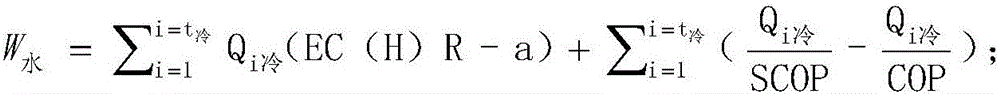Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
261 results about "Heating season" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
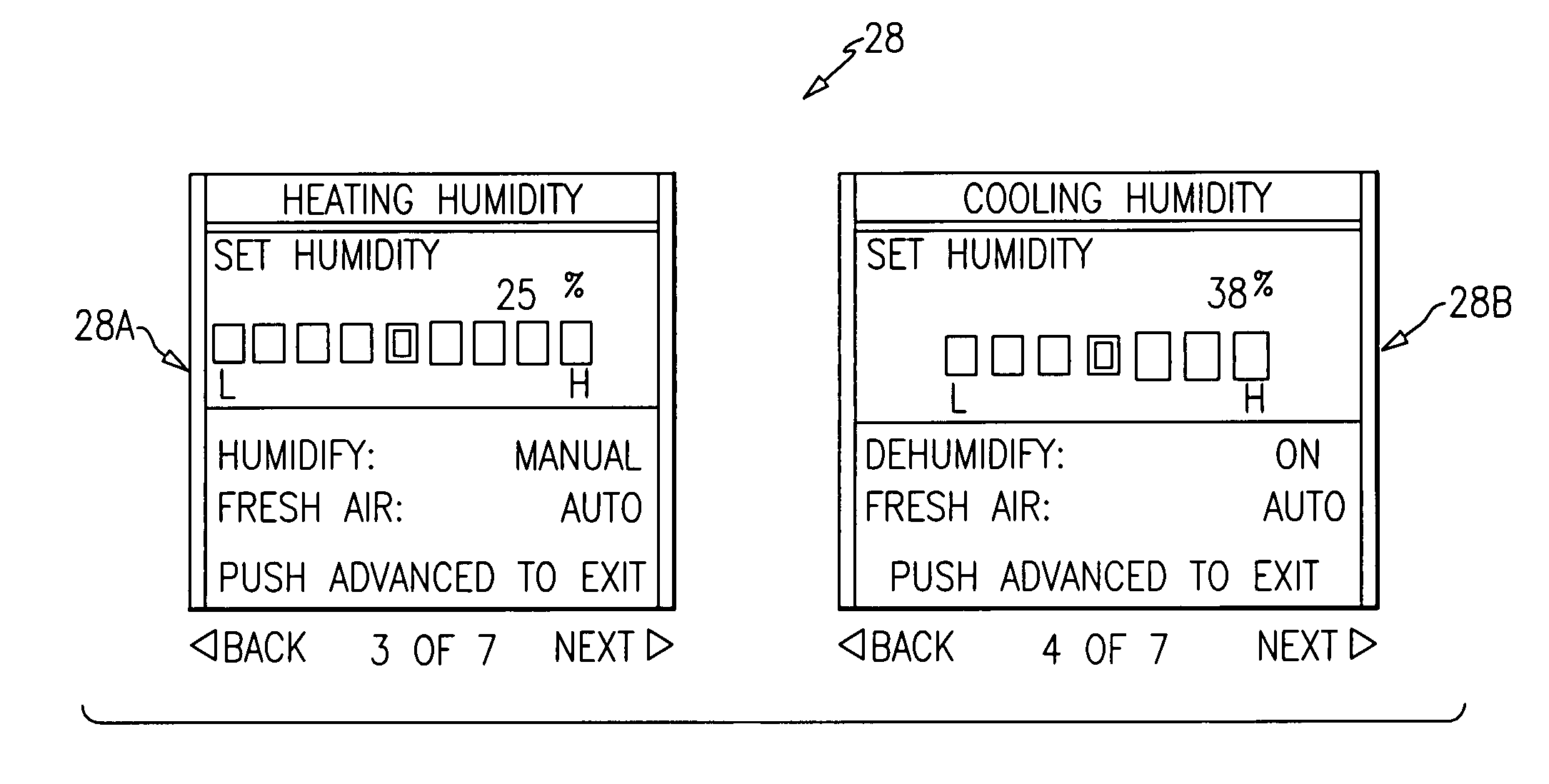
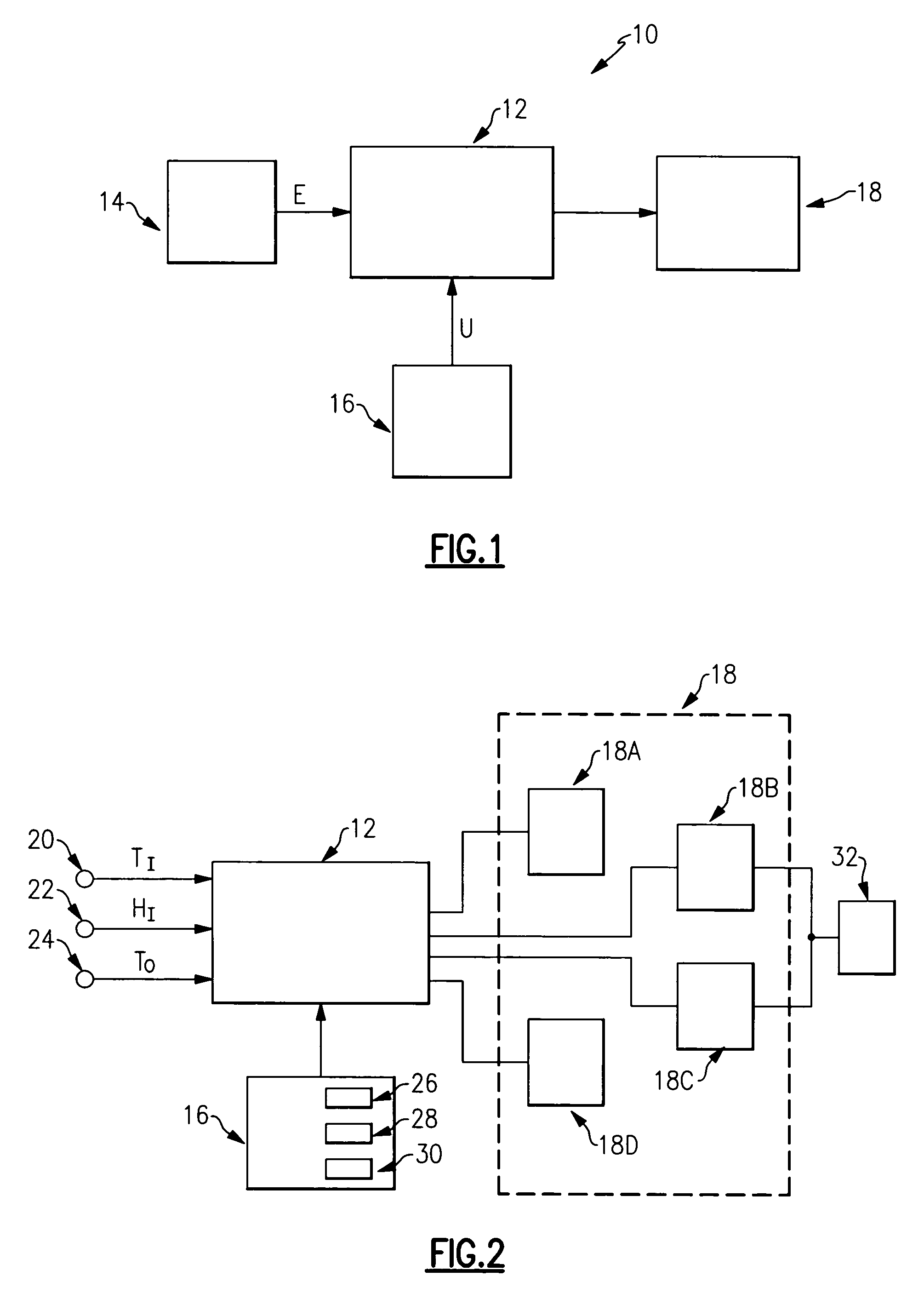
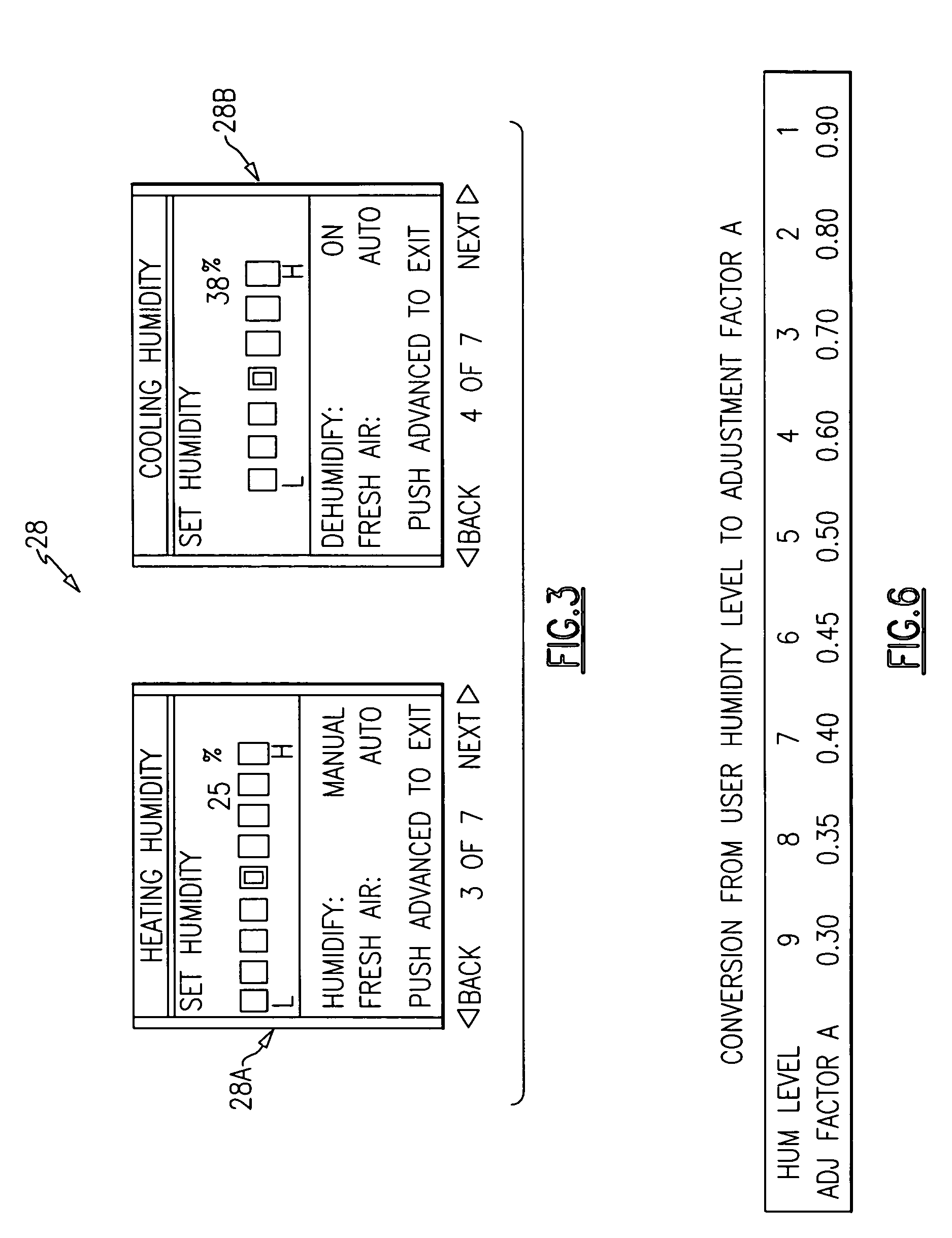
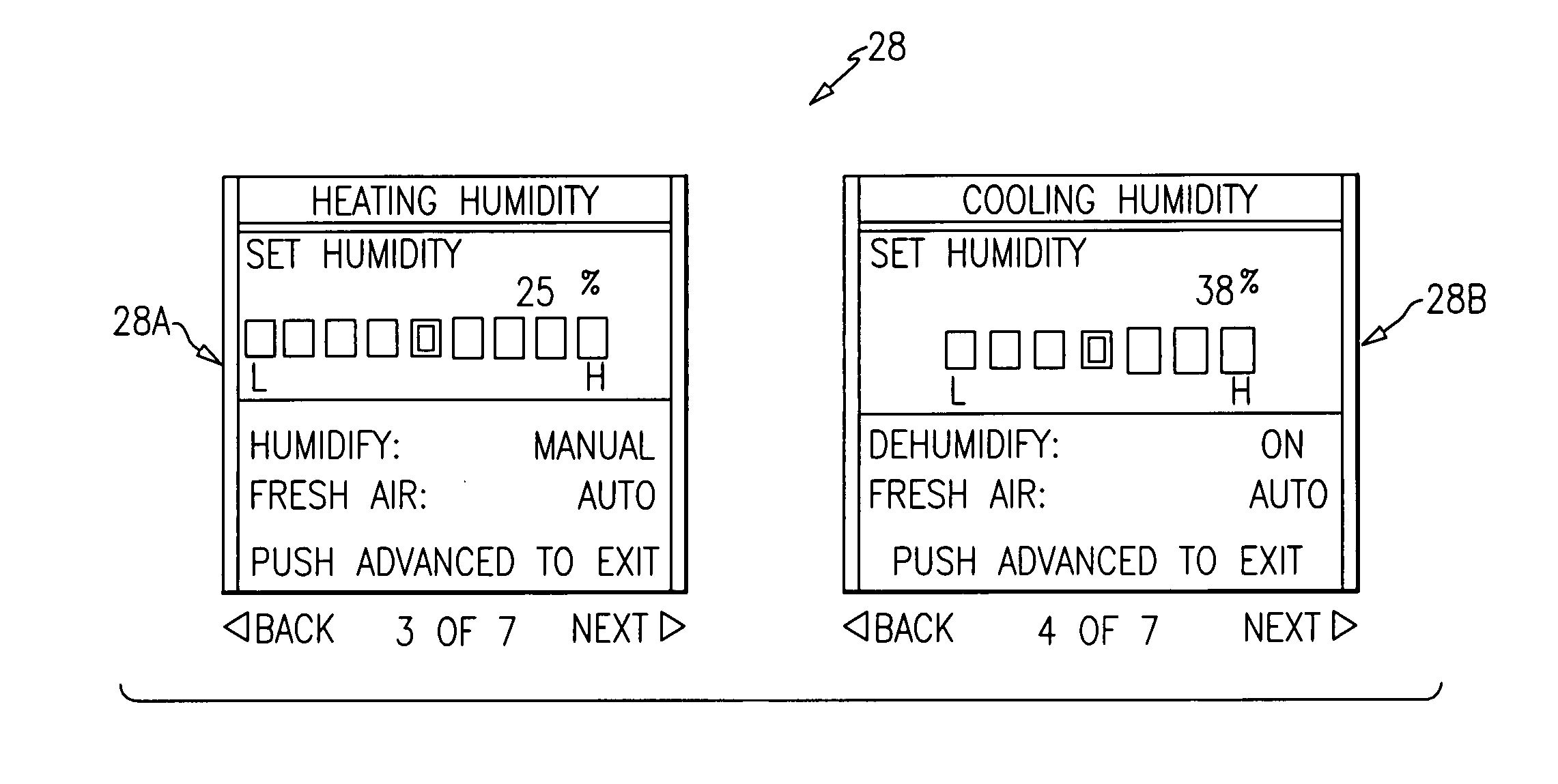
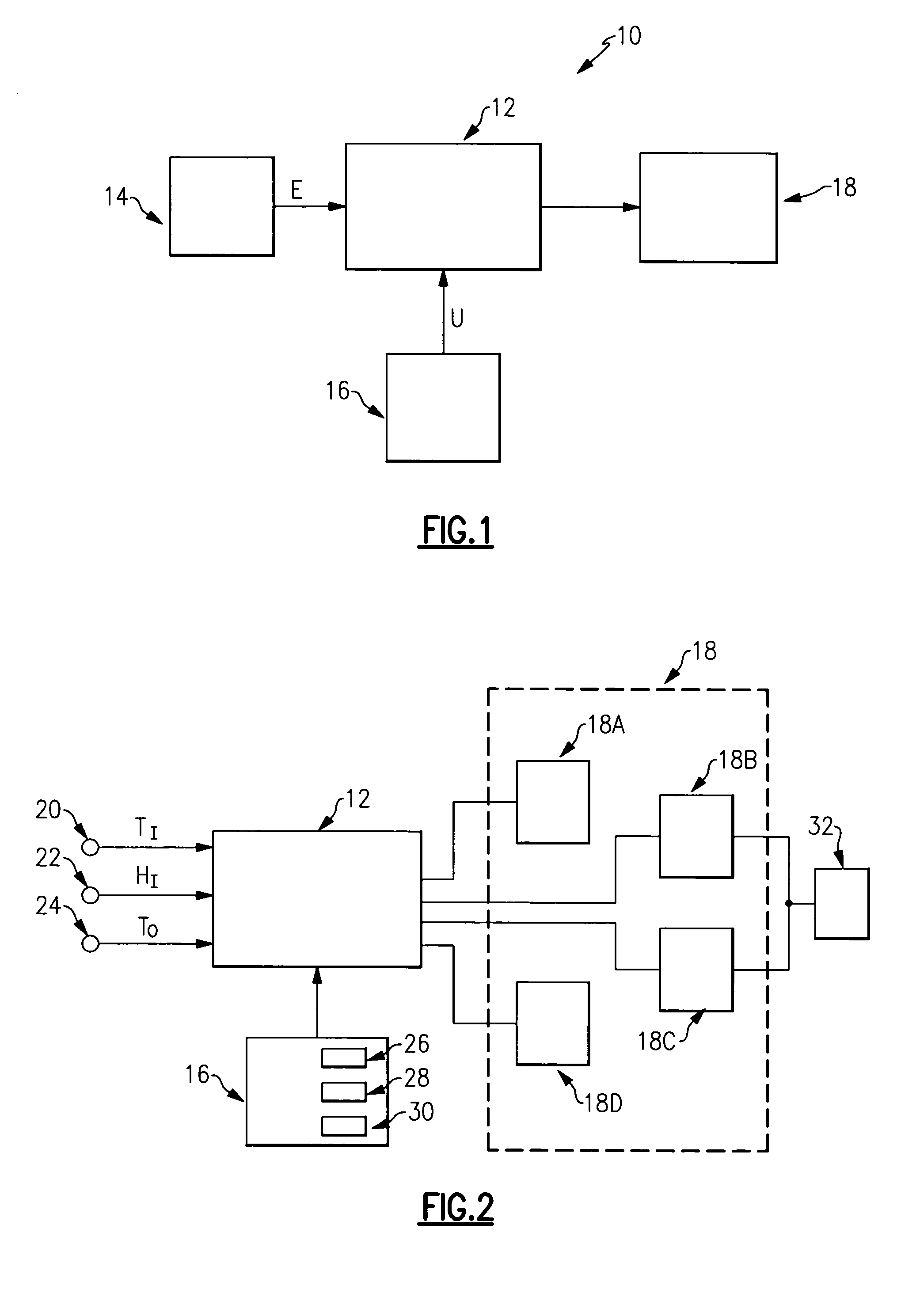
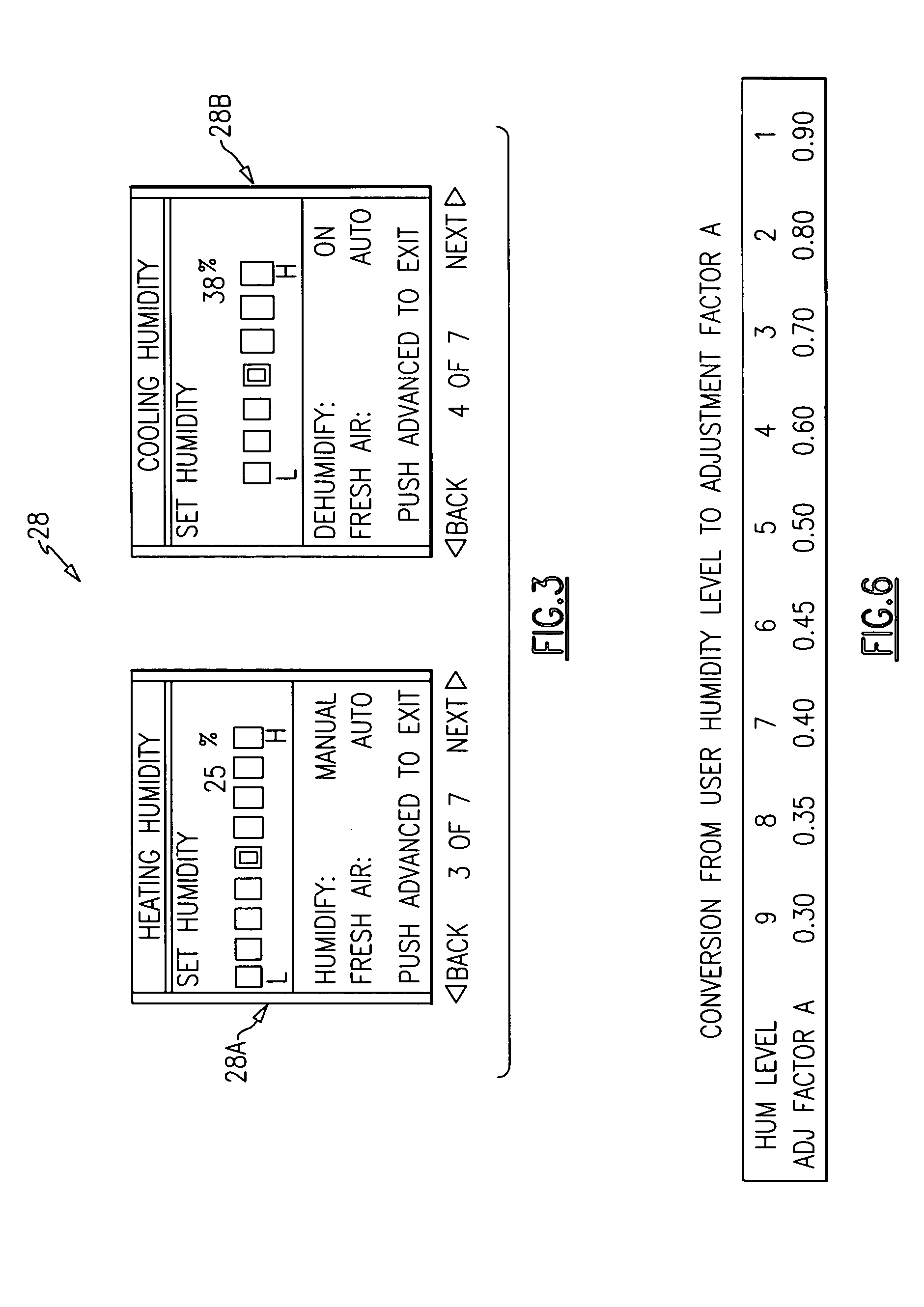
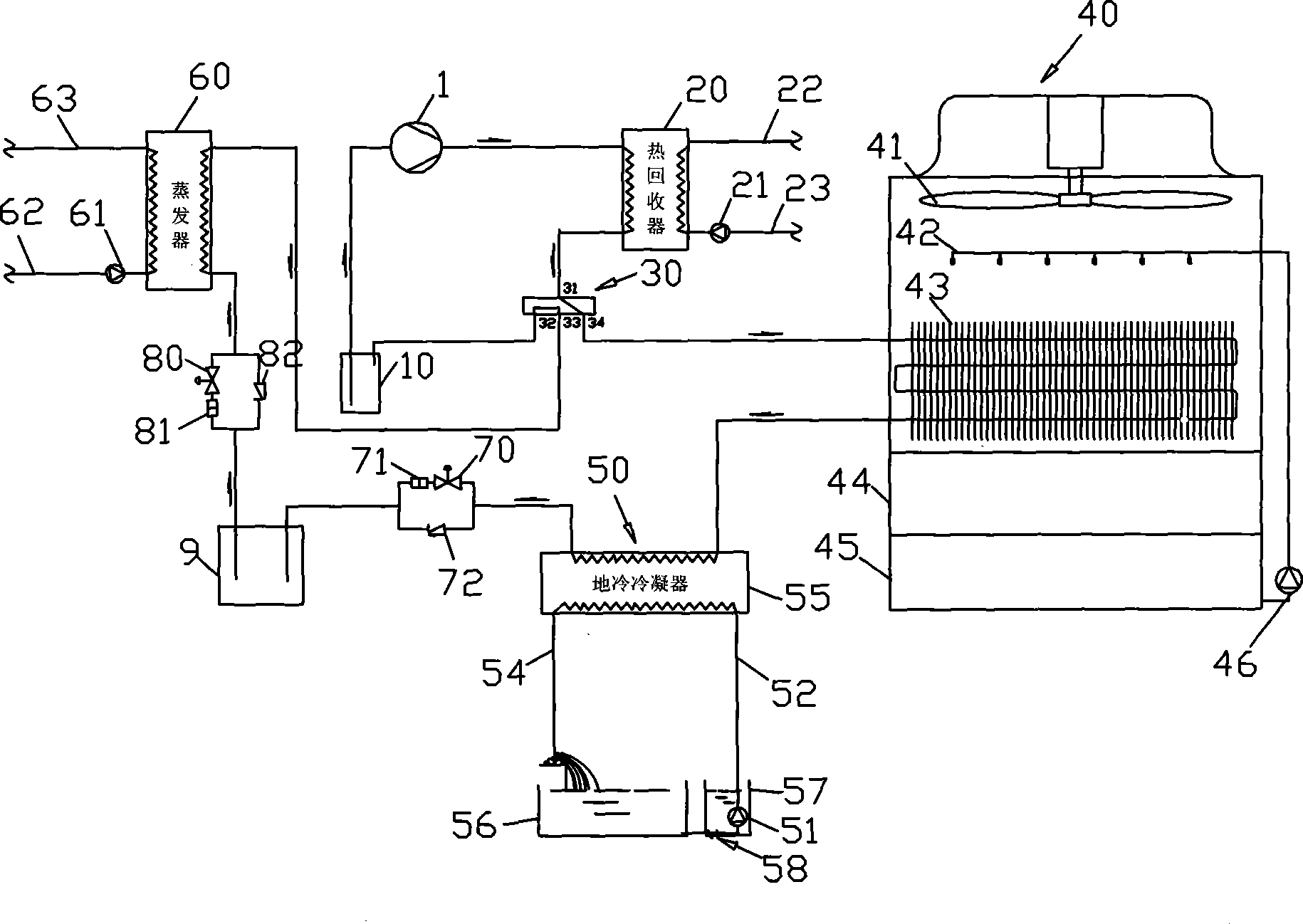
Single integrated humidity and ventilation control in an HVAC system
ActiveUS7266960B2Avoid condensationMechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsFresh airHeating season
HVAC systems are employed to control the indoor environmental characteristics of a building structure to make it comfortable for its inhabitants. An HVAC system includes one single integrated central control to regulate an indoor temperature level, an indoor relative humidity level and an indoor fresh air level of a building structure during both a heating season and a cooling season. Further, the single integrated central control is operable to selectively activate / deactivate an indoor blower to control a sensible ratio within a building structure. In addition, a protection feature for avoiding condensation on the interior surfaces of the building structure is included as an user selectable option.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
