Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
82results about How to "Reduce bites" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
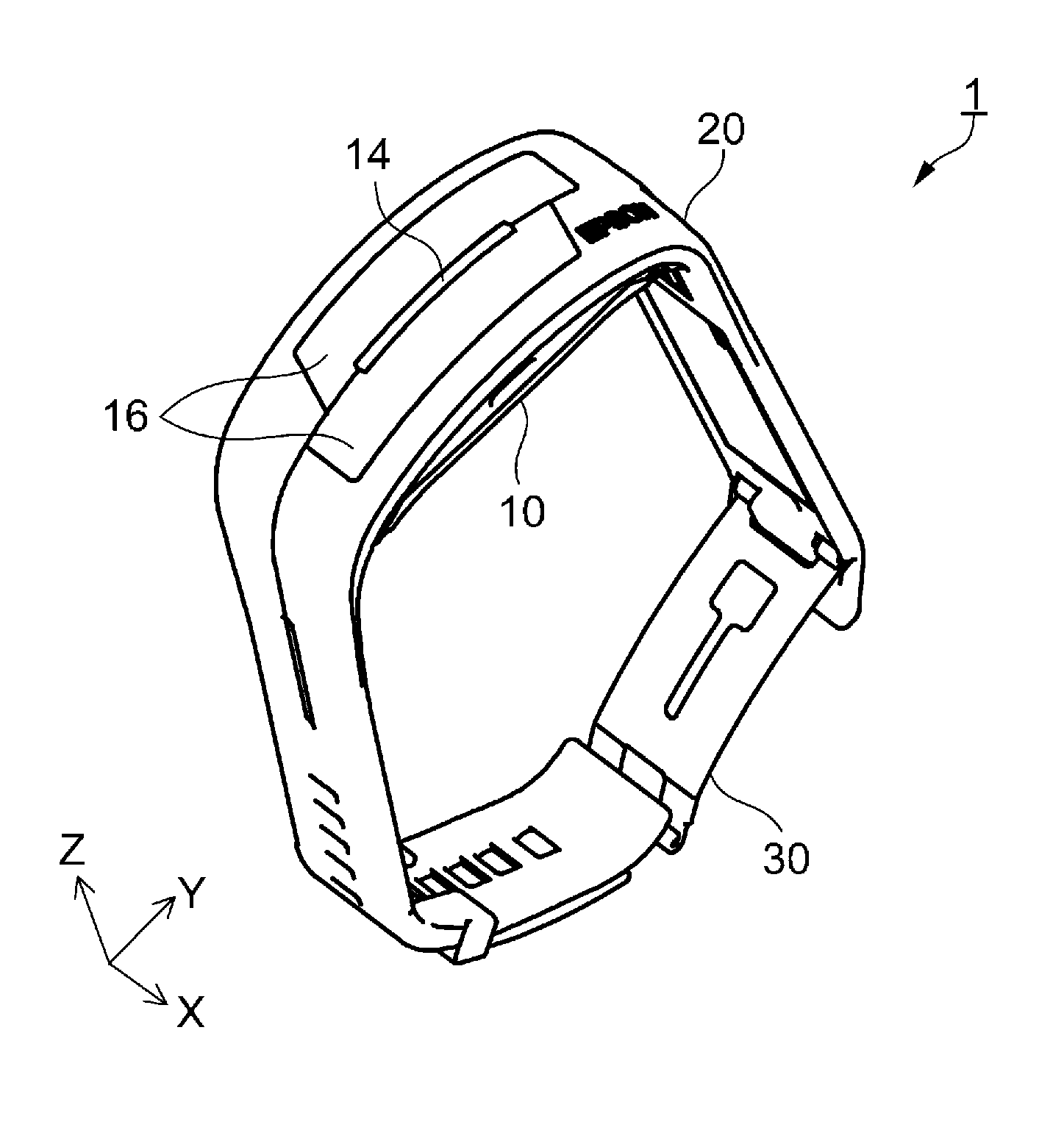
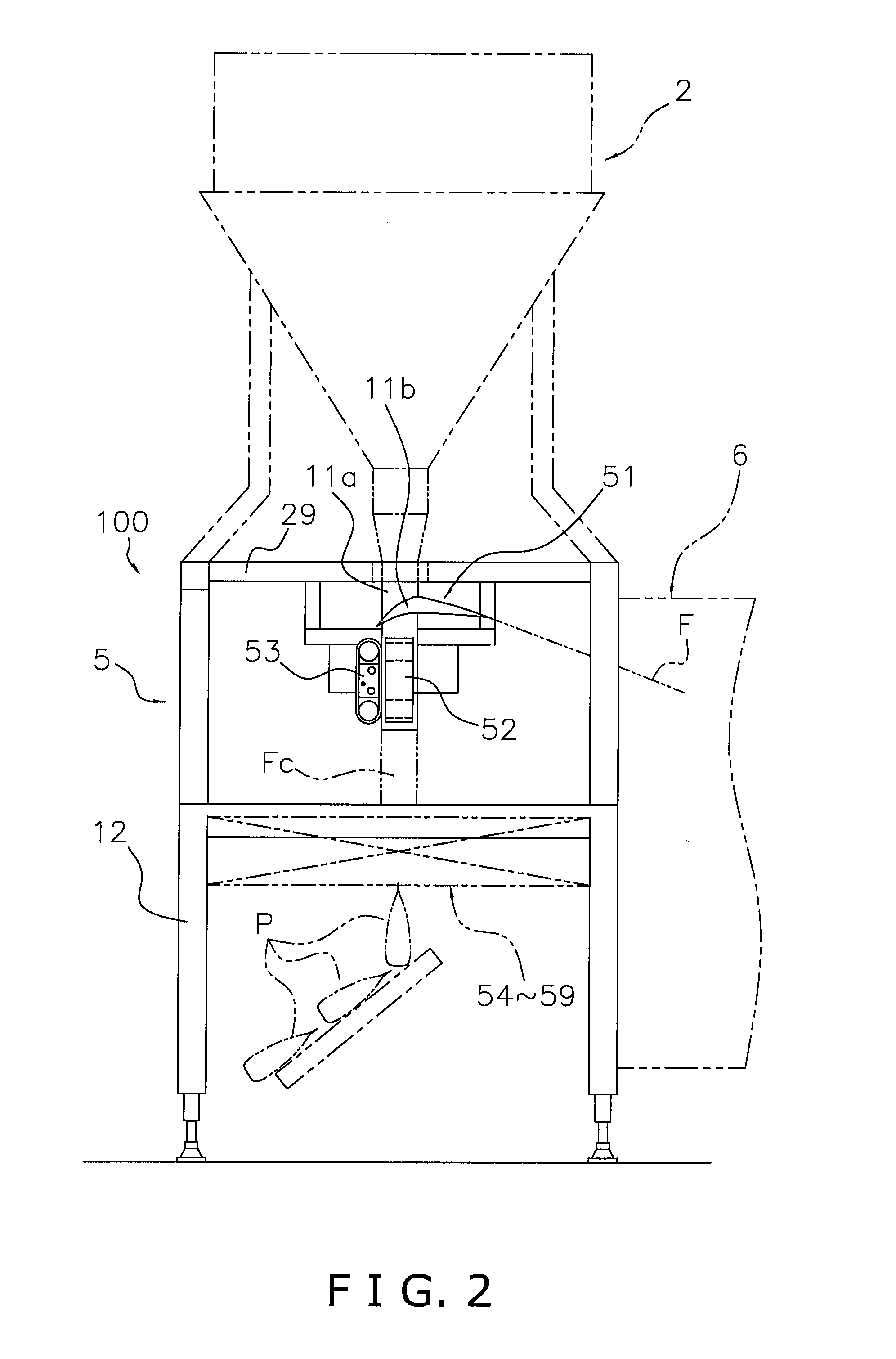
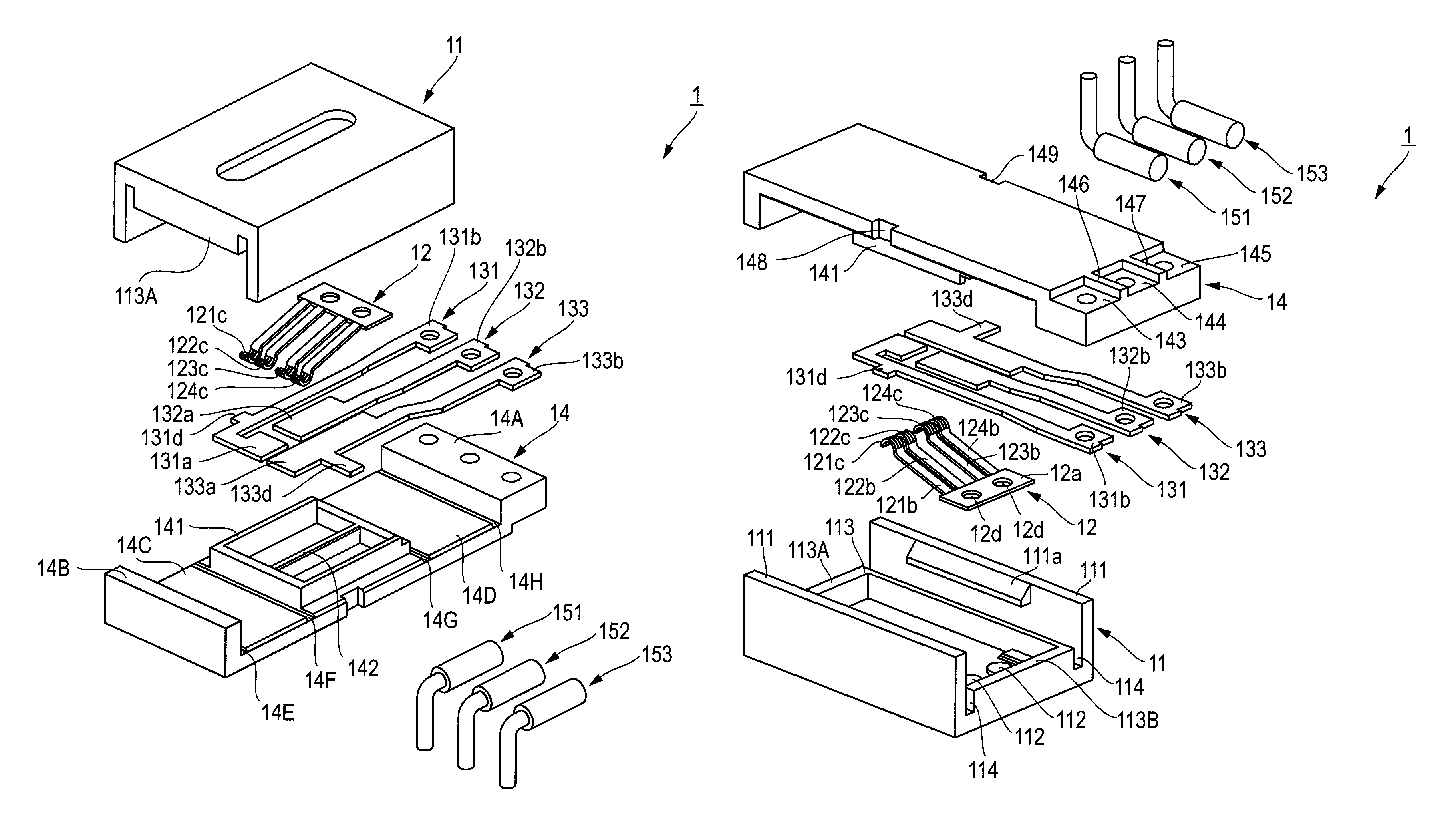
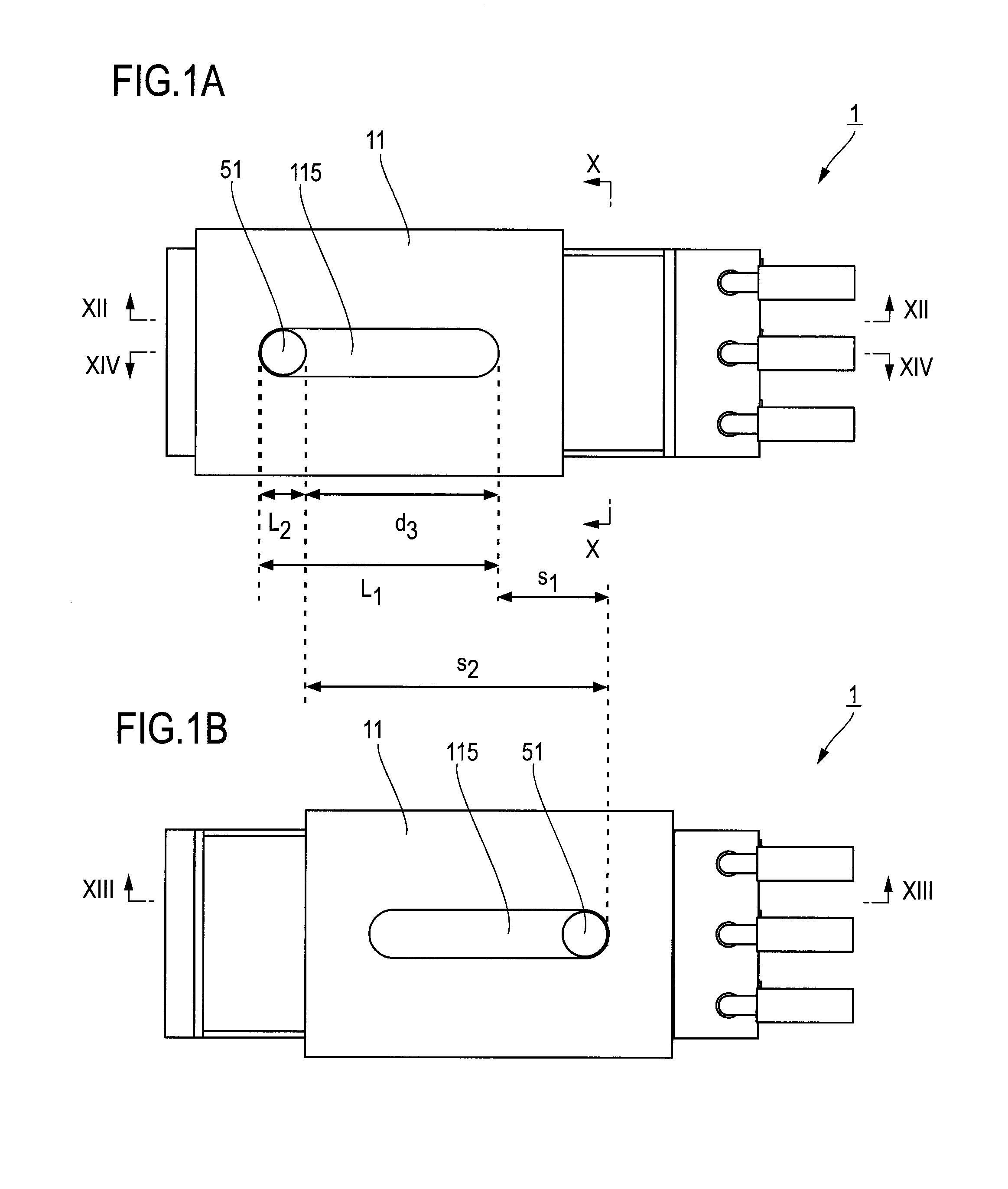
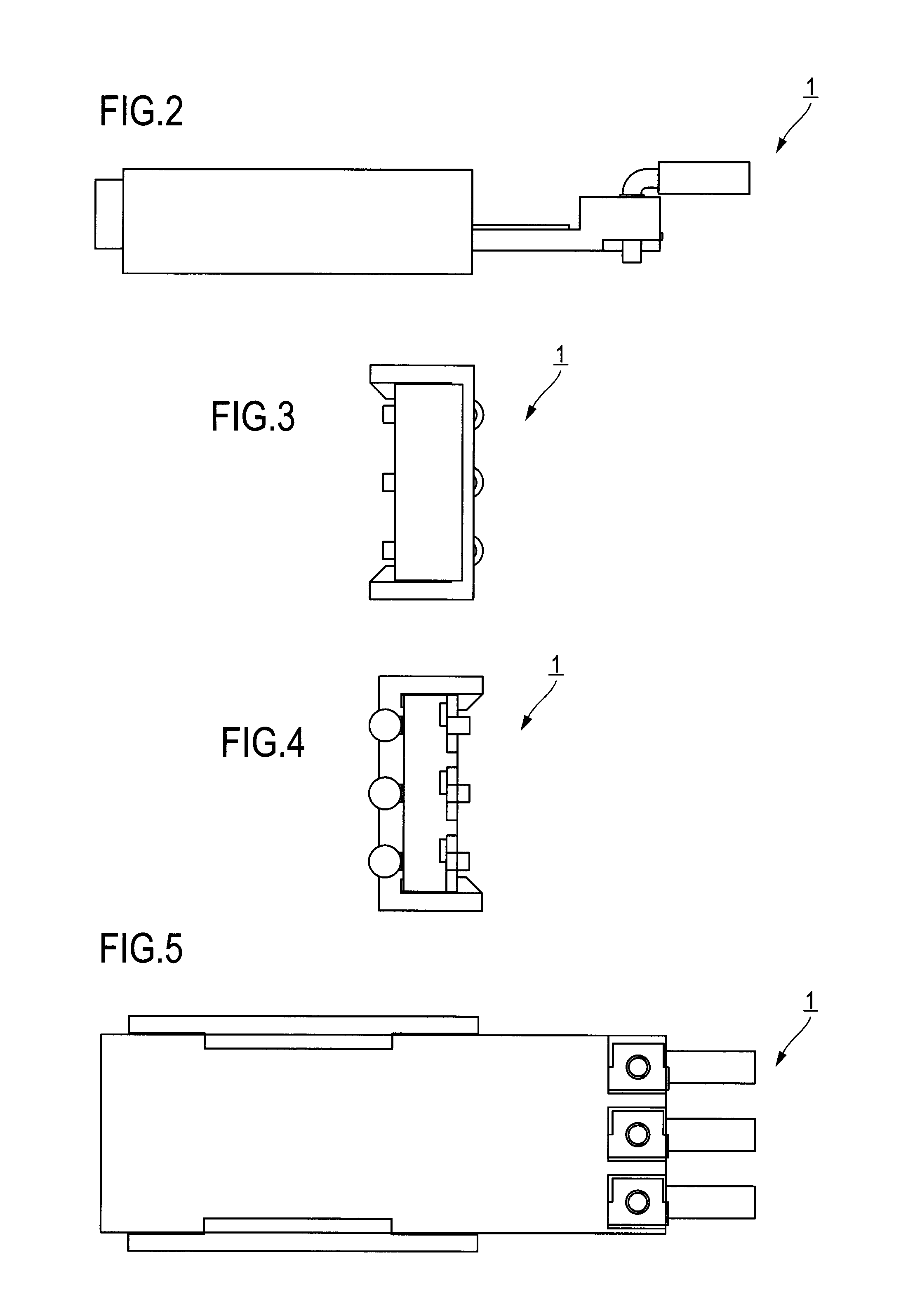
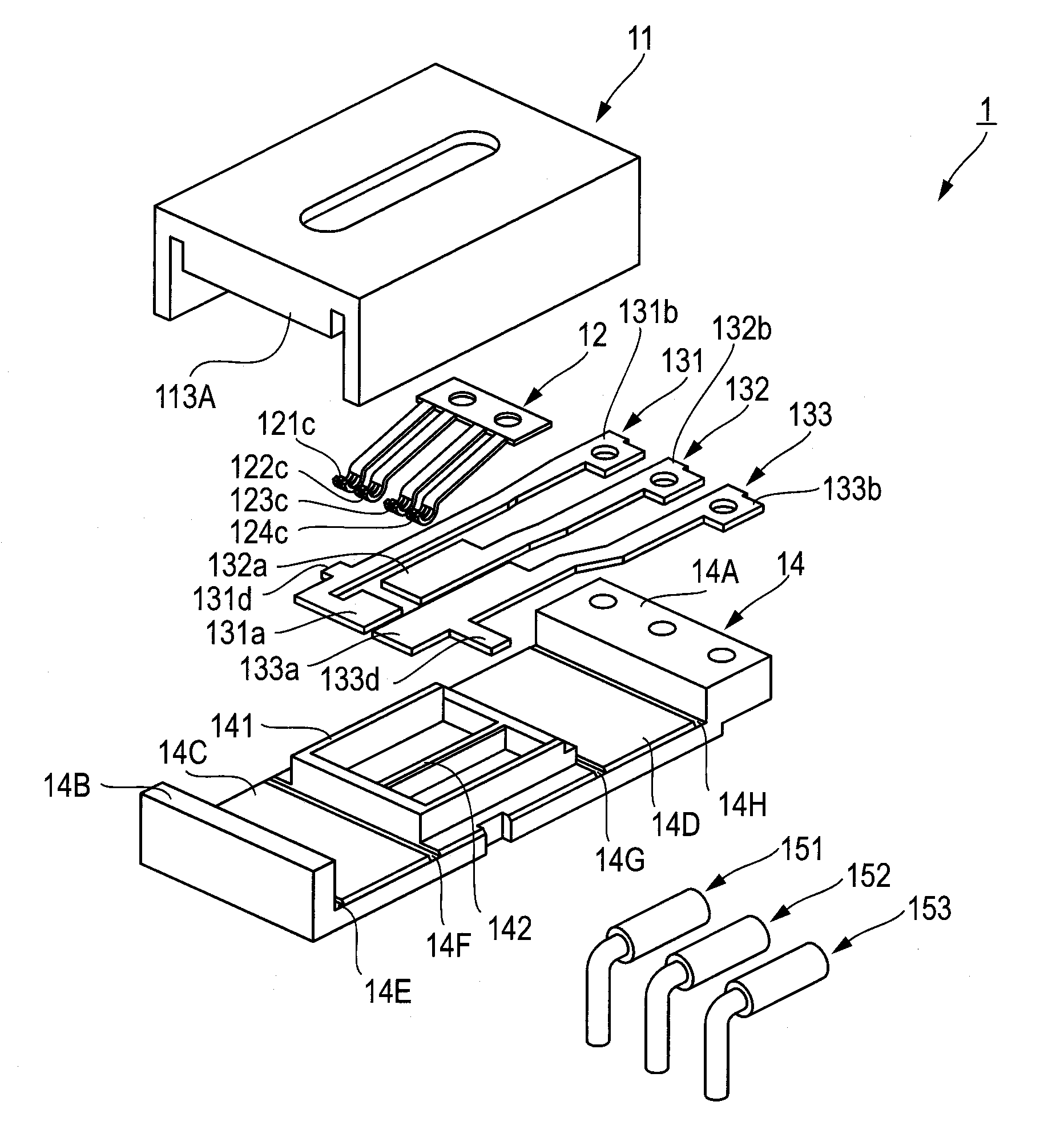
Biological information measuring apparatus
ActiveUS20160143584A1Reduce intensitySpoiling sensation of wearingInertial sensorsTelemetric patient monitoringBiological bodyMeasuring instrument
A biological information measuring apparatus (measuring apparatus) includes a band which fixes a case unit to a living body. The band is provided with a recessed groove part on a side facing the living body. The groove part has a depth of 1020 μm or more and 1140 μm or less.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
