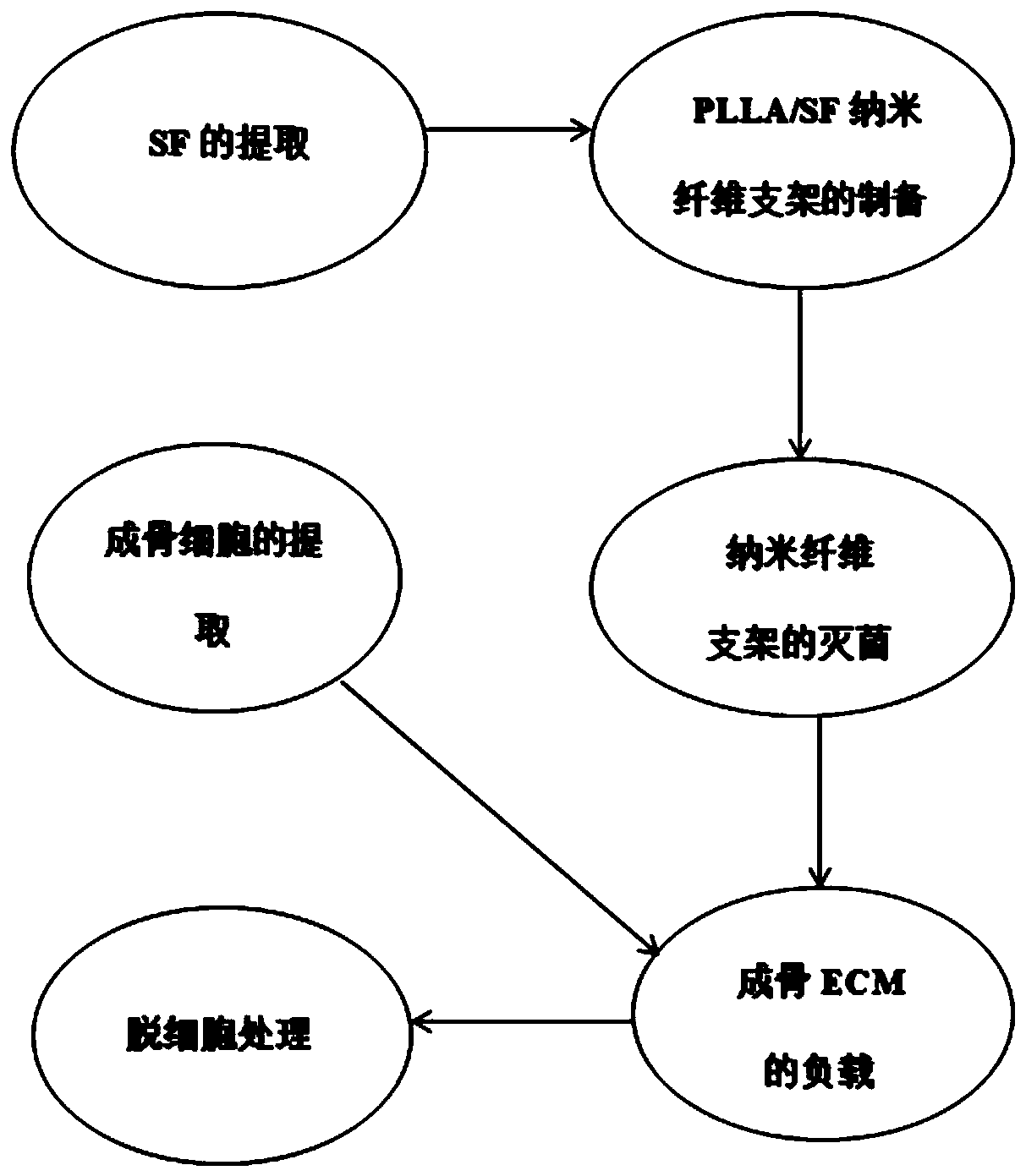
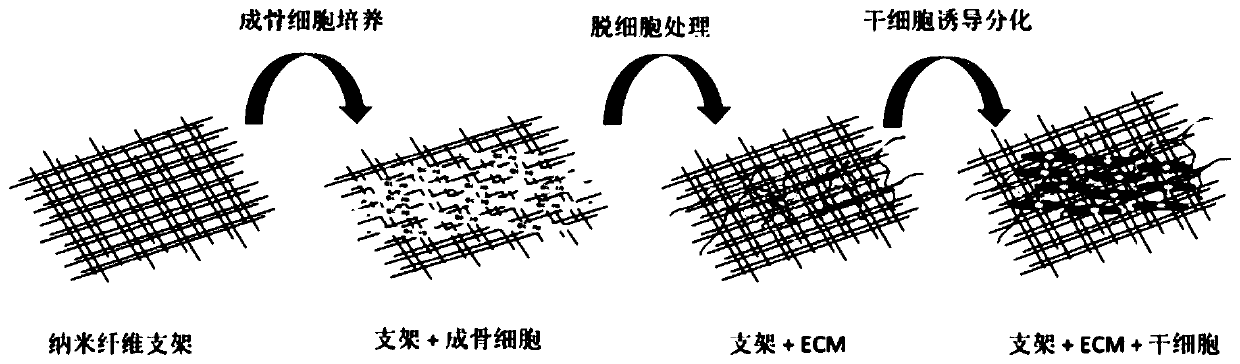
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
40 results about "Extracellular matrix scaffold" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
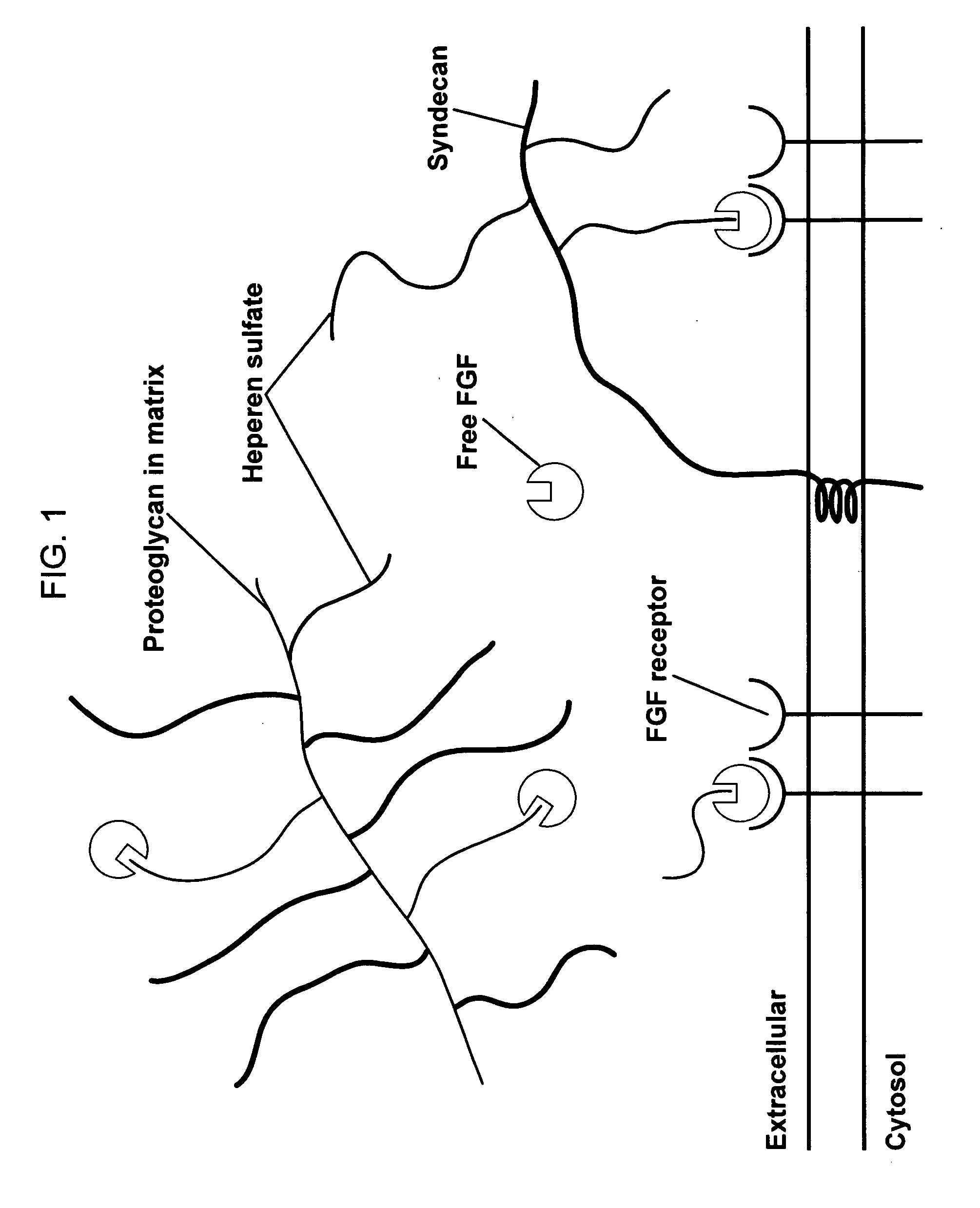
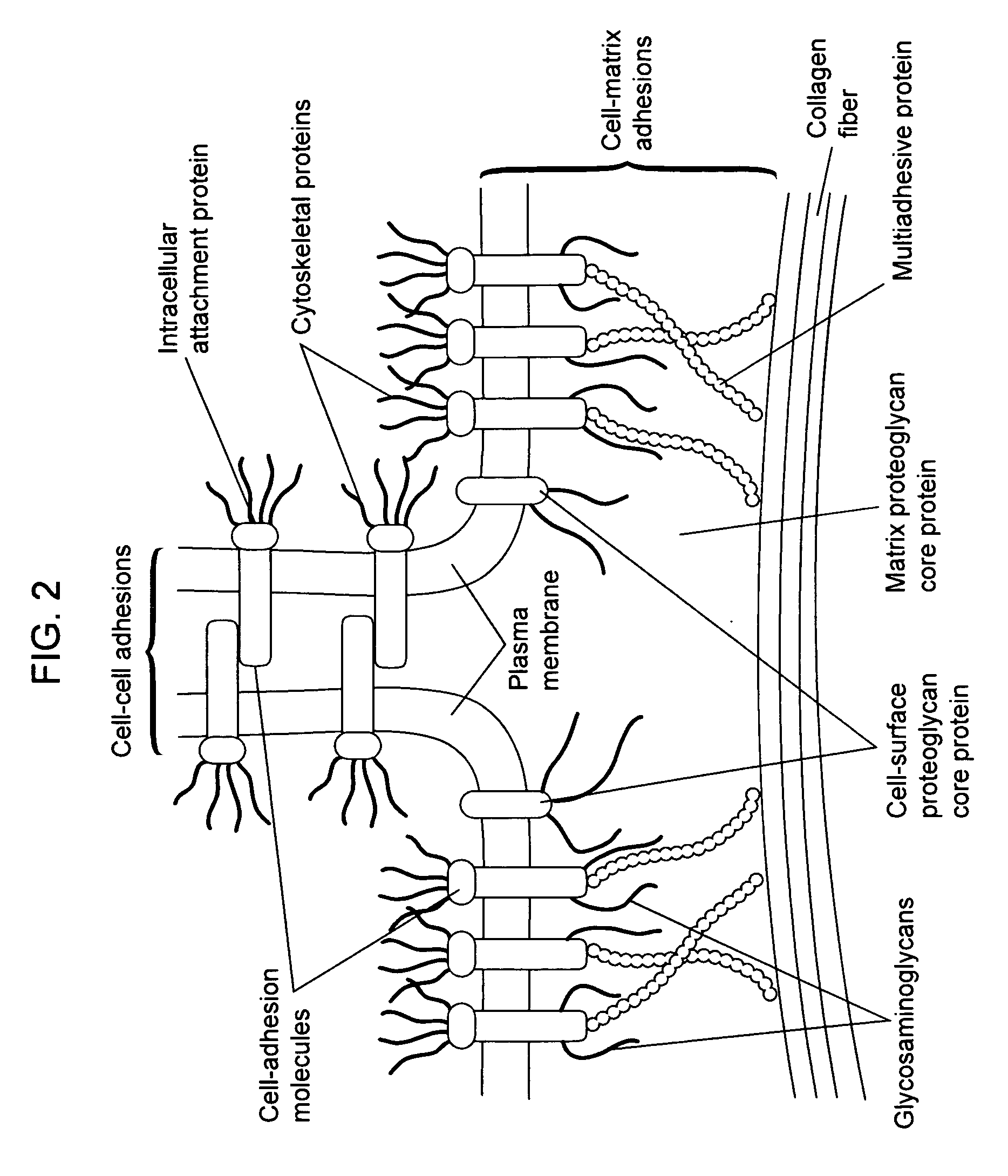
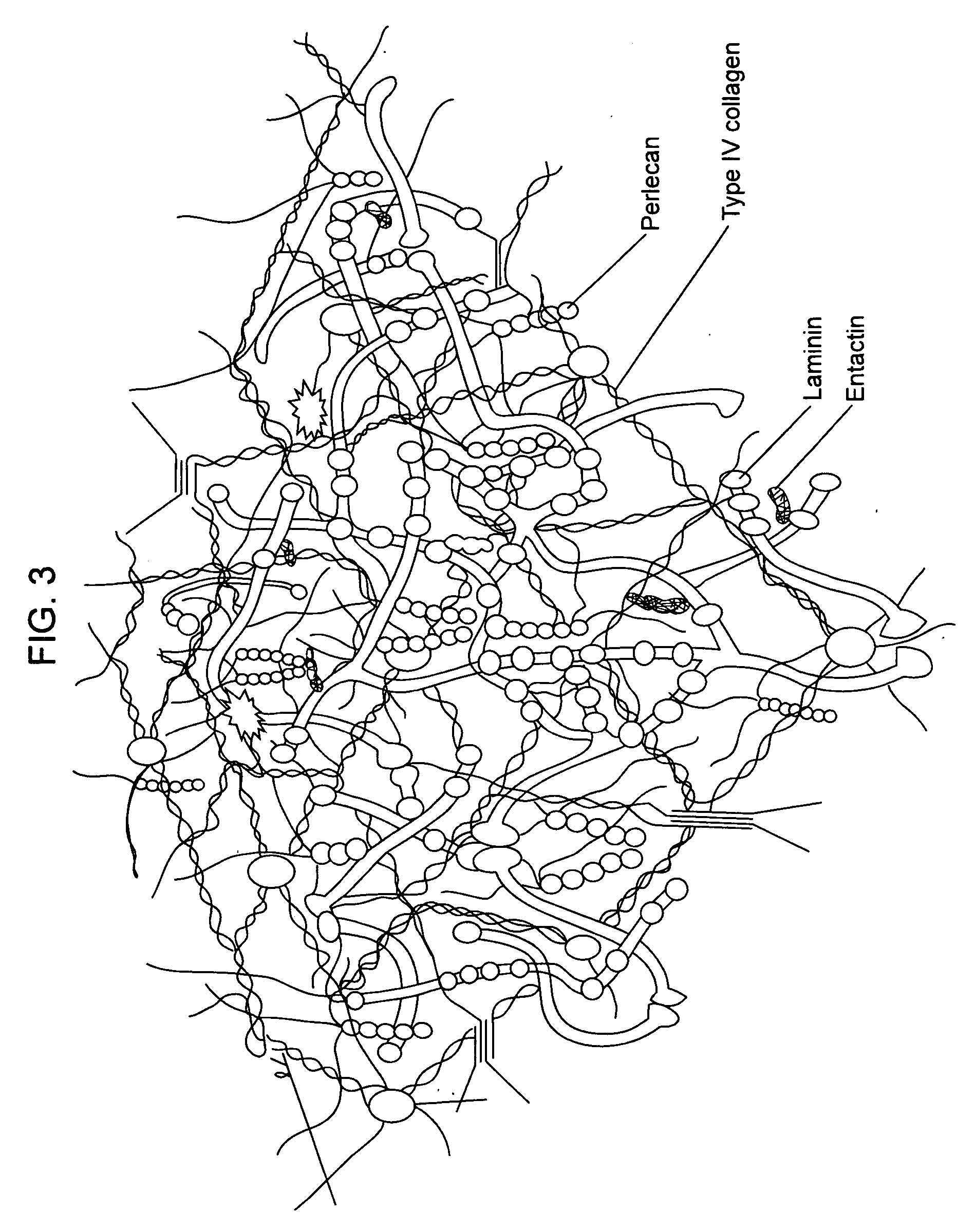
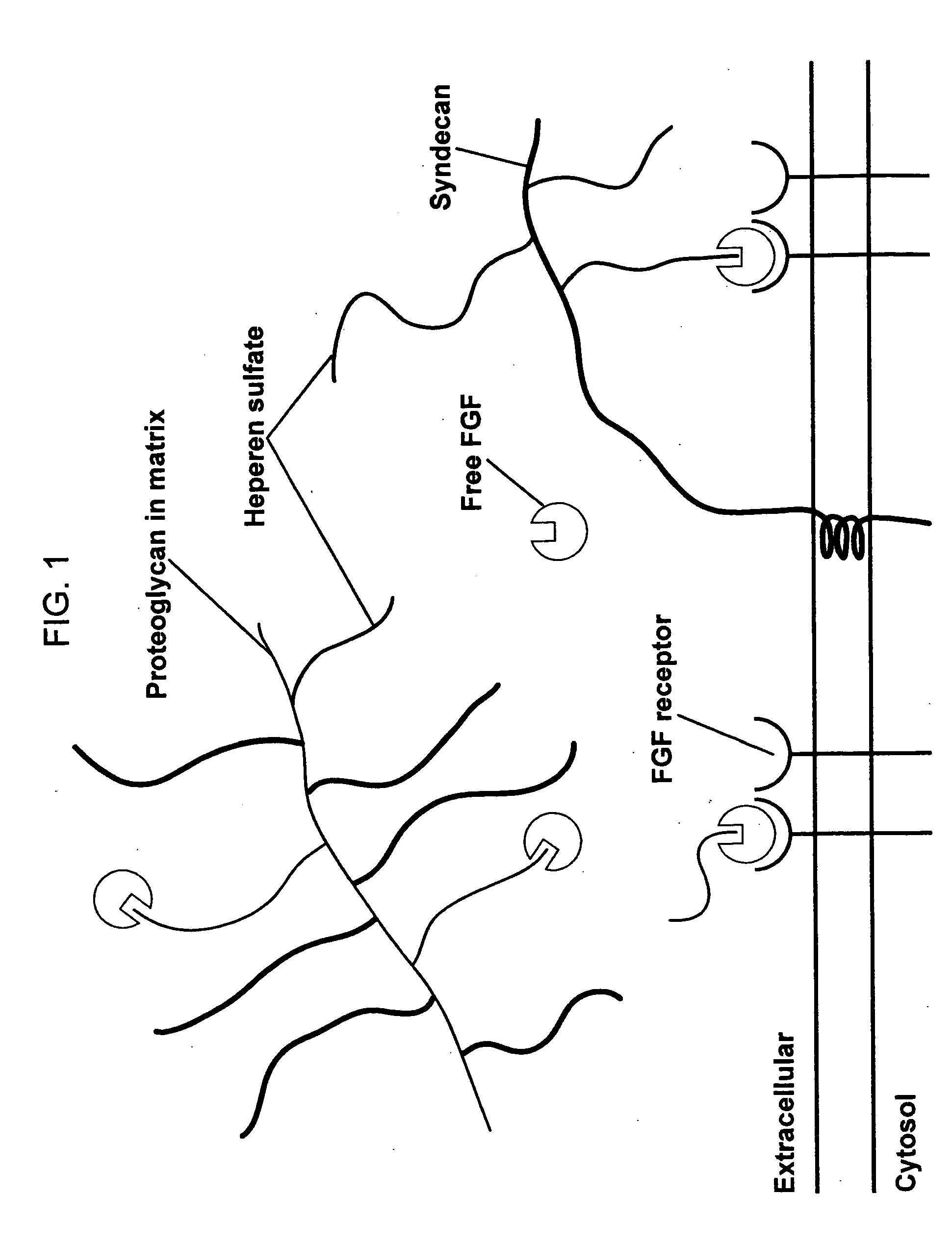
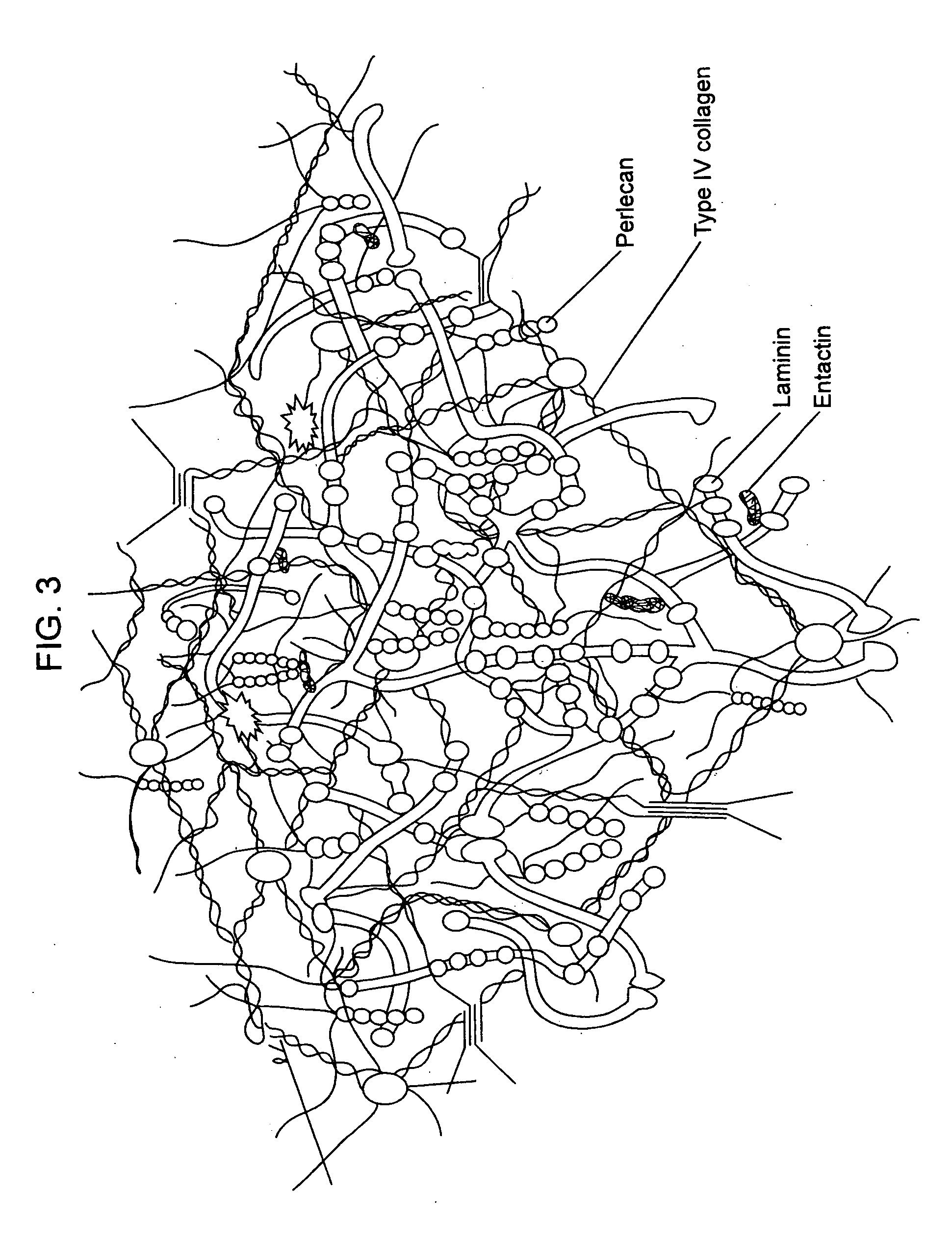
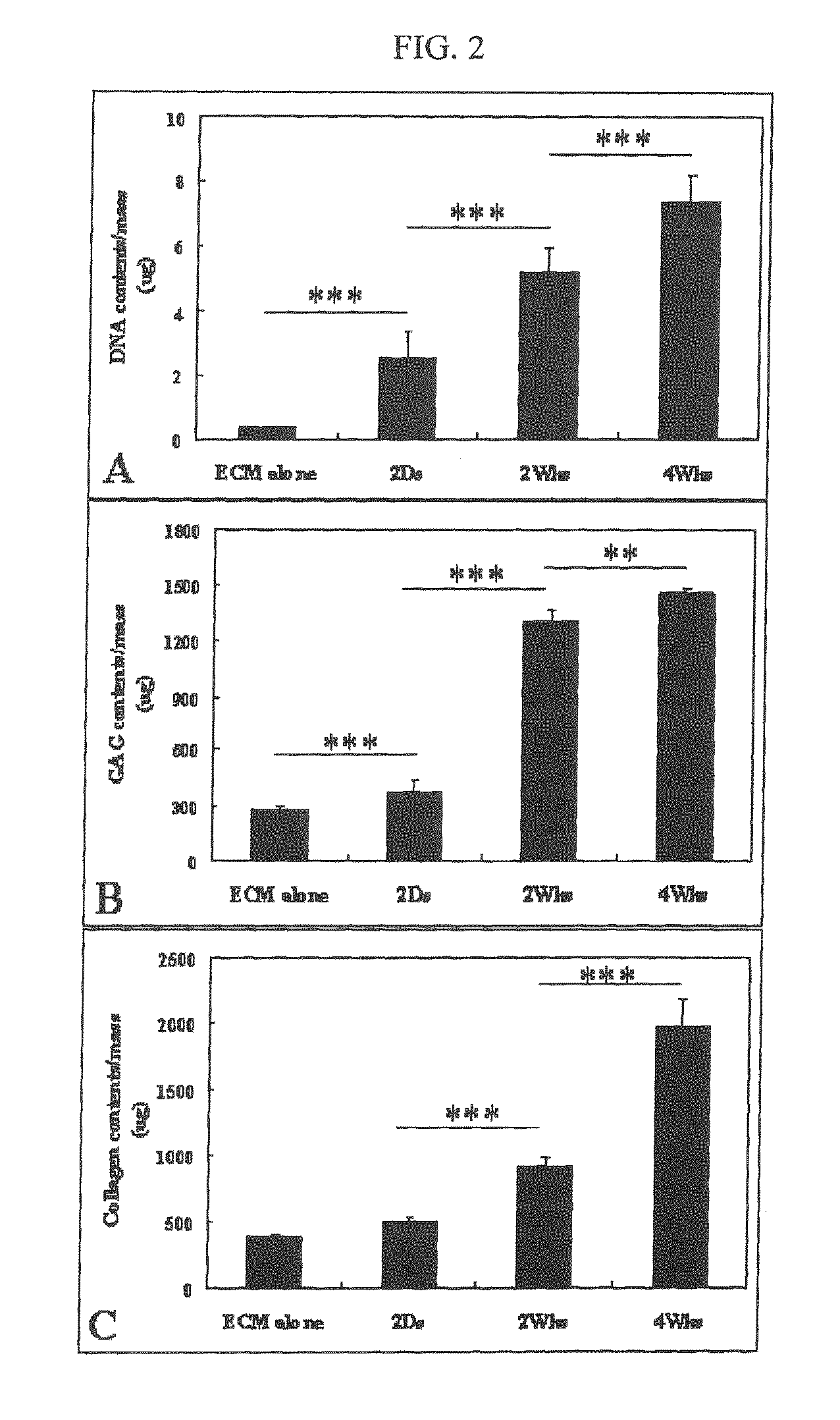
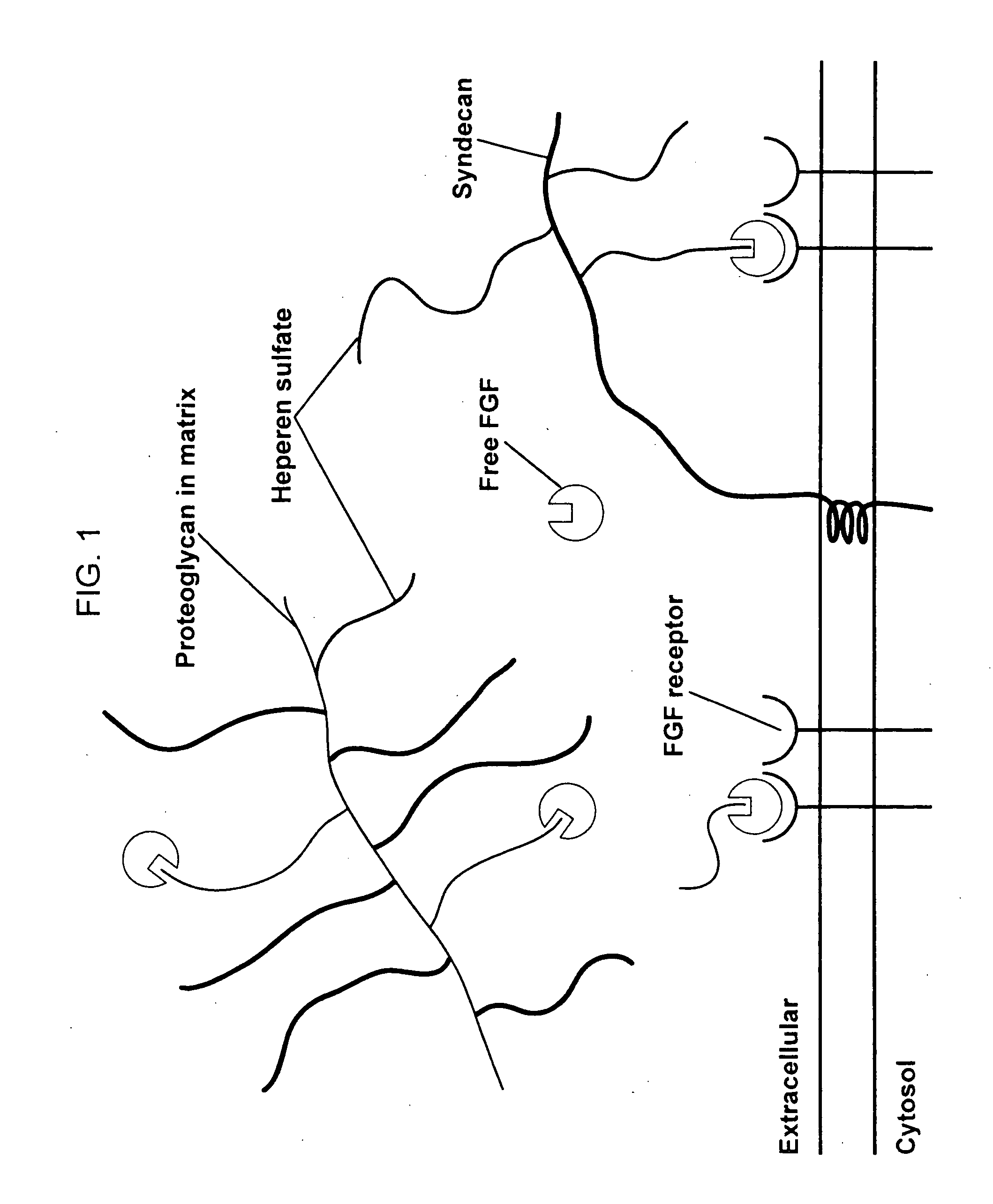
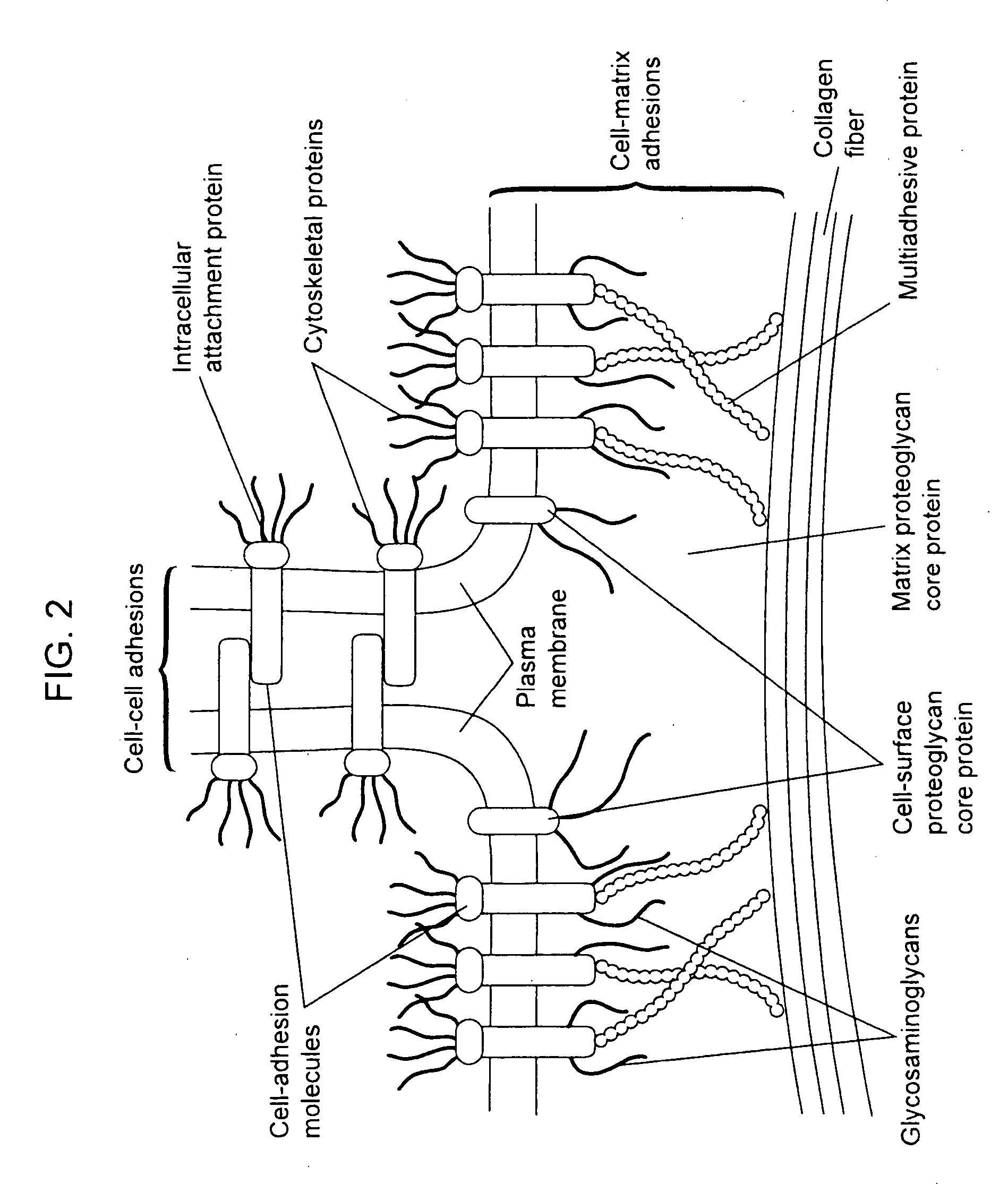
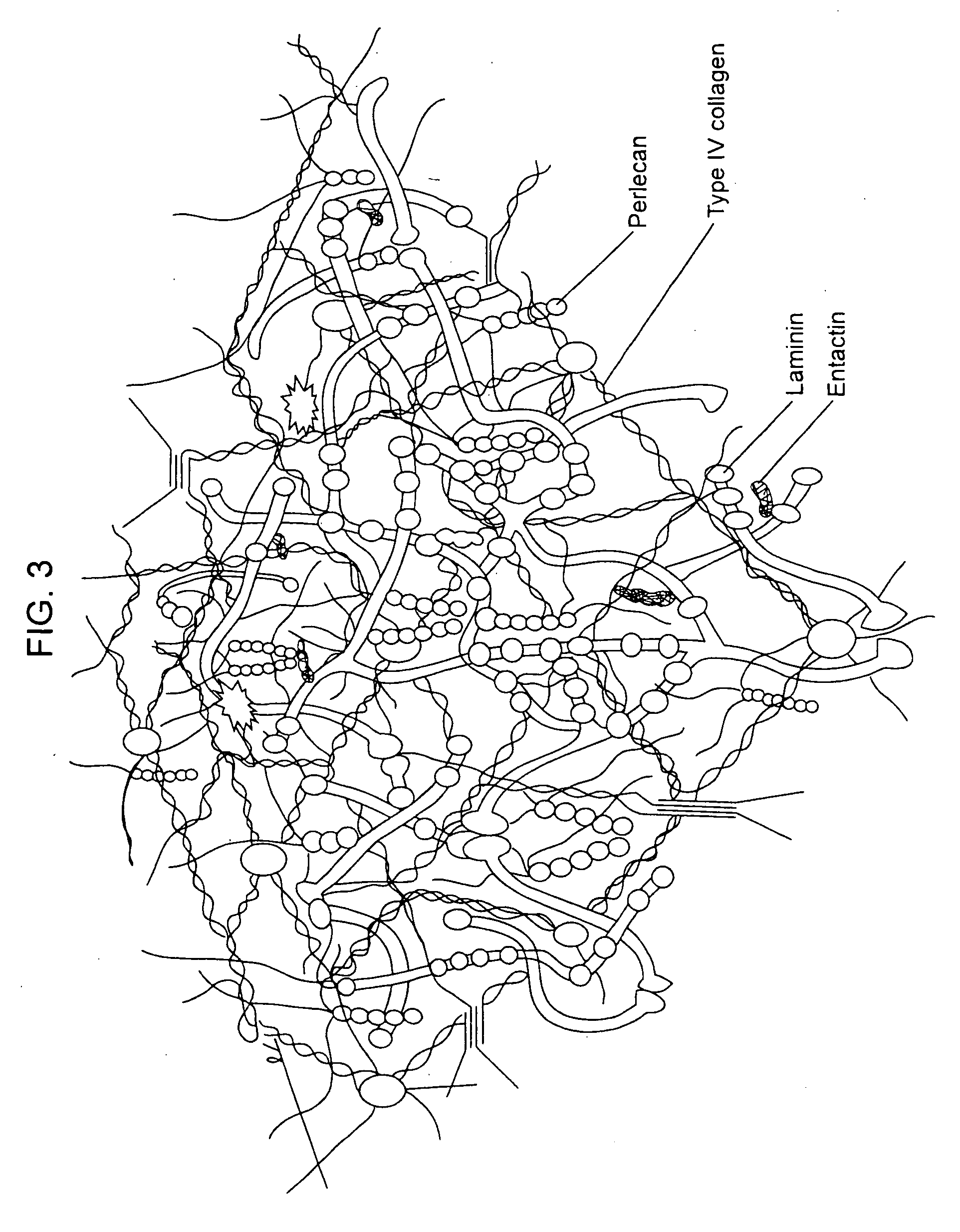
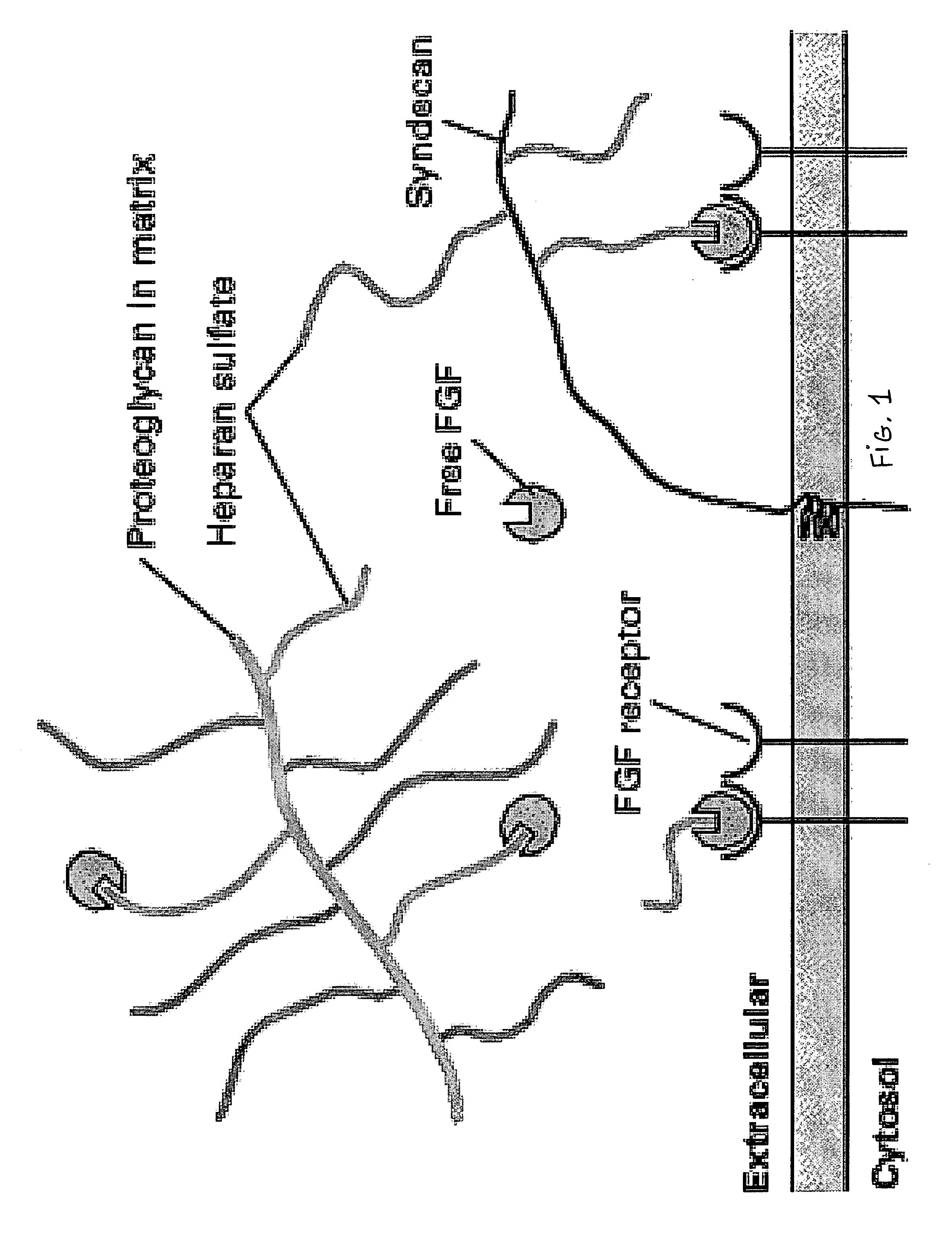
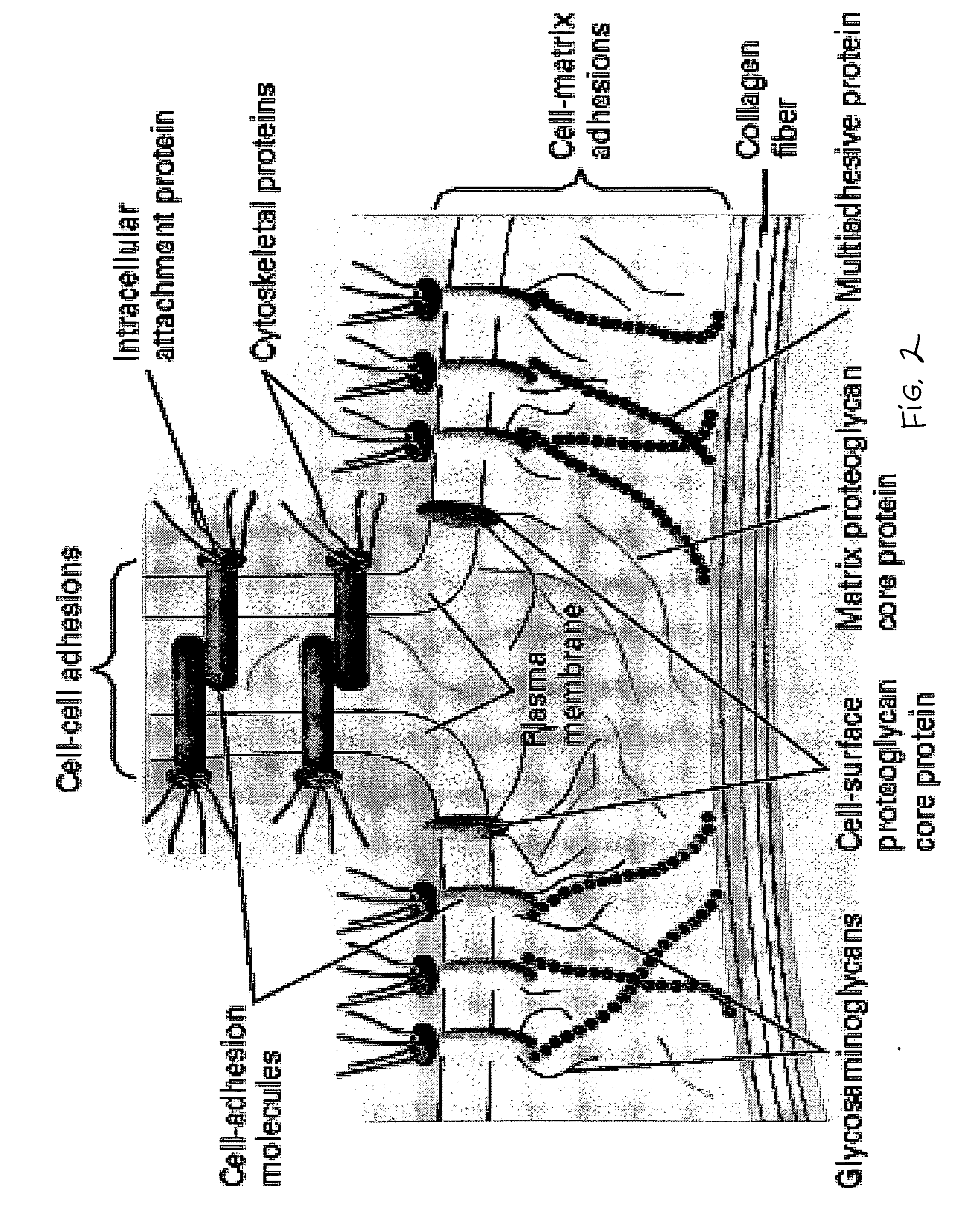
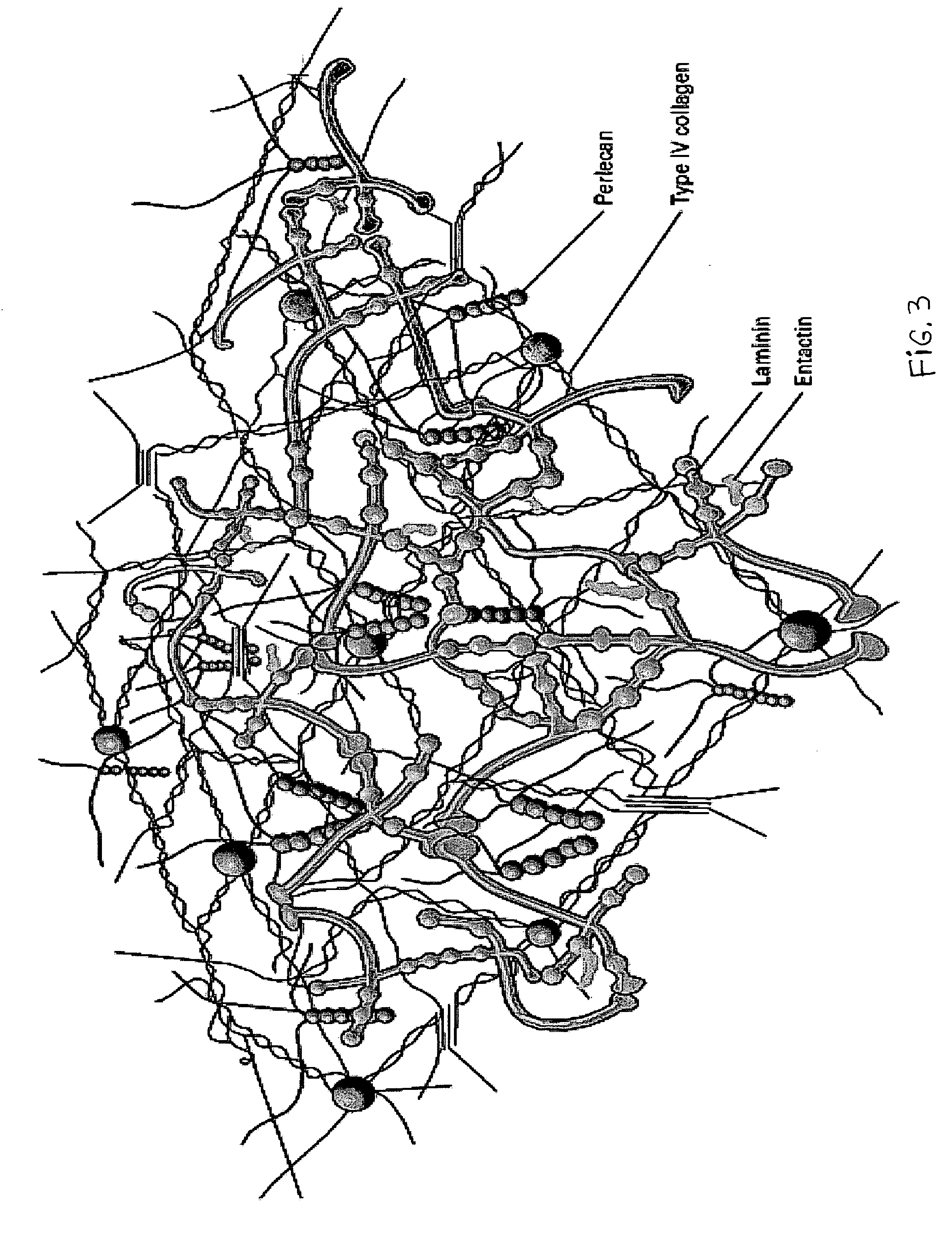
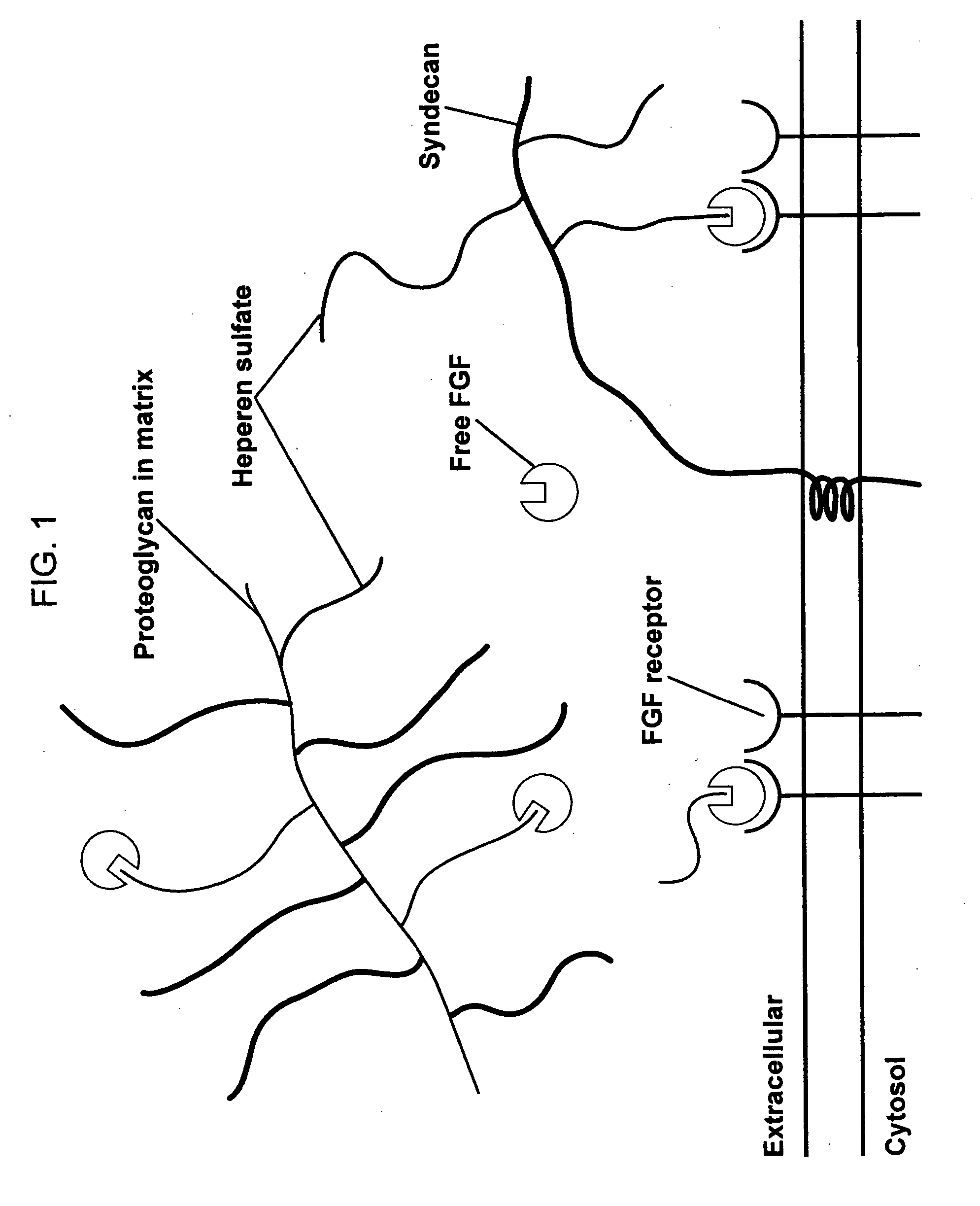
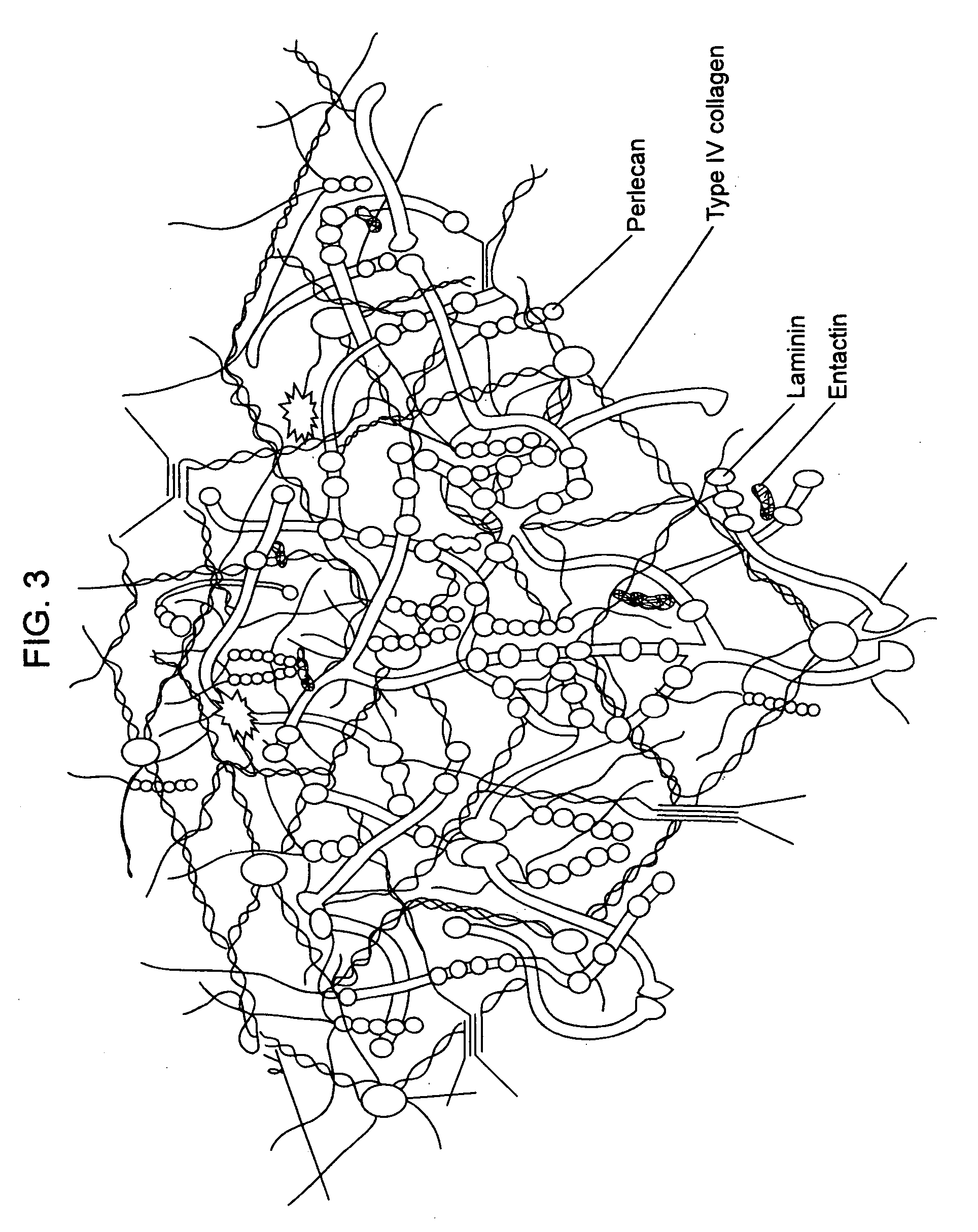
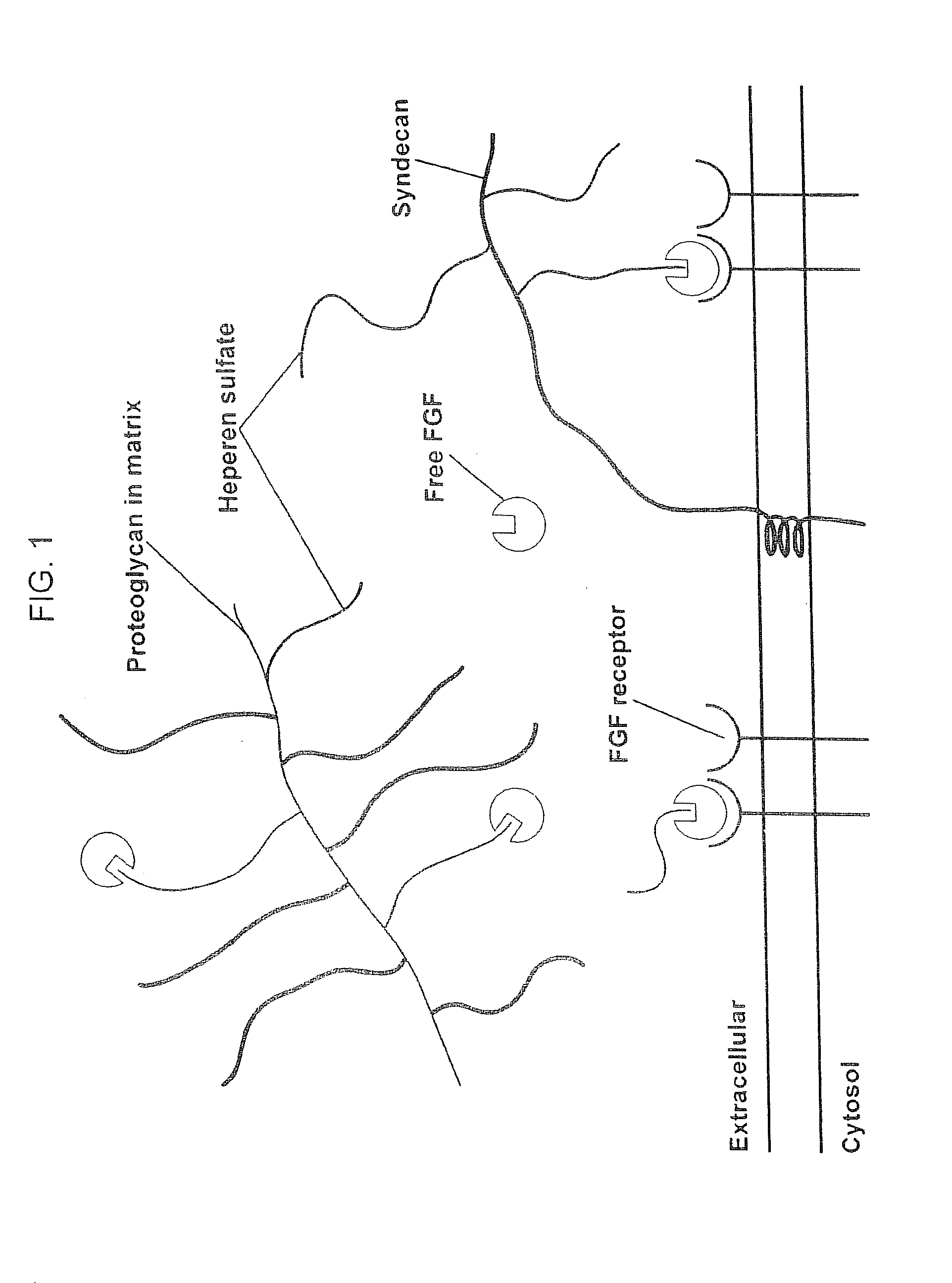
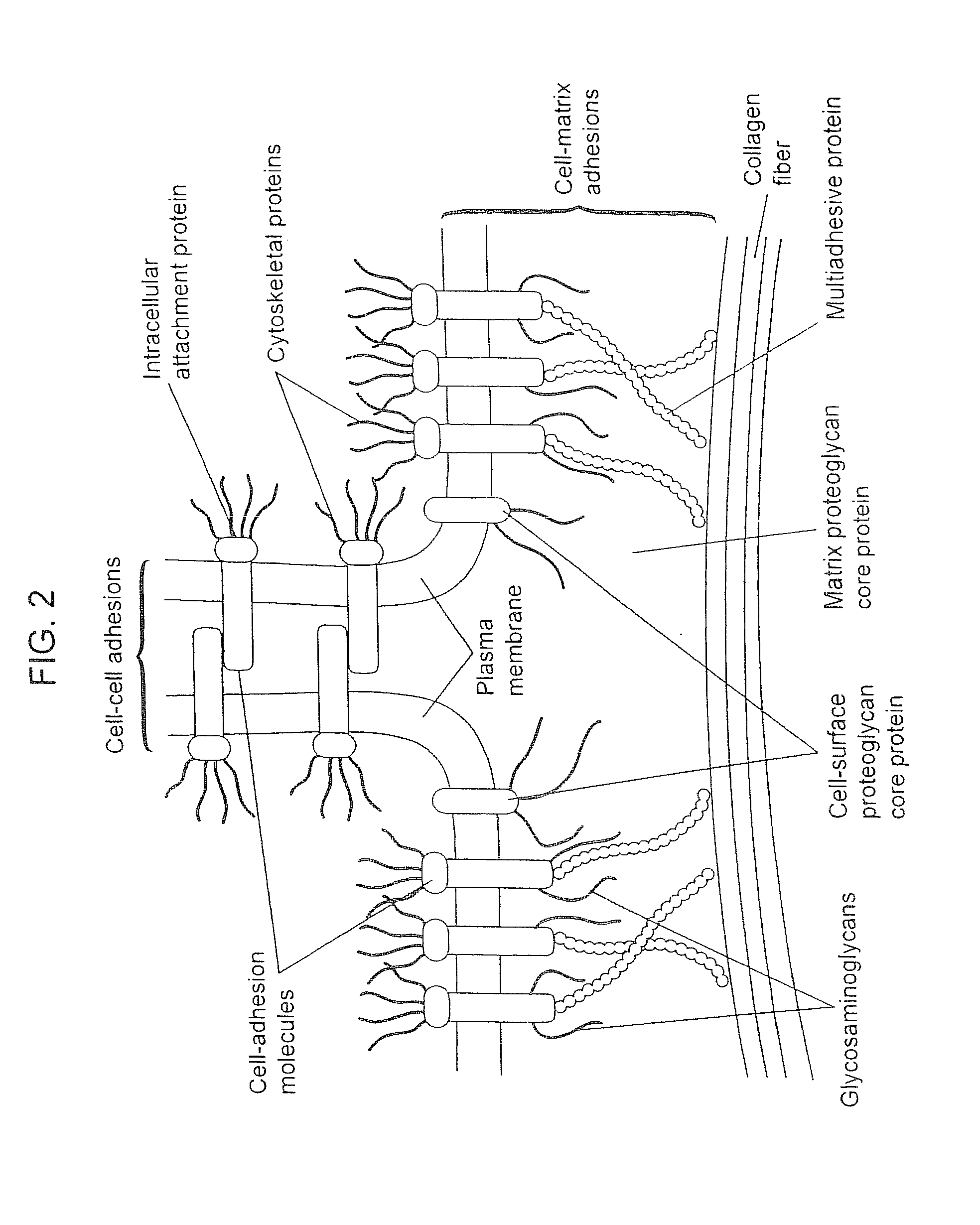
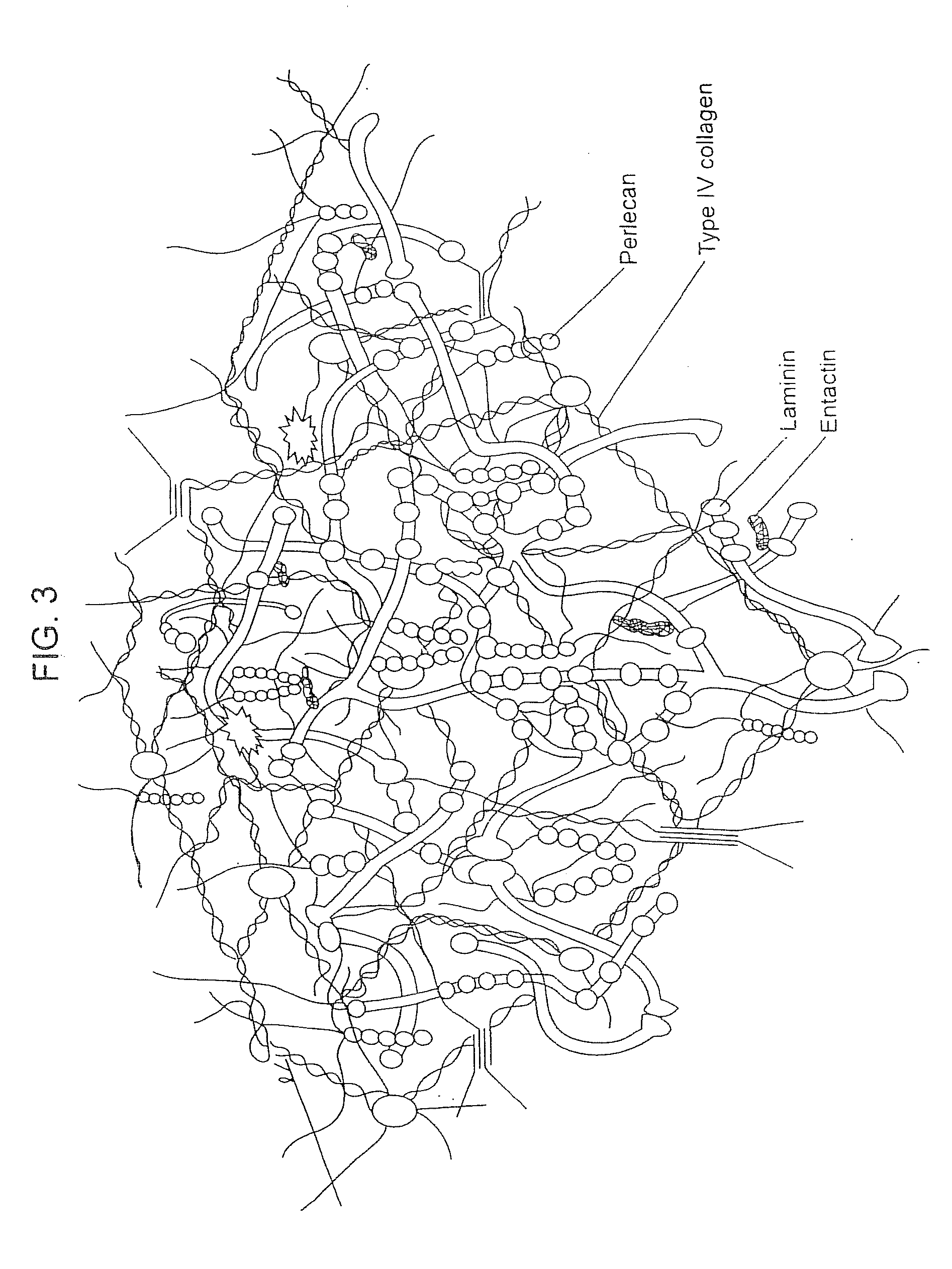
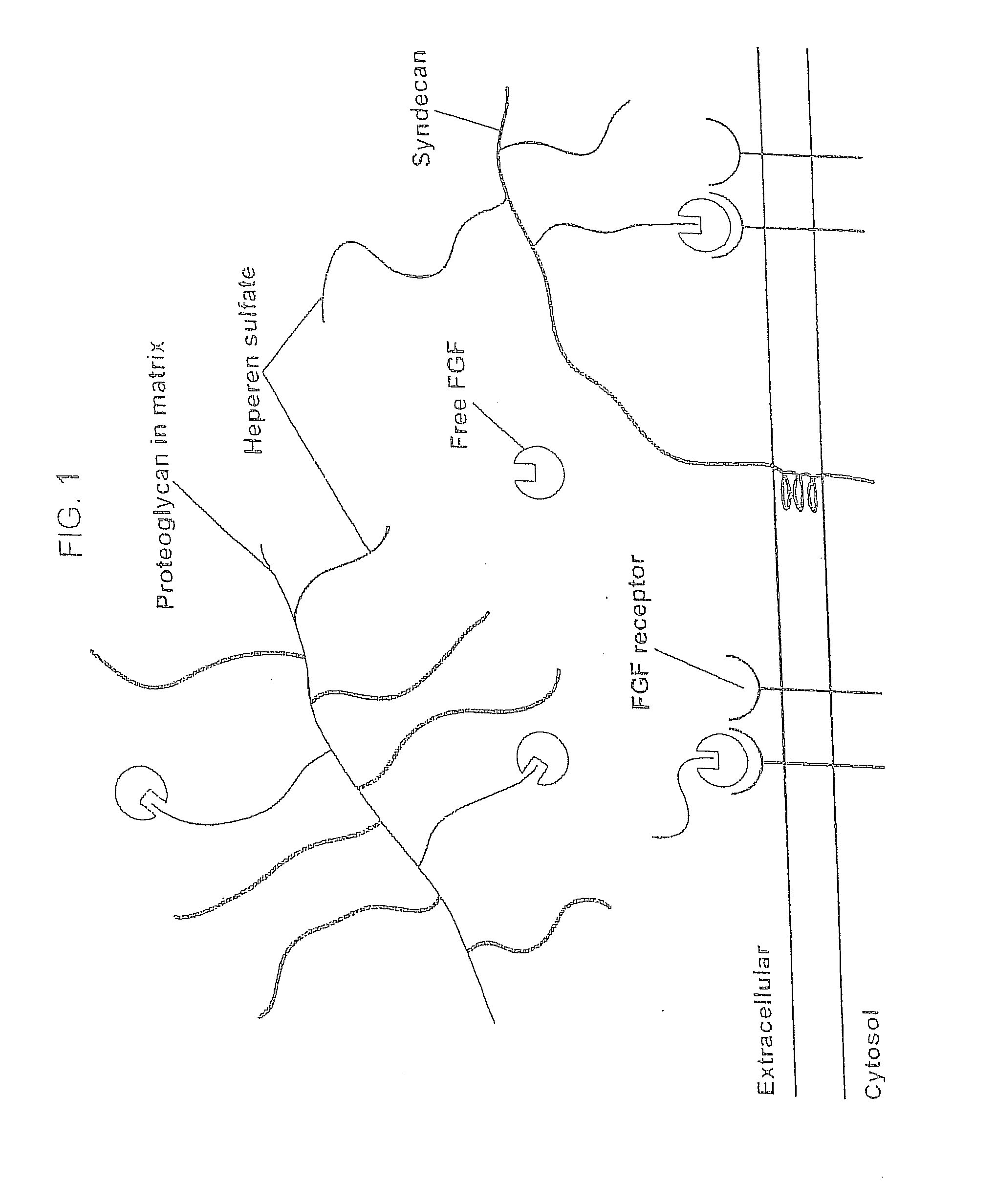
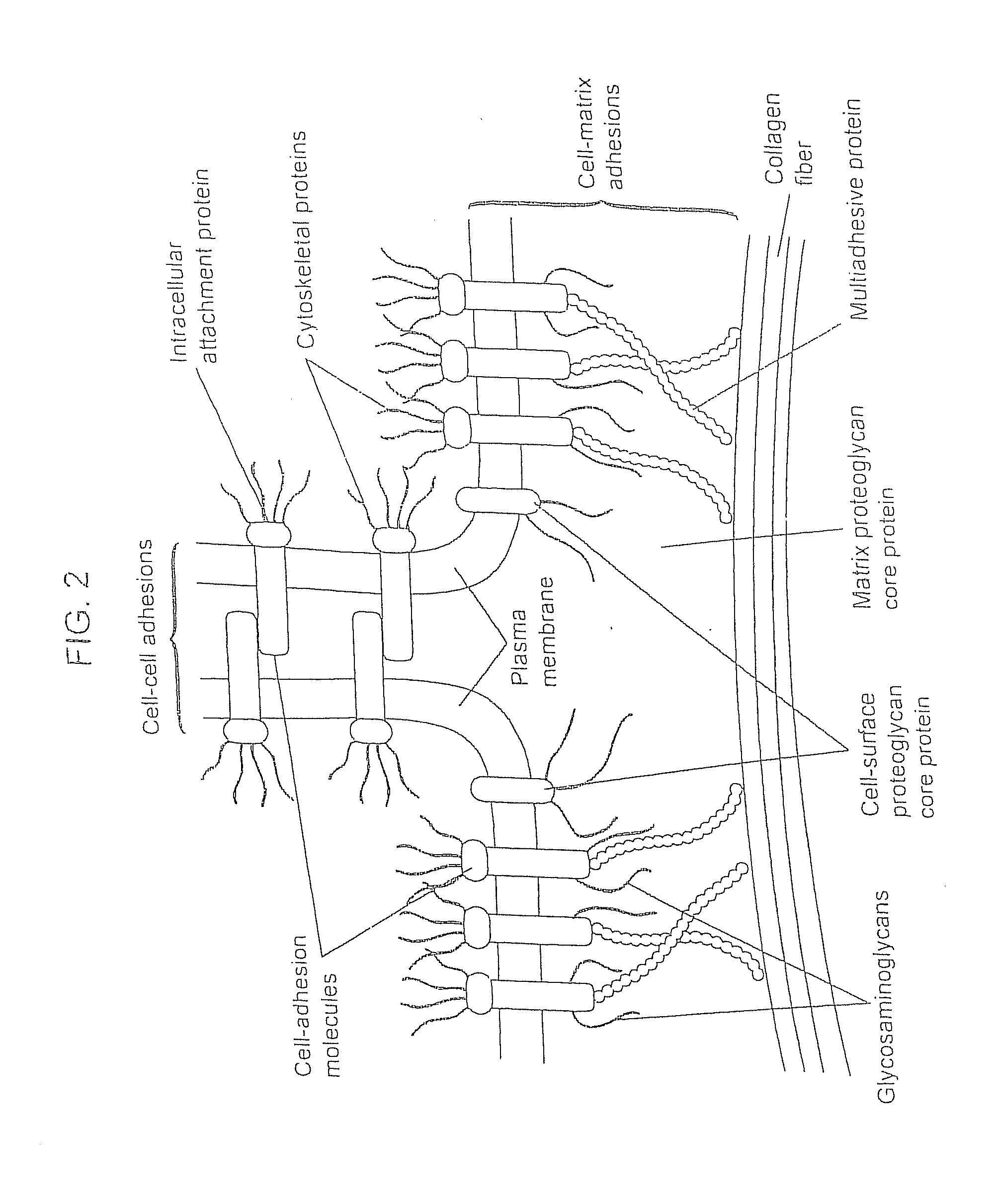
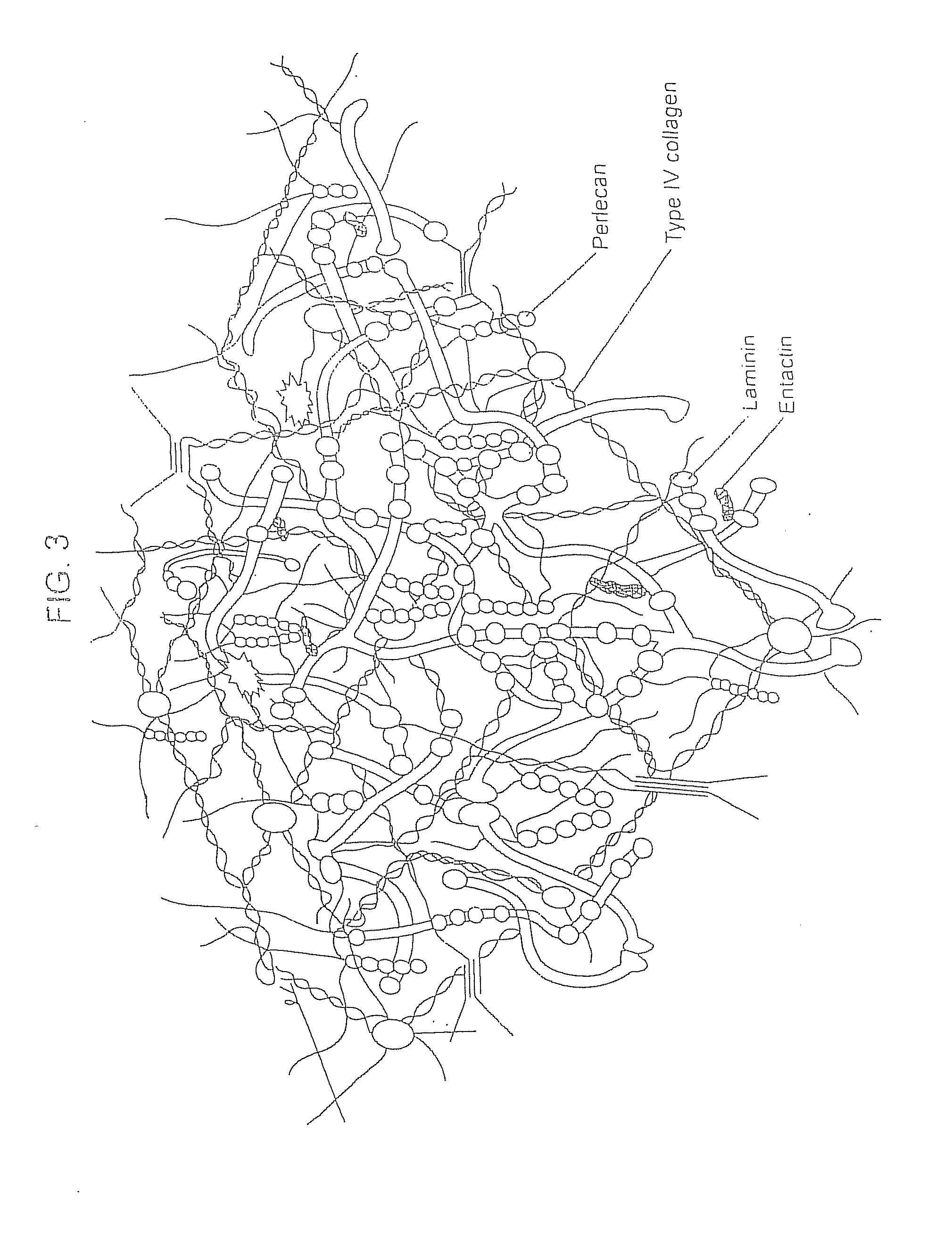
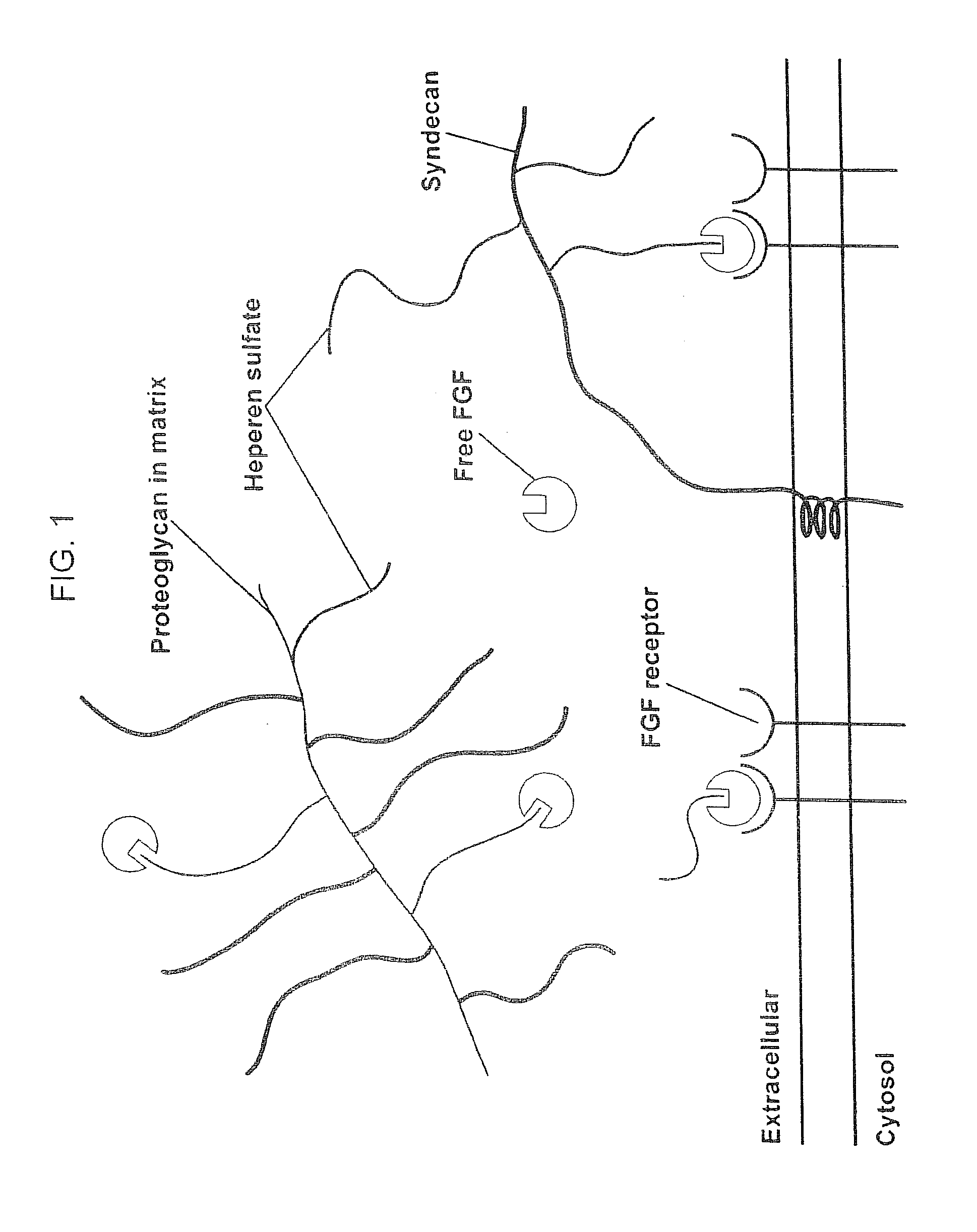
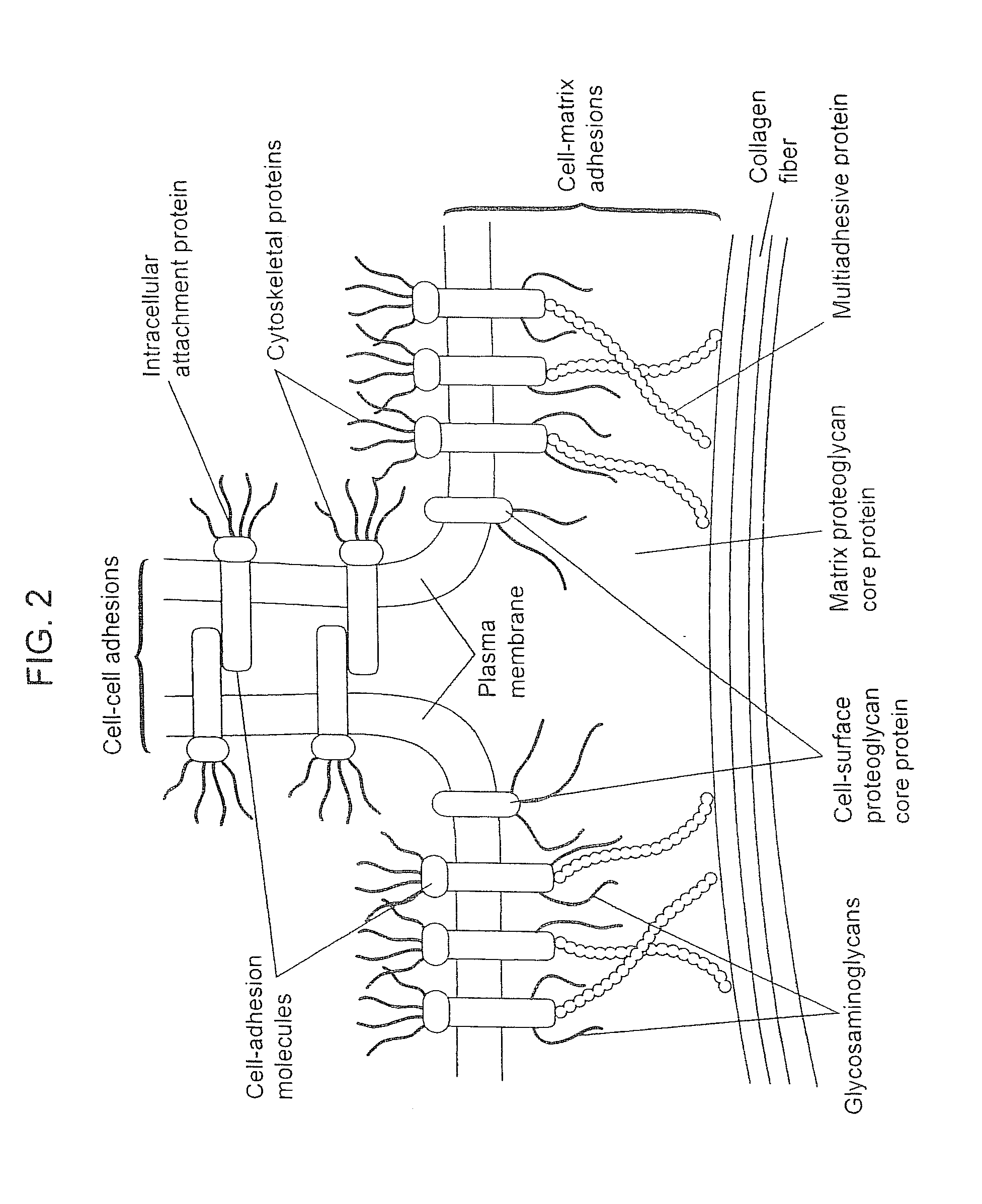
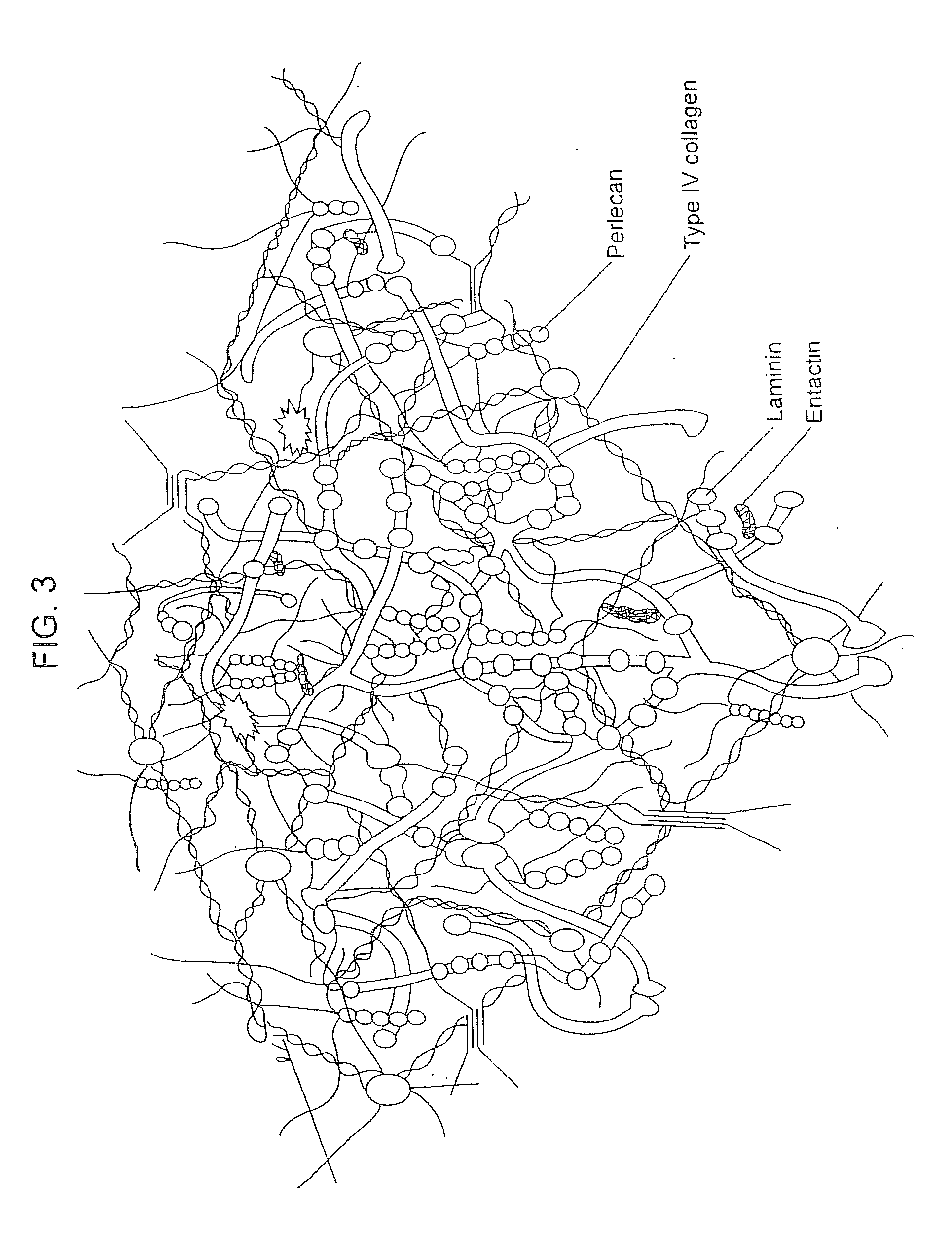
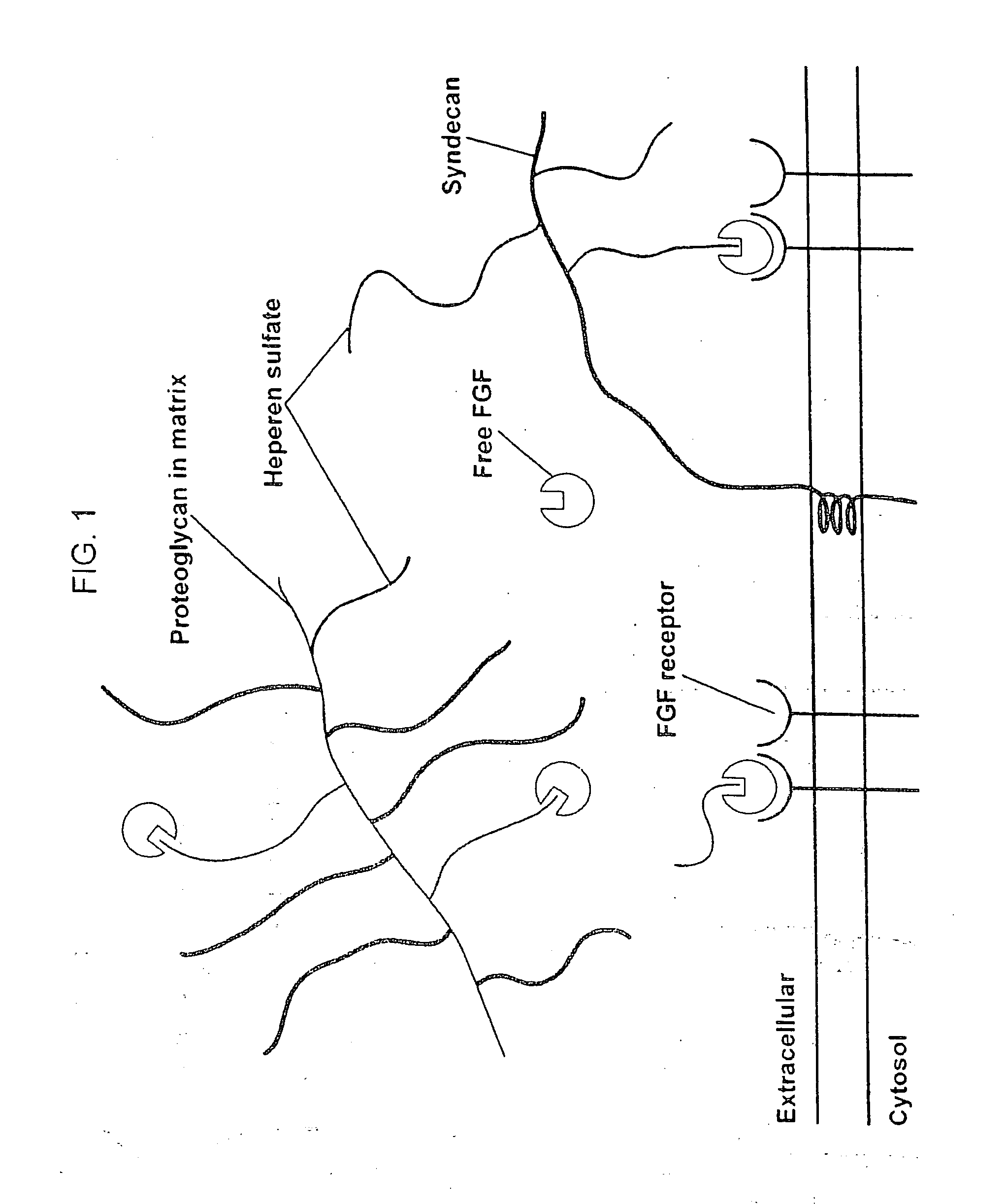
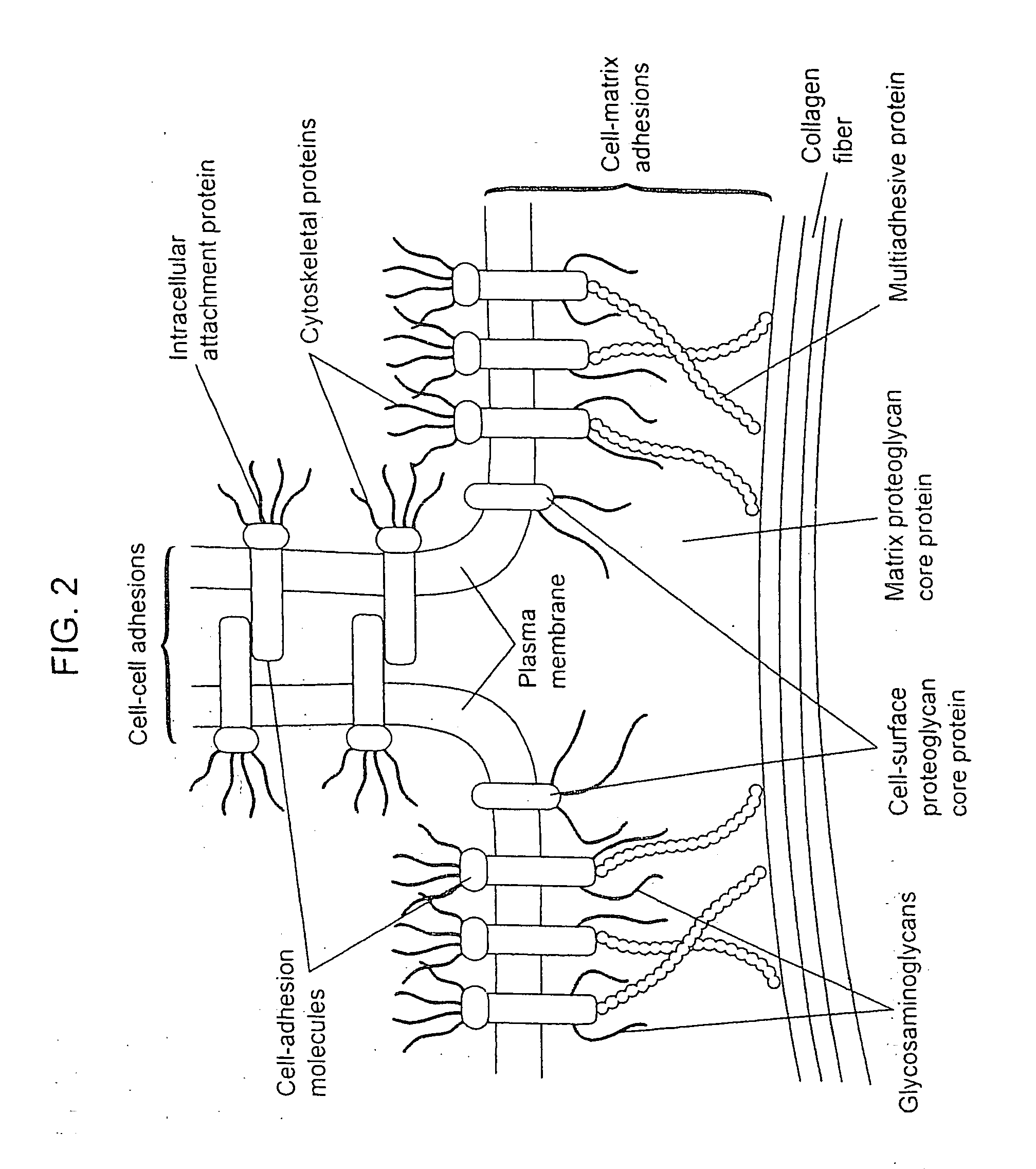
