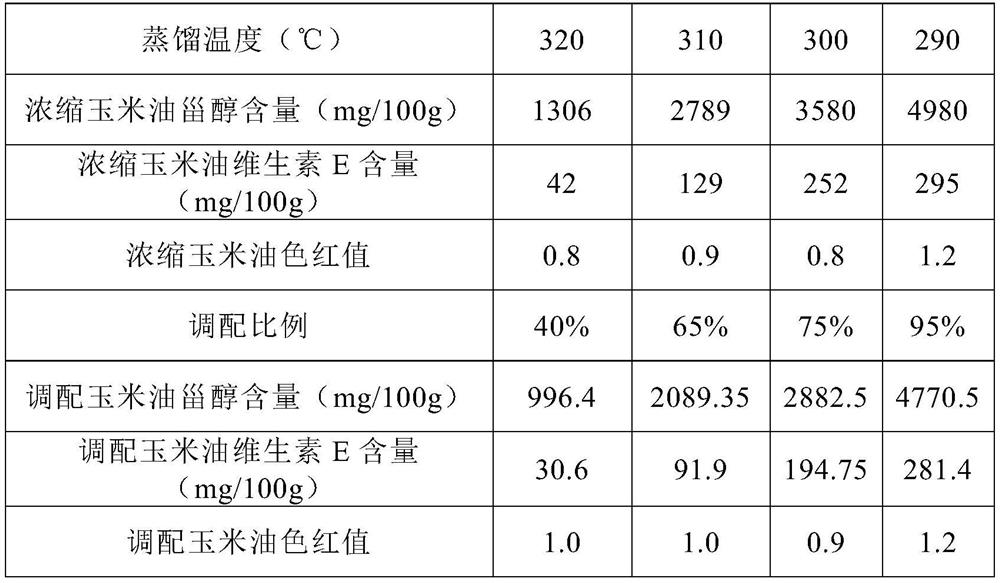
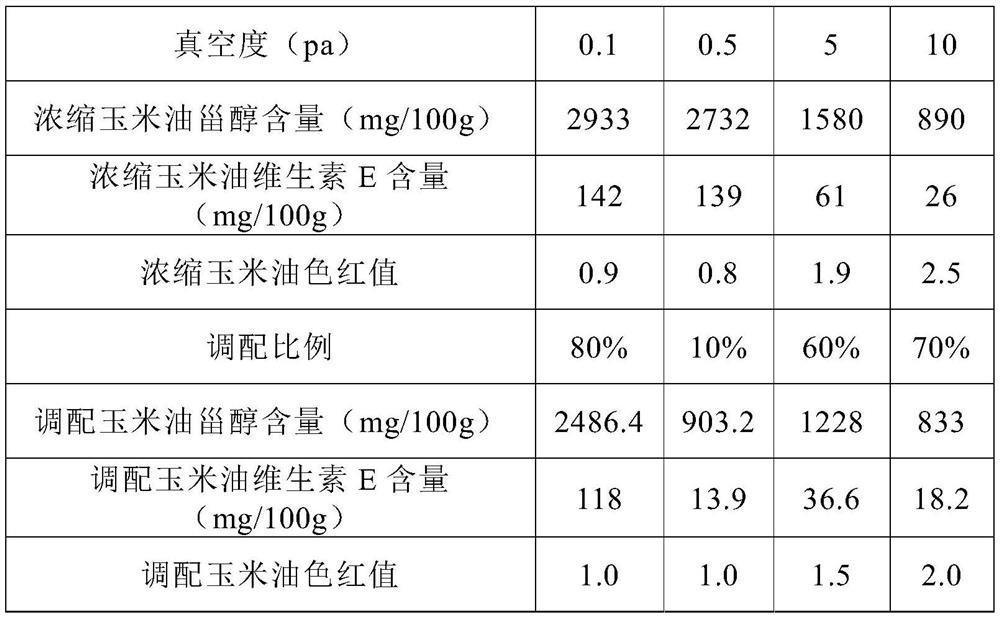
A kind of corn oil with the function of regulating lipid metabolism and its preparation method
ActiveCN111543497BEfficient SupplementIncreased sterol contentFatty-oils/fats refiningEdible oils/fatsSterolBlood triglycerides
Owner:COFCO NUTRITION & HEALTH RES INST +1
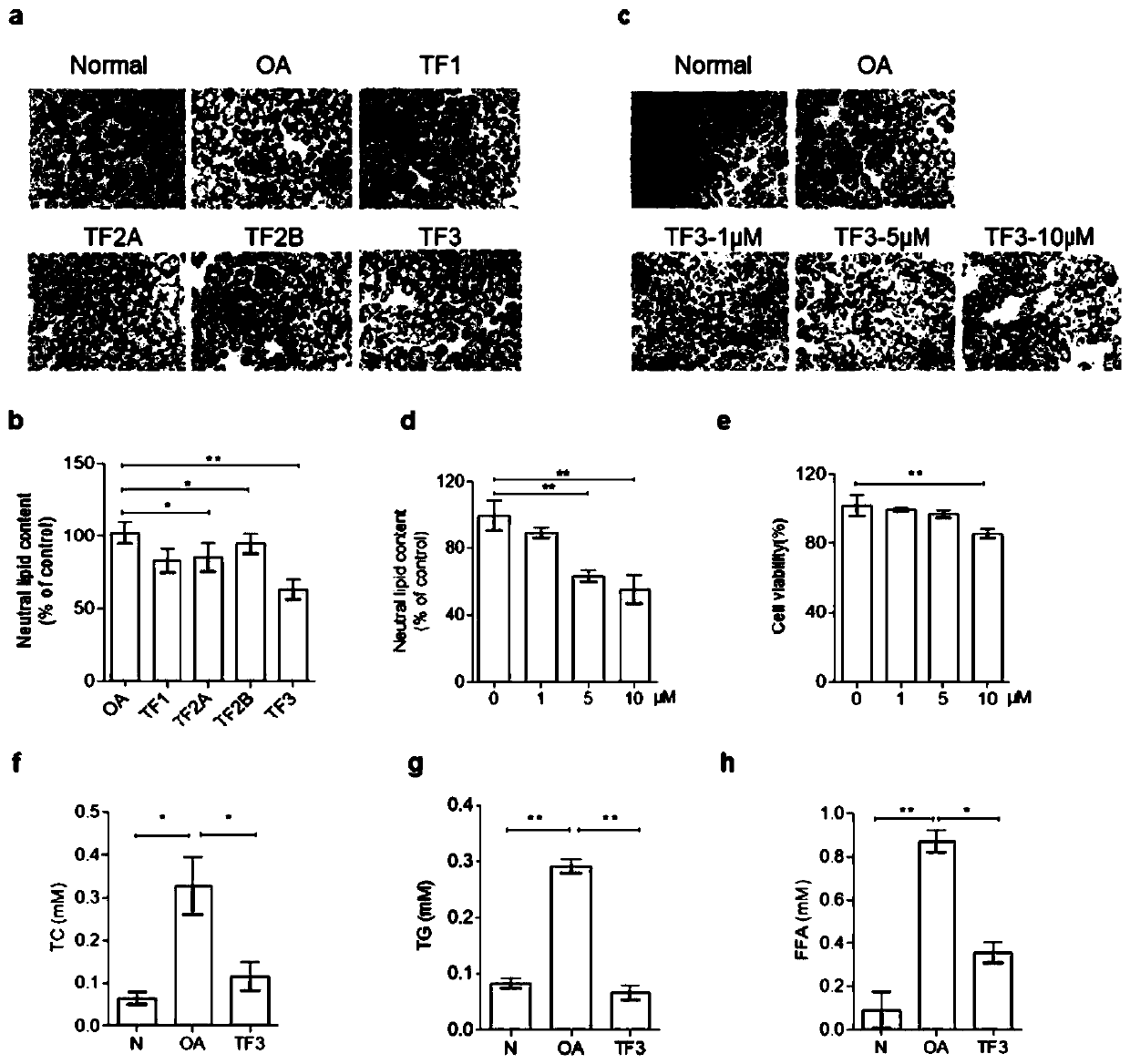
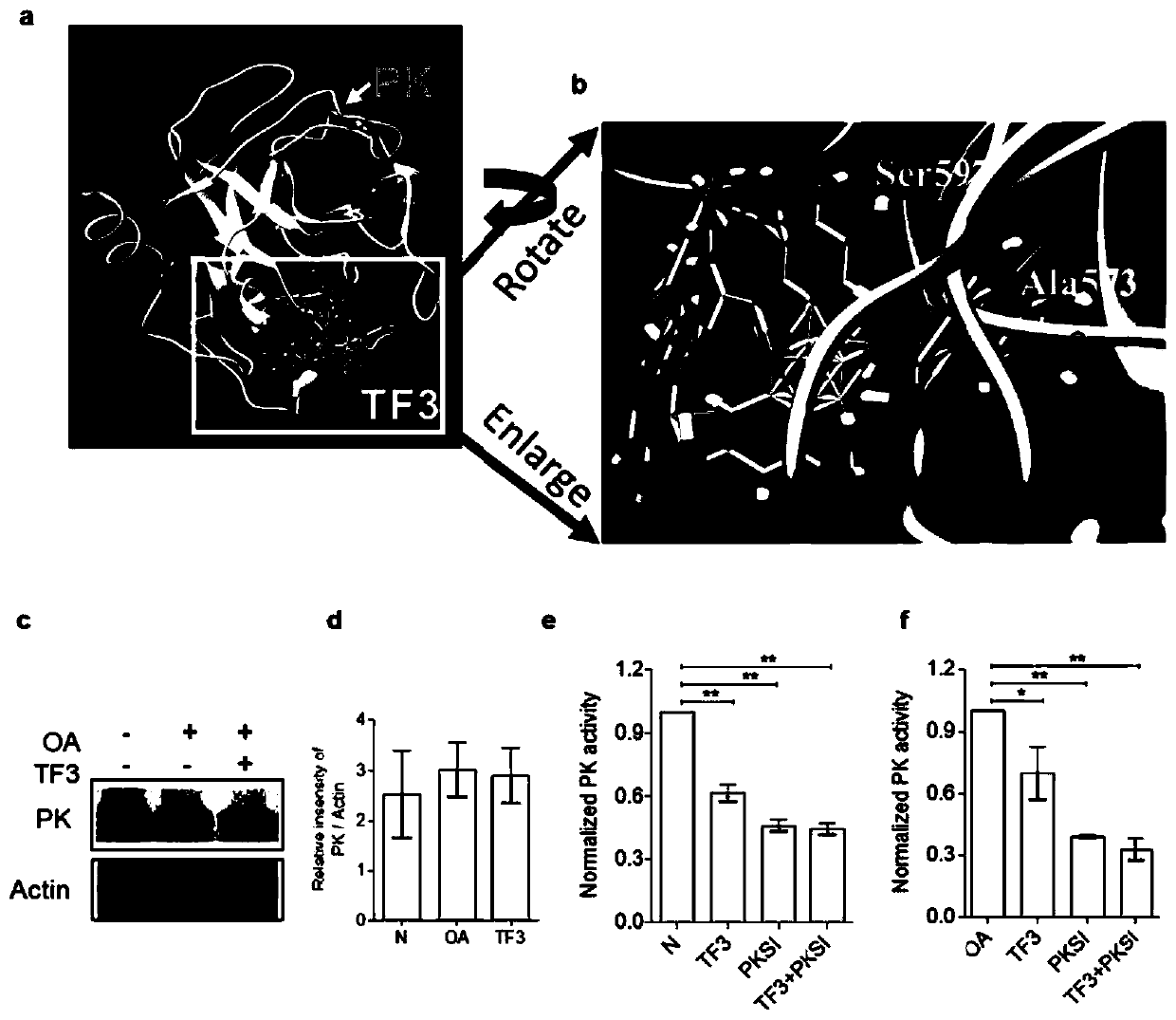
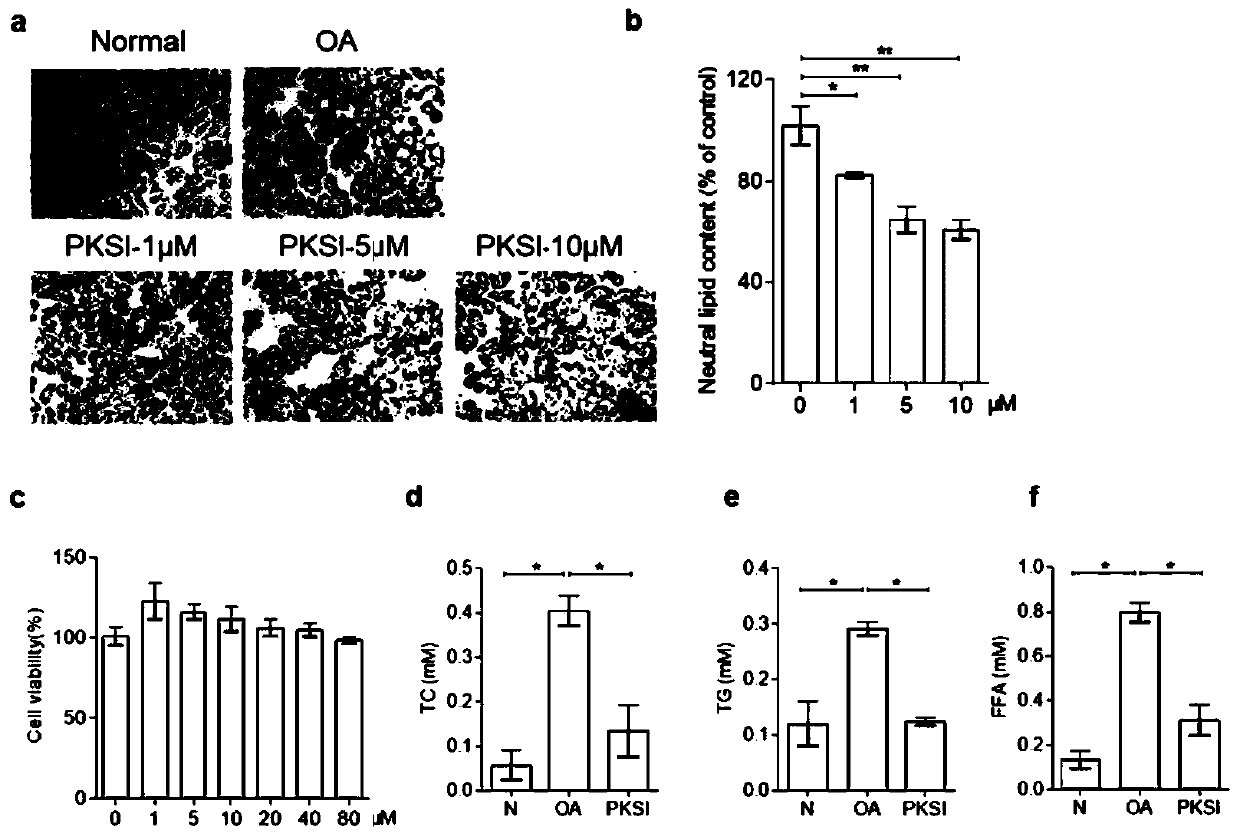
Application of theaflavin TF3 to preparation of PK (plasma kallikrein) inhibitor and medicines for NAFLD (non-alcoholic fatty liver disease) treatment
InactiveCN110840881ANo biological toxicityReduce accumulationOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemKininTheaflavine
The invention belongs to the technical field of pharmaceutical preparations and particularly relates to application of theaflavin TF3 to preparation of a PK (plasma kallikrein) inhibitor and medicinesfor NAFLD (non-alcoholic fatty liver disease) treatment. By a direct inhibition effect of tea monomer theaflavin TF3 (theaflavin-3, 3'-gallate) on PK targets in NAFLD liver cells, TF3 is capable of remarkably inhibiting PK enzymatic activity and further remarkably activating AMPK signal routing after PK inhibition to reduce lipid synthesis protein expression and activate or stimulate lipidolysisprotein expression and is also capable of reducing accumulation of intracellular lipids through PK activity inhibition. Therefore, the theaflavin TF3 can be used as a newly discovered PK inhibitor with a certain regulation function in fat metabolism pathway, plays a key role in NAFLD improvement, has an effect of NAFLD treatment or alleviation and can be applied to medicines for NAFLD prevention,treatment or alleviation.
