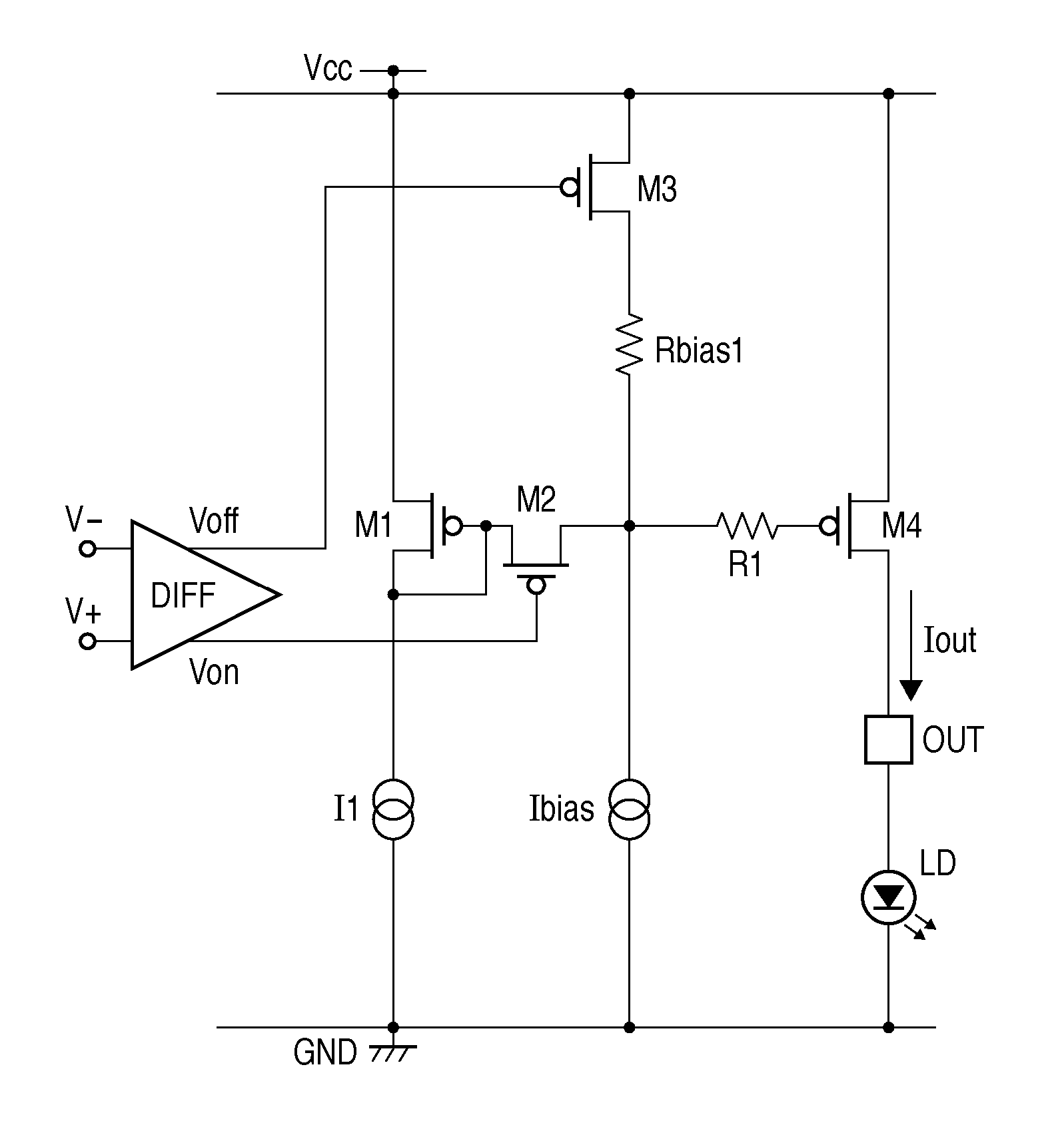
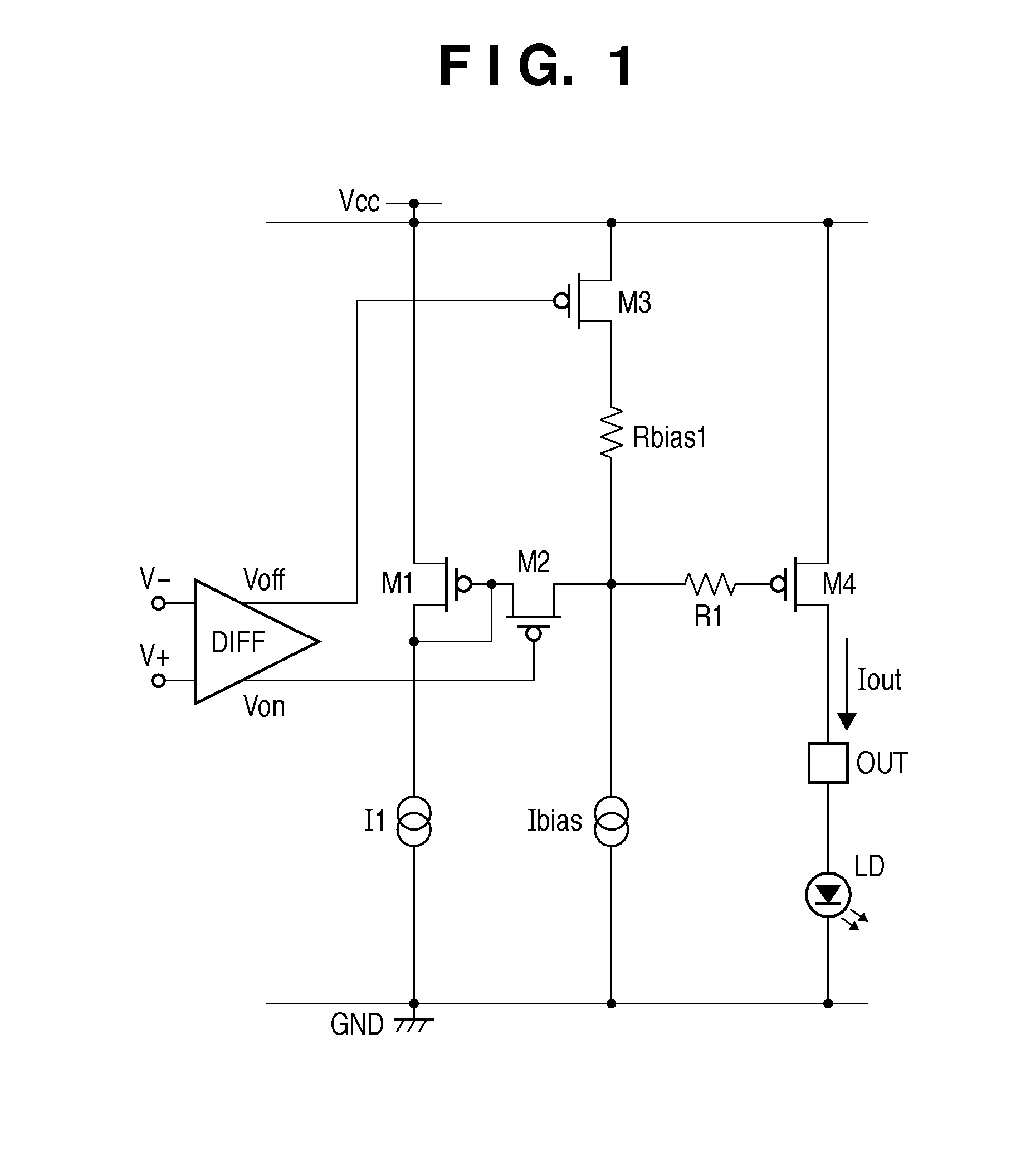
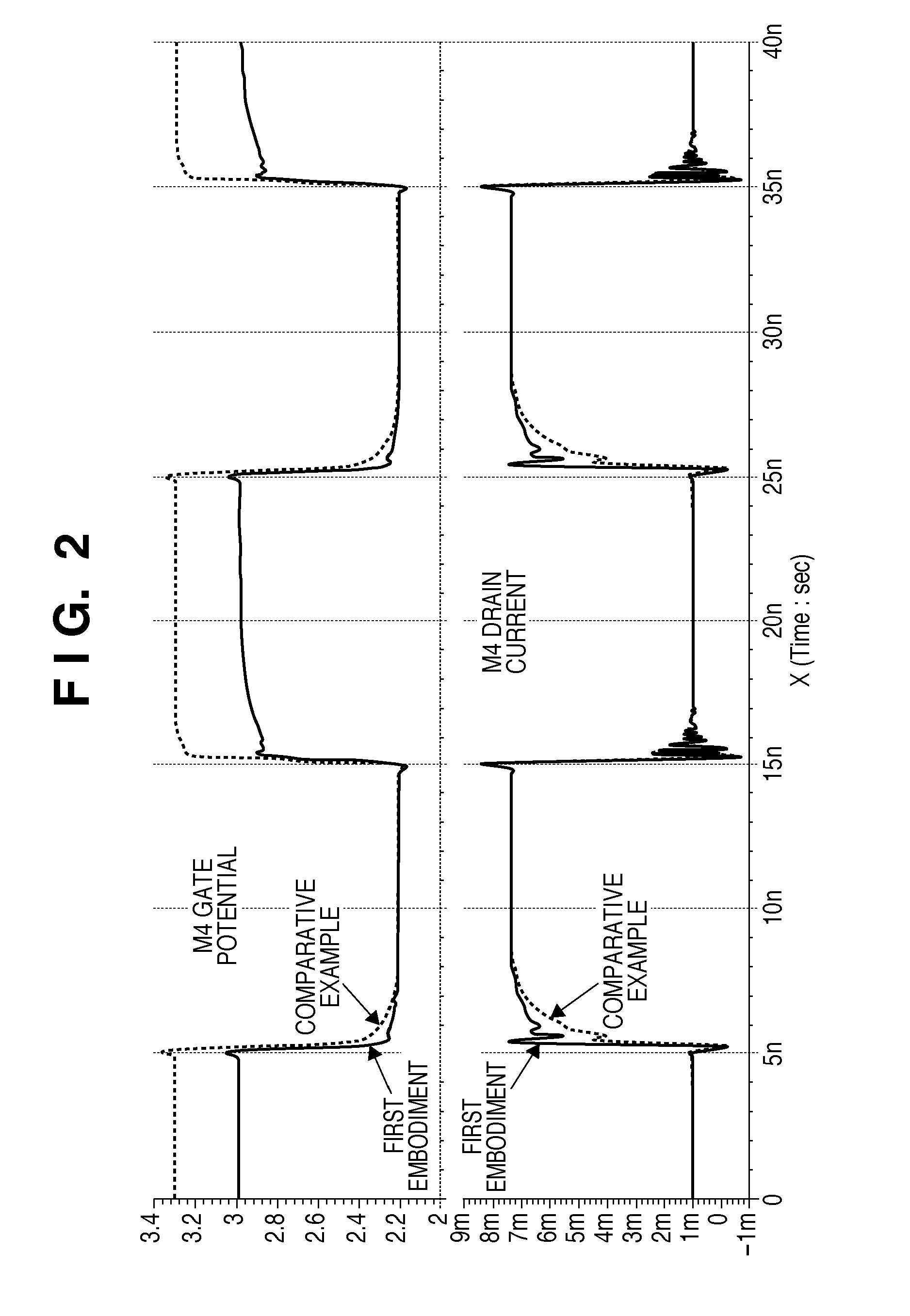
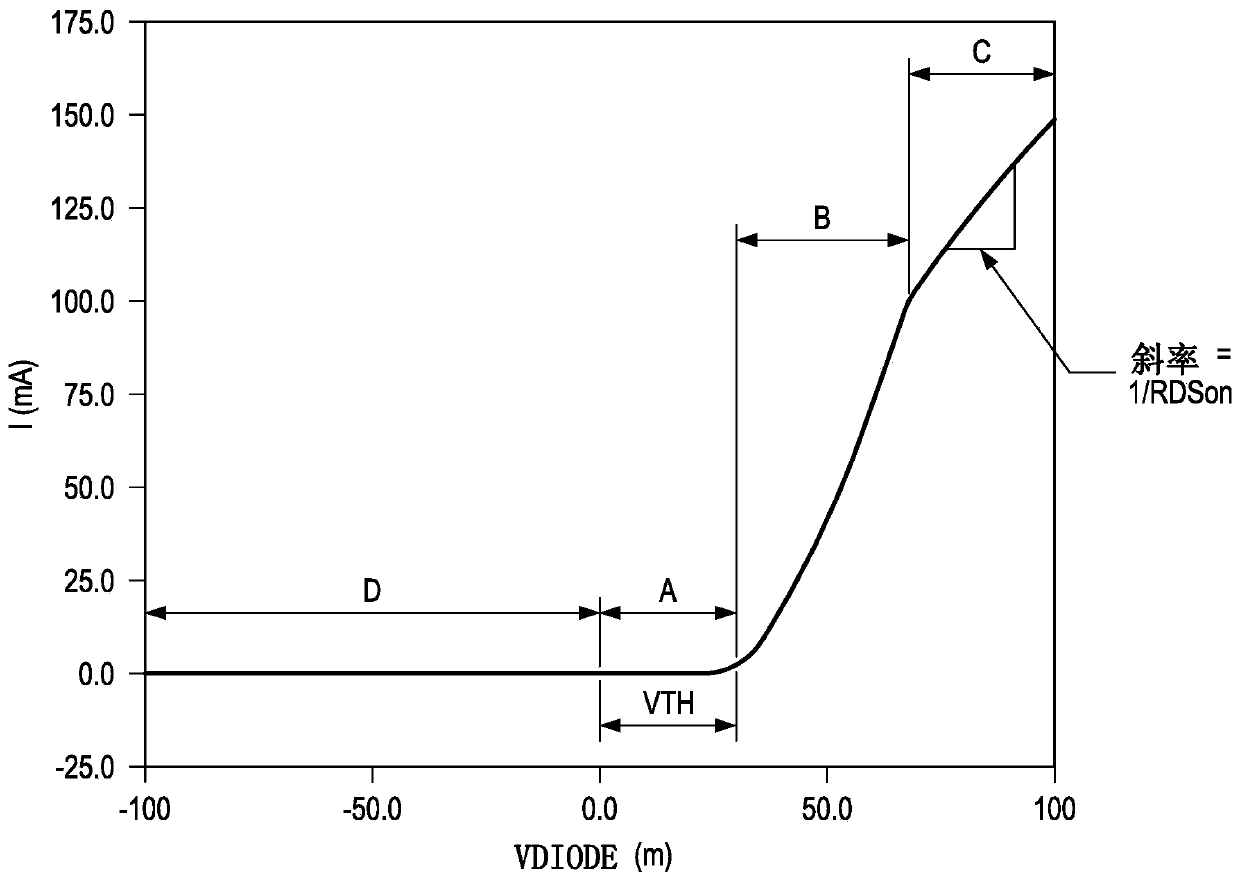
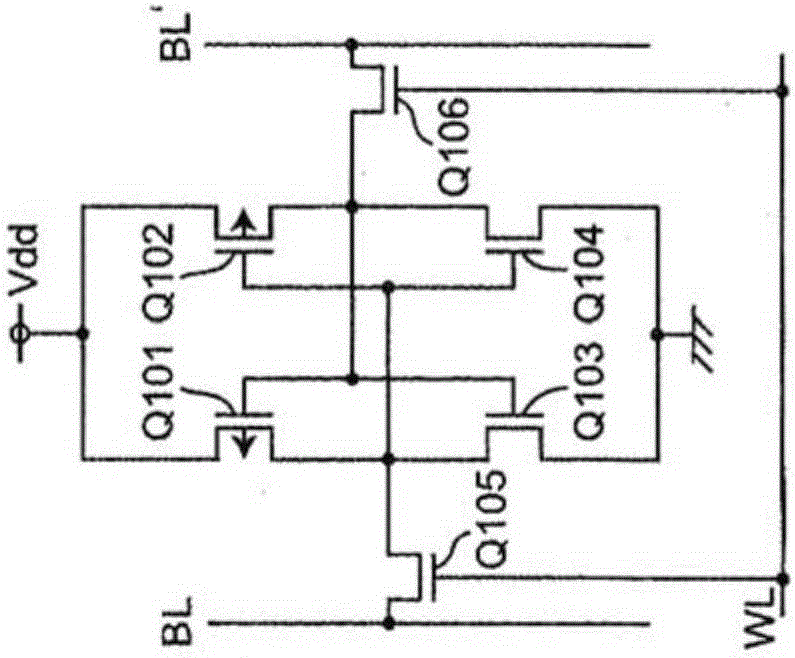
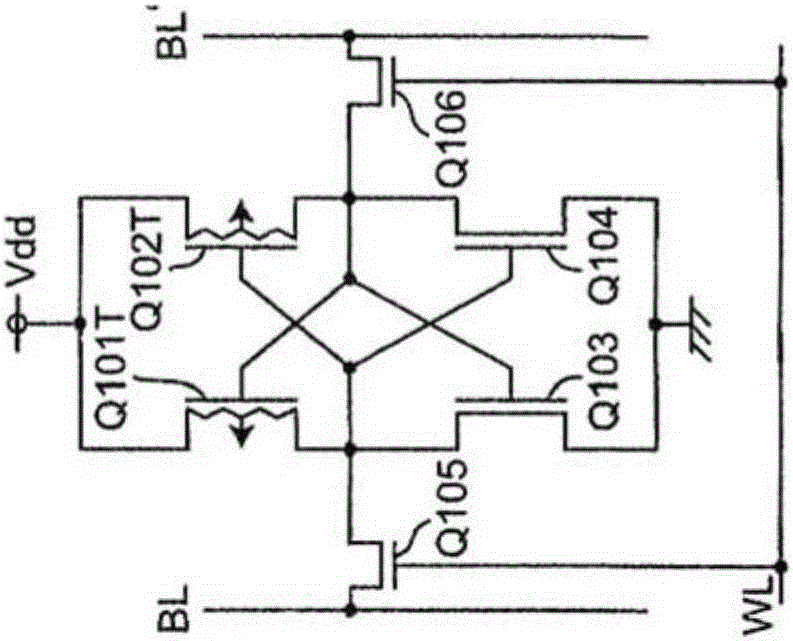
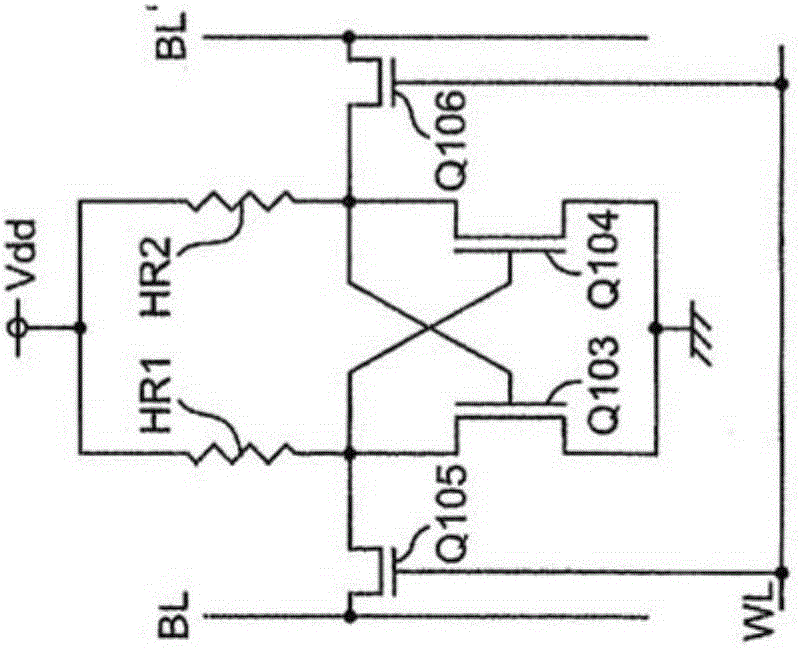
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
33results about How to "Low voltage operation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
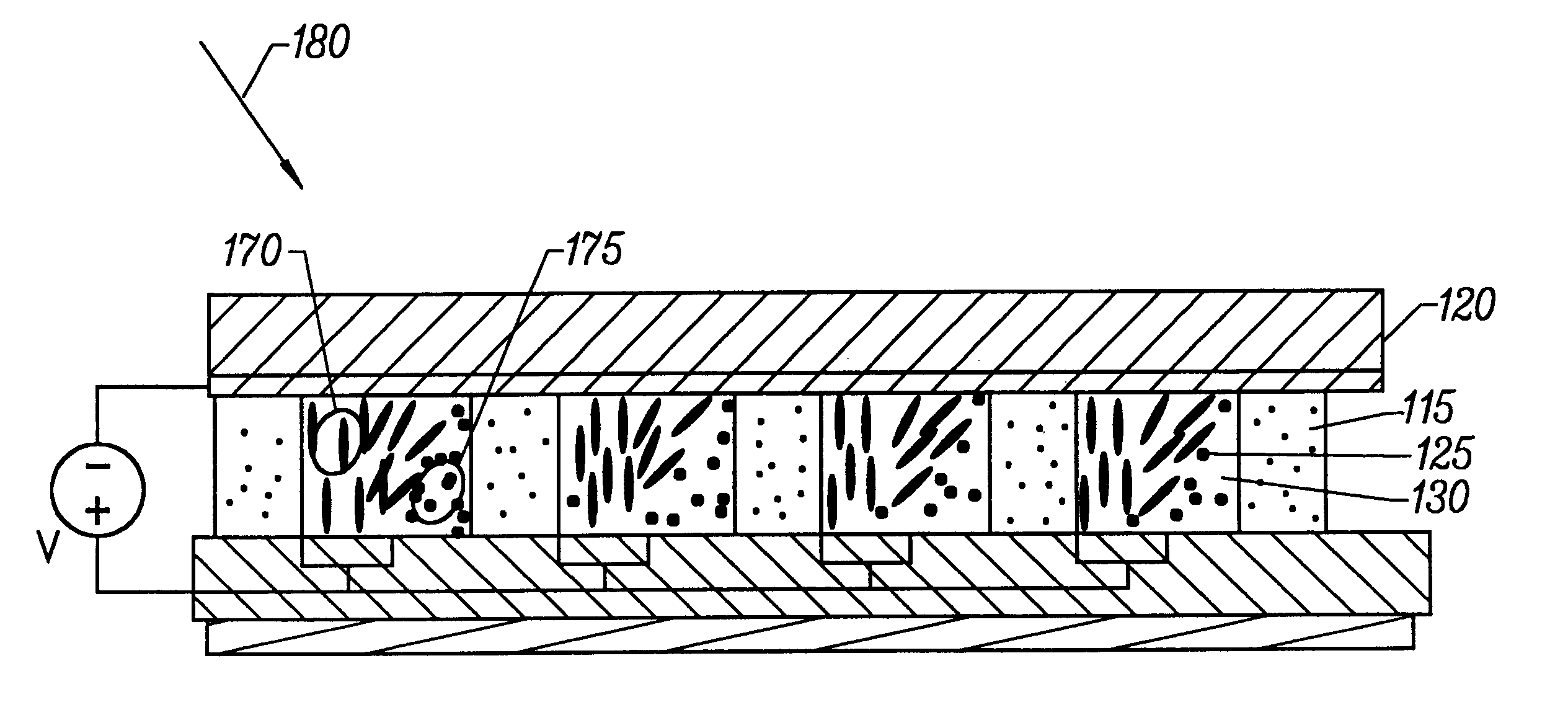
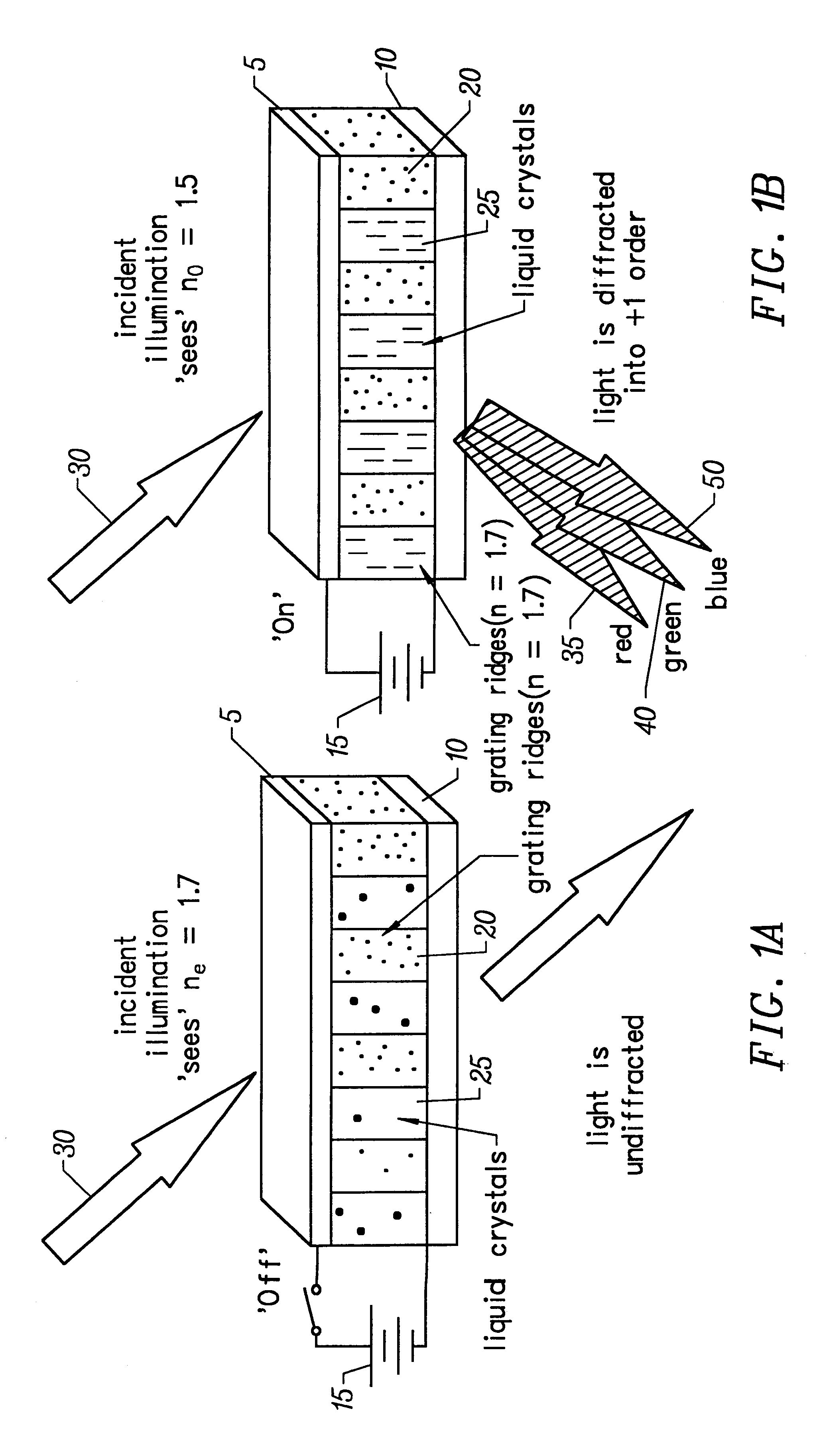
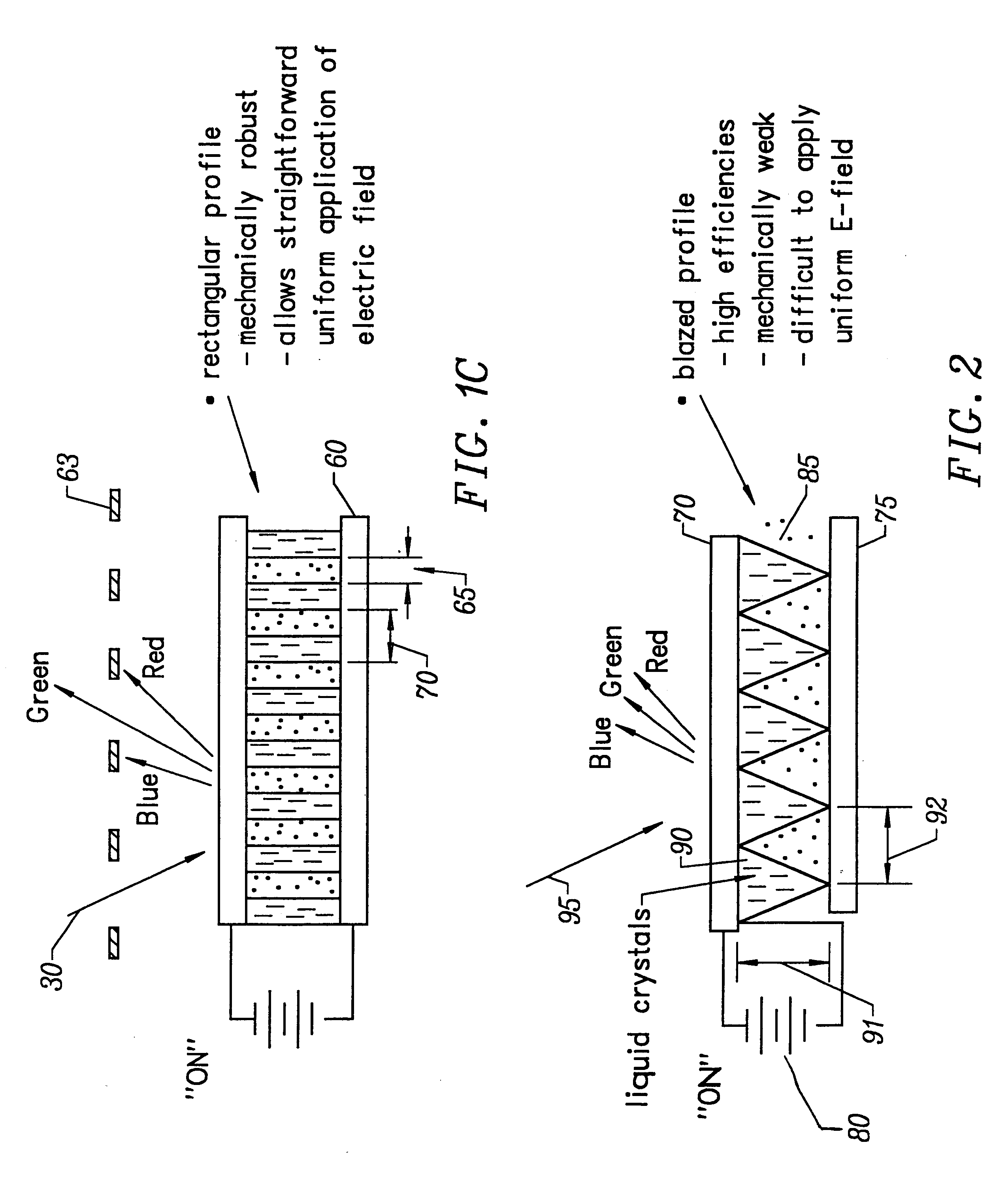
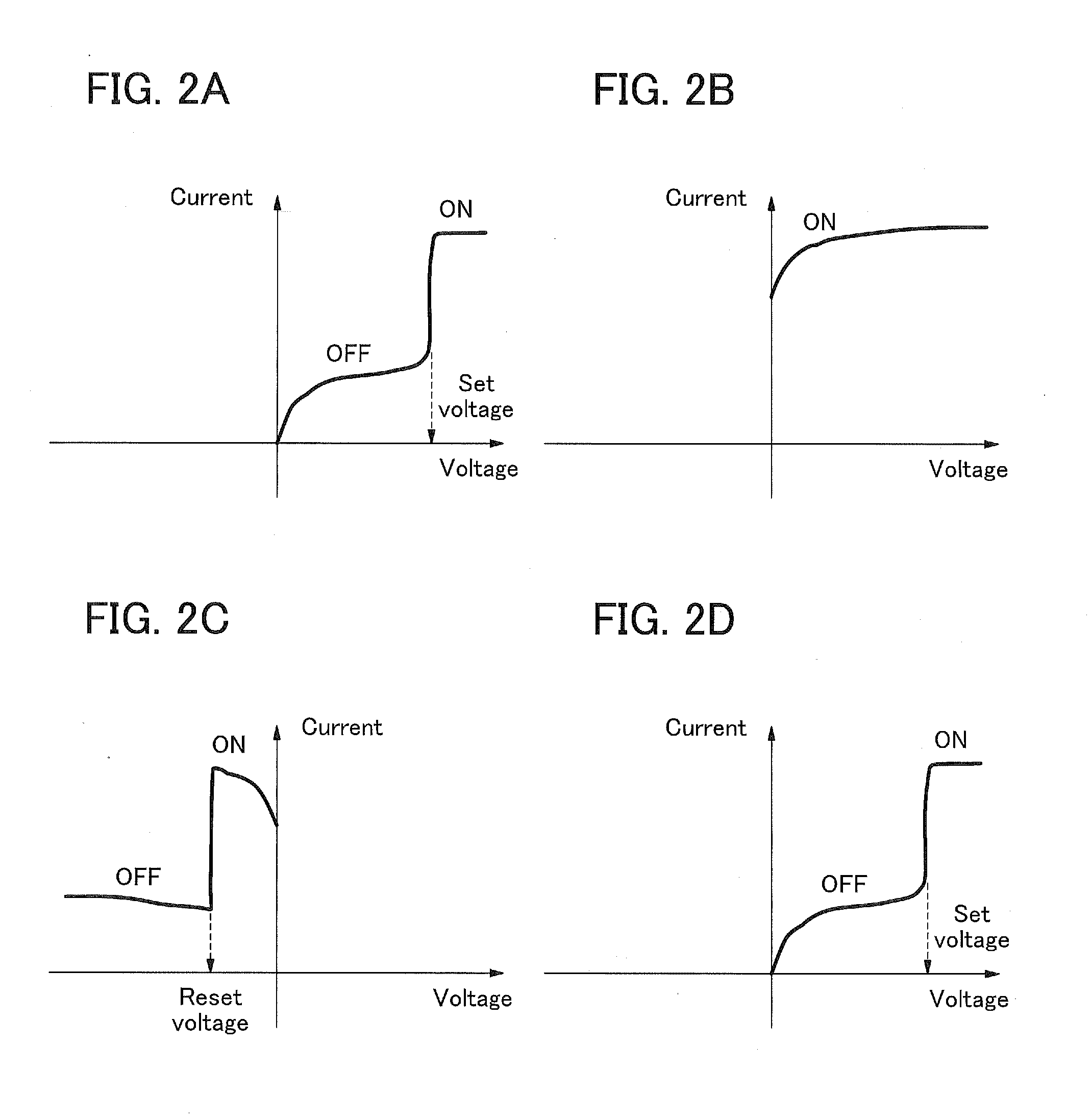
Method and apparatus for forming optical gratings
InactiveUS6172792B1Increase contrastFast response timeDiffraction gratingsNon-linear opticsGratingElectrical field strength
An apparatus for redirecting physical energy includes a substrate defining a first boundary of a region, a first electrode defining a second boundary of the region, the second boundary disposed opposite to the first boundary, a second electrode adjacent to the first boundary for cooperating with the first electrode to apply a non-uniform electric field to the region, the non-uniform electric field having electrical field intensities simultaneously including a first electric field intensity and a second electric field intensity, and a layer of material disposed in the region, the layer having a variable index of refraction responsive to the electric field intensities of the non-uniform electric field, the variable index of refraction including a first index of refraction in response to the first electric field intensity and a second index of refraction in response to the second electric field intensity.
