Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
47 results about "Exopalaemon carinicauda" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Environment-friendly feed for exopalaemon carinicauda
InactiveCN102783563AImprove digestibilityReduce pollutionAnimal feeding stuffCompound organicVegetable oil
The invention relates to an environment-friendly feed for an exopalaemon carinicauda. The feed comprises fish meal, fermented bean pulp, peanut meal, arginine, glycine, wheat gluten, wheat, high protein flour, defatted rice bran, brewers' yeast, shrimp shell powder, clam ferment powder, fish oil, vegetable oil, unshell elements, compound enzyme preparations, compound vitamins, compound organic trace elements, choline chloride and monocalcium phosphate for feed. In addition, feed ingredient further comprises 500-800U / kg of phytase. Due to adoption of the environment-friendly feed for the exopalaemon carinicauda, so that a nutritional demand of an optimal growth of the exopalaemon carinicauda can be met, a feed utilization ratio is improved, and pollution to a water environment during a breeding process of the exopalaemon carinicauda is reduced. Meanwhile, peptides are applied to improve immunity of the exopalaemon carinicauda, and a sustainable development of a seawater breeding industry of the exopalaemon carinicauda can be realized.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY & MARINE FISHERIES JIANGSU
Method for ecologically and early breeding Yangtze River coilia ectenes in pond greenhouse
ActiveCN103636540AEarly emergenceEarly use rateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaExopalaemon carinicaudaGreenhouse
The invention provides a method for ecologically and early breeding Yangtze River coilia ectenes in a pond greenhouse, and relates to coilia ectenes cultivation. The method comprises production steps of parent overwintering and strengthening cultivation, breeding parent stocking, mysis inoculation, daily management, fish fry number estimation and parent removing. The method is characterized in that when the water temperature of an outer pond is reduced to 7-8 DEG C from December to January in the following year, healthy two-age coilia ectenes without surface damage is taken as parent fish and transferred to the pond greenhouse for overwintering and strengthening cultivation; after the parent fish enters the greenhouse, 3 kilograms of exopalaemon carinicauda are put into the pound for each mu, and the mysis is inoculated; from the end of March to the middle ten days of April, the water temperature rises to 15-16 DEG C, overwintered and strengthened parent fish is picked and transferred to an ecological breeding pond, growth and feeding conditions of the fish fry are checked every one week, and the density of fish bait in water is adjusted according to the checked conditions; a seine is used for removing the parent fish in the middle ten days and last ten days of June, 1, 000-2, 000 fish fry can be generally seined each mu, the fish fry specification is that the total length is 7-10 cm and the weight is 1.8-2.5 g, and the fish fry can be taken as culturing offspring seeds.
Owner:上海市水产研究所(上海市水产技术推广站)
Brackish-water ecological cultivation technology for Yangtze-river two-year-old coilia ectenes fingerlings and exopalaemon carinicauda
ActiveCN103960173AIncrease specificationHigh outputClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaExopalaemon carinicaudaGram
The invention discloses a brackish-water ecological cultivation technology for Yangtze-river two-year-old coilia ectenes fingerlings and exopalaemon carinicauda. The technology is characterized by comprising the following steps: firstly, an estuary-area earth pond and natural brackish water with an inflow salinity of 0.5-1.5% are chosen, and food organism is inoculated in the pond; secondly, an aerator is opened before fingerlings are put in the pond in winter or in early spring, wherein the stocking size of the fingerling is a total length of 10 to 20 cm, and the stocking density of the fingerlings is 500 to 600 fishes per mu; thirdly, putting the exopalaemon carinicauda into the pond, wherein the stocking density of the exopalaemon carinicauda is 6 to 12 jin per mu, and the stocking size is 200 to 280 fishes per jin; after the fingerlings and exopalaemon carinicauda are put in the pond, 1 / 3 of water is changed each month from January to June, 1 / 3 of water is changed each half month from July to September, and 1 / 3 of water is changed each month from October to December; fourthly, prawn artificial pellet feed which is adopted as exopalaemon carinicauda feed is fed 1 time per day, wherein the feeding amount is 1 to 3 percent of the weight of the exopalaemon carinicauda; finally, the fingerlings and exopalaemon carinicauda are captured with nets in winter at the temperature of 6 to 8 DEG C, wherein the specification of the captured coilia ectenes is 16 to 20 gram per fish while the specification of the exopalaemon carinicauda is 100 to 150 fishes per jin.
Owner:上海市水产研究所(上海市水产技术推广站)
Method for improving current-year small-specification fingerling overwintering survival rate of fugu obscurus
ActiveCN103858795APromote nutrient accumulationImprove the immunityClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaExopalaemon carinicaudaOpossum
A method for improving the current-year small-specification fingerling overwintering survival rate of fugu obscurus is composed of four production steps which are small-specification fingerling concentrated breeding, temporary culture adaptation, forced domestication and reinforced cultivation. The method is characterized by comprising the steps of placing small-specification thin fingerlings which are yellow in body color in the current year in an indoor cement pool in a concentrated mode ahead of time in the last ten days of October prior to grinding wheel when the water temperature is 20 DEG C, feeding fresh and live opossum shrimp or exopalaemon carinicauda during an adaptation period of 2-3 days for the small-specification fingerlings just subjected to concentrated breeding, starting forced domestication with matched feed after stopping feeding the fresh and live baits for 2-3 days, continuing the domestication for 7-10 days, feeding twice per day during the reinforced cultivation period, sucking the bottom to discharge dirt per day with the feeding for 2 hours as the standard, keeping water quality fresh, adopting circulating water or replacing the water twice per week, replacing 2 / 3 of water each time, maintaining the water temperature at over 15 DEG C, and adopting a fugu obscurus conventional method to overwinter after continuing the reinforced cultivation for 18-22 days.
