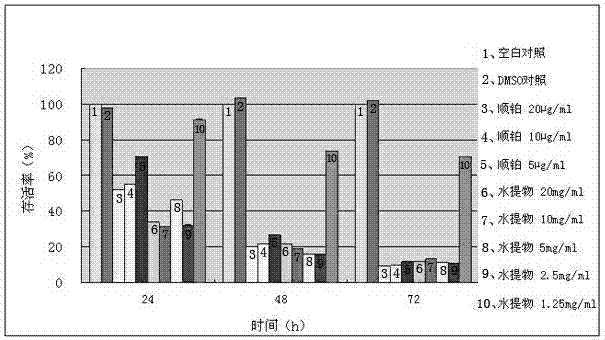
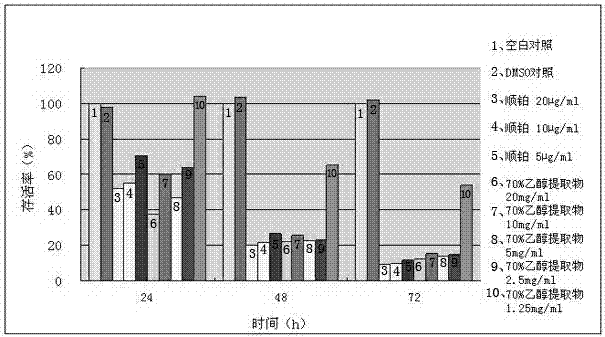
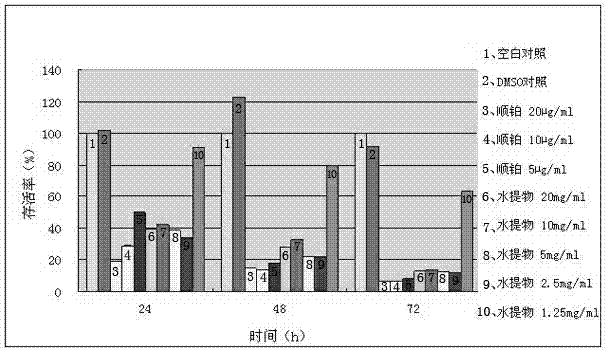
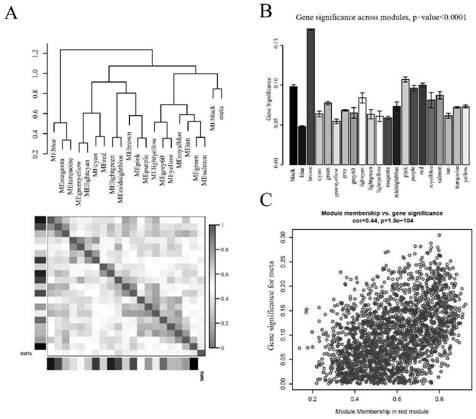
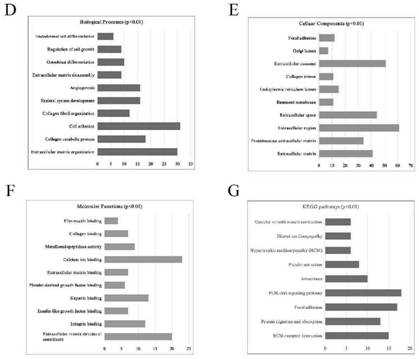
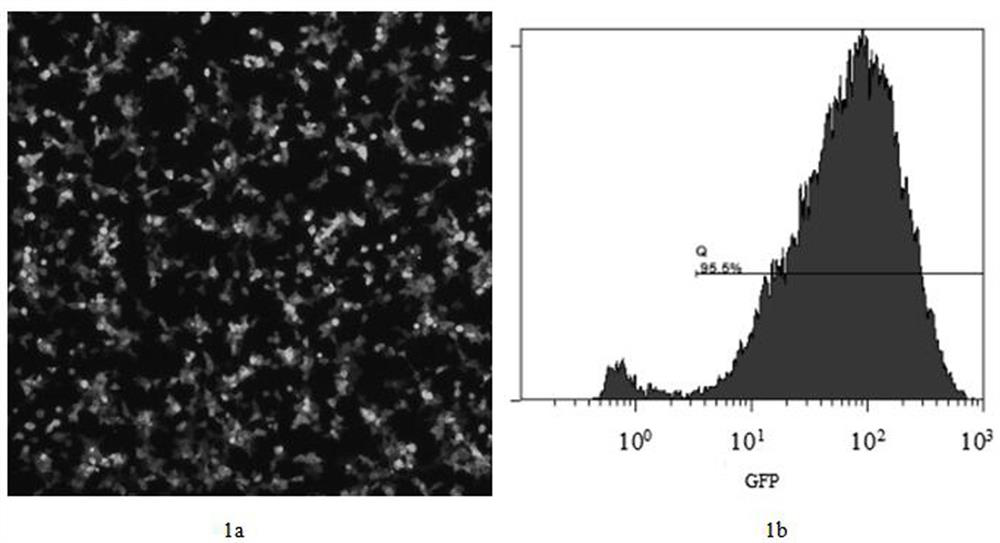
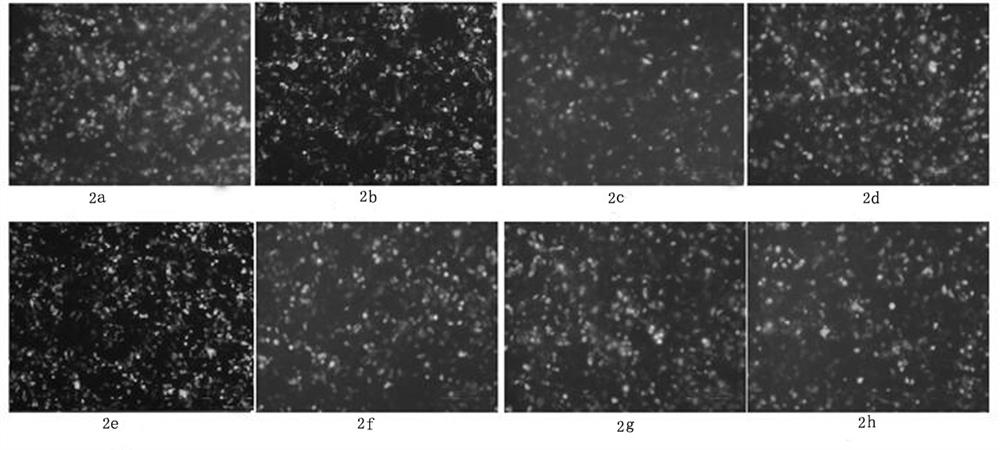
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
45 results about "Colon cancer cell line" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
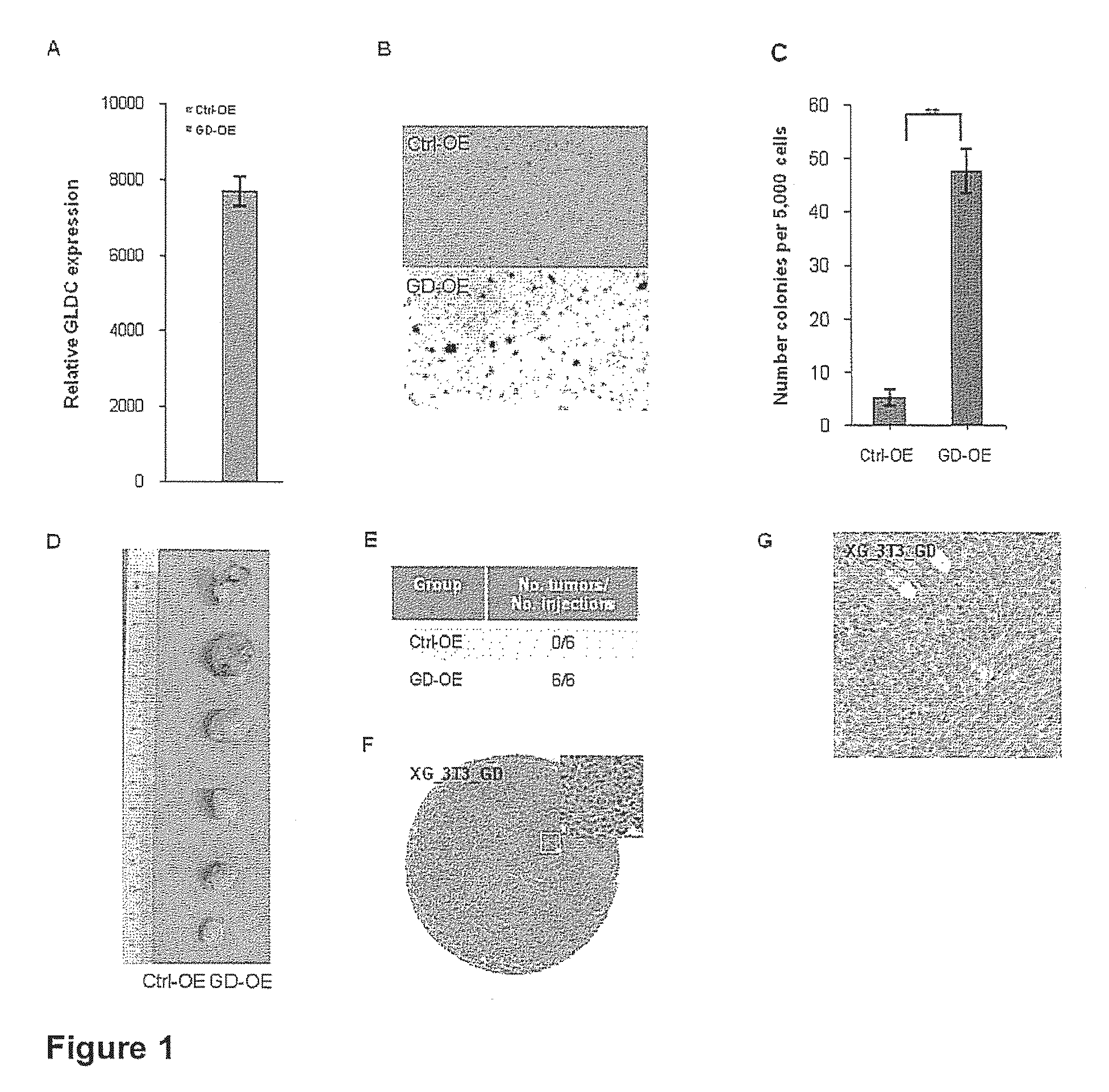
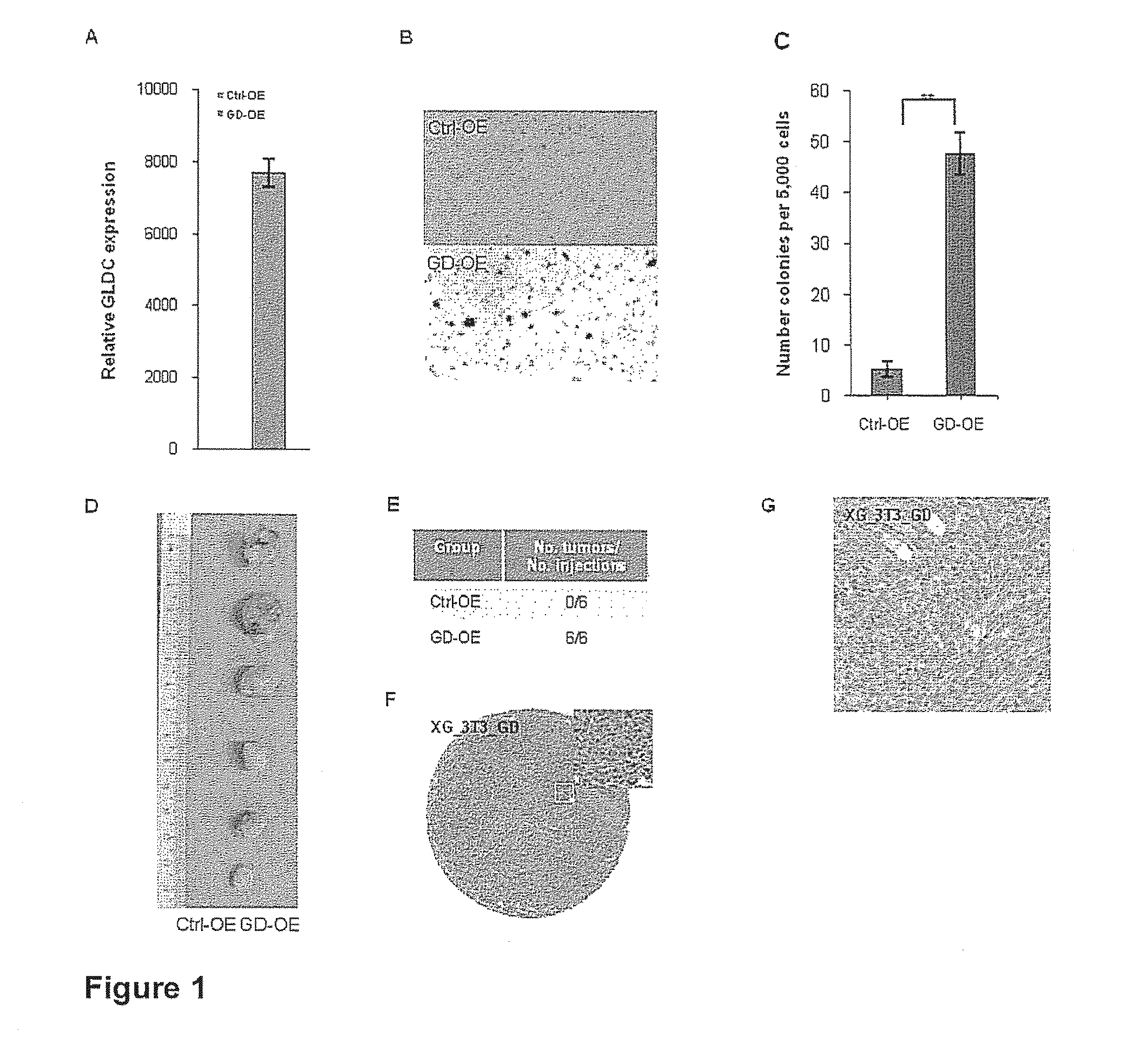
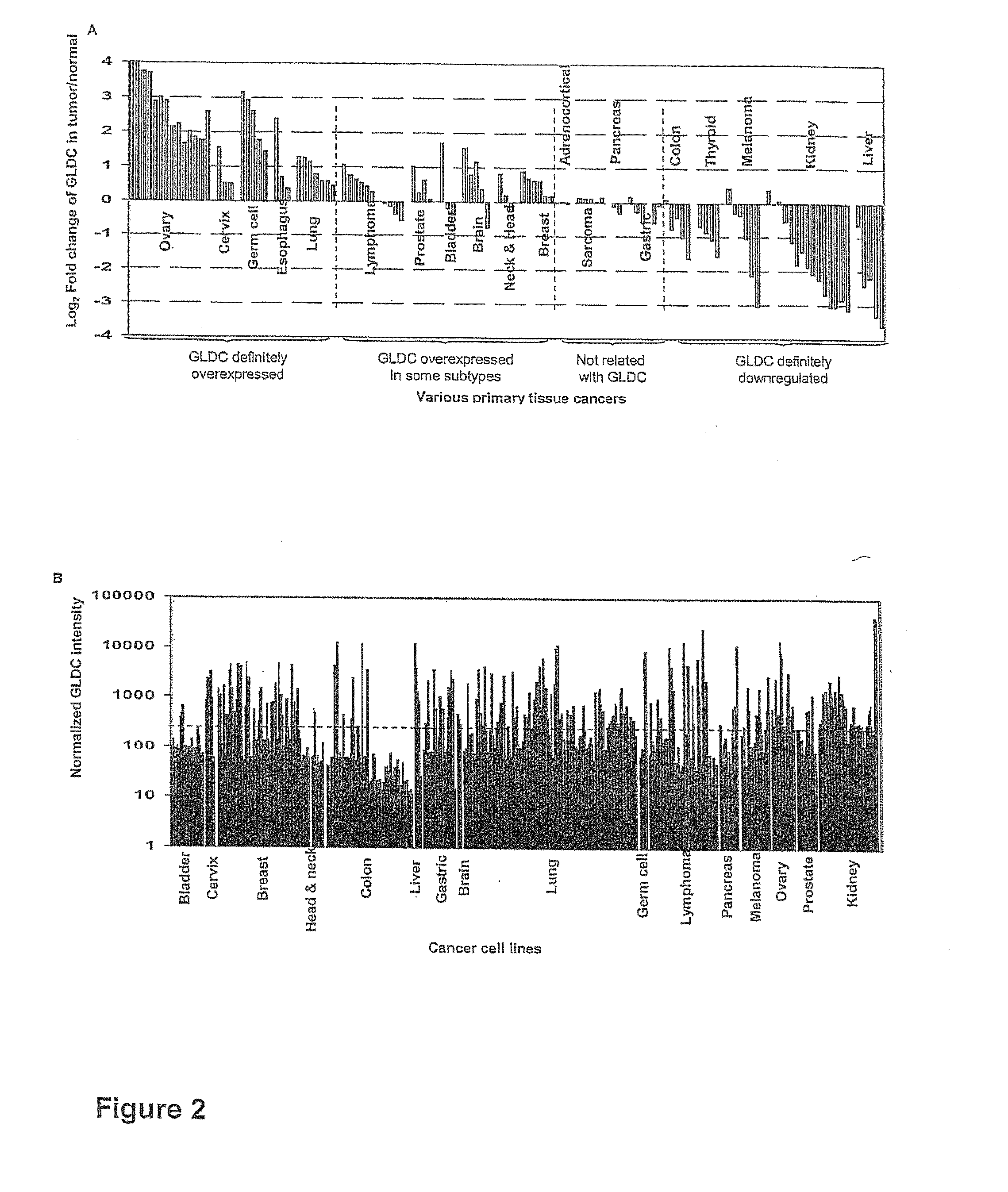
Targeting metabolic enzymes in human cancer
Targeting metabolic enzymes in human cancer Abstract Lung cancer is a devastating disease and a major therapeutic burden with poor prognosis. The functional heterogeneity of lung cancer (different tumor formation ability in bulk of tumor) is highly related with clinical chemoresistance and relapse. Here we find that, glycine dehydrogenase (GLDC), one of the metabolic enzyme involved in glycine metabolism, is overexpressed in various subtypes of human lung cancer and possibly several other types of cancers. GLDC was found to be highly expressed in tumor-initiating subpopulation of human lung cancer cells compared with non-tumorigenic subpopulation. By array studies we showed that normal lung cells express low levels of GLDC compared to xenograft and primary tumor. Functional studies showed that RNAi inhibition of GLDC inhibits significantly the clonal growth of tumor-initiating cells in vitro and tumor formation in immunodeficient mice. Overexpression of GLDC in non-tumorigenic subpopulation convert the cells to become tumorigenic. Furthermore, over-expression of GLDC in NIH / 3T3 cells and human primary lung fibroblasts can transform these cells, displaying anchorage-independent growth in soft agar and tumor-forming in mice. Not only is GLDC is expressed human lung cancer, it is also up-regulated in other types of cancer, such as colon cancer. RNAi knockdown of GLDC in colon cancer cell line, CACO-2 cells, can also inhibit the tumor formation in mice. Thus GLDC maybe a new metabolic target for treatment of lung cancer, and other cancers.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
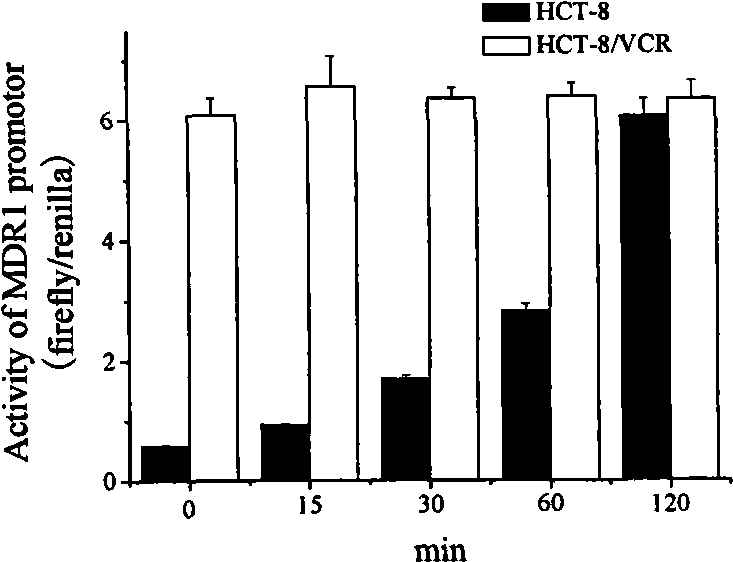
Recombinant plasmid containing MDR1 gene promoter and reporter gene and uses thereof
InactiveCN101481706AHigh sensitivityThe detection process is fastMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationWilms' tumorFhit gene
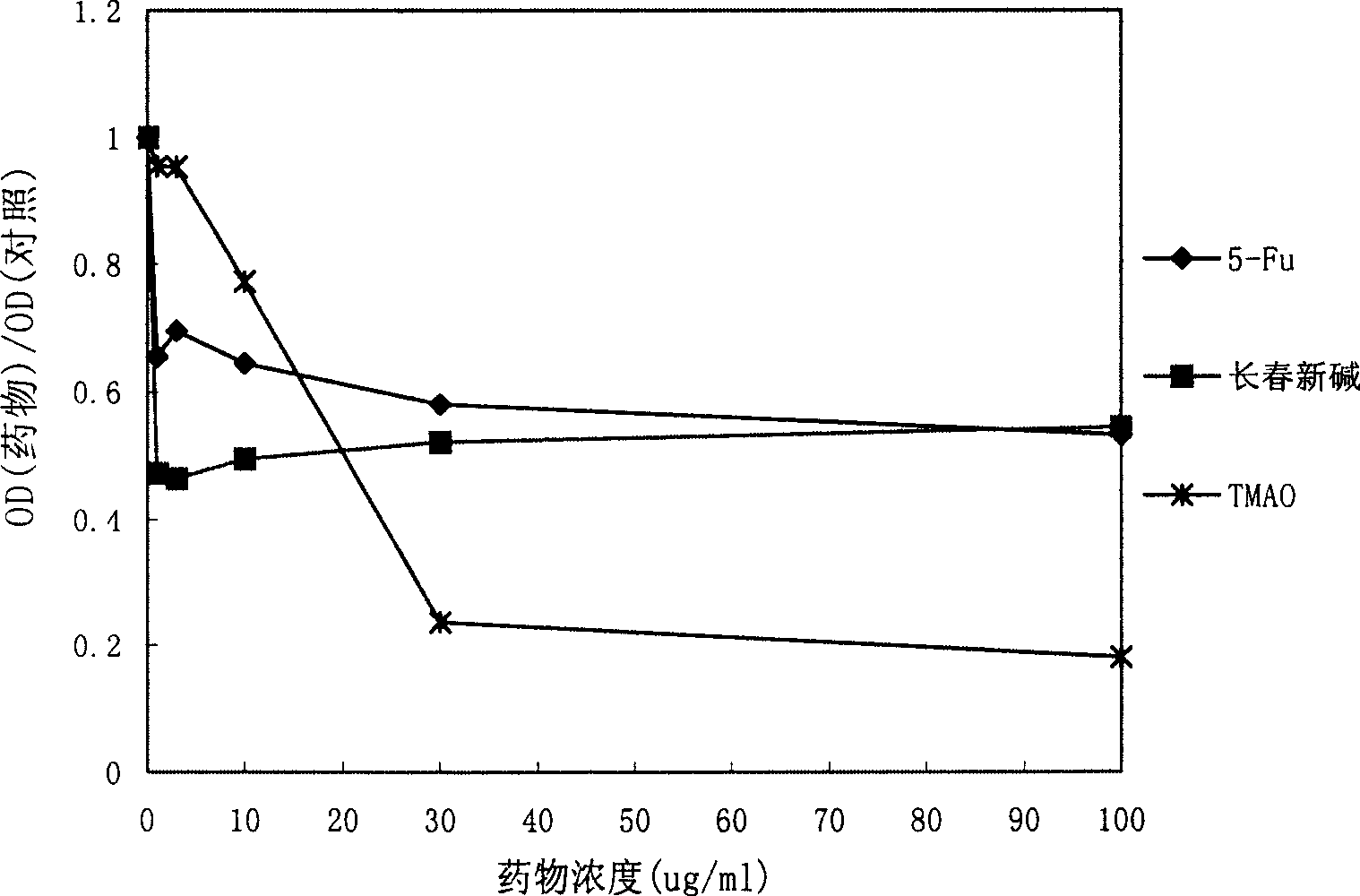
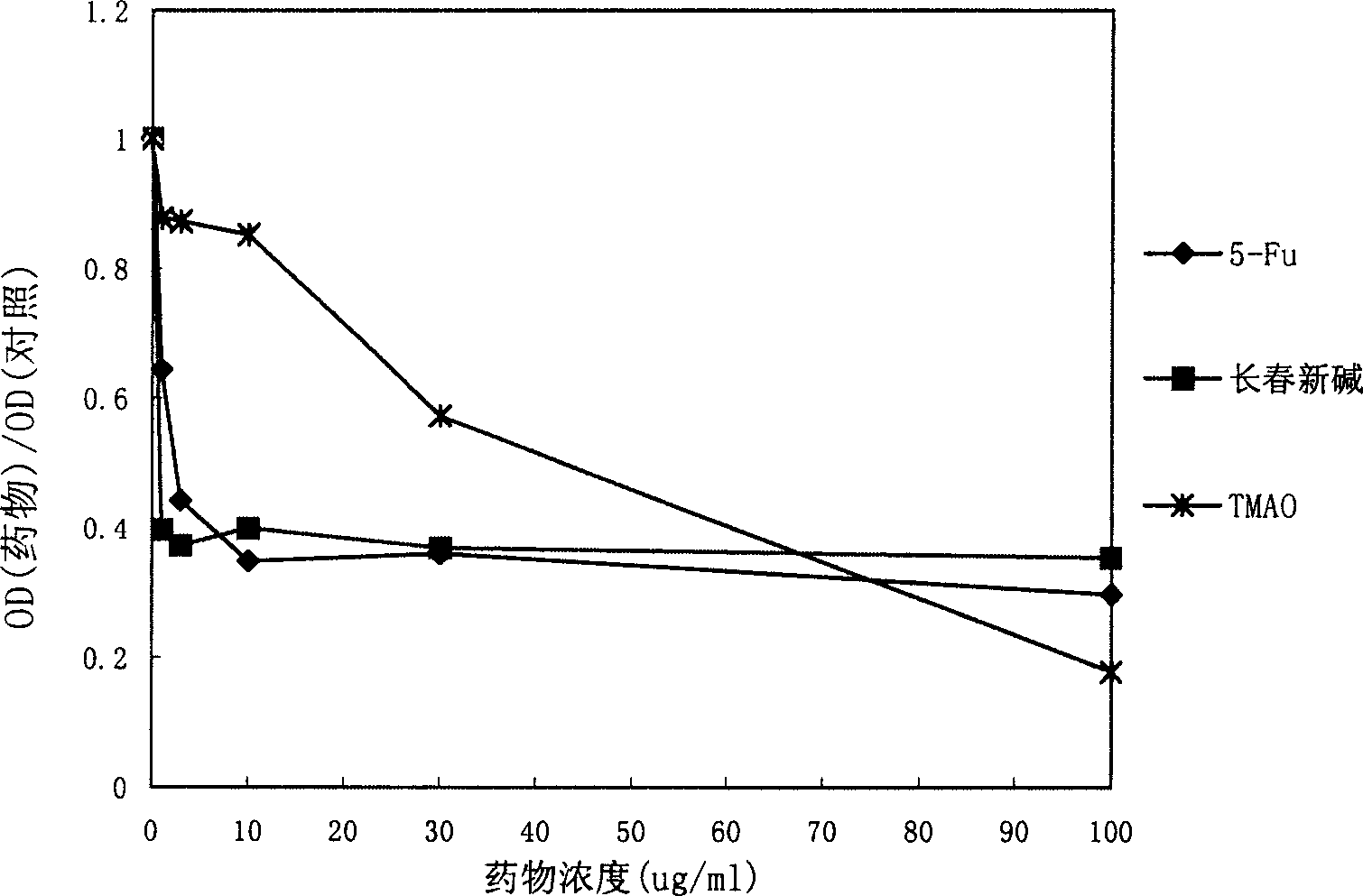
The invention belongs to the biological technical field and relates to a method of screening a tumor multidrug resistance reversal agent. In the method, a promoter specific sequence of a multidrug resistance (MDR1) gene is cloned and regrouped into a firefly luciferase report gene vector promotor sequence, therefore, an MDR1 report gene vector is constructed. The constructed vector and the sea pansy luciferase report gene vector are cotransfected into a sensitive and drug resistant colon cancer cell line. The activities of fireflies and the luciferase are detected simultaneously to reflect the promotor transcription activity of a MDRI gene promoter. Therefore, the method of screening the tumor multidrug resistance reversal agent in a targeted way is constructed. The method has perfect application prospect in screening tumor multidrug resistance reversal agents, researching the mechanism of the tumor multidrug resistance reversal agents and mechanisms of chemotherapeutic drugs inducing humor cells to generate drug resistance, etc.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE PUTUO DISTRICT CENT HOSPITAL
