Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
183results about How to "Suppress dust" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
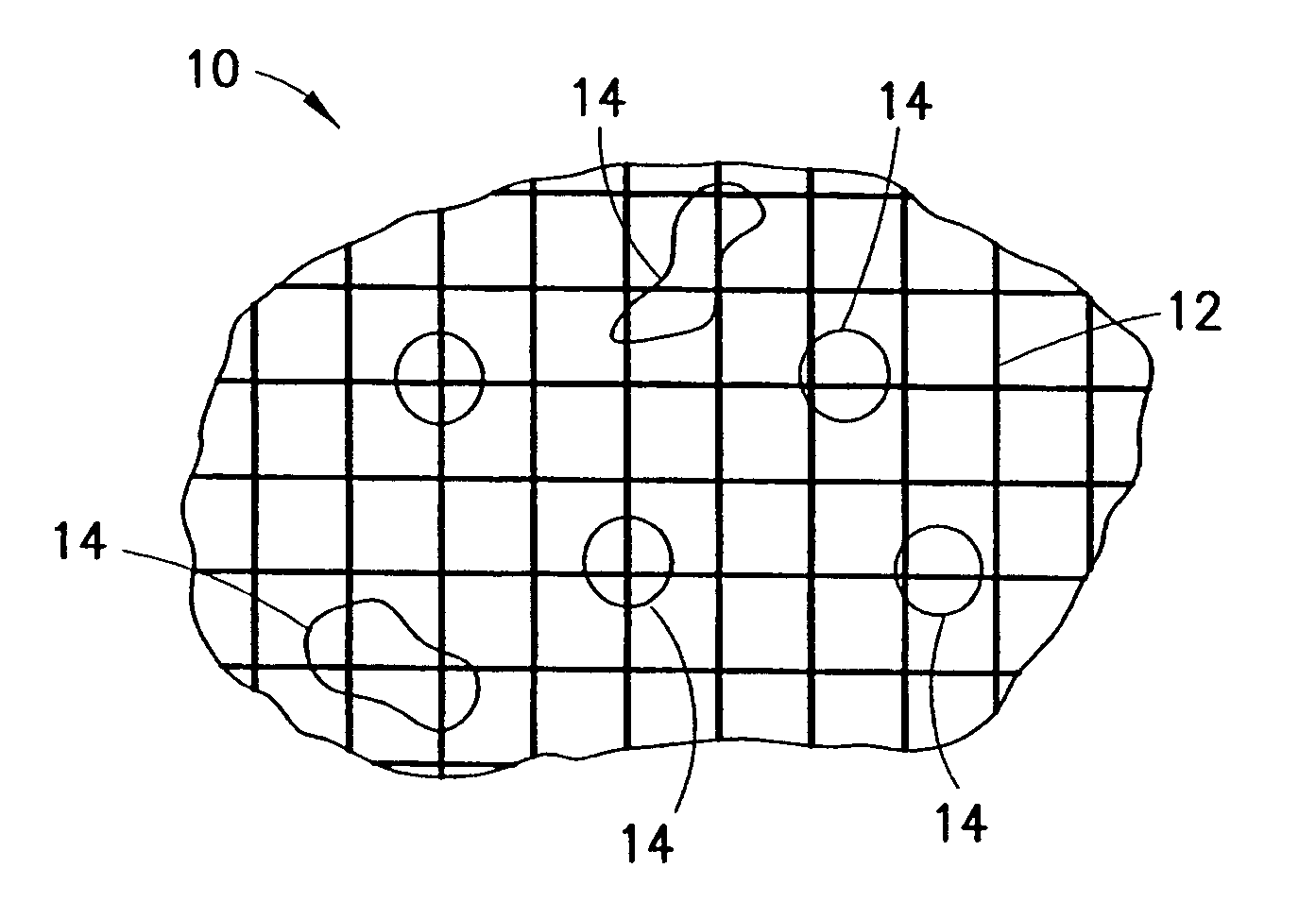
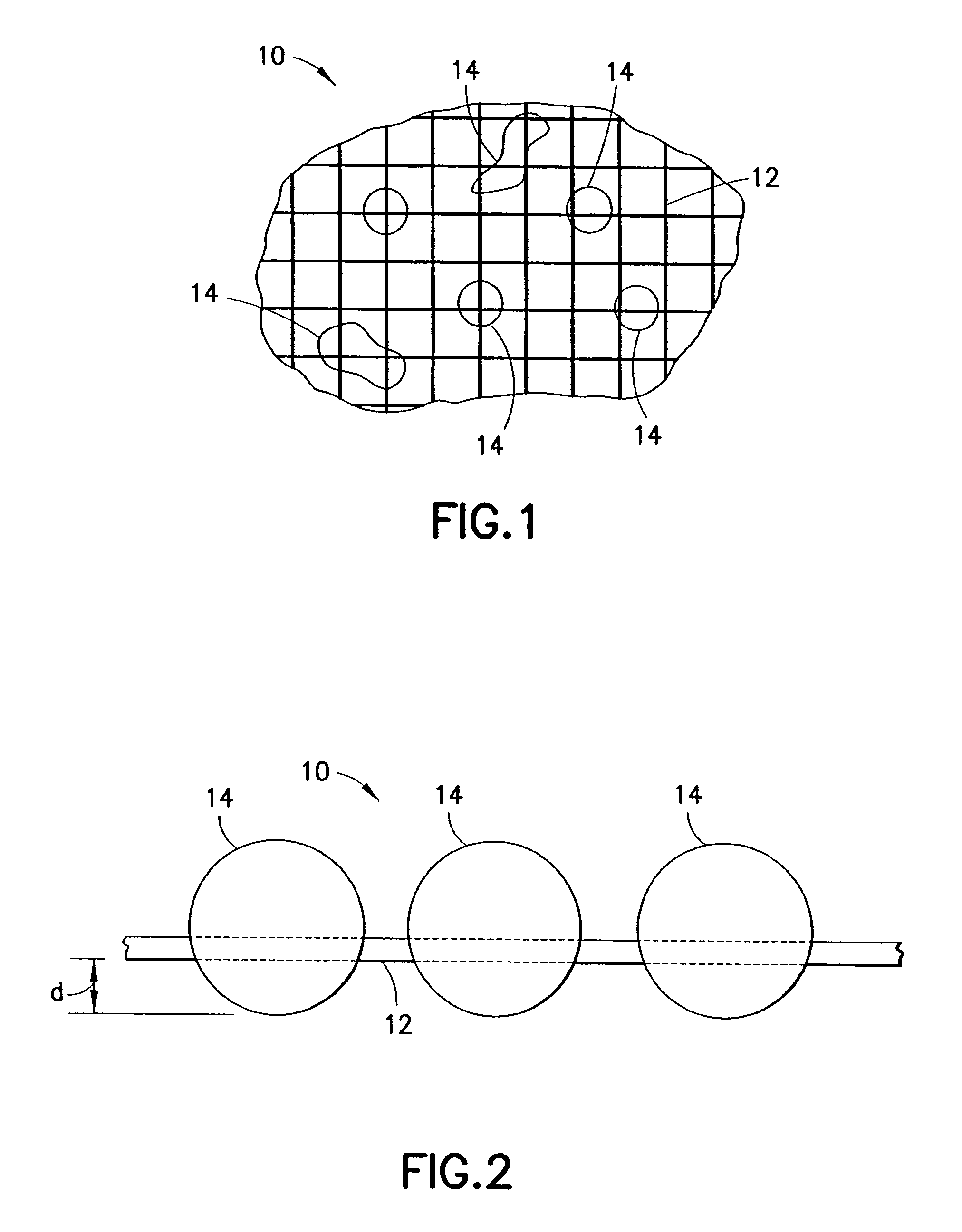
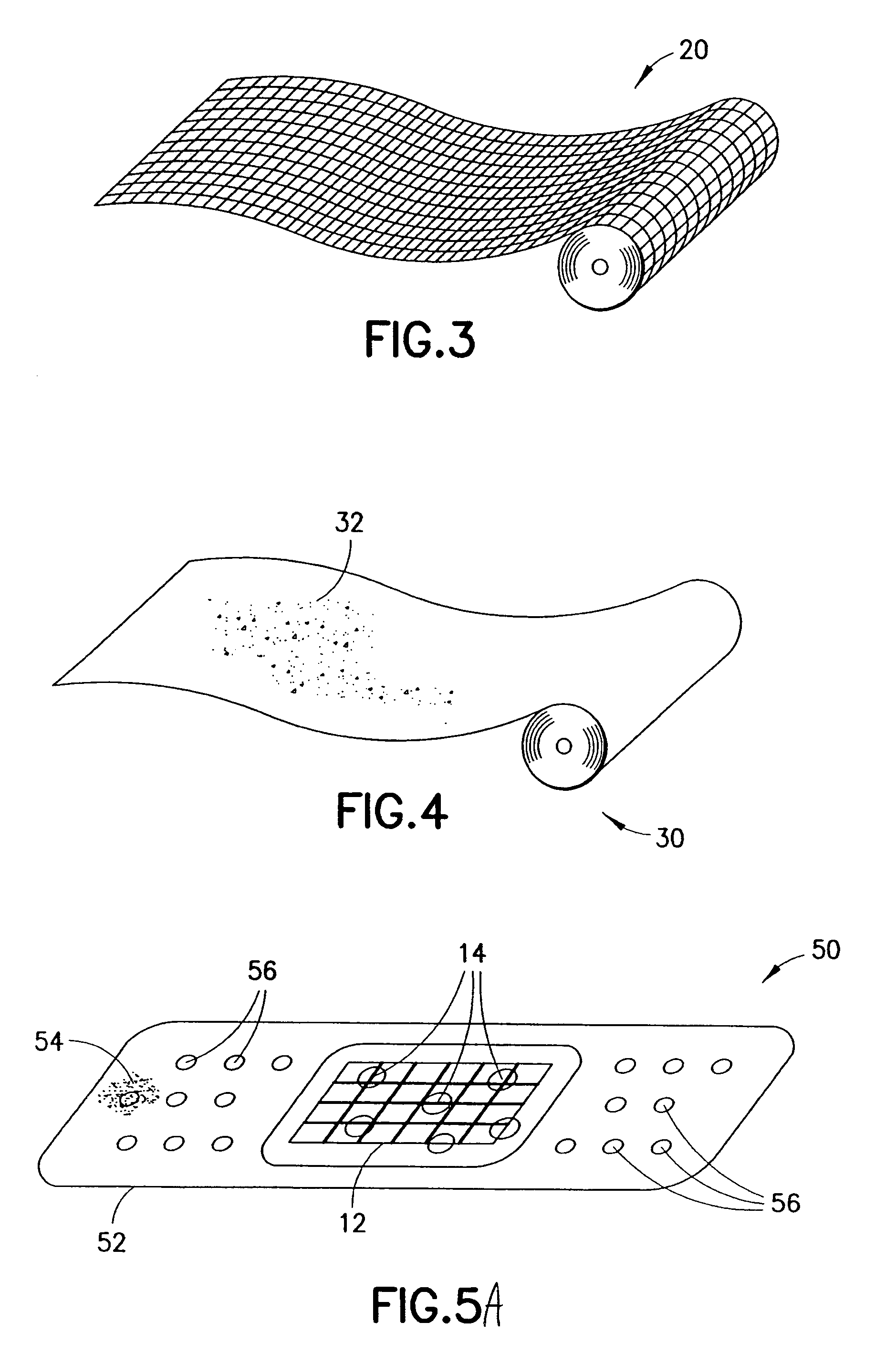
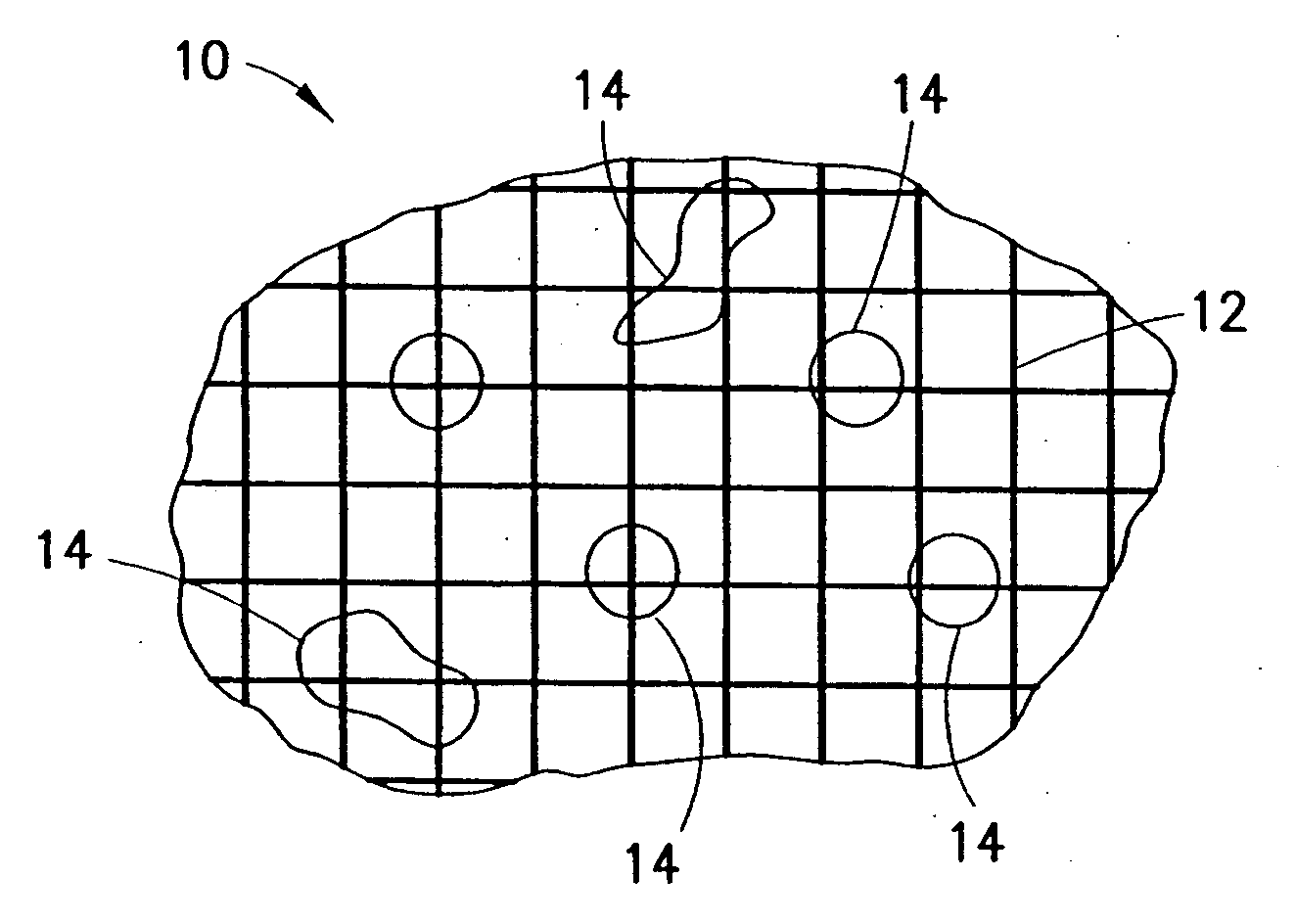
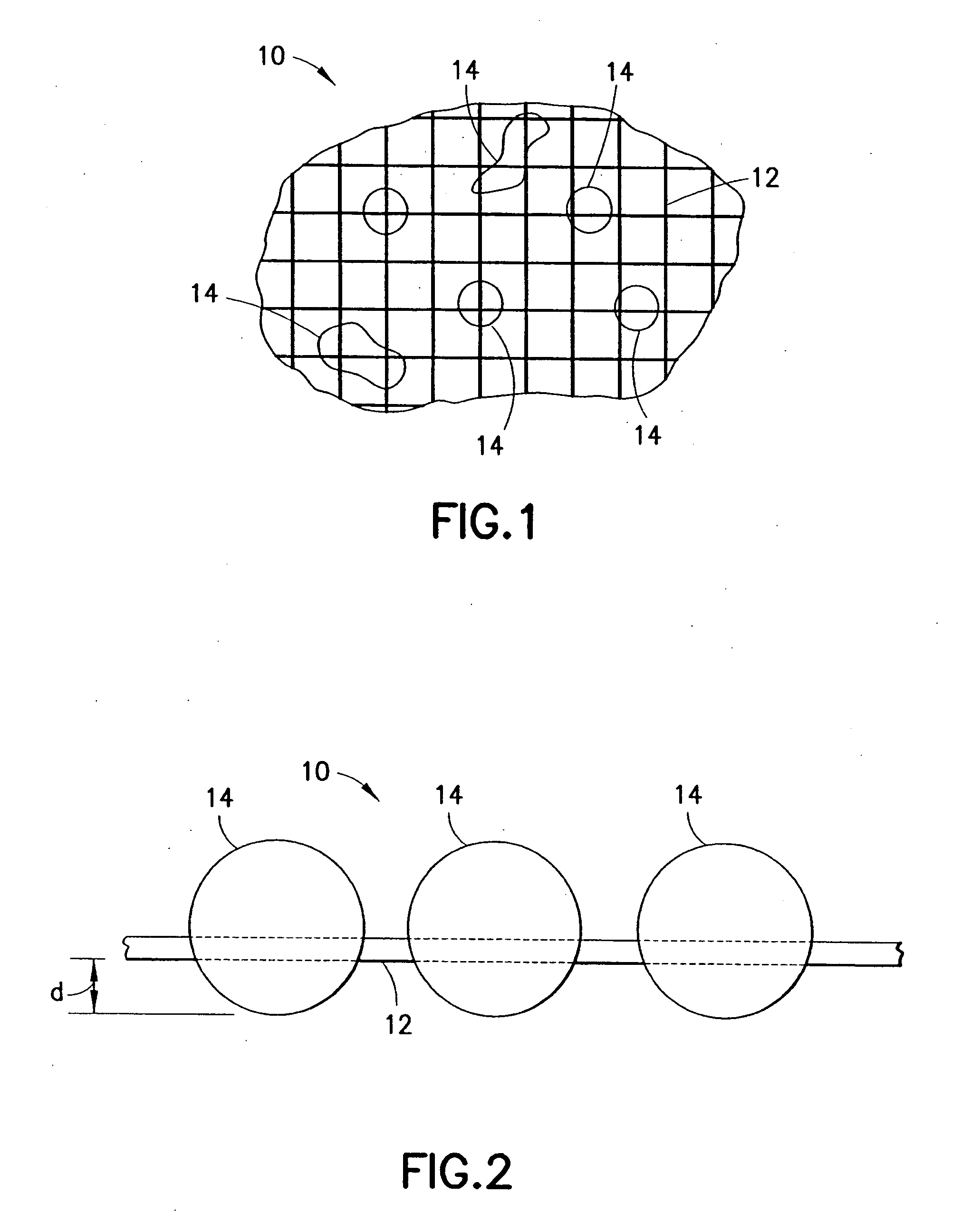
Clay-based hemostatic agents and devices for the delivery thereof
ActiveUS7604819B2Minimizing discomfort and further injuryEliminate feverPowder deliveryPhysical/chemical process catalystsPolyolGlycerol
A hemostatic device for promoting the clotting of blood includes a gauze substrate, a clay material disposed on the gauze substrate, and also a polyol such as glycerol or the like disposed on the gauze substrate to bind the clay material. When the device is used to treat a bleeding wound, at least a portion of the clay material comes into contact with blood emanating from the wound to cause the clotting. A bandage that can be applied to a bleeding wound to promote the clotting of blood includes a flexible substrate and a gauze substrate mounted thereon. The gauze substrate includes a clay material and a polyol. A hemostatic sponge also includes a gauze substrate and a dispersion of hemostatic material and a polyol on a first surface of the substrate.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
Revegetation method for tailings dams in northern region
InactiveCN102668835ASuppress dustImprove adaptabilityHorticultureSoil-working methodsRevegetationTailings dam
A revegetation method for tailings dams in the northern region includes the following steps: (A) slopes are cleaned up and leveled in order to eliminate potential geological hazards; (B) the surface layer of a tailings dam is covered by 10 to 15 centimeters of planting soil; (C) slurry-like plant-growing soil culture medium is sprinkled on the surface of the covering soil, so that a plant-growing substratum with a stable, excellent crumble structure is formed; (D) plant seeds with high stress resistance combined with artificial soil are chosen to be sowed on the surface of the plant-growing substratum, so that a seed layer which is about 2 centimeters in thickness is formed; (E) a management measure with a spray irrigation system and protective nets is adopted to maintain epigaeous seedlings at the late stage. The revegetation method has the advantages that the revegetation method can enhance the adaptability of plants to the complex adverse environment of a tailings pond, including stronger drought-resisting, saline-alkali tolerant, barren-tolerant and nutrient-obtaining capabilities, the method can be utilized to restore the ecology of the slopes of the tailings dam and build a steady vegetation layer, and also has the effects of stabilizing the slopes, conserving water and soil and inhibiting runoff and flying tailings sand.
