Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3563results about "Testing circuits" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
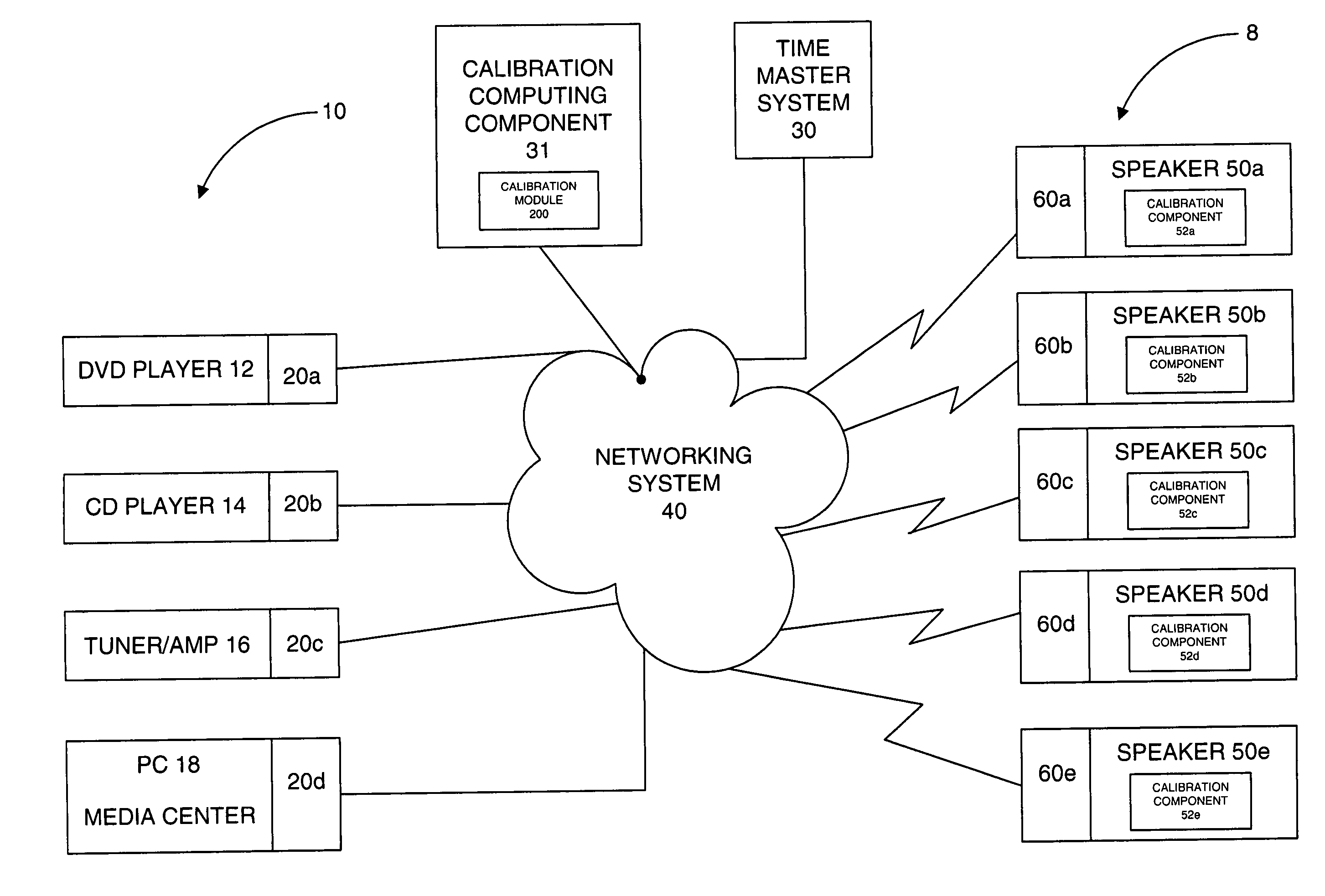
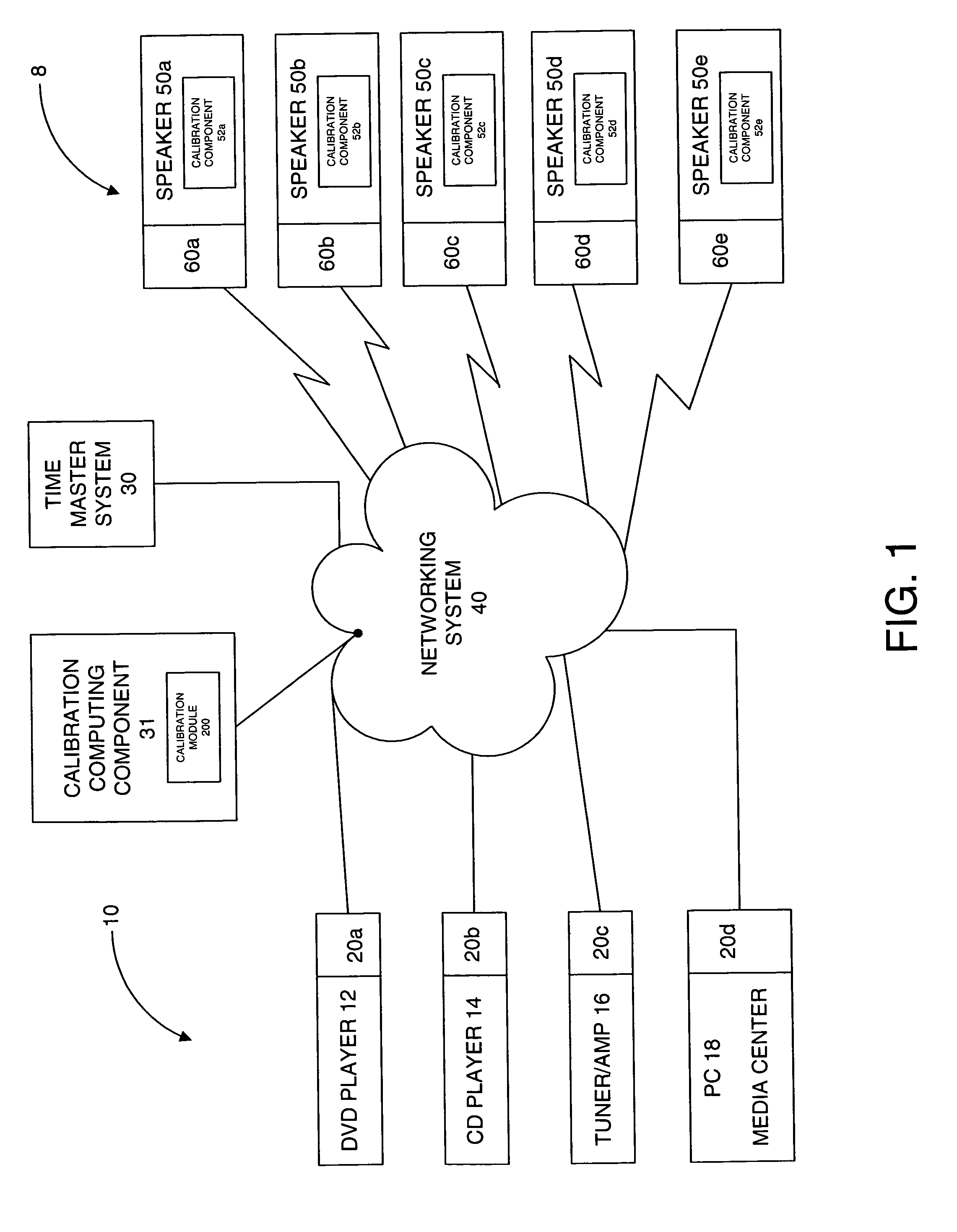
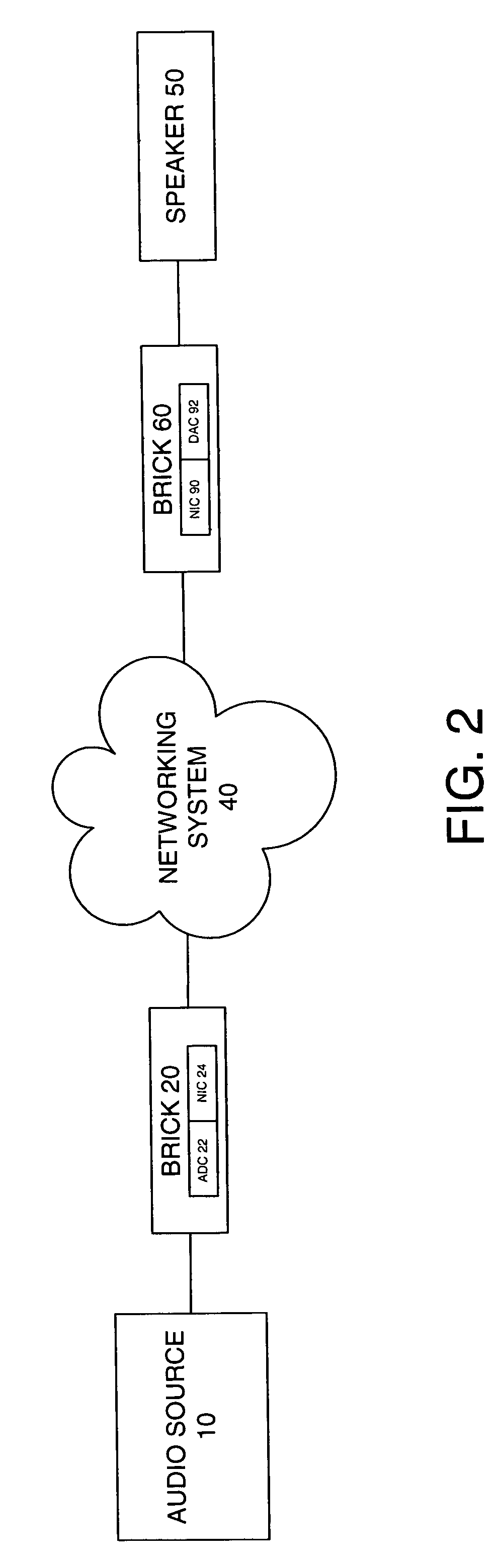
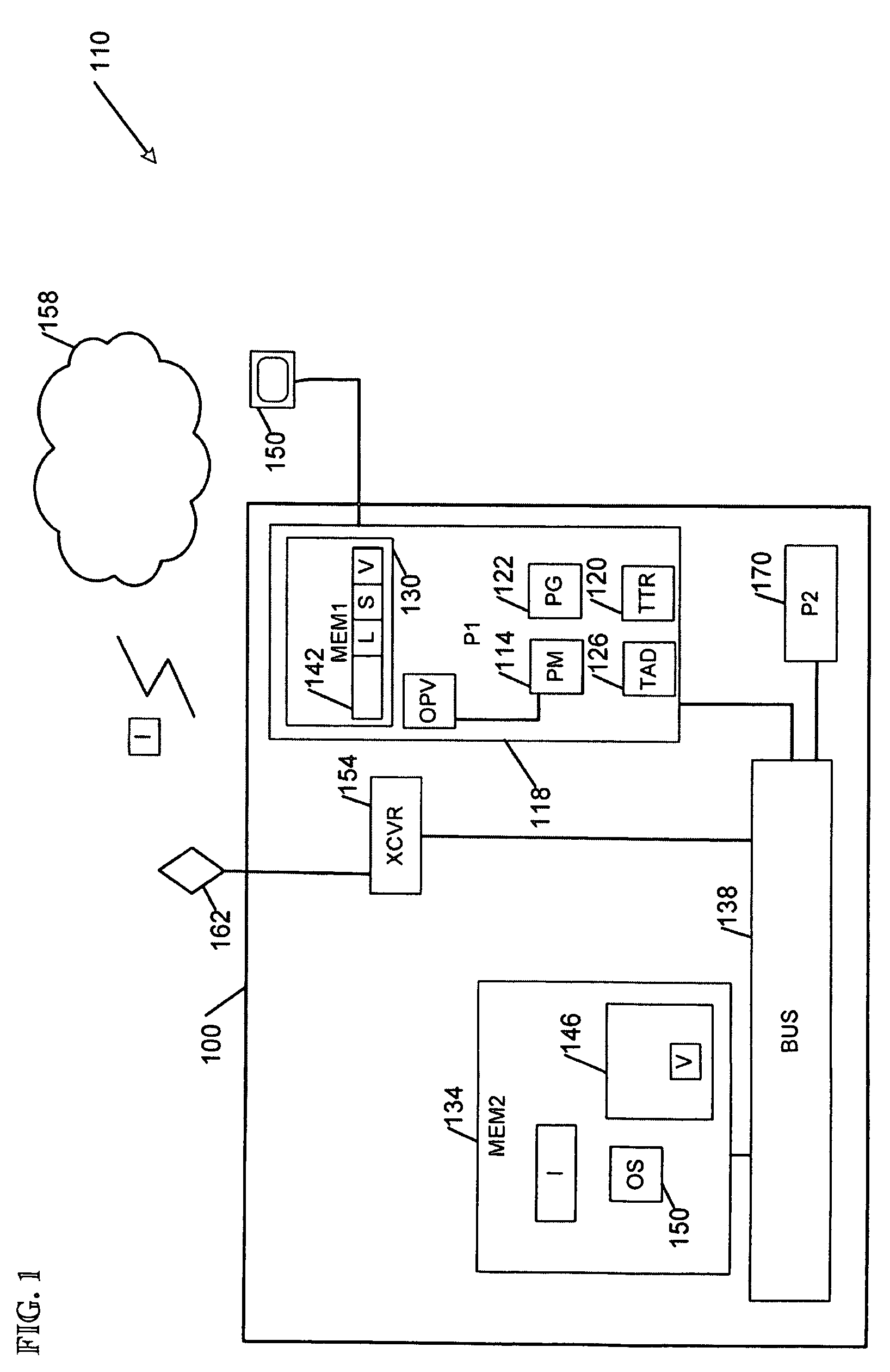
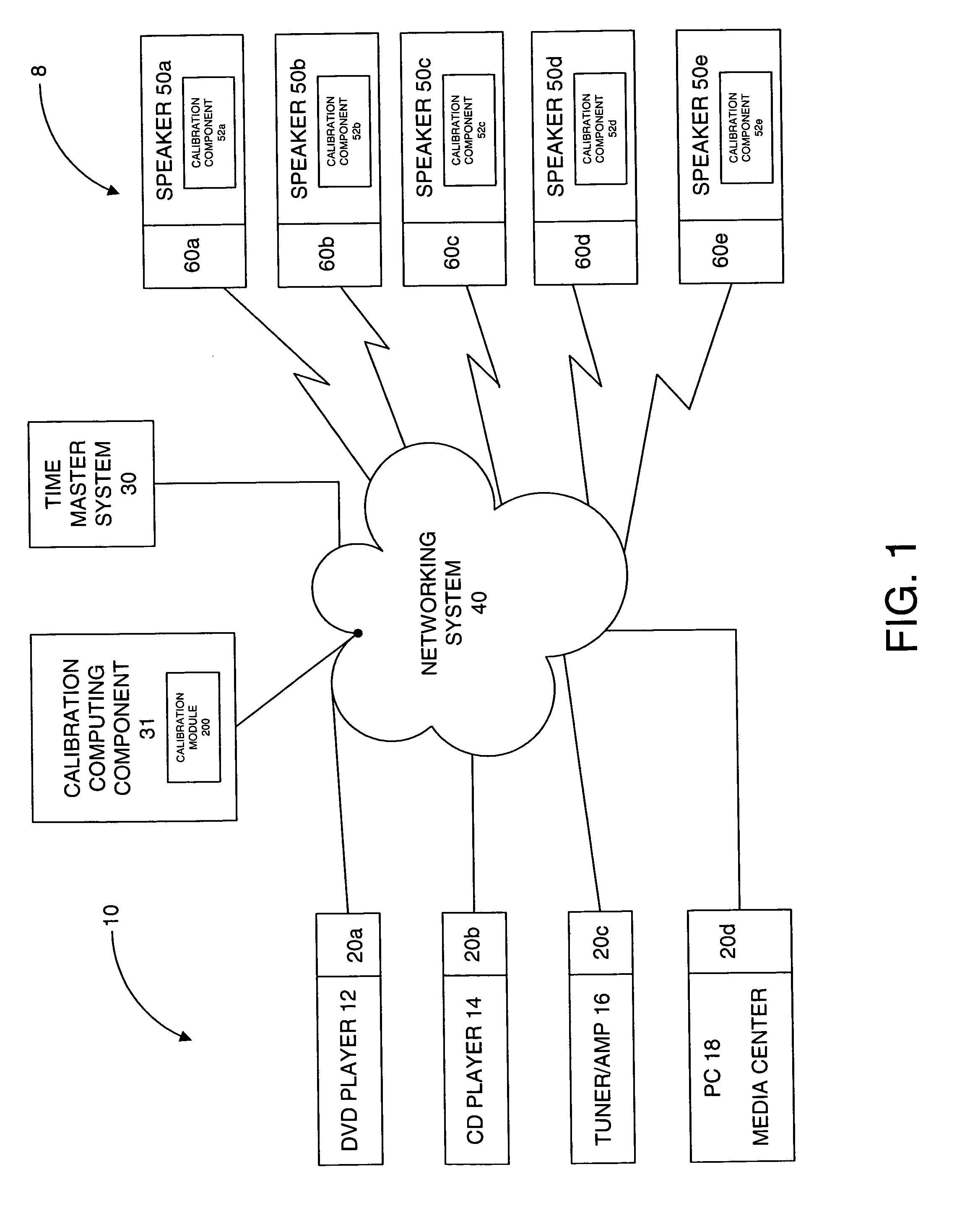
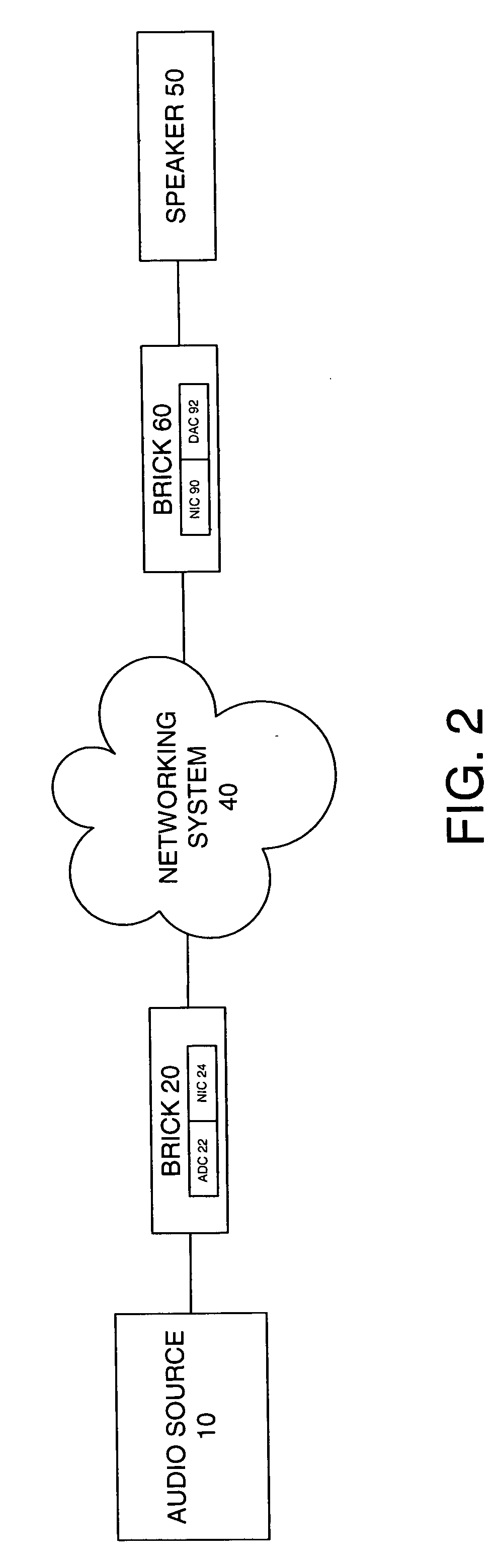
System and method for calibration of an acoustic system
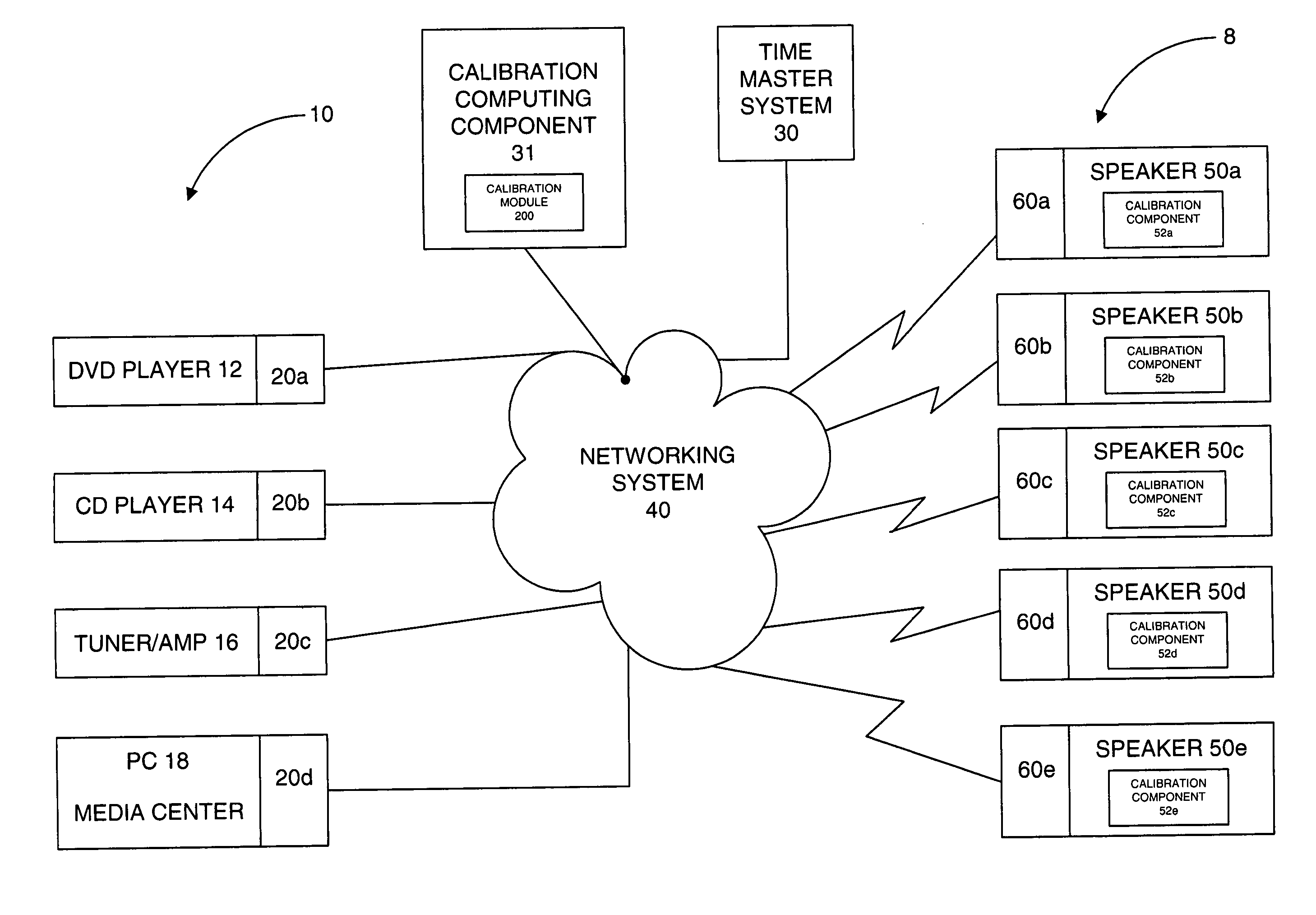
The present invention is directed to a method and system for automatic calibration of an acoustic system. The acoustic system may include a source A / V device, calibration computing device, and multiple rendering devices. The calibration system may include a calibration component attached to each rendering device and a source calibration module. The calibration component on each rendering device includes a microphone. The source calibration module includes distance and optional angle calculation tools for automatically determining a distance between the rendering device and a specified reference point upon return of the test signal from the calibration component.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
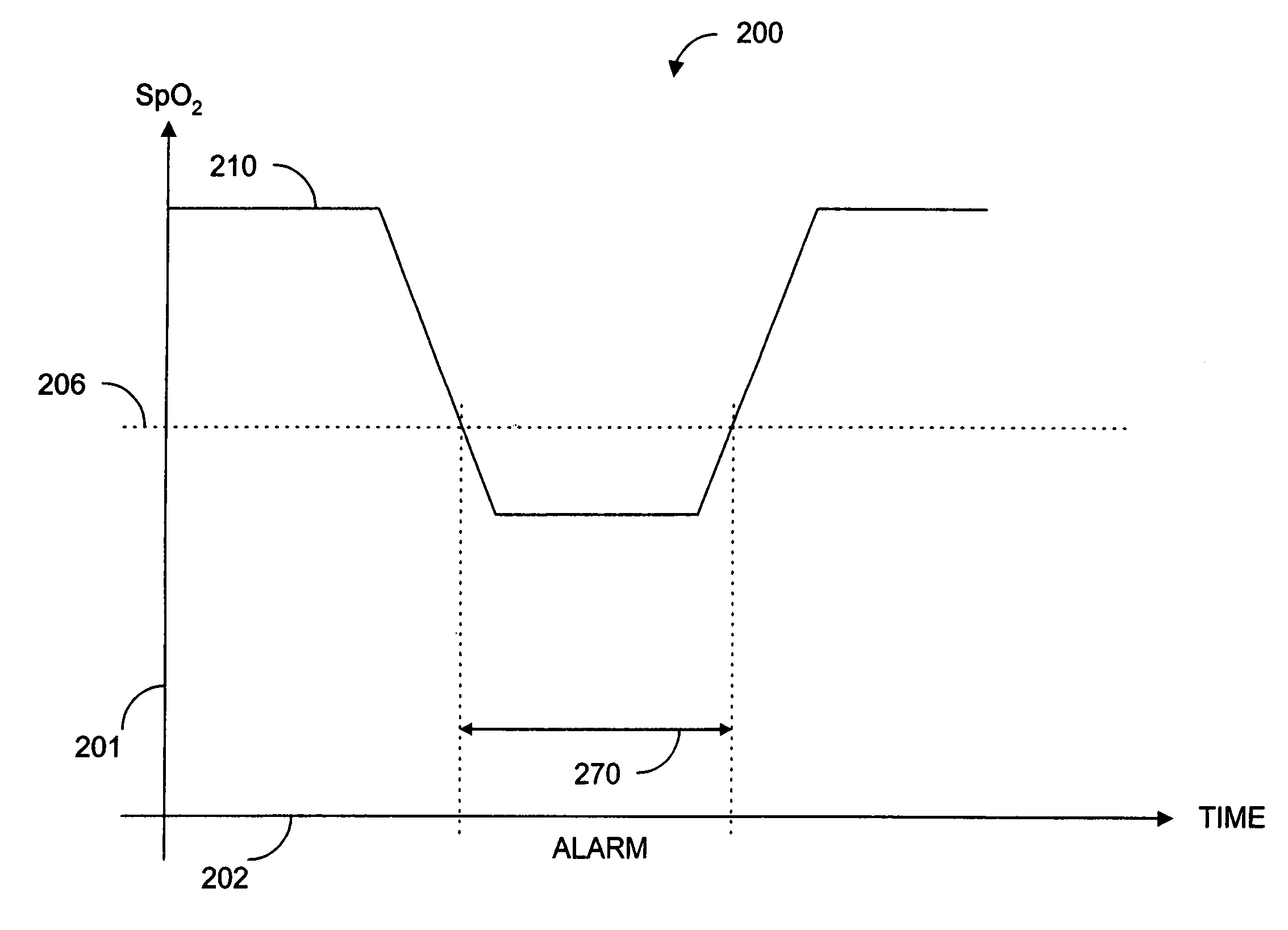
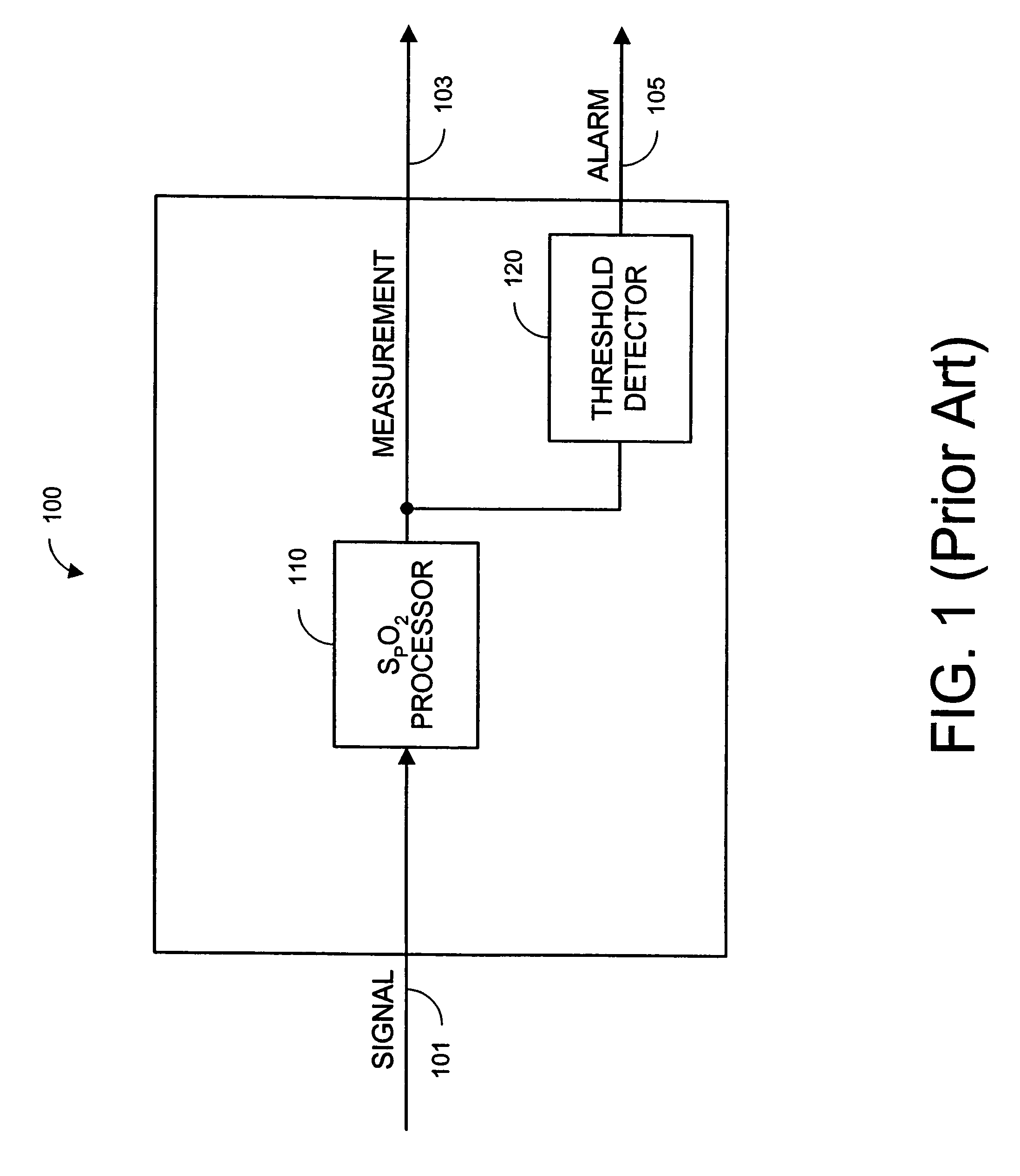
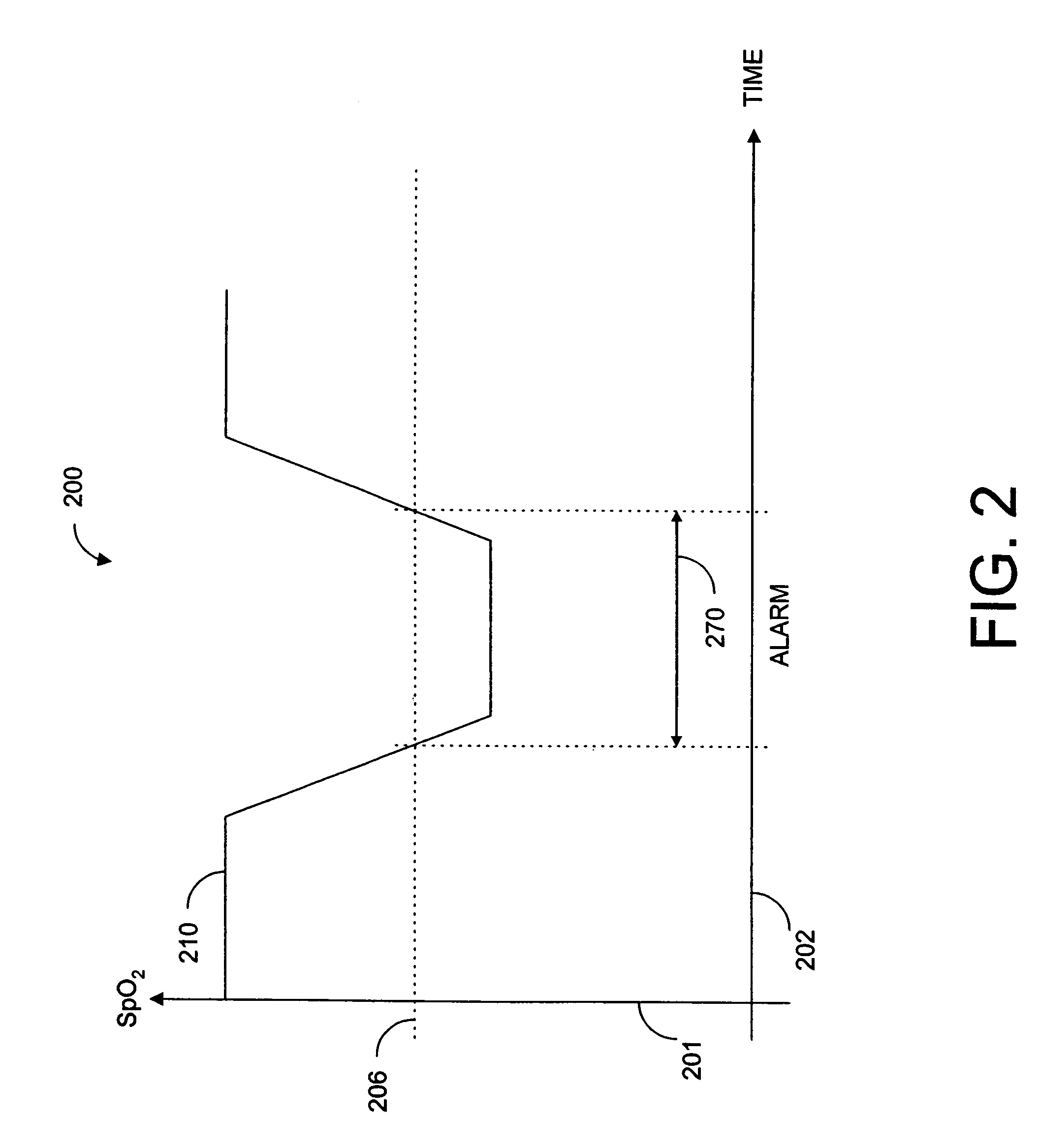
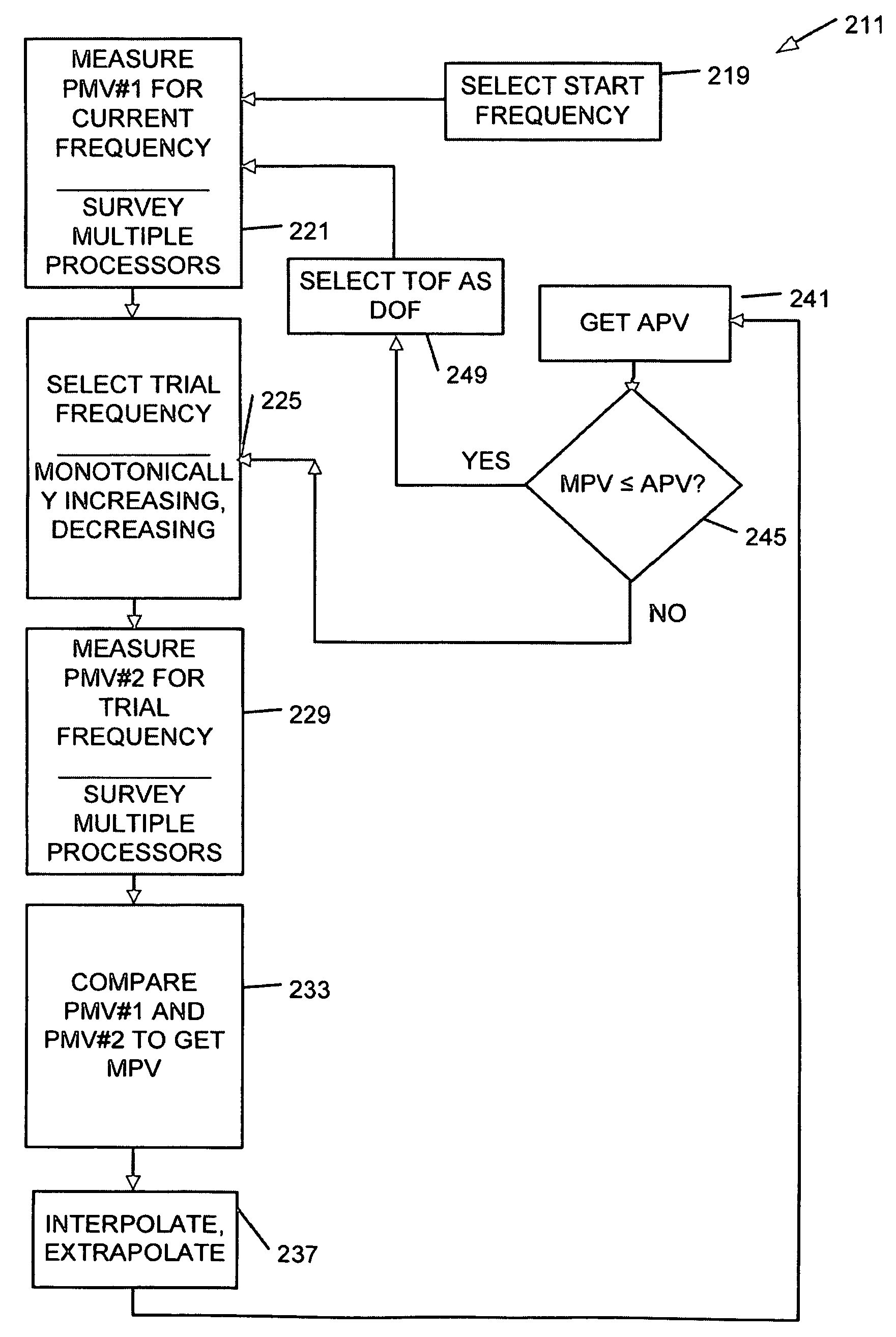
Parallel measurement alarm processor
InactiveUS7030749B2Waste caregiver resourcesReduce false alarm rateComputer controlResistance/reactance/impedenceNormal rangeComputer science
An alarm processor suppresses alarms when a physiological parameter is below a predetermined value but recovering toward a normal range.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
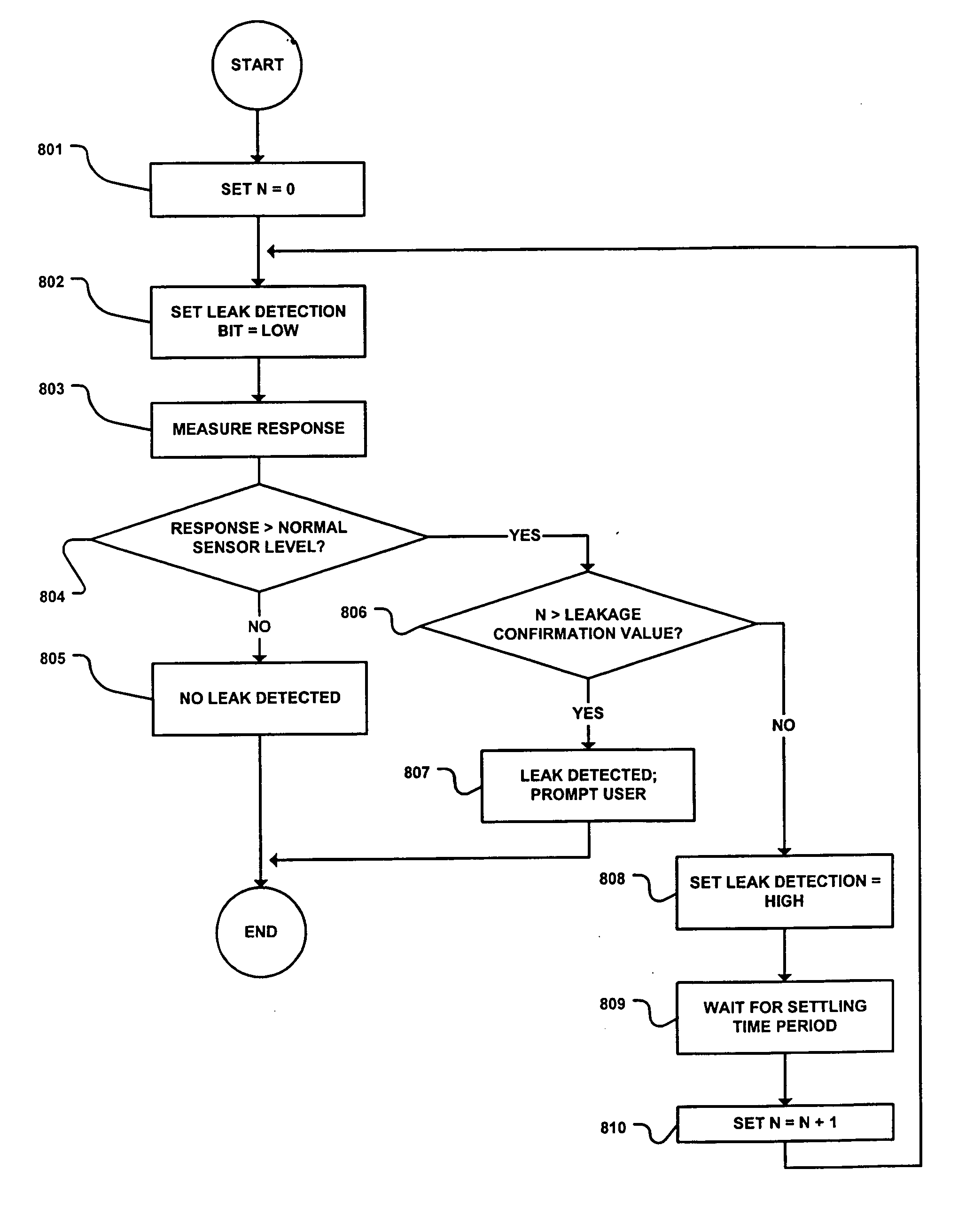
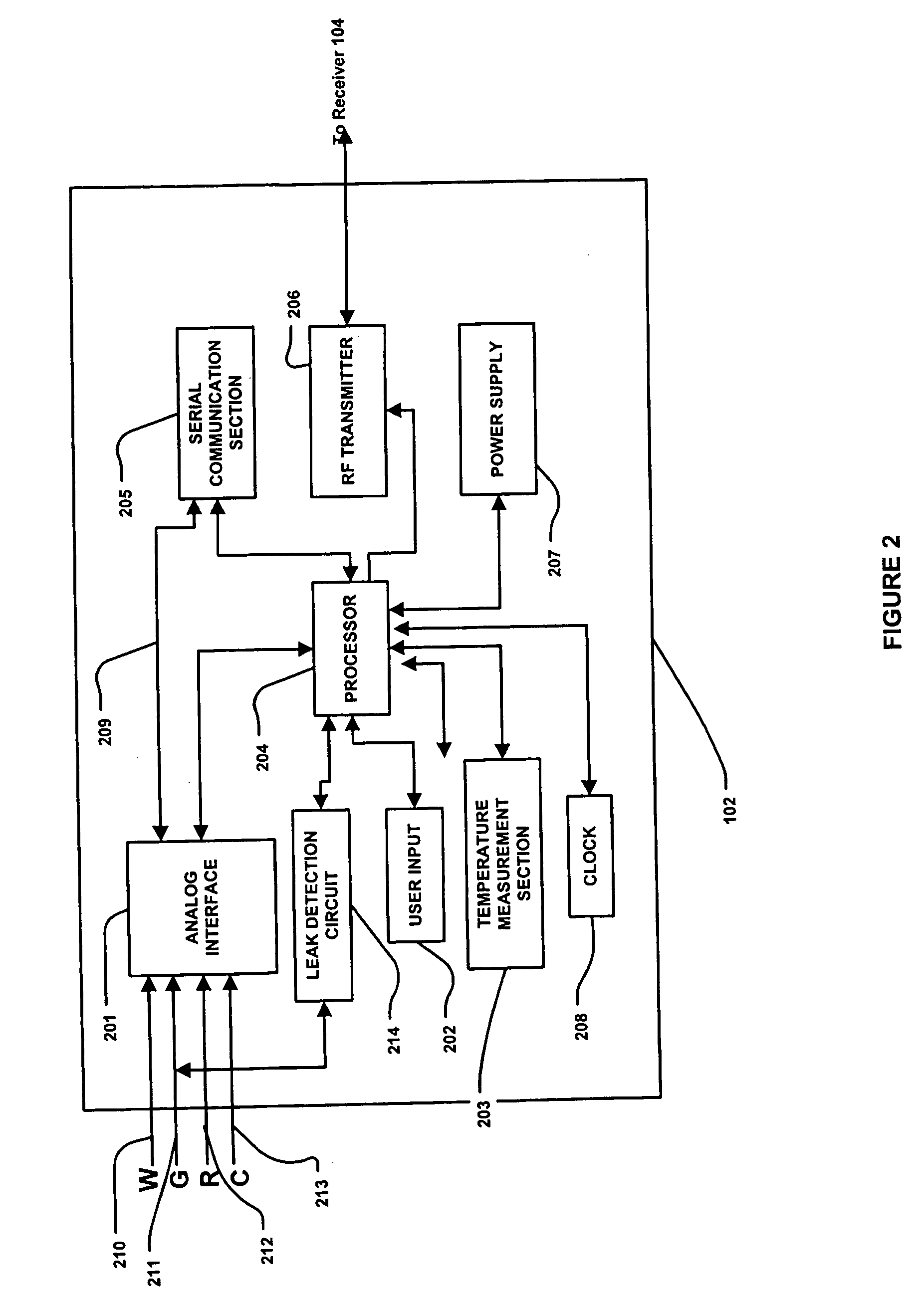
Method and apparatus for providing leak detection in data monitoring and management systems
InactiveUS20060247508A1Resistance/reactance/impedenceFlow propertiesGlucose sensorsMonitoring system
Method and apparatus for providing a leak detection circuit for data monitoring and management system using the guard trace of a glucose sensor by applying a leak detection test signal to determine whether a leakage current is present is provided. The leak detection circuit may includes an interface circuit such as a capacitor coupled to the guard trace to detect the leakage current when the leak detection test signal is applied to the guard trace, such that the user or patient using the data monitoring and management system such as glucose monitoring systems may be promptly and accurately notified of a failed sensor, and to alert the user to replace the sensor.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
