Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
203 results about "Infinite loop" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An infinite loop (or endless loop) is a sequence of instructions in a computer program which loops endlessly, either due to the loop having no terminating condition, having one that can never be met, or one that causes the loop to start over. In older operating systems with cooperative multitasking, infinite loops normally caused the entire system to become unresponsive. With the now-prevalent preemptive multitasking model, infinite loops usually cause the program to consume all available processor time, but can usually be terminated by the user. Busy wait loops are also sometimes called "infinite loops". Infinite loops are one possible cause for a computer "freezing"; others include thrashing, deadlock, and access violations.
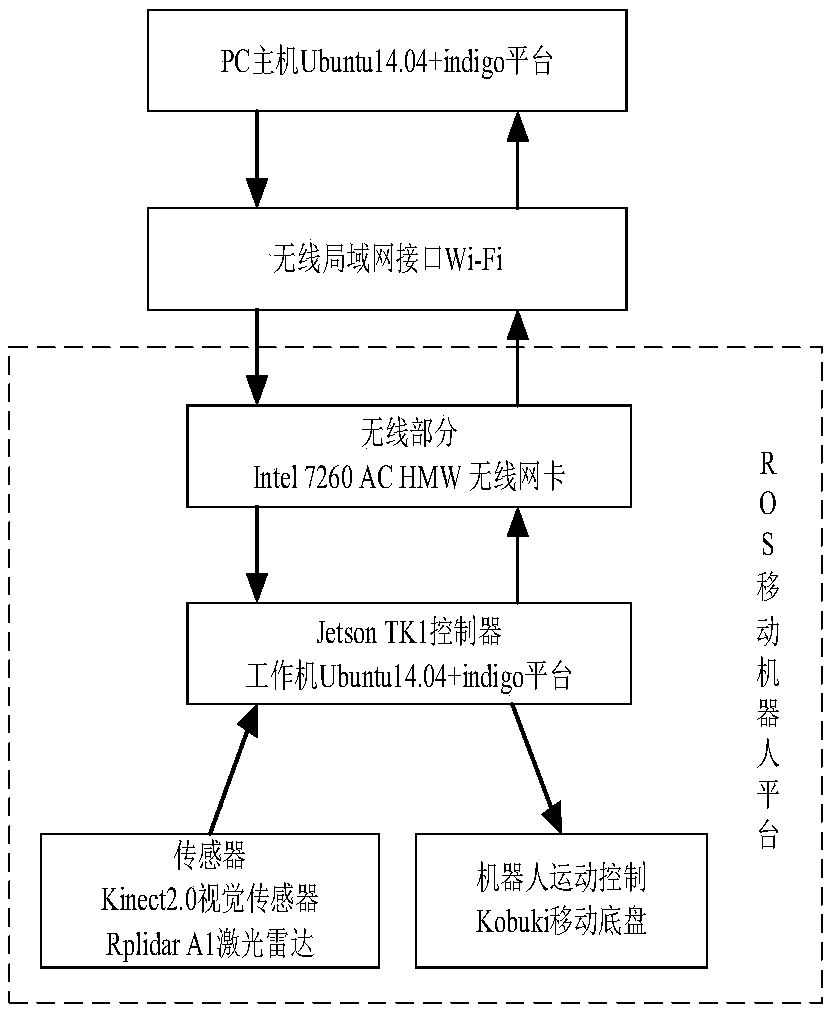
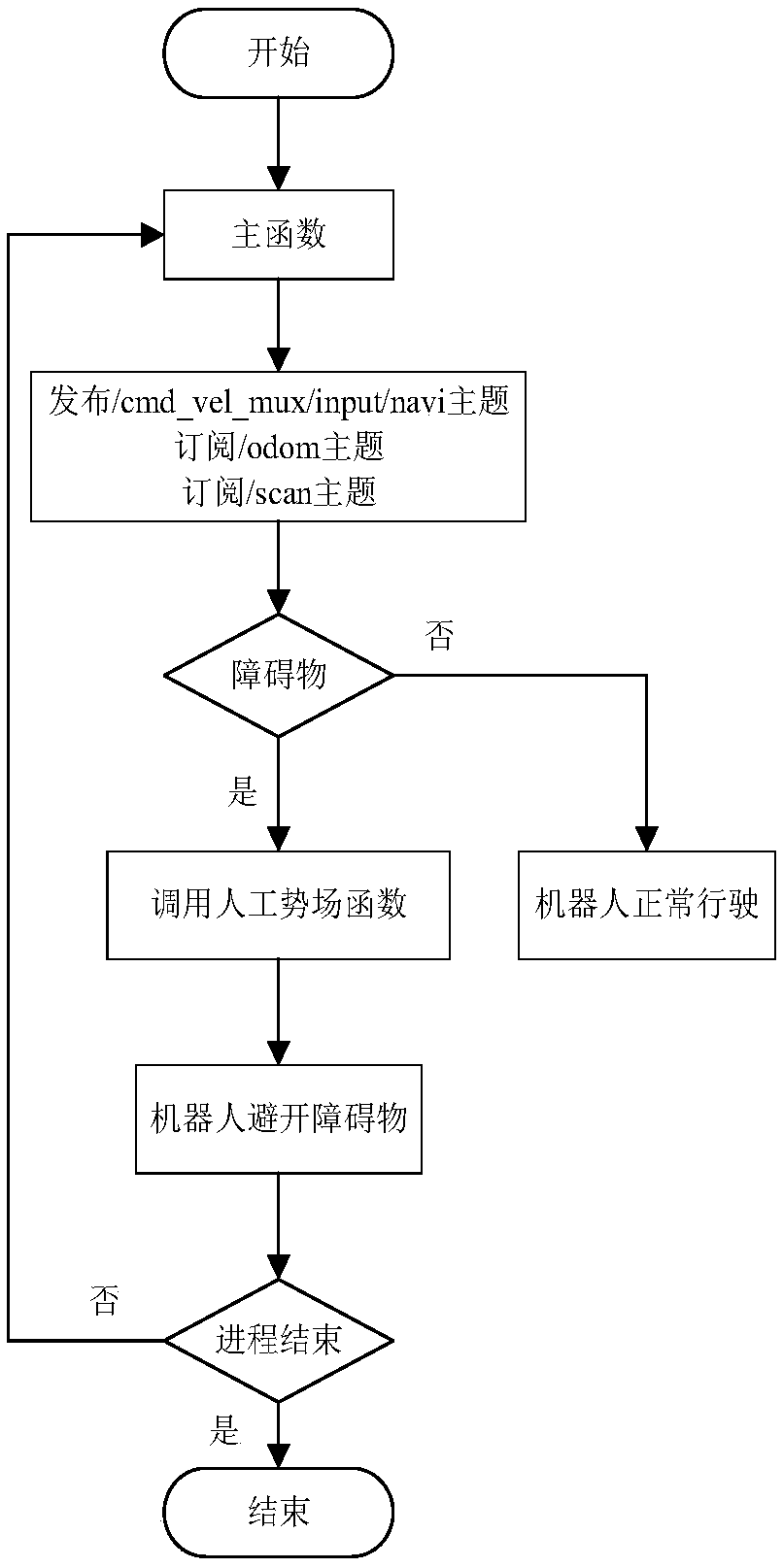
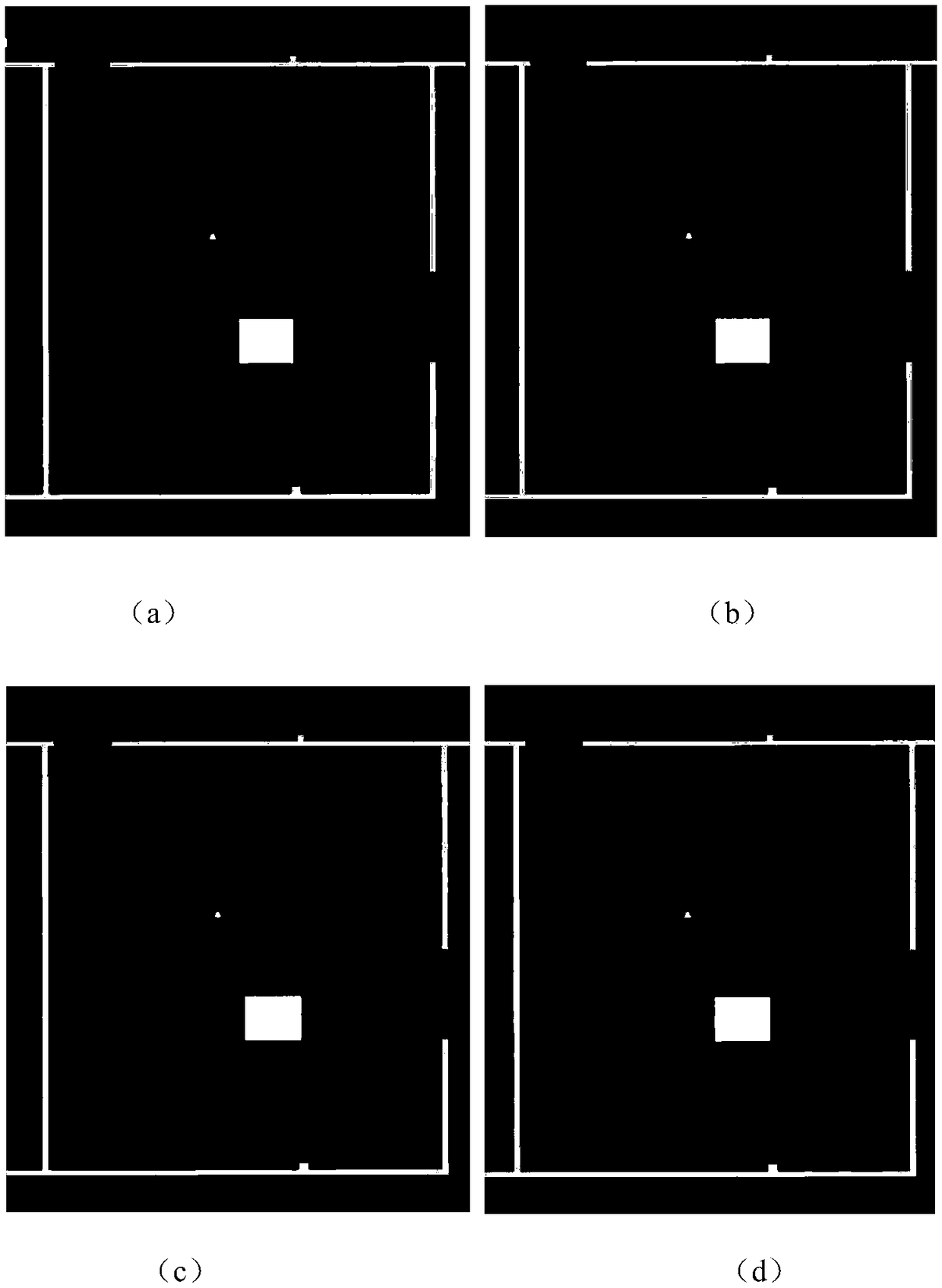
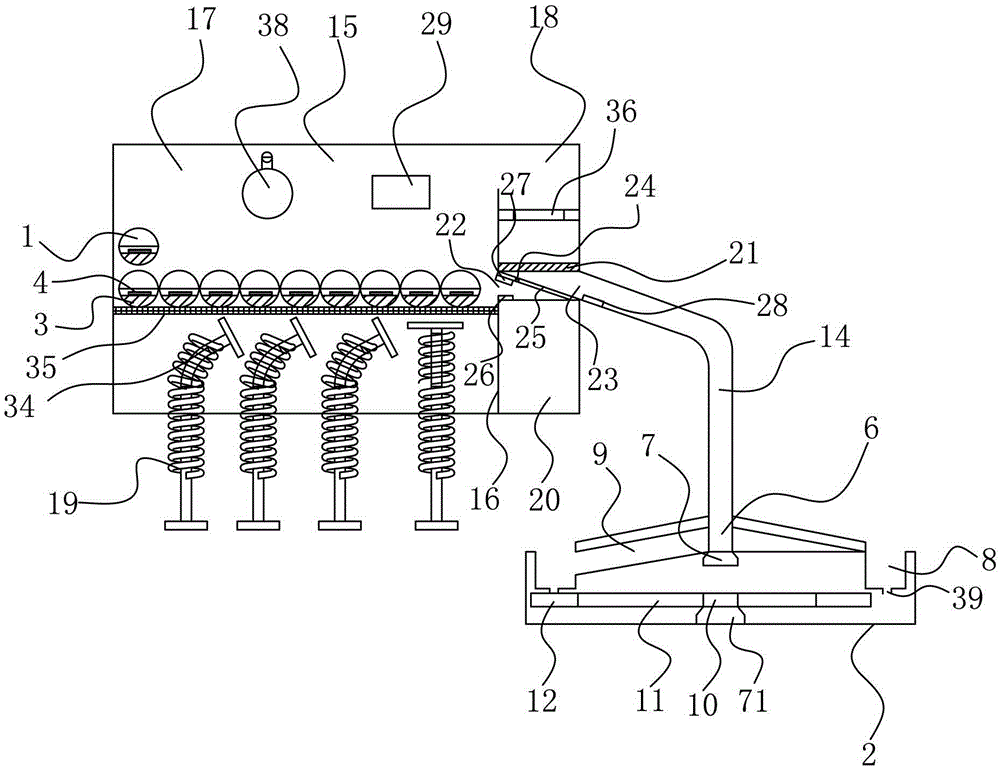
Robot indoor environment exploration,obstacle avoidance and target tracking method based on ROS
ActiveCN108646761AAvoid local exploration infinite loopReduce search timePosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesRadarObstacle avoidance
The invention provides a robot indoor environment exploration,obstacle avoidance and target tracking method based on a ROS. Based on a grid map established through laser radar information,combined with local map deduction and global boundary searching,an independent exploration strategy is designed so that a moving robot can be prevented from getting into a local exploration infinite loop,and whole-indoor-environment exploration can be completely guaranteed. According to the method,real-time tracking nodes and shielding tracking nodes are designed with an improved Kalman