Owner:TEA RES INST GUANGDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Application of Nomilin in Preparation of Drugs for Improving Liver Damage Caused by Cholestasis and Metabolic Diseases
The invention relates to the application of nomilin in the preparation of medicines for improving liver damage caused by cholestasis and metabolic diseases, and belongs to the technical field of medicine preparation. The present invention provides the application of nomilin in the preparation of medicines for improving liver damage caused by cholestasis and metabolic diseases. Nomilin can significantly improve liver damage by improving bile acid metabolism, anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidative stress, and reducing lipid synthesis.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV OF T C M
Compositions comprising pyridine carboxylate herbicides and fatty acid and lipid synthesis inhibitor herbicides
Disclosed herein are compositions comprising (a) a pyridine carboxylate herbicide or an agriculturally acceptable N-oxide, salt, or ester thereof and (b) a fatty acid and lipid synthesis inhibitor (FA / LSI) herbicide, an agriculturally acceptable salt or ester thereof, or mixtures thereof. Also disclosed herein are methods of controlling undesirable vegetation, comprising applying to vegetation or an area adjacent the vegetation or applying in soil or water to control the emergence or growth of vegetation (a) a pyridine carboxylate herbicide or an agriculturally acceptable N-oxide, salt, or ester thereof and (b) a fatty acid and lipid synthesis inhibitor (FA / LSI) herbicide, an agriculturally acceptable salt or ester thereof, or mixtures thereof.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Glycopeptides that increase lipid synthesis
Owner:TFCHEM
Citric acid transport protein and application thereof in lipid synthesis
ActiveCN112661821AImprove biosynthetic abilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicrobial oilMembrane lipid metabolism
The invention discloses a citric acid transport protein and application thereof in lipid synthesis, belonging to the technical field of genetic engineering and microbial engineering. The citric acid-ketoglutarate transport protein with an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID No. 1 has the function of promoting microorganisms to produce fatty acid; after recombinant mortierella alpine containing the citric acid-ketoglutarate transport protein is subjected to shaking culture for 7 days, the fatty acid content of mortierella alpine containing the citric acid-ketoglutarate transport protein can reach 36.1% of the dry weight of cells, and is increased by 30.4% compared with the fatty acid content of mortierella alpine not containing the citric acid-ketoglutarate transport protein. Through a genetic engineering means, the lipid synthesis accumulation capacity of oil-producing microorganisms such as mortierella alpine is improved on a gene level, and meanwhile, the normal growth of the oil-producing microorganisms can be ensured, so a technical support is provided for more efficient microbial oil industrial production.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Productivity and bioproduct formation in phototropin knock/out mutants in microalgae
ActiveUS10590398B2Increase productivityImprove productivityHydrolasesUnicellular algaeElectron micrographsChlamydomonas reinhardtii
Phototropin is a blue light receptor, which mediates a variety of blue-light elicited physiological processes in plants and algae. In higher plants these processes include phototropism, chloroplast movement and stomatal opening. In the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, phototropin plays a vital role in progression of the sexual life cycle and in the control of the eye spot size and light sensitivity Phototropin is also involved in blue-light mediated changes in the synthesis of chlorophylls, carotenoids, chlorophyll binding proteins. We compared the transcriptome of phototropin knock out (PHOT KO) mutant and wild-type parent to analyze differences in gene expression in high light grown cultures (500 μmol photons m−2 s−1). Our results indicate the up-regulation of genes involved in photosynthetic electron transport chain, carbon fixation pathway, starch, lipid, and cell cycle control genes. With respect to photosynthetic electron transport genes, genes encoding proteins of the cytochrome b6f and ATP synthase complex were up regulated potentially facilitating proton-coupled electron transfer. In addition genes involved in limiting steps in the Calvin cycle Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase / oxygenase (RuBisCO), Sidoheptulose 1,7 bisphosphatase (SBPase), Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (3PGDH) and that mediate cell-cycle control (CDK) were also up regulated along with starch synthase and fatty acid biosynthesis genes involved in starch and lipid synthesis. In addition, transmission electron micrographs show increased accumulation of starch granules in PHOT mutant compared to wild type, which is consistent with the higher expression of starch synthase genes. Collectively, the altered patterns of gene expression in the PHOT mutants were associated with a two-fold increase in growth and biomass accumulation compared to wild type when grown in environmental photobioreactors (Phenometrics) that simulate a pond environment. In conclusion, our studies suggest that phototropin may be a master gene regulator that suppresses rapid cell growth and promotes gametogenesis and sexual recombination in wild type strains.
