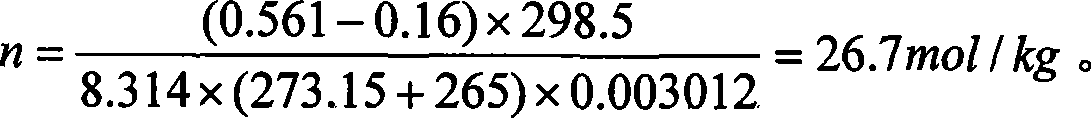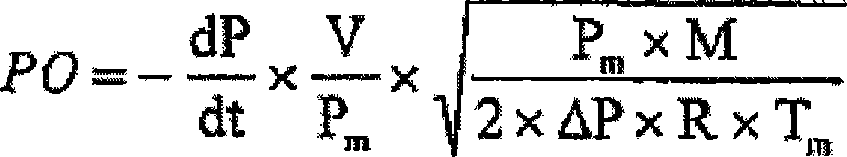Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
209 results about "Ideal gas" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An ideal gas is a theoretical gas composed of many randomly moving point particles whose only interactions are perfectly elastic collisions. The ideal gas concept is useful because it obeys the ideal gas law, a simplified equation of state, and is amenable to analysis under statistical mechanics.
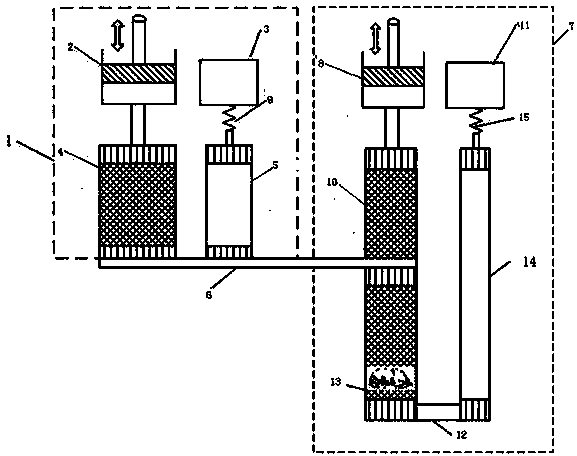
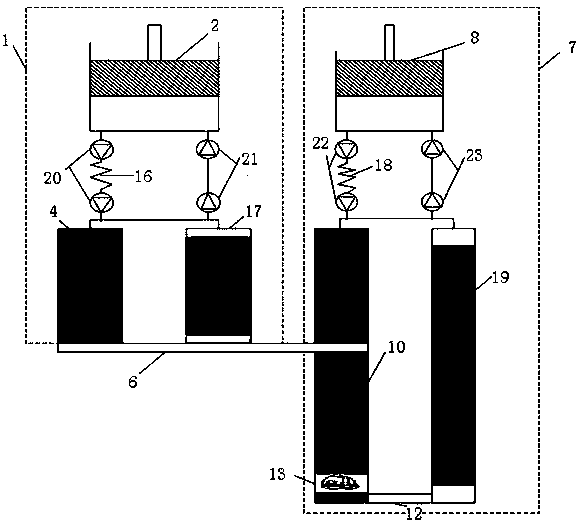
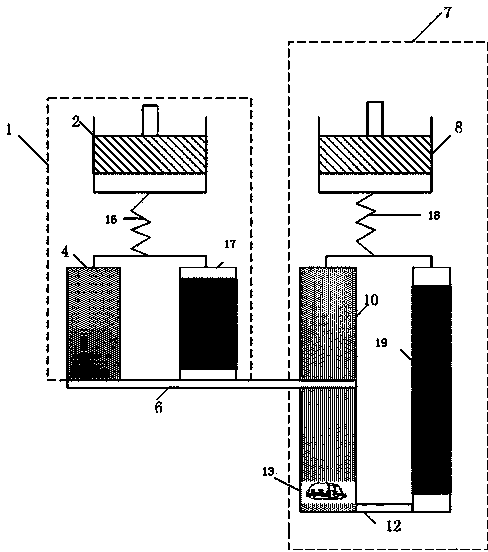
Method for processing information in a tire pressure monitoring system
InactiveUS6868358B2Improve utilizationAccurate detectionInflated body pressure measurementRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesEngineeringTire-pressure monitoring system
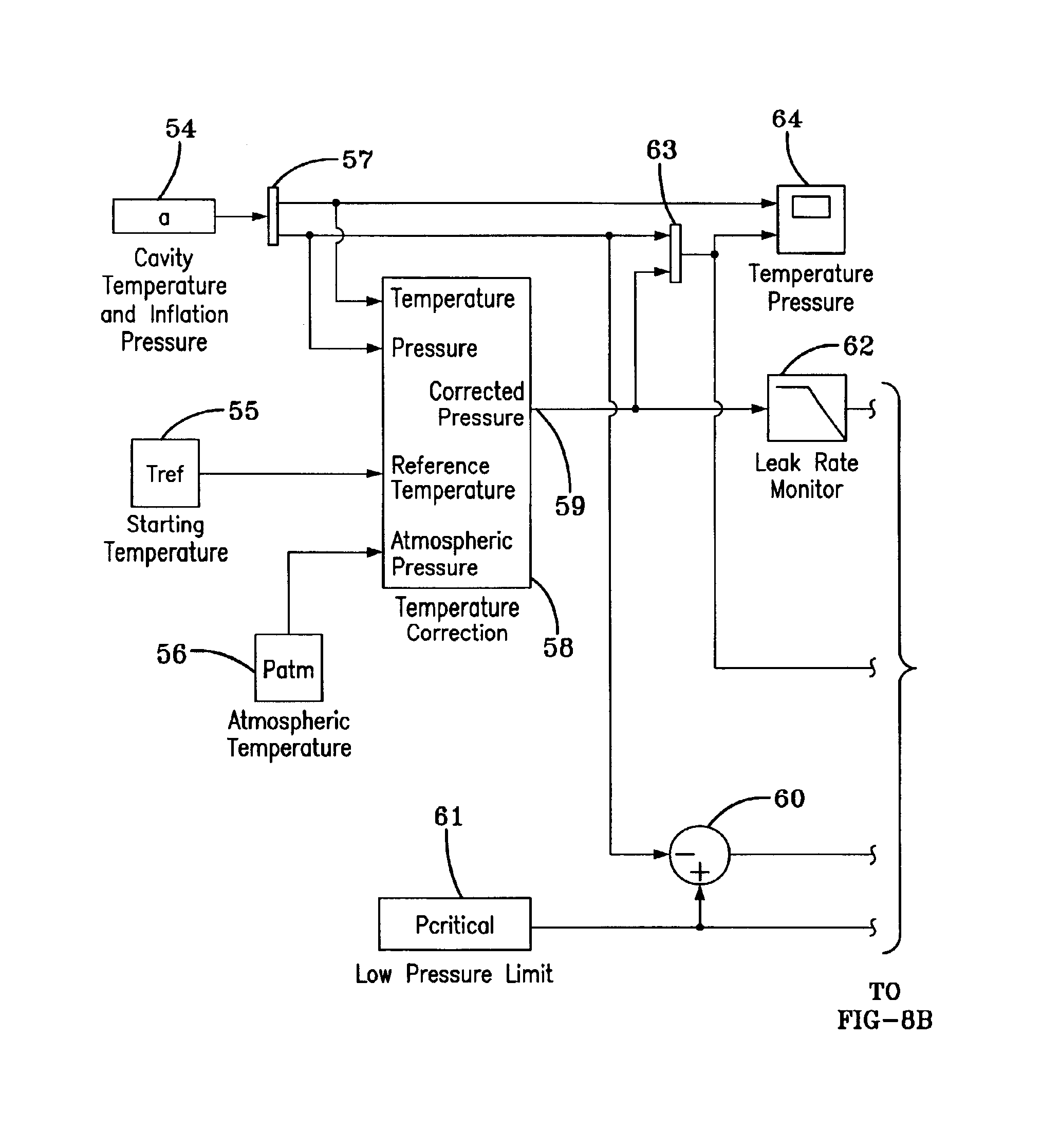
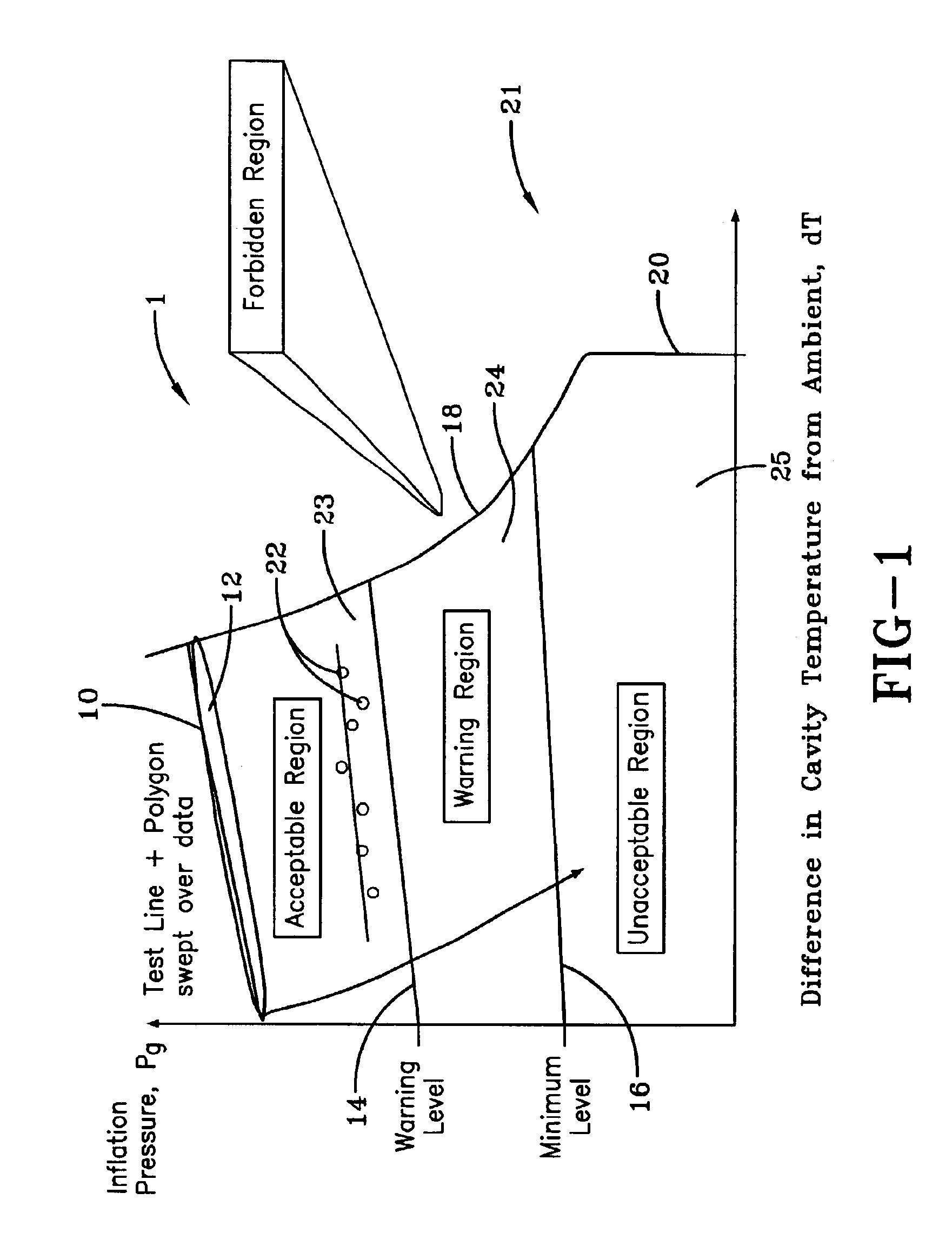
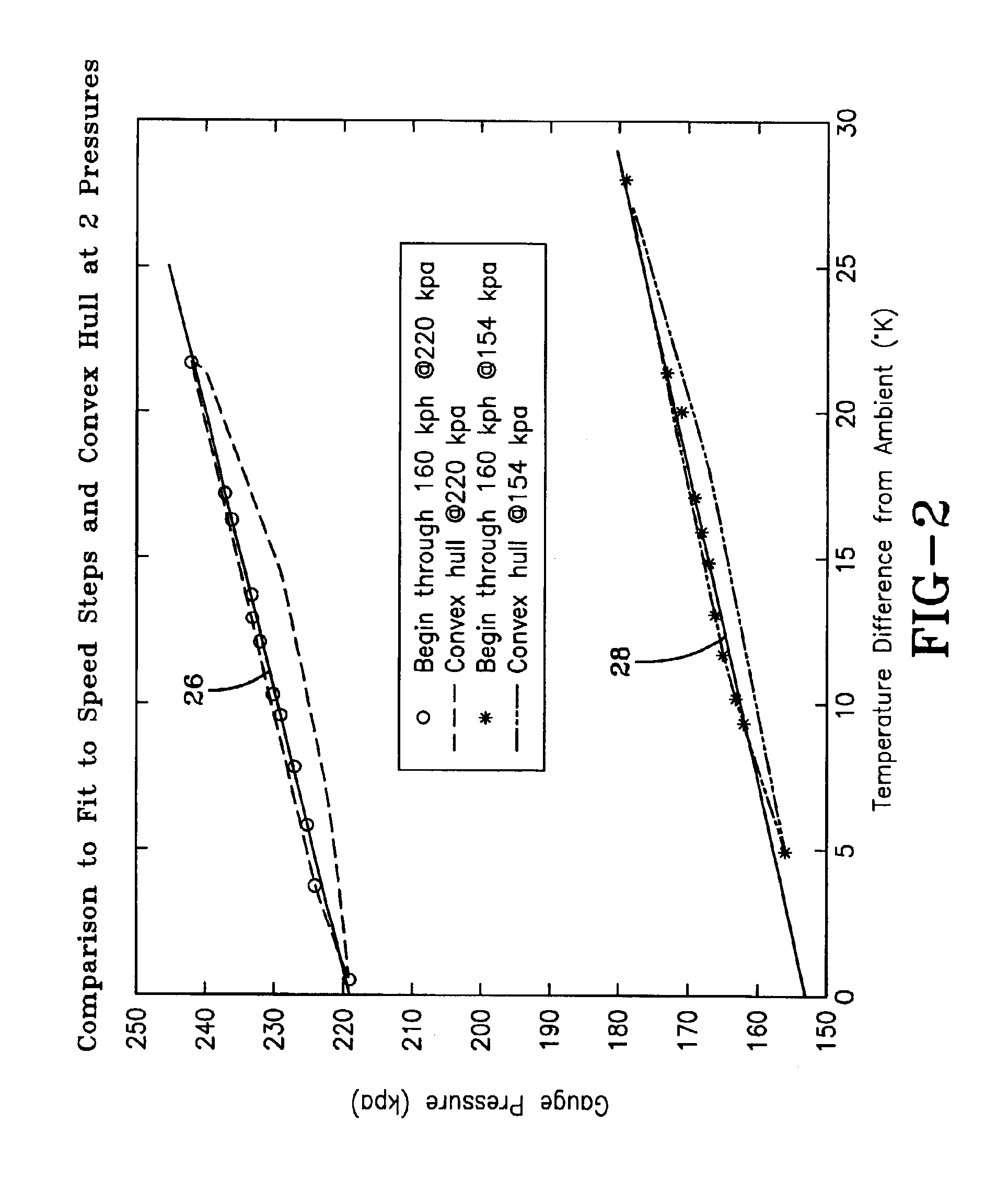
A method of processing information in a tire pressure monitoring system includes the steps of: establishing a reference temperature; determining a pressure warning threshold at the reference temperature; measuring gauge pressure and gauge temperature within a tire cavity; correcting the gauge pressure to a filtered pressure value at the reference temperature using the Ideal Gas Law; and comparing the filtered pressure value against the pressure warning threshold to determine the necessity for a warning signal. In an advanced form of the invention, the method includes determining a pressure leak rate; predicting the time interval that the filtered pressure value will cross the pressure warning threshold at the leak rate and generating progressive warnings to the driver over the time interval. Fuzzy logic is used to quantify the probability of a warning state for each data point, allow for measurement error; and report the state of maximum probability to minimize the occurrence of false warning. A warning utility function is derived based upon a combination of the filtered pressure and leak rate.
