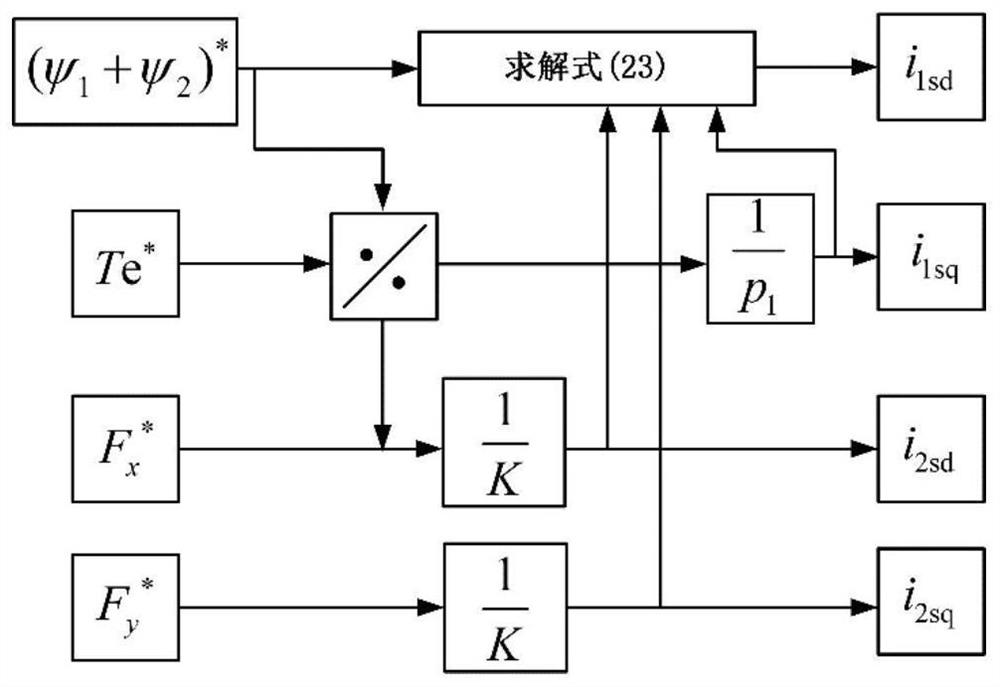
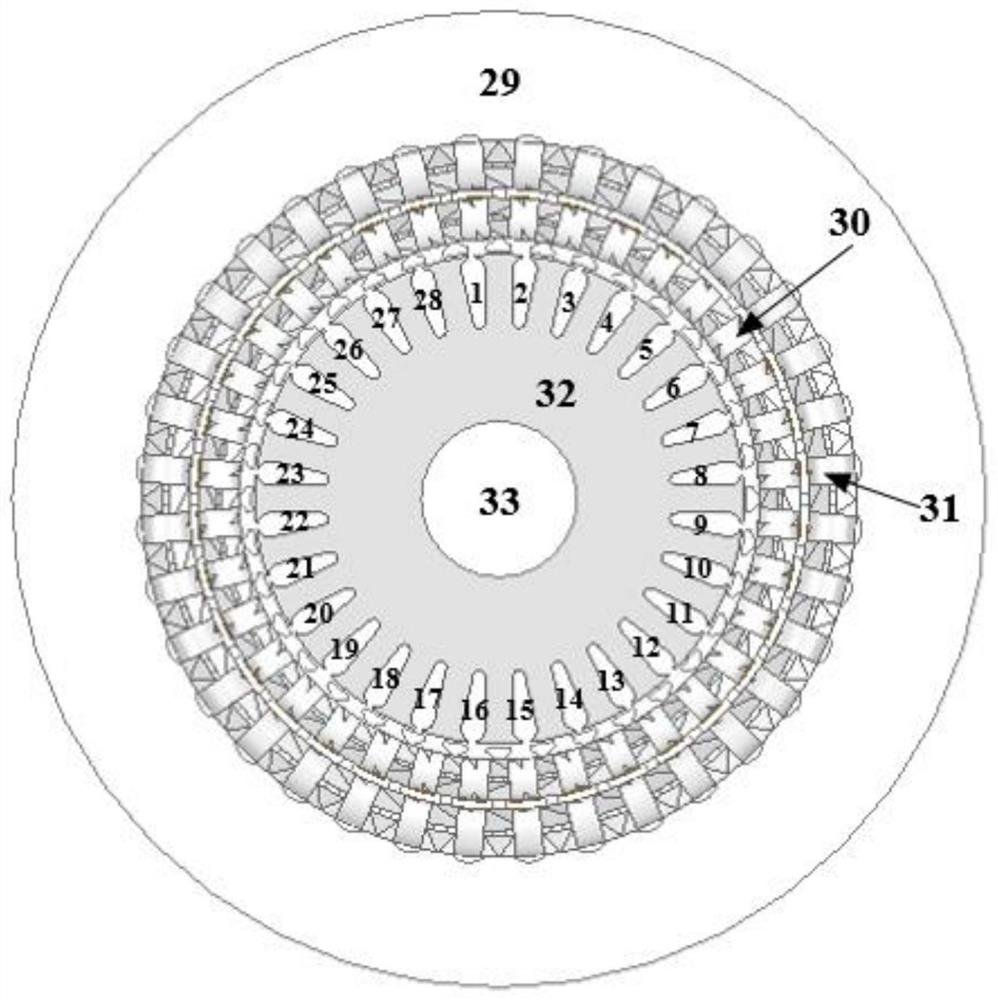
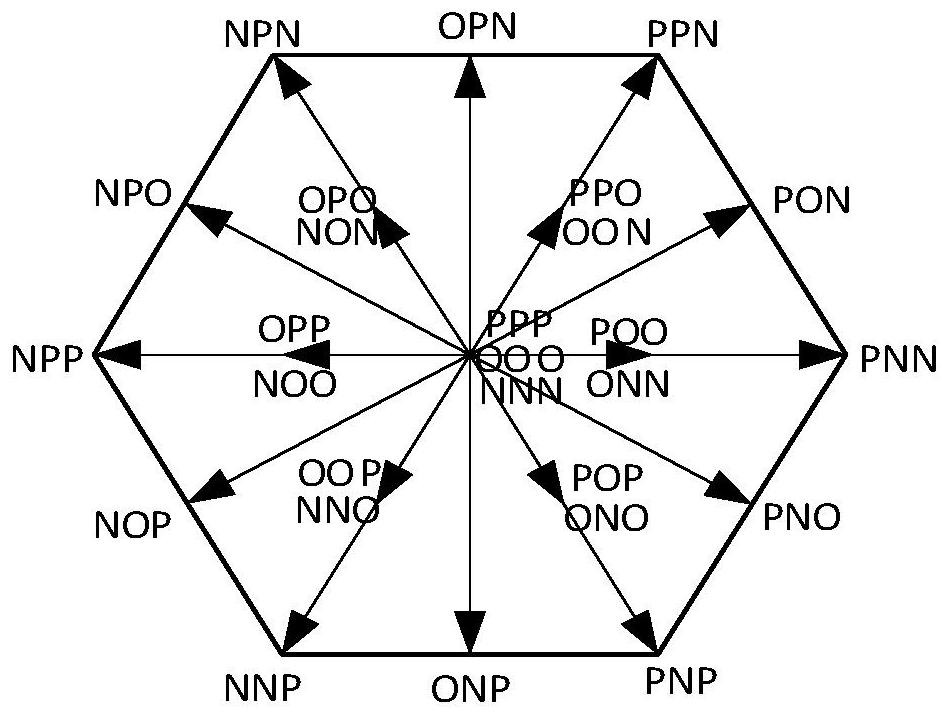
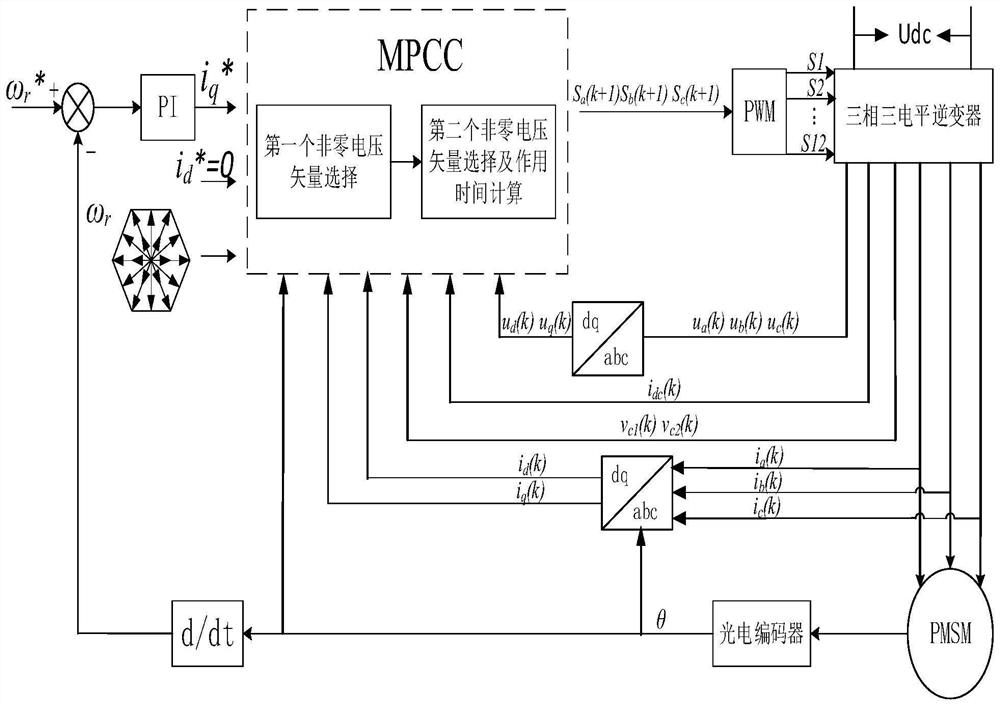
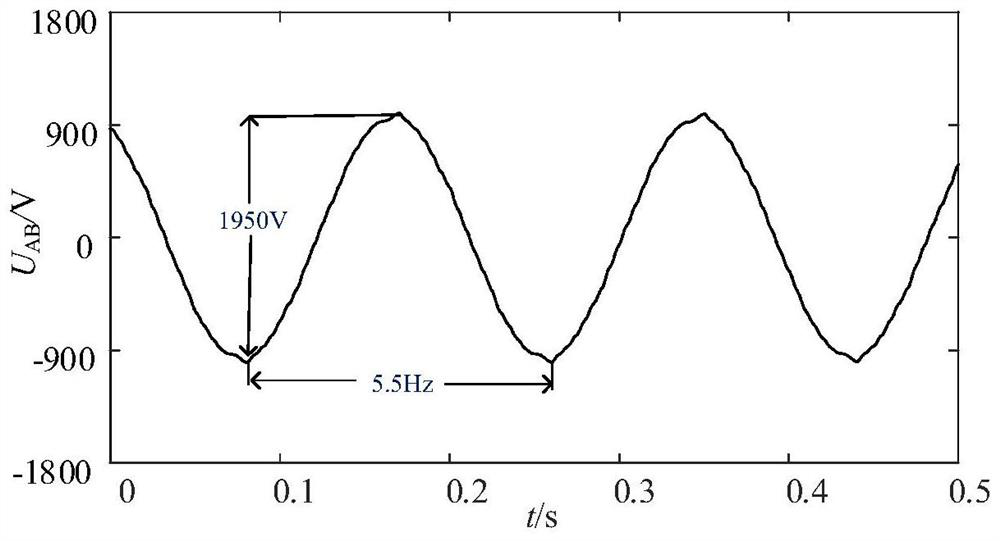
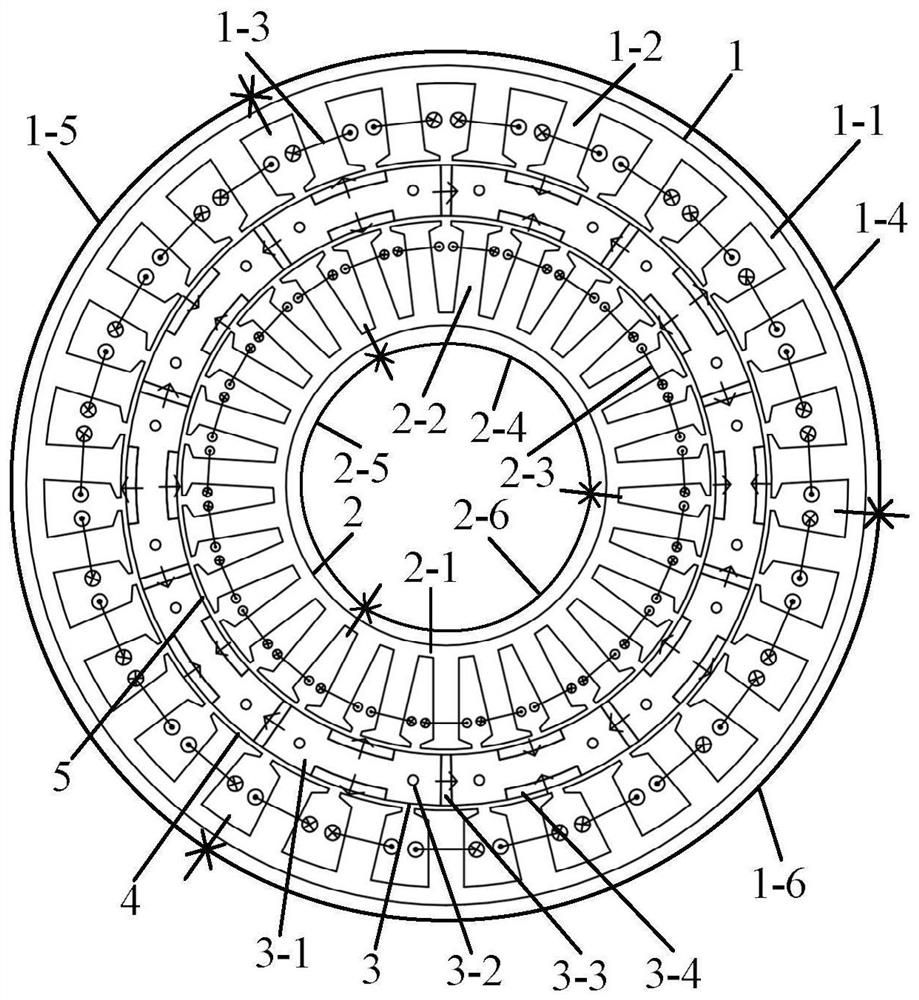
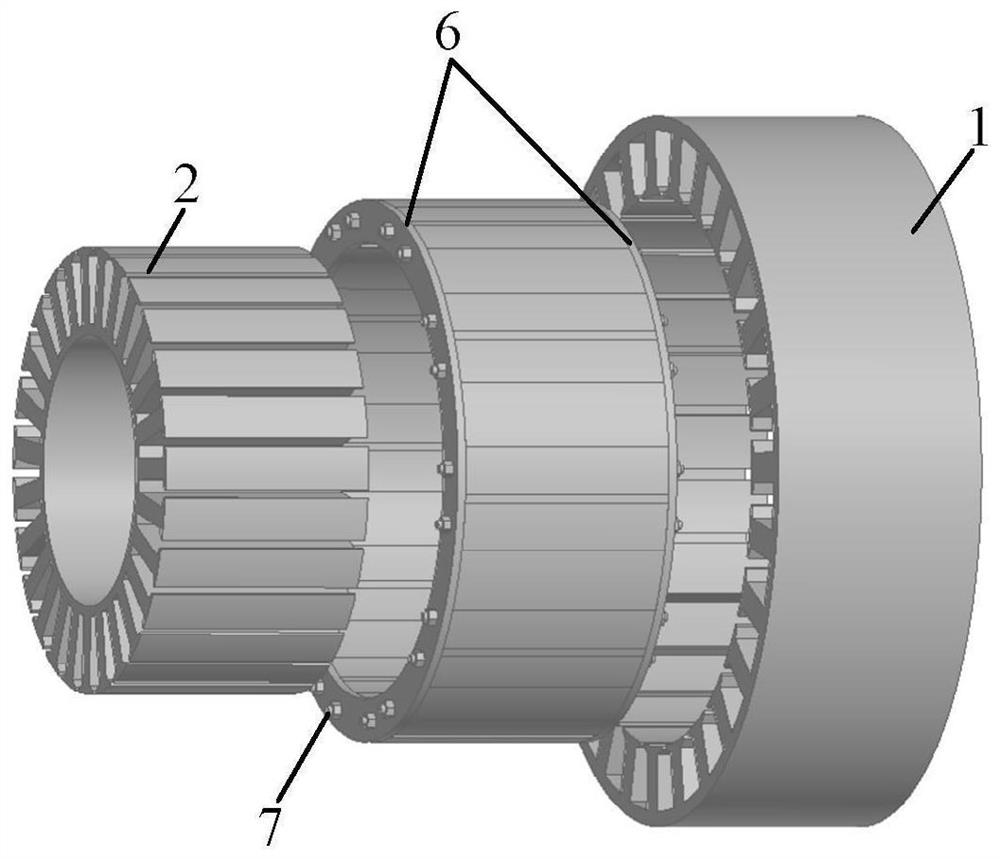
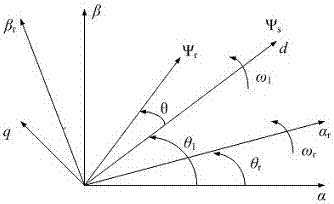
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
38results about How to "Reduce electromagnetic torque ripple" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
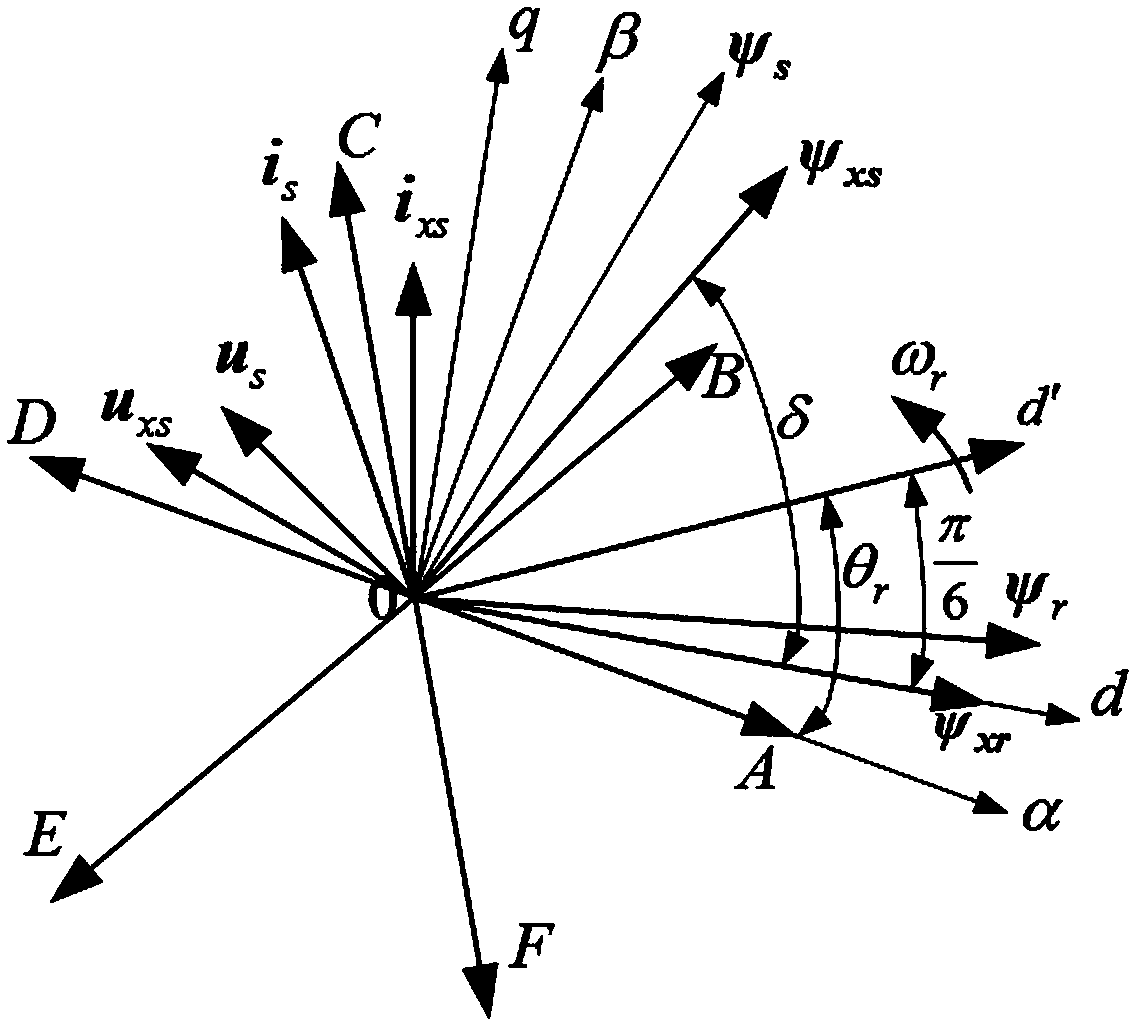
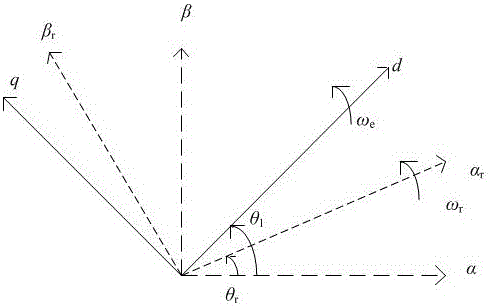
One-phase-failure fault-tolerant torque control method of 60-degree offset six-phase permanent magnet synchronous motor
ActiveCN104184380AQuick controlSolving Instantaneous Torque ControlElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsPosition anglePermanent magnet synchronous motor
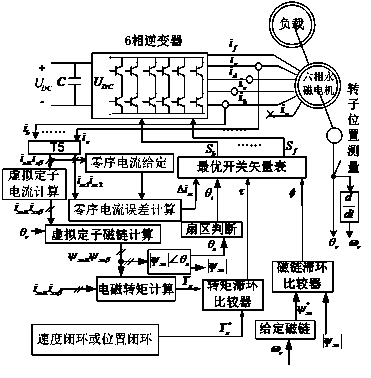
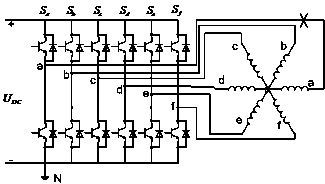
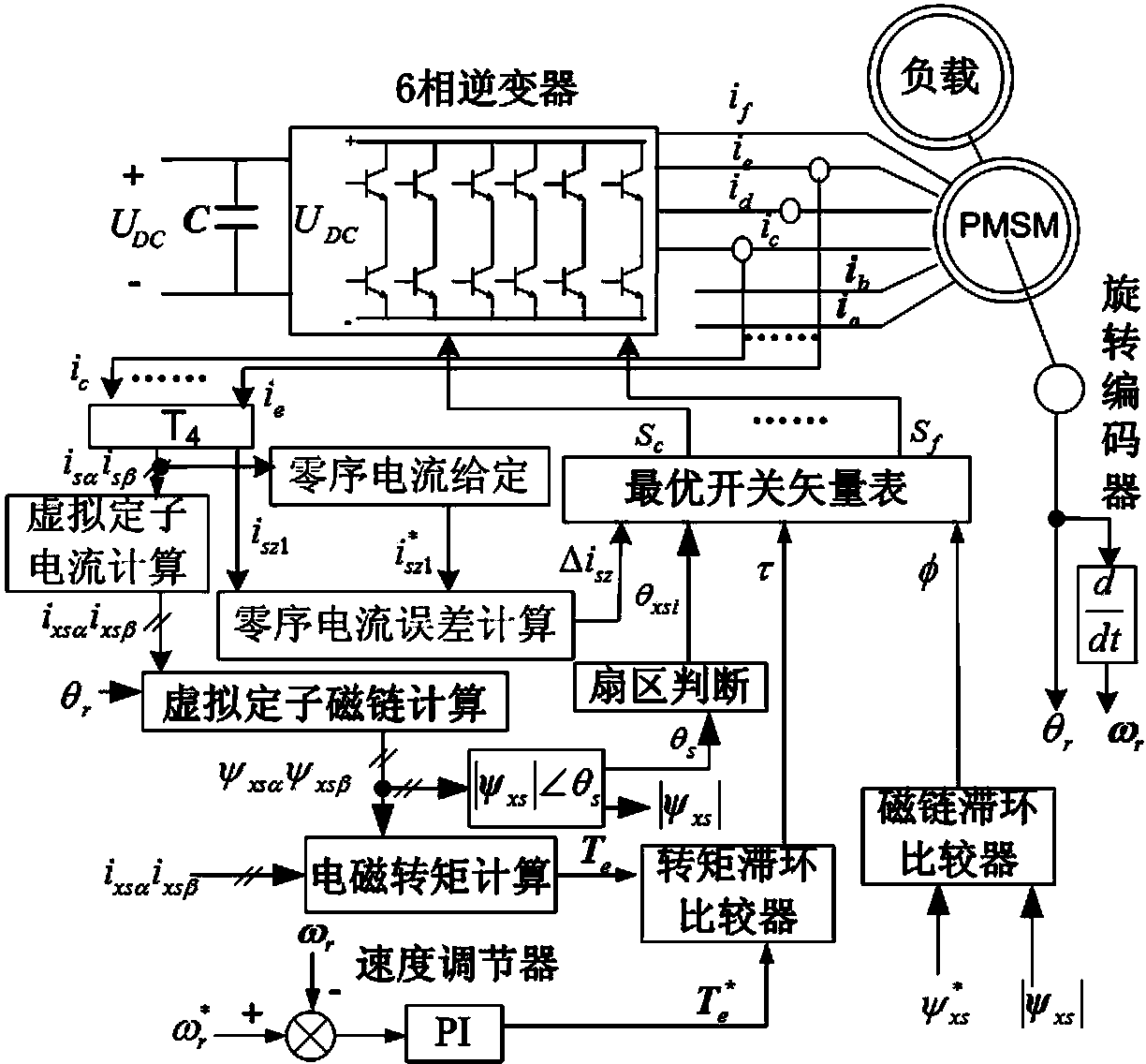
The invention relates to a one-phase-failure fault-tolerant torque control method of a 60-degree offset six-phase permanent magnet synchronous motor. The method includes the steps that currents from ib to if of the remaining healthy phases and the position angle of a rotor are acquired; the currents ib to if of the remaining five healthy phases are transformed into i5alpha, i5beta, i5z1, i5z2 and i5z3; the virtual stator currents iz5alpha and iz5beta are calculated; the virtual stator flux linkages psiz5alpha and psiz5beta are worked out; the serial number thetai of the virtual stator flux linkages psiz5alpha and psiz5beta on the alpha and beta plane sector is judged; the variable phi for controlling the virtual stator flux linkage amplitudes is output; the electromagnetic torque (please see the symbol in the specification) is calculated; the electromagnetic torque control variable tau is output; the zero-sequence current error vector (please see the symbol in the specification) is output; the zero-sequence current error vector, the tau, the phi and the thetai are sent to an optimum switch vector table to obtain an optimum