Adipose extracellular matrix scaffold and production method and application thereof
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0035] Such asfigure 1 As shown, the preparation method of the adipocyte extracellular matrix scaffold in one embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0036] Step S110: Perform pretreatment on the adipose tissue.
[0037] Wherein, the step of pretreating the adipose tissue includes: washing the adipose tissue with physiological saline to remove the blood in the adipose tissue; then mixing the washed adipose tissue with water for homogenization and collecting the precipitate.
[0038] Specifically, the adipose tissue may be animal fat or isolated human fat, wherein the isolated human fat may be extracted human fat, for example.
[0039] Specifically, the step of washing the adipose tissue with physiological saline includes: chopping the adipose tissue, mixing it with physiological saline, and centrifuging at 1000 rpm to 2000 rpm for 3 minutes to 10 minutes to remove blood in fat.
[0040] Specifically, the step of mixing the washed adipose tissue with water for homogenizat...
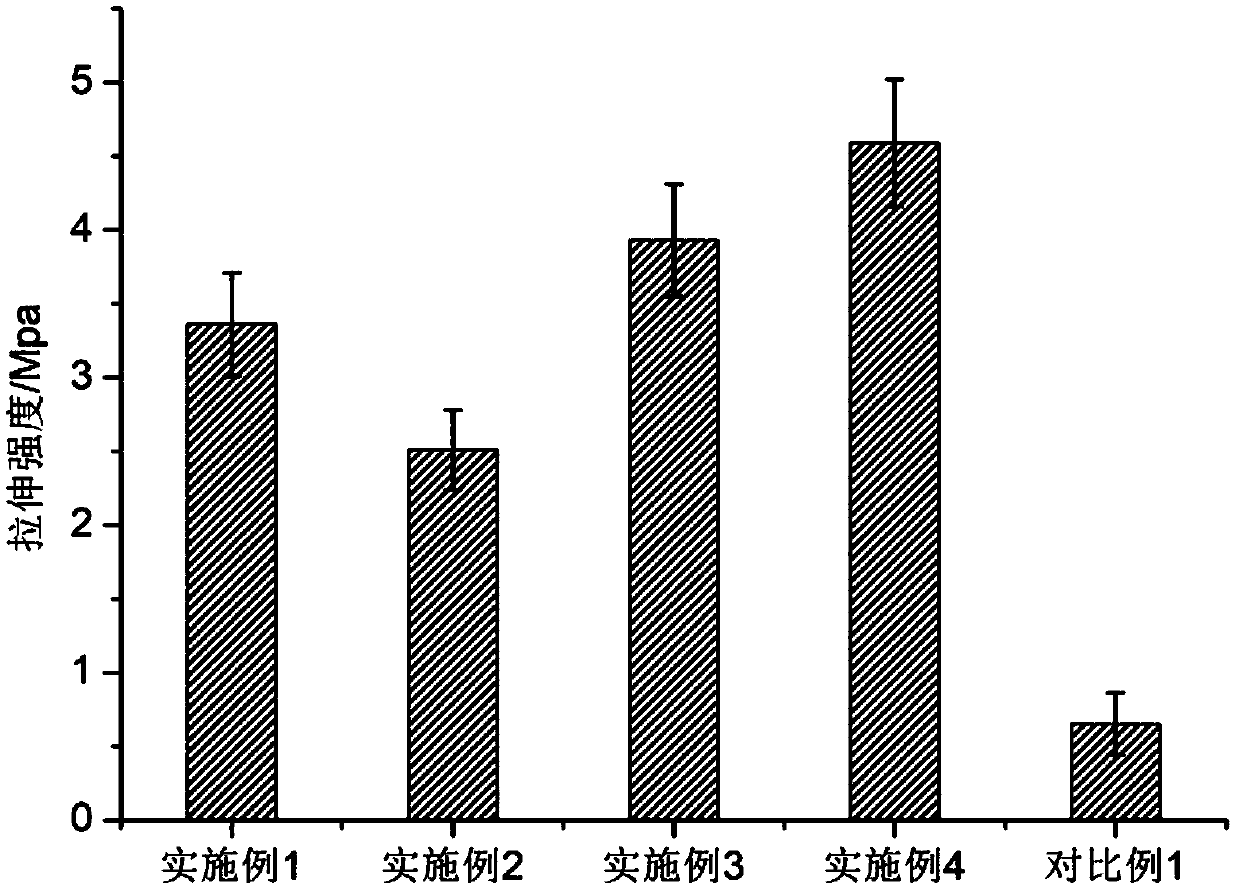
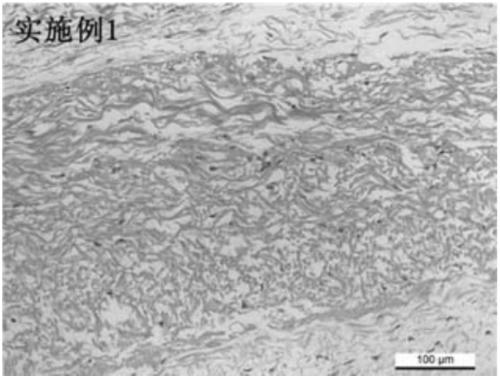
Embodiment 1
[0076] The preparation process of the adipocyte extracellular matrix scaffold of the present embodiment is as follows:
[0077] (1) Pretreatment of adipose tissue: cut fresh porcine adipose tissue into small pieces with a size of about 1cm×1cm×1cm, then mix with normal saline, and centrifuge at 1200 rpm for 8 minutes to remove fat in the blood. Mix the washed adipose tissue with pure water at a mass ratio of 0.5:1, then homogenize in a high-speed homogenizer at room temperature at a speed of 12,000 rpm for 6 minutes, and place the homogenized tissue suspension to obtain a suspension The suspension was centrifuged at 4° C. for 3 minutes at a speed of 3000 rpm, and the white precipitate was collected to obtain pretreated adipose tissue.
[0078] (2) Decellularization treatment: mix the pretreated adipose tissue obtained in step (1) with an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide with a mass percentage concentration of 1.0% in a mass ratio of 1:20, and then at 25° C. Incubate in a...
Embodiment 2
[0084] The preparation process of the adipocyte extracellular matrix scaffold of the present embodiment is as follows:
[0085] (1) Pretreatment of adipose tissue: the body fat collected by liposuction was mixed with normal saline, and centrifuged at 2000 rpm for 10 minutes to remove the blood in the fat. Mix the washed adipose tissue with pure water at a mass ratio of 3:1, then homogenize in a high-speed homogenizer at room temperature at a speed of 10,000 rpm for 3 minutes, and let the homogenized tissue suspension stand still to obtain a suspension Liquid, the suspension was centrifuged at 10° C. for 10 minutes at a speed of 5000 rpm, and the white precipitate was collected to obtain pretreated adipose tissue.
[0086] (2) Decellularization treatment: mix the pretreated adipose tissue obtained in step (1) with an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide with a mass percentage concentration of 2% in a mass ratio of 1:10, and then at 20° C. Incubate in a shaking shaker for 4 hou...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com