Owner:THE GOODYEAR TIRE & RUBBER CO
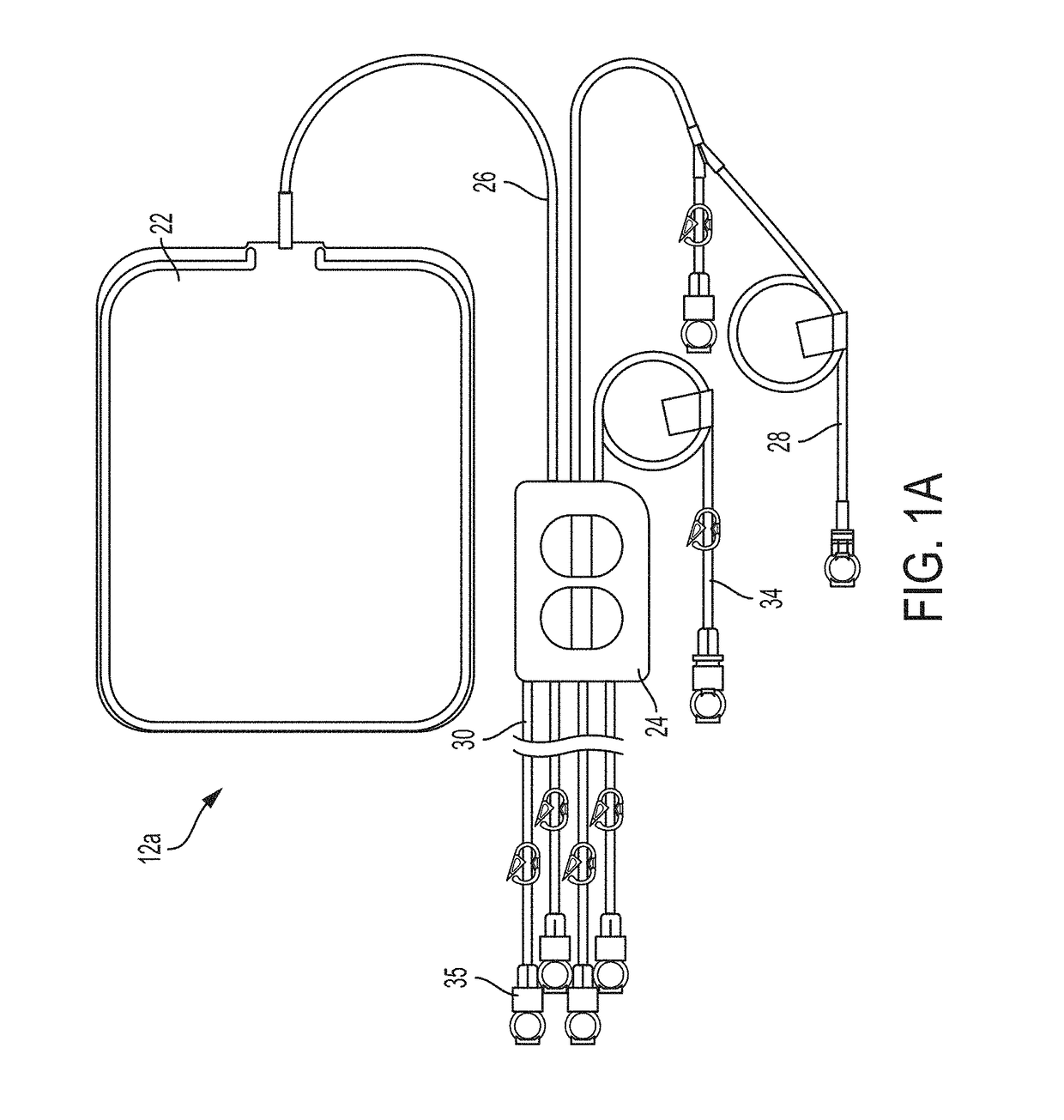
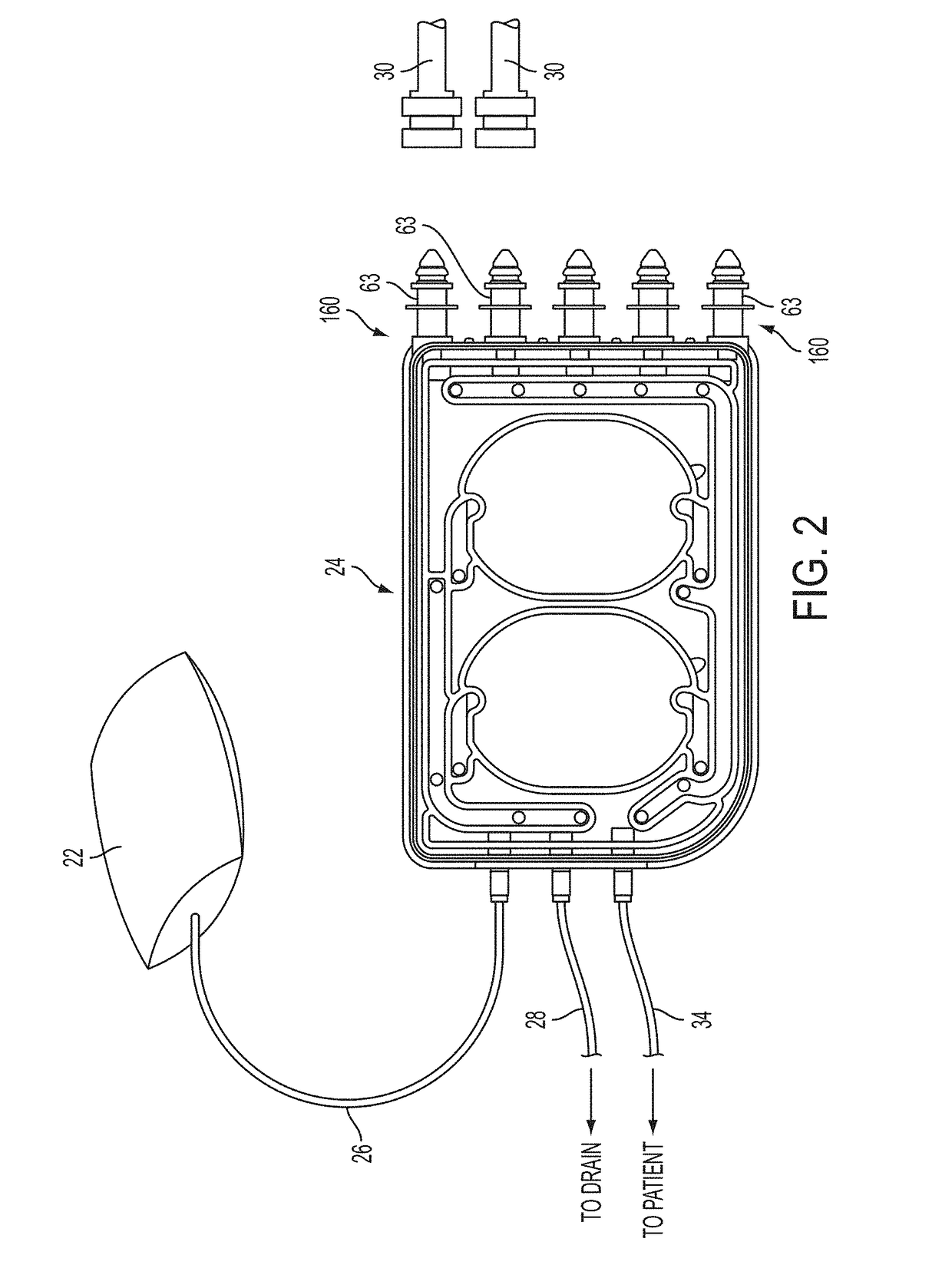
Infusion pump and method for use
InactiveUS7008403B1Small and lightLess componentsContracting/expanding measuring chambersVolume variation compensation/correction apparatusSolenoid valveContact method
A fluid dispensing system provides a non-contact method of monitoring the change in the fluid volume over time. This approach avoids the use of probes or sensors that come into direct contact with the fluid to be dispensed. The system comprises an apparatus comprising three chambers. The first chamber has a fixed volume and contains a pressurized gas. A solenoid valve is used to control the flow of gas from the first chamber into the second. The second chamber is sealed so that the combined mass of air in the first and second chambers remains fixed. The third chamber is adjacent to the second and contains medication in the form of incompressible fluid that is to be administered to a human or animal subject via a suitable delivery port. A piston is disposed between the second and third chambers and is movable responsive to the flow of gas into the second chamber to dispense fluid from the third chamber as desired. By sensing the pressure in the first and second chambers at any point in time, a processor is programmed to calculate the flow rate or dispensed volume of the fluid being delivered using principles derived from the Ideal Gas Law.
Owner:TANDEM DIABETES CARE INC
Method and system for controlling an extraction pressure and temperature of a stoichiometric egr system
The present invention provides a system and method that yields an exhaust stream that includes a relatively high concentration of a desirable gas and is also substantially oxygen-free. This desirable gas includes, but is not limited to: Carbon Dioxide (CO2), Nitrogen (N2), or Argon. The present invention also provides a way to control the physical property of the exhaust stream.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Infusion pump and method for use
InactiveUS20060150747A1Increased riskMeasurement is limitedContracting/expanding measuring chambersVolume variation compensation/correction apparatusSolenoid valveContact method
A fluid dispensing system provides a non-contact method of monitoring the change in the fluid volume over time. This approach avoids the use of probes or sensors that come into direct contact with the fluid to be dispensed. The system comprises an apparatus comprising three chambers. The first chamber has a fixed volume and contains a pressurized gas. A solenoid valve is used to control the flow of gas from the first chamber into the second. The second chamber is sealed so that the combined mass of air in the first and second chambers remains fixed. The third chamber is adjacent to the second and contains medication in the form of incompressible fluid that is to be administered to a human or animal subject via a suitable delivery port. A piston is disposed between the second and third chambers and is movable responsive to the flow of gas into the second chamber to dispense fluid from the third chamber as desired. By sensing the pressure in the first and second chambers at any point in time, a processor is programmed to calculate the flow rate or dispensed volume of the fluid being delivered using principles derived from the Ideal Gas Law.
Owner:TANDEM DIABETES CARE INC
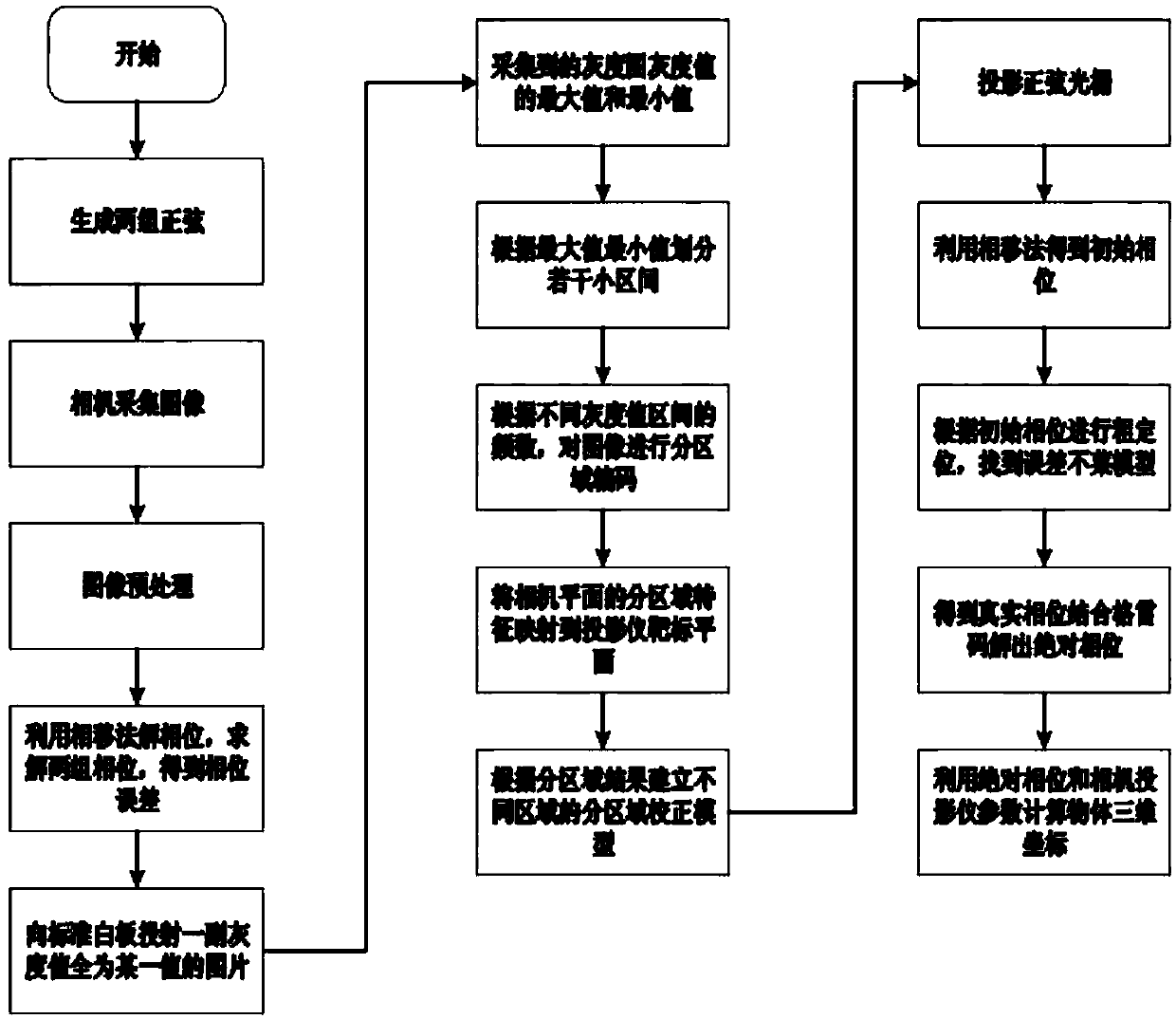
Phase error compensation method applied to grating three-dimensional projection measurement
The invention discloses a phase error compensation method applied to grating three-dimensional projection measurement. The method includes the following steps: generating sine grating stripes; collecting grating stripes that are modulated by the surface of an object; pre-processing images; carrying out phase unwrapping through a phase shift method on the basis of the pre-processed stripe images; projecting a grey-scale image with a single gray value onto the surface of a standard white board; mapping regional results in the step (5) onto a target surface of a projector through an obtained ideal phase; establishing regional correction models for different regions according to the regional results; projecting the sine grating stripes onto the object; solving an initial phase through a phaseshift method, compensating the phase on the basis of established regional error compensation, and solving an actual phase; and through calibrated camera parameters and a solved absolute phase, calculating three-dimensional coordinate information of a to-be-measured object through a spatial intersection method. The method overcomes phase errors and measurement errors caused by Gamma non-linearity.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Instrument and method for measuring the volume of a hermetically sealed variable volume and pressure conforming container
An instrument and method for measuring the volume of a hermetically sealed, variable volume, pressure conforming container. The instrument includes a needle, a vacuum pump, a mass flow rate sensor and an integrator. The needle has a lumen operable for sealingly perforating a container and thereby placing the lumen of the needle in fluid communication with a retention chamber defined by the container. The vacuum pump evacuates the gaseous content from the retention chamber through the lumen defined by the needle and past a mass flow rate sensor for sensing mass flow rates pulled through the lumen and transmitting corresponding mass flow rate signals over time to the integrator. The integrator is programmed to integrate the received mass flow rate signals over time through achievement of an evacuated retention chamber to generate a total mass value, and calculate a volume from the total mass value employing the Ideal Gas Law.