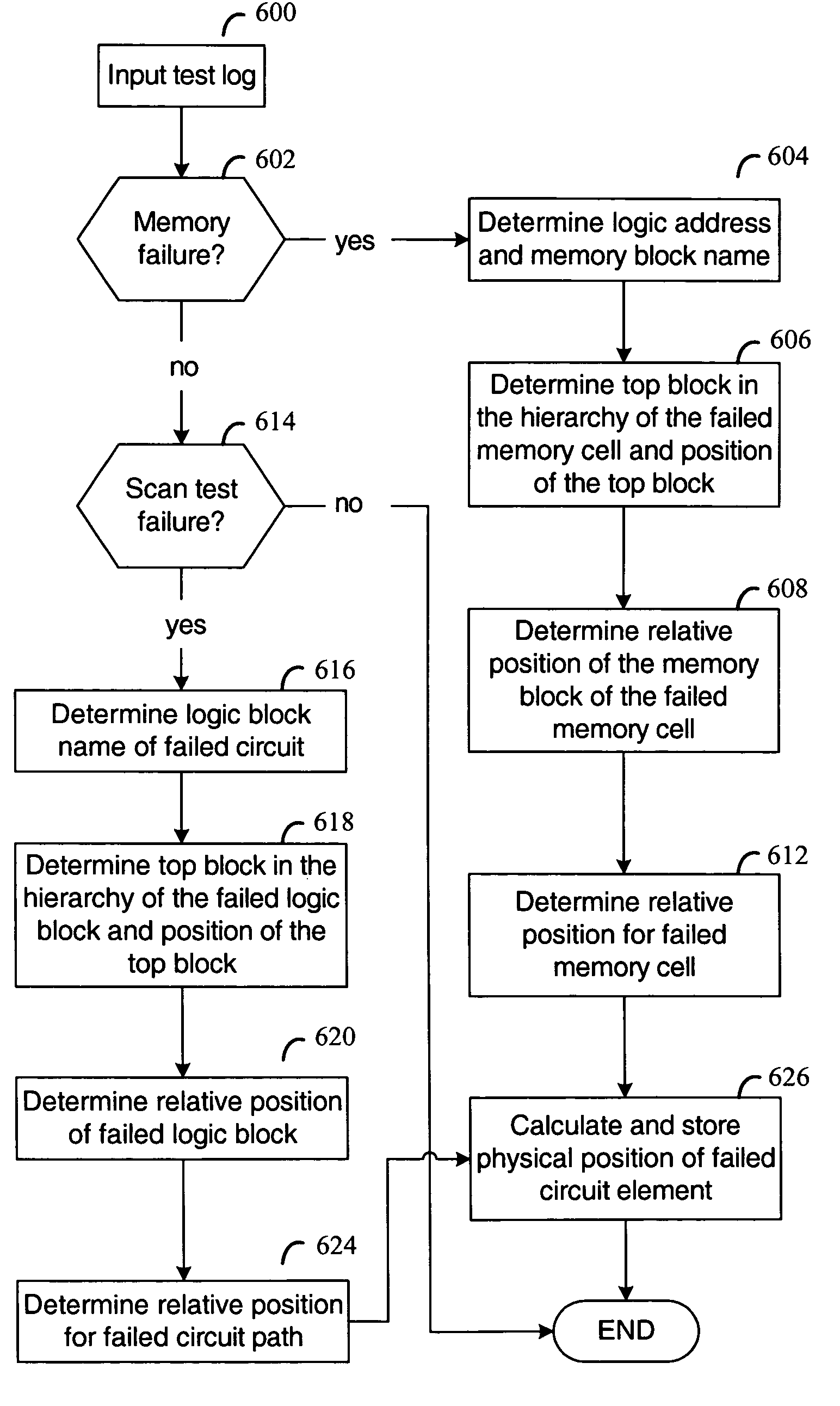
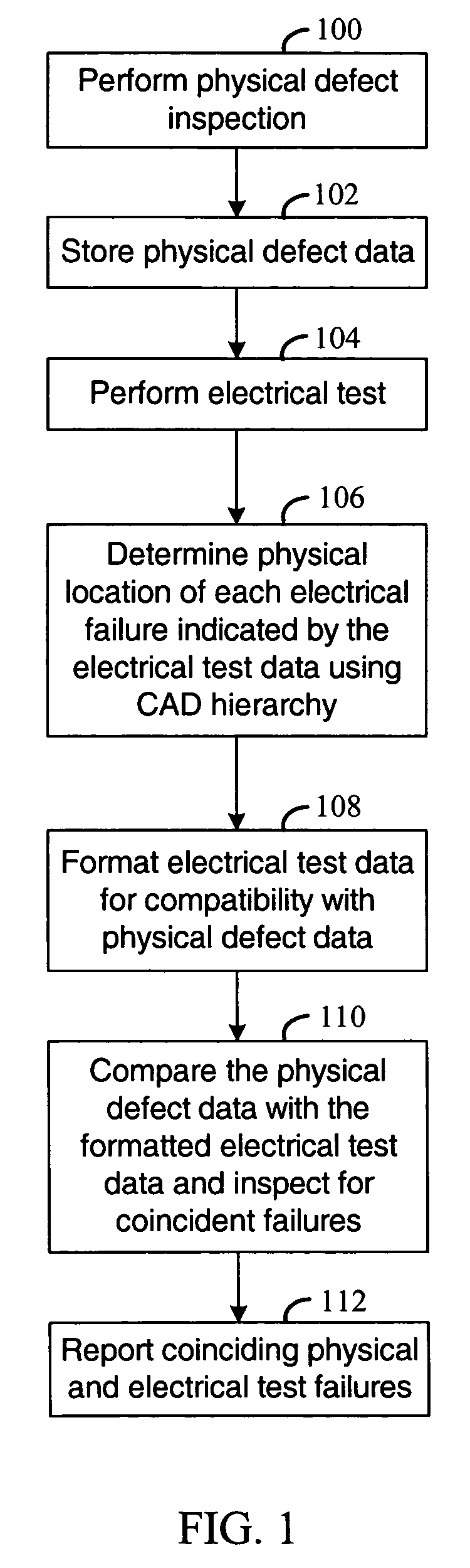
Correlation of electrical test data with physical defect data
ActiveUS6950771B1Improve yield analysisEasy to analyzeResistance/reactance/impedenceElectronic circuit testingData setDesign testing
Method and apparatus are disclosed for analyzing defect data produced in testing a semiconductor chip from a logic design. In various embodiments, input for processing is a first inspection data set that identifies a first set of physical locations that are associated with defects detected during fabrication of the chip. Also input is a second test data set that includes one or more identifiers associated with failing circuitry in the chip. A second set of physical locations is determined from the one or more identifiers of failing circuitry, hierarchical relationships between blocks of the design, and placement information associated with the blocks. Each of the one or more identifiers is associated with at least one of the blocks. Correspondences are identified between physical locations in the first inspection data set and the second set of physical locations.
Owner:XILINX INC
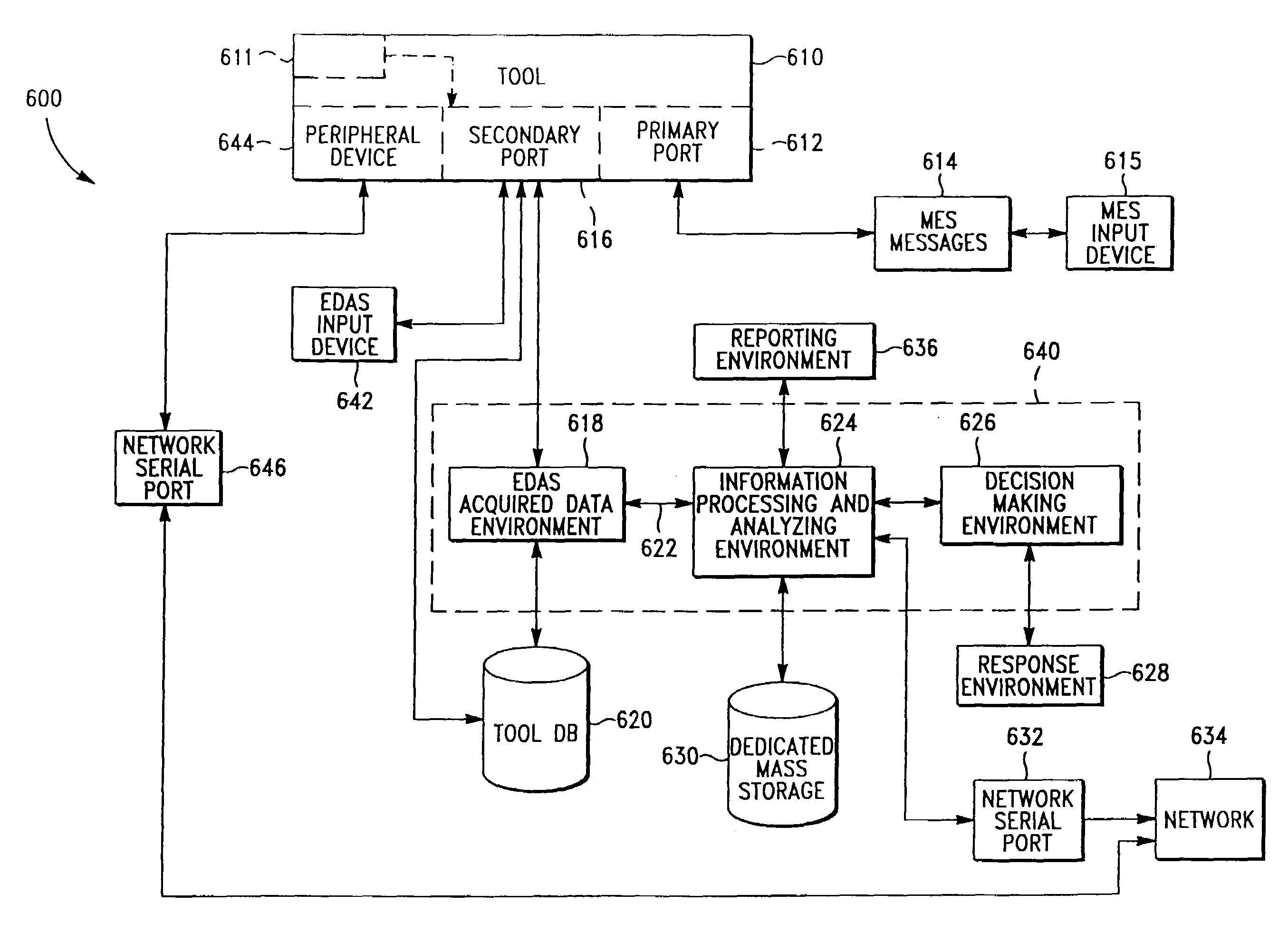
Wafer fabrication data acquisition and management systems
InactiveUS6952656B1Improve data transfer performanceIncrease costResistance/reactance/impedenceComputer controlWafer fabricationData acquisition
The present invention provides a semiconductor processing device (800) including a tool (802) having one or more sensors, a primary data communication port (804) and a secondary data communication port (806). A sensor data acquisition subsystem (808) acquires sensor data from the tool via the secondary port (806). The data acquisition subsystem (808) acquires MES operation messages via the primary port (804). Sensor data are communicated to a sensor processing unit (828) of a sensor data processing subsystem (810). The sensor processing unit (828) processes and analyzes the sensor data. Additionally, the processing unit (828) can be adapted for making product or processing related decisions, for example activating an alarm if the process is not operating within control limits. In another embodiment, the present invention provides a method and apparatus for processing data from a wafer fab facility (1000) including a plurality of tools (1004–1010) each having a primary data communication port (1012–1018) and a secondary data communication port (1042–1048).