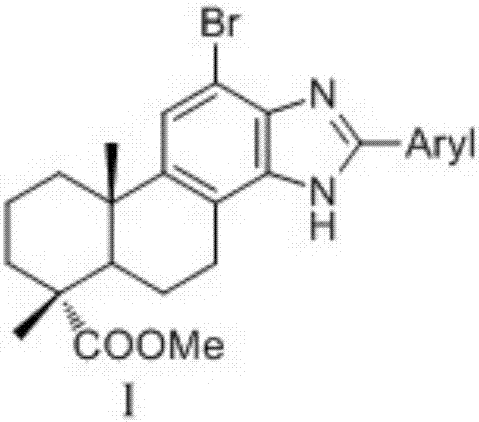
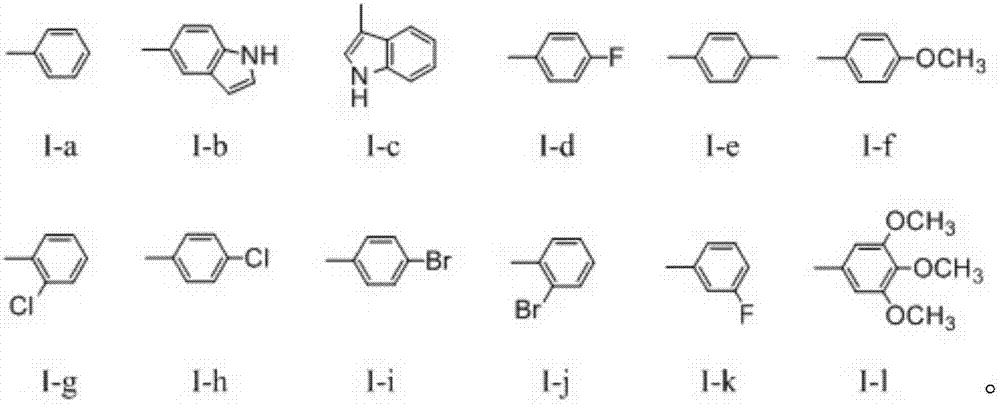
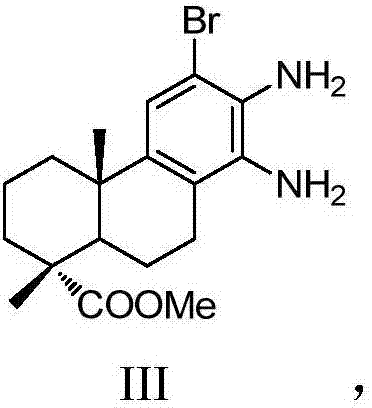
Dehydroabietic acid benzimidazole derivatives with antitumor activity as well as preparation method and application of dehydroabietic acid benzimidazole derivatives
InactiveCN107501387ASteroidsAntineoplastic agentsBenzimidazole derivativeNitrogenous heterocyclic compound
The invention discloses dehydroabietic acid benzimidazole derivatives with antitumor activity as well as a preparation method and an application of the dehydroabietic acid benzimidazole derivatives. The dehydroabietic acid benzimidazole derivatives I-a to I-l with the structures shown in a general formula I and pharmaceutically acceptable salt of the derivatives are shown in the description, wherein corresponding Aryl of dehydroabietic acid benzimidazole derivatives I-a to I-l are shown in the description respectively. Nitrogen-containing heterocyclic compounds are pharmaceutically acceptable salt of the dehydroabietic acid benzimidazole derivatives and have good antitumor bioactivity. Pharmacology experiments prove that the compounds have a remarkable inhibition effect on hepatoma cell lines SMMC-7721, breast cancer cell lines MDA-MB-231 and colon cancer cell lines CT26.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Compound Chinese actinidia root Chinese medicinal composition and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102204974AGood effectHas a tumor suppressive effectAntineoplastic agentsPlant ingredientsActinidiaHep G2
The invention discloses a compound Chinese actinidia root Chinese medicinal composition and a preparation method and application thereof, belonging to the technical field of traditional Chinese medicines. The Chinese medicinal composition is characterized by comprising the following traditional Chinese medicines in parts by weight: 40-80 parts of Chinese actinidia root, 20-40 parts of salvia chinensis, 20-40 parts of herba scutellariae barbatae, 20-40 parts of herba oldenlandiae and 20-40 parts of giant knotweed. The compound Chinese actinidia root Chinese medicinal composition has remarkable proliferation inhibition effects on various cancer cells such as a hepatoma cell line Hep-G2, a lung cancer cell line NCI-H460, a gastric cancer cell line MGC-803, a breast cancer cell line MCF-7, a colon cancer cell line HCT-116 and the like, and can be used for reducing physical and psychological pains of a cancer patient in the chemo-treatment process and solving the problems of difficult and expensive administration.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SIXIAN PHARMA
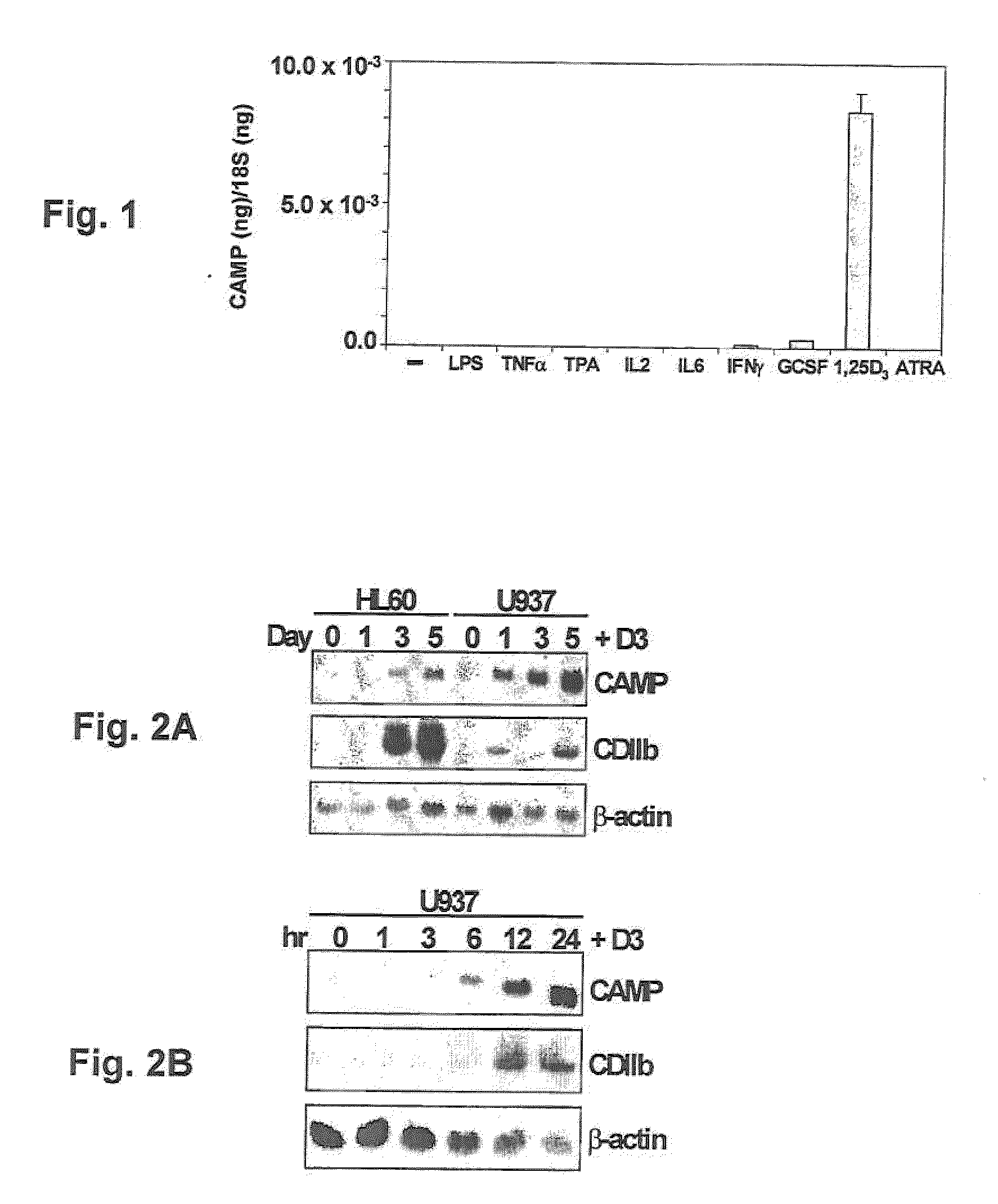
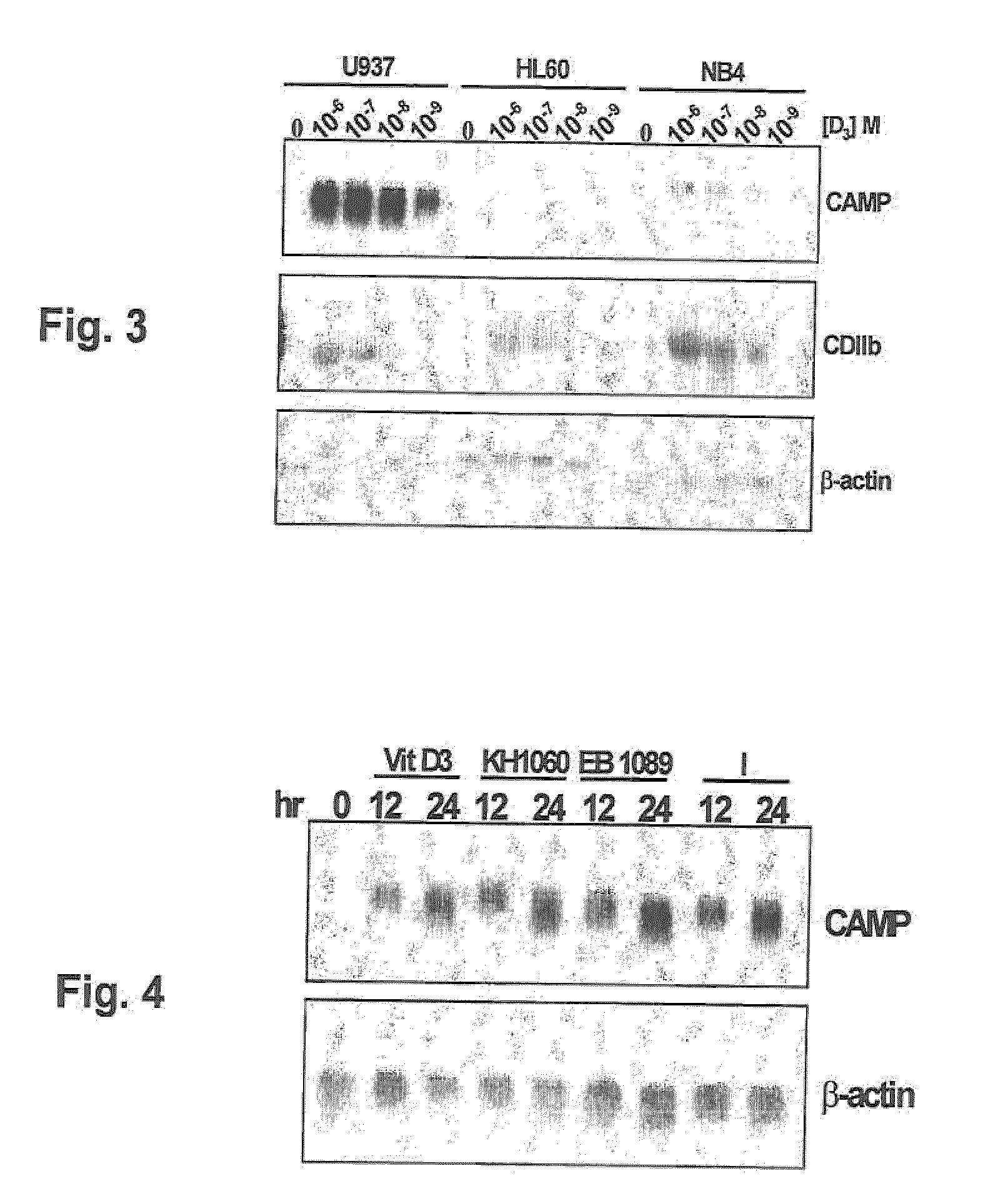
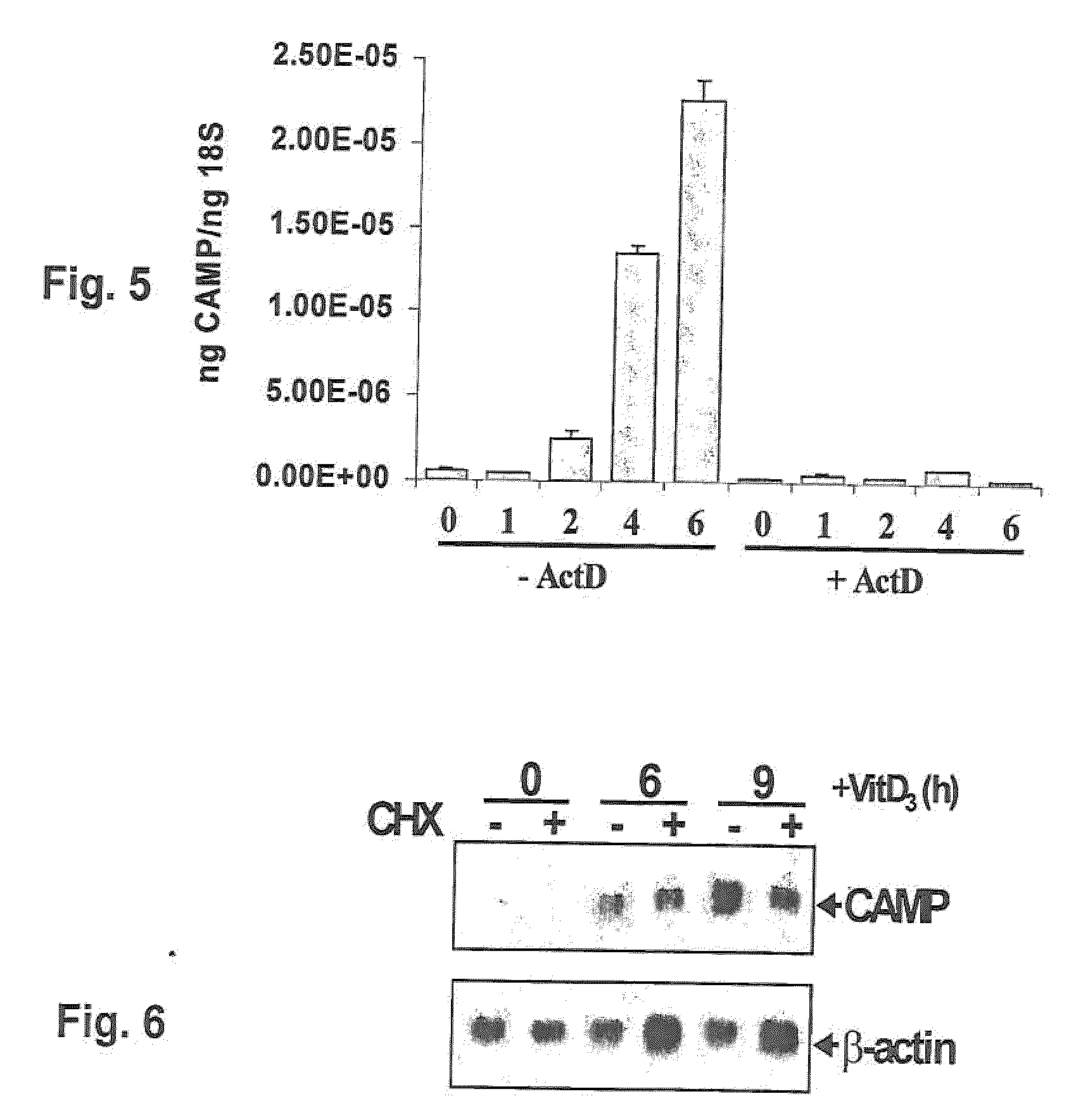
Induction of innate immunity by vitamin d3 and its analogs
Cationic antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are an integral part of the innate immune system. Cathelicidin and defensin homologs from a variety of species exhibit broad-range bactericidal activity. The human cathelicidin analog, hCAP18, is encoded by the CAMP gene. Vitamin D3 and its analogs upregulate transcription of CAMP and defensin β2 (defB2) genes, leading to increased expression of hCAP18 mRNA and defB2. Induction of CAMP was observed in acute myeloid leukemia (AML), immortalized keratinocyte and colon cancer cell lines, as well as normal human bone marrow (BM)-derived macrophages and fresh BM cells. The present invention provides methods of inducing cathelicidin production by administering Vitamin D3 or Vitamin D3 analogs, as well as methods of treating skin infections and infections of the colon, sepsis and wound healing, preventing bacterial growth on skin grafts, promoting angiogenesis, and promoting chemoattraction by administering Vitamin D3 or Vitamin D3 analogs to upregulate cathelicidin and defensin expression.