Owner:MODERN CONTROLS
Medical treatment system and methods using a plurality of fluid lines
ActiveUS10201647B2Improve accuracyAvoid accumulationOther blood circulation devicesMedical devicesPeritoneal dialysisPolytropic process
Improvements in fluid volume measurement systems are disclosed for a pneumatically actuated diaphragm pump in general, and a peritoneal dialysis cycler using a pump cassette in particular. Pump fluid volume measurements are based on pressure measurements in a pump control chamber and a reference chamber in a two-chamber model, with different sections of the apparatus being modeled using a combination of adiabatic, isothermal and polytropic processes. Real time or instantaneous fluid flow measurements in a pump chamber of a diaphragm pump are also disclosed, in this case using a one-chamber ideal gas model and using a high speed processor to obtain and process pump control chamber pressures during fluid flow into or out of the pump chamber. Improved heater control circuitry is also disclosed, to provide added or redundant safety measures, or to reduce current leakage from a heater element during pulse width modulation control of the heater. Improvements are also disclosed in the application of negative pressure during a drain phase in peritoneal dialysis therapy, and to control the amount of intraperitoneal fluid accumulation during a therapy. Improvements in efficiency are also disclosed in the movement of fluid into and out of a two-pump cassette and heater bag of a peritoneal dialysis cycler, and in the synchronization of the operation of two or more pumps in a peritoneal dialysis cycler or other fluid handling devices using a multi-pump arrangement.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
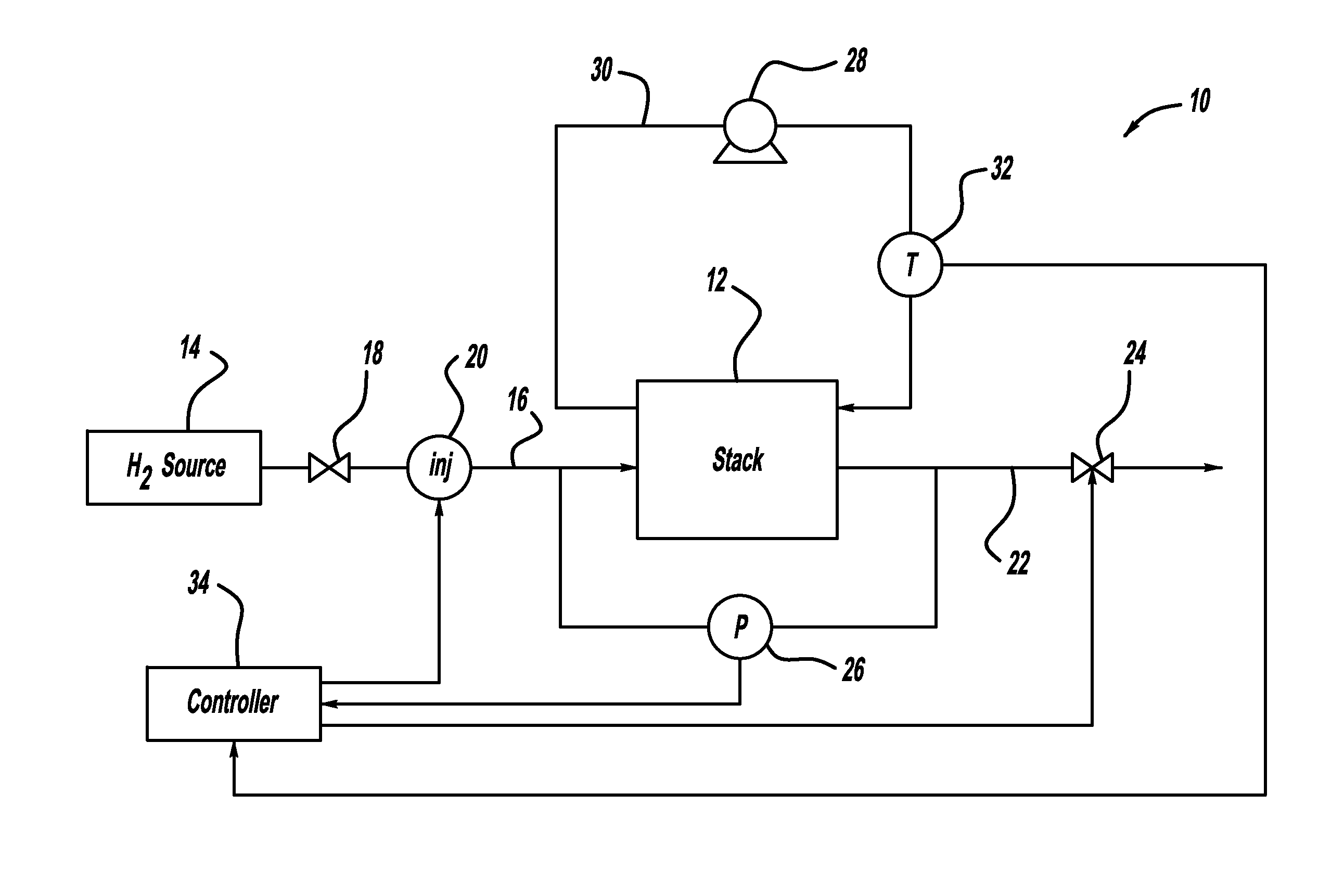
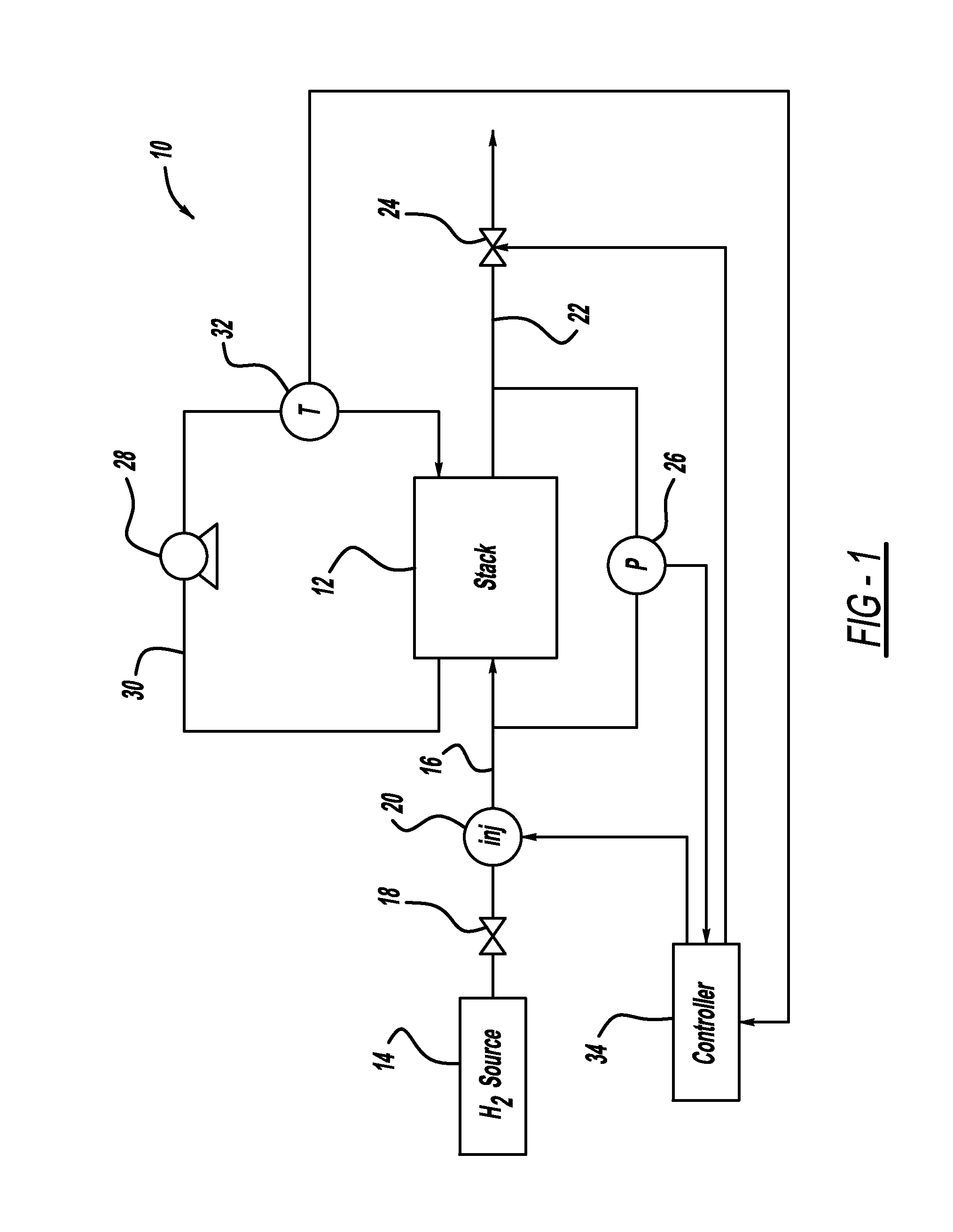
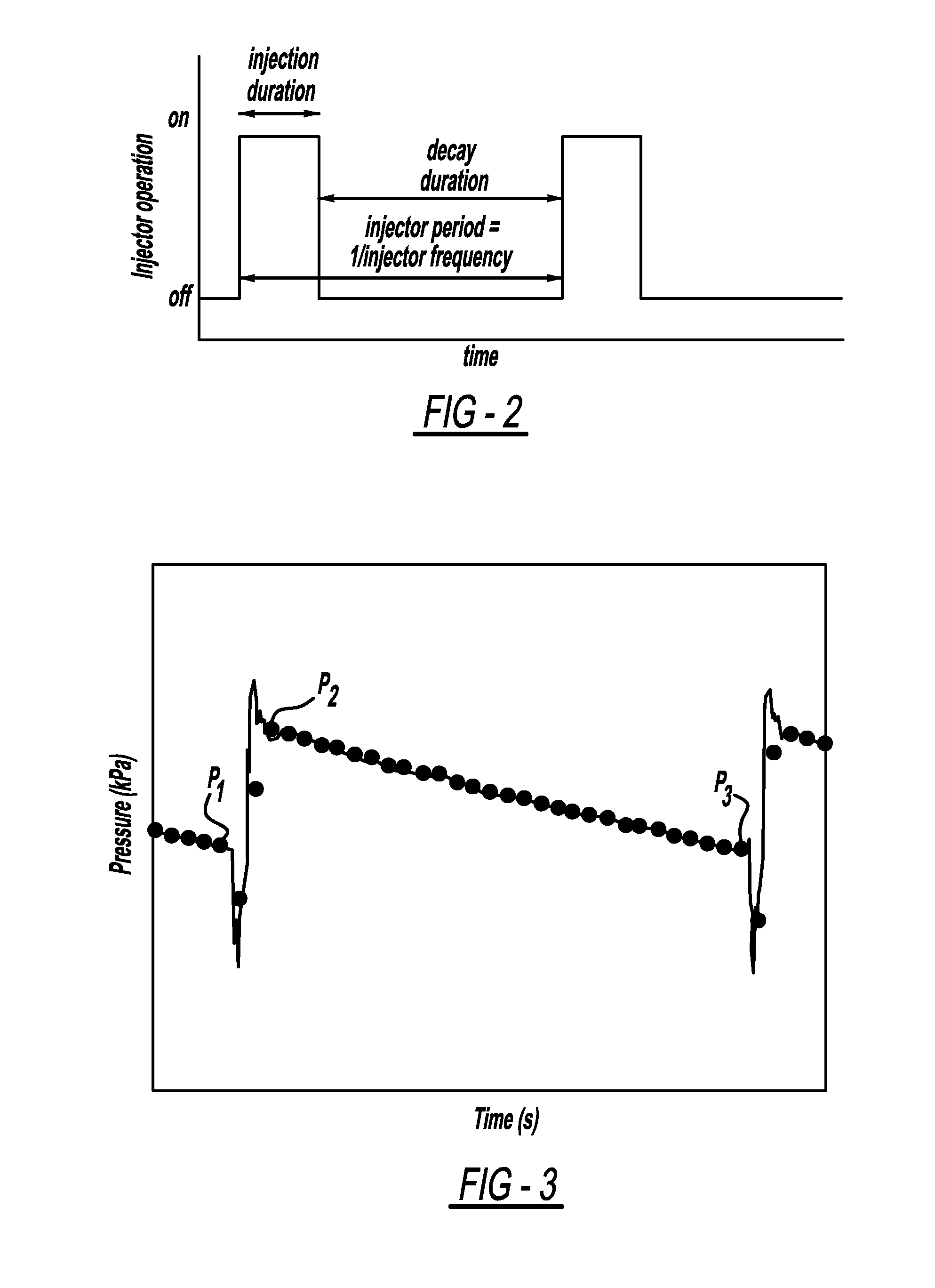
Injector flow measurement for fuel cell applications
ActiveUS8387441B2Detection of fluid at leakage pointMeasurement of fluid loss/gain rateFuel cellsHydrogen
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Method for measuring object density based on air pressure process
InactiveCN104807720AVolume of influenceHigh precisionSpecific gravity measurementDensity basedProduct gas
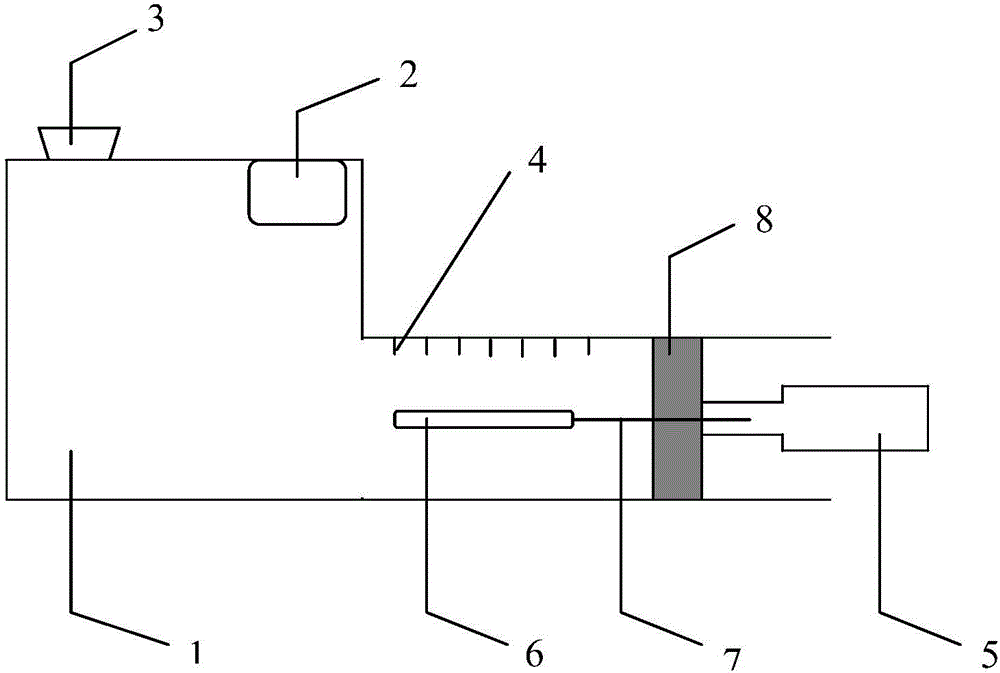
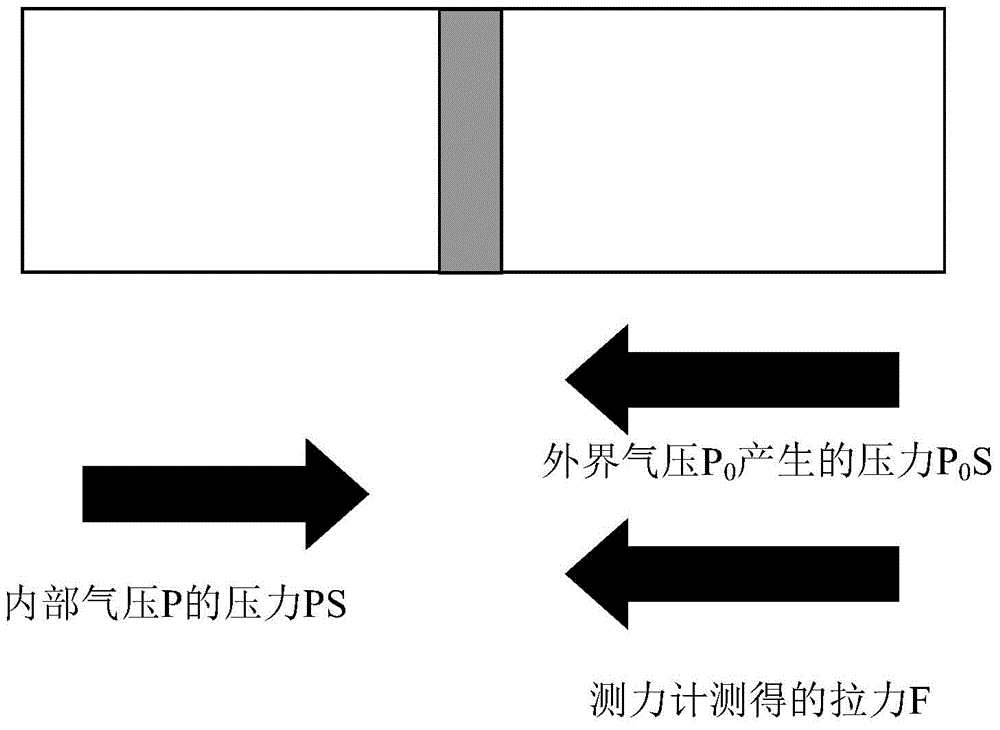
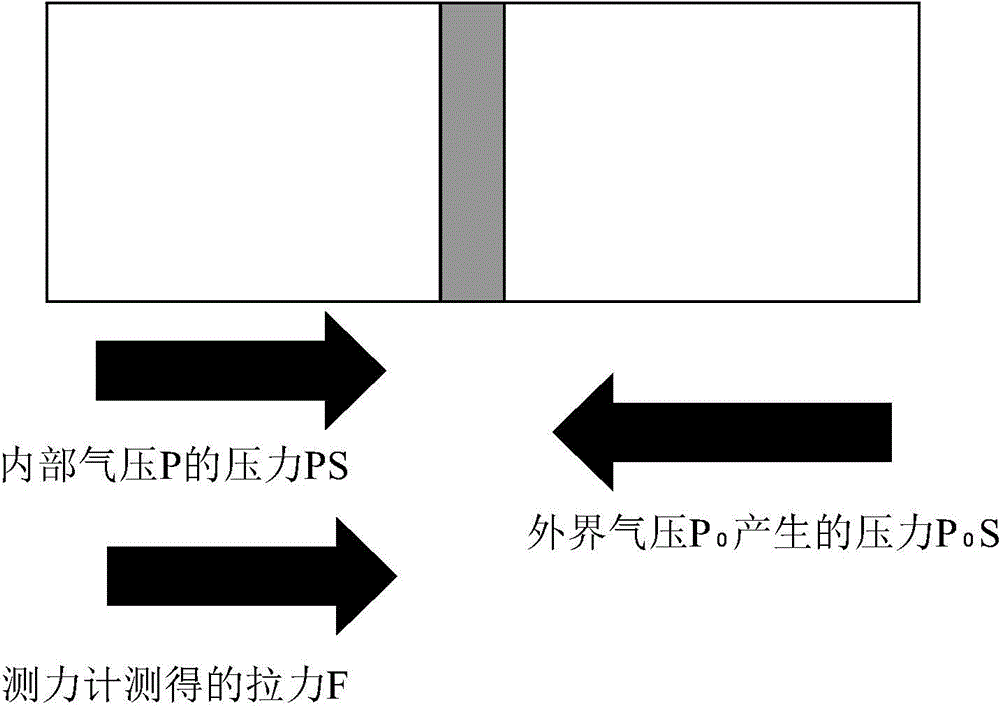
The invention provides a novel method for measuring object density based on an air pressure process. According to the method, the density of an object can be measured by a device capable of measuring an air pressure coefficient. The device comprises a sealed container provided with a sealing cover and volume scales, a thermometer, a dynamometer and a pressure sensor, wherein a piston is arranged on the sealed container; during measurement, the piston is pushed to different scales to change the pressure in the container; the volume V0 in the container is calculated by utilizing an ideal air equation PV=nRT on the premise that the temperature is the same and the mass is the same; after a to-be-measured object is arranged in container, the volume V1 in the container is measured by the same method; the difference of the volume V0 and the volume V1 is the volume V of the to-be-measured object; finally the density of the to-be-measured object can be obtained according to a formula Rho=m / V. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of preventing influences on the volume of the object caused by existence of liquid, improving the measurement accuracy by calculating the volume changes by air pressure and temperature changes and being suitable for measuring the density of objects such as cotton and sponge.