Owner:ROSSELLA
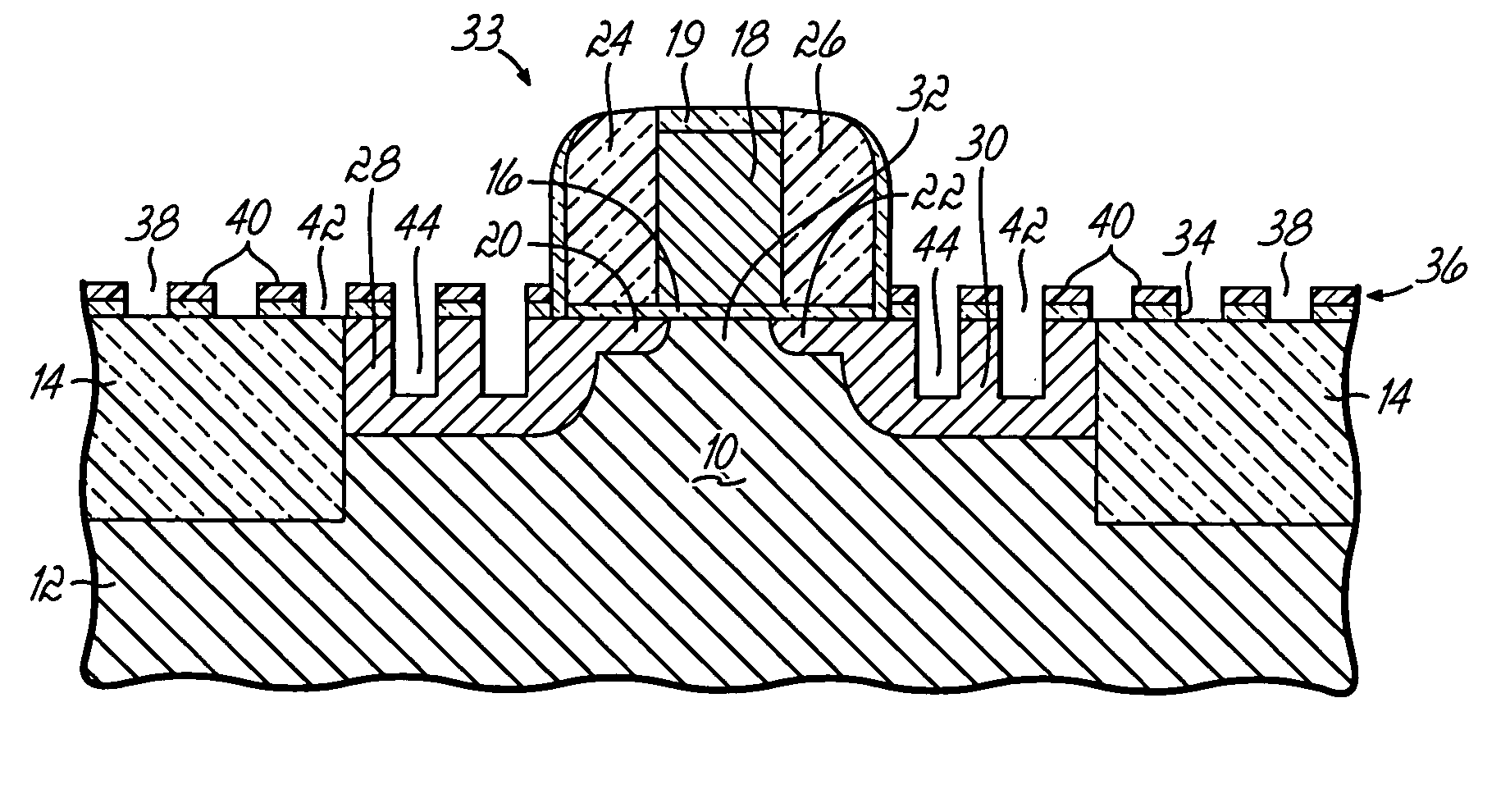
Method for fabricating strained semiconductor structures and strained semiconductor structures formed thereby
InactiveUS20060011990A1Improve performanceAdding to cost and complexityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSemiconductor materialsSemiconductor structure
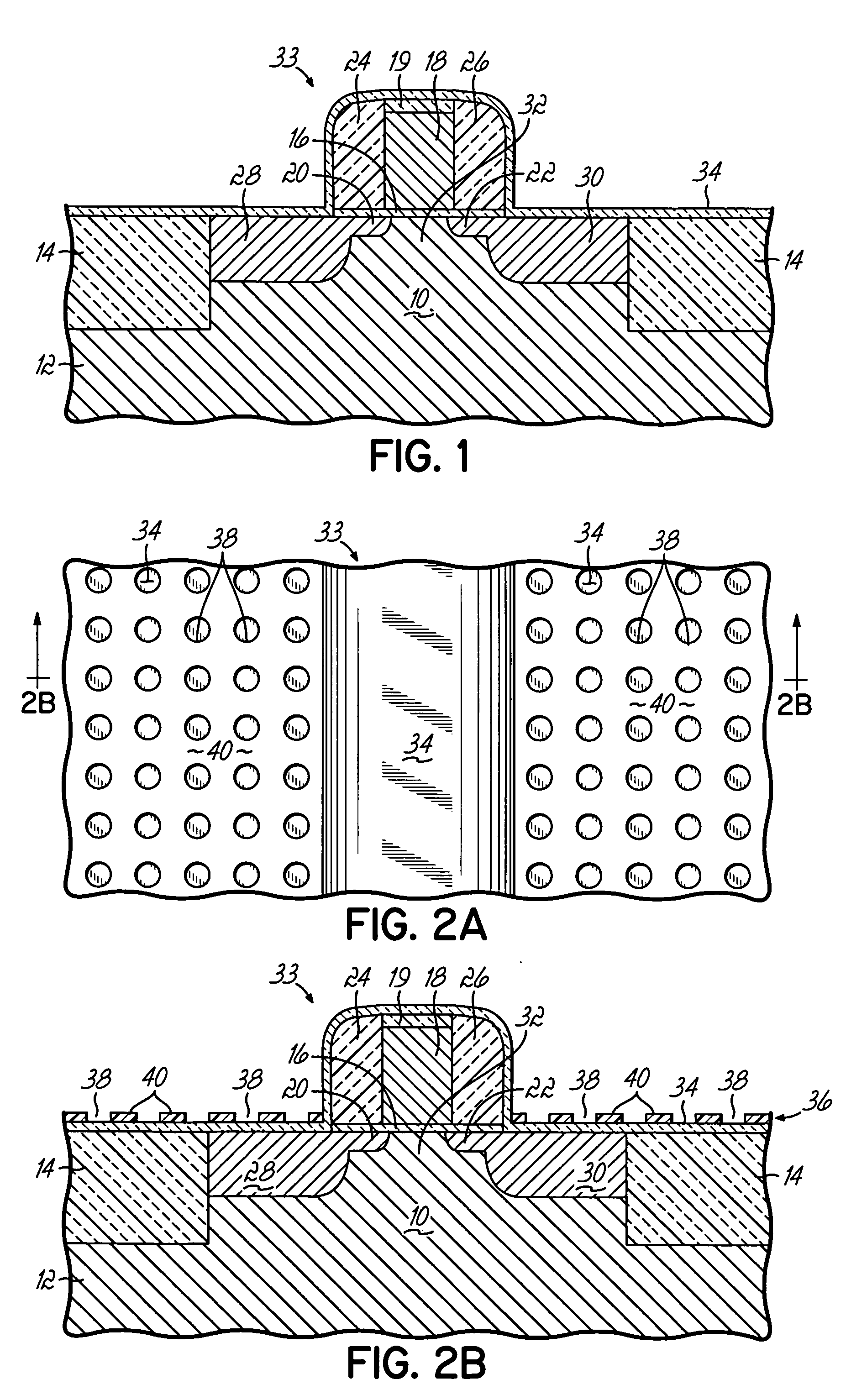
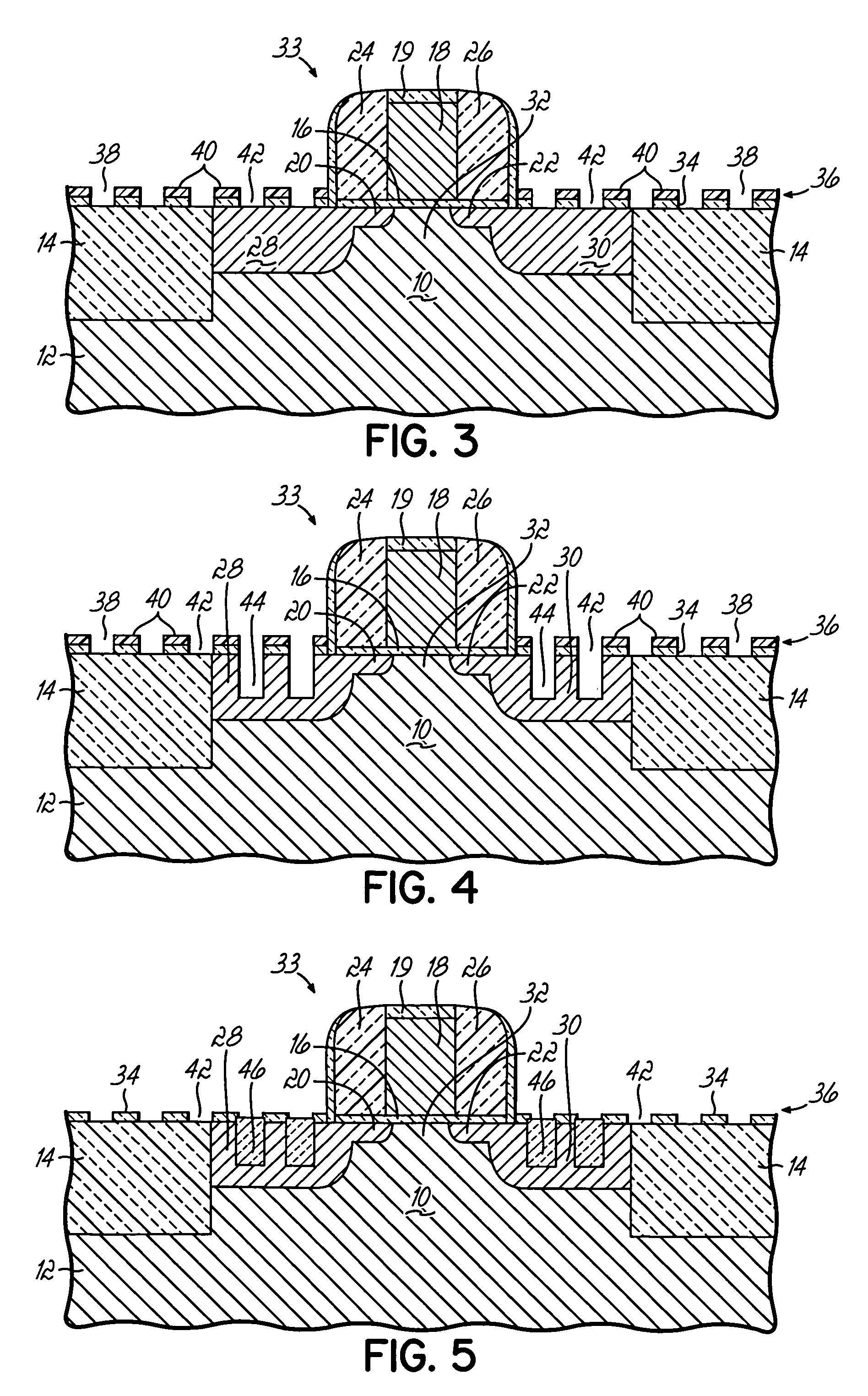
Semiconductor fabrication methods and structures, devices and integrated circuits characterized by enhanced operating performance. The structures generally include first and second source / drain regions formed in a body of a semiconductor material and a channel region defined in the body between the first and second source / drain regions. Disposed in at least one of the first and second source / drain regions are a plurality of plugs each formed from a volume-expanded material that transfers compressive stress to the channel region. The compressively strained channel region may be useful, for example, for improving the operating performance of p-channel field effect transistors (PFET's).
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
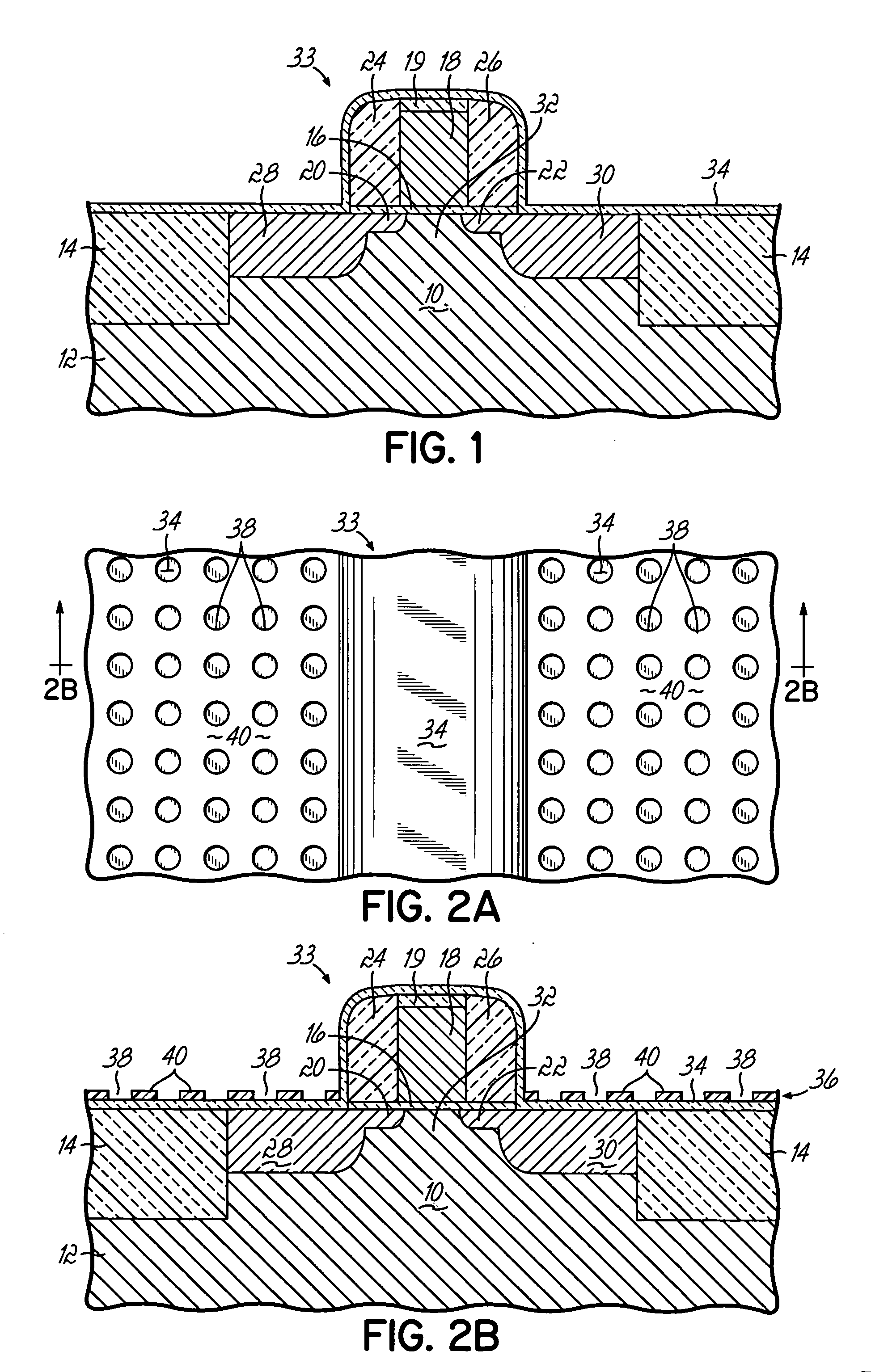
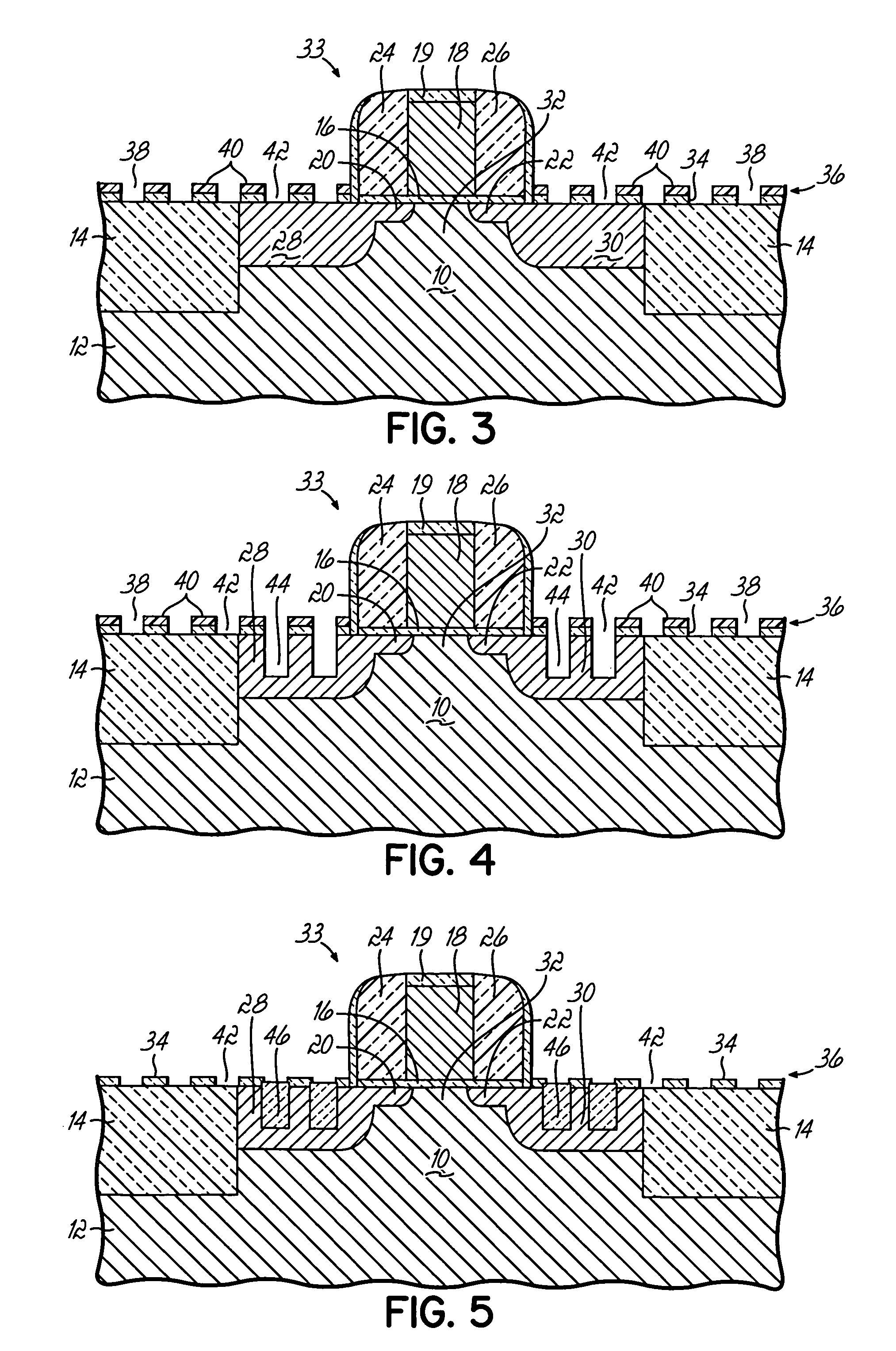
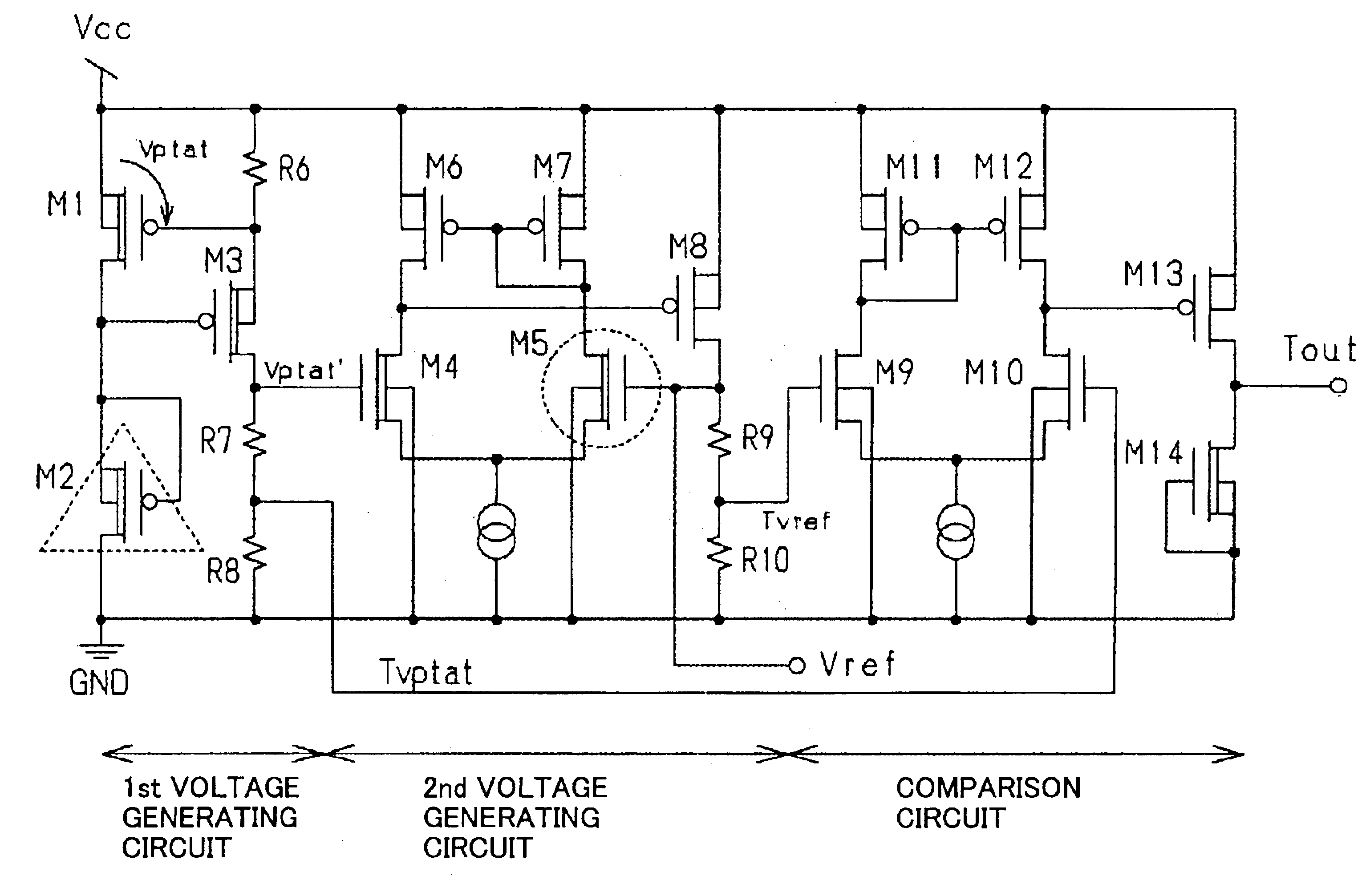
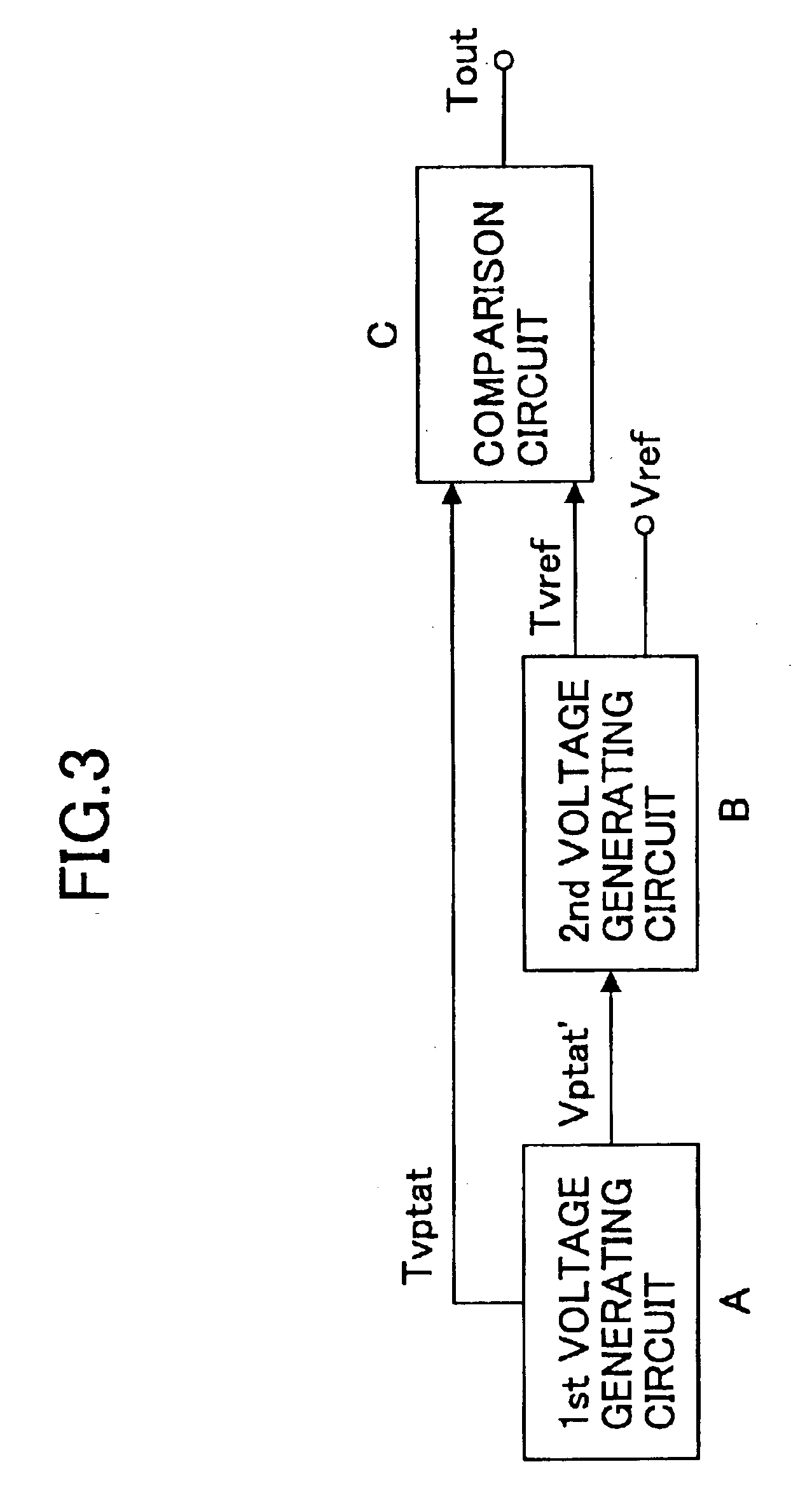
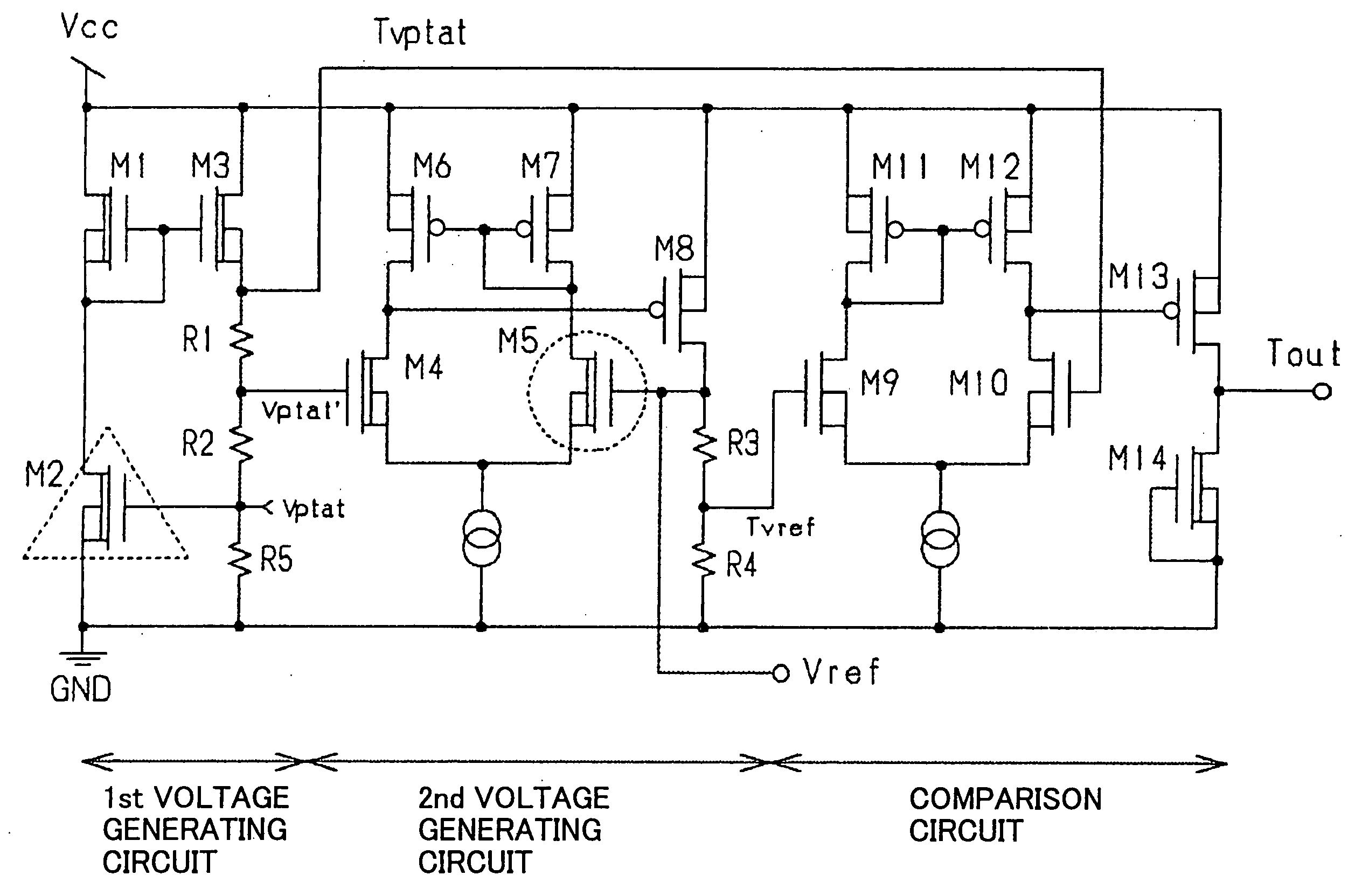
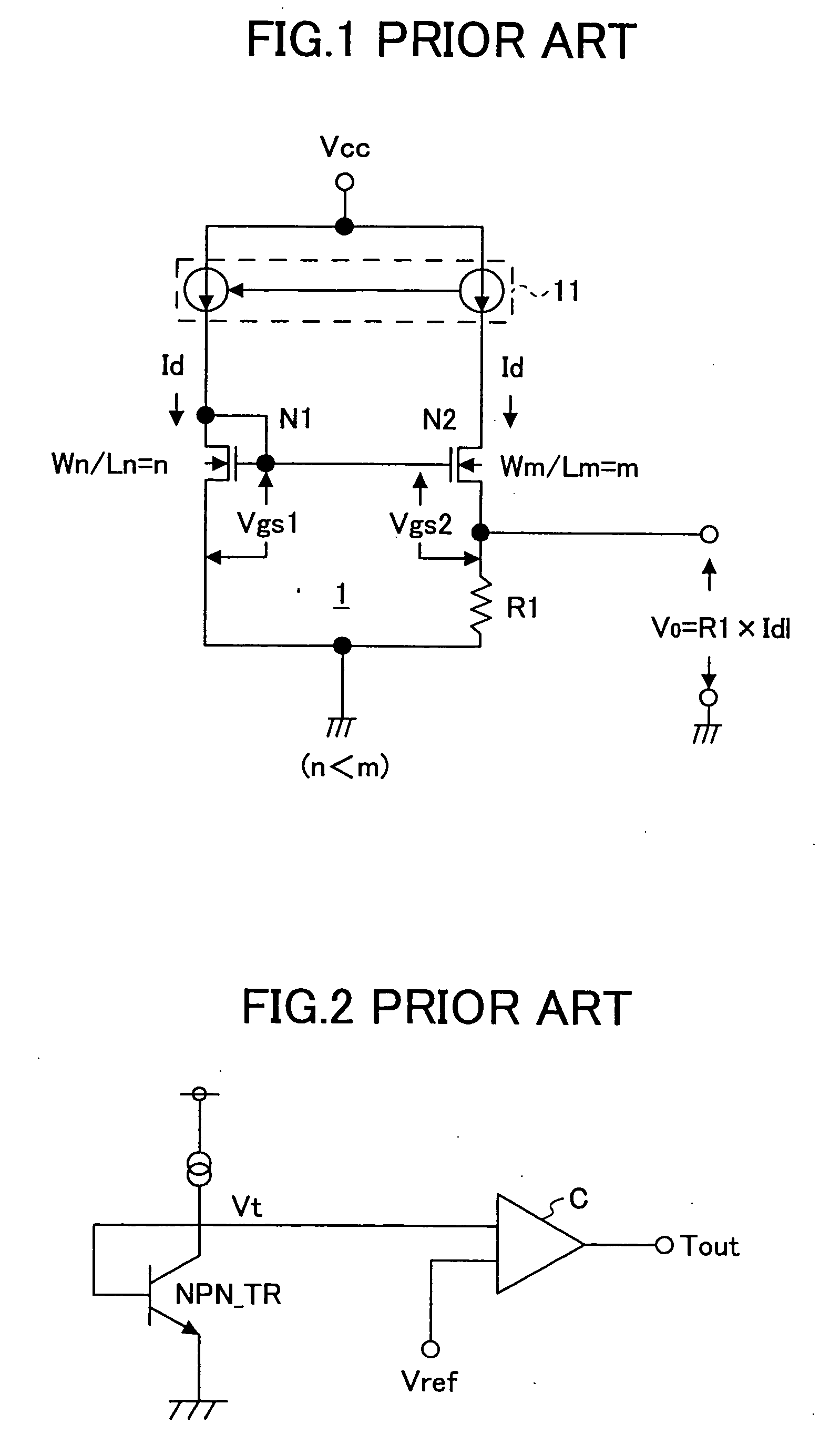
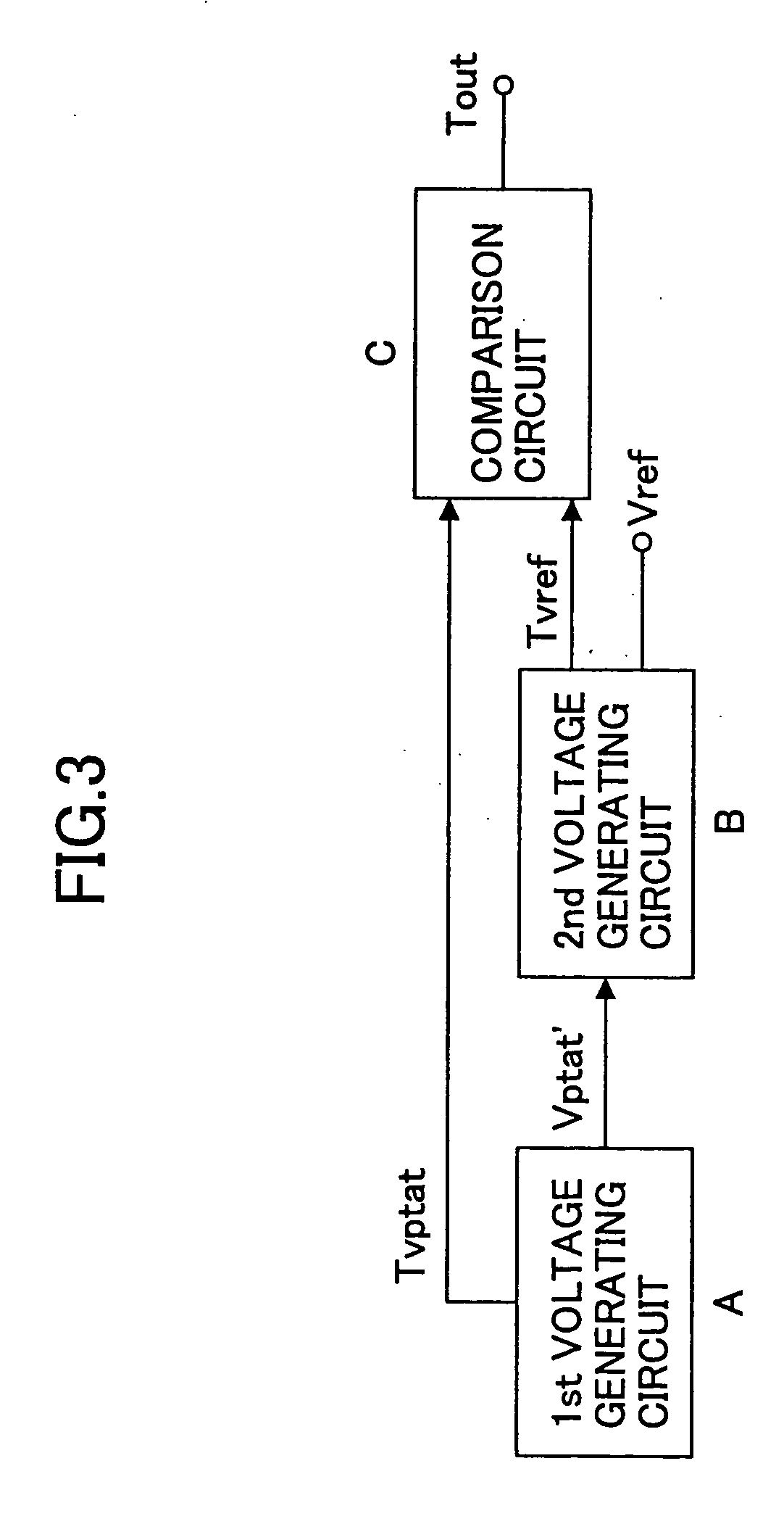
Temperature sensor
InactiveUS6921199B2High sensitivityLow-voltage operationThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsUsing electrical meansNegative temperatureEngineering
A temperature sensor comprises (a) a first voltage generating circuit that generates and outputs a first voltage having a positive or negative temperature coefficient in proportion to the absolute temperature; (b) a second voltage generating circuit that generates a second voltage having an opposite sign of temperature coefficient compared to the first voltage and outputs a reference voltage that does not have a temperature coefficient based on the second voltage; and (c) a comparator that compares the first voltage output from the first voltage generating circuit with the reference voltage output from the second voltage generating circuit.
Owner:RICOH KK
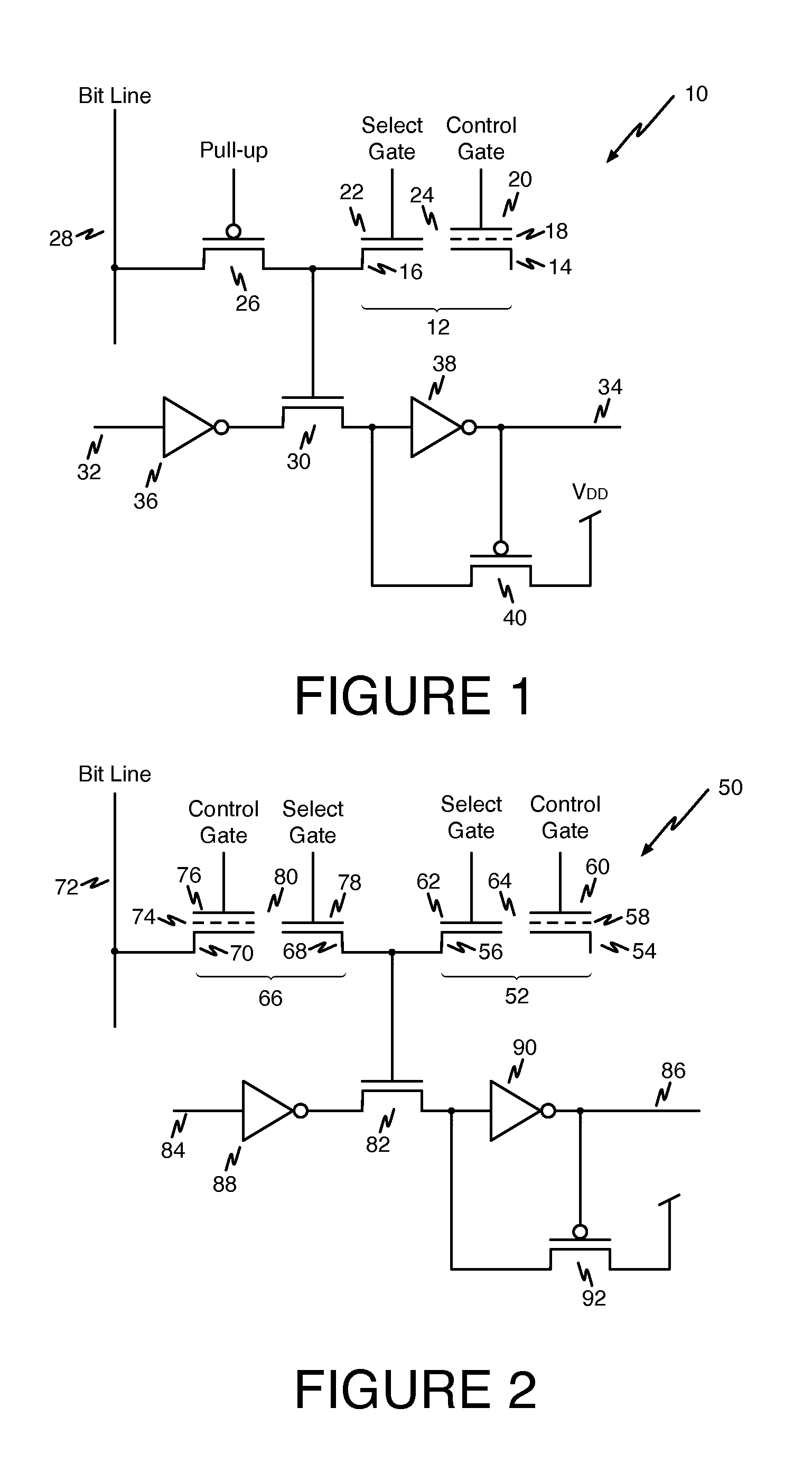
Split gate memory cell for programmable circuit device
ActiveUS7692972B1Leakage of standby current is reducedSmall cell sizeRead-only memoriesDigital storageThin oxideBit line
A split-gate memory cell, includes an n-channel split-gate non-volatile memory transistor having a source, a drain, a select gate over a thin oxide, and a control gate over a non-volatile gate material and separated from the select gate by a gap. A p-channel pull-up transistor has a drain coupled to the drain of the split-gate non-volatile memory transistor, a source coupled to a bit line, and a gate. A switch transistor has first and second source / drain diffusions, and a gate coupled to the drains of the split-gate non-volatile memory transistor and the p-channel pull-up transistor. An inverter has an input coupled to the second source / drain diffusion of the switch transistor, and an output. A p-channel level-restoring transistor has a source coupled to a supply potential, a drain coupled to the first source / drain diffusion of the switch transistor and a gate coupled to the output of the inverter.
Owner:MICROSEMI SOC