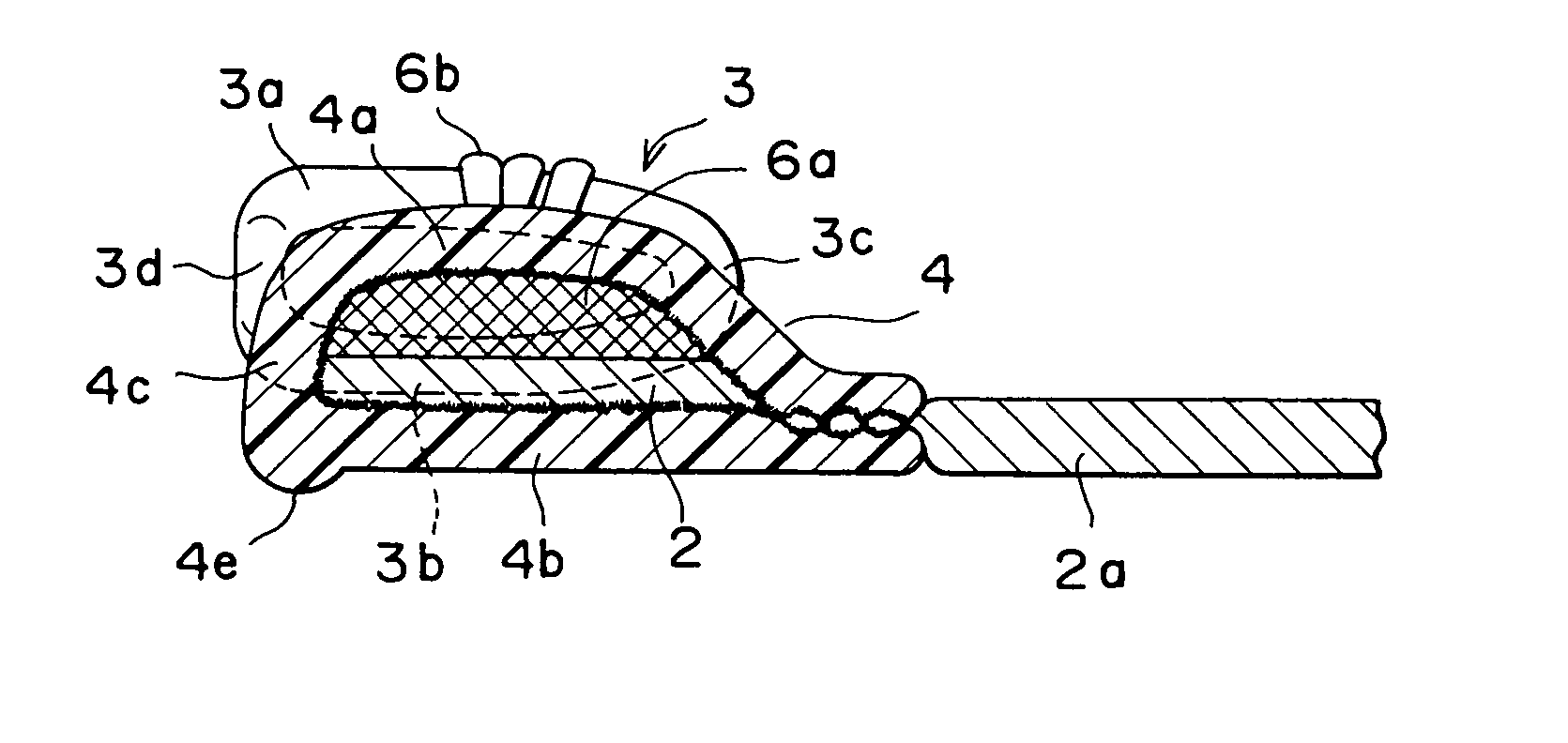
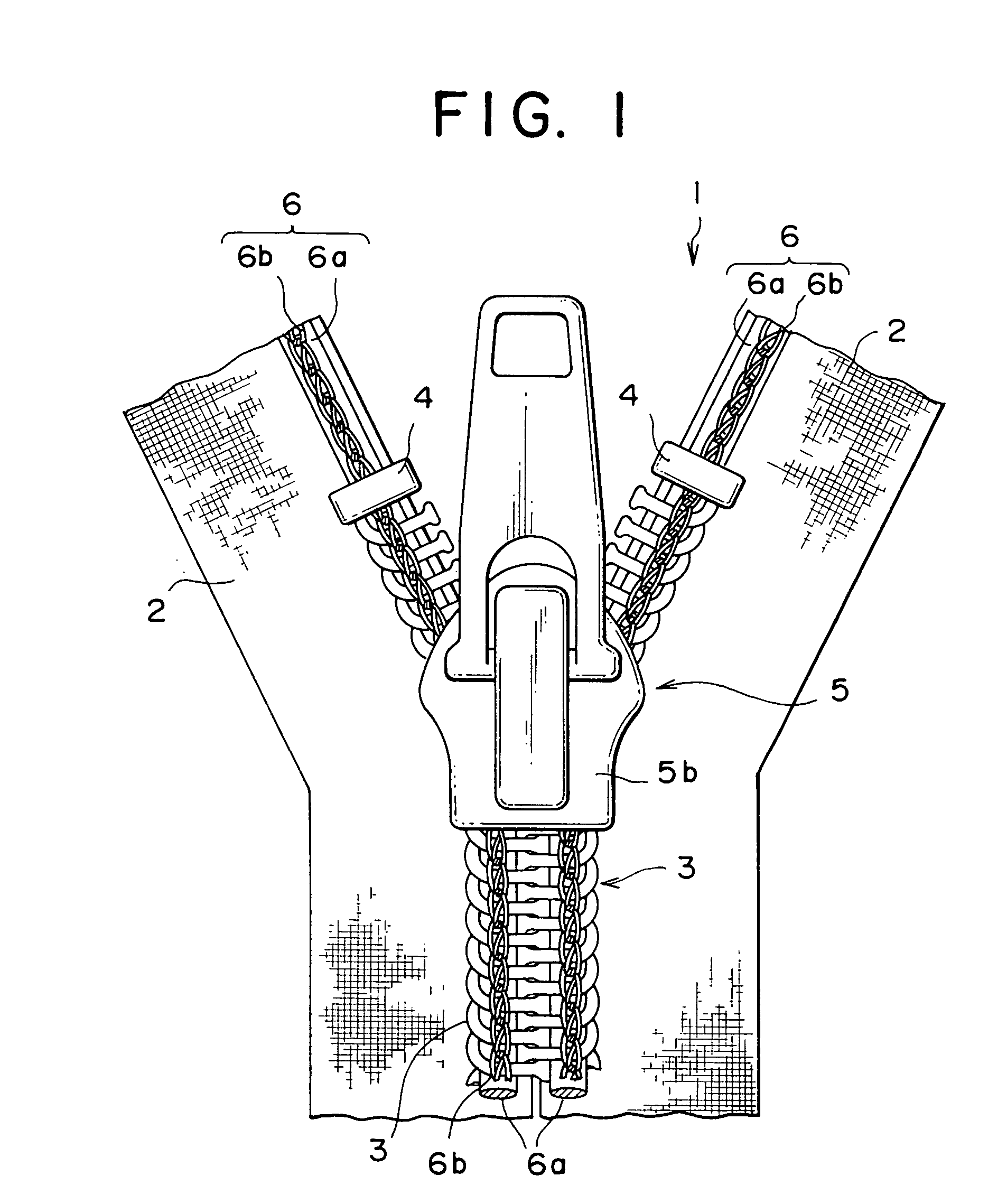
Slide fastener
A stopper portion has a minute protrusion on part of an outer peripheral face except a side face in the length direction of a fastener tape. This protrusion is a rib-like protrusion extended linearly in the length direction of the fastener tape formed on a vertex of the surface of a bent portion, a protrusion extended so as to be expanded in a curved shape in the length direction of the fastener tape or a rib-like protrusion protruded along a boundary portion between the bent portion of the stopper portion and a bottom face thereof. Existence of this protrusion not only reduces a sliding resistance when the slider is started but also eliminates prickly feeling and feeling of disharmony originating from a shape of an upper stopper which is a kind of the conventional stopper portion.