Owner:闫语童
Temperature corrected tire pressure gauge and method
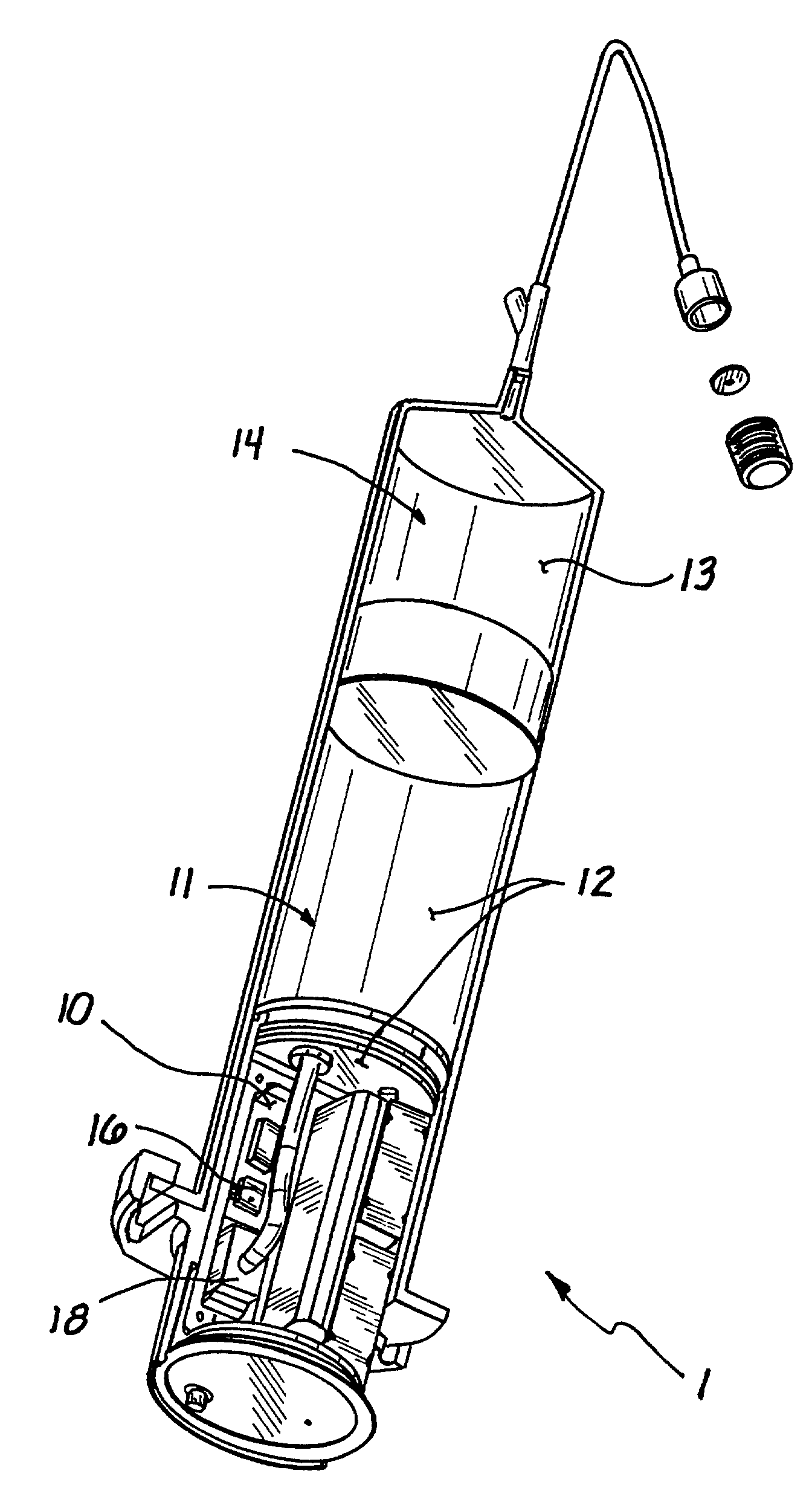
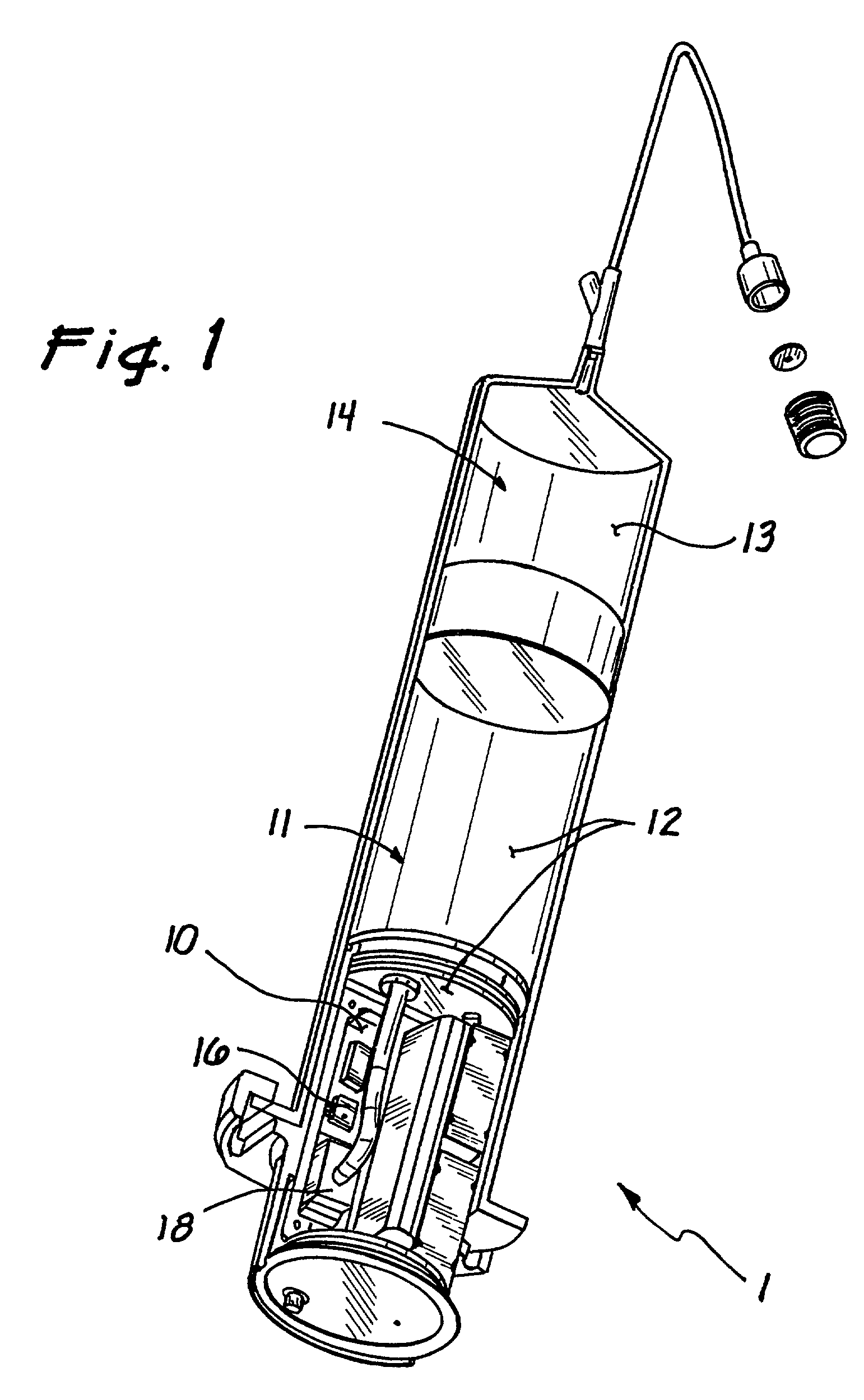
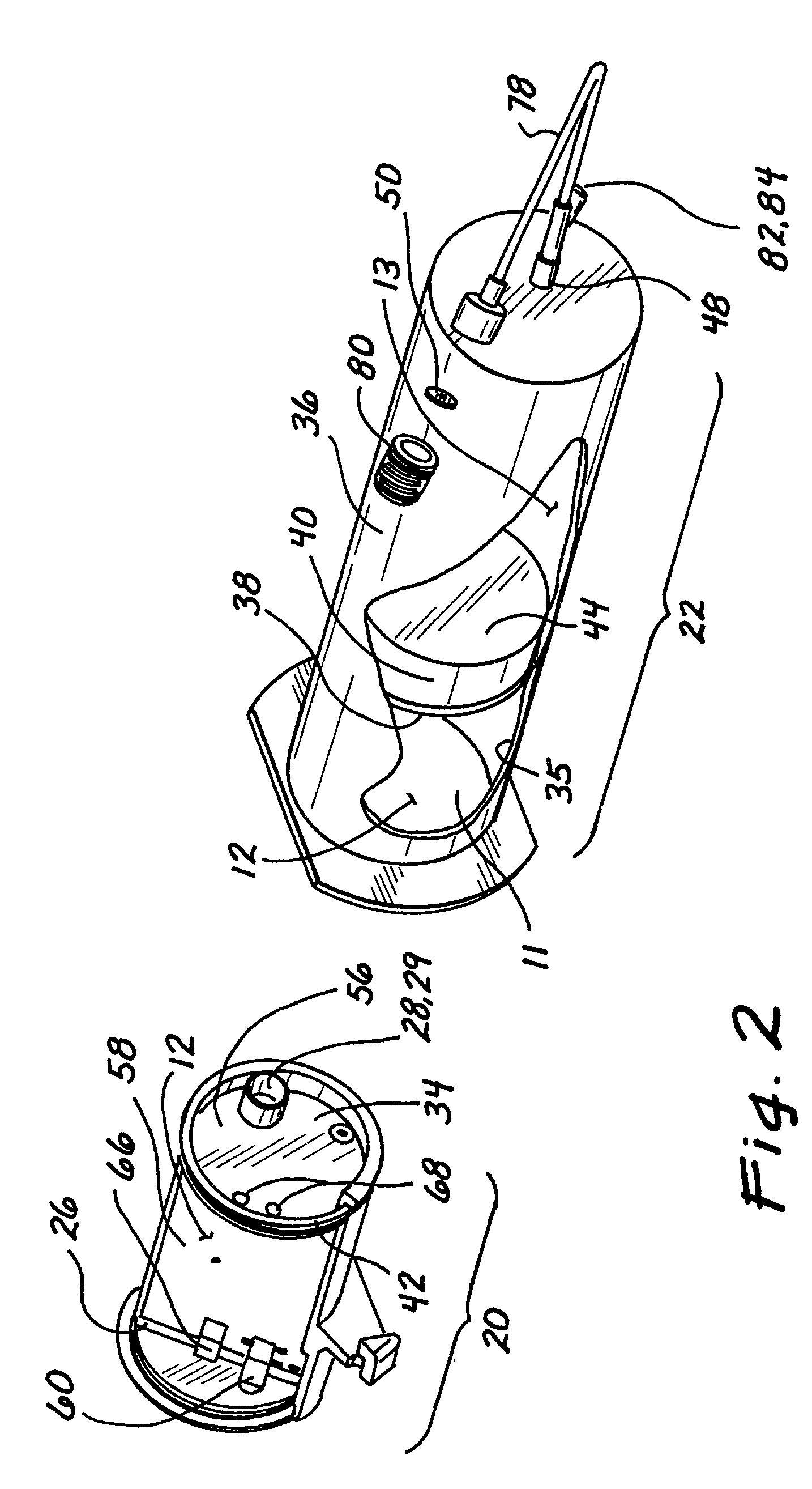
Disclosed is a device (10) and method for determining a temperature-corrected tire pressure. A preselected baseline temperature (26) is measured or selected. A second temperature (28) is measured using a temperature probe (22). An actual tire pressure (30) is measured (24). A programmed processor calculates and displays (14) a corrected tire pressure (32) corresponding to the baseline temperature (26) according the ideal gas law.