Strained semiconductor device structures
InactiveUS7102201B2Improve performanceAdding to cost and complexityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSemiconductor materialsCompressive strength
Semiconductor fabrication methods and structures, devices and integrated circuits characterized by enhanced operating performance. The structures generally include first and second source / drain regions formed in a body of a semiconductor material and a channel region defined in the body between the first and second source / drain regions. Disposed in at least one of the first and second source / drain regions are a plurality of plugs each formed from a volume-expanded material that transfers compressive stress to the channel region. The compressively strained channel region may be useful, for example, for improving the operating performance of p-channel field effect transistors (PFET's).
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Long wavelength pseudomorphic InGaNPAsSb type-I and type-II active layers for the gaas material system
InactiveUS6859474B1Improve efficiencyReduce transition energyLaser active region structureNanoinformaticsQuantum wellNitrogen
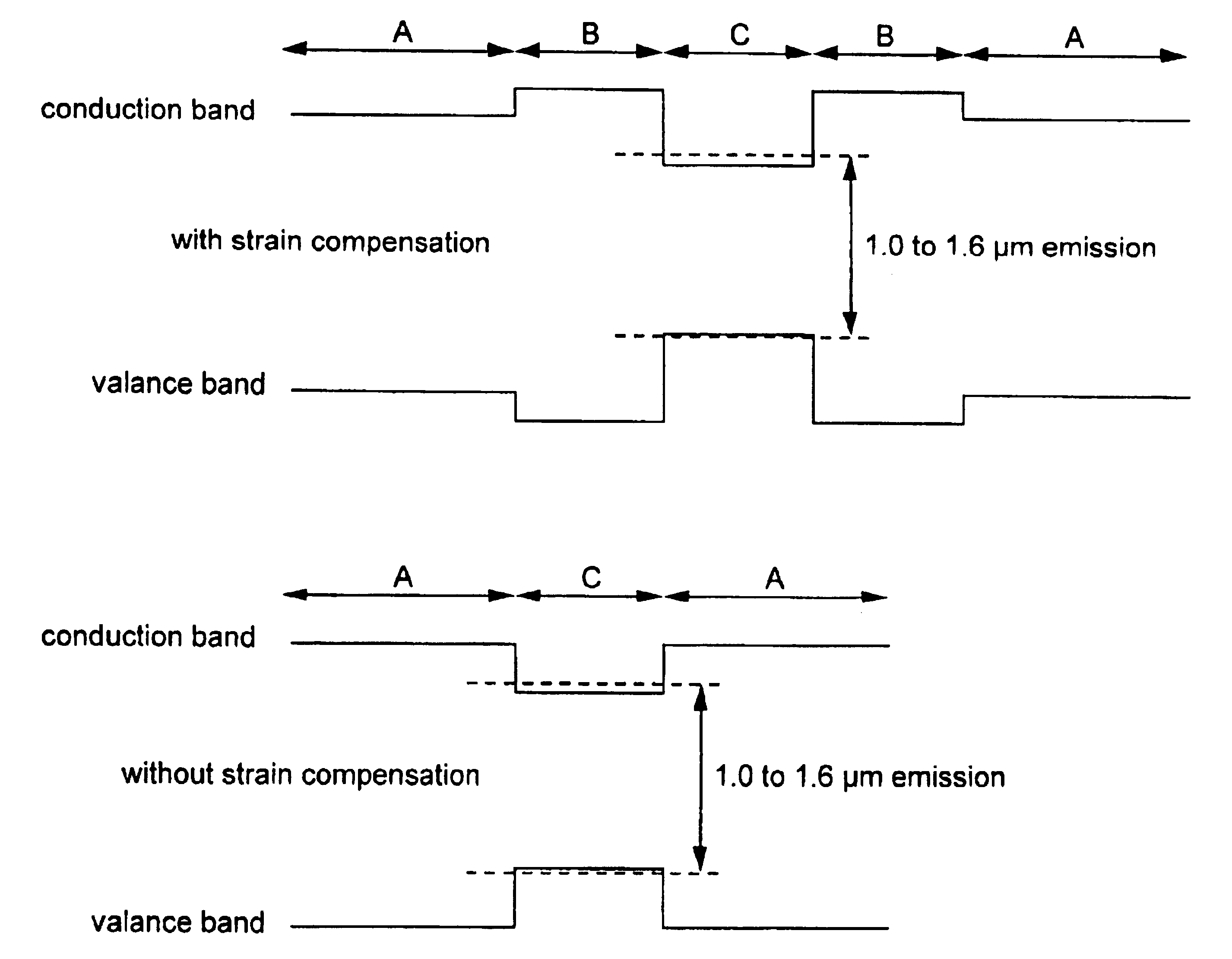
The invention discloses improved structures of light-processing (e.g. light-emitting and light-absorbing / sensing) devices, in particular Vertical Cavity Surface Emitting Lasers (VCSELs), such as may find use in telecommunications applications. The disclosed VSCAL devices and production methods provide for an active region having a quantum well structure grown on GaAs-containing substrates, thus providing processing compatibility for light having wavelength in the range 1.0 to 1.6 μm. The active region structure combines strain-compensating barriers with different band alignments in the quantum wells to achieve a long emission wavelength while at the same time decreasing the strain in the structure. The improved functioning of the devices disclosed results from building them with multicomponent alloy layers having a large number of constituents. The invention discloses as a key constituent in the proposed alloy layers for the active region a substance, such as nitrogen (N), suitable for reducing bandgap energy (i.e., increasing light wavelength) associated with the layers while at the same time lowering the lattice constant associated with the structure and hence lowering strain.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA
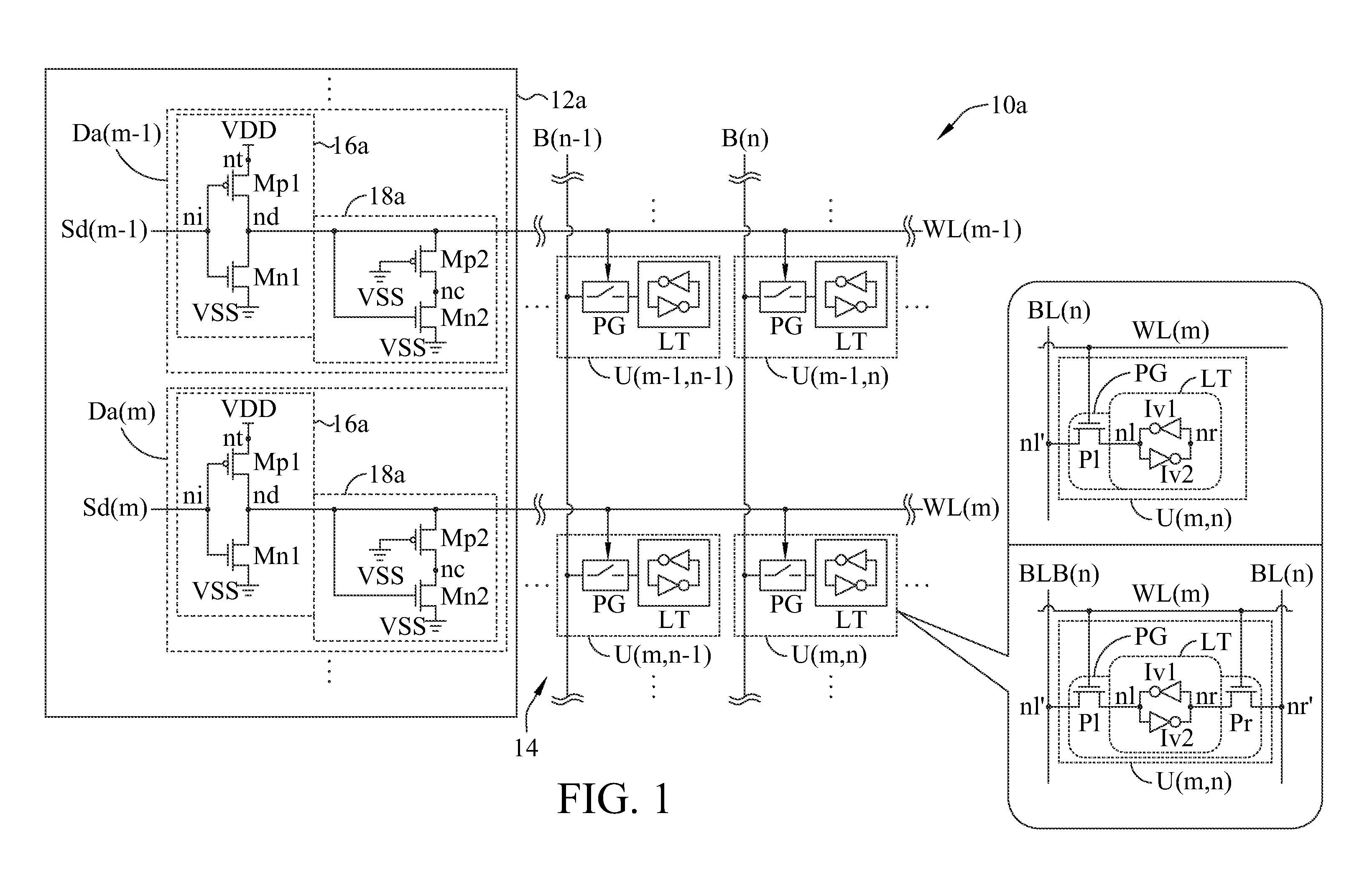
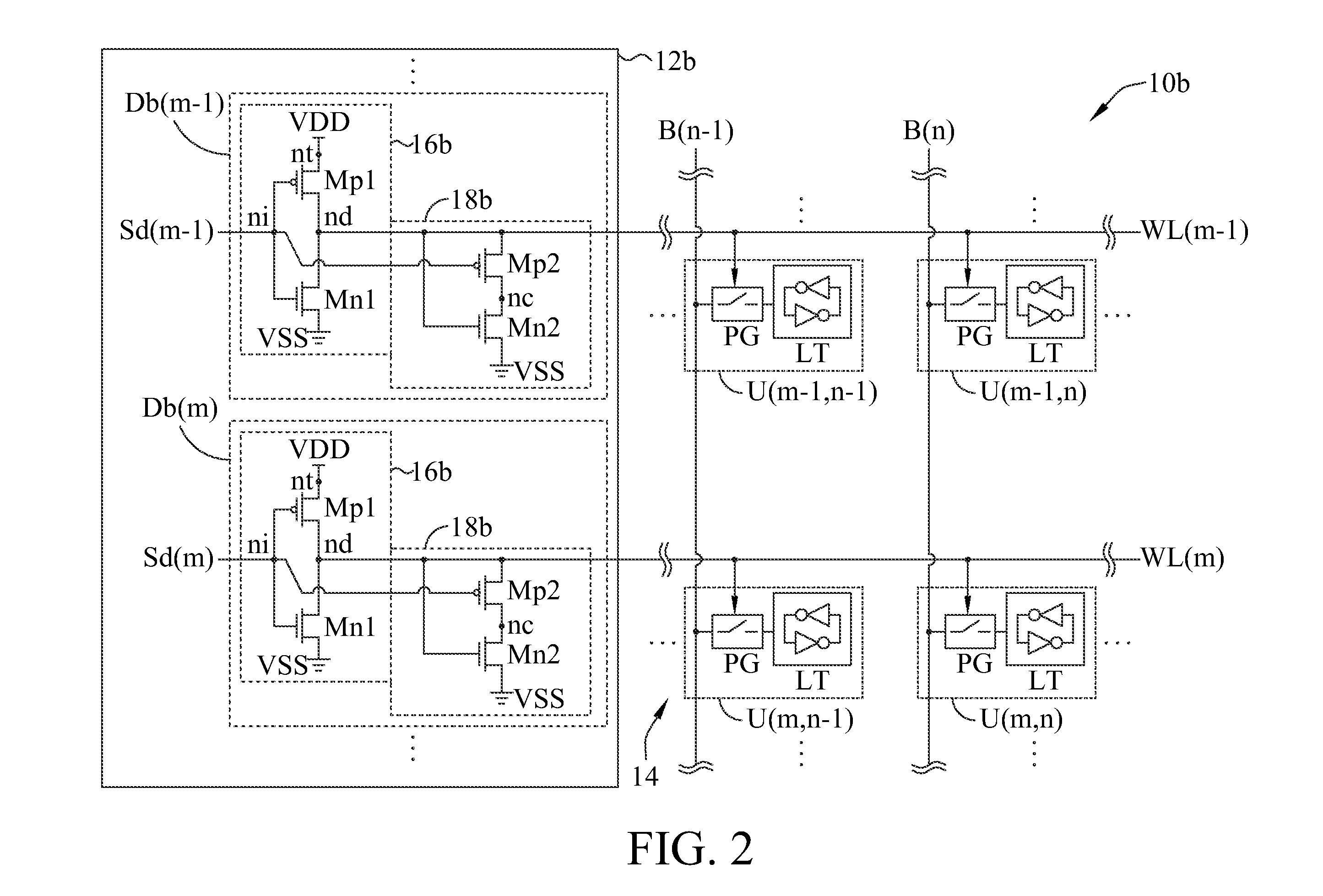
Variation-tolerant word-line under-drive scheme for random access memory
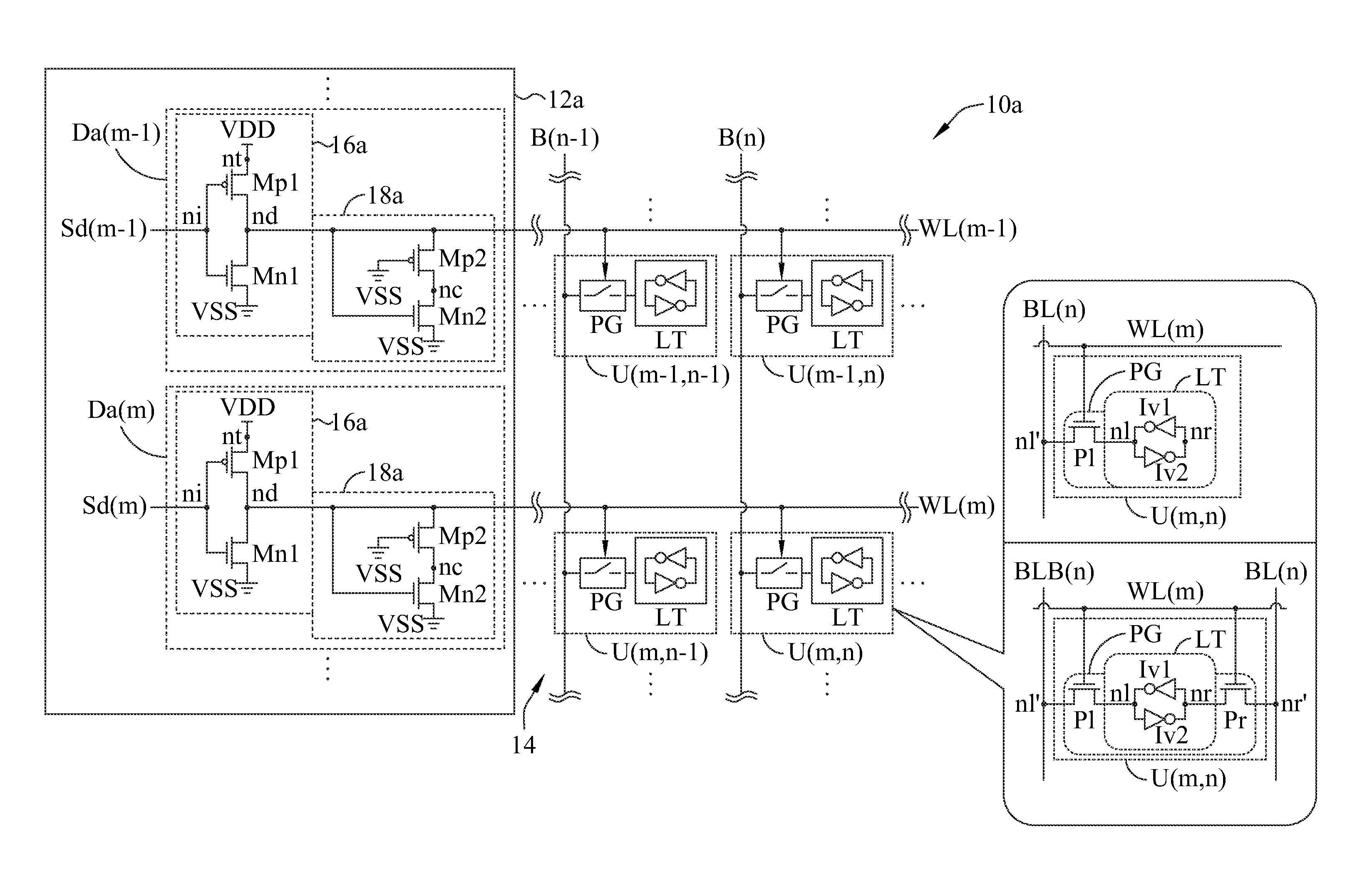
A Random Access Memory (RAM) is provided. The RAM includes a plurality of word-line drivers, at least a first tracking transistor and a second tracking transistor. Each word-line driver has an input node receiving a decoding signal, a power node receiving an operation voltage and a driving node driving a word-line. In an embodiment, the first tracking transistor has two channel terminal nodes respectively coupled to the driving node of one of the word-line driver and a channel terminal node of the second tracking transistor; wherein the first tracking transistor has electronic characteristics tracking those of a driving transistor of word-line driver, and the second tracking transistor has electronic characteristics tracking those of pass-gate transistor(s) in each cell of the RAM.
