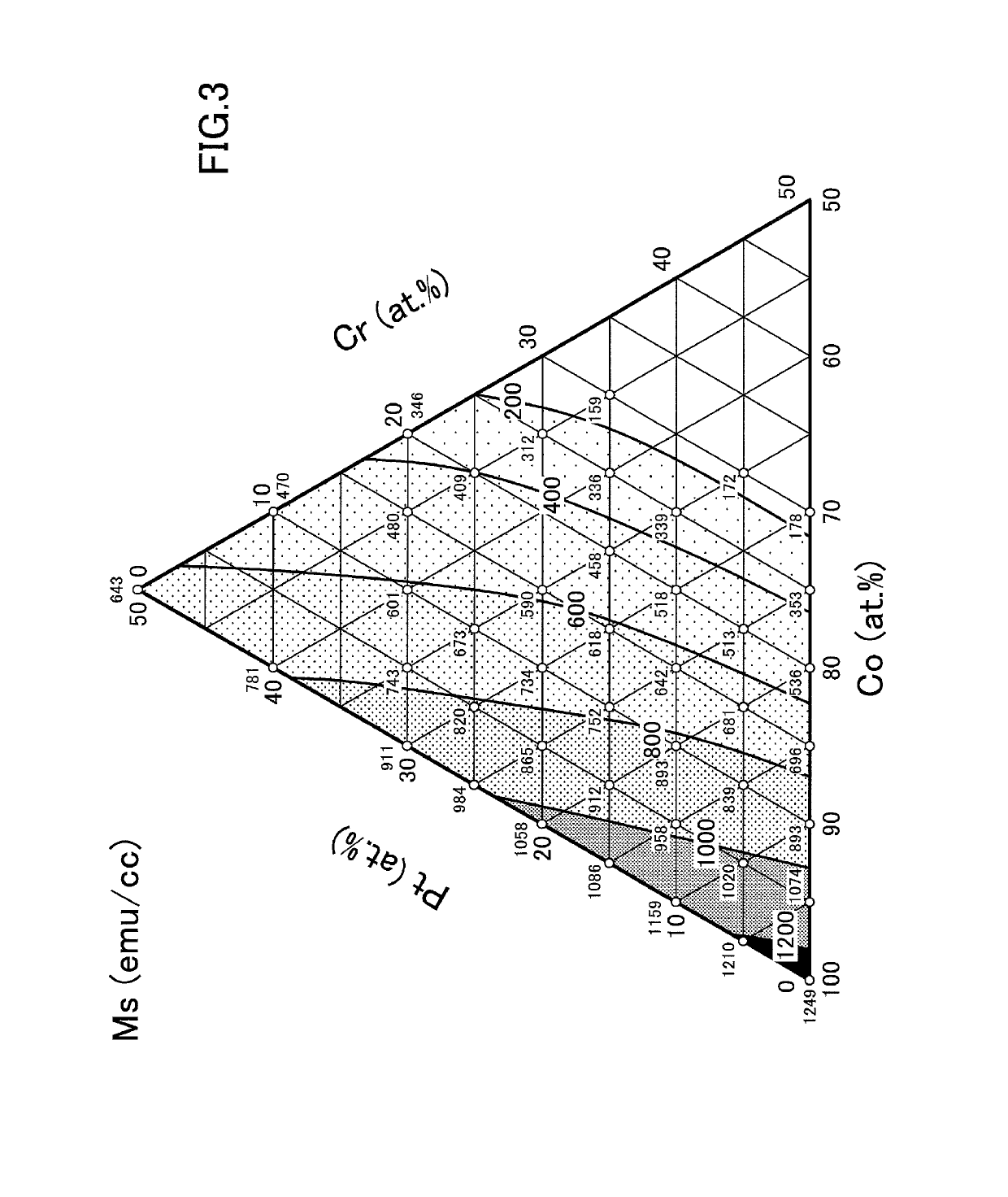
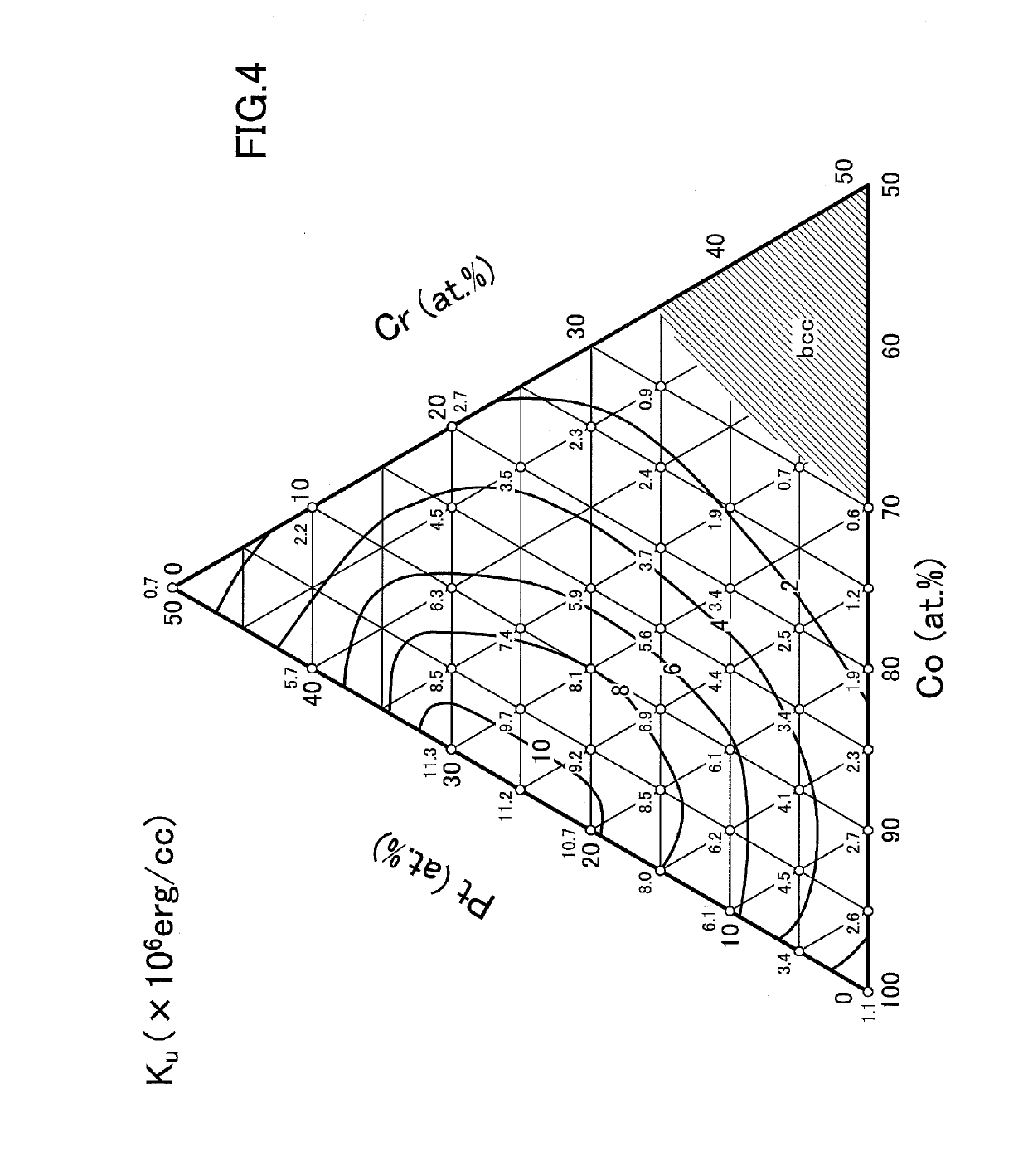
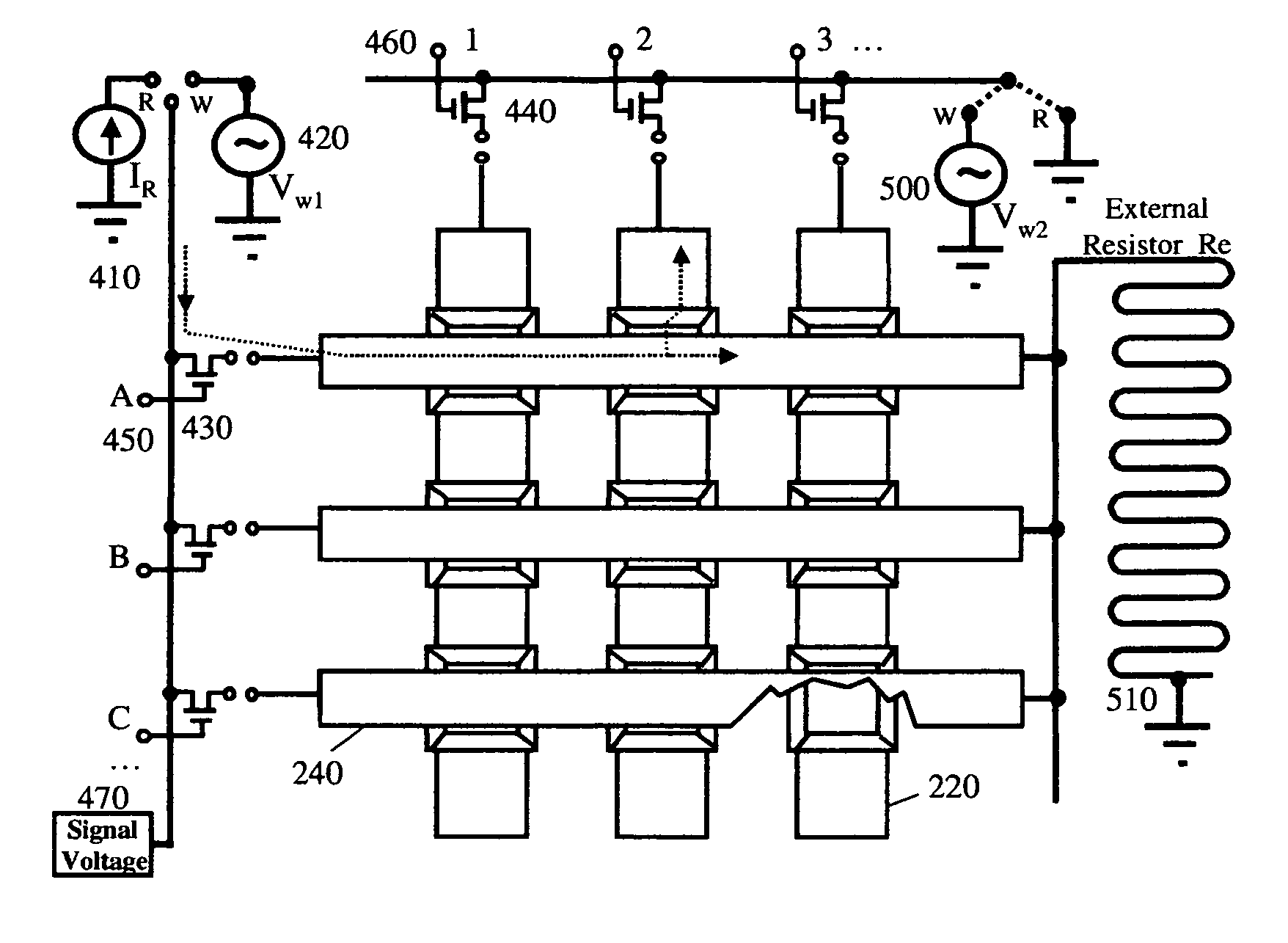
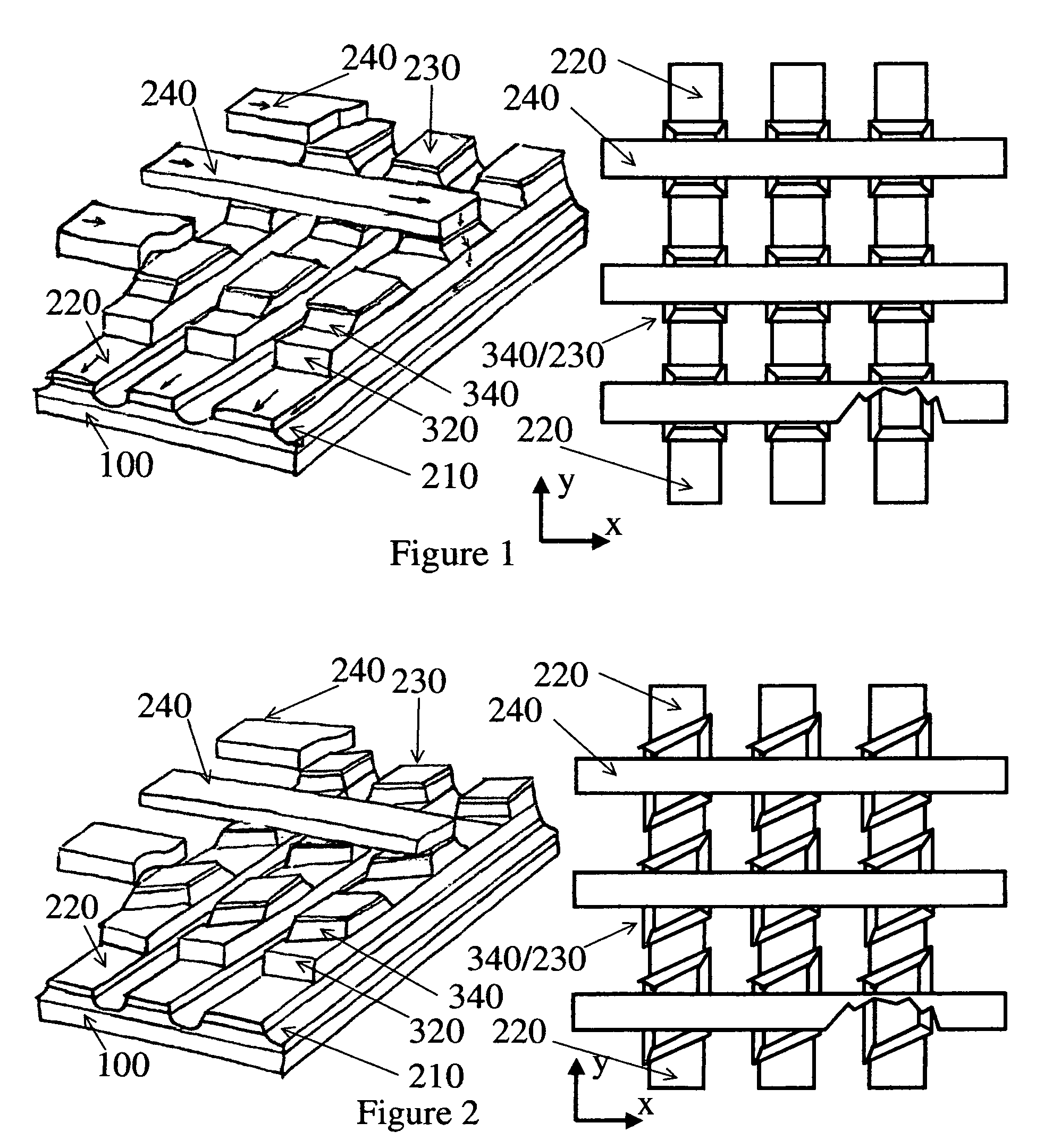
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