Owner:YKK CORP
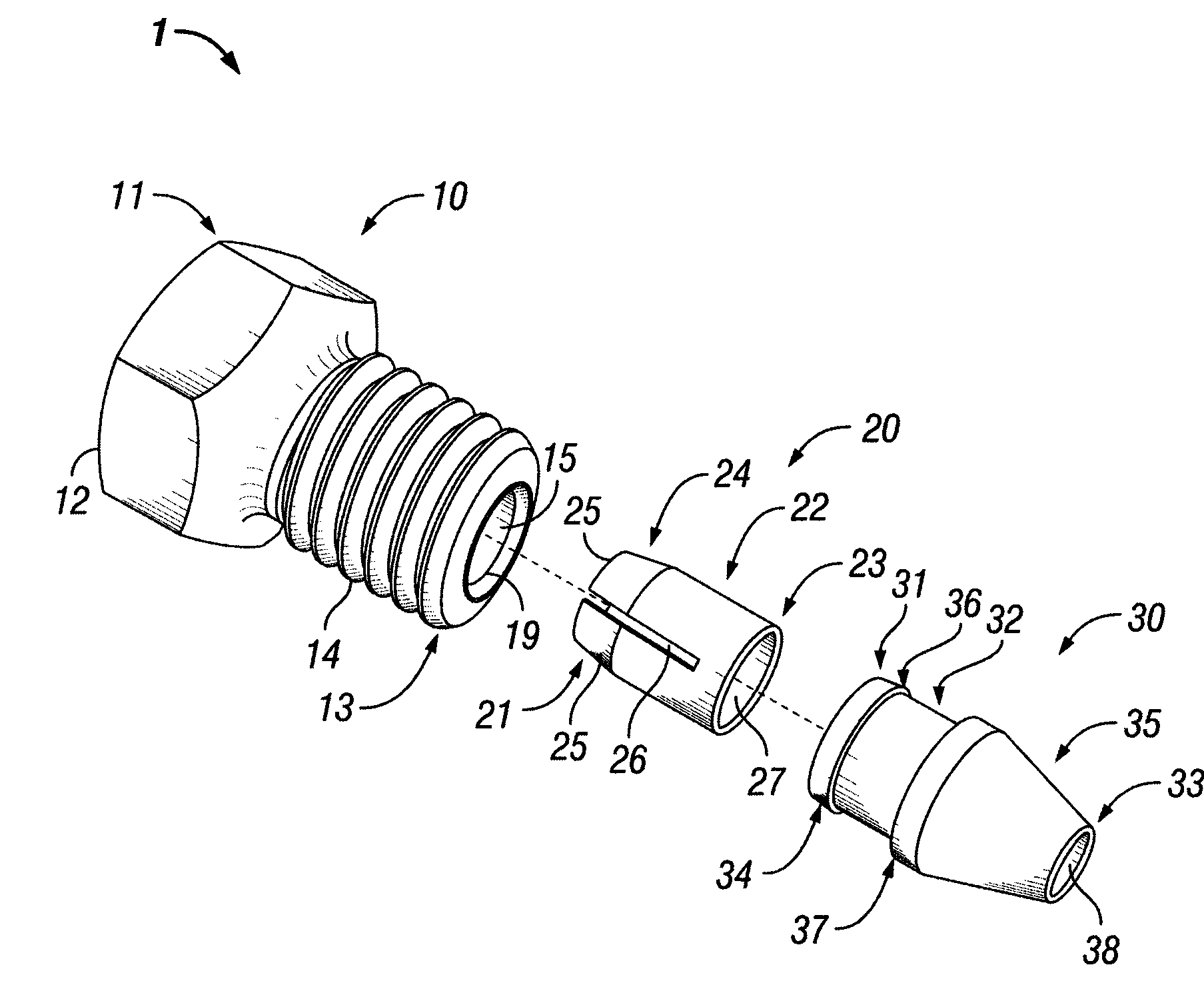
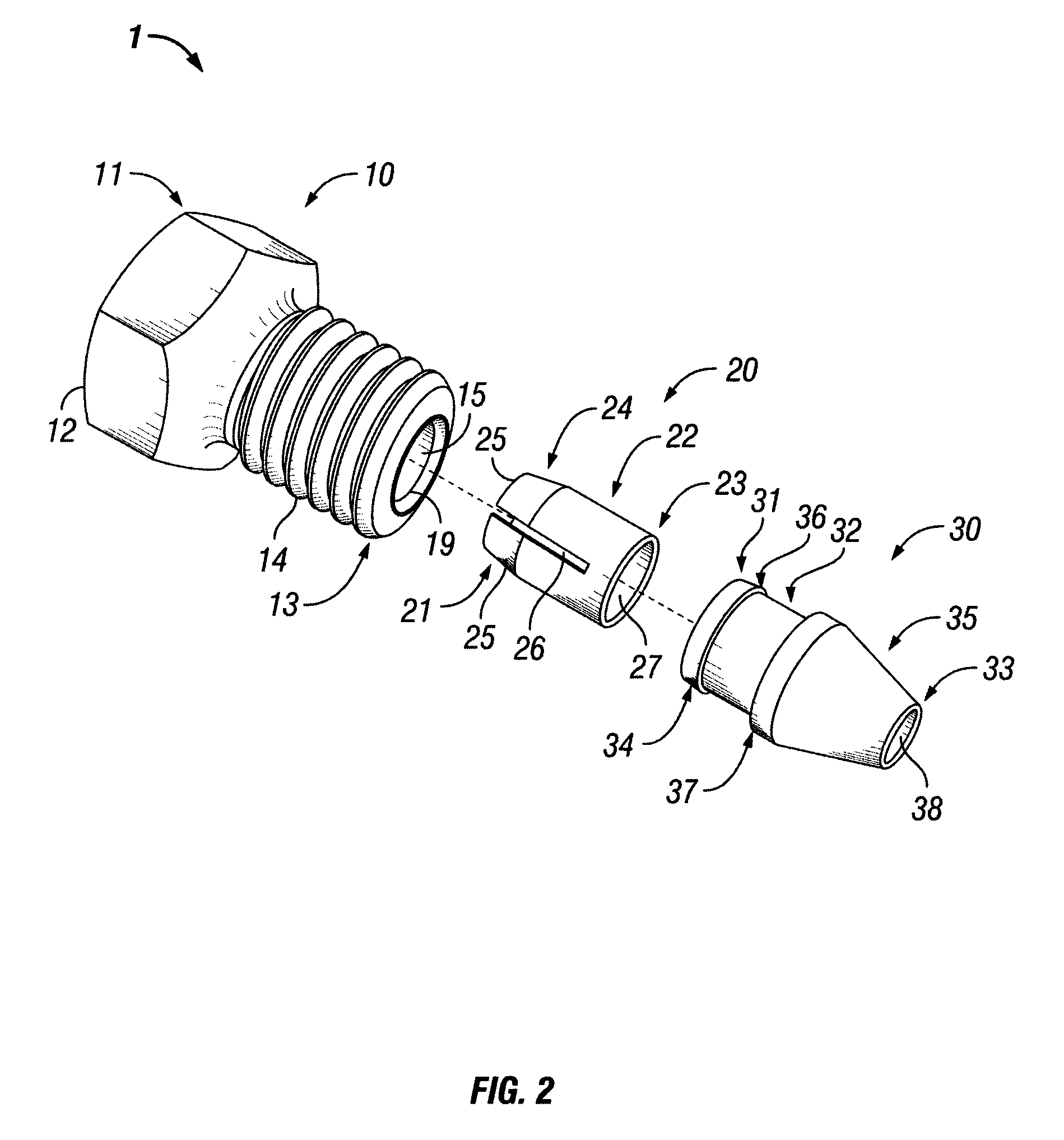
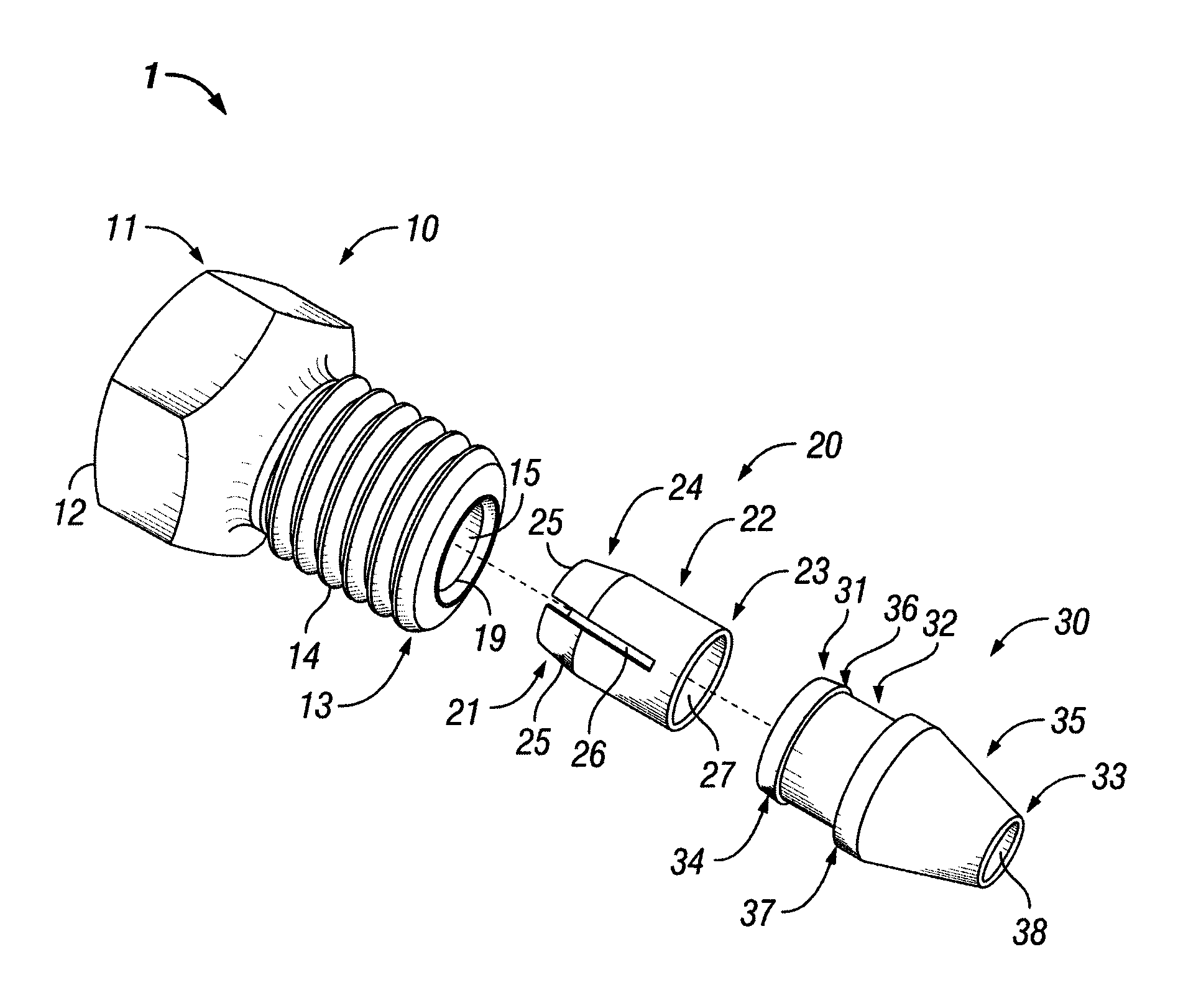
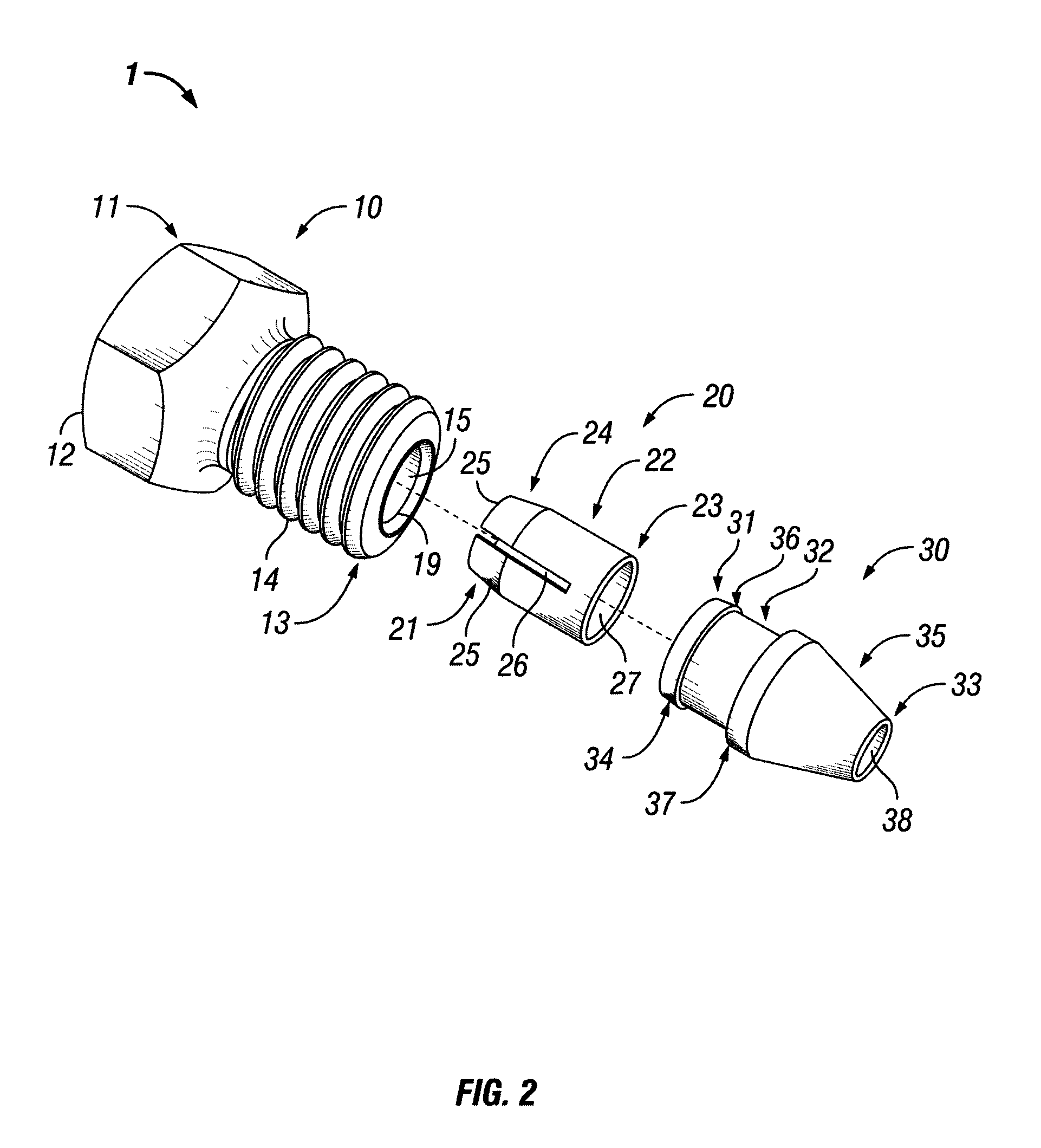
Connection assembly for ultra high pressure liquid chromatography
ActiveUS8569070B2Reduce bitesIncrease forceIon-exchange process apparatusSleeve/socket jointsUltra high pressureMechanical engineering
A fitting assembly having a nut, a ferrule, and a ferrule tip that may be assembled by an operator. The fitting assembly includes a nut with first and second ends, with the second end adapted to receive the first end of a ferrule, and a ferrule tip with a first end having an externally tapered portion adapted to abut the second end of the ferrule and a second end adapted to be received in a component or fitting of a liquid chromatography system. The nut, ferrule and ferrule tip of the fitting assembly have passageways therethrough for receiving and removably holding tubing.
Owner:IDEX HEALTH & SCI
Connection Assembly for Ultra High Pressure Liquid Chromatography
ActiveUS20120014848A1Reduce bitesIncrease forceIon-exchange process apparatusSleeve/socket jointsUltra high pressureEngineering
A fitting assembly having a nut, a ferrule, and a ferrule tip that may be assembled by an operator. The fitting assembly includes a nut with first and second ends, with the second end adapted to receive the first end of a ferrule, and a ferrule tip with a first end having an externally tapered portion adapted to abut the second end of the ferrule and a second end adapted to be received in a component or fitting of a liquid chromatography system. The nut, ferrule and ferrule tip of the fitting assembly have passageways therethrough for receiving and removably holding tubing.