Owner:FARADAY TECH CORP +1
Temperature sensor
InactiveUS20050270011A1High sensitivityLow-voltage operationThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsUsing electrical meansNegative temperatureVoltage reference
A temperature sensor comprises (a) a first voltage generating circuit that generates and outputs a first voltage having a positive or negative temperature coefficient in proportion to the absolute temperature; (b) a second voltage generating circuit that generates a second voltage having an opposite sign of temperature coefficient compared to the first voltage and outputs a reference voltage that does not have a temperature coefficient based on the second voltage; and (c) a comparator that compares the first voltage output from the first voltage generating circuit with the reference voltage output from the second voltage generating circuit.
Owner:RICOH KK
Low voltage, high speed multiplexer
InactiveUS6137340AFast outputReduce in quantityTransistorElectronic switchingResistive couplingMultiplexer
A multiplexer for selecting a single output signal from a plurality of input signals. For a plurality of complementary input signal pairs in particular, the multiplexer includes for each pair of complementary input signals a control sub-circuit having a selection switch and a common resistance in parallel. The switch and the common resistance have a common low-potential node that is tied to a pair of resistances that are in parallel, wherein each of the parallel resistances is coupled to the respective high-potential nodes of a differential amplifier. A particular pair of incoming complementary input signal pairs controls the differential amplifier. An off-circuit selection signal selects which switch of a plurality of control sub-circuits is activated. When a switch is on, it creates a bypassing of the common resistance, thereby enabling the turn-on of output drivers coupled to the differential amplifier. When a switch is off, the potential drops across the common resistance and the parallel resistances reduce the potential at the output drivers' control nodes enough to block their turn-on. As a result, the only output drivers providing signal output are those associated with the one selected control sub-circuit having its switch turned on.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
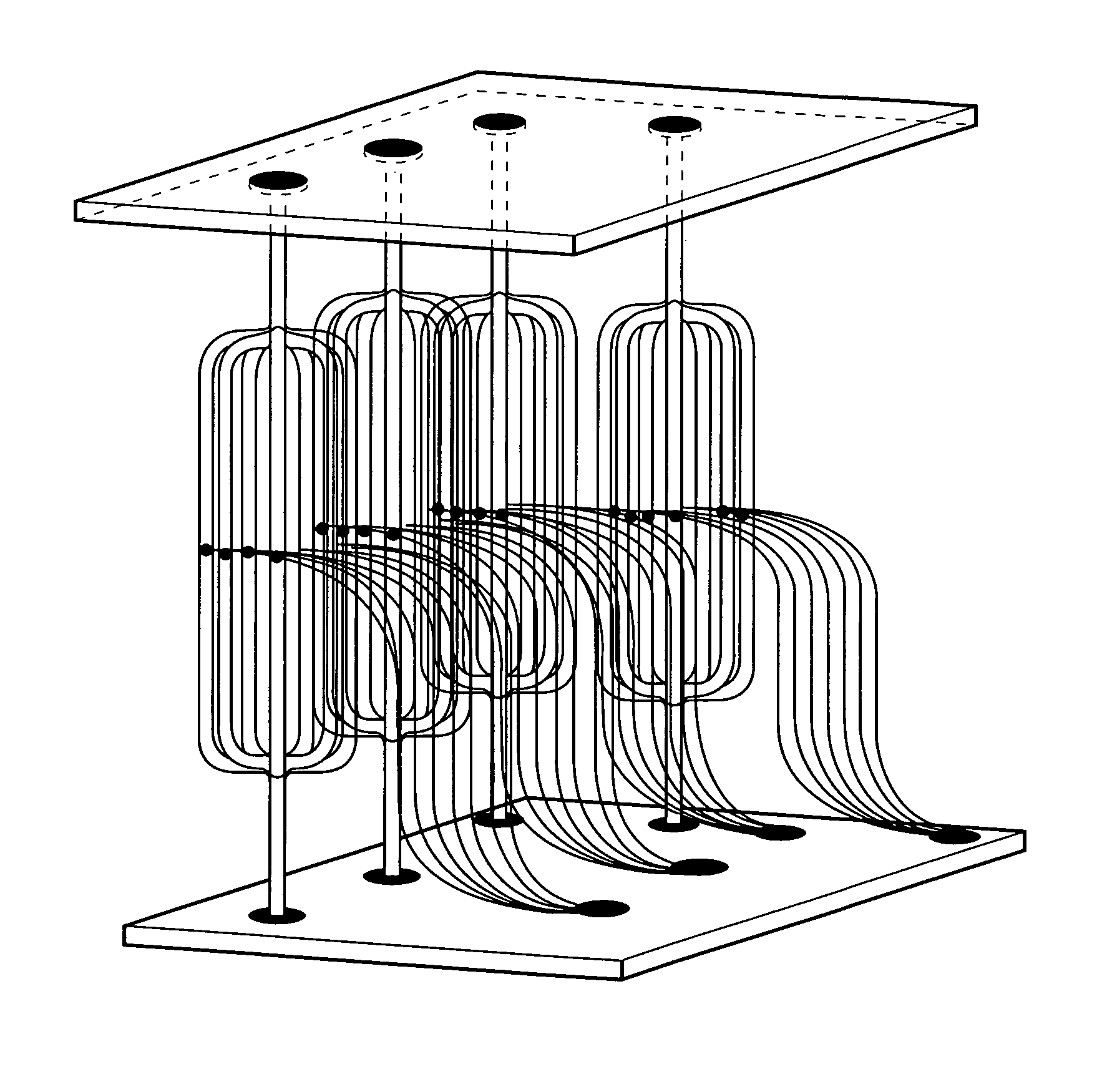
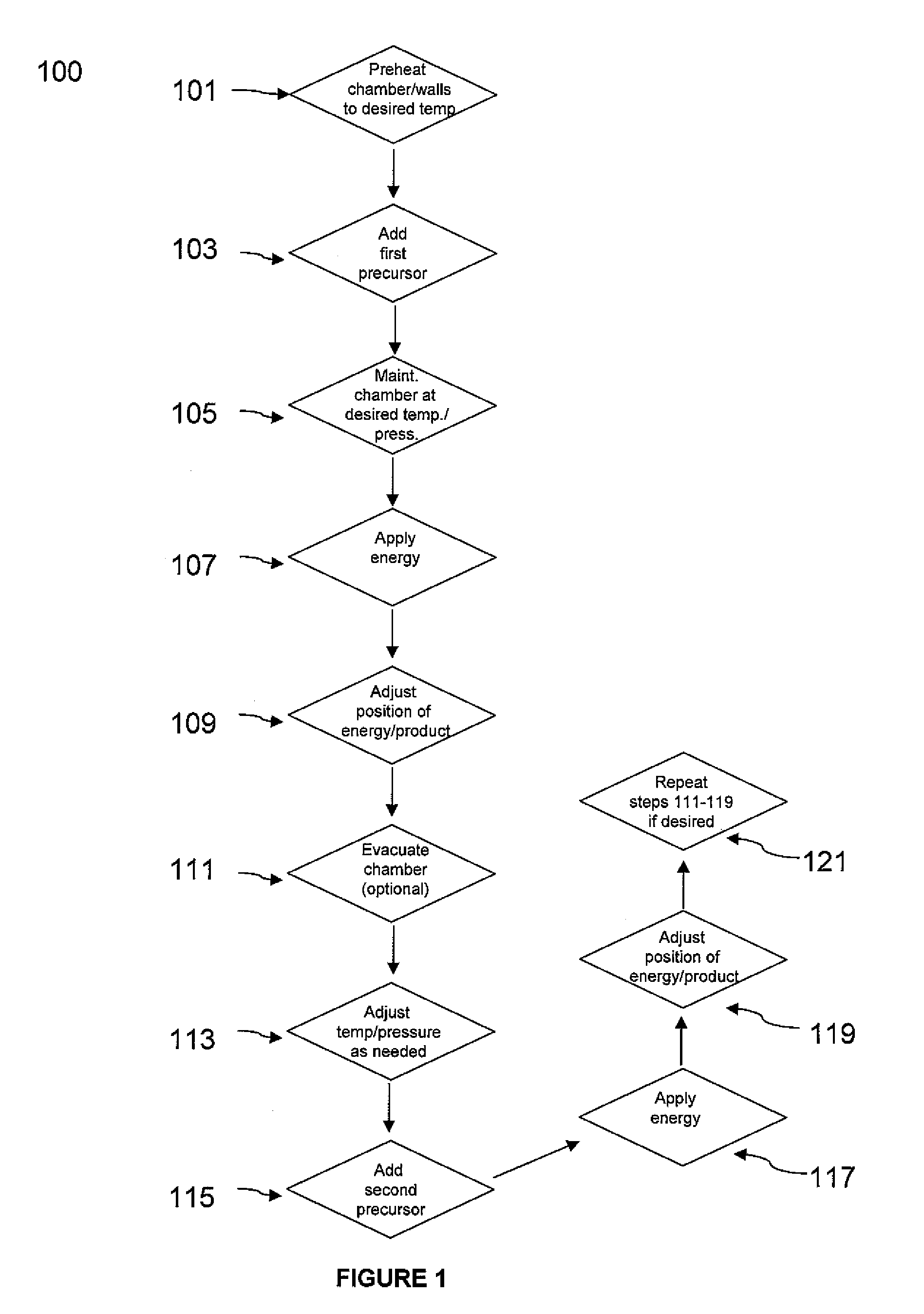
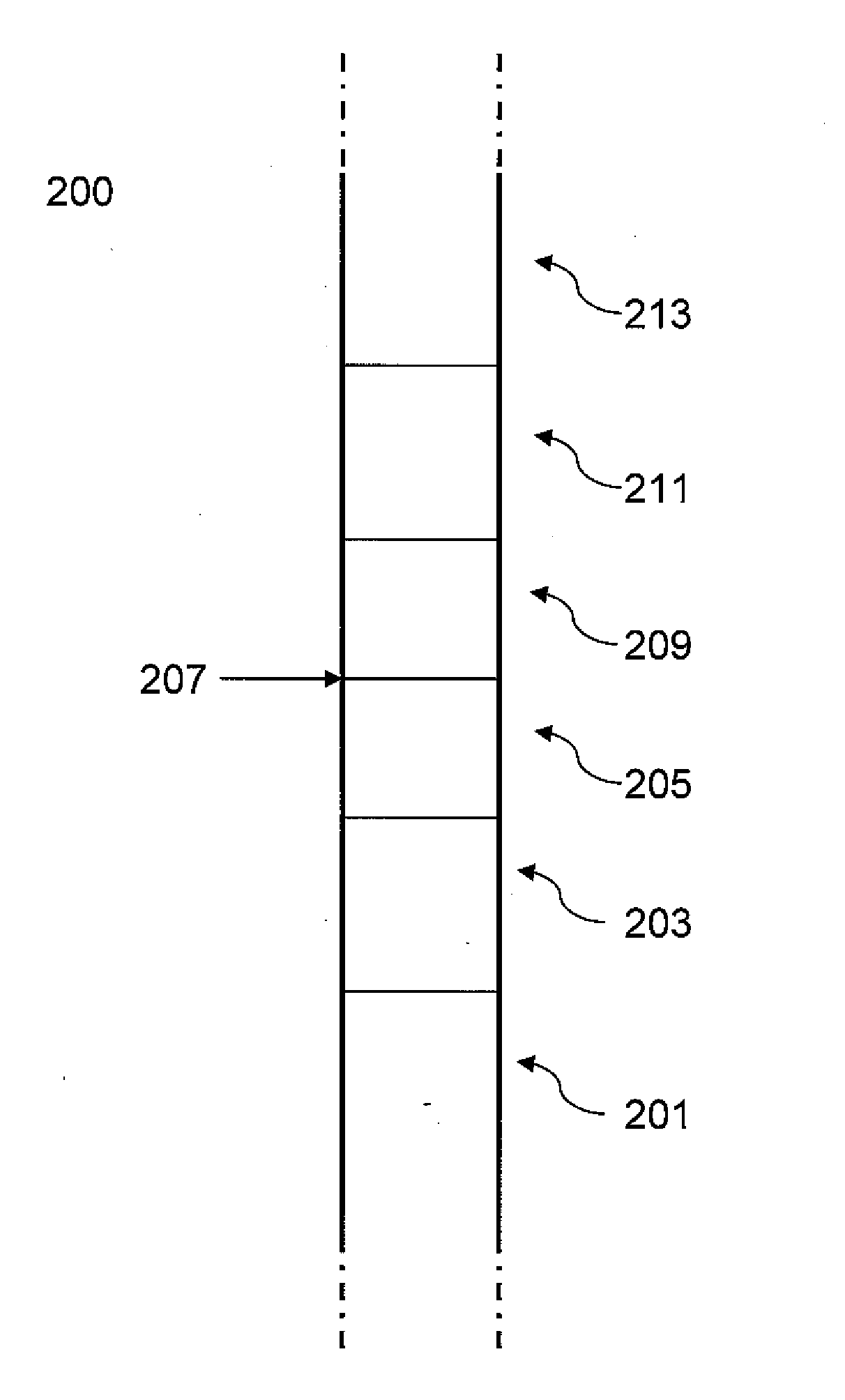
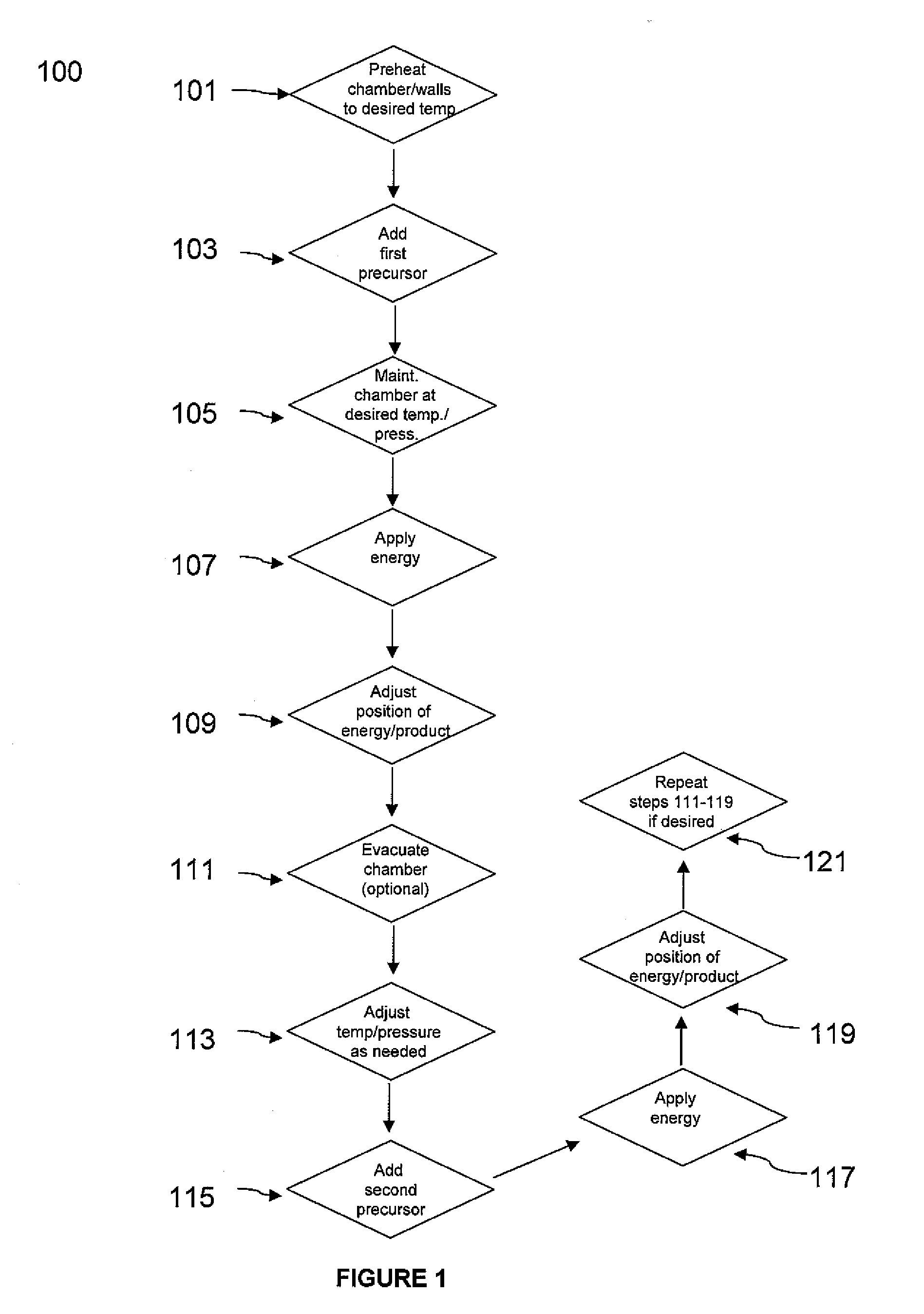
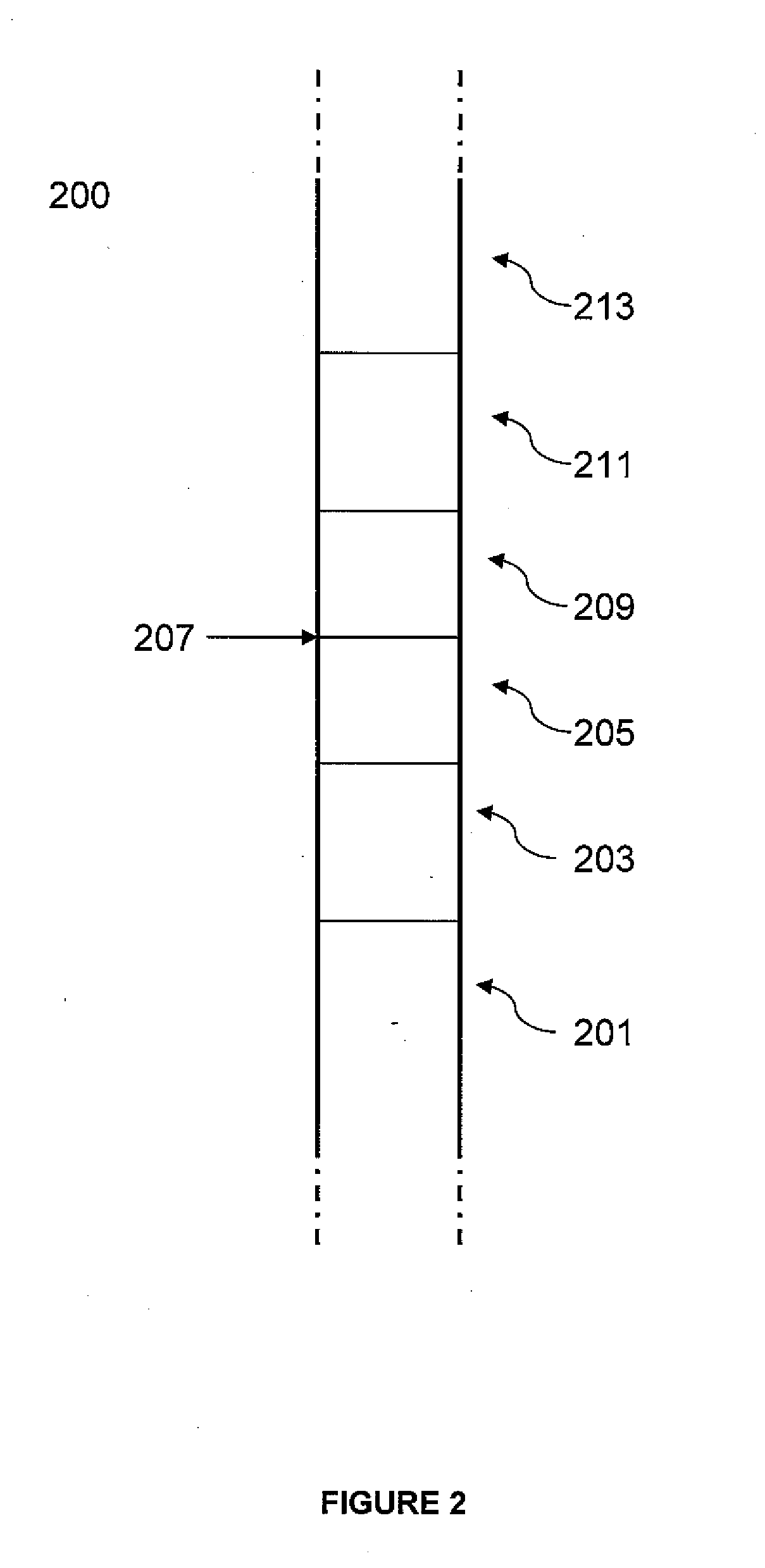
Method of fabricating free-form, high-aspect ratio components for high-current, high-speed microelectronics
InactiveUS8669164B2Easy dischargeUnprecedented performanceSiliconSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectronic structureFree form
Microelectronic structures and devices, and method of fabricating a three-dimensional microelectronic structure is provided, comprising passing a first precursor material for a selected three-dimensional microelectronic structure into a reaction chamber at temperatures sufficient to maintain said precursor material in a predominantly gaseous state; maintaining said reaction chamber under sufficient pressures to enhance formation of a first portion of said three-dimensional microelectronic structure; applying an electric field between an electrode and said microelectronic structure at a desired point under conditions whereat said first portion of a selected three-dimensional microelectronic structure is formed from said first precursor material; positionally adjusting either said formed three-dimensional microelectronic structure or said electrode whereby further controlled growth of said three-dimensional microelectronic structure occurs; passing a second precursor material for a selected three-dimensional microelectronic structure into a reaction chamber at temperatures sufficient to maintain said precursor material in a predominantly gaseous state; maintaining said reaction chamber under sufficient pressures whereby a second portion of said three-dimensional microelectronic structure formation is enhanced; applying an electric field between an electrode and said microelectronic structure at a desired point under conditions whereat said second portion of a selected three-dimensional microelectronic structure is formed from said second precursor material; and, positionally adjusting either said formed three-dimensional microelectronic structure or said electrode whereby further controlled growth of said three-dimensional microelectronic structure occurs.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
Electron-accepting compound and composition for charge-transporting film, and luminescent element using same
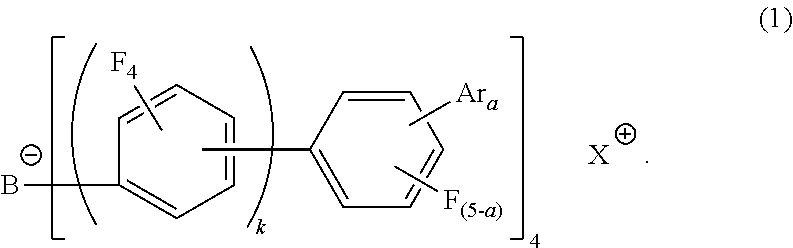
ActiveUS20190019956A1Improve thermal stabilityHigh hole injection/transporting abilitySolid-state devicesPretreated surfacesElectronStereochemistry
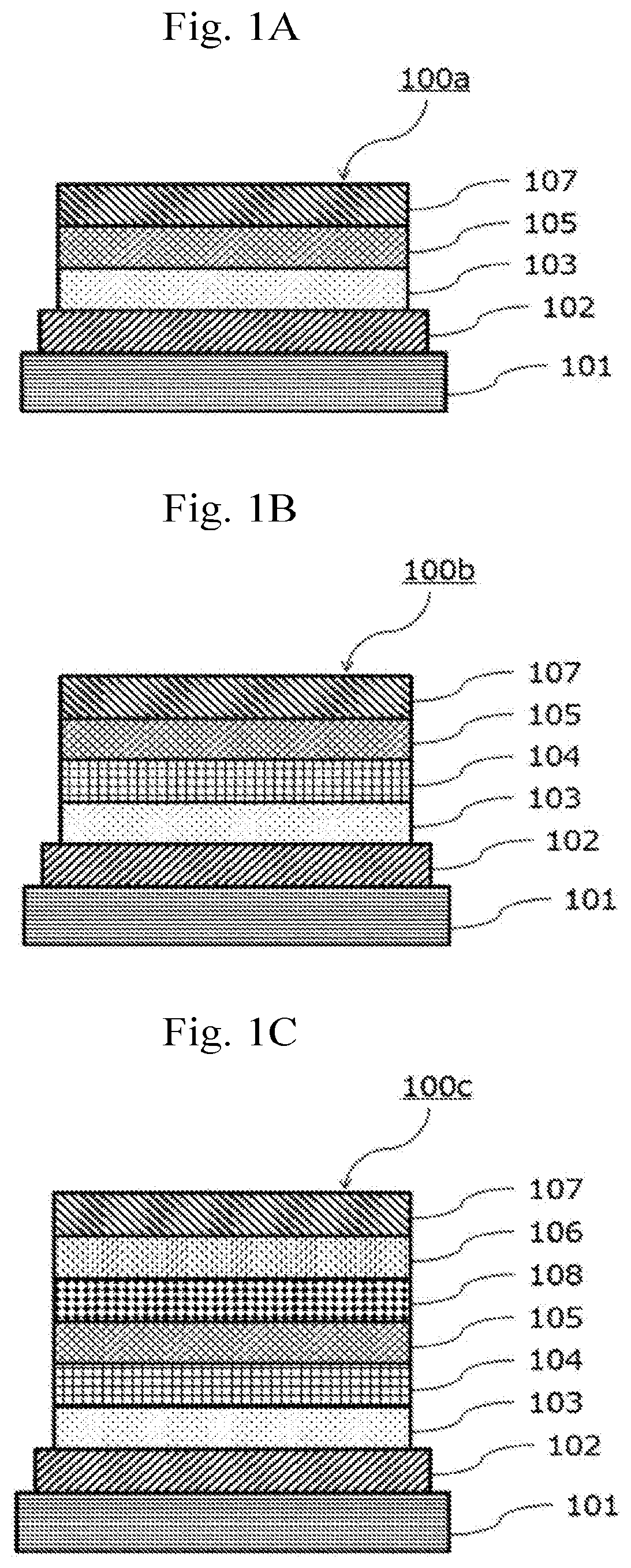
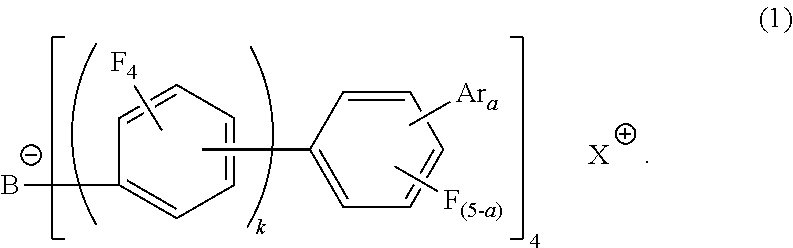
The present invention provides with an electron-accepting compound having a structure of the following formula (1):
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Semiconductor device and operation method for same
ActiveUS20130092895A1Improve reliabilityLow-voltage operationSolid-state devicesDigital storageElectrical conductorDevice material
A semiconductor device includes a first switching element, a second switching element, and at least one third switching element; wherein the third switching element includes a first terminal and a second terminal, wherein each of the first switching element and the second switching element includes an ion conductor, a first electrode which is disposed so as to have contact with the ion conductor and supplies metal ions to the ion conductor, and a second electrode which is disposed so as to have contact with the ion conductor and is less susceptible to ionization than the first electrode; and wherein(a) the first electrode of the first switching element and the first electrode of the second switching element are electrically connected each other, and the first terminal of the third switching element is electrically connected to only the first electrodes which are electrically connected each other or(b) the second electrode of the first switching element and the second electrode of the second switching element are electrically connected each other, and the first terminal of the third switching element is electrically connected to only the second electrodes which are electrically connected each other.