filtering method and aMeanShift method in the ROS,the real-time problem and the complete-shielding problem of target tracking of the moving robot are solved,the computing speed of the system is increased,target search time is shortened,and the real-time requirement of tracking is met; when a target is completely shielded,the shielding tracking nodes forecast and track the target according to previous state information,and after shielding is ended,a target is newly locked,tracking modes are automatically switched,and the target is tracked through the real-time tracking mode.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
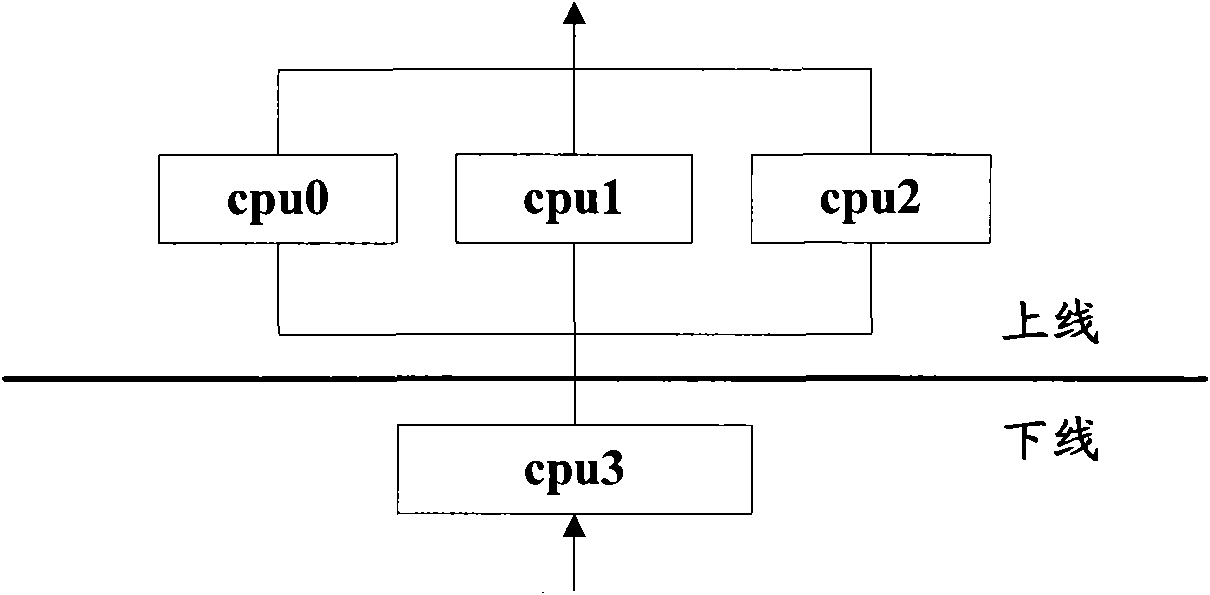
Method for building multi-core operating environment
ActiveCN101770401ARealize comprehensive utilizationEfficient wayResource allocationData switching networksData streamMulticore architecture
The invention provides a method for a building multi-core operating environment, which is characterized in that: a plurality of pieces of cpu are divided into two groups in advance, wherein one group is on-line cpu which operates a standard Linux operating system for checking message content, and the other group is an off-line cpu for operating a specified target code; when all cpu relevant resource finishes initializing, parts of on-line cpu become the off-line cpu; the off-line cpu operates one endless loop function cpu_idle so as to embed the code inlet function of a specified target into the endless loop function cpu_idle; the off-line cpu operates the specified target code to classify and distribute received network message to the corresponding on-line cpu according to data flow. Theinvention can solve the problem that cpu cost sharp increases along with the increase of cpu amount under the Linux environment and provides a new efficient path for multi-core framework development.
