Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
40results about How to "Improved data retention features" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
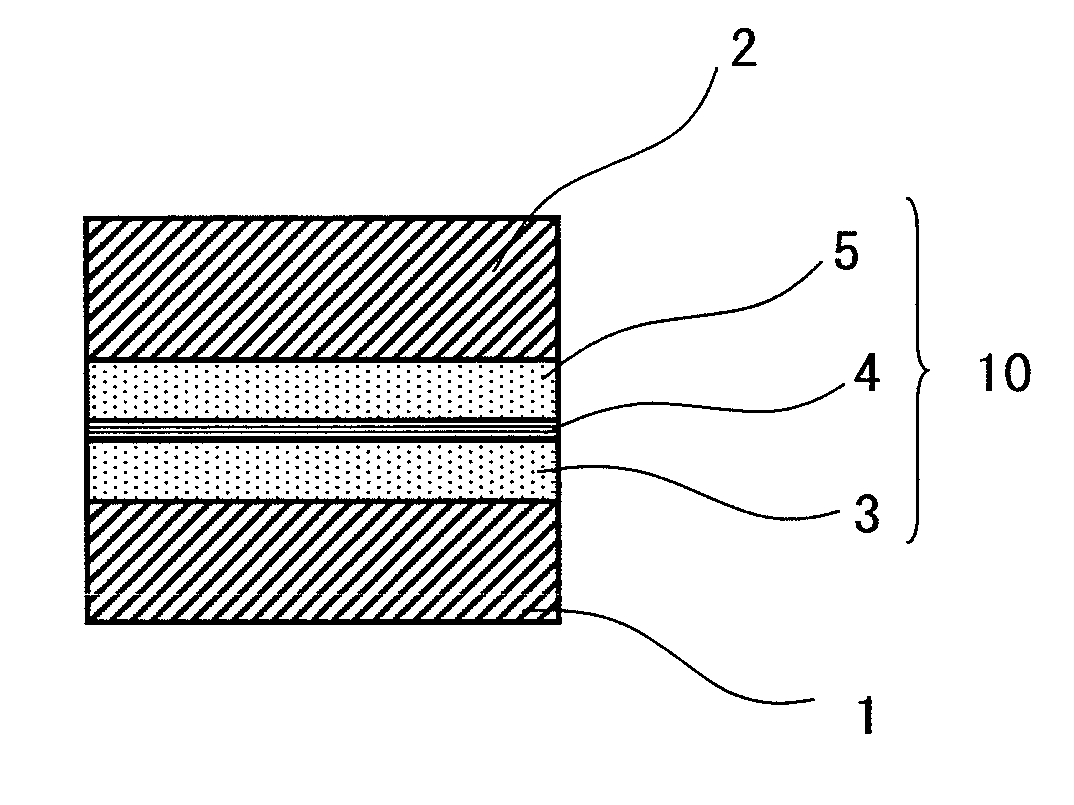
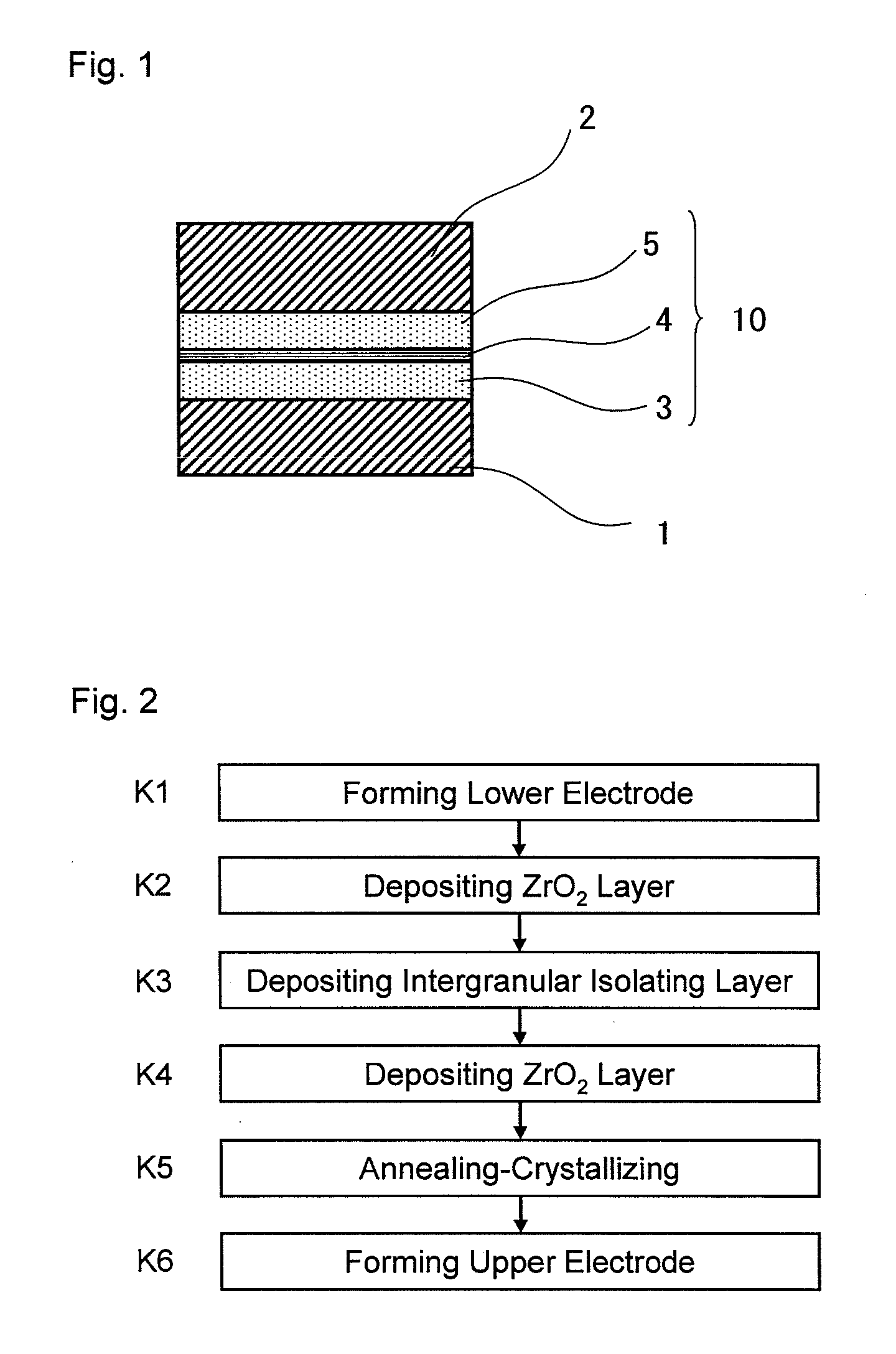
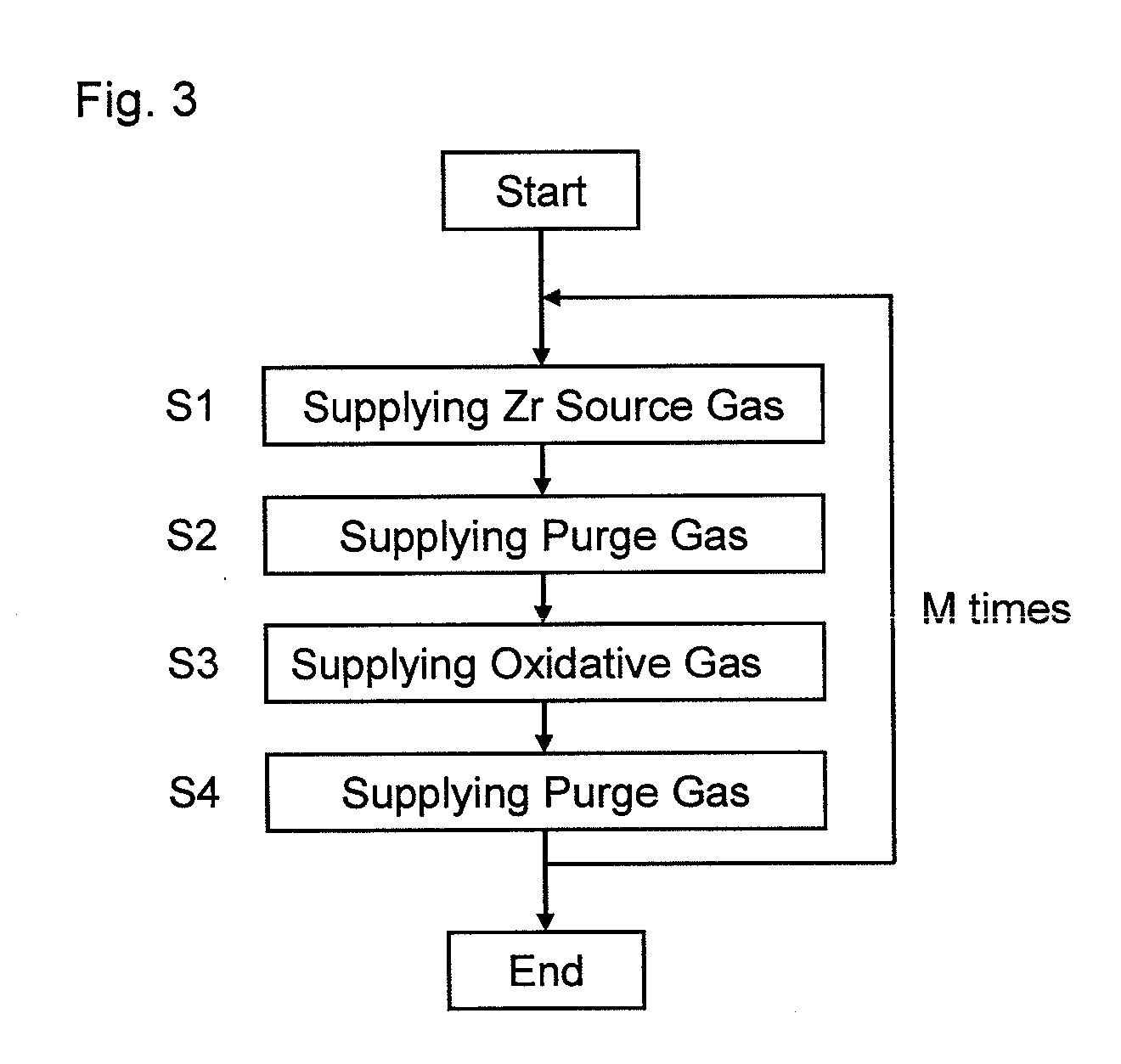
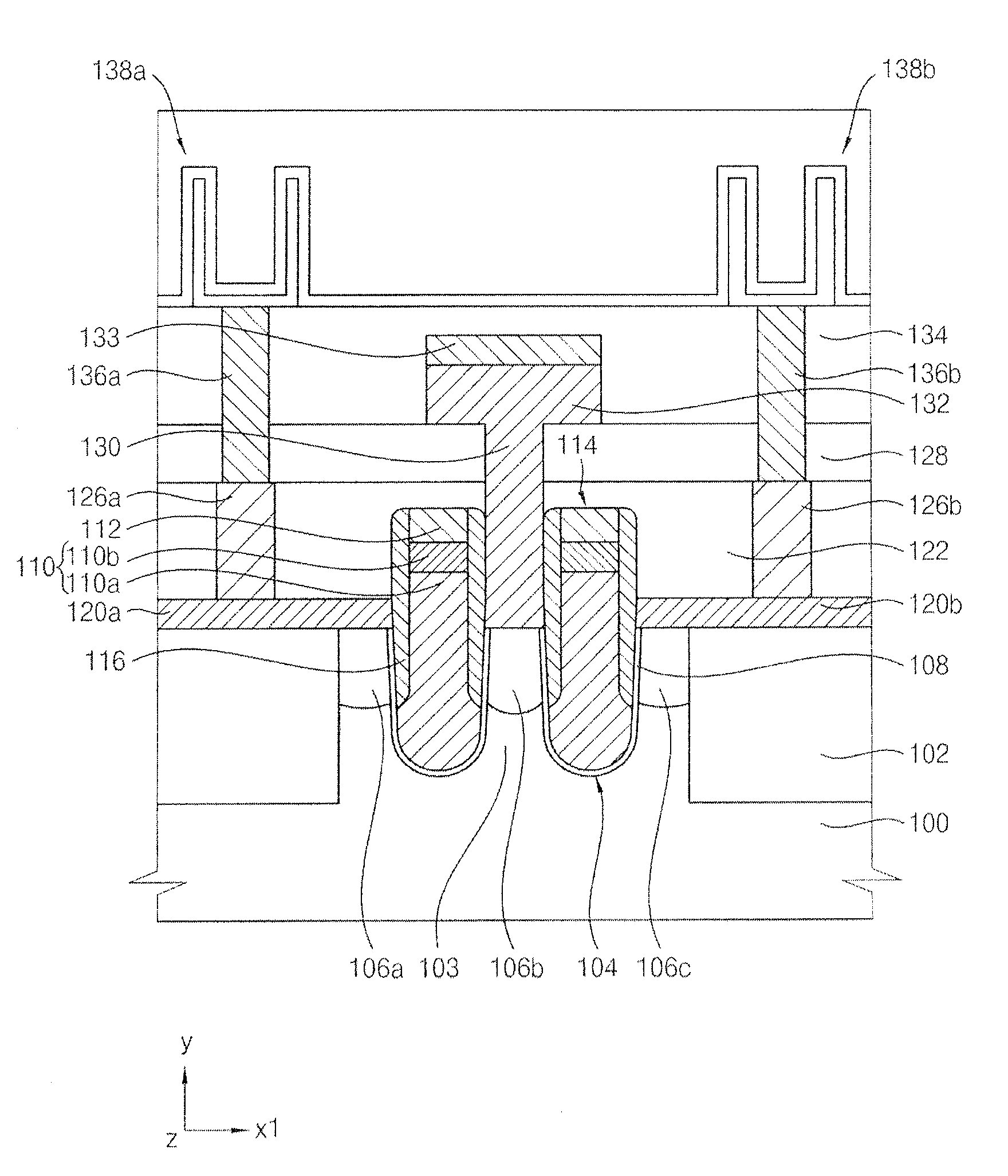
Insulating film, method of manufacturing the same, and semiconductor device
InactiveUS20110048769A1High dielectric constantSmall currentThin/thick film capacitorCeramicsCapacitanceSemiconductor
An exemplary aspect of the invention provides an insulating film which has a high dielectric constant and has small leakage current even when it is sandwiched between electrodes. The insulating film comprises two zirconium oxide layers in crystallized state; and an intergranular isolating layer composed of an amorphous material having a dielectric constant higher than that of zirconium oxide in crystallized state; wherein the intergranular isolating layer is sandwiched between the two zirconium oxide layers. The insulating film is properly used as a capacitive insulating film in a semiconductor device comprising a memory cell including a capacitor element having the capacitive insulating film between an upper electrode and a lower electrode, or as an intergate insulating film in a semiconductor device comprising a nonvolatile memory device having the intergate insulating film between a control gate electrode and a floating gate electrode.
Owner:ELPIDA MEMORY INC
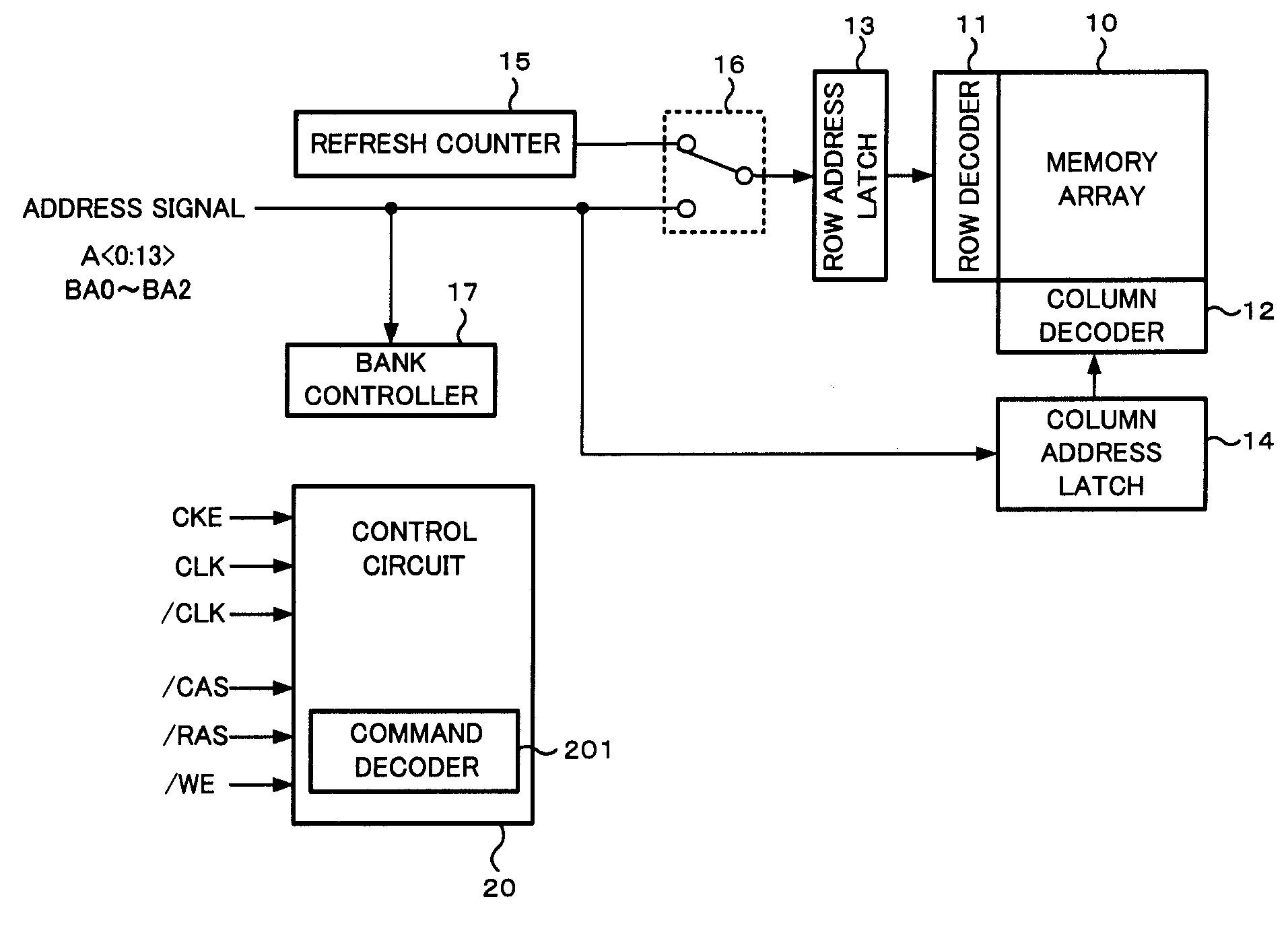
Semiconductor memory device
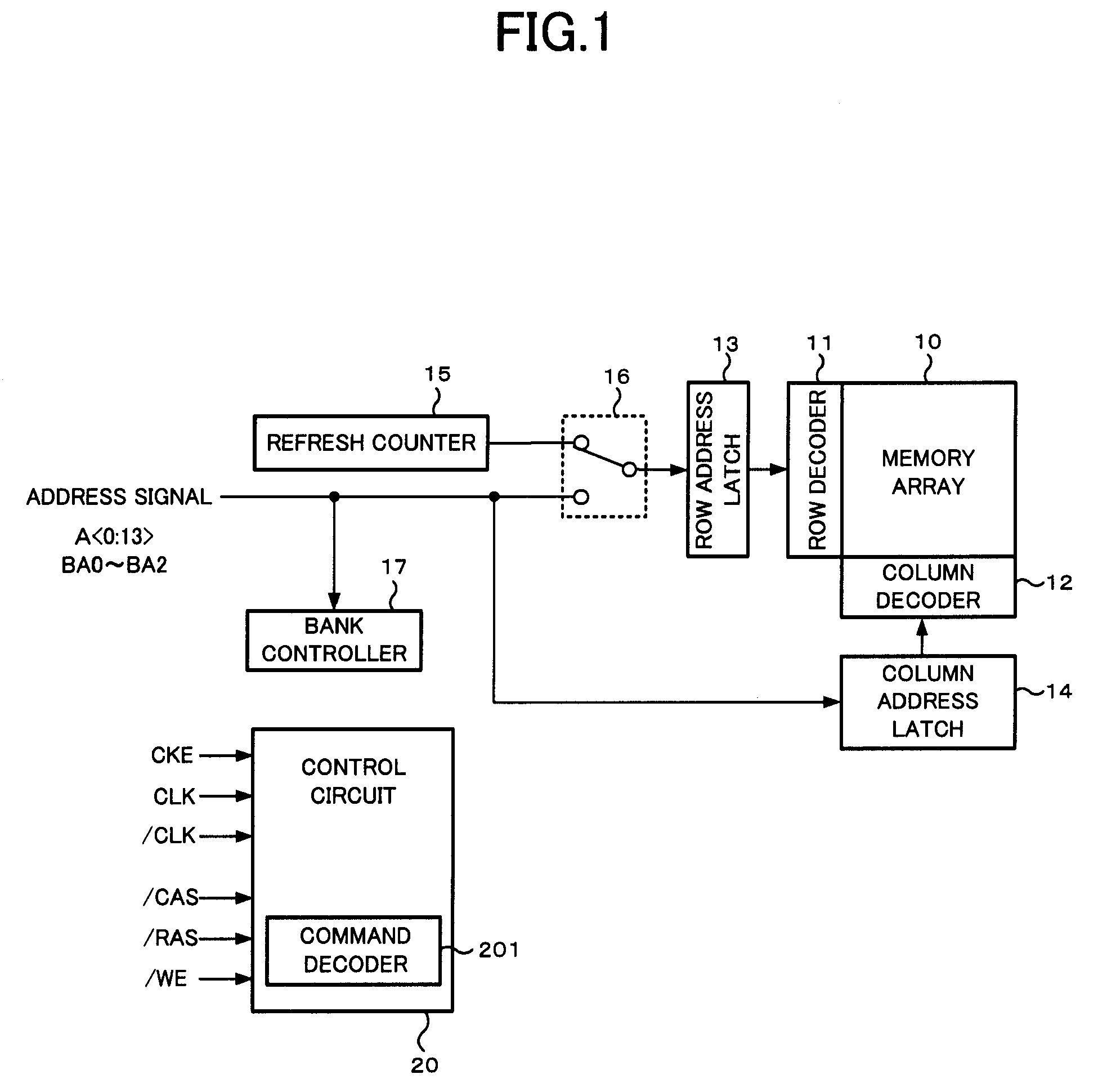
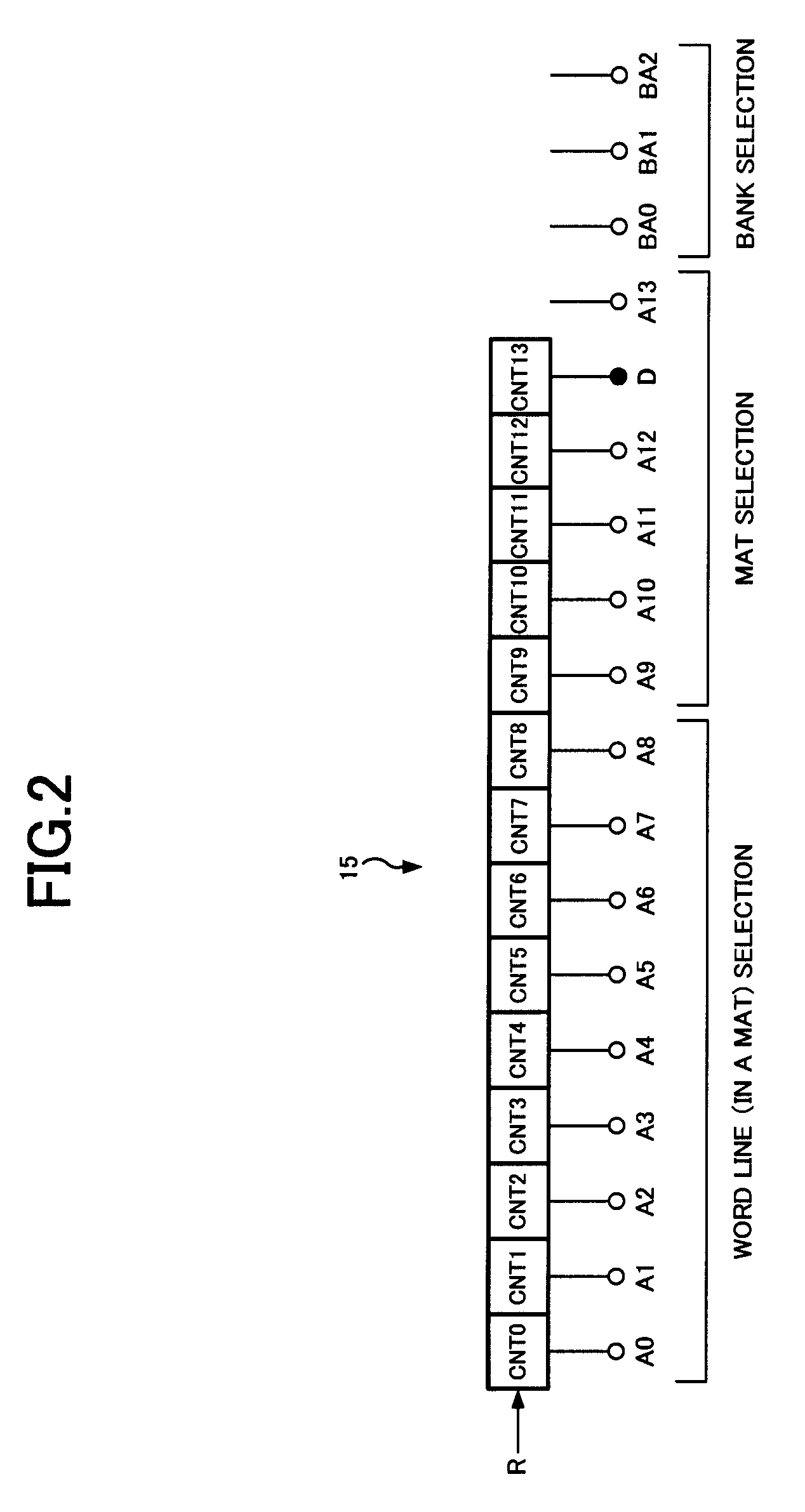
ActiveUS20070242546A1Optimize characteristicsOptimize currentDigital storageLeast significant bitSemiconductor
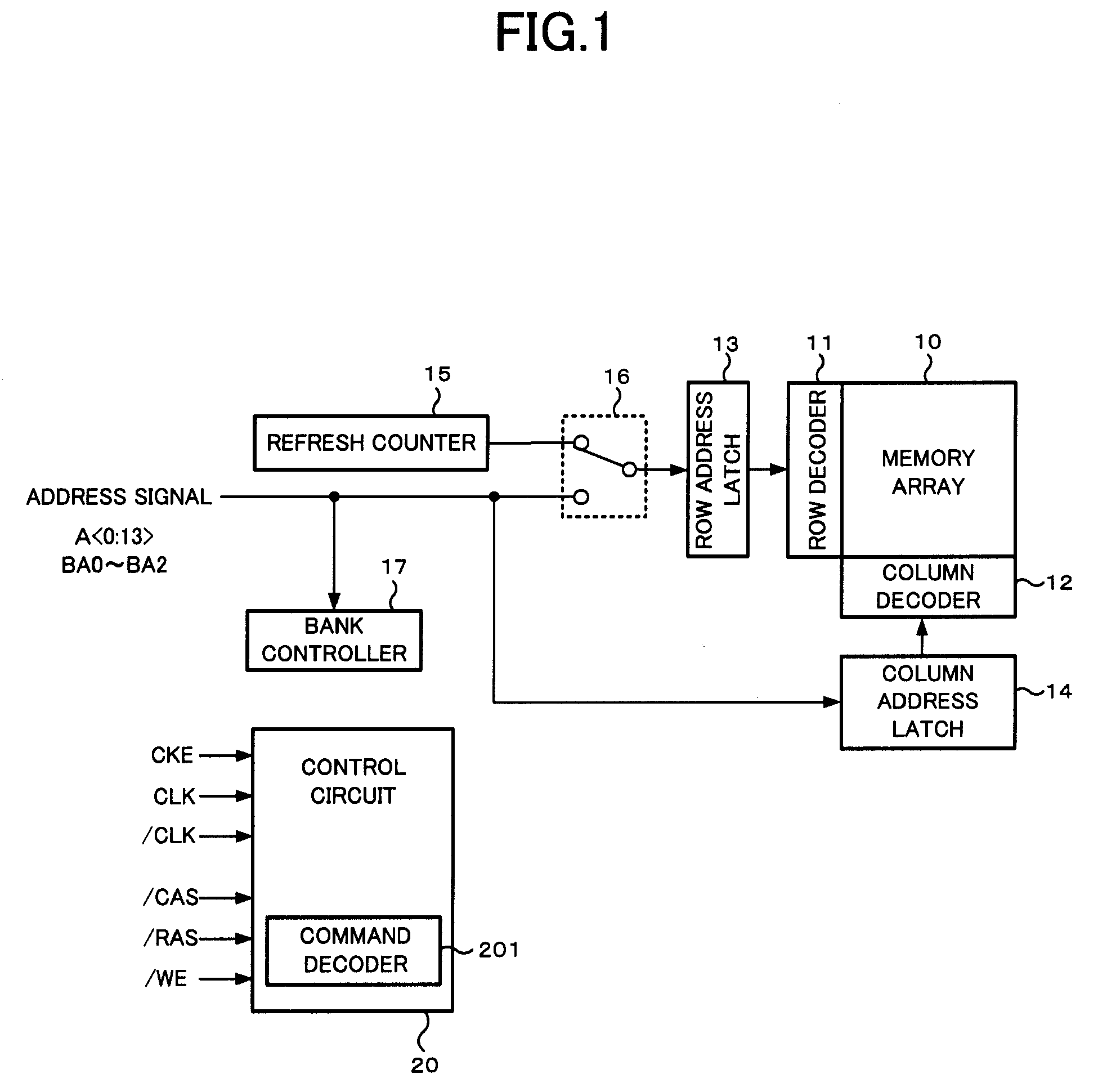
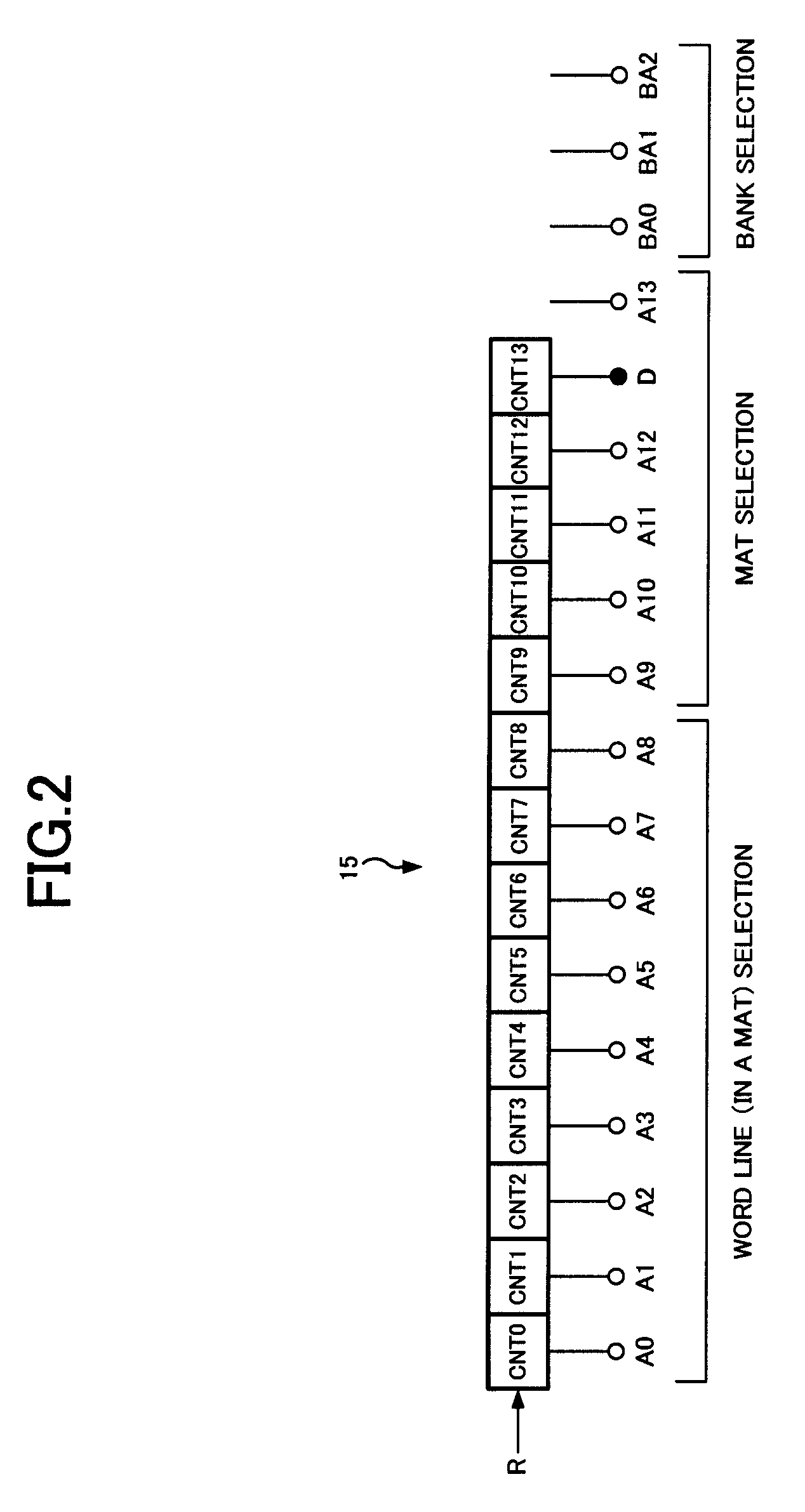