Heat quantity apportionment measuring method and device for central heating
ActiveCN101598611ASolve the real problemAddressing deviations in heat allocationTariff metering apparatusCalorimeterRoom temperatureEngineering
The invention relates to a heat quantity apportionment measuring method and a device for central heating. In the method, aiming at a heating system of a switching-on / switching-off type heat supply control mode, the apportionment measurement of the heating heat consumption is carried out according to a switching-on / switching-off time area method, modification with the time is carried out on the opening time of a switching-on / switching-off valve according to an built-in special modification computation program by the real-time measurement of the water supply and return water temperature values of heating users, and accumulation is carried out to calculate a modified opening specific value; when the heating season is over, the final modified opening ratio and the heating area of each user are used for apportioning the total heat quantity to determine heating charge which needs to be charged by each user; and the special modification computation program is designed in such a way that under the opening state of the switching-on / switching-off control valve, the water supply temperature value and the return water temperature value are read, the modified opening ratio is calculated, so the apportionment of the heat quantity used by the users is calculated. The device is suitable for the heat quantity apportionment measuring method for central heating and comprises a room temperature controller, the switching-on / switching-off control valve, a water supply temperature sensor, a return water temperature sensor, a heat supply control / opening time modification integrating instrument and the special modification computation program.
Owner:HEBEI GONGDA KEYA ENERGY TECH
Development of certain mechanical heat profiles and their use in an automated optimization method to reduce energy consumption in commercial buildings during the heating season
InactiveUS20160195887A1Reduce thermal energyGeometric CADMechanical apparatusOperating energyProcess engineering
The invention teaches a system and method for reducing energy consumption in commercial buildings. The invention provides development of certain mechanical heat profiles and use of such profiles in an automated optimization method. Outputs communicate with the building management system of the commercial building, and regulate the heating system during a season when the building activates the heating system. Various embodiments are taught.