Owner:BEIJING TOPSEC NETWORK SECURITY TECH
Method and device for detecting and processing system faults
InactiveCN104102572ARealize automatic fault detectionFault responseHardware monitoringSoftware systemSelf recovery
The invention discloses a method and a device for detecting and processing system faults. The method comprises the following steps: sending a first-grade dog feeding signal by an interrupt service routine and receiving a second-grade dog feeding signal of a system detection task; when detecting a task endless loop or task exception, carrying out system exception handling according to a pre-set processing strategy; when the interrupt service routine cannot receive the second-grade dog feeding signal in pre-set time, stopping feeding the first-grade dog feeding signal by the interrupt service routine and restarting the system. According to the method and the device, automatic detection of faults of a software system can be realized and the system is automatically recovered according to a user strategy; the system exception of a system starting process and a system operation process can be detected simultaneously and is automatically recovered; exception types in an operation process of the system can be identified by classifying, and the exception judgment and self recovery can be carried out according to the user strategy; system exception detection and self-recovery strategies can be configured by a user; exception reasons can be recorded and can be inquired.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Beamcast (continuous infrared data beaming system)
InactiveUS20020181060A1Effectively achieves one-touch wireless synchronizationEfficient implementationElectromagnetic transmissionLight beamBrief periods
A Continuous Data Beaming System that is capable of continuously and automatically beaming data by direct transmission from one Host Device (source device or "beaming station") to another Remote Device (receiver device) every time the receiver needs the data. The Host Device constantly searches to find an IrOBEX compliant Remote Device, checks availability for an infrared connection, completes the connection to the Remote Device and transfers a data object through the respective infrared ports. If a failure occurs during any of the foregoing steps, the program automatically returns to searching. This progresses in an infinite loop, thereby accomplishing continuous, wireless, infrared data transmission. During the continuous transmission, no Remote Device other than BeamMaster can interrupt the continuous beaming. The BeamMaster Device allows the system to halt for a brief period, thirty seconds or less, so that files or data objects may be swapped. Continuous beaming resumes once the files are swapped or the time has expired. The Host Device automatically transmits data to the receiver device every time a receiver shows up and needs the data, thereby effectively achieving one-touch wireless synchronization.
Owner:HUANG CHIANG LUNG
English word memorizing turntable
