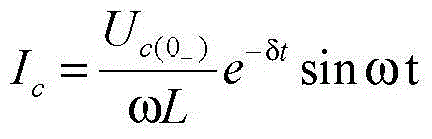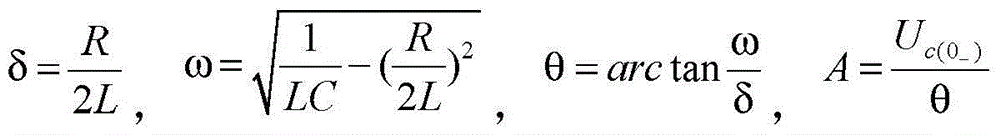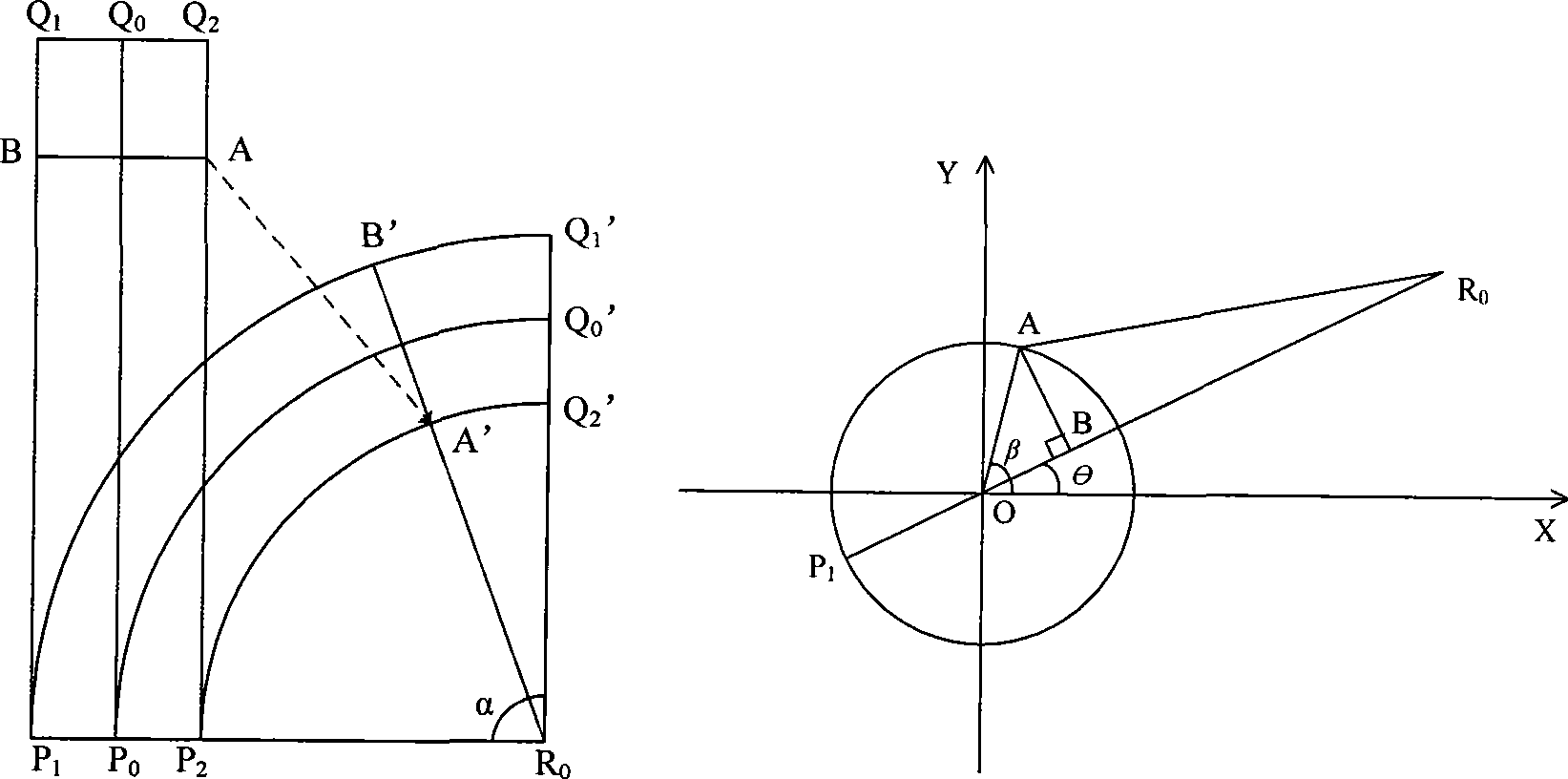Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
132 results about "Damped oscillations" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
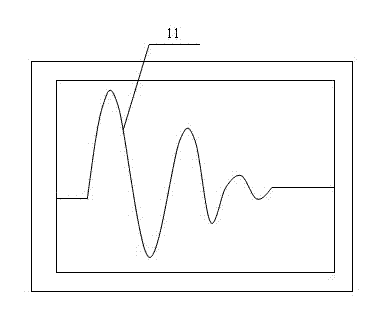
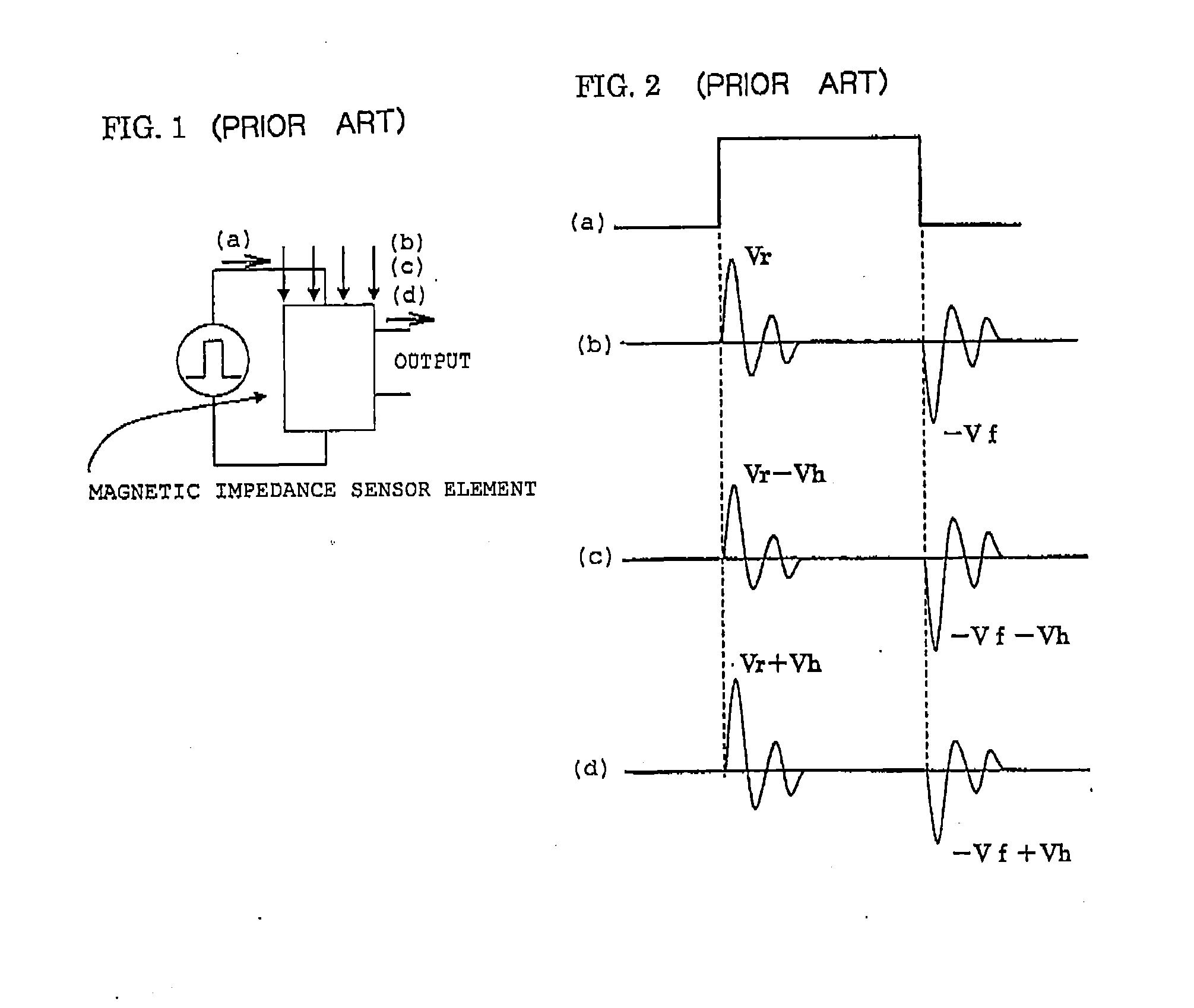
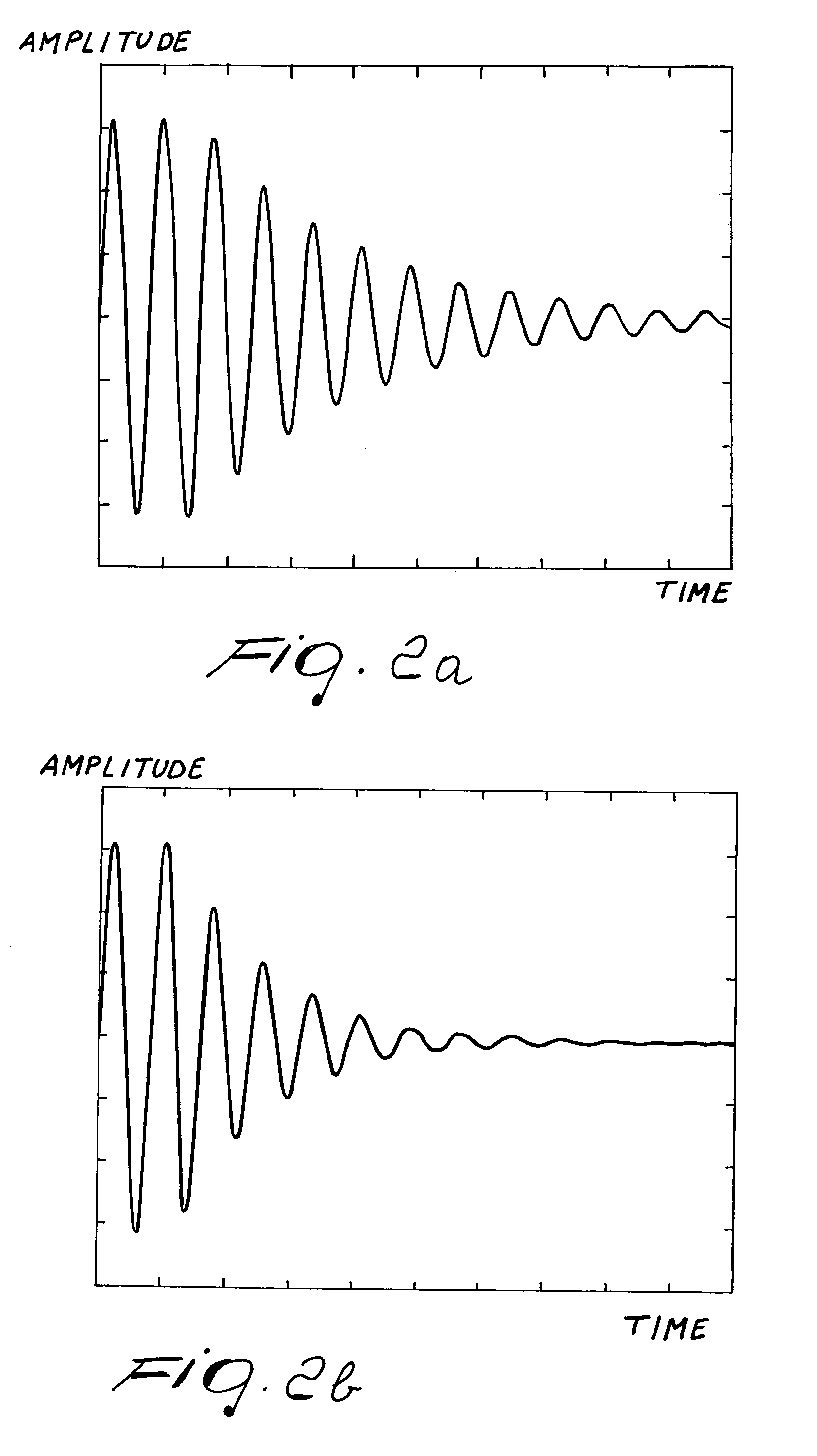
Damped oscillation. [¦dampt ‚äs·ə′lā·shən] (physics) Any oscillation in which the amplitude of the oscillating quantity decreases with time.
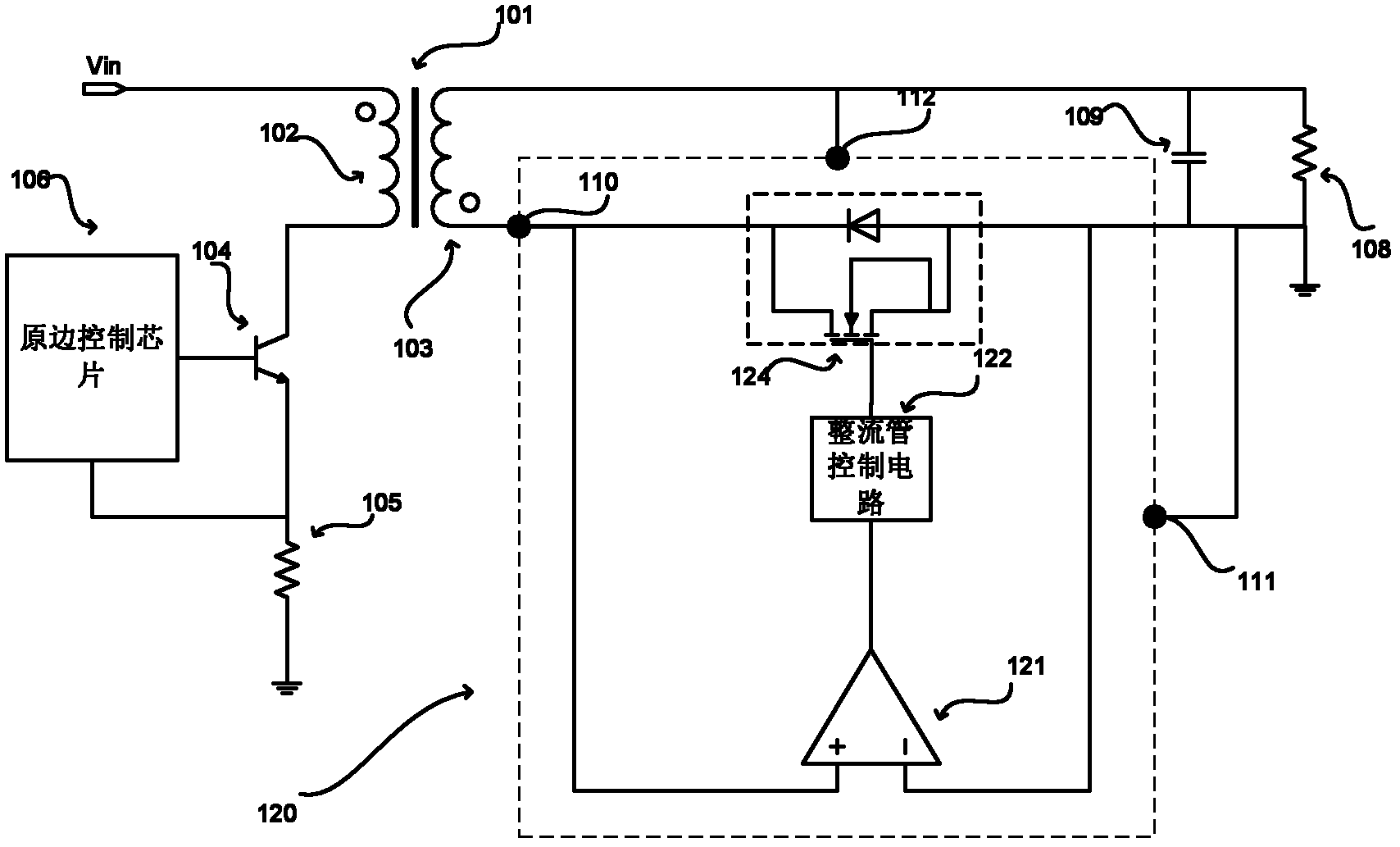
Synchronous rectification control circuit of switch power supply secondary and flyback switch power supply
ActiveCN102231605AImprove efficiencyDetection status is correctEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionSynchronous controlEngineering
The invention discloses a synchronous rectification control circuit of a switch power supply, which is used for the the secondary rectification control of the switch power supply. The circuit comprises a primary state detection unit and a rectifier tube control circuit, wherein the primary state detection unit is used for receiving the voltages of the two ends of the secondary winding of the switch power supply and outputting a state signal to the rectifier tube control circuit; and the rectifier tube control circuit is used for outputting a synchronous control signal according to the state signal and the drain-source voltage of a secondary rectifier tube of the switch power supply so as to control the on and off of the rectifier tube. By adopting the embodiment of the invention, the voltages and parasitic damped oscillation at two ends of the secondary winding, which are excited by normal primary switch actions, can be distinguished based on the voltage second procuct of the voltages of the two ends of the secondary winding, thereby achieving the secondary rectification control which can be adaptively regulated and ensuring a correct detection state.