Owner:SHIEL PATRICK ANDREW
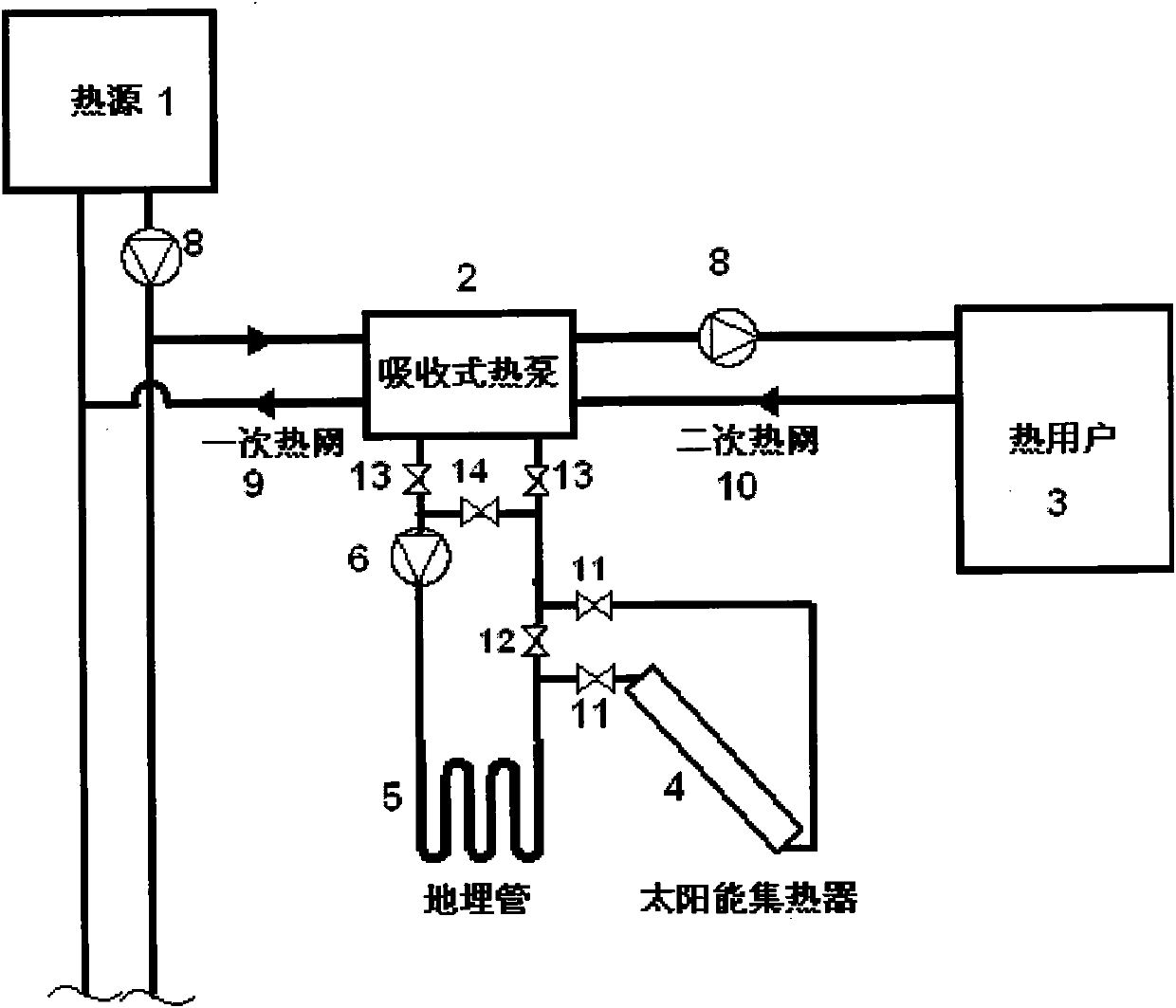
Solar energy and geothermal energy assistant centralized heating system
ActiveCN101922753AIncrease heat supplyIncrease profitHeat pumpsSolar heat devicesHeating seasonEngineering
The invention discloses a solar energy and geothermal energy assistant centralized heating system belonging to the technical field of centralized heating. A heating station is provided with a geothermal source adsorption heat pump unit, a centralized heating system once-network high-temperature hot water drives the adsorption heat pump, a soil source serves as the low-order heat source of the adsorption heat pump, heating medium adsorbs heat from earth and releases heat in a heat-pump evaporator, and adsorbed geothermy is used for secondary network heat supply. In order to restore soil temperature, the system adopts solar energy to serve as an assistant heat source; in the heating season, solar energy and geothermal energy mutually supplements; in the non-heating season, solar energy is independently used to recharge heat into ground so as to restore soil temperature and keep the soil temperature balanced in the whole year. The system takes the adsorption heat pump to replace a water-water heat exchanger and improves system heat supply amount by recovering environment heat; a solar energy soil heat accumulation mode is used for improving the utilization ration and system stability of the solar energy heat collector; and heat network water is used for driving the heat pump, thus saving a great quantity of electric power consumption, and lowering operation cost.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Single integrated humidity and ventilation control in an HVAC system
ActiveUS20050155363A1Avoid condensationMechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsFresh airControl of respiration
HVAC systems are employed to control the indoor environmental characteristics of a building structure to make it comfortable for its inhabitants. An HVAC system includes one single integrated central control to regulate an indoor temperature level, an indoor relative humidity level and an indoor fresh air level of a building structure during both a heating season and a cooling season. Further, the single integrated central control is operable to selectively activate / deactivate an indoor blower to control a sensible ratio within a building structure. In addition, a protection feature for avoiding condensation on the interior surfaces of the building structure is included as an user selectable option.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
Composite multi-source central air-conditioning machine set using geothermal energy
InactiveCN101418971AOvercome limitationsOvercome efficiencyEnergy recovery in ventilation and heatingHeat pumpsPlate heat exchangerWarm season
The invention is applicable to fields of air conditioners and provides a combined multi-source earth-energy central air-conditioning unit. The central air-conditioning unit comprises a primary heat exchanger, a secondary heat exchanger and a heat recovery system which are connected with other parts of a central air conditioner through pipes, wherein the primary heat exchanger, the secondary heat exchanger and the heat recovery system are serially connected through pipes. With the technical proposal, the central air-conditioning unit can use earth source and air source as cold and heat sources and uses the primary heat exchanger and the secondary heat exchanger to achieve a double cooling effect in cooling seasons and uses only the secondary heat exchanger in warming seasons with higher heat exchange efficiency, thereby overcoming the problem of limitation in the use of cold and heat sources and low heat exchange efficiency of earth source heat and air source heat pumps in the prior art. The central air-conditioning unit is also provided with a heat-recovery heat exchanger, so as to enable a user to make hot water for daily use during use of the air conditioner and bring great convenience in use of hot water in daily life.
Owner:巢民强
Solar heating system for geological trans-seasonal heat accumulation
InactiveCN103423799AMake up for deficienciesConducive to heating dynamic heat balanceCentral heating with accumulated heatSolar heat devicesThermal energyPlate heat exchanger
The invention discloses a solar heating system for geological trans-seasonal heat accumulation. A solar heating unit is in matched connection with a solar heat collector and a floor-heating-pipe radiant heating system respectively through pipelines. A geological heat reservoir in matched connection with the solar heating unit is buried in the earth's crust under the surface of the earth. The geological heat reservoir is composed of a heat-insulating shell, a solid heating accumulator and heat exchangers, and is arranged in a pit dug on the surface of the earth and positioned below a tundra of the earth's surface. The solid heat accumulator is wrapped and sealed by the heat-insulating shell, and the heat exchangers and a heat-exchanging working medium delivery pipeline are buried in the solid heat accumulator. The heat-exchanging working medium delivery pipeline is composed of a heat-exchanging working medium input pipeline and a heat-exchanging working medium output pipeline. A heat-exchanging working medium inlet at the first end of a geological heat-exchanging unit composed by the heat exchangers is correspondingly communicated with a heat-exchanging working medium outlet of the solar heating unit through the heat-exchanging working medium input pipeline. A heat-exchanging working medium outlet at the tail end of the geological heat-exchanging unit is correspondingly communicated with a heat-exchanging working medium inlet of the solar heating unit through the heat-exchanging working medium output pipeline. The solar heating system can convert solar energy in hot seasons into heat energy which is trans-seasonally stored for heating in heating seasons.