Owner:JAYNES HARRY M
Test method of supercritical carbon dioxide content in coal
InactiveCN101936861AEasy and accurate measurementThe testing process is simpleMaterial analysisCarbon dioxide cylinderGas cylinder
The invention discloses a test method of supercritical carbon dioxide content in coal. A determination device consisting of a vacuum pump, a coal sample tank, a carbon dioxide cylinder, a pressure device and a high-accuracy balance is used in the test method. The test method comprises the following steps of calculating the quantity of gas filled into an adsorption tank by measuring the mass variation of the adsorption tank, substracting the gas phase content increased in a free space of the adsorption tank to obtain the excess adsorption quantity of a coal sample under balance pressure, and calculating the gas phase carbon dioxide content in a coal pore by utilizing a non-ideal gas equation according to the pore pressure. The supercritical carbon dioxide content in coal is a sum of the excess adsorption quantity and the gas phase content of the pore space in coal, tests of a plurality of balance pressures can be finished by measuring carbon dioxide contents in the coal sample under different balance pressures. The test method has the advantages of simpleness and low requirement to an instrument and equipment, can accurately and conveniently measure the carbon dioxide content in coal and is beneficial to test research on the carbon dioxide content in coal.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
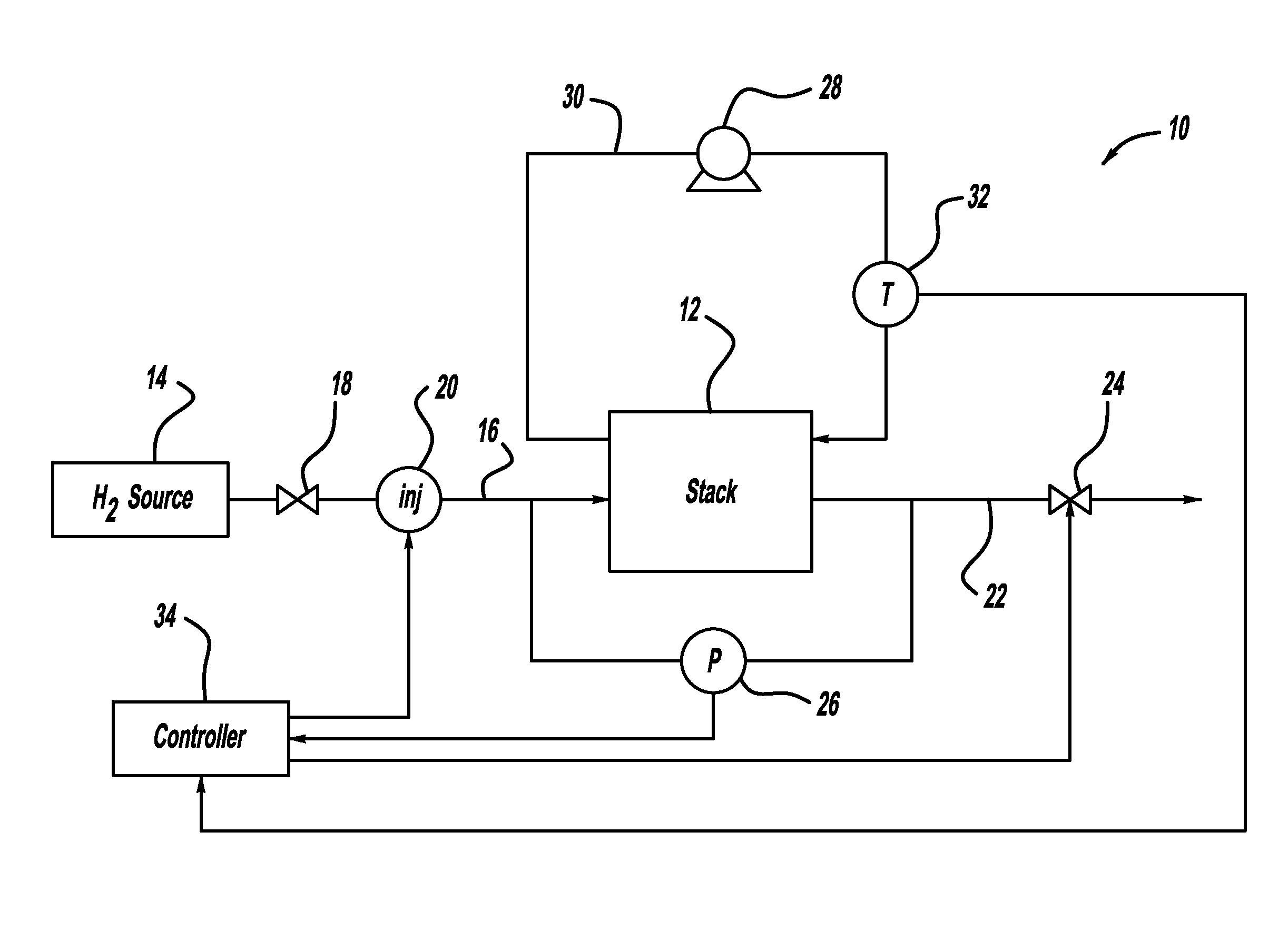
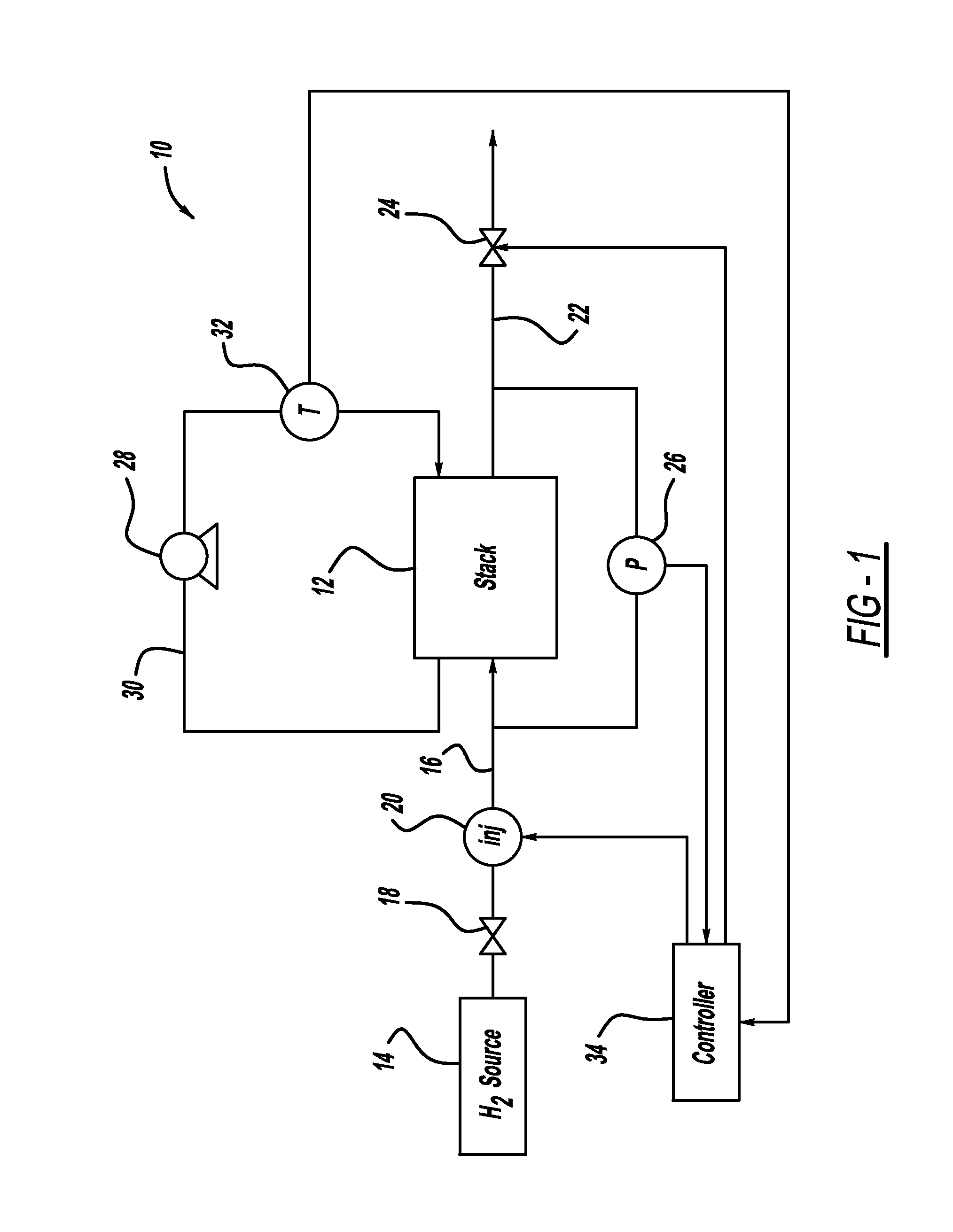
Injector flow measurement for fuel cell applications
ActiveUS20110138883A1Detection of fluid at leakage pointMeasurement of fluid loss/gain rateFuel cellsHydrogen
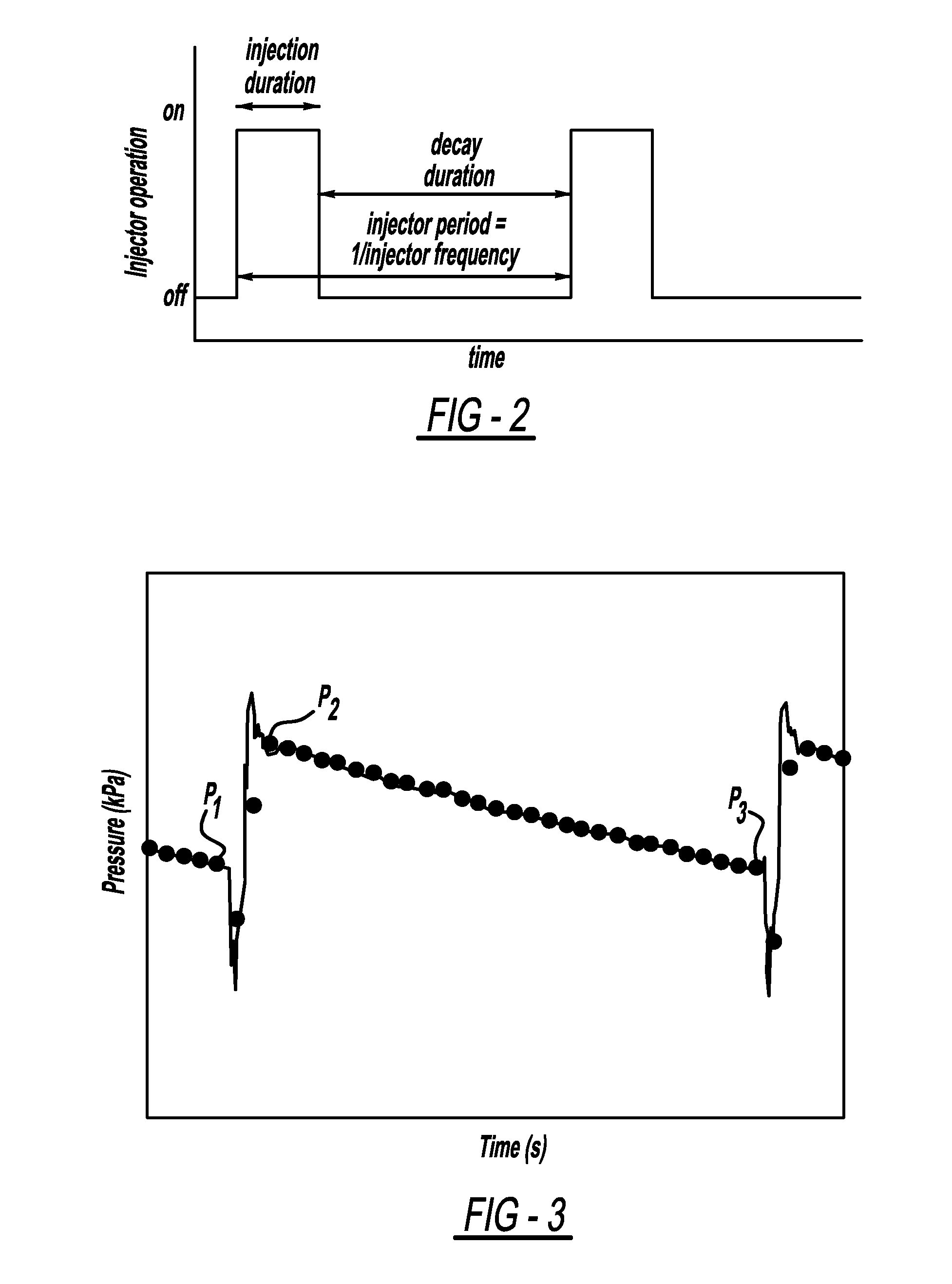
A method for determining the amount of fuel flow from a high pressure gas tank to the anode side of a fuel cell stack through pulsed injector. The anode sub-system pressure is measured just before the injector pulse and just after injector pulse and a difference between the pressures is determined. The difference between the pressures, the volume of the anode sub-system, the ideal gas constant, the anode sub-system temperature, the fuel consumed from the reaction in the fuel cell stack during the injection event and the fuel cross-over through membranes in the fuel cells of the fuel cell stack are used to determine the amount of hydrogen gas injected by the injector.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
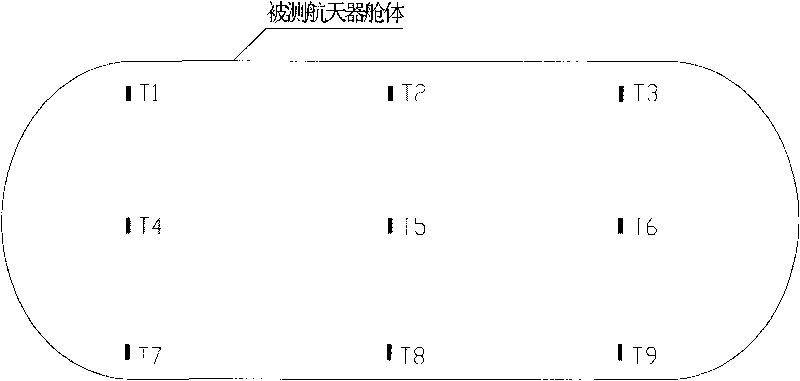
Method for detecting leakage of spacecraft cabin by differential pressure
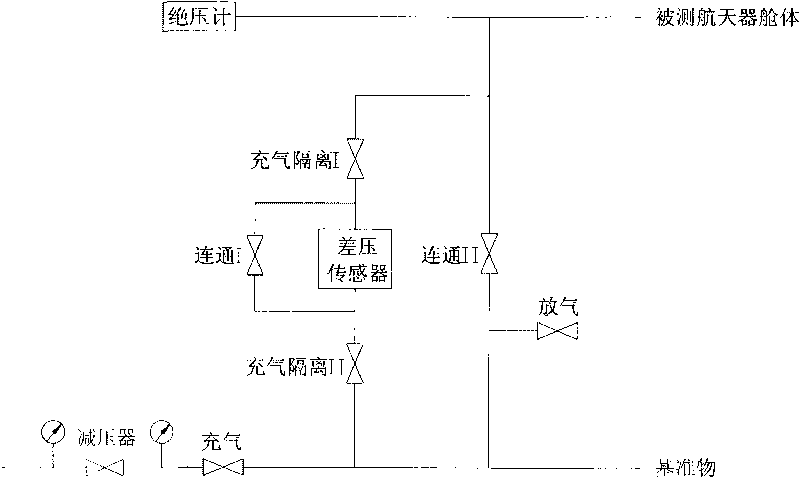
InactiveCN101738296AReduce differential pressureAccurate leak rateMeasurement of fluid loss/gain ratePrimary standardDifferential pressure
The invention provides a method for detecting leakage of a spacecraft cabin by differential pressure. The method comprises the following processes: aerating, balancing, testing and gas deflating. In the method, a small-volume primary standard substance is put in a large-volume spacecraft cabin; standards and a temperature inside the measured cabin are measured when the differential pressure is measured; actually measured differential pressure is compensated by a temperature lagging for some time according to an ideal gas state equation; and finally integral leakage of the measured spacecraft cabin is acquired. In a gas path of the method, an aerating isolating valve is arranged on both sides of a differential pressure sensor respectively and used for avoiding an overrange phenomenon of the differential pressure sensor in the process of aerating or deflating.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT ENVIRONMENT ENG
Gas distribution detection method in coal mine underground goaf
The present invention relates to a gas distribution detection method in a coal mine underground goaf. According to the present invention, the method is the streamline method, which adopts in situ direct sampling, transmission, collection and storage, detection, calculation, analysis and comparison according to the condition of the coal mine underground goaf to carry out the detection; a computer technology and sensors are adopted for collecting data of the gas; microcomputer programs are adopted for completing various analysis functions; the detection method adopts in situ direct sampling in the goaf, transmission, analysis, data printing, such that the process is rapid, the data is abundant and accurate, the gas distribution condition of the goaf can be directly mastered so as to provide the firsthand field data for treatment and elimination of the gas hazard; the detection method is rigorous, advanced, in site, intuitive, convenient, accurate and safe, and is an ideal gas distribution detection method in the coal mine underground goaf.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
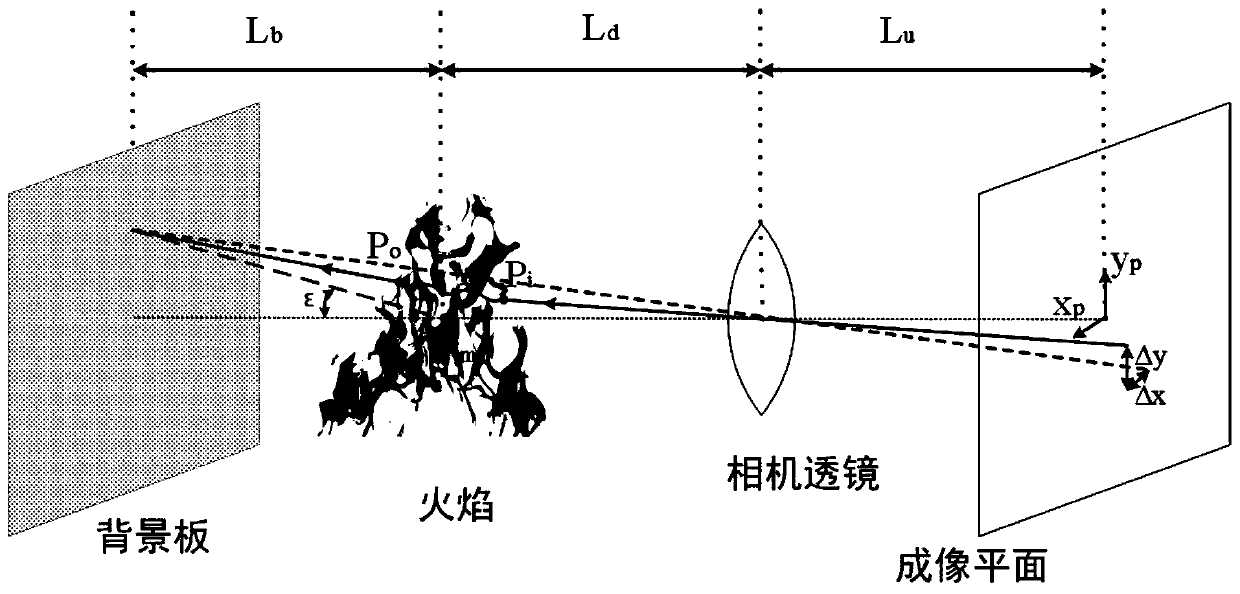
Flame temperature field measuring device and method
InactiveCN111257497ALow costEliminate the problem of out-of-sync shotsChemical analysis using combustionThermometers using physical/chemical changesRefractive indexEngineering
The invention relates to the technical field of flame three-dimensional detection and reconstruction. More specifically, the present invention provides a device and a method for measuring a flame temperature field based on a single-camera endoscopic background schlieren tomography technology. An imaging system combining a high-speed camera and an all-in-one endoscope is adopted, a background schlieren chromatography technology based on a refractive index gradient measurement principle is utilized, and the deflection angle of light passing through to-be-measured gas is obtained by shooting twopictures when to-be-measured flame exists and does not exist and combining an optical flow algorithm or a cross-correlation algorithm. And then a refractive index field of the flame is reconstructed through an algebraic iterative algorithm, the refractive index field is deduced to a density field in combination with a Gladstone-Dale formula, and the density field is deduced to a temperature fieldaccording to an ideal gas state equation. The device is simple, the test cost is low, and the reconstruction of a transient flame three-dimensional temperature field can be realized only by one high-speed camera.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Device and method for production and injection of PLIF flow field diagnosis tracer
ActiveCN105548100AModerate concentrationRealize determinationFluorescence/phosphorescencePlanar laser-induced fluorescenceEngineering