Owner:BCD (SHANGHAI) MICRO ELECTRONICS LTD
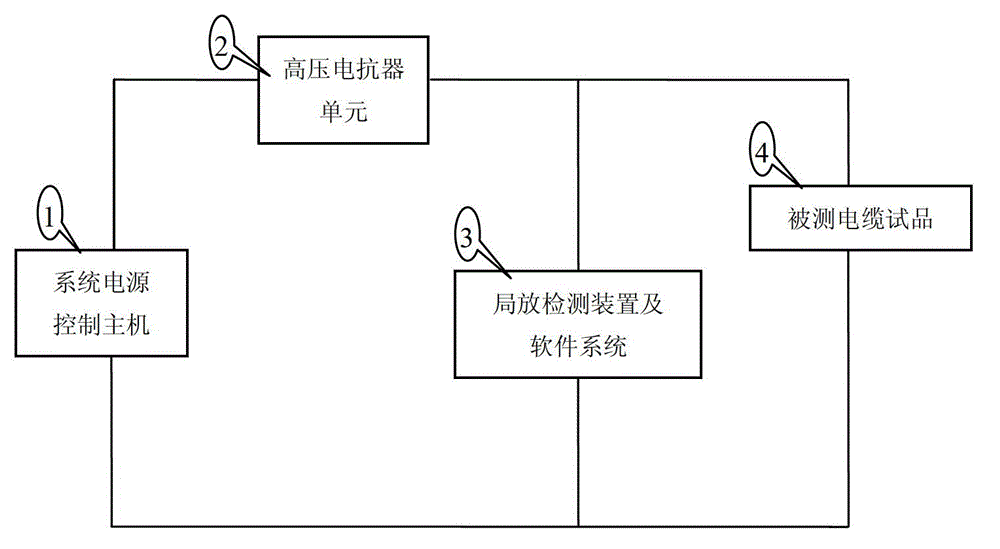
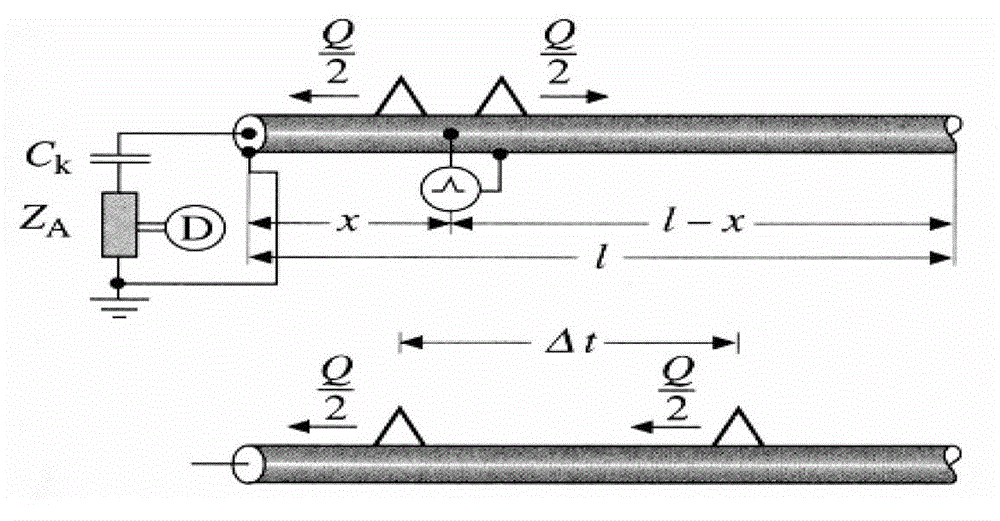
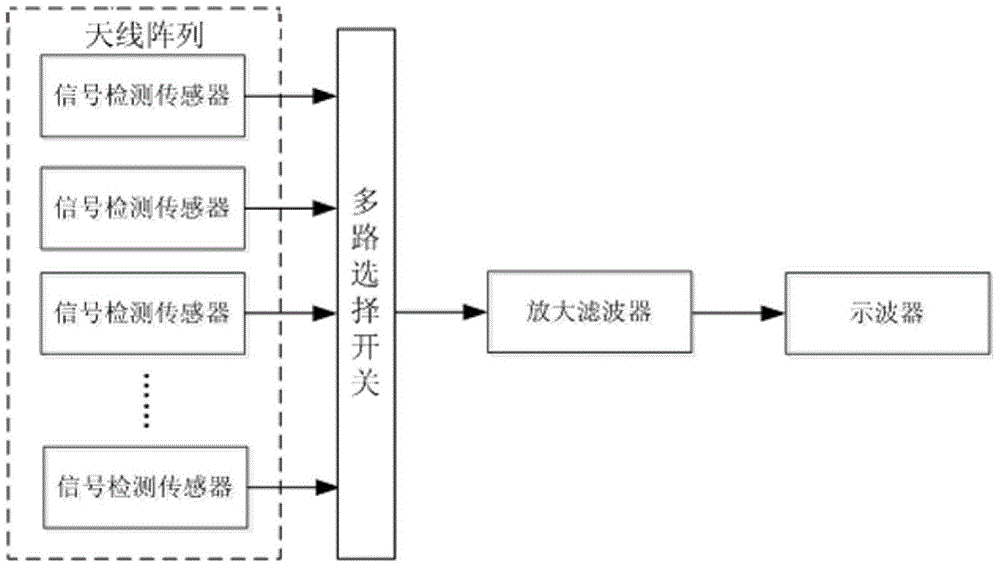
Device and method for detecting cable oscillatory wave partial discharge and fault location
The invention discloses a device and a method for detecting cable oscillatory wave partial discharge and fault location, wherein the device comprises a system power supply control host, a high voltage reactor unit, a partial discharge detection device, a software system and a cable sample to be tested, 220V alternating voltage is input into the system power supply control host, and is converted into direct voltage through a rectifier, and the direct voltage is converted into the alternating voltage with adjustable frequency and amplitude through an inverter. The system power supply control host automatically searches the system resonant frequency, the output voltage is adjusted to reach the initial set test voltage value of the system, users carry out cable withstand voltage tests or damped oscillation wave partial discharge detection tests according to the requirements, and the system locates the fault location through analysis and diagnosis according to the acquired cable partial discharge signals.
Owner:西安博源电气有限公司
In-situ detecting method for partial discharge of damped oscillation wave of large-length ultrahigh voltage crosslinked cable
InactiveCN102914733AImprove operational reliabilityPerfect state detection meansTesting circuitsUltra high voltageHigh pressure
The invention provides an in-situ detecting method for partial discharge of a damped oscillation wave of a large-length ultrahigh voltage crosslinked cable. According to the method, a damped oscillation wave voltage of which the attenuation period is 300mS is adopted to take the place of a power frequency sine-wave voltage to be used as an excitation voltage for testing the partial discharge in a cable line having potential insulation defects; during a voltage boosting process, the partial discharge testing mode is changed into an electrified detection or distributed monitoring mode that the off-line single end fixation measurement is changed into a mode of measuring along middle joints of the line; for signal pickup, a high frequency pulse current coupling sensor is clamped on a cable metal sleeve outtake line so as to take the place of a coupling capacitor and a detection impeder which are connected with a cable terminal in parallel; for data processing, a PD quantity value is calculated by using a pulse current frequency domain integration method. With the adoption of the method, a technical support for diagnosing the defects of ultrahigh voltage crosslinked cable lines and evaluating the insulation states of the cables is provided, the cable state detection means is further enriched and completed for cable operation and maintenance units, and powerful guarantee for improving the operation reliability of the cable lines is provided.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST
Distributing cable partial discharge test method based on oscillatory wave test
InactiveCN104808121AWon't hurtNarrow down testing blind spotsTesting dielectric strengthCapacitanceEngineering
Disclosed is a distributing cable partial discharge test method based on oscillatory wave test. The method includes that a cable partial discharge testing and locating system based on oscillatory wave test is established; by means of the testing system, a cable is charged through a method of voltage increasing to a preset value at a tested cable end, and damped oscillation voltage is generated at the tested cable end through resonance oscillation that occurs by an inductor and a tested cable capacitor in the system; when partial discharge occurs at a position of the tested cable in a distance from a testing end, pulses can spread in two directions along the cable, and the position where the partial discharge occurs can be determined according to time difference that two pulses such as incident wave and radioactive wave reach the testing end. According to the distributing cable partial discharge test method based on oscillatory wave test, oscillatory wave is applied to partial discharge test of the distributing cable, and voltage increasing is performed on the cable through sine oscillatory wave that is generated by resonance oscillation of fixed inductor and the cable. By means of the distributing cable partial discharge test method based on oscillatory wave test, insulating conditions of the cable can be timely known within short time by the system, and thereby, accidents of the cable can be effectively prevented.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
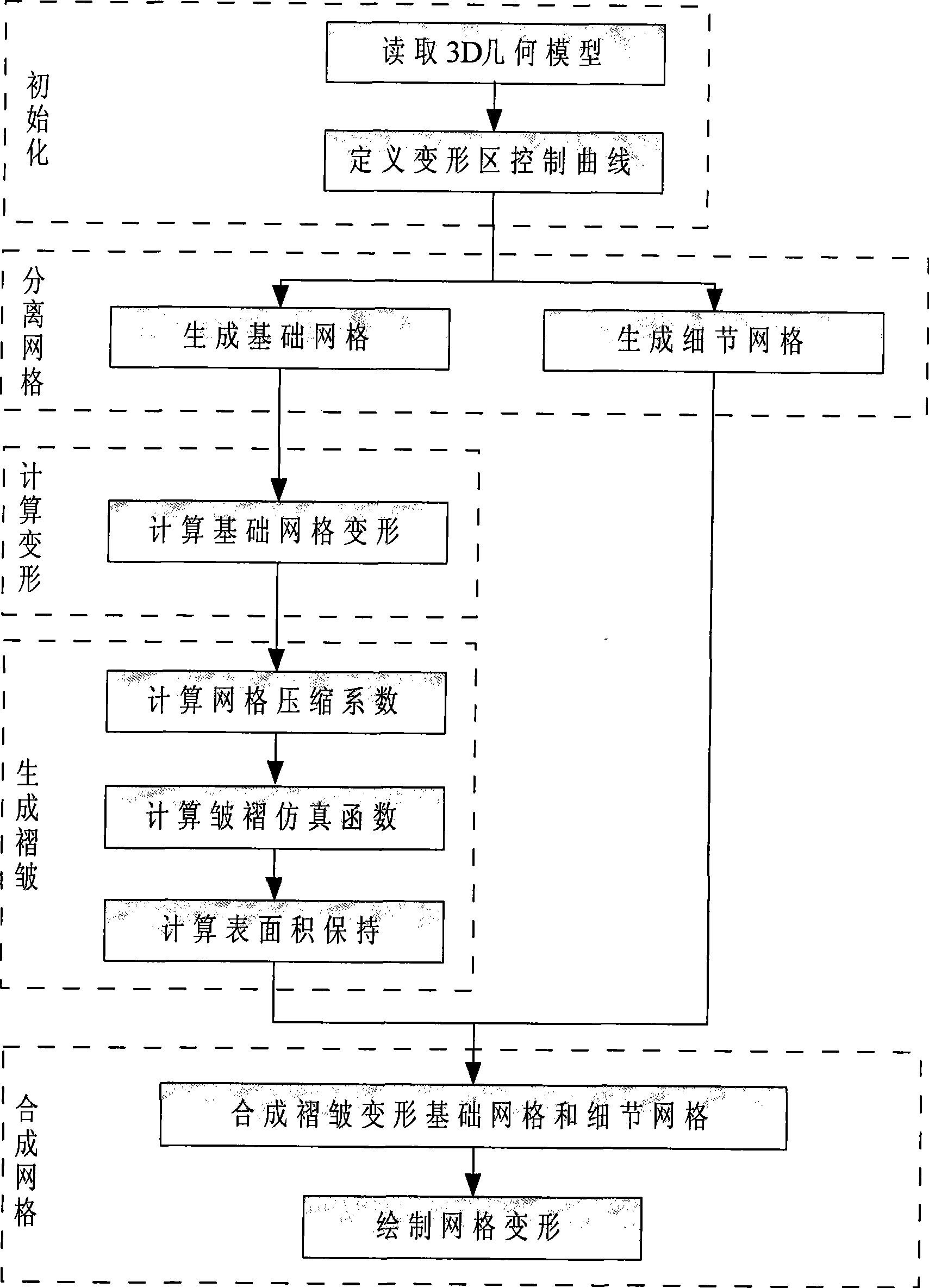
3D grid deforming method based on surface area keeping
The invention relates to a three-dimensional grid deformation method based on surface area maintenance and provides an effective, fast and vivid deformation method for three-dimensional grid objects aiming at the deformation problem of a three-dimensional model of a soft object, which belongs to the field of computer application, in particular to the technical field of computer graphics and virtual reality. In the method, various forms of deformations are seen to be respectively composed of basic bending deformations, the local regions of the basic bending deformations are independently calculated, and a global deformation result is obtained through the joint of the regions; deformation regions are divided according to control curves, and a basic grid deformation algorithm irrelevant to an original grid model is proposed through separating and synthesizing basic deformation grids and detail grids; damped oscillation curves are used to simulate surface wrinkles at the bent and deformed inner sides of the soft object, and the vertex column length of a basic model is maintained to realize the surface area maintenance and improve the third dimension of grid deformation so as to realize the deformation of a three-dimensional grid model.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Method for judging negatively-damped oscillation and forced oscillation on basis of straight line method
InactiveCN102928695ASolve difficult to identifyEasy to implementRate of change measurementElectrical testingPower Management UnitLow-frequency oscillation
The invention provides a method for judging negatively-damped oscillation and forced oscillation on the basis of a straight line method. The method comprises the steps: (1) acquiring an actually-measured oscillation curve; (2) selecting the maximum moment point in each oscillation period for analysis; (3) confirming the oscillation as increasing oscillation; (4) selecting two points, the spacing of which is greater than four oscillation periods, to form a linear equation; and (5) calculating difference to numerical values on the straight line and the actually-measured curve at the same one time point one by one, and judging the type of oscillation according to the obtained result. According to the method for judging negatively-damped oscillation and forced oscillation on the basis of the straight line method, through the data of a PMU (Power Management Unit) or a WAMS (Wide Area Measurement System), that certain low-frequency oscillation is of low-frequency negatively-damped oscillation caused due to damp lack of the system, or the forced oscillation caused due to a forced disturbance source existing in the system can be judged so as to fast take measures to restrain the low-frequency oscillation.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