switch combination, the optimum switch combination further acts on windings of the remaining five healthy phases to achieve the control target that the zero-sequence current, the virtual stator flux linkage amplitudes and the electromagnetic torque error are zero. Through the control method, a direct torque control driving system of the 60-degree offset six-phase permanent magnet synchronous motor can continue running after one phase of the motor fails or one phase of an inverter bridge fails.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Fault-tolerant direct torque control method for six-phase permanent magnet synchronous motor lacking any two phases of windings
ActiveCN104270063AQuick controlSolving Instantaneous Torque ControlElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsPhase currentsPosition angle
The invention relates to a fault-tolerant direct torque control method for a six-phase permanent magnet synchronous motor lacking any two phases of windings. The method includes the steps that remaining healthy phase currents from ic to if and a rotor position angle are collected; the remaining healthy four phases of currents from ic to if are converted into isalphaisbeta and iszlisz2; virtual stator currents ixsalphaixsbeta are calculated; a virtual stator flux linkage psixsalphapsixsbeta is calculated; the number thetaxsi of an alphabeta plane sector where a vector of the virtual stator flux linkage psixsalphapsixsbeta is located is judged; a variable phi for controlling the amplitude of the virtual stator flux linkage is output; an electromagnetic torque Te is calculated; a variable tau for controlling the electromagnetic torque is output; a zero-sequence current error delta isz is output; delta isz, tau, phi and thetaxsi are sent to an optimal switch vector table so that an optimal switch combination can be obtained, and the optimal switch combination acts on remaining four healthy phases of windings so that the control target that the error of zero-sequence currents, the amplitude of the virtual stator flux linkage and the electromagnetic torque is zero can be achieved. The control method solves the problem of how to make a 60-degree-bias six-phase permanent magnet synchronous motor direct torque control drive system continue to operate when two phases of the windings of the motor are disconnected or two phases of windings of an inverter bridge break down.