Owner:NANOBRIDGE SEMICON INC
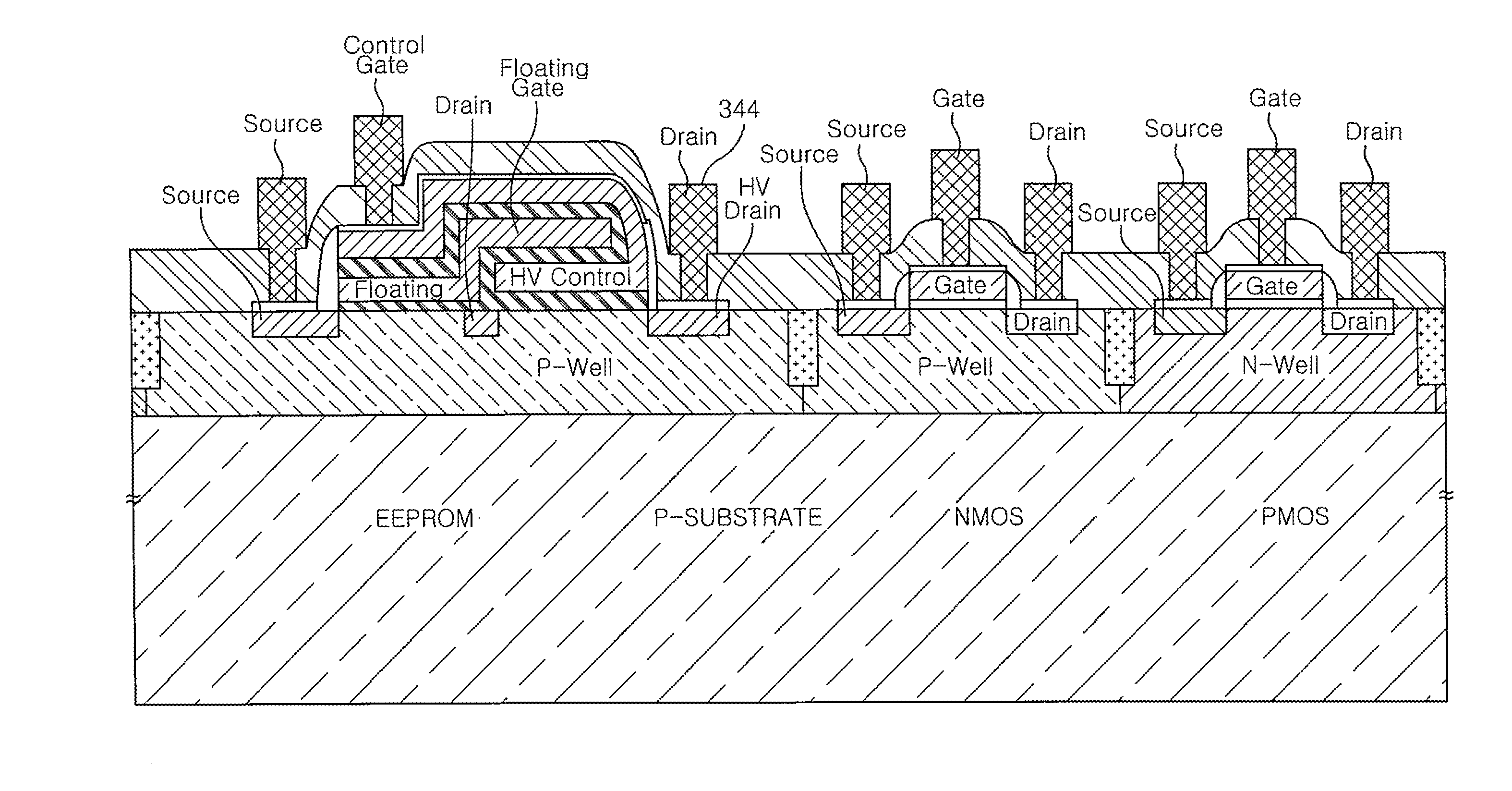
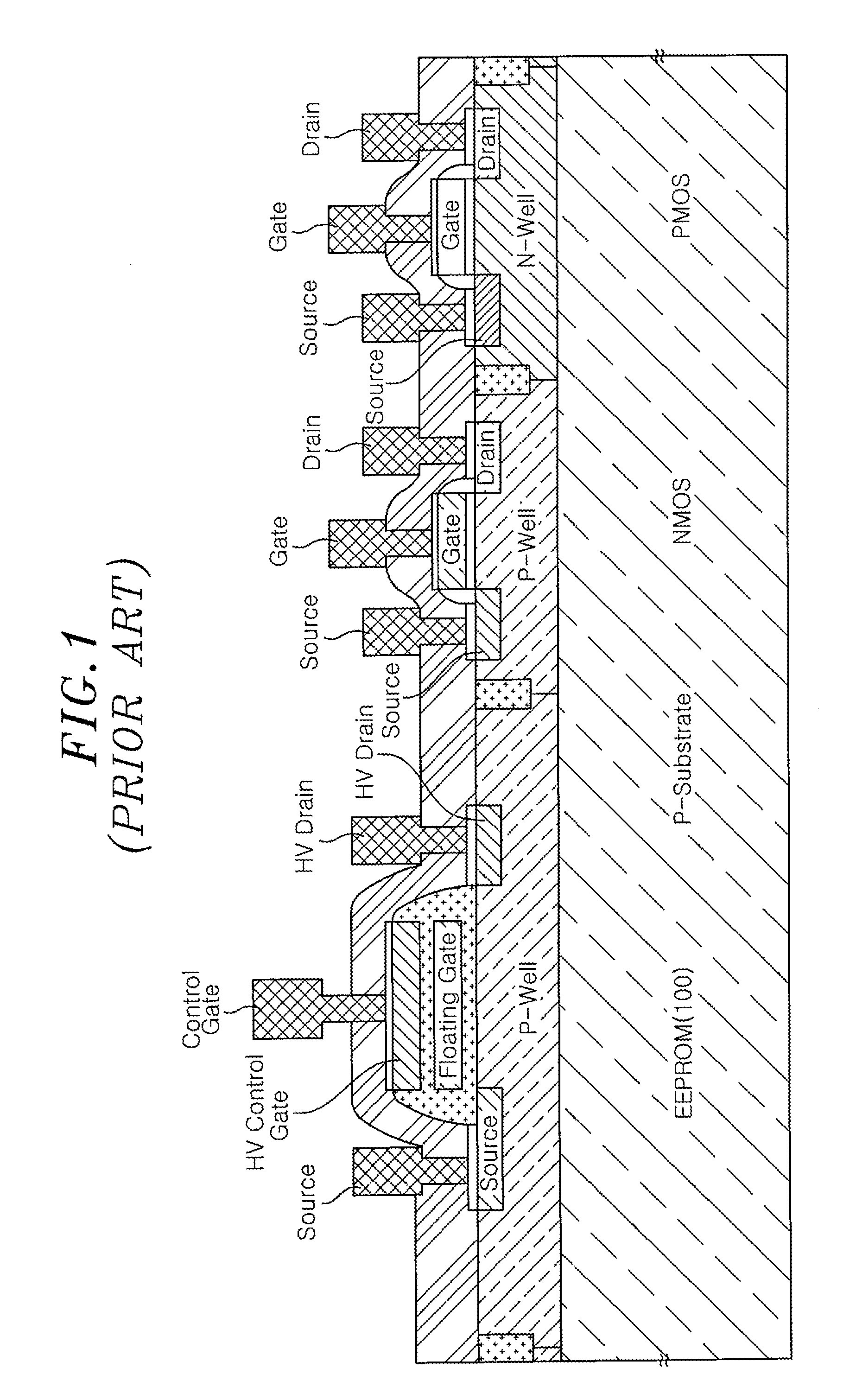
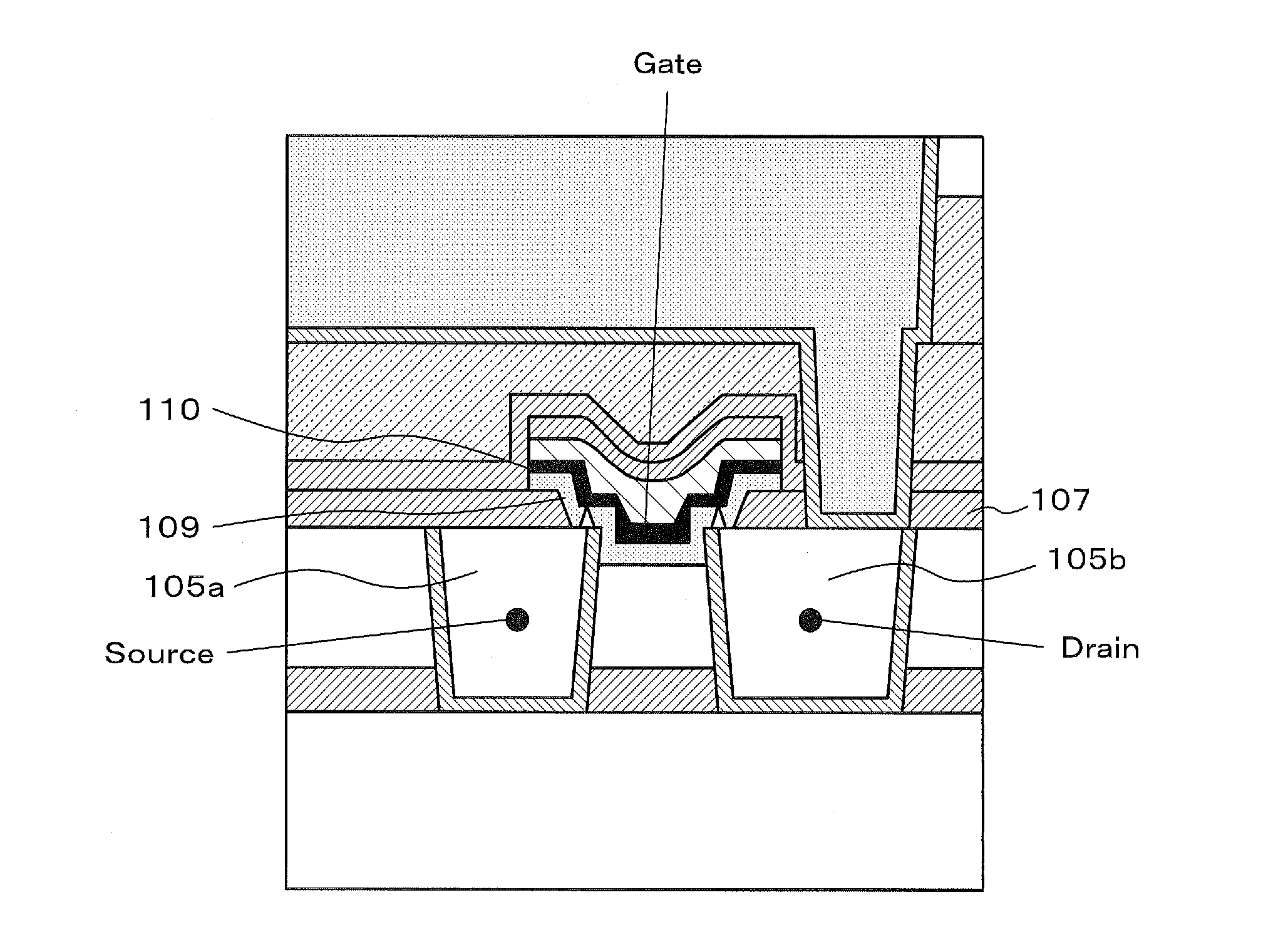
Non-volatile semiconductor memory device having an erasing gate
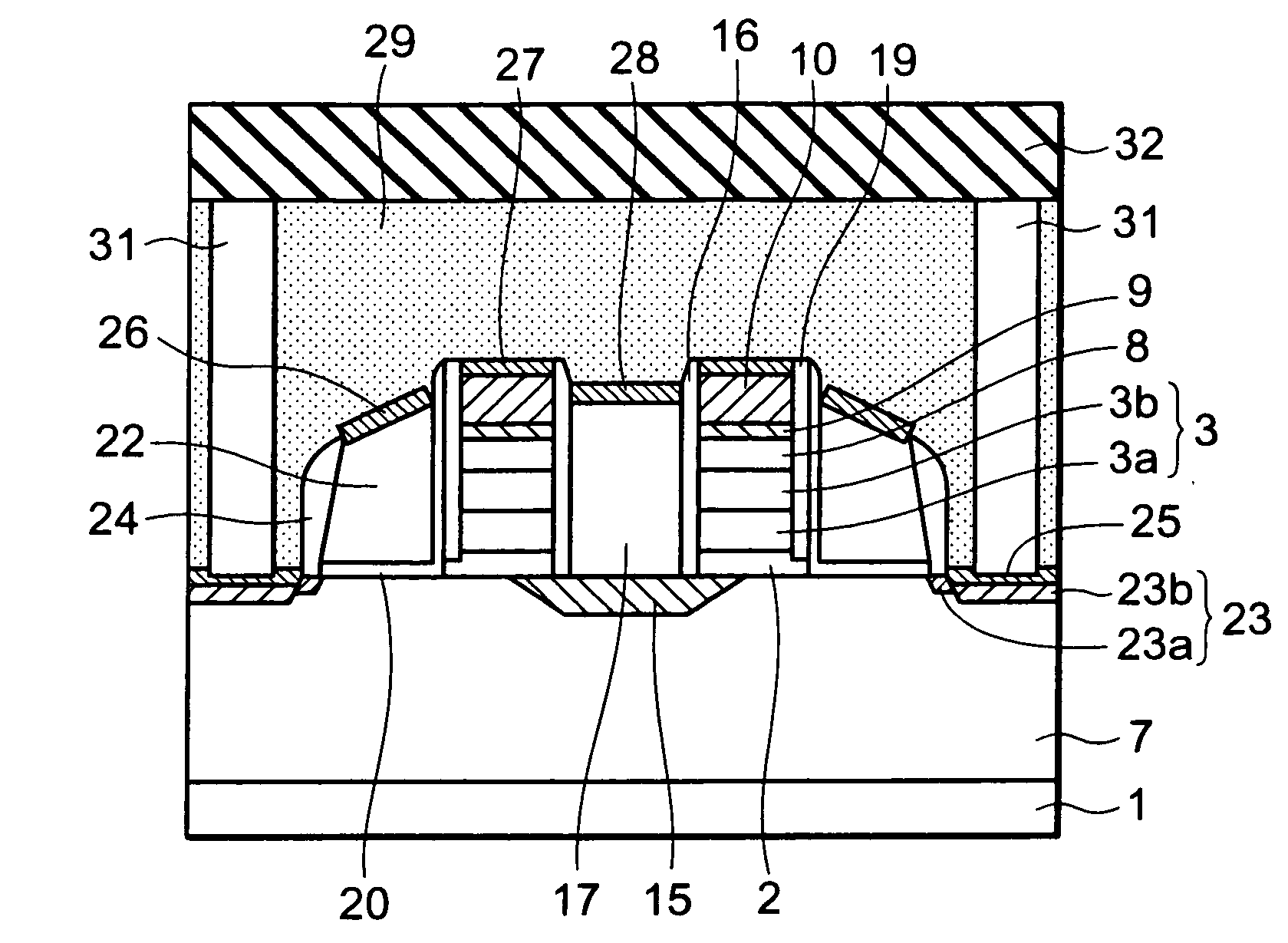
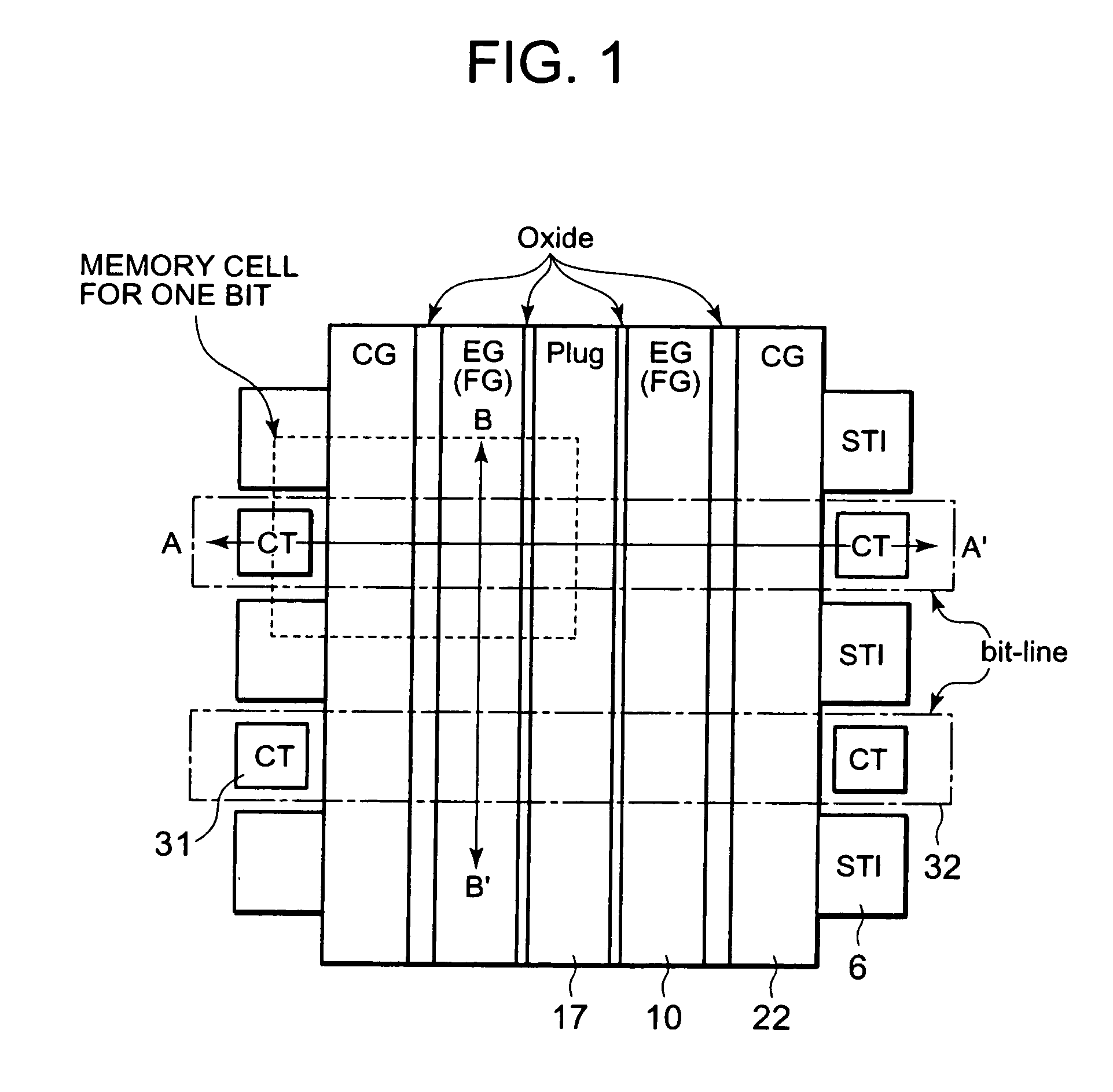
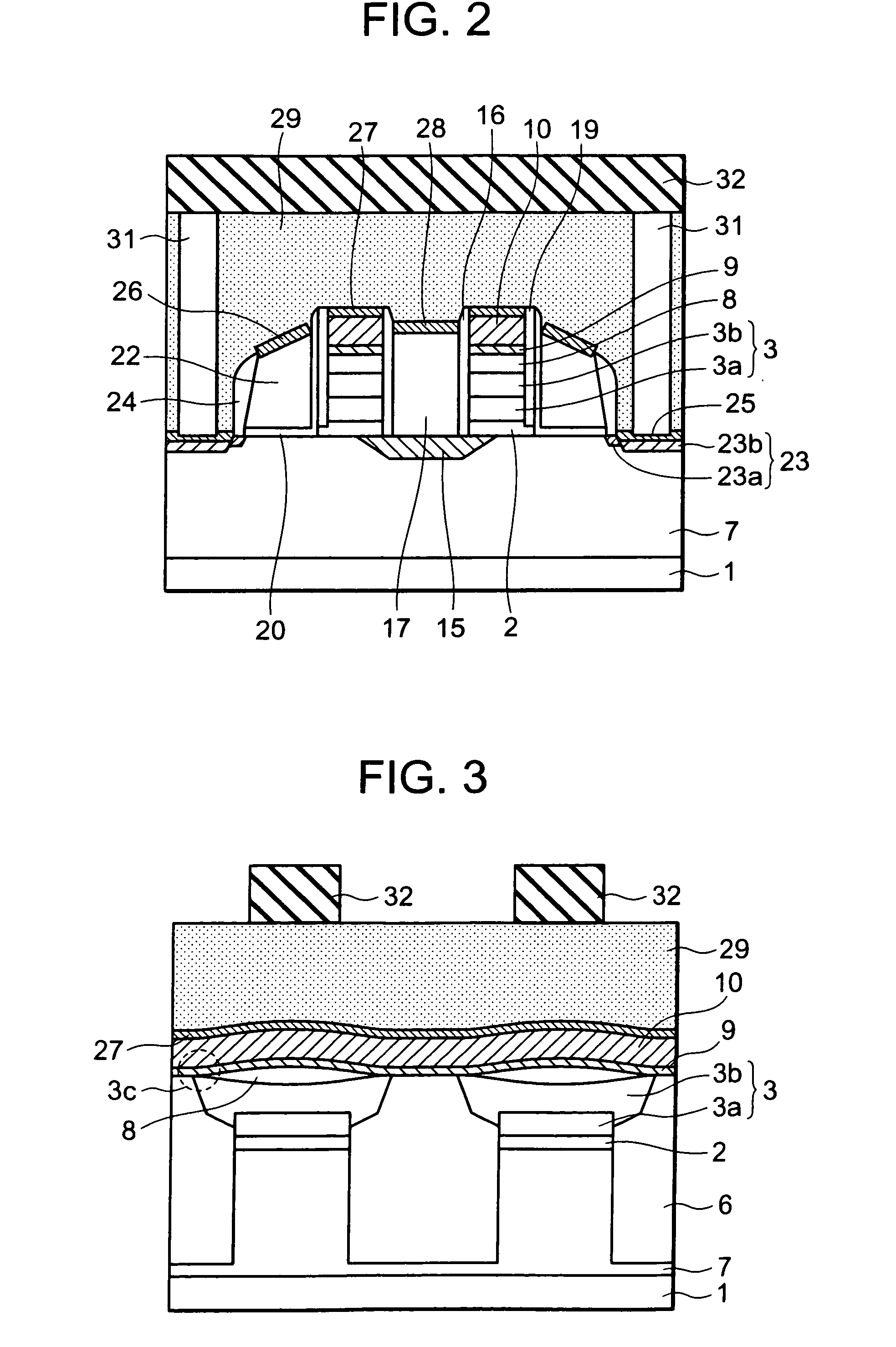
InactiveUS20090085092A1High speed operationLow voltage operationTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringDiffusion layer
A non-volatile semiconductor memory device includes: a floating gate formed above the semiconductor substrate; an erasing gate formed above the floating gate; a control gate formed above a channel region of a surface layer of the semiconductor substrate at a position corresponding to one lateral side of the floating gate and the erasing gate; a diffusion layer formed on the semiconductor substrate at a position corresponding to another lateral side of the floating gate and the erasing gate; a plug formed above the diffusion layer, the plug coupled to the diffusion layer; a first silicide film formed on an upper surface of the erasing gate; and a second silicide film formed on an upper surface of the plug, in which a height of the upper surface of the plug is flush with / or lower than a height of the upper surface of the erasing gate.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
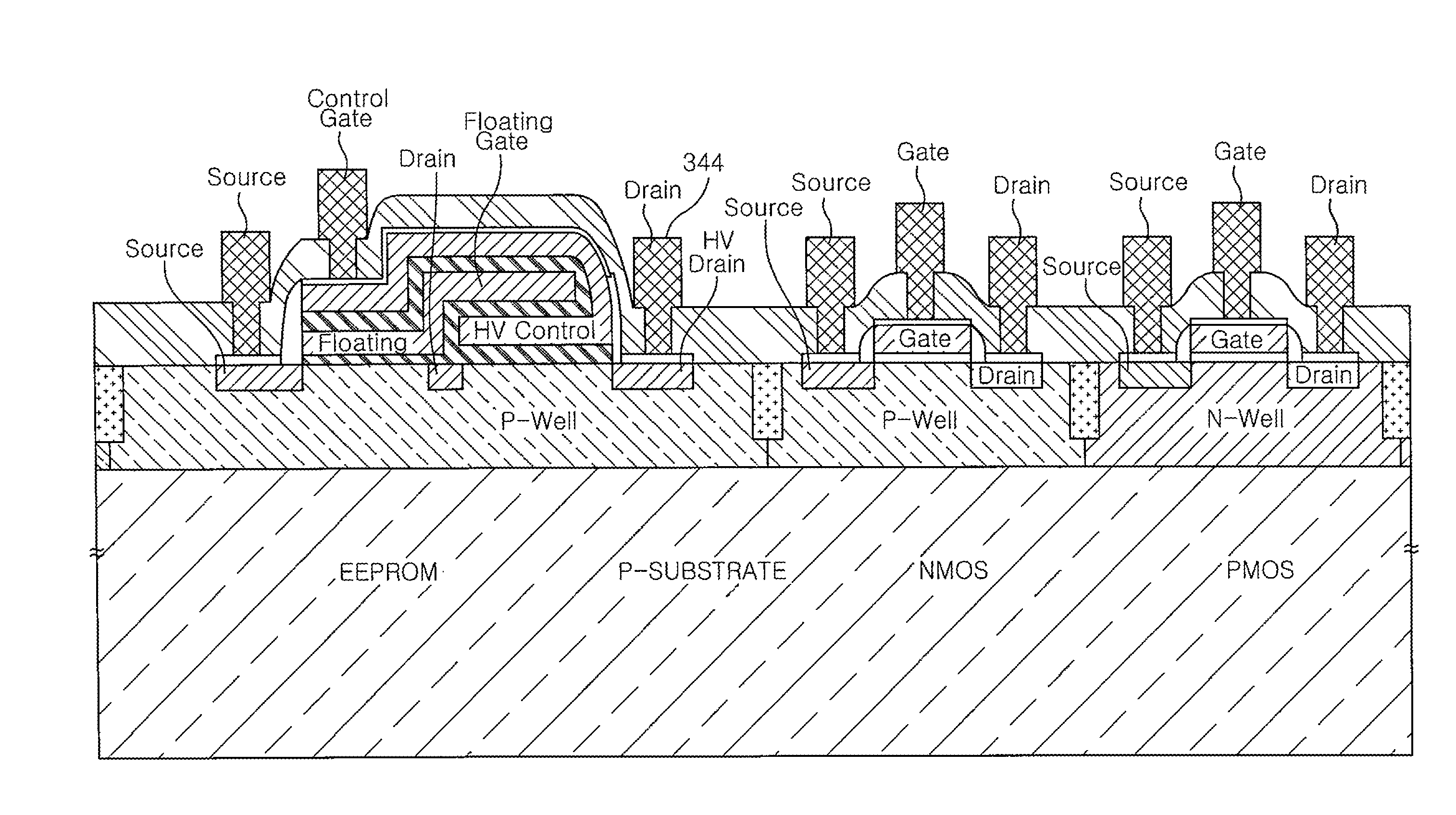
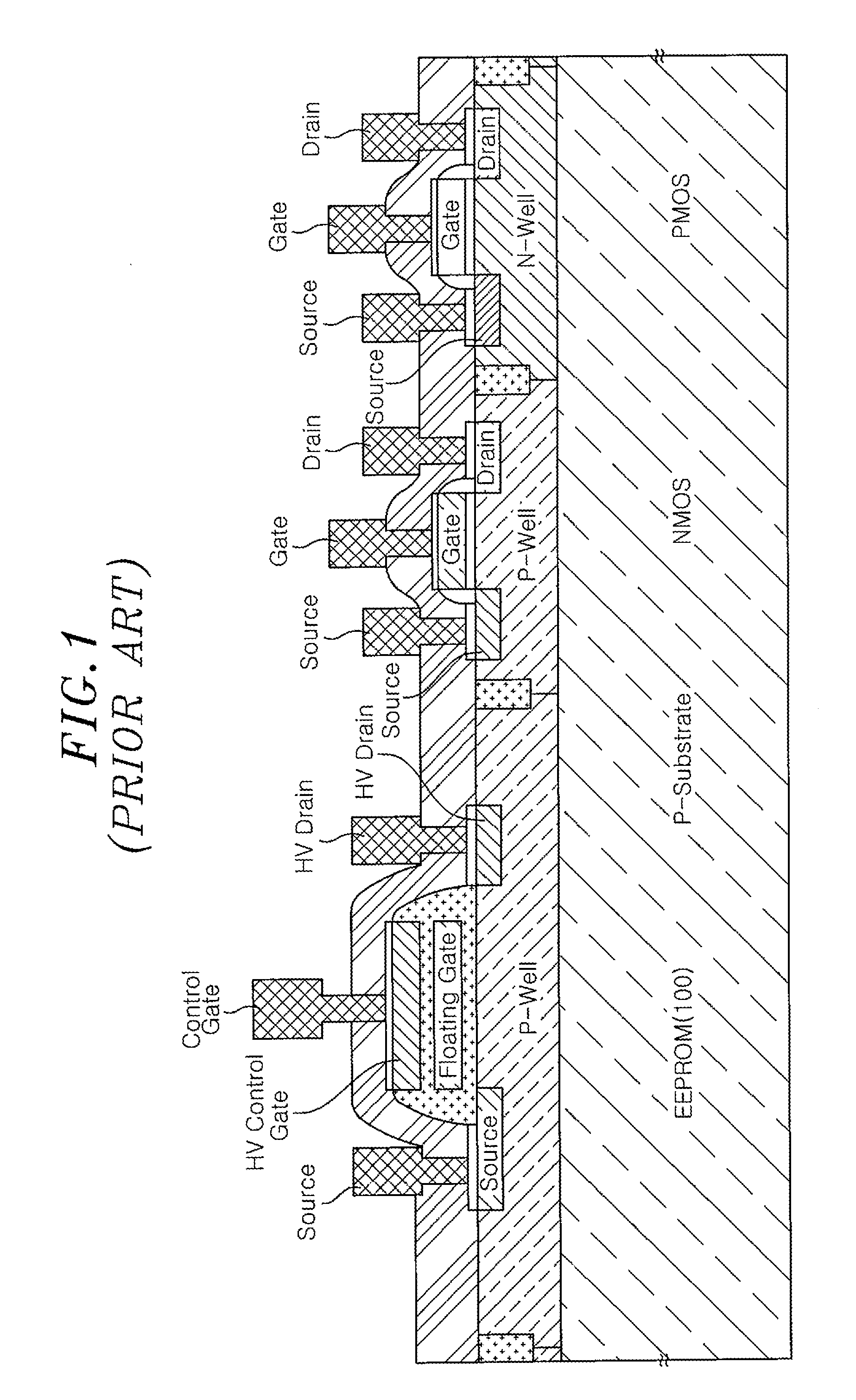
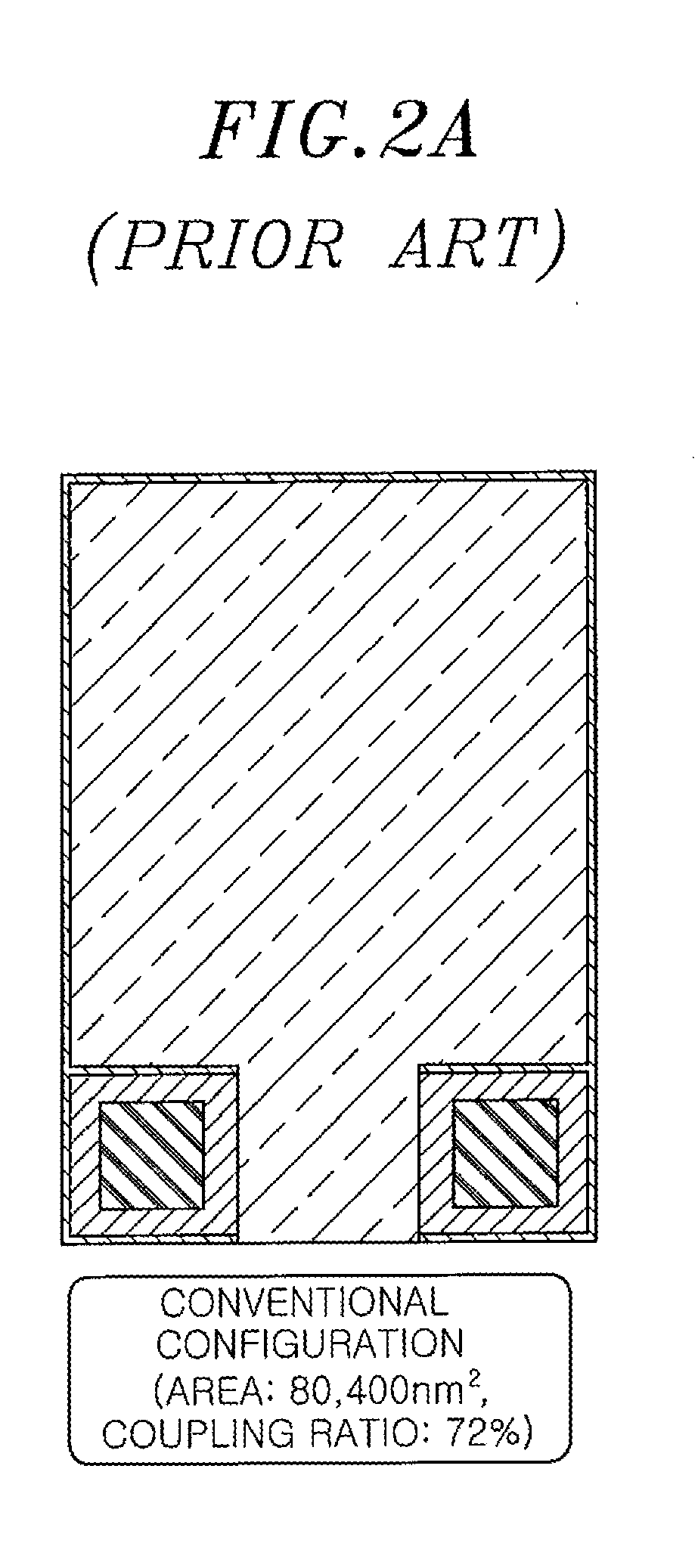
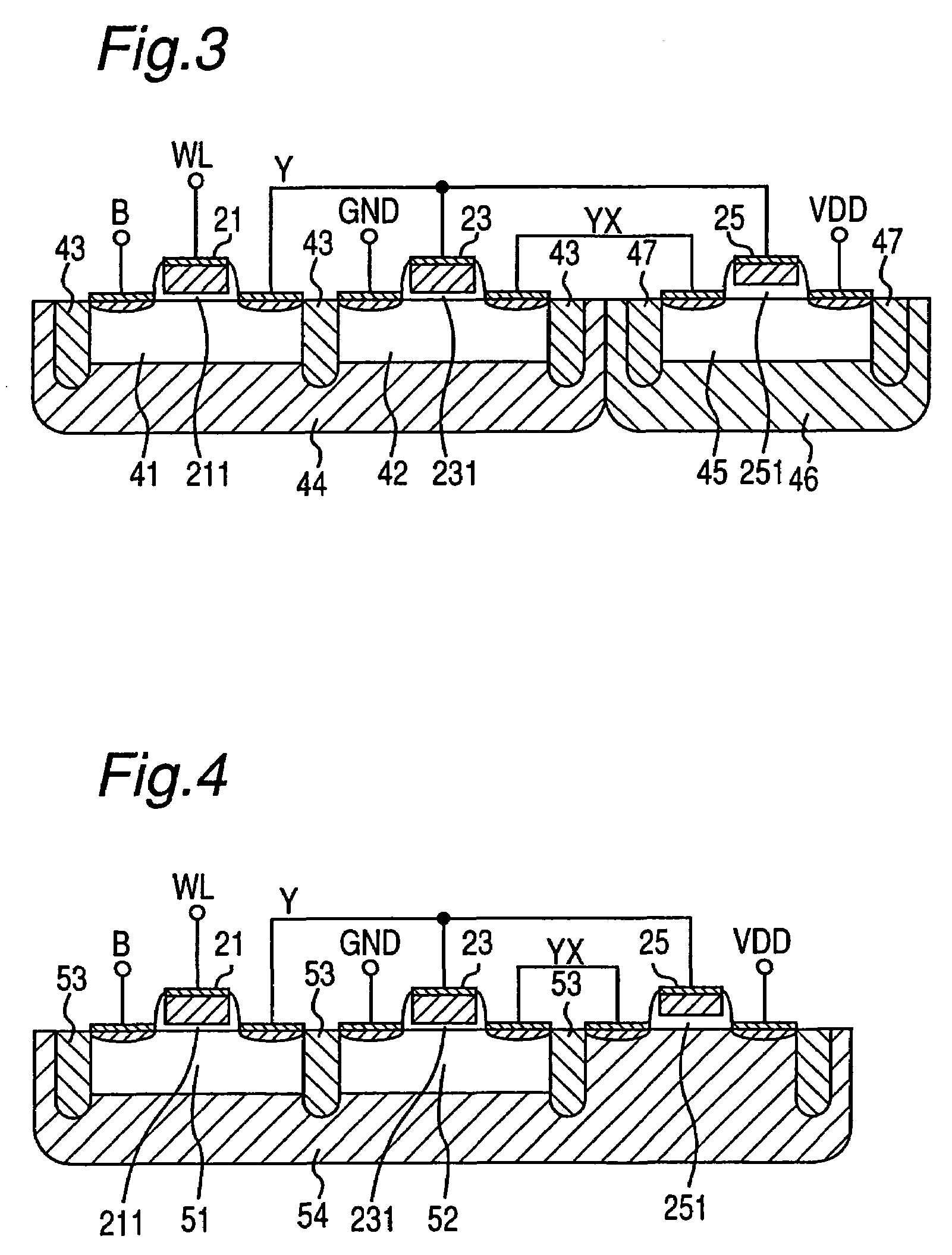
Electrically erasable programmable read-only memory and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS8421144B2Improve the coupling ratioLow-voltage operationTransistorSolid-state devicesProgrammable read-only memoryEngineering
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
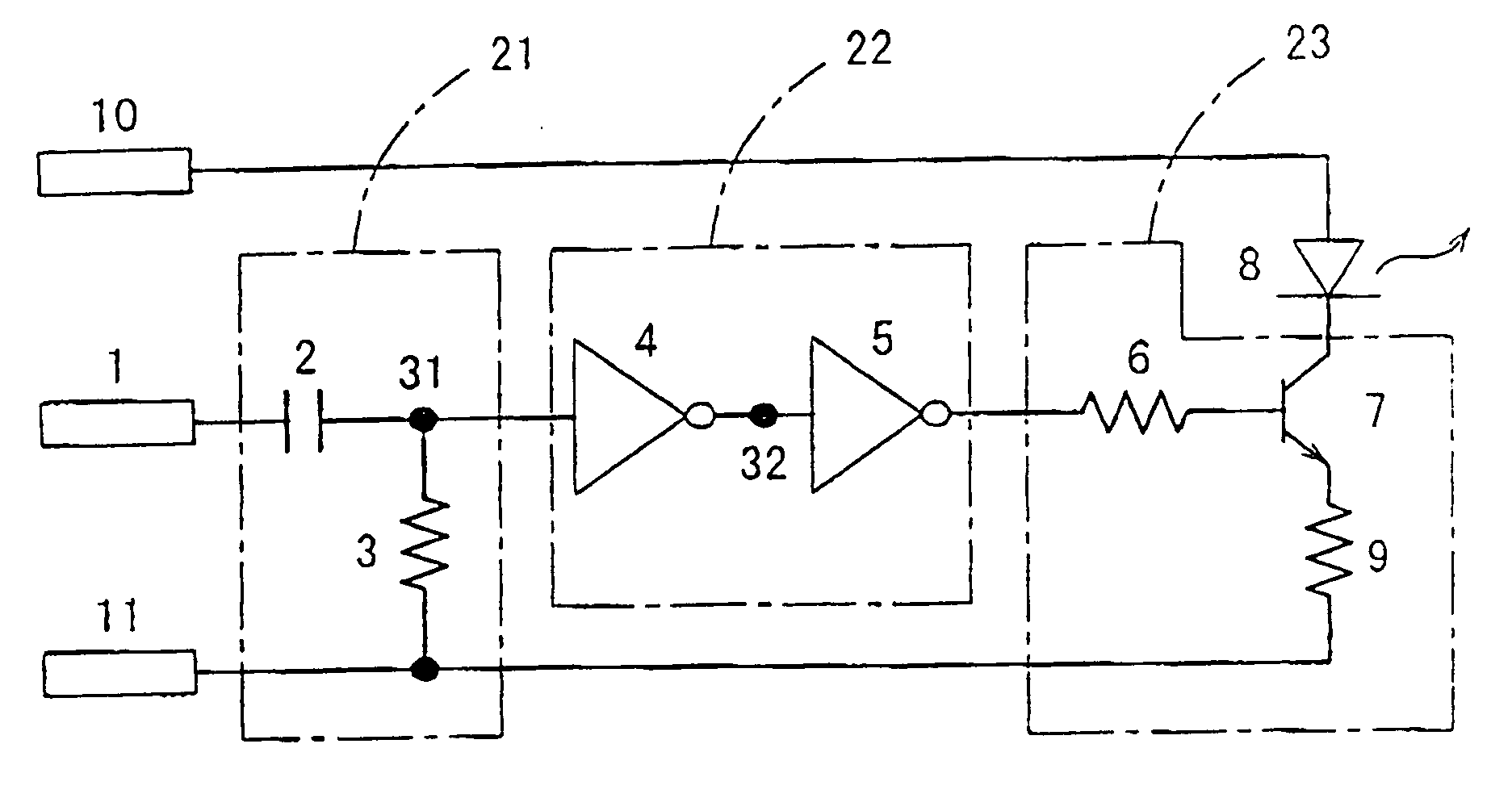
Optical transmitter
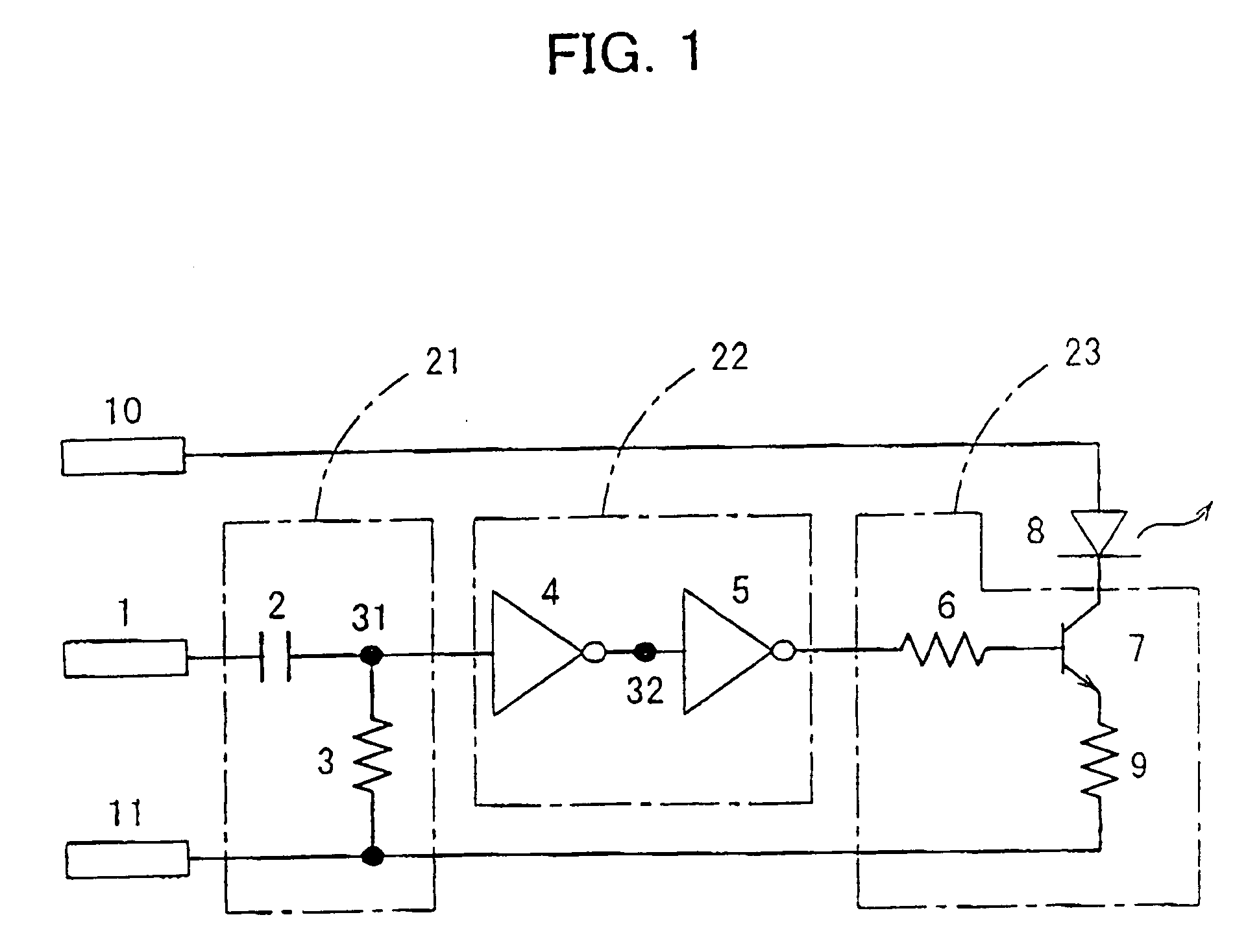
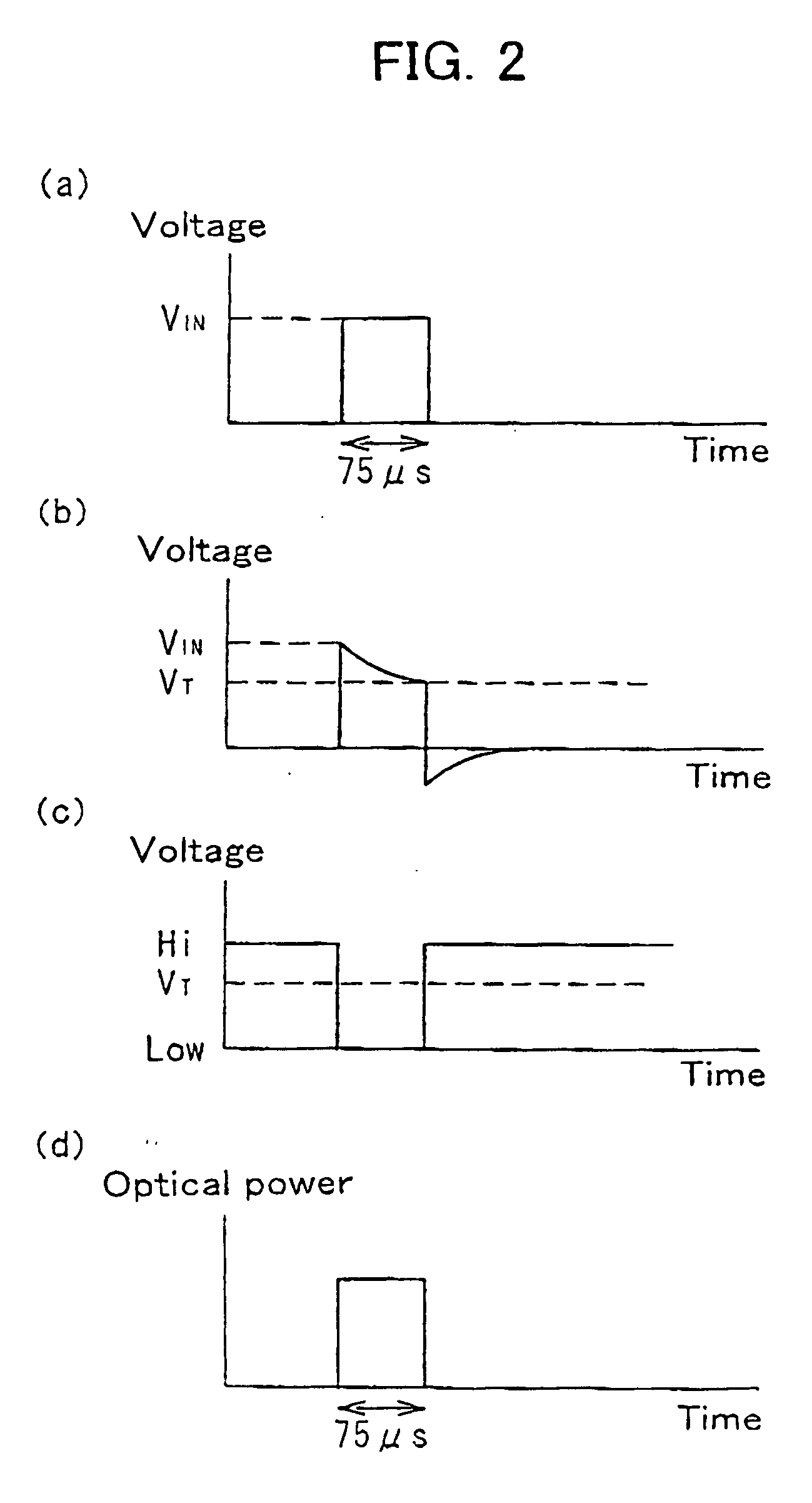
InactiveUS20050063710A1Low costAvoid fatiguePhotometry using reference valueMaterial analysis by optical meansDriver circuitEngineering
The present invention is intended to prevent a light-emitting diode from emitting light continuously in the case when the level at an input terminal is fixed high because of software or the like and to avoid various problems, such as battery exhaustion and breakdown of the light-emitting diode, in PDAs, cellular phones, etc. For these purposes, a high-pass filter 21 for passing the high-frequency components of an optical transmission input signal having a pulse waveform and a binary circuit 22 for binarizing the output signal of the high-pass filter 21 so as to be returned to a pulse waveform are provided in the preceding stage of a light-emitting device driving circuit 23 for driving a light-emitting diode 8 for optical transmission.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Static random access memory and semiconductor device using MOS transistors having channel region electrically connected with gate