A semiconductor memory device is comprised of a refresh counter for sequentially generating a count value indicating one or more row addresses corresponding to one or more word lines to be refreshed when receiving a refresh request at a predetermined interval in normal operation, in which the refresh counter includes n+1 stage counters assigned to n bits included in the row address and a dummy bit not included in the row address, and a counter portion from the least significant bit to the dummy bit forms an N-ary counter, so as to control whether or not refresh is performed in response to a value of the dummy bit when receiving the refresh request.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
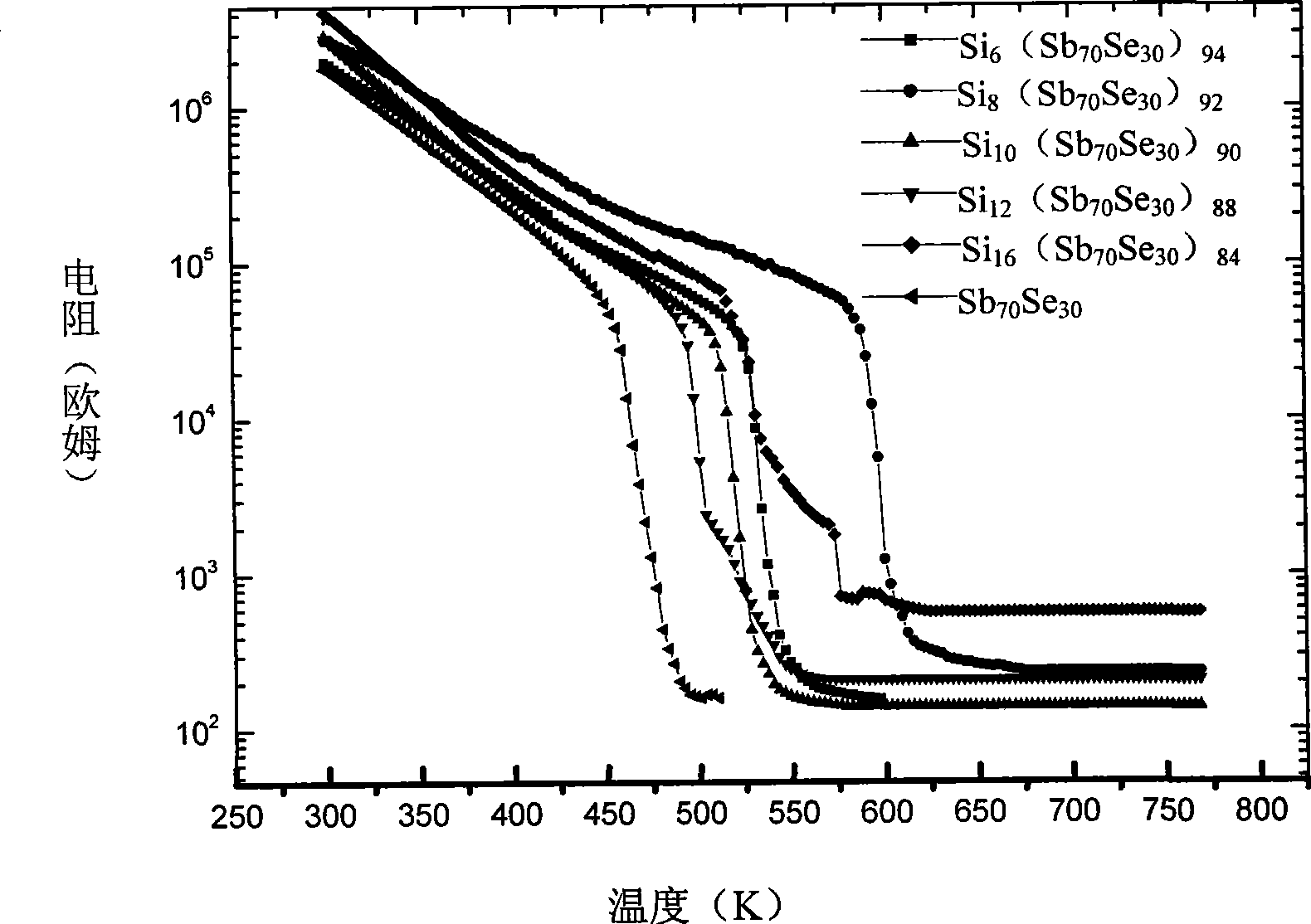
Si-Sb-Se phase changing thin-film material used for phase changing memory
ActiveCN101488557ACrystallize fastFast operationElectrical apparatusDigital storageCMOSPhase-change memory
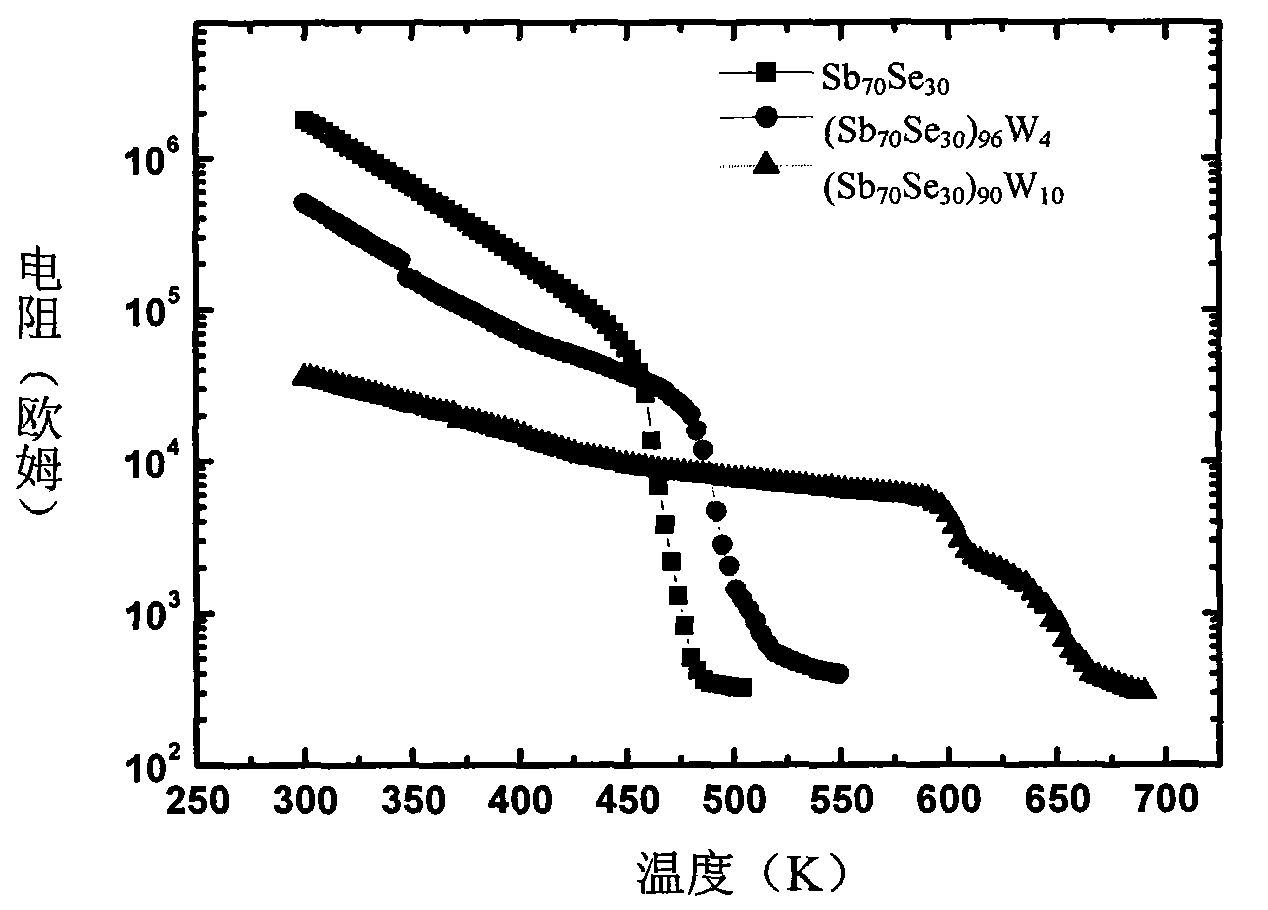
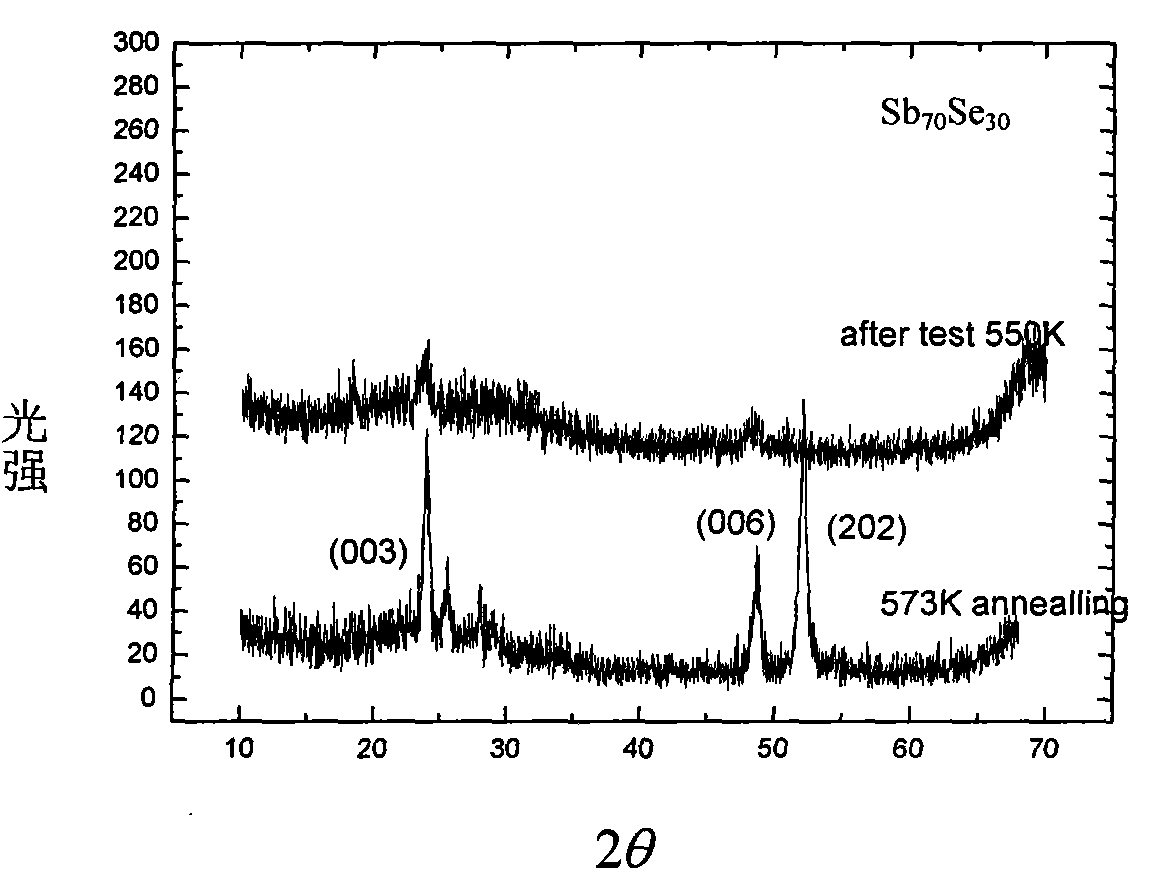
The invention discloses a Si-Sb-Se phase transition film material used for a phase transition storage and the ingredient thereof is SicSbaSeb, wherein b is equal to or more than 48 and equal to or less than 60, a is equal to or more than 20 and equal to or less than 40, c is equal to or more than 8 and equal to or less than 40, and a plus b plus c is 100; or b is equal to or more than 60 and equal to or less than 80, a is equal to or more than 20 and equal to or less than 40, c is equal to or more than 3 and equal to or less than 20 and a plus b plus c is 100. Compared with the prior art, the Si-Sb-Se phase transition film material has faster crystallization rate, faster read-write rate and better data holding property than the commonly used Ge2Sb2Te5 material and better thermal stability than SbSe binary material. Meanwhile, the material is free from element Te, thereby being environment friendly, and the material has good compatibility with the CMOS technique.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Semiconductor Device and Electronic Device
ActiveUS20160172009A1Large memory capacityHigh data reliabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringData reliability