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
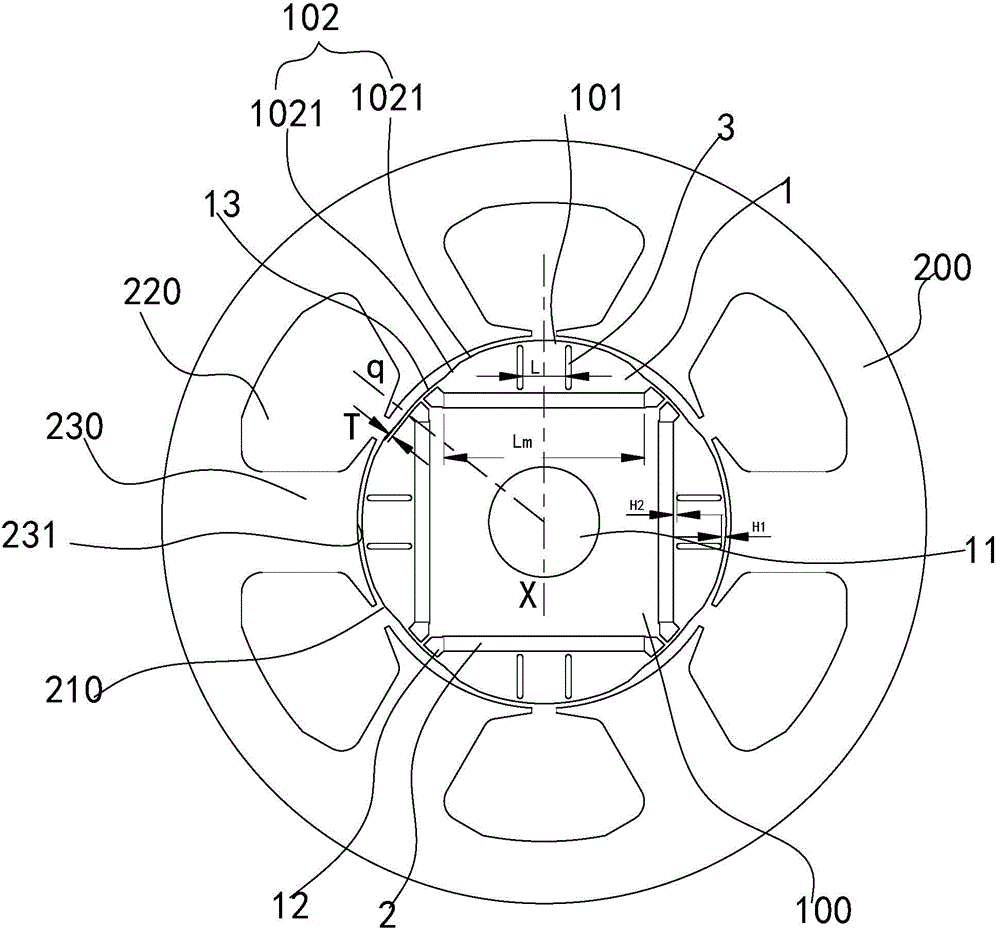
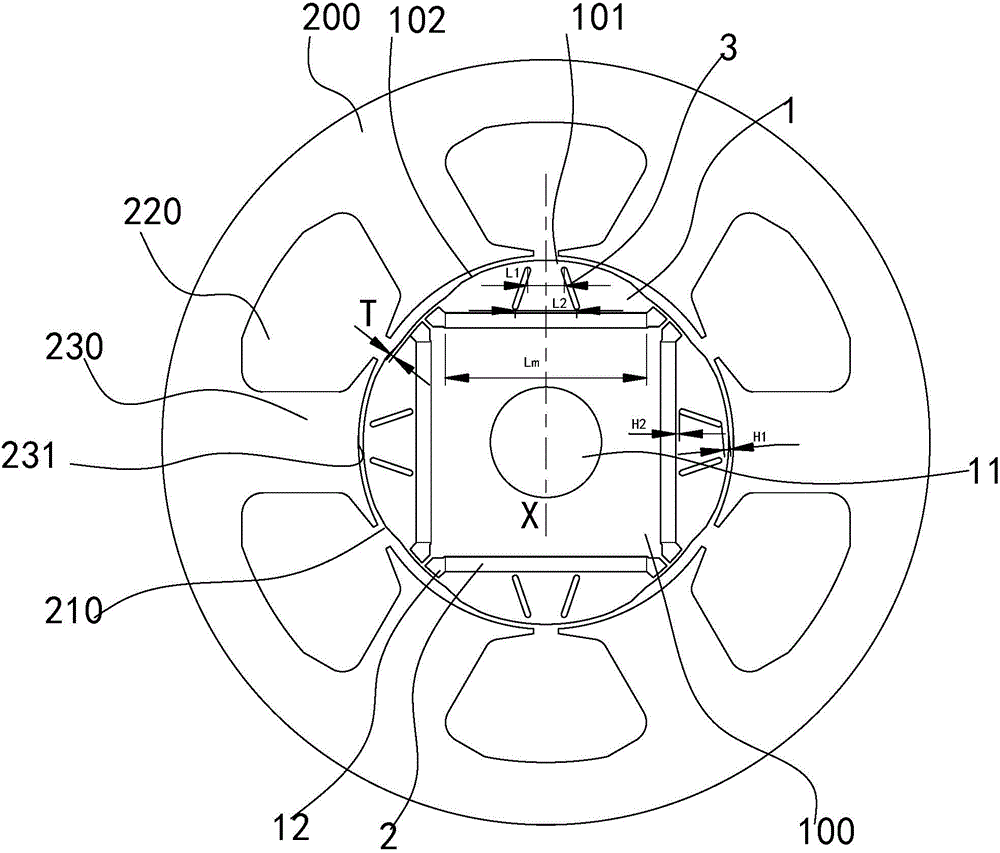
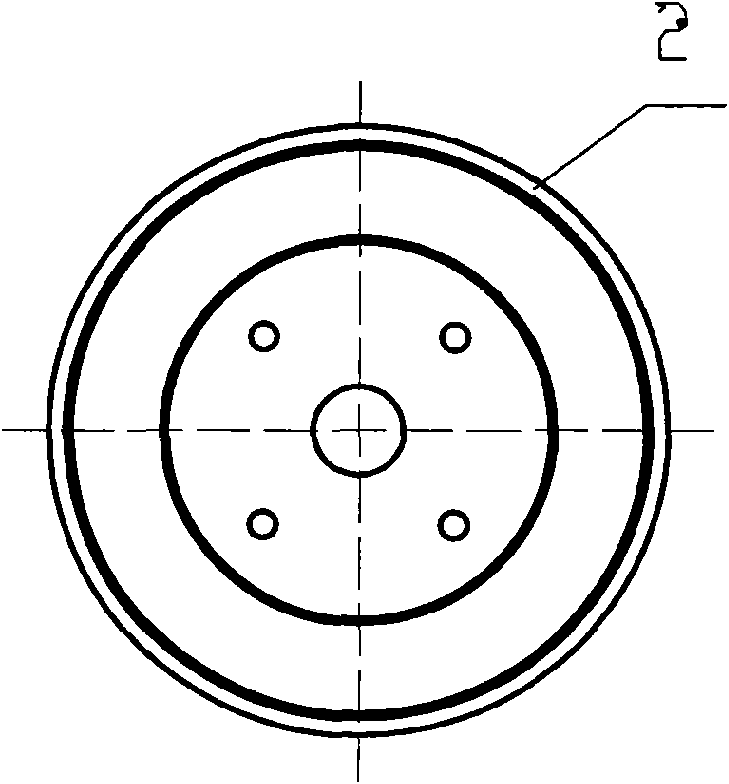
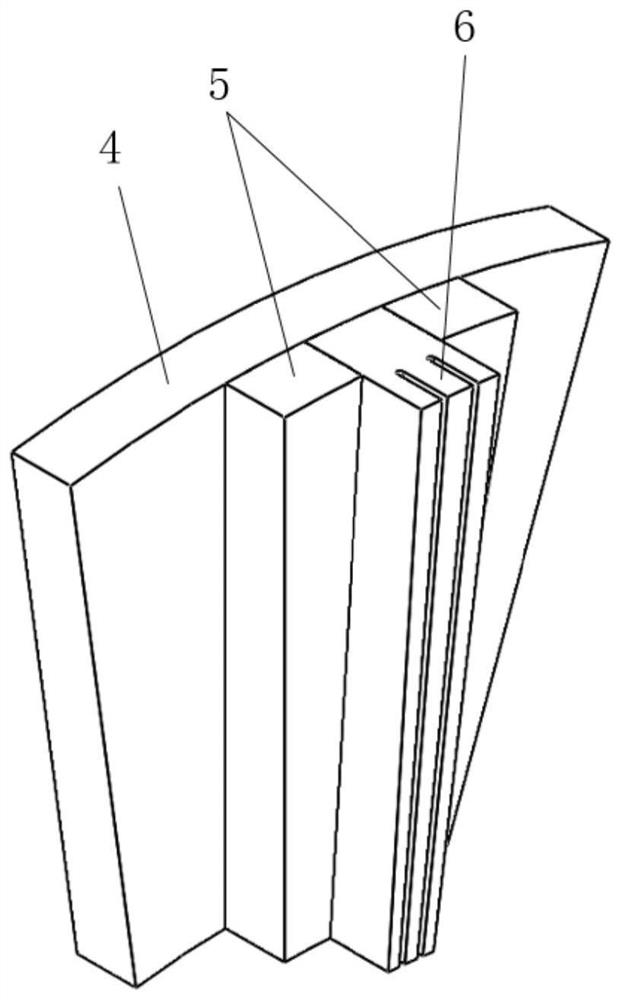
Motor rotor and motor with same
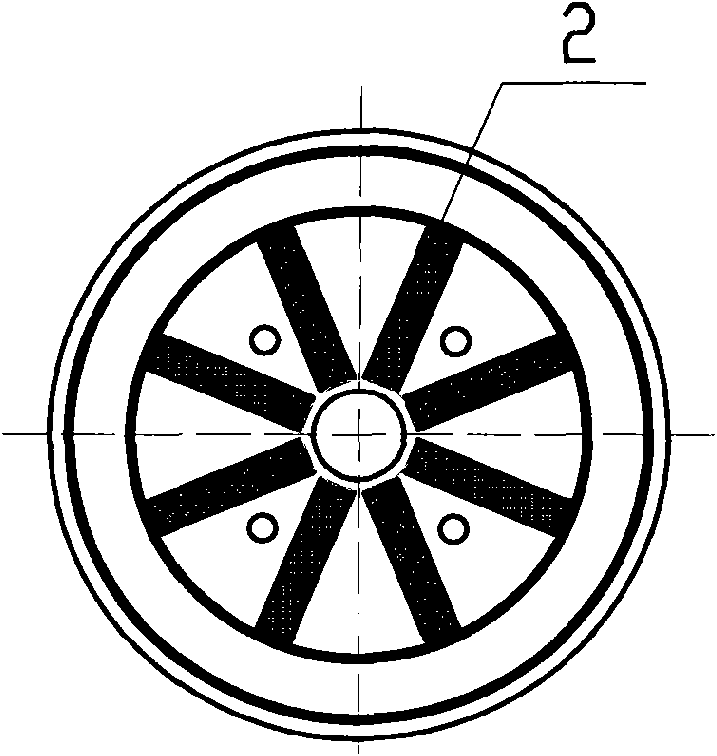
ActiveCN104158322AReduce back EMF harmonic contentReduce electromagnetic torque rippleMagnetic circuit rotating partsLine segmentElectromagnetic torque
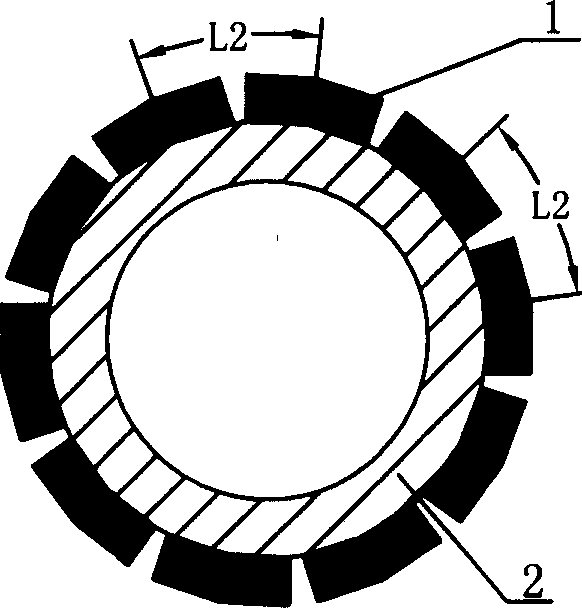
The invention discloses a motor rotor and a motor with the same. The motor rotor comprises a main body and multiple steel magnets, wherein the main body is provided with a rotor hole and multiple steel magnet grooves encircling the rotor hole; the outer profile of the main body comprises a plurality of concentric arc sections concentric with the rotor hole and connecting line segments connected between adjacent concentric arc sections; the concentric arc sections are in one-one correspondence with the steel magnet grooves in the radial direction respectively; each connecting line segment comprises one or more straight line segments; the included angle beta between the central normal line of each straight line segment and the connected line of the midpoint of the central normal line and the center of the rotor hole is not smaller than 0 degree and not greater than 20 degrees; at least one steel magnet is arranged inside each steel magnet groove. According to the motor rotor provided by the embodiment of the invention, the outer profile of the main body comprises the concentric arc sections and connecting line segments connected between adjacent concentric arc sections, so that the reduction of the counter potential harmonic content of the motor is facilitated, and the cogging torque pulsation and electromagnetic torque pulsation of the motor are reduced.