Owner:SHANGHAI FISHERIES RES INST +1
Artificial maturing method for exopalaemon carinicauda in anestrous seasons
InactiveCN103125413APromote gonad developmentImprove controllabilityClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaTemperature controlExopalaemon carinicauda
The invention relates to an artificial maturing method for exopalaemon carinicauda in anestrous seasons, in particular to an artificial reproduction method for exopalaemon carinicauda in autumns and winters by means of regulating and controlling the temperature and the illumination cycle and enriching nutrients for the exopalaemon carinicauda. The artificial maturing method mainly includes controlling the temperature of water; regulating and controlling the illumination cycle; and enriching nutrients for the exopalaemon carinicauda. Temperature control equipment simulates a procedure that the temperature of water in springs rises gradually so as to control the temperature of the water; fluorescent lamps and a timer simulate a procedure that the illumination cycle is gradually prolonged in the springs so as to regulate and control the illumination cycle; and fresh baits such as nereid are fed to the exopalaemon carinicauda to enrich nutrient supplied for the exopalaemon carinicauda in a gonad development procedure. The exopalaemon carinicauda can smoothly reproduce by laying eggs after being bred for 2-3 weeks under the condition. The artificial maturing method has the advantages that characteristics that the temperature of the water gradually rises in the springs and the illumination cycle is gradually prolonged under natural conditions are simulated, so that gonads of the exopalaemon carinicauda are developed in the anestrous seasons, the exopalaemon carinicauda reproduces by laying the eggs in the anestrous seasons, and the purpose of controlling reproduction of the exopalaemon carinicauda throughout the year is achieved.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for obviously improving survival rate of exopalaemon carinicauda in artificial breeding process
InactiveCN103210852AReduce predation rateEfficient separationClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaExopalaemon carinicaudaPhototaxis
The invention relates to a method for obviously improving the survival rate of exopalaemon carinicauda in the artificial breeding process, in particular to a method for carrying out larva separation and collection by utilizing phototaxis of larvae. The method comprises the following steps of dividing different functional regions in a spawning pool; regulating illumination in different functional regions; and installing a lifting adjustable larva collection net. In the step of dividing the functional regions, a large-aperture screen is utilized to isolate and divide the spawning pool into a parent shrimp action region and a larva collection region; and illumination regulation comprises the steps of covering the parent shrimp action region with a sunshade net and carrying out lure in the larva collection region by a fluorescent lamp. The method has the advantages that division of different functional regions and illumination regulation enable larvae and parent shrimps to be spatially and effectively separated and reduces the predation rate of the parent shrimps for the larvae, so that post-larvae yield is greatly improved; meanwhile, embryo abscission and death of the parent shrimps, which are caused by frequent sorting of the parent shrimps, are also avoided and the survival rate in the breeding process is improved; and the lifting adjustable larva collection net can be used for collecting larvae in due time according to the hatching condition of larvae, so that labor intensity is reduced and the practical value on production is improved.
Owner:南通中国科学院海洋研究所海洋科学与技术研究发展中心 +1
Scutellaria composite immune reinforcing agent, preparation method thereof and application thereof
InactiveCN101642488AOrganic active ingredientsClimate change adaptationWhite spot syndromeMortality rate
The technology belongs to the technical field of aquiculture disease prevention, in particular to the preparation method of the immune reinforcing agent for cultivating crustacean, and the applicationmethod thereof. The aquiculture composite immune reinforcing agent comprises 2-4 parts of aquiculture extractive or baicalin and 2.5-5 parts of levamisole. The composite immune reinforcing agent caneffectively enhance non-specific immunity for cultivating blue crab, improve the activity of the blood serum phenol oxidase, the superoxide dismutase and the alkalinephosphatase of the blue crab, andimproves the disease resistance of the blue crab to common pathogens such as white spot syndrome virus, vibrio, hematodinium, etc. The composite immune reinforcing agent can be applied to the cultivation of the blue crab by being injected or added into blue crab fresh fish bait and granulated feed for preventing and controlling the disease at the disease peak and reducing the disease rate and themortality rate of the blue crab. The immune reinforcing agent is added into the feed for preventing and controlling the disease of the penaeus vannamei boone and exopalaemon carinicauda.
Owner:ZHEJIANG INST OF FRESH WATER FISHERIES
Ecological breeding method for jointly breeding exopalaemon carinicauda in takifugu flavidus
ActiveCN103636545AImprove water qualityTap production potentialClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaAnguilla malgumoraEvery Two Weeks
An ecological breeding method for jointly breeding exopalaemon carinicauda in takifugu flavidus comprises fingerling breeding, seed shrimp breeding, daily management and harvesting of the takifugu flavidus and the exopalaemon carinicauda, and is characterized in that when the water temperature of an outer pond is kept to be 14-15 DEG C, overwintered fingerling is bred in the outer pond, and one aerator is equipped for each 3-5 mu of a pond; before breeding, firstly, the pond is cleared and sterilized; the pond is filled with water after 48 hours of sterilization, the water occupies two thirds of the pond, and the salinity is 5-15; after one week of water filling, the fingerling is bred, and summerlings are bred according to the breeding density of 3,000-5,00 0 fish per mu in the beginning of July; the breeding density of two-age fingerling is 1,000-1,200 fish per mu; the breeding density of three-age fingerling is 800-1,000 fish per mu, and water is added to 1.5m after breeding of the fingerling; in June and July, seed shrimps are scattered into a takifugu flavidus aquaculture pond, and 1.5-3 kilograms of seed shrimps are bred for each mu; feeding is performed for two times every day, the feeding amount per day is 3-8% of the weight of fish, fish bait is eel feed containing 45% of crude protein, and water is changed once every two weeks; and in the mid-to-end November, the takifugu flavidus is caught firstly, the exopalaemon carinicauda is harvested in December, and finally, the pond is cleared for fish catching.
Owner:上海市水产研究所(上海市水产技术推广站)
Method for synchronous line establishment of small-population parents in artificial breeding of exopalaemon carinicauda
ActiveCN104542408ASimple temperature control measuresNo effect on growth and developmentClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaExopalaemon carinicaudaTemperature control
The invention discloses a method for synchronous line establishment of small-population parents in artificial breeding of exopalaemon carinicauda. In non-high-breeding season at relatively low water temperature, water temperature is regulated and controlled in three development stages (parent prawn gonad development stage, zygote embryo development stage and larval development stage) by virtue of a temperature control method, so that families established by small-population parents in different gonad development stages can develop into a post-larval stage at the same time as much as possible, and the synchronous line establishment of the small-population parents is finally achieved. By respectively setting temperature gradients according to the suitable temperature ranges of the exopalaemon carinicauda in different development stages, the method disclosed by the invention is conducive to the shortening of development time difference of various parent progenies, and capable of achieving the synchronous line establishment and multi-generation breeding per year of the small-population parents in the artificial breeding of the exopalaemon carinicauda.