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
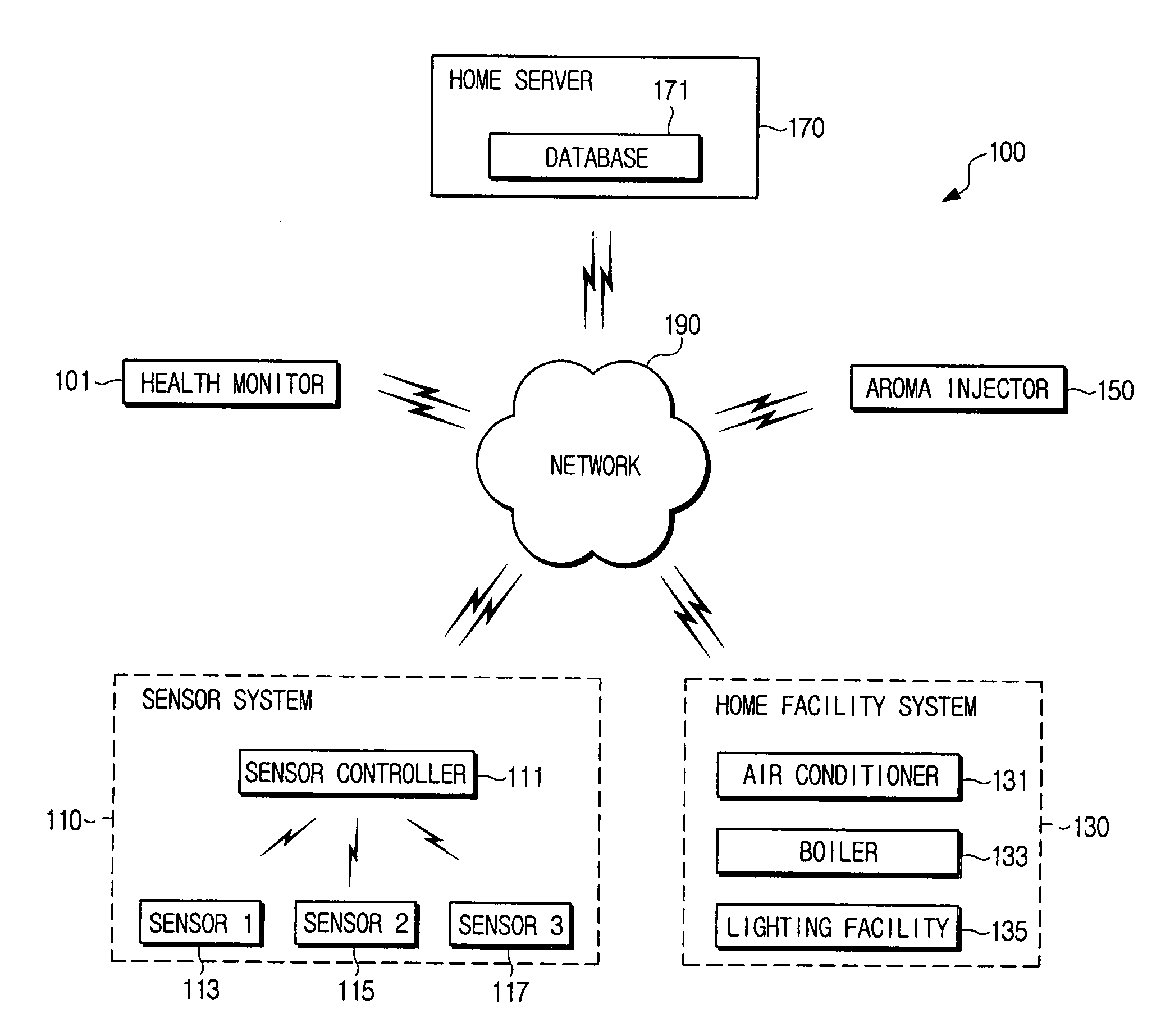
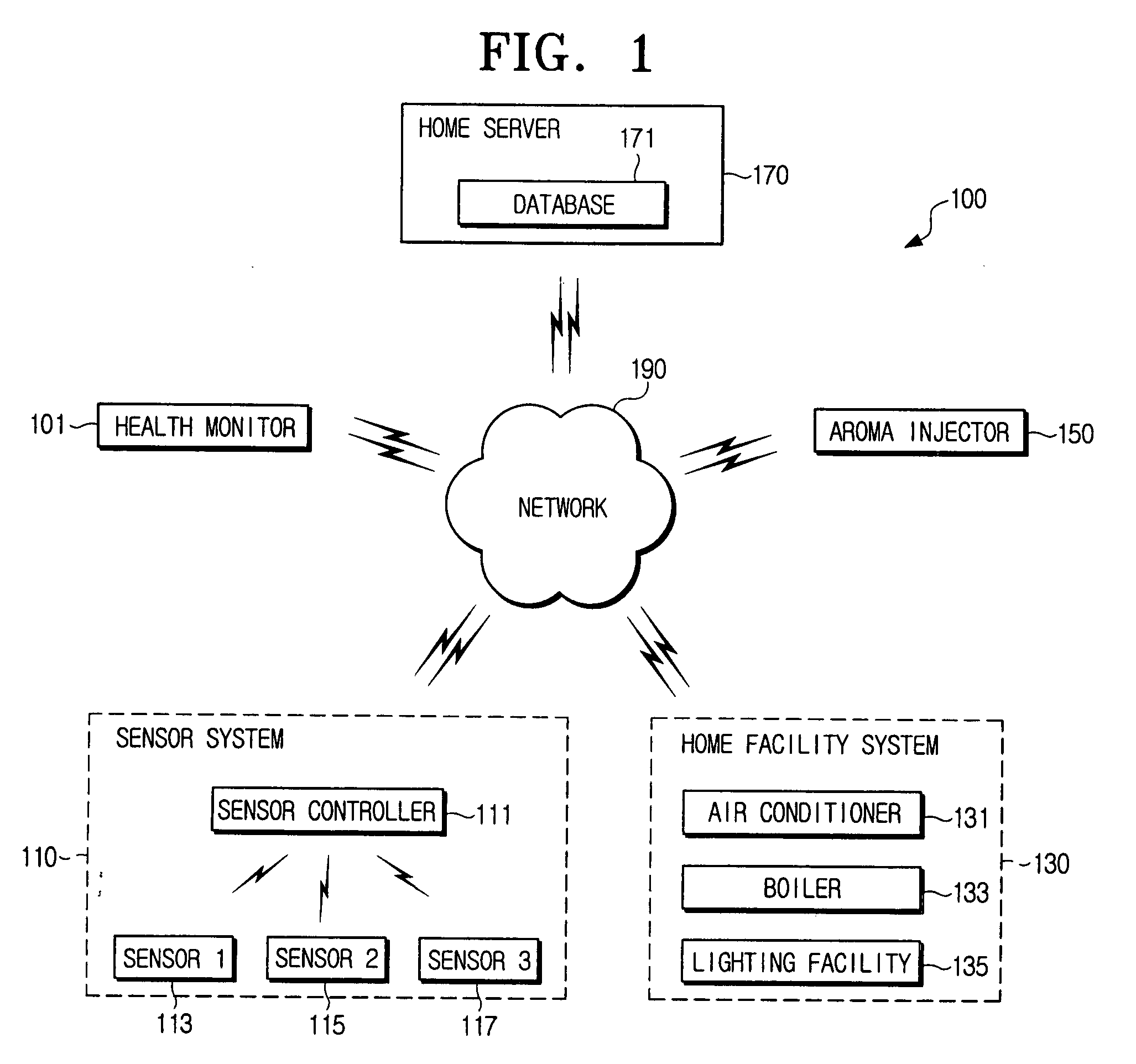
Home control system using galvanic skin response and heart rate and method thereof
InactiveUS20060142968A1Improve sleep environmentSpecial service provision for substationMechanical apparatusElectricitySleep state
A home control system using galvanic skin responses and heart rate information and a method thereof. Whether a user is awake is judged using a galvanic skin response sensor, and the extent of stress of a user is determined using the user's heart rate, thereby extracting a user's emotional state and sleeping state. Furthermore, based on these, various systems in the home network of a user are controlled according to the user's emotional state and sleeping state. In addition, those control results are stored in a database so as to create the optimum control conditions.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
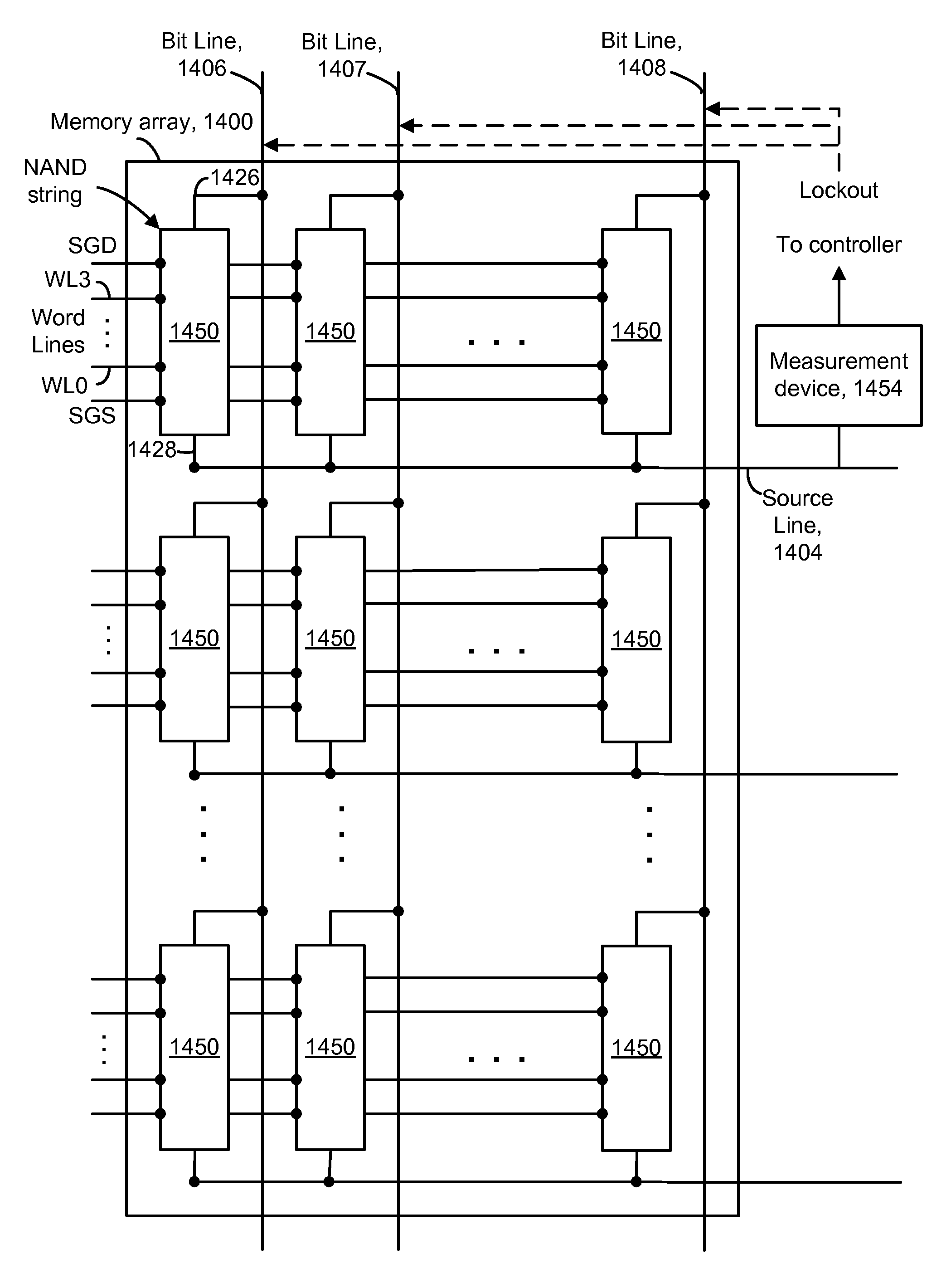
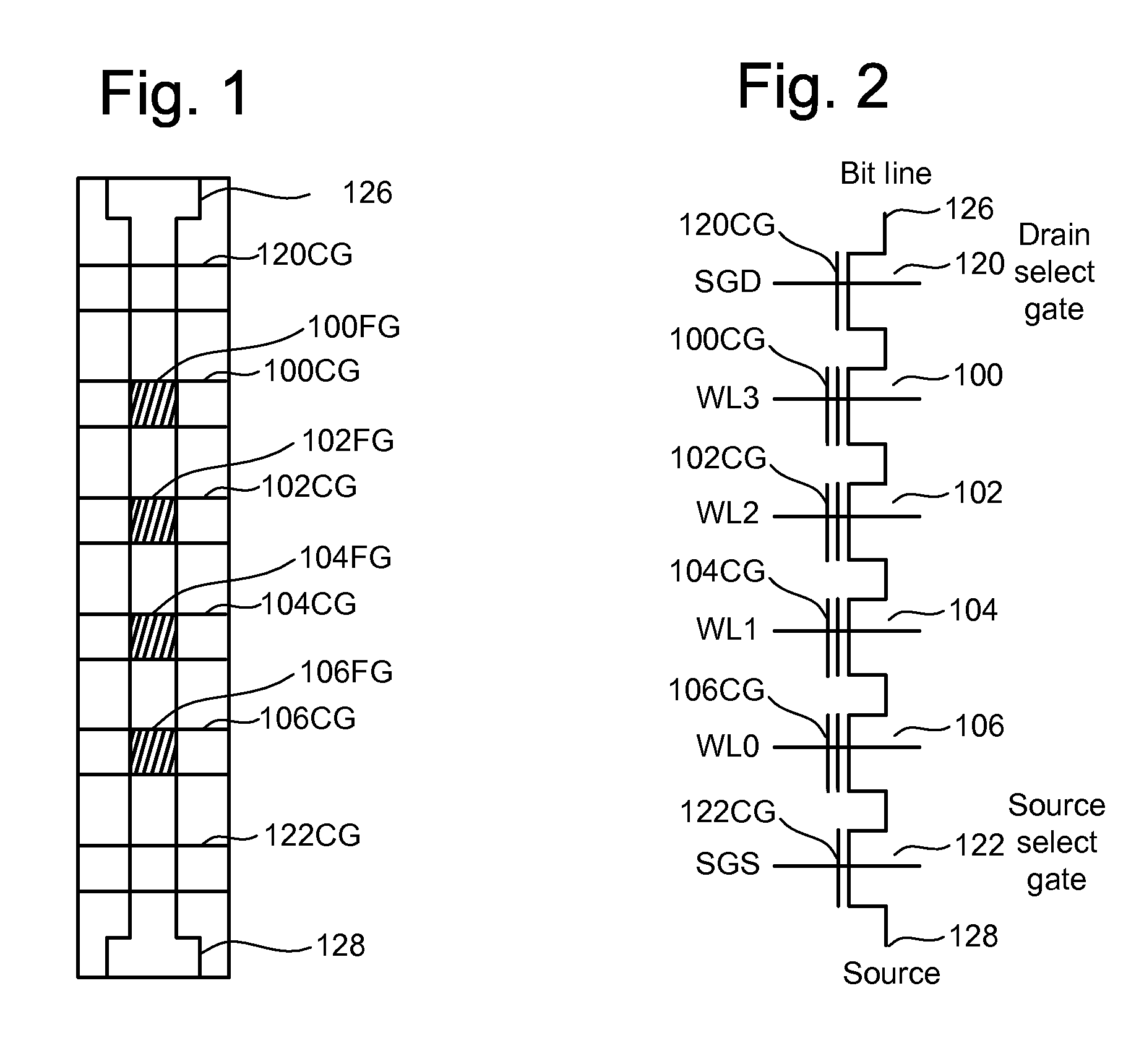
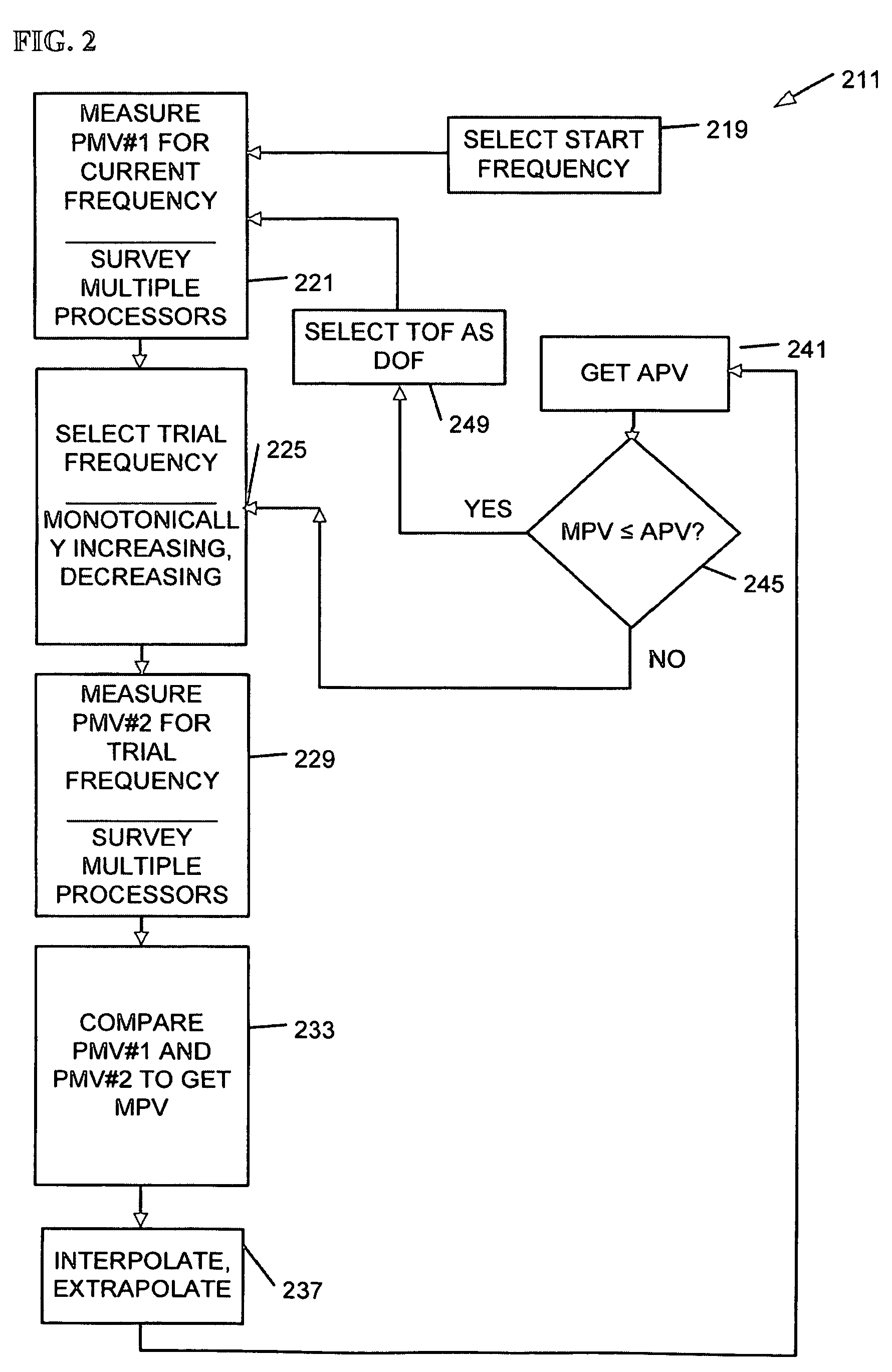
Measuring threshold voltage distribution in memory using an aggregate characteristic
ActiveUS20080285351A1Reduce errorsResistance/reactance/impedenceRead-only memoriesBit lineCapacitance
A threshold voltage distribution of a set of storage elements in a memory device is measured by sweeping a control gate voltage while measuring a characteristic of the set of storage elements as a whole. The characteristic indicates how many of the storage elements meet a given condition, such as being in a conductive state. For example, the characteristic may be a combined current, voltage or capacitance of the set which is measured at a common source of the set. The control gate voltage can be generated internally within a memory die. Similarly, the threshold voltage distribution can be determined internally within the memory die. Optionally, storage elements which become conductive can be locked out, such as by changing a bit line voltage, so they no longer contribute to the characteristic. New read reference voltages are determined based on the threshold voltage distribution to reduce errors in future read operations.
Owner:SANDISK CORP +1
Performance state management
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Performance state management
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
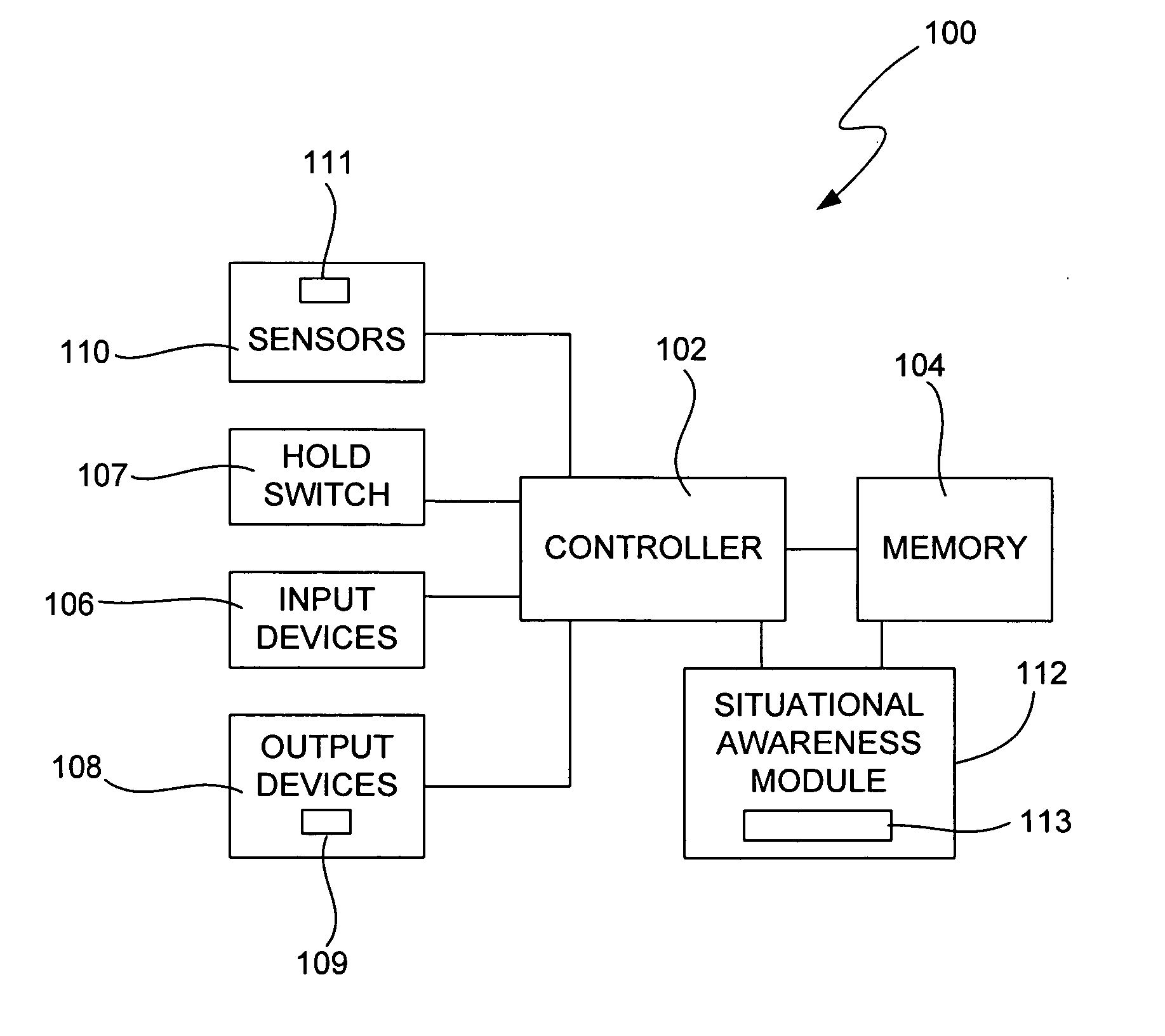
Light activated hold switch
Owner:APPLE INC
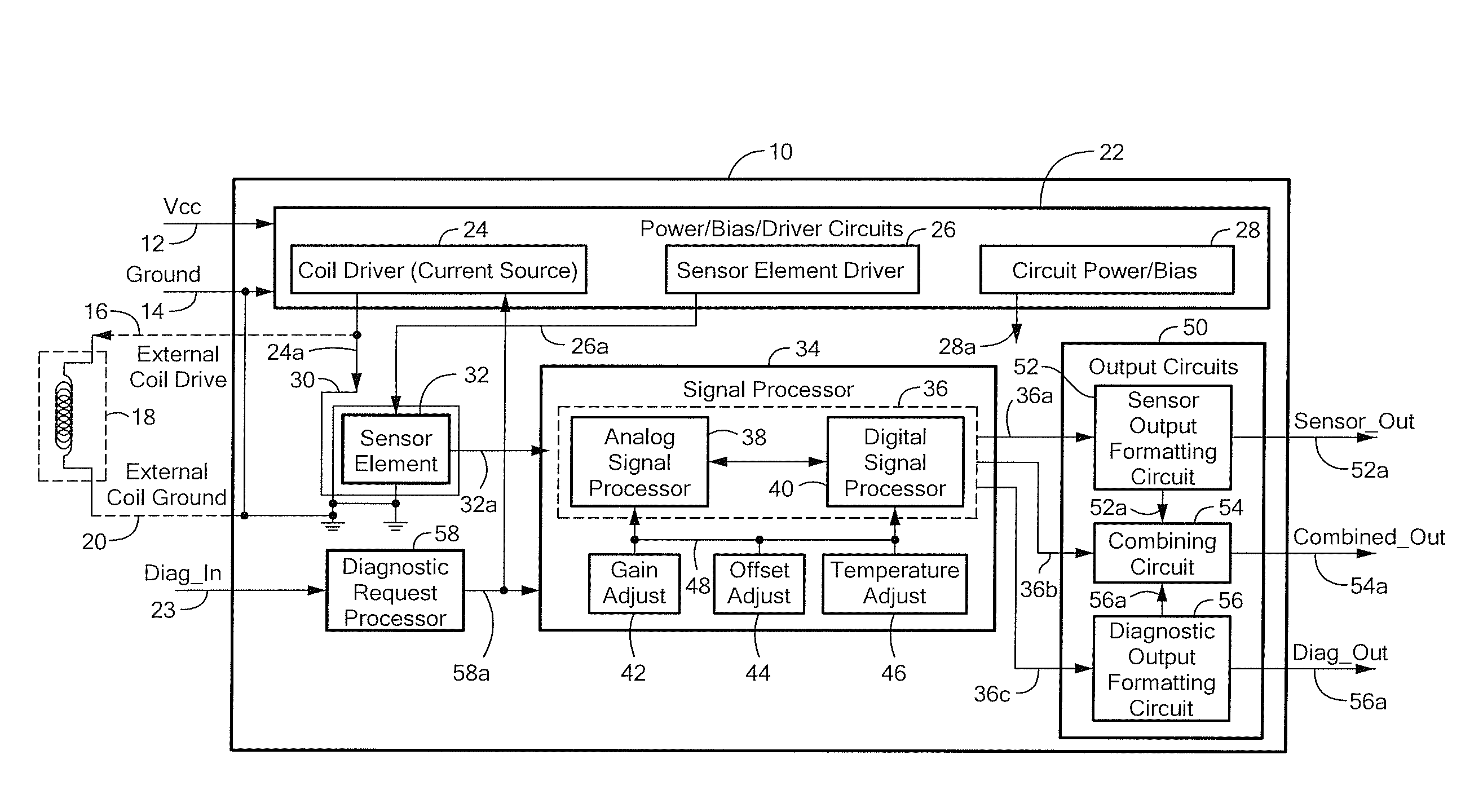
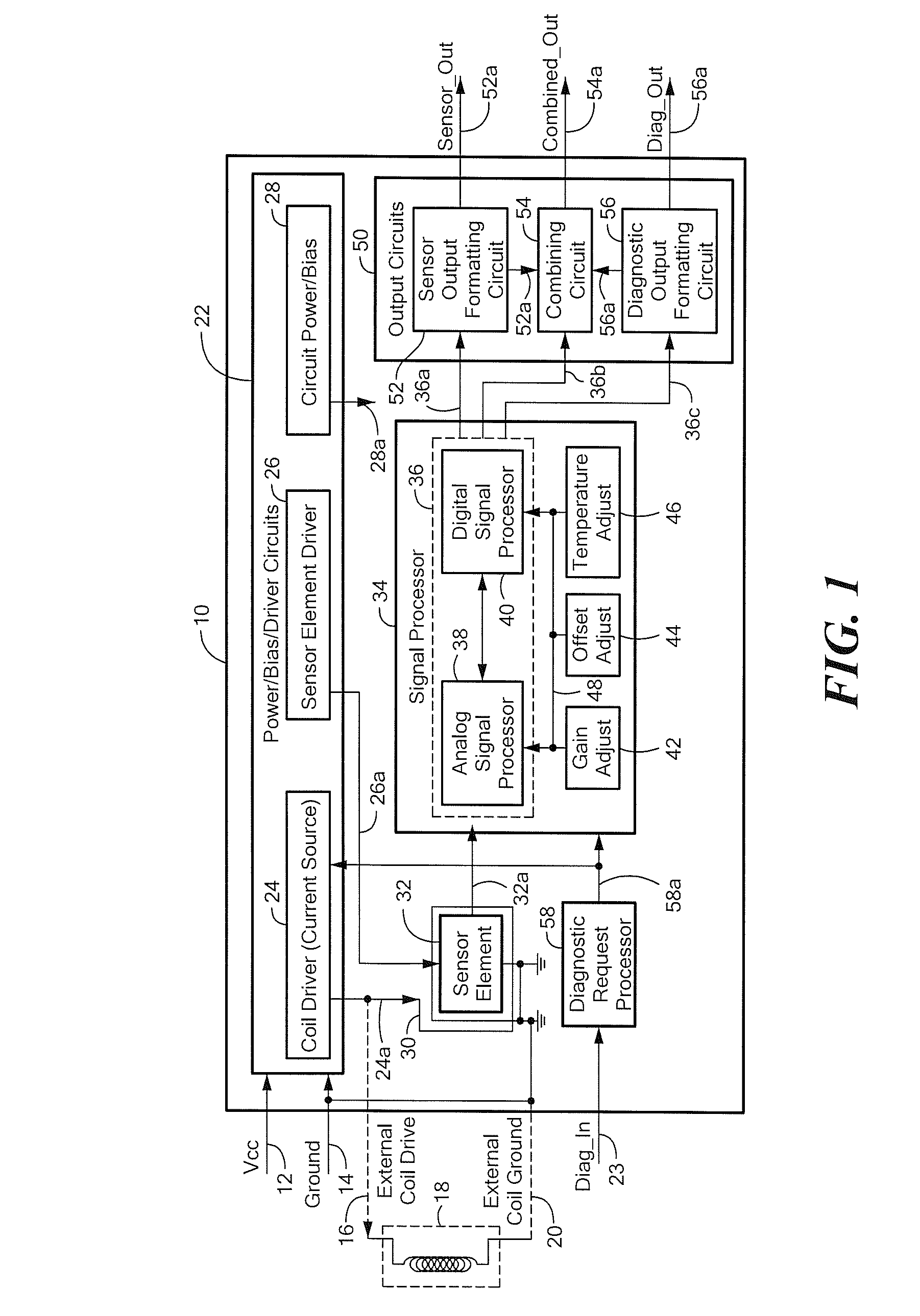
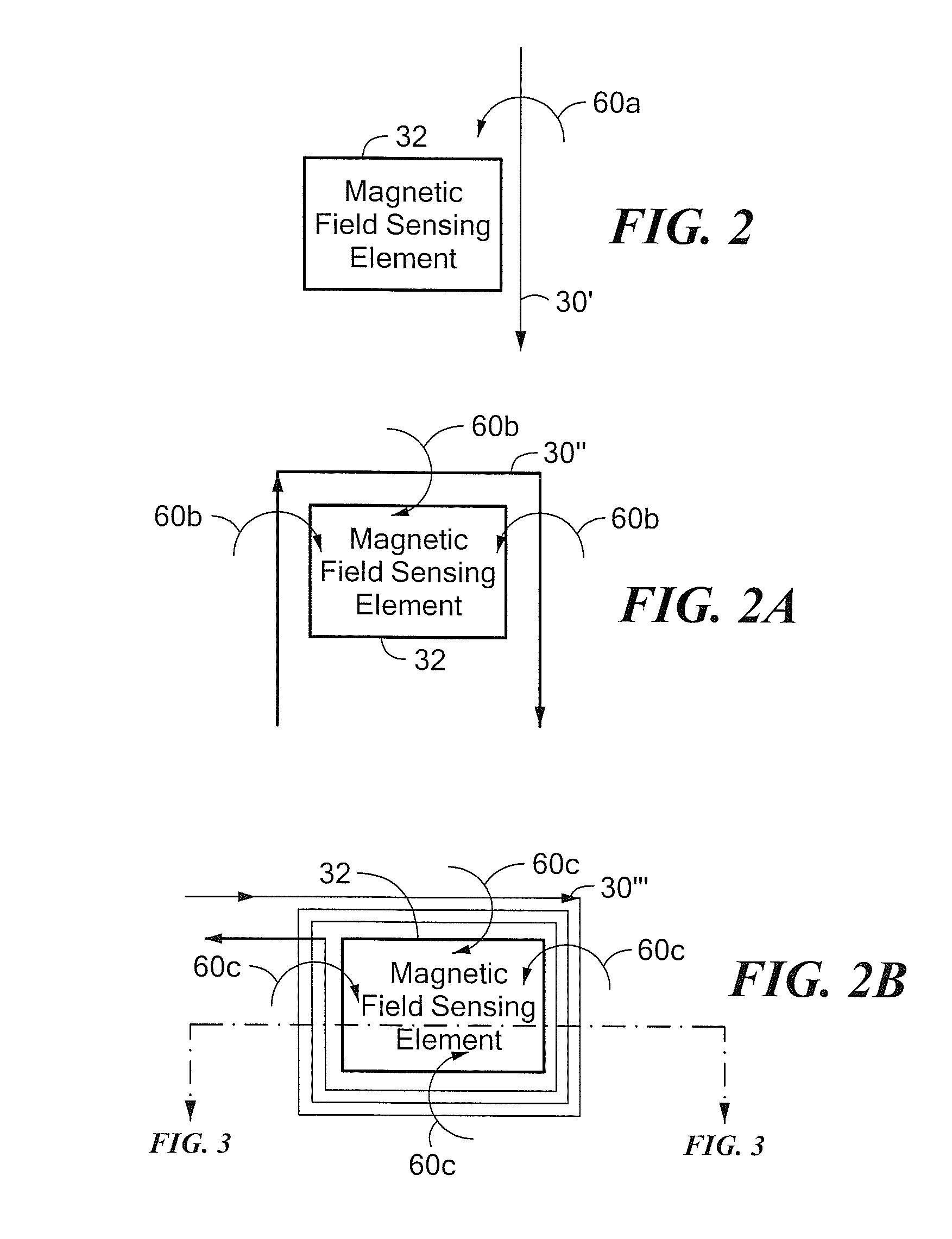
Circuits and Methods for Generating a Self-Test of a Magnetic Field Sensor
ActiveUS20100211347A1Magnetic measurementsAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceBuilt-in self-testCondensed matter physics
A magnetic field sensor includes built in self-test circuits that allow a self-test of most of, or all of, the circuitry of the magnetic field sensor, including self-test of a magnetic field sensing element used within the magnetic field sensor, while the magnetic field sensor is functioning in normal operation.