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
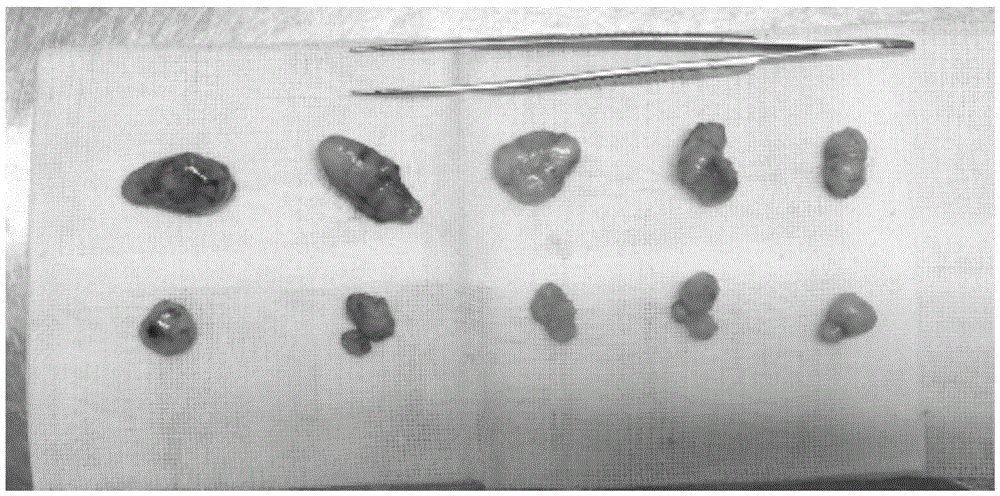
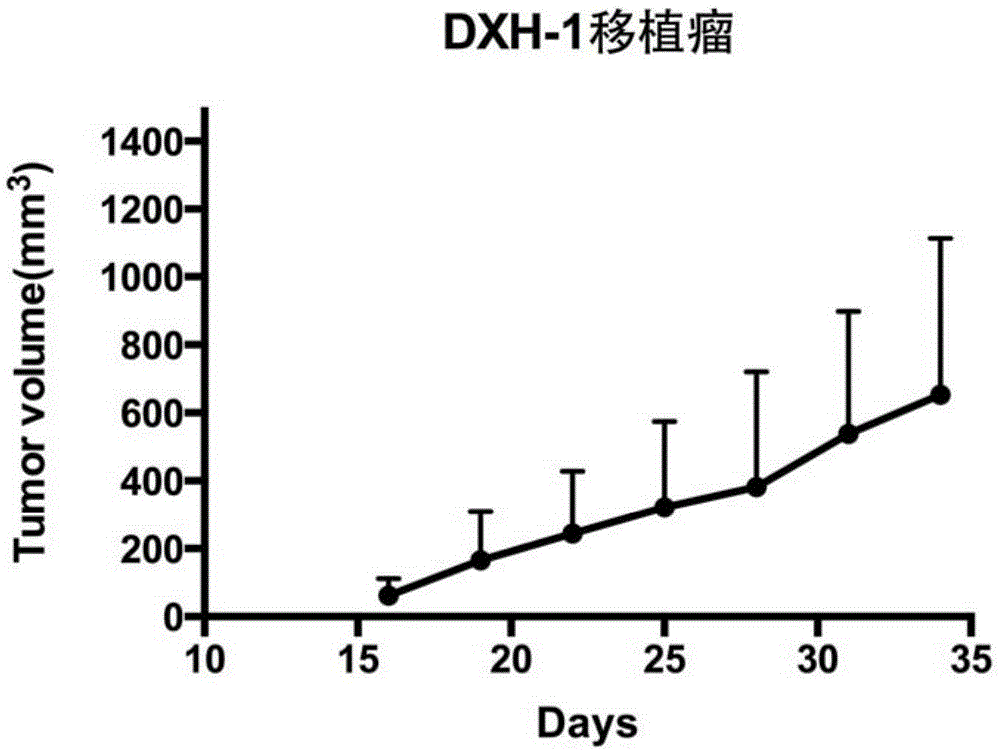
Human colon carcinoma cell line DXH-1 and application thereof
ActiveCN105296430AStrong tumorigenic abilityMicrobiological testing/measurementUnknown materialsTransfer cellSigmoid colon carcinoma
The invention provides a human colon carcinoma cell line DXH-1, which is derived from primary lesion of human sigmoid colon carcinoma, and application of the human colon carcinoma cell line as a human colon carcinoma occurrence, human colon carcinoma development or human colon carcinoma transfer cell model, application of the human colon carcinoma cell line in establishing a human colon carcinoma animal model and application of the human colon carcinoma cell line in researching a human colon carcinoma occurrence mechanism and / or medicines for treating the human colon carcinoma. The human colon carcinoma cell line DXH-1 disclosed by the invention can be stably transferred for more than 50 generations, so that an appropriate material is provided for colorectal carcinoma mechanism and drug screening. In an in-vivo nude mice experiment, the human colon carcinoma cell line shows a relatively strong tumorigenesis cavity, and the cell line, transplanted subcutaneously in nude mice by 1*106 cells, is capable of promoting 100% (5 / 5) tumorigenesis after 35 days; the DXH-1 cell has certain drug resistance to colon carcinoma chemotherapeutics (5FU, such as oxaliplatin, irinotecan and the like), so that a material is provided to the researches on a colon carcinoma chemotherapeutic resistance mechanism; and the human colon carcinoma cell line DXH-1 is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection in Wuhan University, Wuhan, China with number of CCTCC No: C201543.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
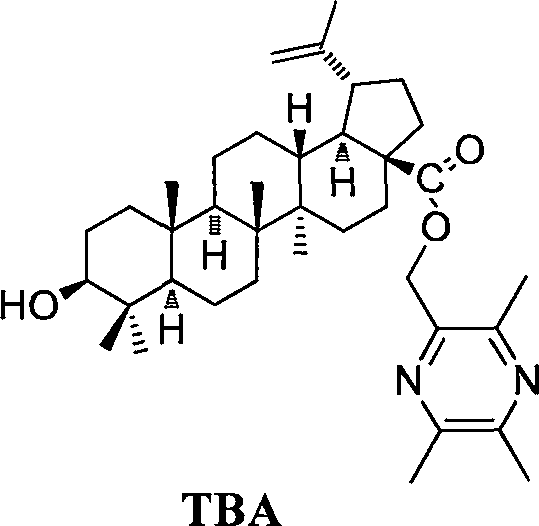
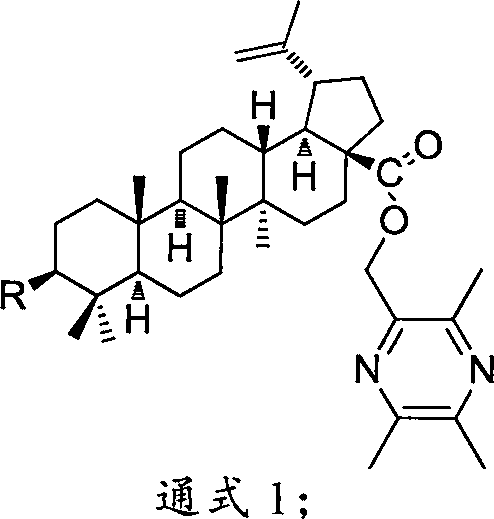
Compound BA-X having antitumor effect, preparation method and applications thereof
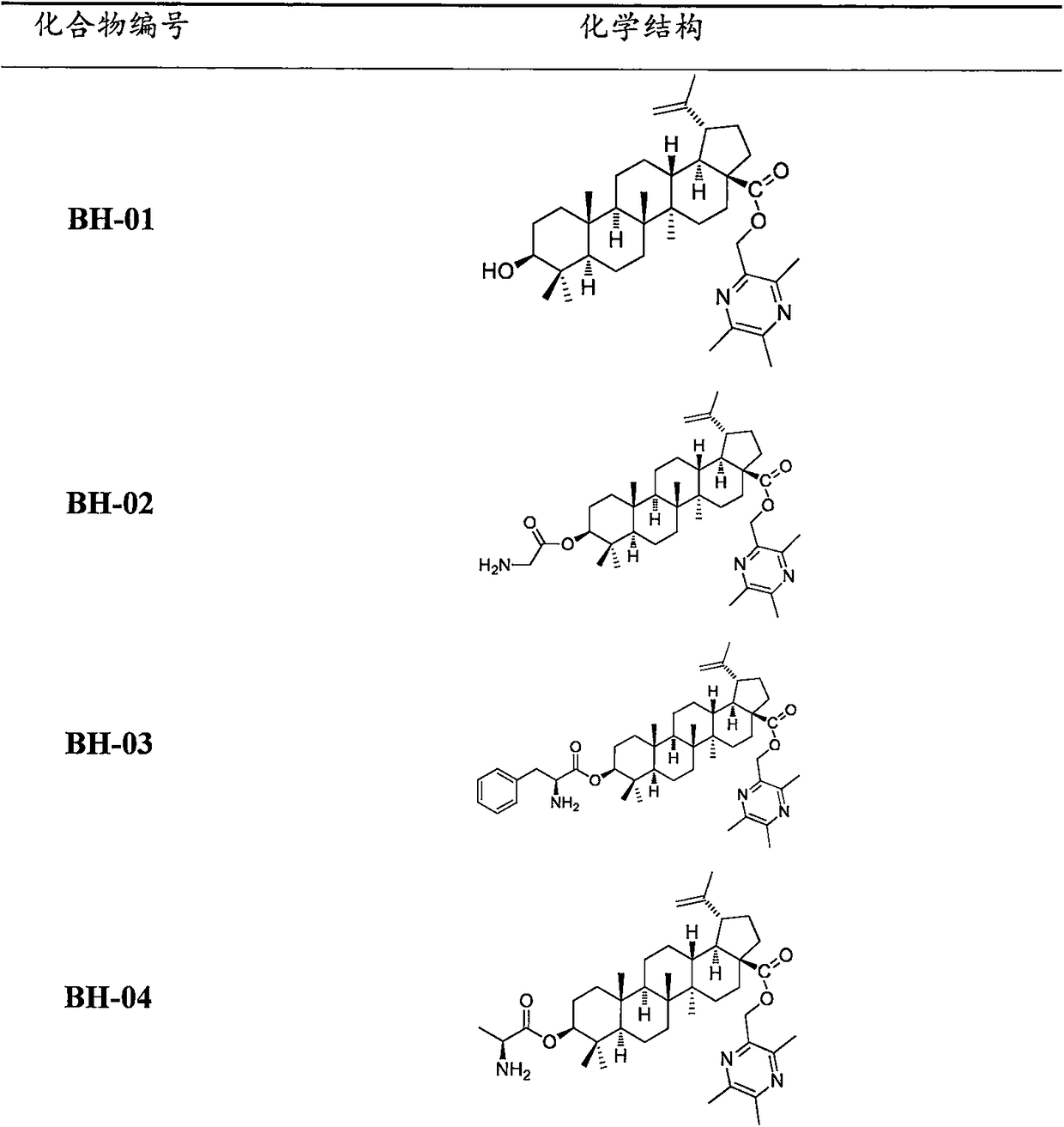
InactiveCN108456239AGood antitumor activityLow cytotoxic activityOrganic active ingredientsSteroidsOncologyTumor cells
The present invention provides a class of compounds having a structure represented by a general formula 1, and a preparation method thereof, and applications in preparation of antitumor drugs. According to the present invention, the compound can significantly inhibit the growth of tumor cell lines (HepG-2, HT-29, Hela, BGC-823 and A549) while has low toxicity on Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells, wherein the compound BH-26 has good anti-proliferative activity against colonic carcinoma cell line HT-29, human cervical cancer cell line Hela and human gastric cancer cell line BGC823 comparedto the positive drug cisplatin, and has significantly low cytotoxicity to normal Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells compared to the positive drug cisplatin. The formula 1 is defined in the specification.