The invention relates to an English word memorizing turntable which effectively settles a problem of no interest in studying English. The technical solution of the English word memorizing turntable is characterized in that the English word memorizing turntable comprises a word ball and a turntable; the center of the turntable is a chamber housing; the inner part of the chamber housing is connected with a ball serving housing through bent pipeline; the inner space of the ball serving housing is divided into a ball serving chamber and a screening chamber; and the ball serving chamber is internally provided with a plurality of uniformly arranged extension springs. The English word memorizing turntable has an ingenious structure and can realize random falling of English words. Furthermore in each English word selection, random selection is realized, thereby preventing infinite loop of some words. Furthermore in English studying, a child can participate in, and playing amusement is improved.
Owner:陈建宝
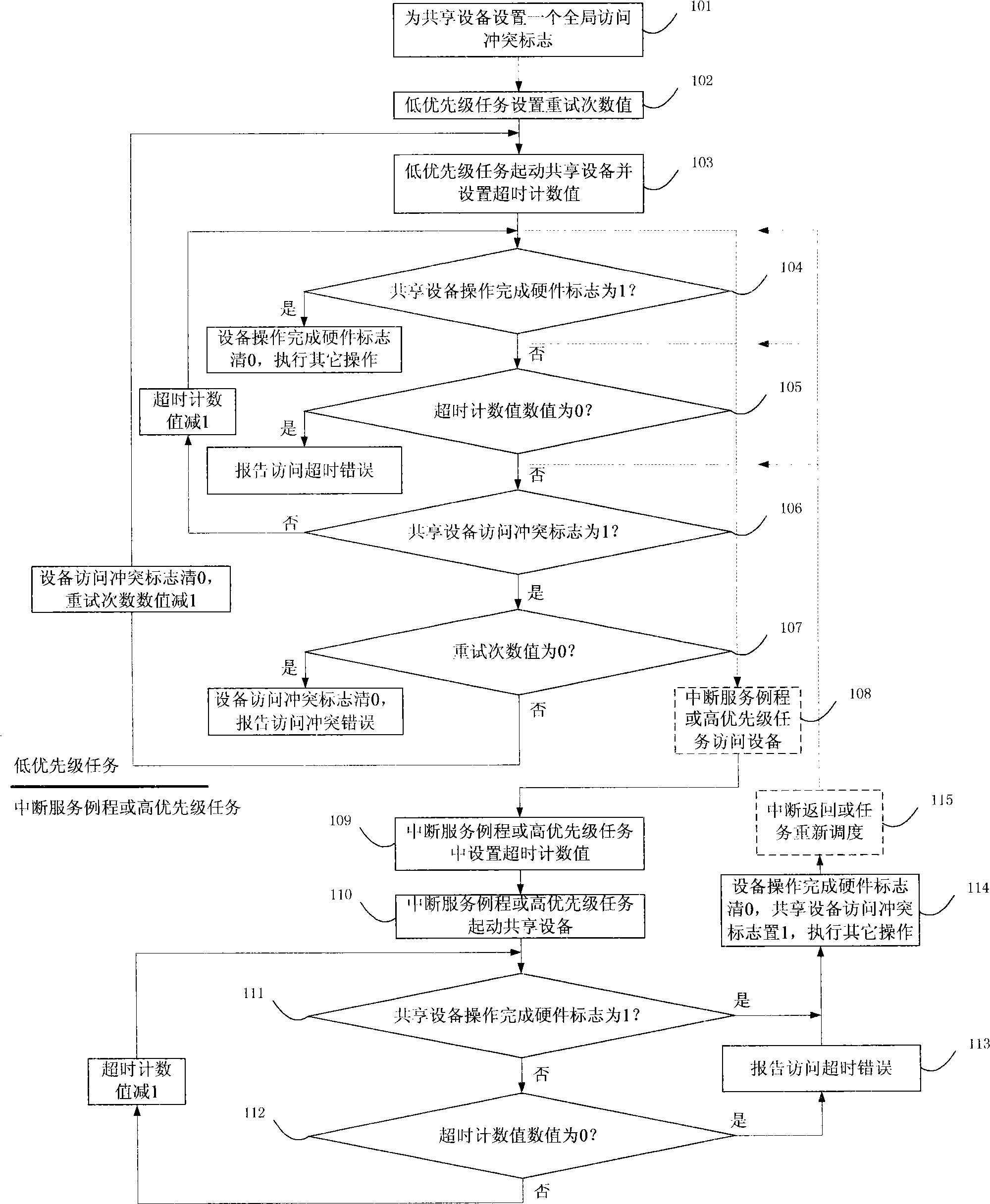
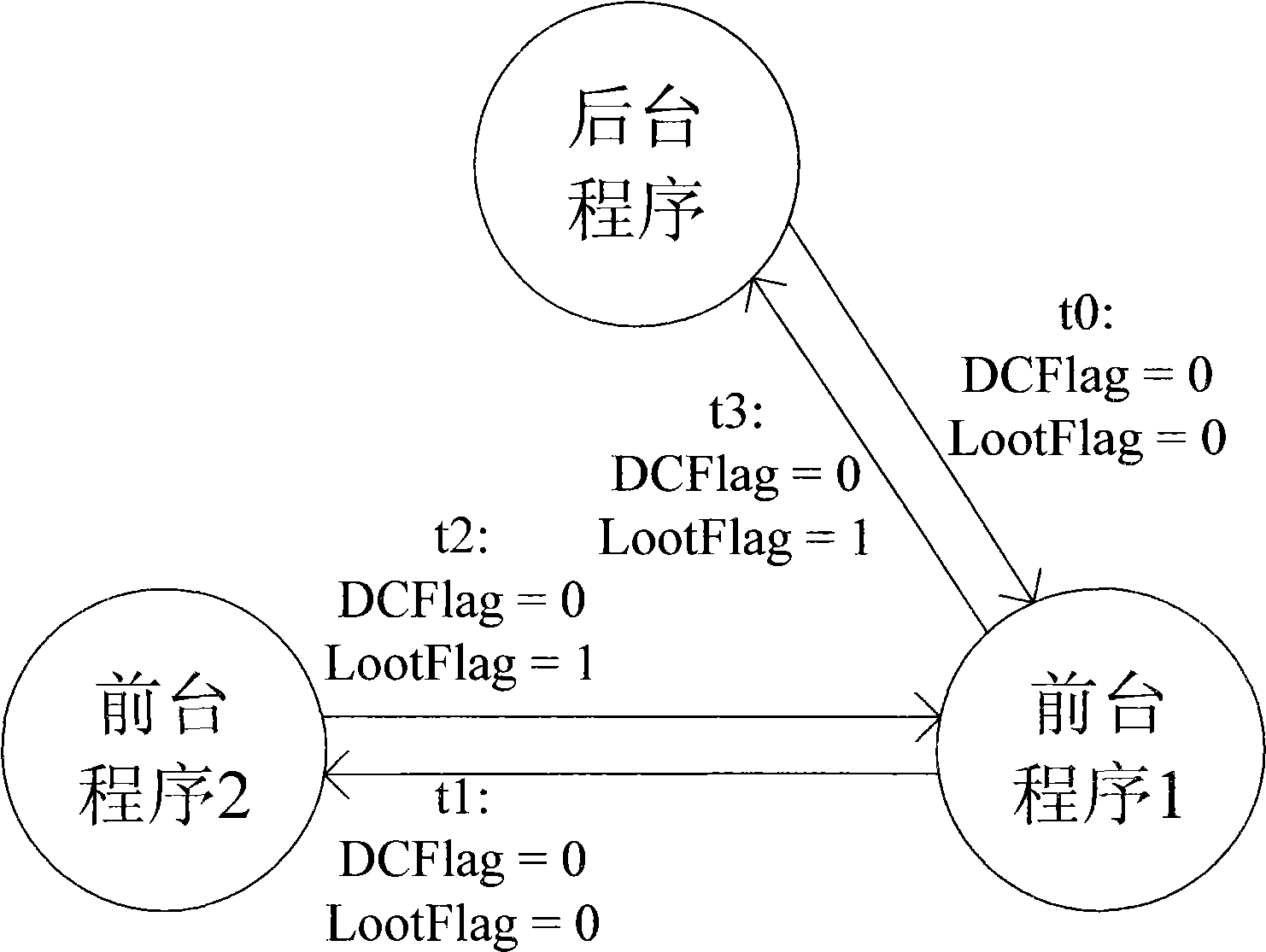
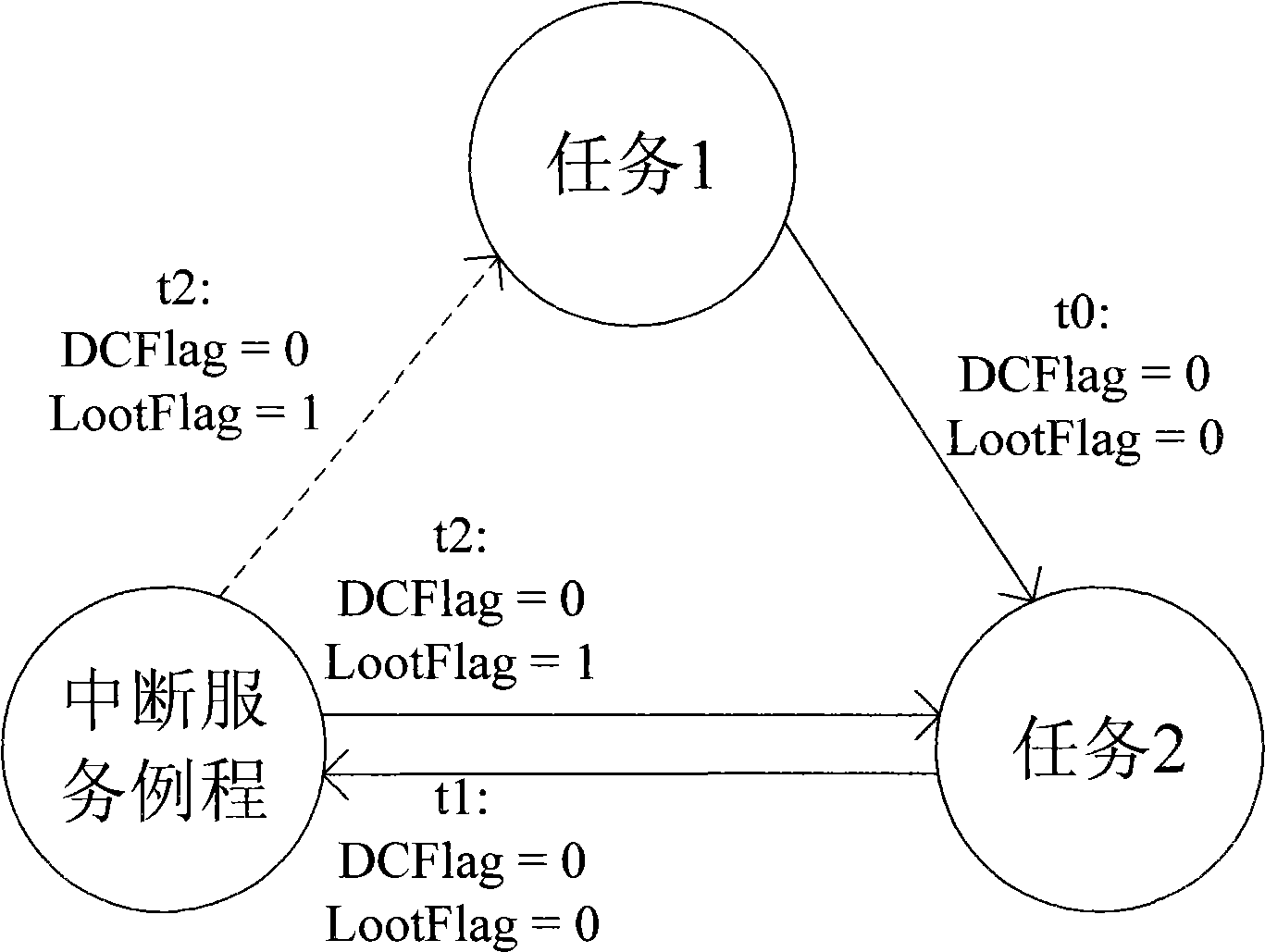
Method for preventing abnormal deadlock of main unit during access to shared devices
InactiveCN101499041ASolve the problem of task deadlockSolve the deadlock problemMultiprogramming arrangementsComputer architectureDeadlock
The invention discloses a method to avoid abnormal deadlock of a host computer in accessing shared device. The host computer sets an access conflict mark for the shared devices. When the low priority task accesses the shared device, and requires whether operation achieving mark of the shared devices is set as 1 in a circular manner, the host computer interrupts a service routine or a high priority task interrupts the lower one and accesses the shared devices, and requires whether operation achieving mark of the shared devices is set as 1, the host computer cleans the mark as 0 and sets the access conflict mark as 1. Along interruption returns or task re-transfer, the low priority task is executed continuously, and detects the operation achieving mark that is 0, the access conflict mark that is 1, the host computer escapes circular requirement (or the task enters deal circle, causing deadlock), re-accesses the shared devices. The technical solution of the invention can avoid the deadlock. Because of simple and reliable method, the invention is in particular applied to the embedded system field with a low-performance processor and inadequate memory resources.
Owner:CHENGDU SUPERXON COMM TECH CO LTD
Method for detecting task endless loop in operating system and operating system
ActiveCN101853191AComprehensive detectionEfficient detectionError detection/correctionOperational systemEngineering
The invention provides a more comprehensive method for detecting task endless loop in an operating system and an operating system for realizing the method. Different from the existing endless loop detection method which compares the continuous running time of a task with a threshold value to judge whether an endless loop exists, the method of the invention compares the accumulated length of time of ready mode with a threshold value to judge whether an endless loop exists. The invention is based on the theory that in the priority-based preemptive operating system, when a task performs an endless loop and does not quit the CPU actively, the task is always in the ready mode in any conditions. By counting the accumulated length of time of the ready mode of one task to judge the endless loop, the omission of the endless loop which quits the CPU passively can be avoided.