Owner:ALLEGRO MICROSYSTEMS INC
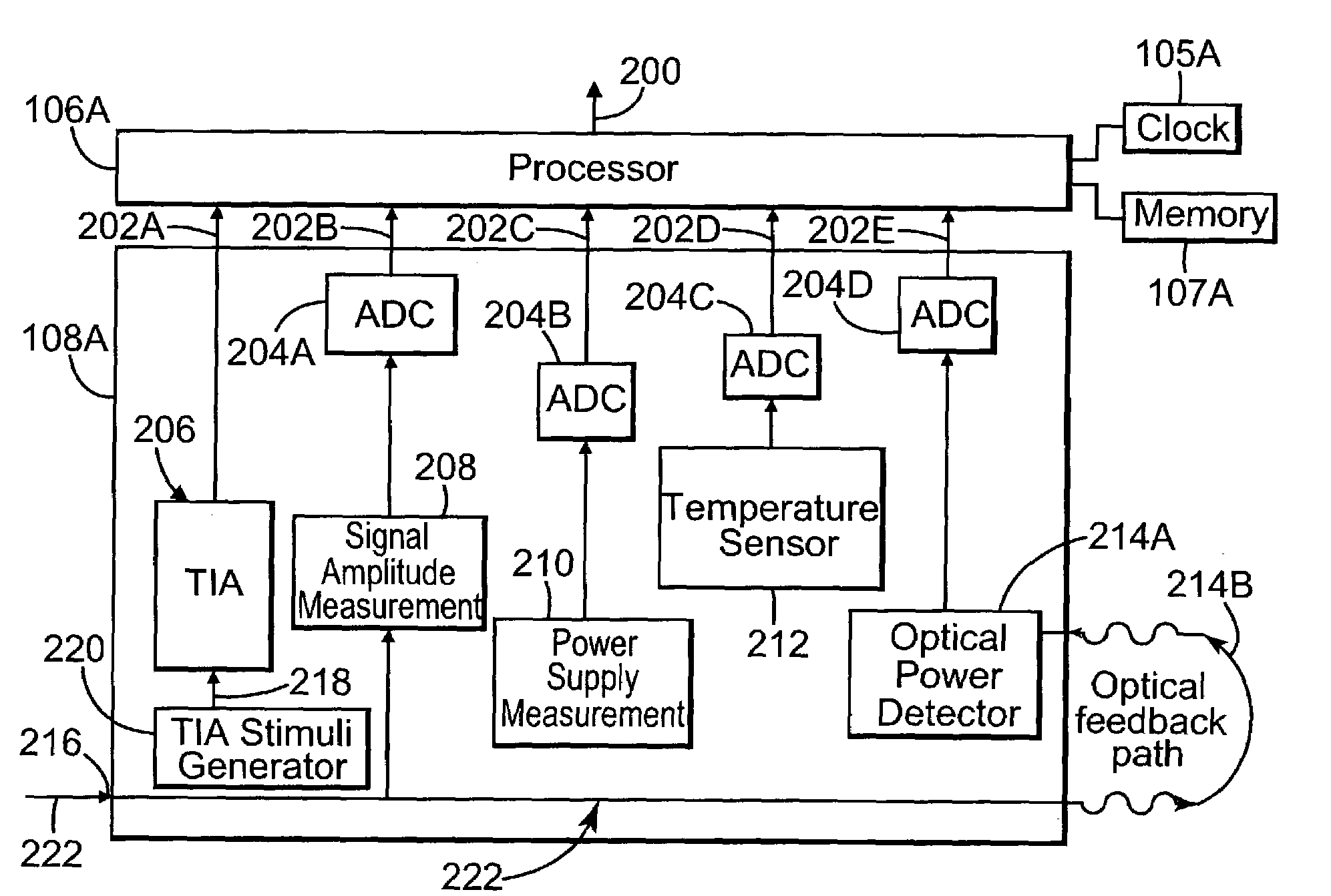
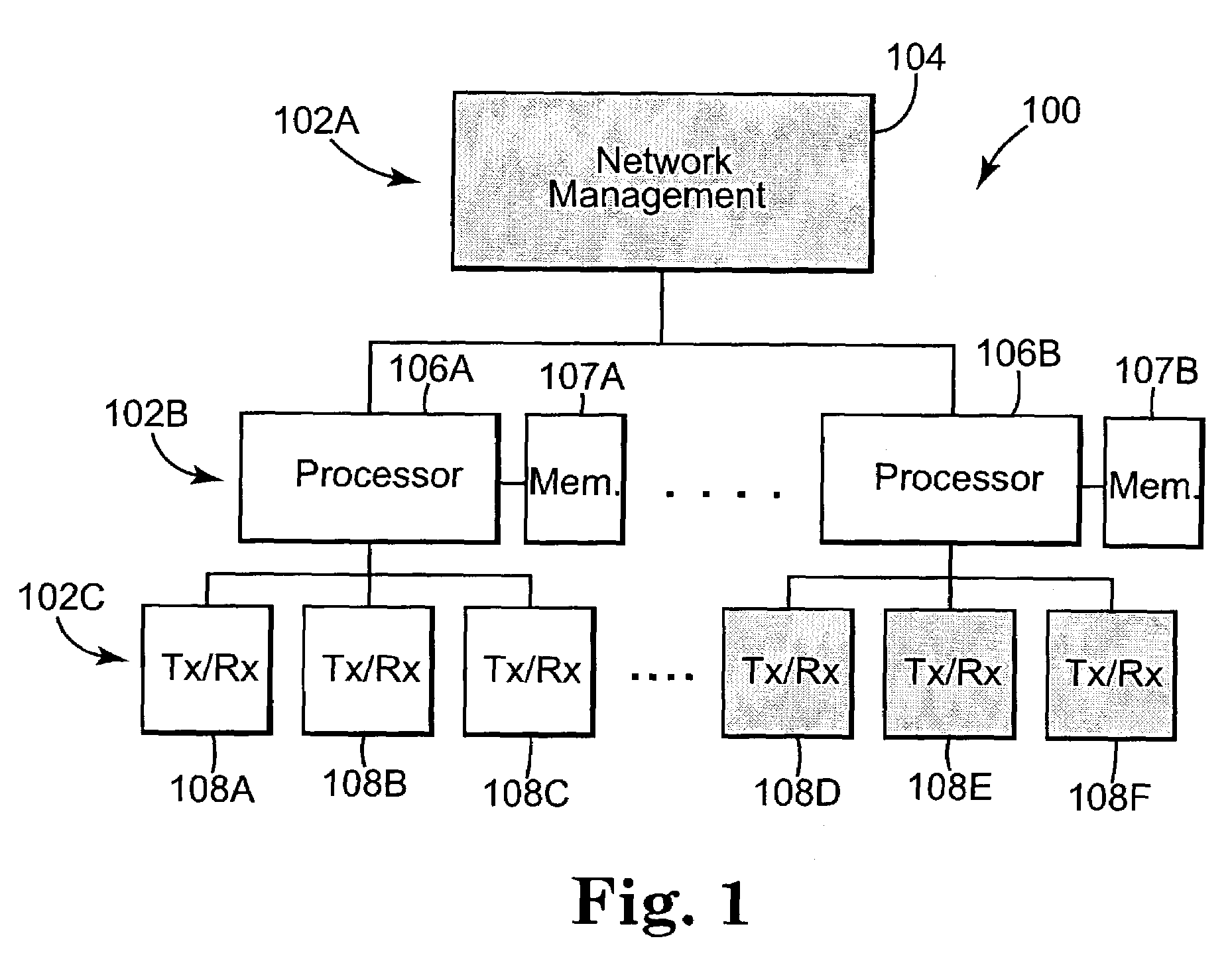
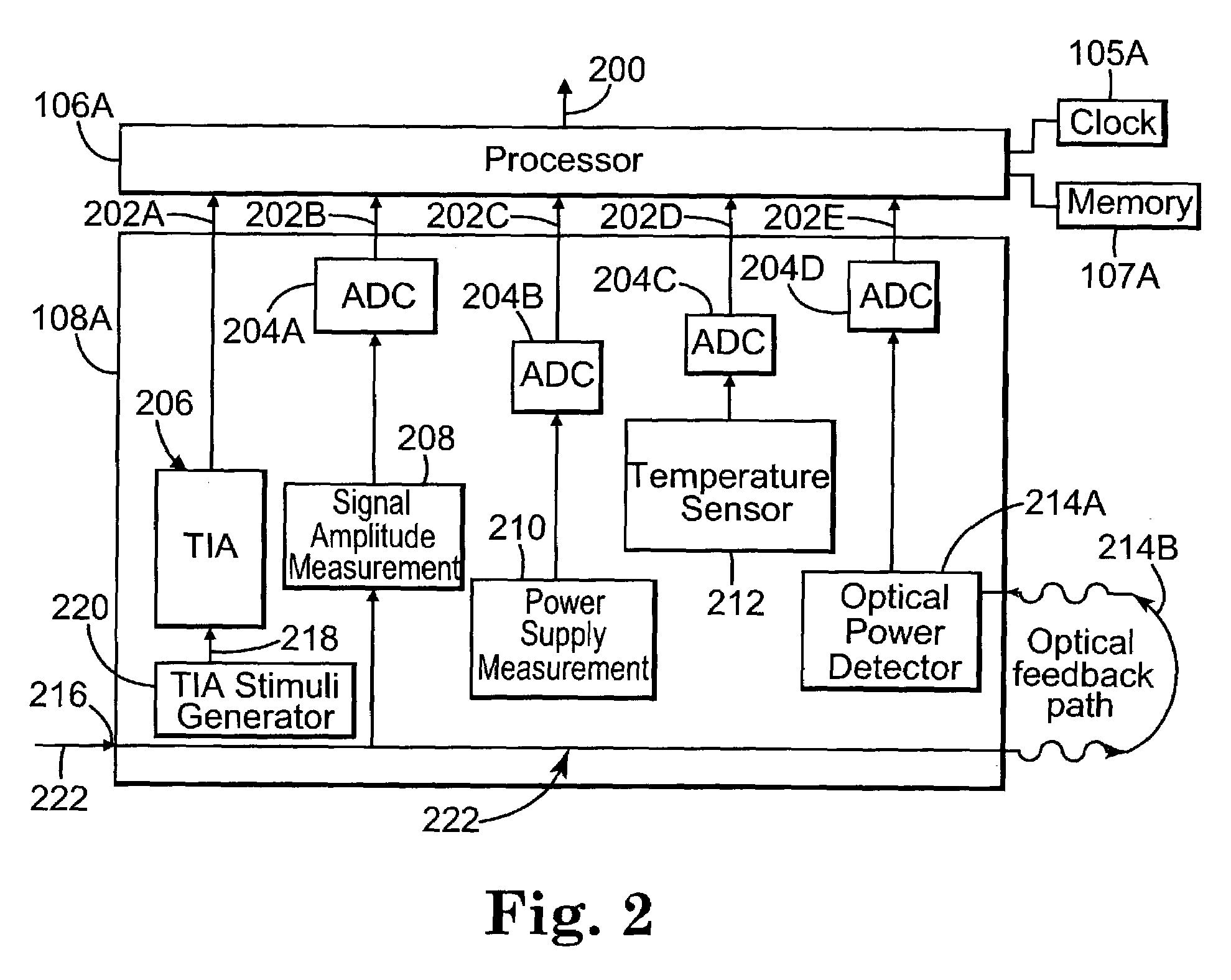
Monitoring system for a communications network
ActiveUS7136772B2Resistance/reactance/impedenceTransmission monitoringMonitoring systemComputer science
A monitoring system for a communications network includes a set of components for transmitting and receiving data signals over the communications network. Each component includes a built-in self-test system for performing tests within the component and outputting corresponding test results. Each self-test system is configured to non-invasively determine waveform characteristics of the data signals. The system includes a set of processors. Each processor is coupled to a subset of the set of components, and is configured to evaluate the test results output by the components coupled to the processor. Each processor is configured to detect and predict faults in the communications network based on the evaluation of the test results.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
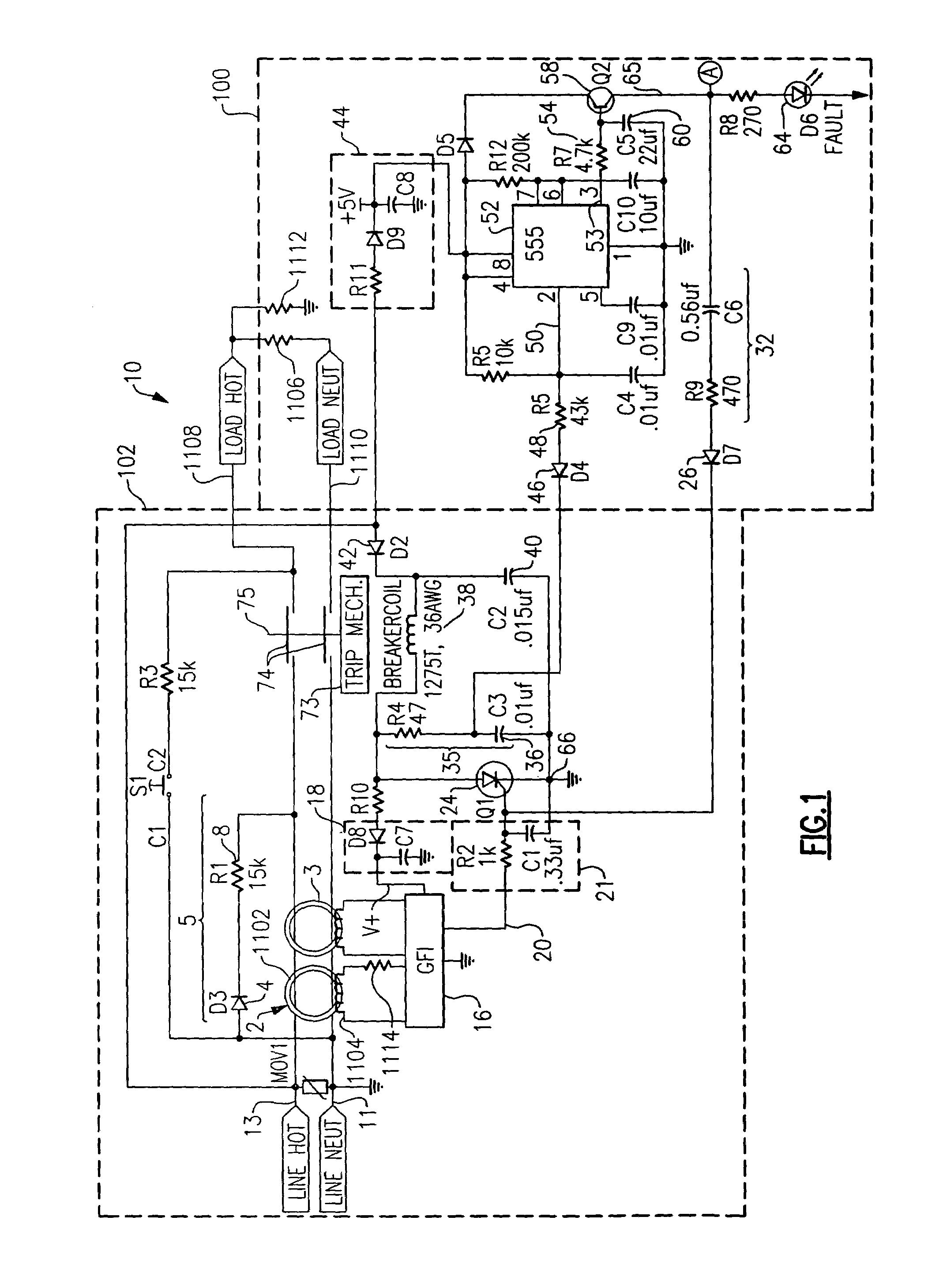
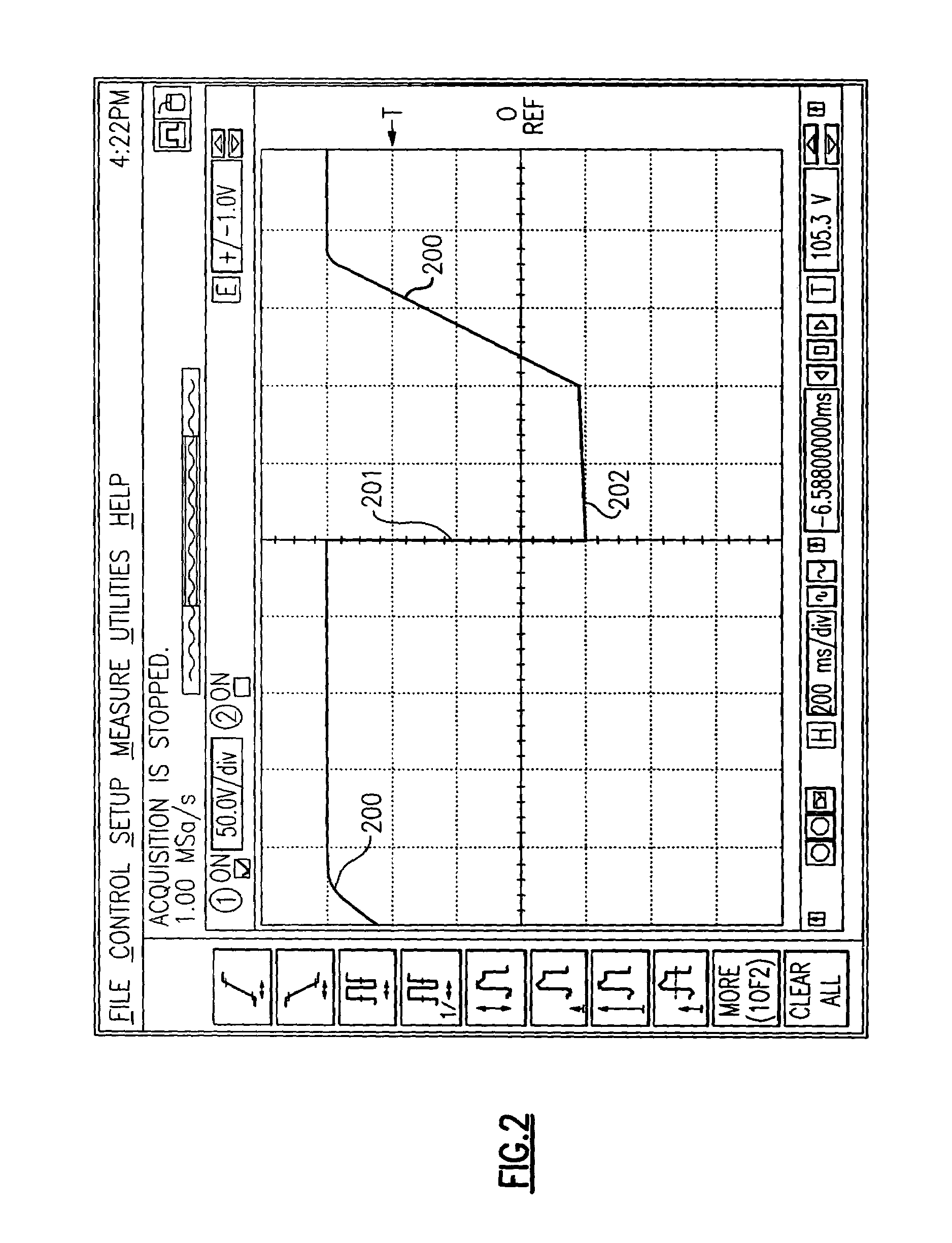
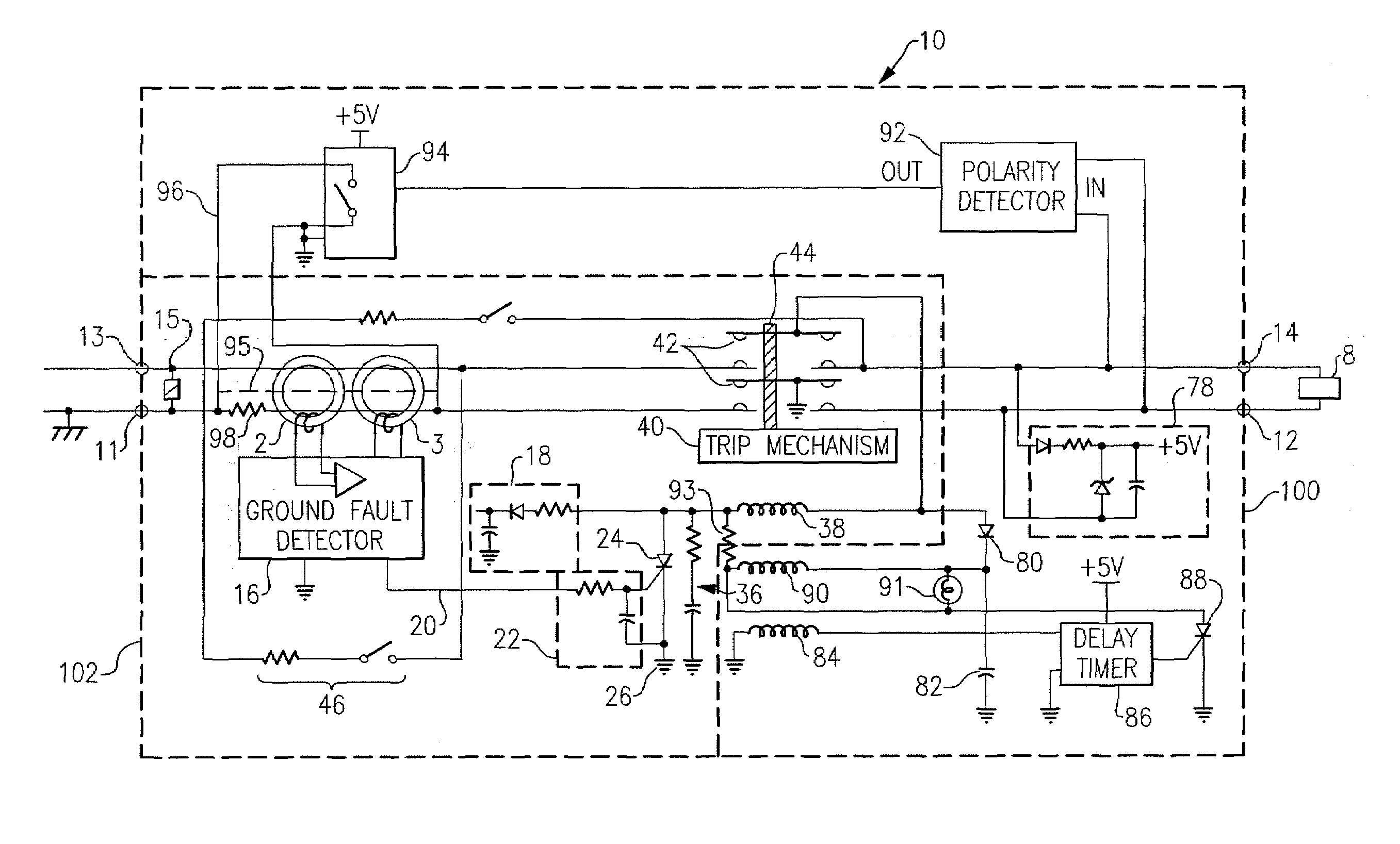
Intelligent life testing methods and apparatus for leakage current protection
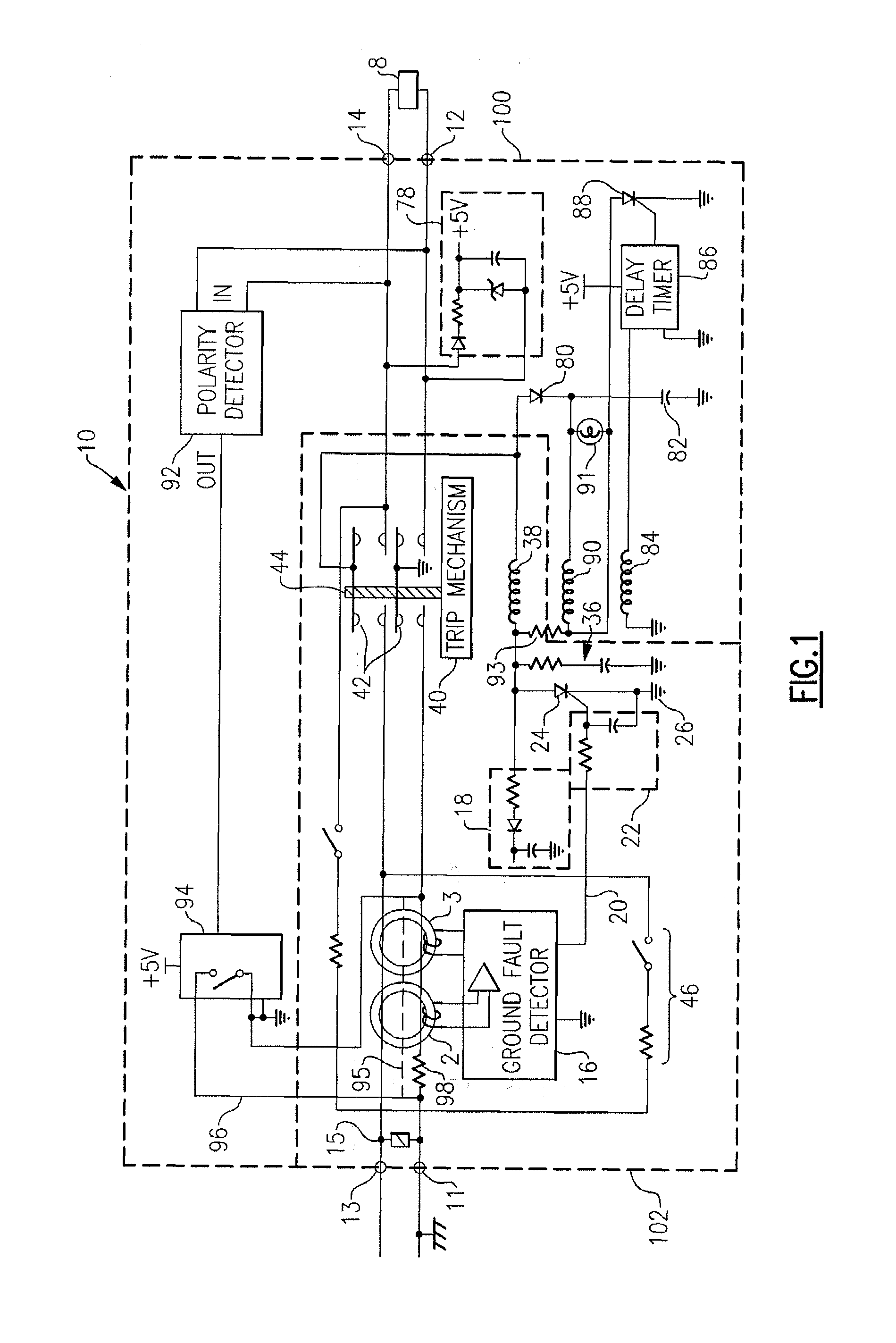
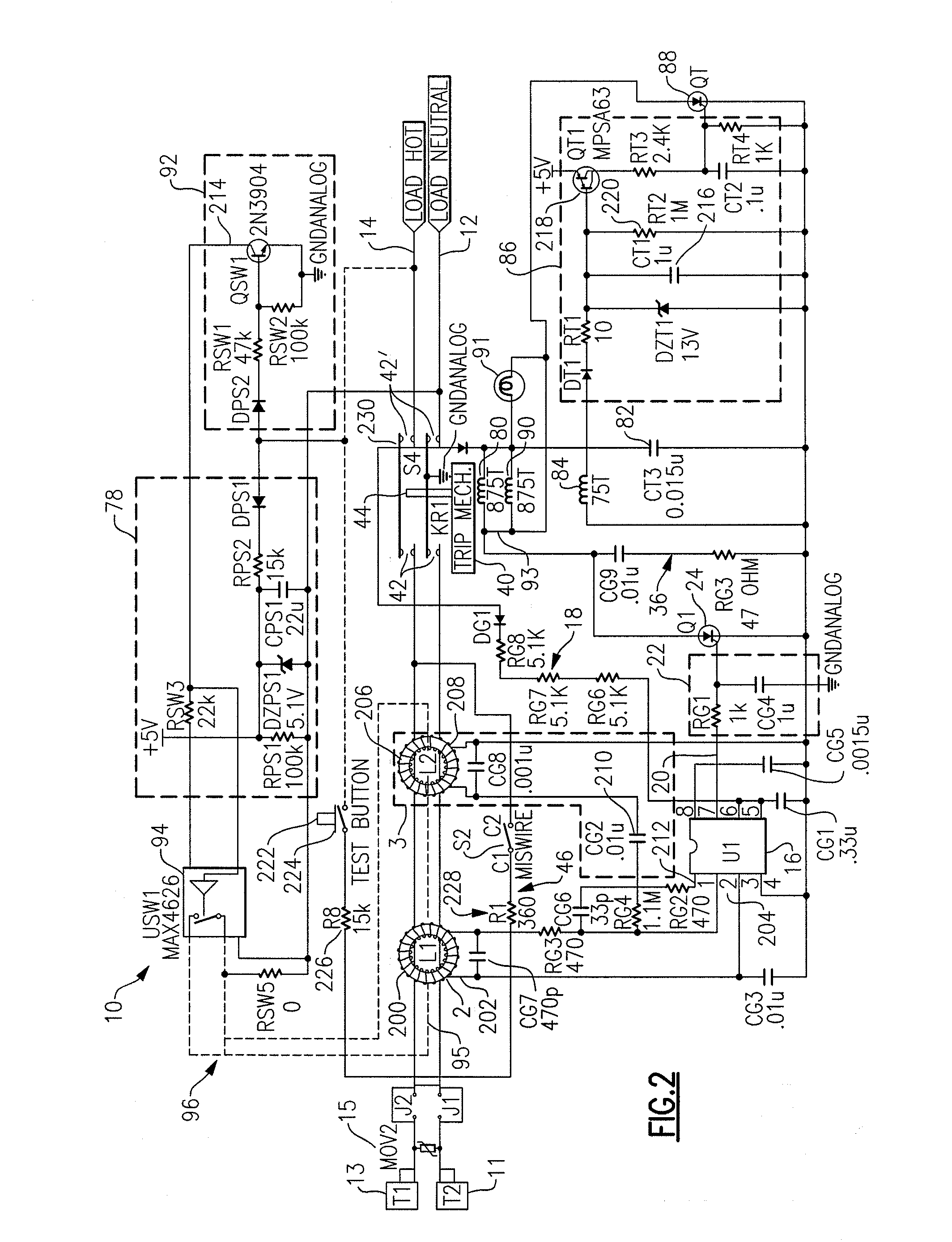
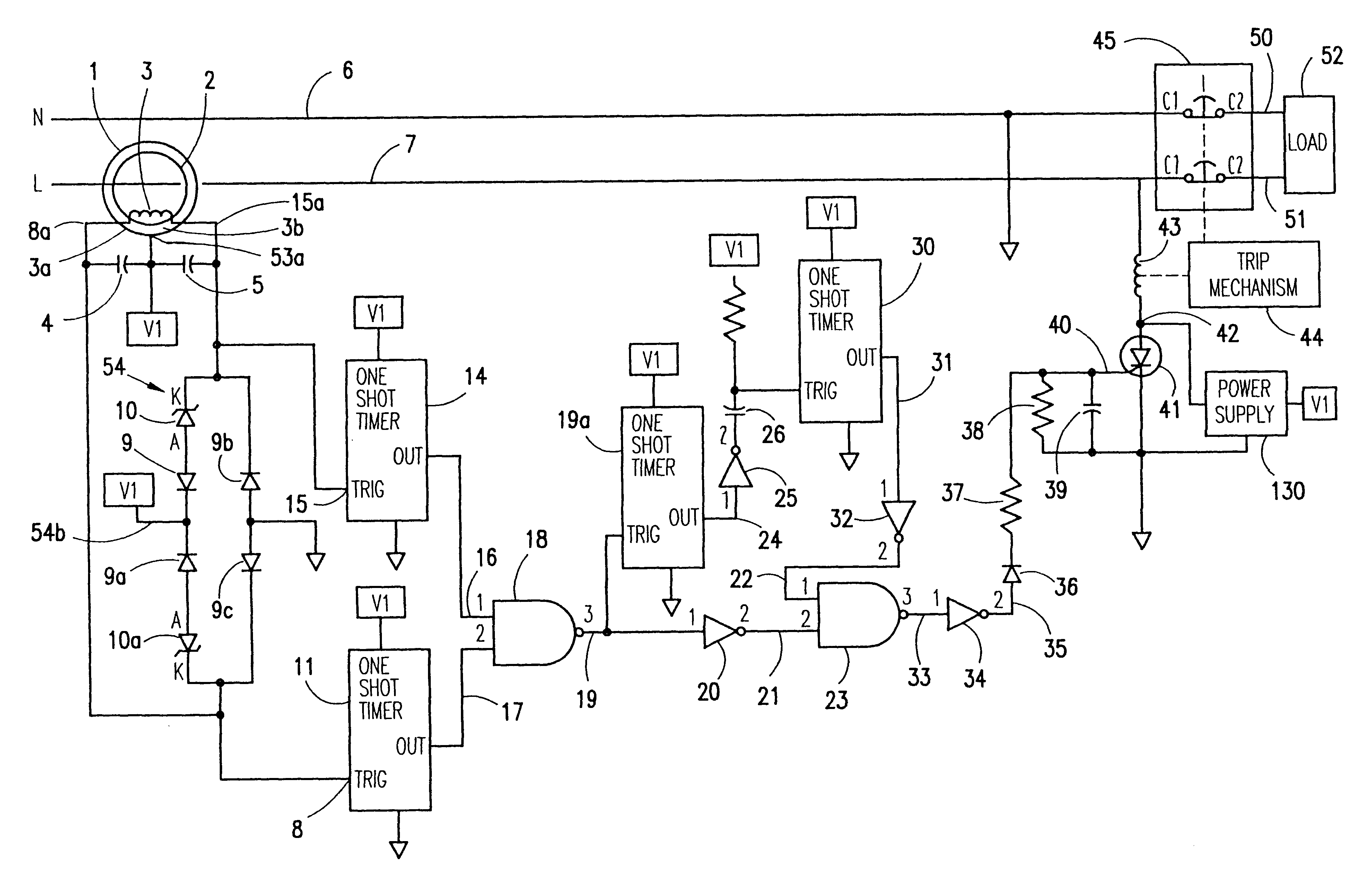
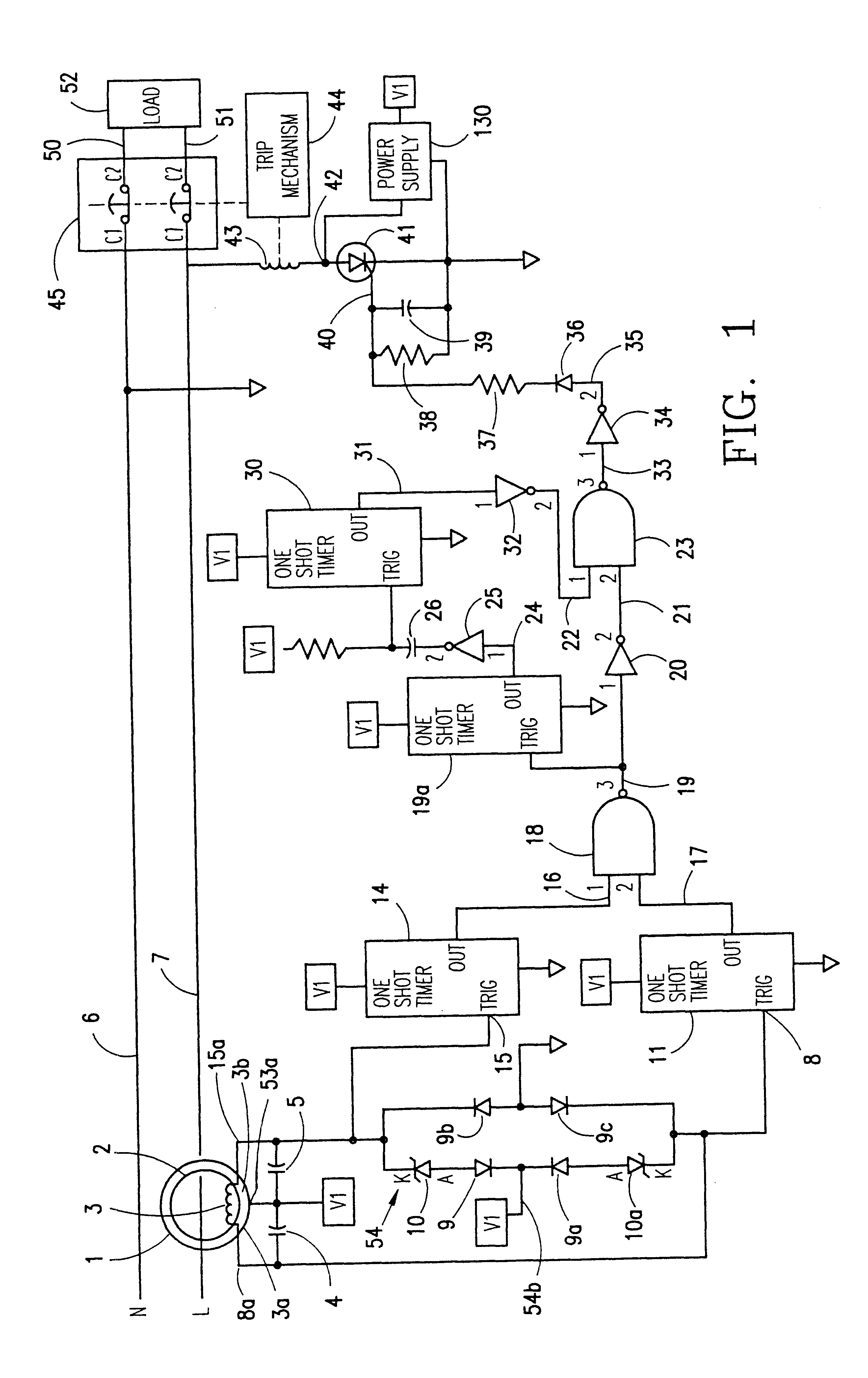
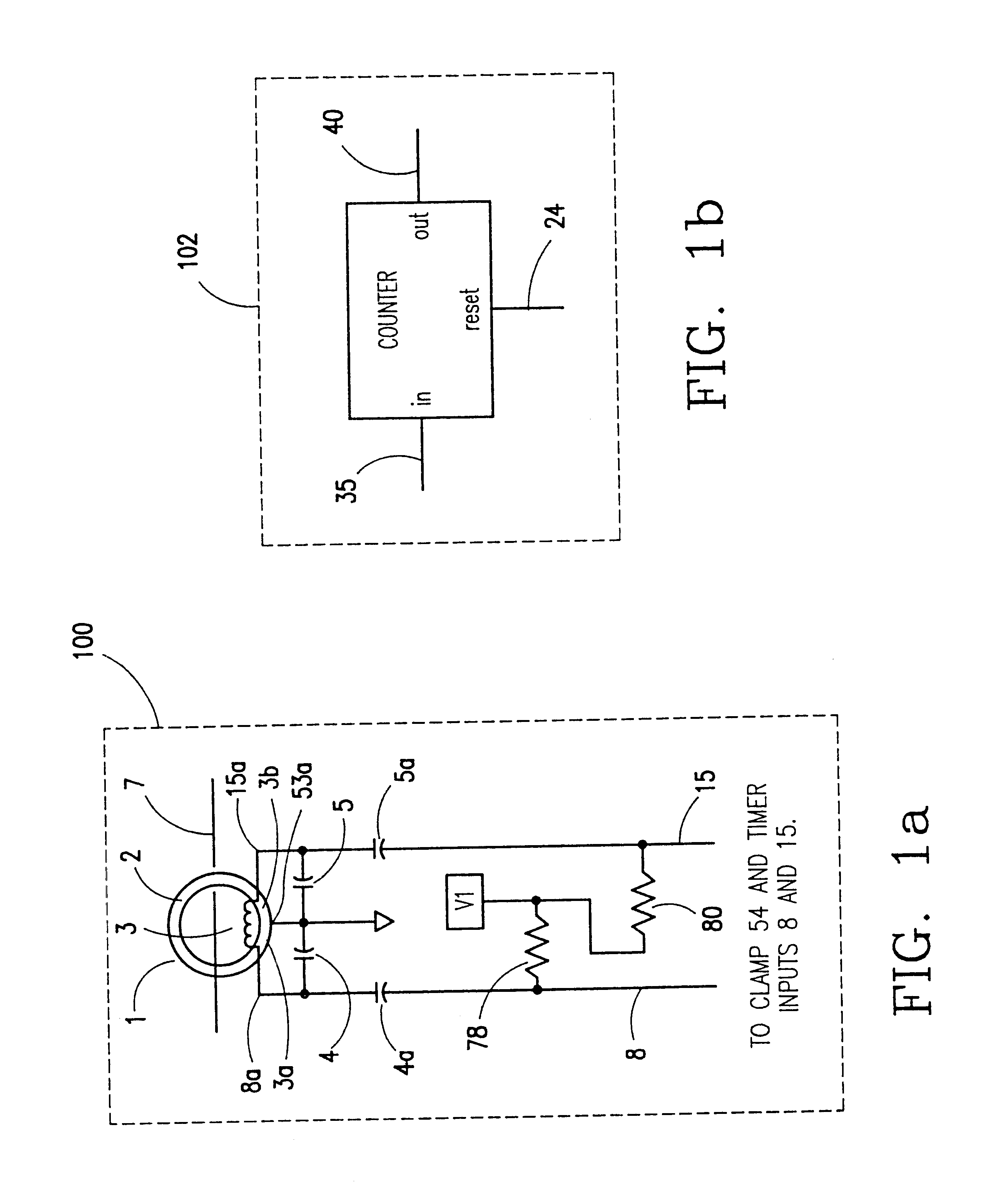
ActiveUS20070164750A1Short-circuit testingEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionEngineeringLife testing
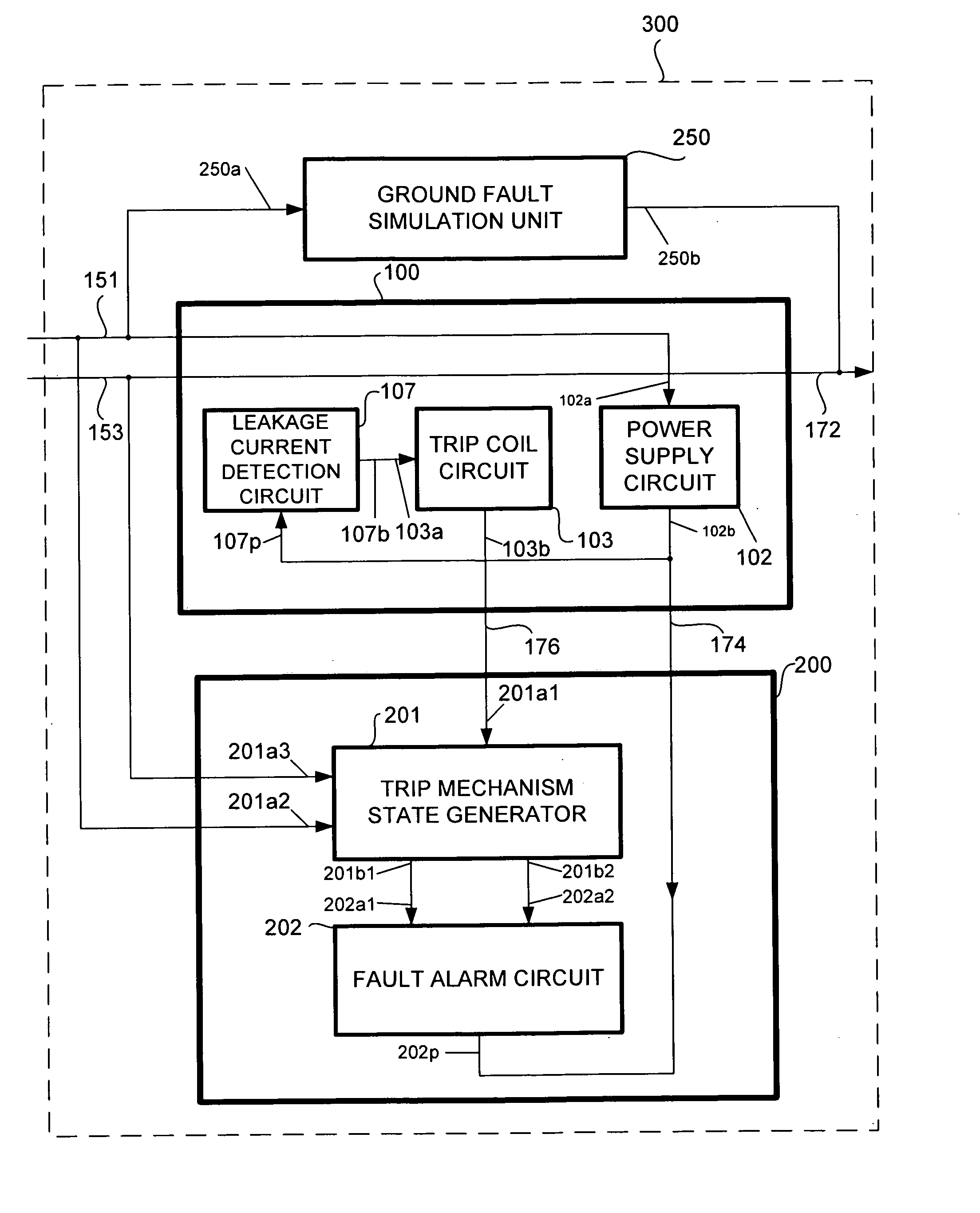
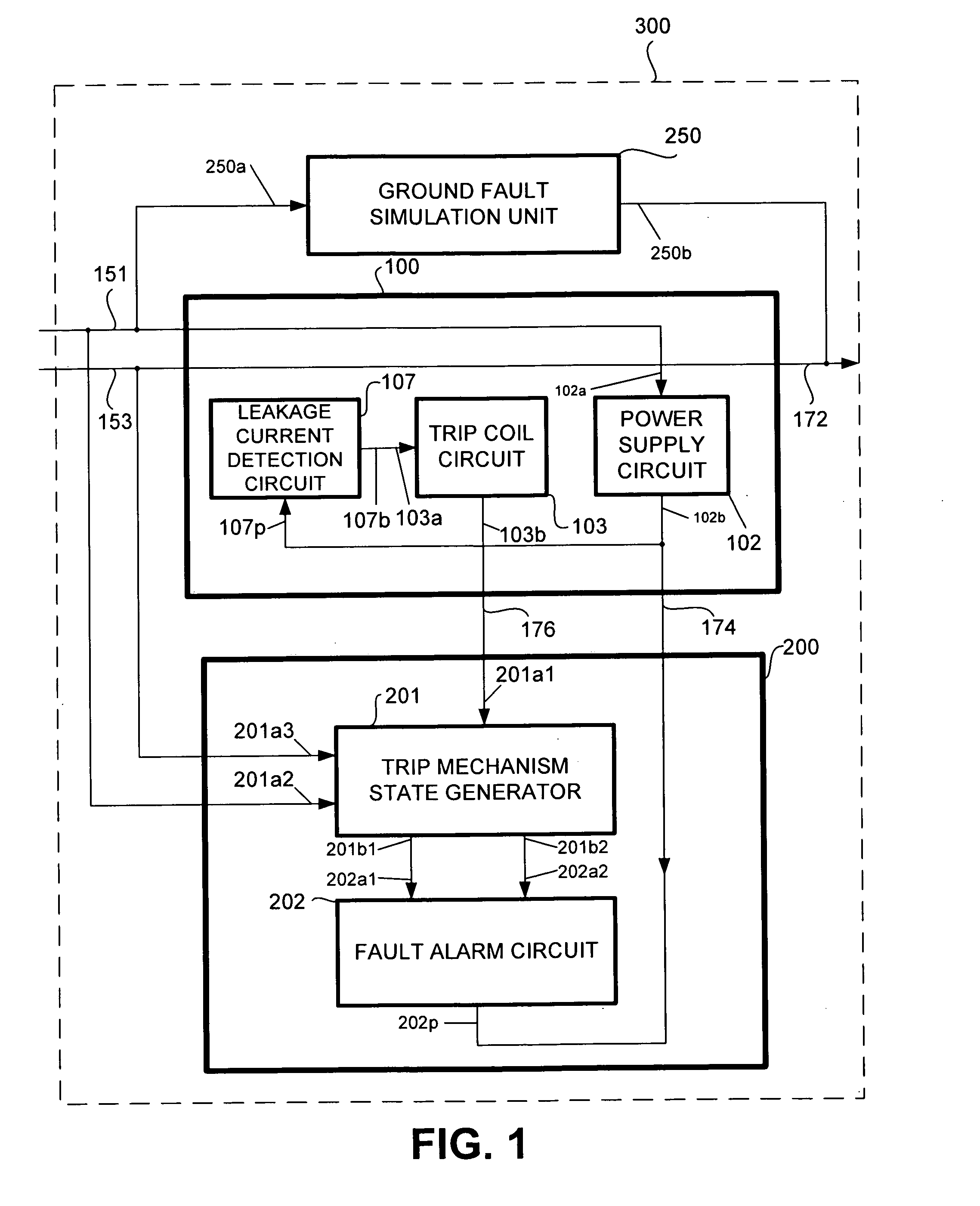
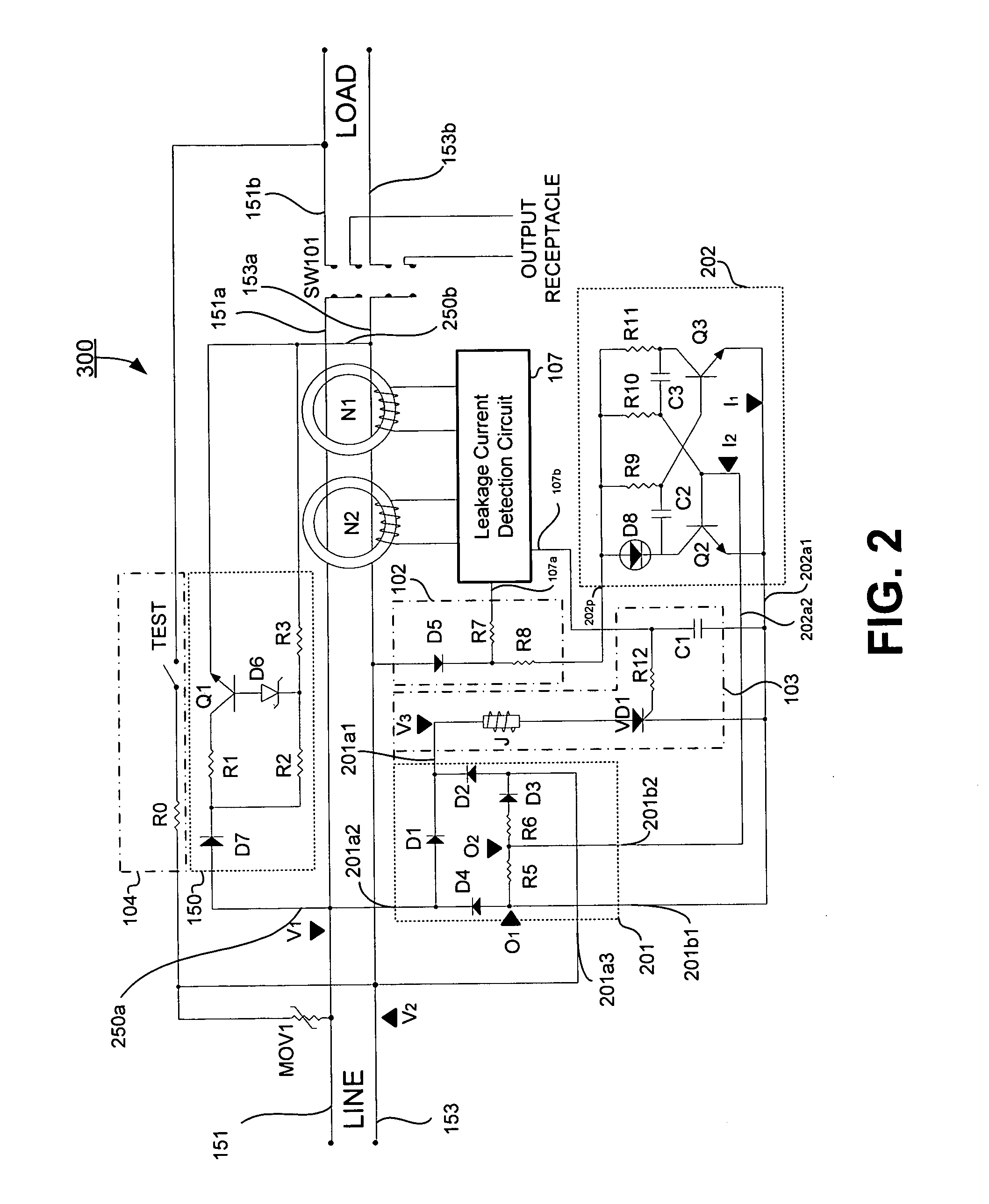
An apparatus for testing the life of a leakage current protection device having a leakage current detection circuit. In one embodiment, the apparatus a trip mechanism state generator, a fault alarm generator, a ground fault simulation unit. In operation, the ground fault simulation unit generates a simulated ground fault signal during every positive half-wave of an AC power, the simulated ground fault signal is detected by the leakage current detection circuit, the leakage current detection circuit responsively generates a signal to turn a switching device into its conductive state so as to allow a current to pass therethrough, the passed current is converted into a DC voltage in accordance with a trip mechanism state generated by the trip mechanism state generator, the fault alarm circuit receives and analyzes the DC voltage and indicates whether a fault exists in the leakage current protection device.
Owner:CHEN HENG
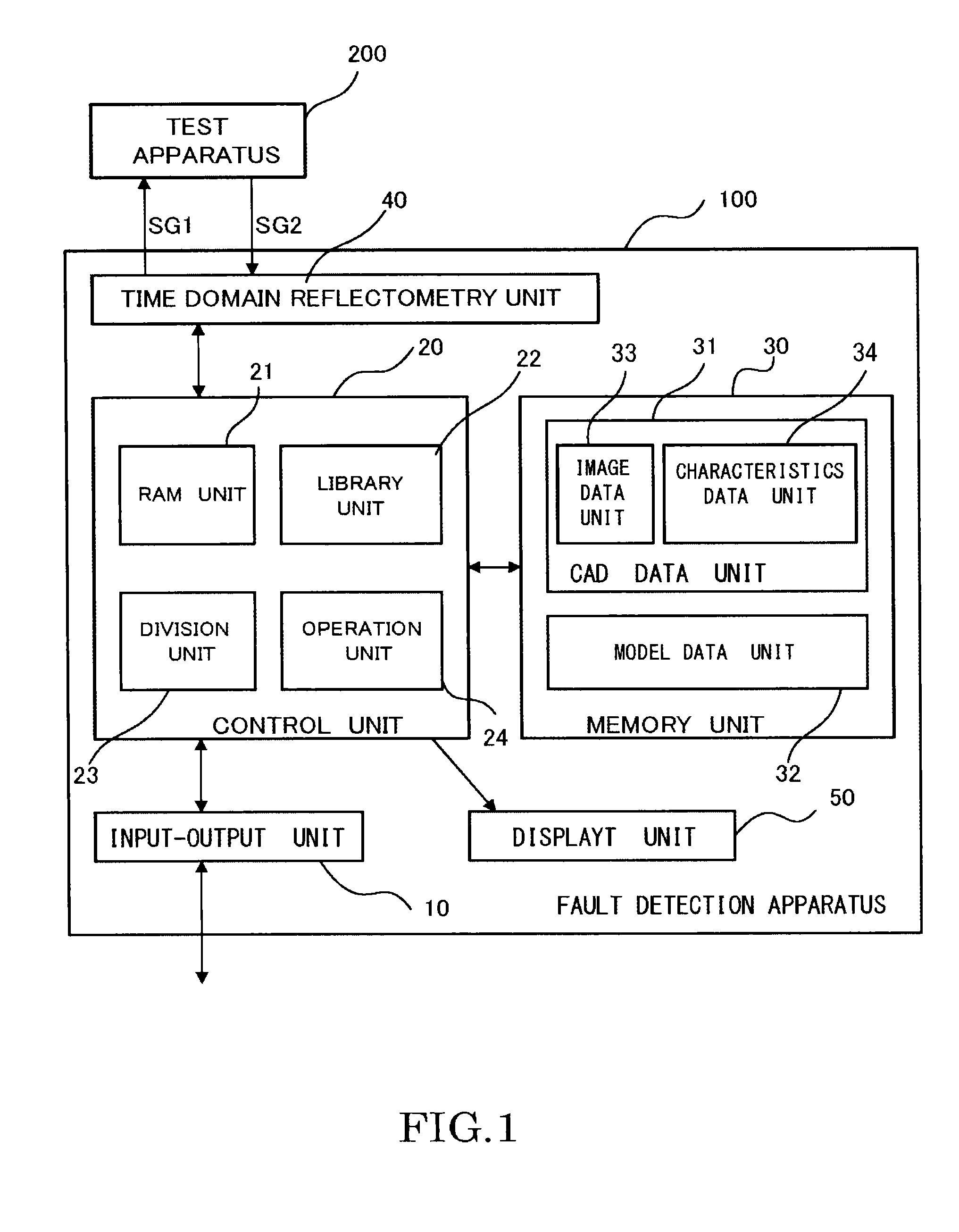
Fault detection apparatus