Owner:IDEX HEALTH & SCI
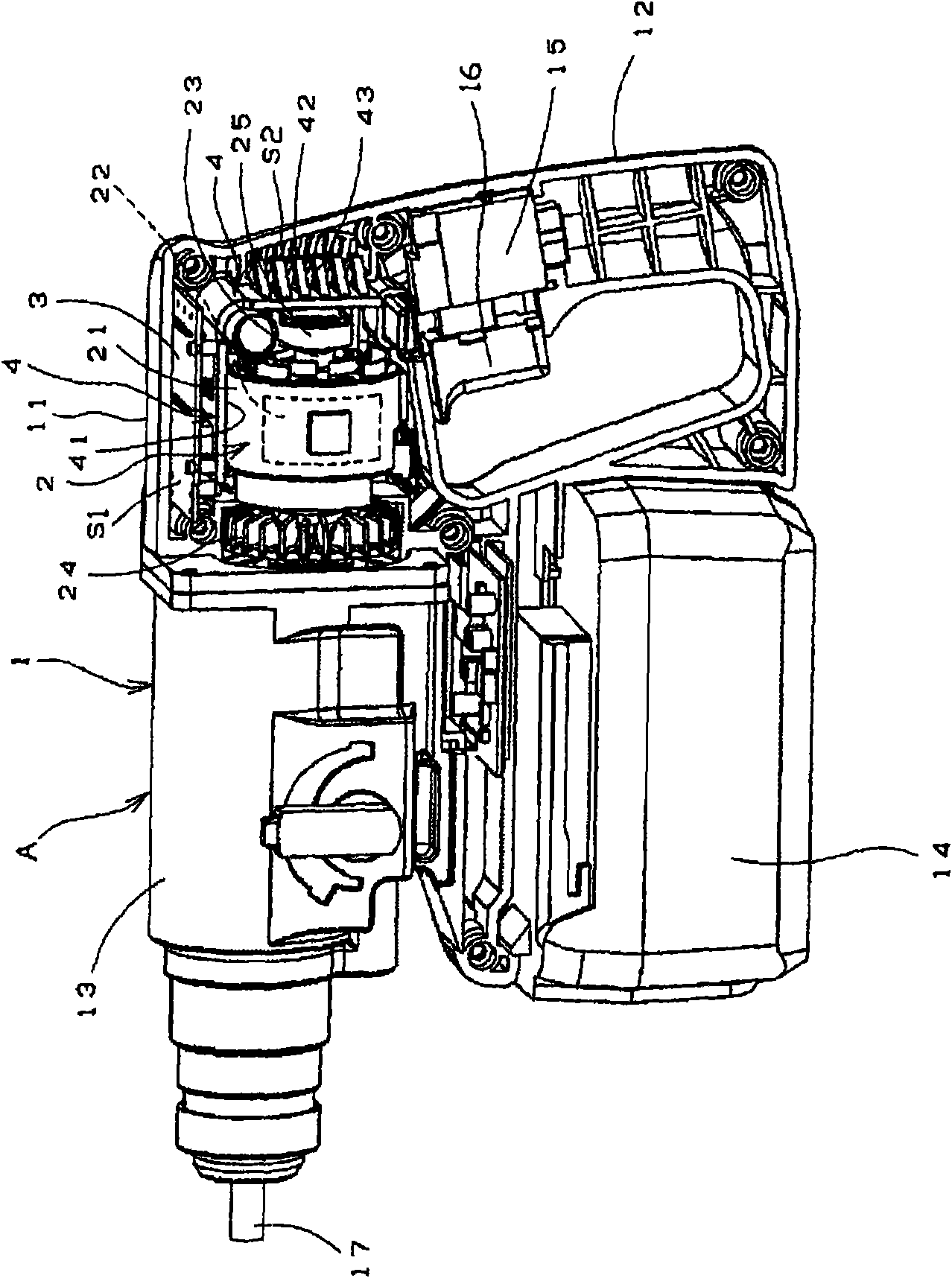
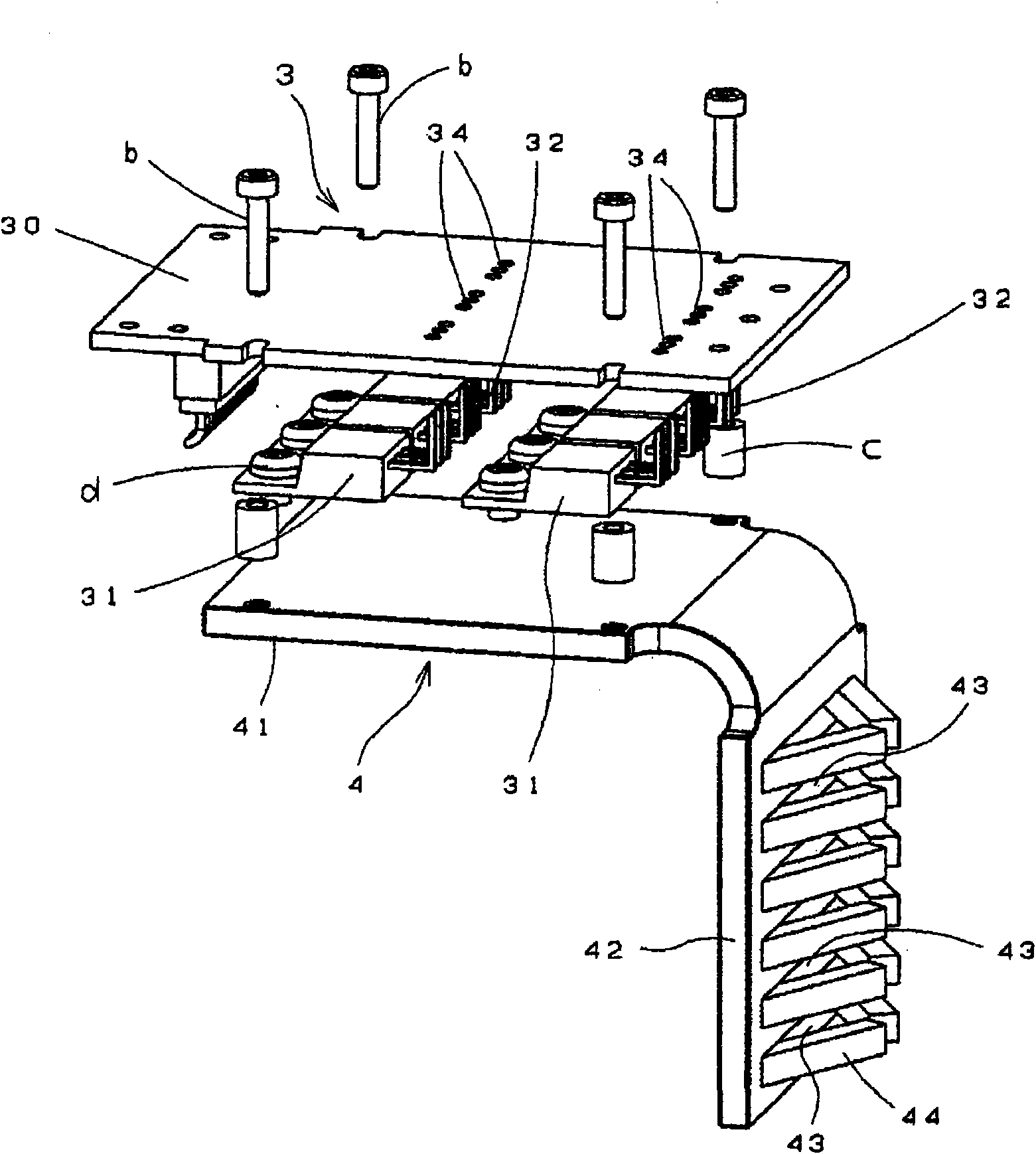
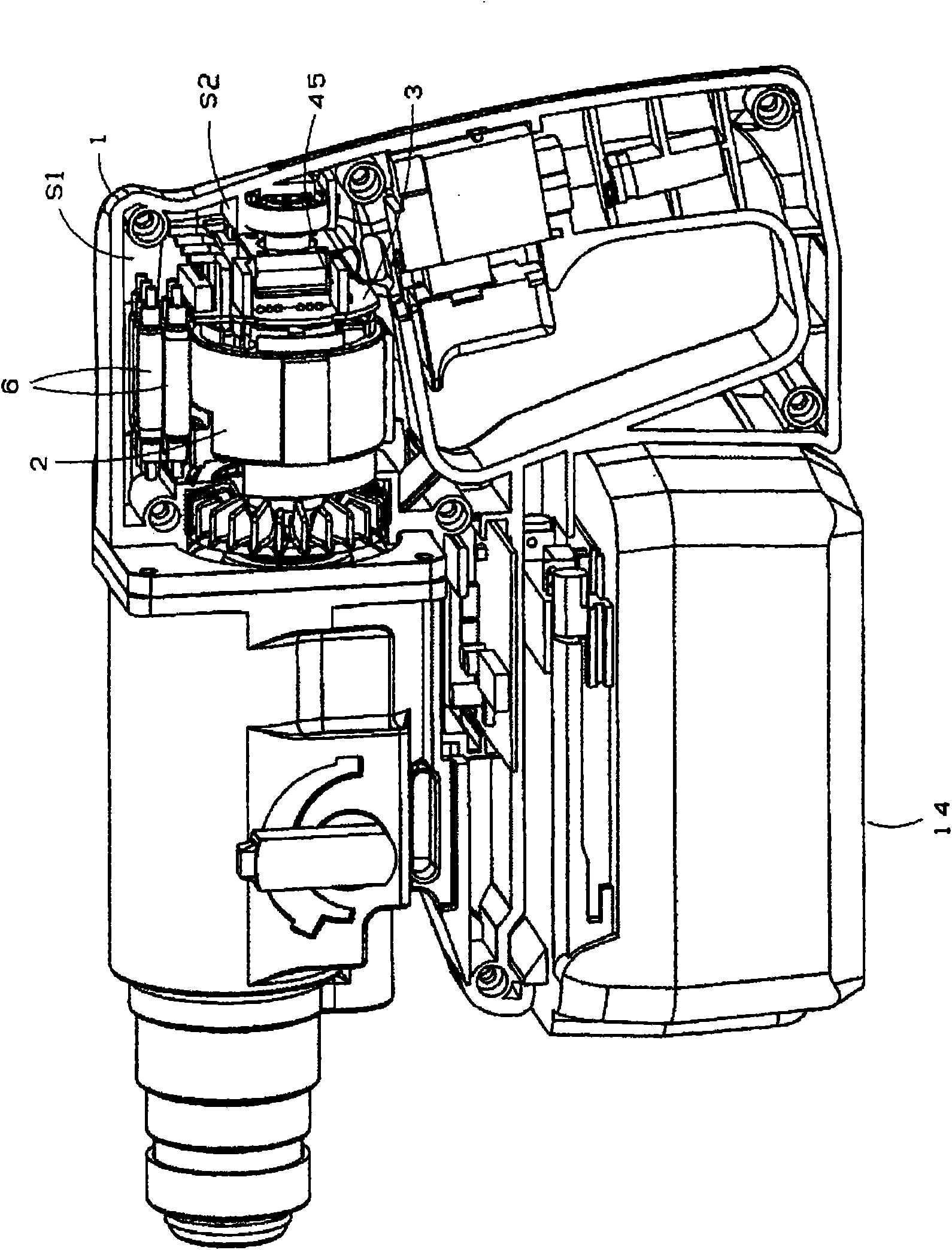
Machine tool having brushless motor
InactiveCN101594969AAvoid overall overheatingImprove workabilityAssociation with control/drive circuitsPortable percussive toolsBrushless motorsPower tool
Disclosed is a machine tool wherein a power substrate (3) having an electronic component for controlling revolution of a brushless motor is arranged in a first space (S1) above the brushless motor and a heat sink for cooling the power substrate (3) is arranged in a second space (S2) in the back of the brushless motor.
Owner:MAX CO LTD
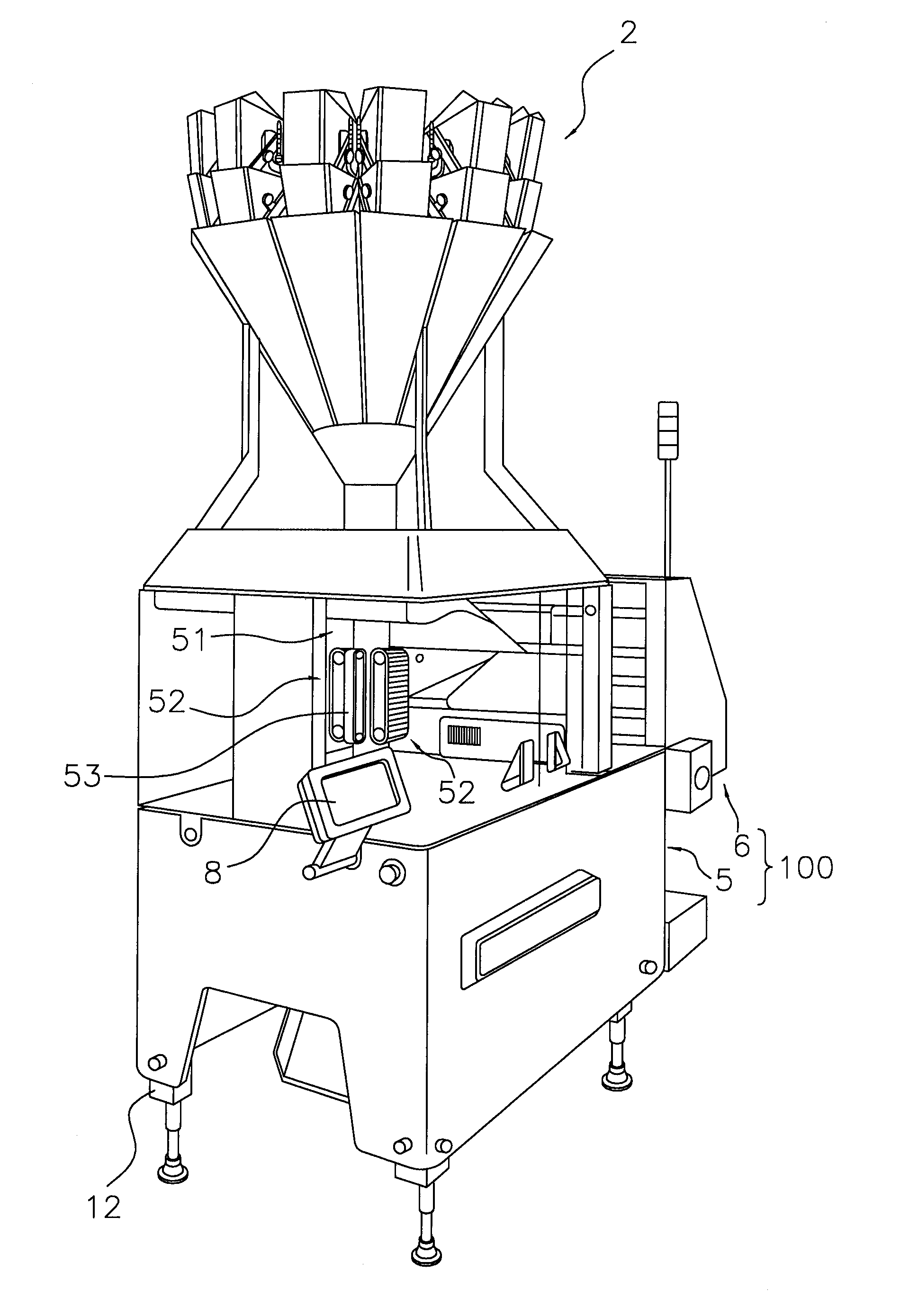
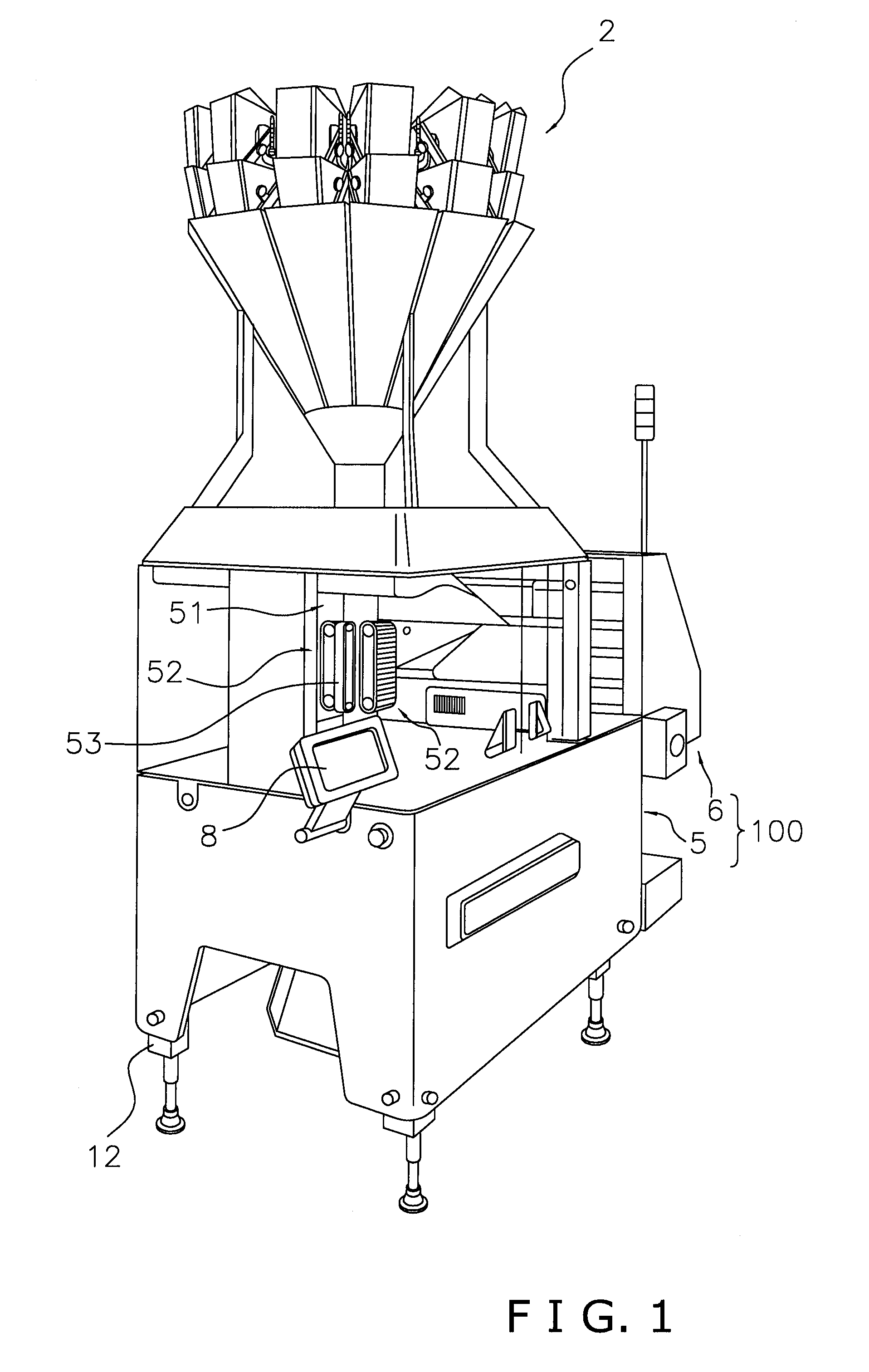
Bag making and packaging machine
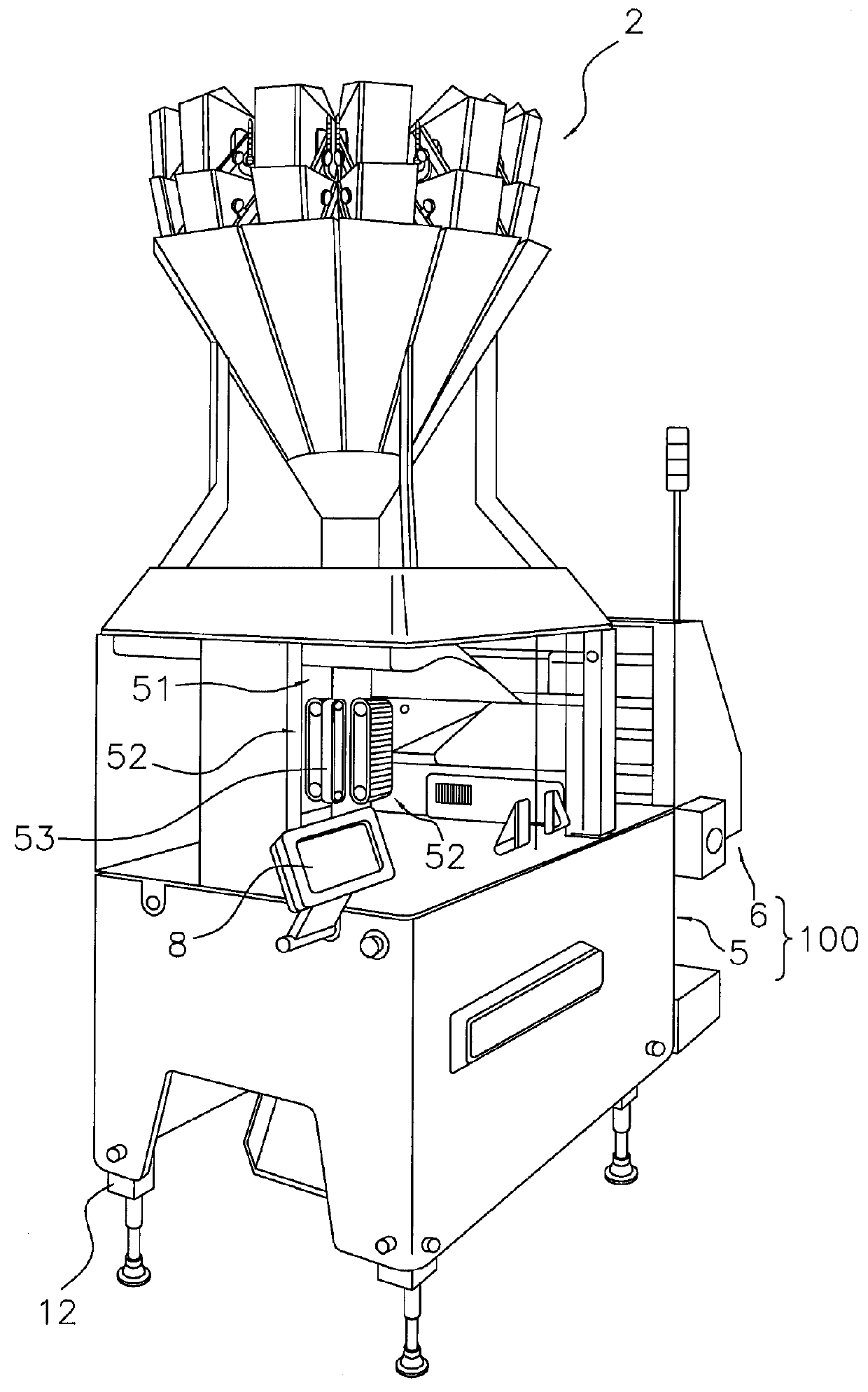
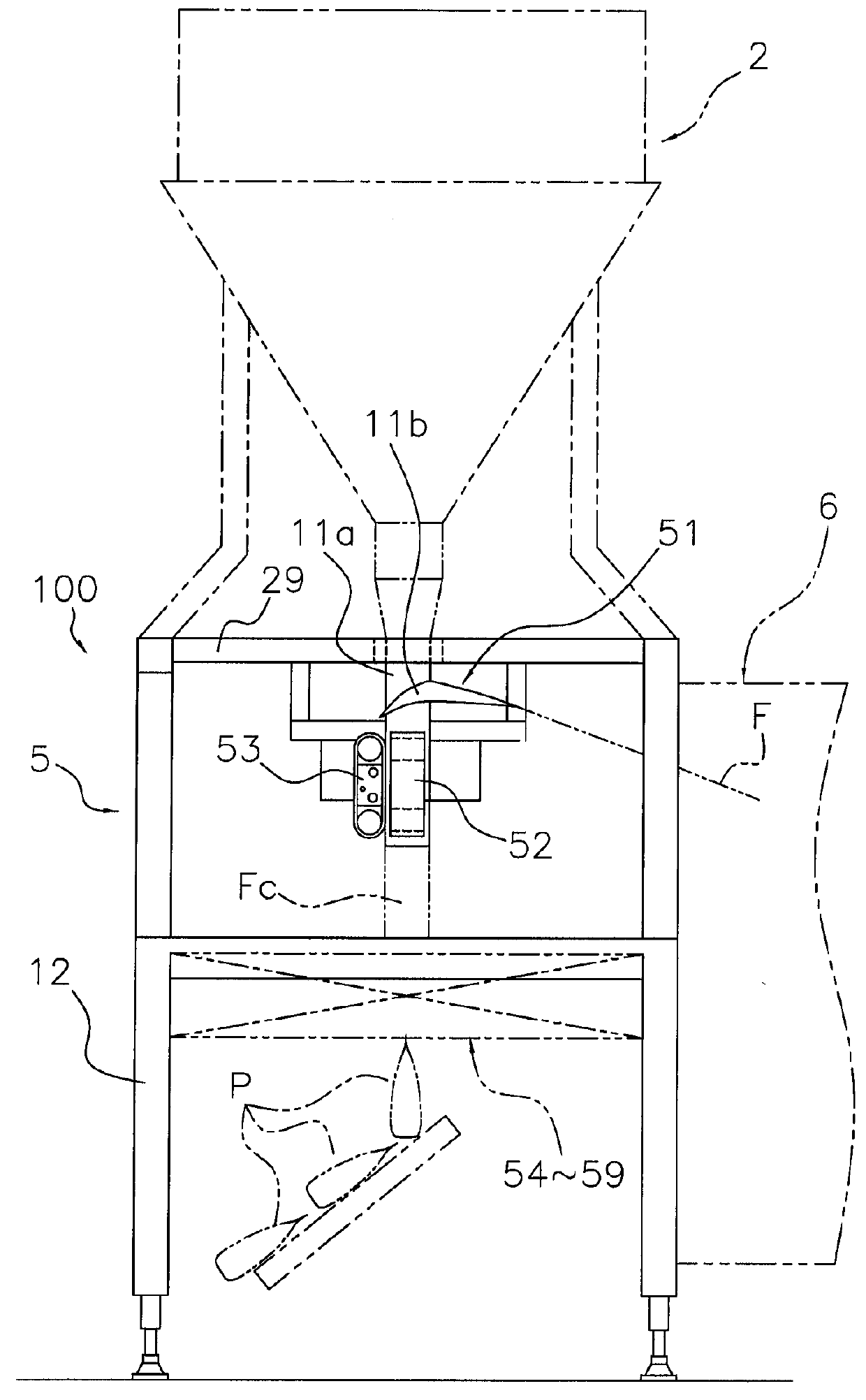
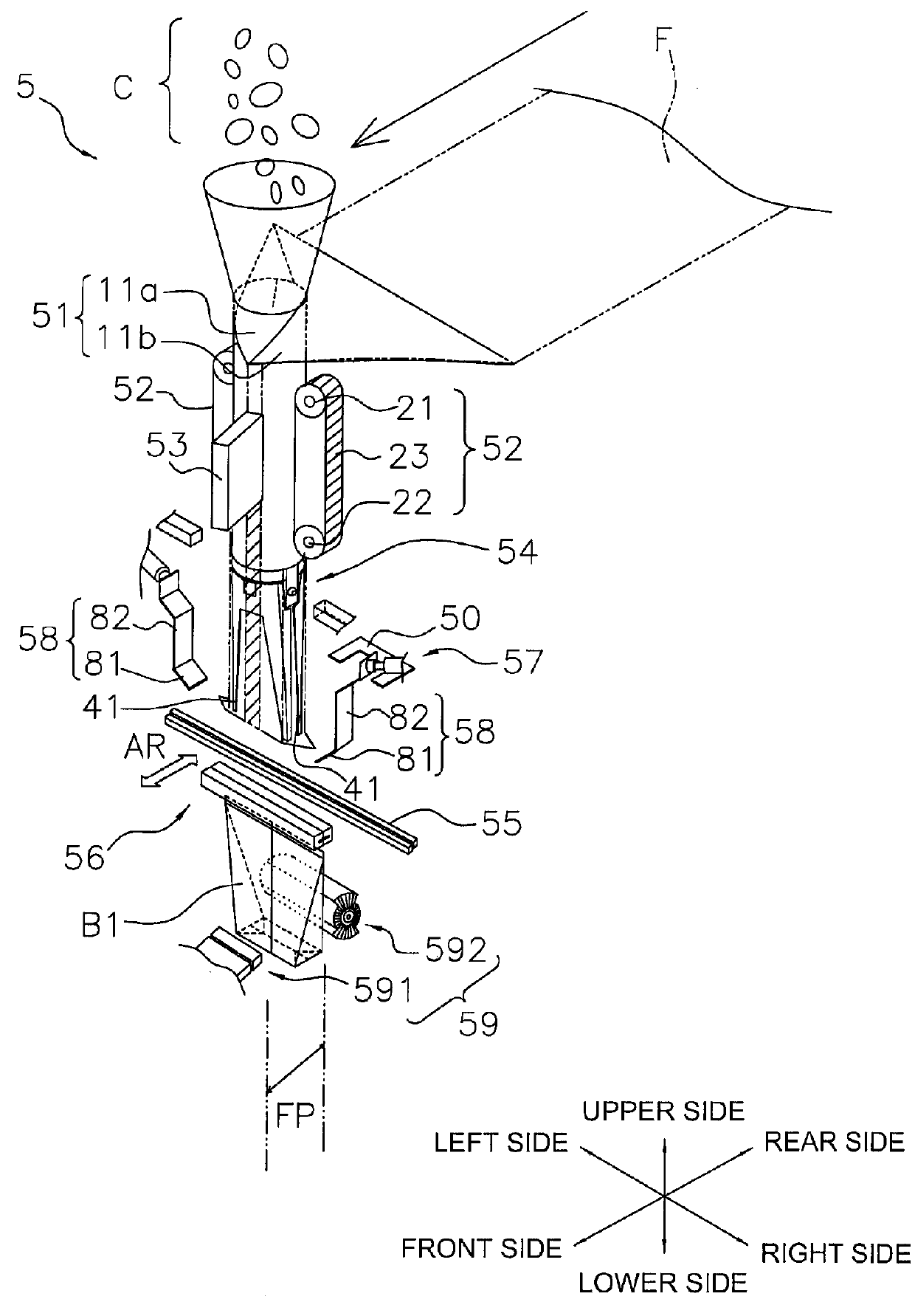
ActiveUS20130059709A1Effective vibrationImprove fill rateEnvelopes/bags making machineryPaper-makingPackaging machine
A bag making and packaging machine forms a first transverse seal portion in a packaging material formed in a tubular shape, fills the packaging material with articles, thereafter further forms a second transverse seal portion to make a bag, and allows the bag to fall, and is equipped with a vibrating mechanism. The first transverse seal portion is formed in a direction perpendicular to a conveyance direction of the packaging material. The vibrating mechanism tilts the packaging material to an outer side of a fall path of the bag and vibrates the packaging material after the packaging material has been filled with the articles and before the second transverse seal portion is formed.
Owner:ISHIDA CO LTD
Antibacterial, mosquito-and-insect-repellent functional loungewear
InactiveCN102628217ABroad-spectrum high-efficiency antibacterial effectReduce stayFibre treatmentStaphylococcus cohniiAedes aegypti
The invention relates to the field of clothing, in particular to a piece of antibacterial, mosquito-and-insect-repellent functional loungewear. The antibacterial, mosquito-and-insect-repellent functional loungewear is characterized in that silver ion antibacterial agent and permethrin mosquito-and-insect-repellent finishing agent are used for processing a textile, and the processing steps are fabric preprocessing, finishing solution preparation, padding, drying, preshrinking and clothing making. The antibacterial, mosquito-and-insect-repellent functional loungewear has a broad-spectrum, high-effective antibacterial effect on a variety of harmful bacteria, such as staphylococcus aureus, pneumobacillus, colibacillus, pseudomonas aeruginosa, candida albicans and trichophyton mentagrophytes, the bacteria inhibition rate of the antibacterial, mosquito-and-insect-repellent functional loungewear on staphylococcus aureus and other harmful bacteria still reaches more than 99 percent after the antibacterial, mosquito-and-insect-repellent functional loungewear is washed for 100 times, the stay and bite of mosquitoes are effectively reduced, the antibacterial, mosquito-and-insect-repellent functional loungewear has repelling and killing effects on various mosquitoes and insects, such as culex, aedes aegypti, tick and bedbug, and the loungewear made of the fabric has remarkable antibacterial, deodorizing, itch-relieving and mosquito-and-insect-repellent functions.
Owner:王建波
Method and equipment for producing flexible cloth possessing hot melt adhesive coating layer applied by wire mesh
InactiveCN1365862AAvoid tensionLow costRotary intaglio printing pressPattern makingMetallurgyDouble coating
The present invention relates to a method and apparatus for producing screen coatings containing hot-melt adhesives on flexible cloth materials such as woven, braided or non-woven fabrics, mainly used in garment processing, by screen embossing the paste forming a protective layer, then powdering with a hot melt adhesive and removing excess powder not adhering to the embossing of the paste, characterized in that the paste is filled into the grooves of an embossing roll or from the outside into the holes of a circular screen stencil, and then almost only this portion of the slurry filler is applied to the cloth and immediately separated from the filler. Afterwards, powdering with the hot-melt adhesive powder, removing excess powder not adhering to the embossing of the paste, and also including a drying and sintering process. The transfer of the slurry from the embossing roll to the coated substrate is accomplished by contact with a backing roll. In the second method, in the process of filling the holes of the screen stencil, the bottom smooth surface on the outside of the stencil is utilized, and the slurry is only filled from the outside without the slurry being pressed through the inside of the screen stencil. An internal doctor blade is provided, without slurry holes, and the slurry is transferred to the coated substrate with the assistance of a rubberized backing roll located below the screen stencil. The resulting double coat of protective layer and hot melt adhesive layer virtually completely covers the surface of the substrate, requiring very few coats while being free from backside seizure and having an even weight distribution. The amount of adhesive required is less and hardly any differences exist, thus reducing costs compared to all coating methods known hitherto, resulting in additional flexibility and good or even enhanced adhesion.
Owner:KUFNER TEXTILWERKE
Mosquito preventing fiber dyed yarn and its production process