InactiveUS7019369B2Improve reliabilityHigh electrostatic withstand voltageTransistorSolid-state devicesStatic random-access memoryRandom access memory
In an SRAM, memory cells are each constructed of four NMOS transistors and two PMOS transistors 25 and 26. The four NMOS transistors are each constructed of DTMOS in which the channel region is electrically connected to the gate. In each NMOS transistor, a threshold voltage Vth is lower in an ON stage than in an OFF stage. The threshold voltage Vth in the OFF stage is equivalent to that of an ordinary NMOS transistor in which the channel region is not electrically connected to the gate. Read and write circuits of the SRAM also include MOS transistors formed of DTMOS in which the channel region is electrically connected to the gate.
Owner:SHARP KK
Electrically erasable programmable read-only memory and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20110140189A1Improve the coupling ratioLow-voltage operationTransistorSolid-state devicesProgrammable read-only memoryEngineering
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
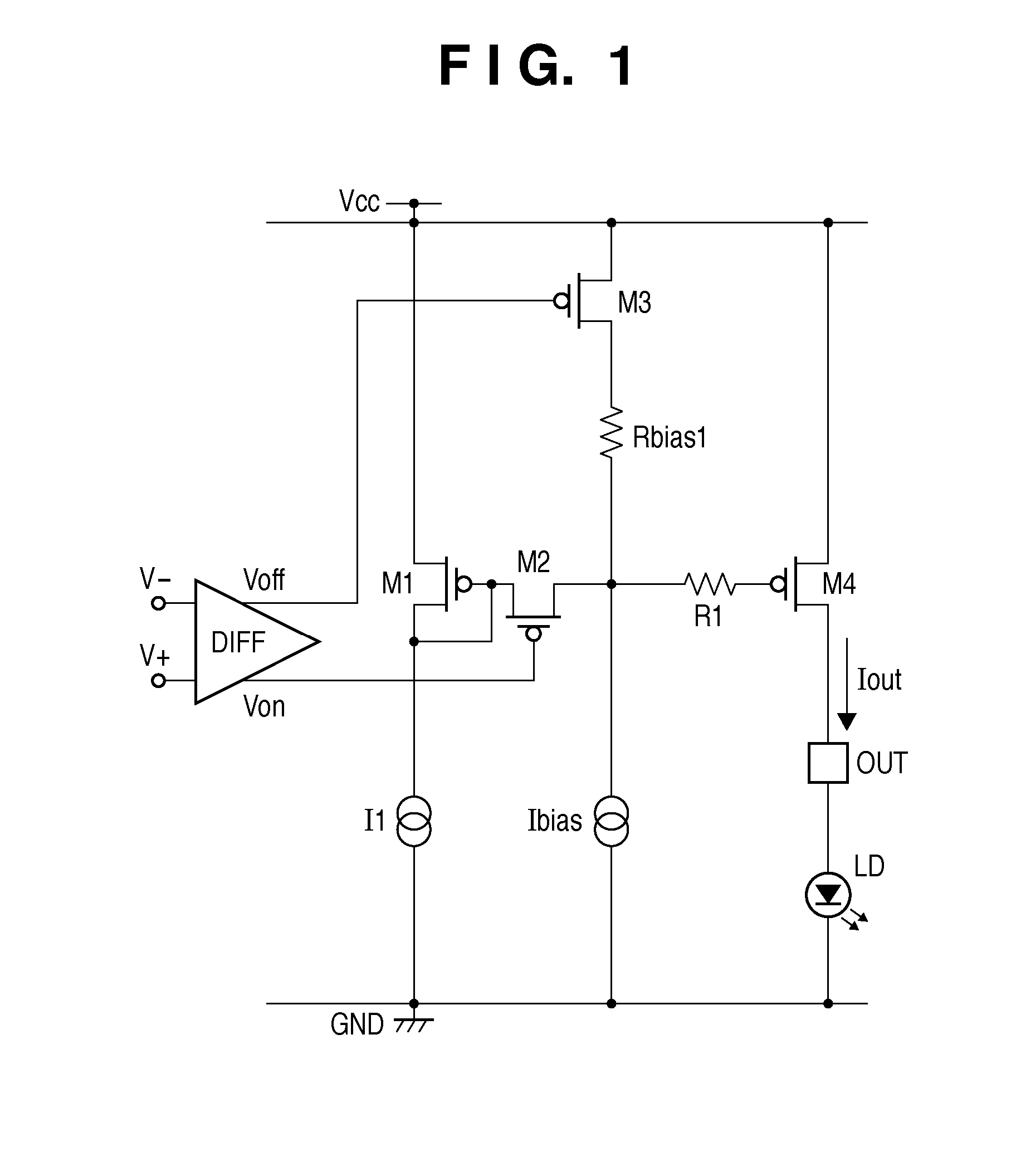
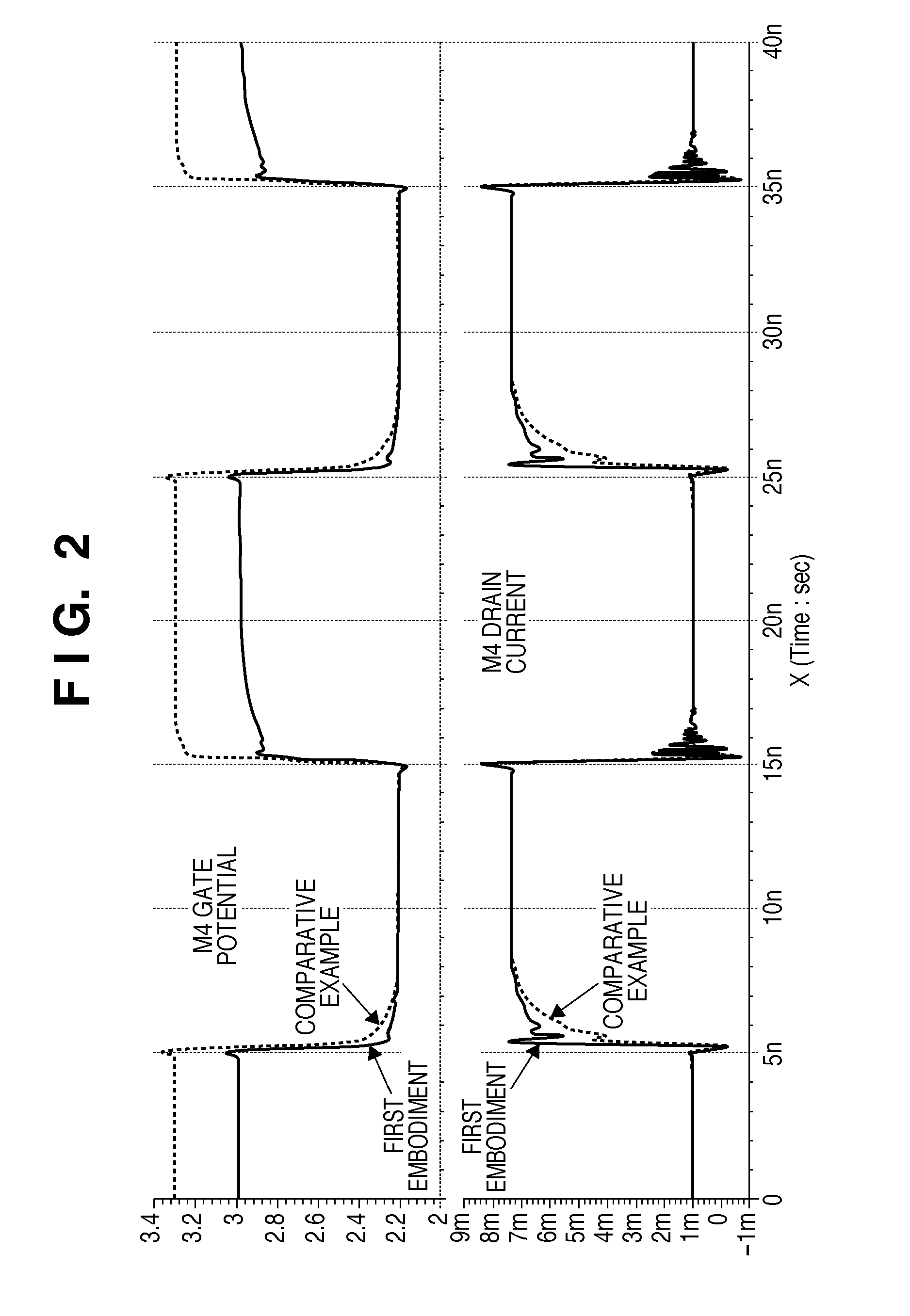
Light emitting element driving circuit
InactiveUS8358080B2High control precisionLow-voltage operationElectrical apparatusStatic indicating devicesElectricityPower flow
Owner:CANON KK
Mixed signal detection experimental device suitable for mechanical and electrical engineering
InactiveCN102881211ASimple designSmall sizeEducational modelsDigital signal processingElectrical engineering technology
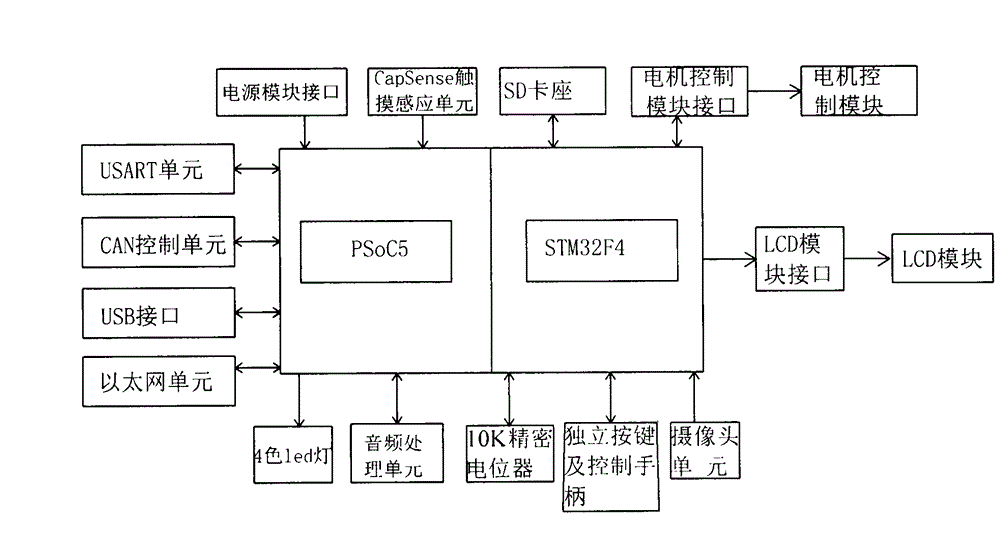
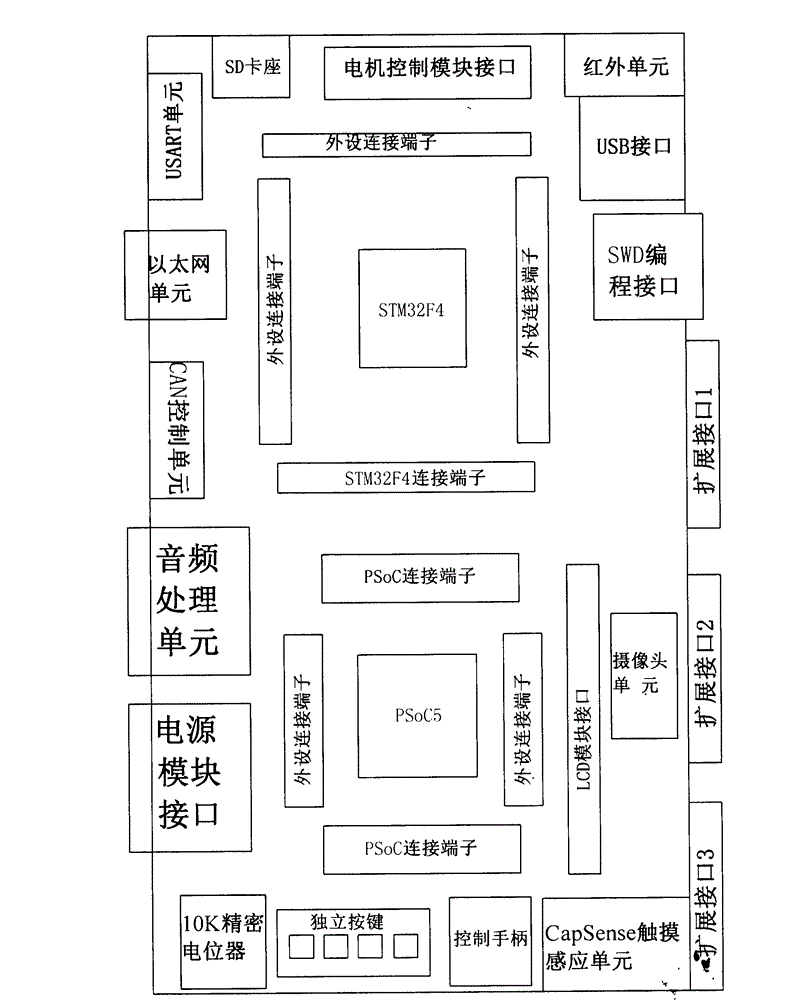
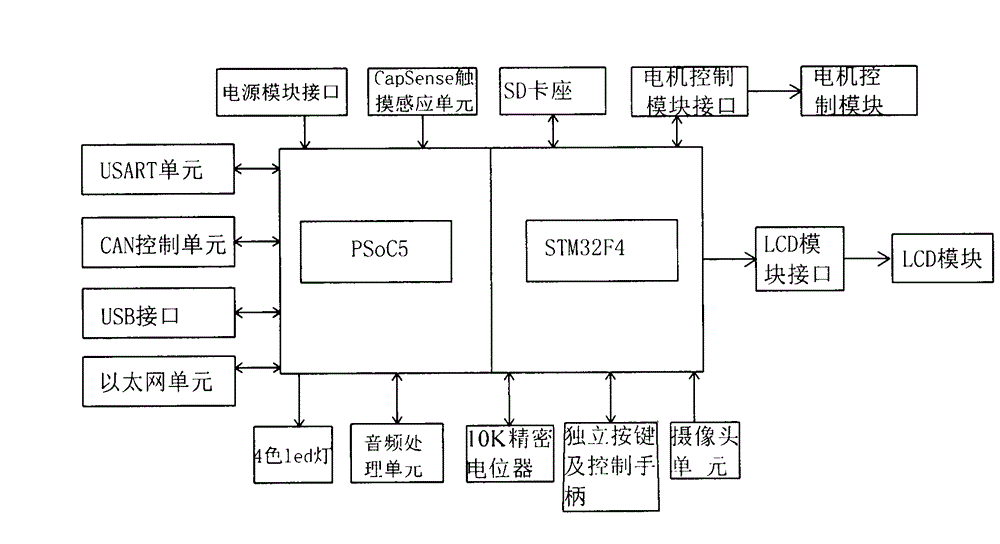
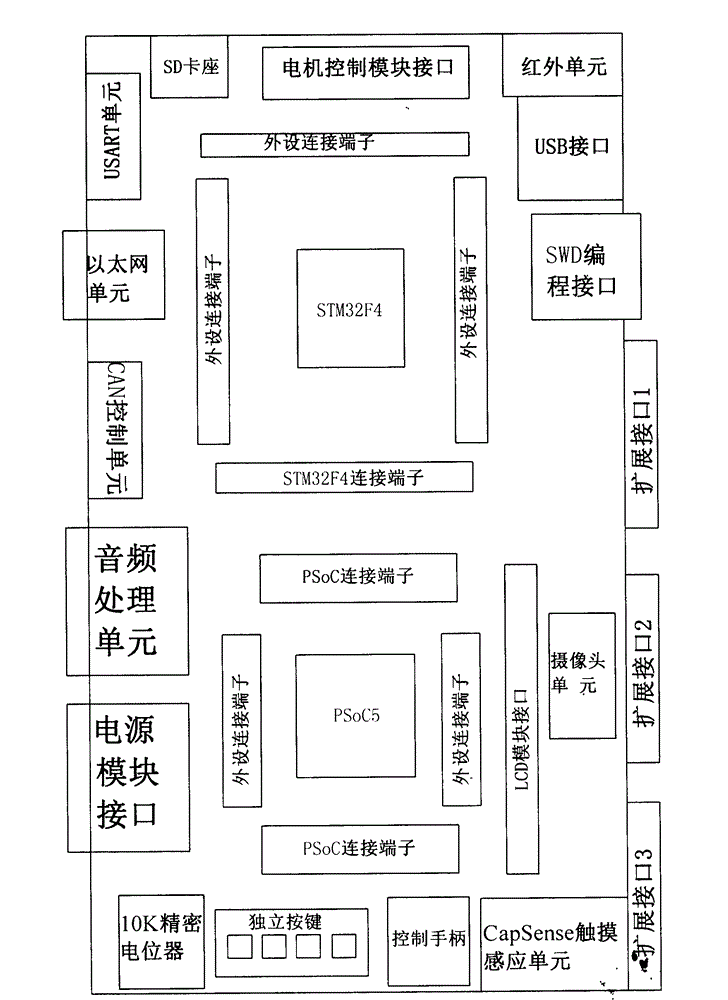
The invention discloses a mixed signal detection experimental device suitable for mechanical and electrical engineering. The device comprises a main board, a power module, a liquid crystal display (LCD) module, a motor control module, a PSoC5 (programmable system on chip) microprocessor module and a STM32F4 (scanning tunneling microscope) microprocessor module; the power module is used for providing power source for every electrical module of the device; the main board is configured with a dual-microprocessor slot; the PSoC5 microprocessor slot in a left half area is used for connecting the PSoC5 microprocessor module, the STM32F4 microprocessor slot in a right half area is used for connecting the STM32F4 microprocessor module; input and output pins of the PSoC5 microprocessor module and the STM 32F4 microprocessor module can enable double rows of contact pins to be connect with external equipment of the main board through connecting leads; the main board is connected with a plurality of external equipment and externally arranged interfaces. By adopting a dual-processor framework, the unique configurable simulative digital property of the PSoC5 is combined with the high performance, the real-time function and the digital signal processing property of the STM32F4, so that the required functions for the electronic system design of the mechanical and electrical engineering are covered.