InactiveUS20140372068A1Improve accuracyElectronic circuit testingElectric connection testingTest objectComputer science
A fault detection apparatus according to an embodiment is provided with a measurement unit, a memory unit, a control unit, and a display unit. The measurement unit measures a first time period taken until a reflection signal reflected on a fault of a test apparatus is received after a first signal is transmitted to the test apparatus. The memory unit includes a CAD data unit having CAD data of the test apparatus, and a model data unit to store model data indicating a relation between the first time period and a predicted conduction distance of the first signal according to the CAD data. The control unit calculates a range of a test object selected in the test apparatus based on the CAD data, calculates the predicted conduction distance from the first time period based on the model data, and specifies a position of a fault of the test apparatus which is separated by the predicted conduction distance from the measurement unit in the range of the test object. The display unit displays the position of the fault in the CAD data.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEMORY CORP
Methods, designs, defect review tools, and systems for determining locations on a wafer to be reviewed during defect review
ActiveUS20080163140A1Resistance/reactance/impedenceDetecting faulty computer hardwareWaferingSoftware engineering
Various methods, designs, defect review tools, and systems for determining locations on a wafer to be reviewed during defect review are provided. One computer-implemented method includes acquiring coordinates of defects detected by two or more inspection systems. The defects do not include defects detected on the wafer. The method also includes determining coordinates of the locations on the wafer to be reviewed during the defect review by translating the coordinates of the defects into the coordinates on the wafer such that results of the defect review performed at the locations can be used to determine if the defects cause systematic defects on the wafer.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
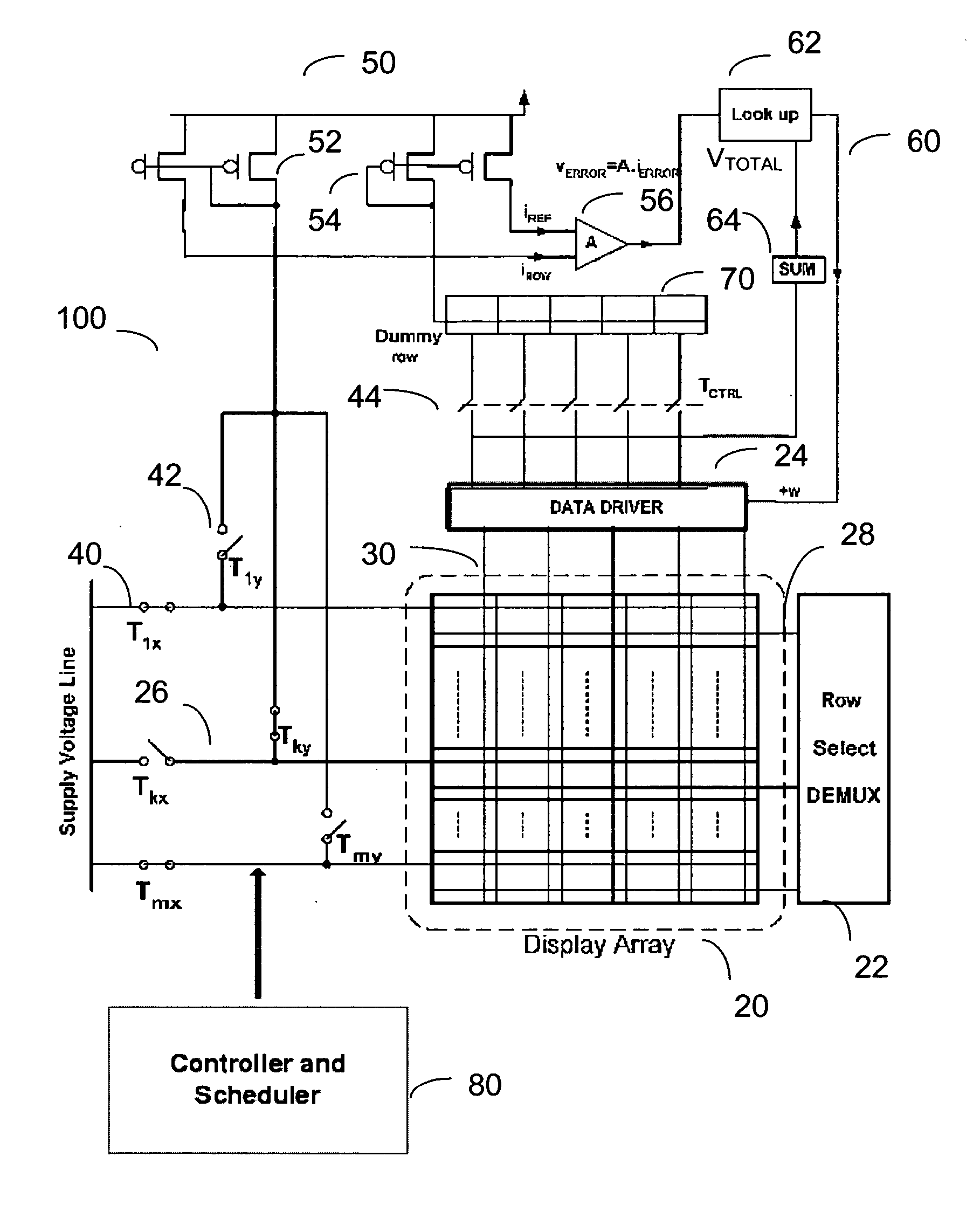
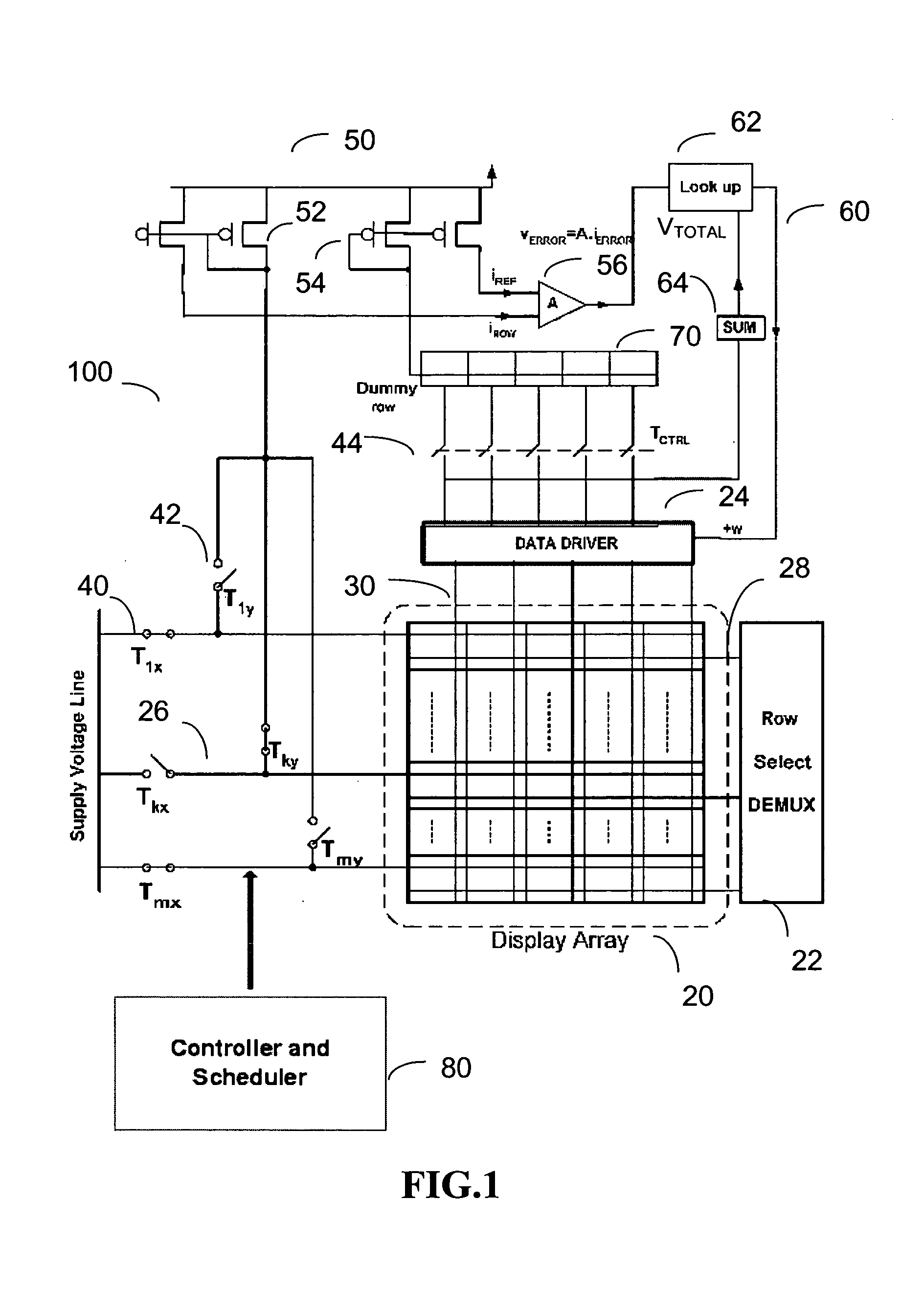
Method and system for calibrating a light emitting device display
ActiveUS20060149493A1Resistance/reactance/impedenceCathode-ray tube indicatorsDisplay deviceLight emitting device
A method and system for calibrating a light emitting device display is provided. The display includes a plurality of pixel circuits, each having a light emitting device. The system for the calibration monitors current drawn from a row of the display array, and generates a correction parameter to correct brightness level of the light emitting device.
