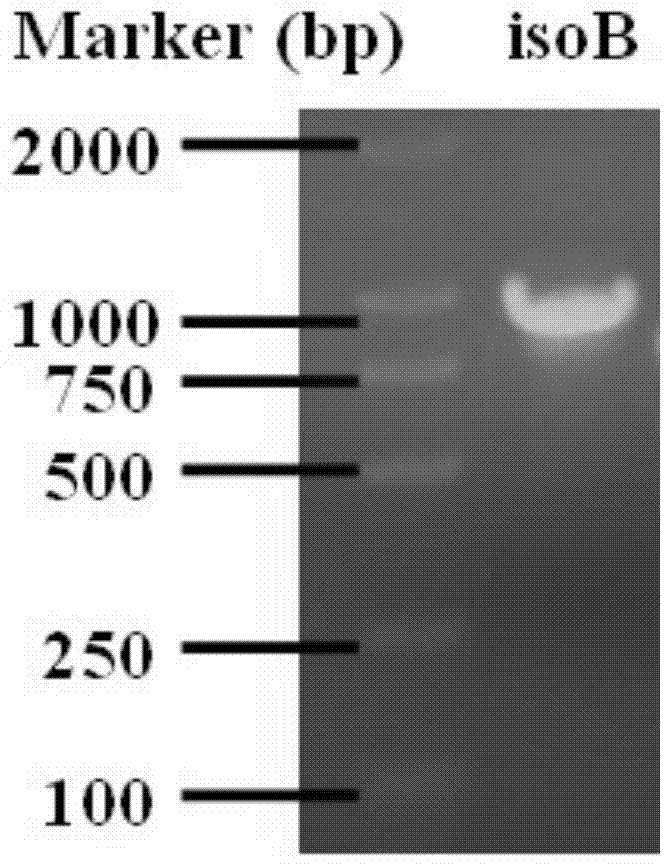
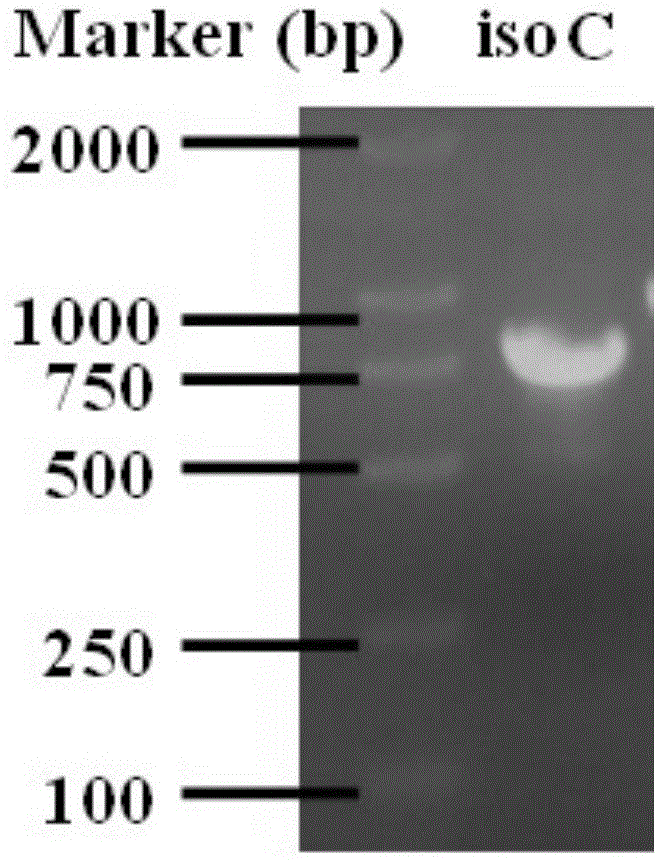
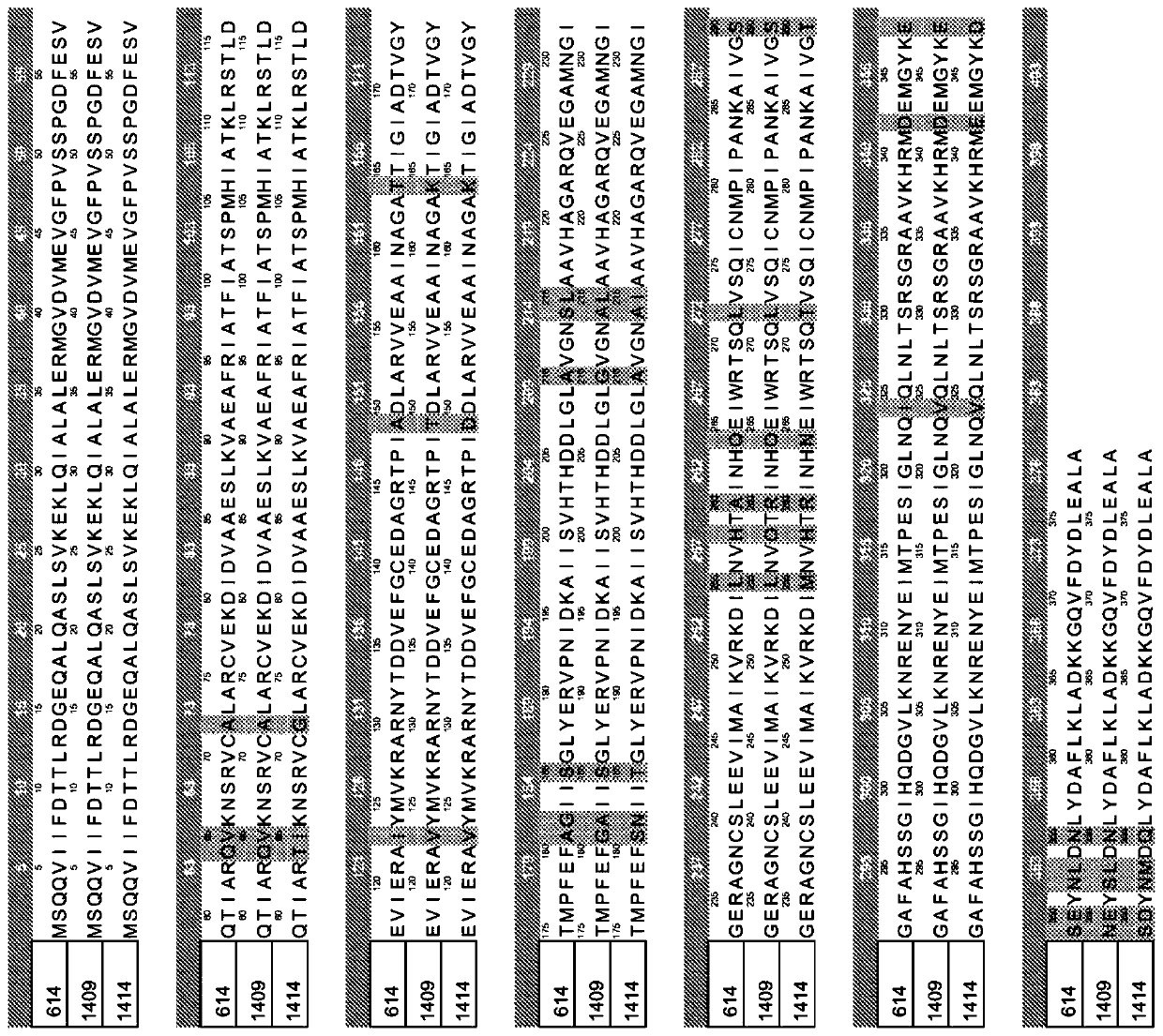
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30 results about "Isopropylmalic acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
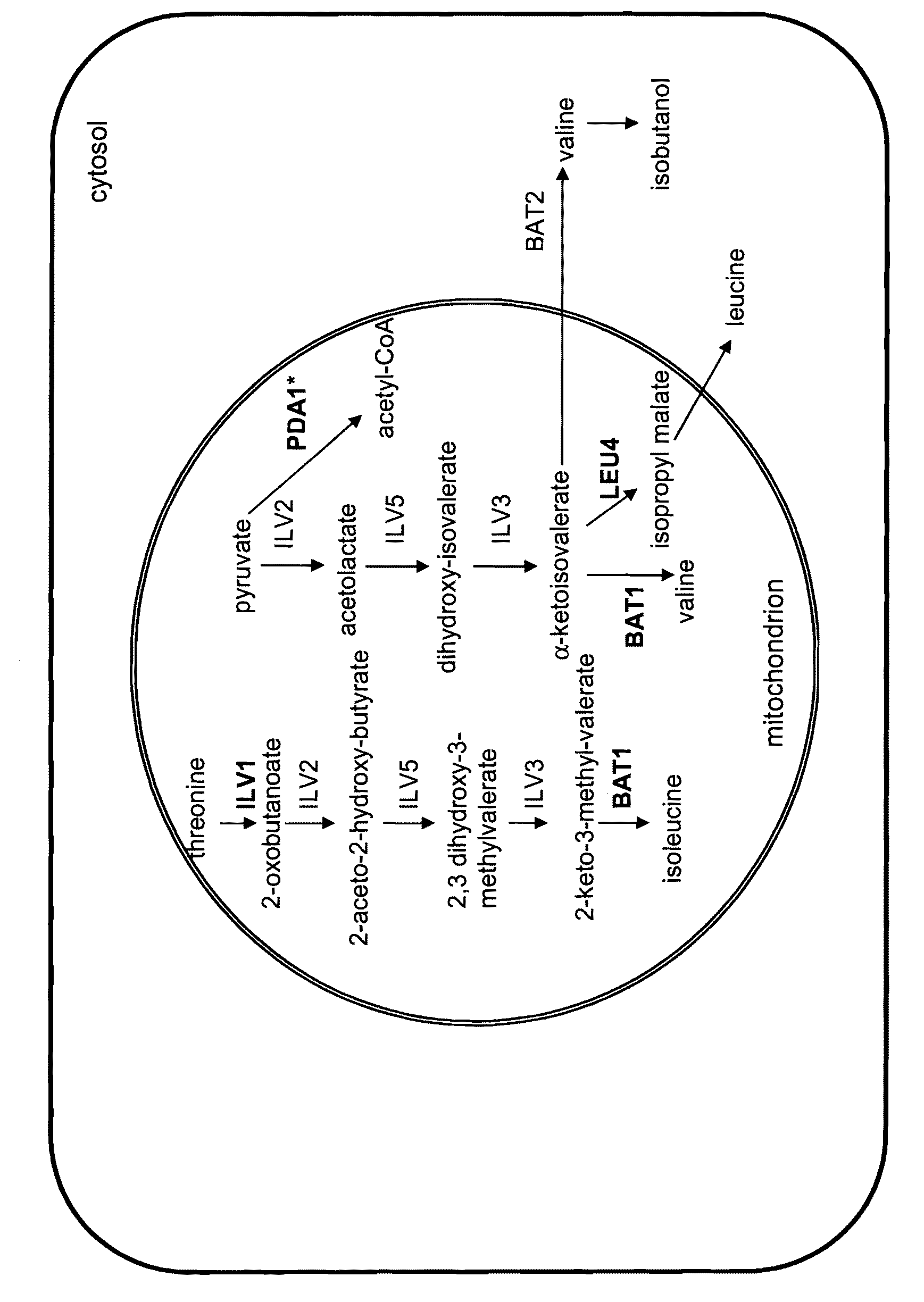
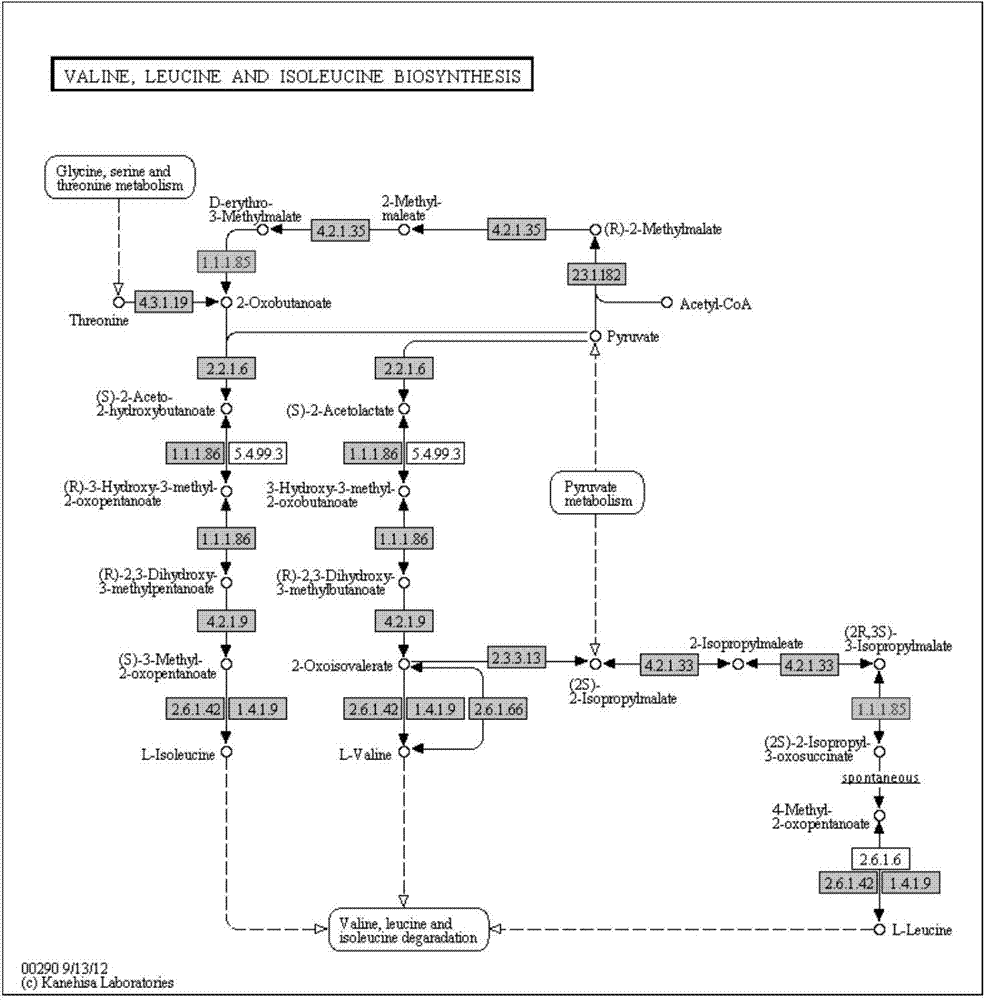
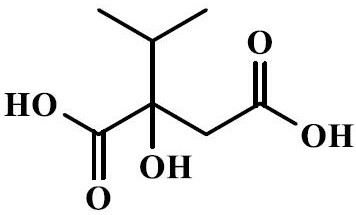
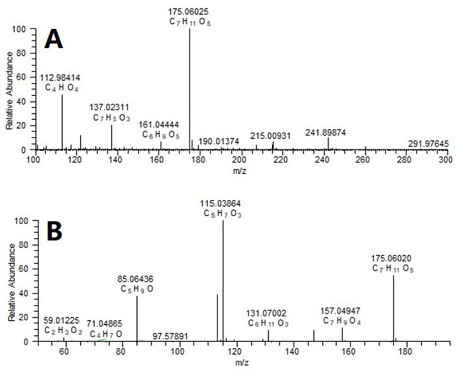
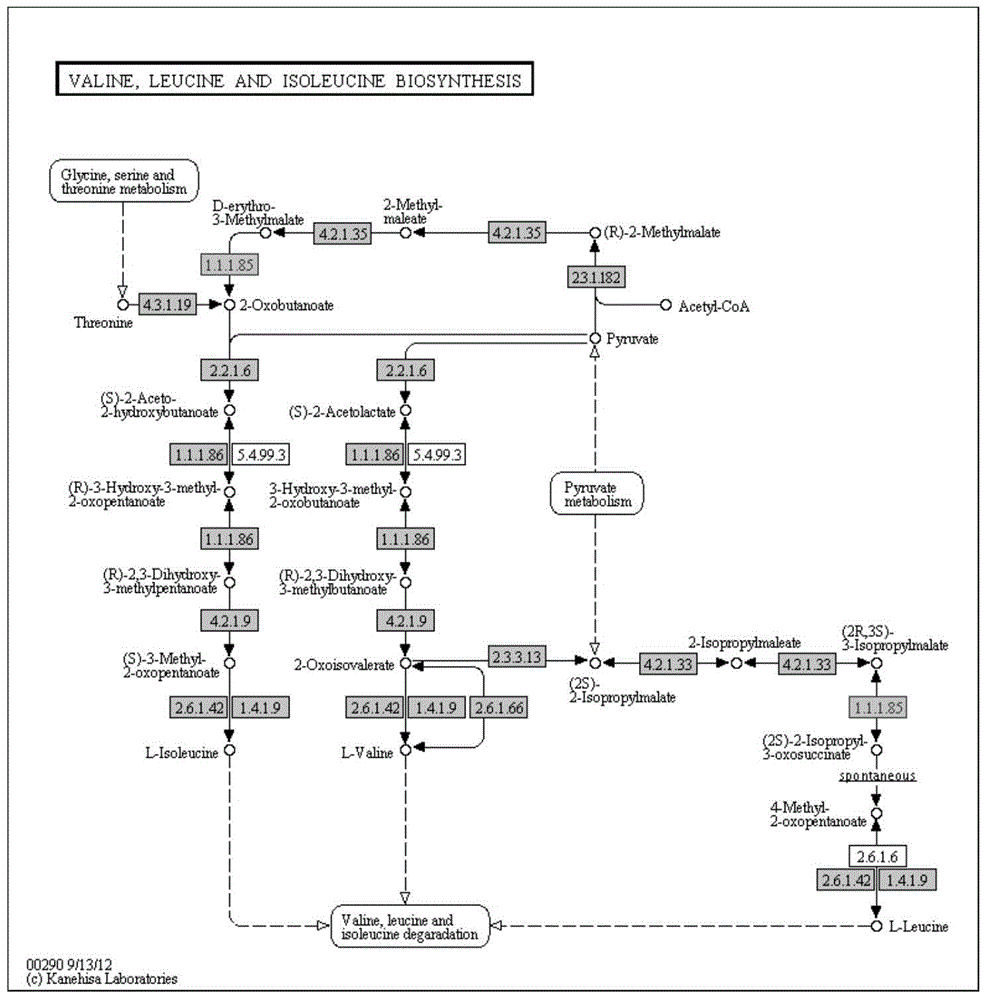
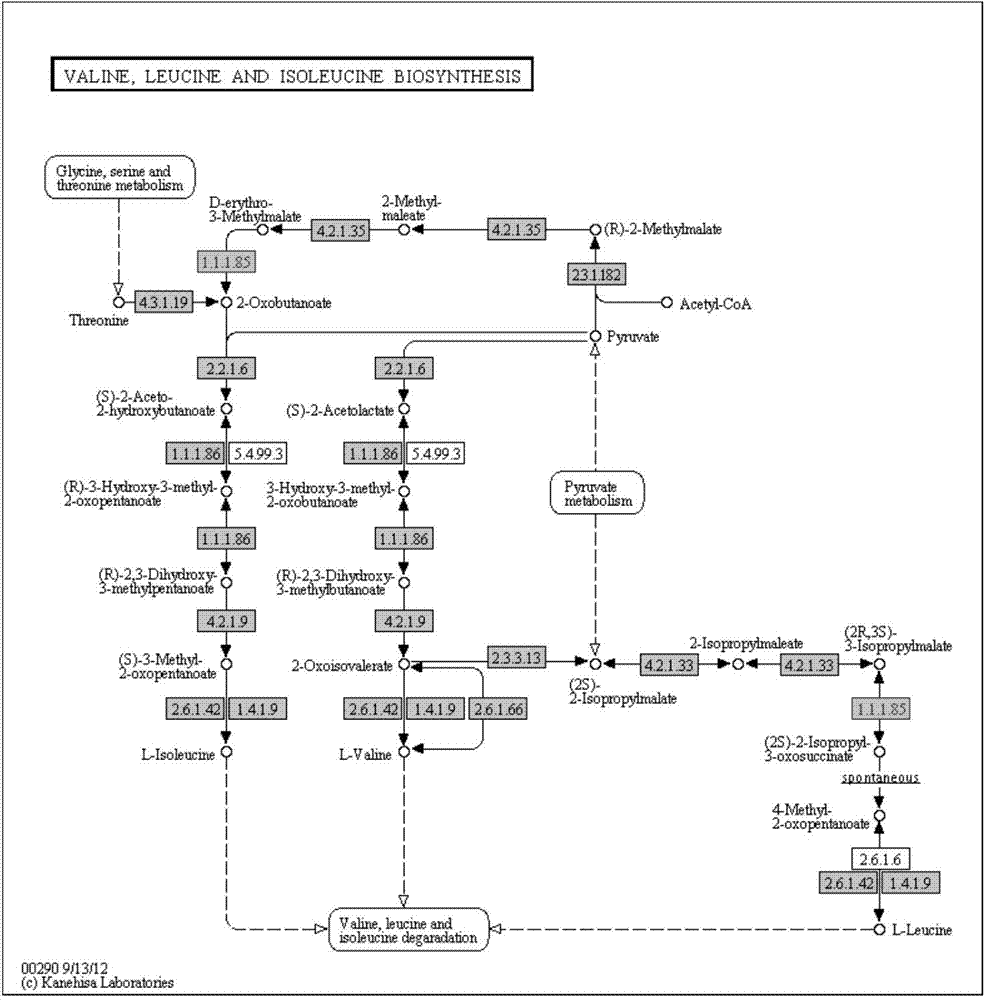
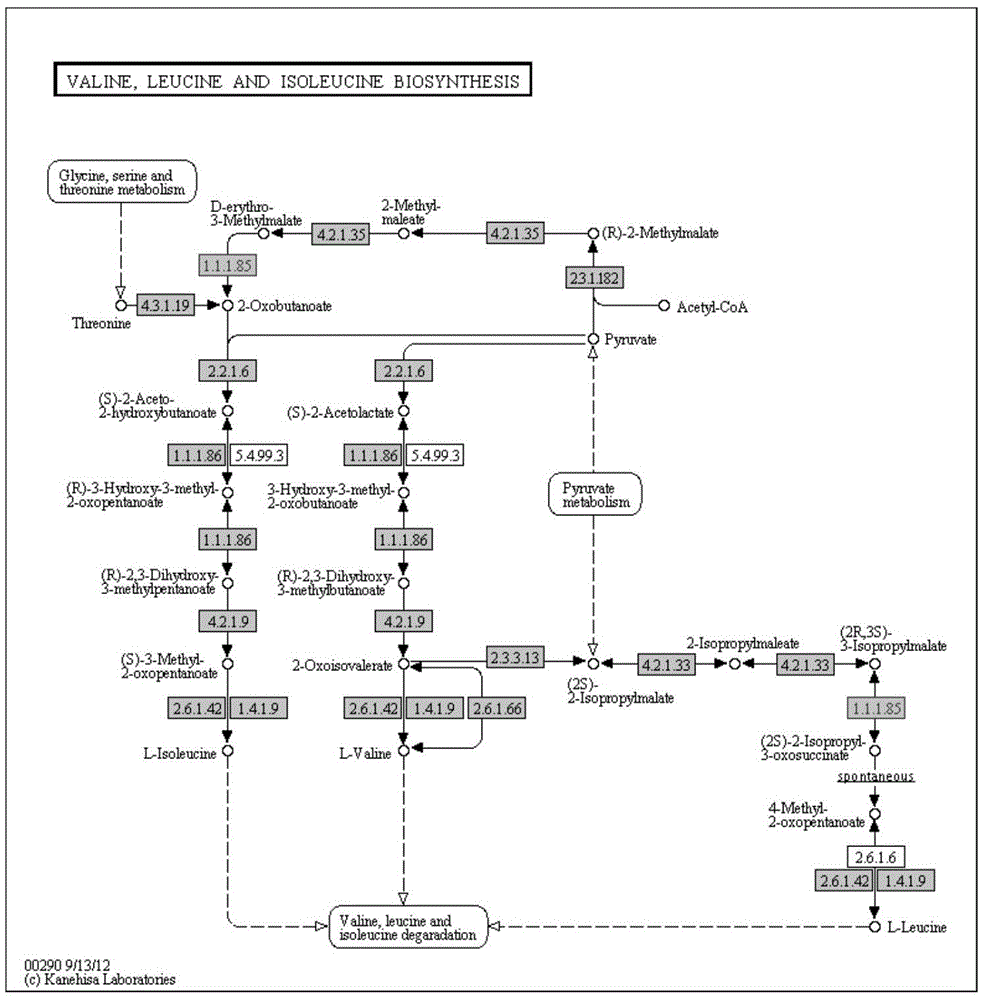
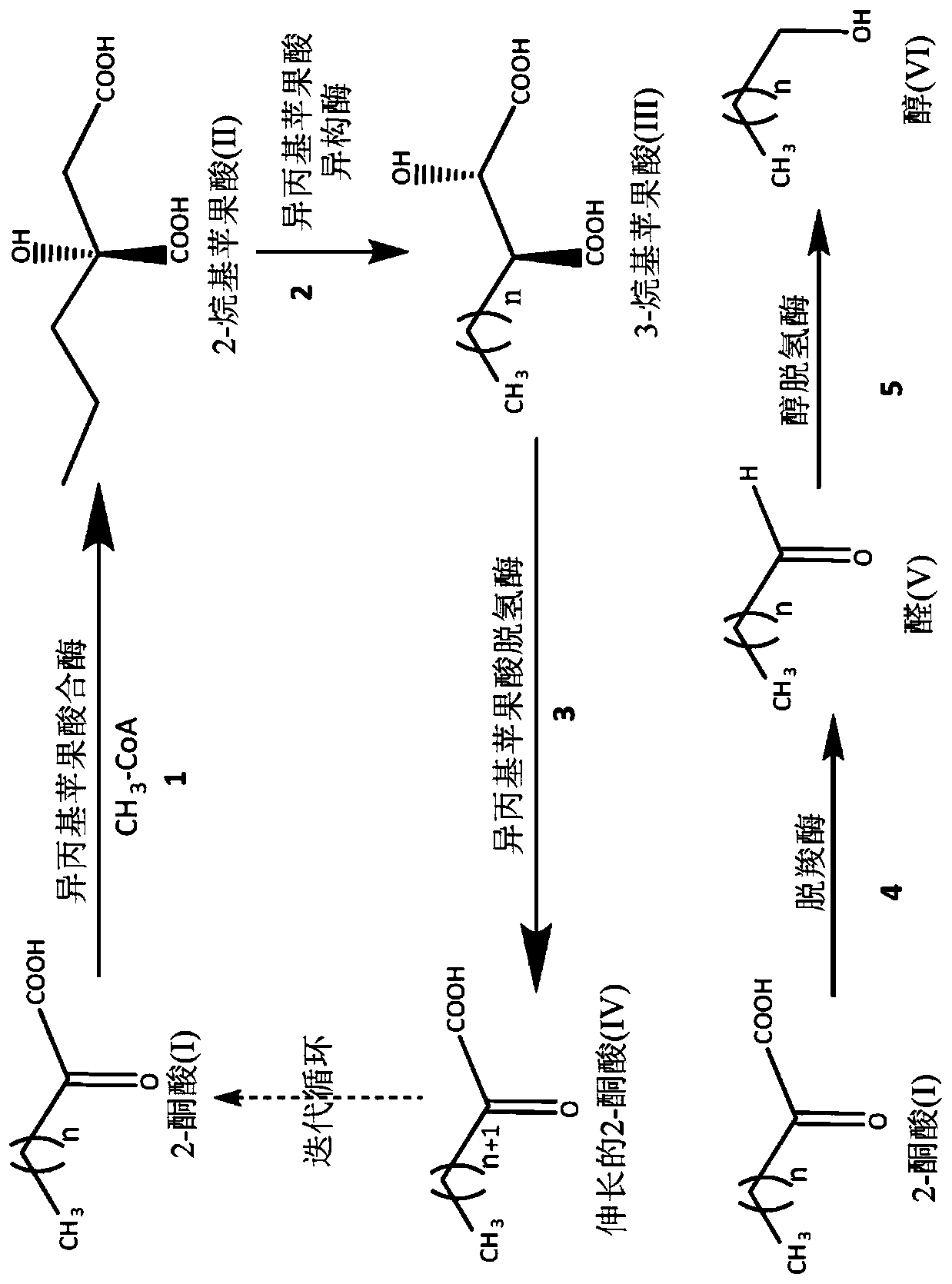
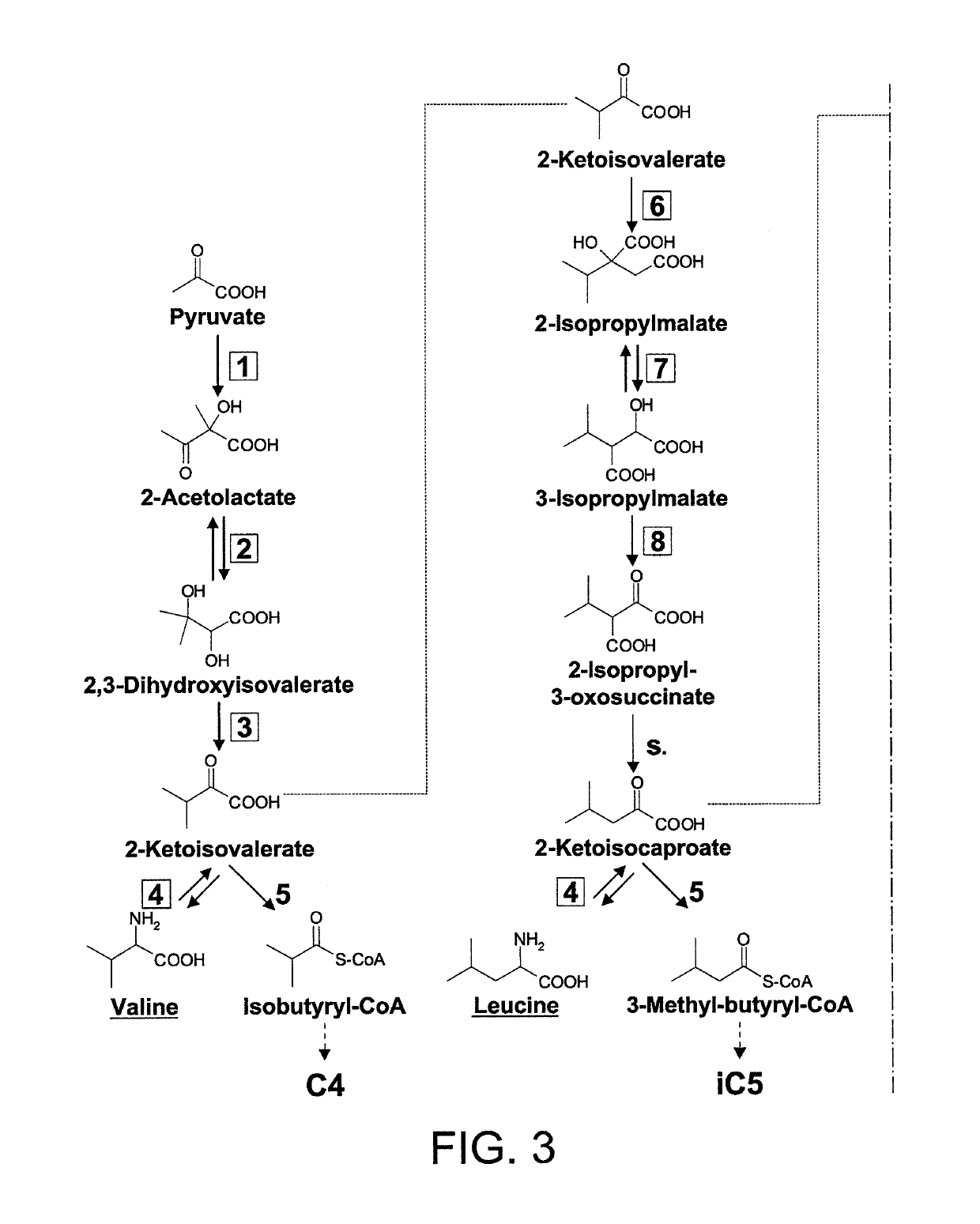
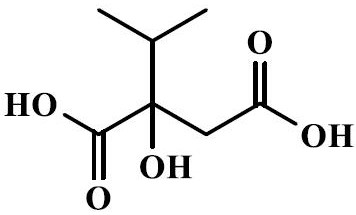
Isopropylmalic acid (isopropylmalate) is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of leucine, synthesized from oxoisovalerate by 2-isopropylmalate synthase and converted into isopropyl-3-oxosuccinate by 3-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase. Two isomers are important, the 2- and 3-isopropyl derivatives, and these are interconverted by isopropylmalate dehydratase.
Increased production of isobutanol in yeast with reduced mitochondrial amino acid biosynthesis
ActiveUS8465964B2Reduced activityCarbon-nitrogen lyasesMicroorganismsIsobutanolBranched-chain-amino-acid transaminase
Owner:GEVO INC
High yield L-leucine engineering bacterium and application thereof
The invention discloses a high yield L-leucine engineering bacterium and an application of the bacterium.The invention provides a method for preparing a recombinant bacterium. The method comprises the following step of importing an alpha-isopropylmolic acid synthetase mutant encoding gene into a target bacterium to form the recombinant bacterium, wherein an alpha-isopropylmolic acid synthetase mutant is enzyme obtained by mutating 494th arginine of alpha-isopropylmolic acid synthetase into histidine, 497th glycine into aspartic acid and 499th leucine into valine.The high yield L- leucine engineering bacterium, particularly corynebacterium glutamicum MD0032, has higher L-leucine yield than bacterial strains produced at home at present, has a unique identification label and is a L-leucine production strain with a high production and application value.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV +1
A novel isopropylmalate synthase variant and a method of producing l-leucine using the same
A novel modified polypeptide having an isopropylmalate synthase activity, a polynucleotide encoding the same, a microorganism comprising the polypeptide, and a method of producing L-leucine by culturing the microorganism.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
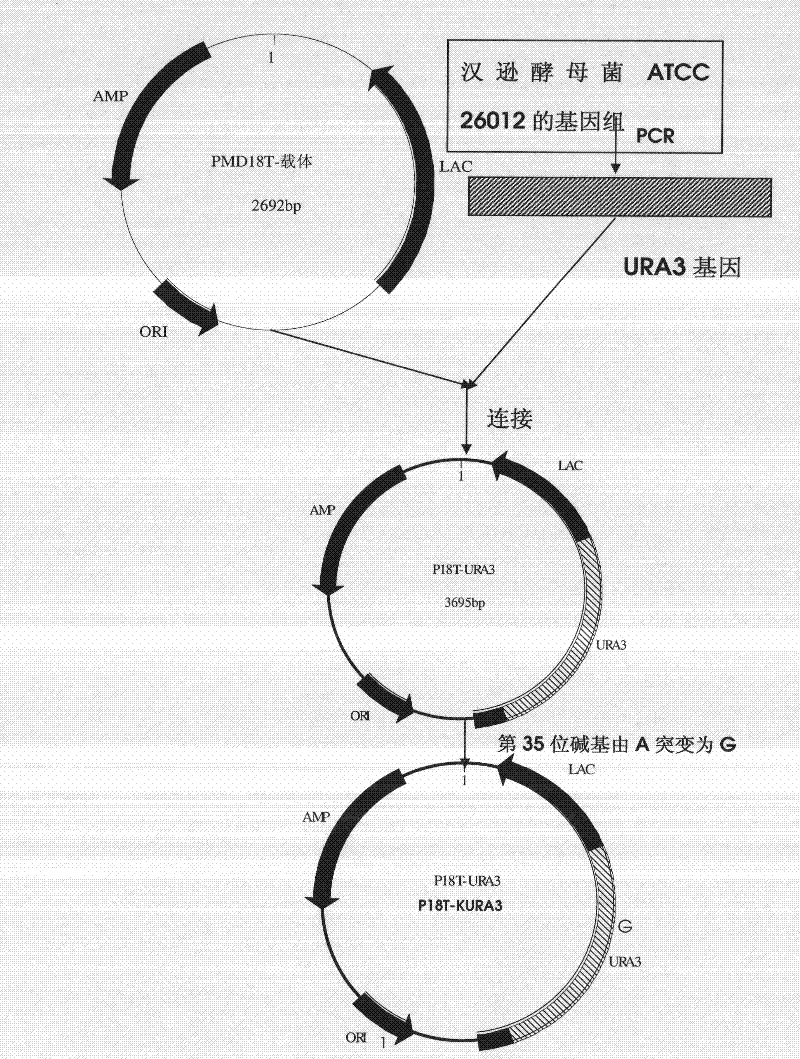
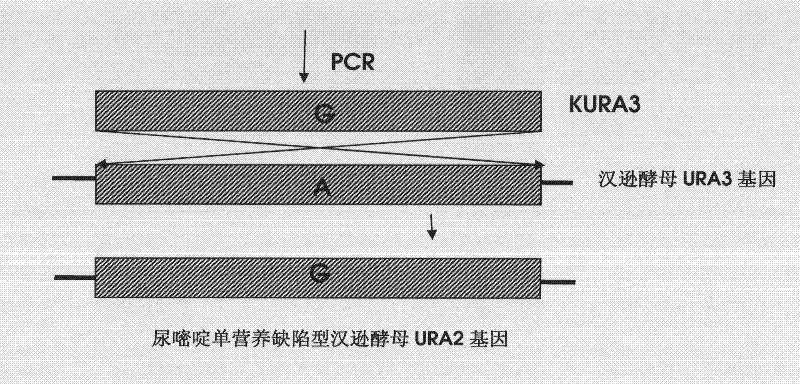
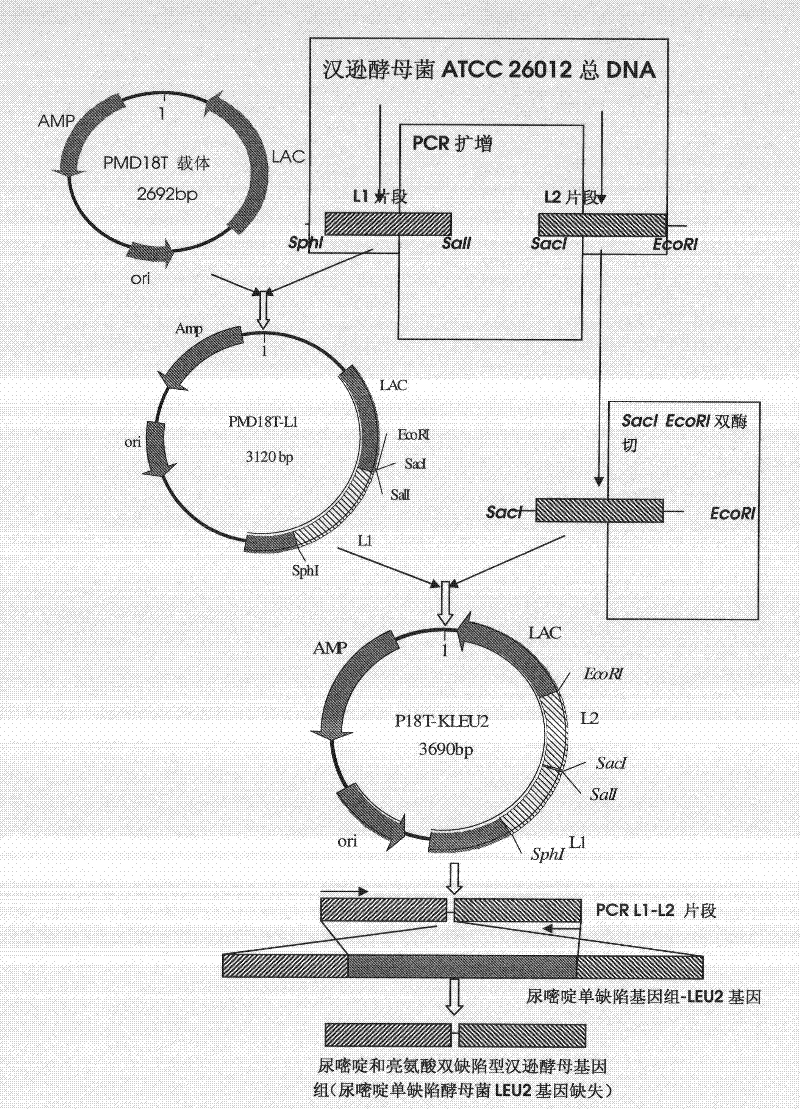
DNA sequence, recombinant vector, single and double auxotrophic Hansenula polymorpha, and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102234620AConvenient sourceSuitable for researchFungiMicroorganism based processesVaccine ProductionPhosphate