Owner:GUANGDONG WELLING ELECTRIC MACHINE MFG +1
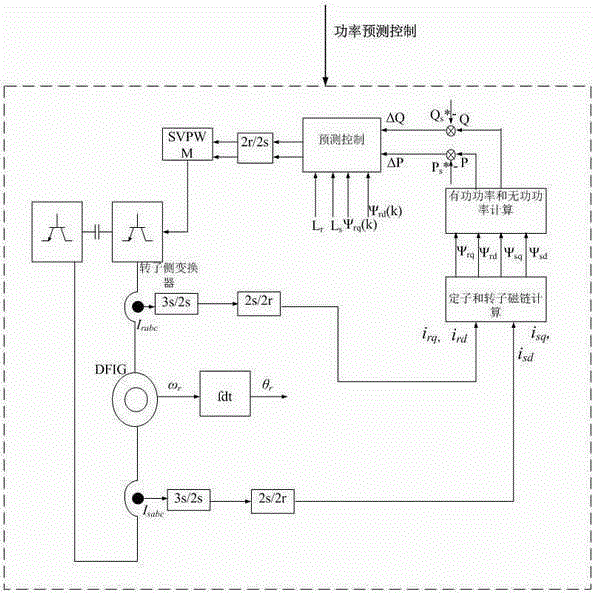
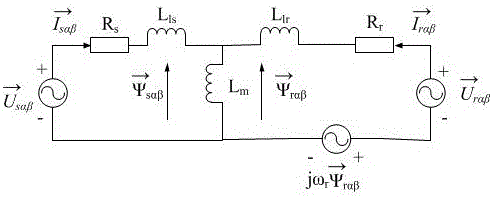
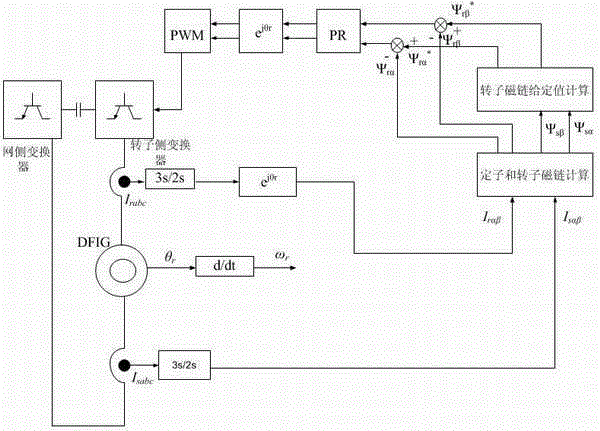
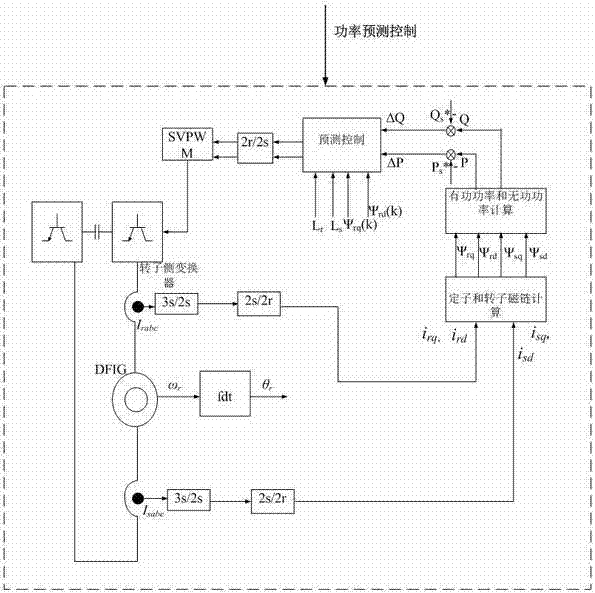
Doubly-fed wind generator rotor linkage deadbeat fault operation method
InactiveCN104967376ANo saturation issuesEase saturationElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsVoltage dropPower grid
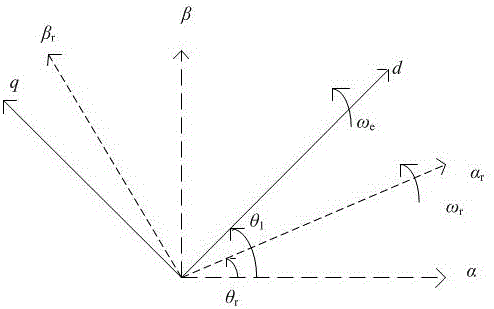
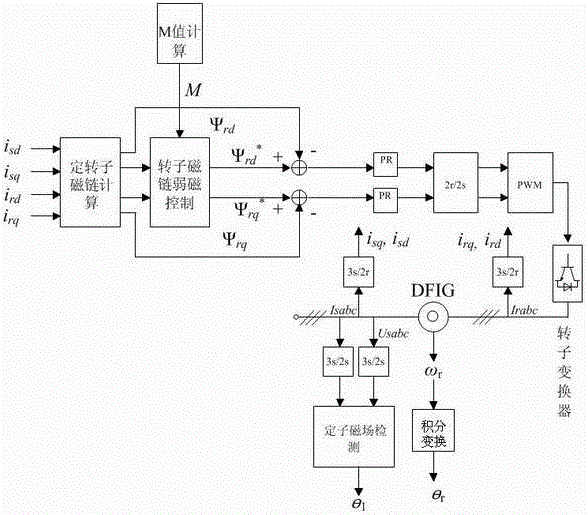
The invention discloses a doubly-fed wind generator rotor linkage deadbeat fault operation method. When power grid voltage drops, by means of a rotor voltage prediction model, in order to make the rotor linkage follow a given value in the model to realize the deadbeat control of the rotor linkage, the value of the rotor linkage at the next moment needs to be replaced by the given value of the rotor linkage at the next moment, the given value of the rotor linkage follows the actual value of the stator linkage, the predicted rotor voltage in a two-phase synchronous rotating coordinate system is subjected to coordinate reversion to obtain the rotor voltage in a two-phase rotor rotating speed rotating coordinate system, and at the end, PWM modulation is carried out. The fault operation method has the advantages of simple operation, good decoupling, fast dynamic response, and high robustness. The rotor linkage deadbeat control method is provided under the power grid fault state, the rotor fault current can be controlled within 1.5-1.6 times of the rated current, the electromagnetic torque ripple during the failure is reduced, the dynamic response speed is fast, and the control precision is high.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
Brushless DC electric machine in structure of short magnetic circuit
InactiveCN1697287AImprove efficiencySmall positioning torqueMagnetic circuit rotating partsElectric machinesNumerical controlElectric vehicle
Improving structure of magnetic path for brushless type DC electric machine, the invention eliminates magnetic coupling between phases in armature. The machine includes stator, multiple permanent magnets, rotor, and excitation winding. There are multiple wide slots and narrow slots opened on inner surface of column sheath of stator. Thickness of pole body between wide slot and narrow slot is same. The excitation winding is wound on root part of pole body. Located at two sides of wide slot, first excitation winding and second excitation winding are connected in series. Sheathed on the rotor, stator and rotor are coaxial, and there is air gap between them. The invention shortens magnetic path of excitation magnetic flux of winding so as to raise efficiency of machine and control precision. Said machine can be used as electromotor or generator, applicable to robot, number control machine tool and electric vehicles.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Doubly-fed wind generator stator and rotor magnetic linkage synchronous flux-weakening control method under power grid failure
InactiveCN104967384AImprove non-off-grid operation capabilityEasy to controlElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsElectric generatorFlux linkage
The invention discloses a doubly-fed wind generator stator and rotor magnetic linkage synchronous flux-weakening control method under power grid failure. When the voltage of the power grid has faults, the high-control-frequency stator and rotor magnetic linkage synchronous flux-weakening control method is adopted by a doubly-fed wind generator rotor side converter. All of the variables of the control method are on the basis of a two-phase synchronous rotating coordinate, when faults occur, a rotor magnetic linkage can be adjusted through the control of the rotor side converter, the synchronous control of the rotor magnetic linkage and a stator magnetic linkage can be realized, the fault impact of the stator magnetic linkage to the rotor magnetic linkage can be weakened, and the rotor fault overcurrent can be reduced. The method can control the rotor fault current be 1.5-1.6 times of the rated current, reduces the electromagnetic torque ripple during the failure, the impact to a set during the failure, and the active power and reactive power fluctuation of the stator side, and can effectively improve the fault ride-through capability of the doubly-fed wind generator under power grid voltage failure.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
Disc type permasyn motor for electric car hub
InactiveCN101764489AImprove power densityReduce power densityMagnetic circuit rotating partsElectric devicesLow speedPermanent magnet synchronous motor
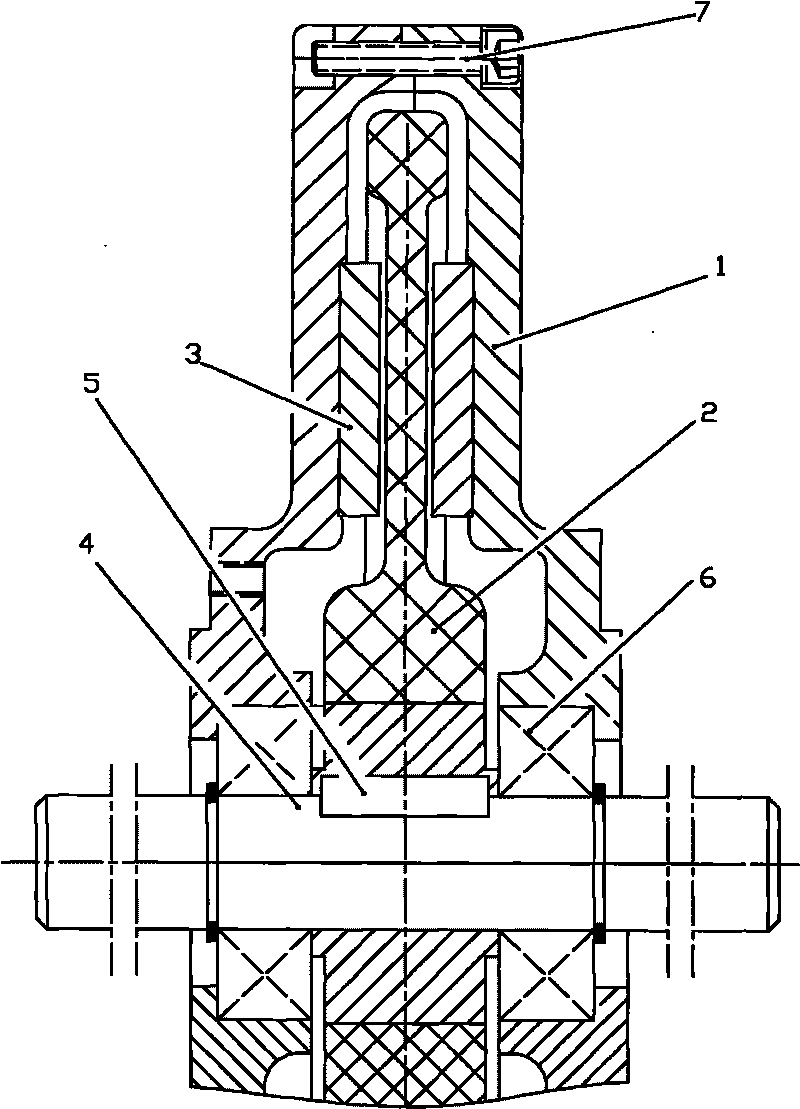
The invention relates to a disc type permasyn motor for an electric car hub, which comprises a fixed mandrel, a rotor outer casing and a stator armature disc, wherein the rotor outer casing is supported on the fixed mandrel; the stator armature disc is fixedly connected with the fixed mandrel. The left and right sides of the rotor outer casing are symmetrically fixedly connected with parallel magnetic steel discs. A circular air gap of which the cross section is in a rectangle shape is formed between the magnetic steel discs. The stator armature disc is arranged in the circular air gap and is provided with an outgoing line. The stator armature disc has no core, and is directly formed by injection molding. The magnetic steel disc adopts a Halbach type permanent magnet array structure. The invention adopts the stator armature disc without a core for direct injection molding, and the magnetic steel disc with the Halbach type permanent magnet array structure, therefore the motor can greatly enhance power density of the motor, decrease the wear and tear of the motor and has the advantages of small volume, compact structure, stable low-speed running, good controllability, light weight, small vortex consumption of the rotor, small rotating inertia, large power density, small electromechanical time constant and the like.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
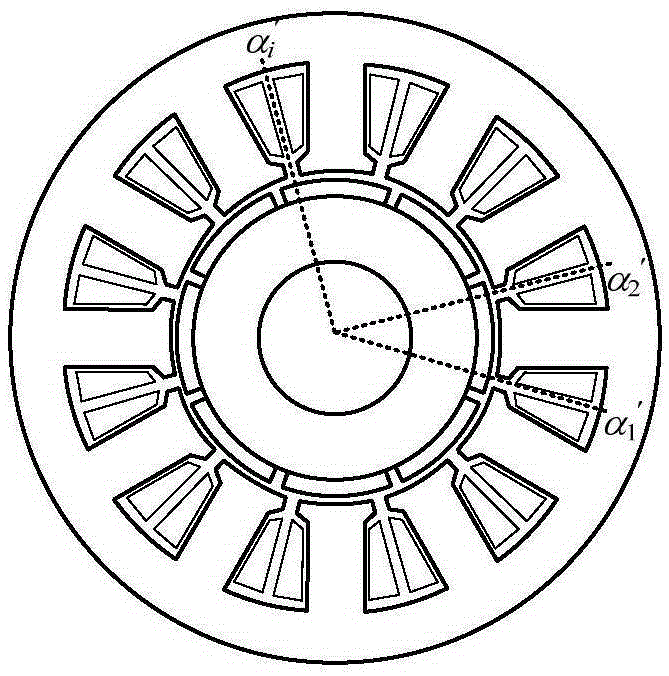
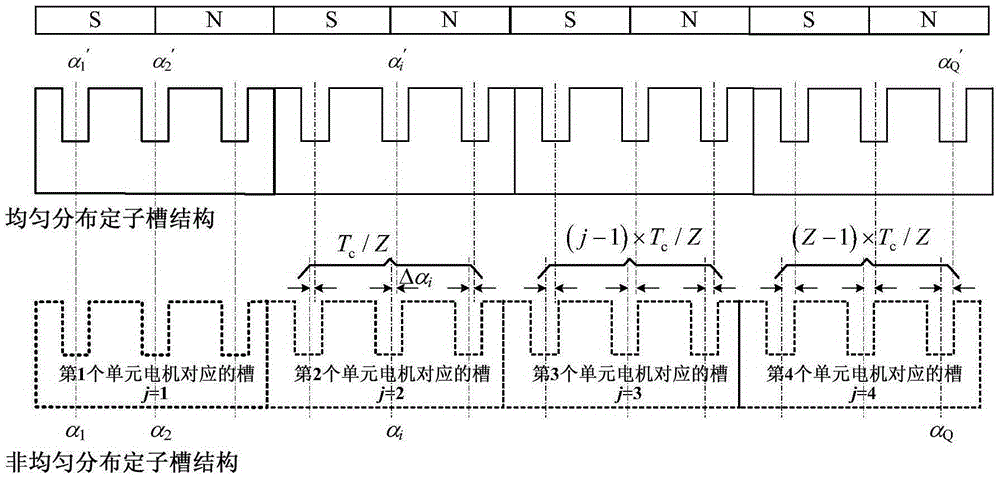
Method using non-uniform stator slots to inhibit cogging torque of permanent magnet synchronous motor
InactiveCN105281449AImprove back EMF waveformImprove performanceMagnetic circuit stationary partsPermanent magnet synchronous motorEngineering
The invention discloses a method using non-uniform stator slots to inhibit the cogging torque of a permanent magnet synchronous motor. Under the condition that the size of stator teeth does not change, center positions of stator slots rotate and deviate in the circumferential direction of a stator. The method is simple in technique and easy for implementation and does not need to increase any extra machining step. The coupling influence of the offset angles of the stator slots and other parameters of the motor is small, and thus the offset angles can be designed independently. While reducing the cogging torque of the motor, the method can also improve the counter electromotive force waveform of the motor, reduce electromagnetic torque fluctuation, avoid asymmetric phenomena of three-phase windings due to non-uniform slot distribution, and effectively improve the overall performance of the motor.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Doubly-fed wind power generator quick weak magnetic control method