The present invention discloses one kind of special functional dyed yarn and its production process, and is mosquito preventing blended dyed yarn containing mosquito preventing cotton fiber. The mosquito preventing blended dyed yarn features its capacity of repelling mosquito, compatibility with fabric finishing agent, high spinnability, etc. The mosquito preventing blended dyed yarn may be used widely in underwear, night dress, bedding, tent and other products.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HUAFU COLOR TEXTILE
Bag making and packaging machine
ActiveUS9227745B2Improve fill rateReduce bitesEnvelopes/bags making machineryPaper-makingEngineeringPackaging machine
A bag making and packaging machine forms a first transverse seal portion in a packaging material formed in a tubular shape, fills the packaging material with articles, thereafter further forms a second transverse seal portion to make a bag, and allows the bag to fall, and is equipped with a vibrating mechanism. The first transverse seal portion is formed in a direction perpendicular to a conveyance direction of the packaging material. The vibrating mechanism tilts the packaging material to an outer side of a fall path of the bag and vibrates the packaging material after the packaging material has been filled with the articles and before the second transverse seal portion is formed.
Owner:ISHIDA CO LTD
Artificial hybridization method for improving peony breeding fecundity
InactiveCN103155856AKeep activeSolve the problem that the flowering period of the hybrid combination does not meetPlant genotype modificationAnthesisPollen
The invention relates to an artificial hybridization method for improving peony breeding fecundity. The artificial hybridization method comprises the steps of: (1). collecting male parent pollen and carrying out refrigerated storage of the male parent pollen; (2). cutting off a part of a female parent petal, removing anther, dipping pollen germination fluid, smearing the pollen germination fluid on a female parent stigma, dipping pollen, smearing the pollen on the surface of the stigma, and then bagging a hybrid flower for isolation; (3). hanging a tag on a corresponding branch of a hybrid plant, and establishing a hybrid file; and (4). after a peony flowering phase, punching a through hole in the isolating bag, retaining the isolating bag until a seed develops to a certain degree, and harvesting timely. The peony artificial hybridization method provided by the invention effectively guarantees the pollen vitality through low-temperature storage of the pollen, thus solving the problem of flowering asynchronism of hybridized combination; the pollen germination fluid is manually smeared to create a pollen germination environment so as to improve the germination rate of the male parent pollen, and effectively overcome the obstacle before hybridized fertilization; and the punched isolating bag is retained, so that the functions of ventilation and rain prevention are achieved, simultaneously the intensity of sunlight direct radiation is reduced, the insect and bird bites are reduced, and the phenomena of early cracking and withering of capsules are reduced.
Owner:LUOYANG ACADEMY OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
Anion containing bamboo carbon fiber quilt with antibacterial and deodorizing functions and preparation method of bamboo carbon fiber quilt
InactiveCN106702572AImproves UV protectionImprove breathabilityCarbon fibresBlanketChemistryAntibacterial effect
The invention relates to an anion containing bamboo carbon fiber quilt with antibacterial and deodorizing functions and a preparation method of the bamboo carbon fiber quilt. The bamboo carbon fiber quilt comprises a core filler which is prepared from, by weight, 10%-20% of bamboo charcoal fiber, 10%-20% of cotton fiber, 10%-15% of nano-silver fiber and 50%-55% of anion viscose fiber. Air permeability and heat dispersion of the product are increased, and antibacterial effect is achieved.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU DEHUI TEXTILE CO LTD
Antibacterial functional medical textile
InactiveCN102912632ABroad-spectrum high-efficiency antibacterial effectReduce stayFibre treatmentEscherichia coliAedes aegypti
The invention relates to the clothing field, particularly to an antibacterial functional medical textile. The textile is characterized in that a silver ion antibacterial agent, a soil-releasing finishing agent and a permethrin mosquito repellent finishing agent are used for processing the textile to enable the textile to acquire antibacterial, soil-releasing and mosquito repellent functions. A processing method includes processing fabric into a semi-product for after-treatment after steps of pretreatment, dyeing or printing and the like; preparing a functional finishing agent which is antibacterial, soil-releasing and mosquito repellent; padding the working solution; drying; baking; packaging; and manufacturing leisure wear. The textile has broad-spectrum high-effect antibacterial functions on a plurality of harmful bacteria such as staphylococcus aureus, pneumobacillus, escherichia coli, pseudomonas aeruginosa, monilia albican and trichophyton mentagrophytes, the bacteriostasis rate of the textile for the harmful bacteria such as staphylococcus aureus after washed for 100 times can still reach above 99%, stay and biting of mosquitoes can be reduced effectively, repellent and contact toxicity functions can be performed on various mosquitoes such as culex, Aedes aegypti, ticks and bugs, and the leisure wear made of the textile is provided with obvious antibacterial, deodorant, itching relieving and mosquito repellent functions.