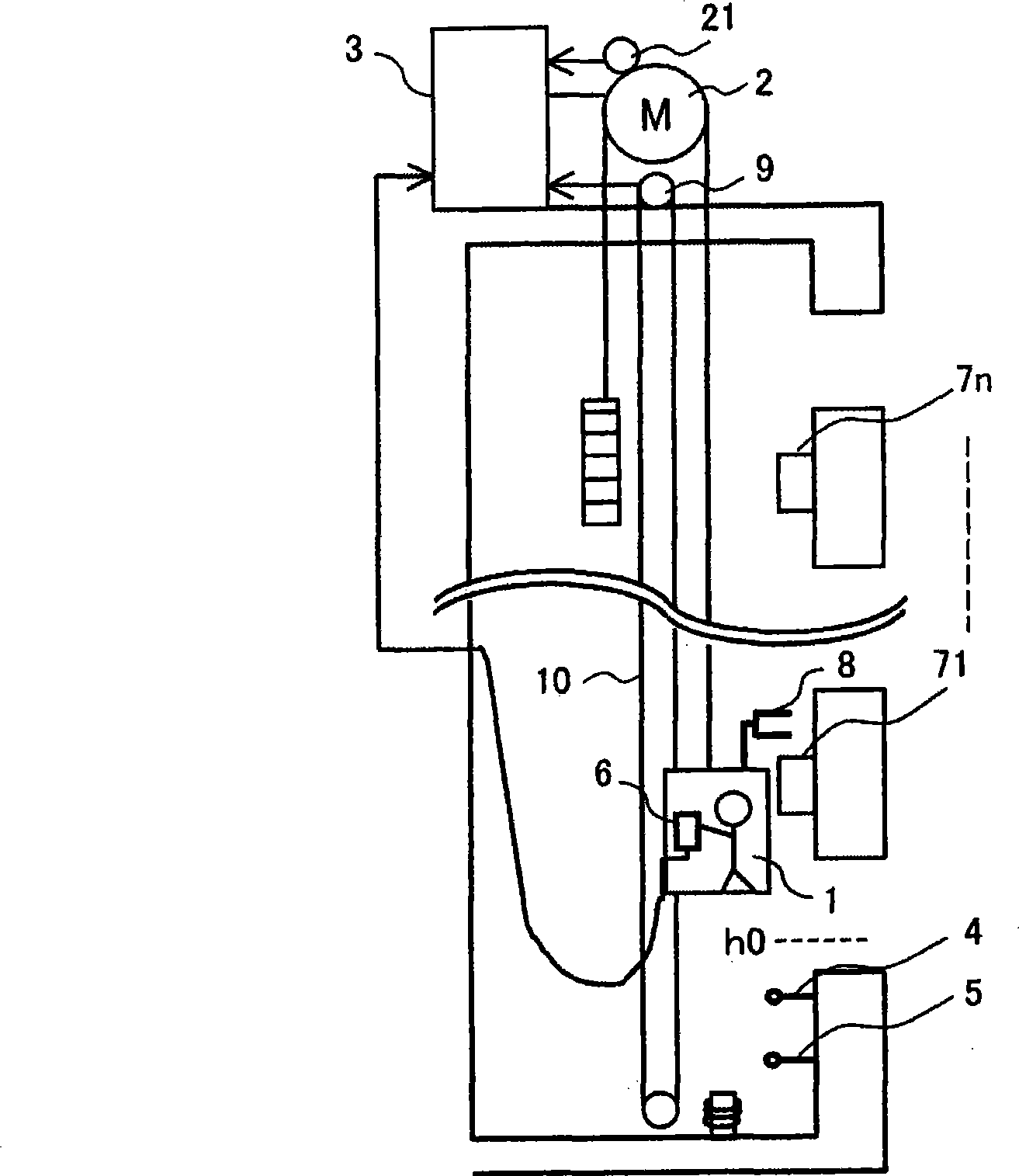
Elevator control system
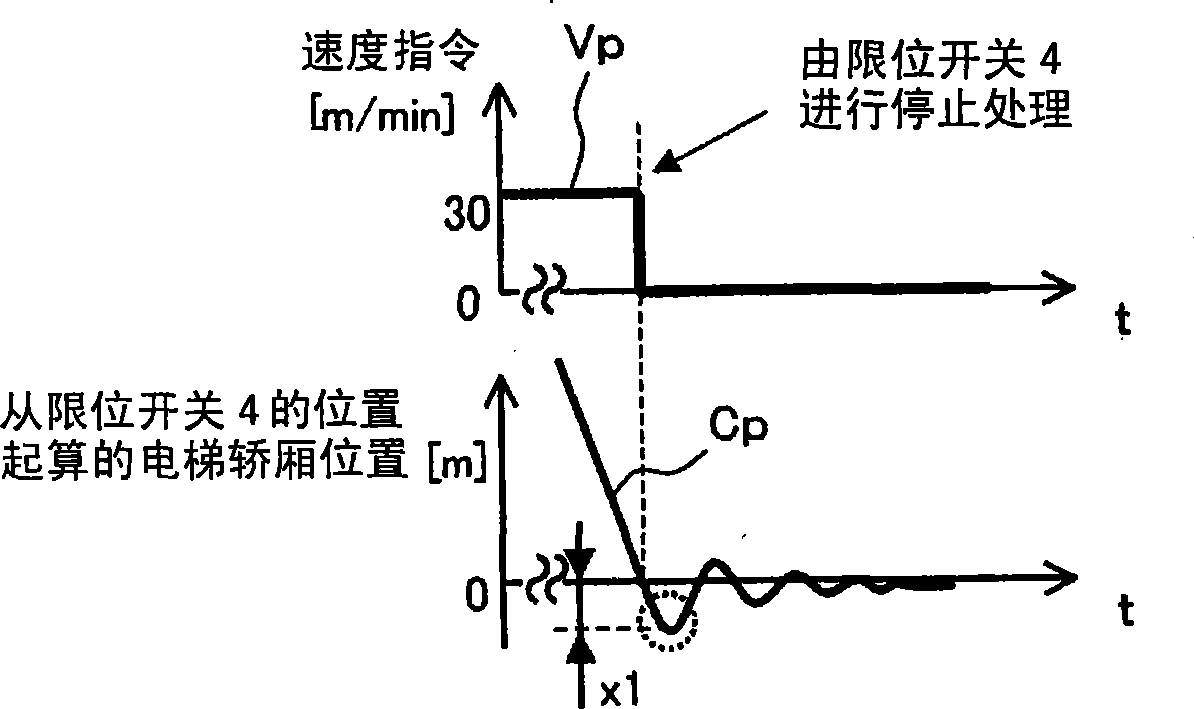
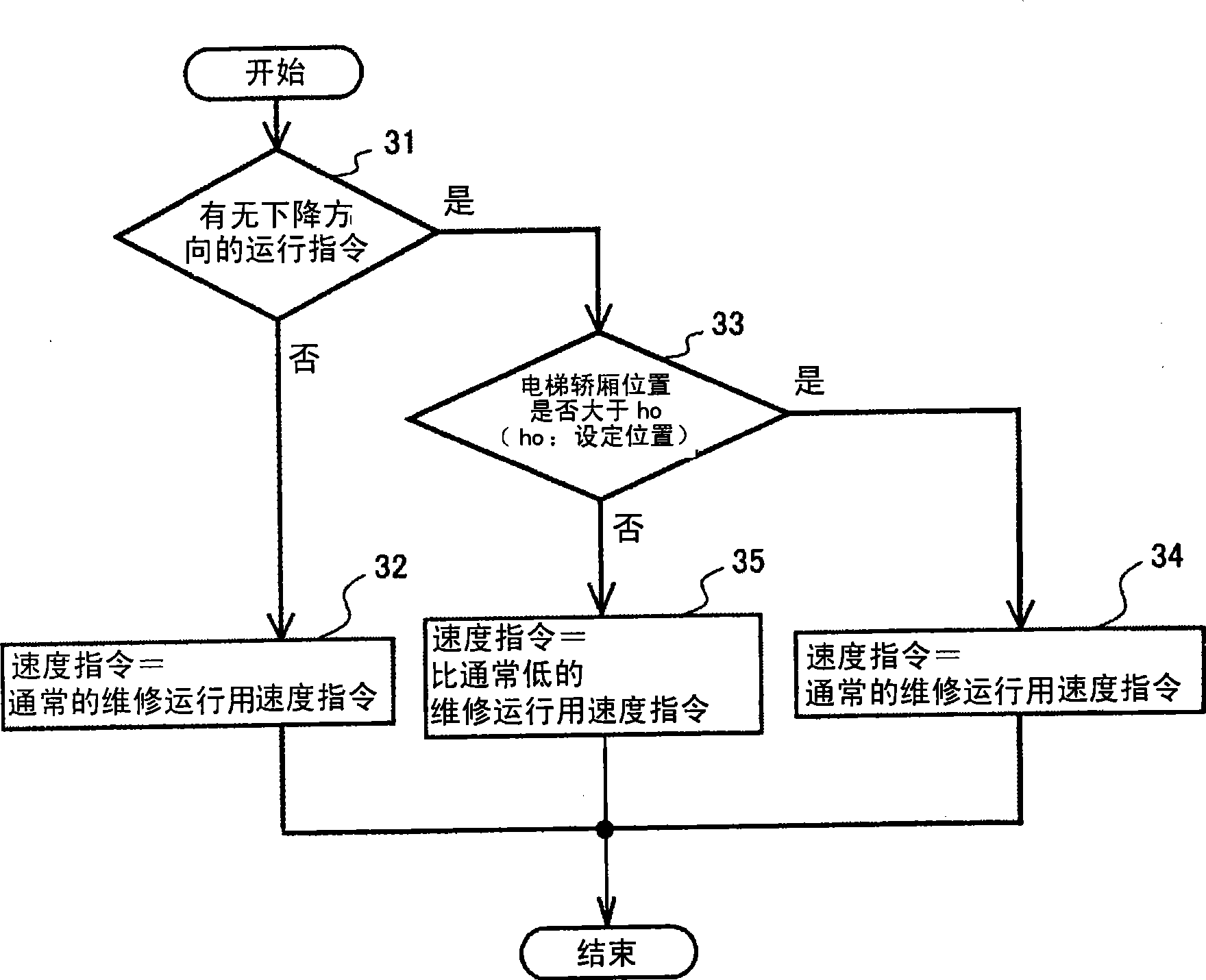
The invention provides an elevator control system associated with maintaining operation of a high-lift elevator, capable of well exerting stopping action near the bottom layer and high-layer testing operation according to the elevator control system. In the maintaining operation of a high-lift elevator, the maintaining operation speed (low-speed operation speed) is reduced from current 30m every minute to 15m every minute when it drops toward the bottom layer and when the elevator carrier exceeds the bottom layer to reach a limit switch (4). According to a preferable exertion mode of the invention, a final limit switch (5) may be prevented from action caused by damped oscillation of the elevator carrier via ladder variable of a speed indication and the maintaining time may be shortened when the high-lift elevator is in maintenance.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
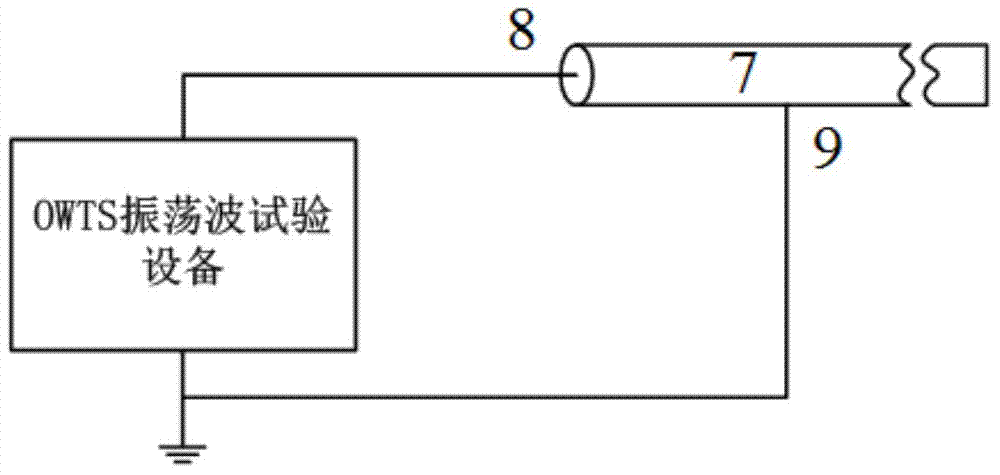
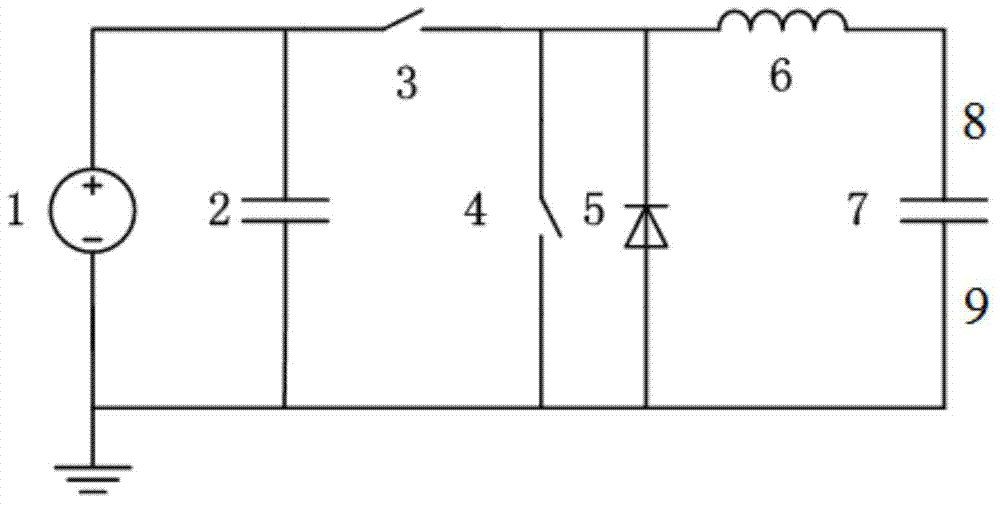
OWTS power cable oscillation wave test equipment and test method
ActiveCN104502825AReduce capacity requirementsReduce weightFault locationTesting circuitsElectronic switchHigh pressure
The invention discloses OWTS power cable oscillation wave test equipment and a test method. The OWTS power cable oscillation wave test equipment comprises a DC high-voltage power supply, a capacitor, high-voltage electronic switches, an electric reactor, a backward diode and a partial discharge detection unit. The DC high-voltage power supply charges the capacitor and controls the high-voltage electronic switch to be conducted after charging is completed. A cable is charged by the capacitor via a quite short period of time, and then the other high-voltage electronic switch is controlled to be conducted. A weak damping loop is formed by the electric reactor, the cable and line resistance, and damped oscillation wave is generated. Acquisition and analysis of partial discharge signals of the cable are realized by using the partial discharge detection unit so that the insulation state of the power cable is finally acquired. The equipment is compact in structure and convenient for onsite testing, and range of cable capacity capable of being detected can be 0.05muF-6muF. Besides, the test process has no long time of DC charging on the cable so that cable insulation is not damaged.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for detecting cable fault point by impact oscillating wave principle
ActiveCN102305901AHigh resolutionEasy to judgeFault location by pulse reflection methodsElectric power systemControl theory
The invention discloses a method for detecting a cable fault point by an impact oscillating wave principle. The method comprises the following steps: the grounding output end of a pulse signal source is connected with the initial end grounding line of a fault cable to be detected; the high-voltage output end of a signal source is connected with one end of a high-voltage resonance reactor; the other end of the reactor is connected with a fault phase; the terminal end groundling line is cut off; the signal source applies the pulse signal by the reactor so that the fault point forms an instant short circuit electric arc; the fault cable generates a damped oscillating wave and radiates an electromagnetic field signal to the outside; the magnetic field signal in the signal is detected; a damped oscillating wave form for reflecting magnetic field signal change is arranged at the left side in the front of the cable fault point; a damped oscillating wave form for reflecting sharp attenuation of the magnetic field signal change is arranged at the right side behind the cable fault point; and the cable position corresponding to the change place of the magnetic field signal is the position in which the cable fault point is located. The invention is suitable for cable fault positioning under various laying conditions, has the advantages of simple structure and convenience in use and is widely used for power systems and all enterprises and public institutions.
Owner:XIAN FRIEND ELECTRONICS T&S
Resistance, inductance and capacitance measurement method based on damping oscillatory wave in oscillation circuit
ActiveCN105277790ANo need to change hardware configurationSimple structureResistance/reactance/impedenceCapacitanceFrequency spectrum
The invention provides a resistance, inductance and capacitance measurement method based on damping oscillatory wave in an oscillation circuit. According to the method, an improved discrete Fourier algorithm is used to realize high-precision measurement of resistance, inductance and capacitance parameters; window function processing is carried out on a detection voltage signal; the influence of a truncation effect in standard discrete Fourier transformation can be effectively suppressed; the accuracy of Fourier transformation is improved; the measurement accuracy of resistance, inductance and capacitance parameters is improved; on the basis that window function processing is carried out on the detection voltage signal, a single spectral line interpolation algorithm is further used; frequency calculation errors caused by non-integer number cycle sampling are corrected; spectral amplitude errors caused by the truncation effect are corrected; and the accuracy of the measurement method is further improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method and device for detecting two parameters of a fluid
An oscillator is excited by a primary oscillator, and the excited oscillator is immersed in a fluid having two parameters, the first parameter of the fluid damping the excited oscillator via a first phase delay, and the second parameter damping the excited oscillator via a second phase delay. The oscillation of the excited and damped oscillator is detected as the oscillation signal. The oscillation signal is mixed with a phase-shifted signal generated from the excitation signal via a third phase delay which corresponds to either the first or the second phase delay. The mixed signal is averaged over time to determine the first or the second parameter according to the selection of the phase delay.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
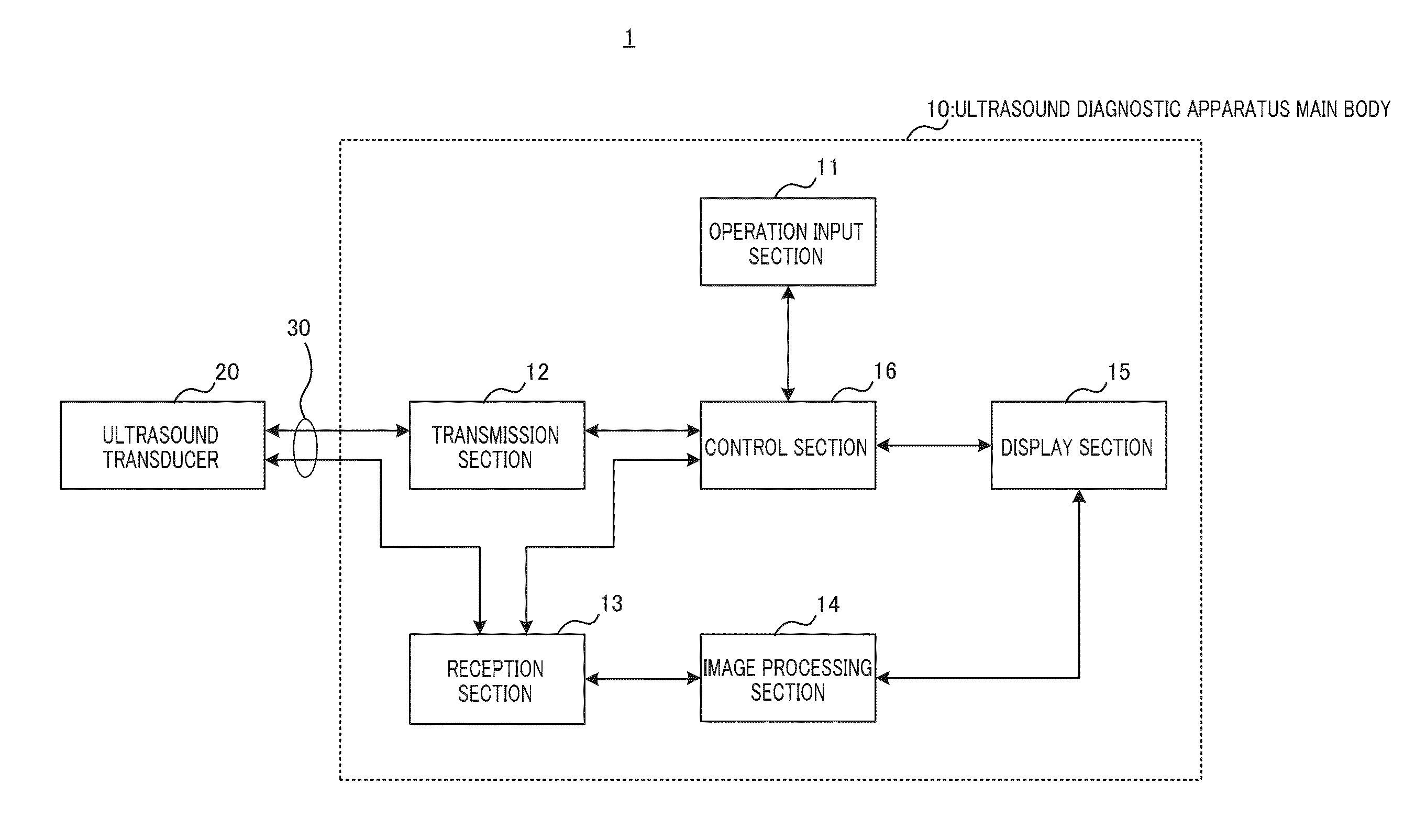
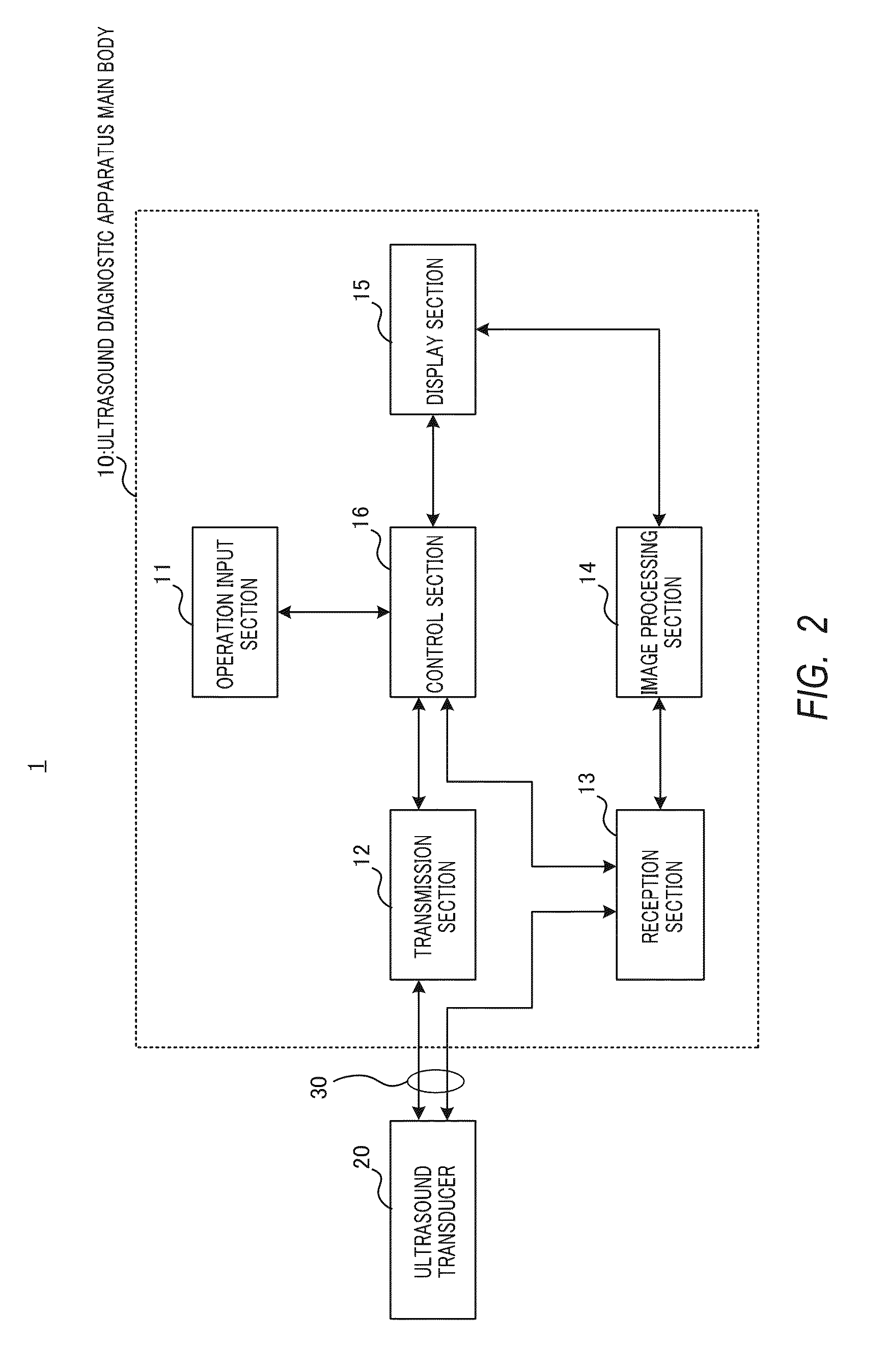
Ultrasound transducer and ultrasound diagnostic apparatus
ActiveUS20160027991A1Broadband characteristicsMagnetostrictive device manufacture/assemblyOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasonic sensorSonification
An ultrasound transducer that achieves broadband characteristics without degrading the sensitivity of the ultrasound transducer. Piezoelectric element (202) includes piezoelectric thin film (203), first electrode (204) that is disposed on a first surface of piezoelectric thin film (203) in a thickness direction of piezoelectric thin film (203), and second electrode (205) that is disposed on a second surface of piezoelectric thin film (203) in the thickness direction of piezoelectric thin film (203), and at least two of parameters of a spring constant, a viscosity coefficient, and a mass in an equivalent single damped oscillation model representing a structure of a diaphragm composed of each piezoelectric cell (200) are each set to a value that is different among the piezoelectric cells (200) such that a relationship between a driving frequency ratio and a phase in the diaphragm is substantially identical among the piezoelectric cells (200).