37results about How to "Improve writing ability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
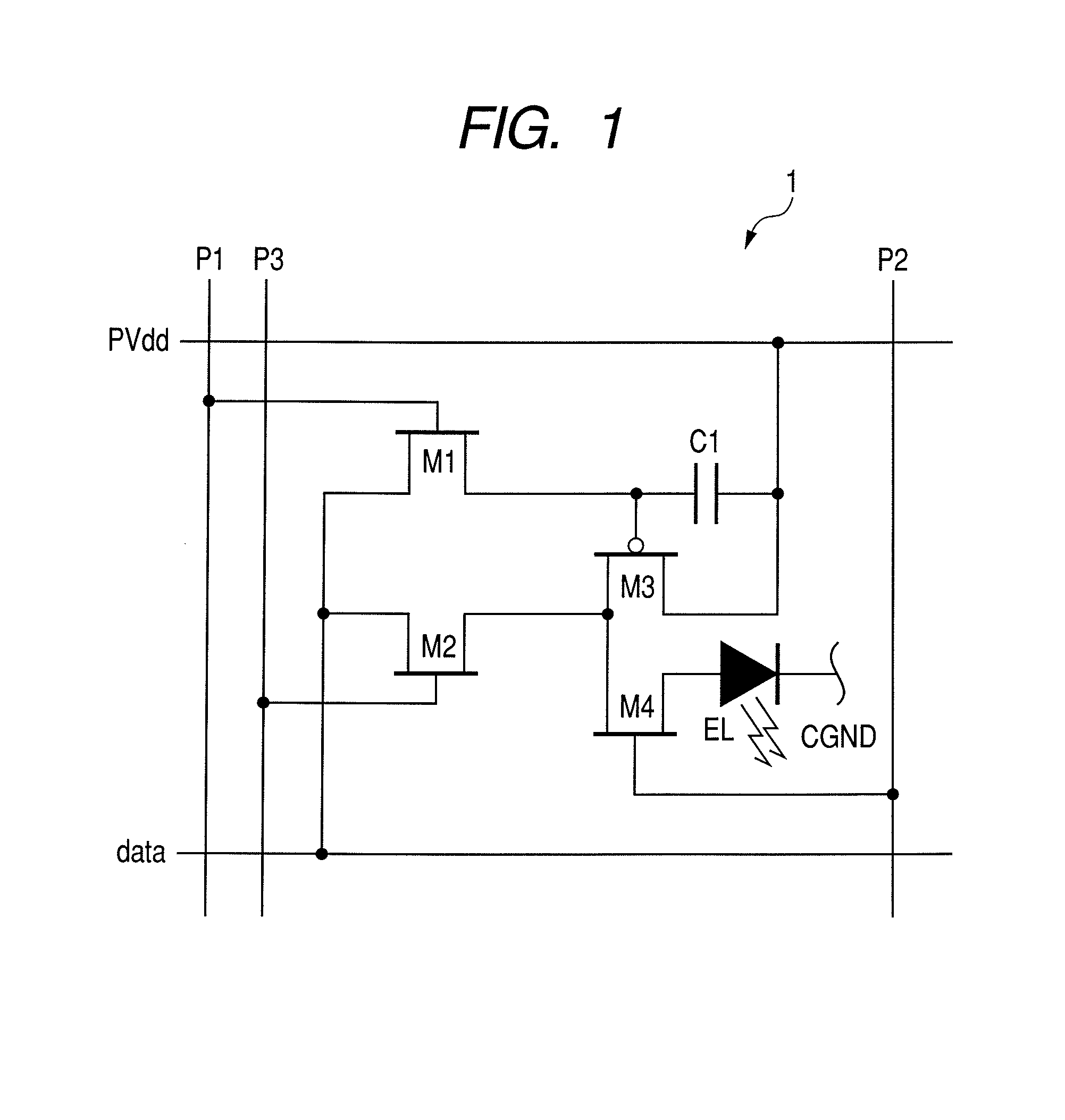
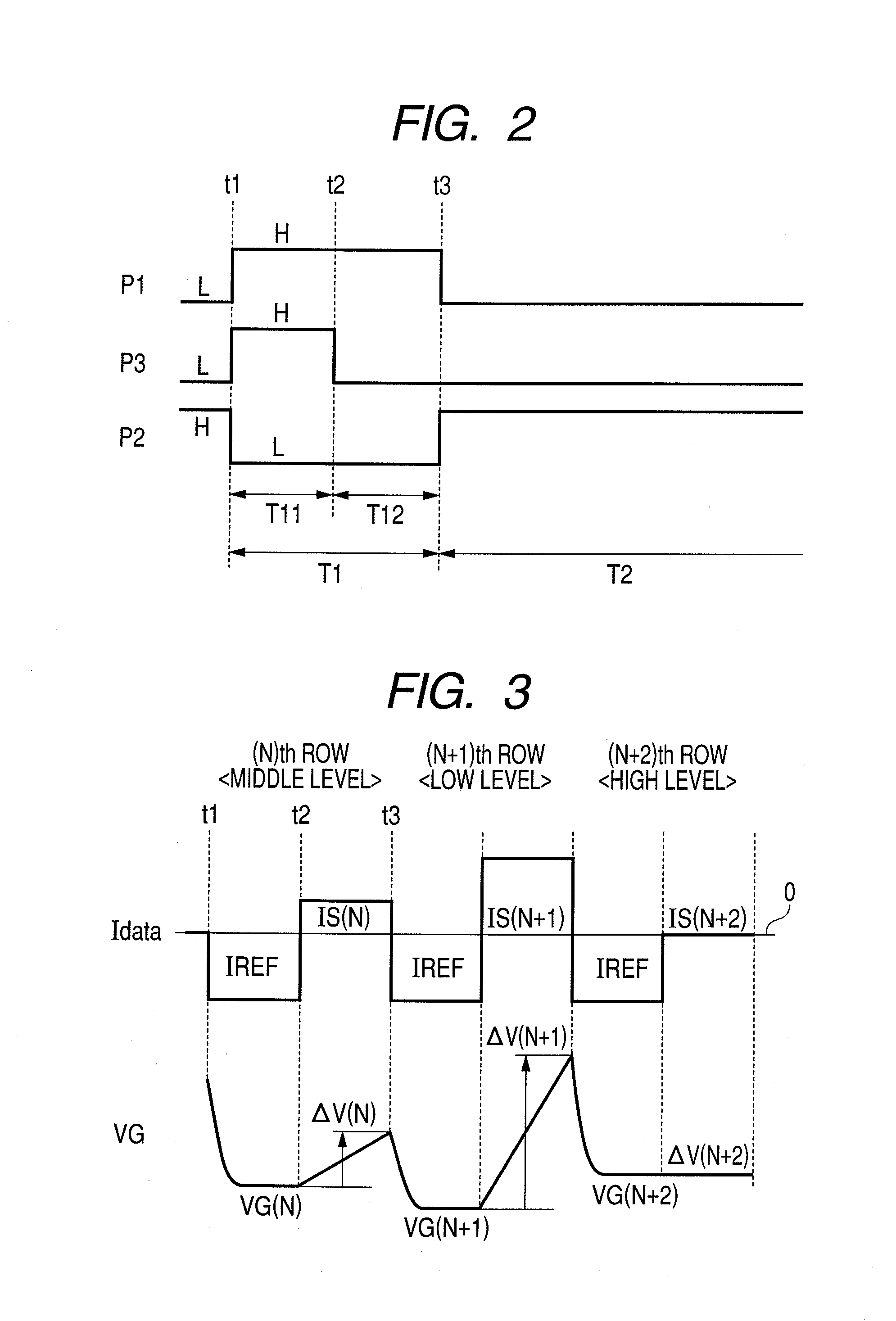
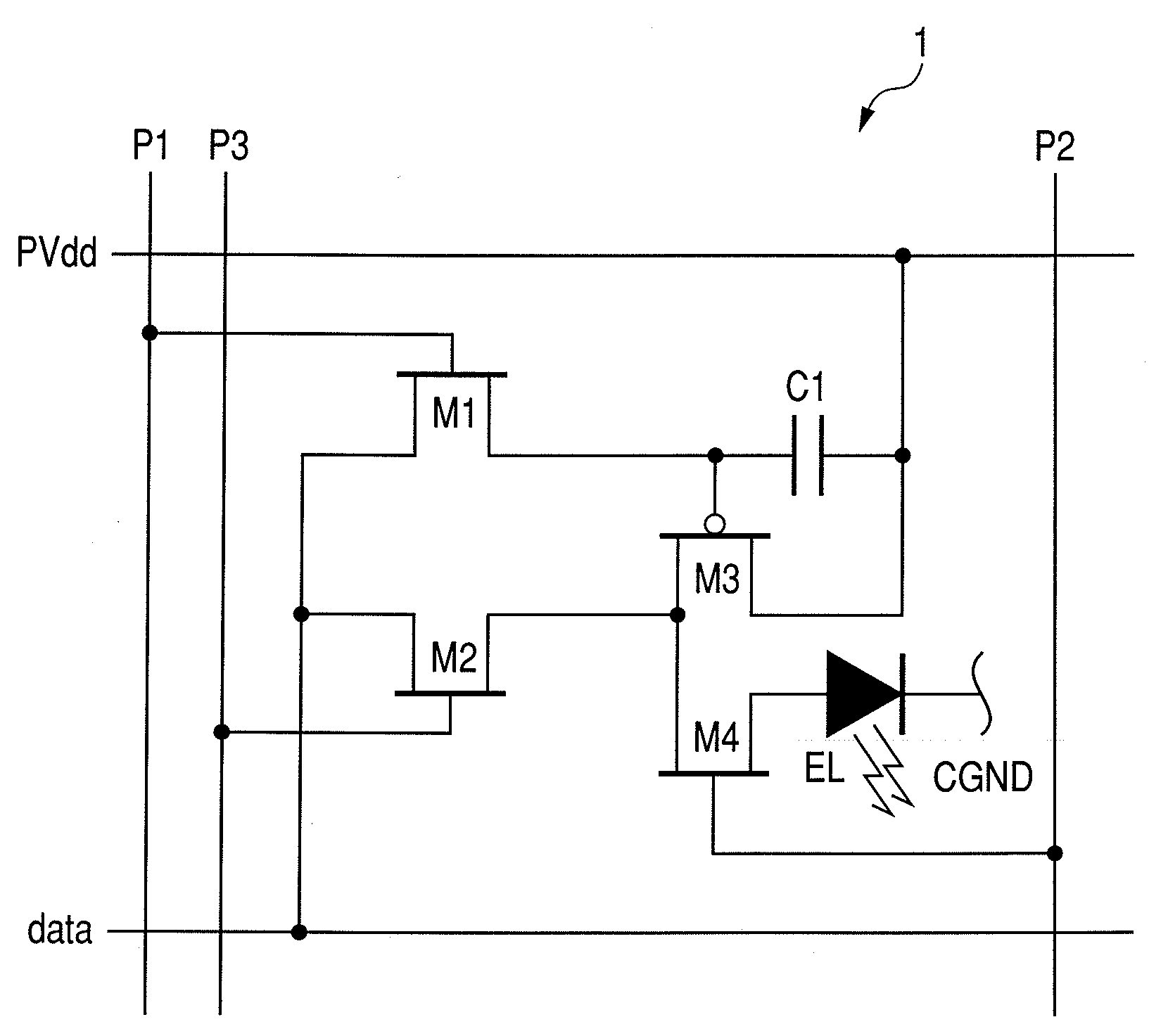
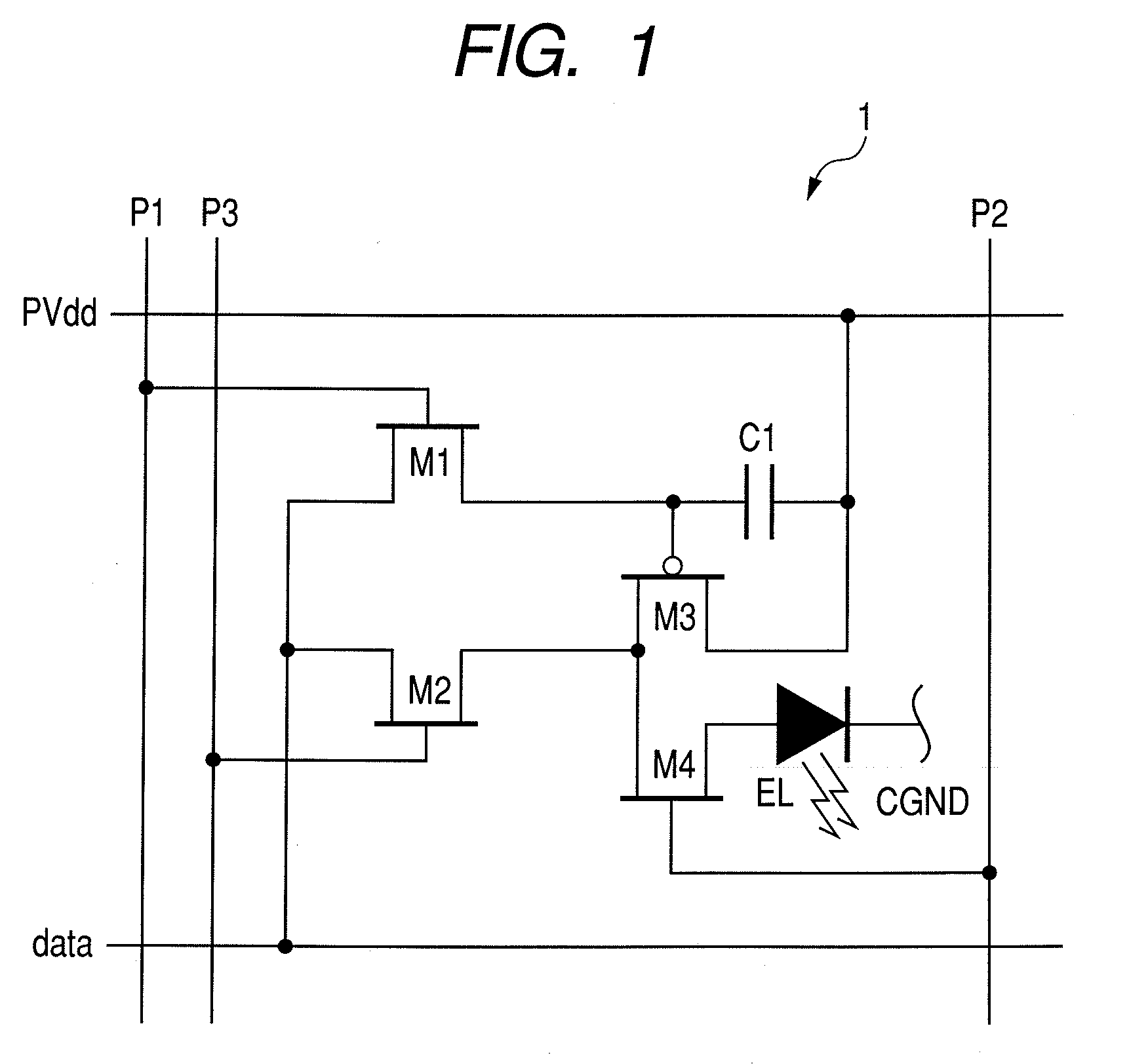