InactiveCN104993759AQuick controlNo saturation issuesElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsEngineeringControl theory
The invention discloses a doubly-fed wind power generator quick weak magnetic control method. In a steady state, all variables are based on a two-phase synchronous rotating coordinate system. The change in active power and the change in reactive power of a stator in a sampling period are predicted; then, the power in the next sampling period is compensated; and finally, the rotor voltage is calculated, and PWM modulation is conducted. By adopting the method, the fluctuation of active power and reactive power of the stator is reduced. When the grid voltage drops, all the variables are based on a two-phase static coordinate system. Quick weak magnetic control on rotor flux is realized through a rotor voltage prediction model, coordinate transformation is performed on the predicted rotor voltage under the two-phase static coordinate system to obtain the rotor voltage under a two-phase rotor speed rotating coordinate system, and finally, PWM modulation is conducted. Through quick weak magnetic control, the rotor current can be controlled within 1.5-1.6 times of the rated current, and the electromagnetic torque ripple is small in the fault period. The operation capacity of a doubly-fed wind power generator in fault is improved.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
Fault operation method under doubly-fed wind power generator stator and rotor flux weak magnetic control
InactiveCN104993756AIncrease control frequencyEasy to controlElectric generator controlPower gridRotor flux
The invention discloses a fault operation method under doubly-fed wind power generator stator and rotor flux weak magnetic control. The technical scheme is as follows: when the grid voltage runs stably, a doubly-fed wind power generator rotor-side converter adopts vector control based on stator flux orientation, and when the grid voltage runs in fault, the doubly-fed wind power generator rotor-side converter performs stator and rotor flux weak magnetic control, and the control frequency of stator and rotor flux weak magnetic control is twice that of vector control based on stator flux orientation. No complex coordinate transformation is needed in the fault period, and quick response to a fault is realized. The rotor current can be controlled within 1.5-1.6 times of the rated current. The electromagnetic torque ripple is small. The fluctuation of active power and reactive power at the stator side is small. The operation capacity of a doubly-fed wind power generator in fault is improved.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
Single-phase capacitor-operated motor
InactiveCN101557148AIncrease productivityThe amount of copper used is obviousWindingsMagnetic circuit rotating partsCapacitanceCopper
The invention provides a single-phase capacitor-operated motor, comprising a motor shaft, a rotor, a stator, a front end cover and a rear end cover; wherein, the rotor is sheathed on the motor shaft and the stator is sheathed at the outer side of the rotor; mutually snap-fit front end cover and rear end cover are arranged at the outer side of the stator; the two ends of the motor shaft are installed on the front end cover and rear end cover via bearings; a stator core of the stator is provided with double-row grooves including a deep-row groove and a shallow-row groove; stator winding is concentrated winding comprising first winding and second winding; coils of the first winding and the second winding are respectively wound in the deep-row groove and the shallow-row groove of the stator core; the adjacent coils of the first winding, which are wound in the deep-row groove, are wound forward and reverse; the adjacent coils of the second winding, which are wound in the shallow-row groove, are wound forward and reverse; the first winding is in parallel connection with the second winding after series connection with capacitance or the second winding is in parallel connection with the first winding after series connection with capacitance. The single-phase capacitor-operated motor can save wires by about 20%; motors with thin iron core and large winding span witness more obvious saving of copper content for windings; in addition, the winding shortens the axial length of the motor; manufacturing of the stator winding achieves machine winding, simplifies the processing flows and improves the production efficiency of the stator; besides, the concentrated stator winding adopted by the invention has high coefficient and good motor property and is suitable for motors with different poles and power.
Owner:MIDEA GRP CO LTD
Independent wheel traction hub motor for railway vehicle
ActiveCN112383163AImprove electromagnetic performanceReduce the magnetic density harmonic distortion rateMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsPermanent magnet synchronous motorElectric machinery
The invention relates to an independent wheel traction hub motor for a railway vehicle. The independent wheel traction hub motor comprises a stator, a rotor, an unequal-width unequal-thickness Halbachaxial annular part segmented permanent magnet array, a rotating shaft and an armature winding, wherein the rotor is installed in the stator, the rotor is fixed on the rotating shaft, the armature winding is installed on the stator, the unequal-width unequal-thickness Halbach axial annular part segmented permanent magnet array is installed on the rotor and located between the rotor and the stator,each magnetic pole is composed of three permanent magnets with the same polarity, and the permanent magnets adopt a Halbach magnetizing mode. The three permanent magnets comprise a main magnetic poleand two boundary magnetic poles, the main magnetic pole is of an axial annular part segmented structure, and the two boundary magnetic poles are located on the two sides of the main magnetic pole andare unequal to the main magnetic pole in width and thickness. The unequal-width unequal-thickness Halbach axial annular part segmented permanent magnet synchronous motor is applied to the interior ofa hub, the harmonic distortion rate of an air gap magnetic field is small, the utilization rate of permanent magnets is high, the torque pulsation is low, and the eddy current loss of the permanent magnets is small.
Owner:LANZHOU JIAOTONG UNIV +1
Low-noise permanent magnet direct current motor
PendingCN112886751AReduce contact areaReduce friction noiseMagnetic circuit rotating partsSupports/enclosures/casingsPermanent magnet direct currentBrush
The invention discloses a low-noise permanent magnet direct current motor. The invention aims to solve the technical problem that a conventional permanent magnet direct current motor is high in noise when working. The low-noise permanent magnet direct current motor comprises a shell and a rotating shaft, wherein one end of the rotating shaft extends out of the shell, the shell is internally provided with a commutator fixed on the rotating shaft and a carbon brush which is in contact with the commutator to transmit current, the inner side face of the carbon brush comprises an axial arc face and a connecting inclined face which are axially connected, one end of the connecting inclined face is connected with the axial arc face, the other end of the connecting inclined face inclines towards the outer side of the shell and is connected with the end face of the carbon brush, and the axial arc face is in face-to-face contact with the peripheral face of the commutator.