Owner:雷鹏程
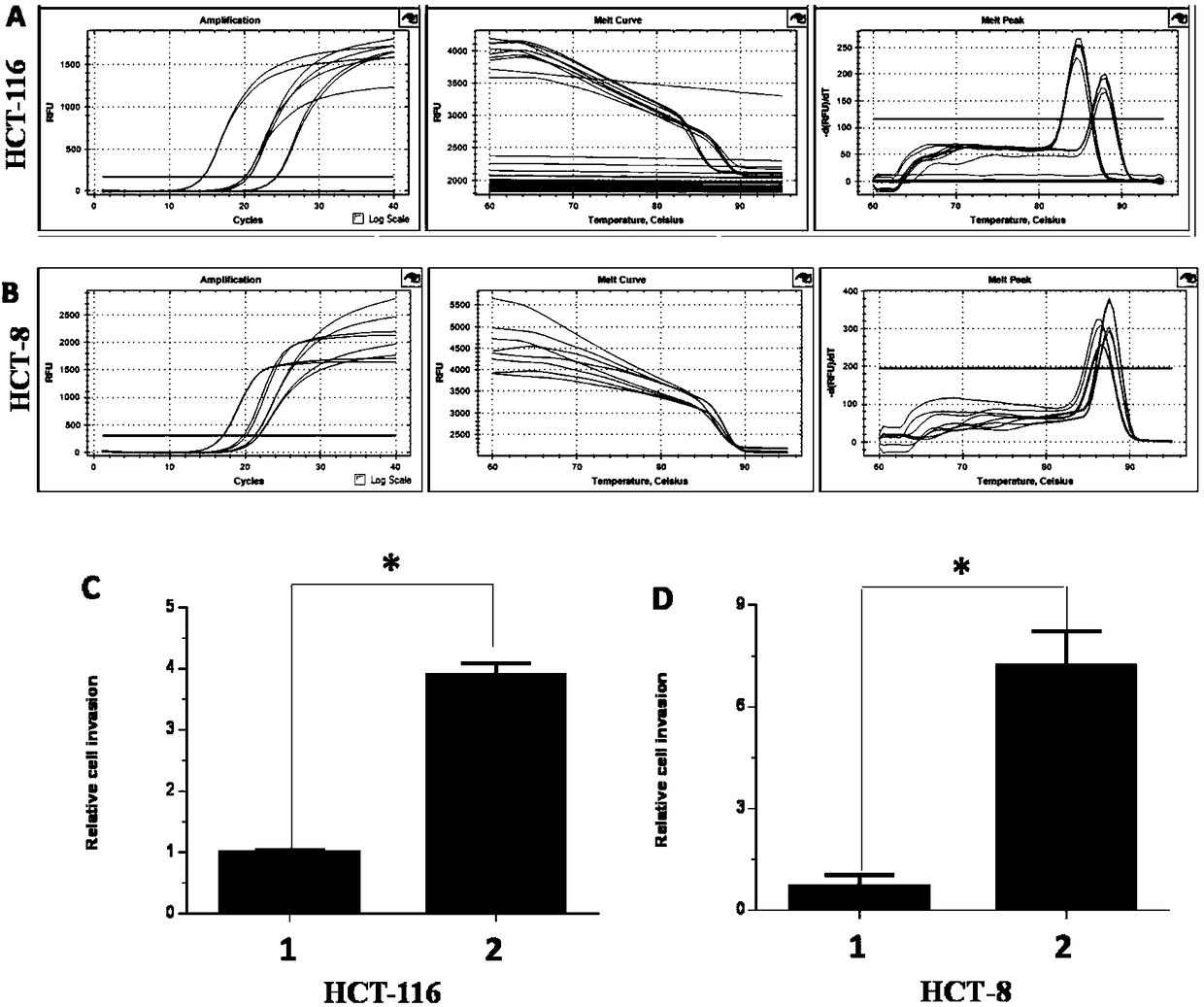
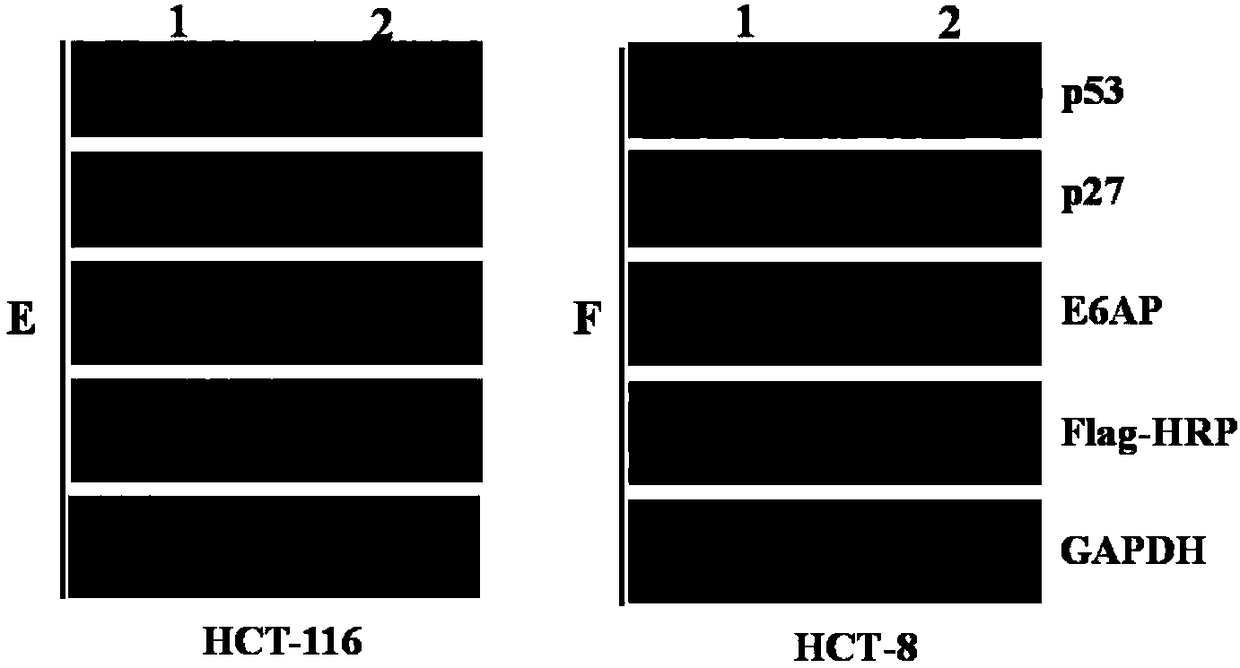
Experimental method for promoting growth and metastasis of colon cancer cells by lentivirus overexpression vector mediated E6-AP
InactiveCN108570453AInhibit apoptosisPromote growthMicrobiological testing/measurementLigasesLymphatic SpreadWestern blot
The invention discloses an experimental method for promoting growth and metastasis of colon cancer cells by lentivirus overexpression vector mediated E6-AP. The experimental method comprises the following steps: detecting the expression of E6-AP in different colon cancer cell lines, and determining low expression E6-AP of HCT-116 and HCT-8 colon cancer cells; co-transfecting human embryonic kidney293FT cells with over-expression PCDH-pCDNA3.0-FLAG-E6-AP plasmid and lentiviral packaging helper plasmids to obtain stable expression cells of lentiviral mediated overexpression of E6-AP, and detecting the overexpression of E6-AP through real-time PCR and Western blot detection; and detecting the influence of overexpression of E6-AP on the growth, migration and invasion of colon cancer cells through CCK-8, scratch healing and Transwell TM experiments. The experimental method provides a new target for colon cancer targeted therapy.
Owner:江西中医药大学第二附属医院
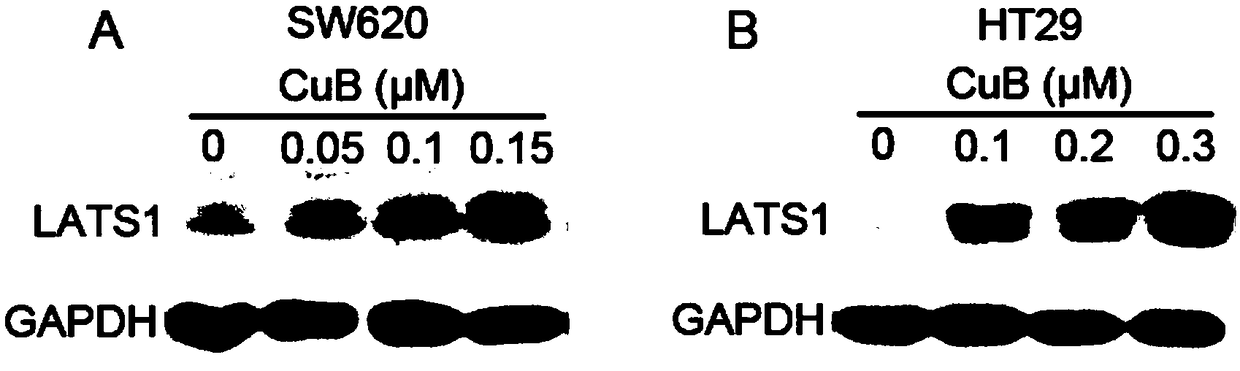
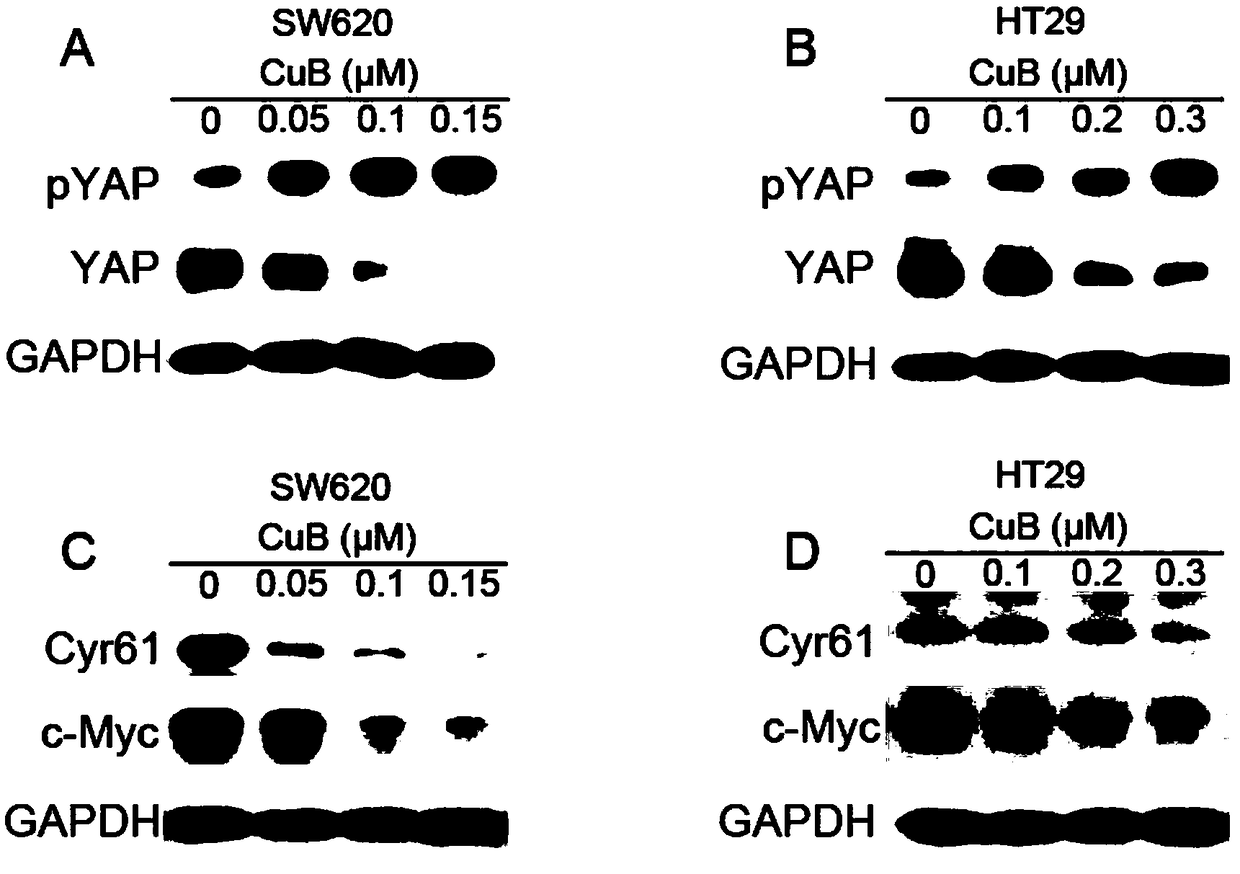
Novel application of cucurbitacin B
InactiveCN108785315APrevent proliferationSmall toxicityOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsSide effectLymphatic Spread
The invention relates to novel application of cucurbitacin B. Particularly, studies find that the cucurbitacin B can upregulate expression of an LATS1 gene and inhibit expression of a YAP gene and downstream related genes thereof in a colon cancer cell line. Moreover, the cucurbitacin B has the effect of inhibiting proliferation, invasion and metastasis of a human colon cancer SW620 cell line andan HT29 cell line, and can promote apoptosis thereof. The invention finds that the cucurbitacin B can be used as an activator for regulating a Hippo-YAP signaling pathway, is a novel promising effective anticancer medicine, can be used as an active component in preparation of medicines for treating cancers such as human colon cancer, and is conducive to improving the targeting ability of medicinalcancer treatment and reducing toxic and side effects of the medicines.