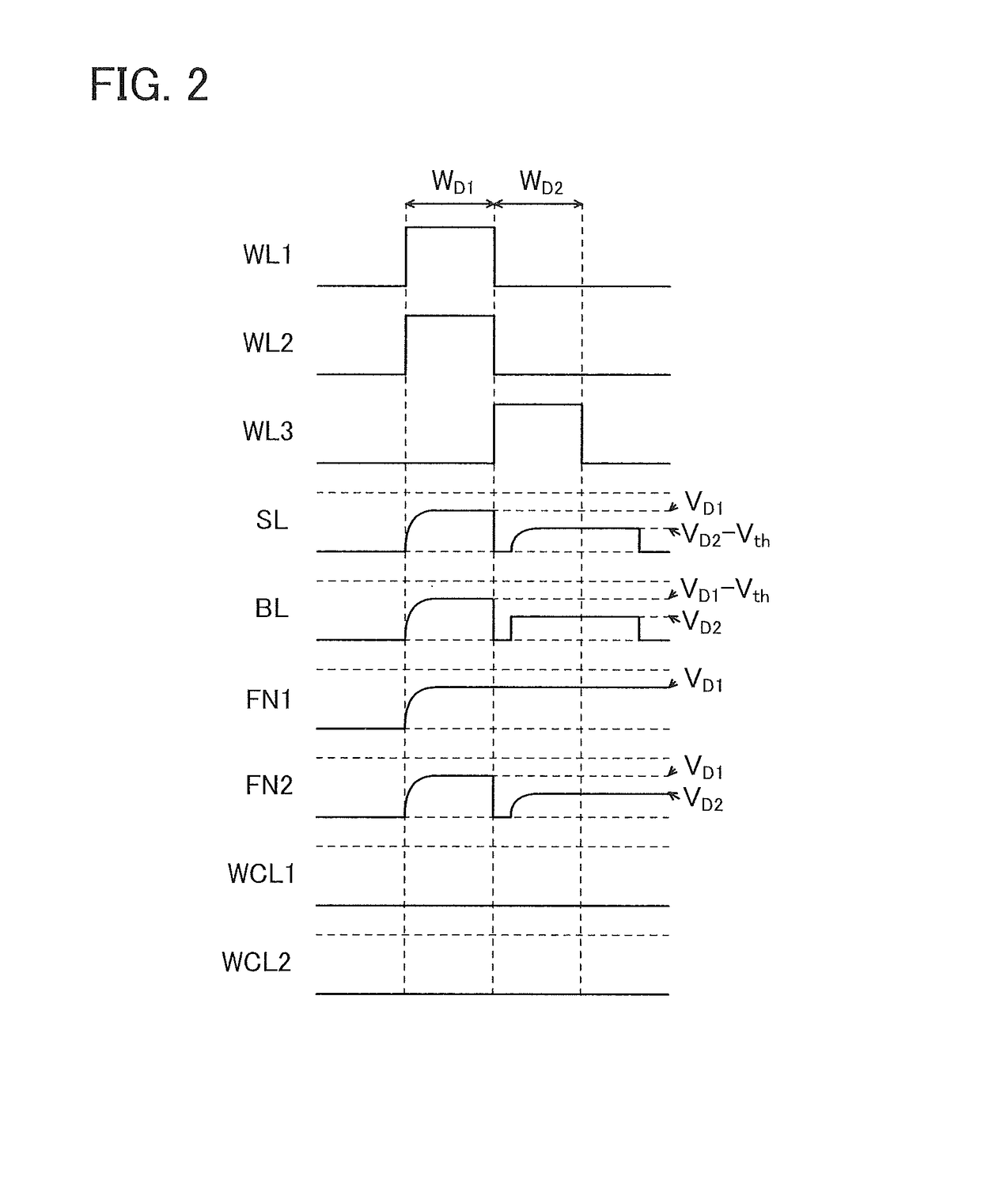
To provide a semiconductor device having large memory capacity and high reliability of data or a small-size semiconductor device having a small circuit area. A memory cell includes first and second data retention portions capable of storing multilevel data. A data voltage is written to the first data retention portion from a first wiring through a transistor for reading the data voltage and a second wiring, and a data voltage is written to the second data retention portion from the second wiring through a transistor for reading the data voltage and the first wiring. With the configuration, data voltages reduced by the threshold voltages of the transistors for reading the data voltage can be retained in the first and second data retention portions. The written data voltages where the threshold voltages of the transistors are canceled can be read by precharging and then discharging the first wiring.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Ferroelectric random access memory
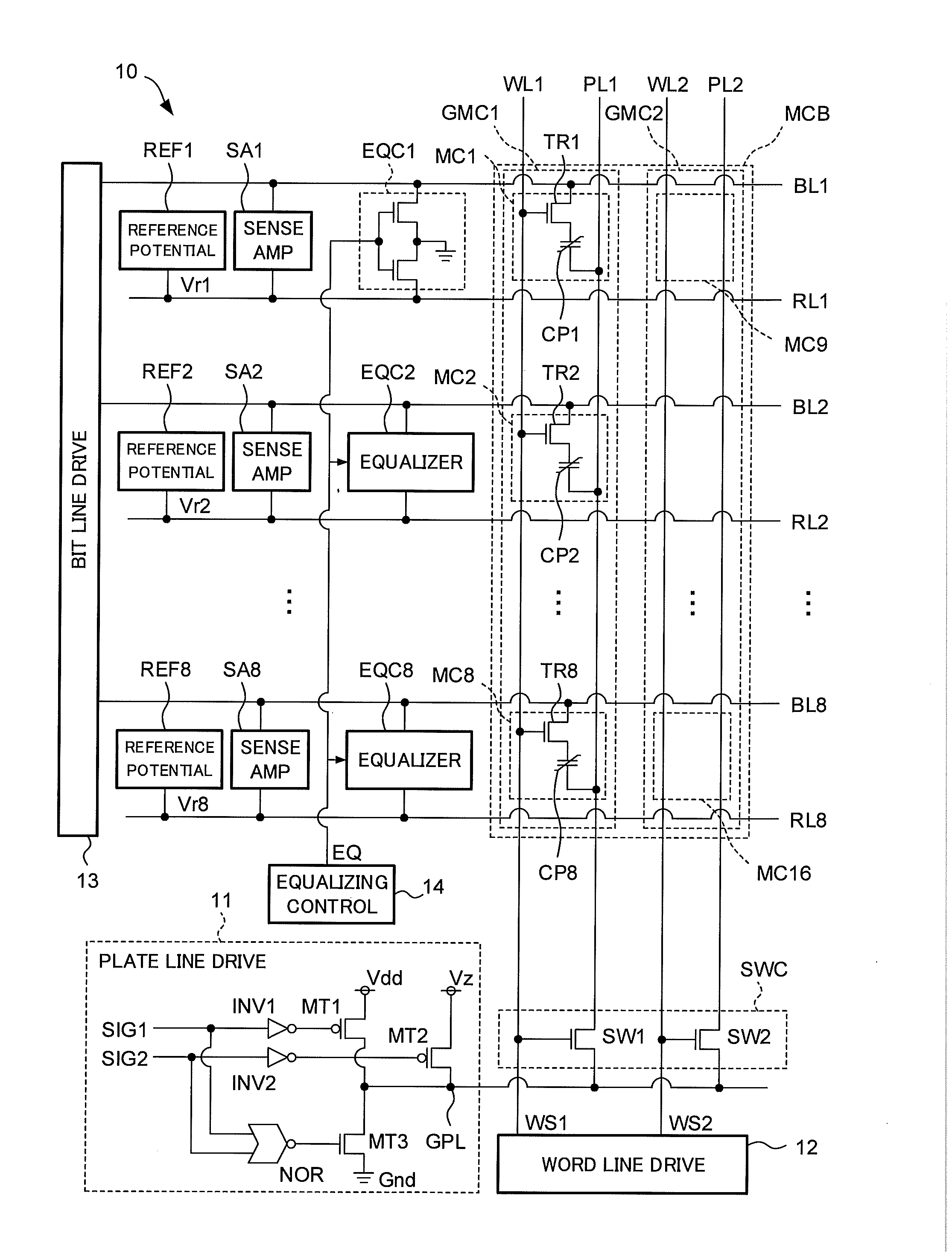
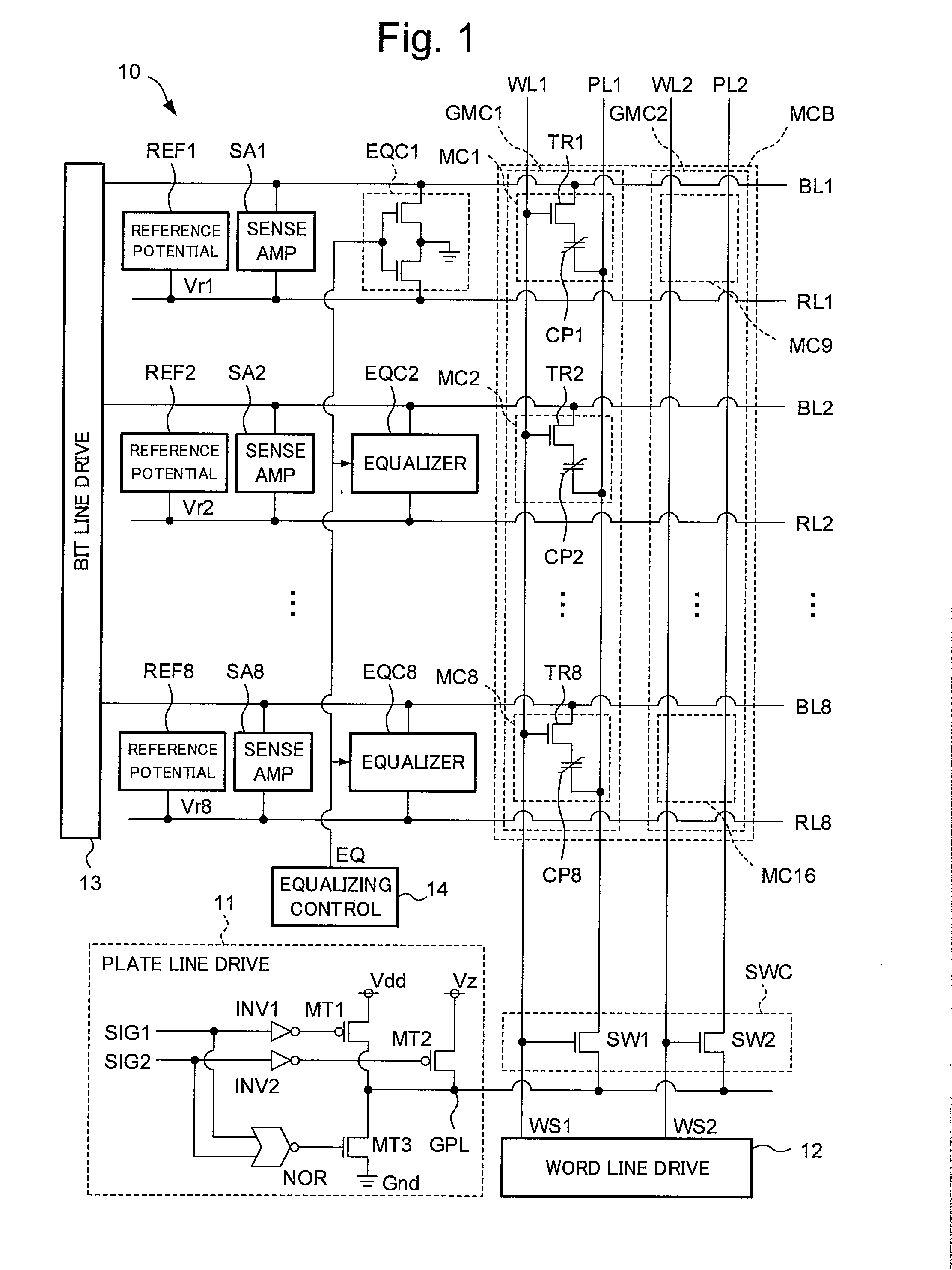
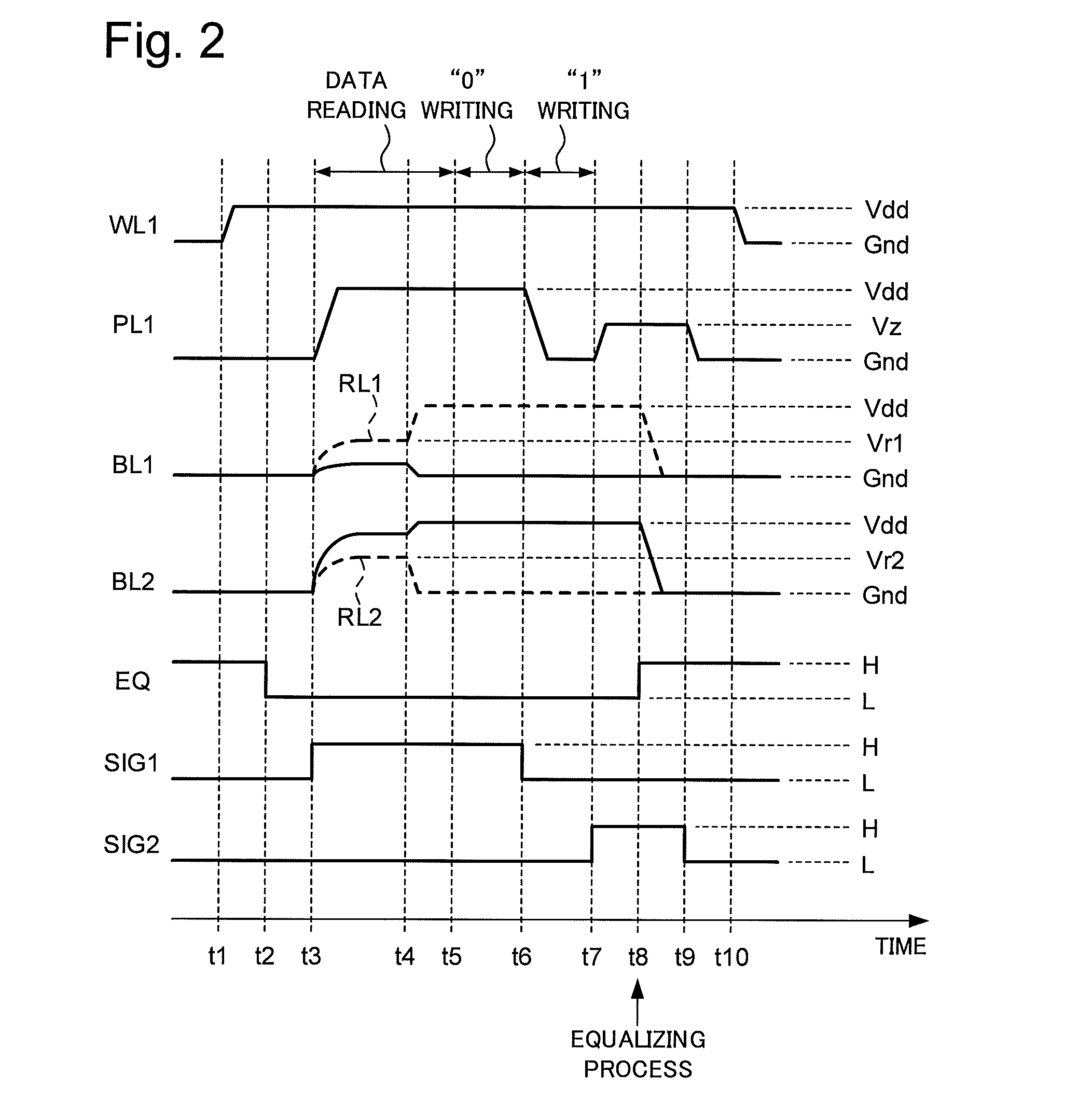
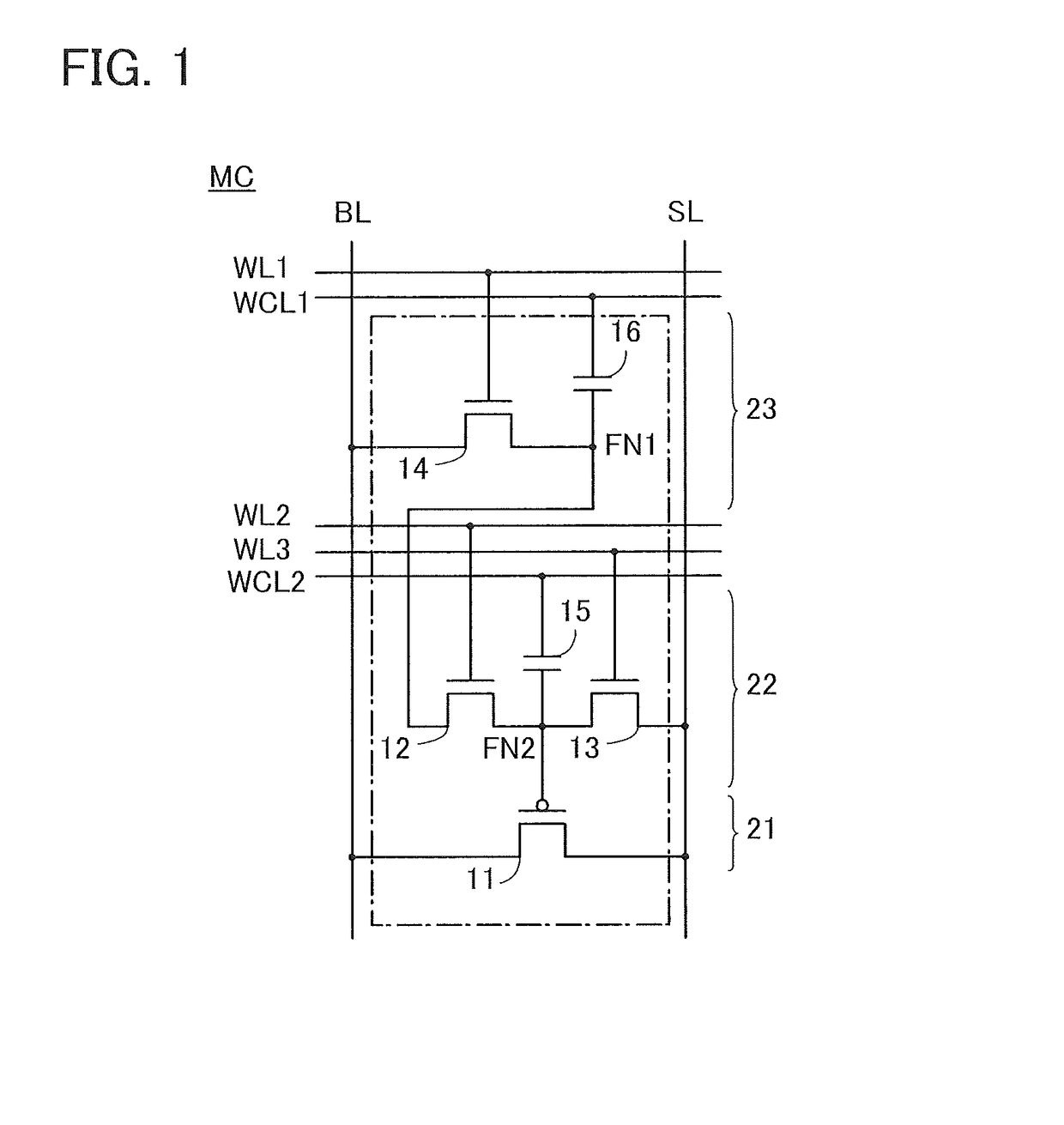
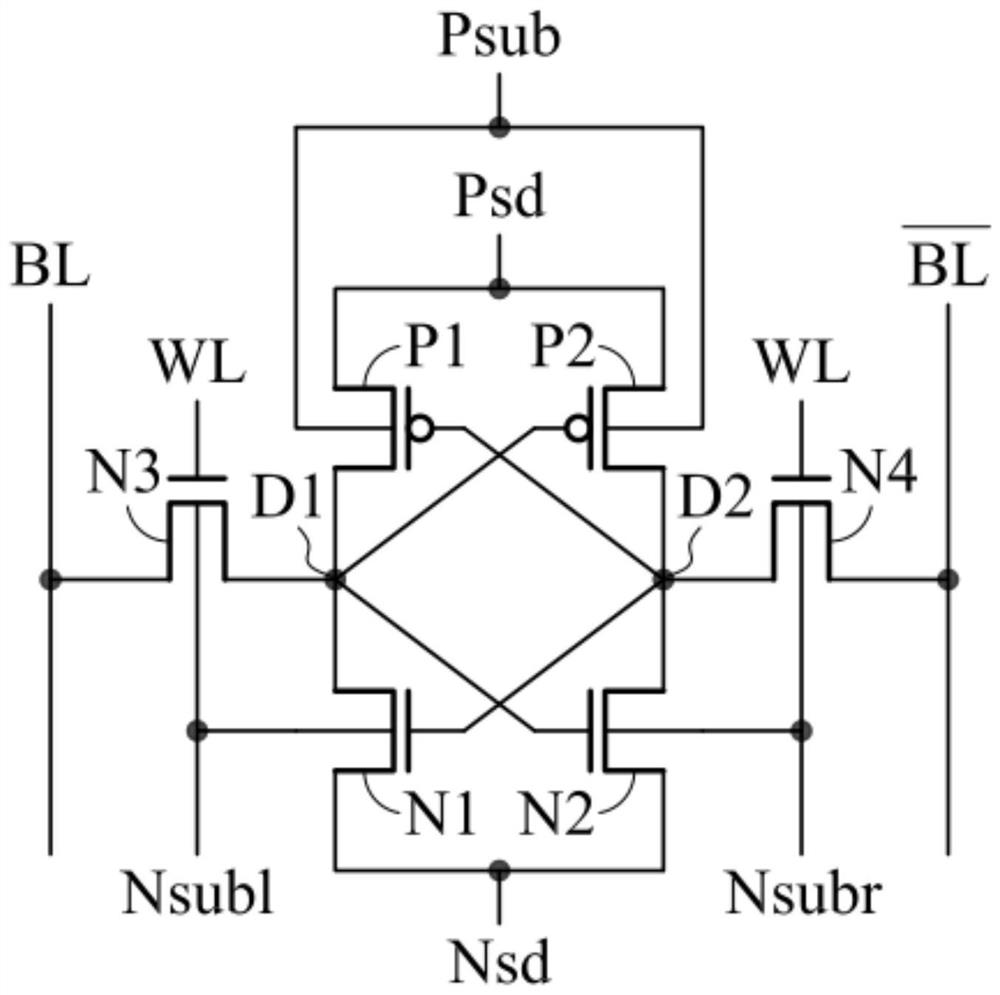
ActiveUS20160086648A1Improved data retention featuresReduce polarizationDigital storageBit lineRandom access memory
A ferroelectric random access memory which comprises a memory cell matrix constituted by a plurality of 1T1C type memory cells of j rows and k columns, and having j bit lines, k word lines, and k plate lines, each of the plurality of memory cells being connected to one of the j bit lines and one pair of the k word lines and the k plate lines, a plate line drive circuit which selectively applies one of a first potential and a second potential having a higher potential level than the first potential to one plate line of the k plate lines, and an equalizing circuit which performs an equalizing process in which the first potential is applied to each of the j bit lines. The plate line drive circuit applies a third potential having a potential level between the first and second potentials to the one plate line, before starting the equalizing process by the equalizing circuit.