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
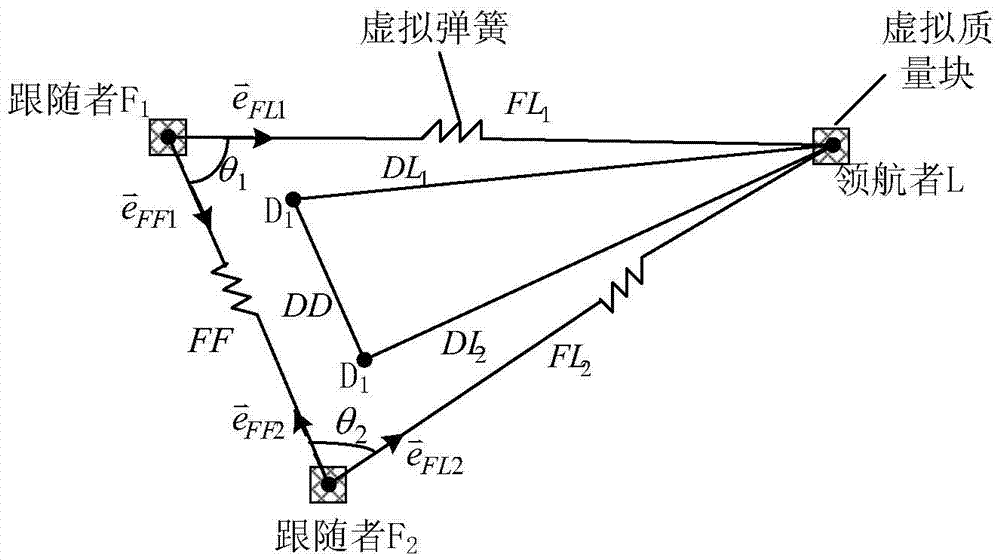
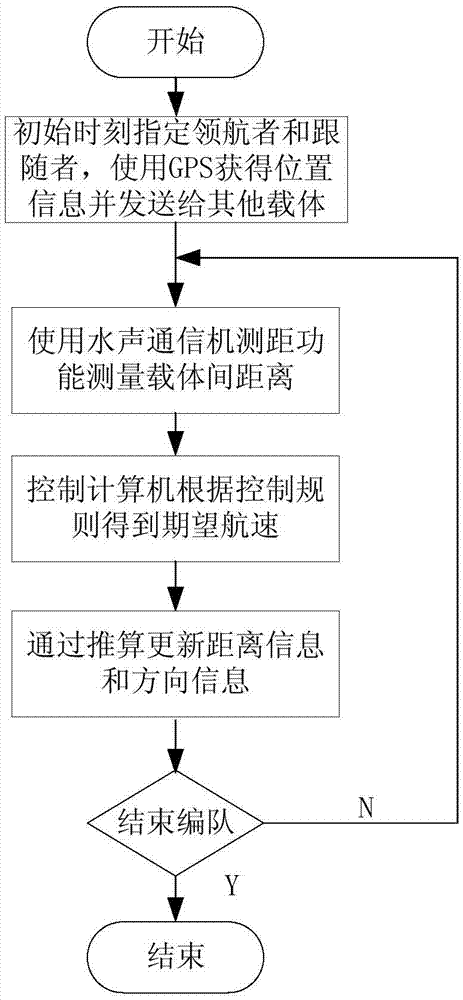
Multi-AUV formation control method based on viscous damped oscillation model
InactiveCN106896817ALess communication informationSure easyAltitude or depth controlUnderwater navigationEstimation methods
The invention discloses a multi-AUV formation control method based on a viscous damped oscillation model. The model is a physical model, and enables an AUV in the formation to be taken as a mass block connected through a virtual spring, through analyzing the condition of virtual force bearing, a formation control rule is obtained. The method is suitable for the multi-AUV formation control in an environment where the communication is limited based on range finding information. The method mainly comprises the parts: an inter-AUV communication rule, an AUV formation control rule based on the viscous damped oscillation model, a condition that reasonable parameters in the formation control rule should meet, and an inter-AUV opposite direction information and distance information real-time estimation algorithm. The method is suitable for the multi-AUV formation under the condition that the communication is limited, is small in needed communication quantity in an underwater navigation process, is high in formation convergence speed, and is easy for popularization.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Distributed mode louspeaker damping oscillations within exciter feet
ActiveUS20160360313A1Improve performanceIncrease amplitudeBending wave transducersDiaphragm dampingEngineeringLoudspeaker
There is provided a flat panel loudspeaker comprising a resonant panel, an exciter comprising a foot generally cylindrical in shape, coupled to the resonant panel and defining an inner region of the resonant panel. The exciter is drivable to vibrate the resonant panel via the foot, whereby to produce a sound. A stiffness of the resonant panel in the inner region is greater than a stiffness of the resonant panel in a region of the resonant panel outside the inner region. Additionally or alternatively, the flat panel loudspeaker further comprises a damping member in contact with the inner region of the resonant panel and arranged inside the foot to generally brace against the vibration of the resonant panel so as to damp a response of the resonant panel in the inner region to a vibration from the exciter.
Owner:AMINA TECH
Positive and negative POSICAST input shaping method-based crane anti-swing control method
The invention relates to a positive and negative POSICAST input shaping method-based crane anti-swing control method. The method includes a positive and negative POSICAST method adopted when a swing angle returns to zero after a time point 3Td / 2, a positive and negative POSICAST method adopted when the swing angle returns to zero after a time point Td, and a positive and negative POSICAST method adopted when the swing angle returns to zero after a time point 3Td / 4, wherein Td is the damped oscillation period of a system. The method of the invention is either applicable to a damped system or an un-damped two-order system. The method of the invention is an open-loop control method. With the method adopted, a measuring sensor for closed-loop feedback is not required. According to the method of the invention, step acceleration input is utilized, and the shaping of step acceleration output is targeted. Compared with a pulse acceleration input method, the method has the advantages of continuous speed change and easiness in engineering realization. The method of the invention is applicable to any damped two-order systems adopting step signals as input, and is used for an anti-swing system or a system of which the output of a certain item is expected to return to an original position.
Owner:SHANGHAI MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Complex wavelet transform partial discharge location test method and device
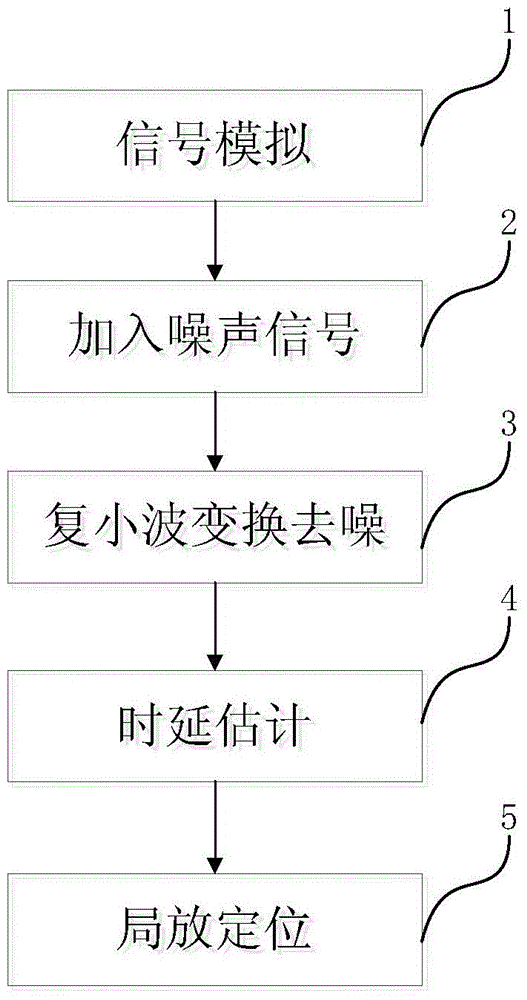
InactiveCN104614647AEliminate distractionsImprove applicabilityTesting dielectric strengthTransformerTime delays
The invention provides a complex wavelet transform partial discharge location test method and device. The method includes the steps of: simulating a partial discharge signal of a transformer substation by exponential damped oscillation pulse, and adding various noise signals of the noise jamming simulation transformer substation based on the partial discharge signal; filtering the signal added with the noise by complex wavelet transform, and thereby obtaining the denoised signal; working out the arrival time delay between two signals by a high-order cumulant detection method; at last estimating the partial discharge location by detecting the arrival time delay between the signals of the sensor. According to the complex wavelet transform partial discharge location test method and device. The interference of the Gaussian noise on the original partial discharge signal; the complex wavelet transform has good applicability for denoising the partial signal, can restore the amplitude, the phase and other characteristics of the partial signal, provides the partial signal with high quality for time delay estimation, and can improve the accuracy of the time delay estimation based on high-order cumulants.
Owner:YUNNAN POWER GRID CO LTD ELECTRIC POWER RES INST
Detecting structure and method for detecting turn-to-turn insulation fault of electric reactor through oscillation method
InactiveCN106226661AReduce the oscillation periodSmall inductanceTesting dielectric strengthUltrasound attenuationCapacitance