The invention relates to a double auxotrophic yeast, wherein the yeast is Hansenula polymorpha, and the orotic glycoside-5-phosphate decarboxylase gene and the beta-isopropyl malate dehydrogenase gene of the Hansenula polymorpha are blocked. The invention also relates to a preparation method of the double auxotrophic yeast. In addition, the invention also provides a DNA sequence and a recombinant vector used to prepared the double auxotrophic yeast. The double auxotrophic yeast of the invention has the advantages of low reverse mutation, high genetic stability, high biomass, and the like, and plays an important role in genetic engineering vaccine production; for example, HPV16-type L1 and 58L2 protein have double expression with high efficiency in the yeast.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF BIOLOGICAL PROD
Application of rice alpha-isopropyl malate synthase gene
InactiveCN108715903AVitality Improvements IncreasedMicrobiological testing/measurementAcyltransferasesMalate synthaseOryza
The invention discloses application of a rice alpha-isopropyl malate synthase gene. The nucleotide sequence of gene OsIPMS1 is shown as SEQ ID NO.1 and the encoded corresponding protein amino acid sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO.2 in a sequence table. According to the application disclosed by the invention, the OsIPMS1 gene can regulate the vitality of rice seeds, which is firstly reported in the rice field; the experiment shows that the mutation of the gene affects the germination speed and seedling growth of seeds under normal conditions. The experiment proves that the OsIPMS1 gene disclosedby the invention regulates the vitality of the rice seeds; the screening and the cultivation of rice varieties with high seed vigor as well as the production of direct-seeding rice are facilitated byutilizing the gene.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for producing L-leucine and related DNA and microorganism
A method for producing L-leucine, comprising the steps of: culturing a bacterium which is transformed with a DNA coding for an alpha-isopropylmalate synthase densensitized in feedback inhibition by L-leucine, in a culture medium to produce and accumulate L-leucine in the medium, and recovering L-leucine from the medium.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Recombinant strain with high lipopeptide yield and application thereof
ActiveCN110331121AIncrease productionEasy to synthesizeBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyIsopropylmalic acid
The invention discloses a recombinant strain with a high lipopeptide yield and application thereof, belonging to the technical field of genetic engineering. The recombinant strain is constructed by transforming a 2-isopropylmolic acid synthase gene in a leucine synthesis pathway into an original strain. Compared with the original strain, the recombinant strain which over-expresses a part of the leucine synthesis pathway (2-isopropylmolic acid synthase, 3-isopropylmolic acid dehydrogenase, 3-isopropylmolic acid dehydratase and branched chain amino acid transaminase) has a surfactin yield increased by 55.6%, can be used for production of lipopeptide type biosurfactants, and has a good industrial application prospect. The average lipopeptide yield in fermentation liquor obtained by shake flask fermentation is 13-16 g / L.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