Owner:MAIPU COMM TECH CO LTD
Method for detecting task closed loop of multi-task operating system
ActiveCN101561778AImprove utilizationEasy to implementSoftware testing/debuggingOccupancy rateOperational system
The invention discloses a method for detecting task closed loop of a multi-task operating system, comprising the following steps: embedding piling code in task inlet function loop bodies, and measuring whether the task is in closed loop state accurately in real time by determining the piling value of the monitored task, the task operation state and the total CPU occupancy factor in the monitoringtask of high priority. The invention is accurate, reliable and efficient and is easy to realize by embedding the piling code in the loop body inlet of the task to be monitored; if the system counts the CPU occupancy rate through the monitoring task of high priority, the piling code determining the closed loop can be added to the monitoring task for counting the CPU occupancy rate, thereby greatlyutilizing the system resources; the piling code can be defined as macro which is embedded at the inlet of the task loop body, thus the invention can be realized flexibly.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Method and apparatus for multi-versioning loops to facilitate modulo scheduling
ActiveUS6993757B2Easy to optimizeFacilitate modulo schedulingSoftware engineeringProgram controlSystems analysisParallel computing
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that facilitates multi-versioning loops to facilitate modulo scheduling. Upon receiving a computer program, the system analyzes the code to locate loops within the program. When a loop is located, the system examines the loop termination condition to determine if it is based on a “not-equal-to” condition that makes it hard to determine beforehand whether the loop will terminate. If the loop termination condition is based on a “not-equal-to” condition, the system creates multiple versions of the loop, at least one of which will terminate and can be modulo scheduled, and at least one of which might be an infinite loop and consequently cannot be modulo scheduled.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
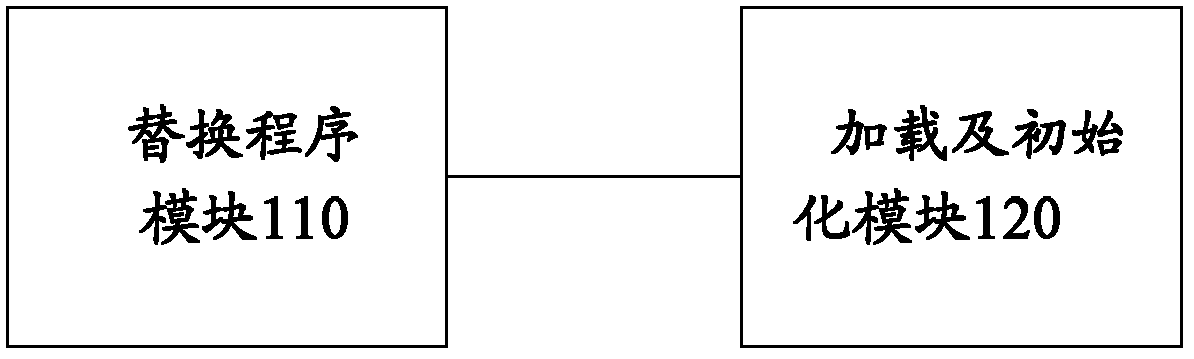
Method and device for dynamically substituting C/C + + function in main program
ActiveCN103294457AImprove efficiencyAvoid endless loopsSpecific program execution arrangementsMemory systemsSubstitution instructionSoftware engineering
The invention provides a method and a device for dynamically substituting a C / C + + function in a main program. The method includes steps as follows: the main program is started, and a substitution program module used for inquiring and modifying a memory is loaded; the loaded substitution program module is initialized, so that the substitution program module is executed in advance of a main function in the main program; symbol table information of a function in the main program is stored in the memory; after the substitution program module receives a substitution instruction, the substitution program module determines a mapping address of a substituted function in the memory according to symbol table information corresponding to the substituted function; and the substituted function is substituted according to the mapping address. The method and the device can dynamically substitute and restore the function during operation of the program, the program is not required to be recompiled, time is saved, high efficiency is realized, and the infinite loop phenomenon when the substituted function is indirectly called inside a substitution function is avoided.
Owner:BAIDU ONLINE NETWORK TECH (BEIJIBG) CO LTD
Multicast randomizing routing method based on virtual Stener tree
InactiveCN101175042AHigh precisionHigh speedSpecial service provision for substationHigh level techniquesRemote controlSensor node
The present invention provides a multicast randomized routing method based on virtual stettner tree and relates to the multicast transmission of radio sensor network data. The present invention adopts a multicast route started by the source and driven by the requirement and introduces probability routing method in the process of choosing route; in this way, the infinite loop of algorithm can be effectively avoided; the node with the maximum probability is chosen as the next hop to ensure a robust route, which guarantees the smooth route and the smooth transmission of data and at the same time greatly prolongs the lifecycle of the network. The present invention is characterized by effective data transmission and long network lifecycle and is especially fit for dangerous environment where people are hard to enter; once the sensor nodes are configurated through a certain measure, the energy replacement in the pattern of battery or other patterns can not be realized and people can only implement the remote control at the base station or management center.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Method and system for checking tasks endless loop
InactiveCN101158913AAvoid the situation of dead loop missing detectionMultiprogramming arrangementsClosed loopComputer science
The invention discloses a method for detection task closed loop, which comprises: in a system of a priority level-based task dispatch strategy, a closed loop detection task with the least priority level shall be preset; when the system clock is interrupted, detect whether the duration of the closed loop detection task for non-operation is greater than the preset threshold value, so as to decide that the task closed loop occurs in the system. The invention also discloses a system detecting the task closed loop. The invention ensures that in the system of the priority level-based dispatch strategy, the situation of missed detection on the low priority level task closed loop won't happen, and the detection of the task closed loop doesn't rely on the task dispatch strategy of the system.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method and device for detecting multi-core CPU
The invention discloses a method and device for detecting a multi-core CPU. The device comprises a monitoring module for monitoring usage rate of each core of the multi-core CPU and running time of each thread in the core; a detection module for detecting the core and thread in fault in the multi-core CPU according to the usage rate of each core of the multi-core CPU and running time of each thread in the core. Through the adoption of the method disclosed by the invention, each core in the multi-core CPU can be independently monitored so as to reflect the real usage condition of each core. In addition, the method comprises the steps of periodically scanning a thread stack of a server and analyzing a thread stack log to detect whether the thread with long running time exists, and then judging the running state of the multi-core CPU in combination with the usage condition of each core. Through the adoption of the method, the fault similar to endless loop in the multi-core CPU can be immediately and fast discovered, thereby immediately notifying a worker to solve the fault problem.
Owner:NUBIA TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
STP link layer state machine optimization method
ActiveCN112559407AImprove the operating mechanismSolve the infinite loop problemElectric digital data processingControl engineeringLink layer
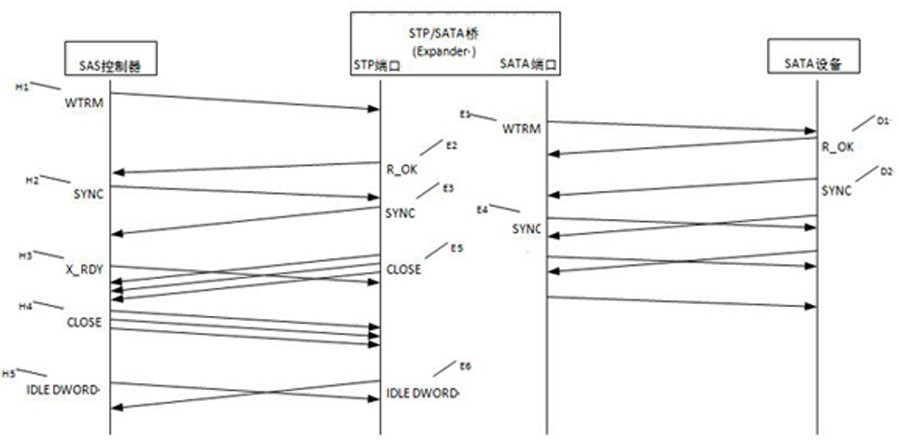
The invention provides an STP link layer state machine optimization method, which comprises the steps of detecting whether an STP link layer state machine is in an HL_SendChkRdy state or not, if the STP link layer state machine is in the HL_SendChkRdy state, determining whether a conflict event occurs in the STP link layer or not, and when the conflict event occurs, migrating the STP link layer state machine to an L_SyncEscape state, and executing state machine skip and subsequent service processing in the L_SyncEscape state. According to the invention, the operation mechanism of the link layer state machine is improved, the endless loop problem of the link layer state machine in the STP scene is solved, and the support of the SATA link layer to the STP scene is perfected.
Owner:无锡众星微系统技术有限公司
System and method for long-time acquisition and playback of multi-specification 10Gbps network signals
PendingCN107995061AStorage real time continuousRealize acquisitionInput/output to record carriersData switching networksTimestampWire speed
The invention discloses a system and method for long-time acquisition and playback of multi-specification 10Gbps network signals, relating to the technical field of high-speed network signal acquisition and playback. The system and method can simultaneously achieve the acquisition and playback of high-speed network signals with various specifications such as 10Gbps Ethernet and 10Gbps SDH, and cansolve the previous single-specification signal acquisition and playback mode. At the same time, by adopting a high-speed large-capacity high-performance SSD memory disc and a multi-threading technology, the system can achieve long-time line speed acquisition and playback of 10Gbps network signals, and the acquired signals can be continuously stored in real time. In addition, the system provides afunction of playing back the signals according to the line speed and a timestamp or in a constant-speed mode, can also specify the number of data playback times, ensures that a default playback modeis an infinite loop playback mode, and further provides various methods for data signal analysis.
Owner:北京卓讯科信技术有限公司
Computer encryption unit and encryption method
Based on chaos principle about sensitive dependence to initial value, infinite looped key stream is generated providing very high security. Length of cryptographic key is variable, could be any length theoretically (recommend 64-4096). Initial process makes subtle change of cryptographic key lead to non-correlative cryptographs. The random number agitation method in the invention adds random unpredictable information into encrypting process. Thus, even plaintext is same, but the cryptographs are different in each time. Thus, it is not possible to attack and explain the cryptograph. Moreover, the time for the method is not dependent to length of the cryptographic key. Thus, the speed is higher than other methods with same intension. The invention is suitable to various platforms. Wide application prospects are used in Internet and handphone.