Owner:新疆品源太阳能科技开发有限责任公司
Method for identifying thermal defects by means of auxiliary heat source under condition of small temperature difference
InactiveCN101806762ASolve the detection problem of thermal defectsSolve the problem of 24/7 detectionRadiation pyrometryMaterial flaws investigationLine tubingHeating season
The invention provides a method for identifying thermal defects by means of an auxiliary heat source under the condition of small temperature difference and relates to an identification method of thermal defects. The invention solves the problem that the current infrared detecting method can only be used for detecting the building thermal defects in the regions with the indoor and outdoor temperature difference of more than 10 DEG C and also solves the problem that the existing thermal defect detecting methods can be influenced by solar radiation and outdoor conditions. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, using the auxiliary heat source to irradiate the inner surface of a building wall and heat the inner surface of the wall body, stopping irritation when the temperature of the inside of the wall body rises; secondly, using a thermal infrared imager to detect the temperature field distribution of the inner surface of the wall body, obtaining a thermal infrared spectrum showing the temperature field distribution of the inner surface; and finally analyzing the temperature difference shown in the thermal infrared spectrum to obtain the thermal defects of the building. The method of the invention is applicable to the thermal defect detection of the inner walls and insulated floor of buildings and can also be used for the pipe locating in non-heating seasons of the floor radiant heating system and the pipe locating in non-cooling seasons of the radiant cooling system.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH +1
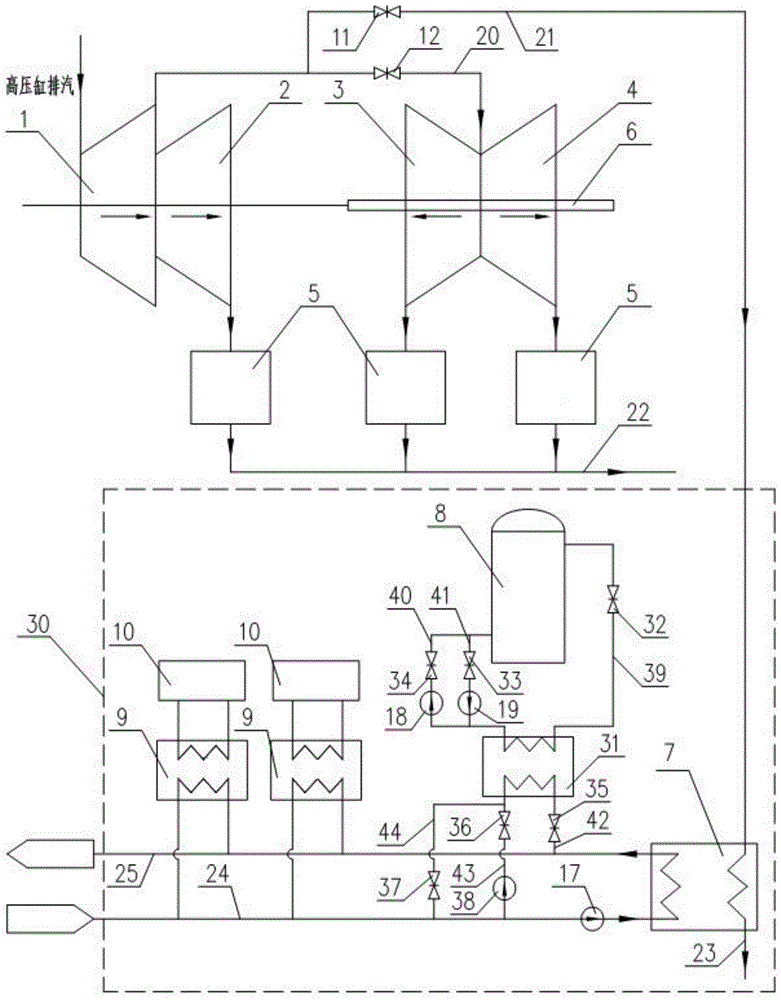
Steam turbine generating heating system with double running modes
InactiveCN103291391ALoss reduced to zeroZero lossSteam useCombined combustion mitigationCouplingEngineering
The invention provides a steam turbine generating heating system with double running modes. The steam turbine electric heating system comprises a generator, a first coupler, a low-pressure rotor, a second coupler, a high- and medium-pressure rotor, a condenser and a low-pressure cylinder flow portion. The low-pressure rotor comprises a pure coagulating rotor and a backpressure heating rotor. The high- and medium-pressure rotor of a steam turbine is connected with one end of the low-pressure rotor through the second coupler, and the other end thereof is connected with the generator through the second coupler to perform generating heating. In an off-heating season, the pure coagulating rotor serves as the low-pressure rotor, and a system is operated in a coagulating mode; in a heating season, the pure coagulating rotor is replaced by the back pressure heating rotor, and the system is operated in a backpressure mode. The steam turbine generating heating system with the double running modes is characterized in that flow grade of the pure coagulating rotor is of 2X6, while flow grade of the back pressure heating rotor which is a one-piece-forged centerless rotor is of 2X4.
Owner:HUADIAN POWER INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION LTD
Energy-saving full-function refrigeration cycle system
ActiveCN101532745AImprove energy efficiency ratioReduce energy consumptionCompression machines with reversible cycleAir conditioning systemsHeating seasonCoefficient of performance
The invention discloses an energy-saving full-function refrigeration cycle system, which consists of an indoor unit and an outdoor unit, wherein the outdoor unit comprises a compressor, an outdoor heat exchanger, a heating expansion valve, a check valve, a heating dry filter, a liquid receiver, a vapor-liquid separator and a pipe joint; and the indoor unit comprises a blower, an electromagnet valve B, an electromagnetic valve A, a refrigerating dry filter, a refrigerating expansion valve B, a check valve B, an indoor heat exchanger B, a check valve A, a refrigerating expansion valve A, an indoor heat exchanger A, an electromagnetic valve C, and a four-way reversing valve. The refrigeration cycle system can meet the requirement of control precision defined by the national standard under the condition of energy-saving operation. The refrigeration cycle system can greatly save heating energy consumption through the energy-saving operation of partial working condition, improve the energy-efficiency ratio in a heating season and annual performance coefficient, and has important practical value.
Owner:NANJING TICA AIR CONDITIONING CO LTD
Air conditioner control method and air conditioner
ActiveCN110500705AFit needsImprove comfortMechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsOperation modeHeating season
The embodiments of the invention disclose an air conditioner control method and an air conditioner, and relates to the technical field of air conditioners. An operating mode can be automatically determined from a professional perspective, the purposes of energy saving and health keeping are achieved, and the comfort of the air conditioner is improved. According to the specific scheme, the currenttemperature and current relative humidity of an indoor environment are detected; and if the current temperature and current relative humidity meet preset conditions, the current operating mode is switched to a target mode, the current operating mode and the target mode are both operation modes included in current season, the current season is any of the cooling season, the heating season and the rainy season, and the air conditioner is controlled to operate according to the target mode. The air conditioner control method disclosed by the embodiments of the invention is used in an intelligent control process of the air conditioner.
Owner:HISENSE (SHANDONG) AIR CONDITIONING CO LTD
Method for calculating pipeline vibration fatigue life of frequency conversion air conditioner
InactiveCN106033498ACalculate Vibration Fatigue LifeAccurate calculationInformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsFatigue damageFrequency conversion
The invention relates to an air conditioner and provides a method for calculating the pipeline vibration fatigue life of a frequency conversion air conditioner. The working conditions of the frequency conversion air conditioner in the refrigerating season and the heating season every year and actual contributions of all frequency points to pipeline vibration need to be combined to estimate the pipeline vibration fatigue life of the frequency conversion air conditioner. The average operating frequency of the frequency conversion air conditioner is calculated through weighting, the working conditions of the frequency conversion air conditioner and the weights of all operating frequency points are determined, fatigue damage of pipelines of the frequency conversion air conditioner in a starting state, an operating state and a halt state within a year is calculated according to fatigue features of pipeline materials and tested vibration maximum stress values at all the frequency points, and the pipeline system vibration fatigue life of the frequency conversion air conditioner is calculated through accumulation of the fatigue damage. The method is suitable for the frequency conversion air conditioner.
Owner:四川长虹空调有限公司
Method for changing pure condensation into back pressure heat supply
The invention discloses a method for changing the heat supply of a large and medium steam turbine, in particular a method for changing pure condensation into back pressure heat supply. In the method for changing the pure condensation into the back pressure heat supply, a high and medium pressure rotor in the steam turbine is connected with one end of a low pressure rotor through a coupler B; the other end of the low pressure rotor is connected with a generator through a coupler A for power generation and heat supply. The method is characterized in that: the low pressure rotor is a pure condensation rotor in non-heating season and the pure condensation rotor is changed into a back pressure heat supply rotor in the heating season. The method for changing the pure condensation into the back pressure heat supply is suitable for transforming an extraction condensing high and low pressure cylinder steam turbine generator unit which has been put into operation; and the back pressure heat supply rotor is used in the heating season and the pure condensation rotor is used in non-heating season, so heat supply efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:SHANDONG HONGAO POWER TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Seasonal heat storage and heating system and heating method thereof
ActiveCN107166499AReduce heat lossHeating fuelLighting and heating apparatusHeating seasonEngineering
The invention provides a seasonal heat storage and heating system and a heating method of the seasonal heat storage and heating system and relates to the technical field of heat storage and heat supply. The heat storage and heating system comprises a solar heat collector, a buffer water tank, a first heat exchanger, a second heat exchanger and an underground heat storage system. The solar heat collector heats water in the buffer water tank through the first heat exchanger. The underground heat storage system comprises a heat storage pool and first heat exchange coil pipes, all of which are buried in the ground. The first heat exchange coil pipes are arranged around the heat storage pool. The second heat exchanger communicates with the first heat exchange coil pipes through the heat storage pool and used for heating a heat storage medium in the heat storage pool and heating soil around the heat storage pool. By the adoption of the seasonable heat storage and heating system and the heating method, solar heat in the non-heating season is stored through the heat storage pool, the soil around the heat storage pool is heated through the first heat exchange coil pipes arranged around the heat storage pool, and the heat storage of the soil around the heat storage pool is used effectively; and furthermore, heat emitted by the heat storage pool can be used for the second time due to the arrangement of the first heat exchange coil pipes around the heat storage pool, and the system efficiency is provided.