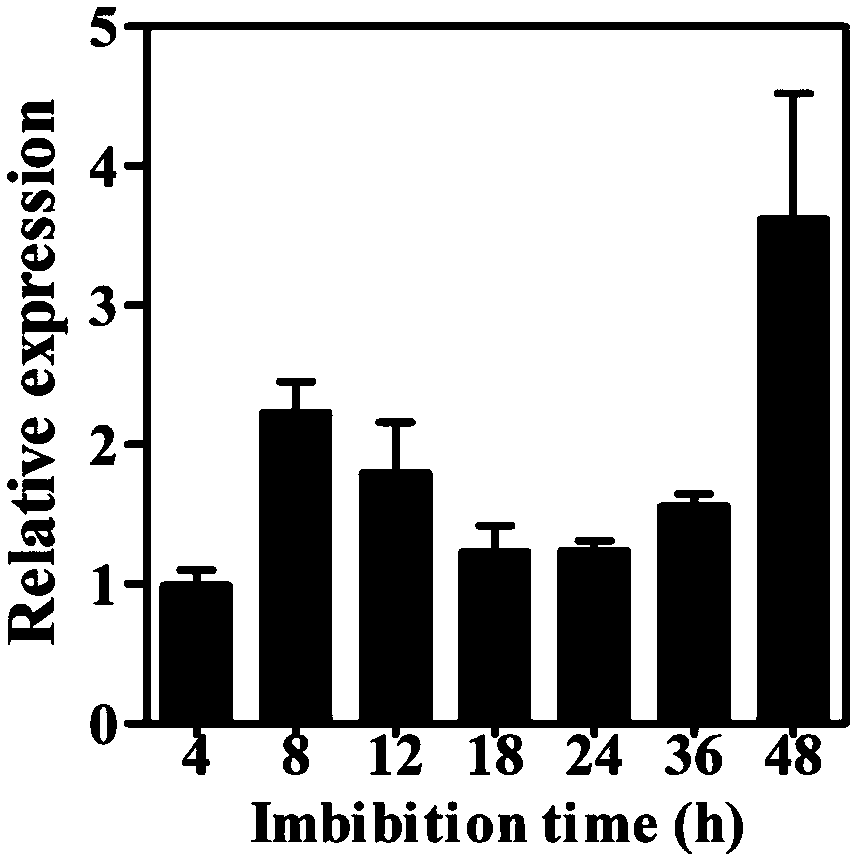
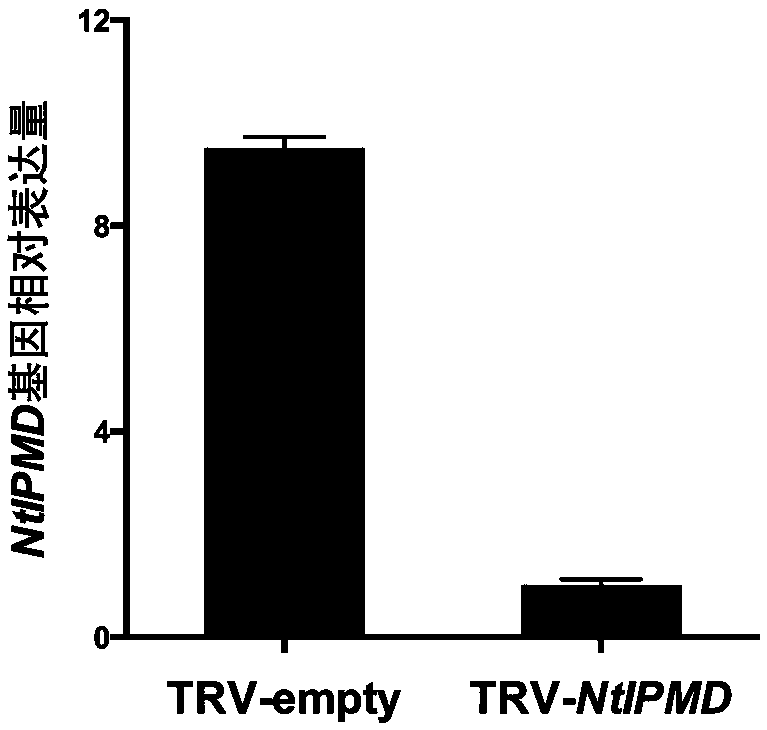
NtIPMD gene affecting differentiation of tobacco axillary bud
The invention belongs to the field of tobacco gene engineering, and particularly relates to a NtIPMD gene affecting differentiation of a tobacco axillary bud. The gene comprises 1218bp basic group with the specific nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO. 1, wherein the nucleotides at the 68-403 sites are specific nucleic acid segments. Isopropyl malic dehydrogenase NtIPMD coded by the gene has thecharacteristic that isopropyl malic dehydrogenase NtIPMD comprises 405 amino acid. The primary research on the NtIPMD gene shows that the gene is related to development of the axillary bud of a plant, after the gene is silenced, development of a lateral branch can be promoted, by taking use of the characteristic, the gene can be silenced or overexpressed through gene silencing or overexpression techniques, accordingly adjustment of the plant shape can be achieved at the molecular level, meanwhile, the gene has the important effect on culturing new species of tobacco, and therefore the gene has the more significant practical value.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC
Method for producing L-leucine and related DNA and microorganism
A method for producing L-leucine, comprising the steps of: culturing a bacterium which is transformed with a DNA coding for an alpha-isopropylmalate synthase densensitized in feedback inhibition by L-leucine, in a culture medium to produce and accumulate L-leucine in the medium, and recovering L-leucine from the medium.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Cordyceps sinensis 3-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase B, as well as encoding genes and application thereof
ActiveCN104120112AEnhance expressive abilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processes3-Isopropylmalate DehydrogenaseNucleotide
The invention provides 3-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase B for preparing 4-methyl-2-oxoglutaric acid from cordyceps sinensis Hirsutella sinensis and biologically catalyzed 3-isopropylmalate as well as encoding genes and an application thereof. The 3-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase B has an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID No.1, and the encoding genes are shown as SEQ ID No.1. Cloning DNA of a nucleotide sequence provided by the invention can be used for being transferred into engineering bacteria through transduction, transformation and combined transfer methods, the host 3-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase B is endowed with high expression by regulating the expression of the 3-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase B genes, an effective path is provided for widening biological application of the 3-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase B, and the 3-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase B has significant application prospects.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +1