Owner:杨斌 +2
Method for testing closed loop or similar closed loop task
InactiveCN1811730ASave resourcesPrecise positioningSoftware testing/debuggingComputer architectureOperational system
An infinite loop or infinite loop like task detection method refers to computer operation system field, especially infinite loop task detecting and processing technology. Present invention overcomes problem of more system resources wasting in current infinite loop or infinite loop like technical detection, determining infinite loop or infinite loop like task and calling system task storehouse accuracy positioning infinite loop position through generating system highest priority infinite loop monitoring task and system lowest priority infinite loop test task. In priority occupying type operation system, present invention only uses two simple tasks effectively detecting infinite loop or infinite loop like task without utilizing system clock interruption handling and task switching processing, to judge whether infinite loop or infinite loop like occurred, having small process frequency and saving CPU resource.
Owner:BEIJING MAIPU HUAXIN INFORMATION TECH
Method and system for verifying business process
InactiveCN102591641AMeet needsSpecific program execution arrangementsSoftware engineeringNetwork model
The invention discloses a method and a system for verifying a business flow. The method includes mapping an original business process in a BPMN (business process modeling notation) model to a Petri network model according to mapping strategy and forming a mapped business process; and verifying the mapped business process to judge whether the original business process is erroneous or not. The method and the system for verifying the business process have the advantages that the business process is mapped to the Petri network model to be verified, the problem that whether the original business process in the BPMN model can be deadly locked or be in infinite loop or not can be verified, accordingly, staff can find out the problem in time to adjust the original business process, and actual needs are met.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Parallel construction method limiting Delaunay triangulation network
InactiveCN106485766AImplement the buildImplement embeddingDrawing from basic elementsParallel programming modelOperand
The invention discloses a parallel construction method limiting a Delaunay triangulation network. Work in aspects including construction of the Delaunay triangulation network, embedding of constraint conditions and parallel calculation of constraint embedding is carried out. The Delaunay triangulation network is constructed via a pointwise insertion method, construction of a convex hull uses a Graham scanning method, constraint embedding uses a method in which a polygon is subdivided into parts, a possible endless loop of an edge switching algorithm is avoided, a constraint embedded non-common influence domain is parallelized in parallel calculating, and time of constraint embedding is shortened greatly. Parallel programming needs to be combined with practical conditions to realize parallel calculating in serial codes which are large in data bulk and operand and can be parallelized, the system cost for developing multiple threads is much lower than benefit from improvement of parallel calculating due to proper task decomposition, effective data conflict processing and correct selection of parallel strategies, and advantages of parallel calculating are made obvious.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Real-time interrupt processing method for Linux system
ActiveCN103389913AImprove real-time performanceMeet the precision requirementsProgram initiation/switchingSoftware engineeringEmbedded operating system
The invention relates to a real-time interrupt processing method for a Linux system. The method comprises the following steps of assigning FPGA (field programmable gate array) external interruption related to business as hardware interruption, and adopting other interruption of the Linux system as software interruption; changing an actuation environment of a software interruption processing program from an interruption context to a progress context, and defining the actuation environment of a hardware interruption processing program as the interruption context; changing other user space process except the user space business program in the Linux system to a non-real-time process, changing the corresponding process of the user space business program and the corresponding process of the software interruption processing program to real-time processes, wherein the real-time process is prior to the non-real-time process; in the real-time process, the corresponding process of the user space business program is prior to the corresponding process of the software interruption processing program. Due to the adoption of the method, the interrupt delay and business delay problems can be solved, the scheduling delay problem is solved through an infinite loop method and a space scheduling method, and the real-time property of the Linux system which is used as an embedded operating system can be improved.
Owner:WUHAN POST & TELECOMM RES INST CO LTD
Small fixed-wing UAV attitude control method based on H infinite loop forming algorithm
PendingCN110377043AHigh steady state accuracyImprove dynamic performanceAttitude controlIntegratorLow-pass filter