Owner:青岛冠中生态股份有限公司
Clay-based hemostatic agents and devices for the delivery thereof
ActiveUS20070276345A1Eliminating generation of heatMinimize discomfort and further injuryPowder deliveryPhysical/chemical process catalystsGlycerolBandage
A hemostatic device for promoting the clotting of blood includes a gauze substrate, a clay material disposed on the gauze substrate, and also a polyol such as glycerol or the like disposed on the gauze substrate to bind the clay material. When the device is used to treat a bleeding wound, at least a portion of the clay material comes into contact with blood emanating from the wound to cause the clotting. A bandage that can be applied to a bleeding wound to promote the clotting of blood includes a flexible substrate and a gauze substrate mounted thereon. The gauze substrate includes a clay material and a polyol. A hemostatic sponge also includes a gauze substrate and a dispersion of hemostatic material and a polyol on a first surface of the substrate.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
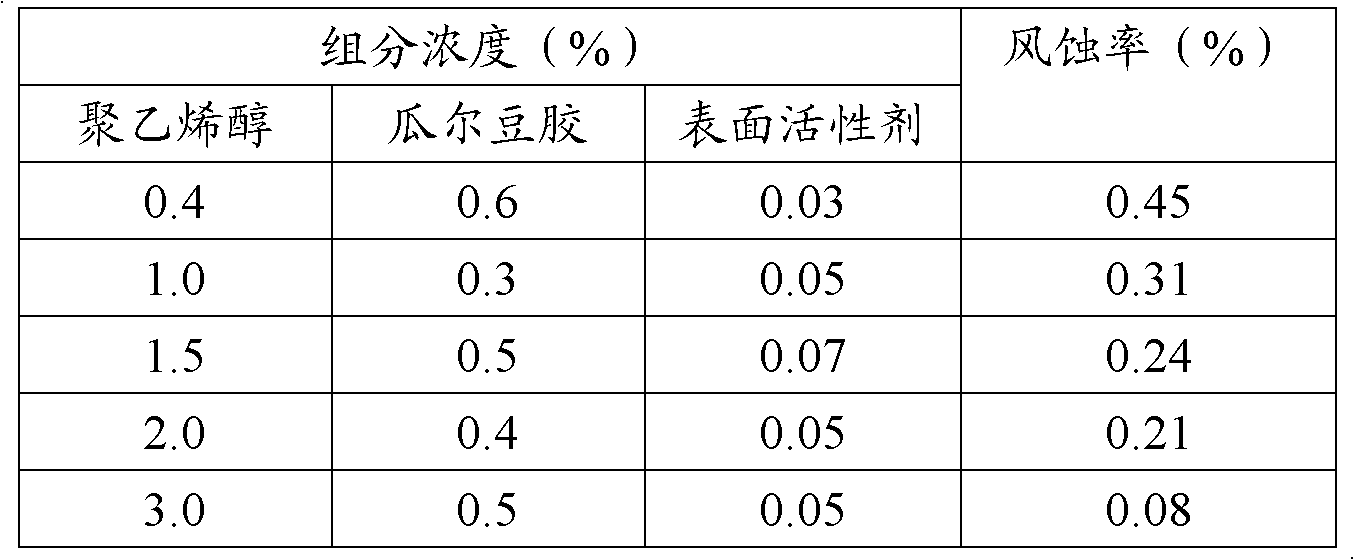
Iron ore dust suppressant composition
ActiveCN102093847ASuppress dustProduce pollutionOther chemical processesWater solubleUltimate tensile strength
The invention relates to an iron ore dust suppressant composition, which consists of styrene butadiene latex, a water-soluble polymer material, a surfactant and water. The iron ore dust suppressant can form a cured layer with certain strength and toughness on the surface of iron ore and mineral powder to adhere large, granular and powdery iron ore together, so that iron ore powder can be effectively prevented from flying. The iron ore dust suppressant also can be used for soil desertification prevention, construction site dust prevention and other ore dust prevention, and cannot pollute environment.
Owner:兰州天际环境保护有限公司 +1
Fertiliser coating containing micronutrients
ActiveUS20150376076A1Different and undesired coatingImprove storage characteristicsAmmonium nitrate fertilisersOrganic fertilisersChemical reactionChelation
A single-step method for preparing a free-flowing, non-dusting micronutrient-coated particulate solid fertiliser material, the method comprising applying a single fluid onto particulate solid fertiliser material at ambient temperature without chemical reaction or chelation, said single fluid comprising a suspension of one or more micronutrient materials in an oil.
Owner:YARA UK LTD
Preparation method of naturally-degradable compound fertilizer anti-blocking agent and application thereof
The invention discloses a preparation method of a naturally-degradable compound fertilizer anti-blocking agent and an application thereof. The naturally-degradable compound fertilizer anti-blocking agent comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 10-20 percent of fatty amine or salt thereof, 20-25 percent of stearic acid, 15-20 percent of oleic acid, 5-15 percent of refined glycerin and 20-50 percent of waste edible oil and fat, and the sum of all the components is 100 percent according to the percentage. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: mixing all the components according to the proportion, heating to be 70 DEG C -85 DEG C, and stirring and reacting for 15 minutes-30 minutes. The used amount of the compound fertilizer anti-blocking agent is 05-2.0kg / t (compound fertilizer), and a granulation mode of a high air-cooling crystallization tower of an all-molten compound fertilizer is adopted to mix the naturally-degradable compound fertilizer anti-blocking agent with the compound fertilizer. In the preparation method and the application thereof, the processing is simple, the use cost is low, the anti-blocking performance is good, the purely natural and environmentally-friendly performances are achieved, the absorption of crops is convenient, the fertilizer effect is enhanced, and the soil is protected.
Owner:福建达安能源实业有限责任公司
Phosphorus ore dust suppressant composition and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102093846ADoes not affect processingDoes not affect transportation handlingOther chemical processesPolyvinyl alcoholPhosphate
The invention relates to a phosphorus ore dust suppressant composition and a preparation method thereof. The phosphorus ore dust suppressant composition comprises water-soluble polyvinyl alcohol, guar gum, microbicide, and water. The phosphorus ore dust suppressant provided by the invention can form a solidifying layer with certain strength and tenacity on the surface of phosphorus ore or powdered ore, which allows granular or powdered phosphorus ores to bond together, so as to effectively suppress dust emission of powder phosphate ores. The phosphorus ore dust can also be used for treatment of soil desertification and dust suppression at construction sites or dust suppression of other ores and can not pollute environment.
Owner:兰州天际环境保护有限公司 +1
End of a moldboard positioned proximate a milling drum
InactiveUS7976239B2Avoid excessive accumulationLimit proximityRoads maintainenceCutting machinesMobile vehicleEngineering
In one aspect of the present invention, the present invention is a system for removing aggregate from a paved surface. The system includes a motorized vehicle with a degradation drum that is connected to the underside of the vehicle. The degradation drum is enclosed by a milling chamber. The milling chamber is defined by having a plurality of plates, including a moldboard positioned rearward of the milling drum. The moldboard comprises an end that is disposed opposite the underside. The end comprises a section that is proximate the milling drum.
Owner:CATEPILLAR SARL +1
Concave elastic screen wheel
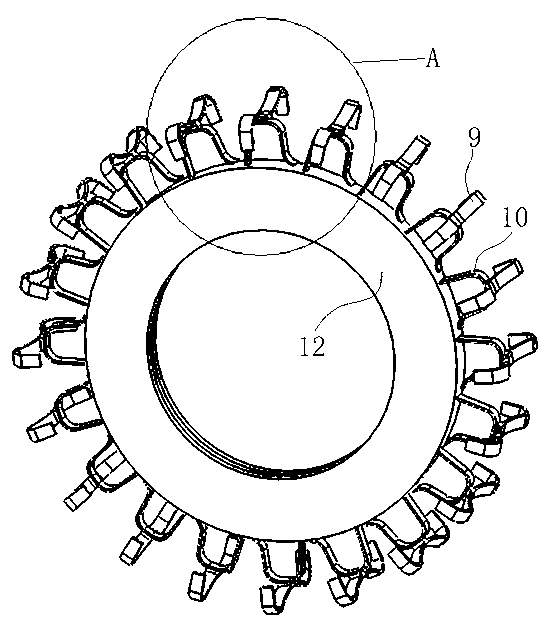
InactiveCN103342084AReduce subsidenceReduce squishingSpecial tyresWheel attachmentsConvex sideEngineering
The invention discloses a concave elastic screen wheel which comprises a hub and a supporting ring arranged on the hub. An annular metal wire mesh is arranged at the outer periphery of the supporting ring, an elastic element for supporting the metal wire mesh is positioned between the supporting ring and the metal wire mesh, an antiskid pawl is positioned at the outer periphery of the metal wire mesh, the metal wire mesh and the antiskid pawl are fixedly connected to form an arch concave elastic screen serving as a tire face, and the tire face is an arch concave face with the concave middle and the two convex sides. The concave elastic screen wheel can carry people to walk in soft, dusty, dry and low-gravity environments, can meet the requirements of high roll stability, high adhesion force and good shock absorption performance, can effectively prevent settlement and can effectively restrain raised dust.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Ecological restoration method for side slope of late dam of tailing pond under condition of no earthing
ActiveCN101974910ASuppress dustConserve soil and waterExcavationsHorticultureVegetationRestoration method
The invention belongs to the technical field of ecological restoration of discarded land in mining area, relating to a stable ecological restoration technology for vegetation on the side slope of a late dam of a tailing pond under the condition of no earthing soil, and realizing a root system network for sand consolidation by planting vetiveria zizanioides and seeding side slope afforesting grass seeds between the seed rows of the vetiveria zizanioides, wherein the proportioning of the side slope grass seeds are Bermuda grass, white clover, alfalfa and astragalus adsurgens the proportion of which is 5-10:1-2:1-2:1-2. The method of the invention can be used for carrying out ecological restoration of the side slope of late dam of the tailing pond under the condition of no earthing, has the effects of stabilizing side slope, conserving water and soil, restraining running water and raising dust of the tailing sands and the stable vegetable layer is established by using the method.