The invention relates to a detecting structure and method for detecting a turn-to-turn insulation fault of an electric reactor through an oscillation method. The structure comprises a discharging ball gap and a pulse capacitor respectively connected to one end of the electric reactor, wherein the other end of the discharging ball gap is connected to the negative electrode of a power supply, the positive electrode of the power supply is connected to the other end of the reactor, and the other end of the pulse capacitor is connected to the negative electrode of the power supply. Since a discharging ball gap and a pulse capacitor are respectively connected to one end of the electric reactor, the power supply provides electric energy, and the pulse capacitor is charged through the power supply. When the pulse capacitor is charged to a certain value, the discharging ball gap discharges, and the pulse capacitor and the reactor form a damped oscillation circuit of a certain frequency. When turn-to-turn short circuit fault occurs to the reactor, the inductance value is reduced, and the active loss is increased sharply. The wave-shaped oscillation period of the reactor is reduced, and the attenuation speed of amplitude is accelerated, so that presence or occurrence of turn-to-turn short circuit fault of the reactor can be detected accurately. The detecting structure and method are highly practical.
Owner:ZHUHAI LANRUIMENG ELECTRIC
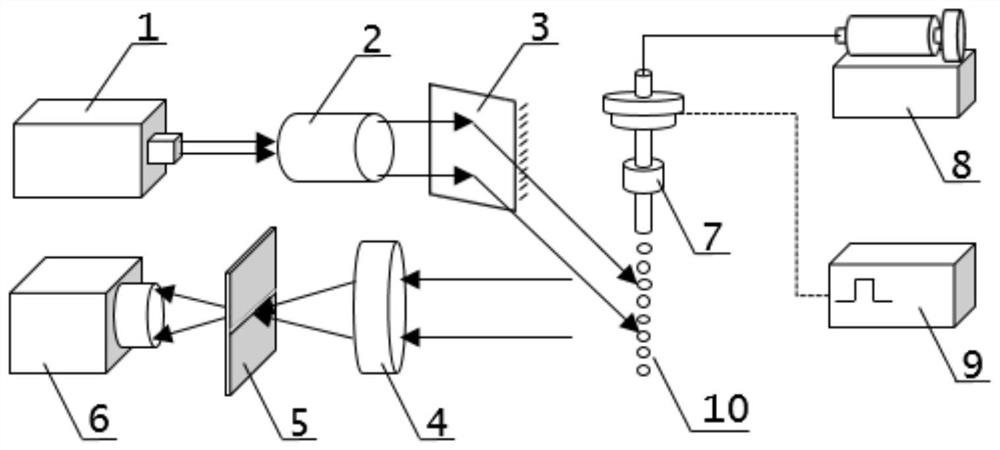
Method and device for simultaneously measuring surface tension and viscosity of liquid on line
PendingCN112098272ACreate pollutionImprove time resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansIndirect flow property measurementTemporal resolutionRainbow
The invention discloses a method for simultaneously measuring surface tension and viscosity of liquid on line. The method comprises the following steps: forming, by a liquid drop generation unit, liquid drops oscillating in a second-order mode, wherein the laser irradiates the oscillated liquid drops and the motion trails of the liquid drops to generate rainbow signals; recording a rainbow image of the spherical liquid drop when the oscillated ellipsoidal liquid drop is in a steady state; obtaining a calibration curve of a pixel column and a scattering angle; extracting signals in the rainbowimage, and aligning the signals to the calibration curve, conducting inversion on the rainbow image, and acquiring the refractive index and the radius of the spherical liquid drop; according to the rainbow angle deviation of the rainbow image, obtaining the evolution condition of the ellipticity in the liquid drop falling process; converting the ellipticity into oscillation amplitude information and fitting to obtain the oscillation frequency and the time constant of the damped oscillation function, and respectively obtaining the surface tension and the viscosity value of the liquid. The invention further discloses a device for simultaneously measuring the surface tension and the viscosity of the liquid on line. According to the method and the device, microsecond-order droplet oscillationtracking is realized, and the spatial and temporal resolution of measurement is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
High-sensitivity spectral absorption damped oscillation cavity gas detection device of transformer oil
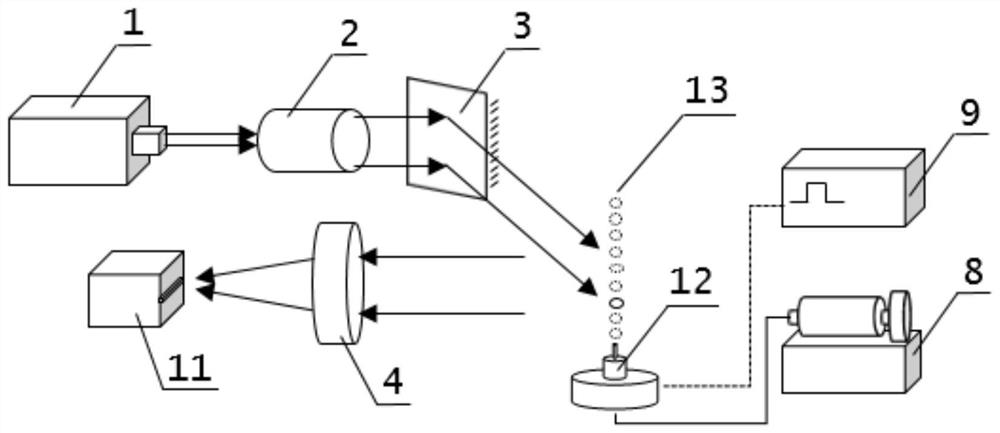
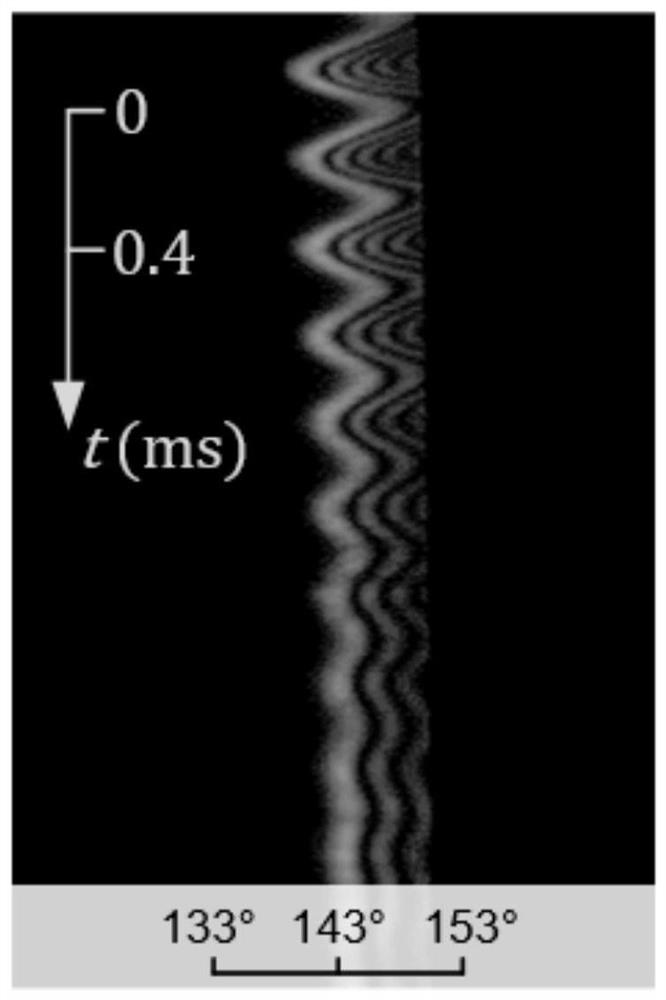
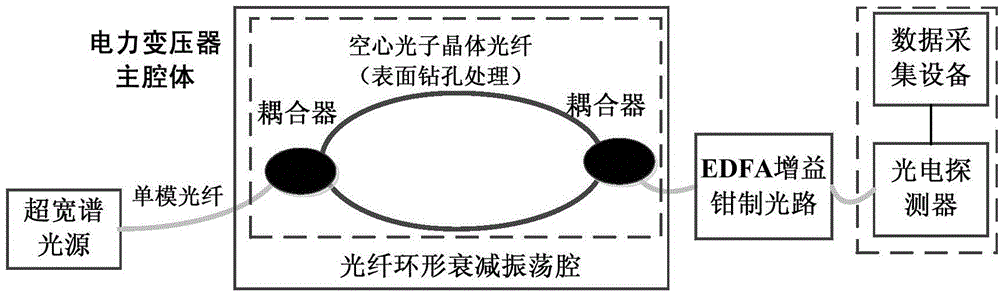
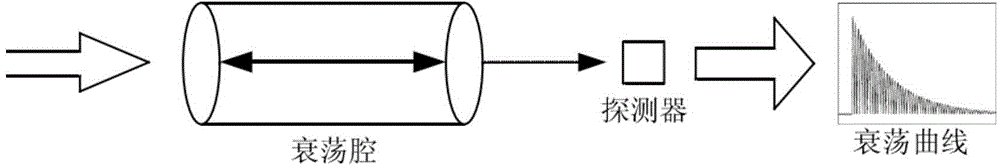
ActiveCN104807765AImprove detection accuracyHigh detection sensitivityColor/spectral properties measurementsHigh reflectivityDamped oscillations
The invention discloses a high-sensitivity spectral absorption damped oscillation cavity gas detection device of transformer oil in the scope of safety detection equipment of a power transformer. The gas detection device comprises a super-continuum spectrum broadband light source, an optical fiber annular damped oscillation cavity, a gain clamping unit and a light intensity detection unit; in a main cavity of the power transformer, the two ends of two columns of hollow photonic crystal fibers are connected high reflectivity optical devices or high reflectivity optical structures to form the optical fiber annular damped oscillation cavity; the two ends of the optical fiber annular damped oscillation cavity are connected with the super-continuum spectrum broadband light source and a gain clamping light path via optical fibers; the gain clamping light path is connected with the light intensity detection unit via an optical fiber; high accuracy time variation measurement is achieved by a topological design of the optical fiber annular damped oscillation cavity and the gain clamping light path; the system detection precision and sensitivity are improved; and the kind and content of dissolved gas in the transformer oil are analyzed and evaluated.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
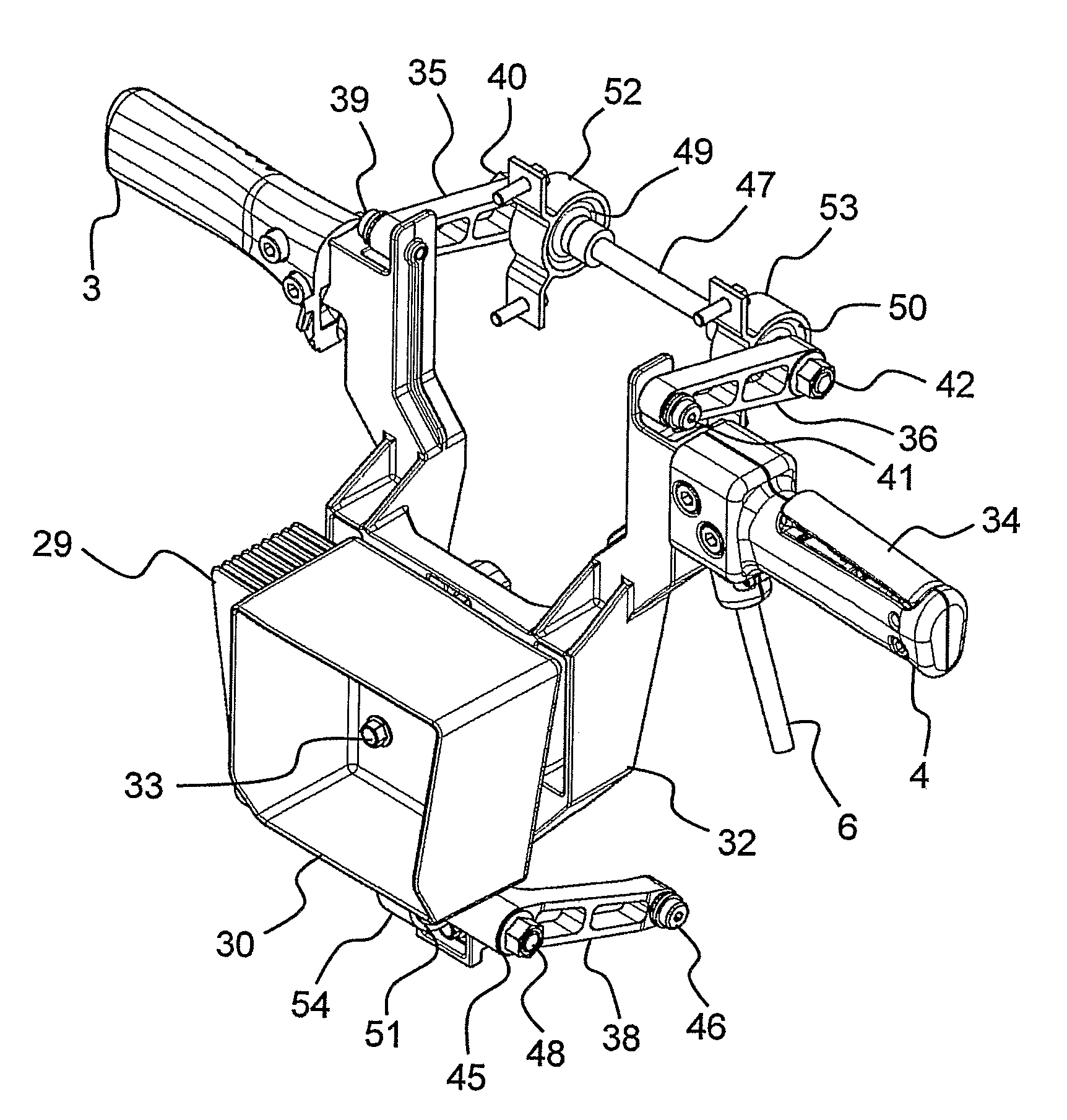
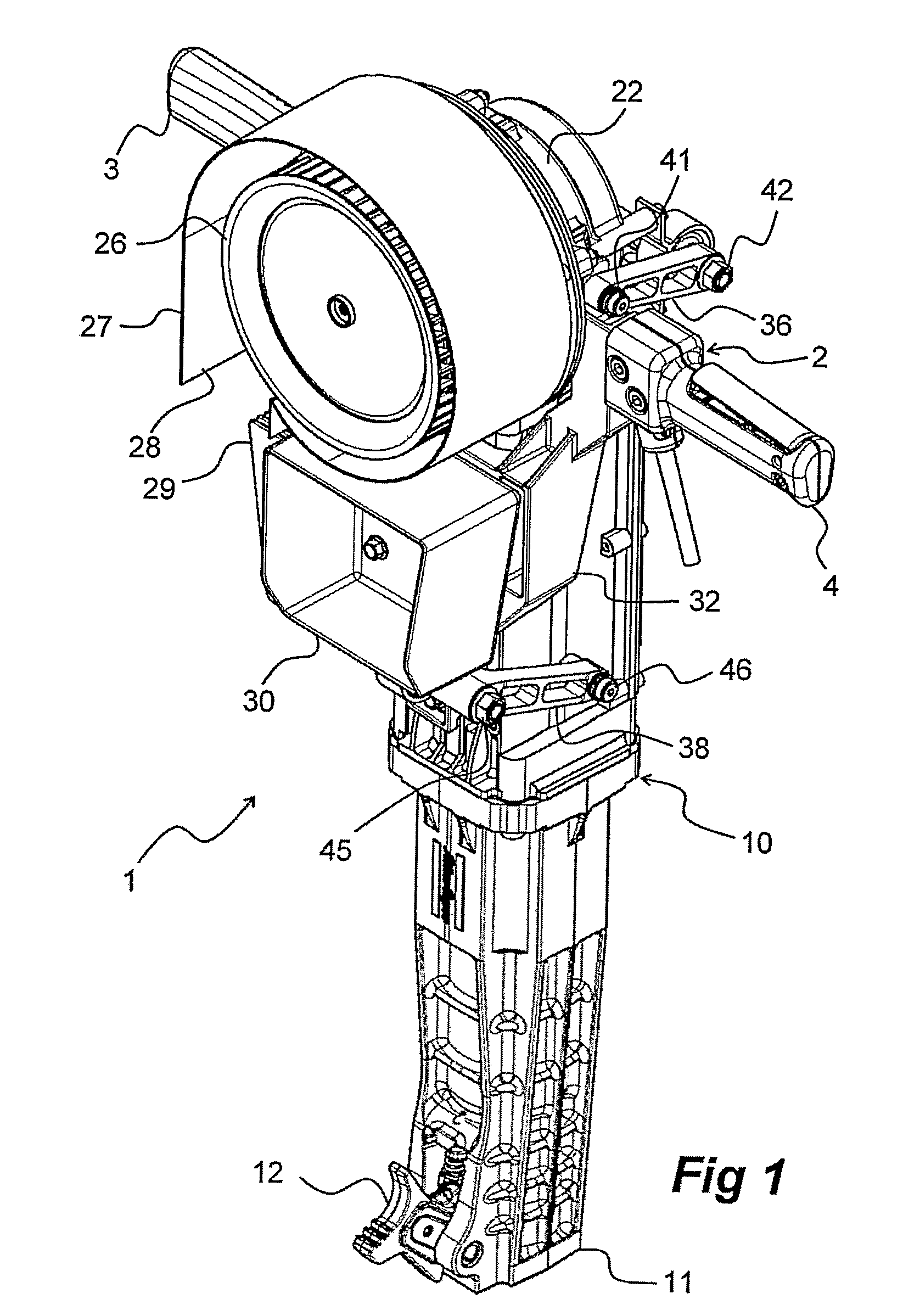
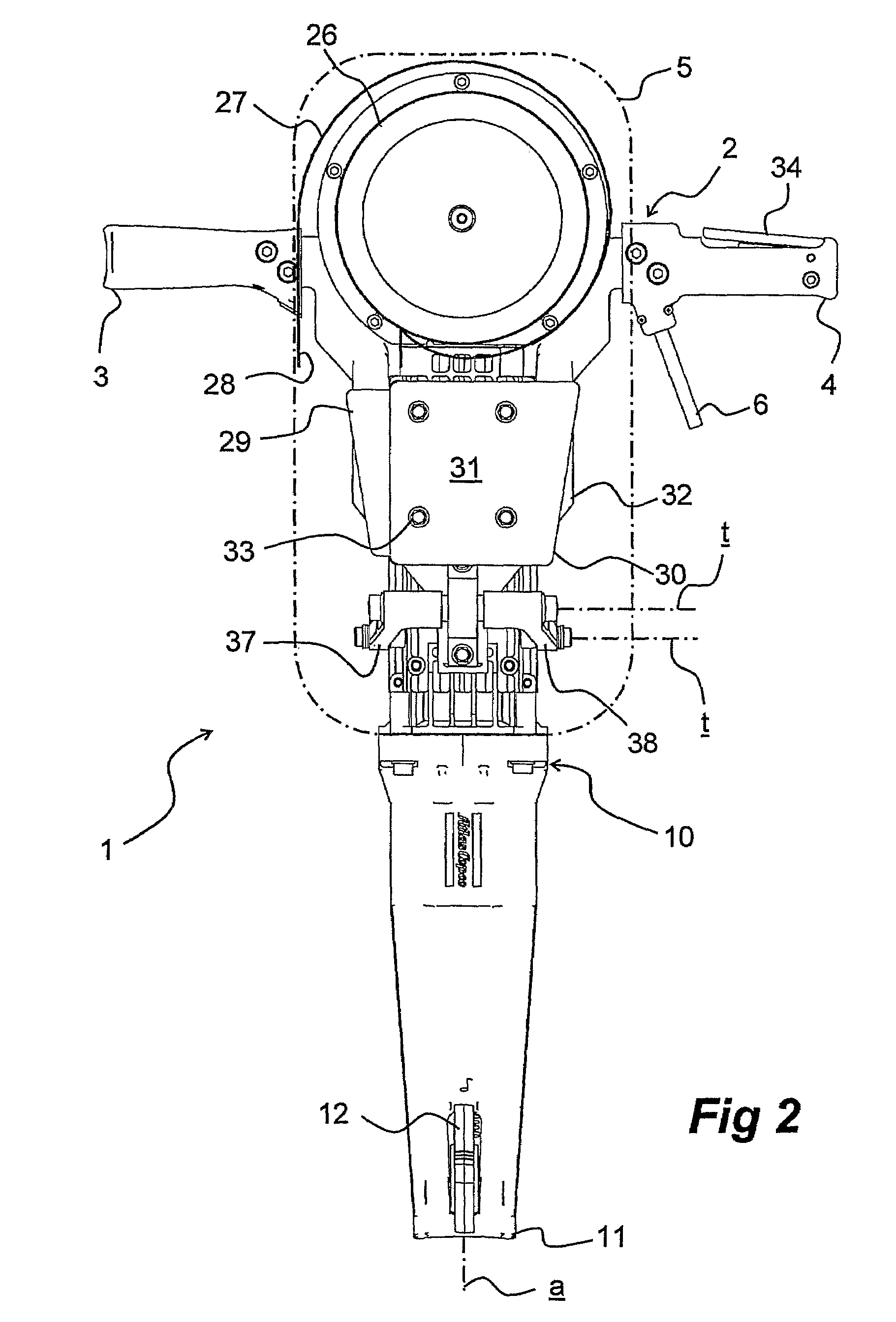
Breaker tool with vibration damped handle device
ActiveUS7640997B2Clean blowingReduce weightPortable percussive toolsPortable power-driven toolsEngineeringDamped oscillations
Owner:ATLAS COPCO AIRPOWER NV
Foreign matter detection method and device of wireless power transmission system
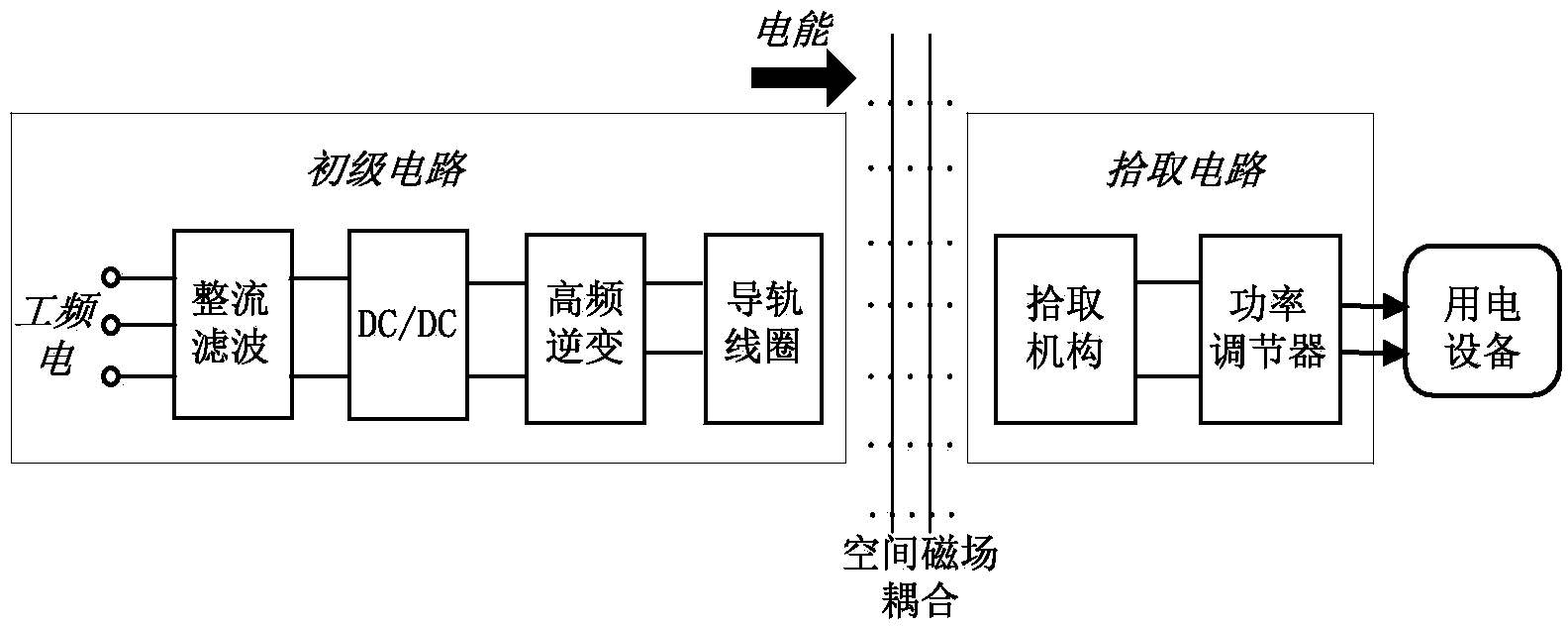
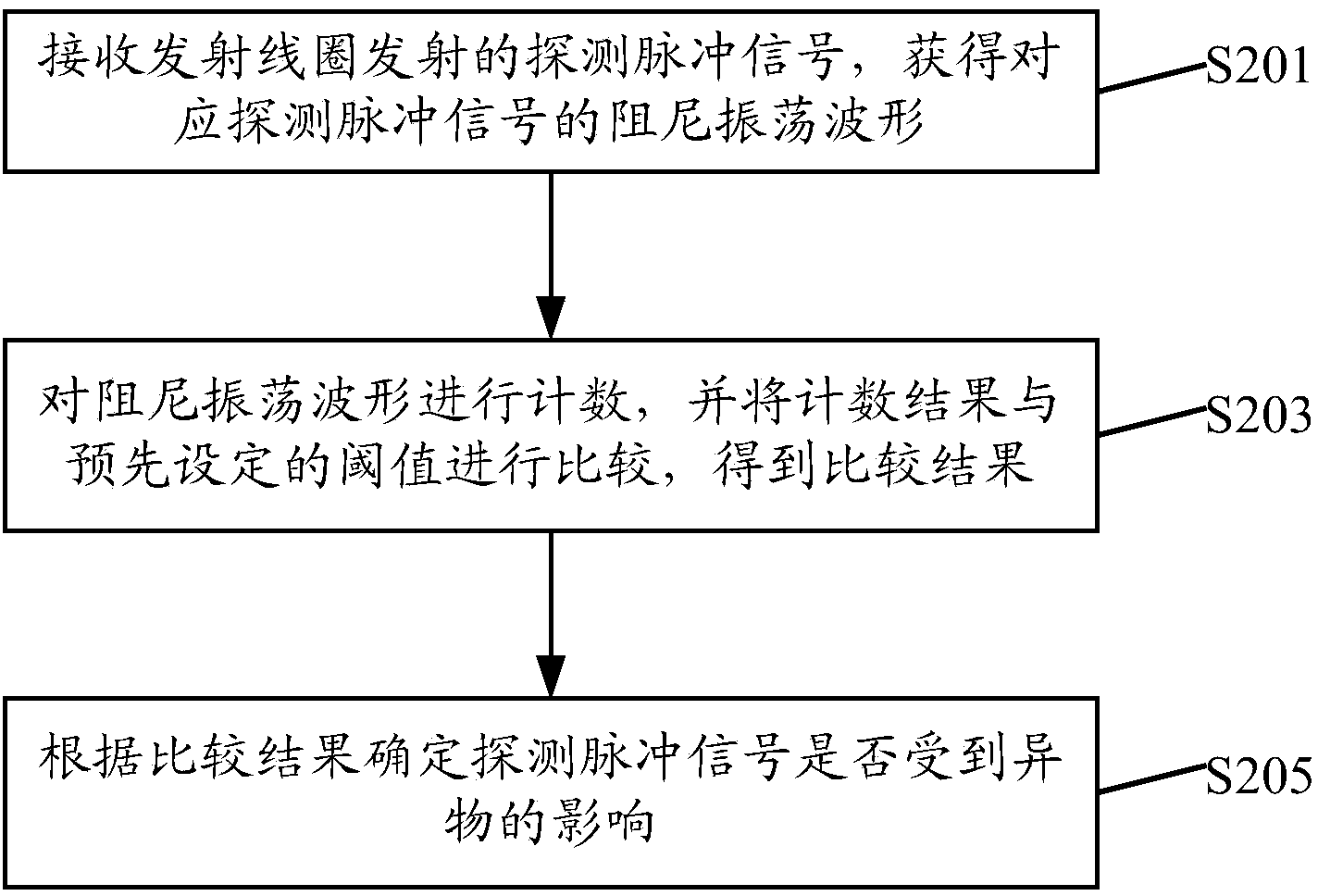
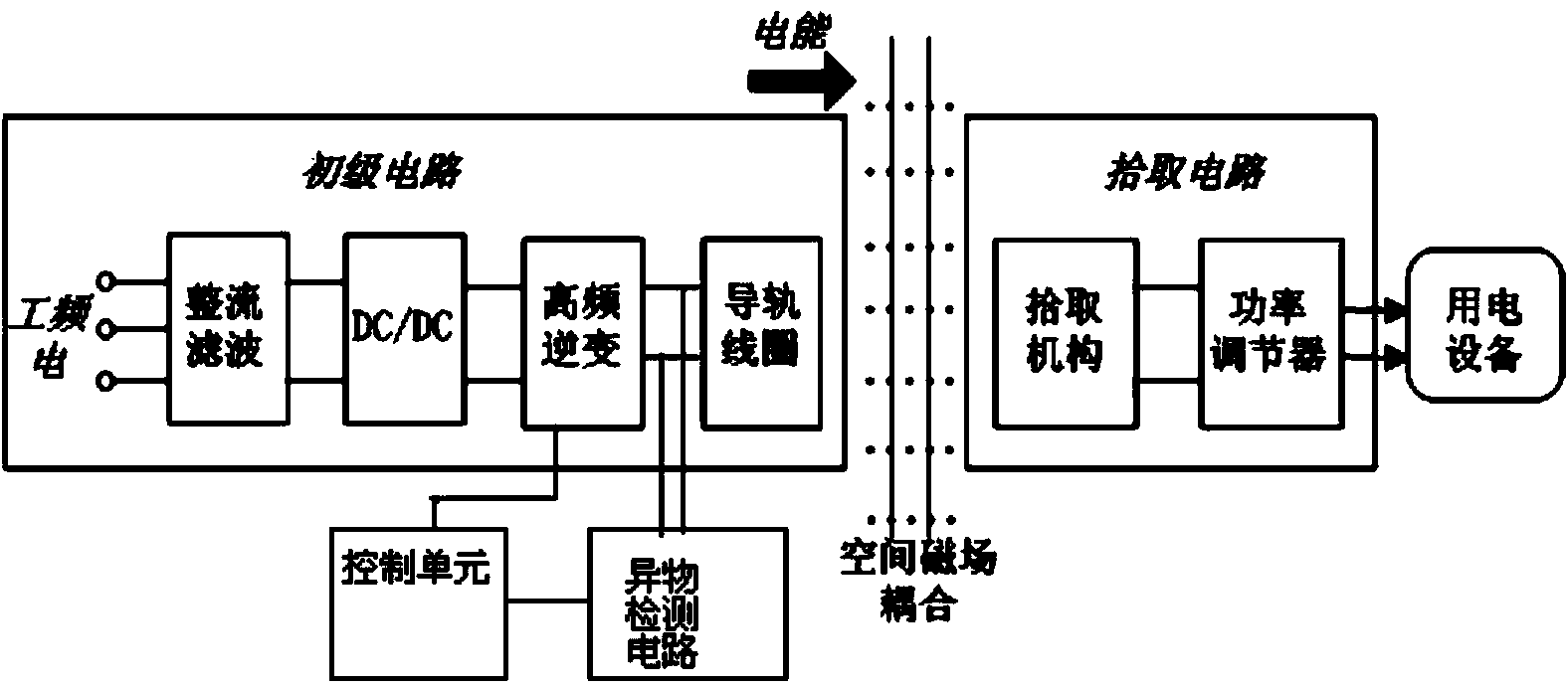
ActiveCN104237954AHigh sensitivityAvoid the influence of powerElectric/magnetic detectionAcoustic wave reradiationElectric power transmissionForeign matter
The invention discloses a foreign matter detection method and device of a wireless power transmission system. The foreign matter detection method includes the steps of receiving detection pulse signals transmitted by a transmitting coil, obtaining damped oscillation waveforms corresponding to the detection pulse signals, counting the damped oscillation waveforms, comparing the counting result with the preset threshold value to obtain the comparison result, and determining whether the detection pulse signals are influenced by foreign matter or not according to the comparison result. The number of the damped oscillation waveforms is obtained through the method of transmitting detection pulses through the transmitting coil, whether foreign matter exists in the wireless power transmission system or not is judged on this basis, the foreign matter detection flexibility is improved, and the influences of the power of the wireless power transmission system on the detection process are avoided.