Relating to a device and method for production and injection of a tracer, the invention provides a device and method for production and injection of a PLIF (planar laser induced fluorescence) flow field diagnosis tracer. During high-time and high-spatial resolution quantitative measurement of mixed fuel gas by a PLIF diagnostic technique, experimental accuracy can be affected due to the incapability of accurate determination of mixed steam's temperature, pressure and concentration. According to the invention, a generation tank is communicated with a gas mixing tank through a first gas transmission pipeline, the generation tank is equipped with a first thermocouple, and the gas mixing tank is equipped with a second thermocouple. The method provided by the invention consists of: step 1. formation of pure tracer steam; step 2. adjustment of mixed gas concentration; step 3. pressurization and dilution of diluent gas in the gas mixing tank according to an ideal gas state equation PV=nRT, thus obtaining a mixed gas meeting the experiment required concentration of A, temperature of T and pressure of P; and step 4. injection of the mixed gas. The device and the method provided by the invention are used for the process of tracer production and injection into an experimental field.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Air supply system of semiconductor process equipment and its gas flow calibration method
ActiveCN101369514ALong calibration timeLow costFlow control using electric meansSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProcess equipmentIsolation valve
The invention discloses a gas supply system of a semiconductor processing device and a method for calibrating gas flow, the gas supply system comprises a gas path box for supplying gas to a reaction chamber, an mass flow controller (MFC) and a pipeline for cleaning the gas path box are provided on the gas path box, a calibrating isolation valve is provided on the pipeline for cleaning the gas path box and can insulate and close the pipeline for cleaning the gas path box, gas with a certain flow is supplied into the pipeline for cleaning the gas path box by the MFC, then actual flow of the gasentered into the pipeline for cleaning the gas path box can be calculated according to an ideal gas state equation, comparing with the actual flow of the gas and a setting flow of the MFC, the gas flow of the gas supply system can be calibrated based on the compared result. The costs of the system and the method are low, the calibrating times of the system and the method are short.
Owner:BEIJING NAURA MICROELECTRONICS EQUIP CO LTD
Method and device for testing content of easily-volatile matters in explosive
The invention discloses a method for testing the content of easily-volatile matters in explosive, and provides a device improved based on a microcalorimeter correspondingly, wherein the device is formed by arranging a presser sensor used for measuring the real-time pressure in a sample cell on the sample cell of the microcalorimeter and arranging a reading device, a searching device and a comparing device on a control system of the microcalorimeter. In testing, the explosive is put into the sample cell firstly, and after vacuumization is carried out, the device provided by the invention is started, parameters including the start temperature, the temperature rise amplitude, the reaction judgment sensitivity, the constant temperature time, the waiting time, the reaction termination conditions and the like of the microcalorimeter are set, the pressure change and the temperature rise rate change in the sample cell are recorded, and then the content of the volatile matters is obtained by an ideal gas state equation. According to the invention, by analyzing the relationship between the gas discharge quantity and the heat flux change, the content of the easily-volatile matters in the explosive can be effectively tested.
Owner:INST OF CHEM MATERIAL CHINA ACADEMY OF ENG PHYSICS
Method and apparatus for determining tire condition using ideal gas law
InactiveUS20140039752A1Vehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesDisplay deviceLaws of thermodynamics
An apparatus is provided for determining a tire operating condition including a tire-based sensor for sensing tire pressure and temperature and transmitting a signal indicative thereof and a vehicle ignition system. A vehicle-based receiver / controller is provided for receiving the signal from the tire-based sensor and for detecting the state of the vehicle ignition system. The controller provides an error signal when the sensed tire pressure is less than a set threshold value Pset and resets the error signal when the sensed tire pressure is greater than a reset threshold value Prst. The receiver / controller determines the set threshold value Pset and the reset threshold value Prst as a function of a calculated warm tire pressure value Pwarm, determines a mole value N of the tire pressure, and adjusts the determined set threshold value Pset and the reset threshold value Prst in response to the vehicle ignition state and a change in the determined mole value N. A display is provided for displaying the error signal from the vehicle-based receiver / controller.
Owner:TRW AUTOMOTIVE US LLC
Numerical simulation of airflow within porous materials
InactiveUS20110010137A1Realistic simulation of structural behavior of porous materialsComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationVolume variationElement analysis
Systems and methods of numerically simulating airflow within porous materials are disclosed. According to one aspect of the present invention, engineering product represented by a finite element analysis model containing in part porous material with permeability. In each solution cycle of a time-marching simulation, each of the elements of porous material is evaluated with airflow in conjunction with the traditional mechanical response. Each element's volume change results into different air-pore pressure hence a pressure gradient, which in turn is used for airflow calculated in accordance with a fluid seepage law that depends upon permeability of the porous material. Therefore, a more realistic simulation of structural behavior of porous materials can be achieved. The volume change and pressure of each element of porous material is evaluated using ideal gas law. A general form of Darcy's law includes user control parameters is used for evaluating airflow based on the pressure gradient and permeability.
Owner:LIVERMORE SOFTWARE TECH
Method, computer program, and device for measuring the amount injected by an injection system
InactiveUS6915683B2Easy to detectReduce gas volumeElectrical controlEngine testingCombustionInternal combustion engine
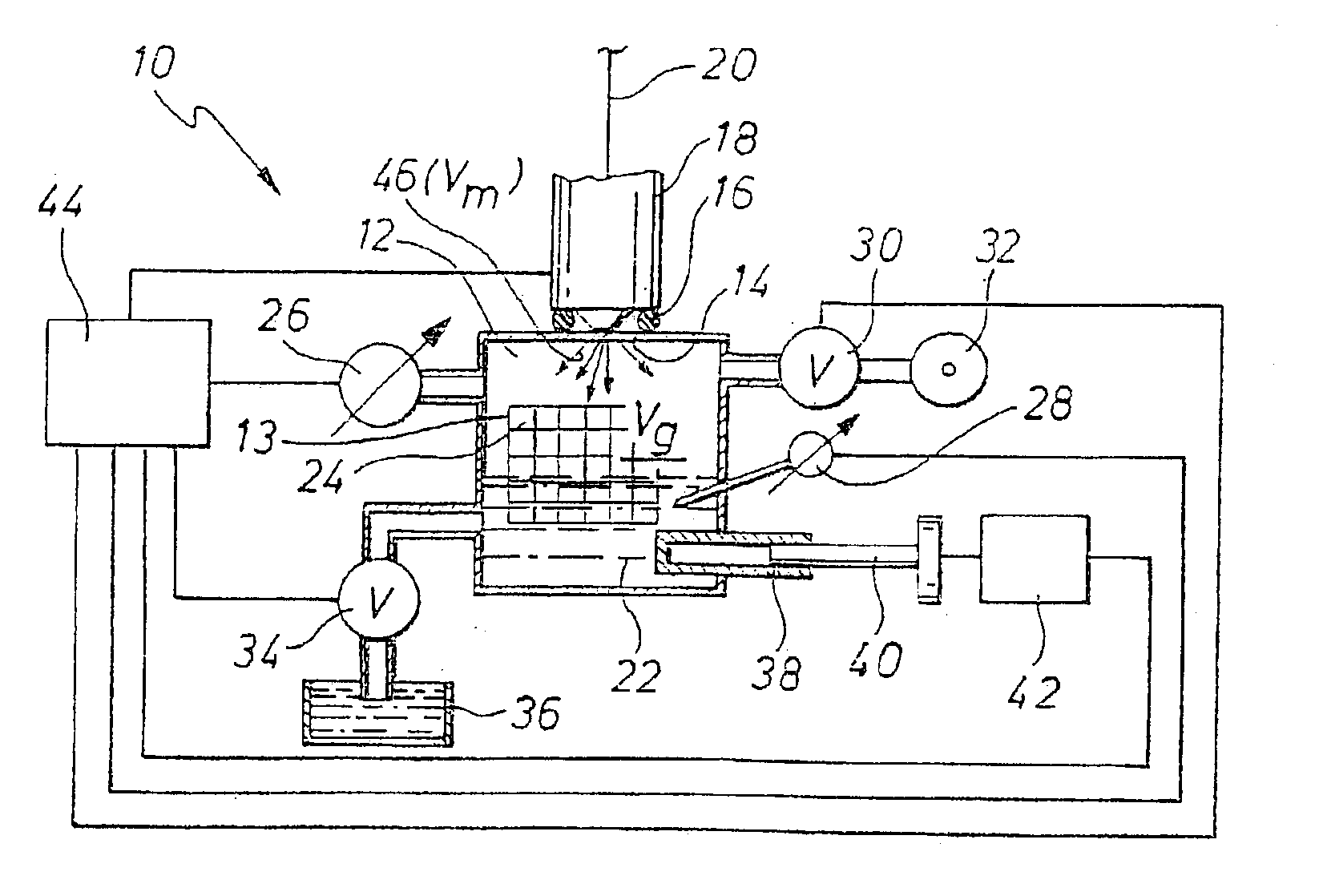
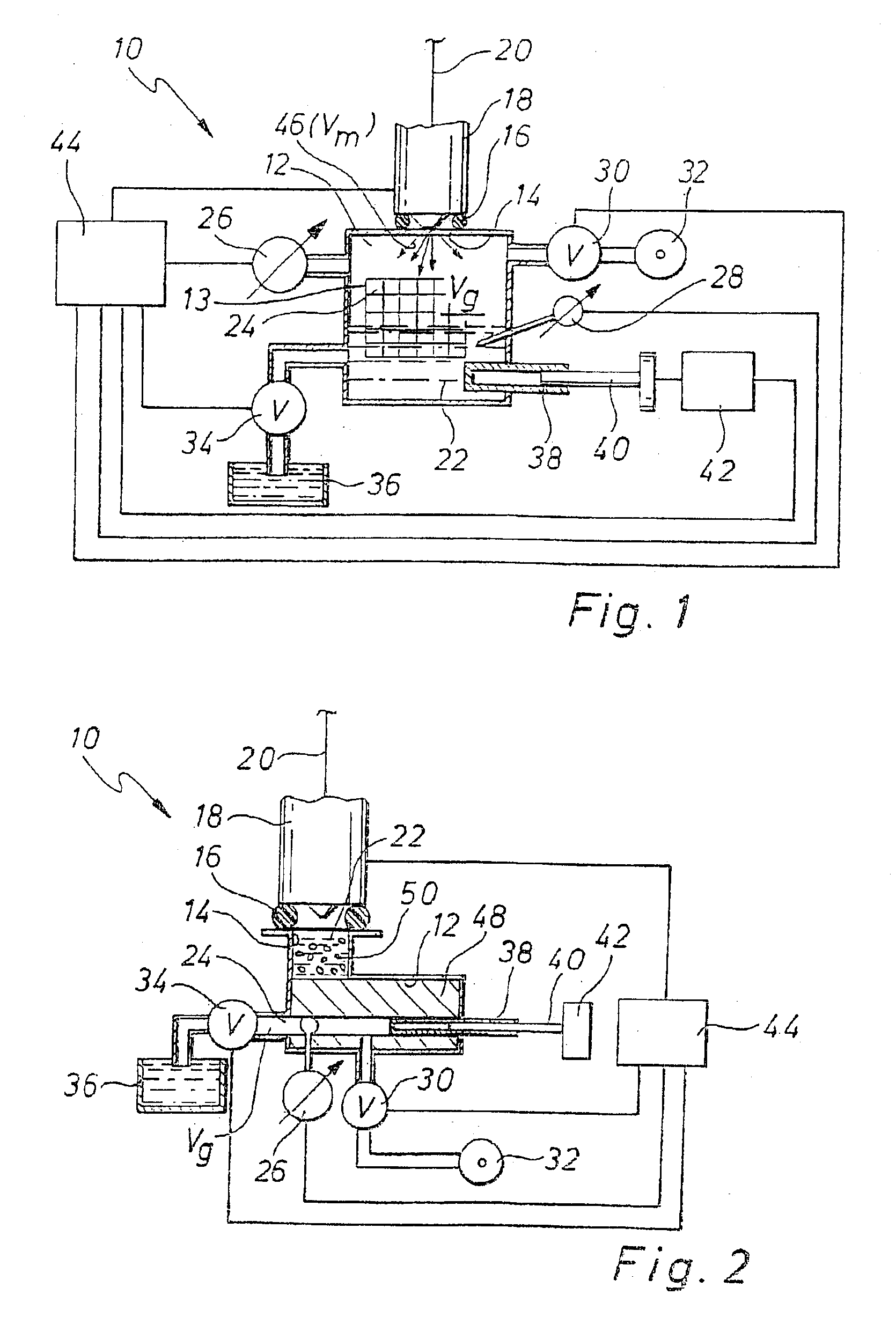
For measuring the injection quantity (Vm) of injection systems (18), in particular in internal combustion engines, test fluid (22) is injected by the injection system (18) into a measurement chamber (12). To increase the precision and stability of the measurement, the volume of the measurement chamber (12) is kept constant during the injection. Moreover, a gas volume (Vg) is present in the measurement chamber (12). The injected volume (Vm) of test fluid (22) is ascertained from the pressure change (dP) in the measurement chamber (12) that occurs upon an injection of test fluid (22). The ascertainment of the injected volume (Vm) is done by means of the state equation for ideal gases.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Propellant burning gas mole number test method and its device
InactiveCN101126694ASolve for moles of gasTests to Solve Specific VolumeVolume measurement apparatus/methodsMaterial analysisSteam pressureEngineering