Owner:BEIJING GENERAL RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY
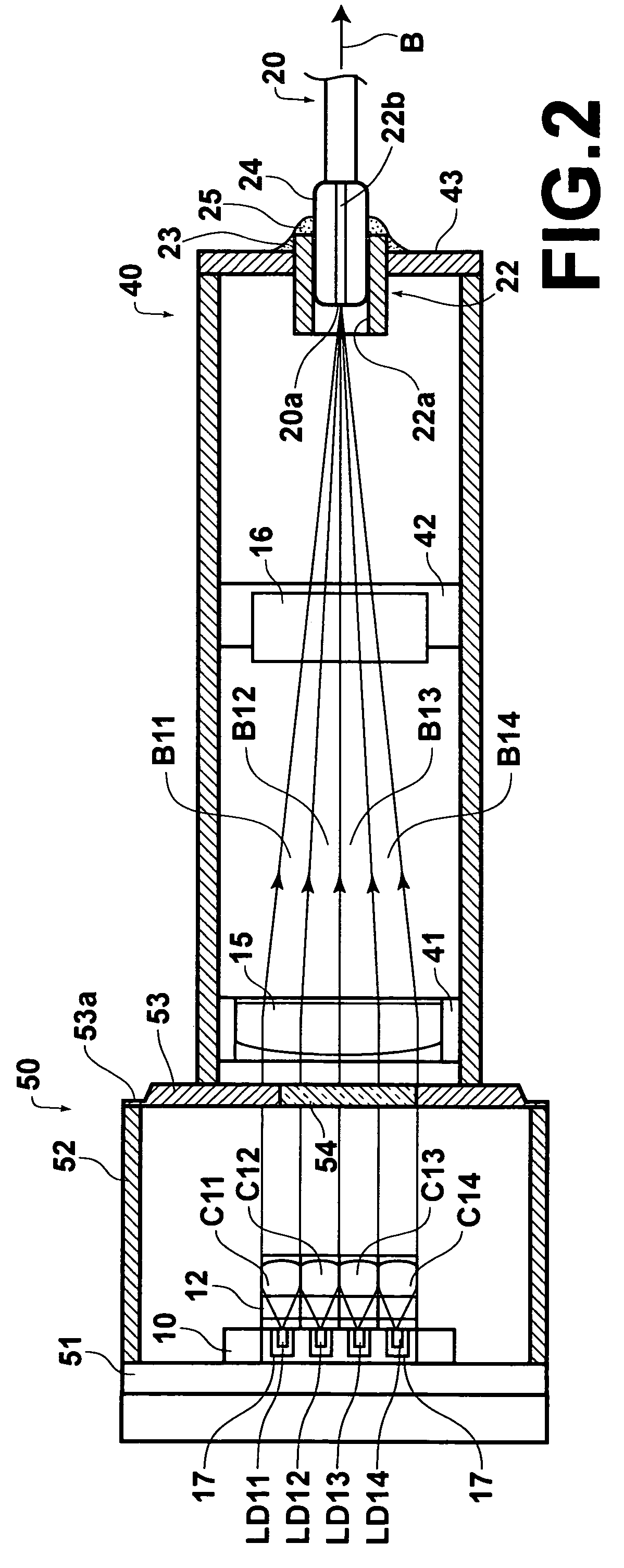
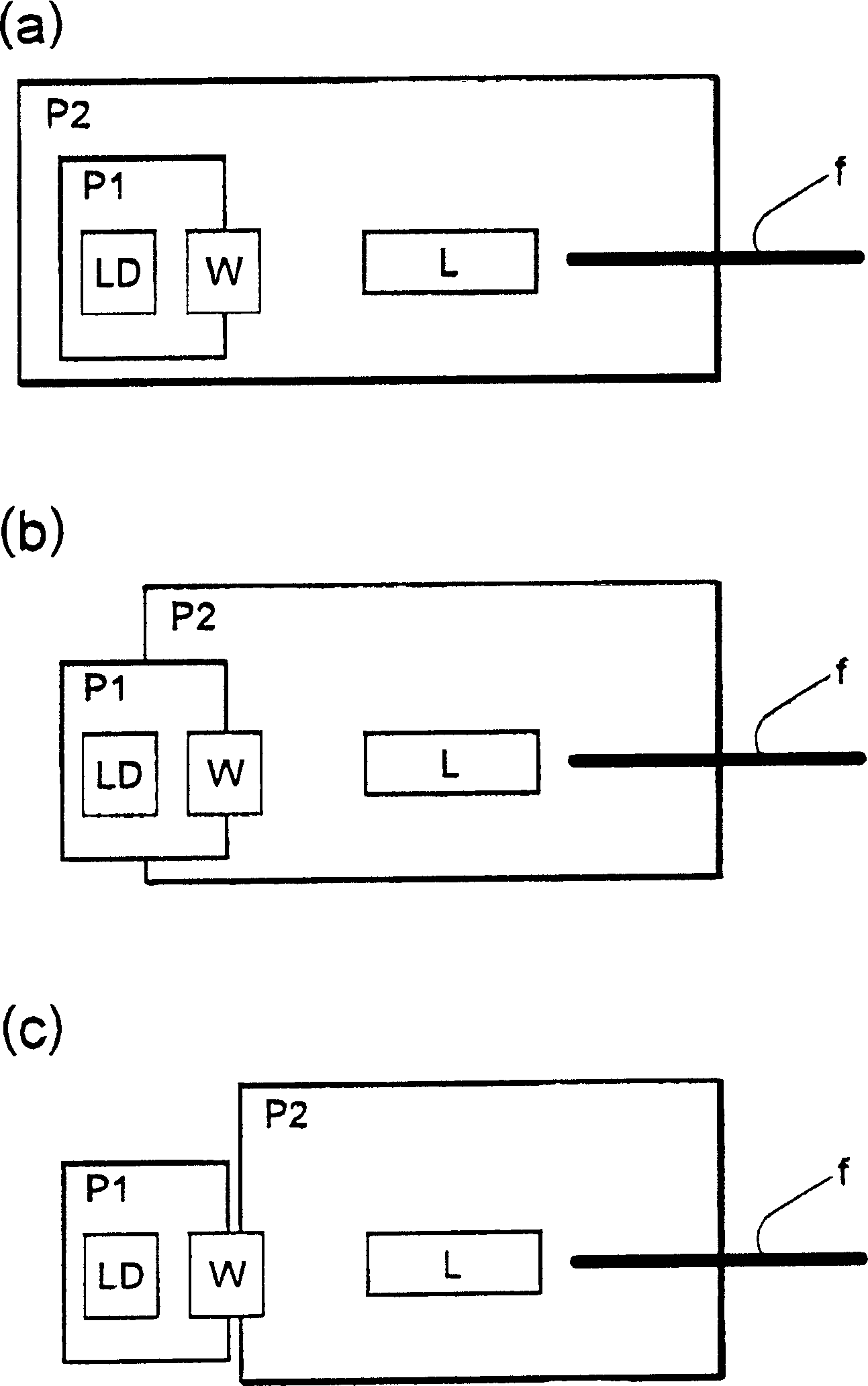
Laser module with sealed packages having reduced total volume
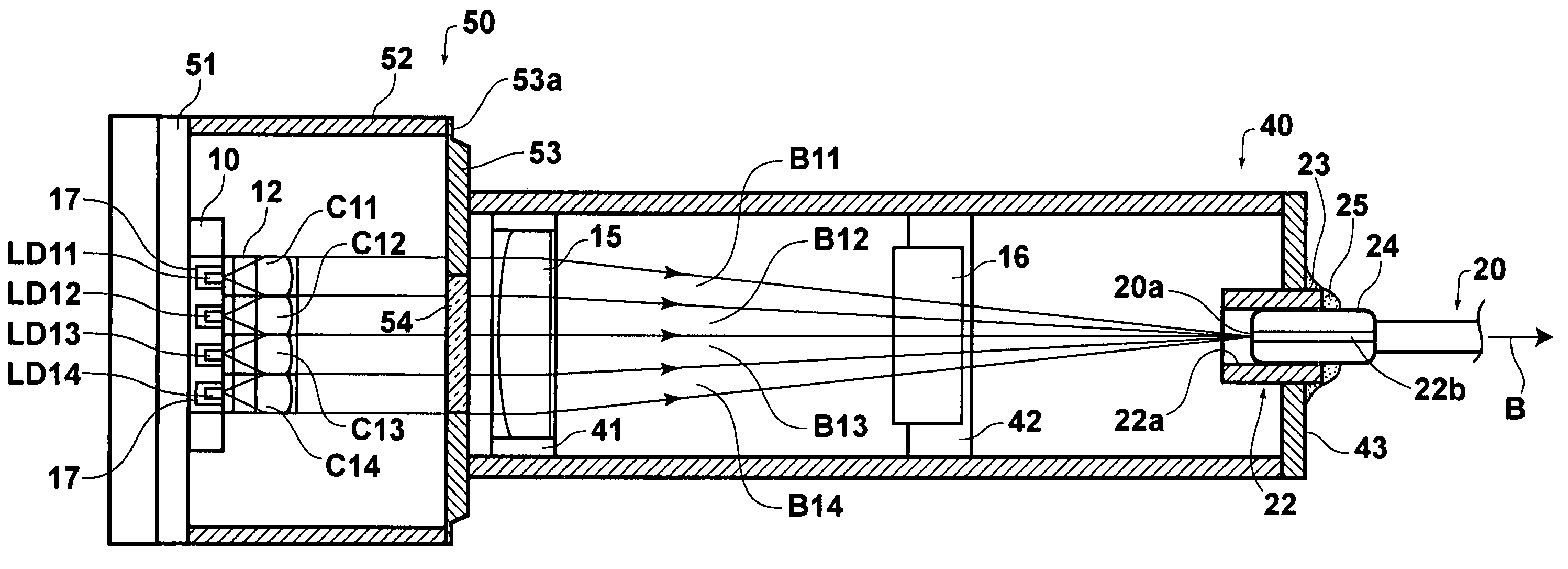
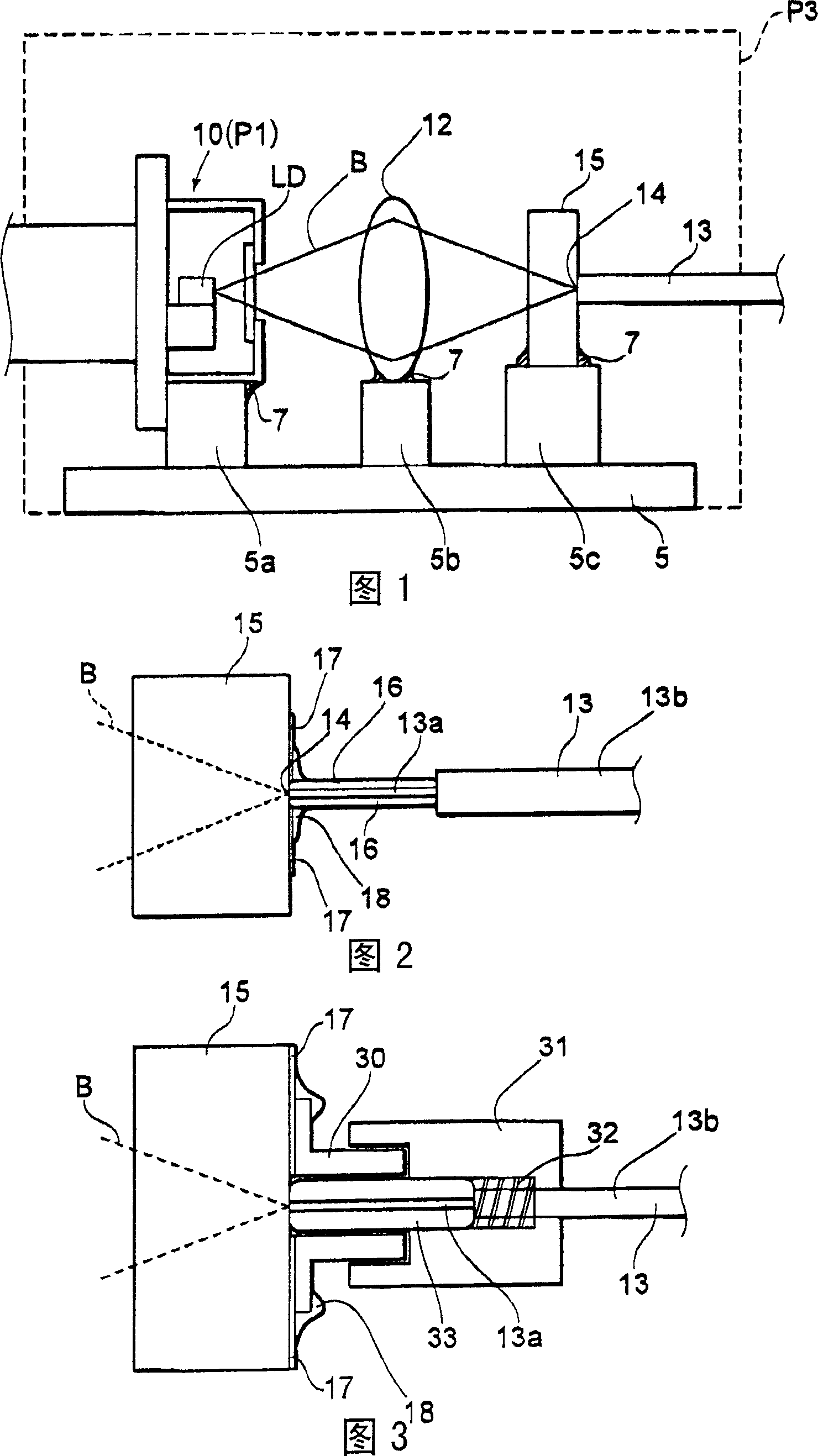
In a laser module in which laser beams emitted from semiconductor laser elements are collimated by collimator lenses, and condensed by an optical condensing system so that the laser beams converge at a light-entrance end face of an optical fiber. The semiconductor laser elements and the collimator lenses are contained in a hermetically sealed, first package which includes a front wall having a window arranged for passage of the laser beams, and a portion of the optical condensing system and the light-entrance end face are contained in a hermetically sealed, second package which is fixed to the front wall. The cross section of the second package perpendicular to the optical axis of the optical fiber at the light-entrance end face is smaller than the cross section of the first package parallel to the cross section of the second package.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Method of preventing emanation of dust from a coal pile or railcar
ActiveUS20060243946A1Effective and long termSuppress emanationIn situ pavingsDisloding machinesCoal dustEnvironmental protection
A method for treating a mass of coal to suppress emanation of coal dust therefrom, the mass of coal having, prior to treatment, an exposed surface from which dust may emanate, comprises applying to the exposed surface an aqueous fluid comprising gelatinized starch to form a layer of the fluid over the surface and drying the layer of the fluid to form a crust over the surface.