Owner:深圳前海贞泰通信技术有限公司
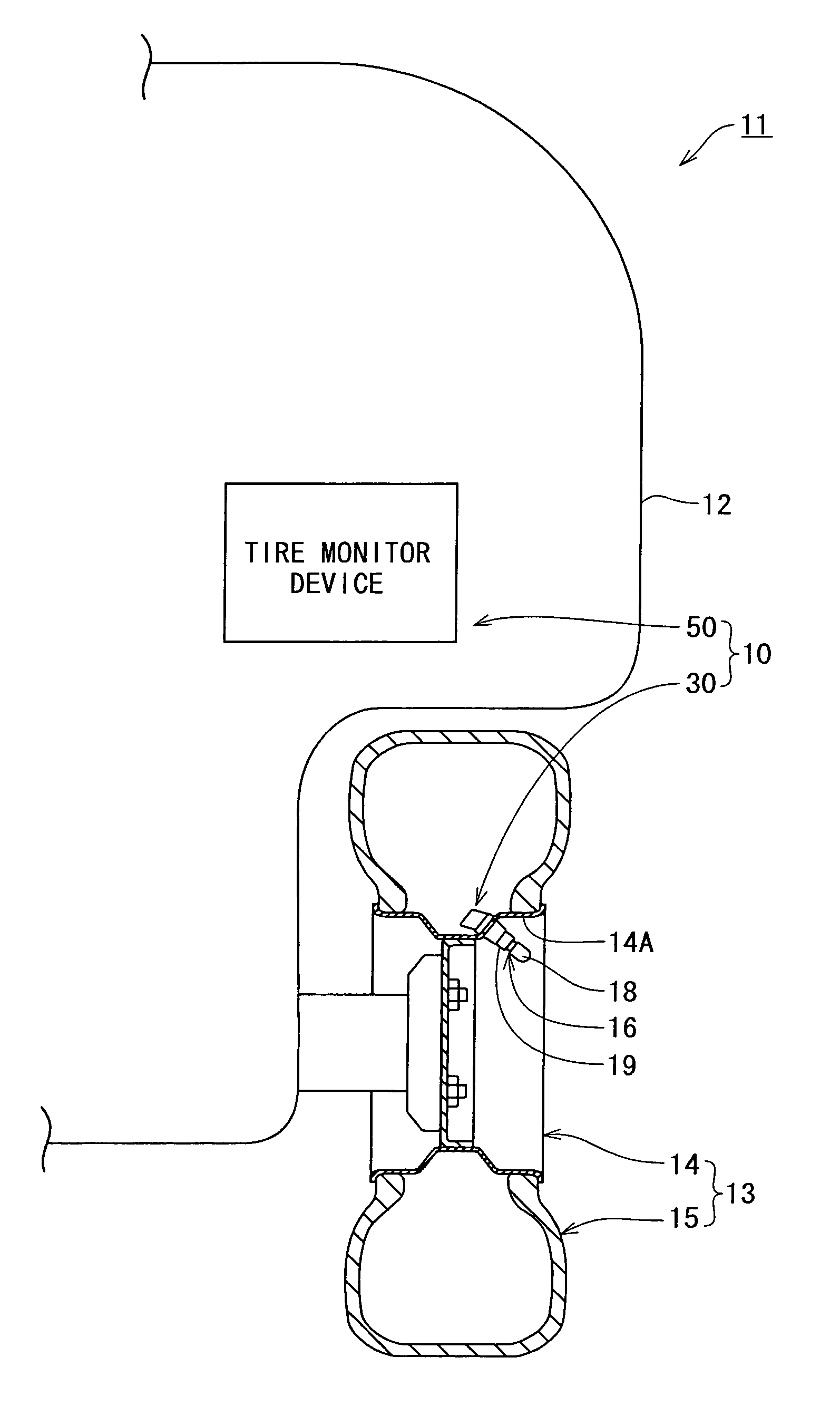
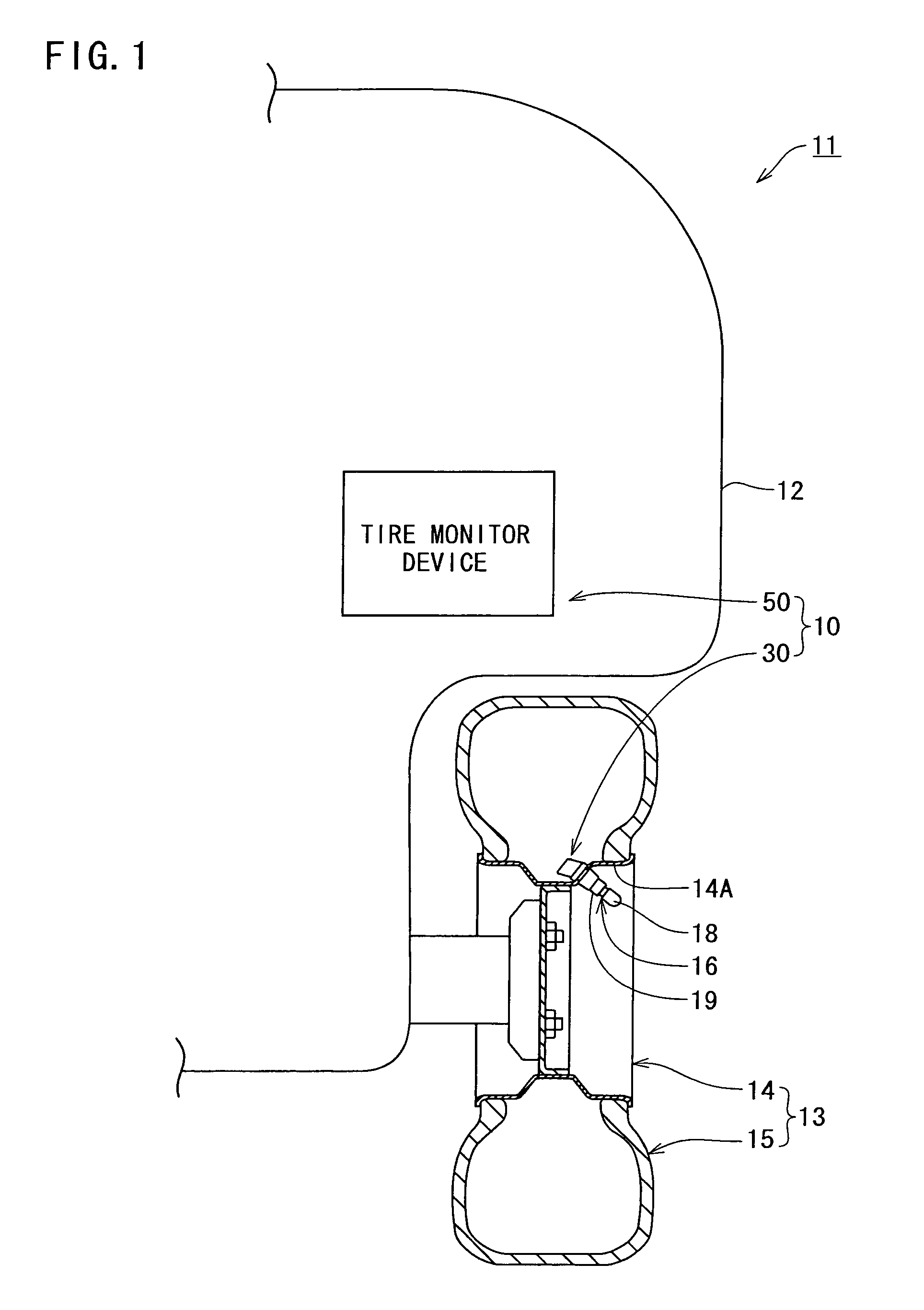
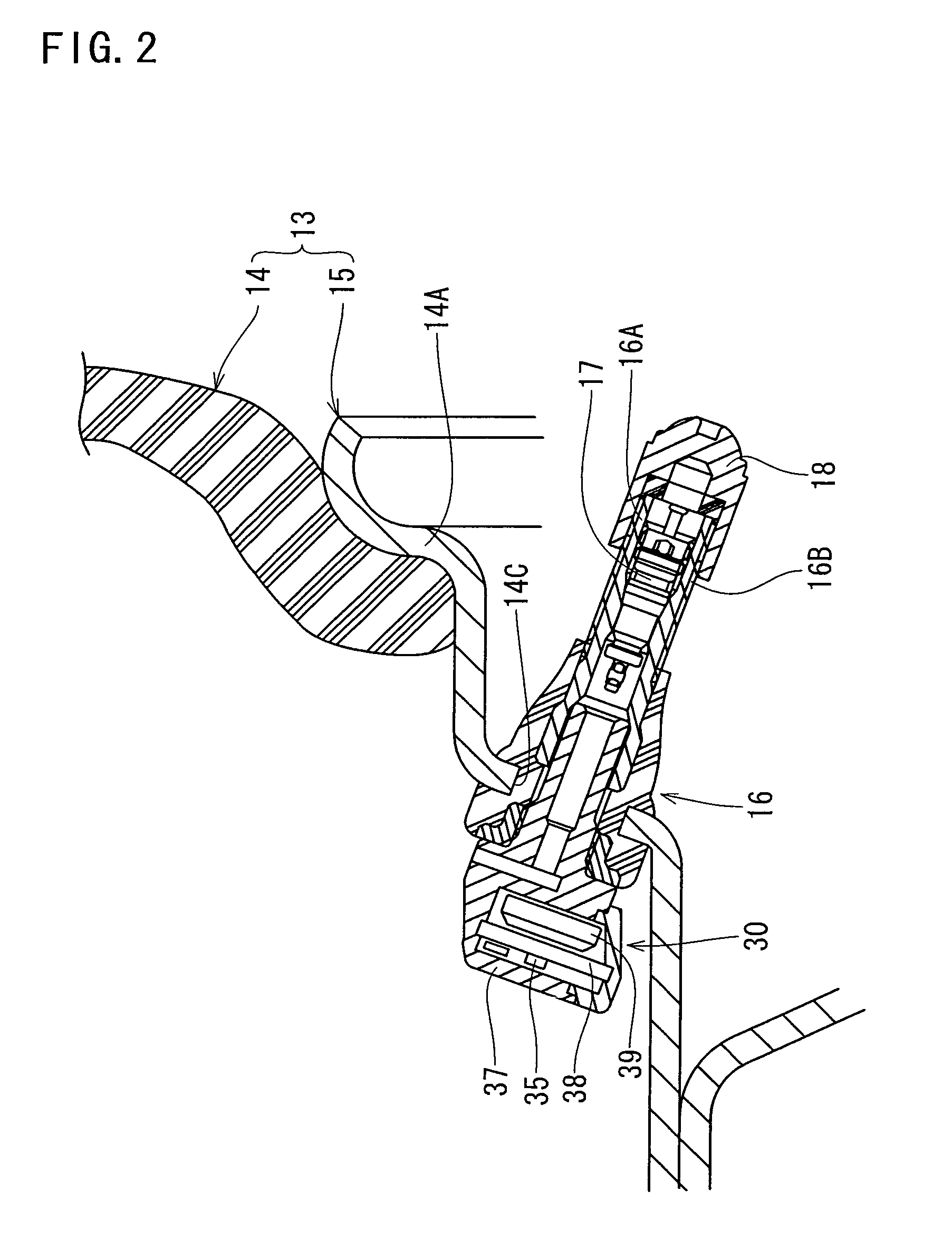
Tire monitor radio circuit and tire monitor system
InactiveUS7421891B2Improve communication reliabilityReduce statically determinate timeInflated body pressure measurementFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsElectrical resistance and conductanceResonance
A tire monitor radio circuit includes a control circuit delivering a binary digital baseband signal, a modulation circuit having an oscillation circuit generating a carrier wave and switched between an oscillatory and a non-oscillatory states, an antenna resonance circuit having a coil and a capacitor both connected together, a resistance damping circuit having a switching element and a resistance and connected to the antenna resonance circuit, the resistance damping circuit being switchable between an operative and an inoperative states, and a compensation circuit putting the resistance damping circuit into the operative state when the modulation circuit is switched to the non-oscillatory state, the compensation circuit returning the resistance damping circuit to the non-operative state when or before the modulation circuit has been or is switched to the oscillatory state. When he resistance damping circuit is on the operative state, resonance current of the damped oscillation in the antenna resonance circuit is applied to the resistance, and the resistance serves as a damper thereby to reduce statically determinate time of damped oscillation. As a result, the digital signal can accurately be detected from the carrier wave at the reception side. Consequently, reliability in the communication can be improved.
Owner:PACIFIC INDUSTRIAL CO LTD
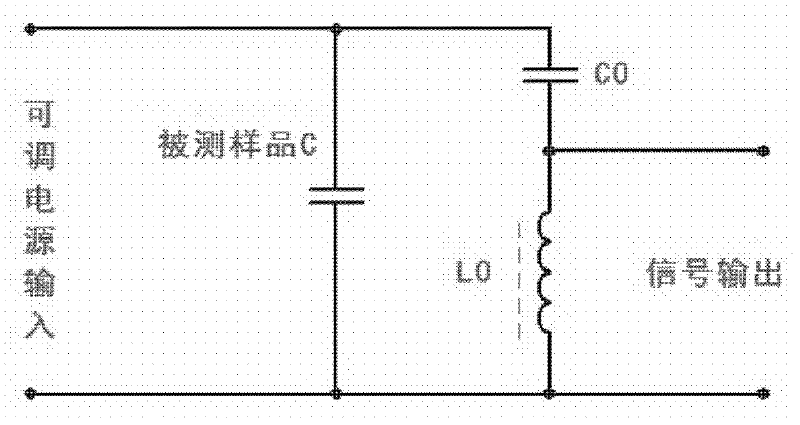
Detection method of self-healing breakdown of capacitor
ActiveCN102654554AEasy to useAccurate detectionTesting dielectric strengthResistance/reactance/impedenceSelf-healingInductor
The invention discloses a detection method of self-healing breakdown of a capacitor. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) connecting a detection capacitor with a detection inductor in series, connecting the detection capacitor and the detection inductor in parallel with a detected sample capacitor to form a detection circuit, and connecting alternating current adjustable power supplies at two ends of the circuit; and (2) adjusting the alternating current adjustable power supplies; when the condition that the detection inductor generates a damped oscillation signal, judging that the detected sample capacitor generates the self-healing breakdown. The detection method disclosed by the invention solves the disadvantage of the conventional detection method of the self-healing breakdown by using the capacitor and has the advantages of convenience for use and accurate detection; and the detection method for a self-healing breakdown test of the capacitor is simple and reliable, has good anti-interference performance and ensures that erroneous judgment does not happen.