Owner:XUZHOU UNIV OF TECH
Electron-accepting compound and composition for charge-transporting film, and luminescent element using same
ActiveUS11316112B2Improve thermal stabilityImprove abilitiesSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMaterials scienceMolecular physics
The present invention provides with an electron-accepting compound having a structure of the following formula (1):
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Method of fabricating free-form, high-aspect ratio components for high-current, high-speed microelectronics
InactiveUS20100289060A1Easy dischargeUnprecedented performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMicrostructural device manufactureElectronic structureFree form
Microelectronic structures and devices, and method of fabricating a three-dimensional microelectronic structure is provided, comprising passing a first precursor material for a selected three-dimensional microelectronic structure into a reaction chamber at temperatures sufficient to maintain said precursor material in a predominantly gaseous state; maintaining said reaction chamber under sufficient pressures to enhance formation of a first portion of said three-dimensional microelectronic structure; applying an electric field between an electrode and said microelectronic structure at a desired point under conditions whereat said first portion of a selected three-dimensional microelectronic structure is formed from said first precursor material; positionally adjusting either said formed three-dimensional microelectronic structure or said electrode whereby further controlled growth of said three-dimensional microelectronic structure occurs; passing a second precursor material for a selected three-dimensional microelectronic structure into a reaction chamber at temperatures sufficient to maintain said precursor material in a predominantly gaseous state; maintaining said reaction chamber under sufficient pressures whereby a second portion of said three-dimensional microelectronic structure formation is enhanced; applying an electric field between an electrode and said microelectronic structure at a desired point under conditions whereat said second portion of a selected three-dimensional microelectronic structure is formed from said second precursor material; and, positionally adjusting either said formed three-dimensional microelectronic structure or said electrode whereby further controlled growth of said three-dimensional microelectronic structure occurs.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
Semiconductor device and operation method for same
ActiveUS9059082B2Improve reliabilityLow-voltage operationSolid-state devicesDigital storageElectrical conductorSemiconductor
A semiconductor device includes a first switching element, a second switching element, and at least one third switching element; wherein the third switching element includes a first terminal and a second terminal, wherein each of the first switching element and the second switching element includes an ion conductor, a first electrode which is disposed so as to have contact with the ion conductor and supplies metal ions to the ion conductor, and a second electrode which is disposed so as to have contact with the ion conductor and is less susceptible to ionization than the first electrode; and wherein(a) the first electrode of the first switching element and the first electrode of the second switching element are electrically connected each other, and the first terminal of the third switching element is electrically connected to only the first electrodes which are electrically connected each other or(b) the second electrode of the first switching element and the second electrode of the second switching element are electrically connected each other, and the first terminal of the third switching element is electrically connected to only the second electrodes which are electrically connected each other.
Owner:NANOBRIDGE SEMICON INC
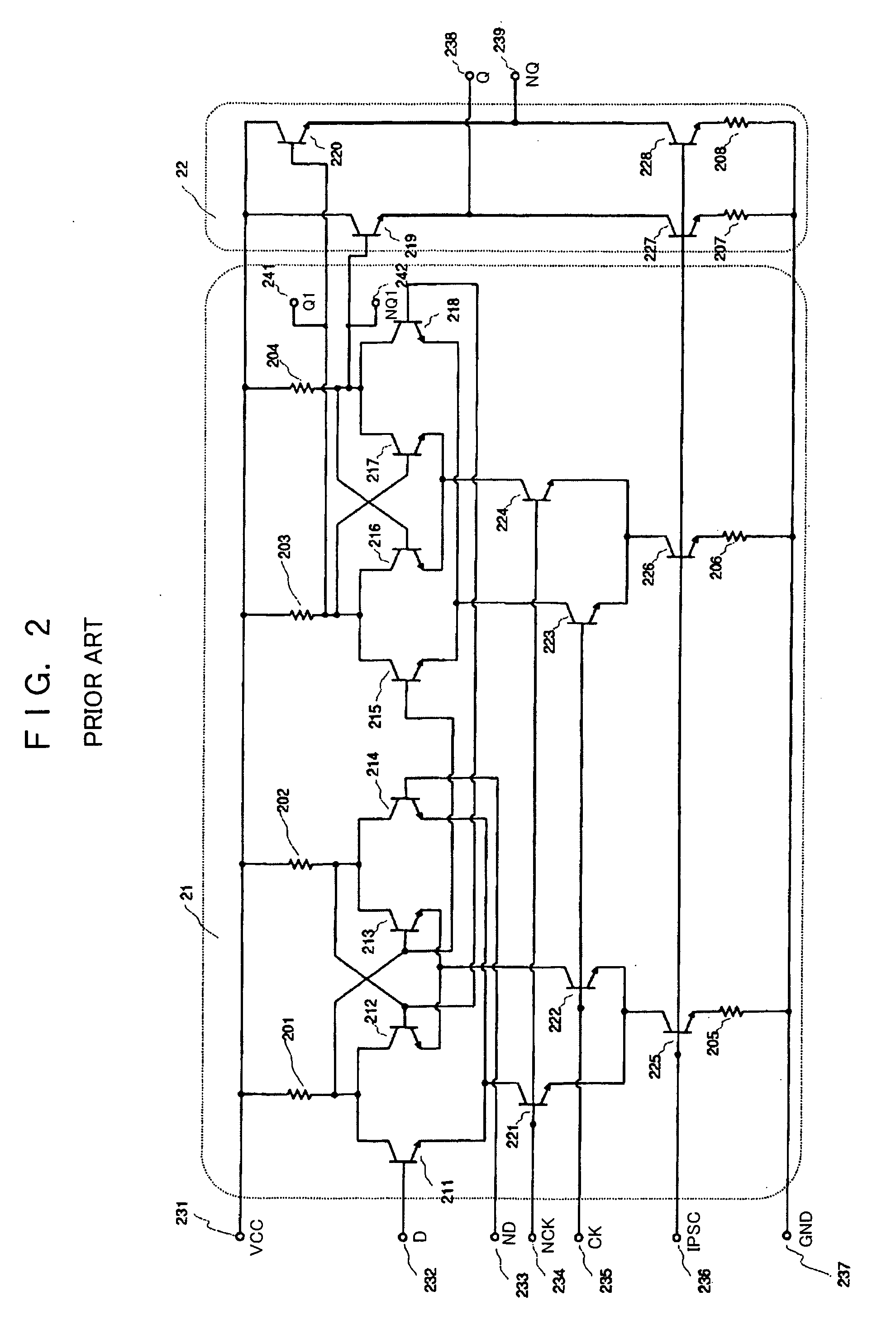
Flip-flop circuit and frequency division circuit using same
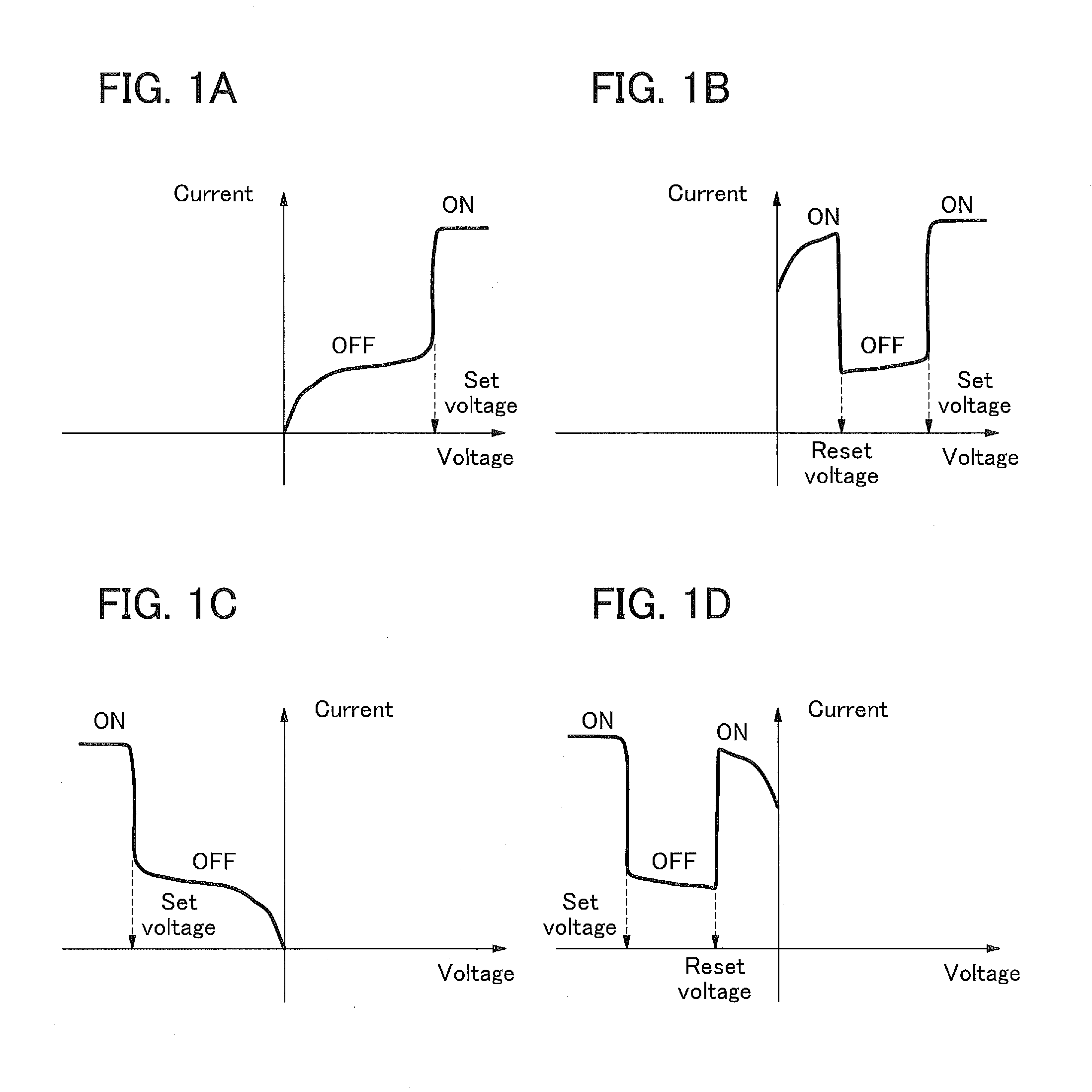
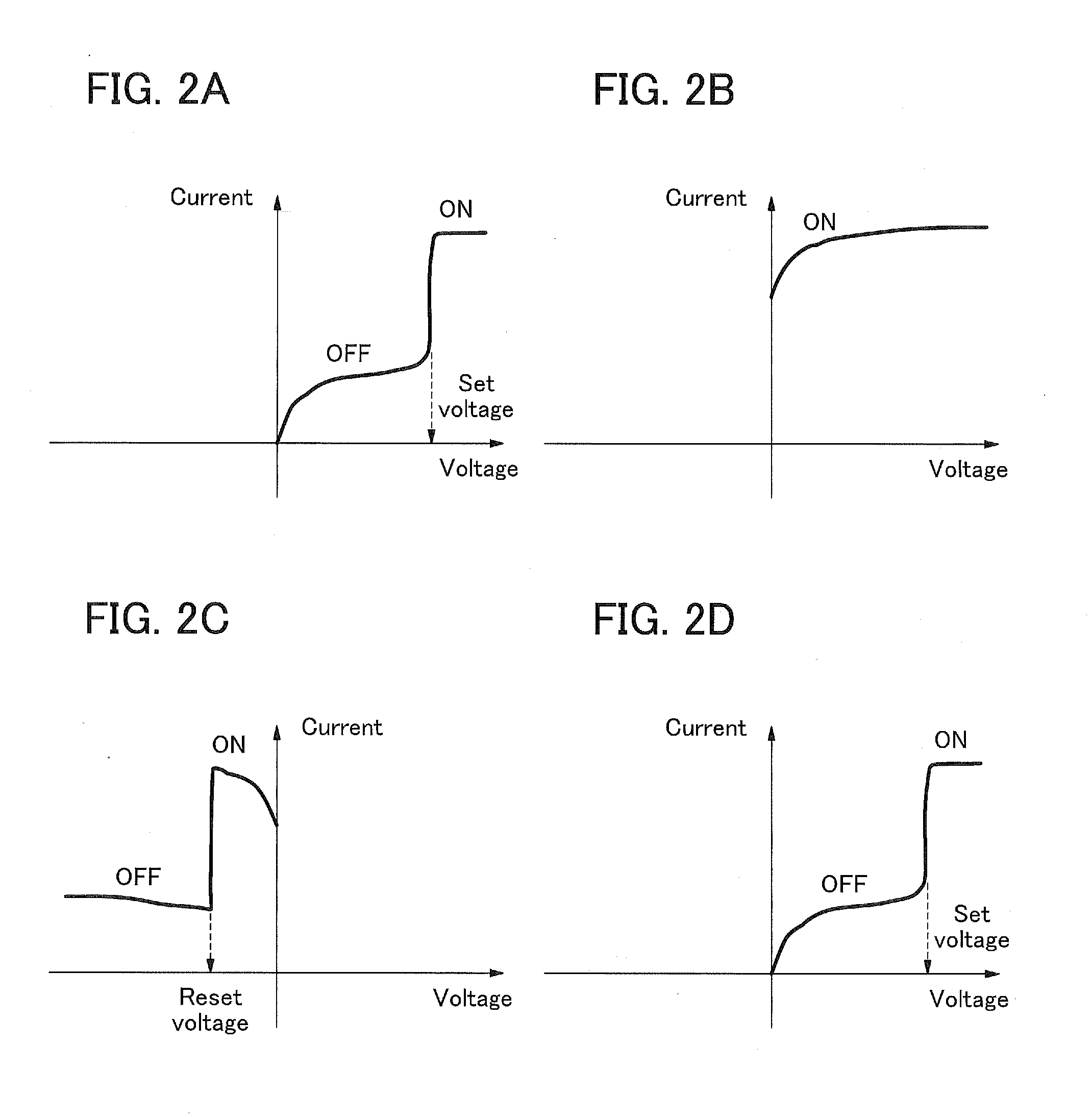
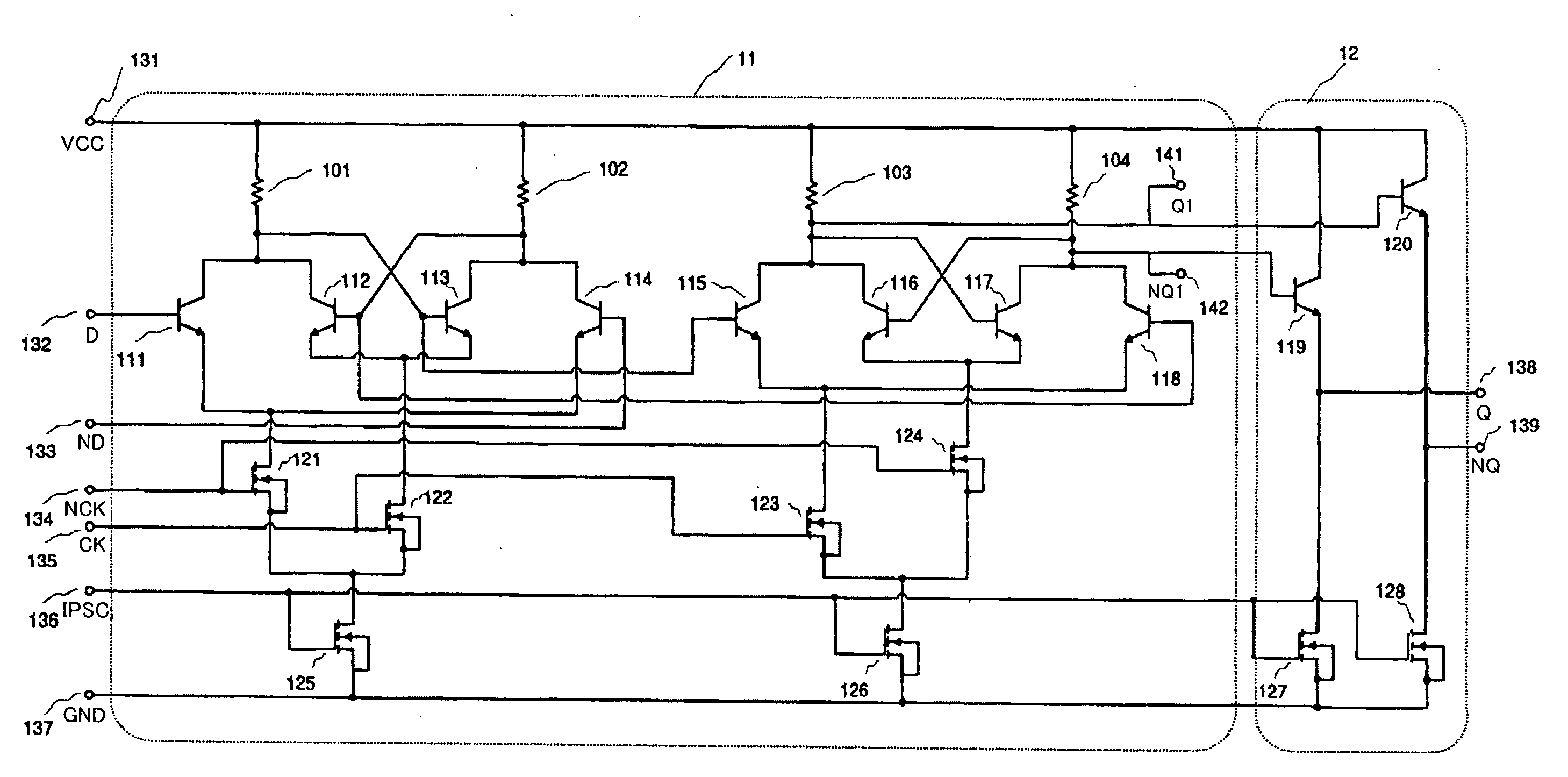
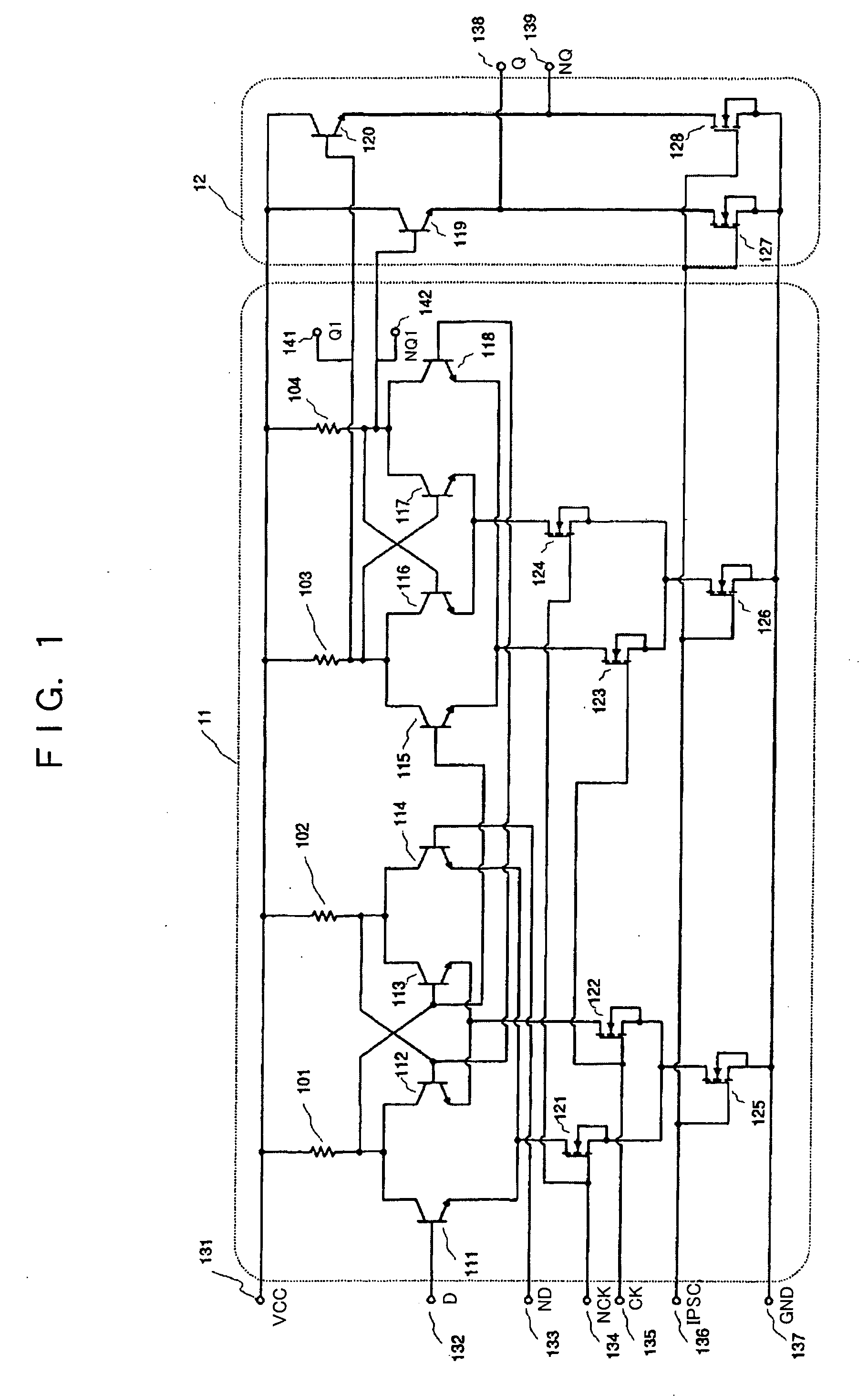
InactiveUS20050218951A1Low-voltage operationLogic circuits using semiconductor devicesElectric pulse generatorLow voltageEngineering
An object of the present invention is to obtain a frequency division circuit including a flip-flop circuit capable of low-voltage and high-frequency operation. The frequency division circuit has bipolar transistors and MOS transistors. Thus, the circuit includes transistors that are connected to the transistor to which the clock input is input, that execute the differential operation after being input with data input signals, and that output signals of resistors, and also transistors that are similarly connected to the transistor to which Ck is input and that hold signals of resistors, transistors that are connected to the transistor to which Ck is input and that output signals of resistors, and transistors that are connected to the transistor to which NCk is input and that hold signals of resistors.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Top-gate thin-film transistors using nanoparticles and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS7972931B2Promote formationLow-voltage operationNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricLow voltage
The present invention relates to a method of manufacturing thin-film transistors using nanoparticles and thin film transistors manufactured by the method. A hydrophilic buffer layers are deposited on the substrates to facilitate formation of nanoparticle films. Sintered nanoparticles are used as an active layer and dielectric materials of high dielectric coefficient are also used as a gate dielectric layer to form a top gate electrode on the gate dielectric layer, thereby enabling low-voltage operation and low-temperature fabrication.