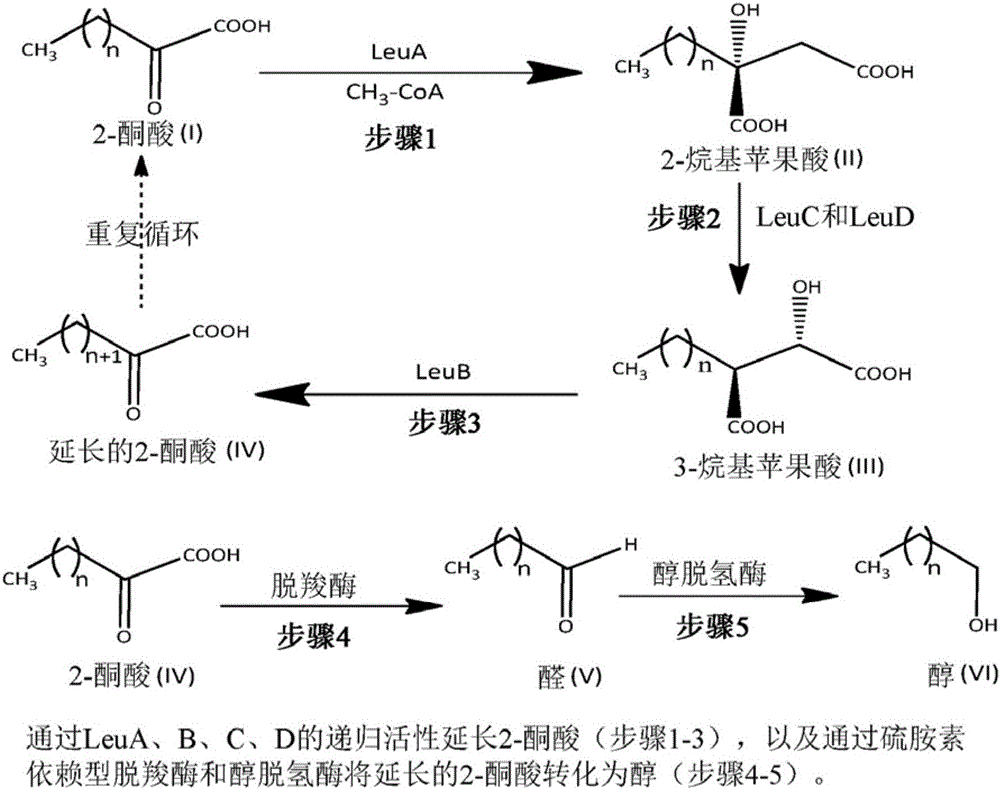
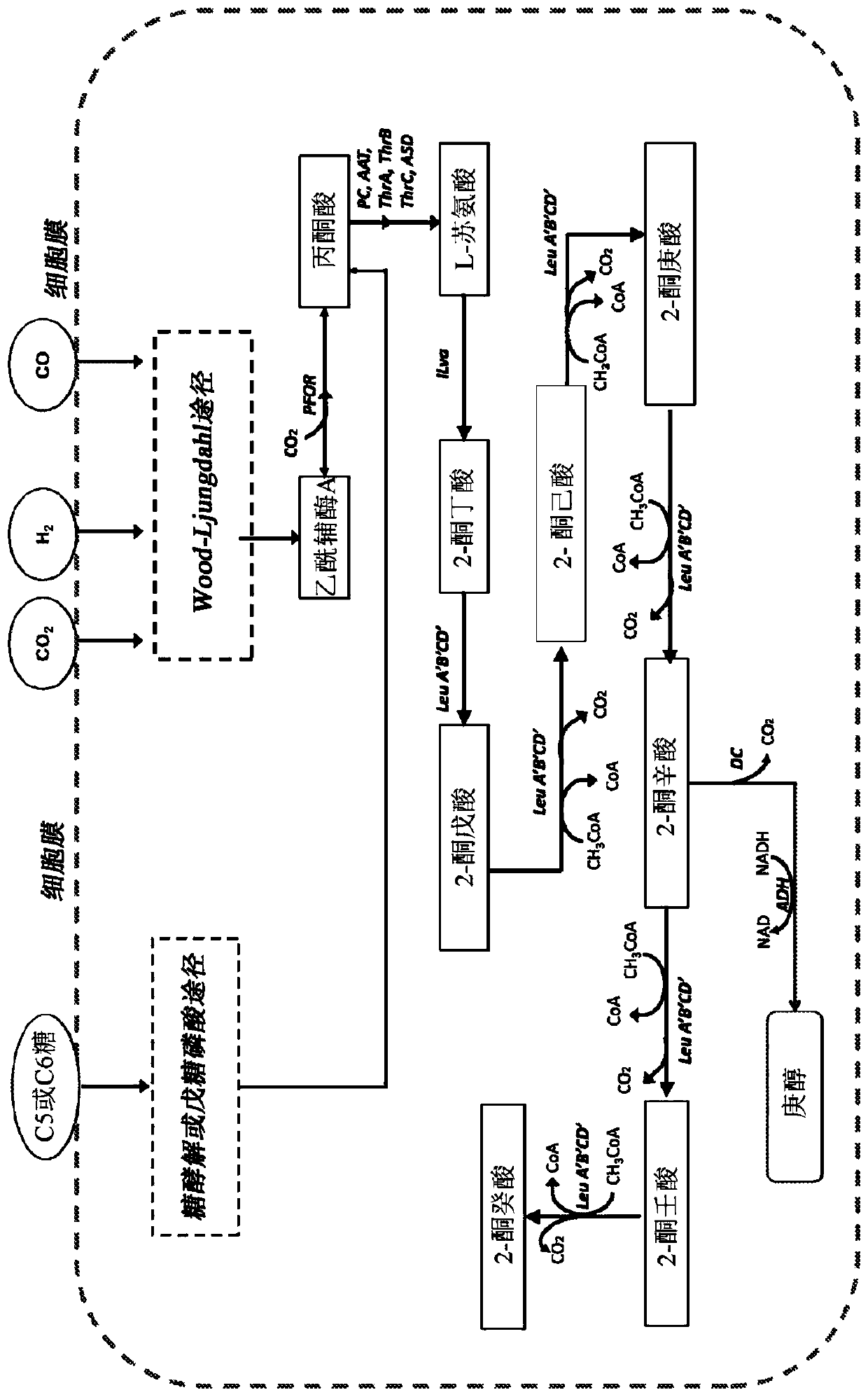
Processes to prepare elongated 2-ketoacids and c6-c10 compounds therefrom via genetic modifications to microbial metabolic pathways
Modification of metabolic pathways includes genetically engineering at least one enzyme involved in elongating 2-ketoacids during leucine biosynthesis, and preferably at least isopropylmalate dehydrogenase or synthase (LeuB or LeuA in E. coli), to include at least such non- native enzyme, enzyme complex, or combination thereof to convert 2-ketobutyrate or 2-ketoisovalerate to a C7-C11 2-ketoacid, wherein the production of such is at a higher efficiency than if a purely native pathway is followed. The C7-C11 2-ketoacid may then be converted, via a native or genetically engineered thiamin dependent decarboxylase, to form a C6-C10 aldehyde having one less carbon than the C7-C11 2-ketoacid being converted. In some embodiments the C6-C10 aldehyde may then be converted via additional native or genetically engineered enzymes to form other C6-C10 products, including alcohols, carboxylic acids, and alkanes. This genetic engineering offers the opportunity for commercial scale of in vivo biosynthetic processes that may be more cost-efficient than non- biobased approaches to produce the same products.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Isopropylmalate synthase from nicotiana tabacum and methods and uses thereof
ActiveUS20140352706A1Undesirable effectReduce yieldEsterified saccharide compoundsTobacco treatmentMalate synthaseNicotiana tabacum
The present invention relates to a mutant, non-naturally occurring or transgenic plant cell comprising: (i) at least one polynucleotide comprising, consisting or consisting essentially of a sequence encoding an isopropylmalate synthase and having at least 60% sequence identity to SEQ ID NO:1 or SEQ ID NO:10 or SEQ ID NO: 12 or SEQ ID NO:14; or (ii) a polypeptide encoded by said polynucleotide(s); or (iii) a polypeptide having at least 60% sequence identity to SEQ ID NO:2 or SEQ ID NO:11 or SEQ ID NO:13 or SEQ ID NO:15; or (iv) a construct, vector or expression vector comprising said polynucleotide sequence(s), optionally wherein said construct, vector or expression vector additionally comprises a promoter comprising, consisting or consisting essentially of the sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:8 or a variant thereof with at least about 60% identity thereto or a trichome promoter.
Owner:PHILIP MORRIS PROD SA
Isopropylmalate synthase variant and a method of producing l-leucine using the same
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
2-isopropylmalate synthetase and engineering bacteria and application thereof
PendingUS20210189354A1Quick upgradeShort maintenance periodOxidoreductasesAcyltransferasesMalate synthaseNutritional deficiency