Owner:南通中国科学院海洋研究所海洋科学与技术研究发展中心 +1
Ecological mixed breeding method of pond mainly used for breeding Sepia esculenta
ActiveCN105409847AMeet water quality requirementsMeet needsClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaExopalaemon carinicaudaWater quality
The invention provides an ecological mixed breeding method of a pond mainly used for breeding Sepia esculenta. The ecological mixed breeding method comprises the following steps: pond preparation: excavating a deep ditch in the middle of the pond, adding gentle slopes on the inner side of the periphery of the pond, covering each gentle slope by using a layer of geotechnical cloth, and paving PVC oxygenation pipelines on the bottom of the pond; stocking Meretrix meretrix Linnaeus seedlings in the pond when the temperature of water in the pond reaches 7-8 DEG C in the spring; stocking Exopalaemon carinicauda and shrimps with eggs when the temperature of the water in the pond rises to be 12-13 DEG C; stocking Sepia esculenta larvae after the temperature of the water in the pond rises to be 14-16 DEG C; and then feeding with baits in a combined manner. According to the ecological mixed breeding method provided by the invention, mixed breeding is implemented by ecological complementarity of the Sepia esculenta, the Exopalaemon carinicauda and the Meretrix meretrix Linnaeus, the Meretrix meretrix Linnaeus purifies water, the Sepia esculenta can eat the Exopalaemon carinicauda, the pond has Exopalaemon carinicauda groups in different stages, and requirements of the Sepia esculenta to live baits are met; and the Sepia esculenta eats sick and weak Exopalaemon carinicauda individuals, and spreading of shrimp diseases is controlled effectively, so that the purposes of high yield, high efficiency and environmental protection are achieved.
Owner:JIANGSU MARINE RESOURCES DEV RES INST LIAN YUNGANG
Detection method of ecssr1024 microsatellite dna marker in white shrimp
ActiveCN102277438ASimple methodAccurate methodMicrobiological testing/measurementExopalaemon carinicaudaMicrosatellite
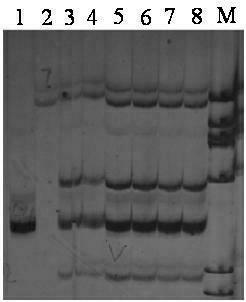
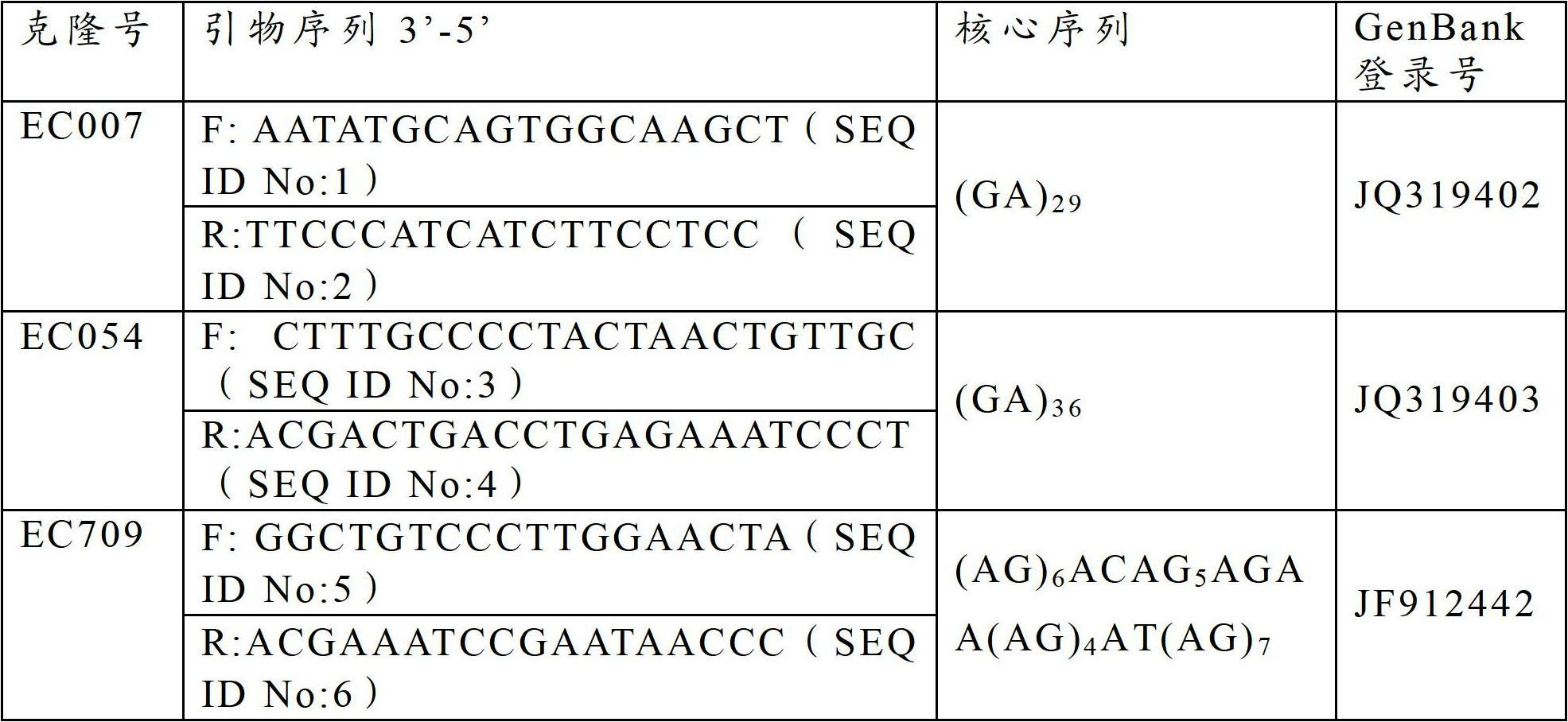
The invention provides a method for detecting an EcSSR1024 microsatellite DNA marker in exopalaemon carinicauda, which comprises: extracting genomic DNA of the exopalaemon carinicauda and diluting the genomic DNA for later use; designing specific primers at the two ends of the core sequence of an EcSSR1024 microsatellite; performing the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification of the genomicDNA of the exopalaemon carinicauda by using the primers, and detecting the product of the PCR amplification; and analyzing by using strips appeared in the product, and obtaining the polymorphic map of a highly-genetic variation in the core sequence area of the EcSSR1024 in the exopalaemon carinicauda. By using the primers and detection method, which are provided by the invention, the genetic variation in the core area of the EcSSR1024 microsatellite in each individual of exopalaemon carinicauda can be detected, and the polymorphic map of the highly-genetic variation in a genetic marker gene locus in the EcSSR1024 in exopalaemon carinicaud can be obtained quickly. The method is suitable to be used in population genetic marking, genealogical identification, genetic map construction and the like.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Method for rapidly breeding Cynoglossus Semilaevis Gunther in soil pond
InactiveCN101699996AImprove survival rateEasy and reasonable operationClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaExopalaemon carinicaudaAquatic product
The invention discloses a method for rapidly breeding Cynoglossus Semilaevis Gunther in a soil pond, comprising the following steps of soil pond selecting, advanced fry stocking, breeding management, harvesting and the like. The invention has convenient and reasonable operation, and the survival rate reaches more than 90 percent. The invention can also be used for breeding aquatic products of Exopalaemon carinicauda and the like.