Owner:王建波
Novel mosquito-repellent cooling hat
ActiveCN103404992AReduce bitesRealize the effect of heat dissipation and coolingHatsHeadwear capsCooling effectEngineering
The invention relates to the field of daily necessities and particularly relates to a novel mosquito-repellent cooling hat. The novel mosquito-repellent cooling hat comprises a hat casing and a fan; an opening is formed in the top of the hat casing; the fan is arranged inside the opening, and the fan blows the air towards the inside of the hat casing. By the aid of the novel mosquito-repellent cooling hat, the cooling effect can be achieved, and mosquitoes can not get close to the face and the neck of a user, so that mosquito bites of the face and the neck of the user are reduced.
Owner:韩宝东
Injection molding sprue cutting device
The invention discloses an injection molding sprue cutting device. The device comprises a base; the base is horizontally arranged; a bracket is arranged on the base; a cylinder is arranged on the bracket, and includes a piston rod; the piston rod is vertically arranged; an upper tool bit is arranged at the bottom end of the piston rod; a limiting plate is mounted on the bracket, is vertically mounted, and is positioned on one side of the upper tool bit; a limiting groove is formed in the limiting plate, and is used for limiting the position of an injection part to be cut; a positioning cushion block is mounted on the base, and is provided with a lower tool bit; the position of the lower tool bit is corresponding to the position of the upper tool bit; the cylinder is connected with a controller; the controller is used for controlling the extension speed of the piston rod; and a switch button is mounted on the base, and is connected with the cylinder. The cutting device has the beneficial effects of smooth cutting and prominent reduction of the reject ratio.
Owner:INJELIC PRECISION MOLD & PLASTICS
Method for increasing bumblebee commodity group propagation speed
ActiveCN104886007AShorten the timeReduce reproductive costsAnimal husbandryBumblebeePropagation time
The invention discloses a method for increasing bumblebee commodity group propagation speed. The method comprises the following steps: preparing bee species and queen bee, preparing propagation environment and feed, inducing the queen bee to lay eggs, performing transfer box feeding to obtain a bumblebee commodity group, packaging the bumblebee commodity group, and adding worker bees into a feeding box in which the queen bee lives after inducing the queen bee to lay eggs and before performing transfer box feeding. The method for increasing bumblebee commodity group propagation speed provided by the invention shortens the time for propagating single queen bee into the commodity group to 55-65 days, which is shortened by 15 days in comparison to the ordinary propagation time of 70-80 days; the propagation cost is reduced by 20%.
Owner:DRY LAND FARMING INST OF HEBEI ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
Mosquito-repelling sachet and production method thereof
InactiveCN106417396AEnhanced anti-mosquito effectImprove aroma profileBiocidePest repellentsHedera helixMosquito bite
The invention provides a mosquito-repelling sachet and a production method thereof. The mosquito-repelling sachet has the advantages that the sachet is outstanding in mosquito-repelling effect by improving components in the sachet; the nature flavor and channel tropism of the components show that only camphor wood and camphor in selected natural medicinal materials have a definite mosquito-repelling effect, auxiliary components such as folium artemisiae argyi and Agastache rugosus are added on the basis of the camphor wood and the camphor serving as the main components, the effects of the components are synergically coordinated to increase the mosquito-repelling effect; especially when components such as Drymoglossum piloselloides Presl, hedera helix and Lysimachia foenum-graecum Hance are added, the mosquito-repelling effect is further enhanced, the fragrance feature of the sachet is improved favorably, and the use effect of the sachet is increased; compared with chemical mosquito-killing products, the traditional Chinese medicine sachet has a long history, does not pollute indoor environments, has unique advantages of purifying air, lasting effect, carrying convenience and improving sub-health status of human bodies, and is a powerful approach for preventing mosquito bite.
Owner:天承南运(天津)科技有限公司
Silk quilt containing negative ions and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN106724473AImprove permeabilityAdjust pHArtificial filaments from viscoseBed-coversPhysical chemistryViscose
The invention relates to a silk quilt containing negative ions and a manufacturing method thereof. The silk quilt containing negative ions comprises a quilt core filler. The quilt core filler is manufactured from, by weight, 45-50% of pure natural silk and 50-55% of negative ion viscose. The silk quilt manufactured through the method is stored for a long time, and the concentration of released negative ions is 500 / cm<3> or above; the body temperature and body friction can be well utilized, the negative ion release amount in silk is increased, and the mulberry silk can store negative ions for a long time, so that the concentration of the negative ions is kept to be large, and the wide application prospect is achieved.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU DEHUI TEXTILE CO LTD
Slide switch
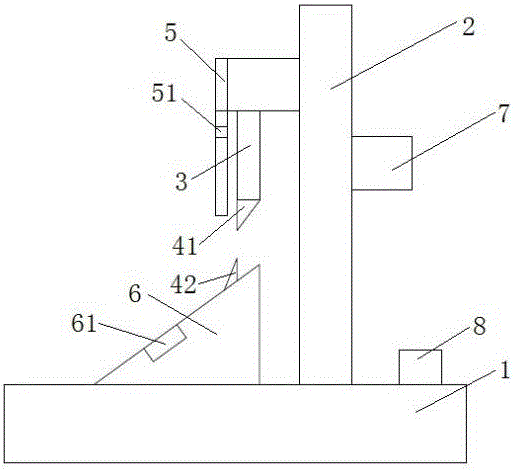
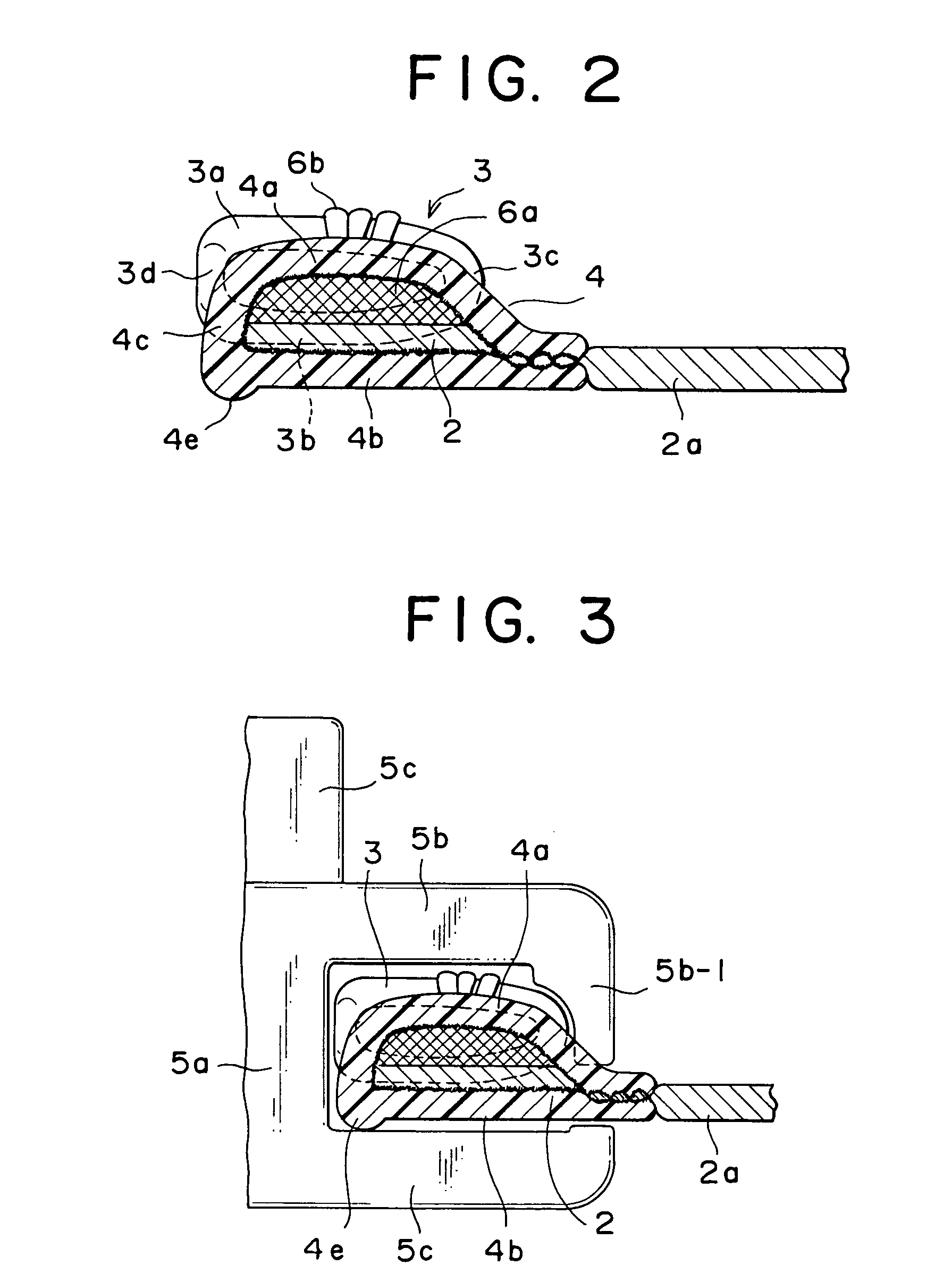
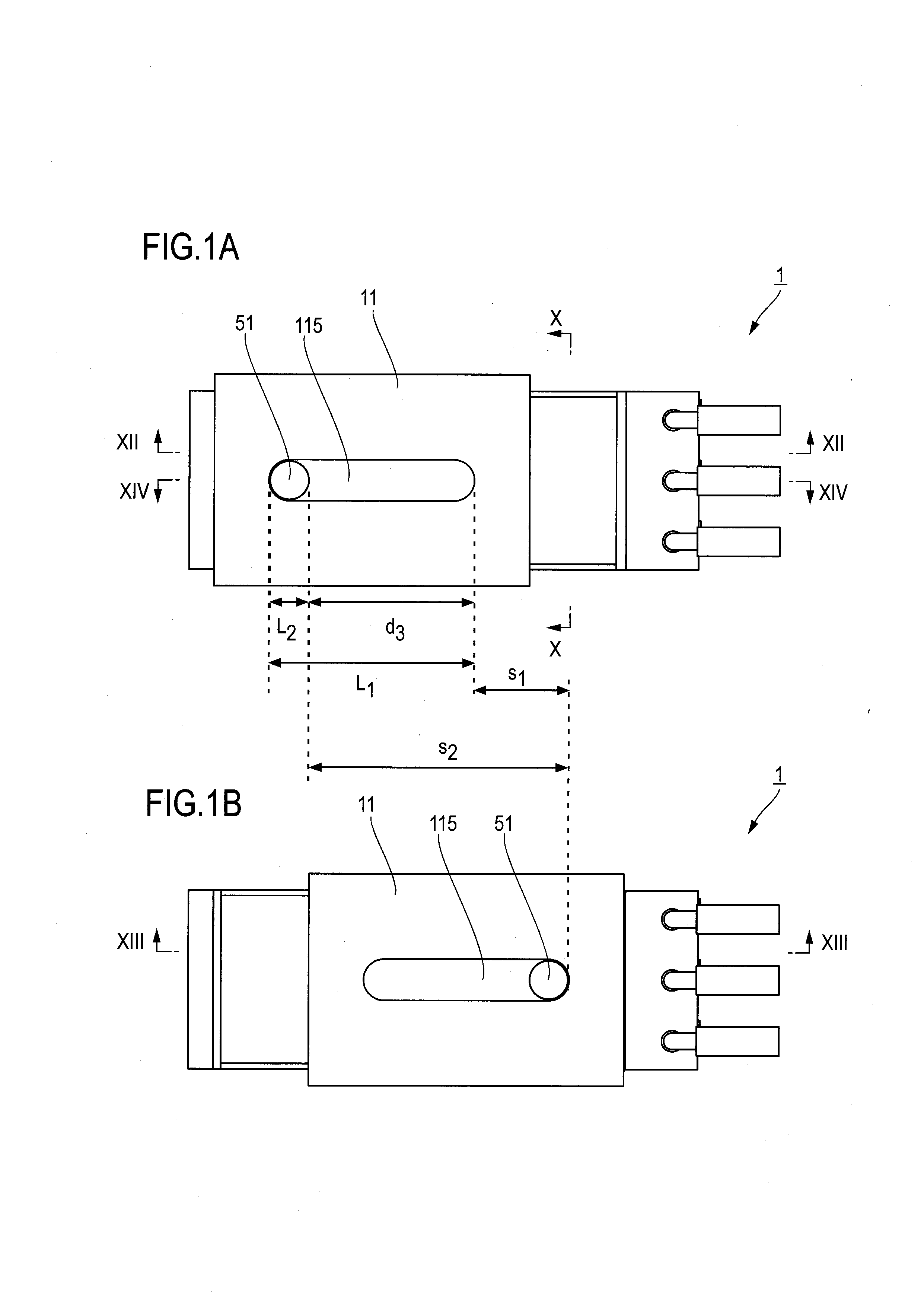
InactiveUS8921723B2Reduce entranceReduce bitesBelt control systemsContact operating partsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:HOSIDEN CORP
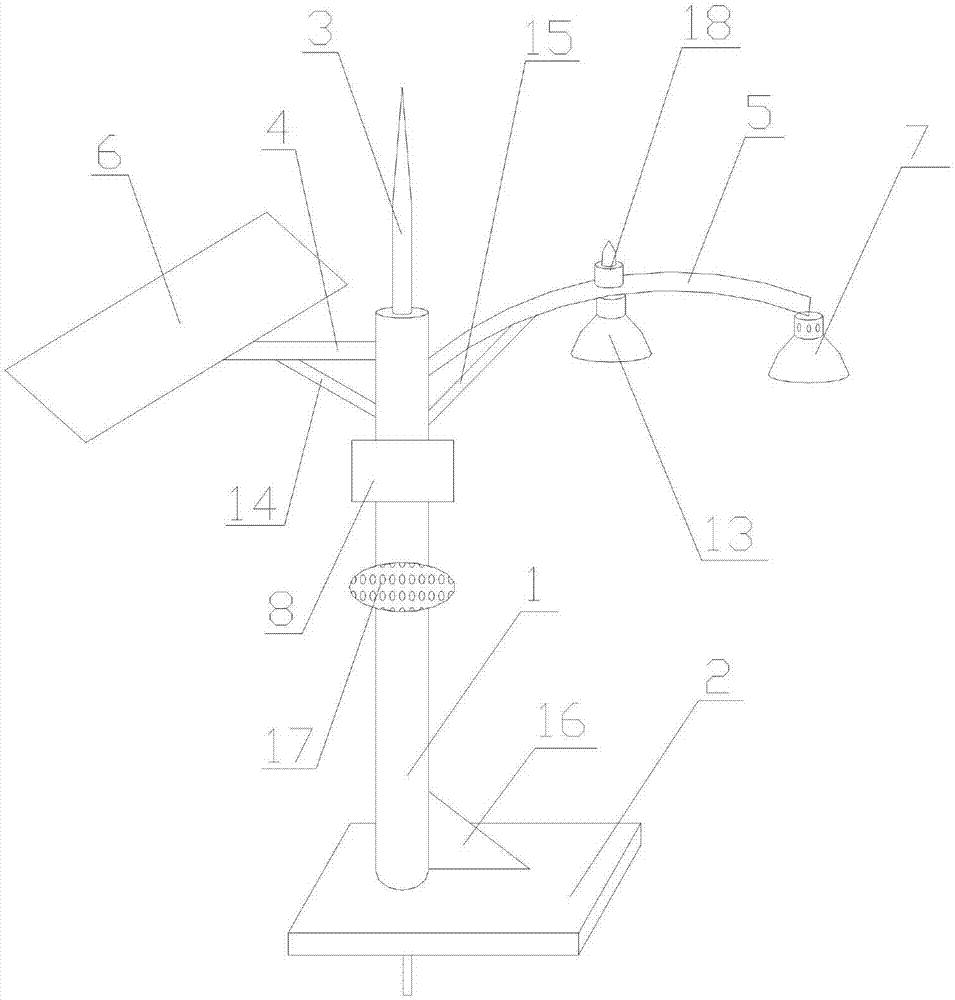
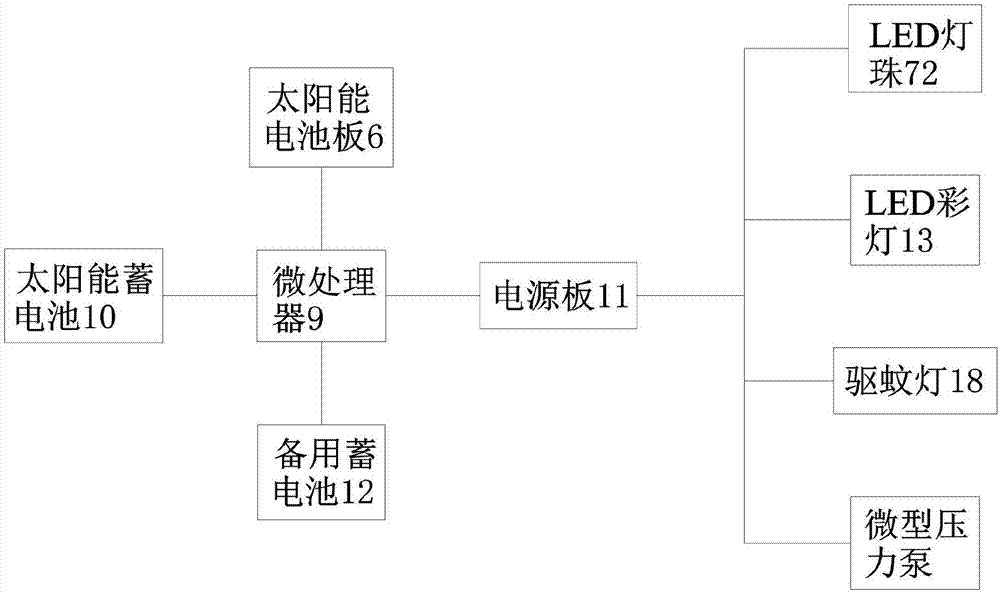
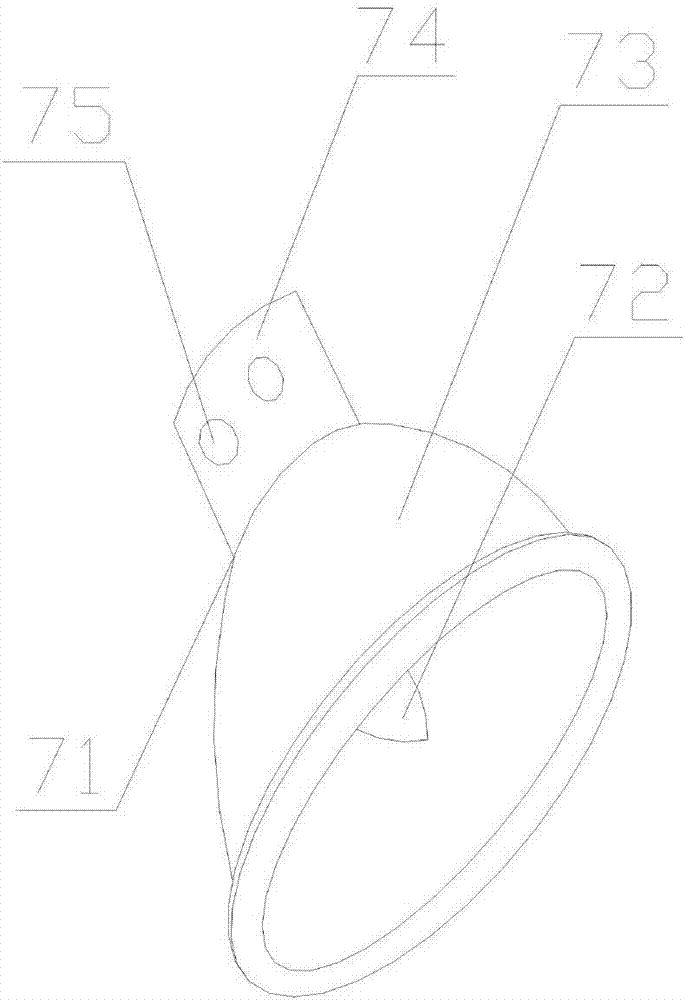
Safe type efficient energy-saving anti-lightning street lamp with mosquito repelling function
InactiveCN107101168AAvoid damageSimple structureMechanical apparatusLighting support devicesPlastic materialsLightning rod
The invention discloses a safe type efficient energy-saving anti-lightning street lamp with a mosquito repelling function. By adoption of the safe type efficient energy-saving anti-lightning street lamp, the problems that street lamps of the prior art are poor in lightning protection effect, high in energy consumption and insufficient in solar power supply are solved. The street lamp comprises a lamp pole, a lamp pole base, a lightning rod, a first cross rod, a second cross rod, a solar cell panel, an LED lamp and a control box. The control box is internally provided with a microprocessor, a solar storage battery and a power panel. The lamp pole base is internally provided with a standby storage battery. The second cross rod is provided with an LED lantern and a mosquito repelling lamp. The LED lamp comprises a lampshade and LED lamp beads. The lampshade comprises a reflection cover and a mounting base which is provided with cooling holes. The reflection cover is provided with an annular flanging. The lamp pole is provided with a humidification device which is provided with a micro pressure pump and vapor spray holes. The area of the solar cell panel is 0.9 square meter, and the solar cell panel comprises a tempered glass layer, an E / VAC layer and a battery piece layer. The whole lampshade is made from flame retardant ABS plastic materials. The safe type efficient energy-saving anti-lightning street lamp is simple in structure and scientific and reasonable in design, saves energy, protects the environment and has humidification and mosquito repelling functions.