The invention discloses a small fixed-wing UAV attitude control method based on an H infinite loop forming algorithm. A fixed-wing UAV attitude controller is designed by combining related knowledge ofthe classical control theory and the modern control theory. A control loop includes a PID controller, a low pass filter, an anti-integrator saturator, and an H infinite controller. The PID controlleris arranged at a forward channel to increase the low frequency gain of the system and reduce the steady state error. The low pass filter is applied to a feedback channel and is mainly used for suppressing high frequency noises in UAV sensor data. The anti-integrator saturator is used for preventing the flight performance from being affected by output saturation of the steering engine. The H infinite controller is used for improving the attitude control robustness of the UAV. Therefore, the fixed-wing UAV can keep the high robustness in a complicated environment or on the condition of changingparameters of the UAV; and the error of command tracking is reduced and the control accuracy is enhanced.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Elastic Key-Value pair data storage method based on RDMA and HTM
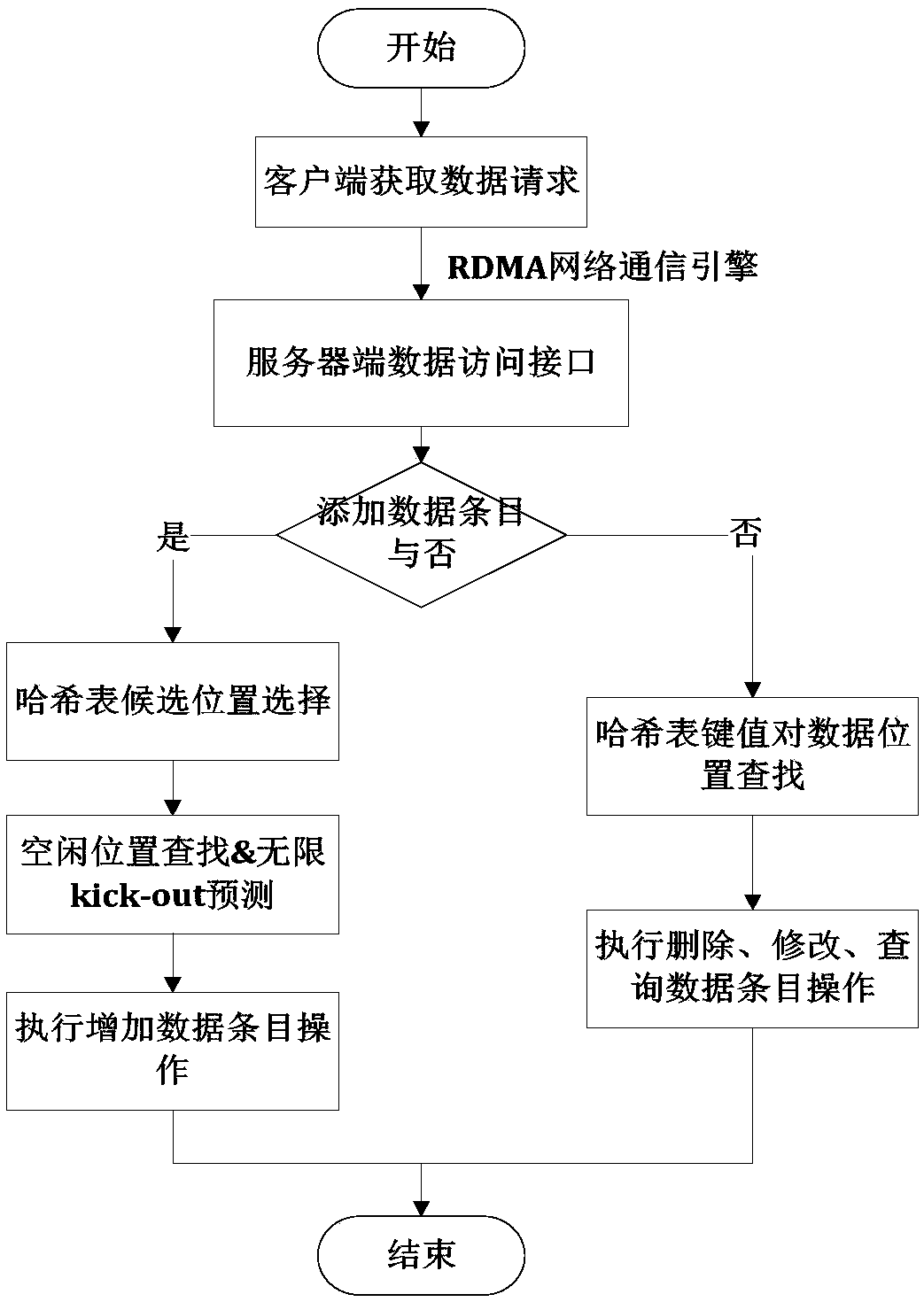
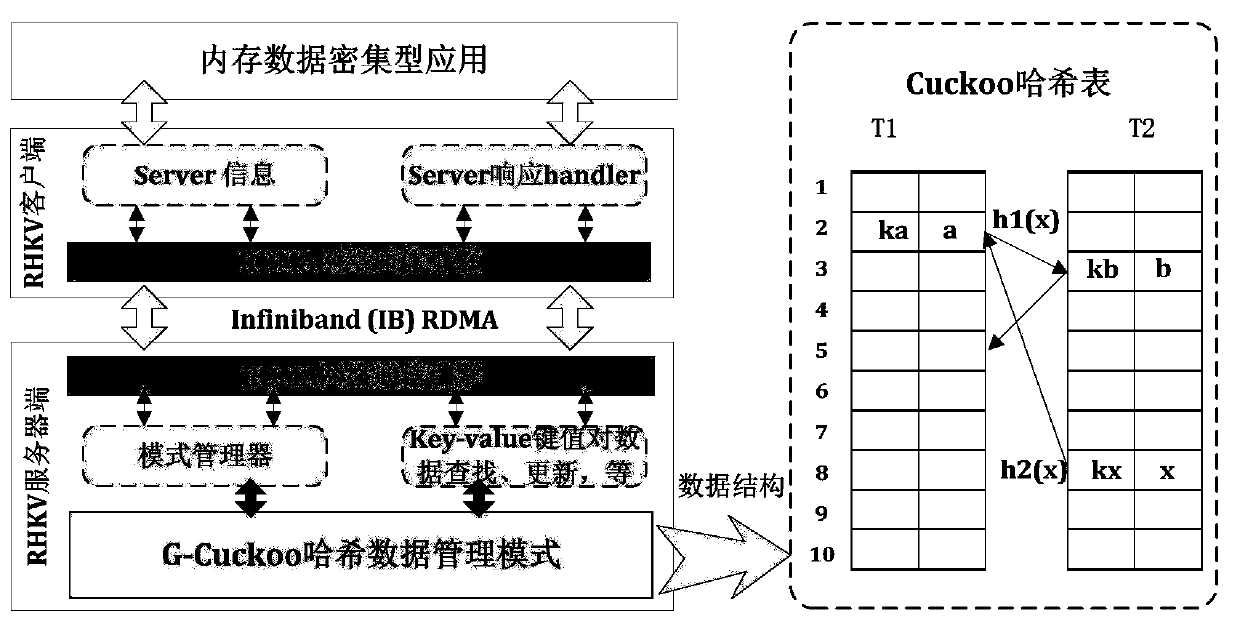
ActiveCN110069431AAlleviate the infinite loop problemImprove throughputTransmissionSpecial data processing applicationsPaired DataPrimitive operation
The invention provides an elastic Key-Value pair data storage method based on RDMA (Remote Direct Memory Access) and HTM (High Temperature Modulation). A server-client architecture mode is designed and followed, and the method comprises the steps that at a server side, an improved G-Cuckoo Hash data management mode is given in combination with a Hashmap; the kick-out infinite loop between Hash tables caused by searching for idle positions in the data insertion process is avoided. the bottleneck problem of key value pair storage performance caused by round response required by the traditional network message transmission between the client and the server is analyzed; an Infiniband remote direct memory access RDMA technology is used, an RDMA network communication engine is designed, a data access request is received, and a data request result is sent back; a hardware transaction memory HTM technology is utilized to realize a two-section lock protocol lock operation and ensure the atomiccharacteristics of data operation; and a key value is used for self-verifying the check code of the data to guarantee data consistency. The basic operation speed of the key value on the data can be greatly improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Screen Printing Device with Infinite Loop Stencil
A screen printing device is disclosed. The screen printing device includes a screen printer workstation having a work path. The work path has an input end, an output end, and a conveyor for transporting a workpiece between the input end and the output end. A stencil assembly is adapted to engage the workpiece as the workpiece is transported between the input end and the output end. The stencil assembly includes a stencil having an endless loop. A method of applying a substance to a workpiece using an endless loop stencil is also disclosed.
Owner:MONCAVAGE CHARLES
Infinite loop or similar infinite loop detection method in multitask system
ActiveCN102622300AReduce consumptionEasy to troubleshootSoftware testing/debuggingPresent momentOperational system
The invention relates to a computer technology. The invention solves the problems that too many system processor resources are consumed, and the detection process is complex in the conventional infinite loop or similar infinite loop detection task, and provides an infinite loop or similar infinite loop detecting method in a multitask system. The technical scheme comprises the steps of: firstly generating a highest priority infinite loop monitoring task and a lowest priority infinite loop detection task, wherein the infinite loop detection task runs and records the present moment after sleeping for a period of time, and the infinite loop monitoring task runs and detects whether the system is in the infinite loop or similar infinite loop after sleeping for a period of time, if so, the infinite loop task or similar infinite loop task is positioned and hung; then positioning and debugging the hung infinite loop task or similar infinite loop task by the system, recording information and performing subsequent treatment; and finally releasing the processed resources. The method has the advantages that the occupation rate of the processor resources is low, and the method is suitable for a preemptive priority type operation system cycled by non-time slice.
Owner:MAIPU COMM TECH CO LTD
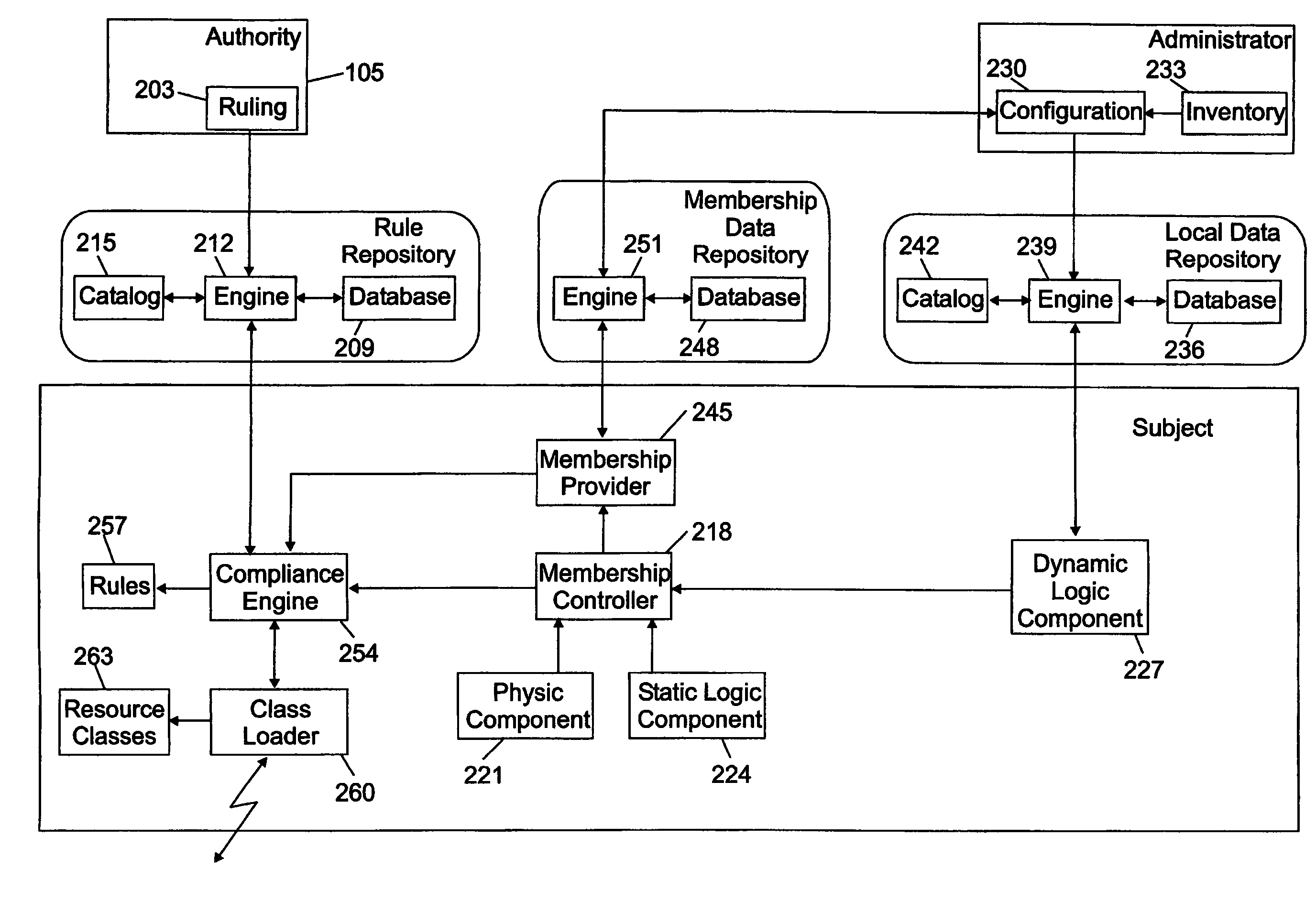
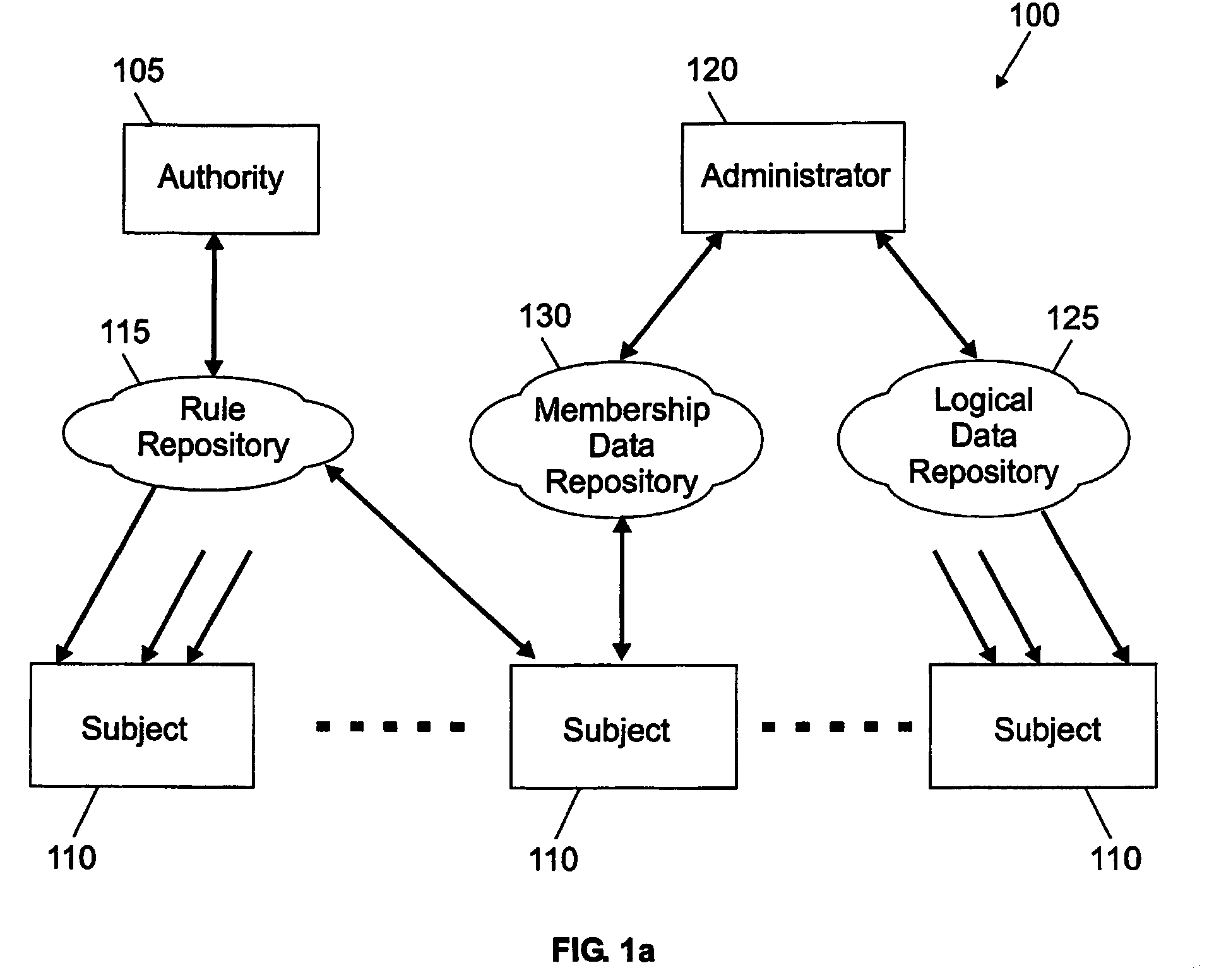
Adaptive management method and system with automatic dependency resolution
InactiveUS7228407B2Data processing applicationsDigital computer detailsAdaptive managementRandom order
A resource management method (300) and a corresponding system are proposed. In the solution of the invention, an authority publishes (324) multiple rules, each one defining a desired target configuration for a category of subjects (without any information about their dependencies). Each subject retrieves (320–322, 326) the rules corresponding to its category in a random order. The rules are then applied (427–439) on the subject according to a trial-and-fail approach. Particularly, the application of any failed rule is continually repeated (427–448), until all the rules are successfully applied (463) or a deadlock condition is detected (451). In this way, any dependency is automatically resolved on the subject at run time. Moreover, as soon as all the rules have been successfully applied the compliance of the subject to the rules is verified (455–457) again; should the subject be not compliant to one or more rules any longer, an infinite loop condition is detected (466).
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Multichannel robustness damping control method based on static state H-infinite loop shaping method