The invention relates to a 2-isopropyl malate synthase, a genetically engineered bacterium for producing L-leucine and application thereof and belongs to the field of metabolic engineering. The genetically engineered bacterium is obtained by overexpressing an isopropyl malate synthase coding gene leuAM for relieving feedback inhibition by L-leucine, an acetohydroxy acid synthase coding gene ilvBNM for relieving feedback inhibition by L-isoleucine, a 3-isopropyl malate dehydrogenase coding gene leuB and a 3-isopropyl malate dehydratase coding gene leuCD in host cells. The genetically engineered bacterium for producing the L-leucine is free from nutritional deficiency, rapid in growth, short in fermentation period, high in yield and high in conversion rate.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A kind of β-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase and its application in lipid synthesis
ActiveCN110499300BImprove biosynthetic abilityOxidoreductasesFermentationIsopropylmalic acidMembrane lipid metabolism
The invention discloses beta-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase and application of the beta-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase in lipid synthesis, and belongs to the technical fields of gene engineering and microbial engineering. An amino acid sequence of the beta-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase is shown in SEQ ID No. 1, and the beta-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase has a function of promoting microorganism to produce fatty acids. Recombinant mortierella alpina containing the beta-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase is subjected to shake cultivation for 7 d, so that the fatty acid content in the mortierella alpinacontaining the beta-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase can reach 46.4% of dry cell weight, and is 20.2% higher than that of mortierella alpina without the beta-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase. According tothe beta-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase, through gene engineering, the fatty acid production ability of the mortierella alpine and other oil producing microorganisms is further improved, and solid theoretical support for improving the fatty acid biosynthesis ability is provided.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Application of high-content 2-isopropylmalic acid in pollen pini authenticity evaluation
InactiveCN111707761AImprove featuresHigh sensitivityComponent separationIsopropylIsopropylmalic acid
The invention relates to the field of food detection, particularly to application of high-content 2-isopropylmalic acid in pollen pini authenticity evaluation, and provides a pollen pini authenticityevaluation method, wherein 2-isopropylmalic acid is used as a characteristic compound, when the content of 2-isopropylmalic acid is 18-35 mg / kg, a sample can be judged as pollen pini, and otherwise, it is determined that the pollen is other pollen or adulterated pollen pini. The method provided by the invention is simple, efficient, high in stability and suitable for accurately determining the content of 2-isopropylmalic acid in pollen pini, is suitable for evaluating the authenticity and purity of the pollen pini, and has important practical significance for protecting legitimate rights and interests of consumers and maintaining healthy development of the pollen pini industry.