Owner:CHENGDU RANUS TECH CO LTD
High-efficiency rolling mill oil film bearing oil composition
The invention discloses a high-efficiency rolling mill oil film bearing oil composition.The composition is prepared from, by weight, 1-85% of API first-type deep refined basic oil, 14.47-92% of API second-type hydrogenation mineral oil, 0.5-3.0% of high-efficiency complexing agent, 0.01-2.0% of anti-wear reagent at extreme pressure, 0.01-1.0% of demulsifier and 0.01-1.0% of pour point depressant.The composition is prepared by using API first-type deep refined basic oil and API second-type hydrogenation mineral oil as the basic oil, selecting import high-efficiency complexing agent, compounding anti-wear reagent at extreme pressure, demulsifier and pour point depressant through scientific matching and optimal designing; the composition has excellent anti-wear performance at extreme pressure and excellent oil-water separation performance, scratching and meshing between toothed surfaces can be effectively reduced, sintering during startup is prevented, the actual service life of an oil product is greatly prolonged, maintenance expenditures are greatly reduced, the service life of a machine is prolonged, and huge resource waste caused by unexpected shutdown is reduced.
Owner:KASONG SCI & TECH
Textile anti-mosquito, moisture-proof and antibacterial finishing agent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109082890AImprove use valueReduce mosquito bitesBiochemical fibre treatmentDipropylene glycolBiting
The invention discloses a textile anti-mosquito, moisture-proof and antibacterial finishing agent and a preparation method thereof, and relates to the technical field of textile finishing. The textileanti-mosquito, moisture-proof and antibacterial finishing agent comprises geranium, tuberose, lavenders, wind medicated oil, chitosan powder, ammonium dihydrogen phosphate, eutrema yunnanense, montmorillonite clay drying agents, silica gel, fiber drying agents, ethyl alcohol, dipropylene glycol dimethyl ether and clear water. According to the batching ratio, raw materials are taken and processedto prepare the textile anti-mosquito, moisture-proof and antibacterial finishing agent by the preparation method of the finishing agent. By the aid of the technical scheme, the finishing agent has theadvantages that the finishing agent is high in use value, a textile fabric is coated with the finishing agent, biting of mosquitoes can be decreased, the finishing agent has a sterilization function,the textile fabric is not easily damped, physical health of people can be protected, ever-increasing demands of people are met, and popularization of the textile fabric is facilitated.
Owner:SHAOXING KEQIAO HAOZHI HUAJU TEXTILE PROD DESIGN CO LTD
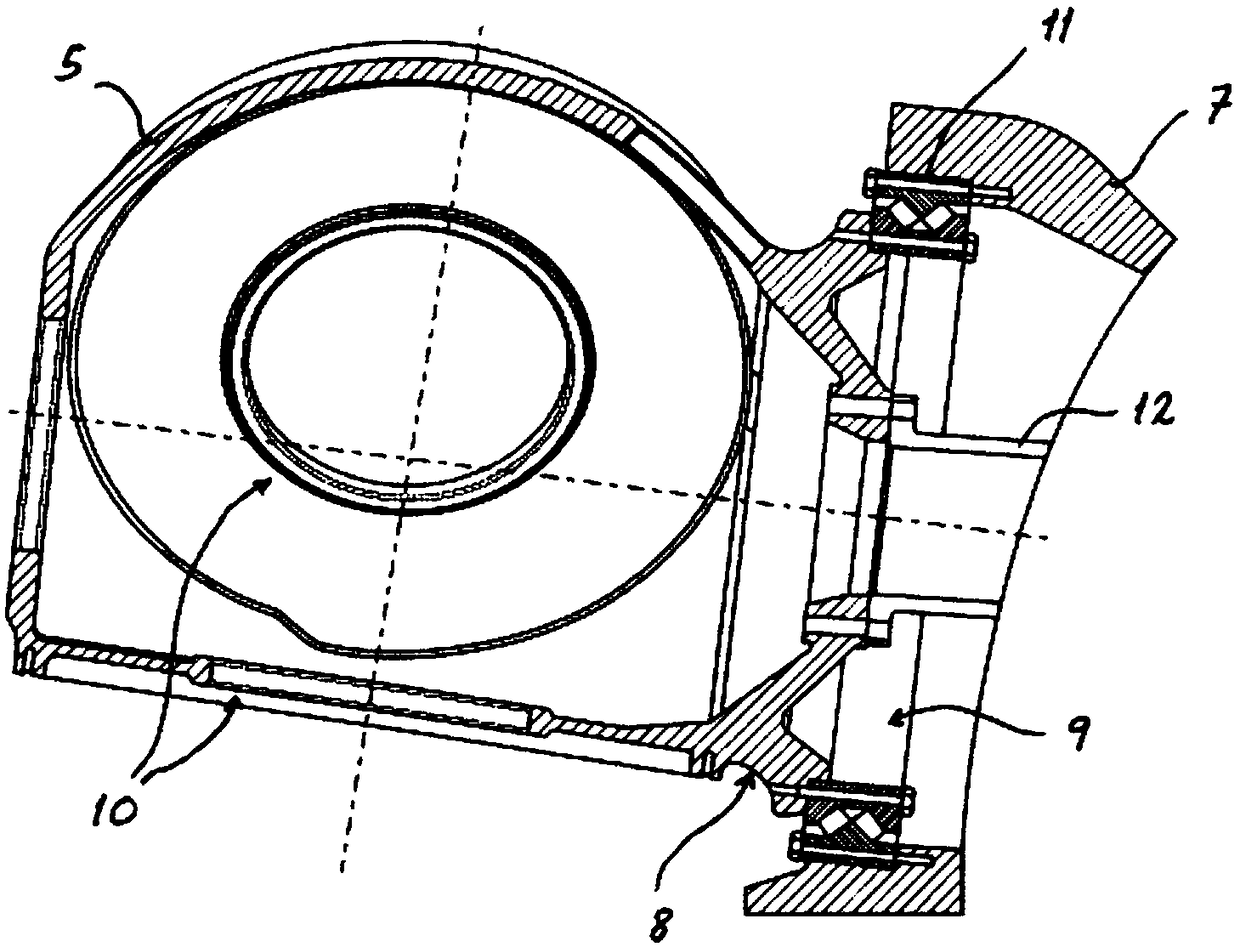
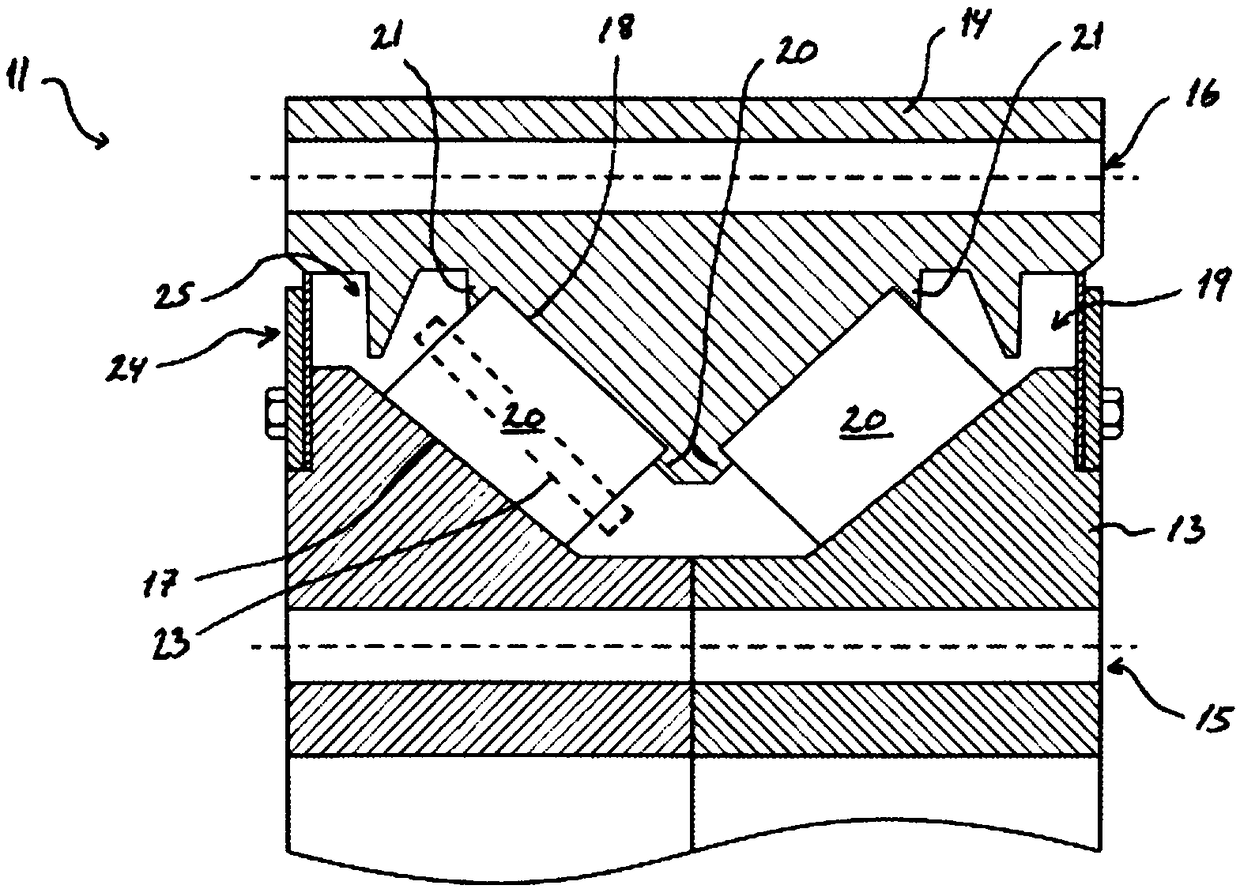
Wind turbine comprising a moment bearing
The invention relates to a wind turbine comprising a rotor with a hub, a nacelle with a mainframe, and a moment bearing arranged between the hub and mainframe. The moment bearing comprises an inner ring and an outer ring between which at least one row of rotatable bearing elements is arranged. The individual bearing elements are substantially held in place by a cage located between the inner and outer rings. The outer ring further comprises a first and a second shoulder for transferring axial loads in both directions from the bearing elements to the outer ring. The moment bearing further comprises at least a first seal element configured to close off the chamber de- fined by the inner and outer rings, wherein said first seal element contacts a contact surface on the outer ring. This provides an improved heat transfer where most of the generated heat is transferred to the mainframe.
Owner:YUANJIAN WIND POWER JIANGYINENVISION ENERGY CO LTD
Slide fastener
A stopper portion has a minute protrusion on part of an outer peripheral face except a side face in the length direction of a fastener tape. This protrusion is a rib-like protrusion extended linearly in the length direction of the fastener tape formed on a vertex of the surface of a bent portion, a protrusion extended so as to be expanded in a curved shape in the length direction of the fastener tape or a rib-like protrusion protruded along a boundary portion between the bent portion of the stopper portion and a bottom face thereof. Existence of this protrusion not only reduces a sliding resistance when the slider is started but also eliminates prickly feeling and feeling of disharmony originating from a shape of an upper stopper which is a kind of the conventional stopper portion.
Owner:YKK CORP
Slide Switch
InactiveUS20130175146A1Substance reductionReduce entranceBelt control systemsContact operating partsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A slider is slidably held in a body and is pushed by insertion of an object to slidingly move. Terminals are provided with fixed contact points disposed on a surface, facing the slider, of the body along a sliding movement direction. The armature is attached to the slider and is provided with moving contact points that slide on a fixed contact point disposition surface of the body in association with sliding movement of the slider. The slider has an armature mounting surface with a side wall protrudingly formed in one end in the sliding movement direction. The body has a facing surface facing an end surface of the side wall in an entire range of sliding movement. At least any one of an end in the sliding movement direction of the end surface of the side wall and an end in the sliding movement direction of the facing surfaces of the body has a foreign substance elimination groove formed therein.