Owner:IGNIS INNOVATION
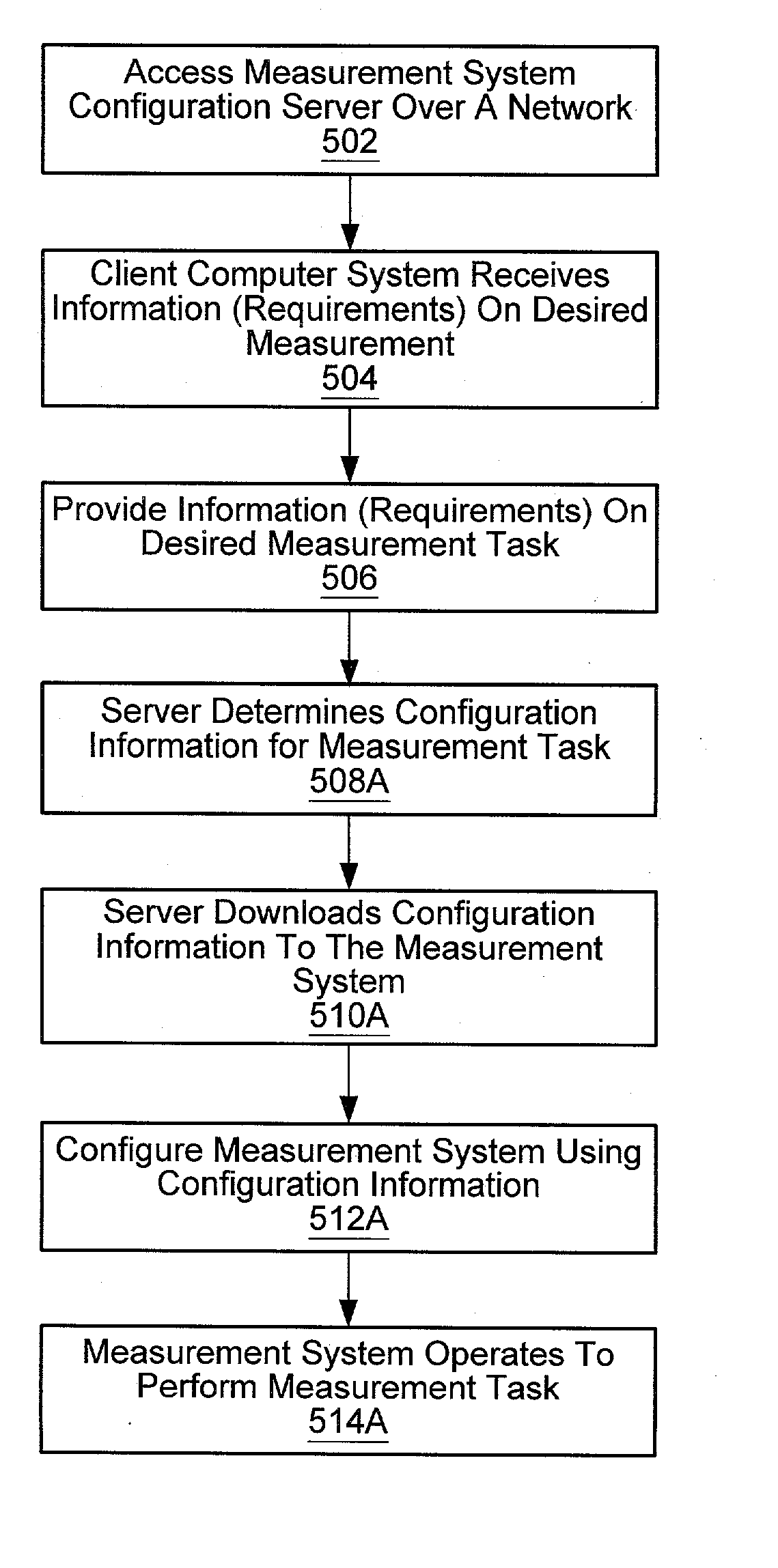
Network-based system for configuring a measurement system using configuration information generated based on a user specification
InactiveUS20030036876A1Measurement arrangements for variableStructural/machines measurementComputer hardwareAuto-configuration
System and method for online configuration of a device for a measurement system. The user accesses a server with a client computer over a network and specifies a task. If the user lacks the hardware to perform the task, hardware specifications are sent to a manufacturer, who sends the hardware to the user. The hardware may be re-configurable hardware (a programmable hardware element or processor / memory based device). Software products (programs and / or data) for configuring measurement system hardware (and / or software) to perform the task may be sent to the user. The hardware may be configured automatically or by the user. The software products may include programs usable by the measurement system to perform the task, configuration information for configuring the client computer or other measurement device, and / or hardware configuration program(s) for configuring a programmable hardware element. Thus, hardware and / or software specific to the user's application are be provided to the user.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
System and method of controlling power consumption in an electronic system
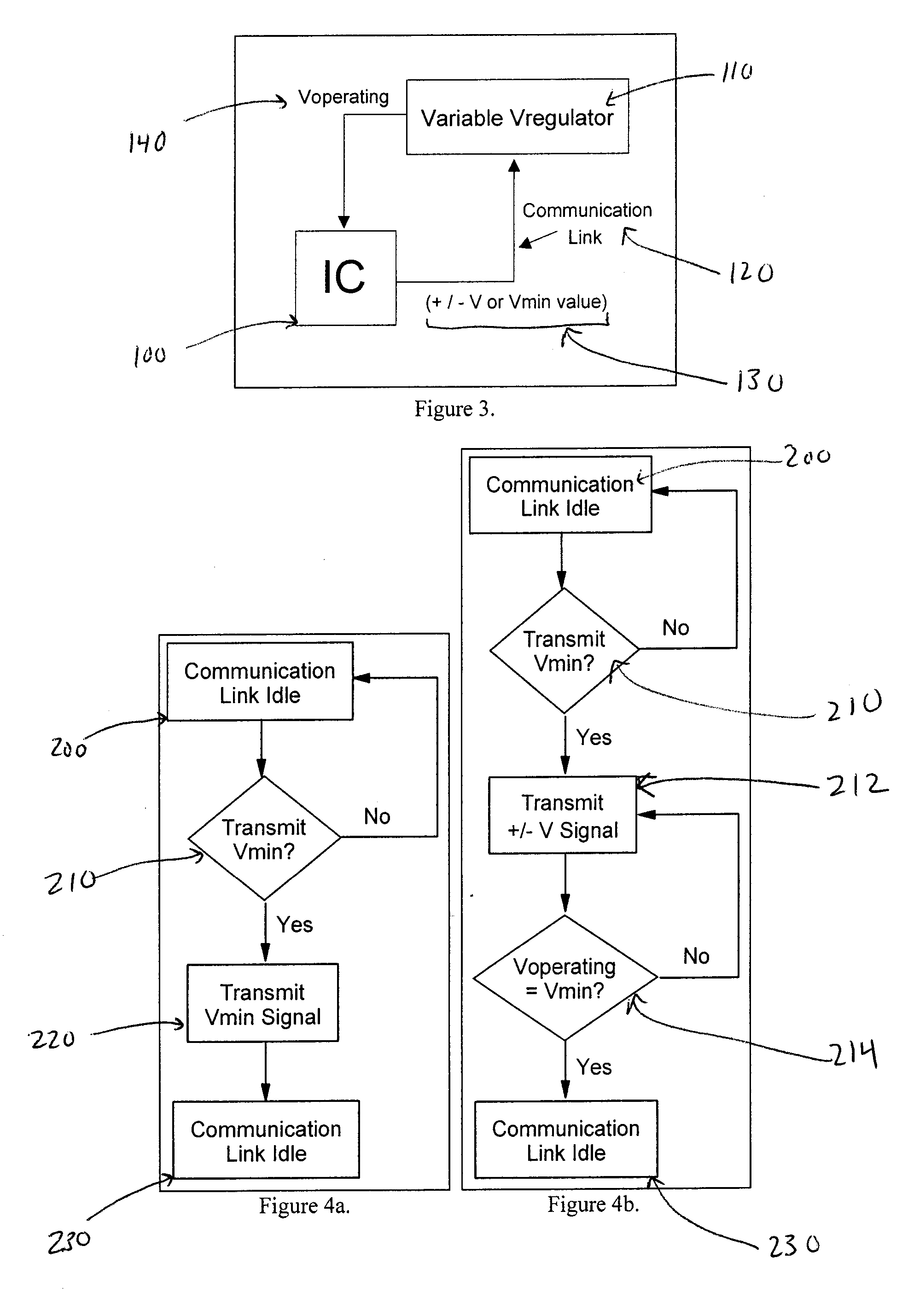
ActiveUS20050188230A1Readily apparentEnergy efficient ICTElectric devicesSystems designElectronic systems
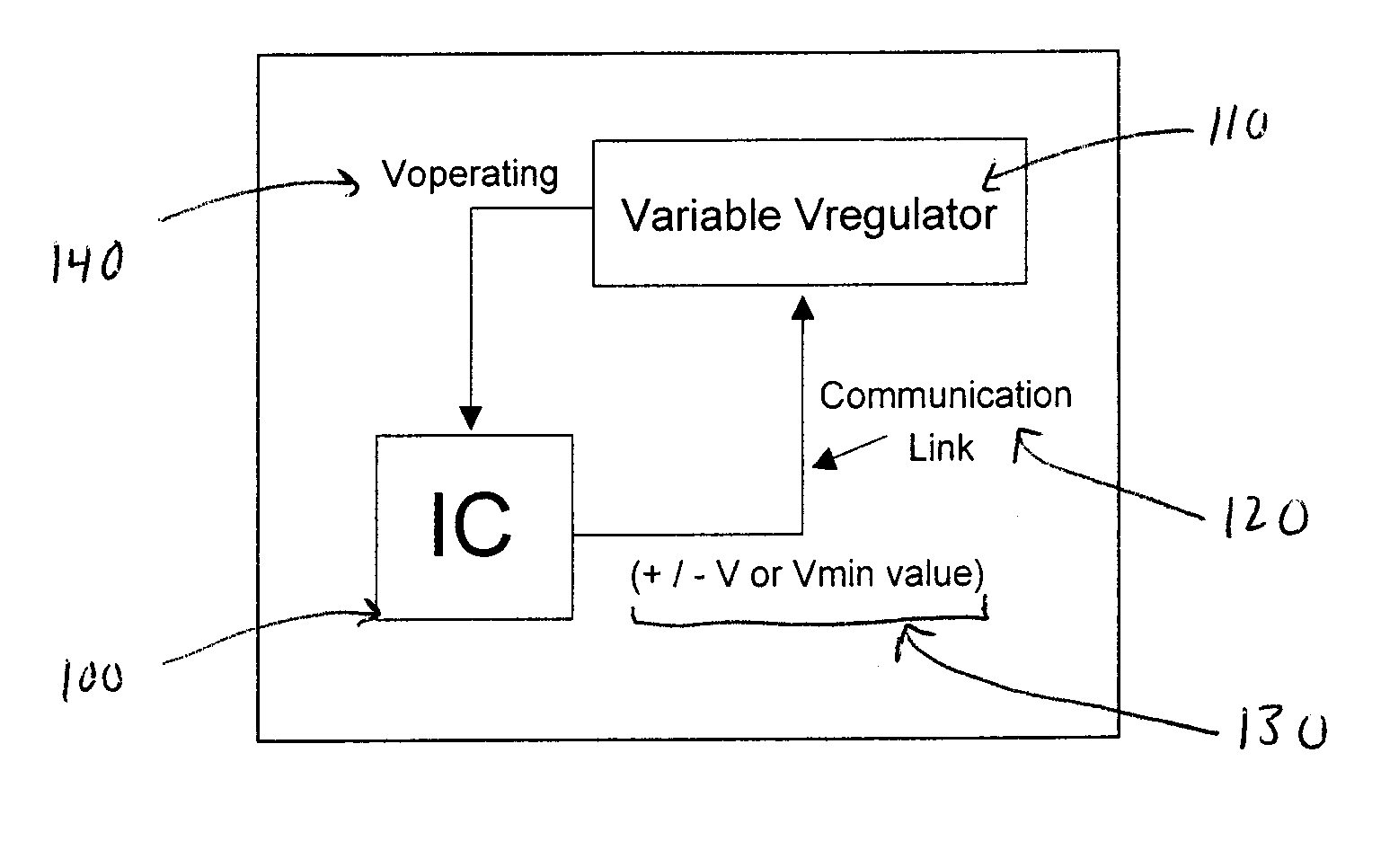
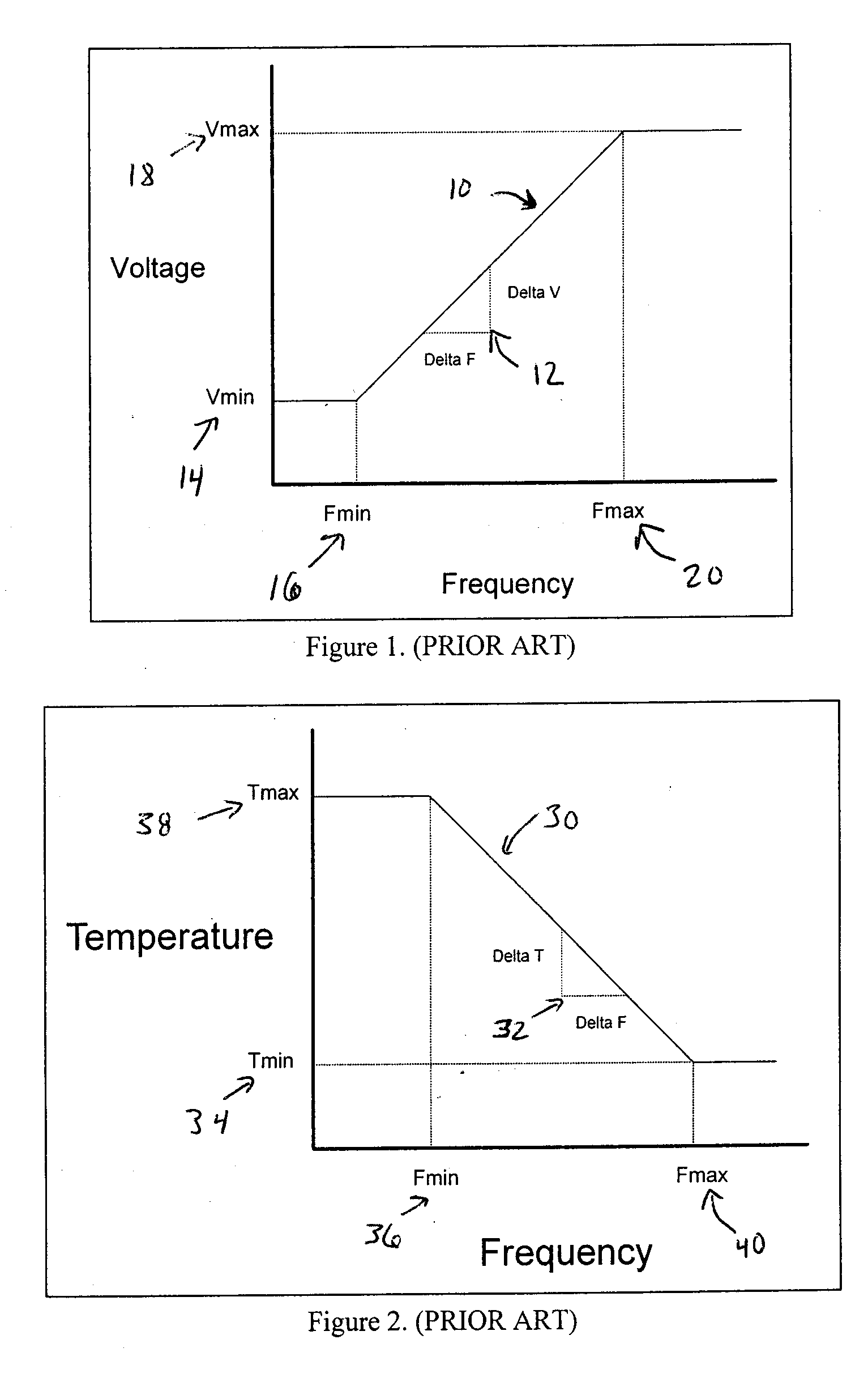
A method and apparatus for adaptively adjusting the operating voltage of an integrated circuit in response to tester-to-system variations, worst-case testing techniques, process variations, temperature variations, or reliability wearout mechanisms. The minimum operating voltage of an integrated circuit is determined either during external testing of the integrated circuit or during built-in-self-testing. The minimum operating voltage is transmitted to a variable voltage regulator where it is used to set the output of the regulator. The output of the regulator supplies the integrated circuit with its operating voltage. This technique enables tailoring of the operating voltage of integrated circuits on a part-by-part basis which results in power consumption optimization by adapting operating voltage in response to tester-to-system variations, worst-case testing techniques, process variations, temperature variations or reliability wearout mechanisms. Alternatively, the invention enables adaptive adjustment of the operating frequency of an integrated circuit. The invention enables system designers to adaptively optimize either system performance or power consumption on a part-by-part basis in response to tester-to-system variations, worst-case testing techniques, process variations, temperature variations or reliability wearout mechanisms.
Owner:IBM CORP
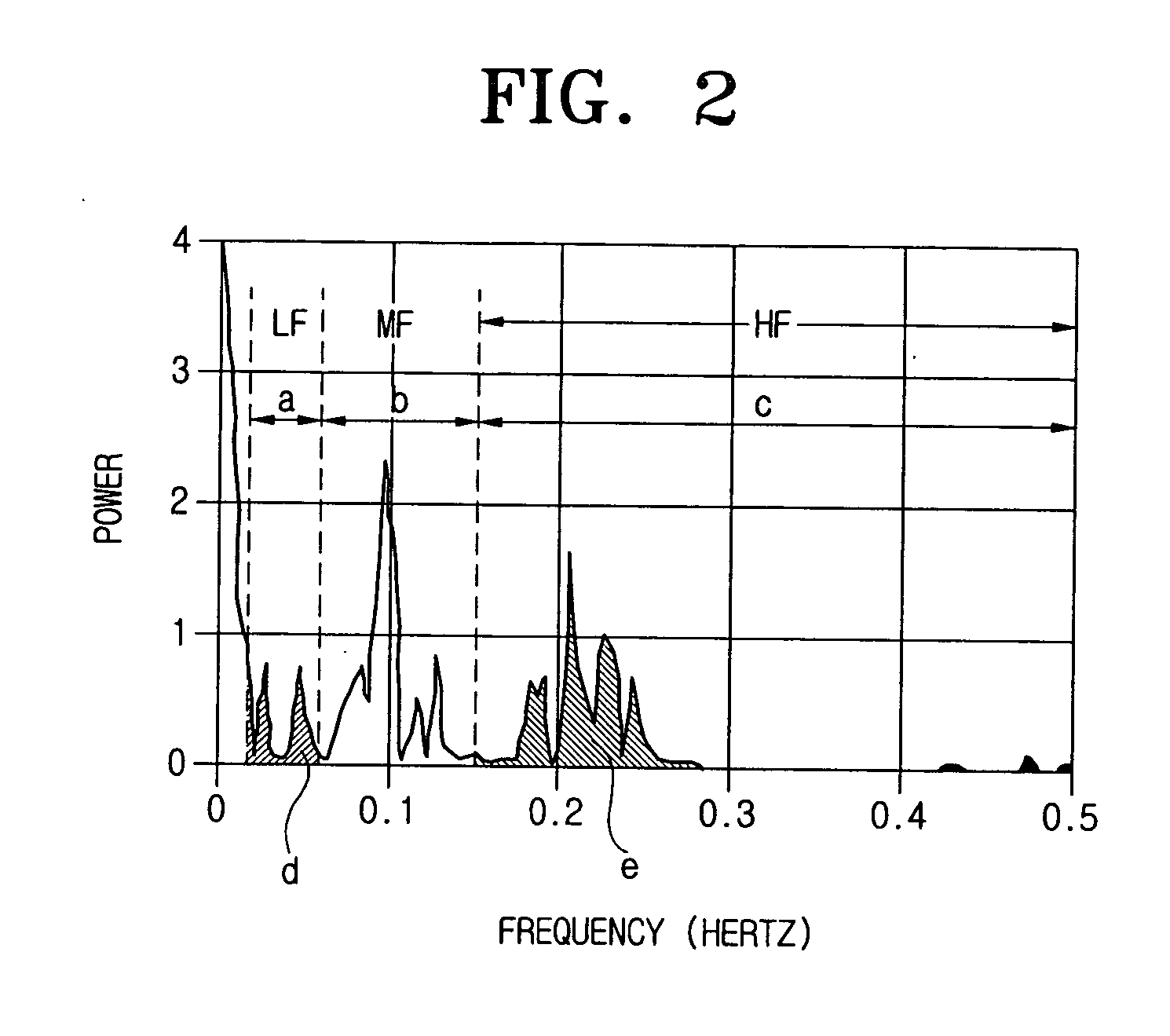
Method for analyzing signal waveform and analyzing vehicle dynamic characteristic
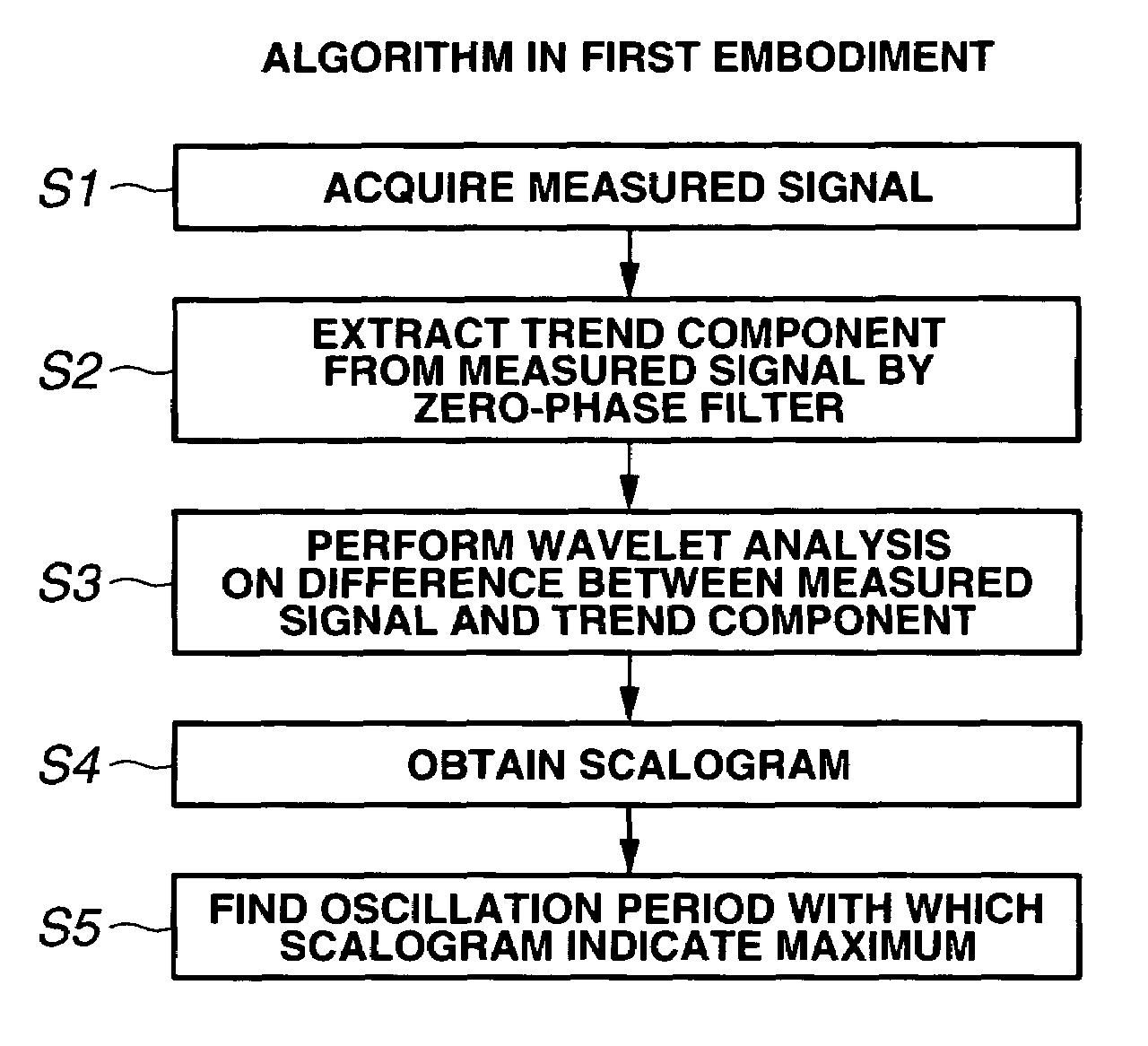
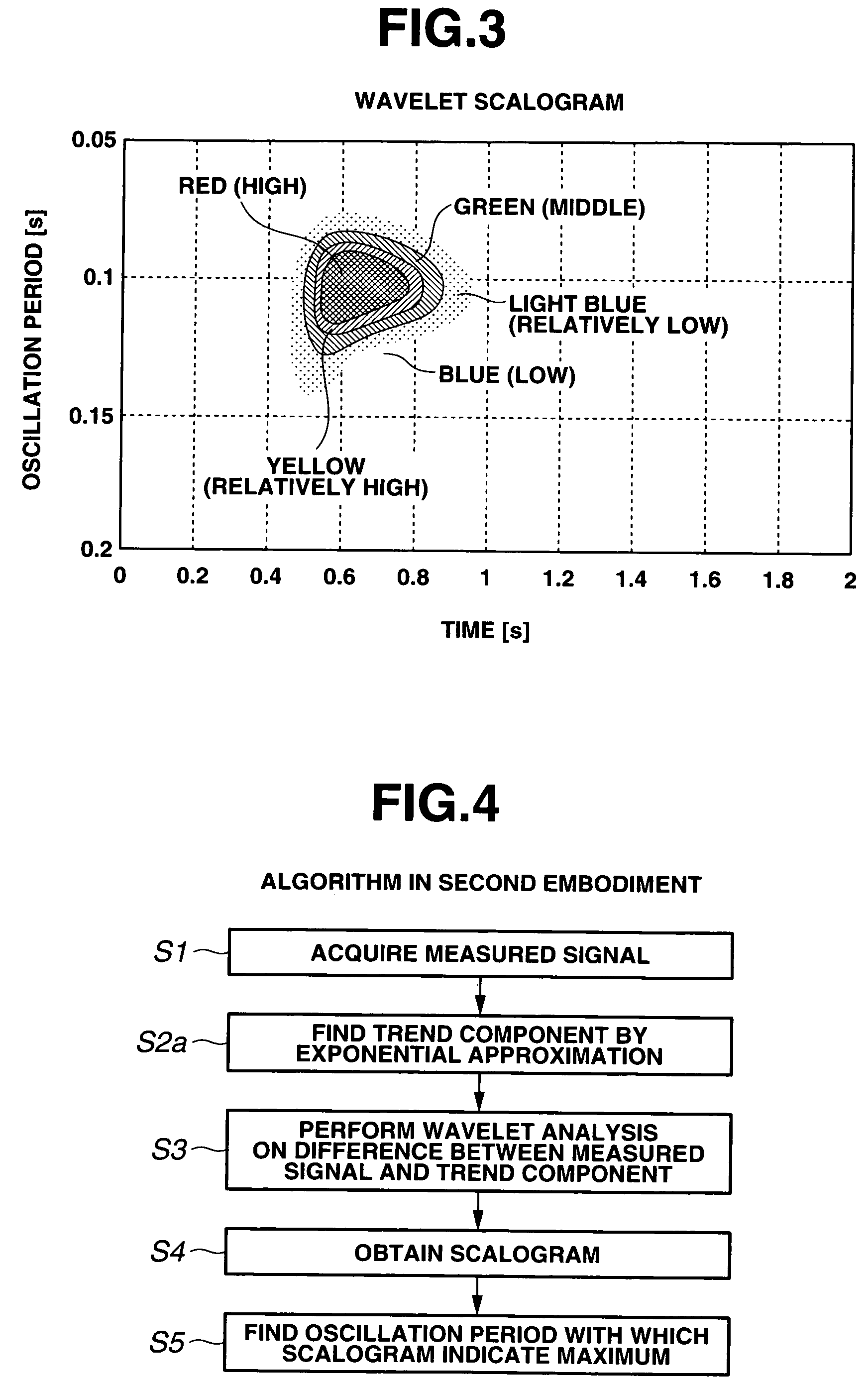
ActiveUS7523011B2Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceResistance/reactance/impedenceVehicle dynamicsWaveform analysis
A signal waveform analysis method includes: determining a trend component of an object signal by applying a zero-phase filter to the object signal; determining an oscillatory component of the object signal by removing the trend component from the object signal; determining a wavelet scalogram by performing a wavelet analysis on the oscillatory component; and determining an oscillation period of the object signal with which the wavelet scalogram indicates a maximum. The signal waveform analysis method is employed to evaluate vehicle dynamic characteristics.