Owner:石斌 +1
Triple-PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection method for exopalaemon carinicauda by using microsatellite mark
ActiveCN102676689AShorten experiment timeImprove experimental efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementExopalaemon carinicaudaDNA paternity testing
The invention provides a triple-PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection method for exopalaemon carinicauda by using a microsatellite mark. The triple-PCR detection method comprises the following steps of: designing and synthesizing a triple-PCR primer; extracting genome DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid); carrying out triple-PCR; and detecting a PCR product, wherein the PCR comprises a triple-PCR system and a triple-PCR program. According to the triple-PCR detection method disclosed by the invention, the triple-PCR system for identifying the family and the paternity of the exopalaemon carinicauda is established and synchronous detection of three microsatellite sites in one PCR is realized, so that the efficiency of the triple-PCR detection method is increased by three times compared with that of an original PCR method. The triple-PCR detection method disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of high efficiency, economy, simplicity, convenience, feasibility and the like and can be popularized and applied in genetic diversity analysis, genetic relationship identification, family management and selective breeding.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
A method of using shrimp eggs to culture in vitro to establish a family of white shrimp
ActiveCN103960182BEffective isolation and cultureStrict isolation cultureClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaExopalaemon carinicaudaMicroscopic observation
The invention relates to a method for establishing an exopalaemon carinicauda family by applying in-vitro egg culture. The method comprises the steps that parent exopalaemon carinicauda are selected and disinfected, and the parent exopalaemon carinicauda and eggs are separated; shaking culture parameters of the eggs are measured; microscopic observation is performed in the culture process; the progressive decreasing control of salinity is performed in the culture process; young exopalaemon carinicauda after incubation are cultured. According to the method, the probability of incubation failure caused by influence of different factors in the egg laying process of the parent exopalaemon carinicauda can be effectively lowered, the incubation rate of the eggs and the survival rate of the young exopalaemon carinicauda are increased, and therefore the method has good application prospects in the application of establishing the exopalaemon carinicauda family.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY & MARINE FISHERIES JIANGSU
Portunus trituberculatus and exopalaemon carinicauda polyculture feed
The invention provides a portunus trituberculatus and exopalaemon carinicauda polyculture feed and belongs to the technical field of fishery industry. The portunus trituberculatus and exopalaemon carinicauda polyculture feed is prepared from the following substances in parts by weight: 20-30 parts of red fishmeal, 5-10 parts of arginine, 8-15 parts of spiral seaweed powder, 4-6 parts of immunopolysaccharide, 10-15 parts of fermented soybean meal, 2-3 parts of pinus massoniana needle powder, 1-5 parts of vinasse, 2-6 parts of bacillus subtilis powder, 2-3 parts of fish oil, 10-15 parts of rice bran, 5-10 parts of nepeta cataria powder, 5-8 parts of cellulase, 0.2-0.5 part of compound vitamin, 0.5-1 part of compound mineral substance and 5-8 parts of houttuynia cordata powder. The portunus trituberculatus and exopalaemon carinicauda polyculture feed has balanced nutrition and can meet the daily requirements of portunus trituberculatus and exopalaemon carinicauda; the feed efficiency is high, the survival rate of the portunus trituberculatus and the exopalaemon carinicauda is high and the weight growth speed is high; after all the raw materials are reasonably compounded, the palatability and the food calling effect are good; the immunity of the portunus trituberculatus can be remarkably enhanced and the antibacterial and anti-virus capabilities of the portunus trituberculatus are improved; and the portunus trituberculatus and exopalaemon carinicauda polyculture feed has good stability in water and is environment-friendly.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
Method for constructing Exopalaemon carinicauda reciprocal backcross family
ActiveCN106386605ABuild method is repeatableEasy to operateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaExopalaemon carinicaudaPhenotypic trait
The invention provides a method for constructing an Exopalaemon carinicauda reciprocal backcross family. The method includes the following steps: (1) parent shrimp selection; (2) parent shrimp mating; (3) cultivation and breeding of F1 offspring seeds; (4) parent-child backcross; and (5) cultivation and breeding of backcross progeny offspring seeds. Male and female Exopalaemon carinicauda parent shrimps which are distributed naturally or bred artificially and have excellent characters are selected, and the reciprocal backcross family can be acquired through completely-artificial breeding, aquaculture and parent-child mating; the success rate of construction of the reciprocal backcross family can reach 75%, and can provide material and technique support for quantitative character genetic analysis, near-isogenic line construction and back cross breeding of the Exopalaemon carinicauda.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Exopalaemon carinicauda feed
An exopalaemon carinicauda feed is prepared by the following raw materials in parts by weight: 2-4 parts of clover powder, 0.2-0.4 part of soya lecithin, 0.3-0.5 part of peanut oil, 10-12 parts of rape cake, 8-12 parts of cottonseed cake, 2-4 parts of Chinese medical stone powder, 1-2 parts of zeolite powder, 3-5 parts of spirulina powder, 2-4 parts of silkworm chrysalis powder, 1-2 parts of earthworm powder, 2-5 parts of chitosan, 3-5 parts of peanut shell, 0.1-0.2 part of radix astragali, 0.3-0.5 part of isatis root, 0.1-0.2 part of finelydivided phtheirospermum root, 1-2 parts of salvia officinalis, 1-2 parts of Chinese angelica, 2-4 parts of chicken liver, 1-2 parts of chicken skin, 1-2 parts of rose root powder, 3-5 parts of potato, 20-25 parts of corn flour, 12-14 parts of wheat flour, and 1-2 parts of EM original liquid.