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
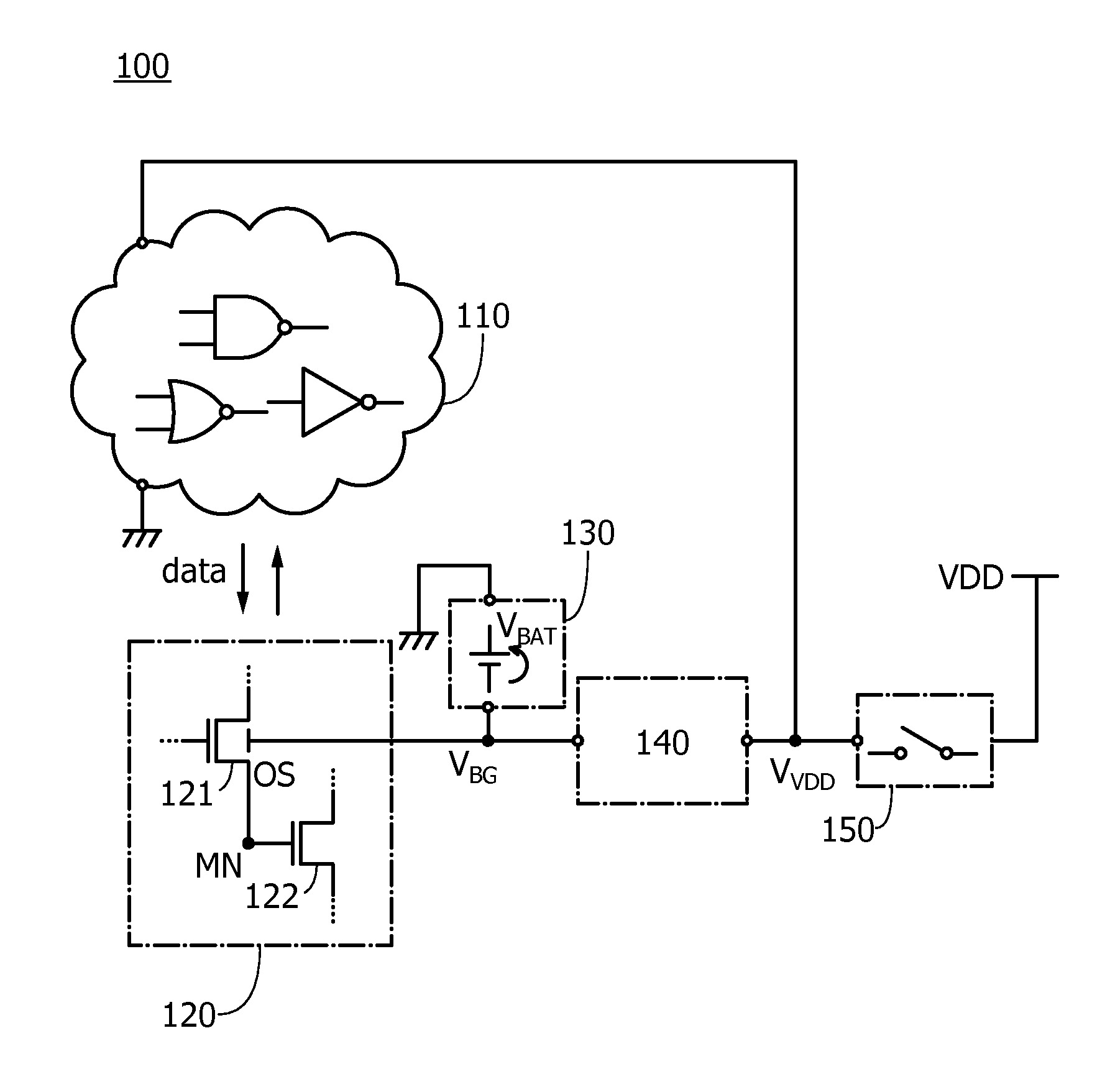
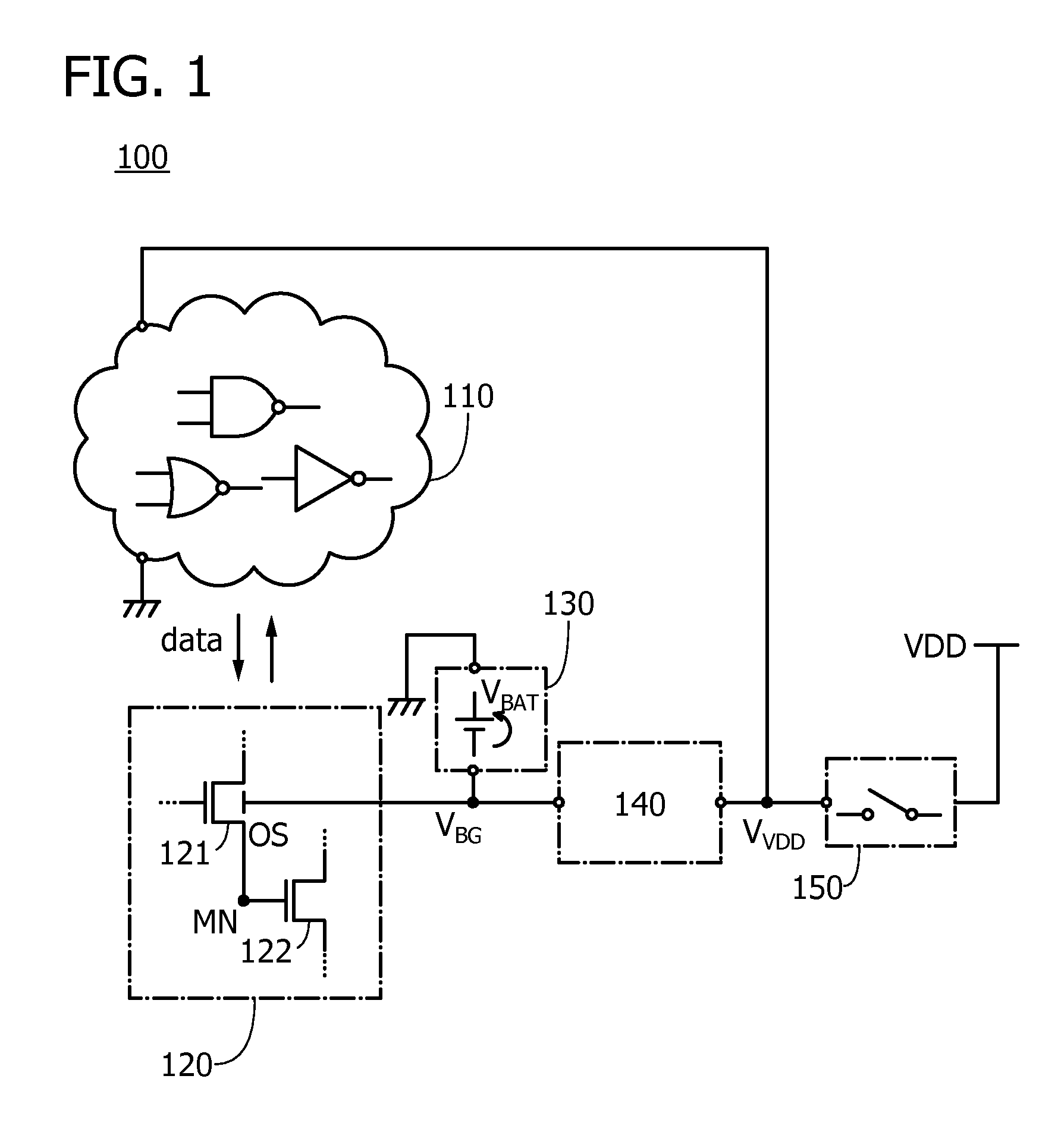
Semiconductor device and electronic device
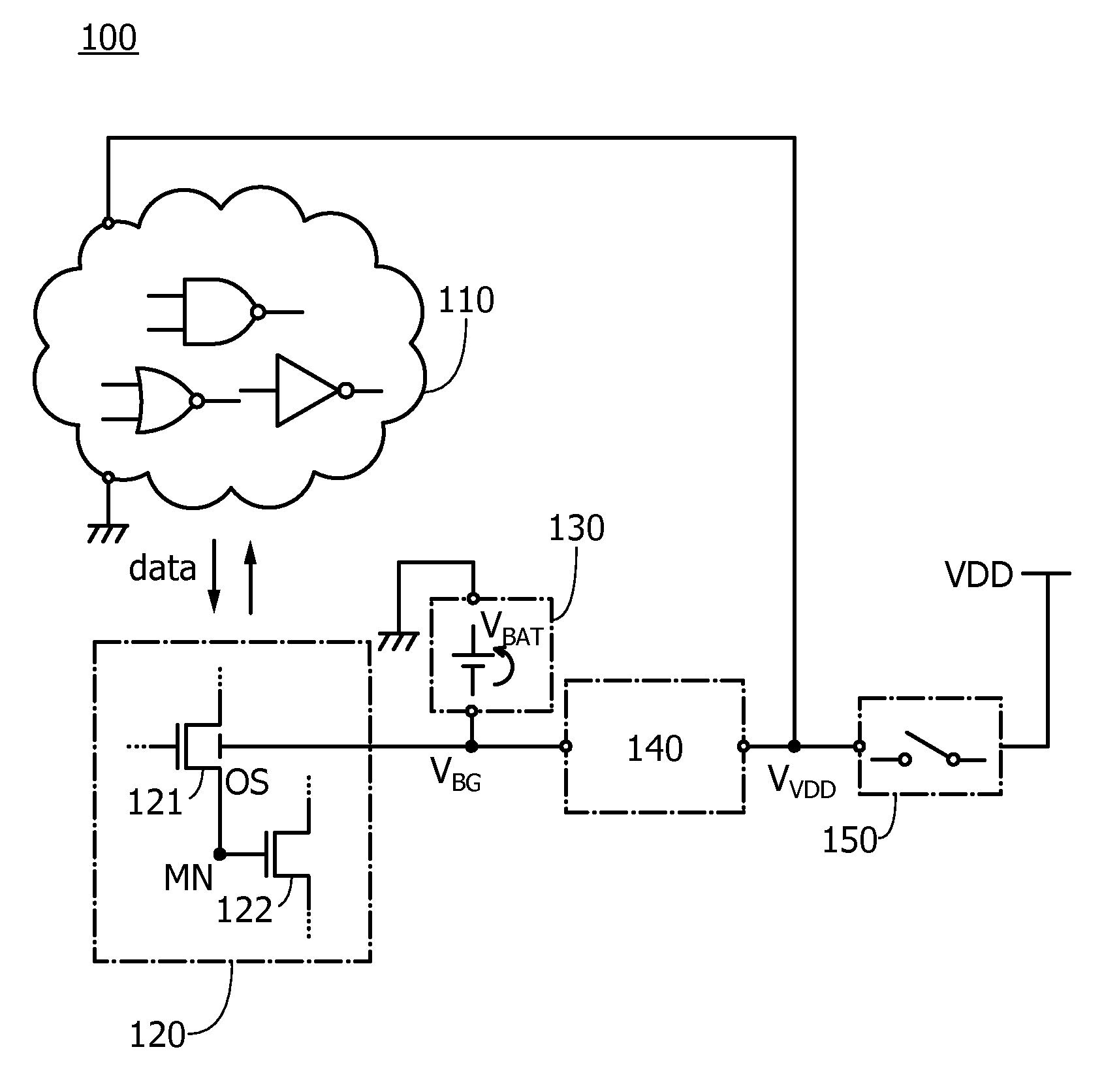
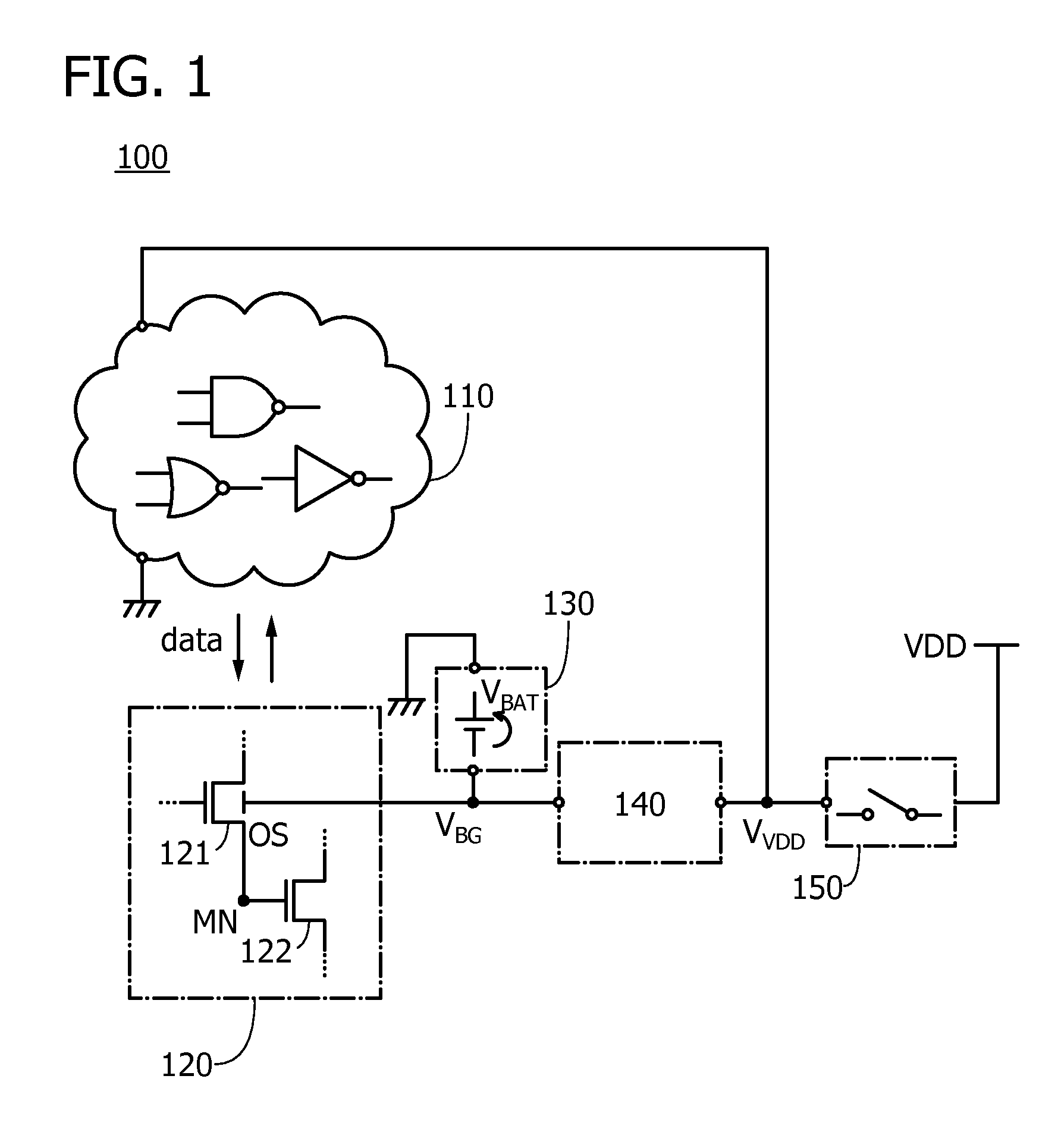
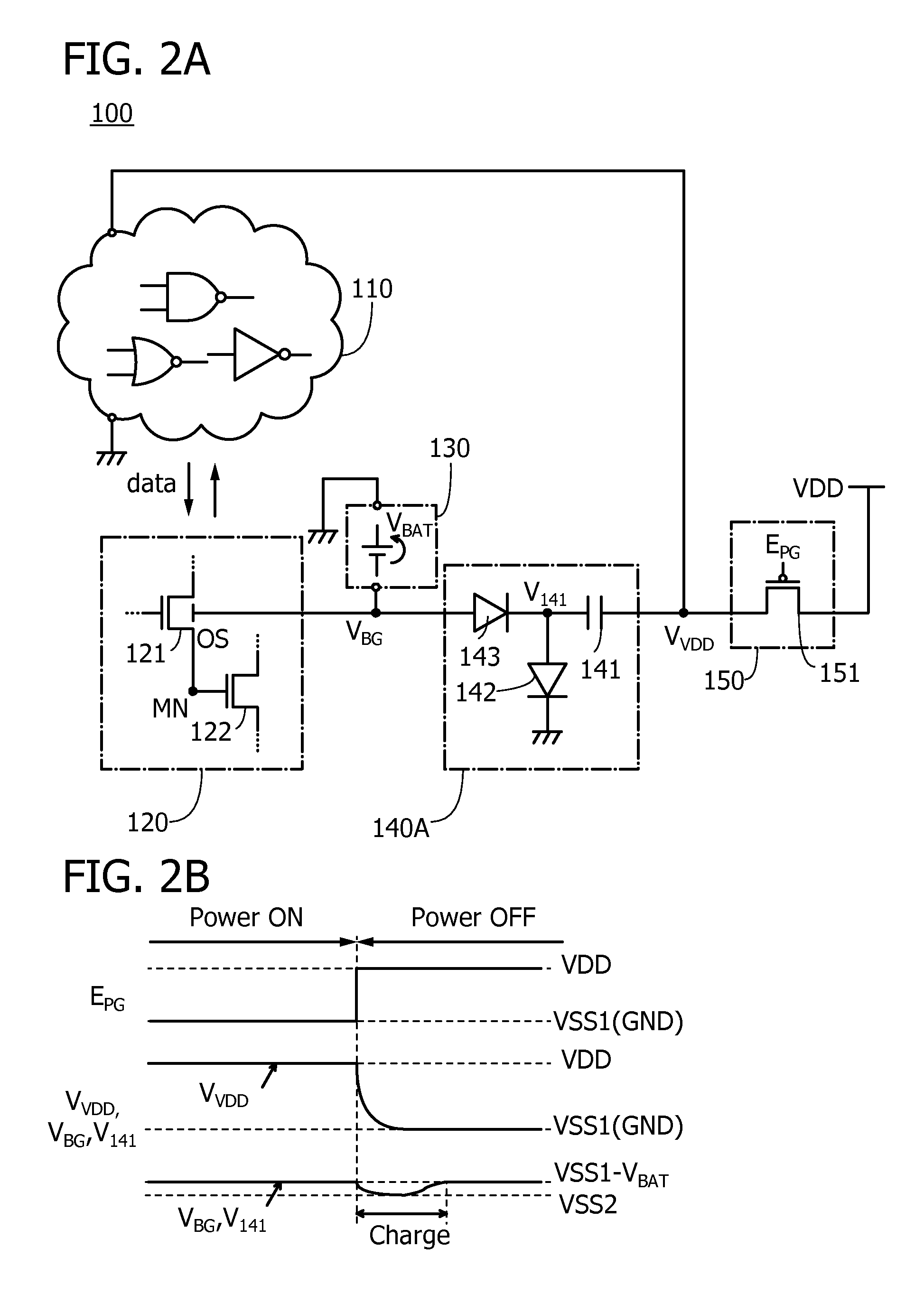
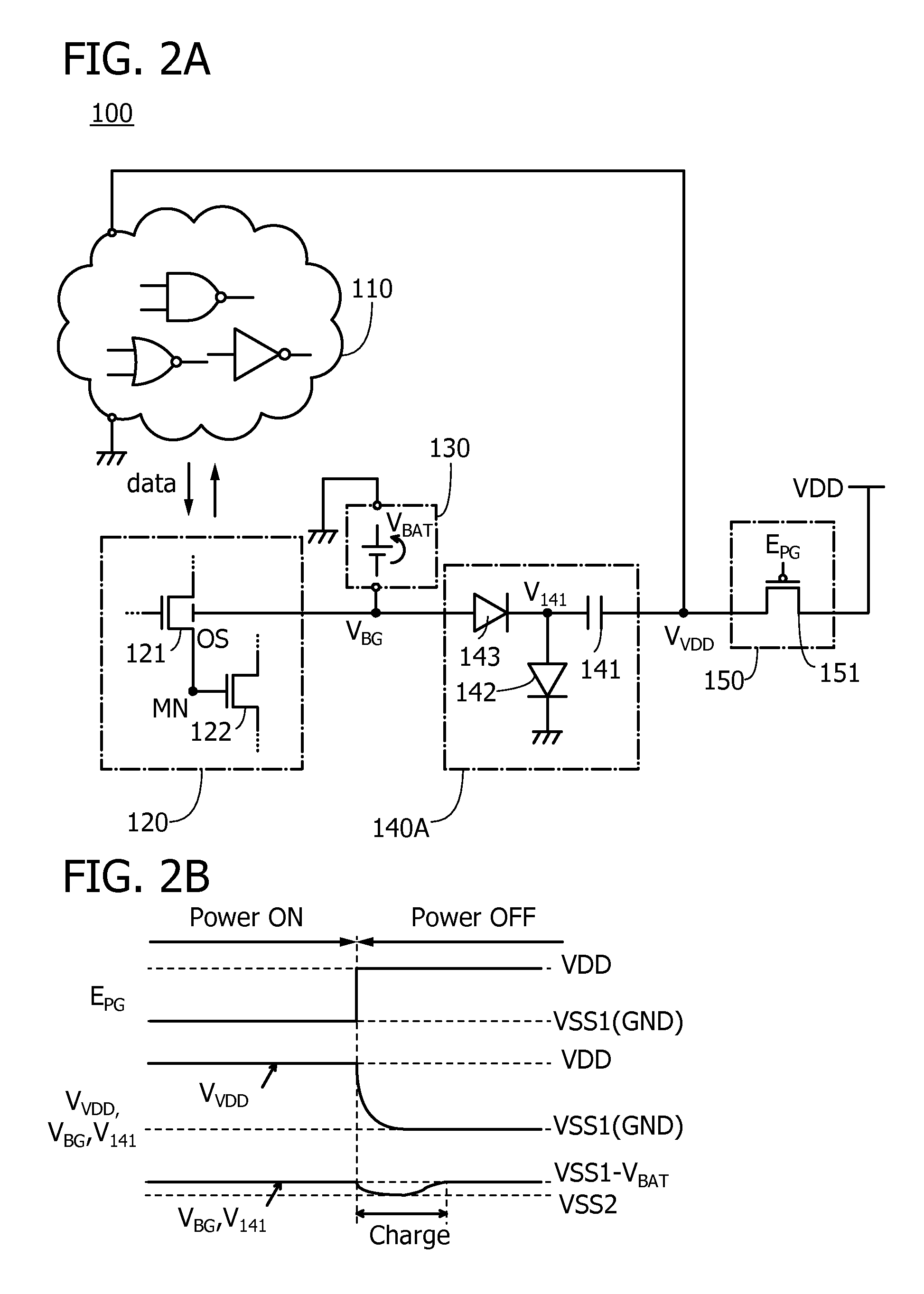
ActiveUS20160043716A1Novel structureImproved data retention featuresPower reduction in field effect transistorsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMemory circuitsData storing
A semiconductor device having excellent data retention characteristics. A transistor with a low off-state current is utilized to save and retain data stored in a memory circuit, and a potential to be applied to a back gate of the transistor is applied from a battery provided for each memory circuit. The potential applied to the back gate of the transistor and a potential for charging the battery are generated in a voltage generation circuit. The battery is charged utilizing power gating of the memory circuit and data retention characteristics is improved.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
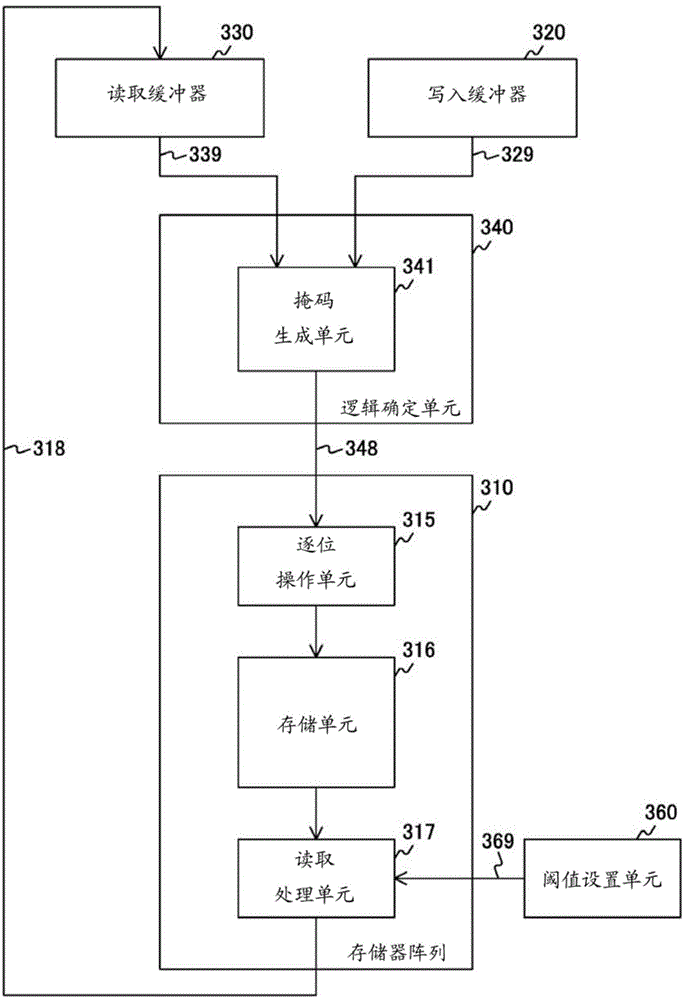
Storage control device, storage device, information processing system, and processing methods therefor
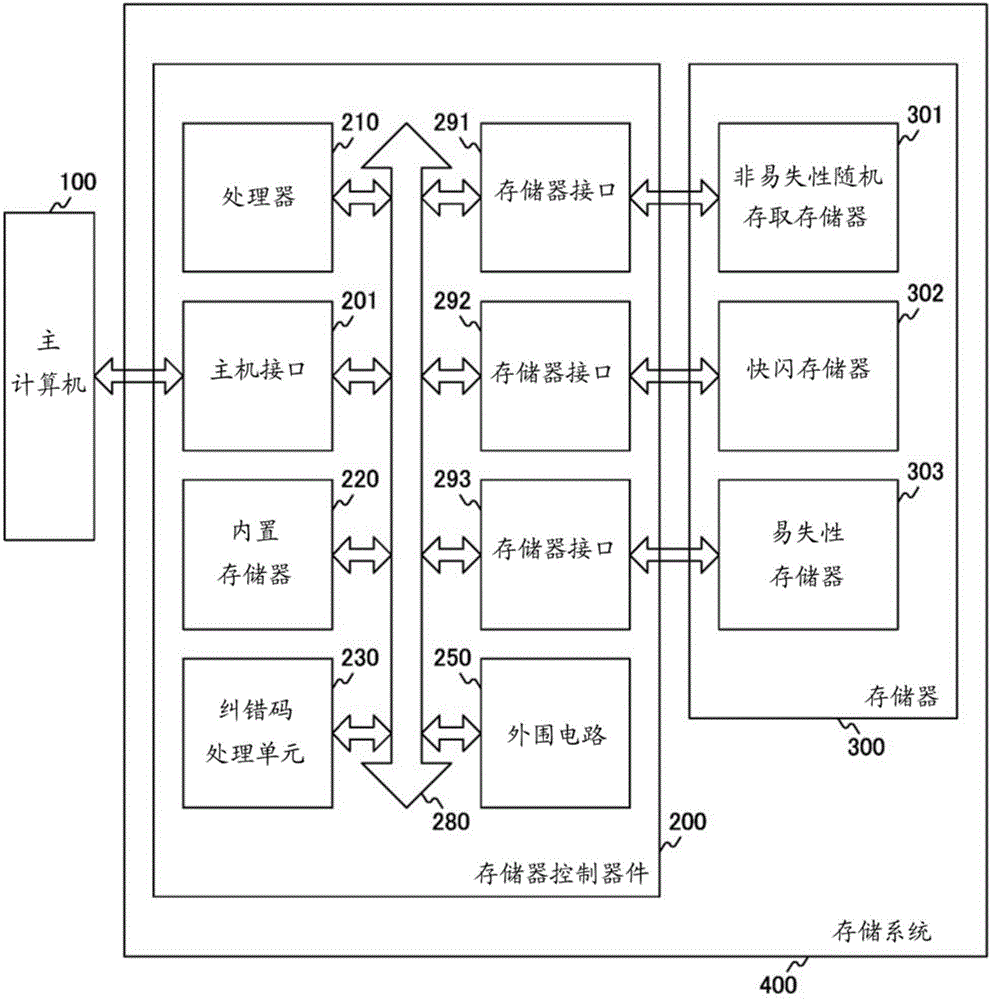
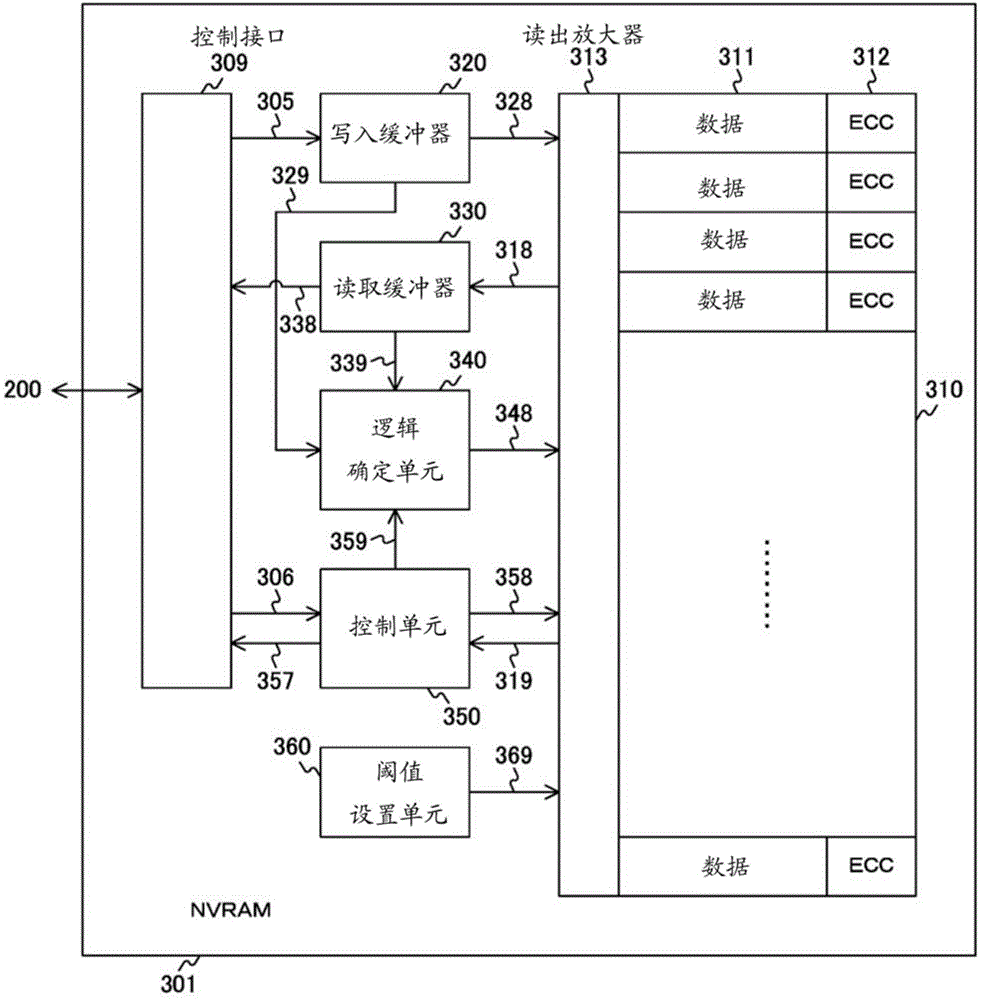
InactiveCN104040634AImproved data retention featuresError detection/correctionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationInformation processingInformation handling system