The utility model discloses a test method and the device for testing the mole number of combustion gas of propellant. A quantitative sample is arranged in a calorimetric bomb; the air in the calorimetric bomb is discharged through charging and discharging inert gas; finally the pressure of the inert gas remained in the calorimetric bomb is lower than 0.2 MPa; the calorimetric bomb is arranged in an oil bath thermostat; the temperature of the oil bath thermostat is higher than 100 DEG C; at the same time, the pressure in the calorimetric bomb is not bigger than the saturated steam pressure of the current temperature. The sample is energized and ignited to combust in the calorimetric bomb; the gas produced by sample combustion is isothermal in the oil bath constant temperature bath; a pressure sensor on the calorimetric bomb is used to detect the pressure change during the whole process from ignition to constant temperature; a temperature transmitter in the constant temperature bath is used for testing temperature. The gas mole number and gas volume under standard state is converted according to ideal gas state equation. The utility model is accurate in water measurement, and solves the problems of testing the specific volume and the mole number of combustion gas of propellant containing chlorine.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Device and method for measuring volume of irregular object through gas
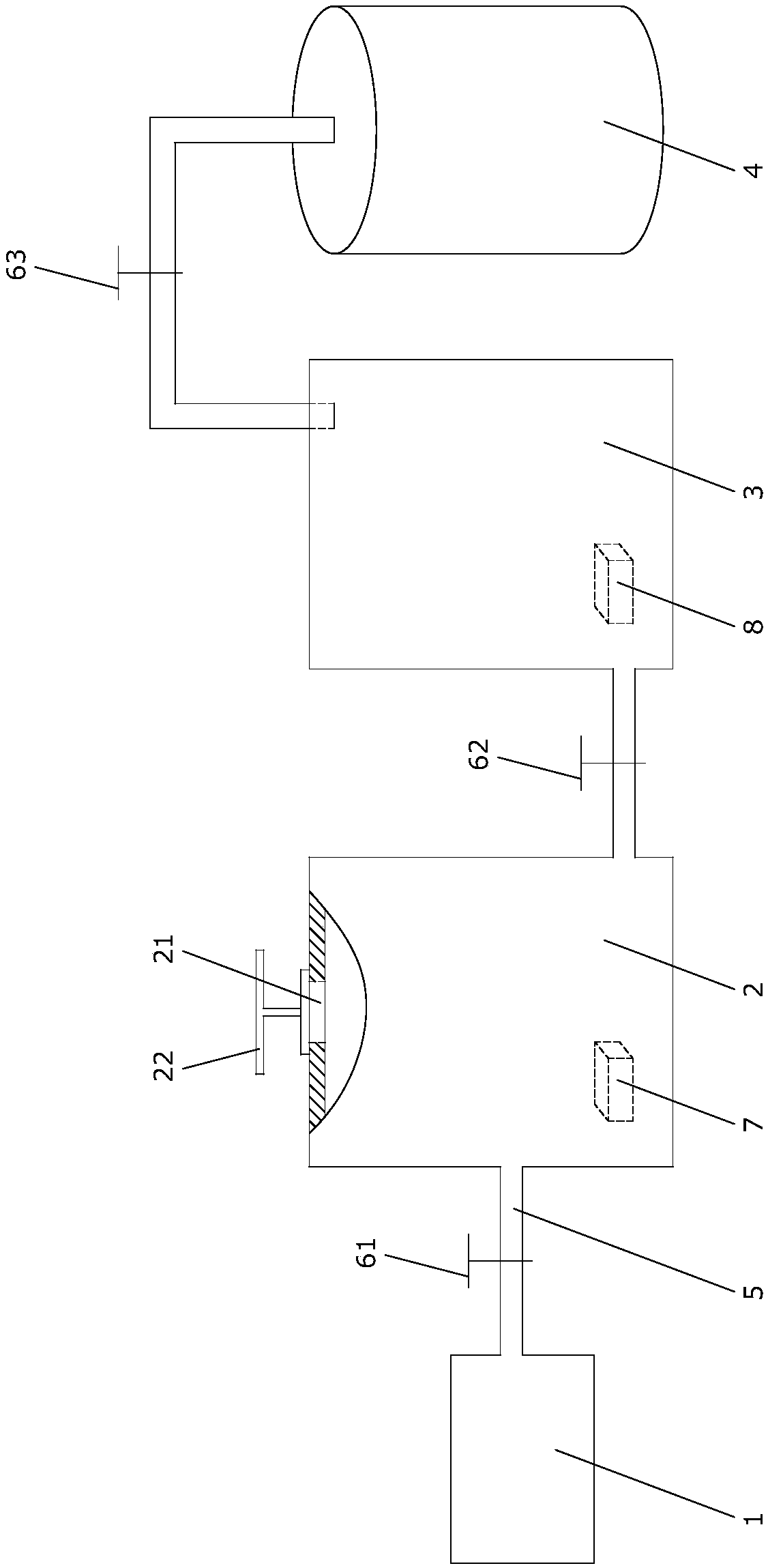
The invention discloses a device for measuring the volume of an irregular object through gas. A vacuum pump is communicated with a pressure tank A through a pipeline; the pressure tank A is communicated with a pressure tank B through a pipeline; the pressure tank B is communicated with a gas tank through a pipeline; a valve A, a valve B and a valve C are arranged on the pipelines in sequence; a pressure gauge A is arranged in the pressure tank A; a pressure gauge B is arranged in the pressure tank B; the pressure tank A is provided with an opening and a cover plate covering the opening; desired gas is arranged in the gas tank. In addition, the invention discloses a method for measuring the volume of the irregular object through the gas. According to the device and the method, the pressureintensity is measured through pressure intensity changes caused by volume changes in the pressure tanks according to a desired gas law and a desired gas equation, and then the volume of the irregularobject to be measured can be calculated; the device has a strict theoretical basis and an accurate measurement result; the measured object is not damaged in the measurement process; the device can beused for measuring the volumes of all types of irregular objects and particularly applicable to measurement of the volumes of objects which cannot be in contact with liquids.
Owner:上海力信能源科技有限责任公司
4K regenerative type low-temperature refrigerating machine and method by adoption of ultrasonic atomization device
InactiveCN103994597AImprove efficiencyCompact structureCompression machinesEnergy industryConduction lossProcess engineering
The invention relates to a 4K regenerative type low-temperature refrigerating machine by the adoption of an ultrasonic atomization device. The refrigerating machine comprises a first-stage compressor, a liquid helium temperature zone regenerative type low-temperature refrigerating machine body and the ultrasonic atomization device. When a refrigerating working medium (helium-4) is located at a low-temperature zone below 20 K, the performance of the helium-4 is closer to liquid in a condensed state because attraction among molecules is remarkably increased, so that pressure enthalpy loss, irreversible regenerative loss and heat conduction loss in a regenerator are increased rapidly, meanwhile, the expansion efficiency of the helium is reduced, and loss caused by an actual gas effect is gradually increased. Therefore, the key is how to decrease the loss caused by the actual gas effect in order to improve the efficiency of the regenerative type low-temperature pulse tube refrigerating machine at a liquid helium temperature zone. Based on the ultrasonic atomization principle, the ultrasonic atomization device is installed at the liquid helium temperature zone, so that liquid helium is atomized, and the helium works in a state closer to ideal gas. The 4K regenerative type low-temperature refrigerating machine is of great significance for the improvement of refrigeration efficiency at the low-temperature zone.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Numerical simulation of airflow within porous materials
InactiveUS20110282637A1Reduce needFeasible solutionGeometric CADComputation using non-denominational number representationCar seatElement analysis
Systems and methods of numerically simulating airflow within porous materials are disclosed. Engineering product (e.g., car seat) represented by a finite element analysis model containing in part porous material with permeability. In each solution cycle of a time-marching simulation, each of the elements of porous material is evaluated with airflow in conjunction with the traditional mechanical response. Each element's volume change results into different pore air pressure hence a pressure gradient, which in turn is used for airflow calculated in accordance with a fluid seepage law that depends upon permeability of the porous material. Therefore, a more realistic simulation of structural behavior of porous materials can be achieved. The volume change and pressure of each element of porous material is evaluated using ideal gas law. A general form of Darcy's law includes user control parameters is used for evaluating airflow based on the pressure gradient and permeability.
Owner:LIVERMORE SOFTWARE TECH
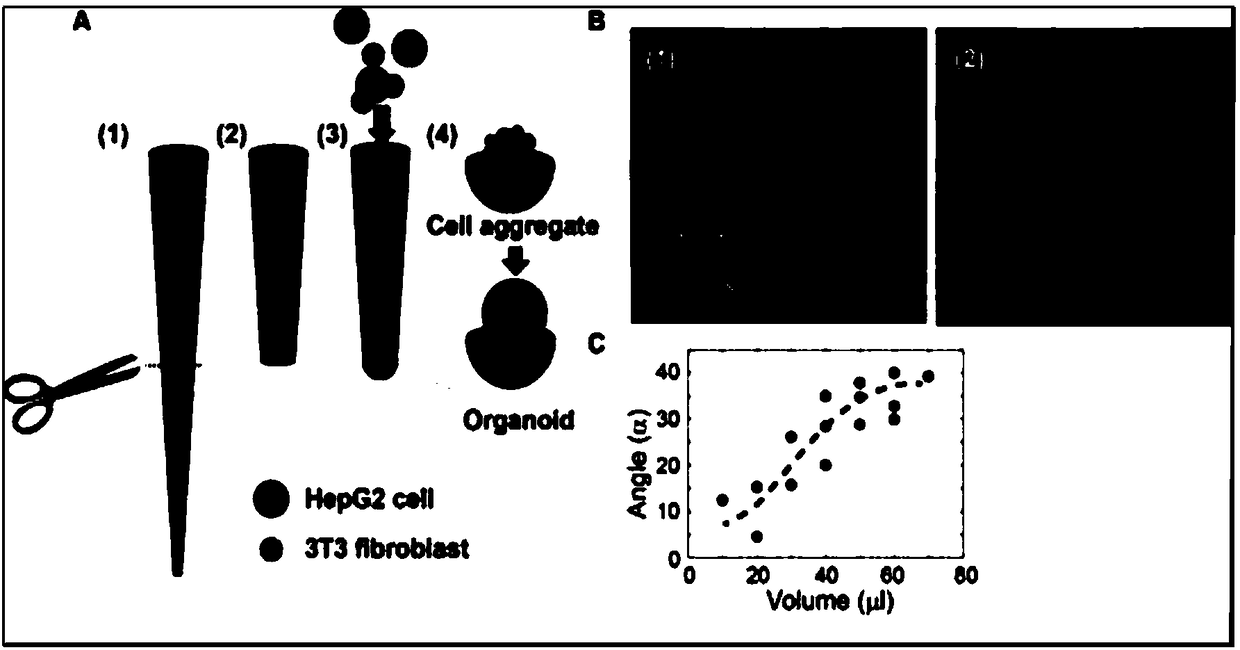
Liquid drop cultivation method of three-dimensional organs
ActiveCN108486035AOvercome effectivenessTo overcome the disadvantage of size)3D cultureGeneral culture methodsPipetteBiology
The invention relates to the fields of a biological technology and a cell culture technology, in particular to a liquid drop cultivation method of three-dimensional organs and application of the three-dimensional organs to biomedicine. A pipette tip and the conventional cell culture method are combined, a liquid drop with spherical conformation is formed by utilizing the pipette tip to serve as aculture carrier, and a millimeter-sized organ tissue is prepared by performing cultivation in the liquid drop. The ideal organ-like liquid drop culture condition is obtained by screening and analyzingfactors such as the cut position of the pipette tip, the volume of the injected liquid as well as the angle of the contact angle between the liquid drop and the section. Meanwhile, the form (shape and size) of the three-dimensional organ is controlled flexibly and effectively by adjusting the condition in a timely manner. In addition, the method provided by the invention has the advantages of being simple and convenient to operate, low in culture cost, high in culture efficiency and the like. The millimeter-sized three-dimensional organ tissue prepared according to the cultivation method canmeet the requirement of performing in-vitro medicine screening in the early personalized treatment stage.