Owner:BENETECH INC
Foaming agent for shield machine
InactiveCN106190136AImprove work performanceReduce wearBuilding constructionsOrganic fertilisersAlpha-olefinMaterials science
The invention belongs to the technical field of foaming agents, and particularly relates to a foaming agent for a shield machine. In order to solve the problems that various properties including the uniformity, the stability, the lubricating properties, the permeability and the like of foams of a domestic foaming agent at current cannot completely meet requirements for foams in shield tunneling, and the adaptability of the foaming agent has certain limit, the invention provides the foaming agent for the shield machine, and the foaming agent is prepared from sodium dodecylsulfate, sodium alcohol ether sulphate, sodium alpha-olefin sulfonate, modified polyethoxylated silicone, and water in a certain proportion. According to the foaming agent disclosed by the invention, the working performance of soil is improved, so that the soil forms plastic deformation to provide uniform and controllable support pressure, and a working surface is stable; leakage is reduced, the sealing properties of the working surface are strengthened, internal frictional force is reduced, abrasion of the soil on cutter heads, conveyors and conveyer belts is reduced, and the energy consumption is reduced; the viscosity of a soil mass is reduced, and generation of plugging is avoided; and the foaming agent has the effect of restraining dust during construction of rock and soil tunnels and mines.
Owner:天津盾构科技发展有限公司
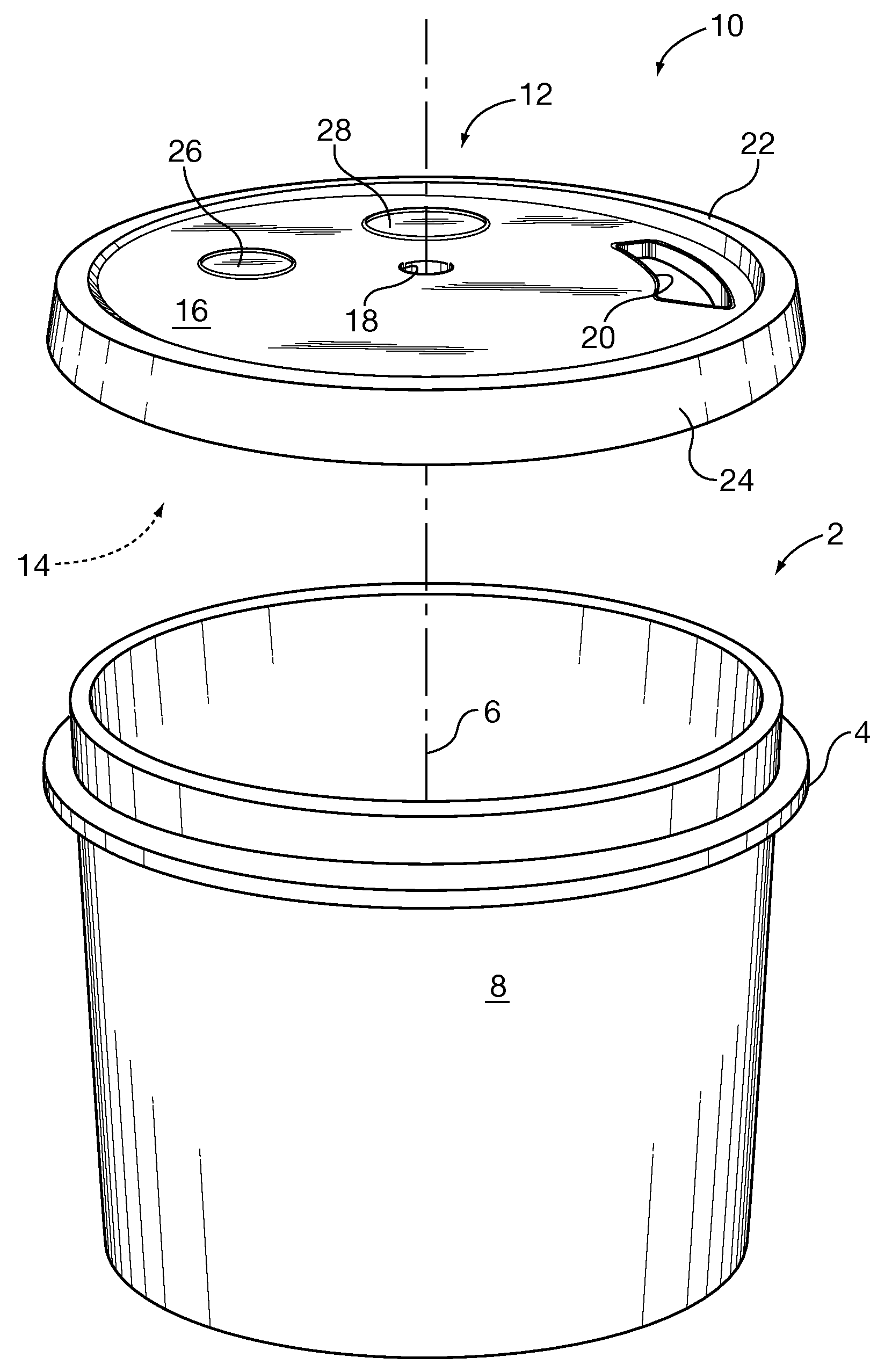
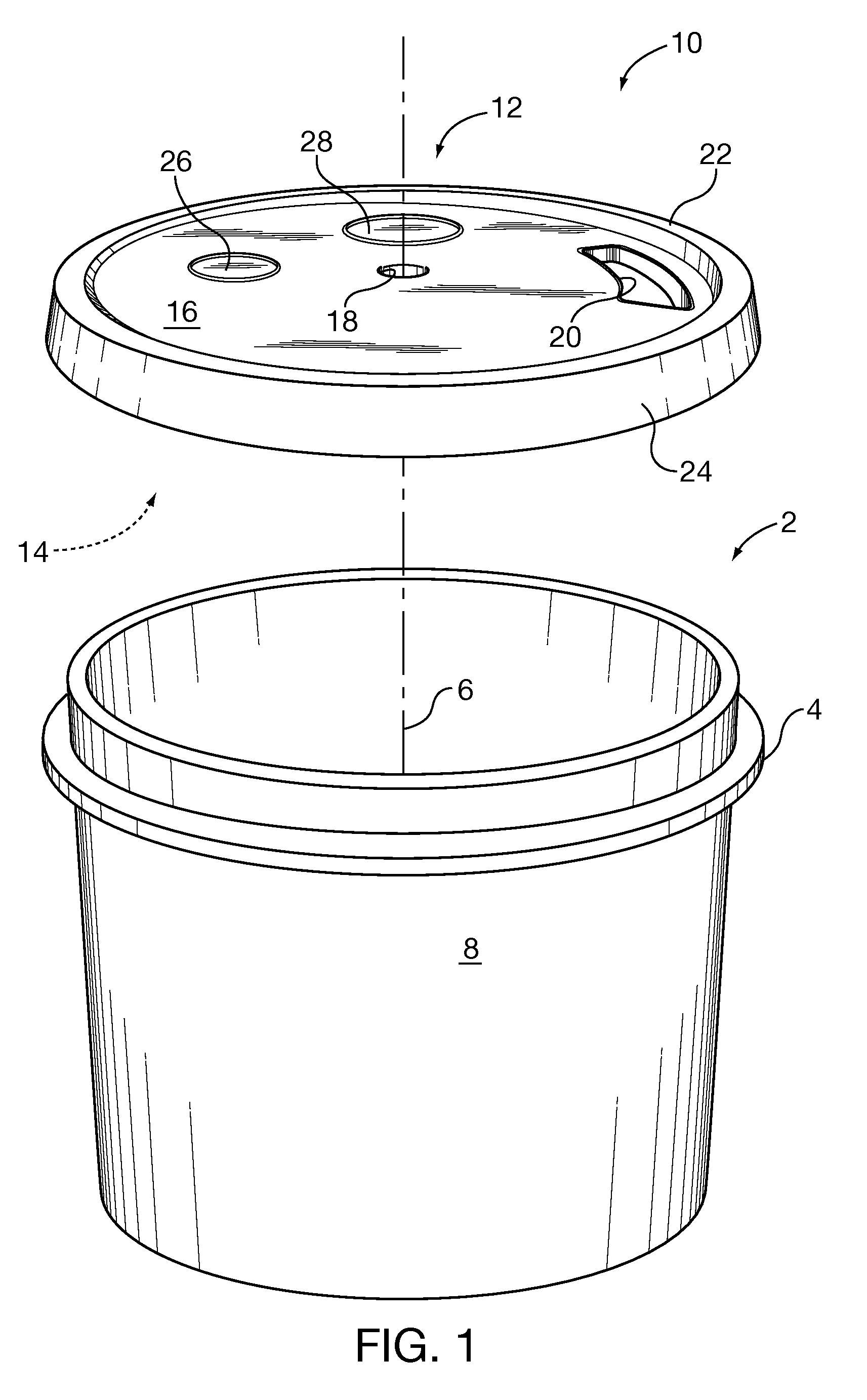
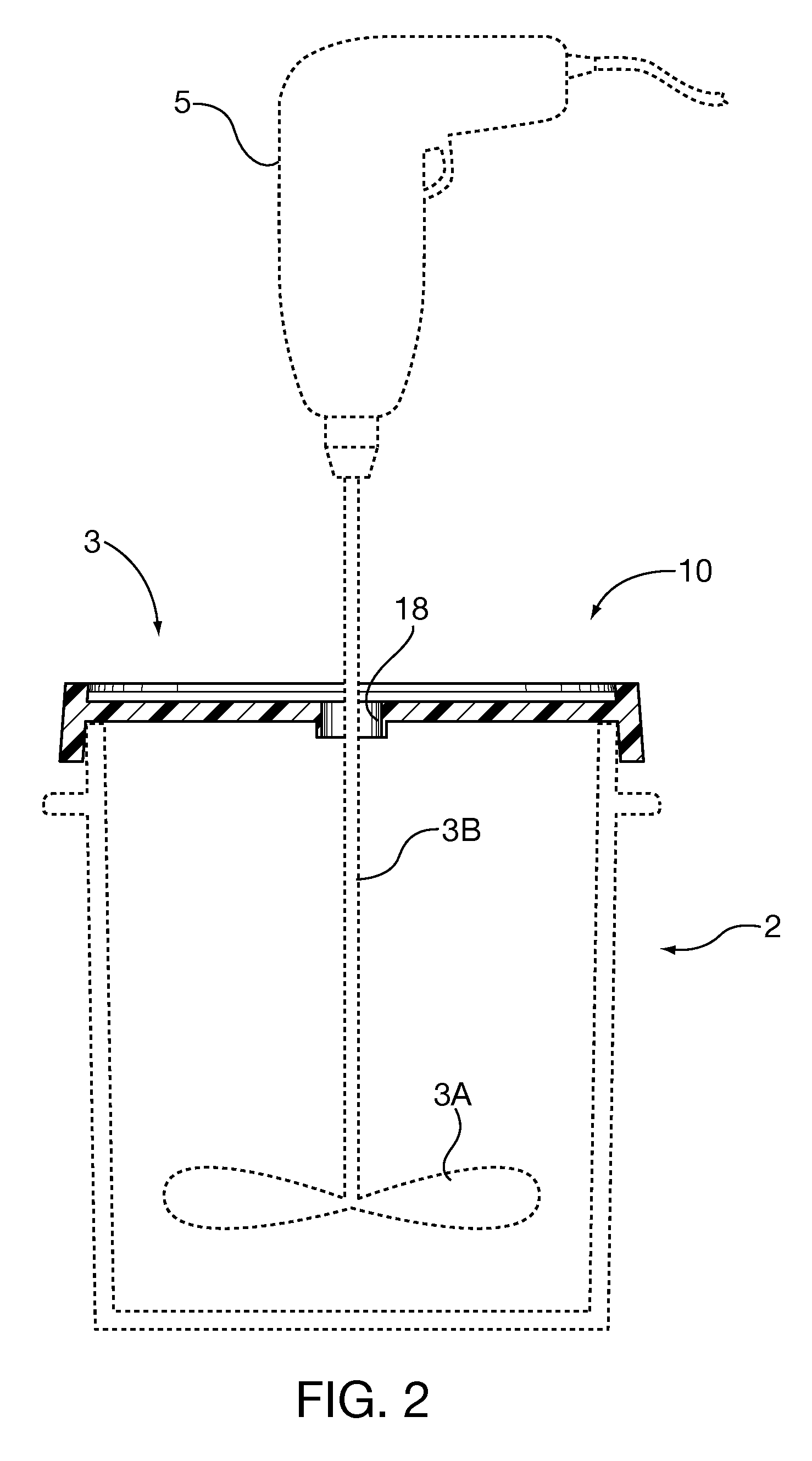
Pouring and mixing lid for cylindrical containers
InactiveUS20100195432A1Suppress dustSuppressing liquidClosuresRotary stirring mixersEngineeringMechanical engineering