In the present invention, if write data is a first value, a threshold setting unit (360) sets a first threshold for a read processing unit (317), whereupon a bit operation unit (315) rewrites a memory cell (316) if read data is a second value. If write data is a second value, the threshold setting unit sets a second threshold for the read processing unit, whereupon the bit operation unit rewrites the memory cell if the read data is the first value. By generating read data using first and second thresholds that are different from a standard threshold, data-hold characteristics are improved.
Owner:SONY GRP CORP
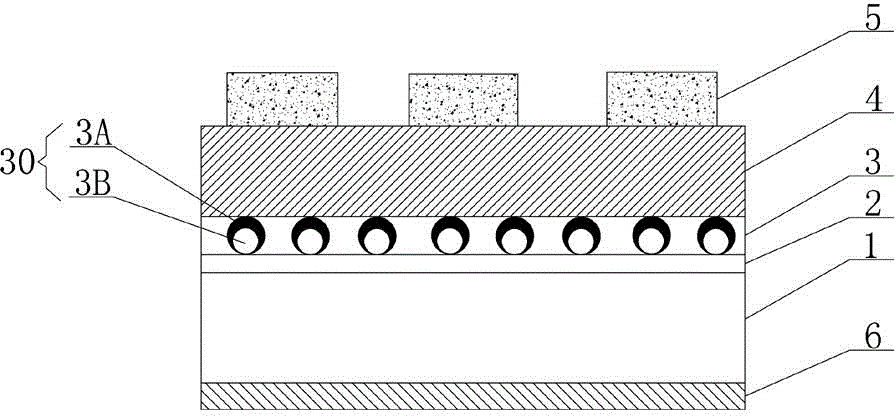
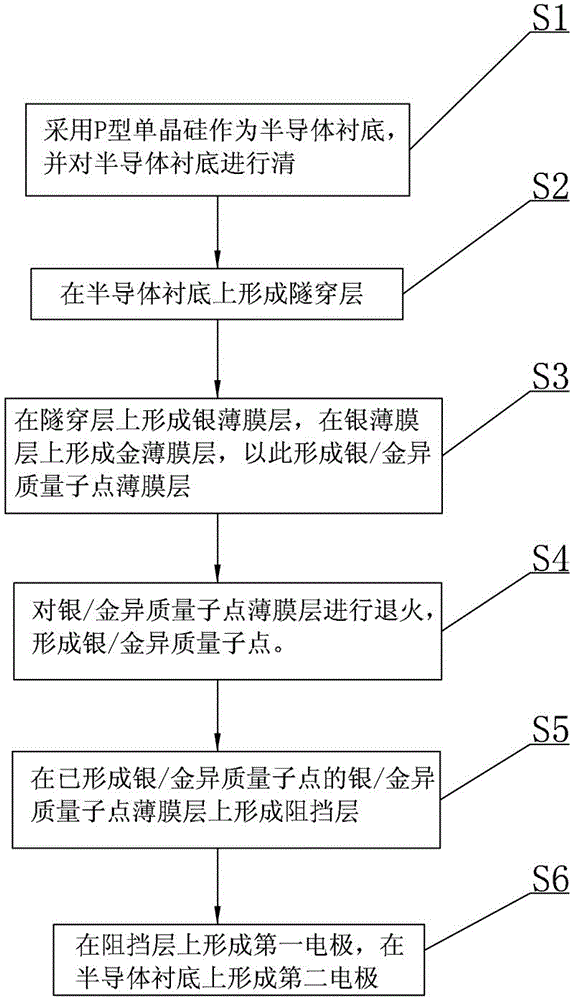
Floating gate memory based on metal heterogeneous quantum dots and preparation method therefor
InactiveCN104882490AExtended storage timeHigh densityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThin layerQuantum dot
The invention relates to a floating gate memory based on metal heterogeneous quantum dots and a preparation method therefor. The floating gate memory based on metal heterogeneous quantum dots comprises a semiconductor substrate. The semiconductor substrate is provided with a tunneling layer. The tunneling layer is provided with a silver / gold heterogeneous quantum dot thin layer. The silver / gold heterogeneous quantum dot thin layer is subjected to annealing to form silver / gold heterogeneous quantum dots. The silver / gold heterogeneous quantum dots achieve information storage by capturing tunneling charges. The silver / gold heterogeneous quantum dot thin layer is provided with a barrier layer for blocking captured charges by the silver / gold heterogeneous quantum dots for entering a first electrode. The barrier layer is provided with the first electrode for supplying power to the barrier layer. The semiconductor substrate is provided with a second electrode for supplying power to the semiconductor substrate. The floating gate memory based on the metal heterogeneous quantum dots is advantaged in that the charge storage density is high, the data holding property is good, the operation voltage is low, the erasing and writing speed is fast and the like.