Owner:HOSIDEN CORP
Peony seed oil-containing skincare essential oil, and preparation method and cosmetics thereof
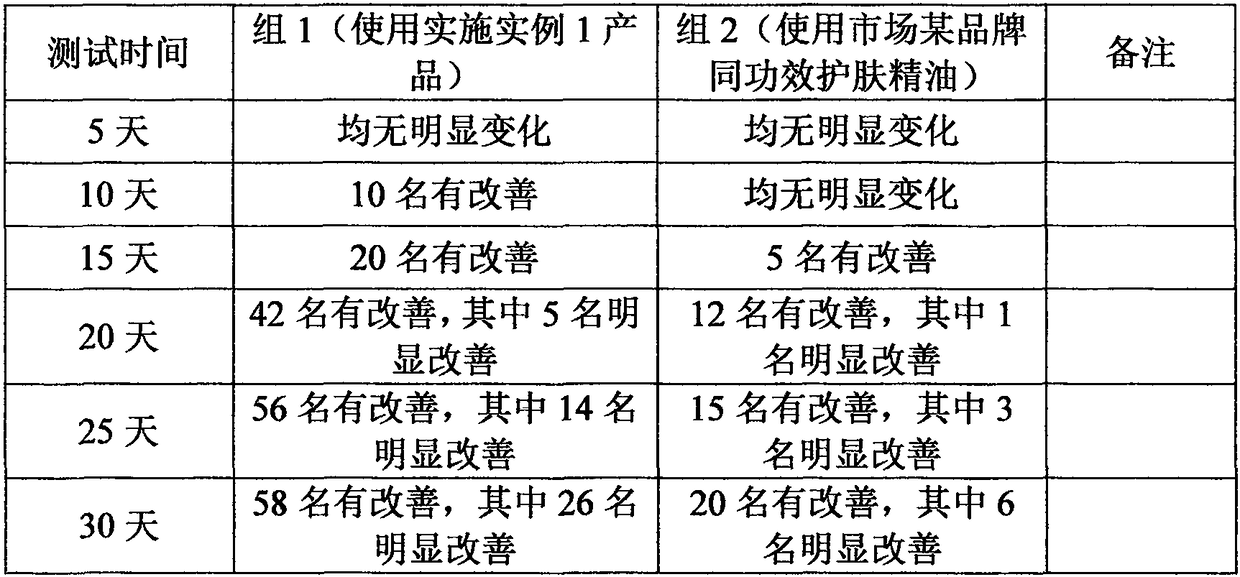
PendingCN108309828AReduce bitesRelieve feverCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsWater bathsCoconut tree
The invention belongs to the technical field of Palmae, such as date palm or coconut tree or Saw Palmetto Berry, and discloses a peony seed oil-containing skincare essential oil, and a preparation method and cosmetics thereof. The peony seed oil-containing skincare essential oil comprises, by weight, 70-90 parts of peony seed oil, 1-5 parts of Boswellia carteri essential oil, 1-15 parts of vitaminE, 1-5 parts of squalane and 0.1-1 part of peppermint essential oil. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding the Boswellia carteri essential oil and peppermint essential oil intoa beaker, placing the beaker in a water bath, and stirring and mixing the essential oils for later use; adding the peony seed oil and vitamin E into a beaker, and stirring the peony seed oil and vitamin E for later use; pouring the mixed Boswellia carteri essential oil and peppermint essential oil into the beaker containing the peony seed oil and vitamin E; pouring the squalane into the beaker containing the Boswellia carteri essential oil, peppermint essential oil, peony seed oil and vitamin E, stirring all above materials, and pouring the obtained mixture into a jacketed beaker after the mixing is completed; and introducing cooling water to the jacket layer of the jacketed beaker containing the obtained mixed liquid, and performing ultrasonic treatment to obtain an ultrasonic mixed essential oil which is the peony seed oil-containing skincare essential oil. The peony seed oil-containing skincare essential oil is a purely natural formula, and contains no chemical substances.
Owner:恒天量子(厦门)科技有限公司
Solar intelligent night fishing lamp detachably connected with rotary seat
InactiveCN107842808AAvoid the hassle of not being able to charge your fishing lightsSolve charging troubleLighting support devicesElectric circuit arrangementsLight energyEmergency light
The invention discloses a solar intelligent night fishing lamp detachably connected with a rotating seat, which comprises a housing, an LED lamp board, a lampshade, a condenser cover and lamp beads, an LED lamp board is arranged inside the housing, and the LED One side of the lamp board is provided with lamp beads, the outside of the lamp beads is provided with a condenser cover, one side of the housing is detachably connected to a lamp shade, the upper end of the housing is fixedly connected to a solar panel, and There is an anti-mosquito lamp, an emergency light is provided on one side of the anti-mosquito lamp, and a handle is provided on the other side of the solar panel. The invention is equipped with a solar panel, which can convert light energy into electrical energy, and charge the storage battery in the case of sufficient sunlight during the day, avoiding the trouble that fishing friends cannot charge the fishing lamp in other places. When fishing friends have a safety accident in the wild, they can turn on the emergency distress light to call for help. The utility model has a simple structure and is convenient to use.
Owner:福品汇(广东)食品开发有限公司
Floating-sinking net cage for deep sea culture
InactiveCN112167134AImprove structural strengthImprove protectionClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaBuoyant flowDeep sea
The invention relates to the technical field of marine culture equipment, and discloses a floating-sinking net cage for deep sea culture. The floating-sinking net cage comprises a central support column and an inner net, the bottom of the central support column is movably connected with a sliding device in a sleeved mode, a first supporting device is movably connected to the position, located above the sliding device, on the central support column, and the top of the central support column is fixedly connected with a second supporting device. Through the arrangement of the central support column, the first supporting device and the second supporting device, the net cage has a middle supporting structure, the structural strength of the net cage is greatly enhanced, and the net cage can resist higher-level stormy waves and can adapt to the changeable weather of deep sea and the rapid change of ocean currents in a water area; and meanwhile through the arrangement of a first solenoid valveand a second solenoid valve, the buoyancy of the net cage can be adjusted, the net cage sinks into the seabed before typhoon comes and is prevented from being in direct contact with stormy waves, then the net cage is protected, the protection performance of the net cage is improved, and the service life is prolonged.
Owner:李卫
Processing technology of single-layer wireless charging coil carrier plate
PendingCN113380529AImprove reliabilityImprove efficiencyCoils manufactureCopper foilInductive charging
The invention discloses a processing technology of a single-layer wireless charging coil carrier plate. The processing technology comprises the following steps: preparing a carrier plate provided with an auxiliary substrate and two ultrathin carrier copper foils, wherein the two two ultrathin carrier copper foils are respectively laminated on the front surface and the back surface of the auxiliary substrate, and are respectively provided with a carrier copper foil and an ultrathin copper foil detachably arranged on one surface of the carrier copper foil; pasting dry films on the two ultrathin copper foils, and forming a circuit pattern after exposure and development; electroplating circuit copper layers on the two ultrathin copper foils according to the circuit pattern, then removing the dry films, and printing resin layers on the two circuit copper layers to obtain a second intermediate plate; splitting the second intermediate plate along the joint of the two ultrathin copper foils and the two carrier copper foils to obtain two third intermediate plates; and etching off the ultrathin copper foils on the third intermediate plates to obtain an effective plate of the single-layer wireless charging coil carrier plate. According to the invention, the processing technology is novel and high in production efficiency, the thickness of the manufactured single-layer wireless charging coil carrier plate is small, the reliability is good, and the coil pattern shape and wiring are not limited.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVISION ELECTRONICS CO LTD
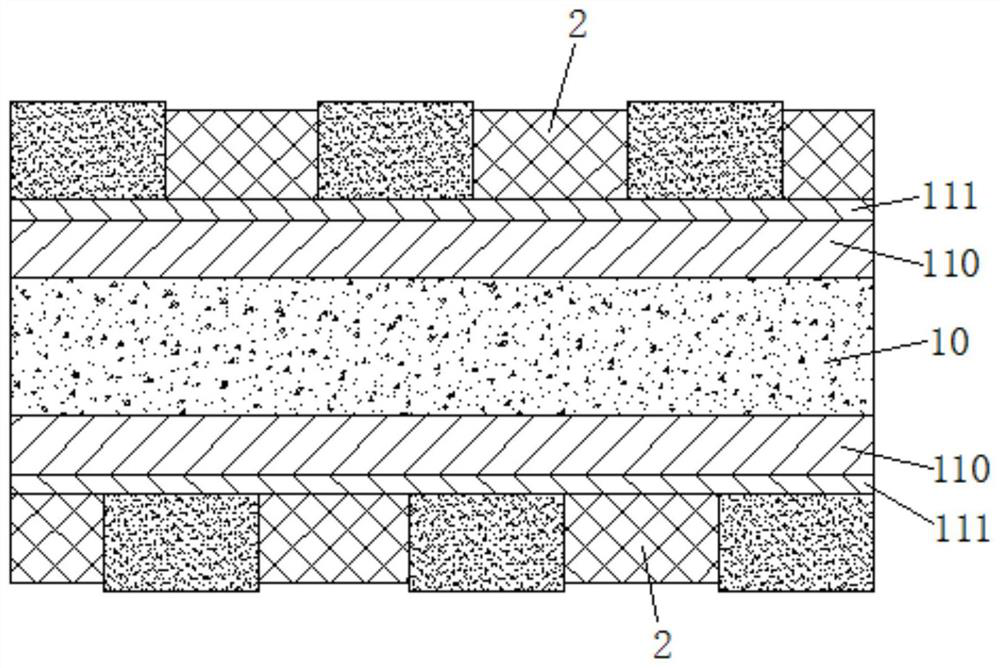
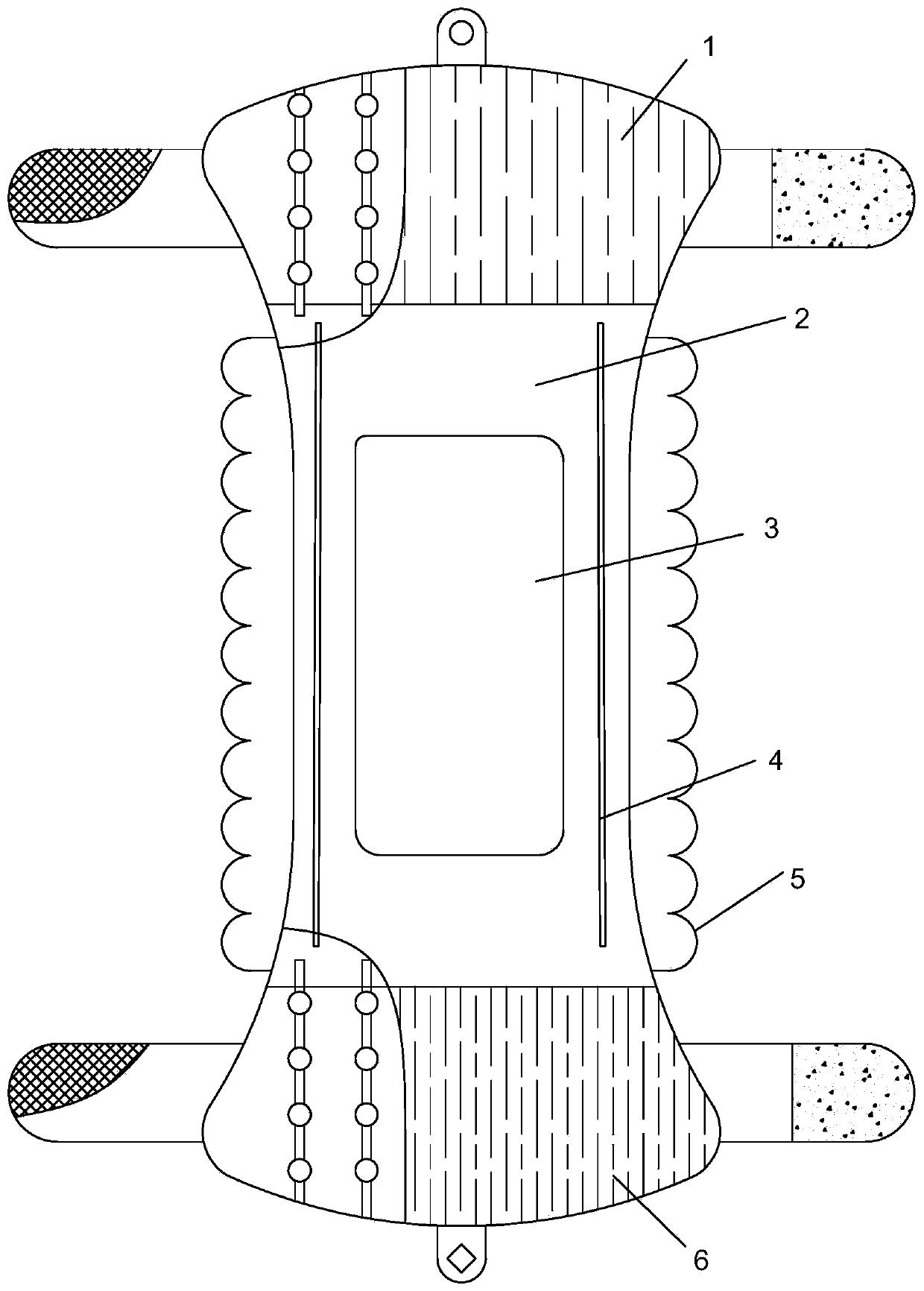
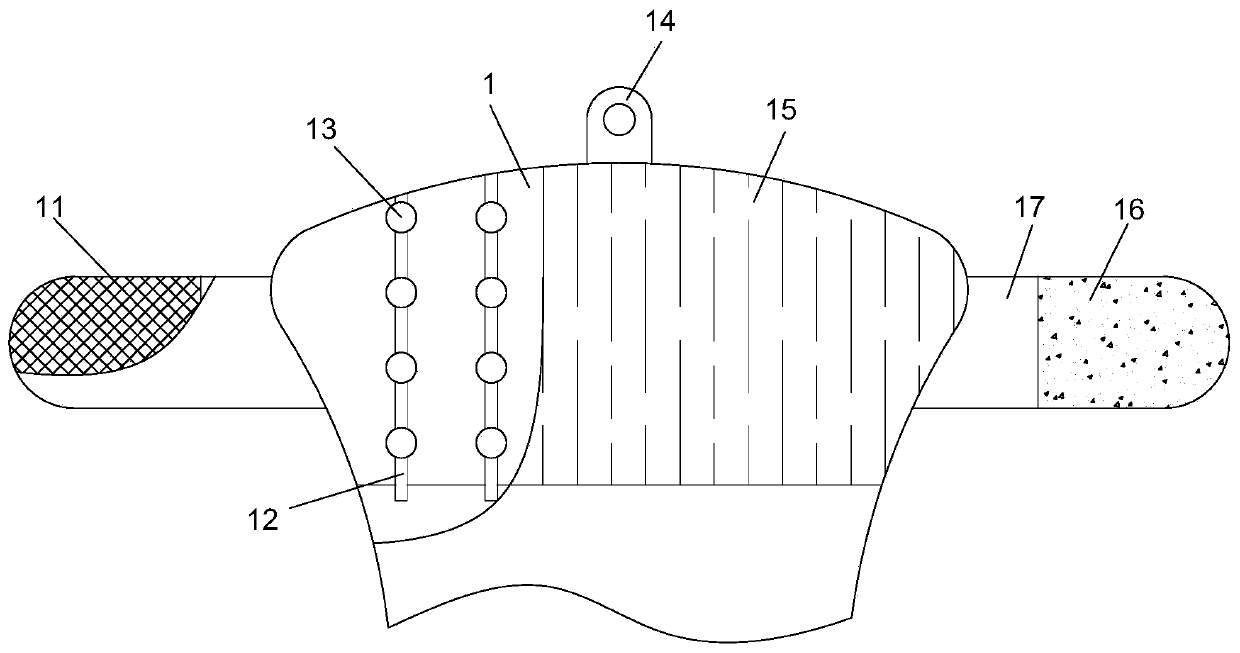
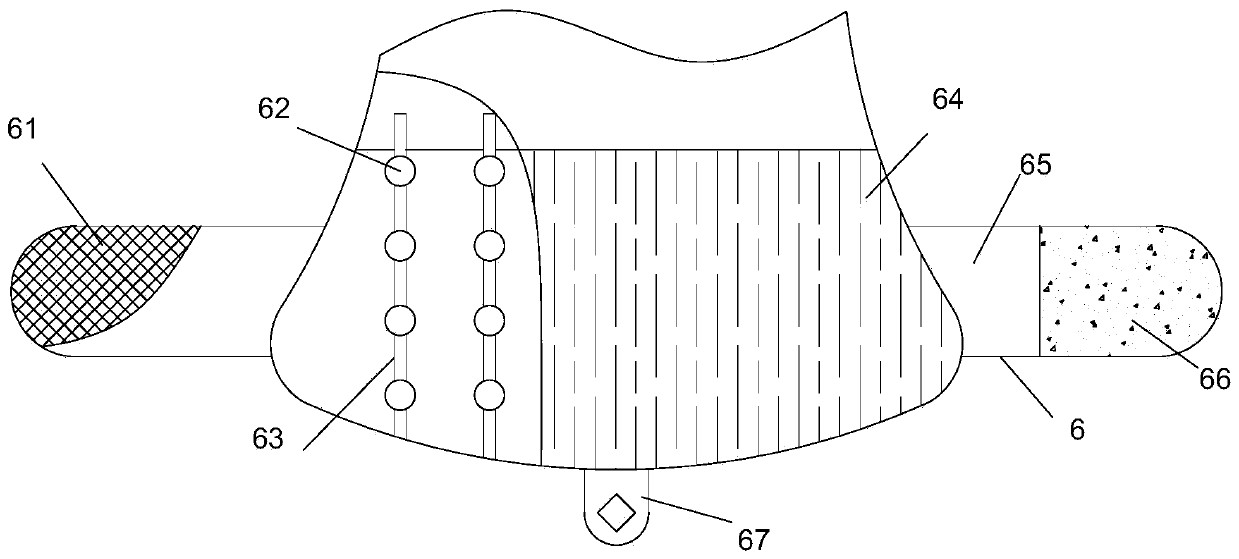
Baby diaper
PendingCN111265366ASpeed up circulationImprove cooling effectAbsorbent padsAnimal repellantsEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention relates to the field of diapers, in particular to a baby diaper. The baby diaper comprises a baby diaper body and a front elastic band mechanism. The front elastic band mechanism is connected with one end of the baby diaper body; the front elastic band mechanism comprises a first hook-and-loop fastener hook face, a first soft silica gel air guide pipe, a first elastic silica gel ball, a front elastic band, a first hook-and-loop fastener loop face and a first side piece. The front elastic band and one end of the baby diaper body are integrally formed, two symmetrically-arranged first side pieces are further integrally formed on the front elastic band, the outer surface of one first side piece is connected with the first hook-and-loop fastener hook face in a sewn mode, and theinner surface of the other first side piece is connected with the first hook-and-loop fastener loop face in a sewn mode. A plurality of mounting grooves which are uniformly distributed and provided with openings in one ends are formed in the front elastic band, and openings of the mounting grooves deviate from the baby diaper body. The baby diaper provided by the invention has the advantages of high air permeability and mosquito repelling effect.
Owner:张德柳
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com