Owner:RICHU DONGFANG SOLAR ENERGY
Seasonal solar energy-phase change energy accumulation graded energy-releasing heating system and method
InactiveCN103712255AReduce dependenceMitigating the problem of large heat loss across seasonsHeat storage plantsEnergy storageThermal energyCollector device
The invention belongs to the field of seasonal energy accumulation heating, and particularly relates to a seasonal solar energy-phase change energy accumulation graded energy-releasing heating system and method. The system mainly comprises a solar heat collector, a phase change energy accumulation heat exchanger, a heating module and a heat exchanger, all of which are connected together through a pipeline, a valve and a circulating pump. According to the system, in non-heating season, solar heat is stored in phase change materials with different temperature levels capable of realizing stable undercooling, so as to stand in an undercooling liquid state; in heating season, two modes, namely, heating load supply by direct heat exchange between heating medium water and the heat collector and heating load supply by direct heat exchange between the heating medium water and the phase change heat exchanger, can be adopted and the phase change material units with different temperature levels are triggered by grades to be solidified and release energy according to loads in different stages. By utilizing the conception that the seasonal phase change energy accumulation graded released energy is utilized to provide heating load in winter, the system has the characteristics of being large in phase change latent heat, stable in heat release temperature, capable of being adjusted by grades, and the like, thus having wide application prospects in a seasonal heat accumulation heat supply system.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Circulating water-cooled plant factory LED (light-emitting diode) surface light source heat dissipation management system and method
InactiveCN103471061AGuaranteed luminous efficiencyReduce light decay ratePoint-like light sourceElongate light sourcesThermal energyMeasuring instrument
A circulating water-cooled plant factory LED (light-emitting diode) surface light source heat dissipation management system and method. The system comprises an LED panel heat dissipation device, a controller, a temperature measuring instrument, a heat energy replacement system and a water channel circulating system, the LED panel heat dissipation device is mounted at the back of a lamp panel, the temperature measuring instrument is mounted on a pipeline of the water channel circulating system entering and exiting the heat dissipation device, the water channel circulating system penetrates the heat dissipation device, the temperature measuring instrument acquires the temperature of inlet and outlet water passing the heat dissipation device, and the controller calculates heat in a replacement water channel of the heat energy replacement system according to the temperature of the inlet and outlet water and controls the rotating speed of a radiator fan to perform heat dissipation. Heat energy generated by LEDs can be timely dissipated, the light-emitting efficiency of the LEDs is ensured, and light attenuation rate is reduced. Besides, the heat energy dissipated from the LEDs can be used for heating the indoor environment of a plant factory in heating seasons, the heat energy is timely discharged from the indoor environment in non-heating seasons, and energy consumption for cooling in the non-heating seasons is reduced.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Solar energy water heater afterheat comprehensive using device
InactiveCN101644509ARunning consumes less powerImprove energy utilizationSolar heat devicesMachines using electric/magnetic effectsHigh energyTemperature difference
The invention relates to a solar energy water heater afterheat comprehensive using device which can maximize the using of the afterheat and realizes the indoor heating and temperature difference powergeneration function through a simple and direct circulating pipeline. In the heating season, the device firstly supplies heating to a bathroom and a bedroom; in other seasons, the afterheat is mainlyused for temperature difference power generation and hot water circulates and returns into the solar energy water heater to be heated again. The whole circulation system is controlled by an electronic self-control device and does not need to be operated manually. In addition, the system is simple and easy to be modified, has strong reliability, high energy utilization efficiency, lower cost and very strong practicability and excellent market development prospect.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
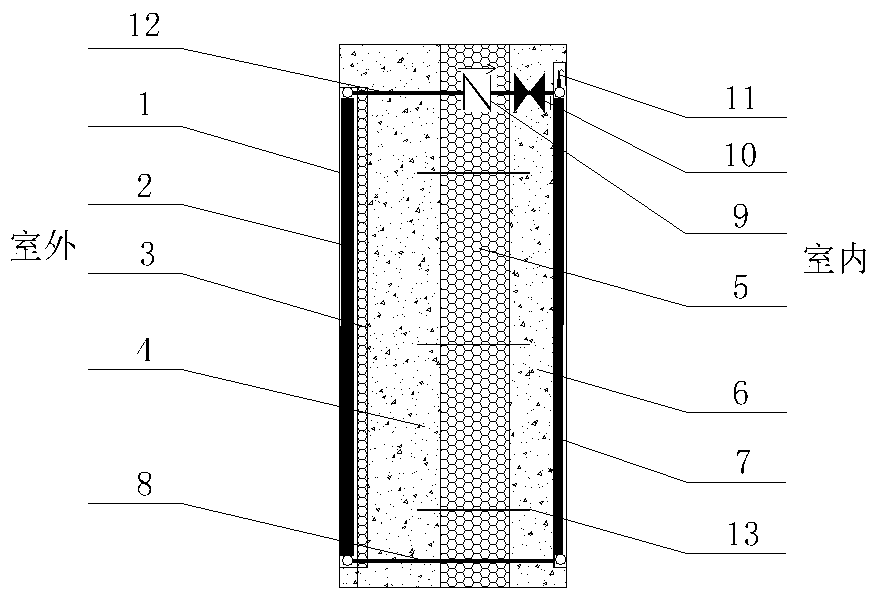
Sandwich heat preservation type solar building integrated wall body
InactiveCN109779086ALarge thermal resistanceBlock deliverySolar heating energySolar heat collector controllersExhaust valveInsulation layer
The invention relates to a sandwich heat preservation type solar building integrated wall, mainly comprising a glass plate, a heat collection plate, a heat collection plate heat insulation layer, an outer bearing wall, a heat preservation layer, an inner bearing wall, a heat radiation plate, a circulating pipe I, a check valve, a control valve, an exhaust valve, a circulating pipe II and a connecting piece. The glass plate, the heat collection plate and the heat collection plate heat insulation layer are embedded in the outer surface of the outer bearing wall. The heat preservation layer is installed between the outer bearing wall and the inner bearing wall. The heat radiation plate is embedded in the inner surface of the inner bearing wall. The heat collection plate and the heat radiationplate are connected through the circulating pipes with the check valve, a control valve and the exhaust valve. The check valve and the control valve are used for controlling heat-carrying fluid to circularly flow in a closed loop formed by the heat collection plate, the circulating pipes and the heat radiation plate, solar heat is transferred to the indoor for heating in the heating season, indoor heat is prevented from being dissipated to the outdoor, and the heating heat load is saved. Outdoor heat can be prevented from entering indoors in the air conditioner season, and the air conditionercooling load is reduced.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
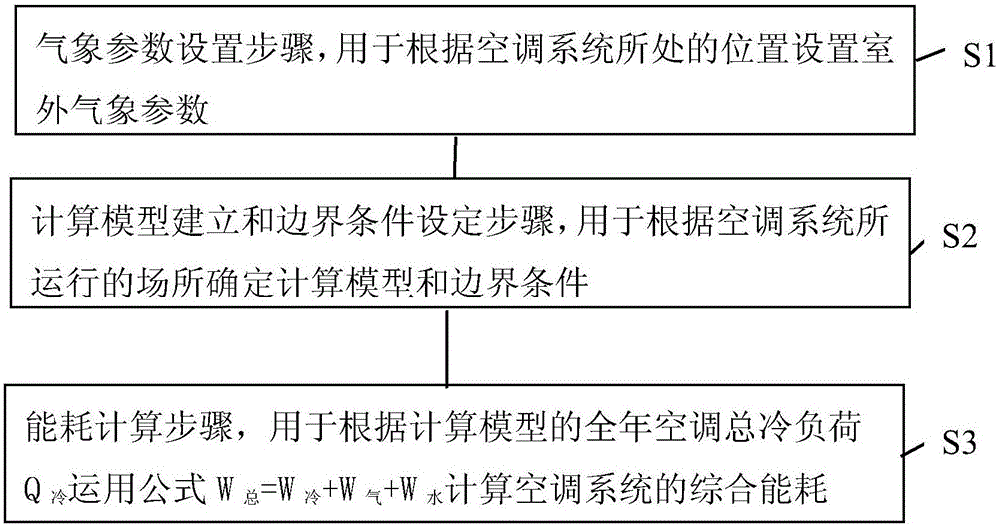
Analysis method for comprehensive energy consumption of air conditioning system in non-heating season
ActiveCN106529167AAccurate calculation of energy consumptionImprove air conditioning systemSpecial data processing applicationsInformaticsSimulationOperation mode
The invention provides an analysis method for comprehensive energy consumption of an air conditioning system in a non-heating season. The method comprises the following steps of a meteorological parameter setting step used for setting an indoor meteorological parameter according to a position where the air conditioning system is located; a computation model building and a boundary condition setting step used for determining a computation model and a boundary condition according to a place where the air conditioning system runs; and a comprehensive energy consumption computation step used for computing the comprehensive energy consumption of the air conditioning system by using a formula: FORMULA, according to an annual air-conditioner overall cooling load of the computation model. According to the energy consumption computation method for the air conditioning system in the non-heating season provided by the invention, computation of the energy consumption of the air conditioning system is more accurate, specific computation modes for refrigeration energy consumption, air system transmission energy consumption and water system transmission energy consumption are particularly provided, so that the different air conditioning systems can be provided for different building types of different cities and the air conditioning systems and operation modes can be improved, and thus energy consumption of the air conditioning system can be reduced.
Owner:深圳市云科设计咨询服务有限公司
Waste heat recovery thermal power plant energy storage method and system
InactiveCN103742964AImprove heating effectExpand profitsHeat storage plantsSpace heating and ventilation detailsThermal energy storageHeating season
The invention discloses a waste heat recovery thermal power plant energy storage method. In the daytime of a heating season, power generated by a power unit is completely used for generating electricity, and all heating systems are borne by energy storage water; at night of the heating season, steam pumped out by a steam pumping opening of a low pressure cylinder of a steam turbine in the power unit drives a first-stage heating unit to enable 60 DEG C heat supply network return water obtained from a heat supply network return water unit to be heated to reach 80 DEG C, then the steam pumped out from the steam pumping opening is heated by the steam turbine to drive a second-stage heating unit to continuously heat the heated 80 DEG C return water to reach 120 DEG C, and the 120 DEG C energy storage water serves as a heat source of the heating system. According to the waste heat recovery thermal power plant energy storage method, the load adjusting and peak adjusting requirements are easily met, the electricity shortage situation in the peak period can be remitted, the electivity resource allocation is optimized, and the electricity utilization efficiency is improved. As for a thermal power plant achieving the designed heating amount upper limit, heating energy storage is carried out at the electricity load low ebb period at night, heating by stored energy released in the daytime and heating of an original heating system are carried out at the same time, the heating capacity of the thermal power plant is improved, the earnings of the thermal power plant are improved, industrial waste heat of the thermal power plant is recycled, the comprehensive saving rate of the heating energy storage water achieves 20%, and the energy dilemma and the environmental pollution are easily remitted.