Owner:HUBEI UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE
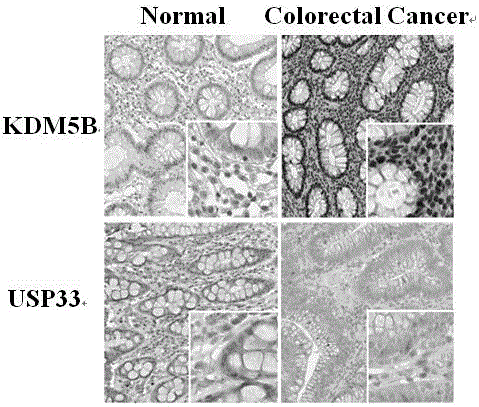
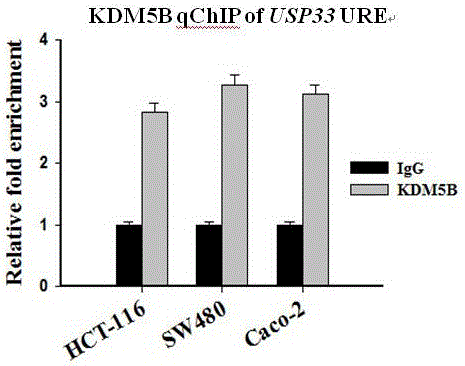
Mutated ubiquitin specific protease 33 gene and application of mutated ubiquitin specific protease 33 gene
ActiveCN106834317AResistance to inhibitionGrowth inhibitionPeptide/protein ingredientsNucleic acid vectorMonoclonal antibodyColorectal cancer cell line
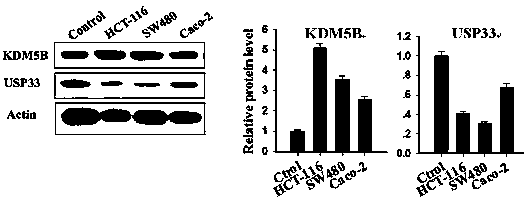
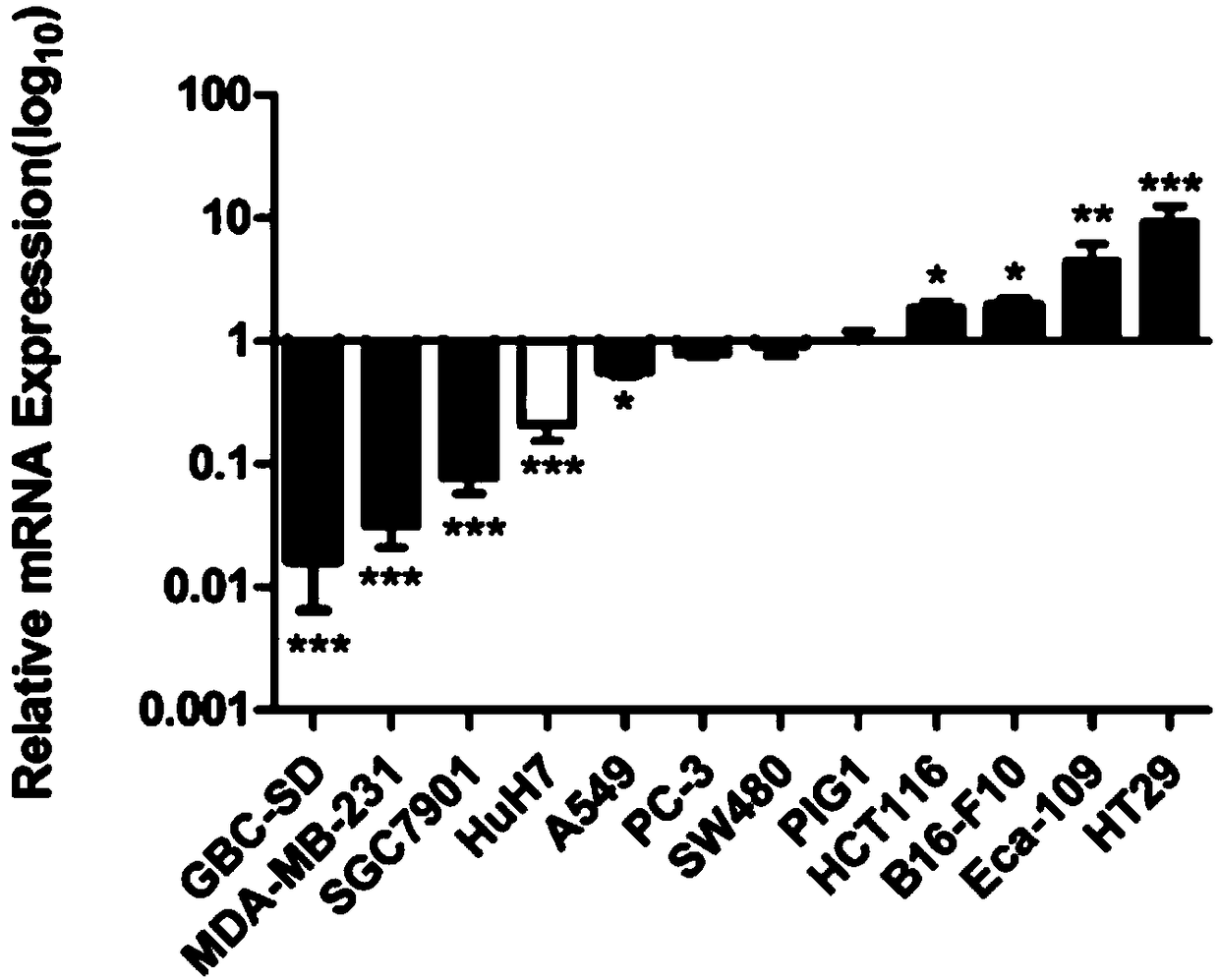
The invention discloses a mutated ubiquitin specific protease 33 gene and application of the mutated ubiquitin specific protease 33 (USP33) gene to production of a medicine for treating colorectal cancer. A research finds out that KDM5B has high expression in a colorectal cancer clinical sample and a colorectal cancer cell line and promotes the proliferation of colorectal cancer cells through inhibiting USP33. A KDM5B inhibitor or a monoclonal antibody of the KDM5B can be used for remarkably inhibiting the proliferation of the colorectal cancer cells. A further research proves that the KDM5B is combined with a USP33 gene promotor region, and the inhibition of the expression to the USP33 gene is realized through combining an upstream specific regulation and control sequence GCACA / C or G / TGTGC. The mutated ubiquitin specific protease 33 gene obtained through a site-directed mutation PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) technology can be used for resisting the inhibition effect of the KDM58B, so that the growth of the colorectal cancer cell line is inhibited.
Owner:XINXIANG MEDICAL UNIV
Compound extracted from eucalyptus plants and use thereof
The invention discloses a tricyclic sesquiterpene compound extracted from eucalyptus, a pharmaceutical composition containing the compound and its application in treating tumors. In vitro and animal experiments have proved that this tricyclic sesquiterpene compound extracted from Eucalyptus can inhibit the growth of liver cancer, gastric cancer, esophageal cancer, prostate cancer, kidney cancer, lung cancer and colon cancer cell lines. Mice inoculated with tumors also had an inhibitory effect.
Owner:中国人民解放军第二军医大学药学院 +2
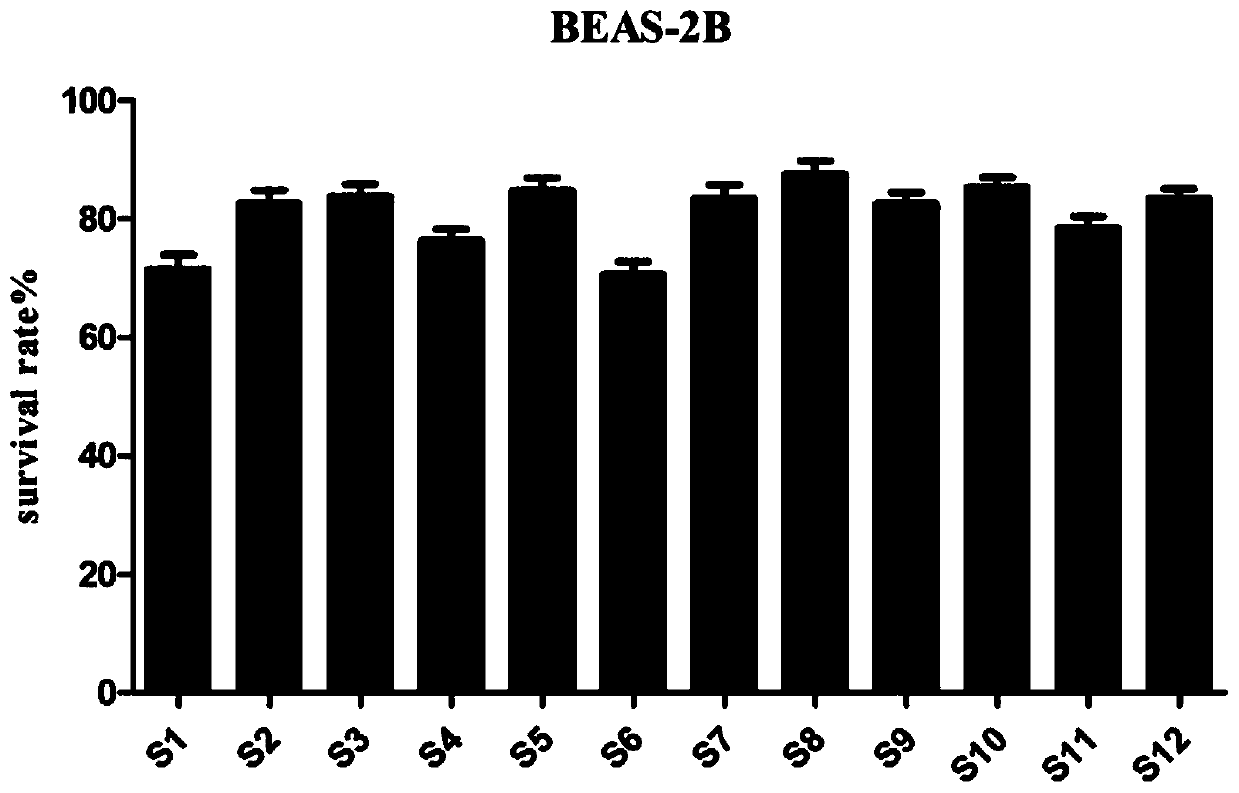
1-(2,6-chlorphenyl)-3-substituted urea colon cancer inhibitor, preparation method and applications thereof.
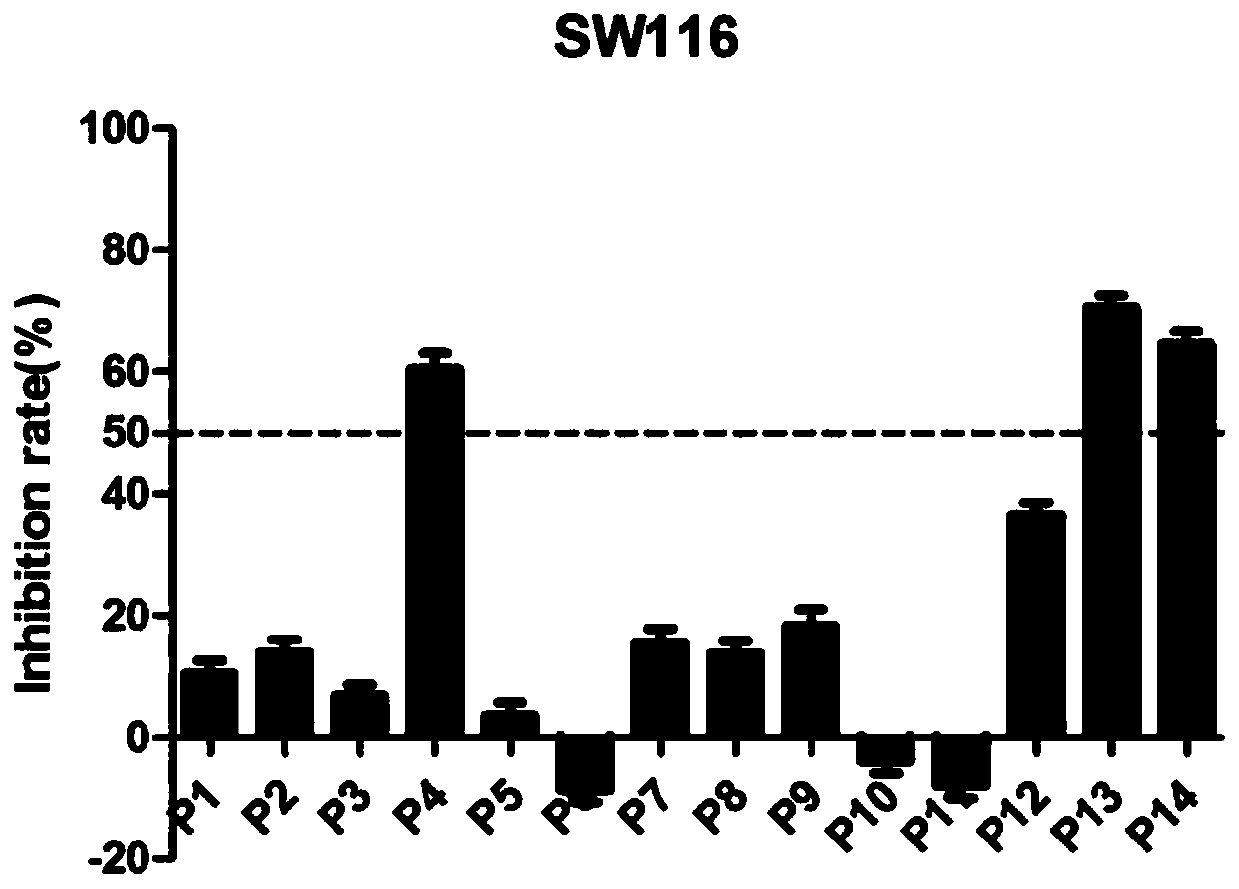
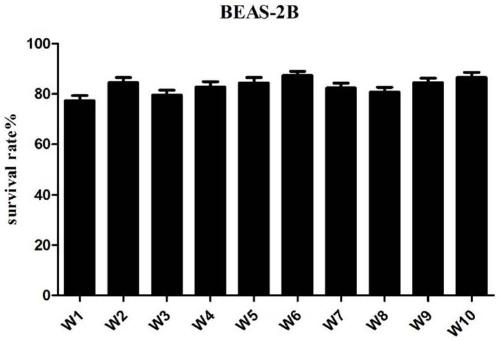
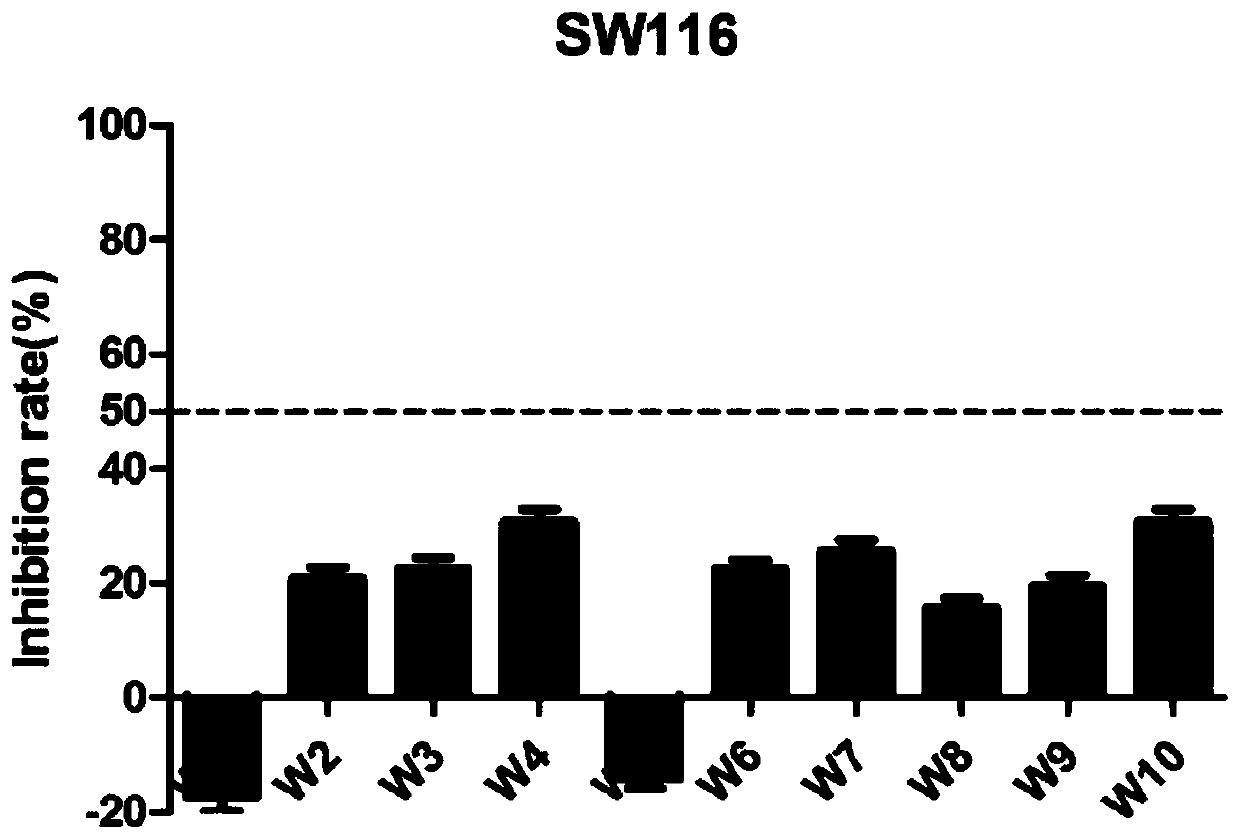
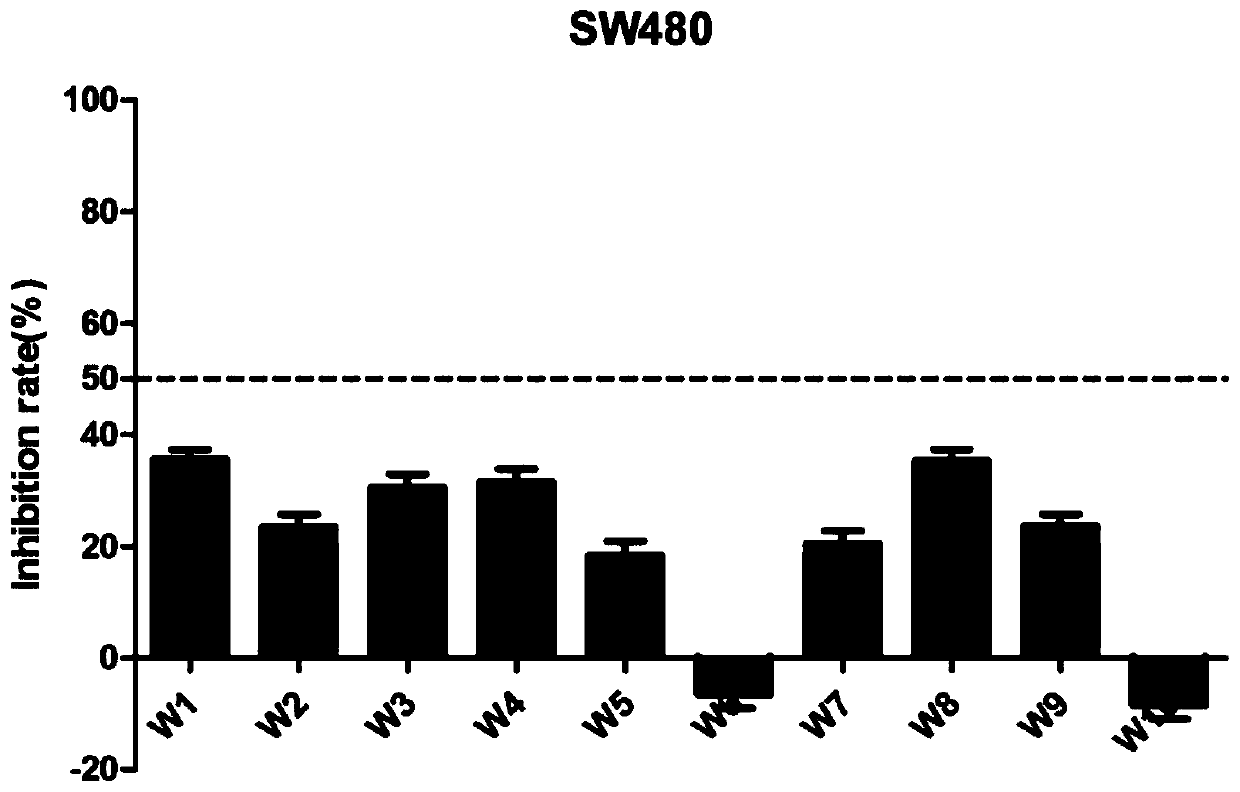
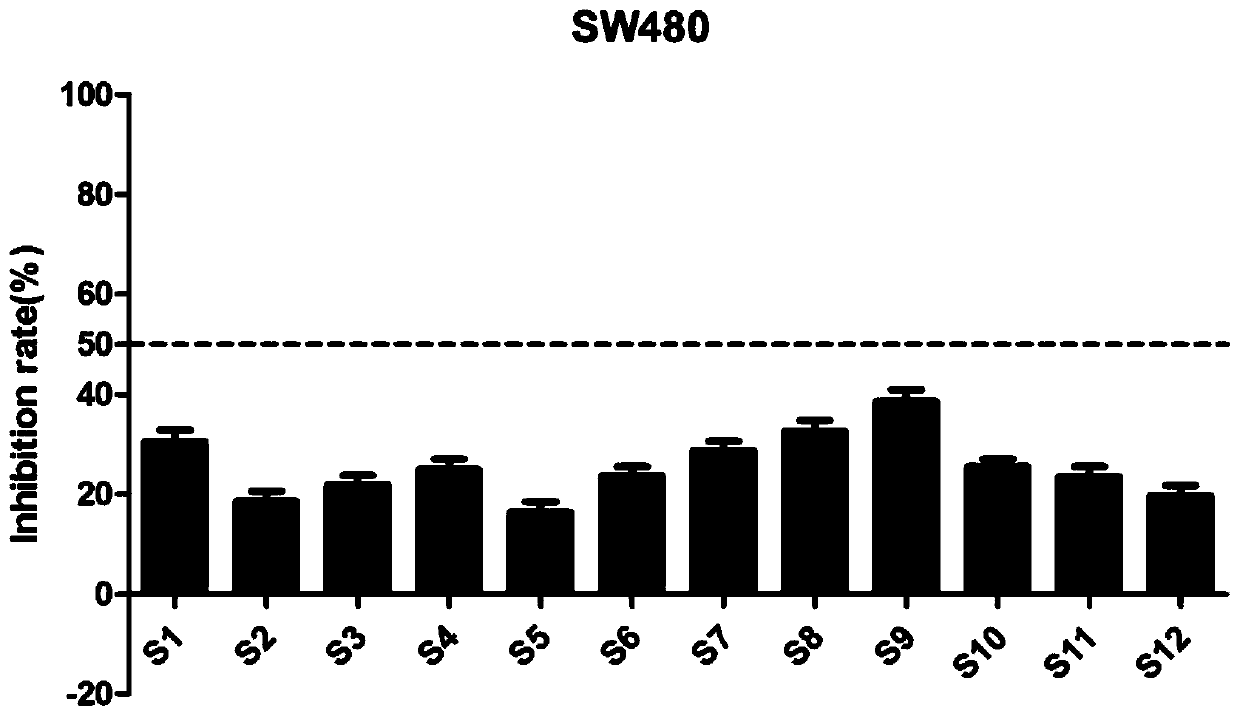
The invention discloses a 1-(2,6-chlorphenyl)-3-substituted urea compound capable of acting on colon cancer, a preparation method and applications thereof. According to the present invention, the 1-(2, 6-dichlorophenyl)-3-(6-(substituted benzylamino)pyrimidine-4-yl) urea compound does not have toxic effect on the proliferation of BEAS-2B cells (normal lung cells), and has a certain inhibitory effect on three selected colon cancer cell lines including SW116 cells (human large intestine cancer cells), SW480 cells (human colon cancer cells) and SW620 cells (human colon cancer cells) so as to provide a certain antitumor activity.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Specific anti-human liver cancer phage single-chain antibody HscFv4-16 gene and its uses
InactiveCN1865285AStrong specificityHigh binding titerImmunoglobulins against animals/humansAntibody ingredientsSingle-Chain AntibodiesChronic hepatitis
The invention discloses an astopic anti-hepatocarcinoma phage single-chained antibody HscFv 4-16 gene and appliance, which is characterized by the following: screening gene in the anti-hepatocarcinoma phage single-chained antibody store to select one astopic anti-hepatocarcinoma phage single-chained antibody HscFv 4-16; possessing high astopic reaction of anti-hepatocarcinoma scFv liver cancer cell system and human liver tissue with lowest combination drip rate than normal liver cell system, stomach cancer cell system and colonocarcinoma cell system by 256 times; making positive rate of reacting rate with human liver cancer tissue at 5.0 percent without combination reaction with normal liver tissue, esophagus cancer tissue and lung cancer tissue; reacting positive rate of liver cancer tissue higher than other tissues obviously. The invention possesses strong astopic property, which can be applied in kinds of liver cancer treatment drug and relative agent.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