Owner:FIFTH ELECTRONICS RES INST OF MINIST OF IND & INFORMATION TECH +1
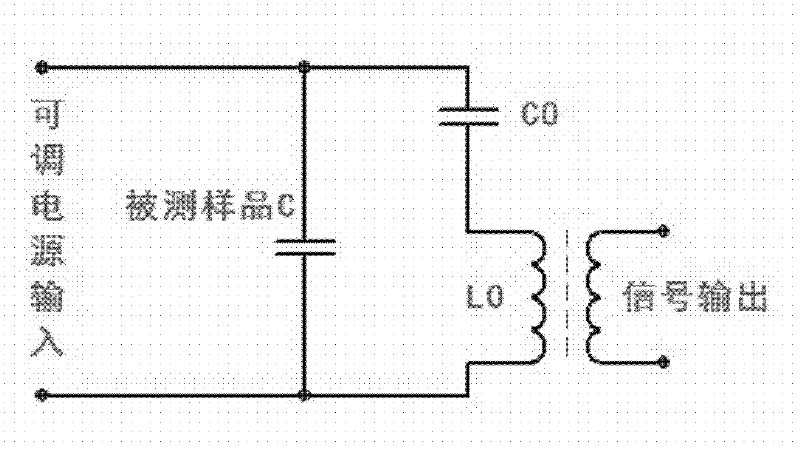
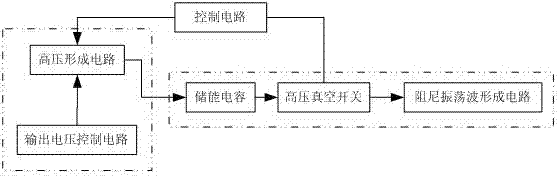
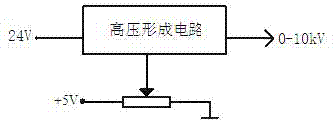
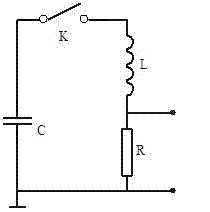
Lightning damped oscillation wave generator
InactiveCN104330598ASimple structural designMeet the test requirementsElectrical measurement instrument detailsElectrical testingCapacitanceControl signal
The invention discloses a lightning damped oscillation wave generator which comprises a continuous adjustable DC high-voltage forming module, a lightning damped oscillation wave forming module and a control circuit. The continuous adjustable DC high-voltage forming module comprises an output voltage control circuit and a high voltage forming circuit which is connected to the output voltage control circuit. The lightning damped oscillation wave forming module comprises an energy storage capacitor, a high voltage vacuum switch and a damped oscillation wave forming circuit which are connected in order. Under the control of the output voltage control circuit, the high voltage forming circuit outputs direct current high voltage to charge the energy storage capacitor. After the charging of the energy storage capacitor is completed, the control circuit outputs a control signal, the high voltage vacuum switch is switched on, and the charging of the energy storage capacitor is stopped. The energy storage capacitor starts discharging through the damped oscillation wave forming circuit, and lightning damped oscillation wave is formed on a load resistor. The lightning damped oscillation wave generator can be connected to a digital memory, and the waveforms of voltage and current of a protection device in the effect of the damped oscillation wave.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Magnetic field detecting device
ActiveUS20150219731A1Improve accuracyLow production costMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsAlternating currentVoltage source
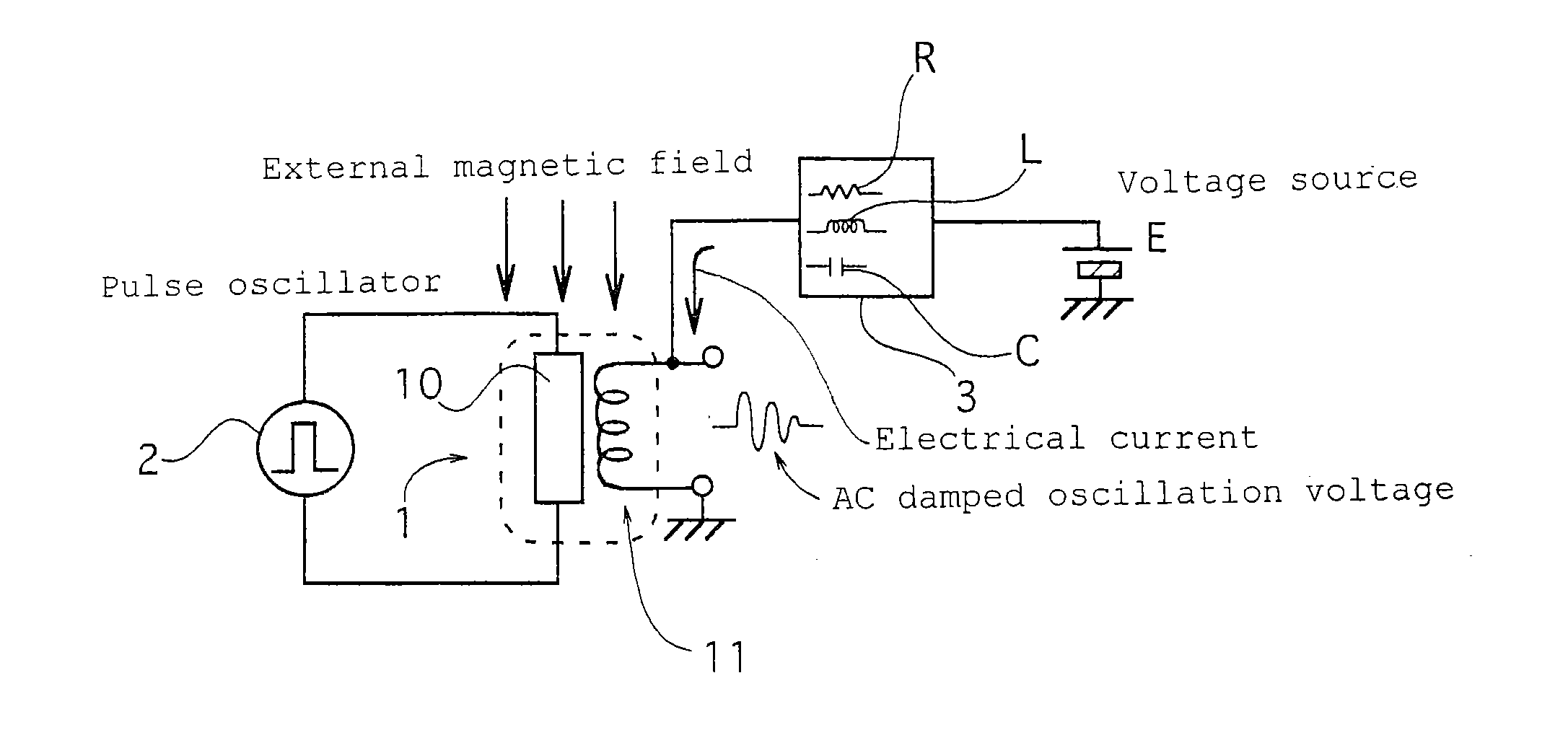
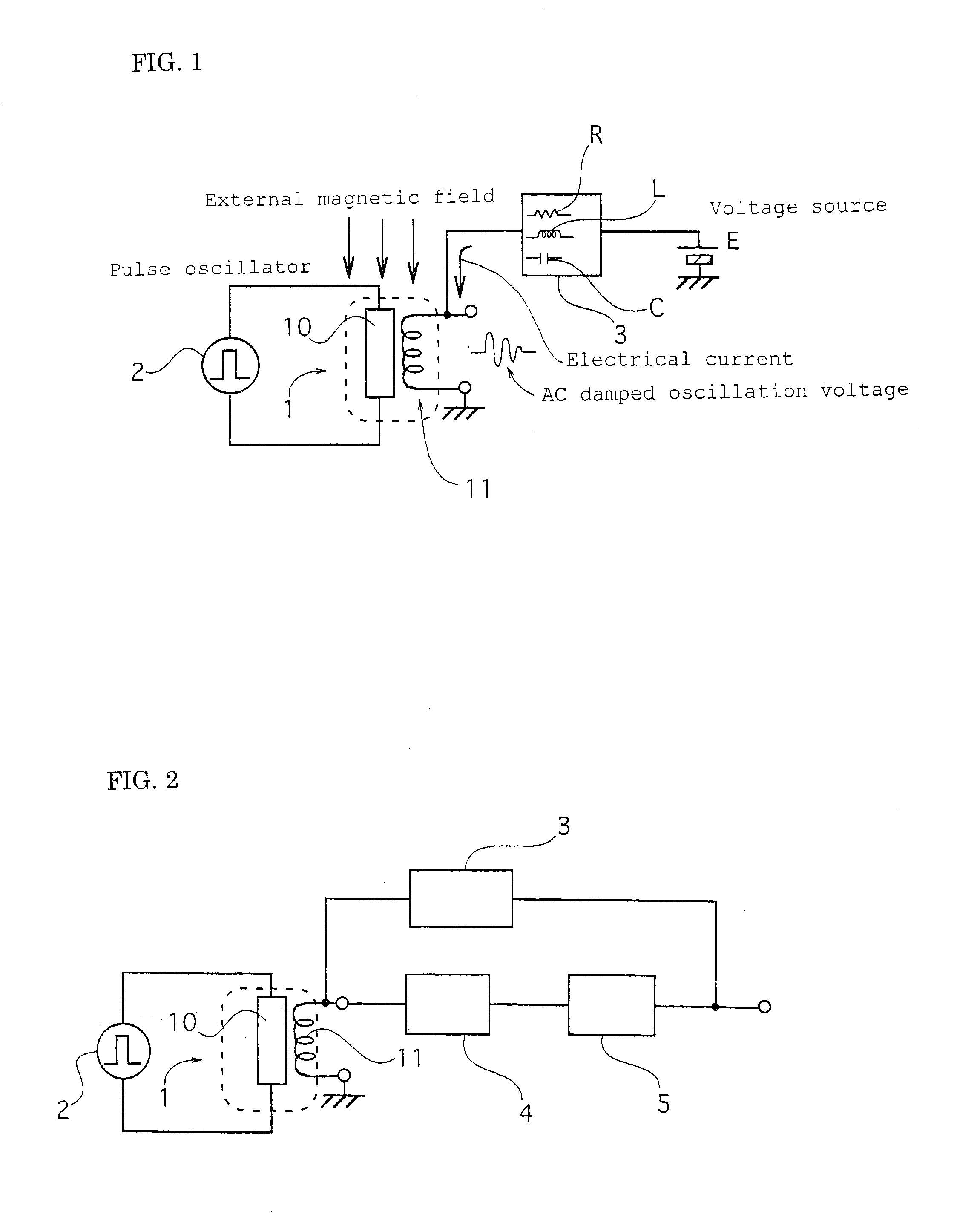
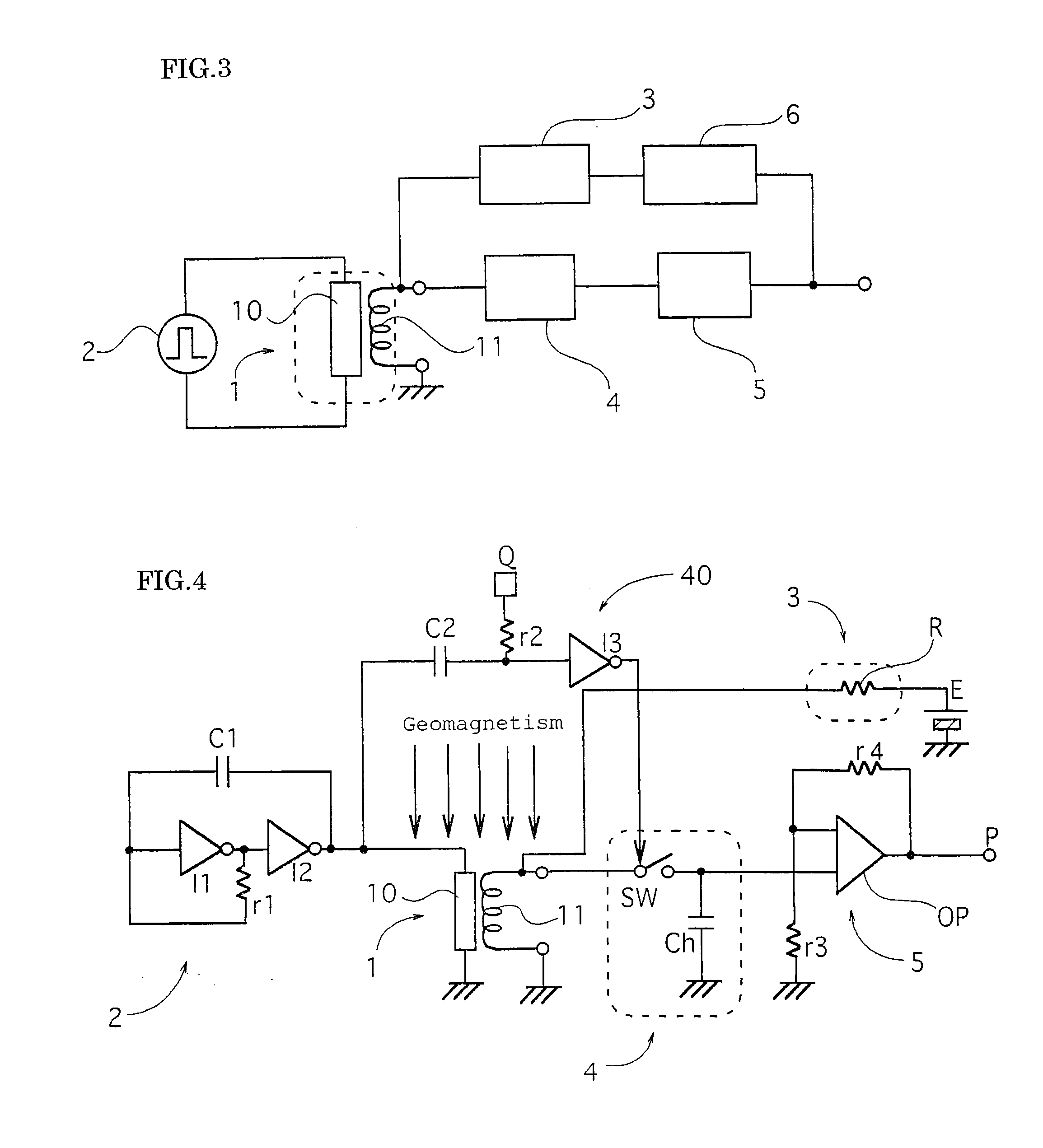
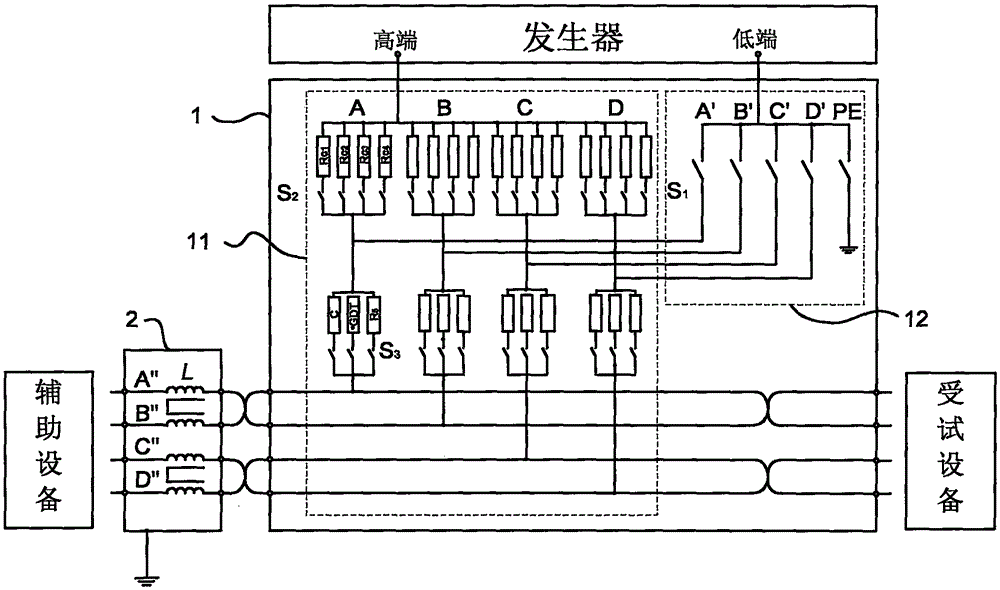
A magnetic field detecting device which comprises a magnetic impedance sensor including a magnetic impedance element 1 in which a pulse electrical current or a high frequency electrical current is applied from an oscillator 2 to an amorphous wire 10 and an alternate current or AC damped oscillation voltage, which is induced in a detecting coil 11 wound around the amorphous wire 10 and has a magnitude corresponding to an external magnetic field, is output, and an arbitrary magnetic field is applied to the amorphous wire by means of the magnetic field generated on the detecting coil 11 energized by connecting the detecting coil 11 to a voltage source or to a current source E through an impedance network 3 comprising of a resistor R or a coil L or a condenser C or comprising a combination of the resistor R, the coil L, and the condenser C.
Owner:AICHI STEEL
Electromagnetic interference eliminator for power system automation apparatus
InactiveCN1764066AImprove electromagnetic compatibilityAvoid pollutionMultiple-port networksHarmonic reduction arrangementPower-system automationLow load
The EMI suppressor as a power system automation device comprises a capacitor and an electric induction coil. Wherein, giving full consideration on load impedance characteristic when designing filter structure; based on testing impedance characteristic of norm port (power, PT, and CT ports), designing two norm circuits: the low load impedance filter circuit fit to condition that load impedance less than 50ª©; or else, selecting the high load circuit. This invention has strong inhibition function to ports with different impedance and fast and damped oscillation wave.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV +1
Multifunctional coupling/decoupling network
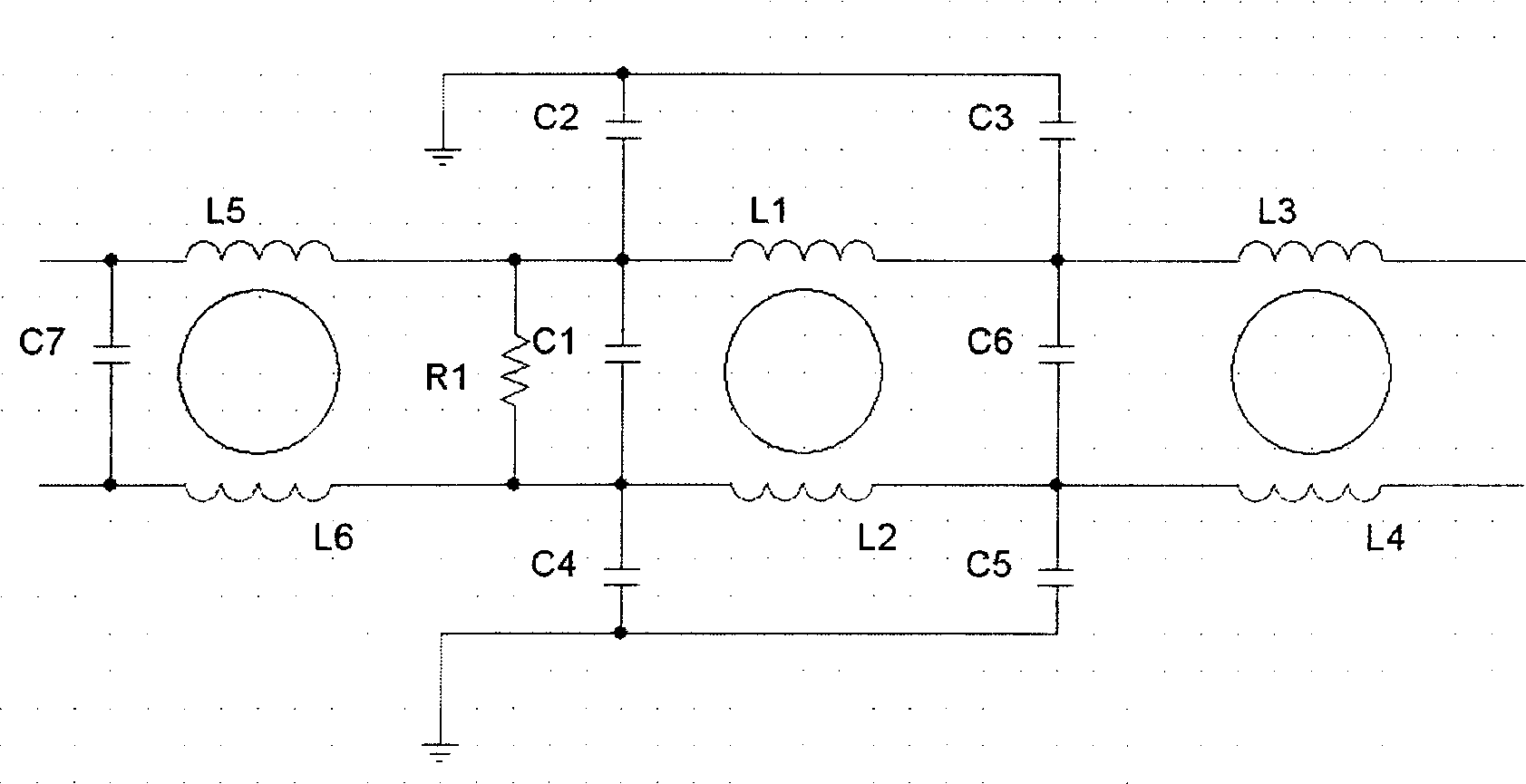
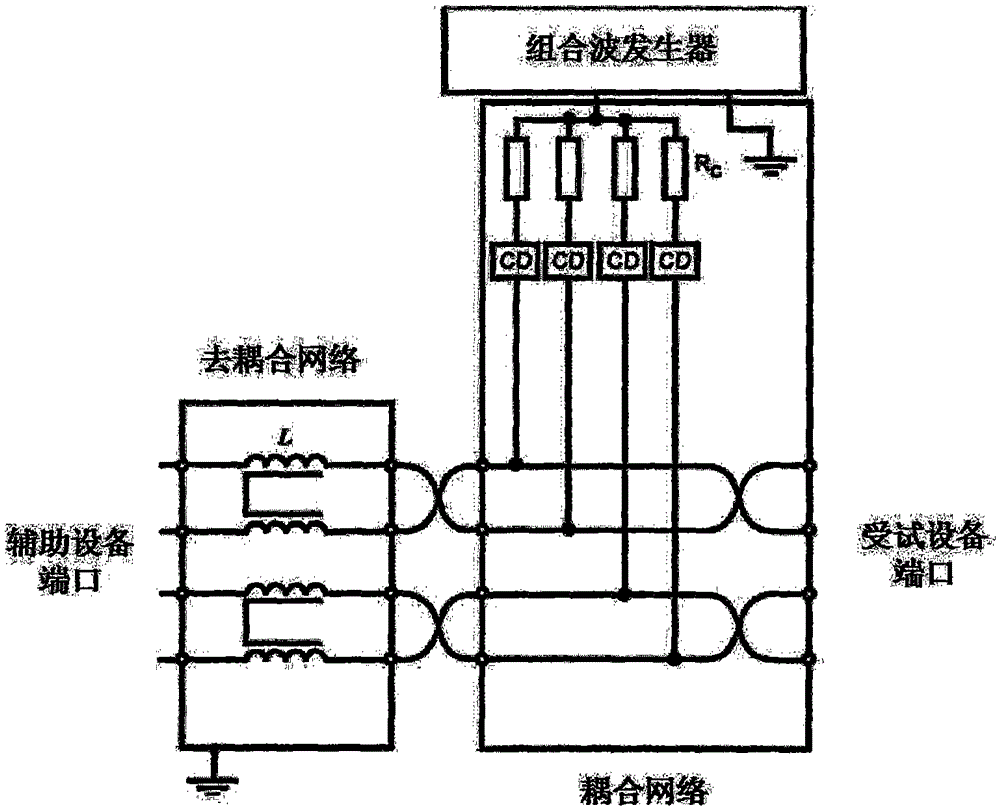
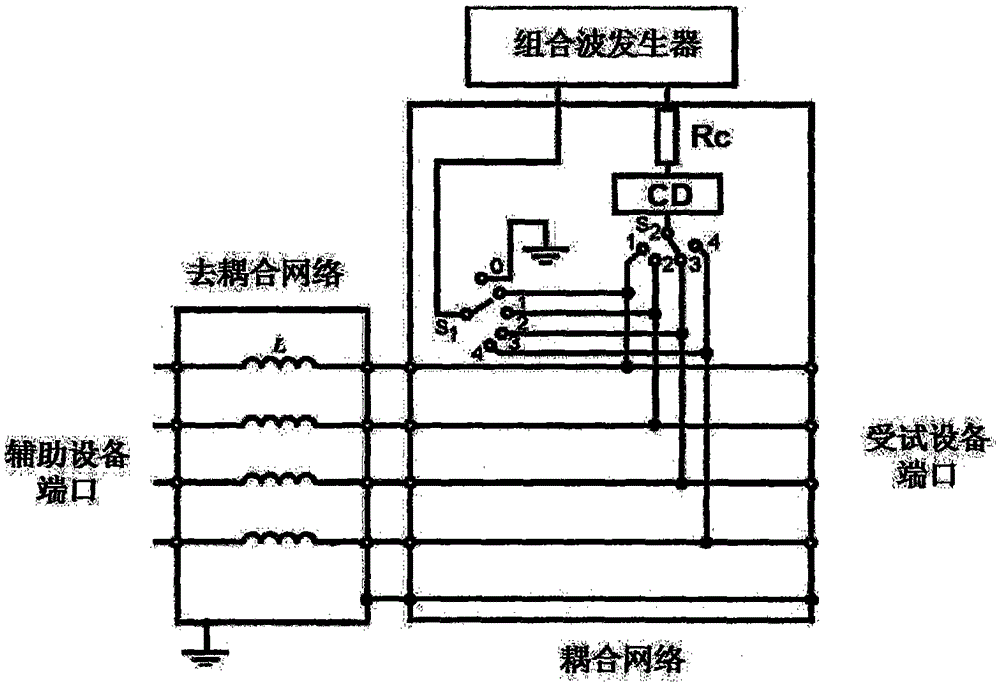
ActiveCN105425074ACompact and reasonable structureLow costMeasuring interference from external sourcesElectrical resistance and conductanceCurrent limiting
The invention discloses a multifunctional coupling / decoupling network, which comprises a coupling circuit and a decoupling circuit, wherein the coupling circuit is provided with multiple paths of coupling circuit high-end lines and coupling low-end lines, and each path of coupling circuit high-end line is serially provided with a switchable current-limiting resistor array comprising various resistance values and a switchable coupling device array comprising various types of coupling elements. When in test, coupling devices, current-limiting resistors and coupling paths are flexibly combined according to different input waveforms, coupling paths and coupling methods, and the unshielded symmetric and asymmetric tests of various kinds of test waveform signal ports including surge waves, ringing waves, damped oscillation waves and the like can be achieved. The multifunctional coupling / decoupling network has the advantages of high integration degree, low cost, convenient operation, wide application range and the like.