Owner:ZHEJIANG JIECHANG LINEAR MOTION TECH
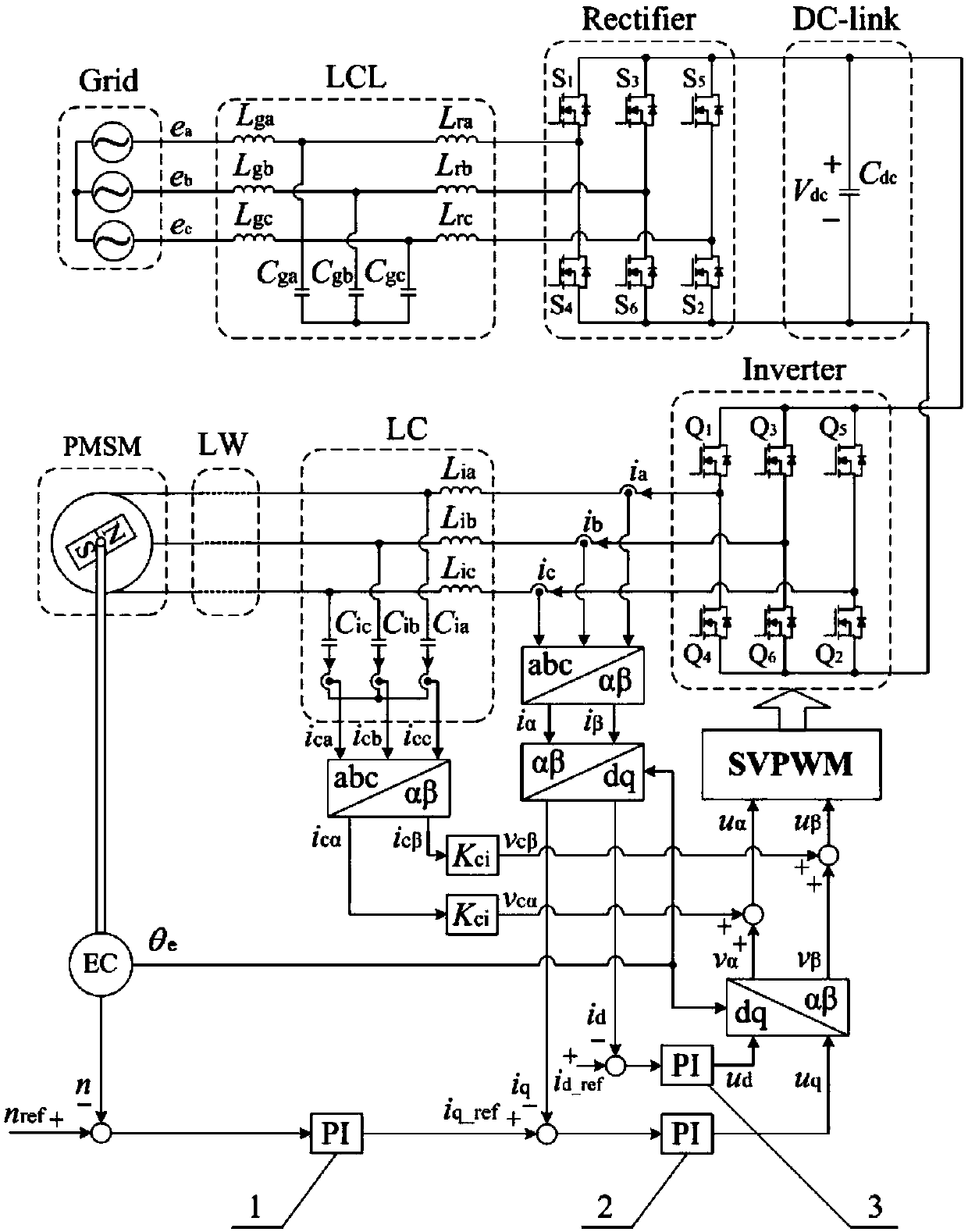
Bilateral filtering permanent magnet synchronous motor driving device adopting SiC MOSFETs
InactiveCN110932646AIncrease working temperatureIncrease the switching frequencyTorque ripple controlAC motor controlMOSFETPermanent magnet synchronous motor
The invention discloses a bilateral filtering permanent magnet synchronous motor driving device adopting SiC MOSFETs, and relates to the technical field of power electronics, and the technical schemeis that the bilateral filtering permanent magnet synchronous motor driving device comprises a three-phase power grid, an LCL filter, a rectifier, a DC bus, an inverter, an LC filter, a long-line cableand a permanent magnet synchronous motor which are connected in sequence; the rectifier and the inverter adopt SiC MOSFETs which are high in switching speed and low in loss as power switching devices. The beneficial effects of the invention are as follows: the SiC MOSFET which is high in switching speed, low in switching loss, small in conduction resistance and high in working temperature is usedas a power switching device. The switching frequency of the driving device can be increased to 50 kHz or above, so that the weight and size of the LCL and LC filters are reduced, the system control precision is improved, the efficiency of the driving device is improved, the working temperature of the driving device is increased, and the cooling link is simplified.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Low-torque pulsating flux reverse motor
InactiveCN111262358AEliminate even harmonicsGuaranteed accuracyMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsElectric machineTorque density
The invention discloses a low-torque pulsating flux reverse motor. The motor comprises a stator and an inner salient pole rotor; the inner salient pole rotor is equally divided into two sections alongthe axial direction of the inner salient pole rotor; two rotor tooth are staggered by a half tooth pitch; permanent magnets are evenly placed on the inner side surfaces of the stator teeth in the circumferential direction of the stator teeth; each permanent magnet is evenly divided into two sections in the axial direction of the permanent magnet and correspond to the two corresponding rotor teethrespectively; the magnetizing directions of the adjacent permanent magnets on the same section are opposite; and the magnetizing directions of the axially opposite permanent magnets on different sections are opposite; air gaps are formed between the permanent magnets on the inner side surfaces of the stator teeth and the inner salient pole rotor; and an armature winding is arranged on the stator.According to the low-torque pulsating flux reverse motor of the invention, the problem of back electromotive force asymmetry of a traditional flux reverse motor is solved; the torque density of the motor of the invention is not influenced; and the electromagnetic torque ripple of the motor is effectively reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
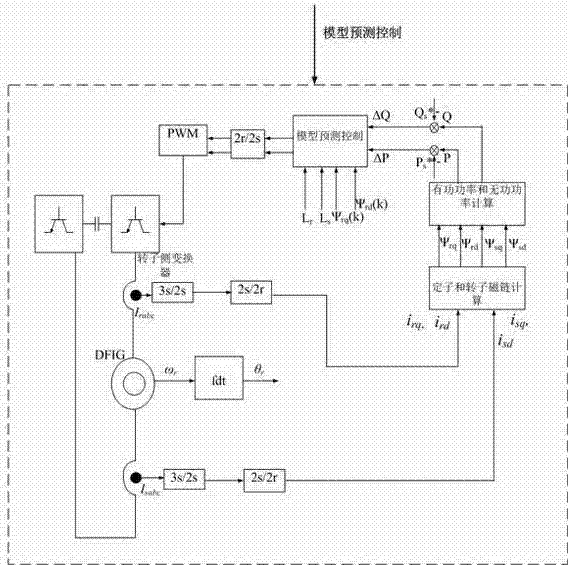
Decoupling method of wound-rotor bearingless asynchronous motor
ActiveCN112332737AGood suspensionReduce electromagnetic torque rippleElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsMotor speedElectric machine
The invention discloses a decoupling method of a wound-rotor bearingless asynchronous motor. The decoupling method comprises a three-phase winding equivalent inductance parameter calculation method, avoltage equation and flux linkage equation construction method and a motor electromagnetic torque and suspension force independent control strategy based on magnetic field orientation. The method comprises the following steps: establishing an inductance matrix of the wound-rotor bearingless asynchronous motor and simplifying the inductance matrix by adopting an equivalence principle; deducing a voltage equation and a flux linkage equation of the motor; and finally, adopting a vector control strategy of torque magnetic field orientation and air gap magnetic field orientation to decompose the original system into two subsystems capable of independently controlling the rotating speed and the flux linkage of the motor. On the basis of establishing an accurate mathematic model of the wound-rotor bearingless asynchronous motor, the purpose of completely decoupling the rotating speed and the flux linkage is achieved by adopting the vector control principle of coordinate transformation and magnetic field orientation, and finally independent control over the electromagnetic torque and the suspension force of the wound-rotor bearingless asynchronous motor is achieved.
Owner:江苏大也环境有限公司
PMSM three-vector model predictive current control method based on NPC type three-level inverter
ActiveCN112821816ASmall amount of calculationGood sine degree of phase currentTorque ripple controlAC motor controlVoltage vectorAlgorithm
The invention discloses a PMSM three-vector model predictive current control method based on an NPC type three-level inverter. The methodcomprises the steps of obtaining the sampling information, and obtaining a rotor position theta of a permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM) through a photoelectric encoder; in a model prediction current control algorithm, reducing the number of alternative voltage vectors of the three-level inverter by using constraint conditions; adding a weight coefficient into a value function of the model prediction current control algorithm, and controlling the neutral-point voltage balance of the NPC type three-level inverter; calculating the action time value of each voltage vector according to the sampling information, and determining the specific action condition of the three-vector control algorithm by adopting a three-vector model predictive current control algorithm based on the time value; and transmitting a control signal obtained by the three-vector model predictive current control algorithm to the NPC type three-level inverter so as to control the permanent magnet synchronous motor.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Asynchronous motor control method based on MRAS
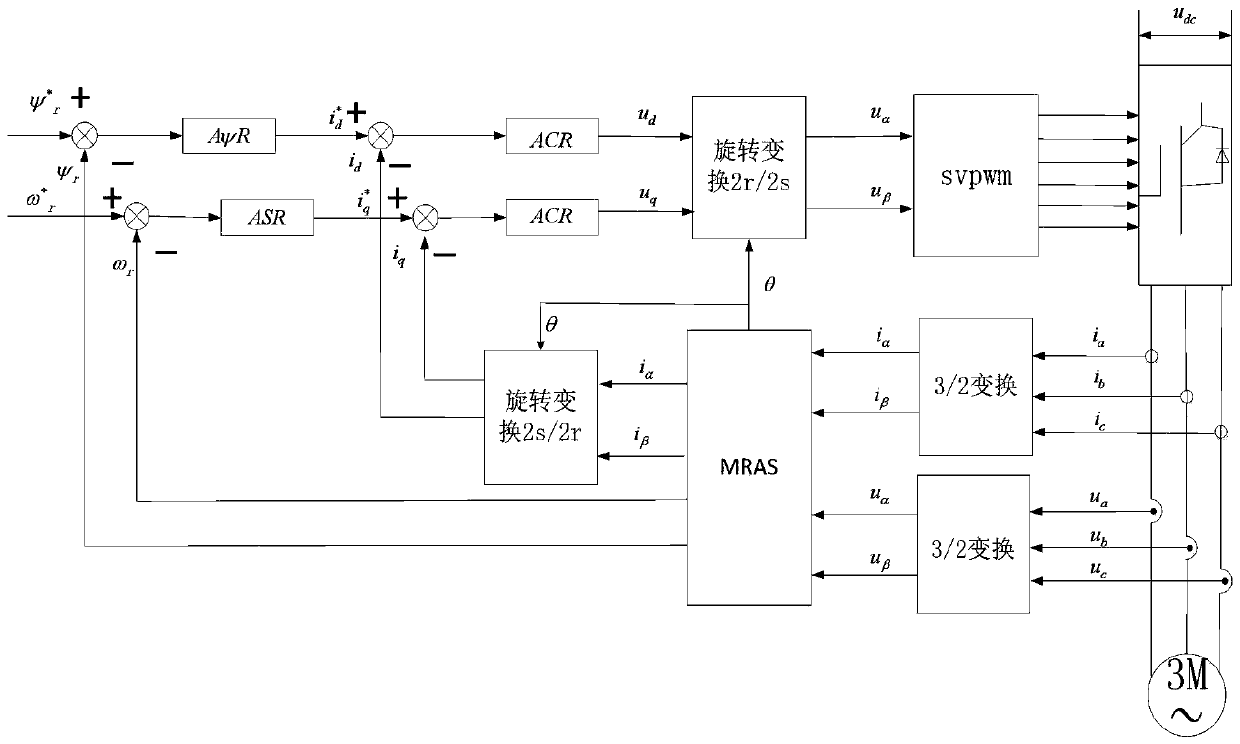
InactiveCN111211721AGuaranteed accuracyImprove stabilityElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlFull bridgeMechanical engineering
The invention discloses an asynchronous motor control method based on an MRAS. The method comprises the steps of acquiring a three-phase stator current and voltage of an asynchronous motor, and generating a torque current feedback quantity and exciting current feedback through Clark and Park conversion in sequence; acquiring a rotor angular speed feedback quantity through an improved MRAS, outputting a torque current after a difference value between the rotor angular speed feedback quantity and a preset rotating speed is adjusted through a speed controller, and outputting a first voltage afterthe difference value between the torque current and the torque current feedback quantity is input into a first PI adjuster; inputting the difference value between a preset exciting current and an exciting current feedback quantity into a second PI regulator and then outputting a second voltage; carrying out Park inverse transformation on the first voltage and the second voltage to generate a two-phase control voltage sum, and inputting the two-phase control voltage sum into SVPWM to be modulated into PWM modulation waves; and controlling a three-phase full-bridge inverter switching device through the PWM modulation waves, and controlling operation of an asynchronous motor. In the invention, low-speed stability of the asynchronous motor is improved, and an electromagnetic torque ripple isreduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A method of suppressing cogging torque of permanent magnet synchronous motor by using non-uniform stator slots