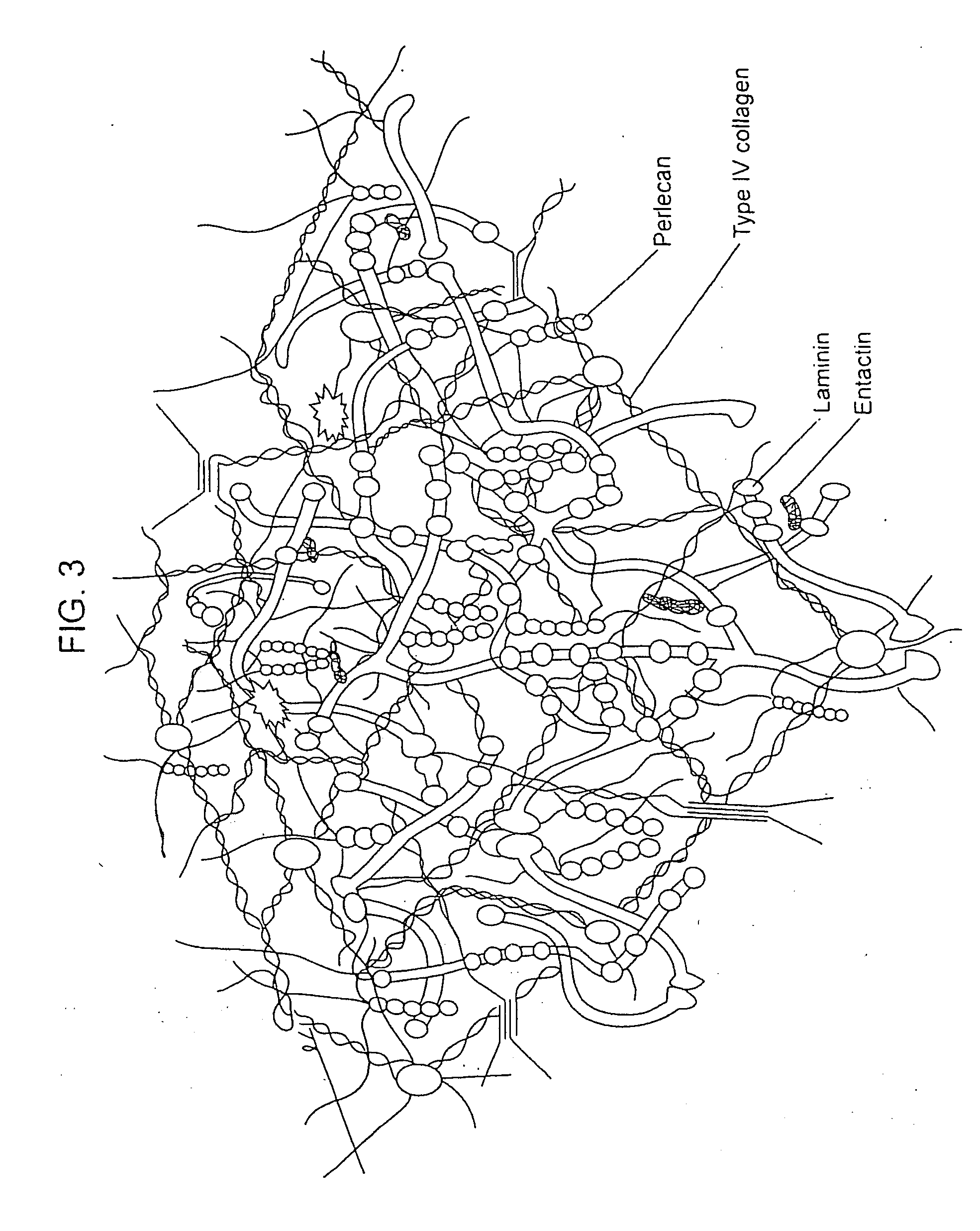
Biological scaffolds derived from extracellular matrix (ECM) have been widely utilised in regenerative medicine. The ECM is an essential non-cellular component of the tissue microenvironment, comprised of a network of macromolecules including polysaccharide glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) and proteins such as collagens, laminins, and fibronectin.
Hybrid biologic/synthetic porous extracellular matrix scaffolds
ActiveUS20030021827A1Wide of injuriesWide supportSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesCell-Extracellular MatrixECM Protein
Methods of making a hybrid biologic / synthetic scaffold for repairing damaged or diseased tissue are provided. The methods include the step of suspending pieces of an extracellular matrix material in a liquid to form a slurry, and coating a synthetic mat with the slurry, or mixing or layering the slurry with a synthetic polymer solution. The liquid is subsequently driven off so as to form a foam. Porous implantable scaffolds fabricated by such a method are also disclosed.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Compositions for regenerating defective or absent myocardium