N-heterocyclic condensed tryptamine-beta-lactam derivative as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN111533732AHas antitumor activityEasy to operateOrganic chemistryAntineoplastic agentsCyanide compoundOrganic synthesis
The invention relates to the technical field of organic synthesis, in particular to an N-heterocyclic condensed tryptamine-beta-lactam derivative as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding an aldehyde compound and propiolic acid into methanol and stirring; then adding tryptamine and isocyanide, and reacting under stirring;removing the methanol in a nitrogen atmosphere; dissolving obtained residues in acetonitrile, adding K2CO3, sealing the mixture, heating the mixture in a microwave oven, removing the acetonitrile, diluting with ethyl acetate, washing with saline water, drying with sodium sulfate, concentrating, purifying the obtained concentrate by silica gel column chromatography, and drying to obtain the N-heterocyclic condensed tryptamine-beta-lactam derivative. The N-heterocyclic fused tryptamine-beta-lactam derivative has a certain inhibition effect on the cell viability of liver cancer, breast cancer, head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and colon cancer cell lines, can inhibit or kill tumor cells, has antitumor activity, and can be applied to preparation of antitumor drugs.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF ARTS & SCI
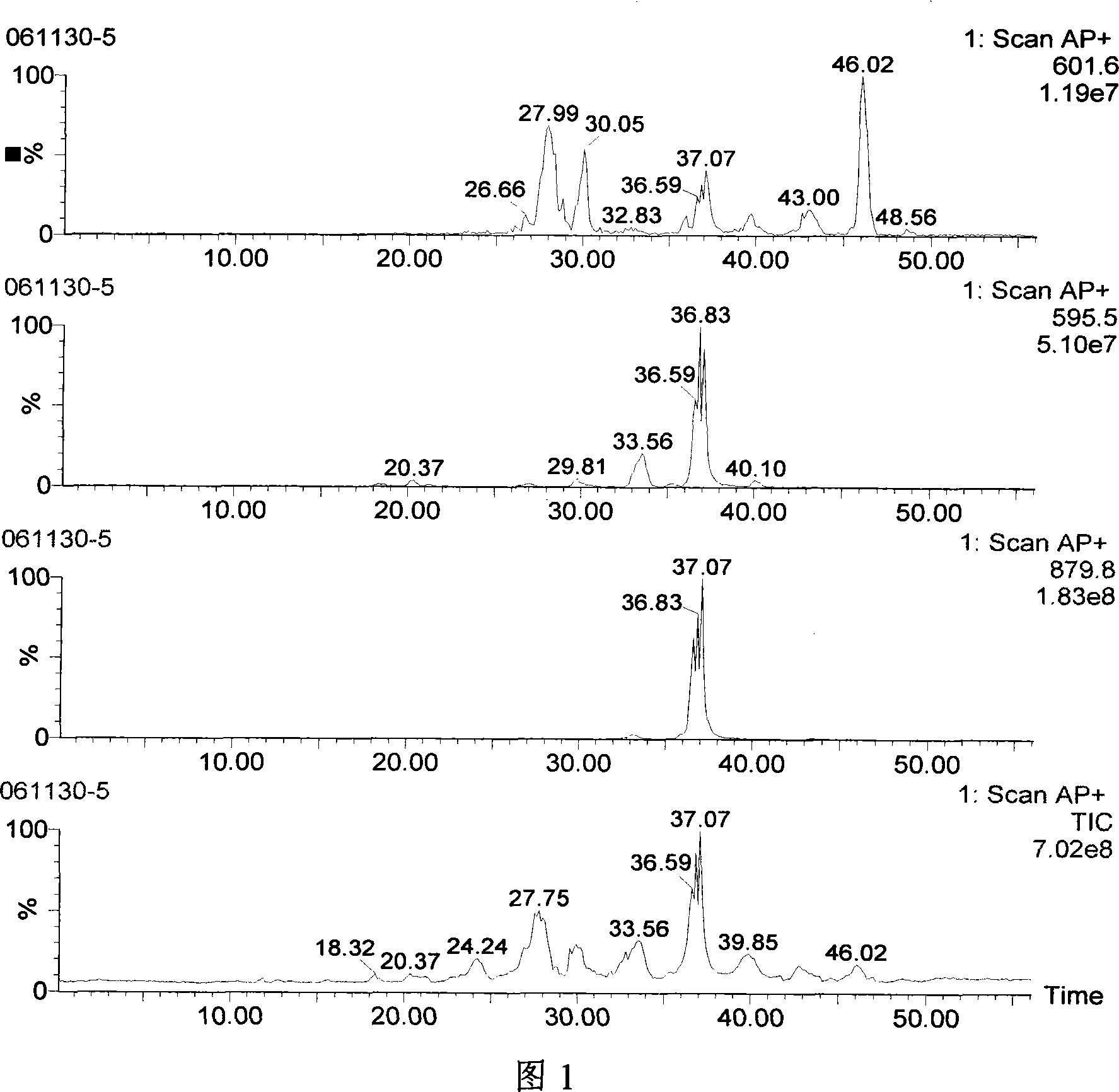
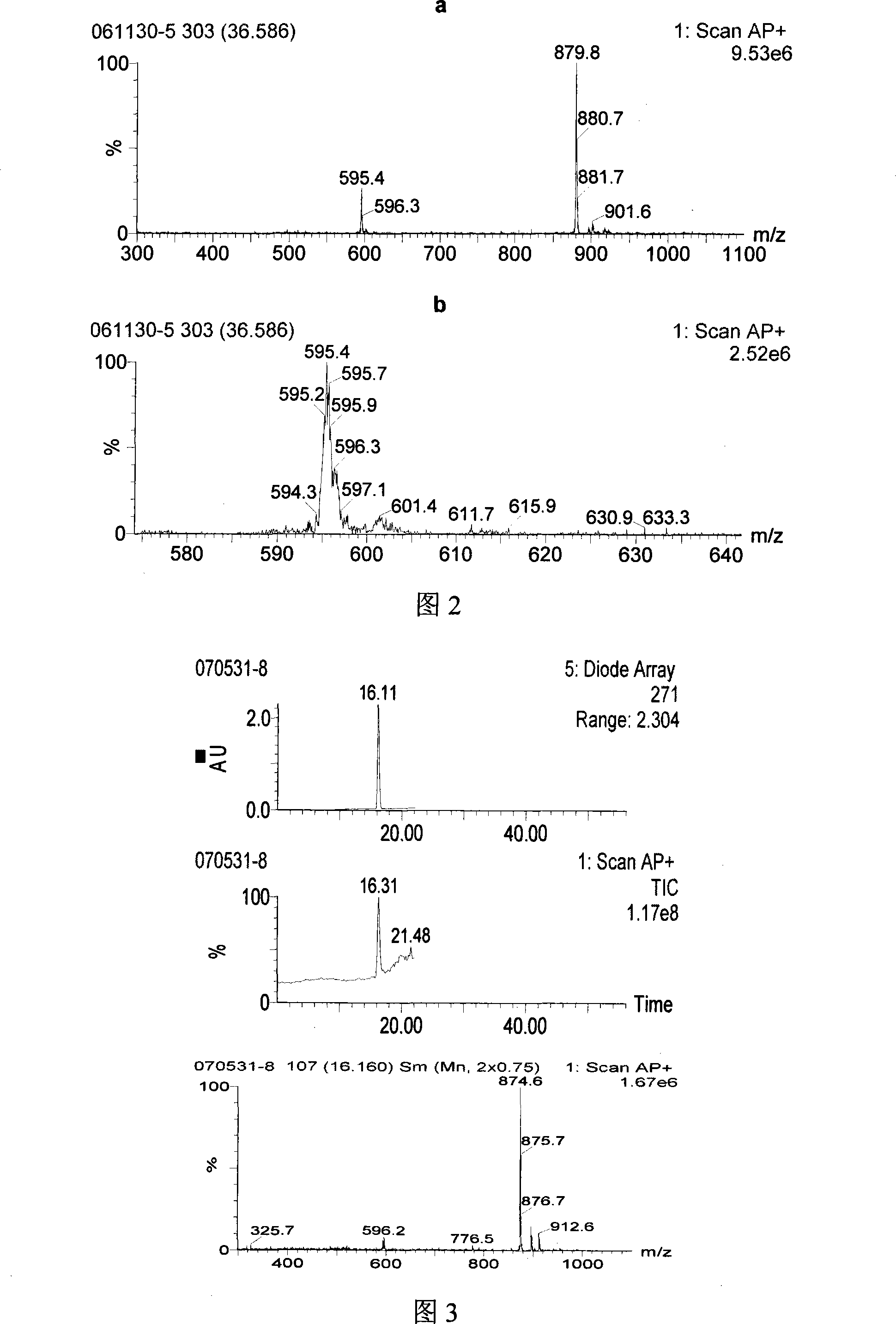
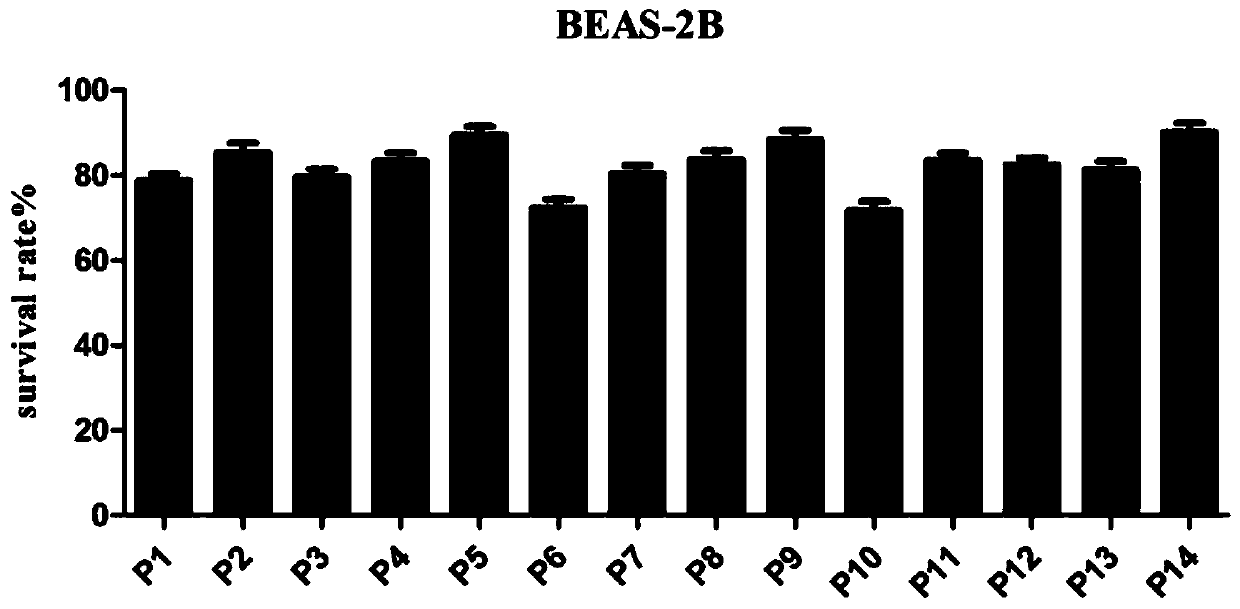
Imidazo[1,2 a] pyridine 6 carboxamide derivatives, their use for the treatment of colon cancer and their method of manufacture
This invention relates to the manufacture of novel chemical compounds which have biological activity, particularly to novel chemical compounds that are cytotoxic against colon cancer cells and colon cancer cell lines. The manufacturing of said chemical compounds displaying anti-cancer properties employs the use of multi-component chemical reactions. The object of this invention is to manufacture and isolate analogues of imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine, namely compounds of Formula 1, which are cytotoxic against colon cancer cells, while concomitantly being relatively inactive against white blood cells.wherein,R is bromo, methyl, phenyl, nitro, hydrogen or an amide functional group;R1 is benzyl, 2,6-dimethylphenyl or cyclohexyl; andR2 is methoxy, benzyloxy or hydroxy.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF THE WITWATERSRAND
Application of compound DY1 in preparation of anti-colorectal cancer drugs
InactiveCN105997992AEnhanced inhibitory effectOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsIc50 valuesNatural product
The invention provides an application of a compound DY1 in preparation of anti-colorectal cancer drugs. According to conventional literature reports, a colorectal cancer surface molecule CD58 newly discovered is researched; a small-molecular compound specifically binding to the CD58 is selected for further drug research; a targeting small-molecular drug originated from natural products is obtained through a computer-aided drug screening technology; cell biology experimental results indicate that the natural product DY1 has significantly inhibiting effect on growth of an SW620 human colorectal cancer cell line, has the IC50 value of 31.30+ / -0.88 [mu]mol, and can be further used for development of new drugs for treatment of colorectal cancer.