Owner:SHAOXING UNIVERSITY
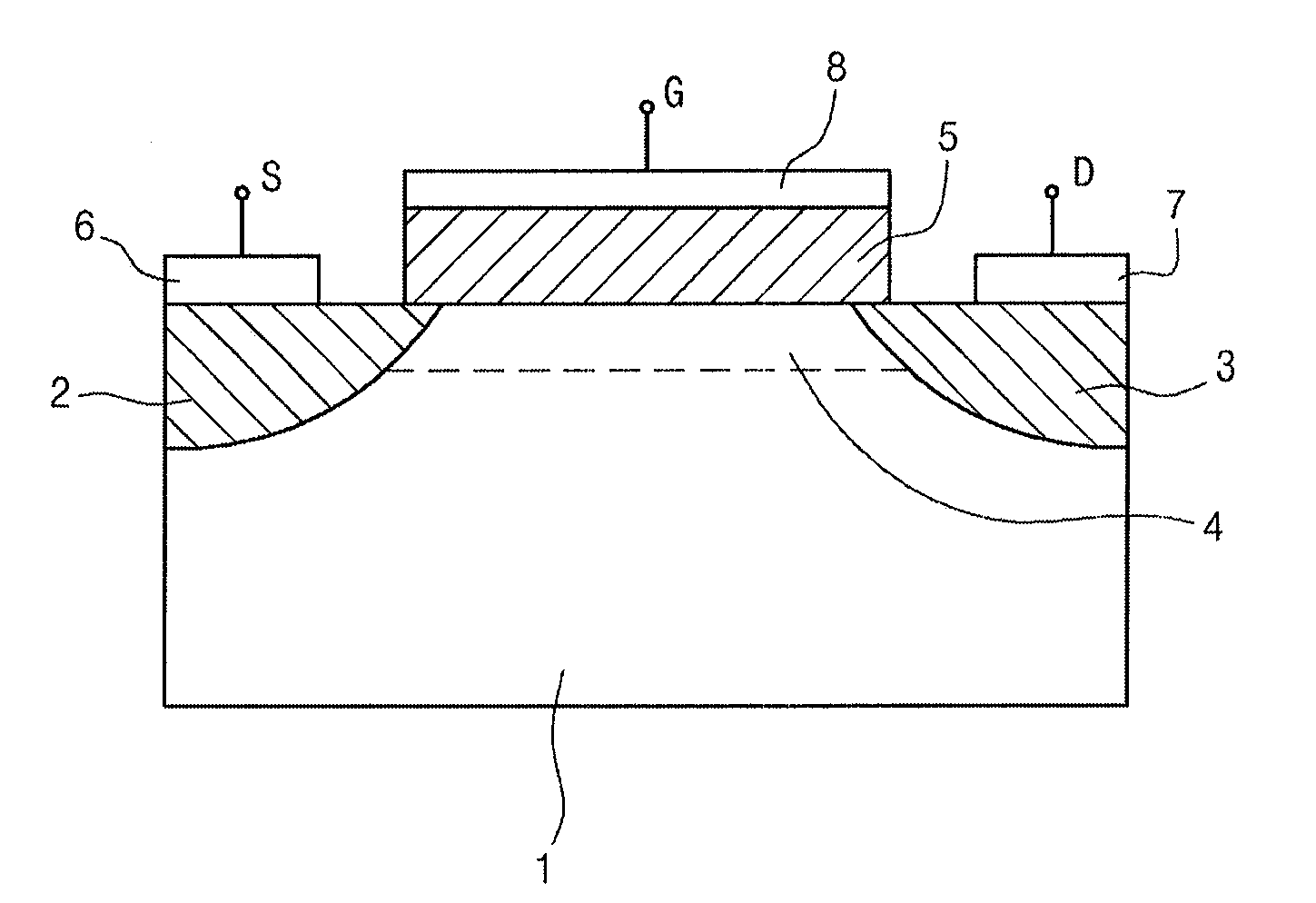
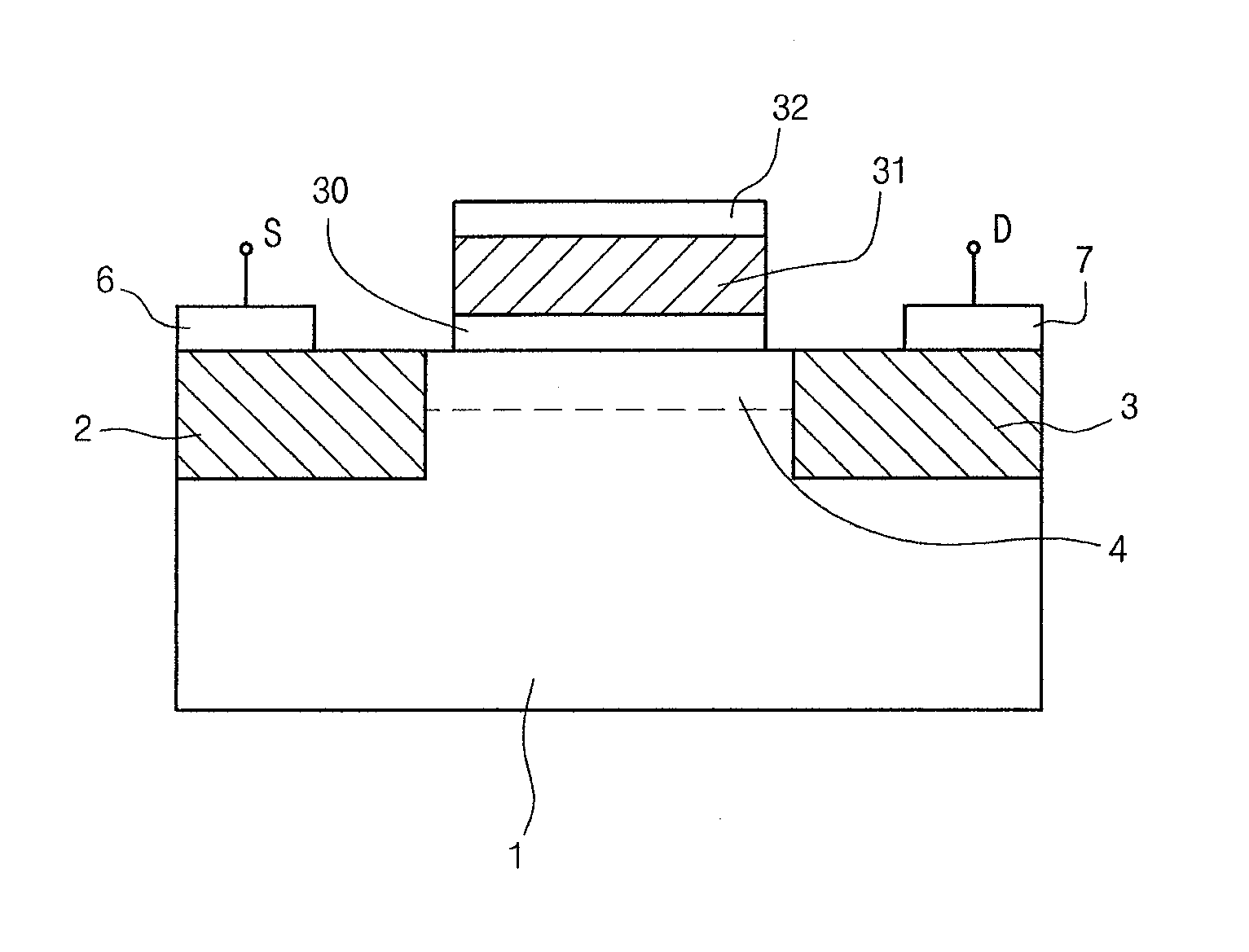
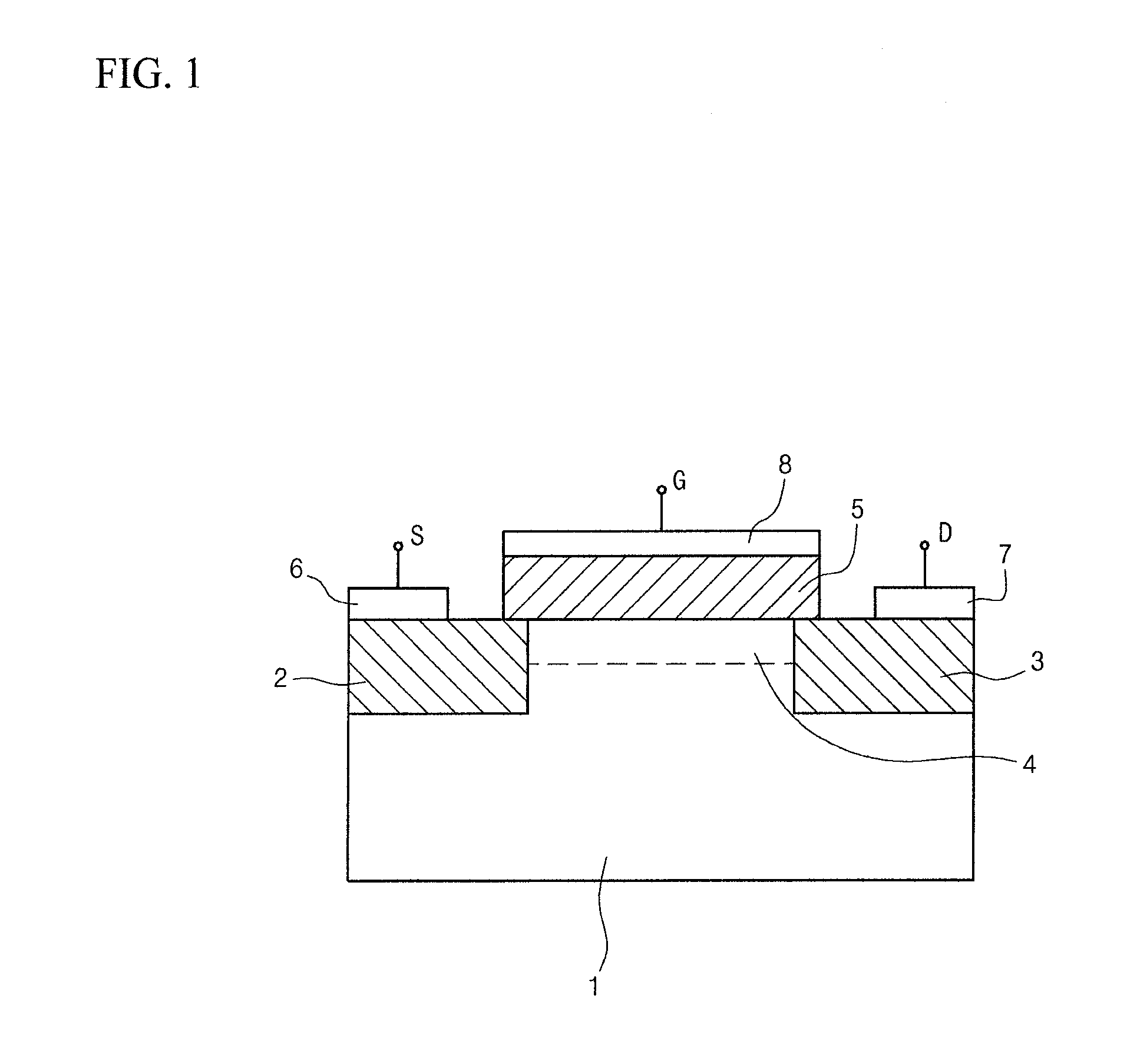
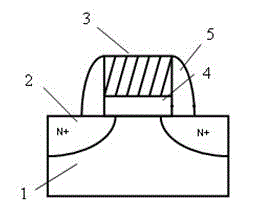
Fet, ferroelectric memory device, and methods of manufacturing the same
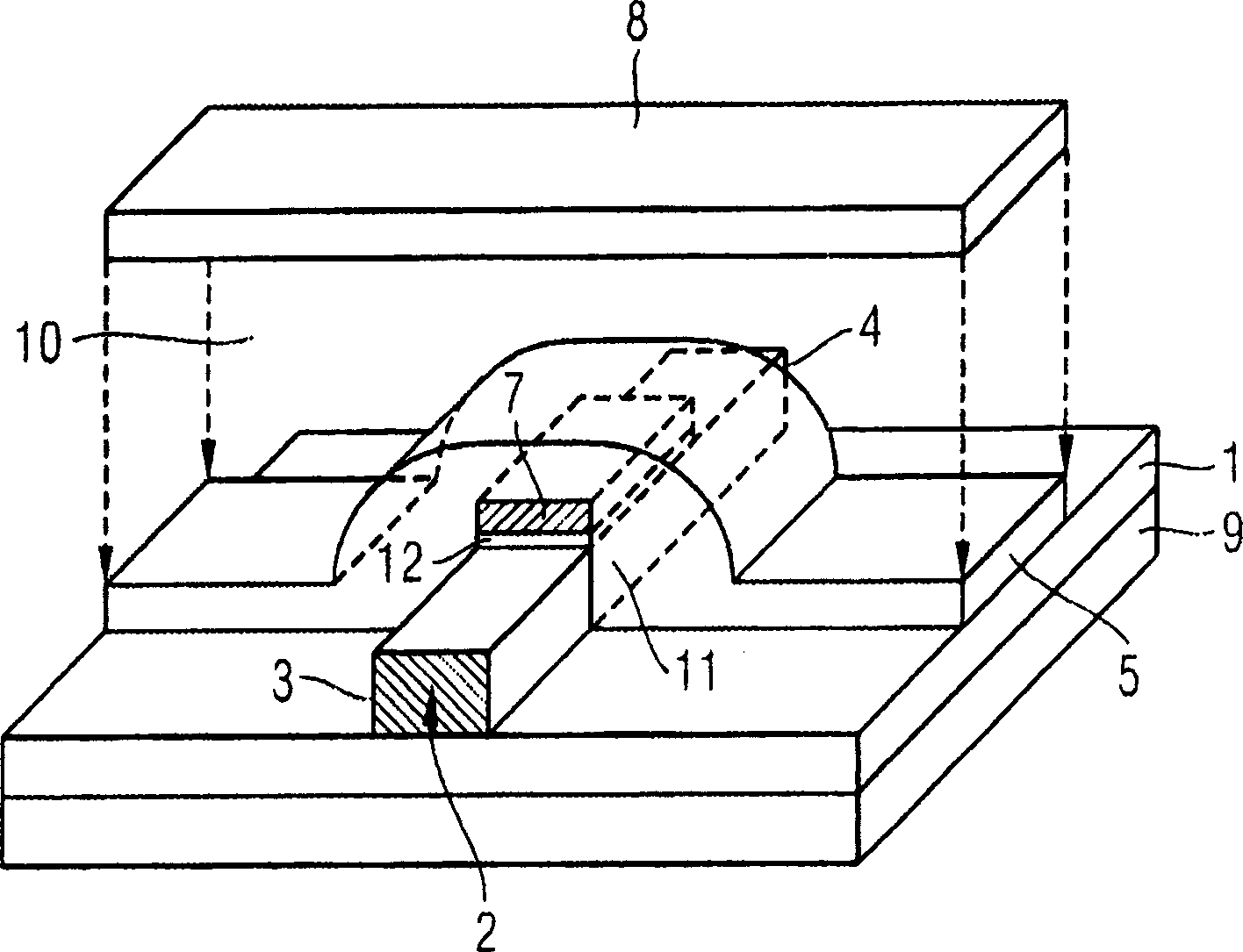
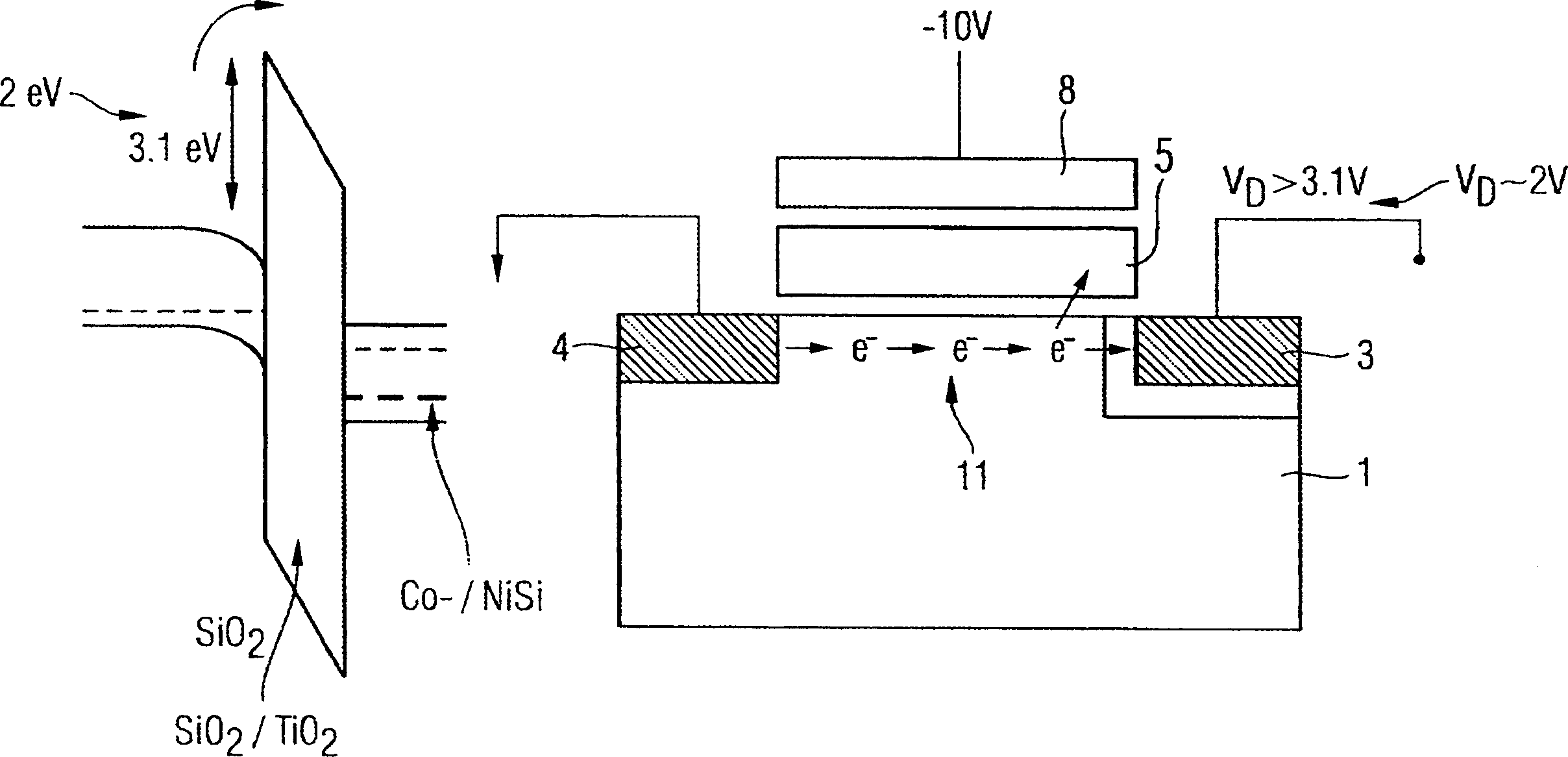
InactiveUS20100096679A1Simple structureImproved data retention featuresSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptoelectronicsField-effect transistor
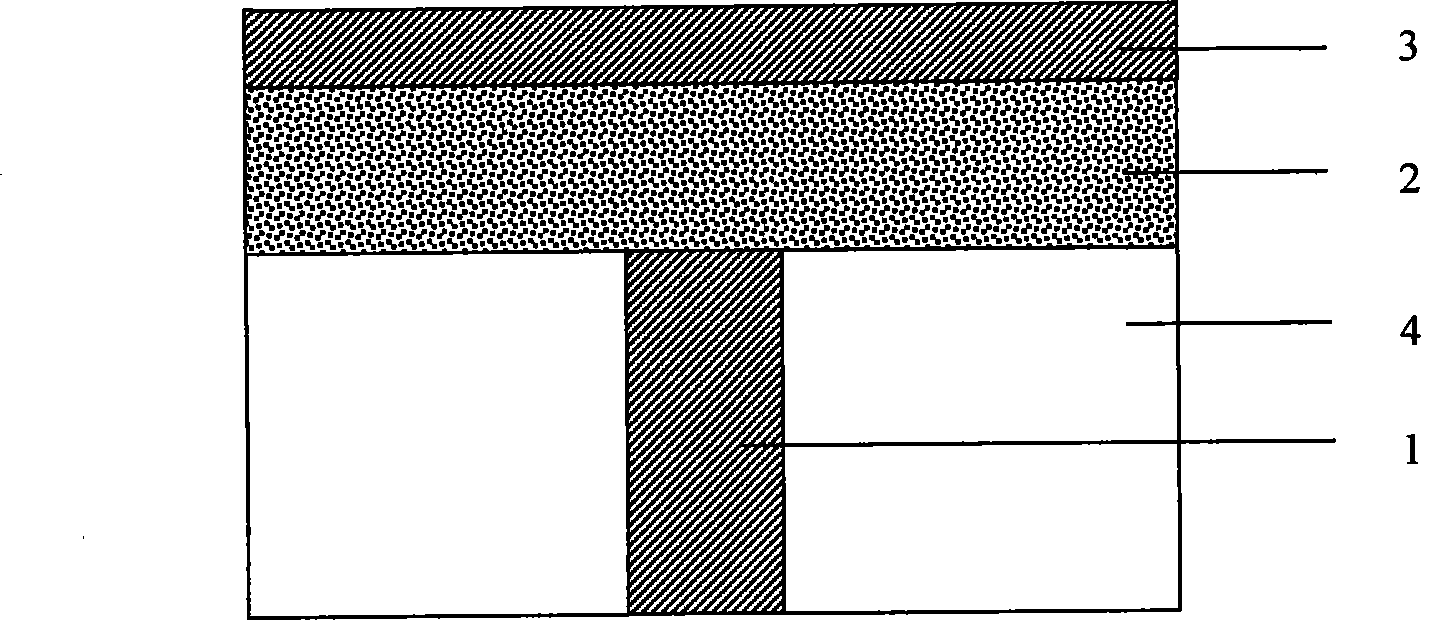
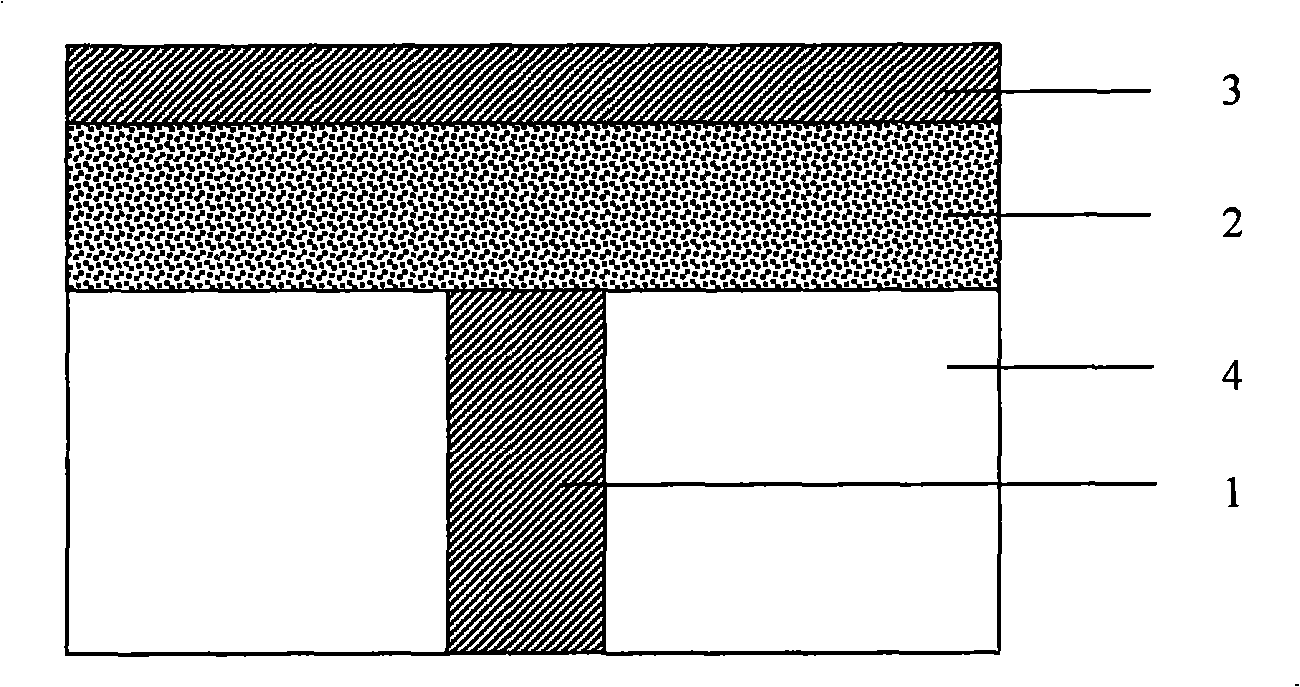
Disclosed herein are a field-effect transistor (FET), a ferroelectric memory device, and methods of manufacturing the same. The FET and the ferroelectric memory device in accordance with the present invention include: a substrate 1; source and drain regions 2 and 3 formed on the substrate; a channel layer 4 formed between the source and drain regions 2 and 3; and a ferroelectric layer 5 formed on the channel layer 4, the ferroelectric layer 5 being composed of a mixture of an inorganic ferroelectric material and an organic material. The ferroelectric layer 5 is formed in a manner that a mixed solution of an inorganic ferroelectric material and an organic material is applied onto the substrate and then subjected to annealing and etching processes.