Owner:全椒县赤镇龙虾经济专业合作社
Method for selecting hypoxia-tolerant Exopalaemon carinicauda
The invention relates to a method for selecting hypoxia-tolerant Exopalaemon carinicauda. The method includes: selecting live adult Exopalaemon carinicauda; preparing water with the dissolved oxygen content being not lower than 4ppm, and placing the adult Exopalaemon carinicauda into the water, wherein the water is isolated from atmosphere; when dead Exopalaemon carinicauda appears in the water along with dissolved oxygen content lowering, removing the dead Exopalaemon carinicauda from the water to prevent the water from being polluted by the decomposed dead Exopalaemon carinicauda; when the number of the live adult Exopalaemon carinicauda lowers to 10% of the initial adding quantity of the adult Exopalaemon carinicauda, collecting the live adult Exopalaemon carinicauda in the water. By the method, the adult Exopalaemon carinicauda individuals good in hypoxia tolerance can be screened out to facilitate follow-up breeding.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY & MARINE FISHERIES JIANGSU
Method for breeding saline-alkaline-tolerant strain of exopalaemon carinicauda
PendingCN112273299AStrong stress resistanceFast growthClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaExopalaemon carinicaudaAnimal science
The invention provides a method for breeding a saline-alkaline-tolerant strain of exopalaemon carinicauda. The method comprises the following steps of selecting artificially bred multi-year exopalaemon carinicauda with excellent growth traits as a basic group; performing an alkalinity stress experiment on young exopalaemon carinicauda growing to 30 days old; performing continuous three-generationalkalinity stress breeding to screen out a saline-alkaline-tolerant strain of the exopalaemon carinicauda; and building a core breeding group capable of being used for culture application after passage propagation. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that a rapid growth group is selected as a basic group; through saline-alkaline-tolerant breeding and polymerization of saline-alkaline-tolerant stress resistance properties, the bred new strain grows rapidly, has high stress resistance, and is suitable for the breeding in saline-alkaline regions; the growth speed is obviouslyaccelerated; the breeding survival rate is obviously improved; the operation of the method provided by the invention is simple and convenient; and the method provided by the invention is suitable forthe breeding of the saline-alkaline-tolerant strain of the exopalaemon carinicauda.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Exopalaemon carinicauda livetin binding protein gene and application thereof
ActiveCN111088257AProve the feasibilityFermentationAnimals/human peptidesBiotechnologyForeign protein
The invention provides an exopalaemon carinicauda livetin binding protein gene and application thereof. The sequence of the gene is shown in SEQ ID NO.1 in the description. The amino acid sequence encoded by the gene is shown in SEQ ID NO.2 in the description. An exopalaemon carinicauda livetin binding protein comprises three structure domains, namely EcVBP-PC1, EcVBP-PC2 and EcVBP-P3 respectively. The invention discloses application of the gene EcVBP in mediating a foreign protein into a zygote of a shelled animal through the livetin binding protein. By adopting the gene provided by the invention, the foreign protein is successfully mediated into a zygote of neocaridina denticulate sinensis, so that feasibility that VBP as a "molecule truck" carries the foreign protein into the zygote ofthe shelled animal is verified, and a basis is made for gene editing and molecular designing breeding of the shelled animal later.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY
Exopalaemon carinicauda compound eye development regulation gene and guide RNA, and acquisition and application thereof
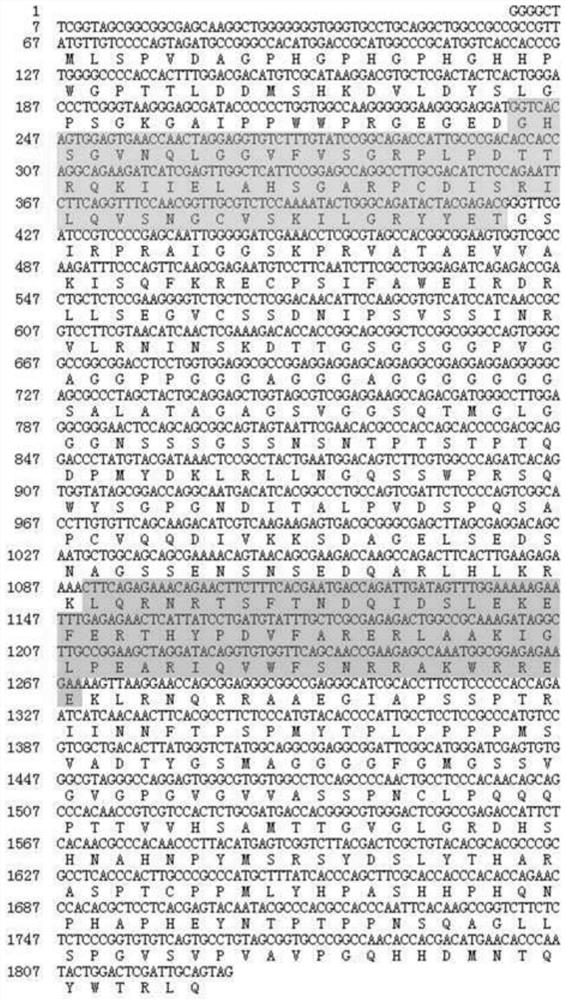
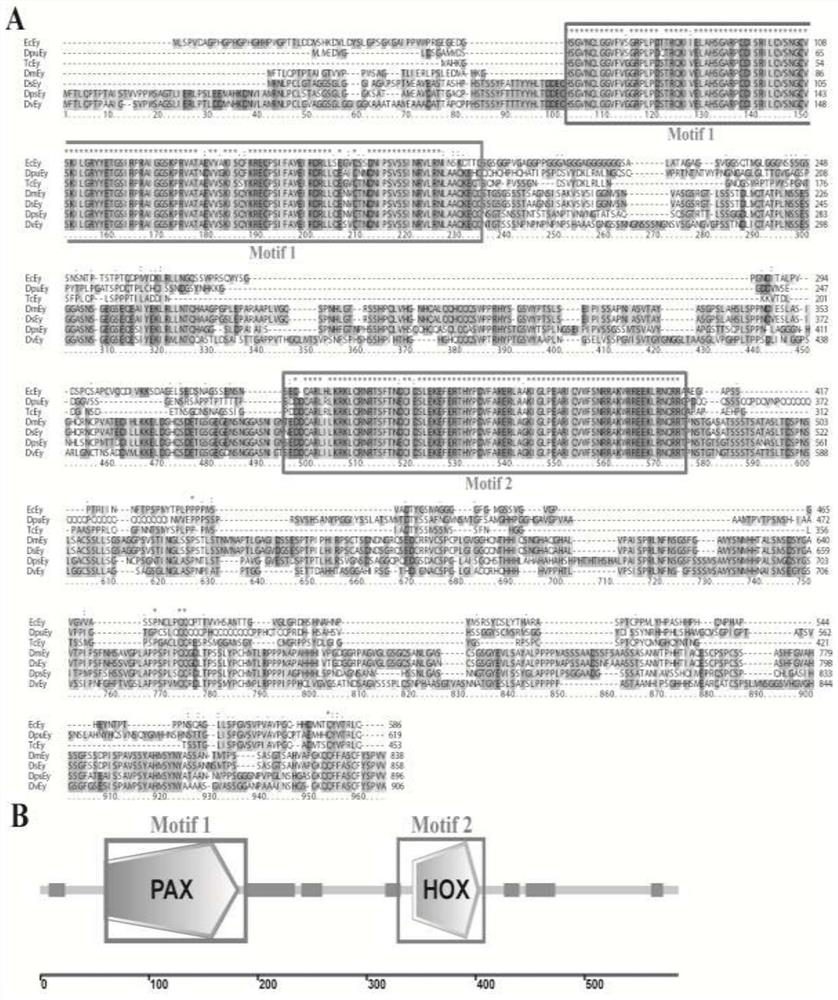
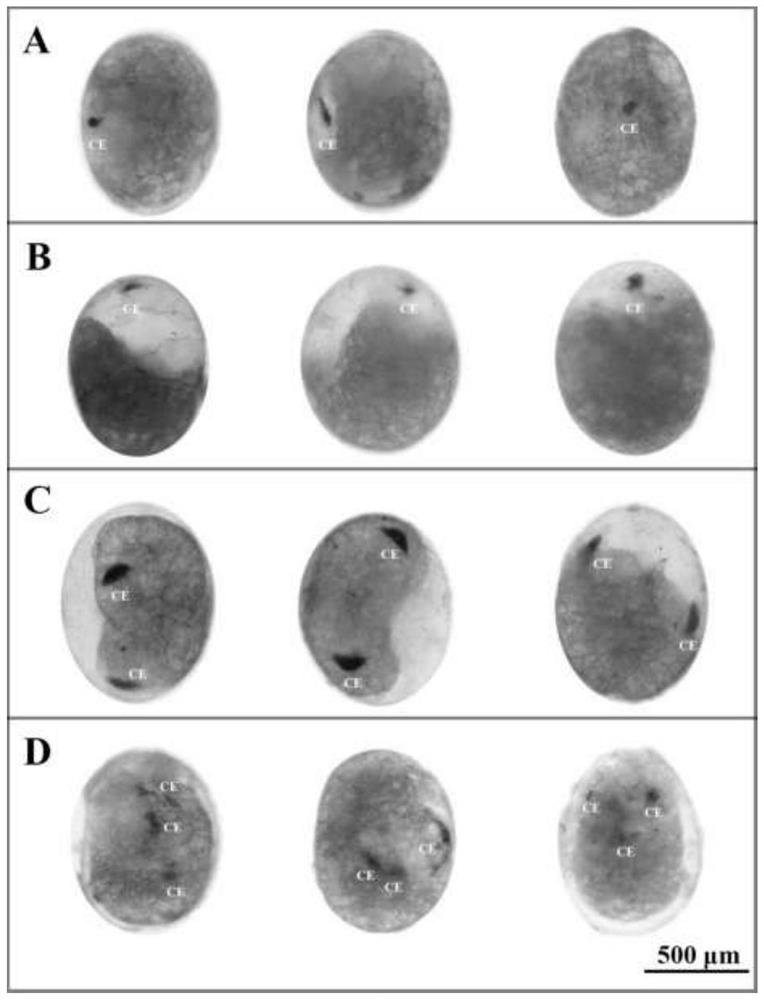
The invention relates to an exopalaemon carinicauda compound eye development regulation gene EcEy which can generate obvious phenotypic change in an embryo period after being successfully edited so asto indicate the success rate of gene editing operation, and the gene can also be applied to the establishment of gene editing platforms of other decapod crustaceans. The EcEy gene of the exopalaemoncarinicauda has a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID No. 1 in a sequence list; the guide RNA (gRNA) designed and synthesized on the basis of the sequence has a ribonucleic acid sequence shown as SEQID No.2 in a sequence list; EcEy-gRNA and commercial Cas 9 mRNA are mixed and injected into fertilized eggs of exopalaemon carinicauda, a PAX structural domain of an EcEy gene can be specifically recognized and cut, and an obvious compound eye defect phenotype is observed in the early stage of embryonic development. The EcEy gene can be used as a target gene for gene editing research of exopalaemon carinicauda, is used for verifying whether gene editing operation succeeds or not, and can also be used for establishing gene editing platforms of other decades of crustaceans.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Quantitative test method of exopalaemon carinicaudamitochondrial genome copy number
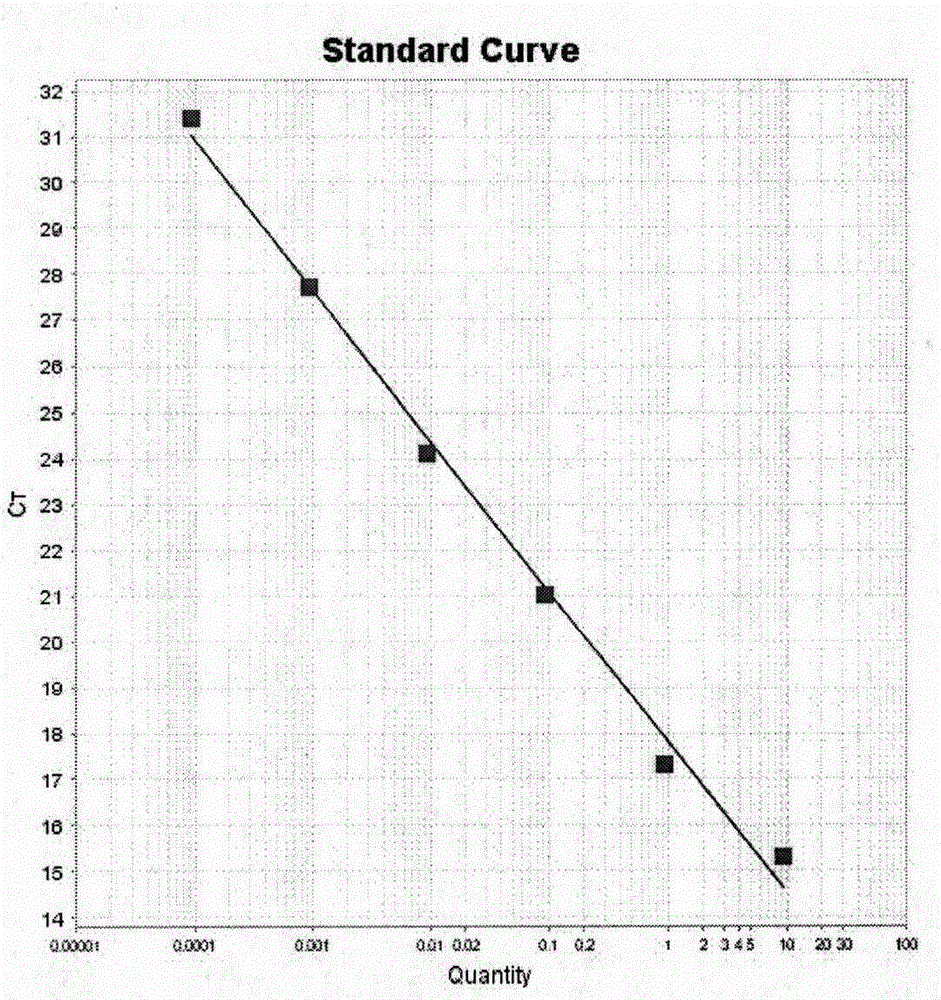
InactiveCN106498044AIncrease concentrationQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceQuantitative PCR instrument
The invention discloses a quantitative test method of exopalaemon carinicauda mitochondrial genome copy number. The method comprises the steps of selecting the adenylyl transferase gene (ANT) and the ATP6 respectively as the single copy genes of the nuclear genome and the mitochondrial genome of white tailed shrimp, designing the primer and the fluorescent probe suitable for the real time quantitative PCR reaction of the ANT and ATP6 genes, preparing real time quantitative PCR reaction standard of the ANT and ATP6 genes, through drawing the standard curve (as shown in the attachment), and using the standard curve as the standard, and quantifying and calculating the copy number of the mitochondrial genome in the to-be-tested sample cells. The method can correctly and quantitatively test the mitochondrial genome copy number of the exopalaemon carinicauda tissue sample cells, and has the advantages of being high in specificity, and simple in operation. Merely the fluorescence quantitative PCR instrument is enough to complete the quantification of the exopalaemon carinicauda mitochondrial genome copy number.
Owner:HUAIHAI INST OF TECH
Method for acquiring ecological early breeding seeds of acanthogobius ommaturus Richardson
ActiveCN103718998ALong growth cycleImprove qualityClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaExopalaemon carinicaudaBroodstock