Owner:HENAN AIMOKA ENERGY SAVING TECH
Multi-energy-complementary heating and heat supply system of nearly zero energy consumption building in alpine region
InactiveCN106439993AImprove insulation effectSolve intermittentSolar heating energyLighting and heating apparatusEngineeringHeating season
The invention relates to a multi-energy-complementary heating and heat supply system of a nearly zero energy consumption building in an alpine region. The solar energy is combined with building foundation storage energy storage to achieve heating in winter, and the solar energy is combined with an air source heat pump to achieve domestic hot water supply. The multi-energy-complementary heating and heat supply system comprises a solar thermal collector, a heat storage coil, a heat-preservation foundation heat storage layer, a plate heat exchanger, warm air blowers, the air source heat pump, a hot water tank and the like. In non-heating seasons, the solar thermal collector is used for heating domestic water which is then stored in the water tank, and the air source heat pump is used for auxiliary heating if heat energy is insufficient. In heating seasons, part of hot water flows into the heat storage coil to be stored for standby use or to be used for supplying heat to the interior of a room through the warm air blowers, and the other part of the hot water flows into the plate heat exchanger to heat domestic water. When solar radiation is weak, the hot water flows from the building foundation heat storage layer into the warm air blowers to supply heat to the interior of the room, and the air source heat pump operates in daytime with the high temperature to heat domestic water which is then stored for standby use. According to the multi-energy-complementary heating and heat supply system of the nearly zero energy consumption building in the alpine region, renewable energy sources are utilized for multi-energy complementation to achieve heating and domestic heat supply of the alpine region in winter, and nearly zero energy consumption operation of the building can be achieved.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Data room heat discharge and waste heat utilization system employing cabinet-level heat pipes
ActiveCN108566761AEfficient heat removalReduce heating energy consumptionEnergy efficient heating/coolingClimate change adaptationWater source heat pumpEnvironmental resistance
The invention provides a data room heat discharge and waste heat utilization system employing cabinet-level heat pipes. The data room heat discharge and waste heat utilization system employing cabinet-level heat pipes includes a cabinet-level heat pipe system, a water source heat pump system, a user end, and a cold source system, wherein the cabinet-level heat pipe system includes at least one heat discharge end and a plurality of heat-absorbing ends; the heat discharge end is arranged outside the data room, and each heat-absorbing end is arranged on the back panel of each cabinet; the water source heat pump system comprises an evaporator, a condenser, a compressor and a throttle valve; and the cabinet-level heat pipe system is connected with the water source heat pump system, can realizedata room heat discharge and building heating in the heating season at the same time, and is also connected with the cold source system to meet the heat discharge requirement for the data room in thenon-heating season. The data room heat discharge and waste heat utilization system employing cabinet-level heat pipes combines the heat pipe system with the heat pump system, thus being able to realize efficient heat discharge of the data room, being able to utilize the large amount of waste heat generated from the data room to heat a building, and having the advantages of being energy saving, being environmentally friendly, and being economical and practical.
Owner:QINGDAO TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
Peak regulation energy storage system for condensed steam type turbine unit and operation adjusting method
InactiveCN105781640AGive full play to the maximum peak shaving abilityReduce electricity loadSteam engine plantsElectricityOptical axis
The invention relates to a peak regulation energy storage system for a condensed steam type turbine unit and an operation adjusting method of the peak regulation energy storage system. By means of the optical axis rotor technology, steam is extracted to be used for supplying heat, so that electrical loads of the unit are reduced; and then a heat storing and releasing system is arranged, the functions of peak clipping and valley filling of the system are utilized, and on the premise of meeting heat loads in the heating season, the electrical loads of the unit are reduced to the minimum. The electricity and heat contradiction within the heating period in the northern area can be relieved, flexibility and elasticity of power grid dispatching are improved, and the system is suitable for being vigorously popularized.
Owner:HUADIAN ELECTRIC POWER SCI INST CO LTD
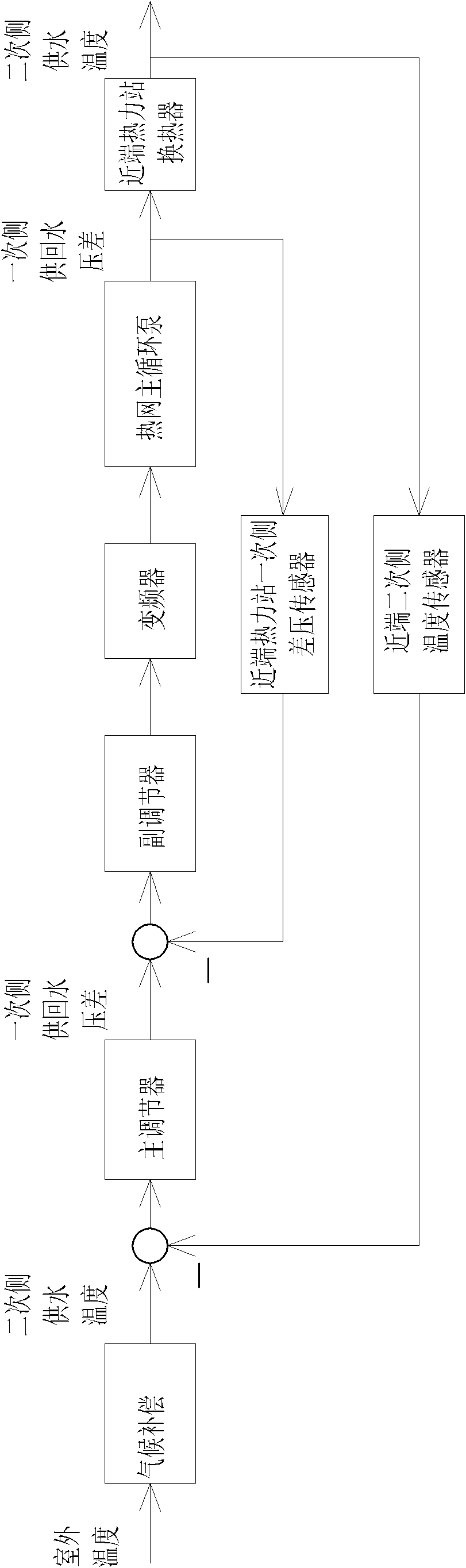
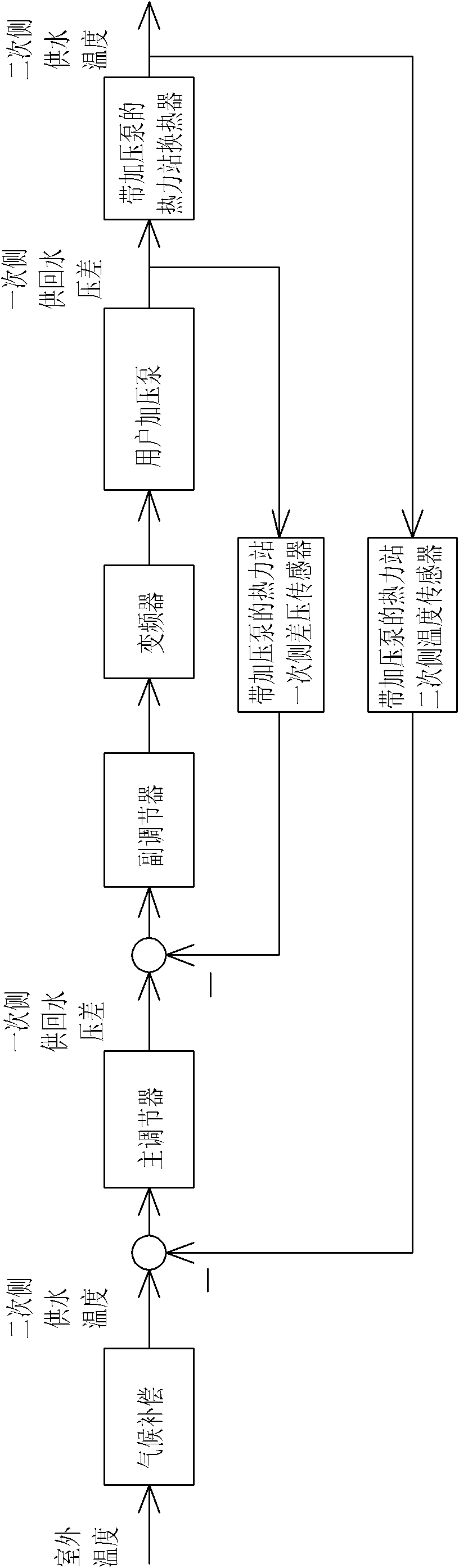
Method for regulating critical zero differential pressure state of distributed water pump variable flow heat supply system
ActiveCN101975417AImprove anti-interference abilityShort transition timeLighting and heating apparatusEfficient regulation technologiesInterference resistanceDifferential pressure
The invention relates to a method for regulating critical zero differential pressure state of a distributed water pump variable flow heat supply system, belonging to a method for regulating the critical zero differential pressure state of the water pump variable flow heat supply system and solving the problems of difficult realization on the maintenance of critical zero differential pressure state of the whole heating season, low system stability, difficult tracing measurement of critical zero differential pressure point, no determined index for main circulating pump regulation, weak system interference resistance capacity and long transition time of a regulating system. The method comprises the steps of: regulating a water supply temperature of a heat source by a heat source controller; regulating a near-end heating power station: meeting the demand on a secondary side user through a rotating speed regulating variable of a heat supply network circulating pump, wherein the rotating speed regulating variable is obtained from a near-end heating station controller; and regulating a heating power station with a pressurizing pump: obtaining the rotating speed regulating variable of the pressurizing pump of the user through the heating power station controller with the pressurizing pump, and meeting the demand on the secondary side user in the heating power station with the pressurizing pump. The method is used for regulating the critical zero differential pressure state of the heat supply system.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Liquid-state compressed air energy storage peak regulation system and method coupled with heat supply system
ActiveCN112096470AReduce heat extraction steam flowReduce energy consumptionPositive displacement pump componentsLighting and heating apparatusThermal energy storage systemHeating season
The invention discloses a liquid-state compressed air energy storage peak regulation system and method coupled with a heat supply system. Air compression heat of a liquid-state compressed air energy storage system is recovered through the heat supply system. In a heating season, the air compression heat is used for primarily heating circulating water of a heat supply network, and heat supply steamextraction flow of a unit is reduced; and in a non-heating season, condensed water is used for recycling the air compression heat, so that the energy consumption of the unit is reduced. Through coupling of a coal-fired unit heat supply system and the liquid-state compressed air energy storage system, the overall operation efficiency of the system is improved. Compared with a conventional liquid-state compressed air energy storage peak regulation system with a heat storage device, an air cooler is adopted to recover the air compression heat to a unit thermodynamic cycle, and configuration of the heat storage system is canceled. The operation efficiency of the whole system is effectively improved, and the overall engineering investment is reduced.