Owner:MEIDENSHA ELECTRIC MFG CO LTD +1
System and method for calibration of an acoustic system
The present invention is directed to a method and system for automatic calibration of an acoustic system. The acoustic system may include a source A / V device, calibration computing device, and multiple rendering devices. The calibration system may include a calibration component attached to each rendering device and a source calibration module. The calibration component on each rendering device includes a microphone. The source calibration module includes distance and optional angle calculation tools for automatically determining a distance between the rendering device and a specified reference point upon return of the test signal from the calibration component.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
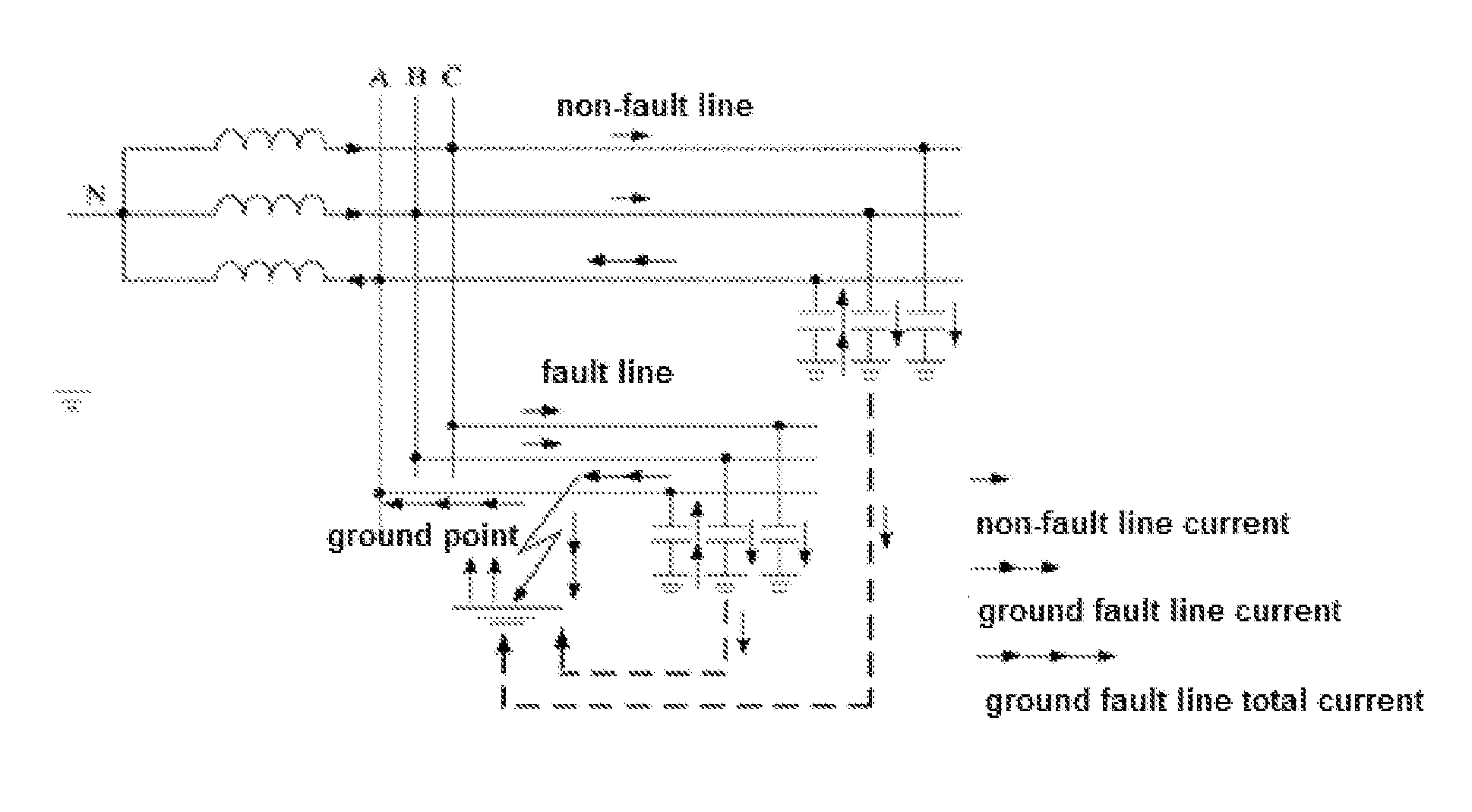
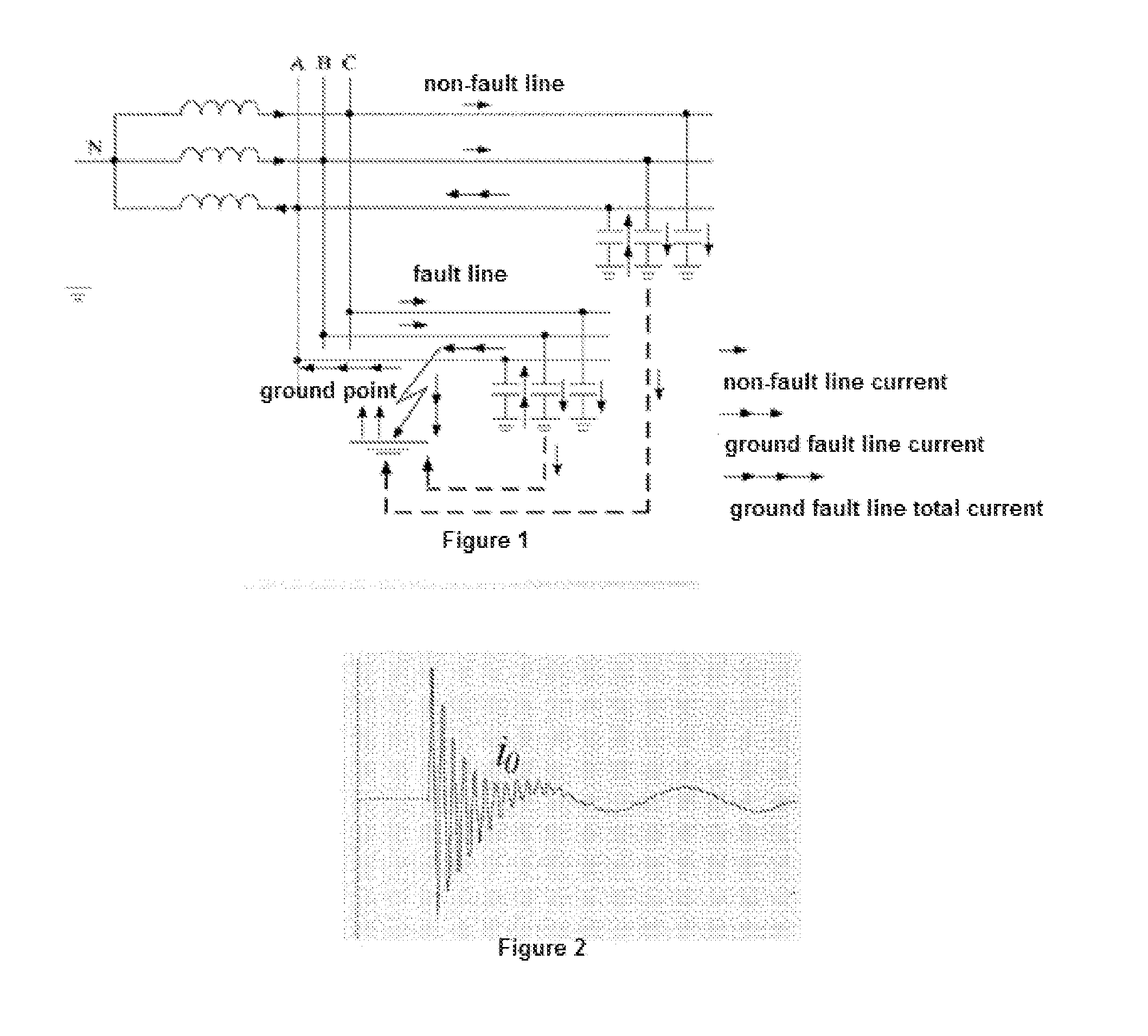
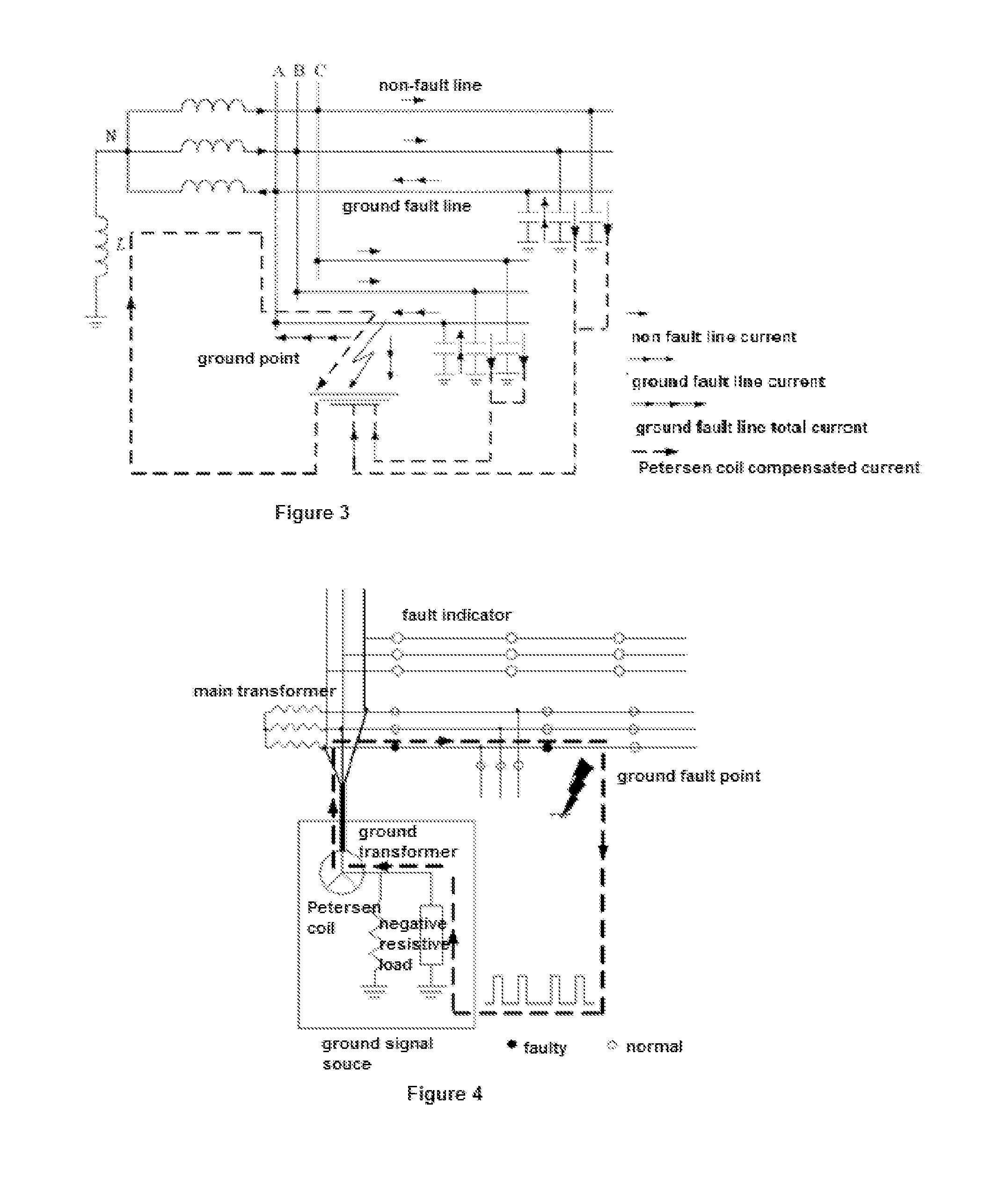
Method and system for detecting and locating single-phase ground fault on low current grounded power-distribution network
ActiveUS20160041216A1Accurate locationFault location by conductor typesShort-circuit testingThree-phaseElectric distribution network
A method and system for detecting and locating a single-phase ground fault on a low current grounded power-distribution network, comprising: respectively testing and picking up the voltage signals and current signals at multiple positions on each phase feeder (61), and determining the corresponding transient voltage signals and transient current signals according to the extraction of the voltage signals and the current signals (62); when the change in the transient voltage signals and the transient current signals exceeds a preset threshold (63), synchronously picking up the voltage signals and current signals at multiple positions on a three-phase feeder (64); calculating corresponding zero-sequence voltages and zero-sequence currents according to the voltage signals and current signals synchronously picked up at multiple positions on the three-phase feeder (65), and then extracting the steady-state signal and transient signal of the zero-sequence voltage and zero-sequence current at each position on the three-phase feeder (66); and determining a specific fault location on a faulty line according to the steady-state signal and the transient signal (67). The method effectively detects and displays a single-phase ground fault on a low current grounded power-distribution network.
Owner:BEIJING INHAND NETWORKS TECH
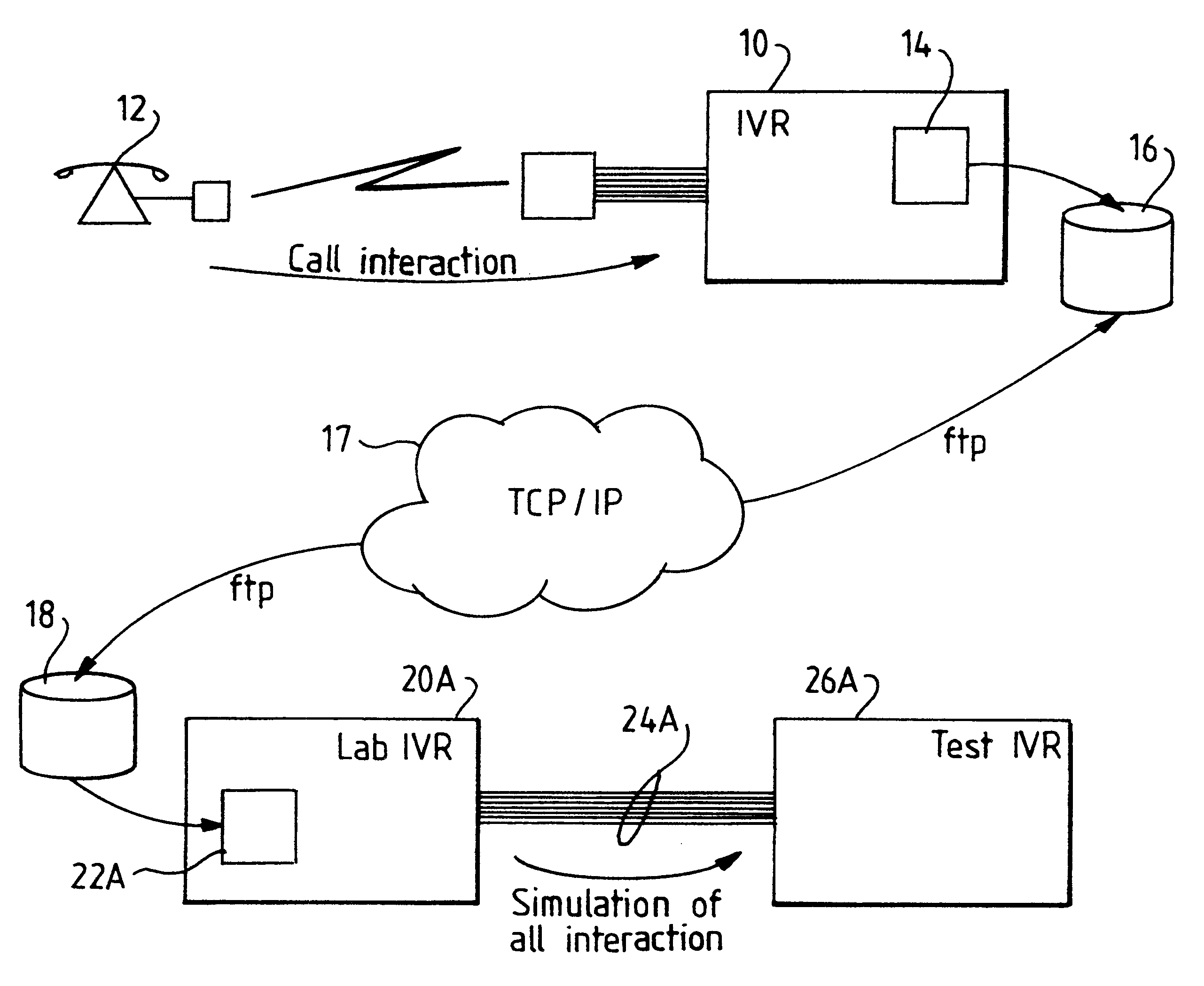
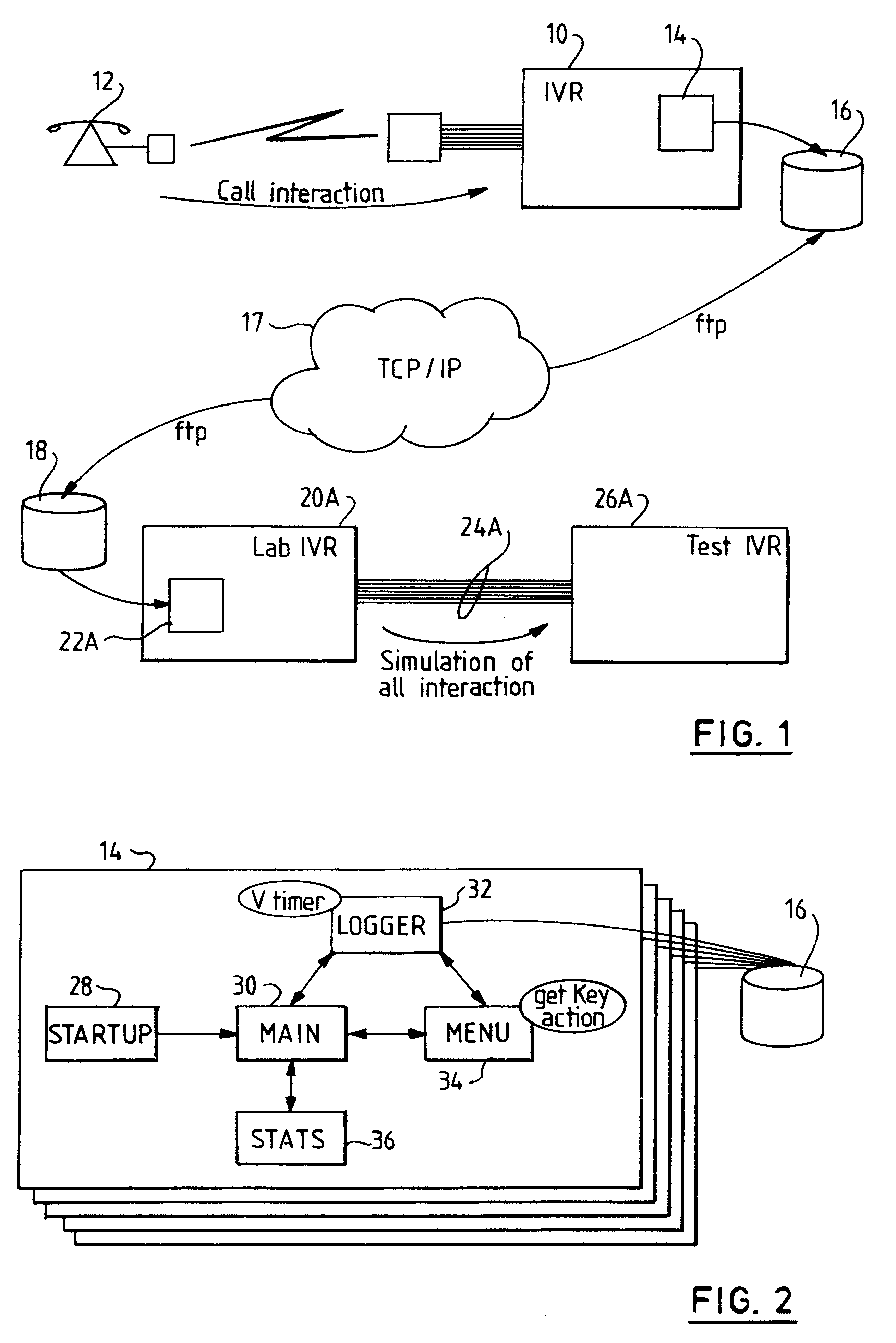
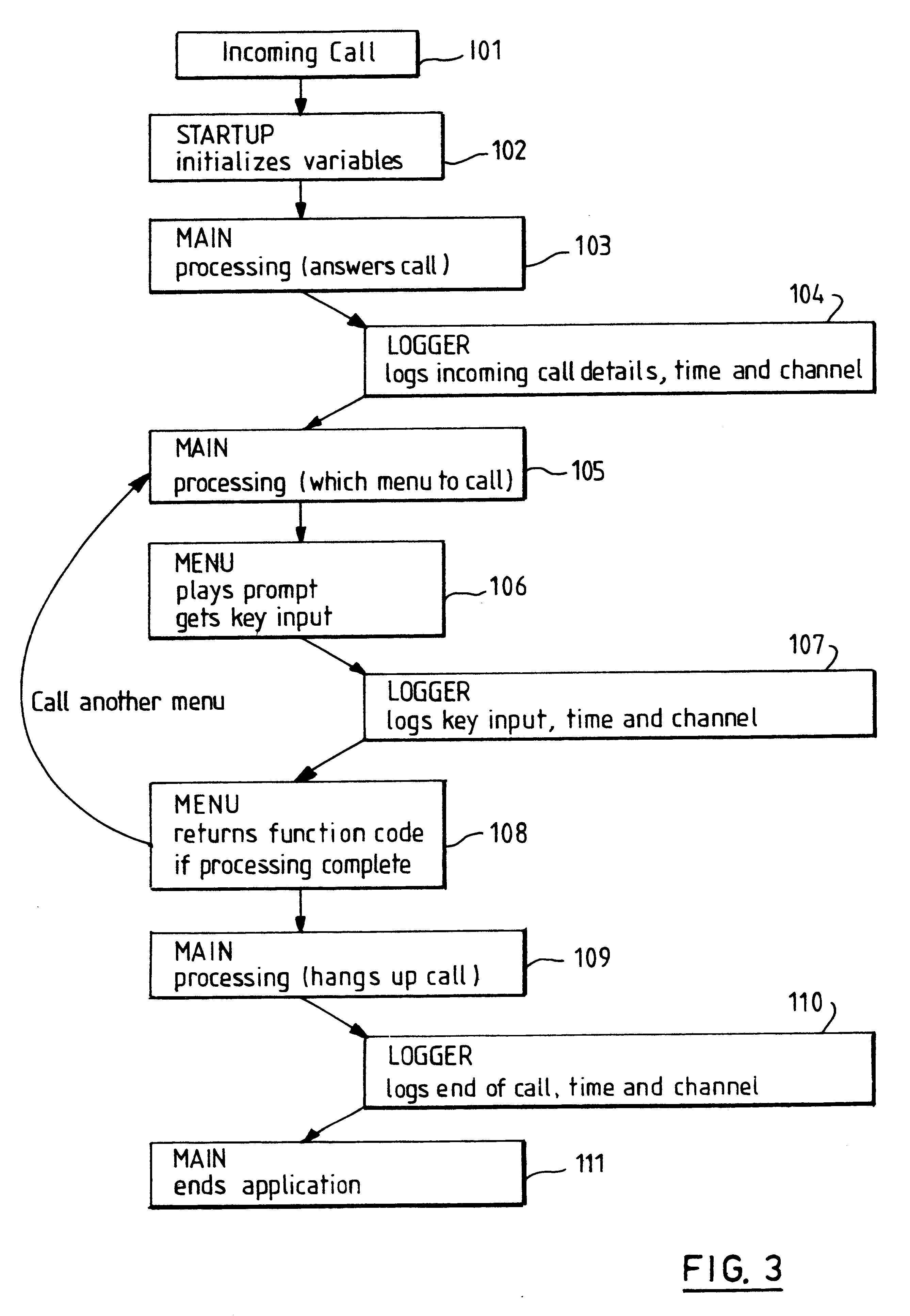
Testing voice message applications
InactiveUS6516051B2Resistance/reactance/impedenceAutomatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingComputer hardwareApplication software
This invention relates to bulk testing of voice messaging applications by playing back an interaction from a recorded script. During development of a voice response system and application it is necessary to simulate a plurality of calls to the system so that the performance under strain can be monitored. Such a simulation can be performed by a bulk call generator which makes real telephone calls to the IVR through a private branch switch. However with bulk call testing some problems occur which rigorous functional and / or performance testing does not find. This is because real callers behave in unpredictable ways which were not expected or assumed by the creators of the functional and / or performance tests. Accordingly there is provided a test system, method and computer program product for testing a voice application in an interactive voice response (IVR) system, said method comprising: acquiring user interactions from a first voice response application dialogue between the IVR system and a user; mapping user interactions from the first voice response application dialogue into machine readable user interaction data such as a script; reproducing user interactions based on the machine readable user interaction data; and sending the simulated user interactions to a second voice response application under test. This solution addresses the problem by providing actual customer data for recreating customer reported problems in the laboratory instead of relying on a programmed bulk call generator.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Circuit protection device with timed negative half-cycle self test
InactiveUS6980005B2Emergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionCircuit interrupters testingElectricityDetector circuits
The present invention is directed to an electrical wiring protection device for use in coupling an AC power distribution system to at least one electrical load. The device includes an automated self-test circuit coupled to the AC power distribution system. The automated self-test circuit is configured to generate at least one simulated fault signal during a first predetermined half-cycle of AC power. A detector circuit is coupled to the automated self-test circuit. The detector circuit generates a detection signal in response to the at least one simulated fault signal. An interval timing circuit is coupled to the test circuit. The interval timing circuit is configured to enable the automated self-test circuit to generate the at least one simulated fault signal during a first predetermined interval and not enable the test circuit during a subsequent second predetermined interval. The first predetermined interval and the second predetermined interval are recurring time intervals.
Owner:PASS SEYMOUR
System and method for creating a boot file utilizing a boot template
InactiveUS6898703B1Convenient and efficient mannerTo offer comfortResistance/reactance/impedenceSoftware engineeringProcessor registerApplication software
The present invention is a system and method of facilitating automatic generation of the source code in a convenient and efficient manner. In one embodiment of the present invention, a programmable system on a chip (PSoC) boot file generation method is utilized to create a boot file. A boot template file is created comprising special symbolic variable names that point to configuration registers within a programmable system on a chip (PSoC). User module selections are received with delineation of preferred configurations and functions associated with components of said programmable system on a chip (PSoC). Application files are automatically generated based upon user selections of PSoC configurations and functions. The special symbolic variable names are substituted or replaced with actual configuration register names. In one embodiment, a present invention programmable system on a chip (PSOC) boot file generation method also facilitates providing interrupt processing routines to the appropriate vector.
Owner:CYPRESS SEMICON CORP
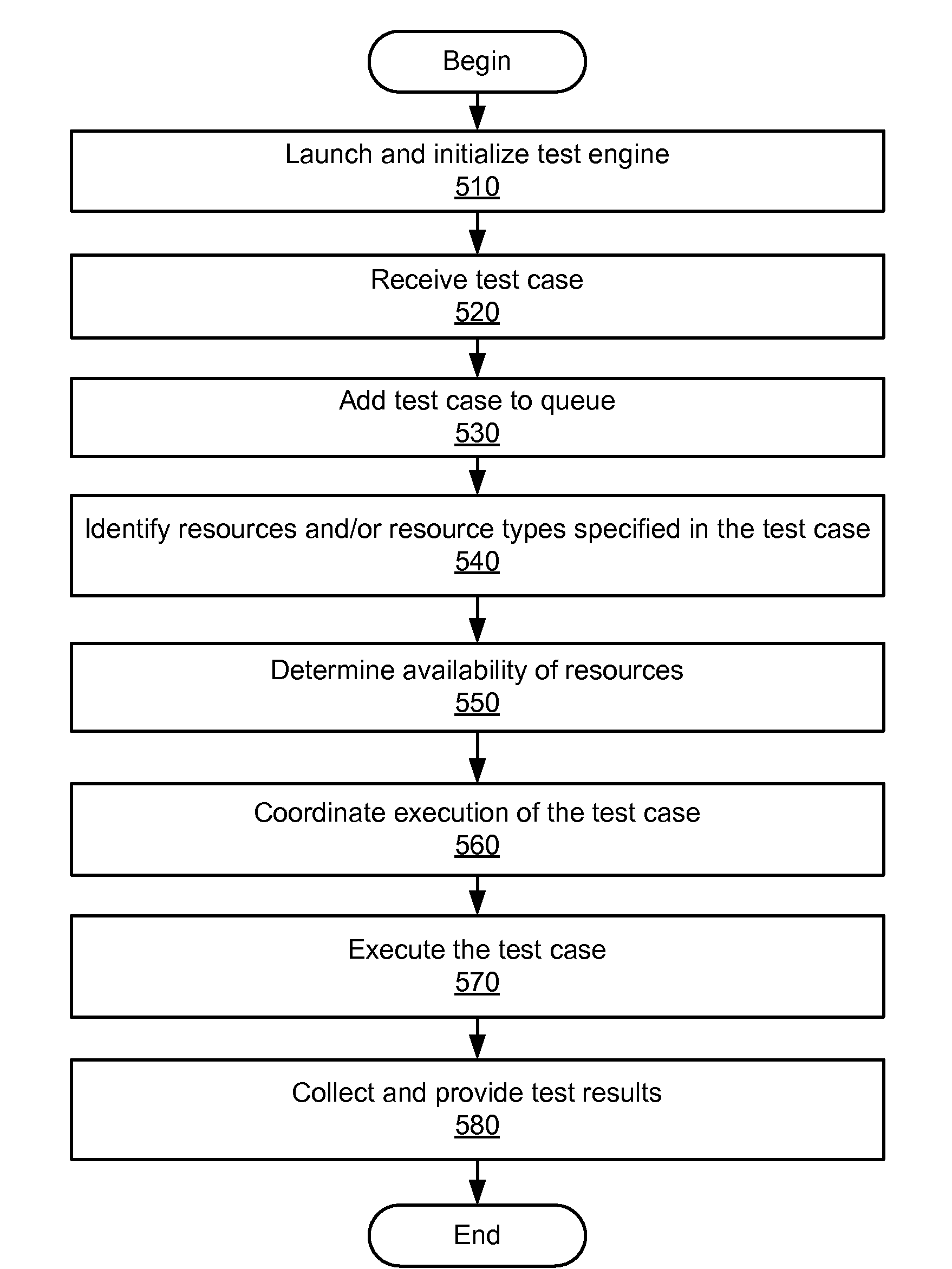
Integrated testing systems and methods
ActiveUS20100070230A1Resistance/reactance/impedenceElectronic circuit testingComputer hardwareCombined test
An exemplary method includes parsing data representative of an automated test case into at least one transaction defined in accordance with a global test language, translating the transaction into at least one command specific to an automated test tool, and providing the command to the automated test tool for execution. In certain examples, the method further includes parsing the data representative of the automated test case into at least one other transaction defined in accordance with the global test language, translating the other transaction into at least one other command specific to another automated test tool, and providing other command to the other automated test tool for execution.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
Circuit protection device with grounded neutral half cycle self test
InactiveUS7253629B1Protective switch detailsEmergency protective arrangement detailsDistribution systemEngineering
The present invention is directed to a circuit and method for self-testing a protection device for use in an AC power distribution system. The device is configured to be coupled between an AC power distribution system and at least one load. The method includes the step of introducing a simulated ground neutral fault during a first predetermined half cycle half cycle of the AC power. An attempt is made to detect the introduced simulated grounded neutral fault during the first predetermined half cycle half cycle. A fault condition is signaled if the introduced simulated grounded neutral fault is not detected within a predetermined period of time.