Owner:NMC INC +1
Heterocyclic modulators of lipid synthesis
Owner:GANNEX PHARM CO LTD
Health products with hypolipemic function, preparation method and usage thereof
ActiveCN101524422BGood effect of lowering blood fatReduce synthesisOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderBiotechnologyGinkgo Biloba Leaf Extract
The invention relates to health products with hypolipemic function and also relates to a preparation method for the health products and the usage thereof. The health products comprise active constituents of hongqu powder, hawthorn extract, ginkgo biloba leaf extract, obtuseleaf senna seed extract and radix salviae miltiorrhizae extract. The active constituents have very obvious synergistic effect, thus playing a positive role in hypolipemic in many aspects such as reducing endogenous lipid synthesis, promoting the transfer and excretion of lipid, regulating lipid metabolism and the like, having obvious hypolipemic effect; safety toxicity test proves that the active constituents are safe, innoxious and harmless.
Owner:WUXI JIANTE PHARM CO LTD +1
Cell culture medium, cell culture kit and cell culture method
ActiveCN111088217AHigh purityEasy to prepareEpidermal cells/skin cellsCulture processDiseaseEndocrine functions
The invention relates to a cell culture medium. The cell culture medium contains a basal culture medium, a serum substitute, linoleic acid, testosterone, vitamin A, L-ascorbic acid, polylysine, putrescine, and 2-mercaptoethanol. The cell culture medium of the invention can efficiently culture sebaceous gland cells in vitro, so that a cell proliferation rate, a survival rate after resuscitation, and an expression amount of lipid synthesis related proteins of different generations of the sebaceous gland cells are significantly increased, and thereby the assistance for extensively researching sebaceous gland physiological and endocrine functions, exploring pathogenesis of sebaceous gland related diseases, and developing drugs is provided.
Owner:GUANGDONG BOXI BIO TECH CO LTD
Method and preparation for regulating lipid secretion of retinal pigment epithelial cells and application thereof
PendingCN113559265AInhibition of activationReduce synthesisOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderMembrane lipid metabolismRetinal pigment epithelial cell
The invention provides a method and a preparation for regulating lipid secretion of retinal pigment epithelial cells, and application thereof, and the method is characterized in that activation of an SREBP-1 site is inhibited by inhibiting a PDGF-D signal channel, so that the lipid secretion amount of the retinal pigment epithelial cells is reduced. The PDGF-D has an adjusting effect on an SREBP-1 signal channel, and activation of SREBP1 can be inhibited by inhibiting expression of the PDGF-D, so that expression of a lipid synthase gene is reduced, lipid synthesis in RPE is reduced, and formation of lipid deposition under the retina is reduced.