Owner:北京北科德源生物医药科技有限公司
Method for establishing HK2 report gene cell line of colon cancer
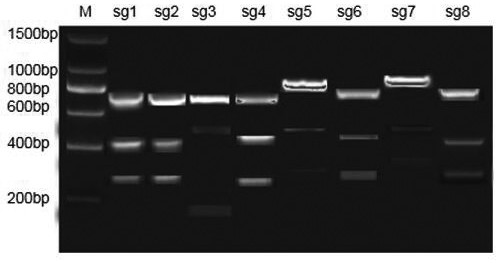
ActiveCN109852586AQuick checkGenetic stabilityGenetically modified cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementGreen fluorescent proteinDNA fragmentation
The invention discloses a method for establishing an HK2 report gene cell line of the colon cancer. The method comprises the specific steps of firstly designing a specificity sgRNA sequence of a HK2 gene site, and performing cloning into a plasmid PX459; integrating a homologous recombination sequence of an HK2 gene and a green fluorescent protein DNA fragment (EGFP), and performing joint electricshock on the plasmid and the integrated fragment to transform a colon cancer cell line HCT116; performing unicellular screening on EGFP expression cells through a flow cytometer, and amplifying a monoclonal cell line; and performing PCR identification and immunoblotting verification on the screened EGFP expression cell line so as to obtain a positive HK2 report gene cell line. The colon cancer cell line cell line HK2 gene and EGFP are in co-expression, and the EGFP expression level and the HK2 gene have high consistency, so that through detecting EGFP expression level changes, the HK2 gene expression level can be accurately judged. The method for establishing the cell line is simple, and easy to operate, and gene sites can be efficiently and accurately positioned.
Owner:GUANGDONG MEDICAL UNIV
Targeting metabolic enzymes in human cancer
Targeting metabolic enzymes in human cancer Abstract Lung cancer is a devastating disease and a major therapeutic burden with poor prognosis. The functional heterogeneity of lung cancer (different tumor formation ability in bulk of tumor) is highly related with clinical chemoresistance and relapse. Here we find that, glycine dehydrogenase (GLDC), one of the metabolic enzyme involved in glycine metabolism, is overexpressed in various subtypes of human lung cancer and possibly several other types of cancers. GLDC was found to be highly expressed in tumor-initiating subpopulation of human lung cancer cells compared with non-tumorigenic subpopulation. By array studies we showed that normal lung cells express low levels of GLDC compared to xenograft and primary tumor. Functional studies showed that RNAi inhibition of GLDC inhibits significantly the clonal growth of tumor-initiating cells in vitro and tumor formation in immunodeficient mice. Overexpression of GLDC in non-tumorigenic subpopulation convert the cells to become tumorigenic. Furthermore, over-expression of GLDC in NIH / 3T3 cells and human primary lung fibroblasts can transform these cells, displaying anchorage-independent growth in soft agar and tumor-forming in mice. Not only is GLDC is expressed human lung cancer, it is also up-regulated in other types of cancer, such as colon cancer. RNAi knockdown of GLDC in colon cancer cell line, CACO-2 cells, can also inhibit the tumor formation in mice. Thus GLDC maybe a new metabolic target for treatment of lung cancer, and other cancers.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
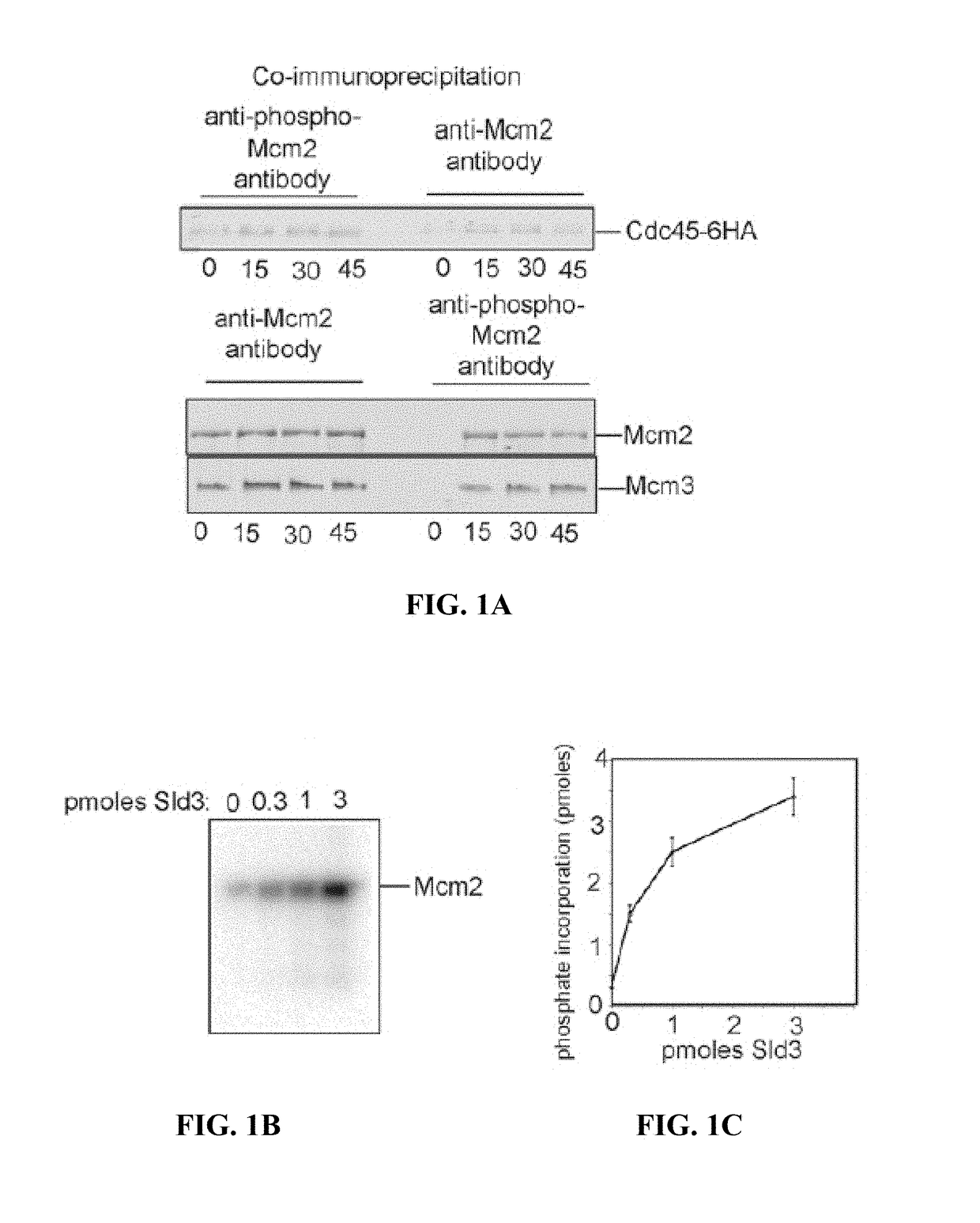
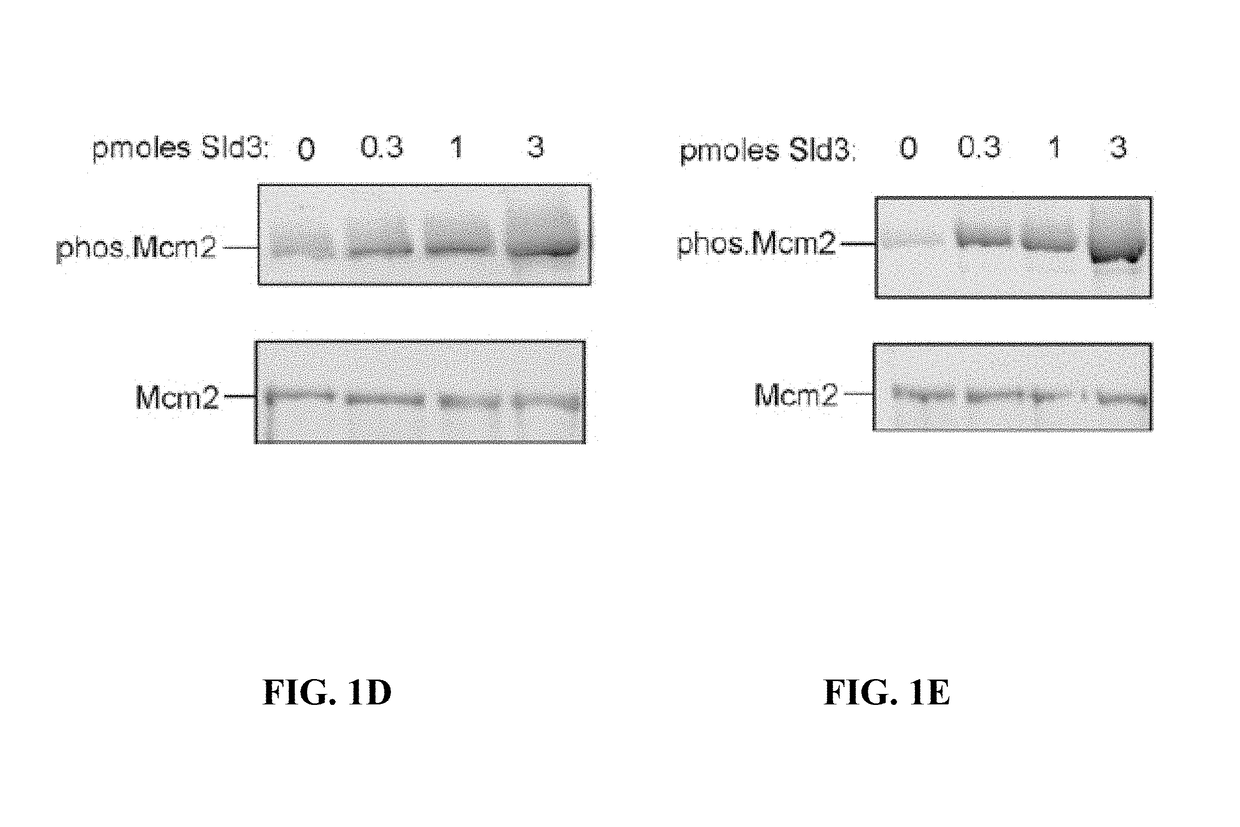
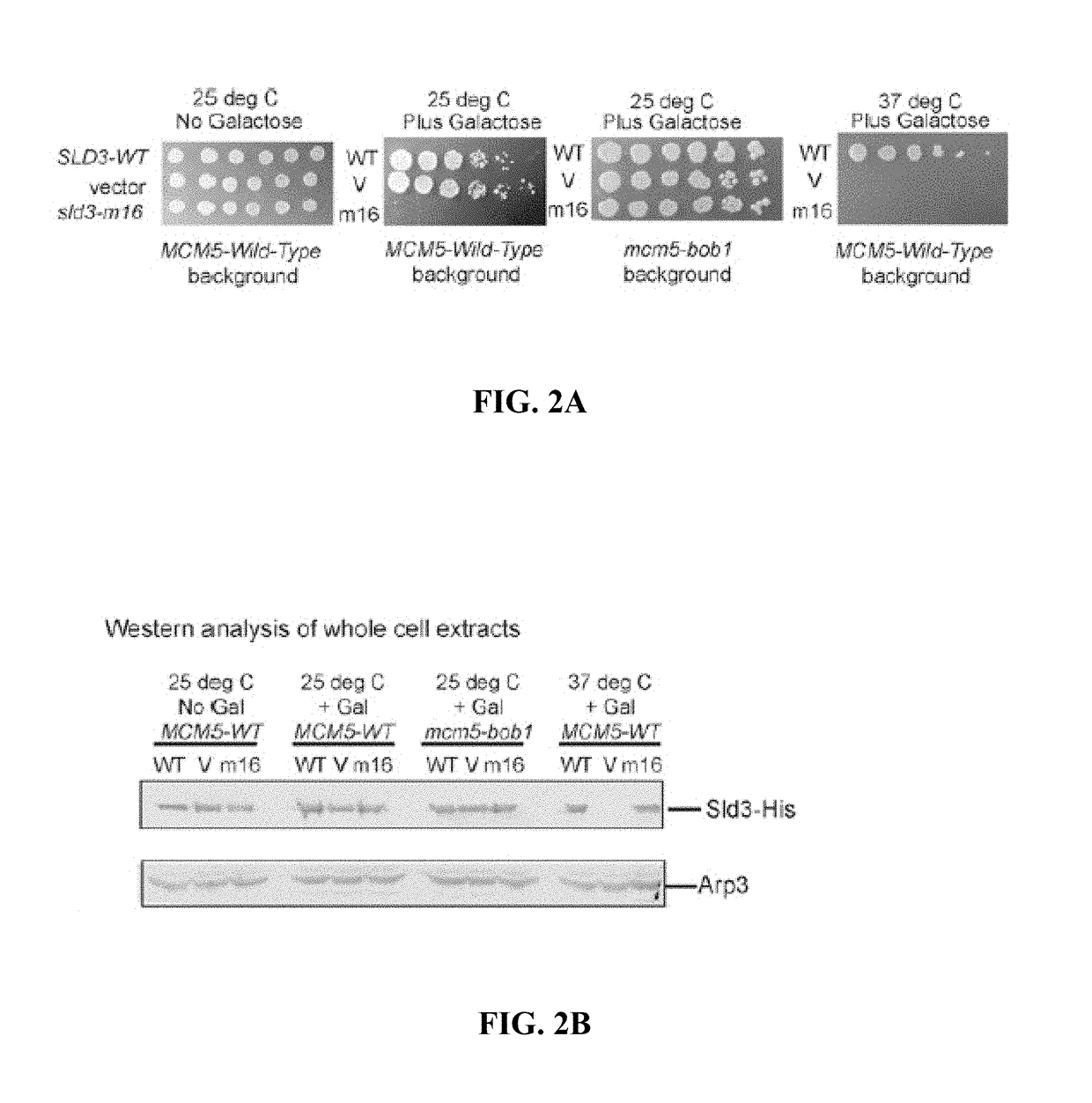
Detection of elevated levels of phosphorylated MCM and method of increasing MCM phosphorylation capacity
InactiveUS9977026B2Increasing capacity for phosphorylationIncreased phosphorylationDetection of post translational modificationsAnhydride/acid/halide active ingredientsCancer cellPhosphorylation
Identified herein is a novel post-translational modification of Mcm2, wherein the residue of serines 53 and 108 are phosphorylated. DDK phosphorylates Mcm2 at serines 53 and 108 when stimulated by Treslin. DDK is overexpressed in many human cancers, including colorectal cancer, suggesting that monitoring the phosphorylation of Mcm2 at serines 53 and 108 may detect early cancer with high sensitivity and specificity. It was also found that the homologous modification in budding yeast is required for DNA replication, and the modification occurs in cells during active DNA replication only. In an embodiment, the current invention is an antibody specific for human Mcm2 that is phosphorylated at serines 53 and 108. This antibody was found to be overexpressed in colon cancer cell line HCT 116, as well as other cancer cell lines, compared to normal cells.