ActiveUS20070014773A1Restoring cardiac functionEffective amountBiocideOrganic active ingredientsCell-Extracellular MatrixRegenerative process
Compositions of the invention for regenerating defective or absent myocardium comprise an emulsified or injectable extracellular matrix composition. The composition may also include an extracellular matrix scaffold component of any formulation, and further include added cells, proteins, or other components to optimize the regenerative process and restore cardiac function. Methods for regenerating defective or absent myocardium apply a composition to a site of myocardium in need of regeneration using a delivery mode appropriate for the particular formulation.
Owner:CORMATRIX CARDIOVASCULAR INC
Compositions for regenerating defective or absent myocardium
InactiveUS20070014871A1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsCell-Extracellular MatrixRegenerative process
Compositions of the invention for regenerating defective or absent myocardium comprise an emulsified or injectable extracellular matrix composition. The composition can also have an extracellular matrix scaffold component of any formulation, then including also added cells, proteins, or other components to optimize the regenerative process and restore cardiac function. Methods for regenerating defective or absent myocardium apply a composition to a site of myocardium in need of regeneration using a delivery mode appropriate for the particular formulation.
Owner:CORMATRIX CARDIOVASCULAR INC
Hybrid biologic/synthetic porous extracellular matrix scaffolds
ActiveUS7914808B2Wide of injuriesWide supportSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesCell-Extracellular MatrixECM Protein
Methods of making a hybrid biologic / synthetic scaffold for repairing damaged or diseased tissue are provided. The methods include the step of suspending pieces of an extracellular matrix material in a liquid to form a slurry, and coating a synthetic mat with the slurry, or mixing or layering the slurry with a synthetic polymer solution. The liquid is subsequently driven off so as to form a foam. Porous implantable scaffolds fabricated by such a method are also disclosed.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Therapeutic composite for cartilage disorder using extracellular matrix (ECM) scaffold
The present invention relates to a method for preparing a cell-derived ECM scaffold to which chondrocytes or stem cells are attached, a method for cartilage regeneration by tissue engineering, which