Owner:BEE RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Cordyceps sinensis 3-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase a, coding gene and its application
ActiveCN104120114BEnhance expressive abilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesExpressivity3-Isopropylmalate Dehydrogenase
The invention provides a 3-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase A (which is derived from Cordyceps Chinese Hirsutella and used for biologically catalyzing 3-isopropylmolic acid to prepare 4-methyl-2-oxo-valeric acid), and a coding gene and application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the 3-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase A is disclosed as SEQ ID No.1, and the coding gene is disclosed as SEQ ID No.2. The clone DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of the nucleotide sequence can be transferred into engineering bacterium by transduction, transformation and conjugal transfer; and the expression of the 3-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase A gene is regulated to endow the host 3-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase A with high expressivity, thereby providing an effective way for widening the biological application range of the 3-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase A, and having great application prospects.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +2
A high-yielding l-leucine engineering bacterium and its application
The invention discloses a high yield L-leucine engineering bacterium and an application of the bacterium.The invention provides a method for preparing a recombinant bacterium. The method comprises the following step of importing an alpha-isopropylmolic acid synthetase mutant encoding gene into a target bacterium to form the recombinant bacterium, wherein an alpha-isopropylmolic acid synthetase mutant is enzyme obtained by mutating 494th arginine of alpha-isopropylmolic acid synthetase into histidine, 497th glycine into aspartic acid and 499th leucine into valine.The high yield L- leucine engineering bacterium, particularly corynebacterium glutamicum MD0032, has higher L-leucine yield than bacterial strains produced at home at present, has a unique identification label and is a L-leucine production strain with a high production and application value.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV +1
A kind of isopropylmalate synthase and its application
ActiveCN110540976BRelease feedback inhibitionNo significant change in activityAcyltransferasesGenetic engineeringIsopropylIsopropylmalic acid
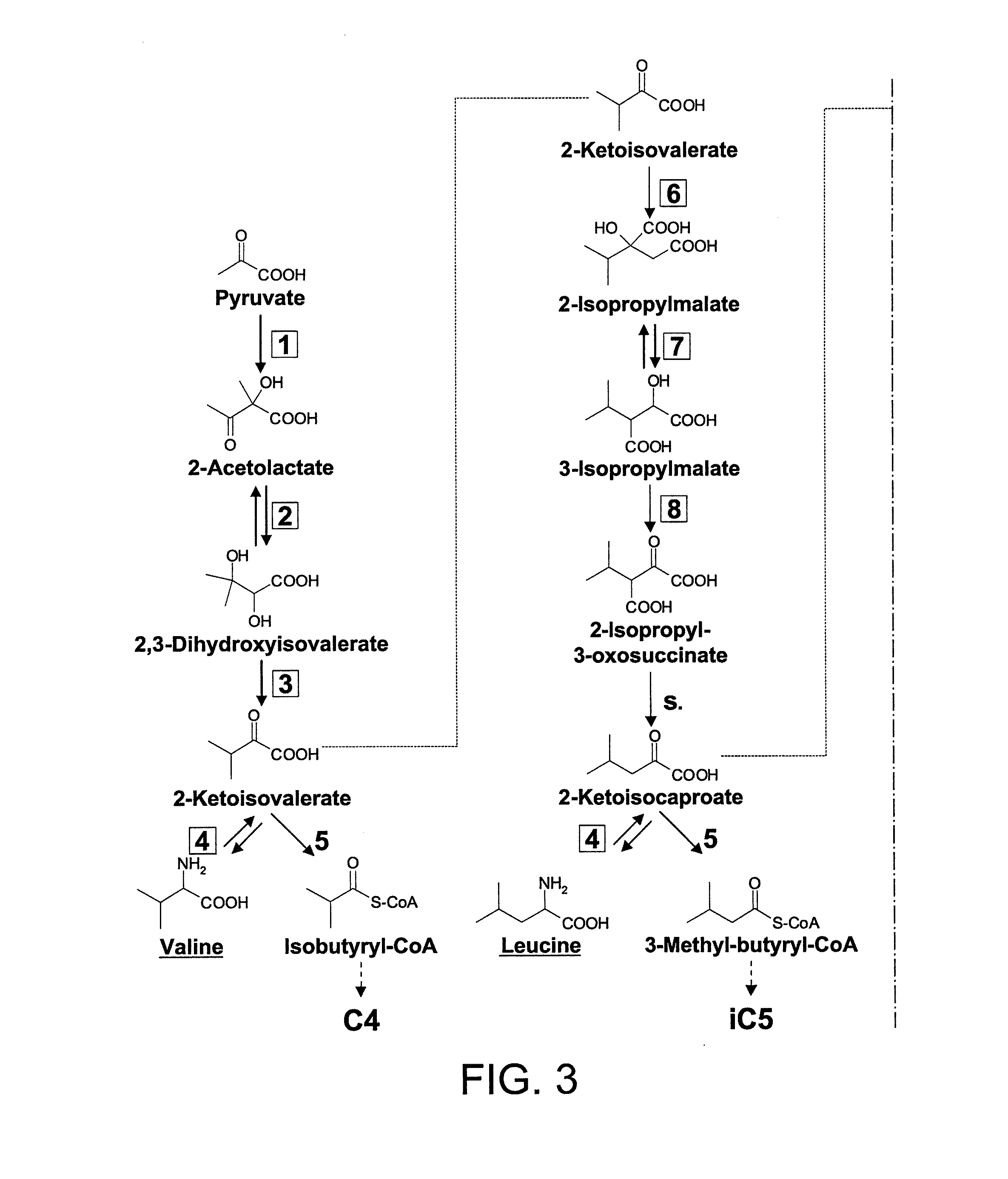
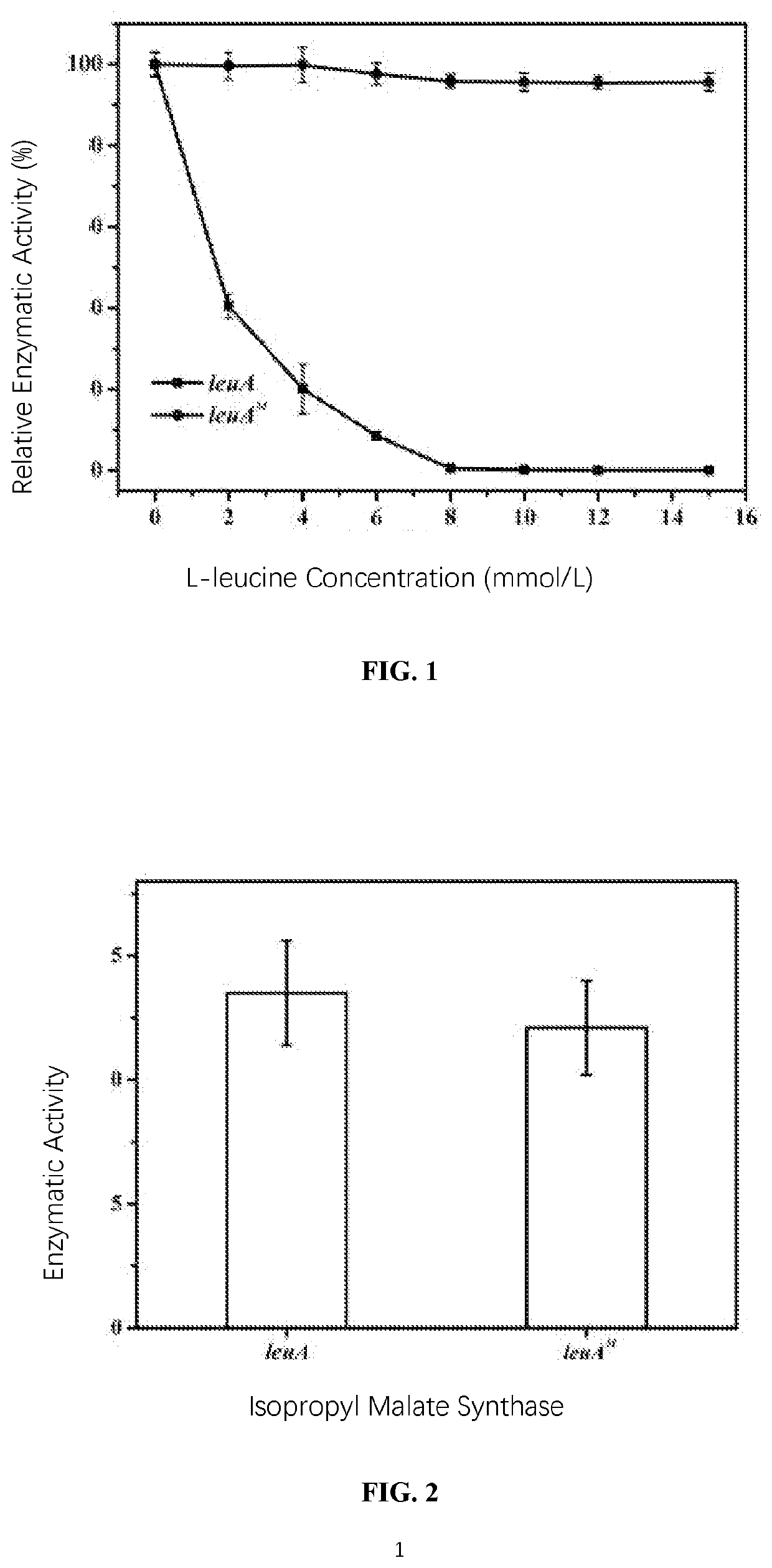
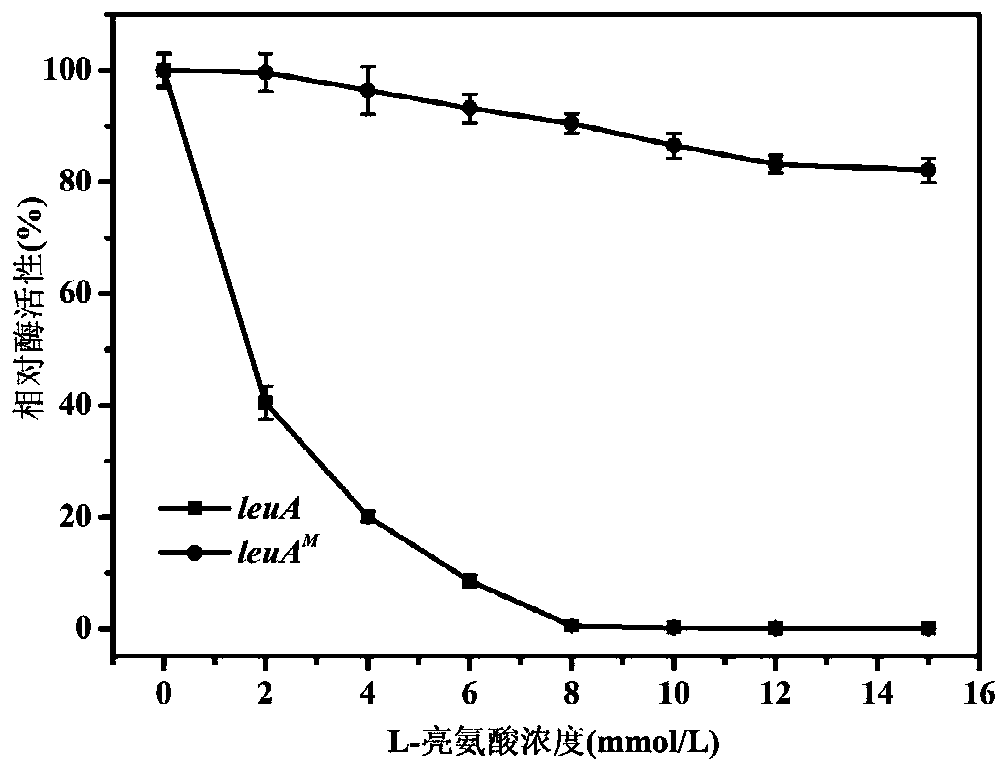
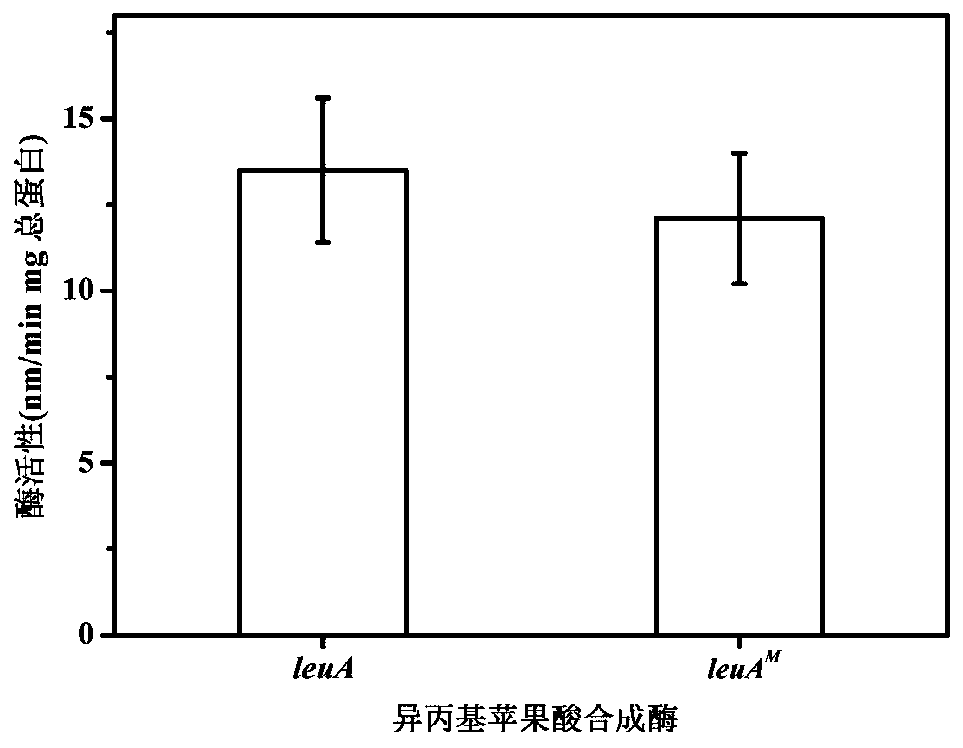
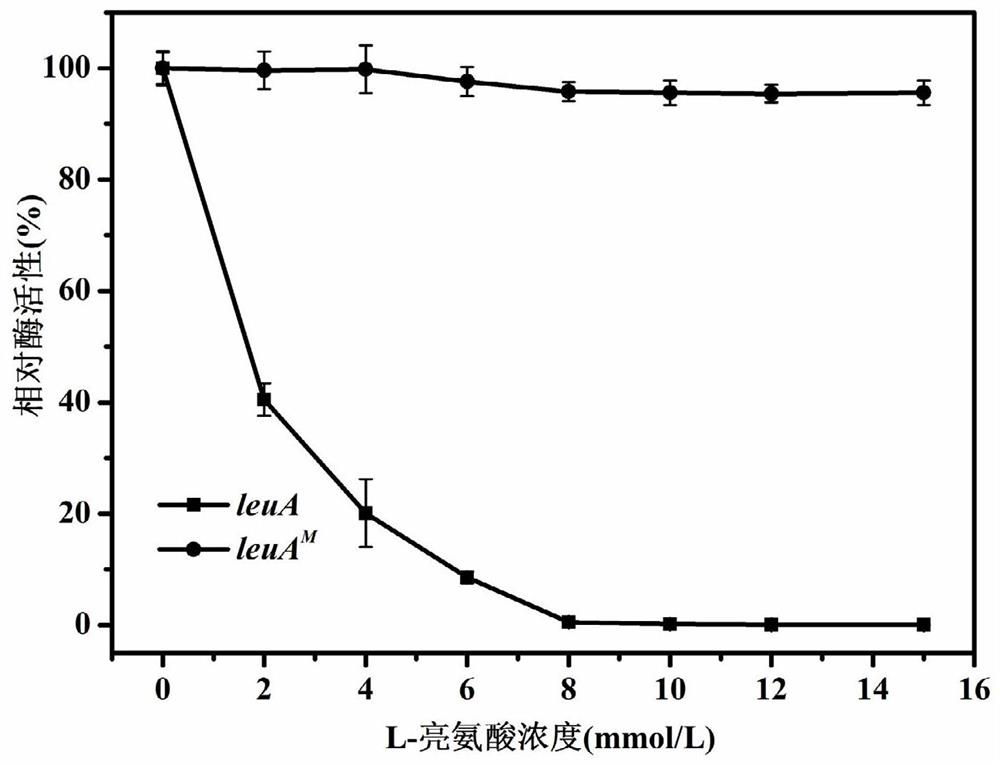
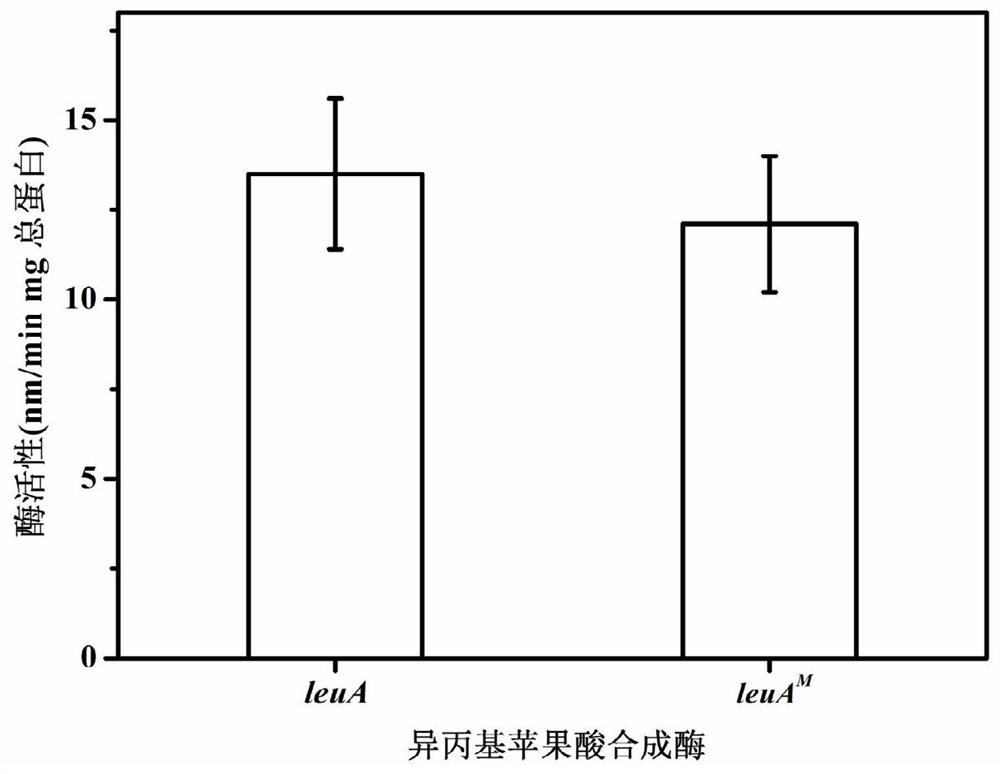
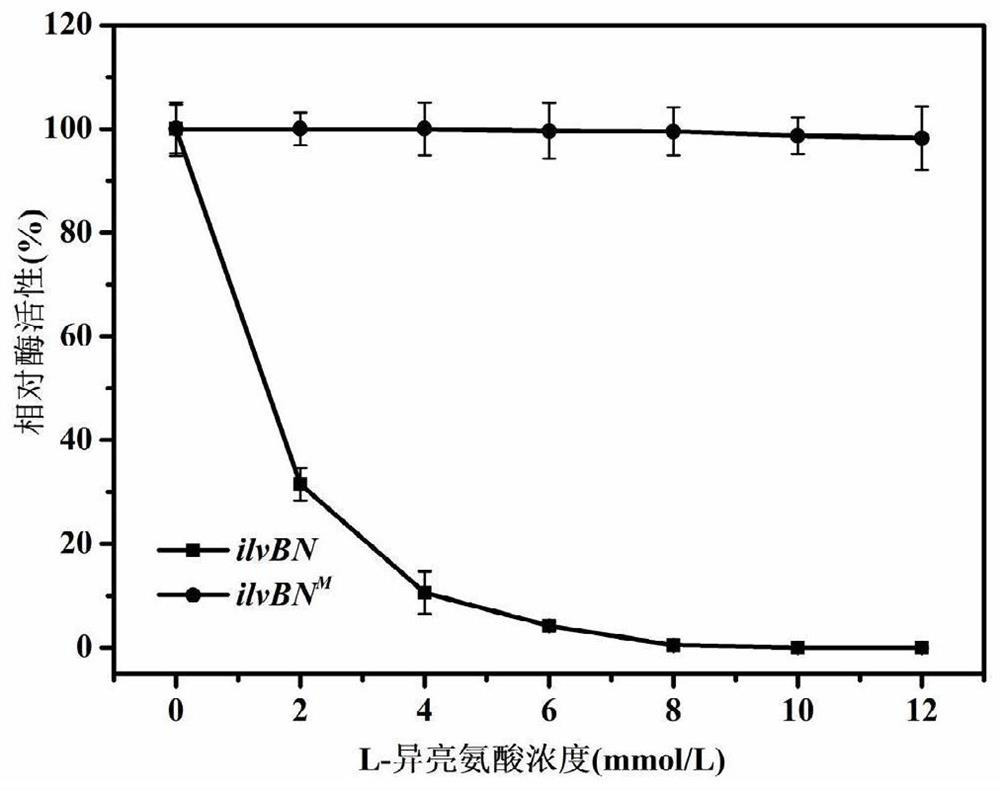
The invention relates to a 2-isopropylmalate synthetase for removing feedback inhibition of L-leucine and an application of the 2-isopropylmalate synthetase, and belongs to the field of metabolic engineering. The leuA<M> gene coded 2-isopropylmalate synthetase has the following characteristics: the synthetase removes the feedback inhibition effect of the L-leucine on the synthetase; under the condition that the concentration of the L-leucine is 0-15 mmol / L, the LEUA<M> activity is not obviously changed; the activity of the 2-isopropylmalate synthetase is not obviously reduced compared with that of a wild LeuA<M> coded 2-isopropylmalate synthetase; and the 2-isopropylmalate synthetase can be applied to the production of the L-leucine.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Cordyceps 3-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase A, and coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN104120114AEnhance expressive abilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesExpressivity3-Isopropylmalate Dehydrogenase