The invention discloses a method for acquiring ecological early breeding seeds of acanthogobius ommaturus Richardson, and relates to technologies for acquiring early seeds for early breeding for acanthogobius ommaturus Richardson. The method includes selecting parent fish; controlling the breeding quantities; selecting heat-insulation sheds of ponds; cultivating the parent fish through the winters; collecting fish fries. The method is characterized in that the parent fish with the weight ranging from 100 grams to 250 grams is selected in periods from November to December, and is cultivated in the ponds for takifugu rubripes through the winters, nylon films are constructed to form heat-insulation greenhouses on the upper sides of the ponds, the areas of the ponds preferably range from 3mu to 8mu, the ratio of female parent fish to male parent fish is 1:1, 10-12 pieces of parent fish is bred in each mu of the ponds under the control, 3-5 kilograms of live exopalaemon carinicauda are placed in each mu in winter cultivation periods and are used as fodders for the parent fish, water is changed regularly, an excellent water quality condition needs to be kept, 1.2-meter water levels of the ponds are kept, and the salinity of the water in the ponds keeps ranging from 6%o to 15%o; the fish fries are sampled after 20th of March in the next year, growth conditions of the fish fries are inspected, and the fish fries are timely collected and distributed when the sizes of the growing fish fries range from 4 centimeters to 6 centimeters.
Owner:SHANGHAI FISHERIES RES INST +1
LAMP detection primers, system and method for detecting health state of exopalaemon carinicauda after WSSV (White Spot Syndrome Virus) infection
PendingCN107365858ALow costEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationExopalaemon carinicaudaWhite spot syndrome
The invention relates to an LAMP detection method for detecting the health state of exopalaemon carinicauda before and after white spot syndrome virus infection. According to the LAMP detection method, in allusion to a cDNA sequence of a gene of which the expression quantity is significantly increased in the early stage of WSSV outburst and which is obtained through massive screening in the exopalaemon carinicauda, 6 primers are designed, and a (Loop-mediated isothermal amplification, LAMP) detection method is established. By the LAMP detection method, nucleic acid extraction and purification are not required, the cost is low, the operation is convenient, and the detection process is fast and sensitive. By the LAMP detection method, diagnosing and prewarning effects can be quickly and effectively achieved in the early stage of the disease outburst of the WSSV-infected exopalaemon carinicauda.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Shrimp pond net cage combination breeding method
ActiveCN108935257AImprove stabilityIncrease production capacityFood processingClimate change adaptationExopalaemon carinicaudaEconomic benefits
The invention relates to a shrimp pond net cage combination breeding method. The method comprises the steps of shrimp pond modification, putting of a net cage, putting of exopalaemon carinicauda berried parent shrimps, putting of young penaeus monodon, putting of young inkfish, putting of stichopus japonicus fry, staged feeding of bait and the like. By means of the protection function of the net cage, exopalaemon carinicauda, penaeus monodon, inkfish and stichopus japonicus are introduced into the same breeding pond, the stability of an ecological system is improved, and the occurrence rate ofdiseases of exopalaemon carinicauda and penaeus monodon is effectively controlled. Meanwhile, a water body is fully utilized, the productivity of the water area is improved, the economic benefit is increased, and the method is suitable for being popularized in northern outdoor shrimp ponds in China.