comprises using the cell-derived ECM scaffold, and a therapeutic composition for treating cartilage disorder, which contains the ECM scaffold as an effective component. More specifically, the present invention relates to a method for cartilage regeneration by tissue engineering, which comprises transplanting ECM scaffold, having chondrocytes or stem cells attached thereto, into cartilage defects, and a therapeutic composition for treating cartilage disorder, which contains the ECM scaffold, having chondrocytes or stem cells attached thereto, as an effective component. According to the present invention, when the inventive ECM scaffold having chondrocytes or stem cells attached thereto is transplanted into a cartilage defect, mature articular cartilage having the same appearance and characteristics as those of natural cartilage tissue, can be regenerated without side effects such as inflammatory responses.
Owner:MIN BYOUNG HYUN
Compositions for regenerating defective or absent myocardium
InactiveUS20070014874A1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsCell-Extracellular MatrixRegenerative process
Compositions of the invention for regenerating defective or absent myocardium comprise an emulsified or injectable extracellular matrix composition. The composition can also have an extracellular matrix scaffold component of any formulation, then including also added cells, proteins, or other components to optimize the regenerative process and restore cardiac function. Methods for regenerating defective or absent myocardium apply a composition to a site of myocardium in need of regeneration using a delivery mode appropriate for the particular formulation.
Owner:CORMATRIX CARDIOVASCULAR INC
Compositions for regenerating defective or absent myocardium
InactiveUS20070014870A1Restoring cardiac functionOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsCell-Extracellular MatrixRegenerative process
Compositions of the invention for regenerating defective or absent myocardium comprise an emulsified or injectable extracellular matrix composition. The composition can also have an extracellular matrix scaffold component of any formulation, then including also added cells, proteins, or other components to optimize the regenerative process and restore cardiac function. Methods for regenerating defective or absent myocardium apply a composition to a site of myocardium in need of regeneration using a delivery mode appropriate for the particular formulation.