The invention provides a 3-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase A (which is derived from Cordyceps Chinese Hirsutella and used for biologically catalyzing 3-isopropylmolic acid to prepare 4-methyl-2-oxo-valeric acid), and a coding gene and application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the 3-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase A is disclosed as SEQ ID No.1, and the coding gene is disclosed as SEQ ID No.2. The clone DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of the nucleotide sequence can be transferred into engineering bacterium by transduction, transformation and conjugal transfer; and the expression of the 3-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase A gene is regulated to endow the host 3-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase A with high expressivity, thereby providing an effective way for widening the biological application range of the 3-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase A, and having great application prospects.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +2
Cordyceps sinensis 3-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase c, coding gene and its application
ActiveCN104120113BEnhance expressive abilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesNucleotideIsopropylmalic acid
The invention provides 3-isopropyl malic dehydrogenase C which is extracted from cordyceps sinensis hirsutella sinensis and joins in biological catalysis on 3-isopropyl malic acid to prepare 4-methyl-2-oxo valeric acid, an encoding gene and application of 3-isopropyl malic dehydrogenase C. The amino acid sequence of 3-isopropyl malic dehydrogenase C is as shown in SEQ ID No.1, and the encoding gene is as shown in SEQ ID No.1; the clone DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) of the nucleotide sequence can be transferred into engineering bacteria by using methods of transduction, conversion and conjugal transfer, by adjusting the expression of the gene of 3-isopropyl malic dehydrogenase C, the host 3-isopropyl malic dehydrogenase C is high in expression property, an effective method is provided to expand the biological application of 3-isopropyl malic dehydrogenase C, and great application prospects are achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +2
Processes to prepare elongated 2-ketoacids and C5-C10 compounds therefrom via genetic modifications to microbial metabolic pathways
Genetically modified isopropylmalate synthases, processes for preparing a C7-C11 2-ketoacids utilizing genetically modified isopropylmalate synthases, and microbial organisms including genetically modified isopropylmalate synthases are described. The genetically modified isopropylmalate synthases, processes for preparing a C7-C11 2-ketoacids, and microbial organisms including genetically modifiedisopropylmalate synthases can be particularly useful for producing corresponding Cn_1 aldehydes, alcohols, carboxylic acids, and Cn_2 alkanes both in vivo and in vitro.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Isopropylmalate synthase from Nicotiana tabacum and methods and uses thereof
ActiveUS10287599B2Undesirable effectReduce yieldEsterified saccharide compoundsSugar derivativesNicotiana tabacumNucleotide
The present invention relates to a mutant, non-naturally occurring or transgenic plant cell comprising: (i) at least one polynucleotide comprising, consisting or consisting essentially of a sequence encoding an isopropylmalate synthase and having at least 60% sequence identity to SEQ ID NO:1 or SEQ ID NO:10 or SEQ ID NO: 12 or SEQ ID NO:14; or (ii) a polypeptide encoded by said polynucleotide(s); or (iii) a polypeptide having at least 60% sequence identity to SEQ ID NO:2 or SEQ ID NO:11 or SEQ ID NO:13 or SEQ ID NO:15; or (iv) a construct, vector or expression vector comprising said polynucleotide sequence(s), optionally wherein said construct, vector or expression vector additionally comprises a promoter comprising, consisting or consisting essentially of the sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:8 or a variant thereof with at least about 60% identity thereto or a trichome promoter.