Owner:FLORIDA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
Compound Chinese actinidia root Chinese medicinal composition and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102204974BHas a tumor suppressive effectAntineoplastic agentsPlant ingredientsActinidiaHep G2
The invention discloses a compound Chinese actinidia root Chinese medicinal composition and a preparation method and application thereof, belonging to the technical field of traditional Chinese medicines. The Chinese medicinal composition is characterized by comprising the following traditional Chinese medicines in parts by weight: 40-80 parts of Chinese actinidia root, 20-40 parts of salvia chinensis, 20-40 parts of herba scutellariae barbatae, 20-40 parts of herba oldenlandiae and 20-40 parts of giant knotweed. The compound Chinese actinidia root Chinese medicinal composition has remarkableproliferation inhibition effects on various cancer cells such as a hepatoma cell line Hep-G2, a lung cancer cell line NCI-H460, a gastric cancer cell line MGC-803, a breast cancer cell line MCF-7, a colon cancer cell line HCT-116 and the like, and can be used for reducing physical and psychological pains of a cancer patient in the chemo-treatment process and solving the problems of difficult and expensive administration.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SIXIAN PHARMA
Biomarker genes for detecting colorectal cancer metastasis, application, kit and pharmaceutical composition
PendingCN113999917AReduce the ability to invadeOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementStainingCancer metastasis
The invention provides a group of biomarker genes for detecting colorectal cancer metastasis, application, a kit and a pharmaceutical composition, and relates to the technical field of biomedical clinical diagnosis. The abnormal expression levels of the biomarker genes BGN, THBS2, SPARC, CDH11, MFAP2, MMP11, SPP1 and THY1 disclosed by the invention are obviously related to the colon cancer metastasis. In the embodiment of the invention, 80 clinical samples are adopted for immunohistochemical staining analysis of the expression conditions of the 8 genes in the clinical samples, then the expression quantity of the corresponding genes in the colon cancer cell line is reduced through the sh-RNA, and transwell cell chamber experiments verify that when the expression level of the target gene is inhibited, the invasion ability of the cell line is weakened. Therefore, the eight genes can be used as biomarkers of colon cancer metastasis, can be used as potential targets for treating colon cancer metastasis, and have important clinical application value.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF BOTANY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Human PD1 gene sgRNA with high knockout rate, plasmid containing sgRNA and T cell
InactiveCN113430202AHighly toxicSignificant specific cytotoxic effectGenetically modified cellsPeptidesNucleotideCytotoxicity
The invention provides a human PD1 gene sgRNA with a high knockout rate. The sgRNA is used for knocking out a PD1 gene; the nucleotide sequence of the sgRNA is shown as SEQ ID NO: 4, SEQ ID NO: 6 or SEQ ID NO: 8 in a sequence table. The sgRNA target spot aiming at the human PD1 gene is transfected into a 293T cell for stably expressing PD1, and the knockout rate of the PD1 gene is 71.92-90.97%; the sgRNA target spot aiming at the human PD1 gene is transfected into the T cell, and the knockout rate of the PD1 gene is 58.26-72.67%; and the sgRNA target spot aiming at the human PD1 gene is transfected into the T cell, and a Crispr-PD 1-T cell is obtained, shows a remarkable specific cytotoxicity effect on a colon cancer cell line LoVo and shows effect-target ratio gradient dependence, namely the higher the effect-target ratio is, the stronger the cytotoxicity effect is.
Owner:SHANDONG XINRUI BIOTECH CO LTD
Mutant ubiquitination-specific protease 33 gene and its application
ActiveCN106834317BResistance to inhibitionGrowth inhibitionPeptide/protein ingredientsNucleic acid vectorMonoclonal antibodyColorectal cancer cell line
The invention discloses a mutated ubiquitin specific protease 33 gene and application of the mutated ubiquitin specific protease 33 (USP33) gene to production of a medicine for treating colorectal cancer. A research finds out that KDM5B has high expression in a colorectal cancer clinical sample and a colorectal cancer cell line and promotes the proliferation of colorectal cancer cells through inhibiting USP33. A KDM5B inhibitor or a monoclonal antibody of the KDM5B can be used for remarkably inhibiting the proliferation of the colorectal cancer cells. A further research proves that the KDM5B is combined with a USP33 gene promotor region, and the inhibition of the expression to the USP33 gene is realized through combining an upstream specific regulation and control sequence GCACA / C or G / TGTGC. The mutated ubiquitin specific protease 33 gene obtained through a site-directed mutation PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) technology can be used for resisting the inhibition effect of the KDM58B, so that the growth of the colorectal cancer cell line is inhibited.
Owner:XINXIANG MEDICAL UNIV
Specific anti-human liver cancer phage single-chain antibody HscFv4-16 gene and its uses
InactiveCN100410274CStrong specificityHigh binding titerImmunoglobulins against animals/humansAntibody ingredientsSingle-Chain AntibodiesChronic hepatitis
The invention discloses an astopic anti-hepatocarcinoma phage single-chained antibody HscFv 4-16 gene and appliance, which is characterized by the following: screening gene in the anti-hepatocarcinoma phage single-chained antibody store to select one astopic anti-hepatocarcinoma phage single-chained antibody HscFv 4-16; possessing high astopic reaction of anti-hepatocarcinoma scFv liver cancer cell system and human liver tissue with lowest combination drip rate than normal liver cell system, stomach cancer cell system and colonocarcinoma cell system by 256 times; making positive rate of reacting rate with human liver cancer tissue at 5.0 percent without combination reaction with normal liver tissue, esophagus cancer tissue and lung cancer tissue; reacting positive rate of liver cancer tissue higher than other tissues obviously. The invention possesses strong astopic property, which can be applied in kinds of liver cancer treatment drug and relative agent.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Application of melanotropin hormone recombinant toxin in preparation drugs treating colon cancer
ActiveCN108619494AInhibit synthesisAchieve the goal of curing tumorsPeptide/protein ingredientsMacromolecular non-active ingredientsNucleotideTumor targeting
The invention relates to an application of melanotropin hormone recombinant toxin in preparation drugs treating colon cancer, and belongs to medicine field. The nucleotide sequencing of the encoding gene of the melanotropin hormone recombinant toxin is expressed as SEQ ID No. 1, the melanotropin hormone recombinant toxin is capable of treating melanocortin receptor 1 as a therapeutic target, specifically capturing and killing the high expressed colon cancer cells which include colon cancer cell line HT29 and colon cancer cell line HCT-116 of the receptor. After the toxicity and pharmacodynamictests of the cell level and animal level, the specific apoptosis function of the melanotropin hormone recombinant toxin to the high expressed MC1R colon cancer cells including the human colon cancercell line HT29, colon cancer cell line HCT-116 and the like. The high expressed MC1R exist to the two cancers. The melanotropin hormone recombinant toxin has new targeting effect, is a potential therapy or add-on therapy for colorectal cancer, and has good application prospect.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Use of Momordica.charantia seed oil riacylglycerol in preparing medicament for inhibiting tumor cell
The invention relates to a usage of the scabies grape-kernel oil tri-acylglycerol during the process of preparing a medicine used for suppressing tumour cells. Besides the toxicity of the carcinoma of colon clone is not as good as alpha-eleostearic acid, the tri-acylglycerol containing conjugate linolenic acid in the scabies grape-kernel oil has quite strong toxicity to the four body tumor clones; while although the tri-acylglycerol has not a high toxicity to the normal liver cell, but the intensity is not high. So the scabies grape-kernel oil tri-acylglycerol has good prospect to suppress the colon cell tumor cells.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
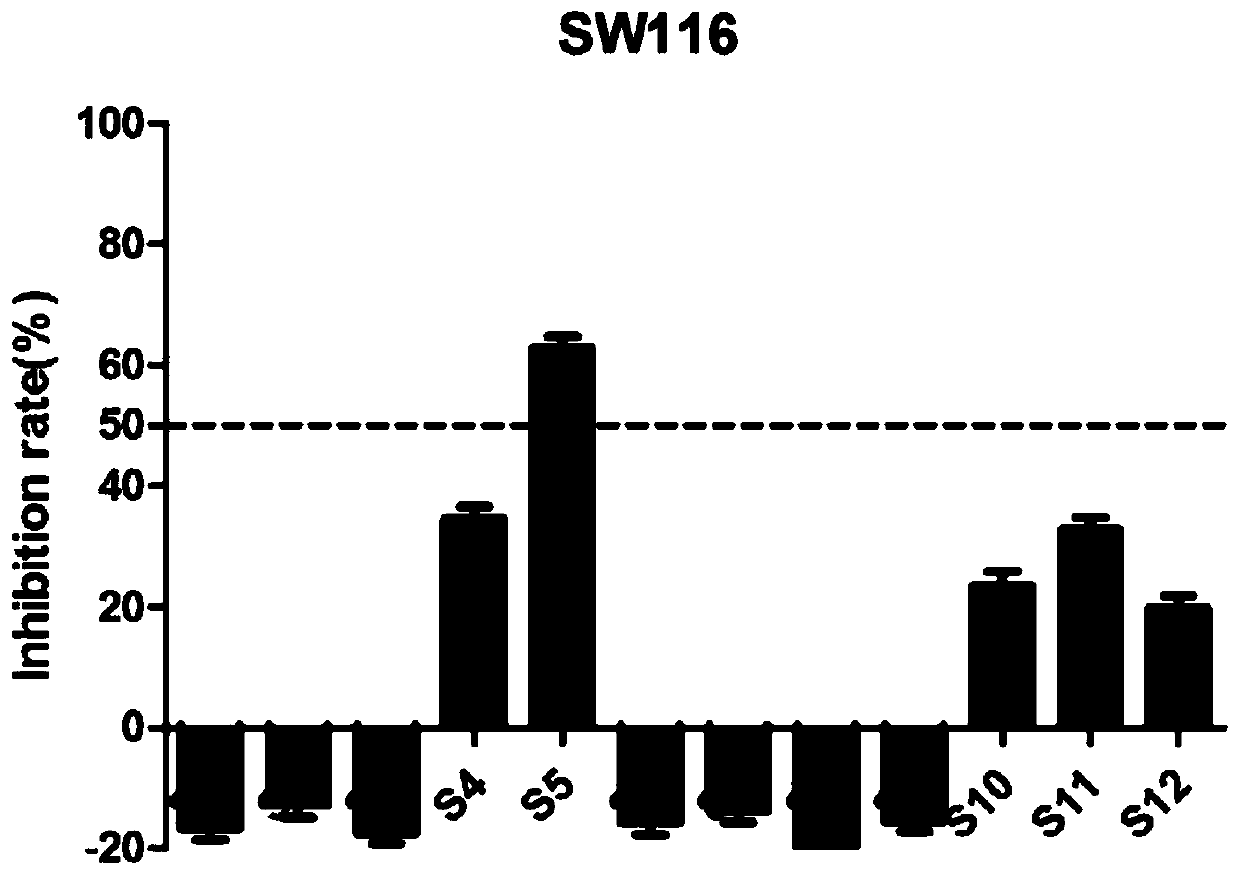
1-(3,5-dimethoxy phenyl)-3-substituted urea colon cancer inhibitor as well as preparation and application thereof
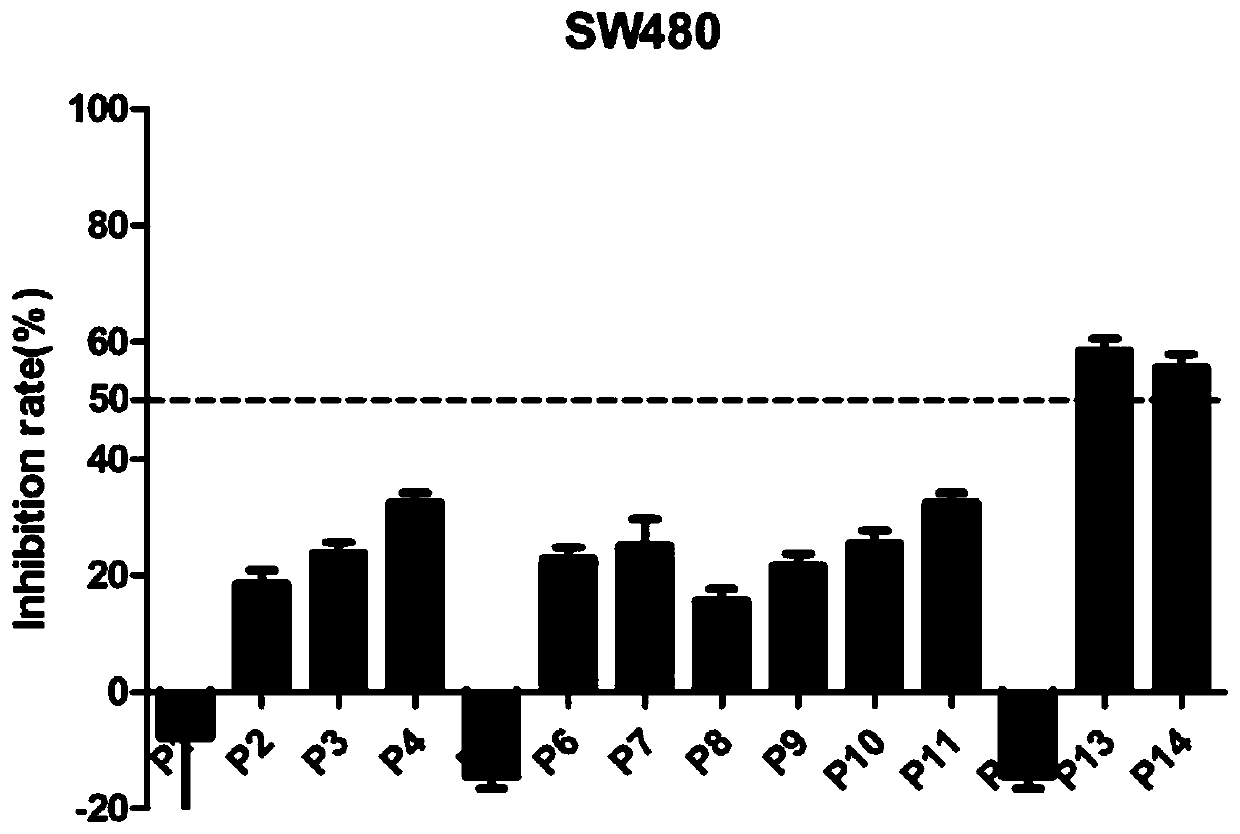
The invention discloses a 1-(3,5-dimethoxy phenyl)-3-substituted urea compound acting on colon cancer, and a preparation method and application of the compound. The compound has no toxic effect on proliferation of BEAS-2B cells, but has a certain inhibition function on three selected colon cancer cell systems, including SW116 cells, SW480 cells and SW620 cells, and has certain anti-tumor activity.Inhibition rates of compounds P13 and P14 upon the three cancer cells are all greater than 50% at a concentration of 10[mu] M, and the compound P13 has a larger inhibition rate. IC50 values of the compound P13 upon three cancer cells are respectively 3.26+ / -0.74[mu] M, 4.62+ / -0.45[mu] M and 3.32+ / -1.21[mu] M. Results show that the compound P13 is an effective colon cancer inhibitor.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Amino acid derivative bithiazole-tryptamine anticancer compound and application
ActiveCN112574192ASignificant inhibitory effectBroad market prospectOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryAnticarcinogenic EffectCarcinoma cell line
The invention discloses an amino acid derivative bithiazole tryptamine compound and the application thereof. The amino acid derivative bithiazole tryptamine compound disclosed by the invention can inhibit colon cancer cell line HCT116, gastric cancer cell line MKN45, non-small cell lung cancer cell line A549 and drug-resistant oral cancer cell line KBV drugs, i.e., preparation of antitumor drugs.The synthetic method provided by the invention is simple in route and high in product purity, and can meet large-scale preparation requirements. The amino acid derivative bithiazole tryptamine compound with the anti-cancer activity has a good anti-cancer effect, has a remarkable inhibition effect on colon cancer, gastric cancer and lung cancer, particularly has an inhibition effect similar to thatof commercially available broad-spectrum anti-cancer drug doxorubicin (DOX) on a drug-resistant oral cancer cell line KBV, and can be applied to the field of tumor resistance.
Owner:YANTAI UNIV
1-(2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-3-substituted ureas colon cancer inhibitor, and preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses a 1-(2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-3-substituted ureas compound capable of acting on colon cancer, and a preparation method and application thereof. The 1-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-3-(6-(substituted benzylamino)pyrimidine-4-yl)ureas compound disclosed by the invention has no toxic effect on the proliferation of BEAS-2B cells (normal lung cells), has certain inhibitory effects on three selected colon cancer cell lines including SW116 cells (human colorectal cancer cells), SW480 cells (human colon cancer cells), and SW620 cells (human colon cancer cells), and shows certain anti-tumor activity.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
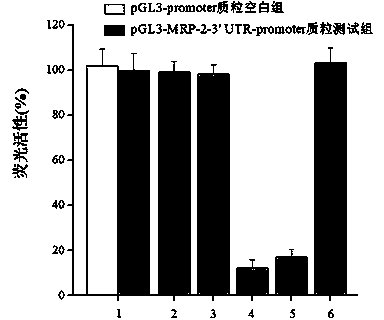
Recombinant plasmid containing MRP (Multidrug Resistance-associated Protein)-2 genes 3' UTR (Untranslated Region) and reporter genes and application thereof
InactiveCN102492712BMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionRenilla luciferaseMicroRNA
The invention discloses a recombinant plasmid containing MRP (Multidrug Resistance-associated Protein)-2 genes 3' UTR (Untranslated Region) and reporter genes and application thereof. Constructed MRP-2 gene 3' UTR and reporter gene carriers and pRL-SV40 carriers and microRNA (Ribonucleic Acid) to be screened are co-transfected into a drug-resistance colon cancer cell line; inhibitory activity of microRNA to MRP-2 gene 3' UTR region is responded by simultaneously detecting activities of firefly and renilla luciferase; and thus, a method for targeted screening of reversal tumor multidrug resistance microRNA is established. The method has excellent application prospect in aspects of screening the reversal tumor multidrug resistance microRNA, researching acting mechanism between the reversal tumor multidrug resistance and microRNA and researching the mechanism of the tumor cell multidrug resistance microRNA level.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com











![Imidazo[1,2 a] pyridine 6 carboxamide derivatives, their use for the treatment of colon cancer and their method of manufacture Imidazo[1,2 a] pyridine 6 carboxamide derivatives, their use for the treatment of colon cancer and their method of manufacture](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/8826e17c-9997-4b66-9fbc-32c305f239e3/US20120101122A1-20120426-D00001.png)
![Imidazo[1,2 a] pyridine 6 carboxamide derivatives, their use for the treatment of colon cancer and their method of manufacture Imidazo[1,2 a] pyridine 6 carboxamide derivatives, their use for the treatment of colon cancer and their method of manufacture](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/8826e17c-9997-4b66-9fbc-32c305f239e3/US20120101122A1-20120426-D00002.png)
![Imidazo[1,2 a] pyridine 6 carboxamide derivatives, their use for the treatment of colon cancer and their method of manufacture Imidazo[1,2 a] pyridine 6 carboxamide derivatives, their use for the treatment of colon cancer and their method of manufacture](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/8826e17c-9997-4b66-9fbc-32c305f239e3/US20120101122A1-20120426-D00003.png)