Owner:CORMATRIX CARDIOVASCULAR INC
Compositions for regenerating defective or absent myocardium
InactiveUS20070014872A1Induce angiogenesisOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsCell-Extracellular MatrixRegenerative process
Compositions of the invention for regenerating defective or absent myocardium comprise an emulsified or injectable extracellular matrix composition. The composition can also have an extracellular matrix scaffold component of any formulation, then including also added cells, proteins, or other components to optimize the regenerative process and restore cardiac function. Methods for regenerating defective or absent myocardium apply a composition to a site of myocardium in need of regeneration using a delivery mode appropriate for the particular formulation.
Owner:CORMATRIX CARDIOVASCULAR INC
Decellularization method for preparing extracellular matrix (ECM) support material
ActiveCN103536967AImprove performanceImprove decellularization effectTissue regenerationProsthesisCell-Extracellular MatrixECM Protein
The invention relates to the field of tissue engineering materials, and in particular relates to a decellularization method for preparing an extracellular matrix (ECM) support material. By using green surfactant glucopyranoside for decellularization treatment, cells can be completely removed, and an ultra microstructure and compositions of an ECM support are maintained.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICROPORT CARDIOFLOW MEDTECH CO LTD
Preparation method of tissue engineering porous extracellular matrix scaffold
ActiveCN105561398AHigh mechanical strengthSolve the problem of holesProsthesisAcellular scaffoldPolymer scaffold
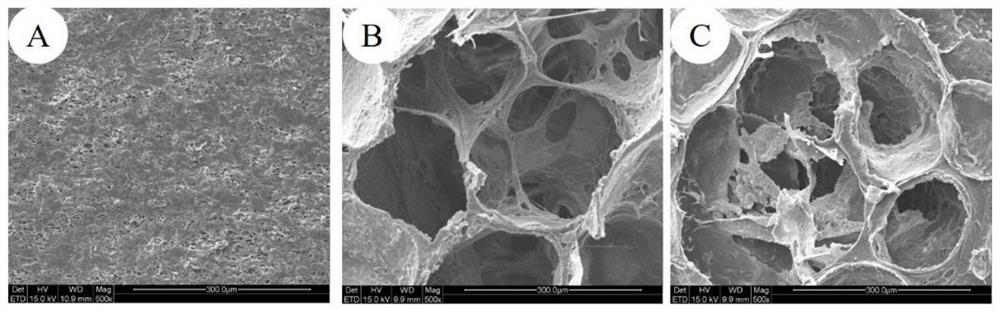
The invention provides a preparation method of a tissue engineering porous extracellular matrix scaffold. The method is characterized in that a nano or micron polymer scaffold is implanted under the skin of or in the abdomen of a host, the polymer scaffold is used as a template to prepare the tissue engineering porous extracellular matrix scaffold with a controllable pore structure and free of immunogenicity after in-vivo implantation by using a host immunoprotection mechanism. The preparation method has the advantages that the problem of hole forming of extracellular matrix scaffold materials is solved; the porous scaffold is animal-source, is used for repairing self-injured tissue or organs, and is free of immunological rejection; since self-repair has no complex decellularization step, the scaffold has significantly better mechanical strength than a decelluarized scaffold material; the extracellular matrix scaffold may be further decelluarized for repairing foreign tissue or organs and has a promising application prospect in the field of organ repairing.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Method for Decellularization of Tissue Grafts
ActiveUS20160030636A1Encourage graft implantationReduced CD4+ T-cell mediated immune responseCell dissociation methodsMammal material medical ingredientsCellular componentCell-Extracellular Matrix
The subject invention pertains to materials and methods for processing tissue to produce a natural, acellular replacement tissue that is immunocompatible with a recipient. According to the subject invention, harvested tissue is subjected to wash solutions wherein only amphoteric detergent(s) are used (e.g., anionic detergents are excluded). Following extraction by amphoteric detergent(s), the tissue is washed with a buffer system to facilitate the clearance of cellular components and detergent. In one embodiment, the subject invention pertains to a replacement tissue that is a nerve graft that supports axonal regeneration, guides axons toward the distal nerve end and / or is immunologically tolerated. Preferably, the nerve graft retains essential extracellular matrix scaffolding as well as biological components that promote nerve regeneration through the nerve graft.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Method for decellularization of tissue grafts
ActiveUS9572911B2Simple preparation stepsDisrupt immunogenic cellular componentsCell dissociation methodsMammal material medical ingredientsCellular componentCell-Extracellular Matrix
The subject invention pertains to materials and methods for processing tissue to produce a natural, acellular replacement tissue that is immunocompatible with a recipient. According to the subject invention, harvested tissue is subjected to wash solutions wherein only amphoteric detergent(s) are used (e.g., anionic detergents are excluded). Following extraction by amphoteric detergent(s), the tissue is washed with a buffer system to facilitate the clearance of cellular components and detergent. In one embodiment, the subject invention pertains to a replacement tissue that is a nerve graft that supports axonal regeneration, guides axons toward the distal nerve end and / or is immunologically tolerated. Preferably, the nerve graft retains essential extracellular matrix scaffolding as well as biological components that promote nerve regeneration through the nerve graft.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Extracellular matrix support material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102743790AAvoid social ethics issuesWide range of organizationsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsProsthesisCell-Extracellular MatrixFreeze-drying
The invention belongs to the field of biological materials and discloses an extracellular matrix support material and a preparation method thereof. The extracellular matrix support material disclosed by the invention is prepared into a three-dimensional porous support material with a certain pore diameter and porosity through performing in-vitro monolayer high-density culture on immature rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and collecting extracellular matrixes secreted by the immature rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by applying the freeze-drying technology and a proper cross-linking agent. The material can be trimmed into proper sizes and shapes according to a cartilage defect zone or the requirement of an in-vitro experiment, and the material is sterilized by ethylene oxide to obtain an integral packaging bag. As the stem cells are used as material sources of an extracellular matrix support, the extracellular matrix support material disclosed by the invention is wide in tissue source and strong in multiplication capacity, therefore, the extracellular matrix support material can obtain enough cell quantity per se, and the problems of social ethics involved by embryonic stem cells are avoided.
Owner:金成哲 +3
Compositions for Regenerating Defective or Absent Myocardium
InactiveUS20130122108A1Restoring cardiac functionGenetic material ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsRegenerative processCell-Extracellular Matrix
Compositions of the invention for regenerating defective or absent myocardium comprise an emulsified or injectable extracellular matrix composition. The composition may also include an extracellular matrix scaffold component of any formulation, and further include added cells, proteins, or other components to optimize the regenerative process and restore cardiac function.
Owner:CORMATRIX CARDIOVASCULAR INC
Compositions for Regenerating Defective or Absent Myocardium
InactiveUS20140342984A1Restoring cardiac functionPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesCell-Extracellular MatrixRegenerative process
Compositions of the invention for regenerating defective or absent myocardium comprise an emulsified or injectable extracellular matrix composition. The composition can also include an extracellular matrix scaffold component of any formulation, and further include added cells, proteins, or other components to optimize the regenerative process and restore cardiac function.
Owner:CORMATRIX CARDIOVASCULAR INC
Nucleus pulposus-cartilage extracellular matrix scaffold and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN105031734AOvercome the disadvantages of small quantities and difficult accessGood biocompatibilityProsthesisArticular surfacesArticular surface
The invention discloses a nucleus pulposus-cartilage extracellular matrix scaffold and a preparing method thereof and belongs to the biological tissue engineering technology. The preparing method comprises the steps that nucleus pulposuses and bony articular surface cartilage are smashed, decellularized, subjected to gradient centrifugation to collect extracellular matrix microfilament suspension, and freeze-dried to obtain a freeze-dried decellularized nucleus pulposus matrix and a freeze-dried decellularized cartilage matrix, the two matrixes are taken in certain proportion and dissolved in ultrapure water to prepare mixed matrix suspension with certain concentration, and the mixed matrix suspension is freeze-dried and subjected to ultraviolet irradiation crosslinking and chemical reagent crosslinking in sequence so that the nucleus pulposus-cartilage extracellular matrix scaffold can be obtained. In this way, the defect that the nucleus pulposuses are hard to obtain due to the small number is overcome; the preparing technology is simple, and decellularizing can be achieved thoroughly; the matrix scaffold is degradable and high in biocompatibility; the matrix scaffold is of a three-dimensional structure, is high in mechanical property and plasticity, and can facilitate the distribution, growth and differentiation of seed cells; the freeze-dried extracellular matrixes are convenient to store and prepare and can be used for constructing a tissue engineered intervertebral disc to repair partial defects of the intervertebral disc, and broad clinical application prospects are realized.
Owner:TIANJIN HOSPITAL
Compositions for Regenerating Defective or Absent Myocardium
InactiveUS20130101563A1Organic active ingredientsBiocideRegenerative processCell-Extracellular Matrix
Compositions of the invention for regenerating defective or absent myocardium comprise an emulsified or injectable extracellular matrix composition. The composition may also include an extracellular matrix scaffold component of any formulation, and further include added cells, proteins, or other components to optimize the regenerative process and restore cardiac function.
Owner:CORMATRIX CARDIOVASCULAR INC
Hydrogel, and preparation method and three-dimensional cell culture method thereof
The invention discloses a hydrogel, and a preparation method and a three-dimensional cell culture method thereof. The preparation method of the hydrogel comprises the following steps: S1, preparing pig acellular dermis and / or pig acellular bladder; S2, freeze-drying the porcine acellular dermis and / or the porcine acellular bladder; S3, grinding the freeze-dried porcine acellular dermis and / or freeze-drying the porcine acellular bladder into fine particles; S4, adding the fine particles into pepsin digestive juice, and stirring for 48-72 hours to form an extracellular matrix scaffold; and S5, adjusting the pH value and the salt concentration of the pepsin digestive juice to inactivate the pepsin, and recombining the protein in the extracellular matrix scaffold to form the hydrogel.
Owner:江苏安泰康健康科技有限公司
Adipose extracellular matrix scaffold and production method and application thereof
ActiveCN111375090AHigh mechanical strengthAppropriate rate of degradation in vivoTissue regenerationProsthesisCell-Extracellular MatrixPhoto irradiation
The invention relates to an adipose extracellular matrix scaffold and a production method and application thereof. The production method of the adipose extracellular matrix scaffold comprises the following steps: subjecting adipose tissue to decellularization treatment, dehydration treatment and degreasing treatment in sequence to obtain an adipose extracellular matrix; crushing the adipose extracellular matrix to obtain matrix powder; subjecting the matrix powder and methacrylic anhydride to a reaction in a first buffer solution to obtain a methacrylated adipose extracellular matrix; and mixing the methacrylated adipose extracellular matrix, a photoinitiator and a second buffer solution, and then carrying out a cross-linking reaction under ultraviolet irradiation to obtain the adipose extracellular matrix scaffold. According to the production method of the adipose extracellular matrix scaffold, the degradation velocity of the adipose extracellular matrix scaffold can be adjusted according to the requirements, and the obtained adipose extracellular matrix has good mechanical strength.
Owner:SHENZHEN LANDO BIOMATERIALS
Marine-derived bionic cartilage material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110193096AReduce the risk of transmissionAbundant resourcesTissue regenerationProsthesisMedicineNetwork structure
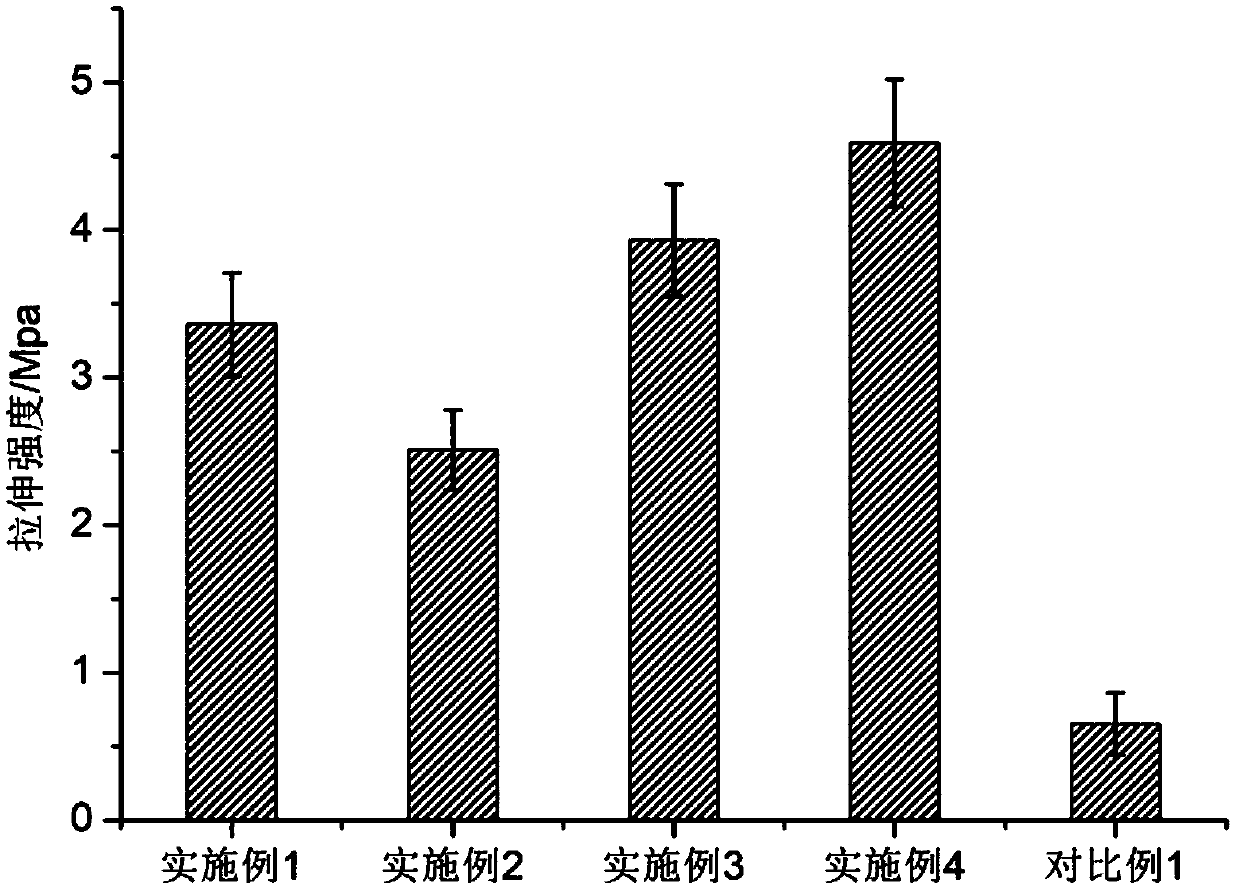
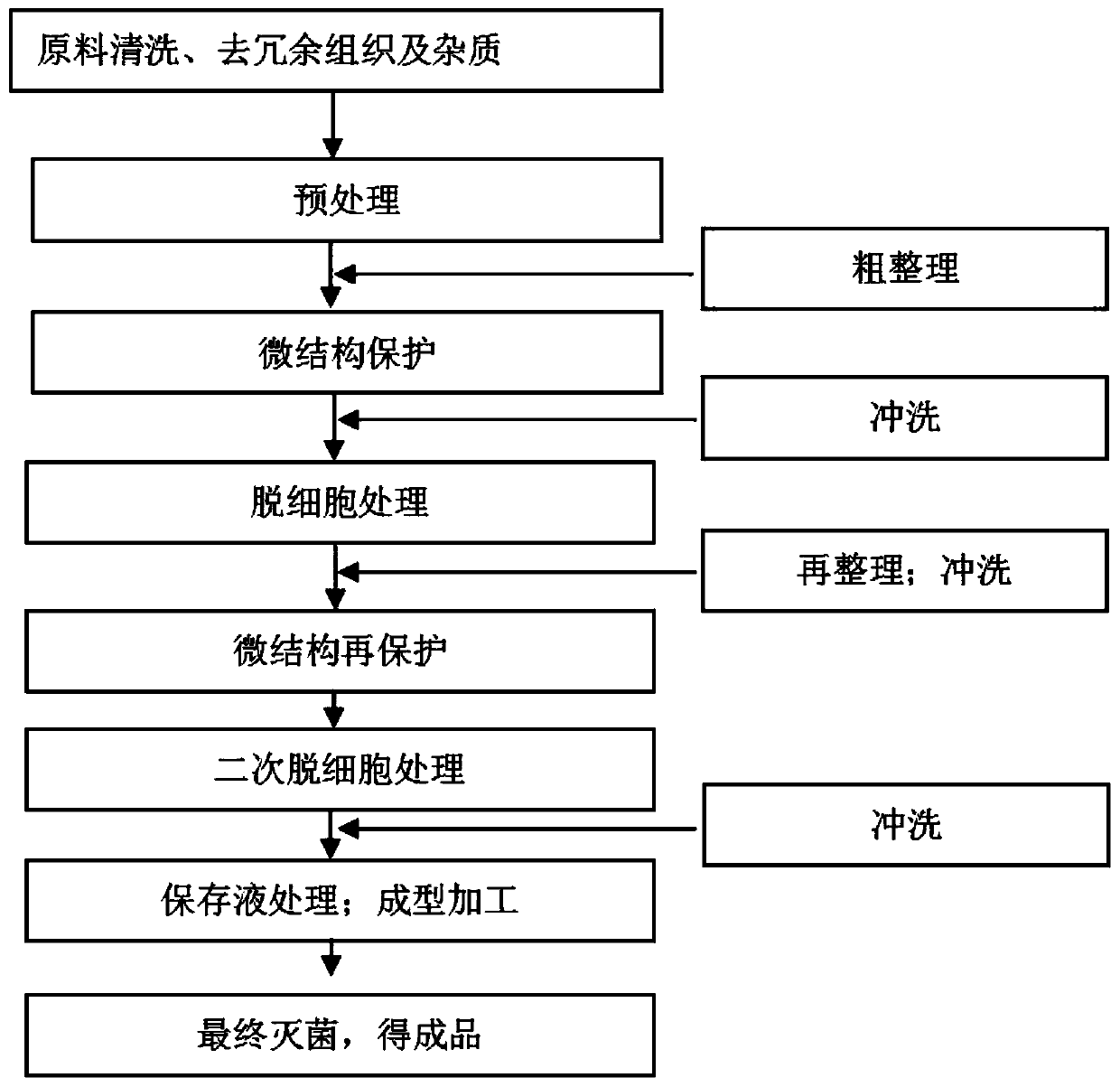
The invention discloses a marine-derived bionic cartilage material and a preparation method thereof, which belong to the field of a medical material. The marine-derived bionic cartilage material is obtained by decellularizing a marine-derived cartilage material by a special process, and has a natural bionic cartilage structure, which can be used for cartilage repair to induce cartilage regeneration; and the preparation method of the marine-derived bionic cartilage material comprises the steps of pretreatment of raw materials, rough finishing, decellularization, re-finishing, preservation liquid pretreatment, molding and the like. The marine-derived bionic cartilage material prepared by the method of the invention has the natural network structure and good mechanical strength, and is a lowimmunogenic bionic extracellular matrix scaffold material, which can solve the problem of clinical cartilage repair; moreover, the marine-derived bionic cartilage material has low risk of carrying andspreading the zoonotic virus, rich resources and low cost, and can fill the market blank of cartilage repair products and has profound social significance.