Owner:PASS SEYMOUR
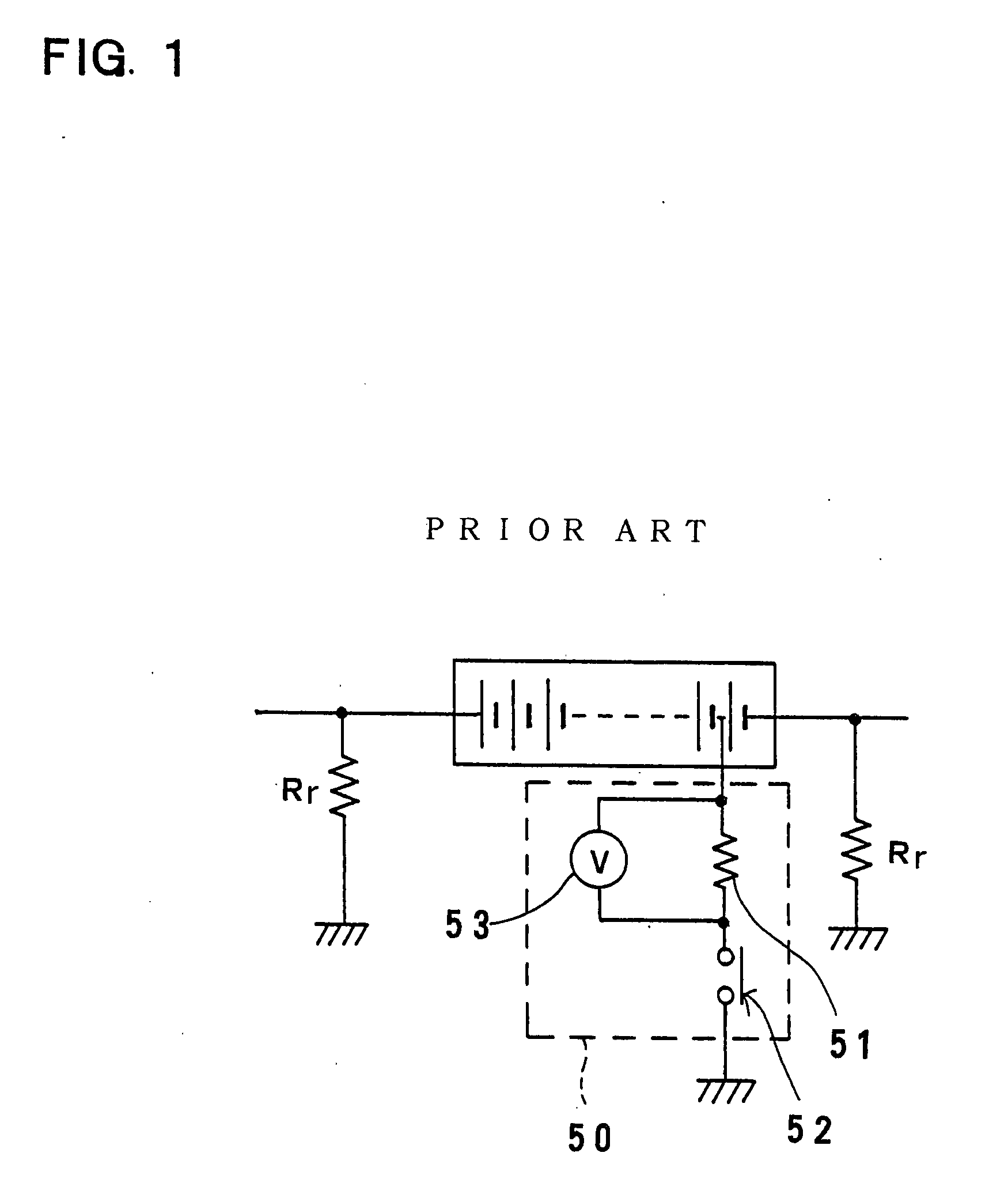
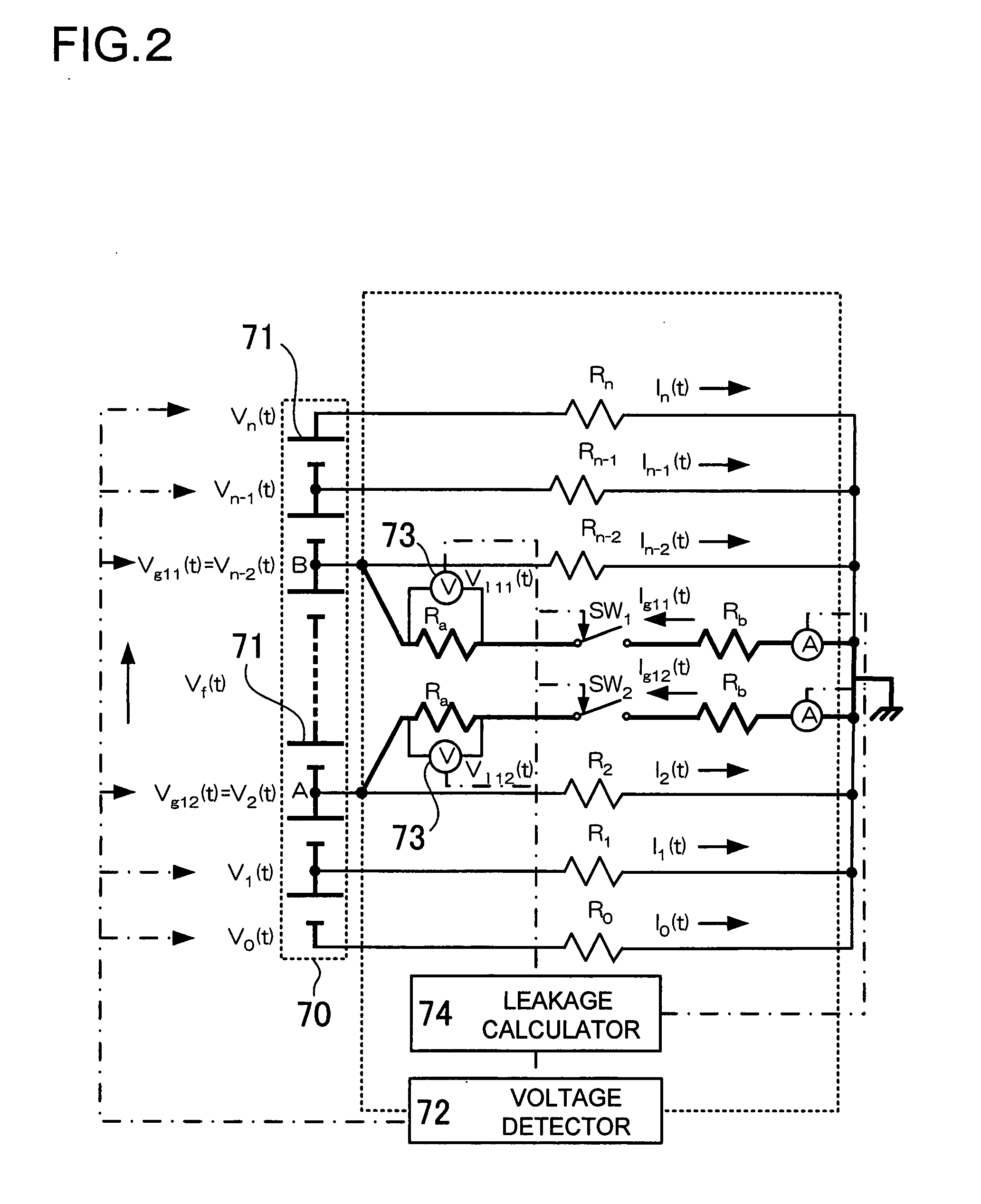
Leakage detection circuit for electric vehicle
ActiveUS20070285057A1Simple and inexpensive structureEasy to useCircuit monitoring/indicationElectric devicesLow voltageEngineering
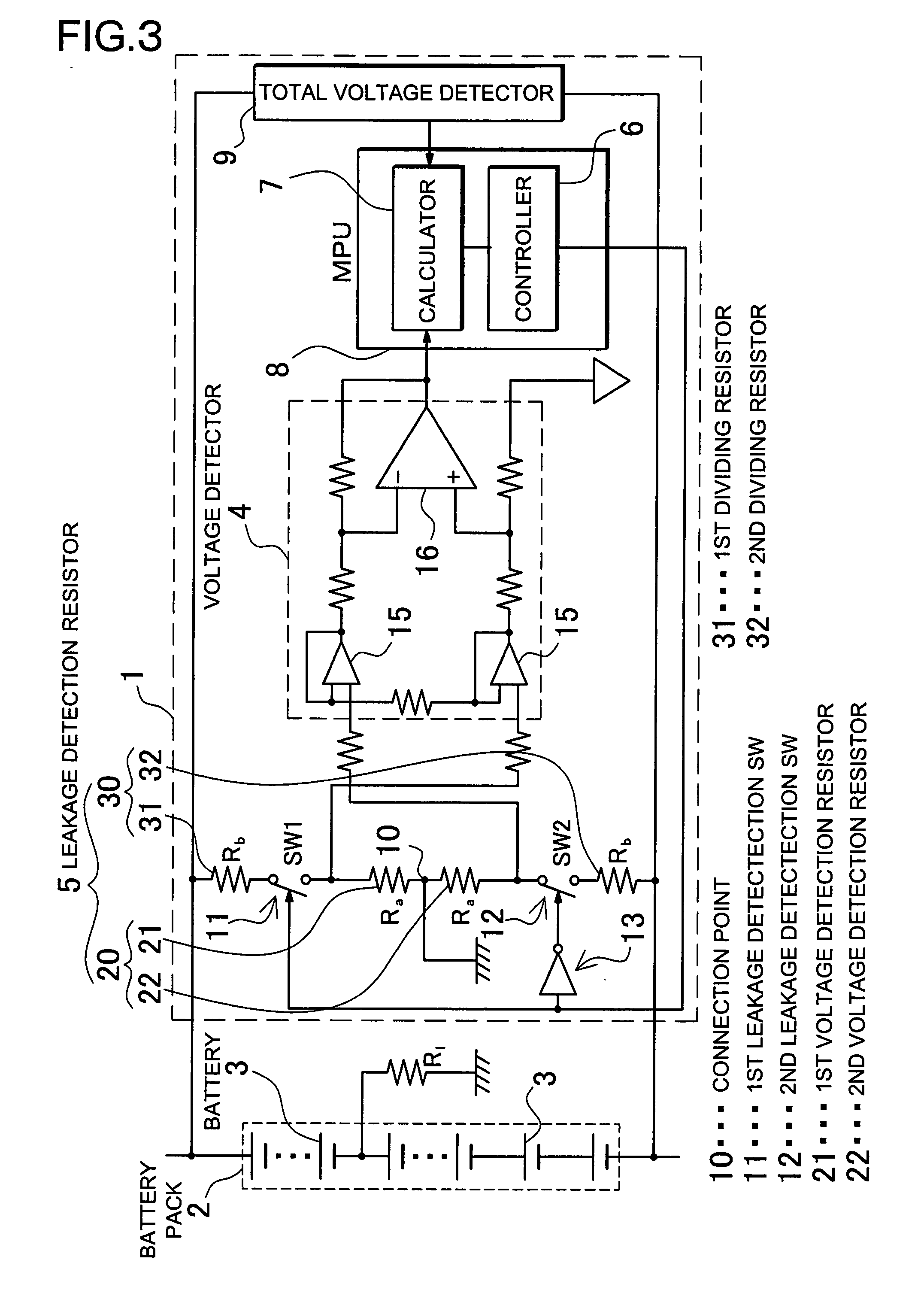
A leakage detection circuit for an electric vehicle includes a battery pack, first and second leakage detection switches, a controller, a leakage detection resistor, a voltage detector, and a calculator. The first and second leakage detection switches are connected to the high and low voltage sides of the battery pack, respectively. The battery pack includes a plurality of batteries that are connected in series. The midpoint of the leakage detection resistor is connected to the ground via the first and second leakage detection switches. The controller alternately turns the first and second leakage detection switches ON. Thus, the voltage detector detects leakage voltage values that are generated in the leakage detection resistor. The controller turns the first and second leakage detection switches ON and OFF, respectively, to detect a first leakage voltage value of the leakage voltage values. On the other hand, the controller turning the first and second leakage detection switches OFF and ON, respectively, to detect a second leakage voltage value of the leakage voltage values. Consequently, the calculator detects leakage based on the first and second leakage voltage values.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
System and method for developing test cases using a test object library
InactiveUS6332211B1Rule out the possibilityResistance/reactance/impedenceSoftware testing/debuggingProgramming languageProgram planning
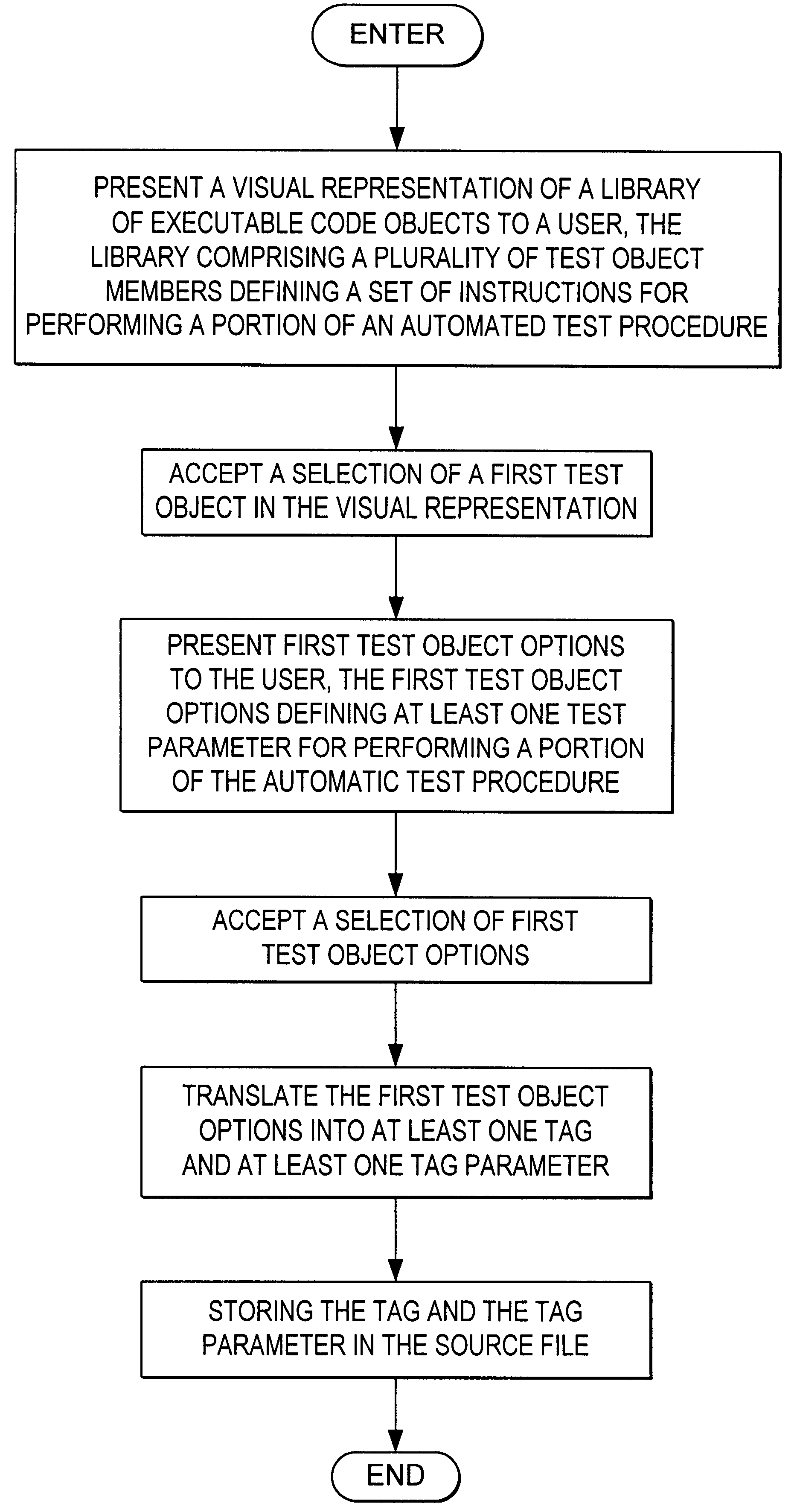
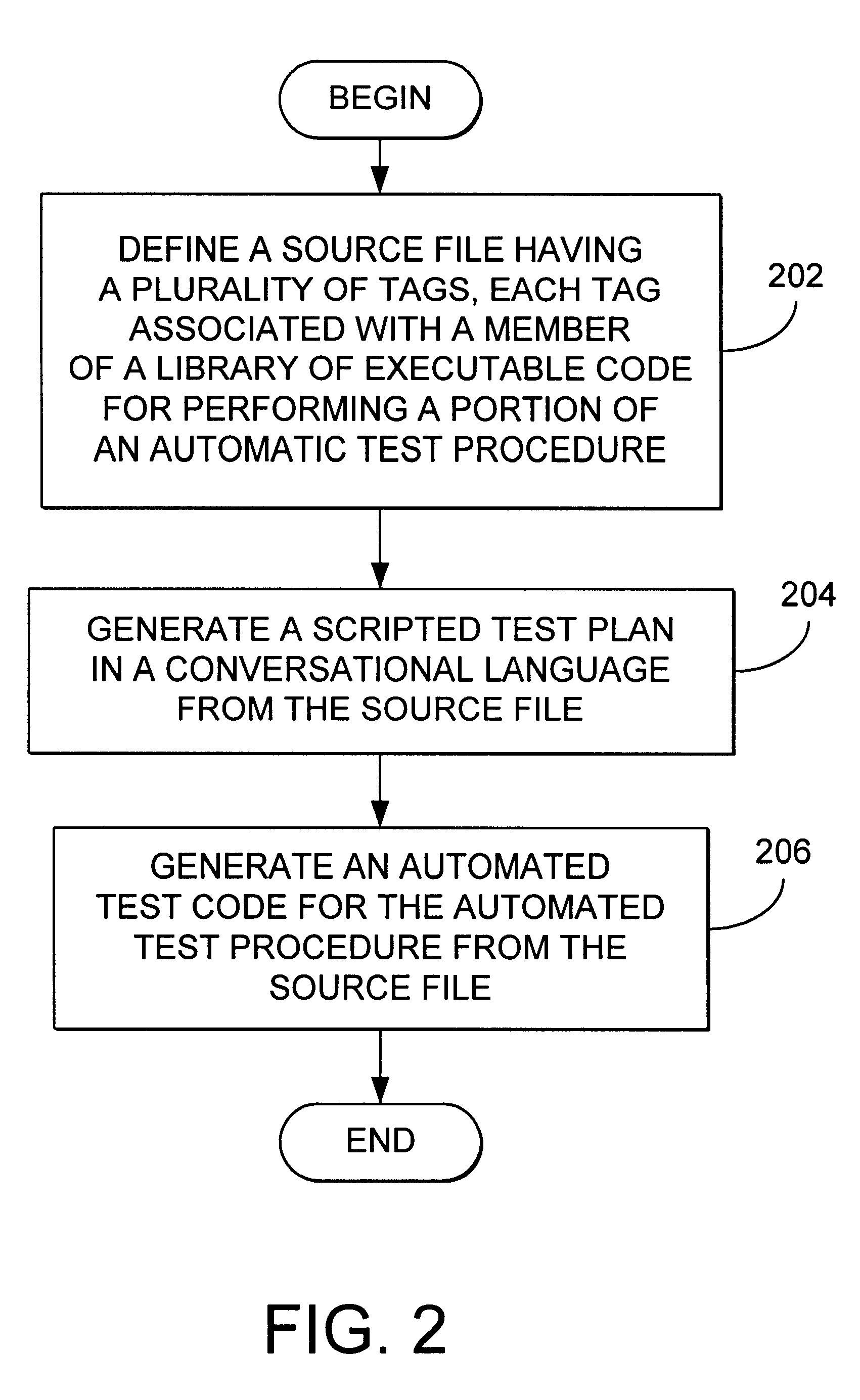
A method, apparatus, article of manufacture, and a memory structure for generating a test code for an automatic procedure is disclosed. The method comprises the steps of defining a source file having a plurality of tags associated with a member of a library of executable code objects defining a set of instructions for performing a portion of the automatic test procedure, generating a test plan in a conventional language from the source file, and generating an automated test code for the automated test procedure from the source file. In one embodiment, a test index identifying system elements tested by the test code is generated and incorporated into the test plan, allowing the user to verify that all desired system elements are exercised by the automated test code. The article of manufacture comprises a data storage device tangibly embodying instructions to perform the method steps described above. The apparatus comprises means for defining a source file having a plurality of tags, wherein each tag is associated with a member of a library of executable code objects defining a set of instructions for performing a portion of an automatic test procedure, means for generating a test plan in a conversational language from the source file, and means for generating an automated test code for the automatic test procedure from the source file.
Owner:IBM CORP
Arc fault circuit interrupter
InactiveUS6373257B1Emergency protective arrangement detailsElectric switchesElectric power systemEngineering
An arc fault detector for detecting electric power lines includes a sensor for sensing the derivative of the current on the electric power line, a converter circuit for converting the derivative of the line current into first and second signals, the first signal responsive to positive step transitions of arc fault current, and the second signal responsive to negative step transitions of arc current, and a temporal detector for signaling the presence of an arc fault when one of the first and second signals follows the other within a predetermined time, or window, and in which a sequence of one of the signals following the other signal occurs in a second predetermined interval of time.
Owner:PASS SEYMOUR
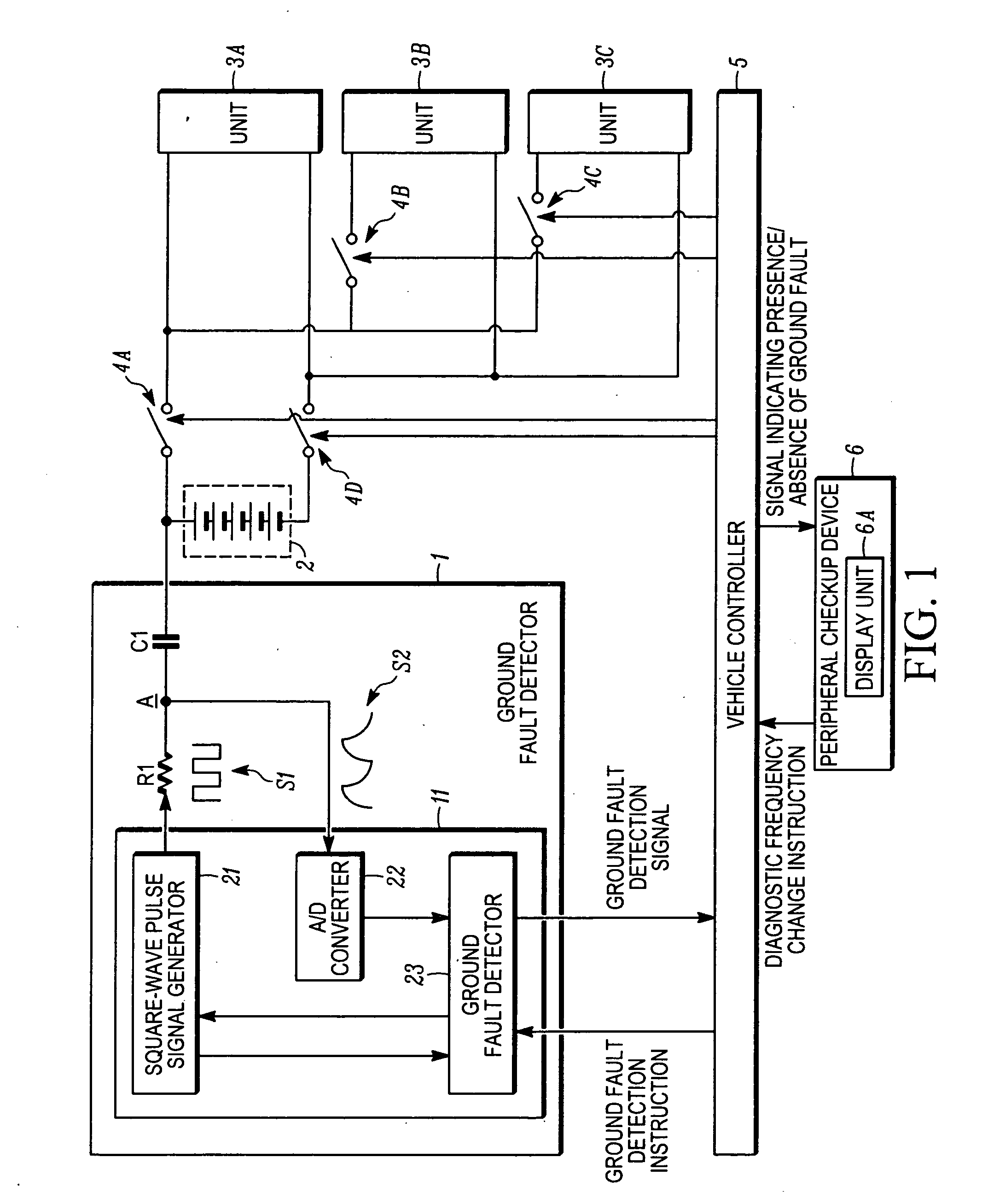
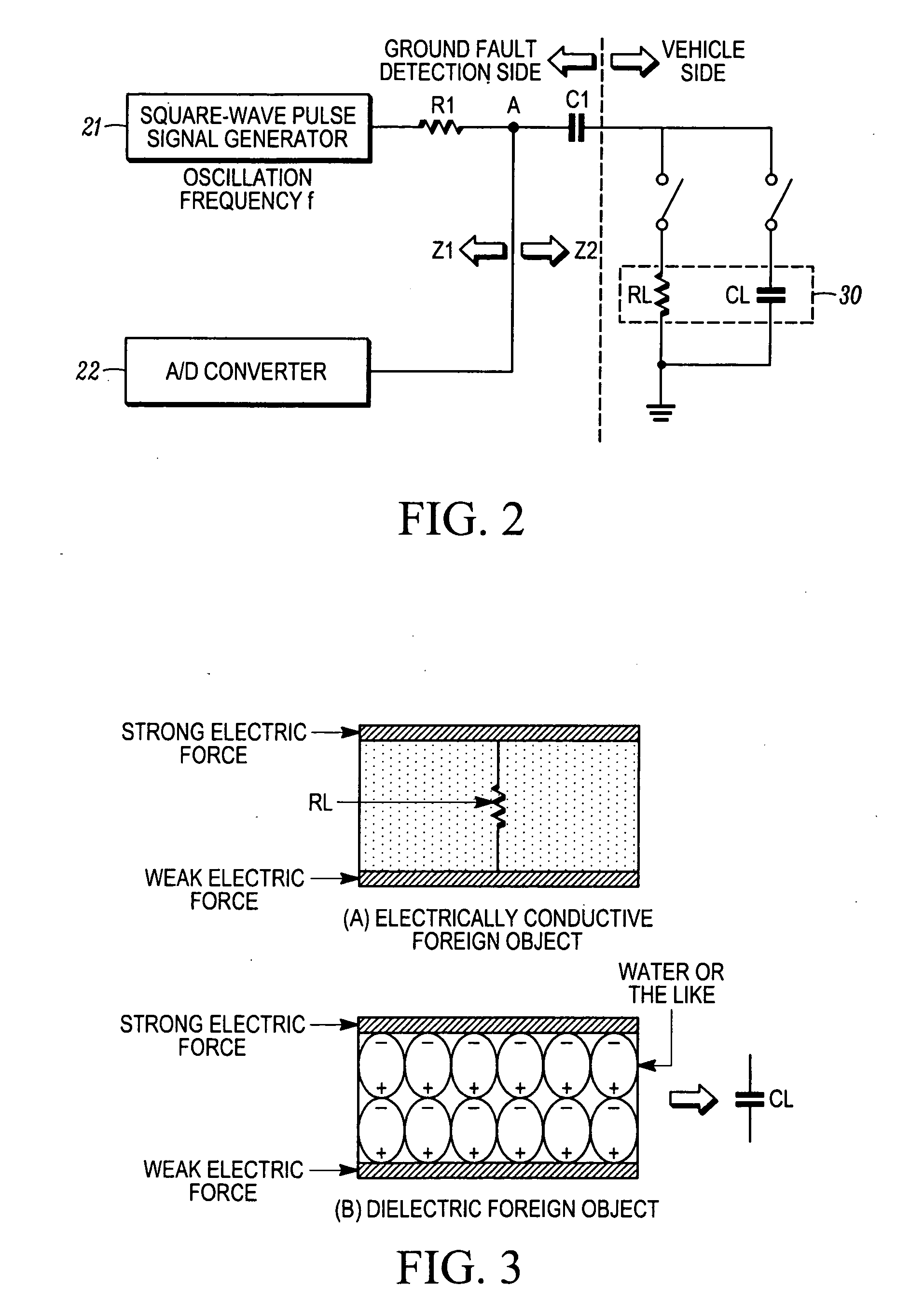
Ground fault detector for vehicle
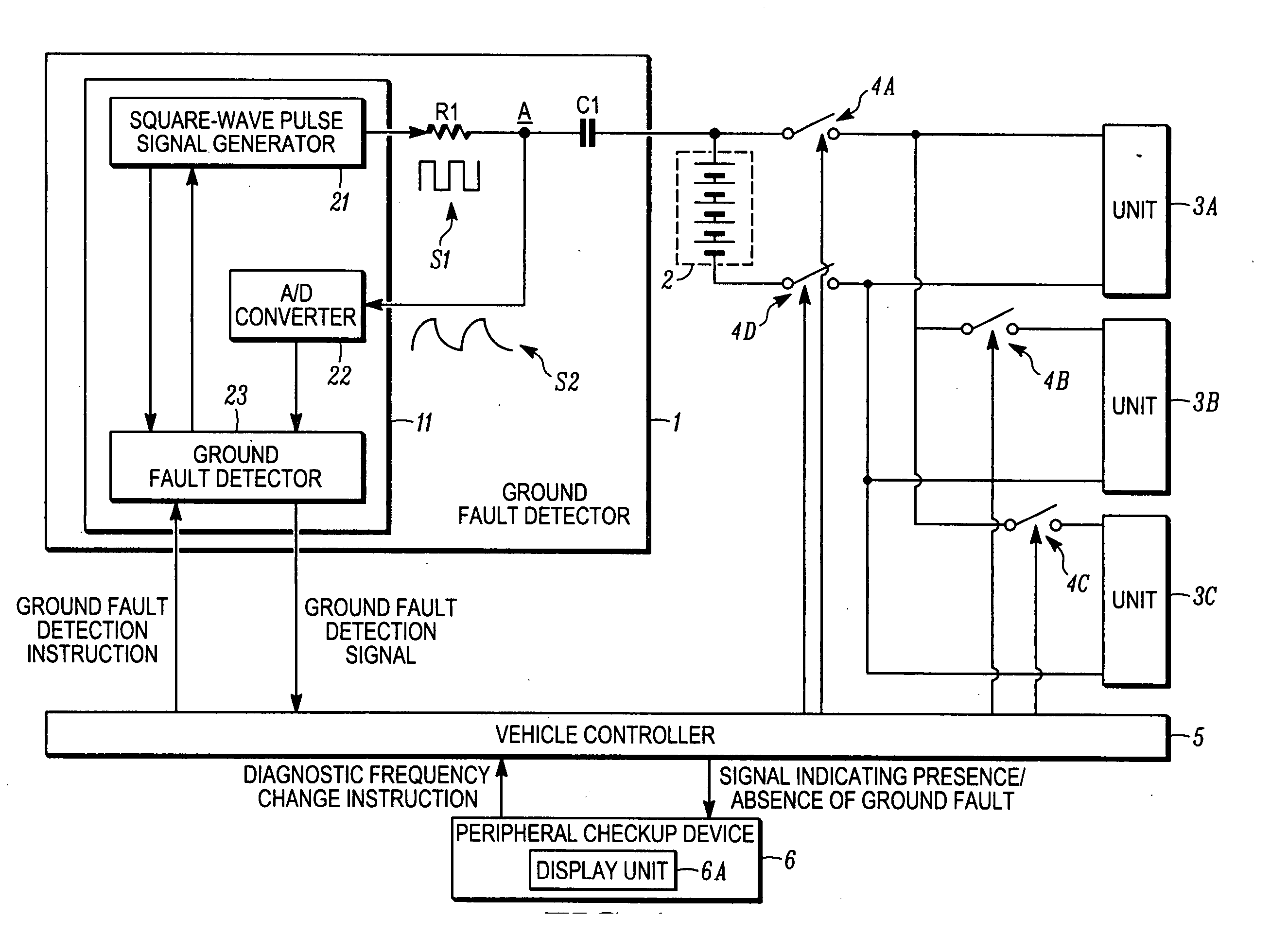
A ground fault detector and detection method for a vehicle that can determine the cause of the occurrence of a ground fault after detecting the presence of the ground fault. The output terminal of a high-voltage battery is connected to one side of a coupling capacitor. In operation, a pulse signal is applied to a measurement point on the other side of the coupling capacitor, and the voltage generated at that point is detected. Whether the high-voltage battery or the electrical equipment units are grounded is determined. To determine the cause of the ground fault, the oscillation frequency of the square-wave pulse signal is changed and applied to the measurement point. From the change in voltage amplitude detected, it is determined whether the cause of the ground fault is a resistive or a capacitive ground fault, according to the change in the impedance of the battery or the units.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com