A cover for blending one or more materials in an open topped container. The cover is adapted to close the open top during blending. The cover may have a central hole for passing the shaft of a powered blender and a peripheral opening for pouring materials from the container or into a container, and to view the progress of the mixing. Optionally, the cover may have a third opening and as a further option, a fourth opening, the third and fourth openings adapted to connect to a commercial vacuum device for evacuating dust from the container during blending. The third and fourth openings may be formed as prescored removable portions of the cover. In a further option, the third and fourth openings may be provided with close fitting removable resilient plugs. The upper surface of the cover may be inclined so that liquids flow towards the peripheral opening and into the container.
Owner:LAURENCE KEVIN +1
Carburization resistant metal material
ActiveCN101946016AExcellent resistance to metal dustingImprove carburization resistanceMetal dustingMetallic materials
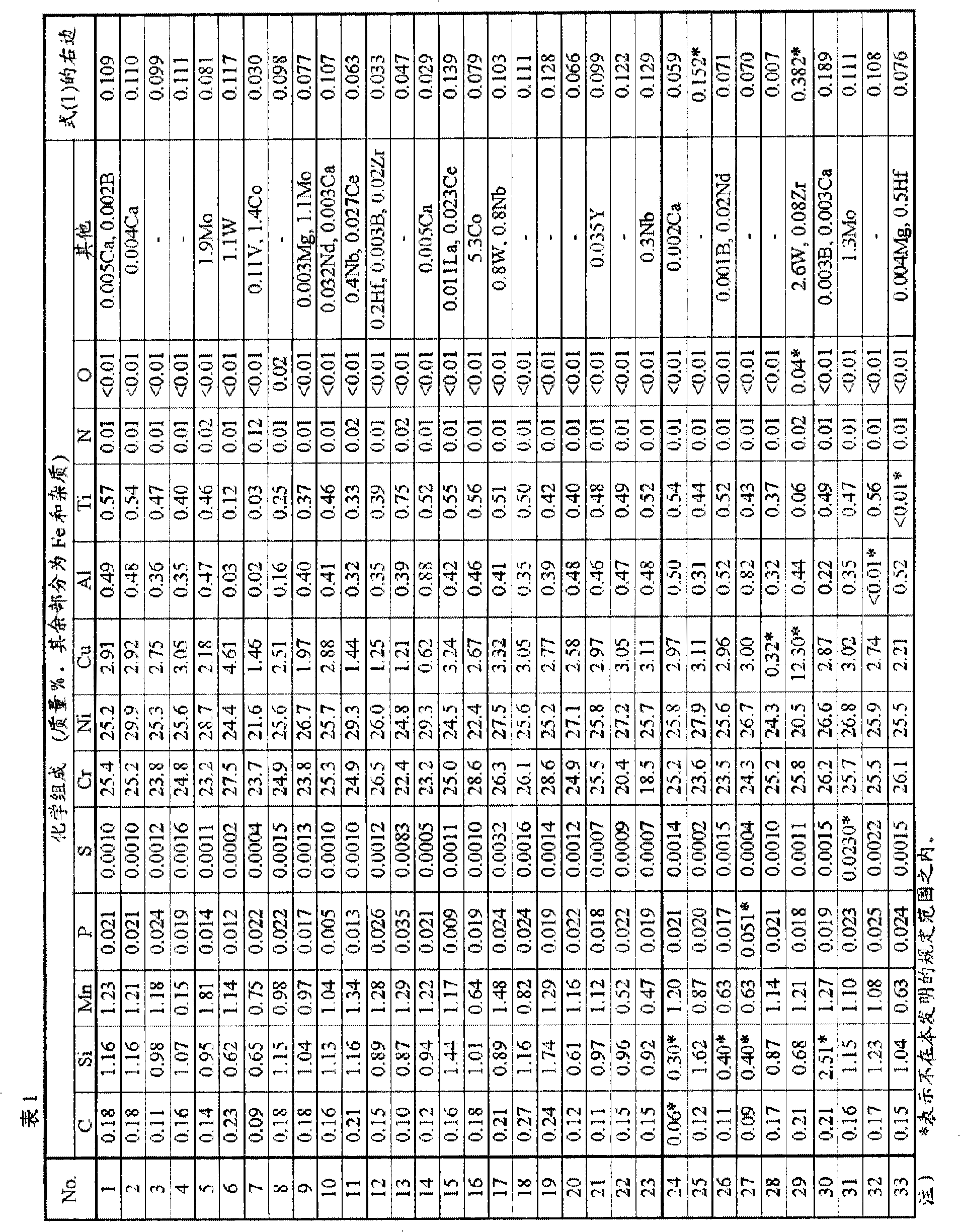
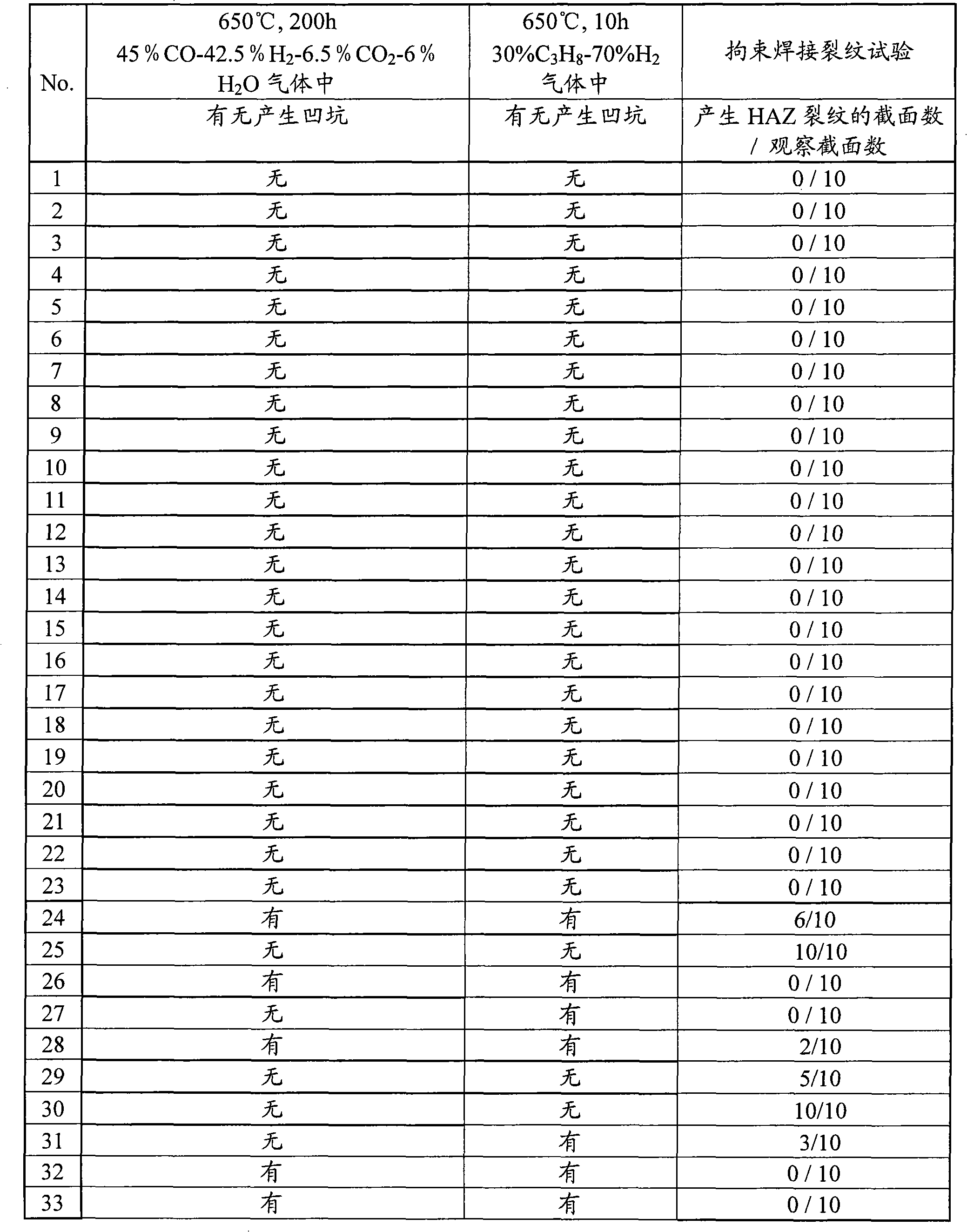
A metal material which exhibits both excellent workability and excellent metal dusting resistance and which is suitable for use as the material in a cracking furnace, a reforming furnace, a heating furnace, or a heat exchanger in petroleum refining or petrochemical plants or the like. A carburization-resistant metal material characterized by containing by mass C: 0.08 to 0.4%, Si: 0.6 to 2.0%, Mn: 0.05 to 2.5%, P: 0.04% or less, S: 0.015% or less, Cr: 18 to 30%, Ni: 20 to less than 30%, Cu: 0.5 to 10.0%, Al: 0.01 to 1%, Ti: 0.01 to 1%, N: 0.15% or less, O (oxygen): 0.02% or less with the balance consisting of Fe and impurities and by satisfying relationship (1). The material may further contain one or more of Co, Mo, W, B, V, Zr, Nb, Hf, Mg, Ca, Y, La, Ce and Nd. C > 0.062Si + 0.033Cu - 0.004Cr + 0.043 (1) (wherein each symbol of element represents the content of the element in mass%).