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN OPHTHALMIC CENT SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Culture method for promoting microalgae fucoxanthin accumulation and lipid synthesis
PendingCN114561295AImprove antioxidant capacityEasy to operateUnicellular algaeBiofuelsBiotechnologyFucoxanthin
The invention discloses a culture method for promoting accumulation of microalgae fucoxanthin and lipid synthesis, which comprises the following steps: inoculating microalgae into a culture medium for culture, and adding 150-350mg / L of L-ascorbic acid into the culture medium. According to the culture method disclosed by the invention, the fucoxanthin content of the phaeodactylum tricornutum can be increased, and meanwhile, the lipid content of the phaeodactylum tricornutum, especially the content of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), is increased.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
A citrate transporter and its application in lipid synthesis
ActiveCN112661821BImprove biosynthetic abilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicrobial oilMembrane lipid metabolism
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
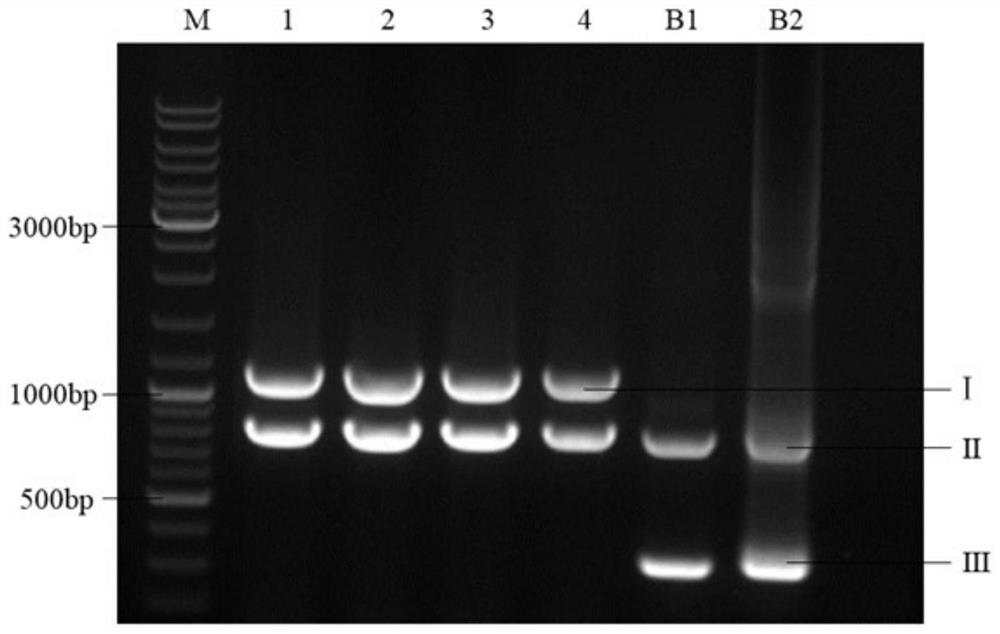
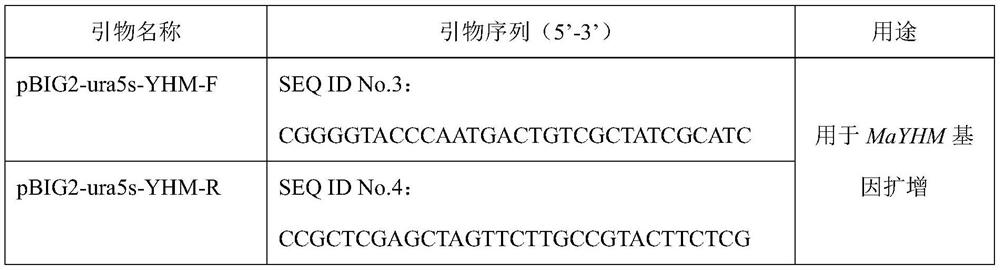
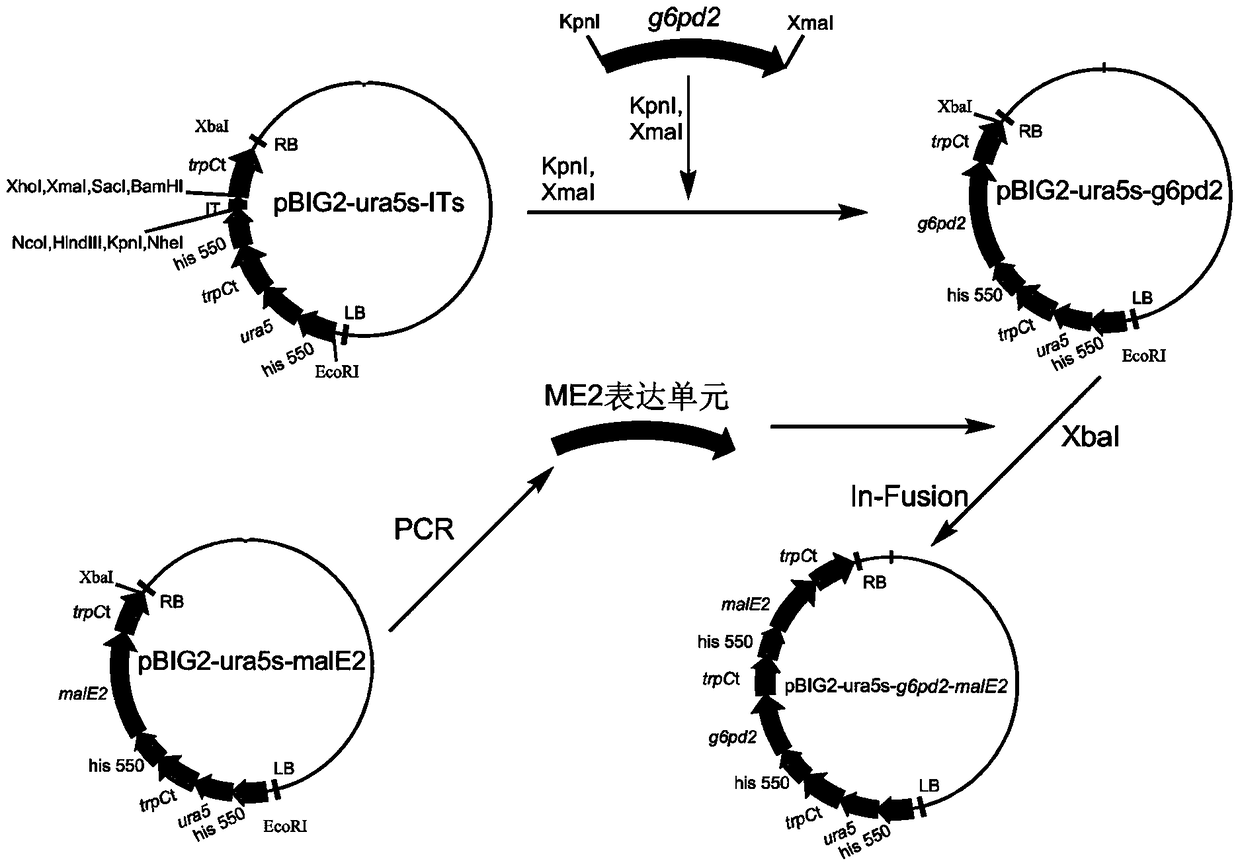
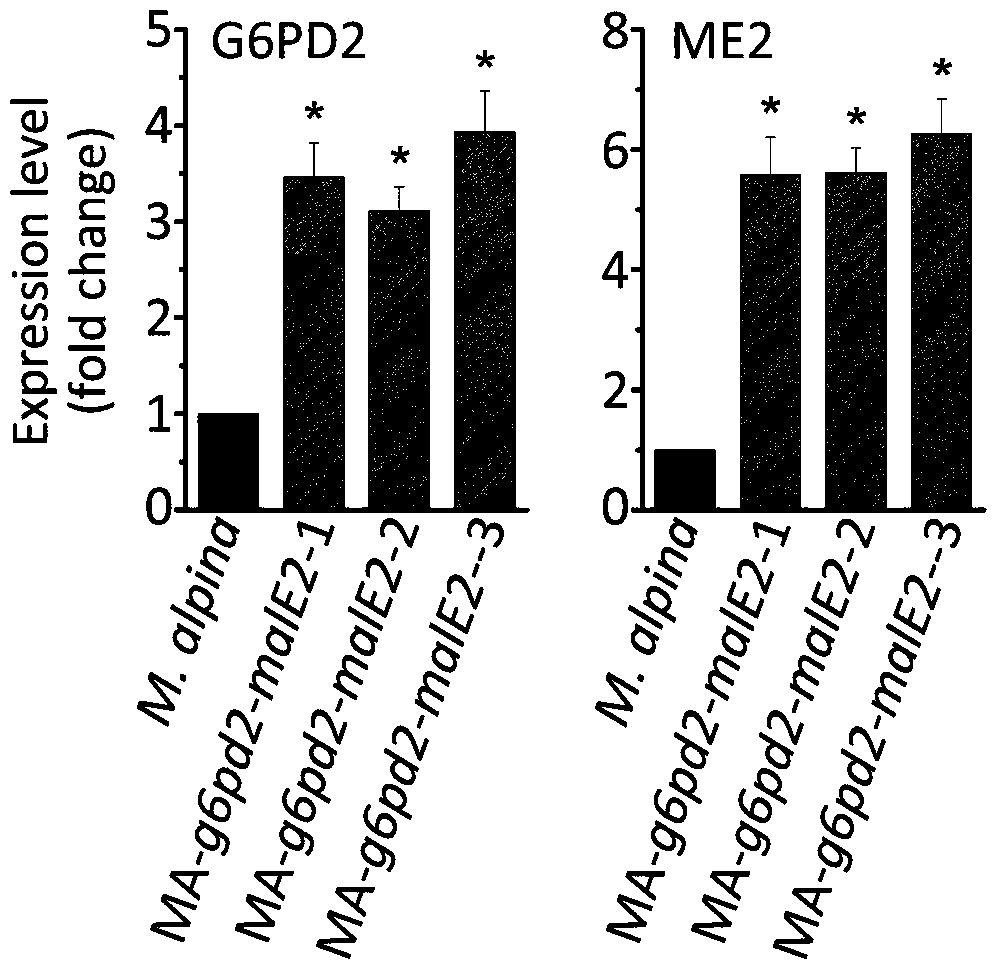