Owner:XIAN THERMAL POWER RES INST CO LTD +1
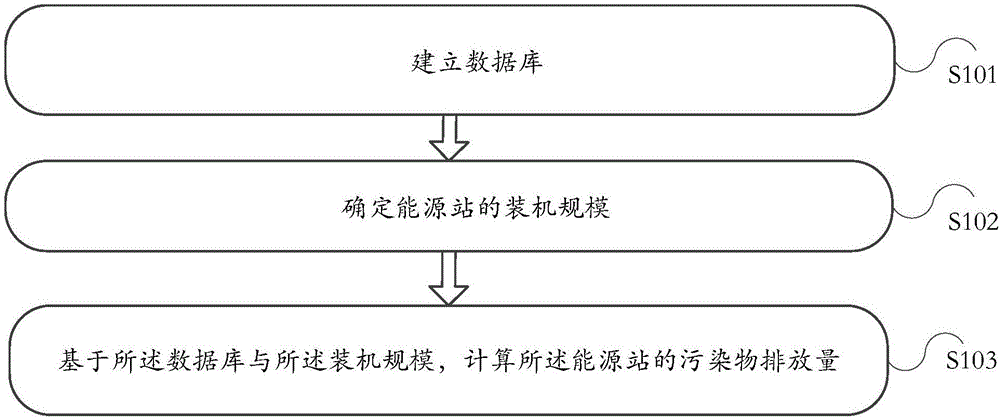
Pollutant discharge amount computing method and electronic equipment
ActiveCN106295145AImprove work efficiencyGood reproducibilitySpecial data processing applicationsInformaticsTime ratioPollutant emissions
The invention discloses a pollutant discharge amount computing method and electronic equipment. The pollutant discharge amount computing method comprises the steps that a database is built; the database comprises hourly cooling load coefficients, hourly heating load coefficients, cooling season time, heating season time, first time proportions of different temperature intervals corresponding to different cooling daily loads in the cooling season time, second time proportions of different temperature intervals under different heating daily loads in the heating season time and pollutant discharge coefficients of different cities in different operating modes; the scale of installation capacity of an energy station is determined; based on the database and the scale of installation capacity, the pollutant discharge amount of the energy station is computed. According to the method, the technical problems that the pollutant discharge amount computing mode in the prior art is complex in computing process and is not intelligent enough are solved.
Owner:ENN ENERGY SERVICE
Building-type combined cooling heating and power system power device selection method
ActiveCN105117557AThe method is simple and fastImprove accuracySpecial data processing applicationsModel selectionEngineering
The present invention discloses a building-type combined cooling heating and power system power device selection method. The method comprises the steps of carrying out dynamic simulation of cooling and heating loads on a target building by using a building CAD drawing in Dest software, thus to obtain full-year cooling and heating load requirements; calculating cooling and heating average daily loads, thus to calculate economic cost and primary energy consumption; calculating average days of a cooling season and a heating season individually, and multiplying the cooling and heating average daily loads by the corresponding days, thus to obtain full-year operation energy consumption and cost situations; and calculating system performance evaluation indexes to different schemes, and determining an ultimate installation model selection result according to performance evaluation optimization. The method is simple, rapid, good in accuracy and capable of comprehensively considering factors at multiple respects; the method can serve as a supplement for a selection method of ordering power by heat; and the method is applicable to a building-type combined cooling heating and power system and also applicable to a regional-type combined cooling heating and power system.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Low-pressure expanded economizer system
ActiveCN103256644ALess investmentSimple operation and maintenanceFeed water supplyHot-water central heatingEngineeringRecuperator
The invention discloses a low-pressure expanded economizer system comprising a turbine, a condenser, a condensate pump, a make-up pump, a drain pump, a low-pressure expanding economizer, a recycle pump, a low pressure steam pocket, a turn-off valve and a heat exchanger. The heat exchanger comprises a heat exchanger high-temperature section and a heat exchanger low-temperature section which are mutually communicated. Non-heating season condensate working condition is utilized as a basis and heating season heat supplying working condition is combined to combine the low-pressure expanded economizer with a smoke heating network heater (heat-supplying economizer) to form one heated surface (the low-pressure expanded economizer), and users can flexibly adjust according to heating demand and electric load condition. Compared with the prior art with the low-pressure expanding economizer and the smoke heater for heating network arranged respectively, the low-pressure expanded economizer system does not need to mount the smoke heating network heater independently, pipelines and valves needed to be arranged are reduced, the structure is simple, system reliability is high, and the problem of non-heating season burning is avoided.
Owner:HANGZHOU BOILER GRP CO LTD
Efficient numerical simulation method and device for urban scale geothermal field group well system
ActiveCN108846245ASolve meshingSolve the speed problemDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsThree dimensional simulationNumerical models
Embodiments of the invention disclose an efficient numerical simulation method and device for an urban scale geothermal field group well system. The method comprises the steps of obtaining geologicaldata of a geothermal field to determine a range of a model calculation area, and building a three-dimensional geological numerical model of a research area according to a geological section map; determining water-heat initial conditions of the model; partitioning heat storage parameters, and distinguishing a heat storage layer and a heat coverage layer; determining water-heat boundary conditions of the whole simulated heat storage system; simplifying geothermal wells into one-dimensional linear geometry, and adding the geothermal well linear geometry into the model according to a distributiondiagram and coordinates of the geothermal wells; setting inflow and outflow boundary conditions of temperatures and fluids for the geothermal wells, and considering a heat exchange process of the fluids in the geothermal wells and surrounding rock masses by adopting an equivalent heat exchange coefficient, wherein the influence of a sleeve pipe and a mortar layer is also contained in the equivalent heat exchange coefficient; and setting a time period function for the model and discretizing each year into two time periods including a heating season and a non-heating season. The difficult problems of grid division and calculation speed of three-dimensional simulation of urban scale geothermal fields can be solved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Building thermal load prediction method based on heat storage system
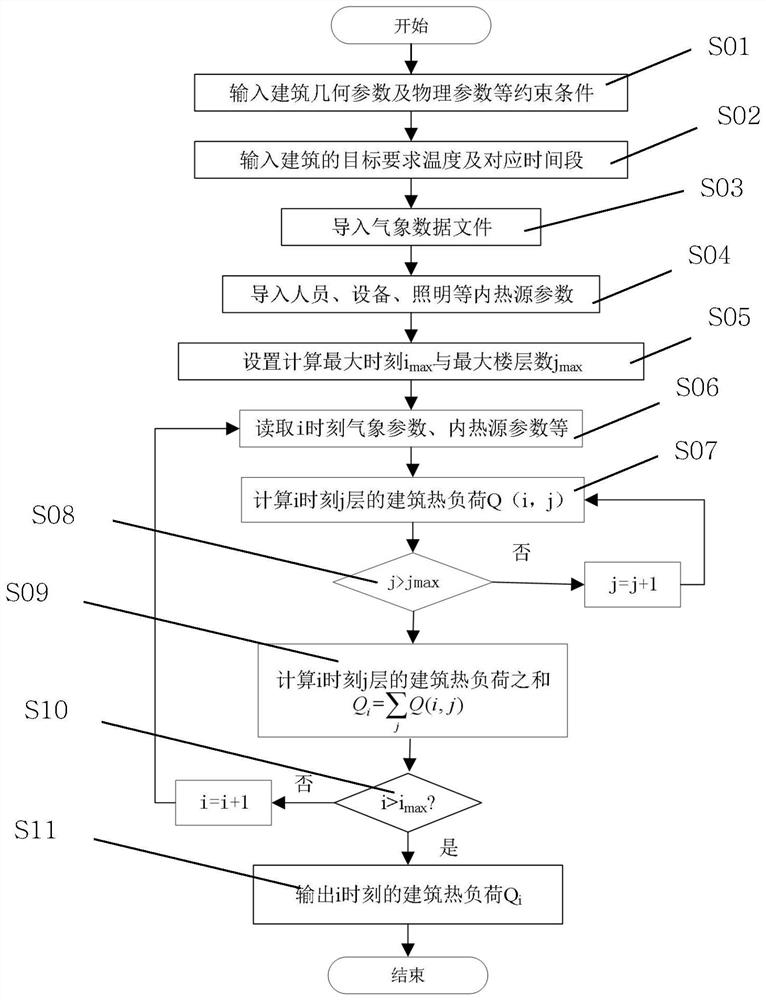
PendingCN112036026AVerify correctnessPublic text cannot be restrictedLighting and heating apparatusElectric heating systemThermodynamicsProcess engineering
The invention discloses a building thermal load prediction method based on a heat storage system. The building thermal load prediction method comprises the following steps: obtaining physical parameters of a building; acquiring a target temperature required by the building and a corresponding time period; obtaining meteorological parameters of the building at each moment; acquiring internal heat source parameters of the building at each moment; building a prediction model by taking the physical parameters, the target temperature, the corresponding time period, the meteorological parameters andthe internal heat source parameters of the building as input quantities and taking the building heat load as an output quantity; and substituting the parameters obtained according to the above stepsinto a prediction model to obtain the building thermal load. According to the technical scheme, the thermal load prediction model is established to obtain hourly thermal load and daily heat demand inthe building heating season, the solid electric heat storage-electric direct heating combined heating equipment power ratio optimization model is established, and the economic optimization in the equipment operation life is taken as the target, the optimal input power ratio of the solid electric heat storage equipment to the electric direct heating equipment is determined, the equipment utilization rate is increased, and meanwhile the equipment initial investment and operation cost are reduced.
Owner:TIANDAQIUSHI ELECTRIC POWER HIGH TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com