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Dust suppressant
Owner:EARTH ALIVE CLEAN TECH
Environment-friendly water-soluble adhesive dust inhibitor and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110373156ALowering the freezing pointWon't freezeOther chemical processesSodium lactateEmulsion
The invention relates to an environment-friendly water-soluble adhesive dust inhibitor and a preparation method thereof. The environment-friendly water-soluble adhesive dust inhibitor comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 0.1-2% of sodium lactate, 0.1-6% of a pregelatinized starch, 2-10% of glycerinum, 0.1-5% of an adhesive, 1-5% of urea, 0.2-2% of a polyacrylic resin, 0.1-1%of a surfactant, 0.1-3% of an emulsion, 0.02-0.5% of texanol, 0.1-2% of an environment-friendly pigment and the balance of water, and the inhibitor is finally prepared through stirring and mixing. Compared with the prior art, the inhibitor is applied to dust inhibition and the like in exposed fields such as mine tailing ponds, city exposed grounds, municipal construction, coal transportation andstorage yards, is not limited by use fields, and is capable of reducing environment pollution and reducing resource waste.
Owner:艾珂(上海)环境技术工程有限公司 +1
Road dust depressor and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105018032ASolve road dust problemGood dust suppression effectOther chemical processesBuilding insulationsMoisture retentionChemistry
The invention discloses a road dust depressor and a preparation method thereof. The road dust depressor is prepared from 0.5-10% of petroleum asphalt, 5-20% of glycerol, 1-5% of anhydrous calcium acetate, 0.5-5% of a surfactant, 1-5% of a cosolvent, 1-2% of sodium metasilicate and 55%-90% of water. The preparation method includes: at room temperature, adding deionized water into a reaction kettle, starting stirring and conducting heating to 50DEG C, adding anhydrous calcium acetate in batches, after complete dissolving, adding glycerol, after dissolving, adding the surfactant, road asphalt, the co-solvent and sodium metasilicate in order, performing stirring dissolving to a homogeneous phase so as to obtain a brown-black brown aqueous solution, and carrying out standing, cooling and filling, thus obtaining a finished product. The road dust depressor has good moisture retention, moisture absorption and adhesion, and has remarkable dust suppression effect and long dust suppression period. The product is safe to use, has no corrosion to metal, is non-toxic, can be biodegradable, has no influence to vegetation, is an environment friendly product, and can be widely applied to dust control of unpaved roads, urban asphalt pavement, strip mine roads and the like.
Owner:宁夏浤森环保科技有限公司
Movable type tubular belt conveyor
ActiveCN103241494ARealize continuous deliveryImprove efficiencyConveyorsSupporting framesTerrainVertical plane
The invention belongs to the field of continuous operating tubular belt conveyors, and particularly relates to a movable pipe belt conveyor. The movable pipe belt conveyor has the technical essentials that, running gears are arranged on the head and the tail of the pipe belt conveyor and enable both the head and the tail of the pipe belt conveyor to perform movements of loading points and emptying points according to practical situations on site, simultaneously middle adjustment machine frames are arranged between the head and the tail of the pipe belt conveyor, the middle adjustment machine frames are all composed of machine frame units and are respectively connected in mode of hinging horizontal planes and vertical planes, slide blocks or universal wheel devices are arranged on the lower portions of the machine frames, and therefore the machine frames can be bent in any horizontal plane, vertical plane and space in a certain bending radius range according to terrain, and materials can be conveyed in a plurality of ranges. The movable pipe belt conveyor can achieve continuous conveying, and thereby is high in efficiency; can effectively restrain dust rising for materials with high dust, and thereby is environment-friendly; and can adapt to topographic change to the upmost, and thereby is strong in adaptability.
Owner:TIDFORE HEAVY IND
Method for controlling earth surface water and soil loss of underground layered mineral product mining subsidence area
ActiveCN104846848AIncrease moisture contentWon't breakProtective foundationSoil preservationEcological environmentSurface water
The invention discloses a method for controlling earth surface water and soil loss of an underground layered mineral product mining subsidence area. According to the method, according to the soil body stress distribution or the deformation feature difference caused by the elevation change of a mining area ground surface subsidence basin, the water physical property of a ground surface soil body in different water containing conditions is utilized, the soil body plasticity is improved, pull cracks of a soil body are reduced, and therefore the depth perpendicular infiltration function caused by the cracks in the soil corrosion process is achieved. On the mining area ground surface, the soil body water containing rate is adjusted through an auxiliary technology for quantitative water spraying, the ground crack development degree of an expanding time zone of the mining subsidence basin is controlled, and the water and soil loss acting degree caused by the crack preferential flow action is lowered. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that a large machine is not needed for construction, the input is low in the mine lot environmental governance technology method, and the governance cost is low; the ground surface soil body does not need to be chemically improved through the method, the micro-ecology environment in the soil body cannot be damaged, and the method is suitable for the fragile ecological environment in a mine lot.
Owner:ANHUI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
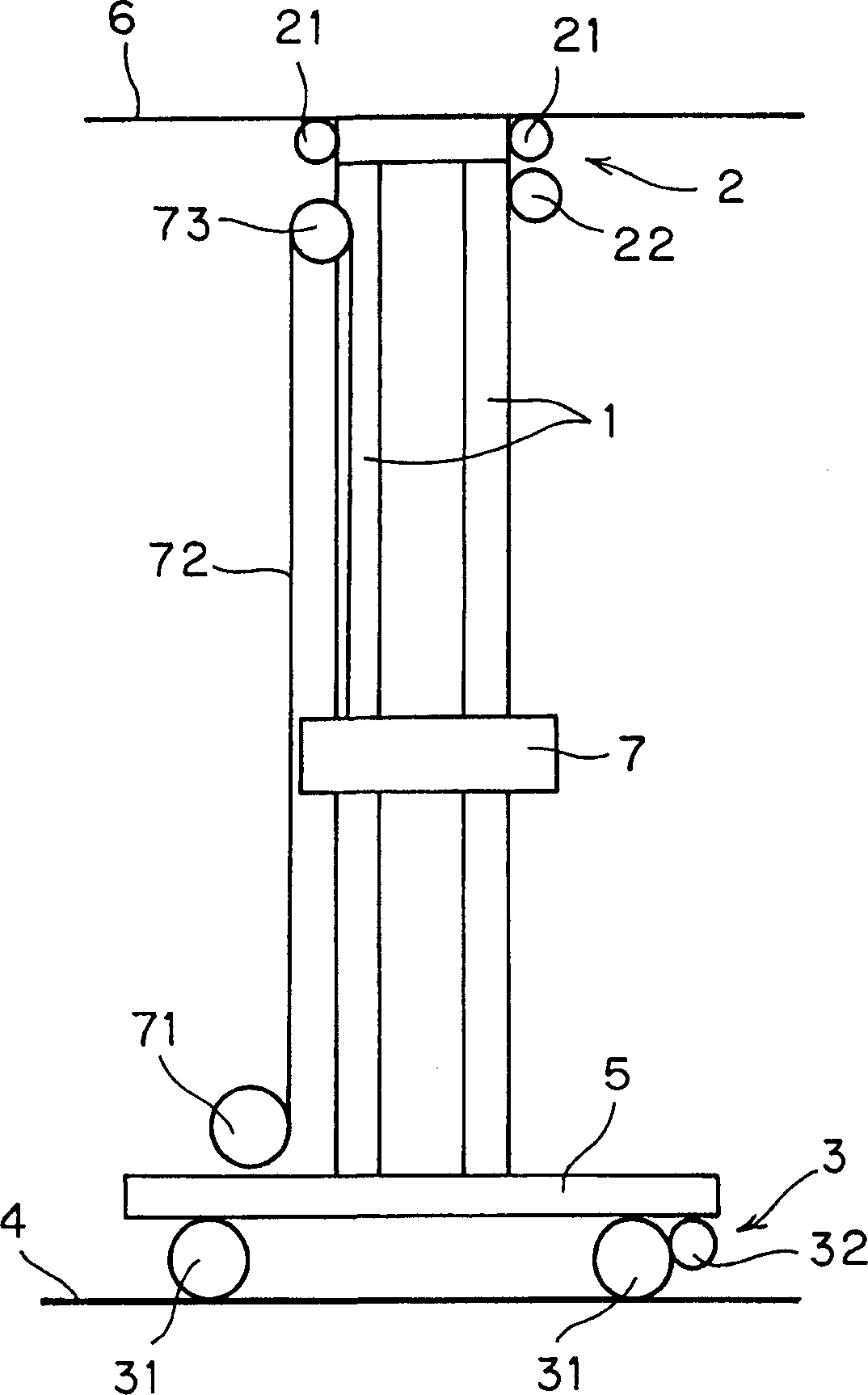
Stacker crane
The upper travelling driving device 2 and a lower travelling driving device 3 are provided in an upper part and a lower part of the mast 1 of the stacker crane. The lower travelling driving device 3 controls travelling and position of the stacker crane, and the upper travelling driving device 2 is driven on the basis of a speed signal of the lower travelling driving device 3 so as to restrict vibration of the mast 1 with the upper travelling driving device 2.