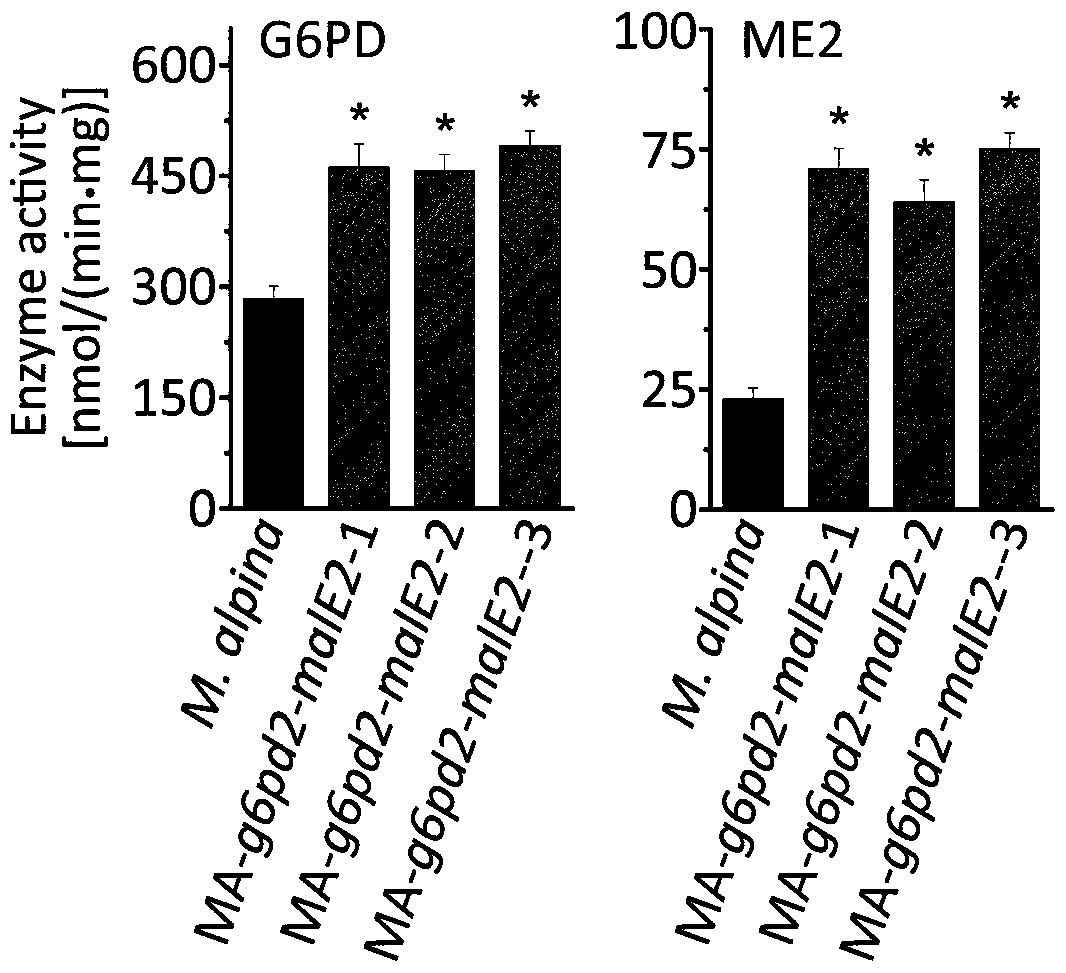
A recombinant Mortierella alpina strain co-expressing glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and malic enzyme and its construction method and application
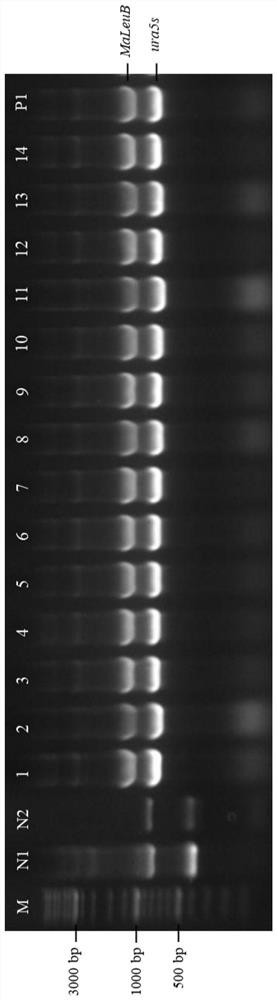
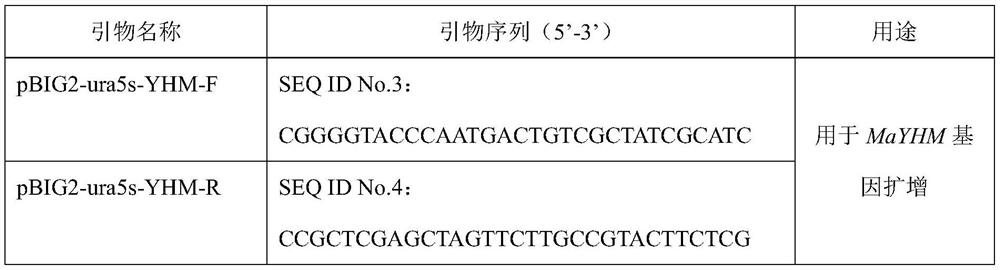
The invention relates to a recombinant bacterium for coordinately expressing glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD)2 and malic enzyme (ME)2 in mortierella alpine, and further relates to a constructing method of the strain and an application of the strain. According to the recombinant bacterium, the constructing method and the application, the high-arachidonic-acid-yield mortierella alpine gene recombinant strain is constructed with mortierella alpine uracil auxotroph as a material; the important effects of the G6PD2 and the ME2 in the fatty acid synthesis process and the fatty acid desaturation process are verified; due to coordinate and ectopic expression of the two genes, the effects of increasing the yield and the desaturation degree of fatty acid are effectively achieved at the same time, the proportion of ARA in the total fatty acid is remarkably increased, fermentation time is effectively shortened, and the recombinant bacterium is of great significance in lipid synthesis basic principle researching and product development of the oil-producing fungus in mortierella alpine ATCC 32222.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com