InactiveCN105281449BImprove back EMF waveformImprove performanceMagnetic circuit stationary partsPermanent magnet synchronous motorPermanent magnet synchronous generator
The invention discloses a method for suppressing cogging torque of a permanent magnet synchronous motor by using non-uniform stator slots. Under the condition that the size of the stator slot remains unchanged, the center position of the stator slot rotates and deviates in the circumferential direction of the stator. The method proposed by the present invention utilizes the non-uniform stator slot distribution structure to weaken the cogging torque of the permanent magnet synchronous motor. Independent design; and this method can not only reduce the cogging torque of the permanent magnet synchronous motor, but also improve the waveform of the back electromotive force of the motor, reduce the fluctuation of the electromagnetic torque, and avoid the asymmetry of the three-phase winding caused by the non-uniform slot distribution phenomenon, which can effectively improve the overall performance of the motor.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
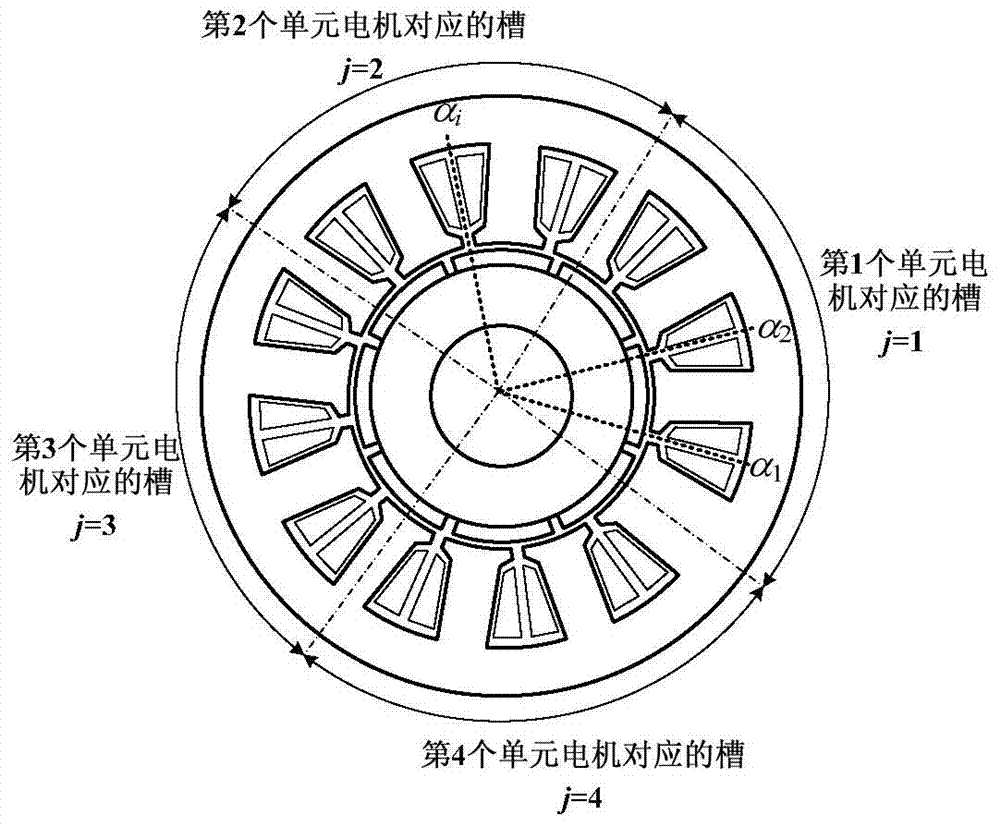
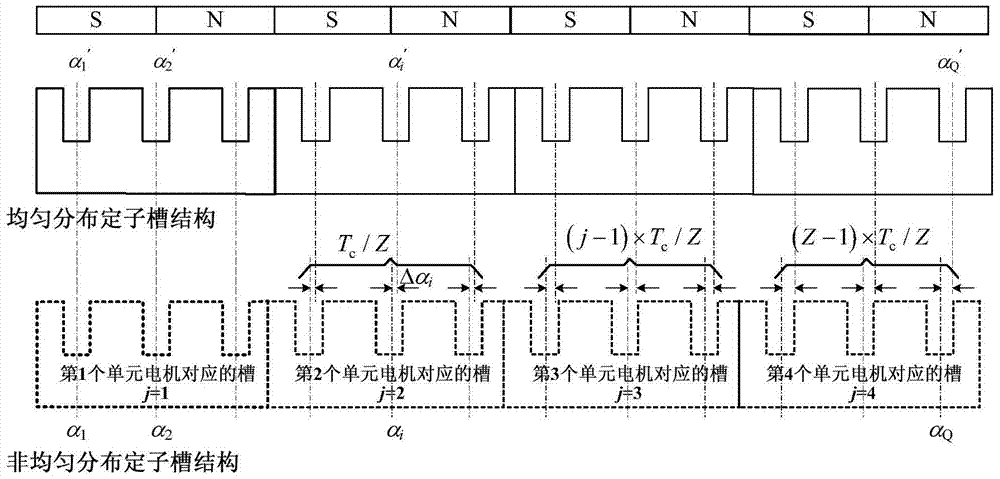
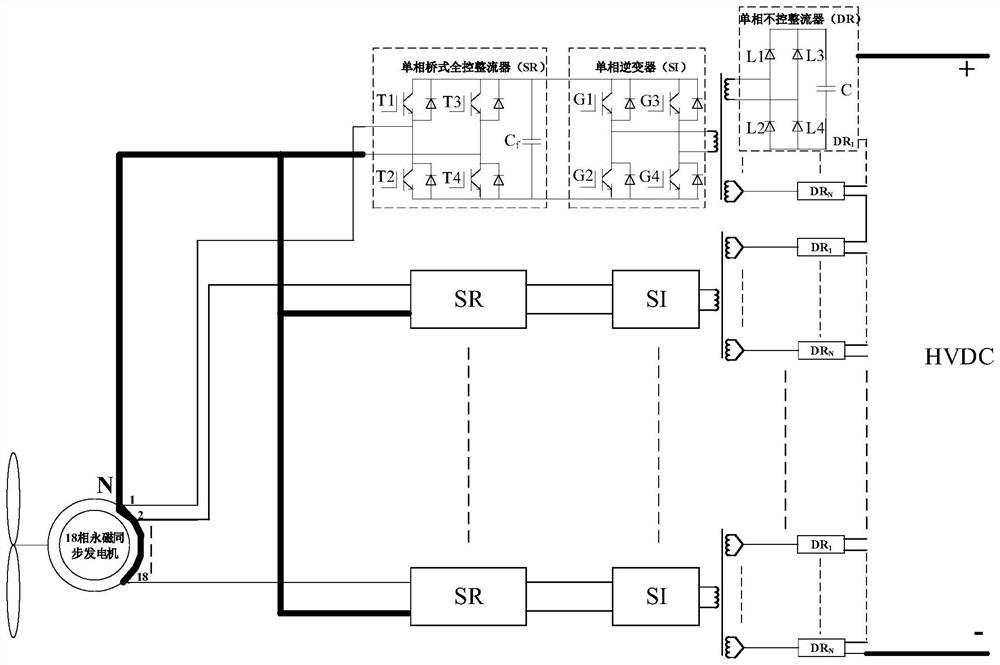
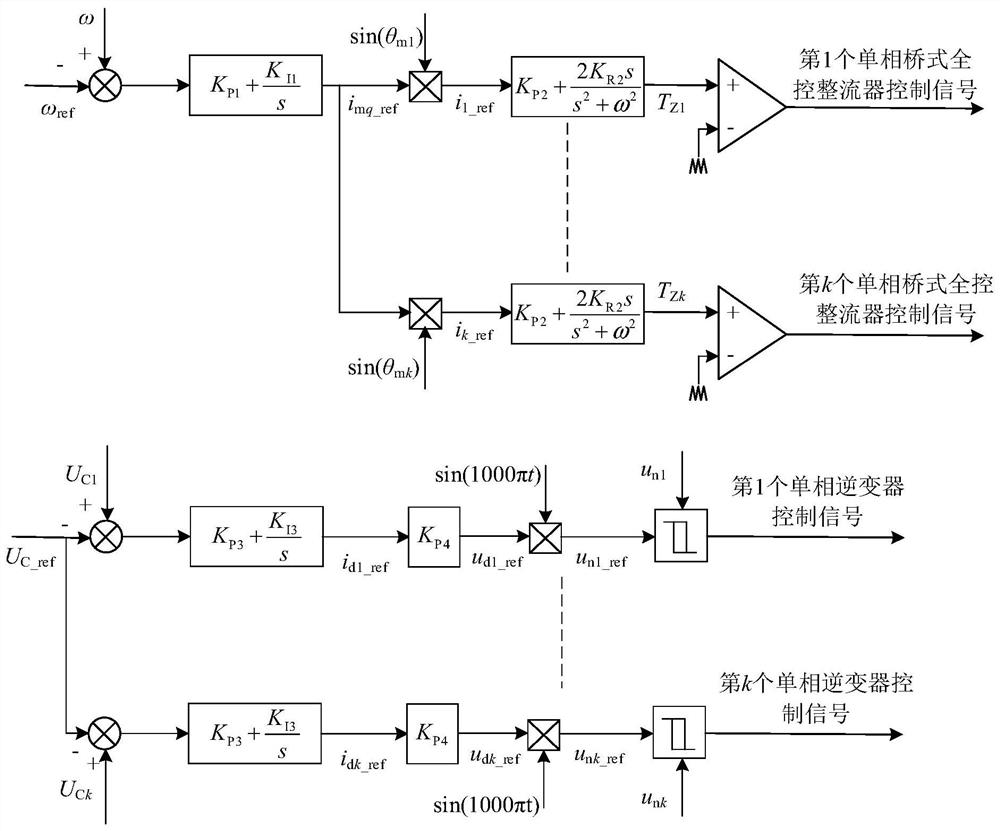
An 18-phase wind power generation system and its control method
ActiveCN112832951BReduce electromagnetic torque rippleImprove reliabilityWind motor controlMachines/enginesHigh-voltage direct currentPermanent magnet synchronous generator
The invention discloses an 18-phase wind power generation system and a control method thereof. The wind power generation system includes an 18-phase permanent magnet synchronous generator, 18 single-phase bridge-type full-control rectifiers and 18 power electronic transformers; Each phase winding of the synchronous generator is rectified by a single-phase bridge fully-controlled rectifier and then passed through a power electronic transformer. The secondary output terminals of all power electronic transformers are cascaded and connected to the high-voltage DC grid. The invention replaces the traditional three-phase motor with an 18-phase permanent magnet synchronous generator. Compared with the traditional three-phase generator, the power transmitted by the 18-phase permanent magnet synchronous generator is larger; at the same time, more phase windings ensure that the 18-phase The permanent magnet synchronous generator can still effectively transmit power when the winding part is broken, and has high fault tolerance; and, under the action of the stator harmonic current, the electromagnetic torque of the 18-phase permanent magnet synchronous generator The lower pulsation greatly improves the reliability of the 18-phase permanent magnet synchronous generator during operation.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSTITUTE, CHINA SOUTHERN POWER GRID CO LTD +1
Direct-drive consequent-pole permanent magnet hub motor
ActiveCN114006489AReduce electromagnetic torque rippleLow costElectric machinesMagnetic circuit stationary partsElectric machinePermanent magnet motor
The invention discloses a direct-drive consequent-pole permanent magnet hub motor. The direct-drive consequent-pole permanent magnet hub motor comprises an inner stator, an outer stator and a consequent-pole rotor located between the inner stator and the outer stator; the inner stator and the outer stator are each formed by combining a plurality of stator modules; the consequent-pole rotor comprises a plurality of modularized iron cores, Spoke permanent magnets and surface-mounted permanent magnets, wherein the Spoke permanent magnets and the surface-mounted permanent magnets are alternately arranged, the Spoke permanent magnets are magnetized in the annular direction, and the surface-mounted permanent magnets are magnetized in the radial direction; positioning holes are formed in the modularized iron cores; non-magnetic pressing plates are arranged on the inner side and the outer side of the consequent-pole rotor; and the non-magnetic pressing plates are fixed with the positioning holes in the modularized iron cores through positioning bolts. According to the direct-drive consequent-pole permanent magnet hub motor of the invention, the problem of counter electromotive force even harmonic caused by asymmetric air gap flux density of the consequent-pole permanent magnet motor is solved, the counter electromotive force waveform quality of the motor is improved, the electromagnetic torque characteristic of the motor is improved, the problem of single-side magnetic leakage of a single-stator Spoke rotor structure is solved, and the permanent magnet utilization rate is improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
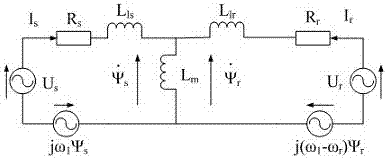
Rotor Flux Linkage Deadbeat Operation Method of Doubly-fed Wind Turbine Generator
InactiveCN104967376BNo saturation issuesEase saturationElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsGrid faultPower flow
The invention discloses a double-fed wind generator rotor flux linkage deadbeat fault operation method. When the grid voltage drops, through the prediction model of the rotor voltage, in order to make the rotor flux follow its given value in the model, the rotor flux is realized. The deadbeat control of the chain needs to replace the value of the rotor flux linkage at the next moment with the given value of the rotor flux linkage at the next moment. The given value of the rotor flux linkage follows the actual value of the stator flux linkage, and the predicted The rotor voltage in the two-phase synchronous rotating coordinate system undergoes coordinate inverse conversion to obtain the rotor voltage in the rotating coordinate system of the two-phase rotor speed, and finally undergoes PWM modulation. The invention has the advantages of simple implementation, good decoupling, fast dynamic response and strong robustness. In the grid fault state, a dead-beat control method for the rotor flux linkage is proposed, which can control the rotor fault current at 1.5-1.6 times the rated value. Within the current, the electromagnetic torque ripple is small during the fault, the dynamic response speed is fast, and the control precision is high.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
A decoupling method for a wound-type bearingless asynchronous motor
ActiveCN112332737BGood suspensionReduce electromagnetic torque rippleElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsMotor speedMathematical model
The invention discloses a decoupling method for a wound-type bearingless asynchronous motor, including a calculation method for equivalent inductance parameters of a three-phase winding, a construction method for a voltage equation and a flux linkage equation, and an electromagnetic torque and levitation force of a motor based on magnetic field orientation independent control strategy; firstly, the inductance matrix of the wound bearingless asynchronous motor is established and simplified by the equivalent principle; then the voltage equation and the flux equation of the motor are deduced; finally, the torque field orientation and the air gap field orientation are used respectively Based on the vector control strategy, the original system is decomposed into two subsystems that can independently control the motor speed and flux linkage. On the basis of establishing a precise mathematical model of the wound-type bearingless asynchronous motor, the present invention adopts the vector control principle of coordinate transformation and magnetic field orientation to achieve the purpose of complete decoupling of the rotating speed and flux linkage, and finally realizes the electromagnetic torque of the wound-type bearingless asynchronous motor and independent control of suspension forces.