Owner:KOREA UNIV IND & ACADEMIC CALLABORATION FOUND
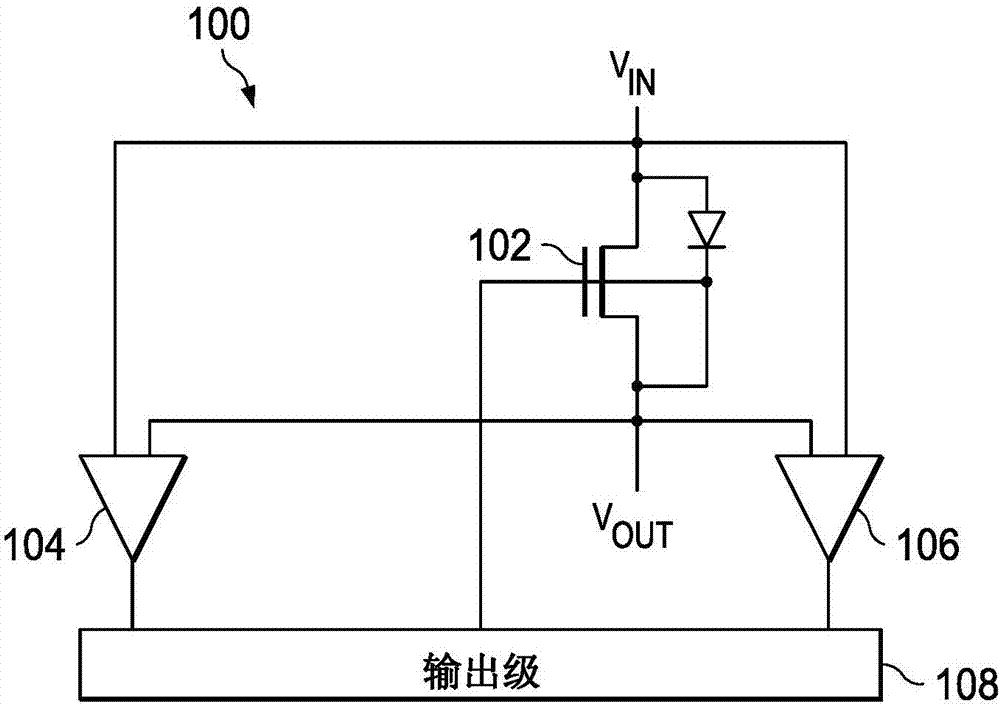
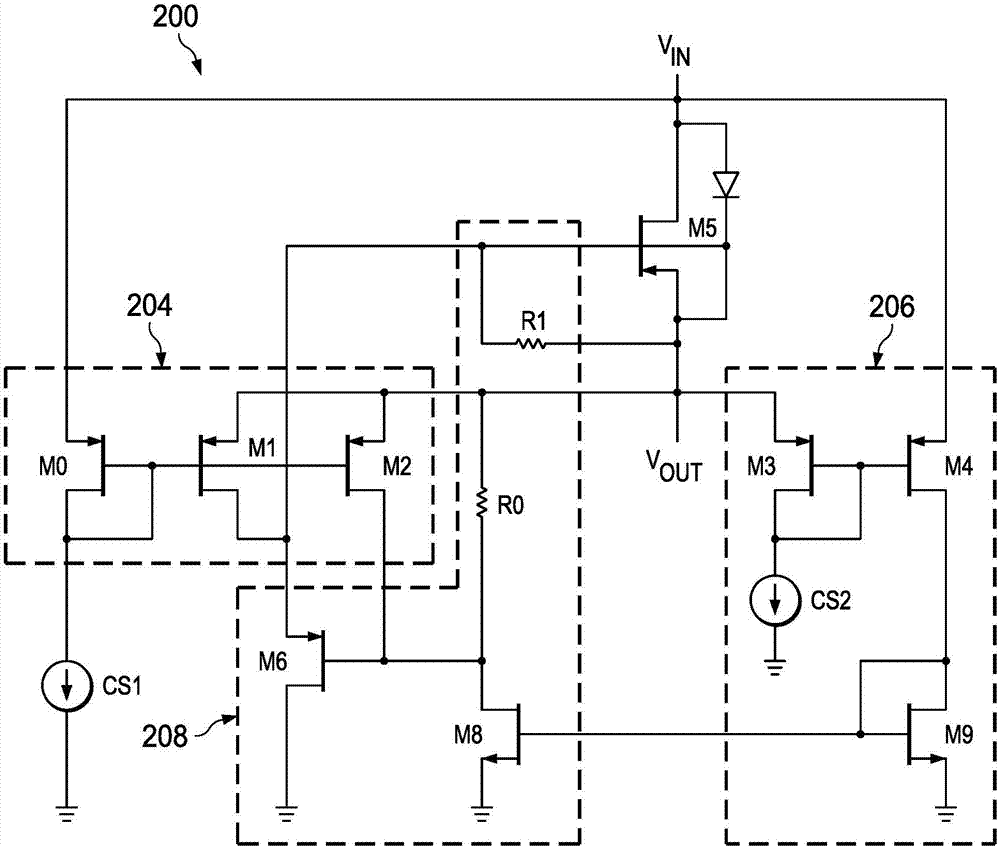
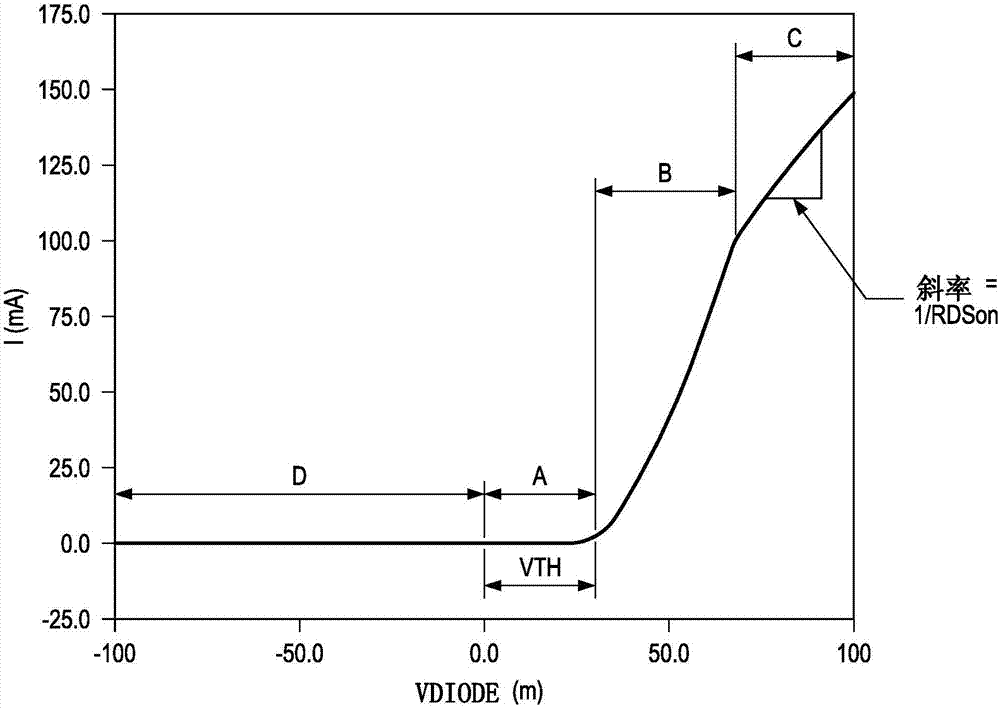
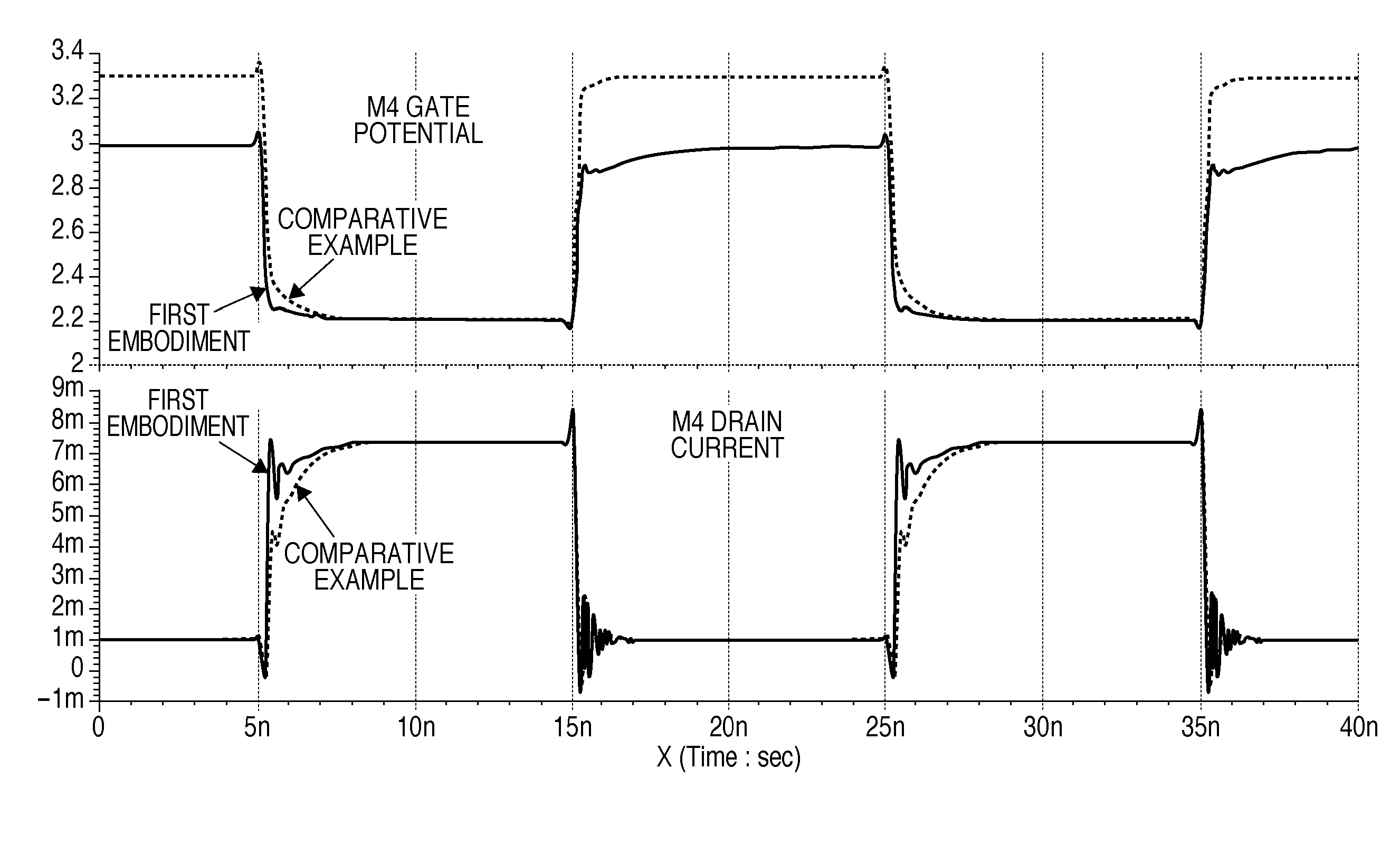
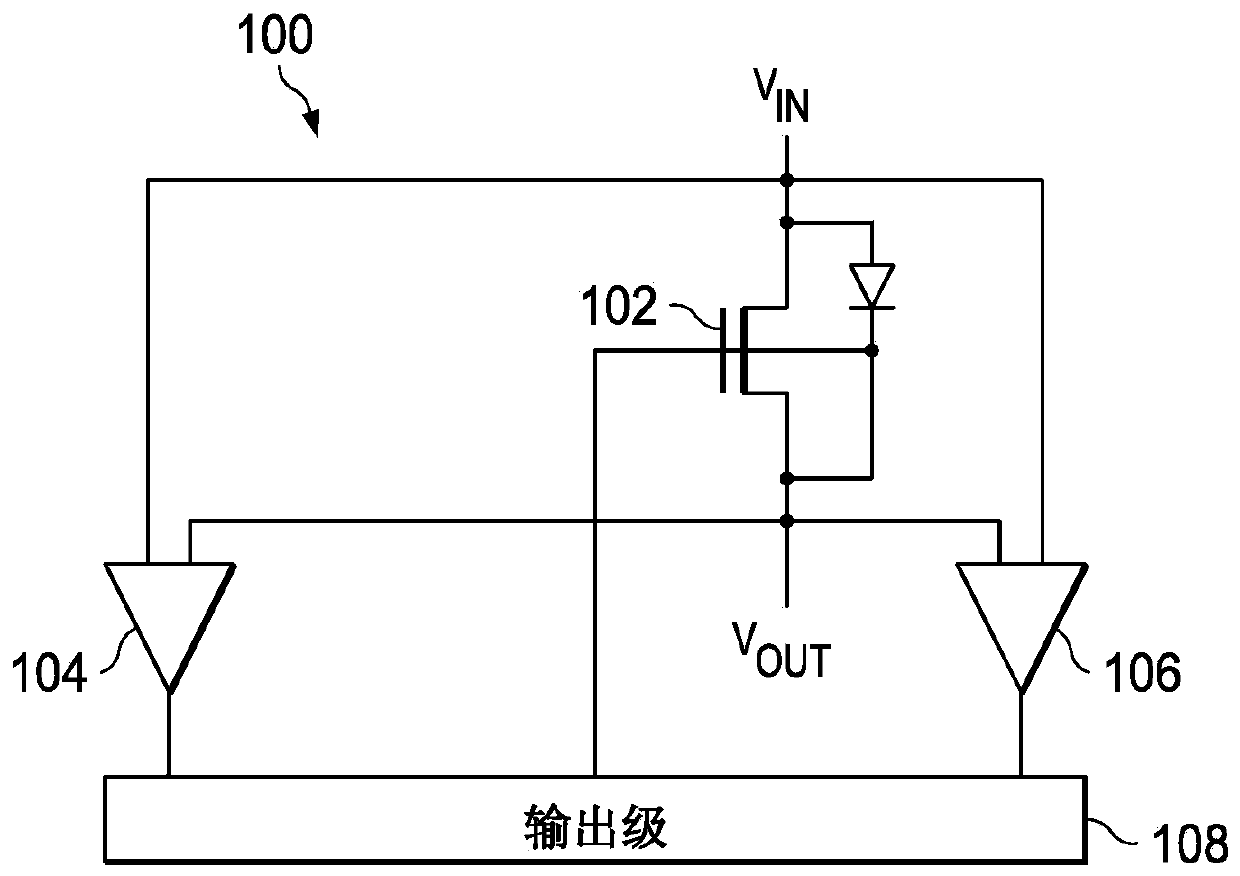
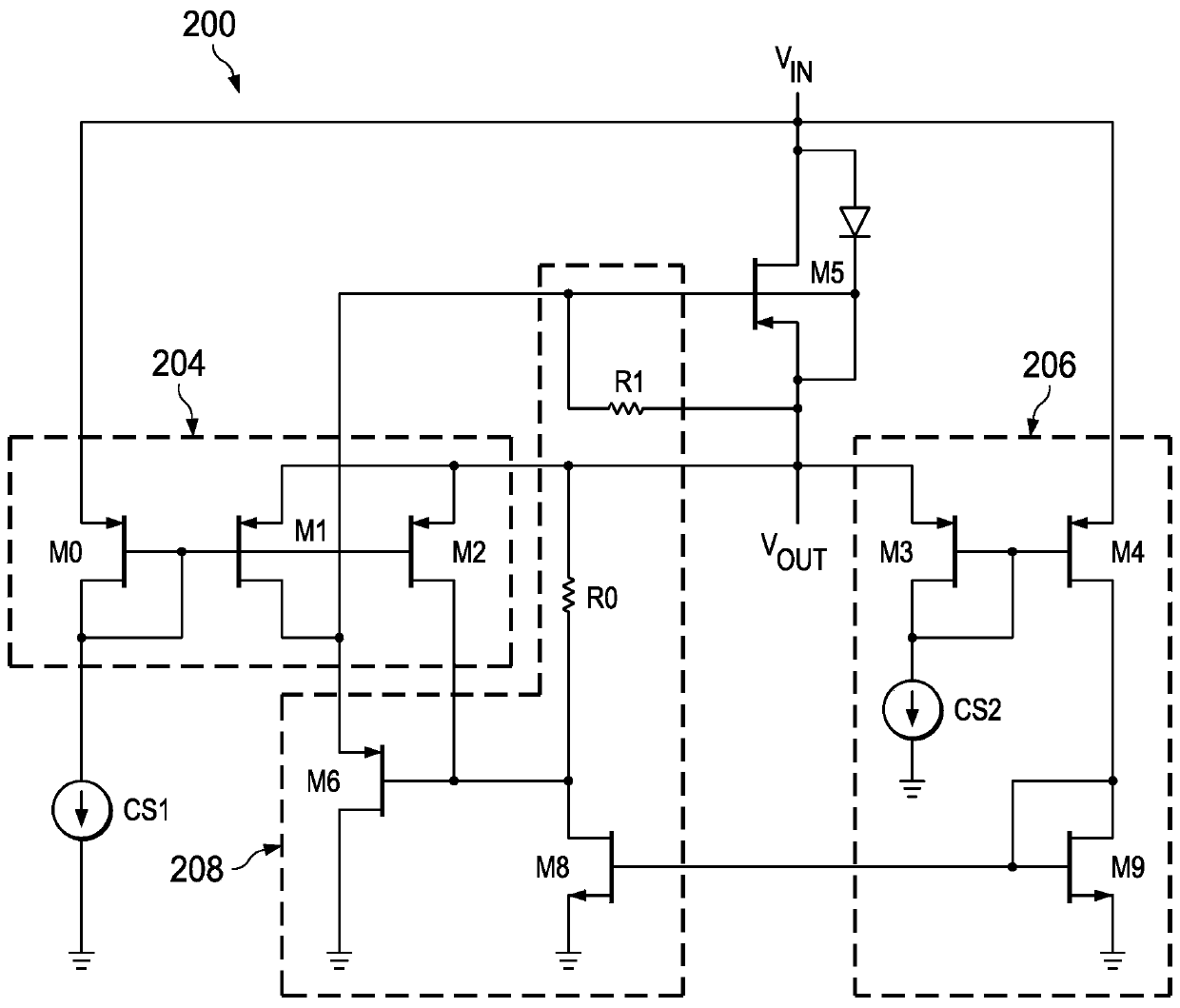
A low power ideal diode control circuit
ActiveCN107112918ALow powerLow voltage operationAc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationAudio power amplifierControl circuit
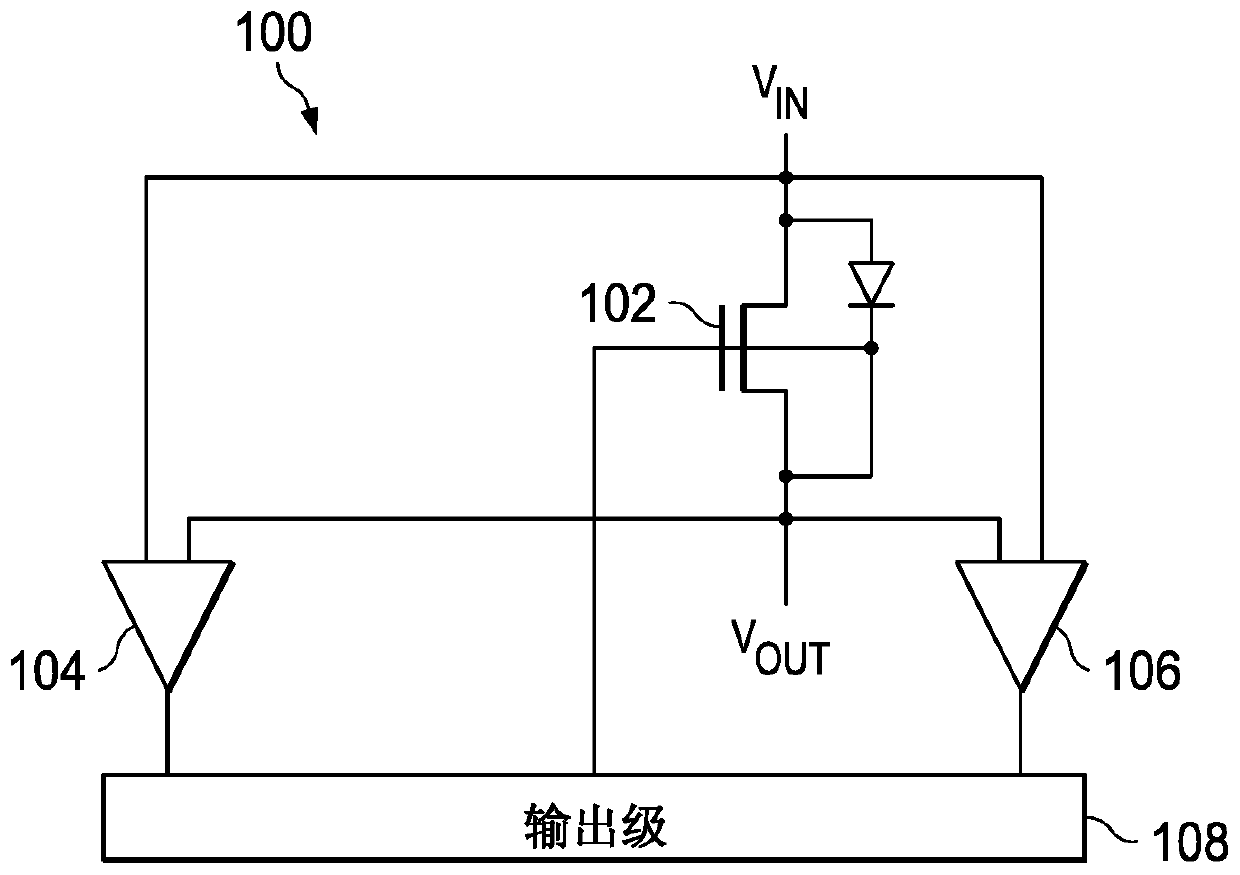
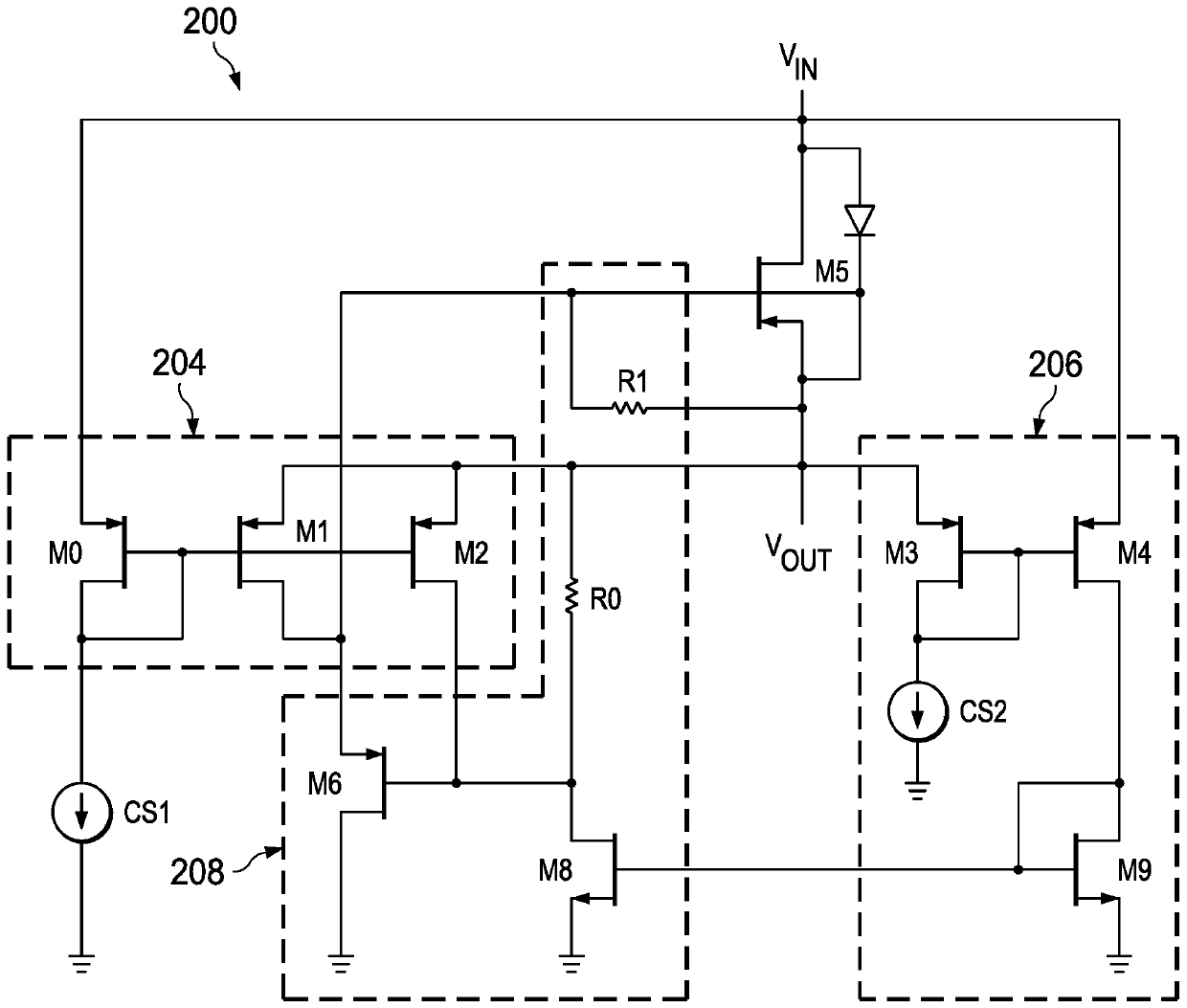
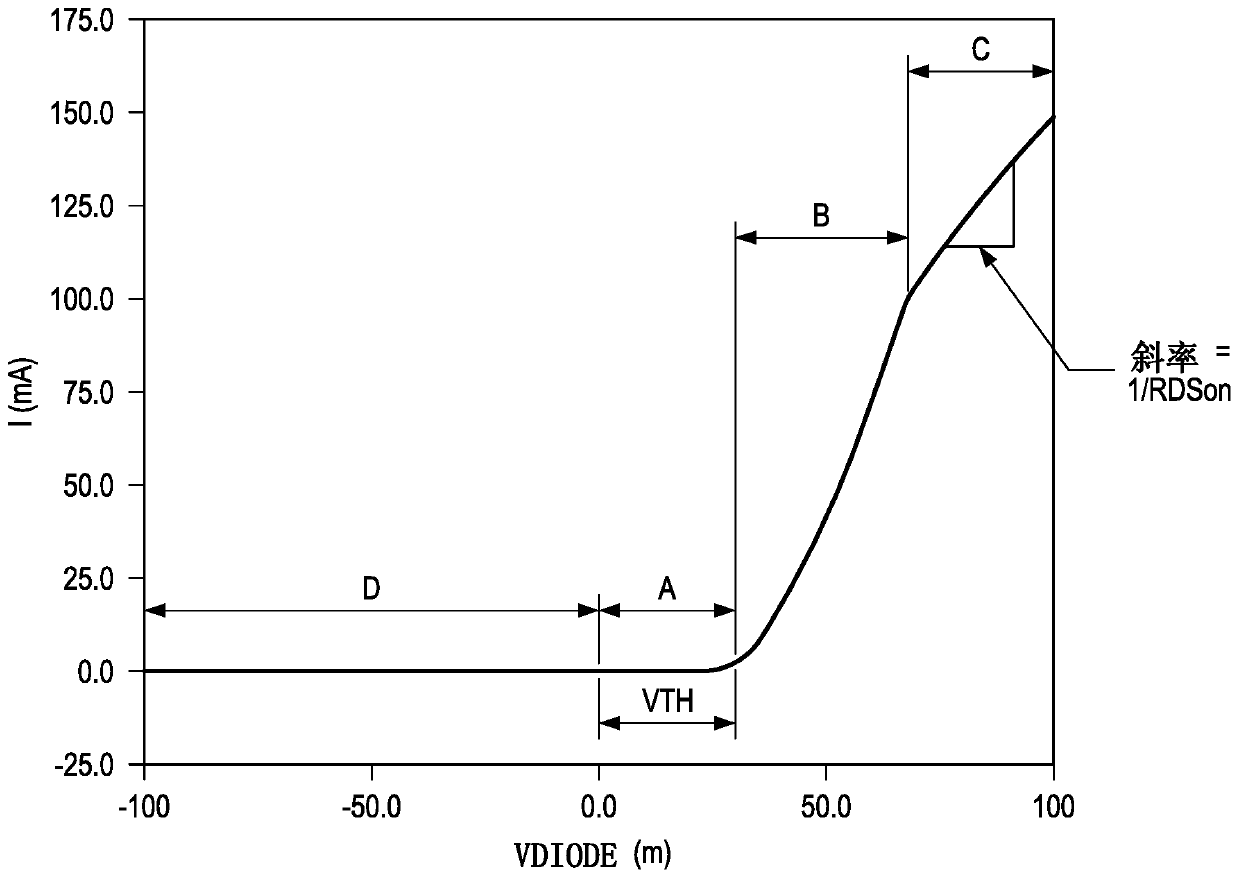
The invention discloses a low power ideal diode control circuit. In described examples of a circuit (100) that operates as a low-power ideal diode, the circuit (100) includes a p-channel transistor (102) connected to receive an input voltage (VIN) on a first terminal and to provide an output voltage (VOUT) on a second terminal, a first amplifier (106) connected to receive the input voltage and the output voltage and to provide a first signal that dynamically biases a gate of the p-channel transistor (102) as a function of the voltage across the p-channel transistor, and a second amplifier (104) connected to receive the input voltage and the output voltage and to provide a second signal that operates to turn off the gate of the p-channel transistor (102) responsive to the input voltage (VIN) being less than the output voltage (VOUT).
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Light emitting element driving circuit
InactiveUS20110187277A1High control precisionLow-voltage operationElectrical apparatusStatic indicating devicesDriver circuitData signal
A light emitting element driving circuit for driving a light emitting element in accordance with a differential data signal for causing the light emitting element to turn on or turn off is provided. The circuit includes a first transistor, a first constant current source connected to a drain and gate of the first transistor and configured to supply a constant current through the drain and source of the first transistor, a second transistor configured to supply a certain current, and a control circuit configured to electrically connect or disconnect the gate of the first transistor to or from a gate of the second transistor via a first resistor. The control circuit may supply, to the gate of the second transistor, an intermediate potential in accordance with the other of the differential data signals, while the gate of the first transistor is electrically disconnected from the gate of the second transistor.
Owner:CANON KK
A low power ideal diode control circuit
ActiveCN110794728ALow powerLow voltage operationProgramme controlComputer controlHemt circuitsControl circuit
The invention discloses a low power ideal diode control circuit. In described examples of a circuit (100) that operates as a low-power ideal diode, the circuit (100) includes a p-channel transistor (102) connected to receive an input voltage (VIN) on a first terminal and to provide an output voltage (VOUT) on a second terminal, a first amplifier (106) connected to receive the input voltage and theoutput voltage and to provide a first signal that dynamically biases a gate of the p-channel transistor (102) as a function of the voltage across the p-channel transistor, and a second amplifier (104) connected to receive the input voltage and the output voltage and to provide a second signal that operates to turn off the gate of the p-channel transistor (102) responsive to the input voltage (VIN) being less than the output voltage (VOUT).
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Semiconductor memory device
ActiveCN106024789ASmall sizeLow costSolid-state devicesDigital storageEngineeringSemiconductor memory
The semiconductor memory device of the invention includes 2 TFT MOS transistors, 2 bulk MOS transistors, a first and second access MOS transistors and a first and second capacitor. The TFT and bulk MOS transistors form a latch for retaining a data that is inverted between a first and second node. The first bulk access MOS transistor switches the first node to connect to a first bit line according to a voltage of a word line. The second bulk access MOS transistor, switches the second node to connect to a second bit line according to the voltage of the word line. The first capacitor is disposed between the first node and a power supply voltage. The second capacitor is disposed between the second node and the power supply voltage. The bulk MOS transistors and the access MOS transistors are formed by a recess gate type MOS transistor.
Owner:POWERCHIP SEMICON MFG CORP
Low Power Ideal Diode Control Circuit
ActiveCN107112918BLow powerLow voltage operationAc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationAudio power amplifierEngineering
In the depicted example of a circuit (100) operating as a low power ideal diode, the circuit (100) includes a p-channel transistor (102) connected to receive an input voltage (V IN ) and provides an output voltage (V OUT ); a first amplifier (106) connected to receive an input voltage and an output voltage and to provide a first signal that dynamically biases the gate of the p-channel transistor (102) according to the voltage across the p-channel transistor pole; and a second amplifier (104) connected to receive the input voltage and the output voltage and to provide a second signal that operates in response to the input voltage (V IN ) is less than the output voltage (V OUT ) to turn off the gate of the p-channel transistor (102).
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Mixed signal detection experimental device suitable for mechanical and electrical engineering
InactiveCN102881211BSimple designSmall sizeEducational modelsDigital signal processingElectrical engineering technology
The invention discloses a mixed signal detection experimental device suitable for mechanical and electrical engineering. The device comprises a main board, a power module, a liquid crystal display (LCD) module, a motor control module, a PSoC5 (programmable system on chip) microprocessor module and a STM32F4 (scanning tunneling microscope) microprocessor module; the power module is used for providing power source for every electrical module of the device; the main board is configured with a dual-microprocessor slot; the PSoC5 microprocessor slot in a left half area is used for connecting the PSoC5 microprocessor module, the STM32F4 microprocessor slot in a right half area is used for connecting the STM32F4 microprocessor module; input and output pins of the PSoC5 microprocessor module and the STM 32F4 microprocessor module can enable double rows of contact pins to be connect with external equipment of the main board through connecting leads; the main board is connected with a plurality of external equipment and externally arranged interfaces. By adopting a dual-processor framework, the unique configurable simulative digital property of the PSoC5 is combined with the high performance, the real-time function and the digital signal processing property of the STM32F4, so that the required functions for the electronic system design of the mechanical and electrical engineering are covered.
Owner:XUZHOU UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com