Owner:陕西融光云生物科技有限公司
Suspension Control System Providing Closed Loop Control Of Hydraulic Fluid Volumes For An Agricultural Machine
ActiveUS20190178695A1Minimize error valueAgricultural vehiclesInterconnection systemsControl systemTransducer
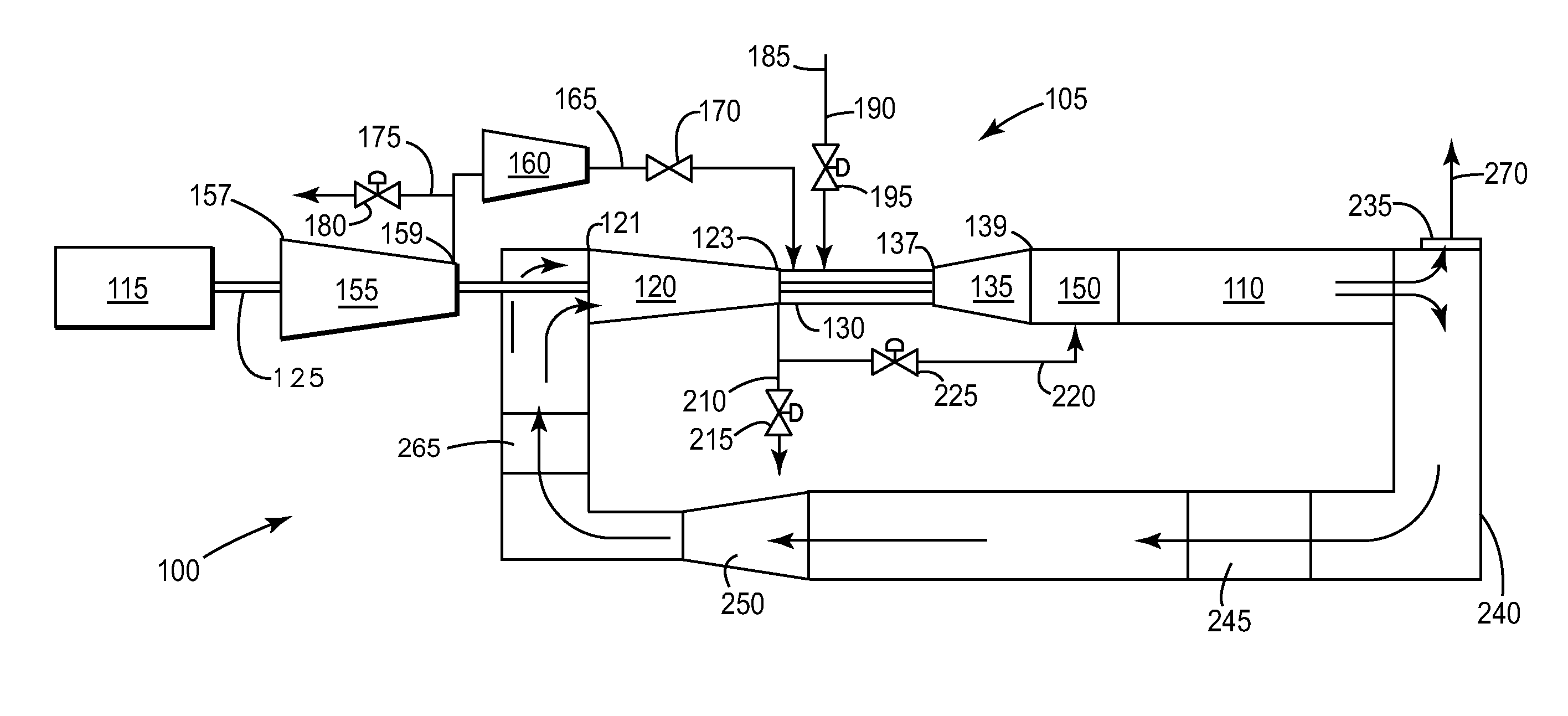
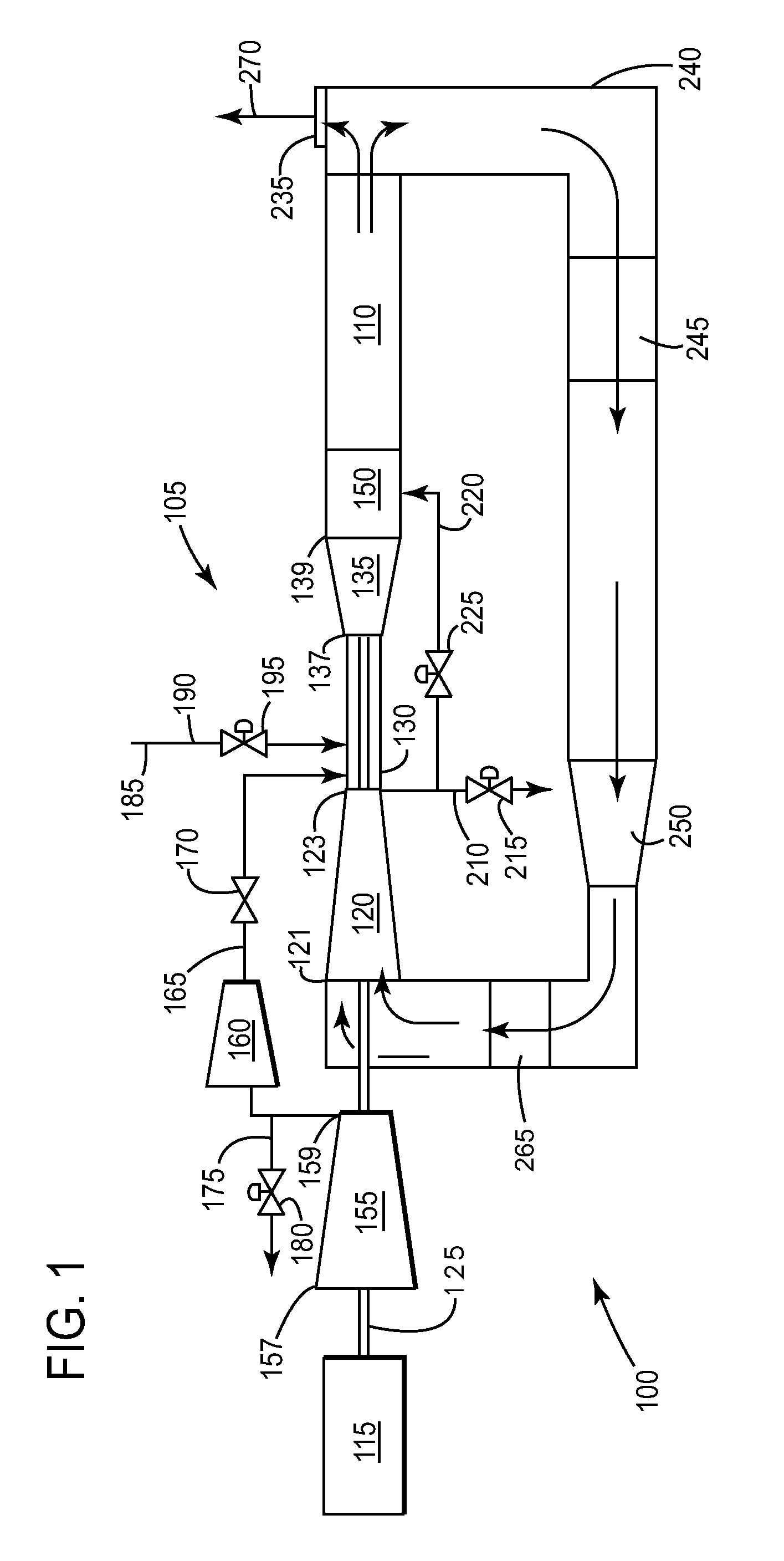
In one aspect, a control system is provided which determines fluid flow in a suspension system for an agricultural machine by determining total fluid in a closed loop piston system. Fluid is determined using position sensors and a pressure transducers and application of the ideal gas with respect to each accumulator. A closed loop control system can then target an amount of fluid for optimum suspension control.
Owner:BLUE LEAF I P INC
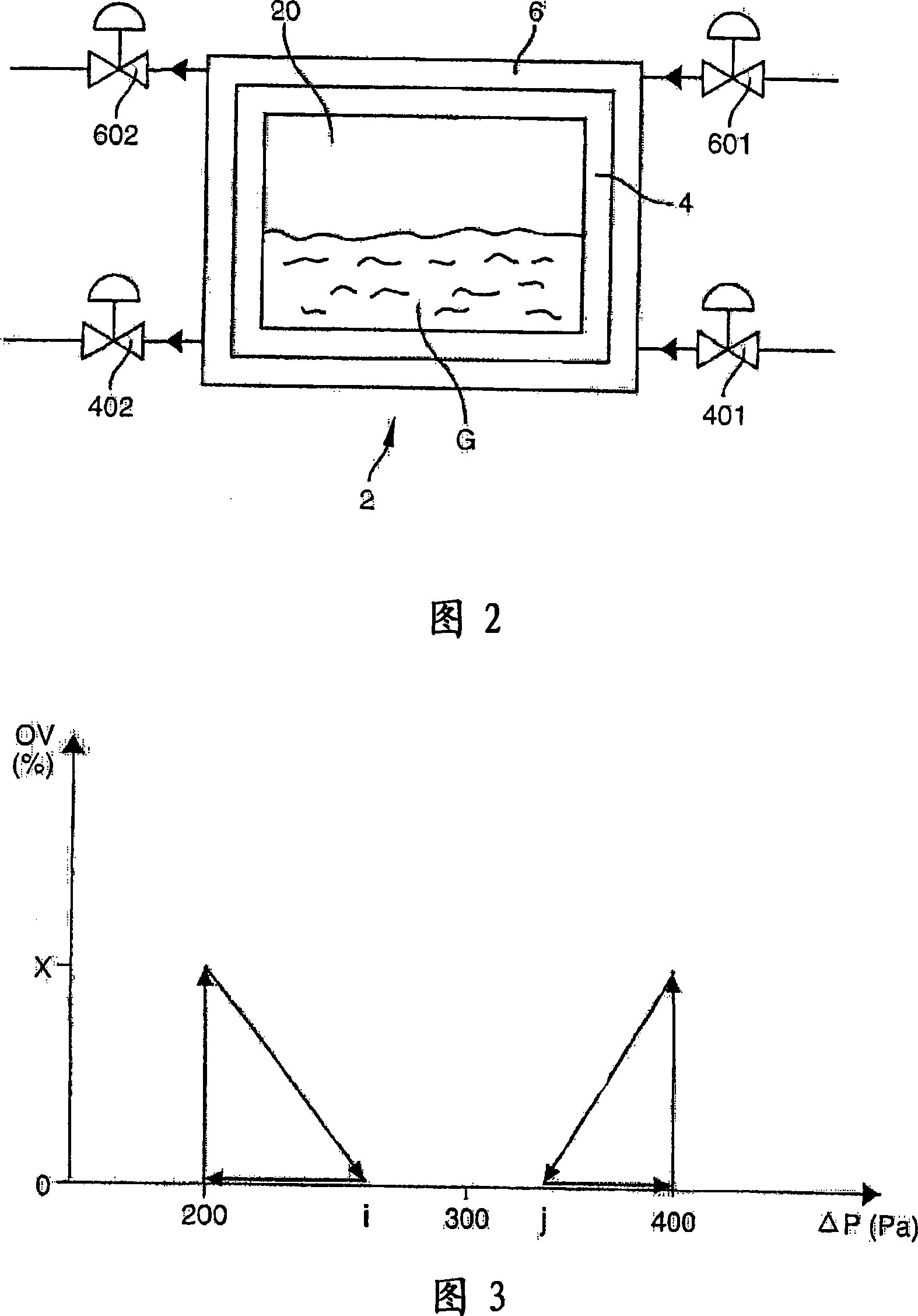
Method for measuring the actual porosity of the watertightness barrier of a fluid containment tank
The method involves measuring values of pressure and absolute temperature inside a free space (60) of a thermal insulation layer (6) at two instants during closing of inert gas i.e. nitrogen, intake and discharge valves (601, 602) or stable usage conditions of an insulated storage tank (20) e.g. membrane tank, to calculate layer's average pressure and temperature. Actual porosity of liquid / gas proof barrier is calculated based on specific formula comprising parameters such as rate of change of pressure inside the space, volume of the space, molar mass of inert gas and perfect gas constant.
Owner:STX EUROPE
Experimental method and device for measuring diffusion coefficient of carbon dioxide in water
InactiveCN104237079AAchieve rotationLearn about changesSurface/boundary effectDiffusionExperimental methods
The invention discloses an experimental method and device for measuring a diffusion coefficient of CO2 in water. The experimental device adopts a fixed diffusion distance and mainly comprises a data acquisition system, a constant temperature heating system, a pH meter probe, a diffusion kettle, a pressure sensor, a temperature probe and the like, wherein the pH meter probe is installed on a lower end cover of the diffusion kettle, the pressure sensor is installed on an upper end cover, one end of the temperature probe is connected with a heating coil outside the diffusion kettle, and the other end of the temperature probe is connected with the constant temperature heating system. When an experiment is performed in the diffusion kettle, the diffusion kettle is installed on a bearing and is turned to simulate a tilted stratum, pressure is utilized to calculate initial concentration of the CO2 according to an ideal gas equation, the hydrolysis amount of the CO2 is calculated according to a pH value acquired by the data acquisition system, a fitted curve of the CO2 hydrolysis amount and time square root is drawn to obtain slope k, and the diffusion coefficient D is calculated according to a calculation model.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
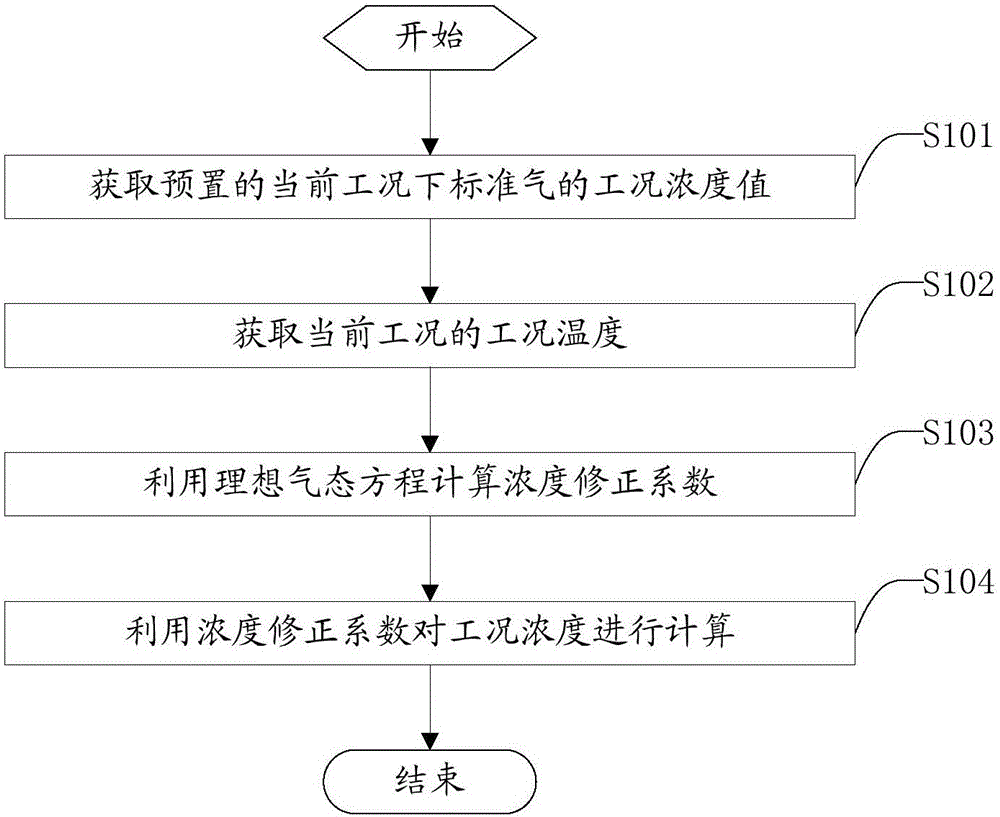
Standard gas distribution control method and system and standard gas distribution instrument
ActiveCN105806681AAvoid errorsTransportation and packagingPreparing sample for investigationGas analysisDistribution control
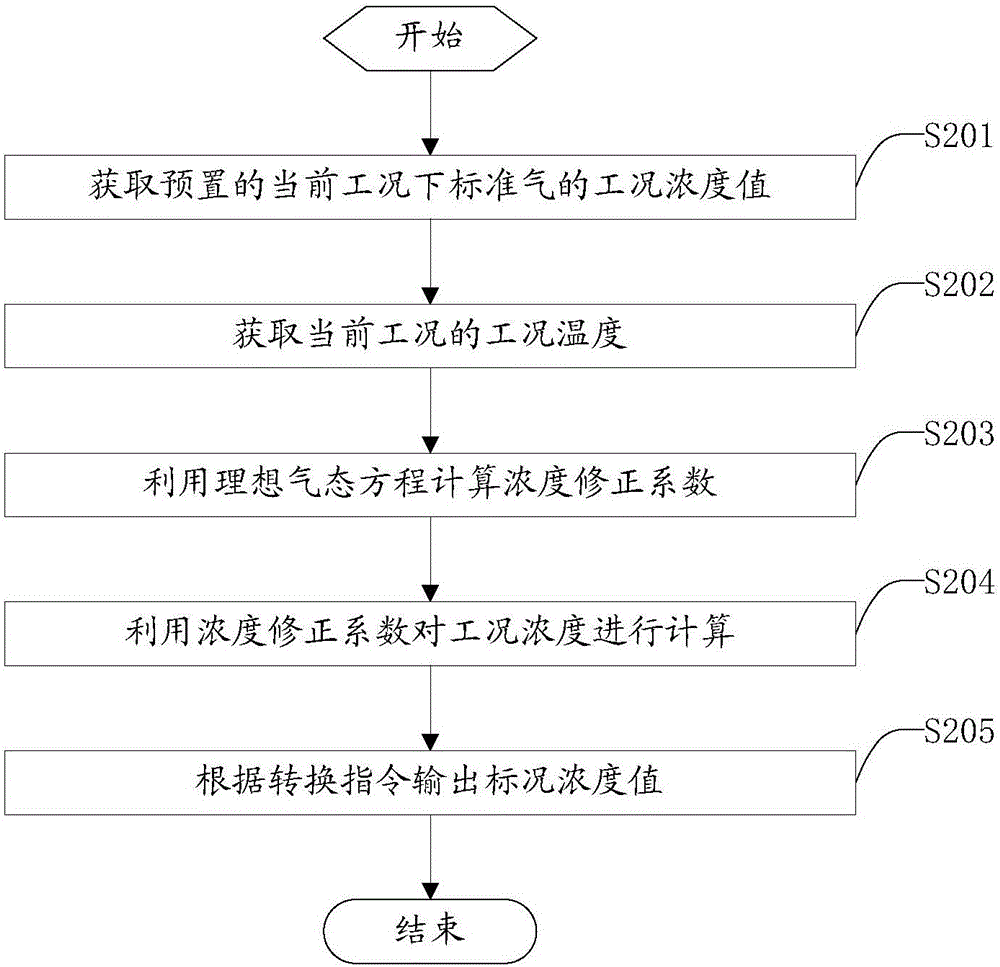
The application discloses a standard gas distribution control method and system and a standard gas distribution gauge.The method comprises the specific steps: acquiring preset condition concentration value of standard gas under current conditions, using a temperature sensor to acquire condition temperature under current conditions, calculating the condition temperature by an ideal gas equation to obtain a concentration correction coefficient, and correcting and calculating the condition concentration value by the concentration correction coefficient to obtain a standard concentration value of the standard gas under standard condition.The condition concentration under working condition can be corrected into the standard condition concentration under standard condition through the above conversion, and an operator can calibrate a gas analysis system according to the standard condition concentration value, thus avoiding errors generated during calibrating of the gas analysis system.
Owner:BEIJING SDL TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com