Owner:DAIFUKU CO LTD
Dust suppression method and apparatus
InactiveUS20060078685A1Suppress dustOther chemical processesLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingFiberMaterials science
The present invention provides a process for suppressing dusting of dusting materials by spraying an aqueous dispersion of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) or modified polytetrafluoroethylene onto the exposed exterior surfaces of the dusting material to fibrillate at least part of the dispersion and coat the exposed exterior surfaces of the dusting material with a web of fibrils of polytetrafluoroethylene or modified polytetrafluoroethylene. The process is especially advantageous for suppressing dusting of dusting materials contained in a pile, stockpile or open-topped container and dusting materials contained in open-topped transport vehicles.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Soil solidifying agent with compound function and use method thereof
InactiveCN102504827ASuppress dustSimple preparation processOrganic fertilisersSoil conditioning compositionsAluminium saltsSodium silicate
The invention discloses a soil solidifying agent with a compound function and a use method thereof. The soil solidifying agent is used for preventing soil, sand dunes and the like from being subjected to wind erosion, water erosion and generating environmental pollution. Anionic polyacrylamide, sodium silicate and aluminum sulfate are selected as the components of the soil solidifying agent. According to an L9 (34) orthogonal design, three levels of concentration is selected for each reagent. An unconfined compressive strength test, an indirect tensile strength test and a water soaking test are used for testing a formed standard test piece, thereby obtaining an optimal formula of the soil solidifying agent. A test result shows that a novel soil solidifying agent developed in a spraying applying form has an excellent solidifying function and obtains an excellent composite economic benefit. The soil solidifying agent is an ideal environment-friendly product and has a huge ecological environmental protection benefit.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Spray and dust reduction device applicable to building construction site
InactiveCN106149610ASuppress dustImprove environmental qualityRoad cleaningEnvironmental qualityWater supply
The invention relates to the technical field of dust suppression in construction, in particular to a spray dust suppression device for construction sites, which is characterized in that it includes a deck, a dust detector, a controller, and a valve; Type groove, a spring is fixed on one side of the half-shaped groove, and the other end of the spring is fixedly connected with the baffle plate. The ends are fixedly connected, the middle part of the outer wall water supply pipe is fixedly connected with one end of an inner wall water supply pipe, the tops of the outer wall water supply pipe and the inner wall water supply pipe are bent downwards in opposite directions, and the outer wall water supply pipe and the inner wall water supply pipe The tops of the water supply pipes are respectively connected through and fixedly to a spherical atomizing nozzle. The invention can effectively capture the dust in the air near the fence inside and outside the construction site, suppress the dust inside and outside the site, improve the environmental quality inside and outside the site, and protect the health of workers.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Coal flow dust suppressant as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN107828380AHigh viscosityWeight increaseOther chemical processesEngineeringSURFACTANT BLEND
The invention belongs to the technical field of control for coal flow flying dust and particularly relates to a coal flow dust suppressant as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The coal flow dust suppressant comprises components in parts by weight as follows: starch-grafted acrylic polymer, a surfactant and water. The coal flow dust suppressant has good coagulation property,wettability and permeability, dust particles are wetted rapidly and coagulated together, grain size and weight of the dust particles are increased, meanwhile, the coal flow dust suppressant can rapidly permeate into the coal flow, and the dust suppression effect is realized. According to the coal flow dust suppressant, the technical defect of low dust suppression speed of a traditional dust suppressant can be effectively overcome.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID
Surfactants
InactiveUS20030162687A1Superior solubility and flowabilitySuppress dustCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsChemistryAmino acid
A surfactant comprising an N-long-chain acyl amino acid or a salt thereof dried by a spray dryer, which contains 280 mesh pass particles at a ratio of 3% by weight or less, and a surfactant comprising an N-long-chain acyl amino acid or a salt thereof dried by a spray dryer, which does not substantially contain 200 mesh pass particles, preferably 140 mesh pass particles. Also provided are surfactants having improved solubility and flowability, which are used for detergents and the like.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method of preventing emanation of dust from a coal pile or railcar
InactiveUS7976724B2Effective and long-termSuppress dustIn situ pavingsDisloding machinesCoalEnvironmental protection
A method for treating a mass of coal to suppress emanation of coal dust therefrom, the mass of coal having, prior to treatment, an exposed surface from which dust may emanate, comprises applying to the exposed surface an aqueous fluid comprising gelatinized starch to form a layer of the fluid over the surface and drying the layer of the fluid to form a crust over the surface.
Owner:BENETECH INC
Laer moudle
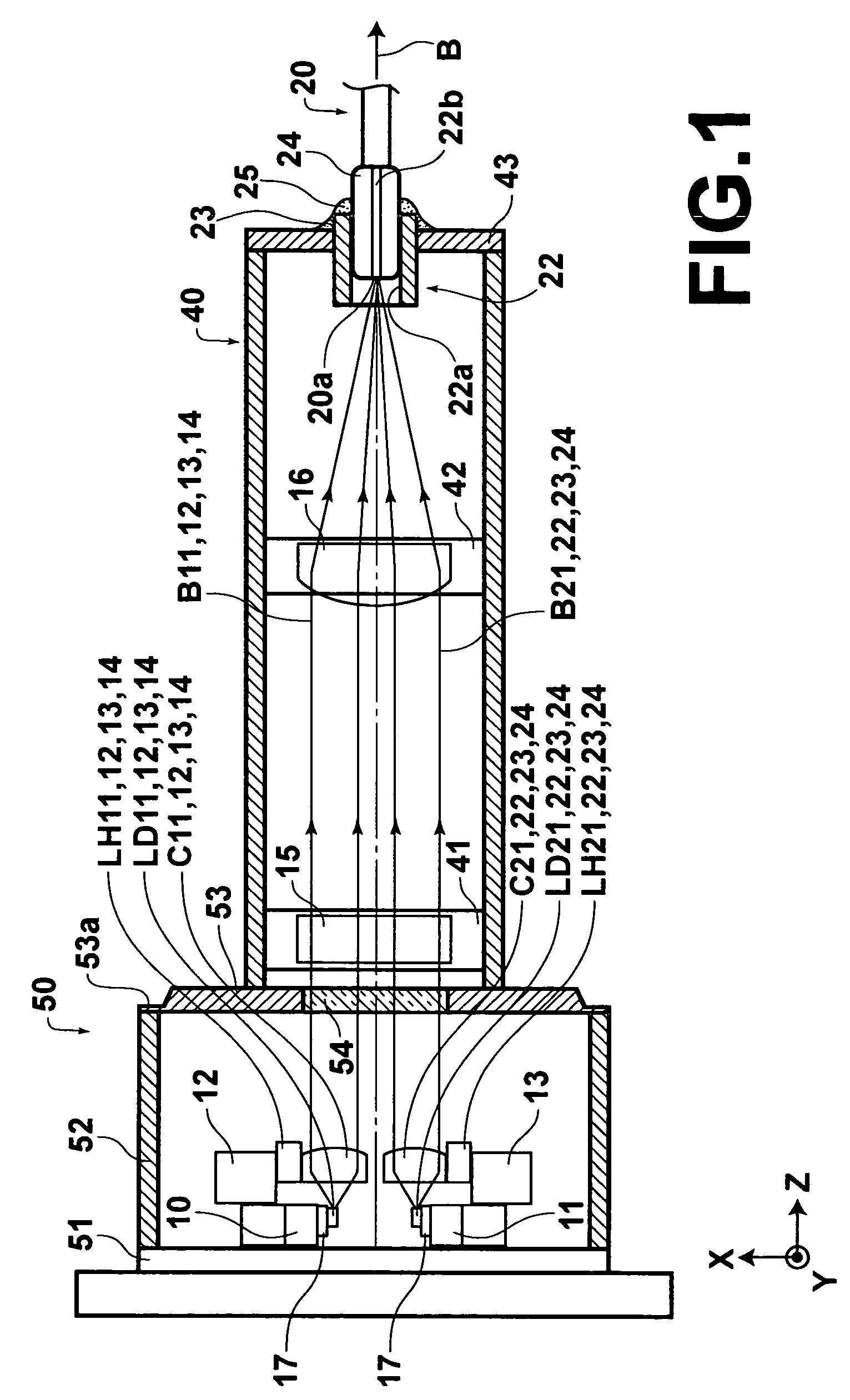
InactiveCN1519997AImprove reliabilitySuppress dustLaser detailsChiropractic devicesCollimatorLaser beams
To obtain high reliability in a laser module provided with a semiconductor laser element, an optical fiber, and a convergence optical system which converges a laser beam emitted from the semiconductor laser element and couples with an incident end of the optical fiber. In a laser module, a semiconductor laser element LD, a collimator lens 19, a condenser lens 12, and an optical fiber 13 are arranged in a positional relation where a laser beam B emitted from the semiconductor laser element LD is collimated by the collimator lens 19, condensed by the condenser lens 12, and converged in an incident end. A CAN package 10 is provided as a first package which is hermetically sealed including the semiconductor laser element LD. Moreover, a second package P2 which is hermetically sealed including the incident end of the optical fiber 13 is provided.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Foam blocking material suitable for volatile organic compound polluted soil and application of foam blocking material
The invention relates to a foam blocking material suitable for volatile organic compound polluted soil and application of the foam blocking material. The material is prepared from the following components of, by weight, 10-20 parts of protein substances, 2-10 parts of inorganic salt substances, 1-5 parts of low-molecular-weight organics, 2-10 parts of starch substances, 1-2 parts of thickening agents and 53-84 parts of deionized water, wherein the weight sum of the components is 100 parts. During application, the foam blocking material is diluted by the deionized water to prepare mixed liquid; the mixed liquid is stirred at a high speed to form even and fine foam; and the formed even and fine foam evenly covers the polluted soil to be treated, and a foam layer is formed on the surface layer of the polluted soil to be treated. Compared with the prior art, the material is stable in property, nontoxic, harmless, degradable and wide in application range, does not cause pollution to the environment, saves energy, is environmentally friendly and can be widely used for inhibiting dust, covering a liquid beach, blocking peculiar smell and isolating air.
Owner:上海化工院环境工程有限公司
Intelligent construction waste classification device
PendingCN109629795AReduce impact noiseEasy access to timingMagnetic separationVertical ductsRefuse collectionWaste collection
The invention relates to an intelligent construction waste classification device. Each floor is provided with a floor waste opening, every two adjacent floor waste openings are connected through a transport passage, the lower part of the lowermost floor waste opening or transport passage is provided with a construction waste transport passage and a decoration waste transport passage, an electric baffle device is arranged between the construction waste transport passage and the decoration waste transport passage, the lower part of the construction waste transport passage is provided with a particle separation passage, and the lower parts of the particle separation passage and the decoration waste transport passage are provided with mobile waste collection carts. The intelligent constructionwaste classification device is ingenious in concept, simple in structure and high practicality, achieves the function of automatically and efficiently classifying construction waste based on stages,types and particle sizes with the powerful intelligent classification capacity, and also has good noise reduction, dust suppression and safety protection effects.
Owner:CHINA CONSTR SEVENTH ENG DIVISION CORP LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com