Owner:UNIV OF SEOUL IND COOP FOUND
NOR memory cell based on resistance-changeable gate dielectric, its array and its operation method
An NOR memory based on a resistance-changeable gate dielectric comprises: a transistor comprising a source electrode, a drain electrode and a control gate electrode; a memory node which is a gate dielectric of the control gate electrode of the transistor, is positioned between the control gate electrode of the transistor and a silicon substrate and stores the resistance change; a word line connected to the control gate electrode of the transistor; a bit line connected to the drain electrode of the transistor; and a source line connected to the source electrode of the transistor. The gate electrode uses a resistance-changeable characteristic material having three different states of insulation, high resistance and low resistance, there is reversible switching between the high resistance and the low resistance, a constant voltage is applied among the word line, the source line and the bit line during reading, and "0" and "1" can be determined according to different currents. The invention also provides an array and an operation method of the NOR memory cell based on the resistance-changeable gate dielectric.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
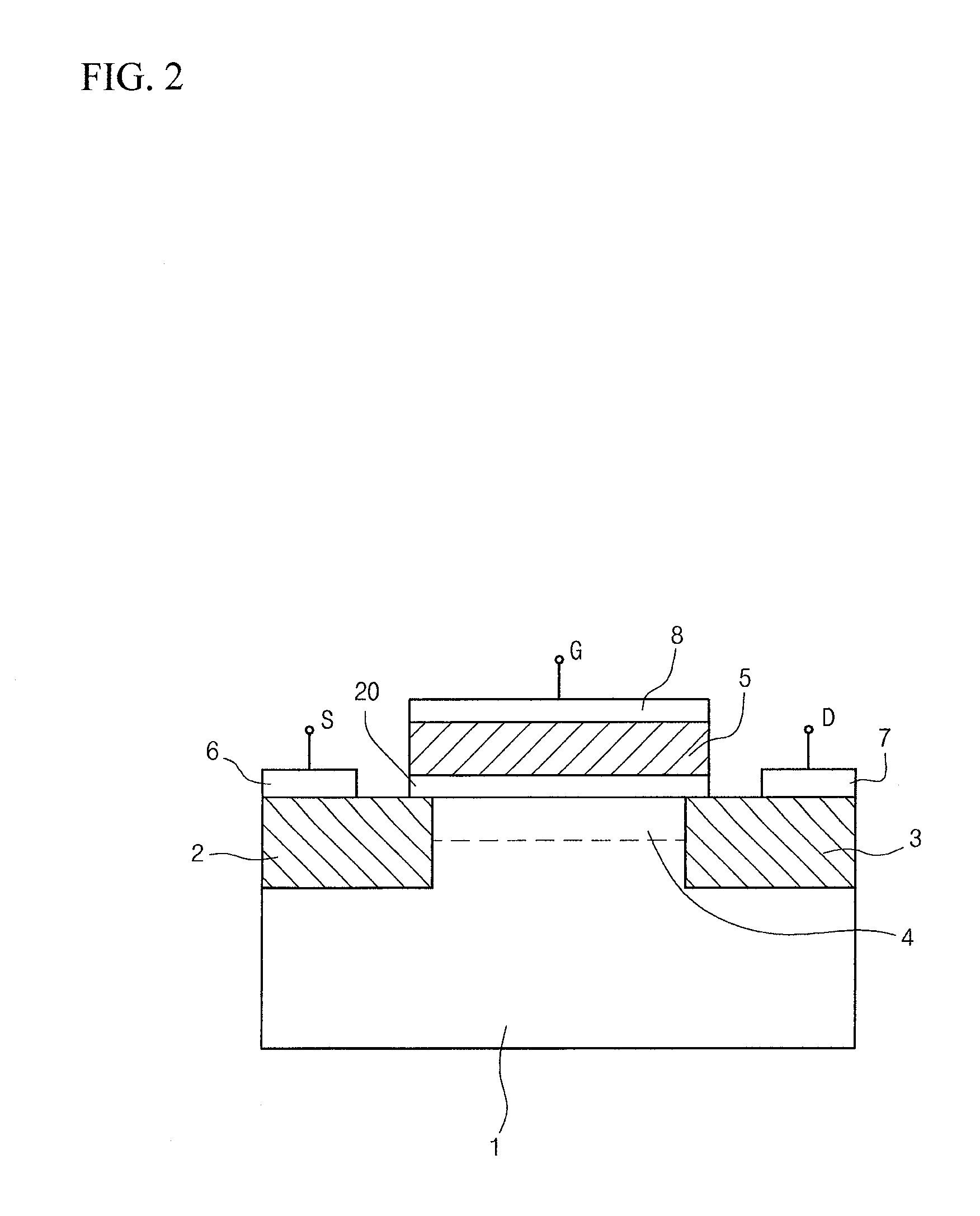
MFMS-FET, Ferroelectric Memory Device, And Methods Of Manufacturing The Same
InactiveUS20100252867A1Simple structureImproved data retention featuresSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingConductive materialsEngineering
Disclosed herein are a metal-ferroelectric-metal-substrate (MFMS) field-effect transistor (FET), an MFMS-ferroelectric memory device, and method of manufacturing the same. The MFMS-FET and the ferroelectric memory device in accordance with the present invention include: a substrate including source and drain regions, and a channel region formed therebetween; a buffer layer formed on the top of the channel region of the substrate; a ferroelectric layer formed on the buffer layer; and a gate electrode formed on the ferroelectric layer, wherein the buffer layer is formed of a conductive material.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF SEOUL
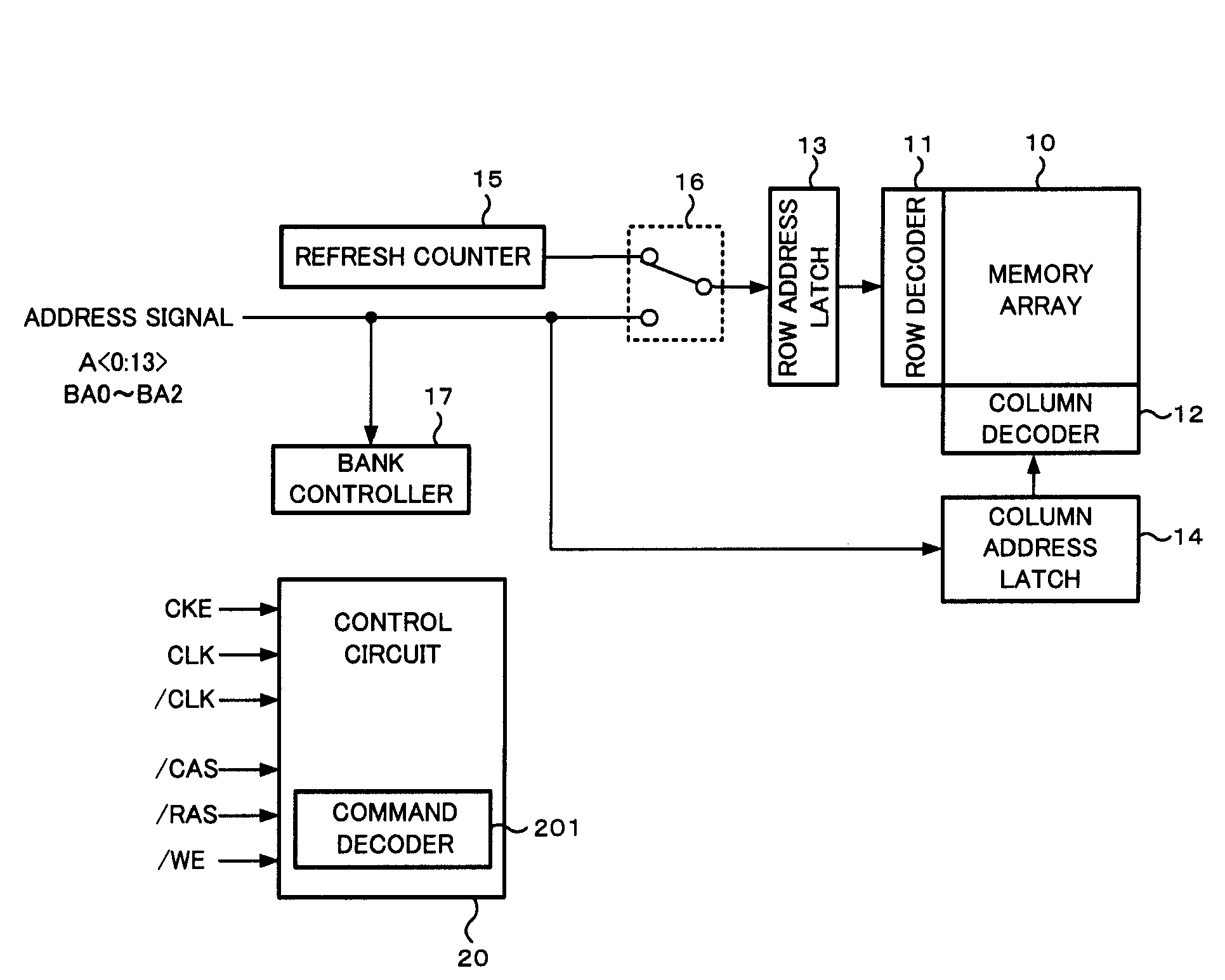
Semiconductor memory device which controls refresh of a memory array in normal operation
ActiveUS7471586B2Optimize characteristicsOptimize currentDigital storageLeast significant bitControl memory
A semiconductor memory device is comprised of a refresh counter for sequentially generating a count value indicating one or more row addresses corresponding to one or more word lines to be refreshed when receiving a refresh request at a predetermined interval in normal operation, in which the refresh counter includes n+1 stage counters assigned to n bits included in the row address and a dummy bit not included in the row address, and a counter portion from the least significant bit to the dummy bit forms an N-ary counter, so as to control whether or not refresh is performed in response to a value of the dummy bit when receiving the refresh request.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
2T dynamic memory unit and array structure based on resistance variation gate dielectric and method for operating same
InactiveCN103123805AReduce the refresh rateLow power applicationsTransistorDigital storageHigh resistanceArray data structure
The invention belongs to the technical field of memories and relates to a 2T dynamic memory unit and array structure based on a resistance-change gate dielectric and a method for operating the same. The 2T dynamic memory unit and array structure comprises a write-in tube, a read tube, a memory part, a write word line, a write bit line, a read word line and a read bit line, wherein the source terminal of the write-in tube is connected with the gate electrode of the read tube; the write-in tube has a programming function; the gate dielectric of the read tube is the memory part; the gate dielectric has an insulation state, a high-resistance state and a low-resistance state, and the conversion between high resistance and low resistance is reversible; a certain voltage is applied to the gate electrode of the read tube and the read word line in a reading process; and '0'and '1' can be judged according to the voltage change or the current value of the read bit line. The 2T dynamic memory unit and array structure is simple and convenient in process, low in cost, superior in effect, low in power consumption and high in performance, and is compatible with the front end of a 32-nm High k CMOS logic process.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
WOx-based resistance type memory and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101826595AStrong process controllabilityIncrease power consumptionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingControllabilityTungsten
The invention belongs to the technical field of microelectronics and relates to a metal oxide non-volatile memory technique, in particular to a WOx-based resistance type memory and a preparation method thereof. The WOx-based resistance type memory comprises an upper electrode, a tungsten lower electrode and a WOx-based memory medium which is arranged between the upper electrode and the tungsten lower electrode; the WOx-based memory medium is formed by performing oxidation treatment on a WSI compound covered on the tungsten lower electrode; and x is more than 1 and less than or equal to 3. Theresistance type memory has the characteristics of improving the controllability of the process and the reliability of devices, along with relatively low power consumption and high data retention performance.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Double gate memory cell with improved tunnel oxide
InactiveCN1812131ALower barrier heightIncreased Fermi level differenceTransistorSolid-state devicesMixed oxideDouble gate
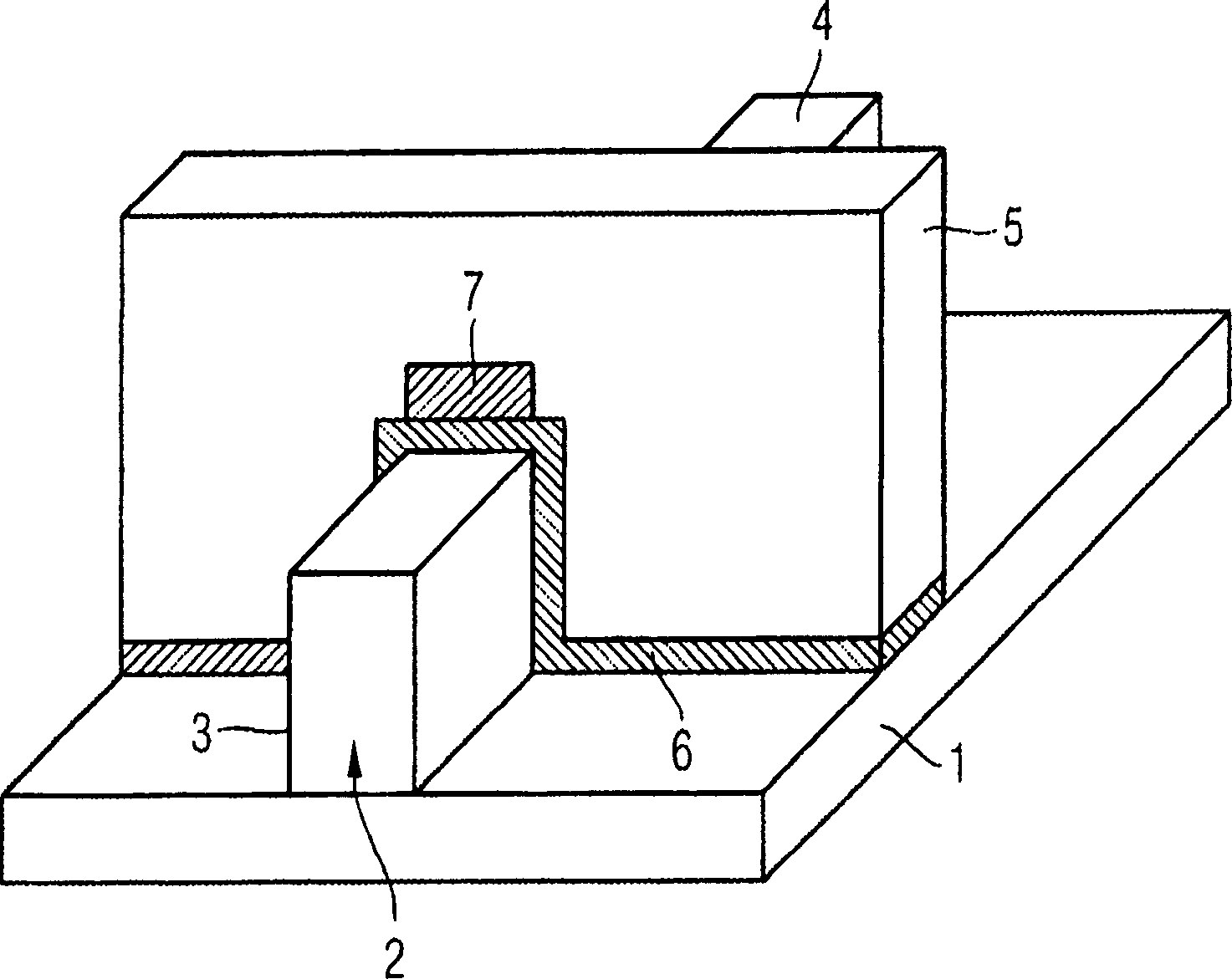
Provides a double gate memory cell having a silicon substrate with an active region having a channel region and source / drain regions, the active region forming a ridgelike fin with at least the channel region. A tunnel oxide layer is formed at least partly on the surface of the ridgelike fin of the active region. A floating gate for storing electrical charges is formed at least partly on the surface of the tunnel oxide layer. An intergate insulator layer made of a dielectric material is formed at least partly on the surface of the floating gate. A control gate is formed at least partly on the surface of the intergate layer, the tunnel oxide layer including an amorphous silicon dioxide / titanium dioxide mixed oxide.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Semiconductor device and electronic device with data voltages read accurately without the influence of threshold voltage variation
ActiveUS9640226B2Novel structureImproved data retention featuresTransistorSolid-state devicesData reliabilitySemiconductor
To provide a semiconductor device having large memory capacity and high reliability of data or a small-size semiconductor device having a small circuit area. A memory cell includes first and second data retention portions capable of storing multilevel data. A data voltage is written to the first data retention portion from a first wiring through a transistor and a second wiring, and a data voltage is written to the second data retention portion from the second wiring through a transistor and the first wiring. With the configuration, data voltages reduced by the threshold voltages of the transistors can be retained in the first and second data retention portions. The written data voltages where the threshold voltages of the transistors are canceled can be read by precharging and then discharging the first wiring.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Tungsten titanium alloy nanocrystalline gate-floating structure and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101494237APrevent leakageImproved data retention featuresSemiconductor devicesCMOSDielectric
The invention discloses a tungsten-titanium alloy nanocrystalline floating grid structure used for a flash memory, pertaining to the technical field of micro-electronics. The structure comprises a silicon substrate as well as a silicon oxide layer, a high k (dielectric constant) thin film, a tungsten-titanium alloy nanocrystalline charge storage layer, a barrier layer and a grid material layer which are covered on the silicon oxide layer successively. The structure improves memory properties of a non-volatile memory unit of the floating grid structure, such as programming / erasing efficiency, programming / erasing (P / E) speed, effective charge memory power, data maintenance property and programming / erasing tolerance. The invention also discloses a method for manufacturing the tungsten-titanium alloy nanocrystalline floating grid structure. The method is simple and convenient and is compatible with the traditional CMOS silicon planar technology.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP +1
M-Sb-Se phase changing thin-film material used for phase changing memory
ActiveCN101488558BFast crystallizationFast reading and writingElectrical apparatusDigital storageCMOSPhase-change memory
The invention discloses an M-Sb-Se phase transition film material used for a phase transition storage and the ingredient thereof is (SbxSe(1-x))(1-y)My, wherein y is an atomic ratio of 0.2%-15%, x is the atomic ratio of 50%-95%, and doping elements of M comprise one or two elements out of tungsten, aluminum, indium, silver, copper, nickel, gallium, titanium , tin, oxygen and nitrogen. The M-Sb-Sephase transition film material of the invention has faster crystallization rate, faster read-write rate and better data holding property than the commonly used Ge2Sb2Te5 material and better thermal stability than SbSe binary material. Meanwhile, the material is free from element Te, thereby being environment friendly, and the material has good compatibility with CMOS technique.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
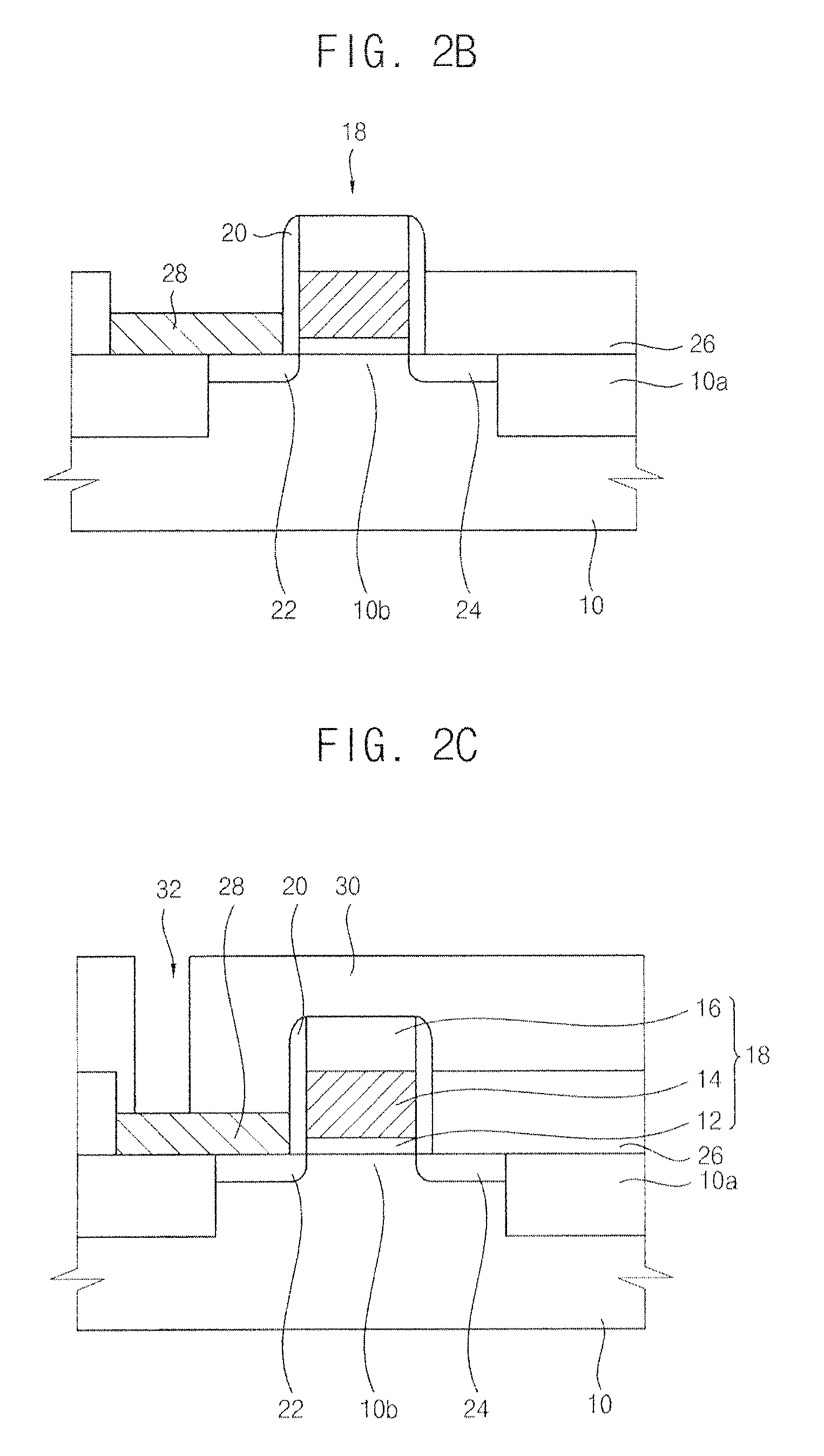
DRAM semiconductor device with pad electrode
InactiveUS8334556B2Avoid leakage currentImproved data retention featuresTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPower semiconductor deviceEngineering
A semiconductor device includes a semiconductor substrate having an active region and an isolation region. A gate structure is provided on the semiconductor device. First and second impurity regions are provided in the substrate on both sides of the gate structure. A pad electrode is provided to contact the first impurity region. Because the pad electrode is provided on the first impurity region of the semiconductor device, the contact plug does not directly contact the active region. Accordingly, failures caused by damage to the active region may be prevented.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
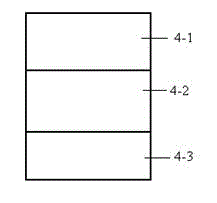
Double capture-silicon oxide nitride oxide semiconductor (SONOS) memorizer with double layer dielectric charge trapping layer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103066074AImprove data retention characteristicsEasy to storeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectricTrapping
The invention relates to the field of semiconductor charge capture memorizers, and discloses a nonvolatile double capture-silicon oxide nitride oxide semiconductor (SONOS) memorizer with a double layer dielectric charge capture layer. The nonvolatile DC-SONOS memorizer with the double layer dielectric charge trapping layer comprises a semiconductor substrate of a channel which is provided with a channel surface, a source terminal adjacent to the channel and a drain terminal adjacent to the channel, a grid electrode, a dielectric stack arranged between the grid electrode and the channel surface, and side walls arranged at two sides of the grid electrode and two sides of the dielectric stack. The dielectric stack comprises a tunneling layer contacted with the surface of the channel, a charge capture layer superimposed on the tunneling layer, the charge capture layer is of a double layer dielectric composite structure, a barrier layer superimposed on the charge capture layer, and the barrier layer is contacted with the grid electrode. The charge capture layer comprises a first layer dielectric contacted with the tunneling layer, wherein the first layer dielectric is made of Si3N4, the thickness of the first layer dielectric is 1-30, a second layer dielectric adjacent to the first layer dielectric, wherein the second layer dielectric is made of SiN, and the thickness of the second layer dielectric is 1-50. According to the DC-SONOS memorizer with the double layer dielectric charge capture layer, performance of traditional SONOS nonvolatile memorizers is improved, data-hold feature of the memorizer is improved, and the memorizer which is capable of keeping high data-hold feature under poor operating conditions is easy to obtain.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY +1
Semiconductor device, and method for fabricating thereof
InactiveCN101315946AImproved data retention featuresImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSilicon oxideNitride
A semiconductor device having silicon-oxide-nitride-oxide-silicon (SONOS) structure that overcomes spatial limitations which trap charges by not utilizing a flat, planar structure of the ONO film including a charging trap layer, thereby making it possible to improve reliability for data preserving characteristic of a SONOS device.