Owner:PHILIP MORRIS PROD SA
A kind of genetically engineered bacteria producing l-leucine and its application
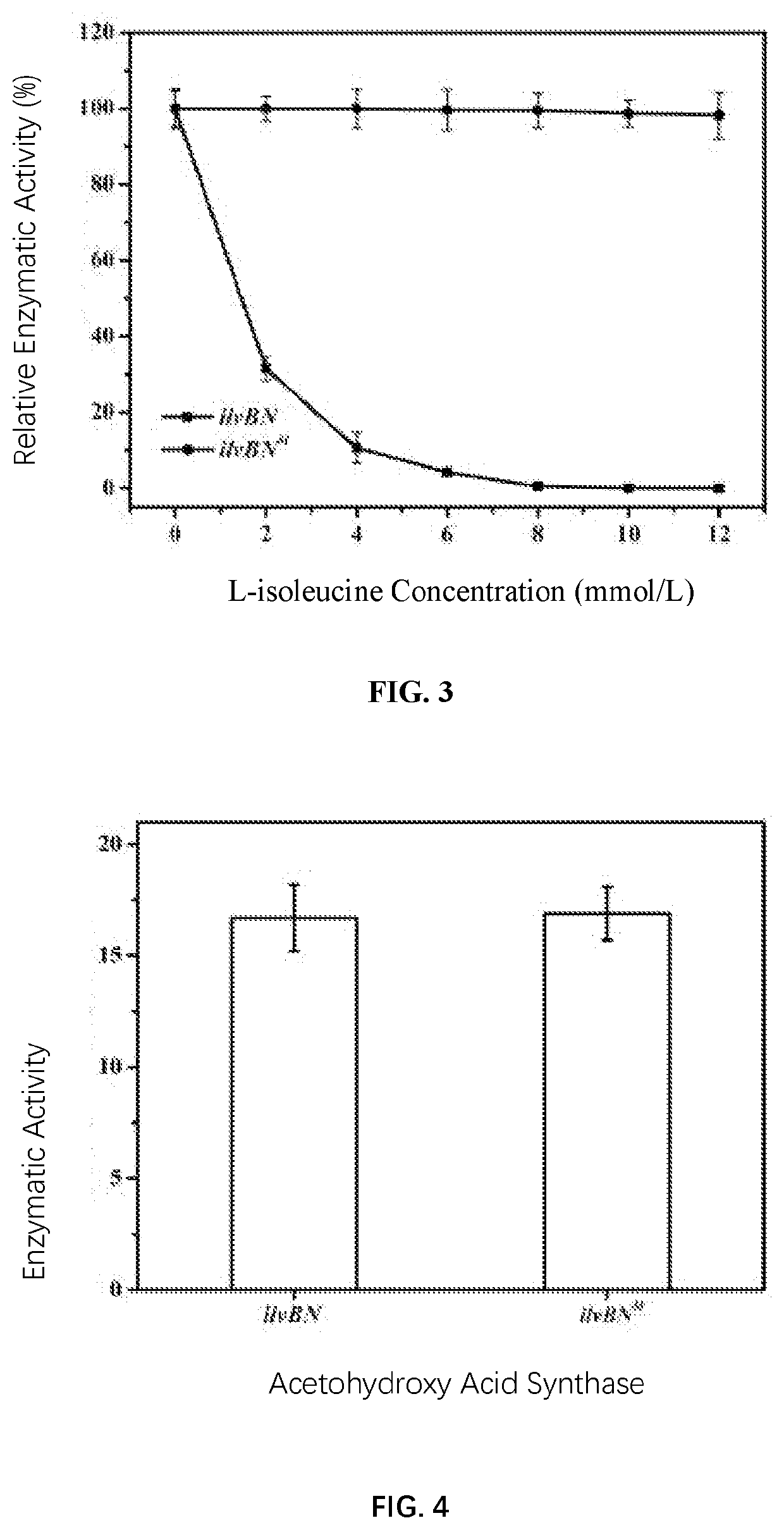
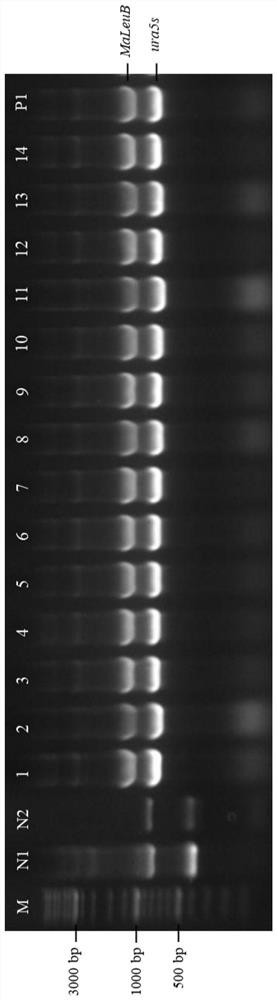
ActiveCN110551670BRelease feedback inhibitionNo significant change in activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesNutritional deficiencyAcetohydroxy Acid Synthetase
The invention relates to a genetic engineering bacterium for producing L-leucine, and application of the genetic engineering bacterium, and belongs to the field of metabolic engineering. The genetic engineering bacterium is obtained by an isopropylmalate synthetase encoding gene leuA[M] capable of relieving L-leucine feedback inhibition through overexpression in a host cell, an acetolactate synthase encoding gene ilvBN[M] capable of relieving L-leucine feedback inhibition, a 3-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase encoding gene leuB and a 3-isopropylmalate dehydratase encoding gene leuCD. Acetohydroxyacid synthase encoded by the leuA[M] relieves the feedback inhibition function of the L-leucine for the acetohydroxyacid synthase, in addition, the activity of the acetohydroxyacid synthase is not obviously lowered than wild leuA encoded isopropylmalate synthetase. The L-leucine genetic engineering bacterium does not have nutritional deficiencies, is quick in growth, and has a short fermentation period, a high yield and a high conversion rate. After fermentation is conducted for 40-44h, the concentration of the L-leucine in fermentation liquor achieves 60.5-69.6g / L.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Cordyceps sinensis 3-isopropyl malic dehydrogenase C, encoding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN104120113AEnhance expressive abilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesNucleotideIsopropylmalic acid
The invention provides 3-isopropyl malic dehydrogenase C which is extracted from cordyceps sinensis hirsutella sinensis and joins in biological catalysis on 3-isopropyl malic acid to prepare 4-methyl-2-oxo valeric acid, an encoding gene and application of 3-isopropyl malic dehydrogenase C. The amino acid sequence of 3-isopropyl malic dehydrogenase C is as shown in SEQ ID No.1, and the encoding gene is as shown in SEQ ID No.1; the clone DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) of the nucleotide sequence can be transferred into engineering bacteria by using methods of transduction, conversion and conjugal transfer, by adjusting the expression of the gene of 3-isopropyl malic dehydrogenase C, the host 3-isopropyl malic dehydrogenase C is high in expression property, an effective method is provided to expand the biological application of 3-isopropyl malic dehydrogenase C, and great application prospects are achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +2
Application of high content 2-isopropylmalic acid in authenticity evaluation of pine pollen
The invention relates to the field of food detection, particularly to application of high-content 2-isopropylmalic acid in pollen pini authenticity evaluation, and provides a pollen pini authenticityevaluation method, wherein 2-isopropylmalic acid is used as a characteristic compound, when the content of 2-isopropylmalic acid is 18-35 mg / kg, a sample can be judged as pollen pini, and otherwise, it is determined that the pollen is other pollen or adulterated pollen pini. The method provided by the invention is simple, efficient, high in stability and suitable for accurately determining the content of 2-isopropylmalic acid in pollen pini, is suitable for evaluating the authenticity and purity of the pollen pini, and has important practical significance for protecting legitimate rights and interests of consumers and maintaining healthy development of the pollen pini industry.
Owner:BEE RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Cordyceps sinensis 3-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase b, coding gene and its application
ActiveCN104120112BEnhance expressive abilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processes3-Isopropylmalate DehydrogenaseNucleotide
The invention provides 3-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase B for preparing 4-methyl-2-oxoglutaric acid from cordyceps sinensis Hirsutella sinensis and biologically catalyzed 3-isopropylmalate as well as encoding genes and an application thereof. The 3-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase B has an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID No.1, and the encoding genes are shown as SEQ ID No.1. Cloning DNA of a nucleotide sequence provided by the invention can be used for being transferred into engineering bacteria through transduction, transformation and combined transfer methods, the host 3-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase B is endowed with high expression by regulating the expression of the 3-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase B genes, an effective path is provided for widening biological application of the 3-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase B, and the 3-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase B has significant application prospects.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +1
An ntipmd gene affecting tobacco axillary bud differentiation
This application belongs to the field of tobacco genetic engineering, and specifically relates to a method that affects the differentiation of tobacco axillary buds. NTPMD Gene. The gene includes 1218bp bases, and the specific nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.1, wherein the 68th to 403rd nucleotides are specific nucleic acid fragments. The isopropylmalate dehydrogenase NtIPMD encoded by the gene is characterized in that the isopropylmalate dehydrogenase NtIPMD includes 405 amino acids. This application is aimed at NTPMD Preliminary research on the gene shows that the gene is related to the development of the axillary buds of the plant. After silencing the gene, it can promote the development of side branches. Using this characteristic, the gene can be silenced or overexpressed through gene silencing or overexpression technology, so as to realize molecular Horizontally, the adjustment of the plant type has an important impact on the cultivation of new tobacco varieties, so it has relatively important practical value.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC
A kind of recombinant bacteria with high lipopeptide production and its application
ActiveCN110331121BIncrease productionEasy to synthesizeBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEnzyme GeneActive agent
The invention discloses a recombinant strain with a high lipopeptide yield and application thereof, belonging to the technical field of genetic engineering. The recombinant strain is constructed by transforming a 2-isopropylmolic acid synthase gene in a leucine synthesis pathway into an original strain. Compared with the original strain, the recombinant strain which over-expresses a part of the leucine synthesis pathway (2-isopropylmolic acid synthase, 3-isopropylmolic acid dehydrogenase, 3-isopropylmolic acid dehydratase and branched chain amino acid transaminase) has a surfactin yield increased by 55.6%, can be used for production of lipopeptide type biosurfactants, and has a good industrial application prospect. The average lipopeptide yield in fermentation liquor obtained by shake flask fermentation is 13-16 g / L.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Beta-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase and application of beta-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase in lipid synthesis
ActiveCN110499300AImprove biosynthetic abilityOxidoreductasesFermentationFatty acid biosynthesisMicroorganism
The invention discloses beta-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase and application of the beta-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase in lipid synthesis, and belongs to the technical fields of gene engineering and microbial engineering. An amino acid sequence of the beta-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase is shown in SEQ ID No. 1, and the beta-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase has a function of promoting microorganism to produce fatty acids. Recombinant mortierella alpina containing the beta-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase is subjected to shake cultivation for 7 d, so that the fatty acid content in the mortierella alpinacontaining the beta-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase can reach 46.4% of dry cell weight, and is 20.2% higher than that of mortierella alpina without the beta-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase. According tothe beta-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase, through gene engineering, the fatty acid production ability of the mortierella alpine and other oil producing microorganisms is further improved, and solid theoretical support for improving the fatty acid biosynthesis ability is provided.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com