Owner:HANGZHOU EVERFINE INSTRUMENT CO LTD
Magnetic field detecting device
ActiveUS20150234017A1SensitiveIncrease output ratioVoltage/current isolationMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsPhysicsDamped oscillations
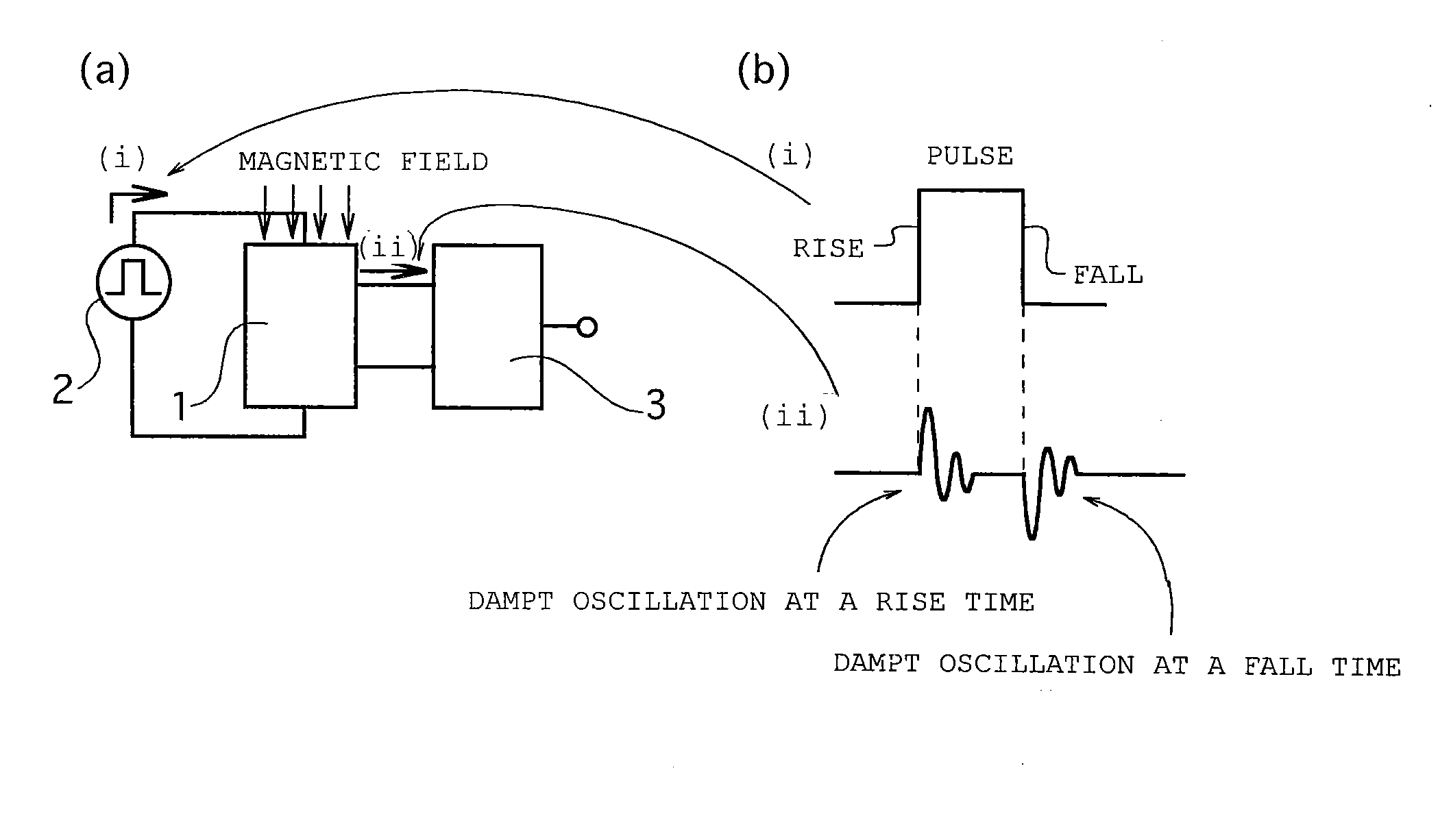
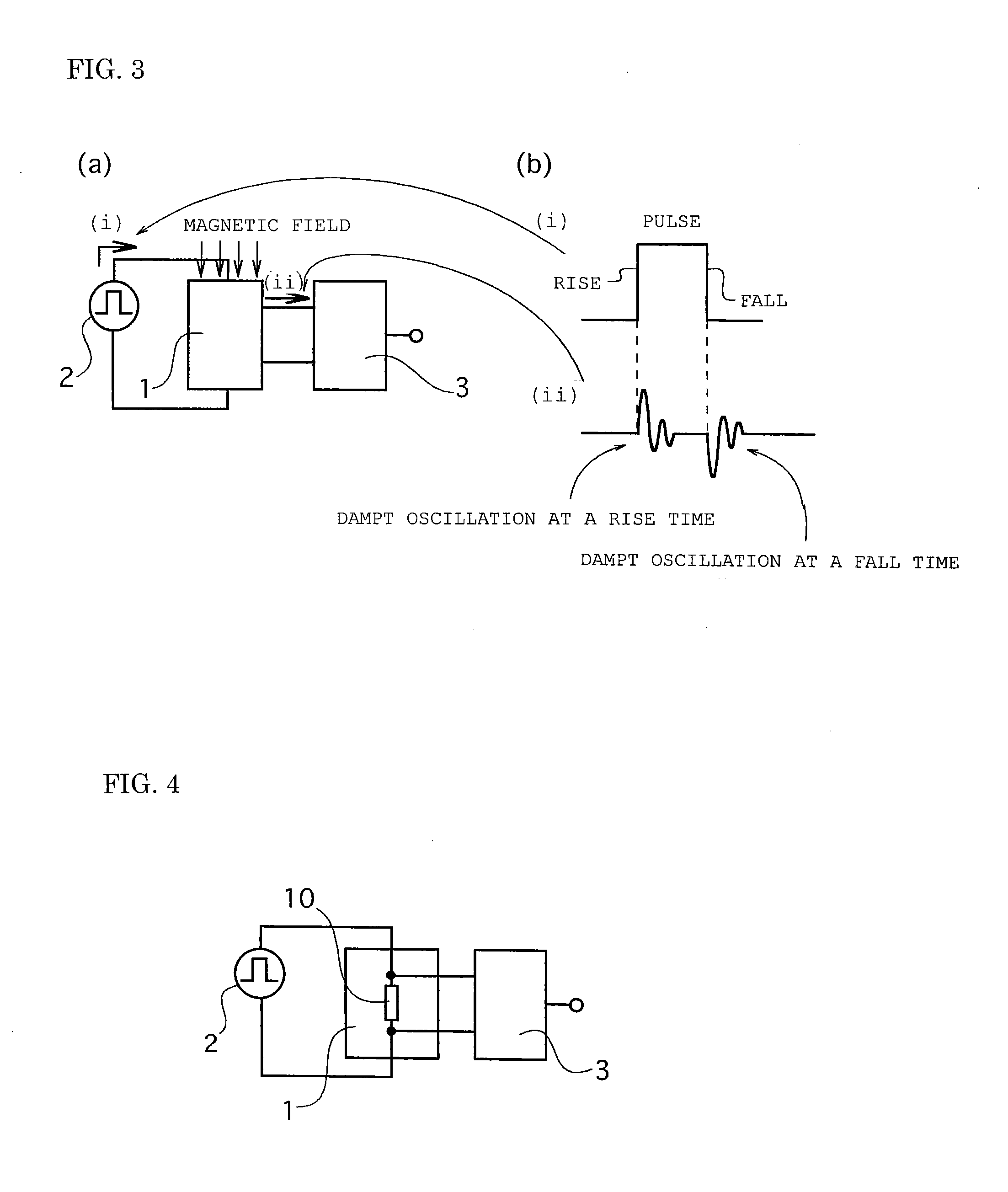
A magnetic field detecting device which comprises a magnetic impedance sensor including a magnetic impedance element 1 in which a detecting coil 11 wound around an amorphous wire 10 for detecting and outputting the external magnetic field around the amorphous wire at a rise time and a fall time of the pulse current in case of the pulse current is applied to the amorphous wire and a signal processing device 3 includes two sample-hold circuit 31, 32 for respectively sample-holding the alternate current damped oscillation voltage at the rise time and the fall time of the applied pulse current, wherein the output signal in response to the external magnetic field around the amorphous wire is output based on the detected two alternate current damped oscillation voltages output at the rise time and the fall time of the pulse current.
Owner:AICHI STEEL
Device for detecting the presence of a transponder around the device
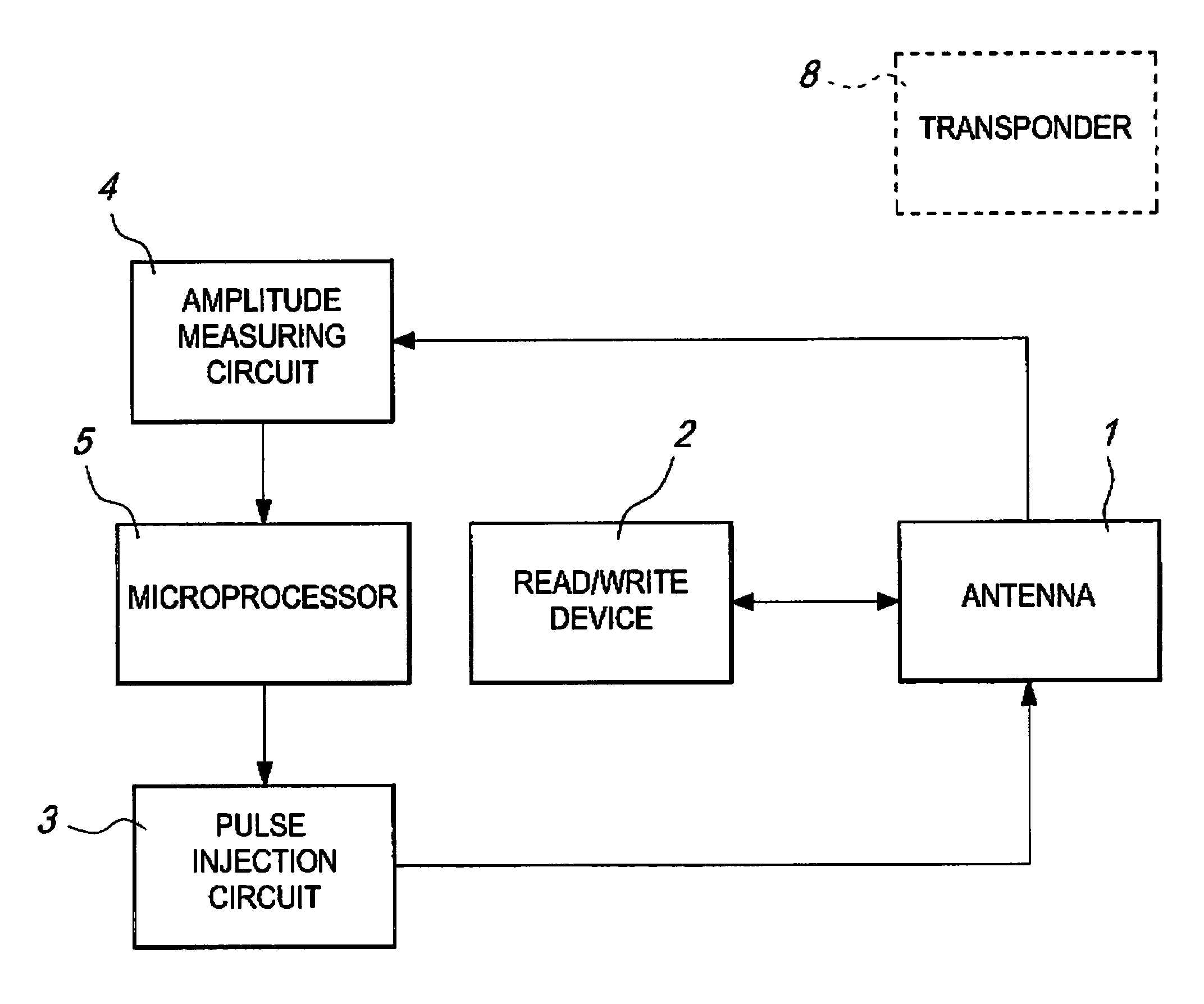
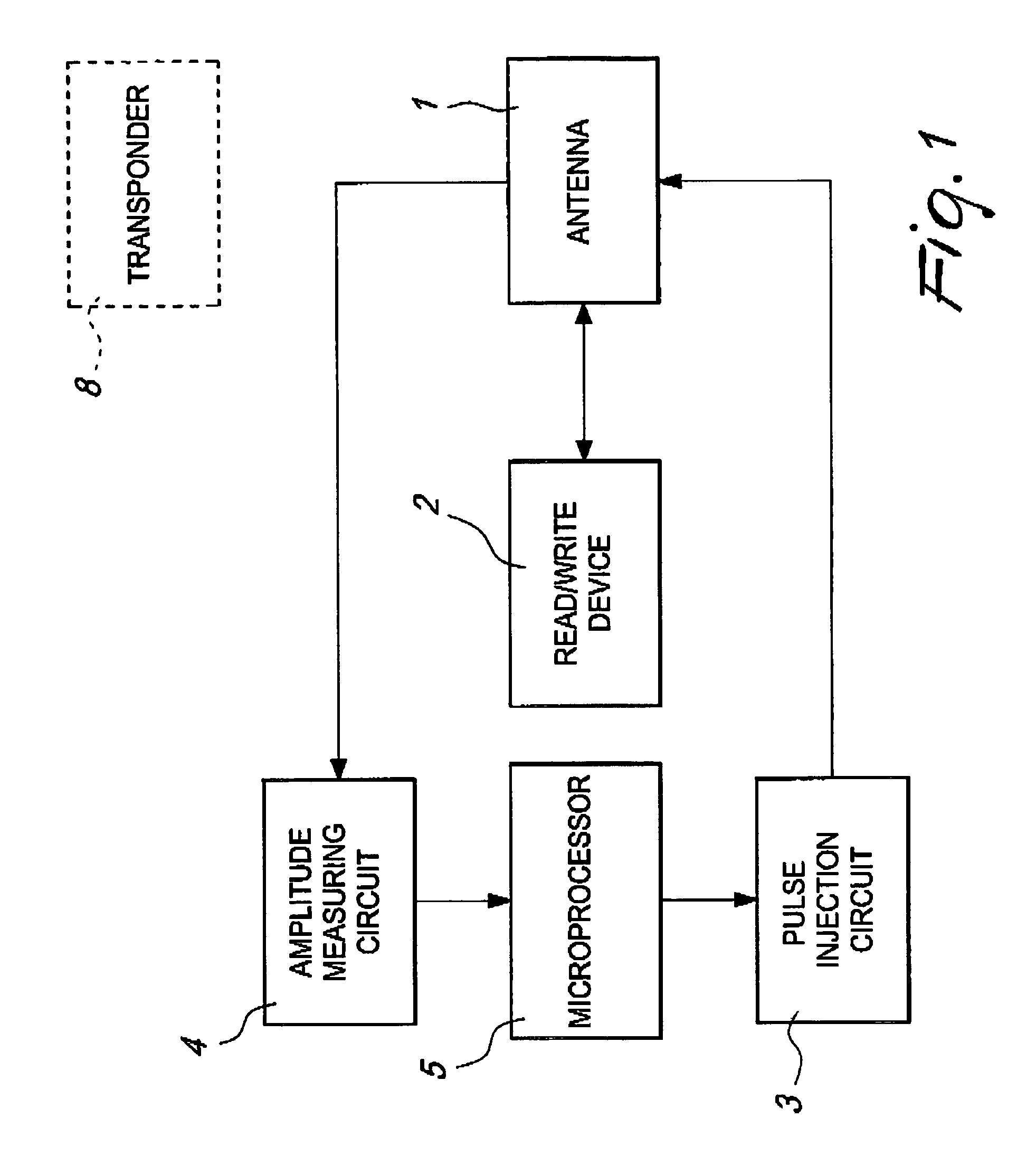
InactiveUS6982645B2Simple to provideCompetitive costMemory record carrier reading problemsNear-field in transpondersDamped oscillationsElectrical and Electronics engineering
A device for detecting the presence of a transponder in its vicinity is provided, which comprises an antenna, a pulse generation unit, a unit adapted to feed the antenna with the pulses and a unit for measuring the damped oscillations of the antenna as a consequence of being fed with the pulses, the unit for measuring the damped oscillations of the antenna determining whether a transponder is present or not in the vicinity of the antenna on the basis of the characteristics of the damped oscillations.
Owner:MICROHARD +1
UPFC-based POD design method of damping wind-power-system-included oscillating characteristic
ActiveCN107968416AReduce reactive powerImprove transient stabilitySingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPower oscillations reduction/preventionTime domainElectricity
The invention discloses a UPFC-based POD design method of a damping wind-power-system-included oscillating characteristic. The method comprises: S1, constructing a model of a unified power flow controller (UPFC); S2, constructing a model of a doubly-fed induction generator (DFIG) set; S3, adding the UPFC model obtained at the S1 and the DFIG model obtained at the S2 into a grid system; S4, analyzing influences on damping characteristics of a grid system by the wind-power grid-connected capacity and a UPFC compensation degree; S5, constructing a model of a damped oscillation controller (POD); S6, connecting an output terminal of the POD controller to a parallel side of the UPFC of the grid system in the S3 and using a signal of a grid system connecting line as an input signal of the POD controller; and S7, for the grid system in the S4, changing the output of a synchronous generator in the grid system and a transmission power of the grid system connecting line and analyzing influences on the damping characteristics of the grid system by the UPFC and the POD controller. Therefore, references are provided for large-scale wind power plant access planning and analyses of the power of the interconnection system connection line and inter-area oscillation characteristics.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com