Owner:DONGBU HITEK CO LTD
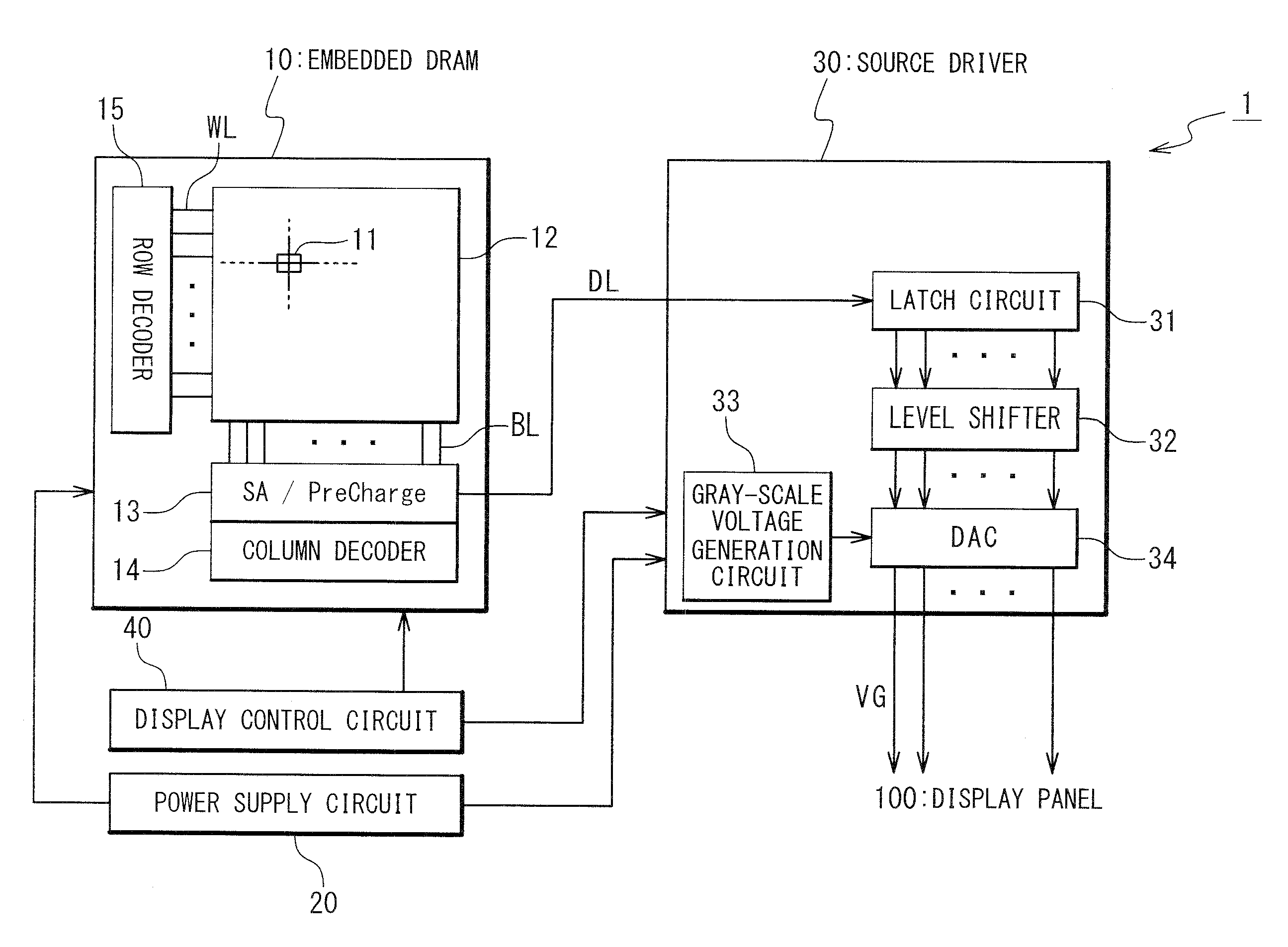
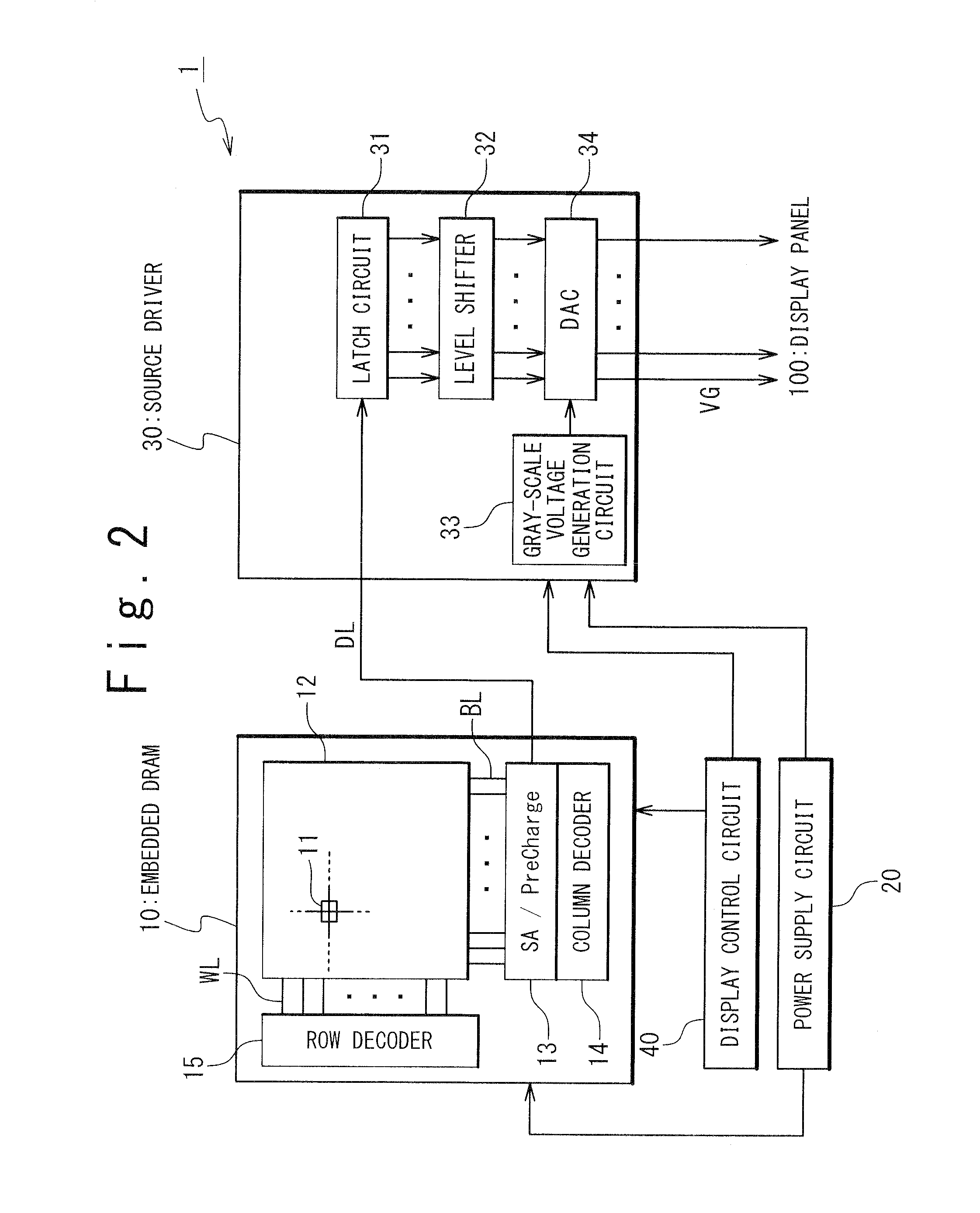
Display driver IC having embedded dram
InactiveUS20080186335A1Improve data retentionLot differenceCathode-ray tube indicatorsDigital storageDigital dataDriver circuit
A display driver IC for controlling display of an image on a display panel is provided with a DRAM and a driver circuit. The DRAM has a plurality of memory cells and stores digital data corresponding to the image. The driver circuit converts the digital data into a gray-scale voltage and outputs the gray-scale voltage to the display panel. The DRAM is configured to store one bit data by using n memory cells of the plurality of memory cells, n being an integer of 2 or more.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
2t dynamic memory cell and array structure based on resistive gate dielectric and its operation method
InactiveCN103123805BAvoid difficultiesOvercoming the problem of poor process compatibilityTransistorDigital storageCMOSGate dielectric
The invention belongs to the technical field of memory, and relates to a 2T dynamic memory unit based on a resistive gate medium, an array structure and an operation method thereof. The present invention includes a write tube, a read tube, a storage unit, a write word line, a write bit line, a read word line, and a read bit line; the source end of the write tube is connected to the gate of the read tube, and the write tube It has the function of programming, and the gate medium of the reading tube is a storage part; the gate medium has three different states of insulation, high resistance, and low resistance, among which the transition between high resistance and low resistance is reversible, and when reading, it is read into the tube grid. A certain voltage is applied to the electrode and the read word line, and "0" and "1" can be judged according to the voltage change or current value of the read bit line. The invention has the advantages of simple process, low cost, superior effect, low power consumption and high performance, and is compatible with the front end of 32nm High k CMOS logic process.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Semiconductor device, and method for fabricating thereof
InactiveCN101315946BImproved data retention featuresImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPower semiconductor deviceEngineering
A semiconductor device having silicon-oxide-nitride-oxide-silicon (SONOS) structure that overcomes spatial limitations which trap charges by not utilizing a flat, planar structure of the ONO film including a charging trap layer, thereby making it possible to improve reliability for data preserving characteristic of a SONOS device.
Owner:DONGBU HITEK CO LTD
Non-destructive read ferroelectric memory, its preparation method and read/write operation method
ActiveCN104637948BSimple structureEasy to makeSolid-state devicesDigital storageNon destructiveHigh density
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Three-dimensional nonvolatile semiconductor memory based on nanocrystalline floating gate and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110137174AIncrease storage capacityPrevent leakageSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesSulfurVertical channel
The invention belongs to the field of three-dimensional flash memory preparation, and more particularly to a three-dimensional nonvolatile semiconductor memory based on a nanocrystalline floating gateand a preparation method thereof. The three-dimensional semiconductor memory includes a plurality of three-dimensional NAND memory strings in a vertical direction, wherein each three-dimensional NANDmemory string includes a semiconductor region, and a four-layered package structure surrounding the semiconductor region and including a tunneling dielectric layer, a charge storage layer, a barrierdielectric layer and a control gate electrode; the material of the charge storage layer comprises a nanocrystalline material; and the nanocrystalline material is a sulfur-based compound nanocrystalline. The sulfur-based compound nanocrystalline having a high hole structure content is used as the material of the charge storage layer, thereby improving the programming / erasing efficiency, the programming / erasing speed, and the charge storage capability of a single memory cell of the three-dimensional flash memory. The process of the nanocrystalline floating gate of the invention is simple and iscompatible with a vertical channel process.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
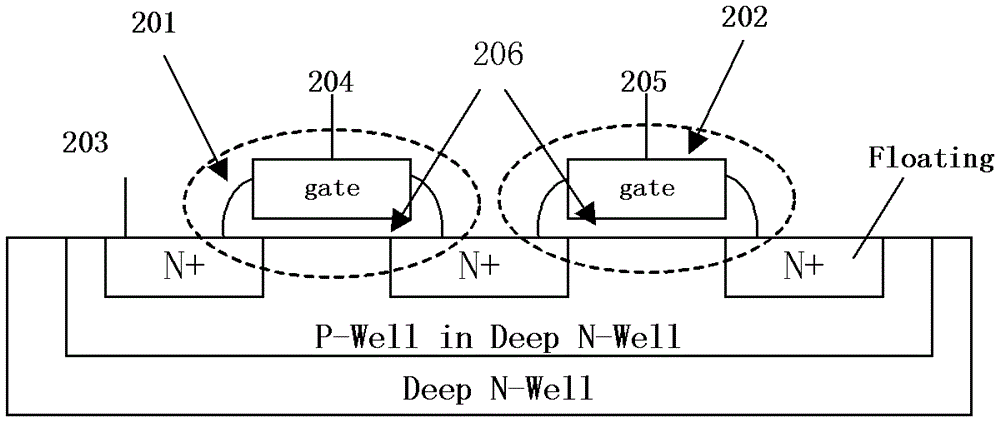
Semiconductor device
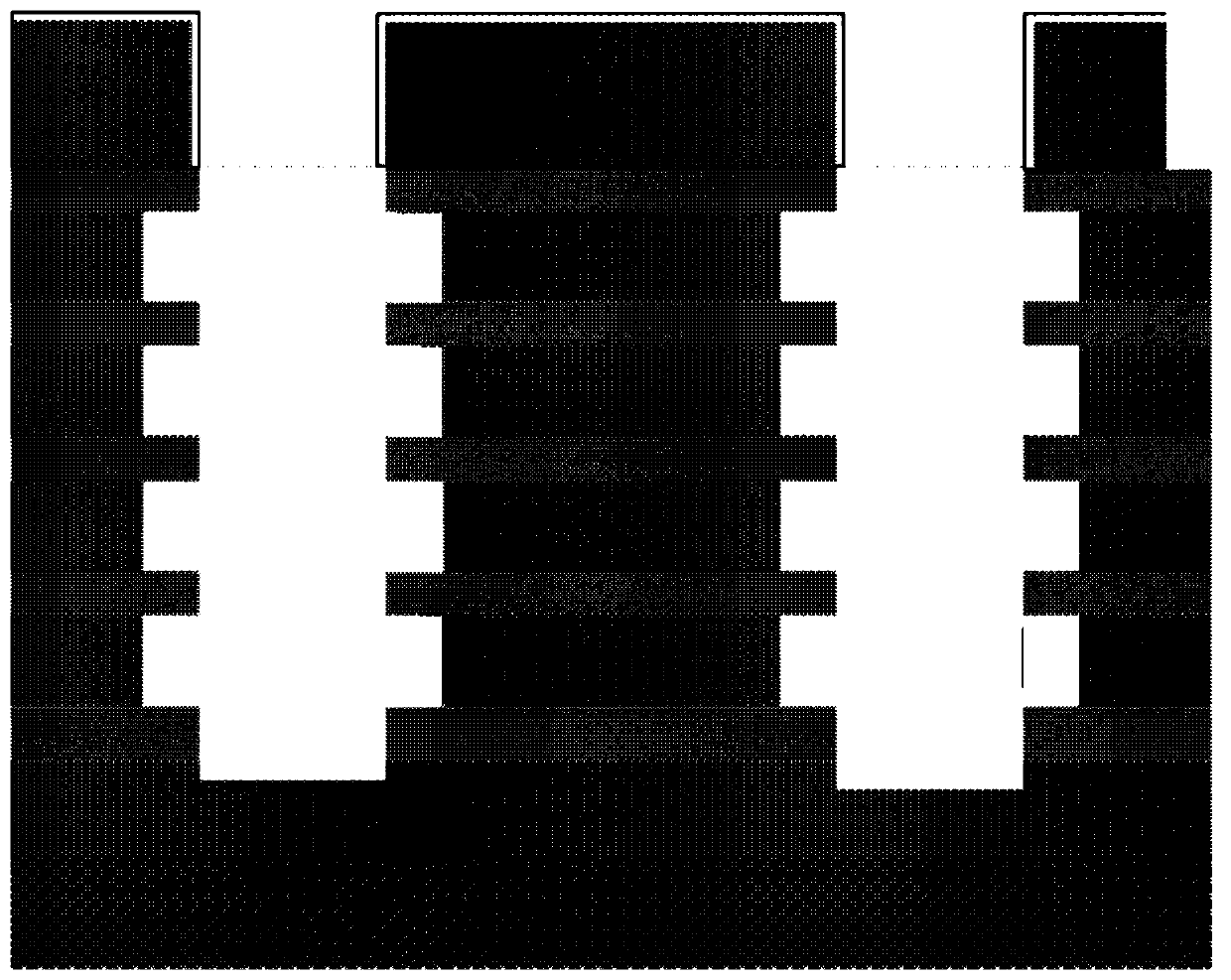
ActiveCN111798899AImproved data retention featuresSmall drain currentSolid-state devicesDigital storageMemory cellDevice material
A semiconductor device is provided. An SRAM of the invention includes P-well regions PW_1 and PW_2, an N-well region NW, a first metal wire M1, and a second metal wire M2. The P-well regions PW_1 andPW_2 extend in a first direction, and pull-down transistors and accessing transistors are formed therein. The N-well region NW extends in first direction, and pull-up transistors are formed therein. The first metal wire M1 extends in the first direction on the N-well region NW and is electrically connected to the N-well region NW. The second metal wire M2 extends in a second direction orthogonal to the first direction and electrically connected to a common S / D region of a pair of pull-up transistors that are formed in the N-well region NW. The semiconductor can apply different voltages to sources and bases of pull-up transistors and improves write margin of memory cells.
Owner:WINBOND ELECTRONICS CORP
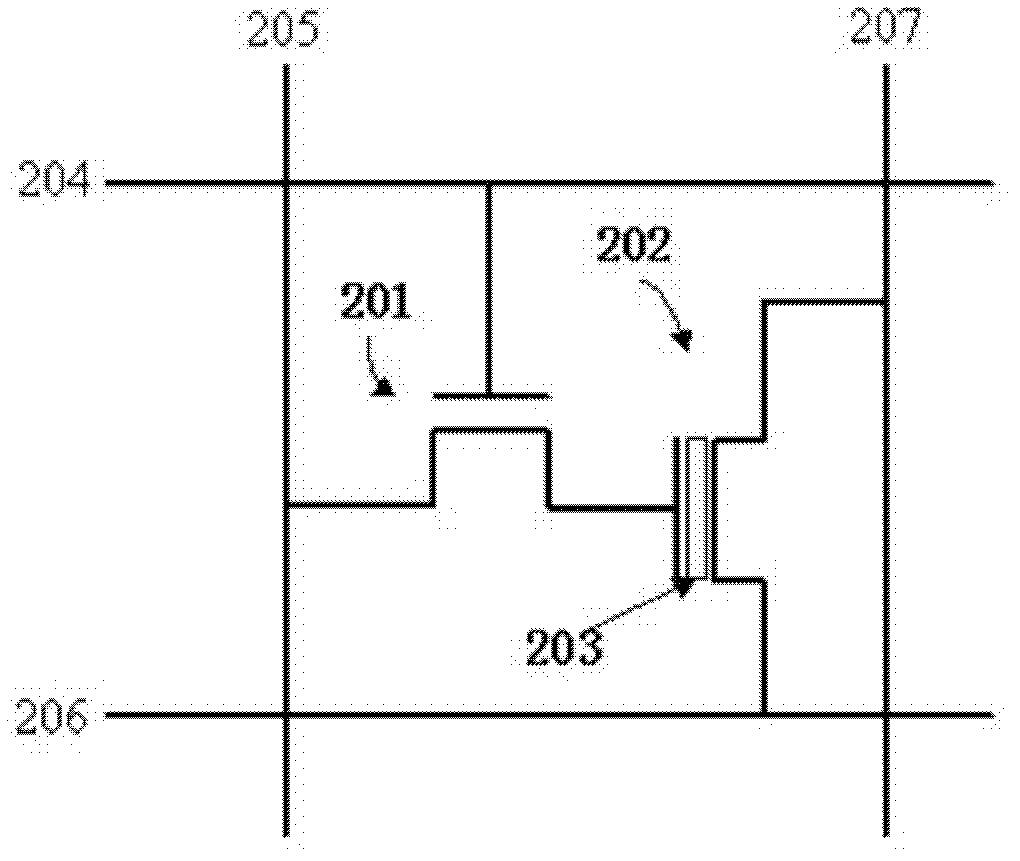
1.5t dynamic memory cell, array and operation method based on resistive switching gate dielectric
InactiveCN103123804BSimple processGood effectTransistorDigital storageHigh resistanceGate dielectric
The invention relates to the field of memory technology, and relates to a 1.5T dynamic memory unit based on a resistive gate dielectric, an array structure, and an operation method thereof. The invention includes: a transistor, including a source, a drain and a control gate; a storage node, that is, the gate dielectric of the transistor control gate, located between the transistor control gate and the silicon substrate, with storage resistance changes; a word line, Connected to the control gate of the transistor; the bit line is connected to the drain of the transistor; the source line is connected to the source of the transistor; among them, the read tube 201 plays the role of gating and current limiting, and 202 is used for programming Components, 203 is the bit line, 204 is the word line of 201, and 205 is the programming word line. The gate has different states of high resistance and low resistance, and the transition between them is reversible. When a certain voltage is applied between the bit line and the word line, there will be currents of different sizes. The invention solves the difficulties of the traditional 1T1C DRAM unit and the problem of poor compatibility with the standard CMOS process, and can be compatible with the standard logic CMOS HfOx high k metal gate technology.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Semiconductor device and electronic device
ActiveUS9520873B2Novel structureImproved data retention featuresPower reduction in field effect transistorsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMemory circuitsData storing
A semiconductor device having excellent data retention characteristics. A transistor with a low off-state current is utilized to save and retain data stored in a memory circuit, and a potential to be applied to a back gate of the transistor is applied from a battery provided for each memory circuit. The potential applied to the back gate of the transistor and a potential for charging the battery are generated in a voltage generation circuit. The battery is charged utilizing power gating of the memory circuit and data retention characteristics is improved.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
WOx-based resistance type memory and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101826595BStrong process controllabilityIncrease power consumptionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringLow power dissipation
The invention belongs to the technical field of microelectronics and relates to a metal oxide non-volatile memory technique, in particular to a WOx-based resistance type memory and a preparation method thereof. The WOx-based resistance type memory comprises an upper electrode, a tungsten lower electrode and a WOx-based memory medium which is arranged between the upper electrode and the tungsten lower electrode; the WOx-based memory medium is formed by performing oxidation treatment on a WSI compound covered on the tungsten lower electrode; and x is more than 1 and less than or equal to 3. The resistance type memory has the characteristics of improving the controllability of the process and the reliability of devices, along with relatively low power consumption and high data retention performance.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com