Owner:SHANGHAI SIXTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Preparation method and application of bionic composite nanofiber stent material
InactiveCN110882416AHigh mechanical strengthGood toughness strengthPharmaceutical delivery mechanismProsthesisCell-Extracellular MatrixBiocompatibility
The invention relates to a preparation method and application of a bionic composite nanofiber stent material. The material comprises an artificial nanofiber scaffold material and an extracellular matrix material derived from cells. According to the composite nanofiber material disclosed by the invention, advantages of no toxicity, degradability and the like of the traditional L-polylactic acid biomedical material are reserved and mechanical properties such as the flexibility and the tensile strength of the stent material are also improved; since the extracellular matrix has high conservative property among different species, decellularized extracellular matrix stent has advantages of low immunogenicity, excellent biocompatibility and the like; and the mesenchymal stem cells that are goingto be implanted into the body of a patient and are amplified can be inoculated and thus a tissue engineering prosthesis stent for being implanted into the human body to replace defective tissues is formed after proper culturing.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Preparation technology of porous extracellular matrix bracket
InactiveCN105999423ANon-immunogenicCompact structurePharmaceutical delivery mechanismProsthesisCell-Extracellular MatrixECM Protein
The invention discloses a preparation technology of a porous extracellular matrix bracket, aiming at solving the problems of an extracellular matrix bracket material that the pore diameter is small and cellularization is poor. Specifically, after a degradable polymer micro-sphere aggregate is planted into a subcutaneous tissue, muscle or an abdominal cavity of a host, a host cell is transferred into a micro-sphere aggregate pore to realize cellularization; after a cellularized micro-sphere aggregate bracket material is subjected to polymer elution and decellularization treatment in sequence, the extracellular matrix bracket can be obtained. The process can be used for controlling the size of the pore diameter of the bracket through controlling the size of the polymer micro-sphere; meanwhile, the connectivity of the bracket is controlled through controlling the splicing degree of the polymer micro-sphere. The porous extracellular matrix bracket prepared by the invention has a good application prospect in the fields of tissue engineering including stem cell transplantation, cartilage repairing, skin repairing and the like.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Bionic artificial bone and preparation method thereof
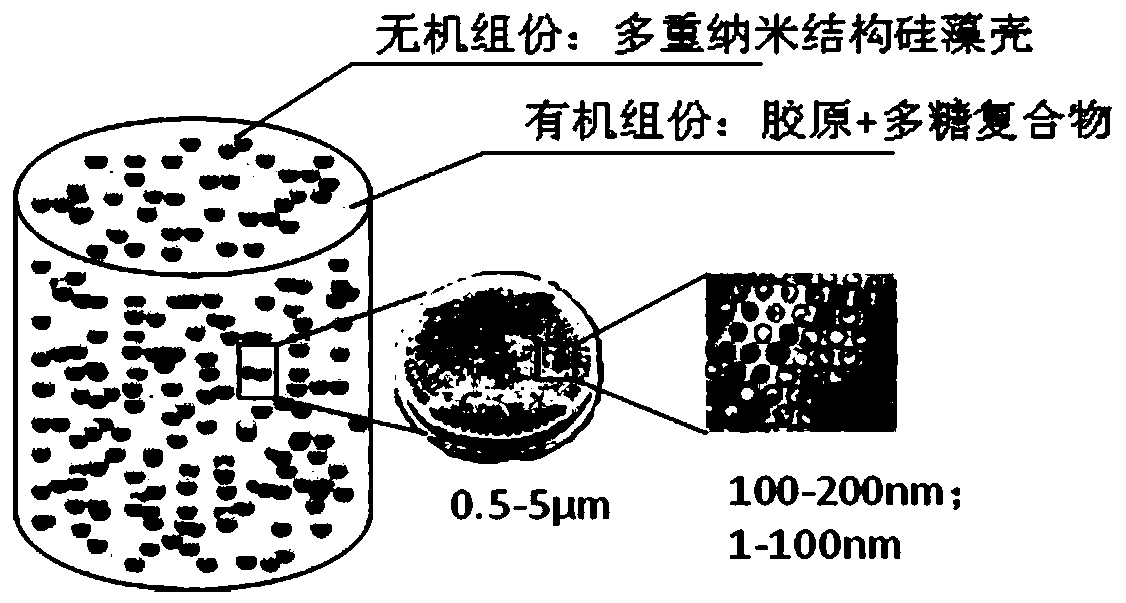
InactiveCN110339399AWide variety of sourcesLow costPharmaceutical delivery mechanismTissue regenerationCell-Extracellular MatrixNano structuring
The invention relates to a bionic artificial bone. The artificial bone comprises a component A and a component B, wherein the component A is a marine-source biomineralized substance with a natural multiple nano structure, and the component B is an artificial extracellular matrix organic substance. Specifically, the component B in a solution form is a complex of collagen and polysaccharide, and thecomponent A mainly consists of a marine organism exoskeleton of bacillariophyta. The invention also relates to a preparation method of the bionic artificial bone. The bionic artificial bone is bionically compounded of marine-source natural inorganic materials and organic materials, has the natural multiple nano bionic structure, can guide and induce the generation of new tissue, and comprises theinorganic mineralized components of the marine-source natural multiple nano structure and the organic components of an artificial extracellular matrix; the sources are wide, the cost is low, the biological safety is high, and therefore the bionic artificial bone is adopted as a natural bionic extracellular matrix stent material. The prepared bionic artificial bone has high processability and clinical operability and can meet the clinical demands of repairing different bone defects.
Owner:SHANGHAI SIXTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Compositions for Regenerating Defective or Absent Myocardium
InactiveUS20140186304A1Restoring cardiac functionBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsRegenerative processCell-Extracellular Matrix
Compositions of the invention for regenerating defective or absent myocardium comprise an emulsified or injectable extracellular matrix composition. The composition may also include an extracellular matrix scaffold component of any formulation, and further include added cells, proteins, or other components to optimize the regenerative process and restore cardiac function.
Owner:CORMATRIX CARDIOVASCULAR INC
Preparation method and application of extracellular matrix scaffold with controllable pore structure
InactiveCN114191612AShort manufacturing cycleShorten the manufacturing cycleTissue regenerationProsthesisCell-Extracellular MatrixMicrosphere
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of an extracellular matrix scaffold with a controllable pore structure, firstly, a polymer microsphere aggregate template is prepared, secondly, tissue is subjected to decellularization treatment to obtain an extracellular matrix material, and the extracellular matrix material is dissolved to obtain an extracellular matrix solution; thirdly, pouring the obtained extracellular matrix solution into pores of the microsphere aggregate to obtain a polymer-acellular matrix composite material; fourthly, cross-linking and neutralizing after freeze drying; and 5, eluting the polymer template to obtain the extracellular matrix scaffold material with the controllable pore structure. The method is short in material preparation period, controllable in matrix component and controllable in mechanics.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Preparation method and application of tissue engineering biological scaffold
PendingCN113648461AImprove biological activityGood biocompatibilityPharmaceutical delivery mechanismTissue regenerationBiologic scaffoldCell-Extracellular Matrix
The invention relates to a preparation method and application of a tissue engineering biological scaffold, and belongs to the technical field of biological medicines. According to the invention, bioactive glass nanospheres and an acellular cartilage extracellular matrix are included; and the bioactive glass nanospheres and the acellular cartilage extracellular matrix are constructed into the composite scaffold. The composite scaffold not only has the advantages of a decellularized cartilage extracellular matrix scaffold, but also overcomes some defects of a pure decellularized cartilage scaffold, the biological activity of the scaffold is increased, meanwhile, the mechanical property of the scaffold is also increased, and the scaffold can better promote regeneration and repair of cartilage and osteocartilage. By utilizing the characteristics that the acellular cartilage extracellular matrix can be subjected to freeze-drying forming and chemical crosslinking, the defect that bioactive glass nanospheres are not easy to form as granular products is overcome, and the advantages of high specific surface area, solubility, ion slow release characteristic and the like of the bioactive glass nanospheres are fully utilized. The invention provides a good biological scaffold for tissue engineering.
Owner:RENJI HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Preparation method of a specific demineralized extracellular matrix scaffold of cross-linked antibiotics
ActiveCN112618797BGood biocompatibilityImprove biological activityTissue regenerationProsthesisTherapeutic effectDrug release
The invention discloses a preparation method of a cross-linked antibiotic specific demineralized extracellular matrix scaffold, and belongs to the technical field of bone infection treatment. The invention discloses a method for preparing a specific demineralized extracellular matrix scaffold of cross-linked antibiotics. The specific demineralized and decellularized cancellous bone extracellular matrix scaffold (SDECM) is used as a substrate, and the specific demineralized and decellularized cancellous bone extracellular matrix scaffold (SDECM) is used as a substrate, and the antibiotic is electrostatically adsorbed and chemically adsorbed. Cross-linking two forms of composite drug loading, releasing antibiotics through rapid pH response and accompanying material degradation in an acidic environment, anti-infection through antibiotics and promoting repair through SDECM, so as to achieve pH-sensitive drug release in an acidic environment in the early stage of infection Rapid sterilization, sustained sterilization by slow release of drugs in the mid-late physiological environment, and permanent sterilization ability to prevent infection recurrence in the absence of infection provide new ideas and tools for the antibacterial and repairing treatment of bone infections.
Owner:杭州源囊生物科技有限公司
A kind of preparation method of tissue engineering porous extracellular matrix scaffold
ActiveCN105561398BHigh mechanical strengthSolve the problem of holesProsthesisCell-Extracellular MatrixAcellular scaffold
The invention provides a method for preparing a porous extracellular matrix scaffold for tissue engineering. In the method, a nanometer or micrometer polymer scaffold is implanted into the subcutaneous or peritoneal cavity of a host, and the polymer scaffold is used as a template to prepare a tissue-engineered porous extracellular matrix scaffold using the immune protection mechanism of the host. Controlled pore structure, and non-immunogenic tissue engineered extracellular matrix scaffold implanted in vivo. The invention solves the problem of pore formation of extracellular matrix scaffold materials; the porous scaffold is derived from the animal itself and is used for repairing autologous damaged tissues or organs without immune rejection; at the same time, since there is no complicated decellularization step for autologous repair, the scaffold The mechanical strength of the cell matrix is obviously better than that of the decellularized scaffold material; the cell matrix porous scaffold can be further decellularized for allogeneic tissue or organ repair, and has a good application prospect in the field of organ repair.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Preparation method of gene-activated poly-lactic acid material for treating liver diseases
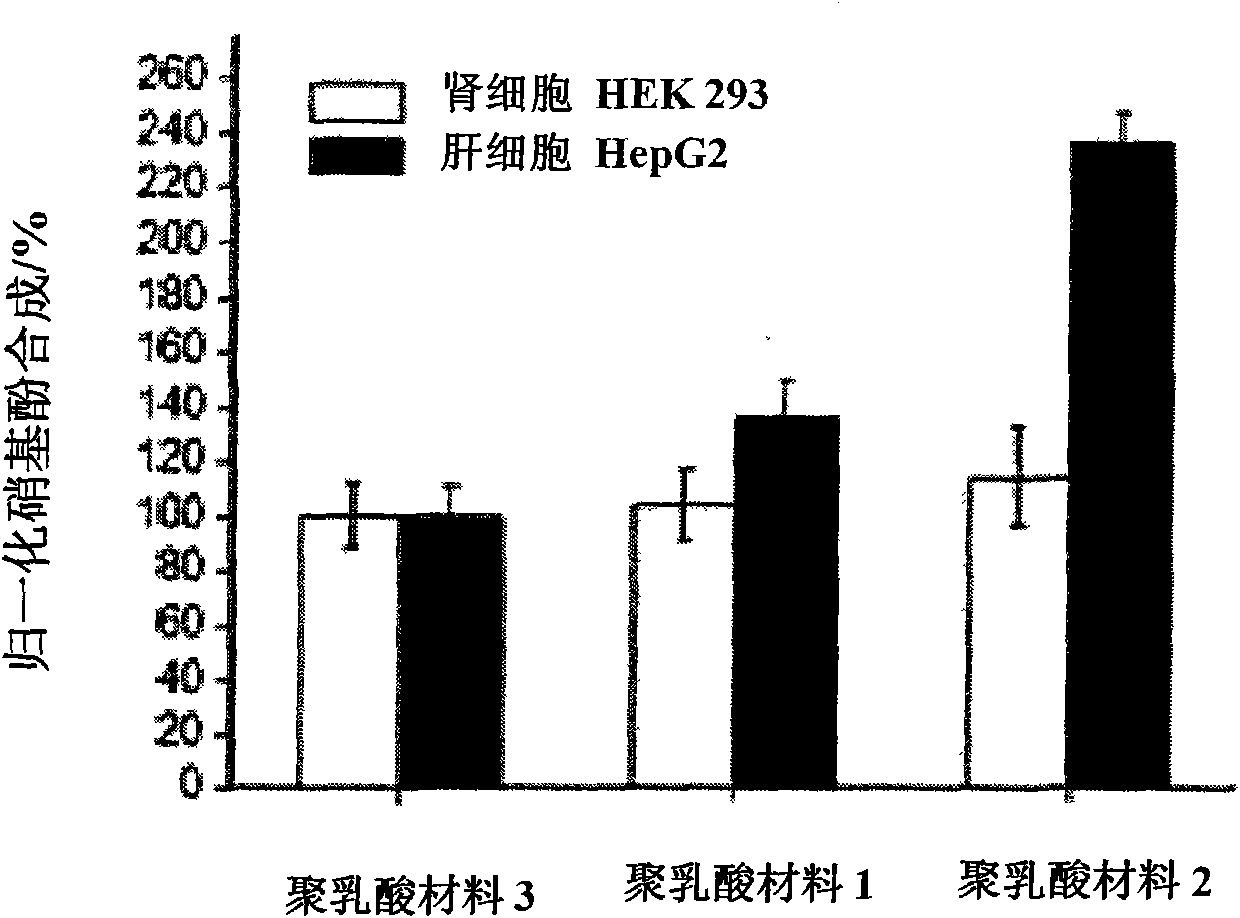
InactiveCN101745151BAdd attachment pointsAchieve targetedGenetic material ingredientsDigestive systemHepatic DiseasesPlasmid dna
The invention discloses a gene-activated poly-lactic acid material for treating a liver disease, comprising a poly-lactic acid material body and an activating layer, wherein the activating layer comprises a plasmid DNA layer and a galactose glycosidation chitosan layer, the plasmid DNA layer and the galactose glycosidation chitosan layer are sequentially arranged from the interior to the exterior at intervals, the gene-activated poly-lactic acid material has excellent cellular compatibility, can induce the growth of liver cells in situ, can strengthen the adhesive performance of the liver cells on an extracellular matrix scaffold material, can improve the stability of an implant, further induces the transfer of liver targeted genes, efficiently regulates and controls the genes to release in a targeted manner, strengthens the activity of cells and increases the transfection efficiency so as to realize the treatment of the liver disease. The invention further provides a preparation method of the gene-activated poly-lactic acid material, wherein the galactose glycosidation chitosan layer and the plasmid DNA layer are sequentially deposited on the surface of the poly-lactic acid material by utilizing the electrostatic interaction between the galactose glycosidation chitosan molecules and the plasmid DNAs, the method has simple operation and low cost and is easy to implement and very suitable for the industrial application.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Ovarian extracellular matrix scaffold and hydrogel as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN112717201AHigh purityImprove the growing environmentPharmaceutical delivery mechanismTissue regenerationGranular leucocyteOvarian tissue
The invention discloses an ovarian extracellular matrix scaffold and hydrogel as well as a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biomedicine and clinical medicine. The preparation method of the ovarian extracellular matrix scaffold comprises the following steps: 1) ovarian tissue pretreatment; 2) multi-decellularization treatment: sequentially putting the ovarian tissue skin and marrow treated in the step 1) into double distilled water, a mixed solution of sodium deoxycholate and triton X-100 and a lauryl sodium sulfate solution, sufficiently shaking and washing, adding DNA enzyme, and culturing in a culture medium at 37 DEG C for 4-8 hours; (3) sterilization and freeze-drying treatment: (4) preparation of the ovarian extracellular matrix scaffold: grinding the freeze-drying tissue prepared in the step (3) into particles with the particle size of less than 1mm, and adding acid liquor, pepsase, alkali liquor and a buffer solution into the particles to prepare the ovarian extracellular matrix scaffold. and continuously adding granular cells and follicles into the ovarian extracellular matrix scaffold to prepare the hydrogel material which can be implanted into a mammal body and has the effects of repairing ovarian injury and reconstructing ovarian functions. The research provides a new strategy for female fertility protection.
Owner:TONGJI HOSPITAL ATTACHED TO TONGJI MEDICAL COLLEGE HUAZHONG SCI TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com