Owner:江苏大也环境有限公司
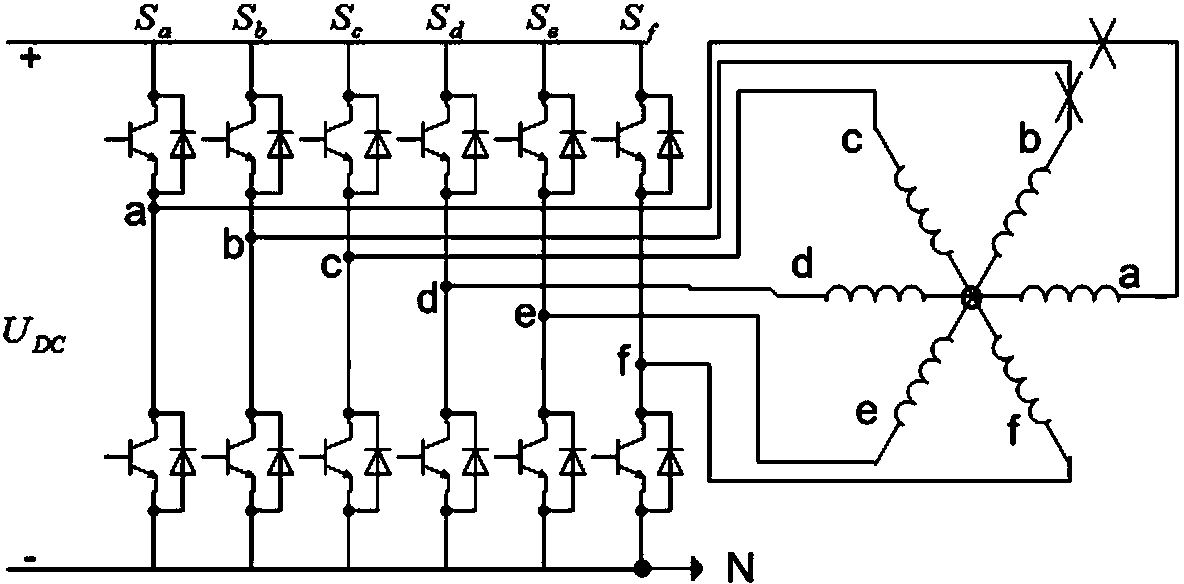
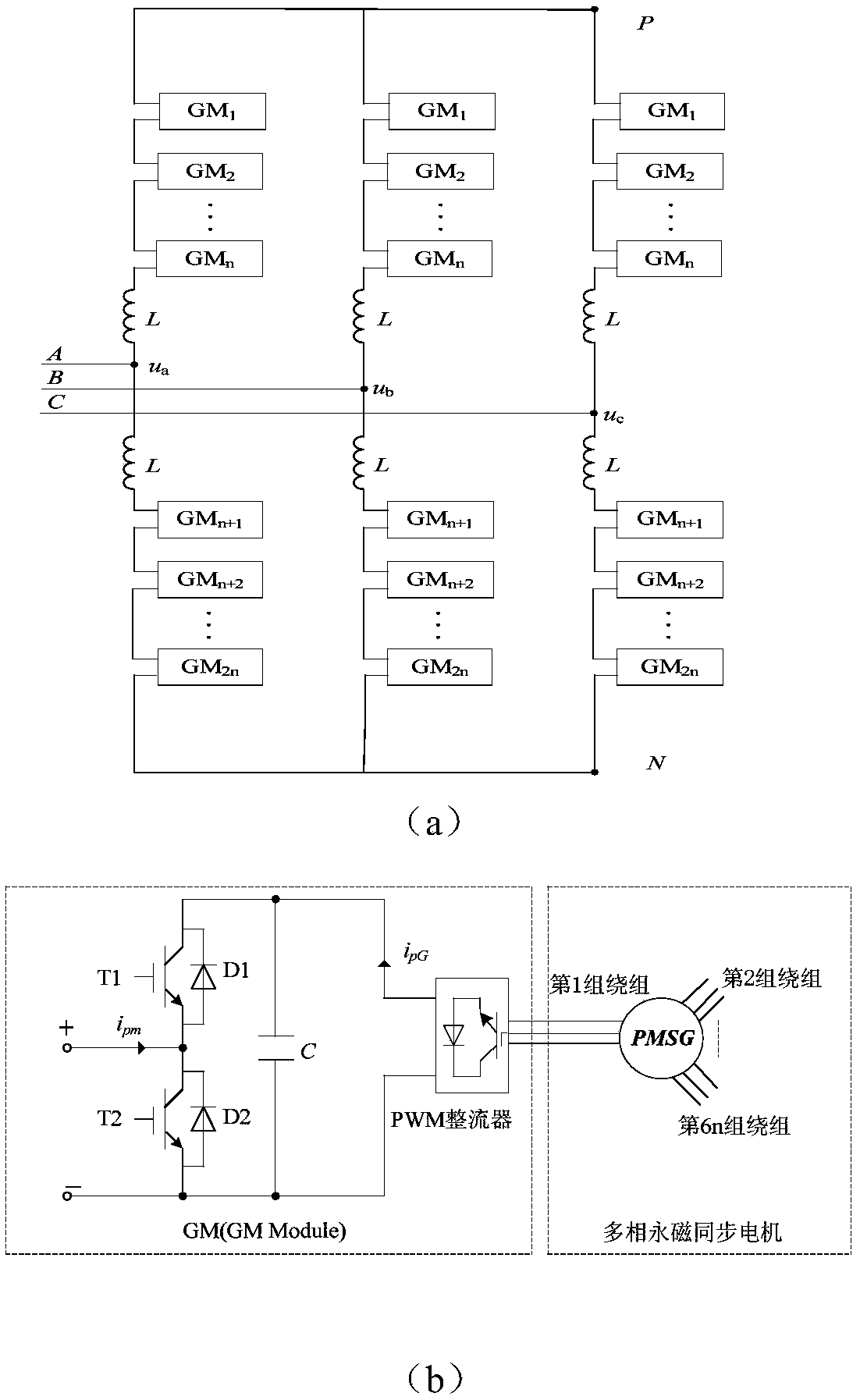
A multi-phase permanent magnet synchronous motor drive system and its control method
ActiveCN106301102BAchieve direct driveReduce torque rippleTorque ripple controlVector control systemsCapacitanceLow voltage
The invention discloses a driving system for a multiphase permanent magnet synchronous motor and a control method of the driving system. The driving system comprises a modular multilevel converter, wherein the modular multilevel converter consists of three phases and six bridge arms; each bridge arm consists of n submodules and one filter inductor; each submodule consists of a PWM (Pulse-Width Modulation) inverter, two IGBTs (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor) and one capacitor; the two IGBTs are serially connected and then are connected with the corresponding capacitor and a direct current side of the corresponding PWM inverter in parallel; an alternating current side of each PWM inverter is connected with one set of three-phase winding of the multiphase permanent magnet synchronous motor; the number of the three-phase winding of the multiphase permanent magnet synchronous motor is 6n (n is 1, 2, 3 and the like). According to the driving system and the control method disclosed by the invention, three-phase branches are subjected to modular series-parallel connection, all the sets of three-phase winding of the multiphase permanent magnet synchronous motor are respectively controlled, the problem that the multiphase permanent magnet synchronous motor is difficult to control in a multidimensional manner is solved, and low-voltage, heavy-power and high-reliability driving of the multiphase permanent magnet synchronous motor can be realized.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Synchronous flux weakening control method for stator and rotor flux linkage of doubly-fed wind turbine under grid fault
InactiveCN104967384BImprove non-off-grid operation capabilityEasy to controlElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsEngineeringFlux linkage
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
Faulty operation method of doubly-fed wind turbine stator-rotor flux linkage flux-weakening control
InactiveCN104993756BImprove fault operation capabilityImprove non-off-grid operation capabilityElectric generator controlControl vectorPower grid
The invention discloses a fault operation method for the flux-weakening control of the stator-rotor flux linkage of a doubly-fed wind power generator. The key points of the technical solution of the present invention are: the faulty operation method of the stator-rotor flux-linkage weakening control of the doubly-fed wind power generator, when the grid voltage is in steady state operation, the rotor-side converter of the doubly-fed wind power generator adopts the vector control based on the orientation of the stator flux linkage , when the grid voltage fault is running, the rotor-side converter of the double-fed wind turbine performs the stator-rotor flux-weakening control, and the control frequency of the stator-rotor flux-weakening control is set to be twice that of the vector control based on the stator flux orientation. The present invention does not need complex coordinate conversion during the occurrence of a fault, realizes a quick response to the fault, can effectively control the rotor current within 1.5-1.6 times the rated current, the electromagnetic torque fluctuation is small, and the stator side active power and The reactive power fluctuation is small, which improves the fault operation capability of the doubly-fed wind turbine.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
radial flux motor
ActiveCN110829643BIncrease pitchAchieve noise reductionMagnetic circuit stationary partsWindings conductor shape/form/constructionElectric machineMagnetic poles
The present invention proposes a radial flux motor, comprising: a motor stator, including: a plurality of stator modules spliced along the circumferential direction, and the stator module includes: a stator core, including an arc-shaped stator yoke and an arc-shaped stator yoke A plurality of stator teeth on the upper part and extending toward the axial direction; the stator windings are respectively wound on the stator teeth one by one to generate radial magnetic flux after electrification, and the motor rotor is nested and assembled with the motor stator. The angle between two adjacent stator teeth satisfies: N t is the number of stator teeth on each stator module, m is the number of phases of the motor, and p is the number of poles of the motor rotor. Through the technical solution of the present invention, compared with the setting direction in which the tooth pitch of adjacent stator teeth is equal to the pole pitch between adjacent magnetic poles in the prior art, by adjusting the tooth pitch, it is possible to maintain low cost and low difficulty process At the same time, it can reduce the electromagnetic torque ripple and achieve noise reduction.
Owner:GUANGDONG WELLING ELECTRIC MACHINE MFG +2
A cast aluminum rotor tooth slot structure
ActiveCN106685113BReduce widthSmall currentMagnetic circuit rotating partsTransverse planeEngineering
The invention discloses a cast-aluminum rotor gullet structure, which comprises a gullet body. Insulating separator plates are arranged in a cavity of the gullet body. The first transverse plane of each insulating separator plate is connected or contacted with one end wall of the gullet body, and extends in a length direction of the gullet body to the second transverse plane. The second transverse plane of each insulating separator plate is connected or contacted with the other end wall of the gullet body. The bottom of each insulating separator plate is connected with the bottom wall of the gullet body. The advantages are that in a condition with the same electric magnetic torque, currents of a rotor are reduced, currents of a corresponding stator are reduced, and thus the efficiency of a motor is increased.
Owner:HEFEI HENGDAJIANGHAI PUMP IND CO LTD
Fast field-weakening control method for doubly-fed wind turbine
InactiveCN104993759BQuick controlNo saturation issuesElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsPower gridEngineering
The invention discloses a fast magnetic field weakening control method for a double-fed wind power generator. In the steady state, all variables are based on the two-phase synchronous rotating coordinate system. By predicting the variation of stator active power and reactive power in a sampling period, and then compensating the power in the next sampling period, the rotor voltage is finally calculated, and then After PWM modulation, this method reduces the fluctuation of active power and reactive power on the stator side. When the grid voltage drops, all variables are based on the two-phase static coordinate system. Through the prediction model of the rotor voltage, the rapid flux-weakening control of the rotor flux linkage is realized, and the predicted rotor voltage in the two-phase static coordinate system is converted into two-phase The rotor speed is the rotor voltage in the rotating coordinate system, which is finally modulated by PWM. Fast field weakening control can effectively control the rotor current within 1.5-1.6 times the rated current, and the electromagnetic torque ripple is small during the fault period, which improves the fault operation capability of the doubly-fed wind turbine.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
Five-phase axial magnetic flux permanent magnet motor for electric vehicle
ActiveCN113659787AShorten the main magnetic circuitShorten the axial lengthMagnetic circuit rotating partsElectric machinesElectric vehicleElectromotive force
The invention discloses a five-phase axial magnetic flux permanent magnet motor for an electric vehicle, which adopts a single-stator / double-rotor structure and consists of a stator and two rotors. The stator is of a back-to-back topology and comprises ten stator iron cores, ten aluminum-nickel-cobalt permanent magnets, twenty armature coils and twenty pulse coils, and the rotor is composed of fifty seven neodymium-iron-boron permanent magnets. The five-phase motor is good in fault tolerance performance, high in reliability and small in torque pulsation; the stator and rotor permanent magnet type axial doubly salient structure is short in axial length, compact in structure, small in size, high in power / torque density, high in back electromotive force sine degree and high in efficiency; the aluminum-nickel-cobalt permanent magnets on the stator are easy to realize magnetization and demagnetization, the air-gap magnetic field of the motor can be flexibly adjusted, the speed regulation range is widened, the loading capacity is enhanced, and the magnetism regulation efficiency is high; and the neodymium iron boron permanent magnets in a special arrangement form on the rotor can obtain a perfect sine air-gap magnetic field, reduce the harmonic content, and further improve the motor efficiency and the power density.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com