ActiveCN106602588AReduce orderGuaranteed accuracyElectric power transfer ac networkBand-pass filterReduced order
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF STATE GRID NINGXIA ELECTRIC POWER COMPANY +1
Data read/write device capable of reading SIM card
InactiveUS20070117587A1Burn out preventionSubstation equipmentSensing record carriersComputer scienceSubscriber identity module
A data read / write device capable of reading SIM (Subscriber Identity Module) card includes a SIM card slot, into which a SIM card is inserted and read; an internally provided SIM card connector for transmitting data of the SIM card inserted in the SIM card slot; a microprocessor for receiving and reading data of a SIM card transmitted from the SIM card connector, and a SIM card carrier detect (CD) pin provided between the SIM card connector and the microprocessor for detecting any SIM card in the SIM card slot. The SIM card CD pin is capable of informing the microprocessor to stop reading data of SIM card when the SIM card is withdrawn from the SIM card slot, so that the microprocessor is prevented from burning out due to faulty operation or falling into infinite loop of reading.
Owner:GOOD WAY TECH CO LTD
Serial attached SCSI broadcast primitive processor filtering for loop architectures
A method and system are provided for broadcast message filtering in SAS expanders. Common SAS topology defined by ANSI T10 specification only supports spanning tree topology (without loops) interconnection among multiple end devices and expander devices. Broadcast message filtering provides a mechanism to selectively discard broadcast messages, or primitives, in the SAS expanders to break the infinite loop path that broadcast primitives can traverse. This enables new SAS physical topologies with loops that are otherwise difficult or impossible to realize using SAS expanders that handle primitive broadcasts according to the definition of the SAS standard. By allowing redundant paths in a SAS topology, the problem of infinite broadcast flooding in SAS topology is reduced. Selectively forwarding broadcast messages can be based on whether the broadcast was originated at the source phy, or received by the source phy, or based on whether the source phy is a filtered phy.
Owner:MICROSEMI SOLUTIONS (US) INC
Method for reducing current consumption in a mobile communication terminal
InactiveUS6973584B2Total current dropExtend standby timeEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementMobile endCurrent consumption
A method for reducing current consumption of a mobile terminal is provided. The method includes setting a task as an initial idle task of the mobile terminal for performing a simple infinite loop in a state where all of the effective tasks performed by a program of the mobile terminal are blocked, counting global variable values of the idle task for a predetermined time according to a timer interrupt signal generated by the timer at regular intervals and storing the global variable values of the idle task as a reference value of an idle task of a program of the mobile terminal, resetting the counted value, measuring by counting the global variable values of the idle task where an effective task occupies the idle task for a predetermined time and storing the global variable values of the idle task as an idle value of the effective task according to a timer interrupt generated every predetermined time by the timer when the program of the mobile terminal performs the effective task, dividing the measured idle value of the effective task by the reference value of the idle task, to thus calculate a program idle rate of the mobile terminal, and storing the program idle rate, and changing a PLL value according to the program idle rate of the mobile terminal and varying a main clock frequency of a CPU of the mobile communication terminal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
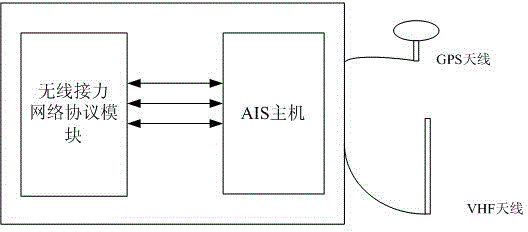
AIS-system-based wireless relay network implementing method
InactiveCN104579447AExpand the scope of monitoringImprove AIS monitoring effectMarine craft traffic controlRadio relay systemsWireless mesh networkNetworking protocol
The invention discloses an AIS-system-based wireless relay network implementing method. The AIS-system-based wireless relay network implementing method comprises the following steps: providing a shore-based AIS base station and wireless relay network ship-borne equipment, wherein the wireless relay network ship-borne equipment comprises a wireless relay network protocol module and an AIS mainframe; according to the shipping dynamic state of a ship in a shipping lane, actively sending an AIS message for monitoring the ship in the shipping lane and automatically forwarding AIS monitoring information of other ships by the wireless relay network ship-borne equipment; setting a forwarding frequency flag bit in a relay message by the wireless relay network protocol module so as to prevent two pieces of equipment from entering an infinite loop state in which the two pieces of equipment repeatedly forward the relay message of the opposite side mutually; periodically broadcasting a coverage identifying message of the AIS base station outwards by the shore-based AIS base station, receiving and indentifying the forwarded ship relay message, and converting the relay message into AIS position information after the relay message is analyzed. After application of the AIS-system-based wireless relay network implementing method, the monitoring ranges of a coastal area and an inland AIS base station can be widened, the AIS monitoring effect on a ship in an inland shipping lane can be improved, communication expenses are not generated and the application value is high.
Owner:TIANJIN 712 COMM & BROADCASTING CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com