Owner:JIANGSU OCEAN UNIV
Acanthogobius ommaturus Richardson ecological breeding method
InactiveCN107211923AEfficient acquisitionSolve supply problemsClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaExopalaemon carinicaudaFemale to male
The invention discloses a Acanthogobius ommaturus Richardson ecological breeding method. The Acanthogobius ommaturus Richardson ecological breeding method comprises the steps of selection of parent fishes, control of the stocking number, selection of the pond size, winter cultivation management and fry collection. The method is characterized in that the parent fishes with the weight of 100-250 grams are selected from November to December and put into a pond with the size of 3-9 mu for cultivation, wherein the proportion of females to males is 1:1, and the stocking number per mu is controlled to 3-5; 1-2 kilograms of live Exopalaemon carinicauda is put in per mu in the period of winter cultivation as fodder of the parent fishes, water is changed at regular intervals to keep the good water quality condition, the water level of the pond is maintained at 1.25 meters, and the salinity is maintained at 5 %. or above; fry sampling is conducted after the next April 20th, the growth situation is examined, and fries are dispersed in time after growing to 2.5 centimeters or above.
Owner:SHANGHAI FISHERIES RES INST
Pond polyculture high-yield method for red-shell meretrix meretrix and exopalaemon carinicauda holthuis
ActiveCN113349122AThe capture operation does not conflictIncrease profitFood processingClimate change adaptationPuccinia xanthiiExopalaemon carinicauda
The invention relates to a pond polyculture high-yield method for red-shell meretrix meretrix and exopalaemon carinicauda holthuis. The method comprises the following steps: a deep water tank and a peripheral platform are dug in the middle of a pond, and water is normally stored in the pond; after disinfection, water quality maintenance is carried out, and initial water fertilization is carried out; in March, seeding of the red-shell meretrix meretrix is completed; fertilizing water mainly in early May, and putting parent exopalaemon carinicauda holthuis from late May to early June; and before the first batch of shrimp seeds grow to 2.5 cm in the current year, the aquatic water body is stably yellow green or yellowish brown mainly by adjusting the algal facies of the water body, after the shrimp seeds grow to 2.5 cm to 3 cm, pellet feed is fed, and feeding is enhanced in September to October. According to the method, by setting the pond stocking sequence and time of the meretrix meretrix and the exopalaemon carinicauda holthuis, the win-win situation of breeding of the meretrix meretrix and the exopalaemon carinicauda holthuis is achieved through ecological niche complementation, close matching of varieties and breeding management operation of key nodes, and the purpose of high yield is achieved.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY & MARINE FISHERIES JIANGSU
A method for artificial breeding of small groups of white shrimp by artificial breeding of synchronous line establishment of parents
ActiveCN104542408BSimple temperature control measuresNo effect on growth and developmentClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaTemperature controlExopalaemon carinicauda
The invention discloses a method for synchronous line establishment of small-population parents in artificial breeding of exopalaemon carinicauda. In non-high-breeding season at relatively low water temperature, water temperature is regulated and controlled in three development stages (parent prawn gonad development stage, zygote embryo development stage and larval development stage) by virtue of a temperature control method, so that families established by small-population parents in different gonad development stages can develop into a post-larval stage at the same time as much as possible, and the synchronous line establishment of the small-population parents is finally achieved. By respectively setting temperature gradients according to the suitable temperature ranges of the exopalaemon carinicauda in different development stages, the method disclosed by the invention is conducive to the shortening of development time difference of various parent progenies, and capable of achieving the synchronous line establishment and multi-generation breeding per year of the small-population parents in the artificial breeding of the exopalaemon carinicauda.
Owner:南通中国科学院海洋研究所海洋科学与技术研究发展中心 +1
A method for ecological early propagation of cuttlefish from the Yangtze River in greenhouses
ActiveCN103636540BEarly emergenceEarly use rateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaExopalaemon carinicaudaBroodstock
The invention provides a method for ecologically and early breeding Yangtze River coilia ectenes in a pond greenhouse, and relates to coilia ectenes cultivation. The method comprises production steps of parent overwintering and strengthening cultivation, breeding parent stocking, mysis inoculation, daily management, fish fry number estimation and parent removing. The method is characterized in that when the water temperature of an outer pond is reduced to 7-8 DEG C from December to January in the following year, healthy two-age coilia ectenes without surface damage is taken as parent fish and transferred to the pond greenhouse for overwintering and strengthening cultivation; after the parent fish enters the greenhouse, 3 kilograms of exopalaemon carinicauda are put into the pound for each mu, and the mysis is inoculated; from the end of March to the middle ten days of April, the water temperature rises to 15-16 DEG C, overwintered and strengthened parent fish is picked and transferred to an ecological breeding pond, growth and feeding conditions of the fish fry are checked every one week, and the density of fish bait in water is adjusted according to the checked conditions; a seine is used for removing the parent fish in the middle ten days and last ten days of June, 1, 000-2, 000 fish fry can be generally seined each mu, the fish fry specification is that the total length is 7-10 cm and the weight is 1.8-2.5 g, and the fish fry can be taken as culturing offspring seeds.
Owner:上海市水产研究所(上海市水产技术推广站)
A method for constructing a reciprocal backcross family of spinytail white shrimp
ActiveCN106386605BBuild method is repeatableEasy to operateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaExopalaemon carinicaudaAnimal science
The invention provides a method for constructing an Exopalaemon carinicauda reciprocal backcross family. The method includes the following steps: (1) parent shrimp selection; (2) parent shrimp mating; (3) cultivation and breeding of F1 offspring seeds; (4) parent-child backcross; and (5) cultivation and breeding of backcross progeny offspring seeds. Male and female Exopalaemon carinicauda parent shrimps which are distributed naturally or bred artificially and have excellent characters are selected, and the reciprocal backcross family can be acquired through completely-artificial breeding, aquaculture and parent-child mating; the success rate of construction of the reciprocal backcross family can reach 75%, and can provide material and technique support for quantitative character genetic analysis, near-isogenic line construction and back cross breeding of the Exopalaemon carinicauda.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com