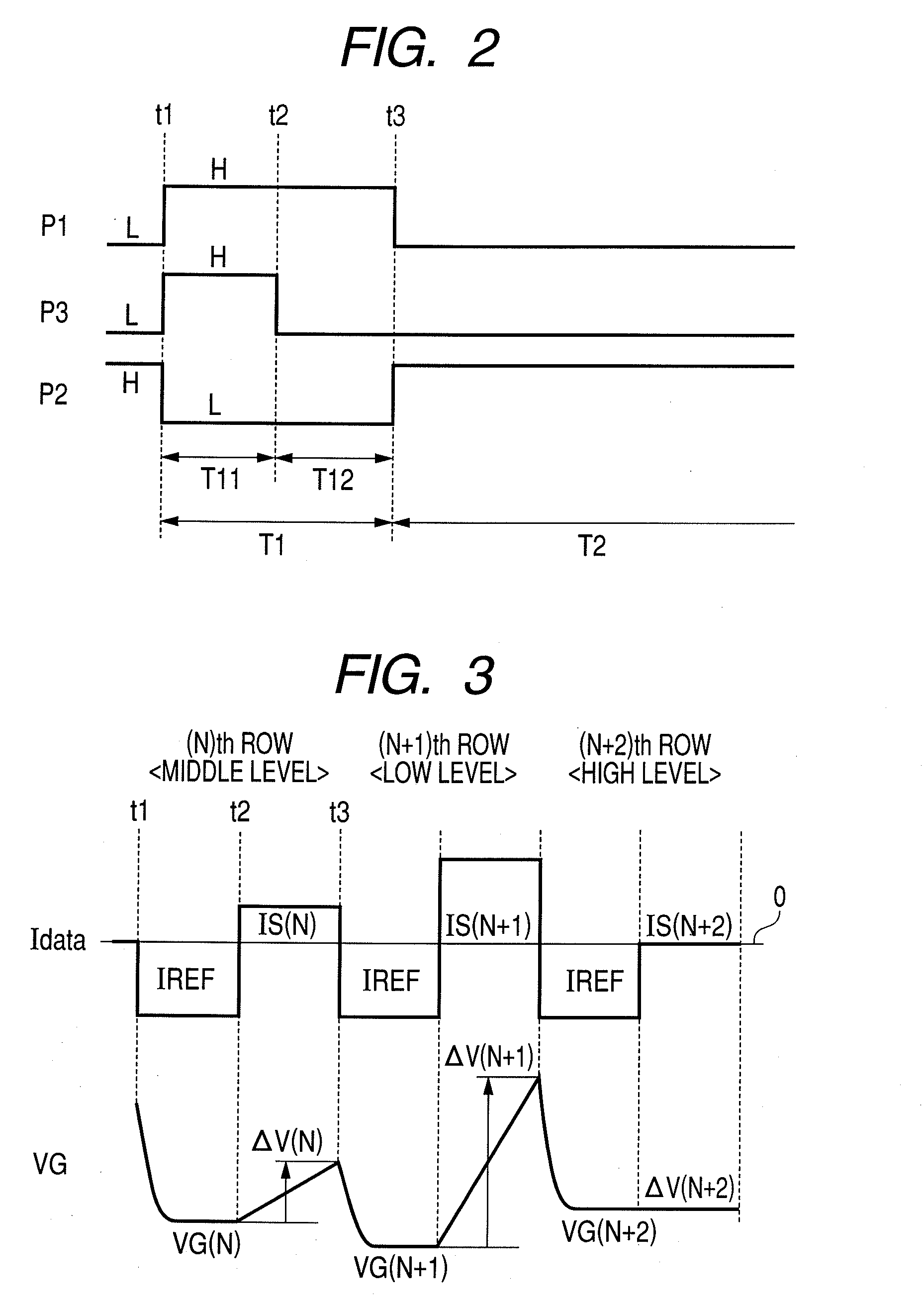
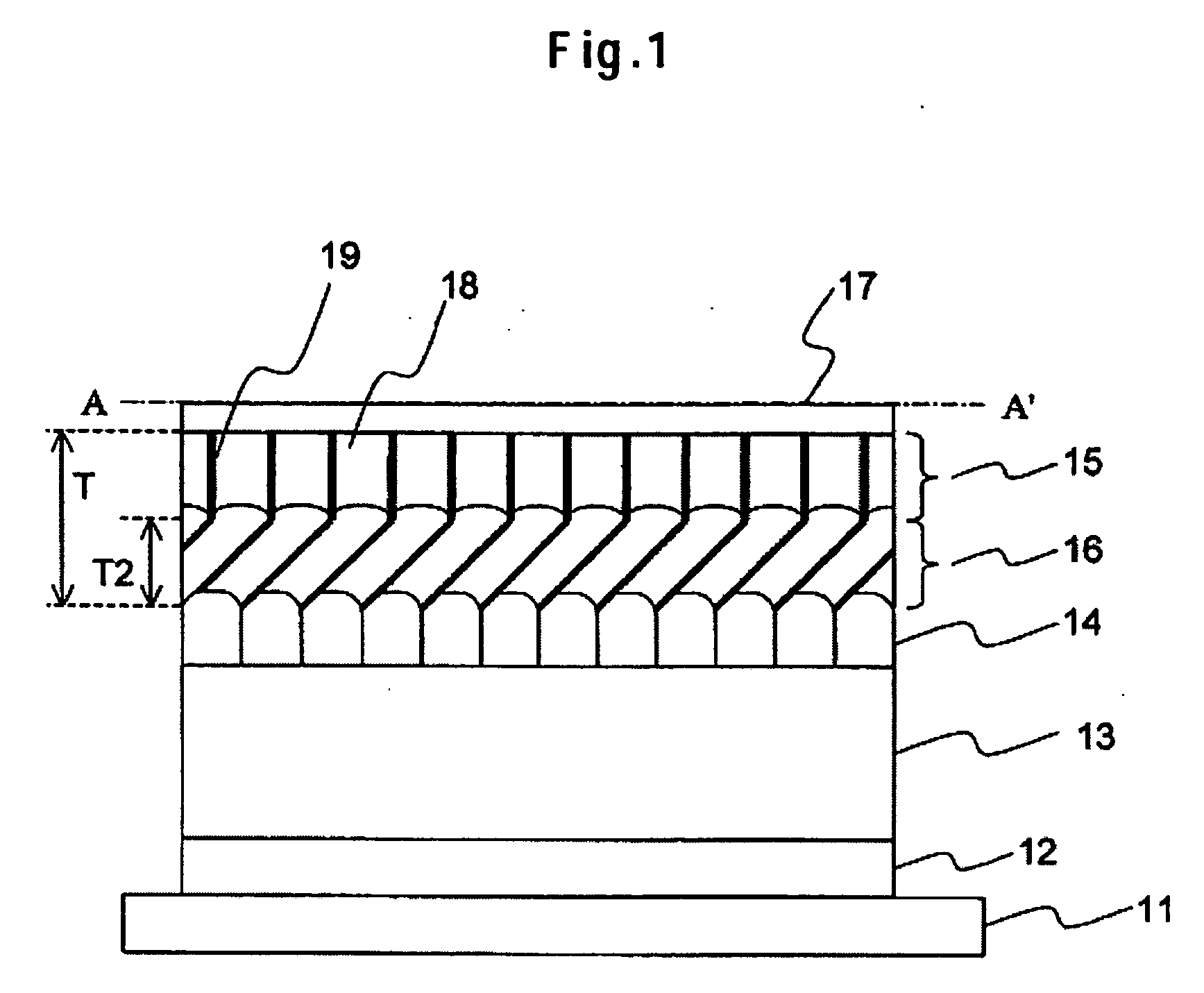
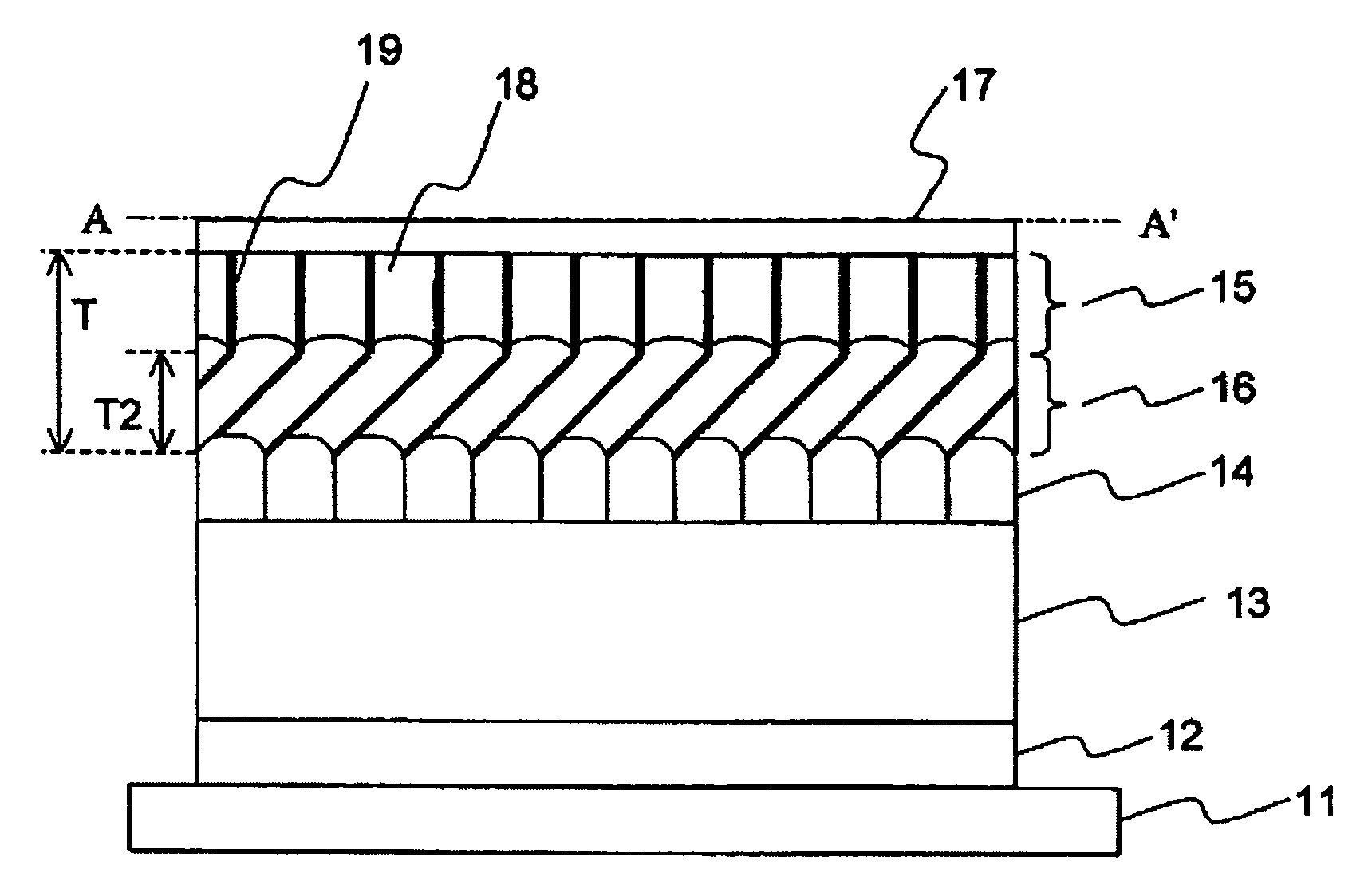
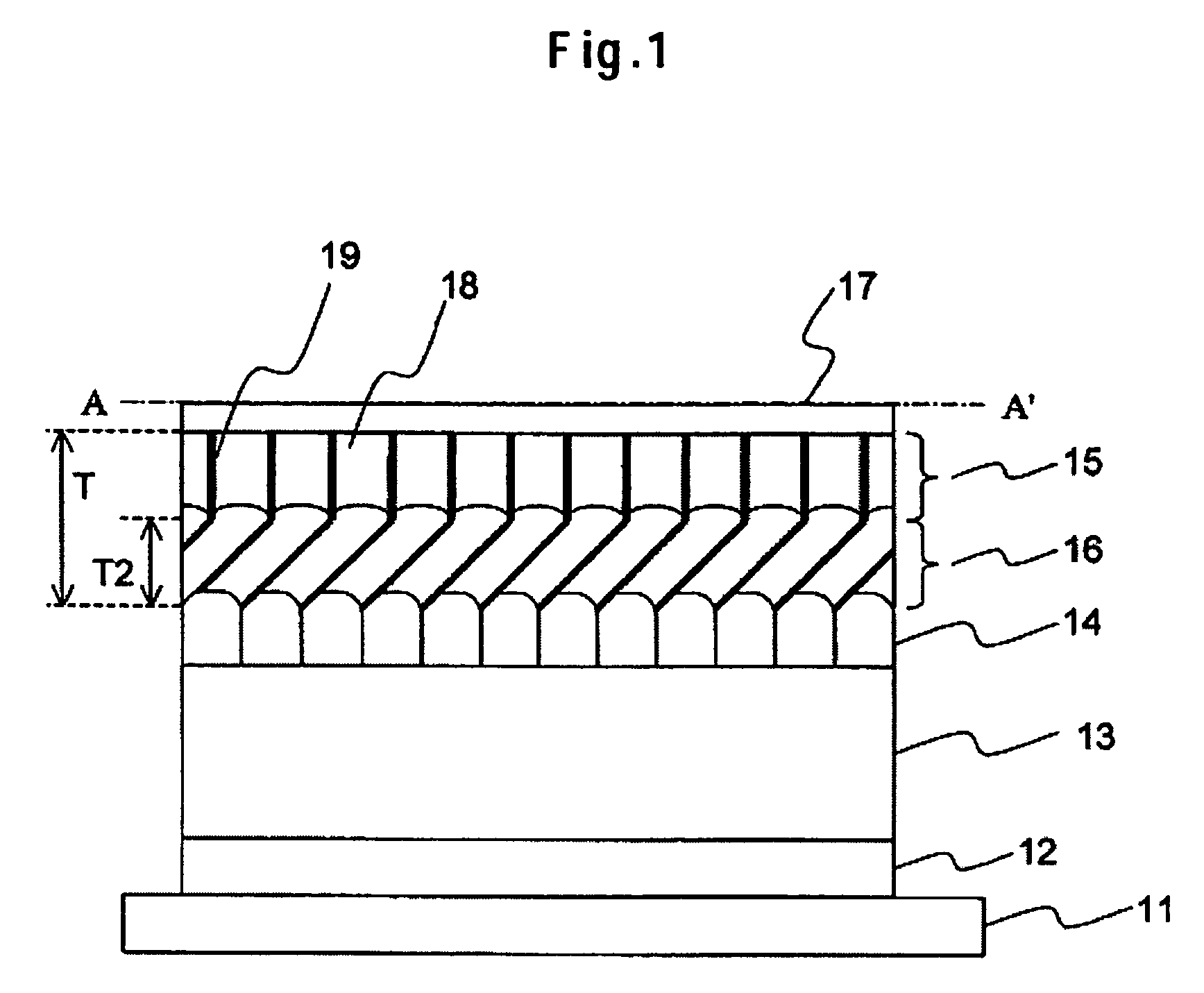
Active matrix type display apparatus and driving method thereof
InactiveUS8354981B2Improve writing abilityImproving current writing abilityCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingCapacitanceDriving current
In an active matrix type display apparatus, during a first selection period, a second main conductive terminal of a drive transistor and a display element are isolated, and at the same time, a control terminal of the drive transistor and the second main conductive terminal and a signal line are connected, and the signal line is supplied with a first current capable of conducting the drive transistor. The first current does not correspond to a signal current corresponding to a current injected to the display element. During a second selection period, a connection of the second main conductive terminal of the drive transistor and the signal line is broken, and the signal line is supplied with a second current. The second current corresponds to a signal current corresponding to the current injected to the display element. During a non-selection period, the second main conductive terminal of the drive transistor and the display element are connected, and the drive current of the drive transistor corresponding to voltage between both terminals of a capacitive element is supplied to the display element.
Owner:CANON KK
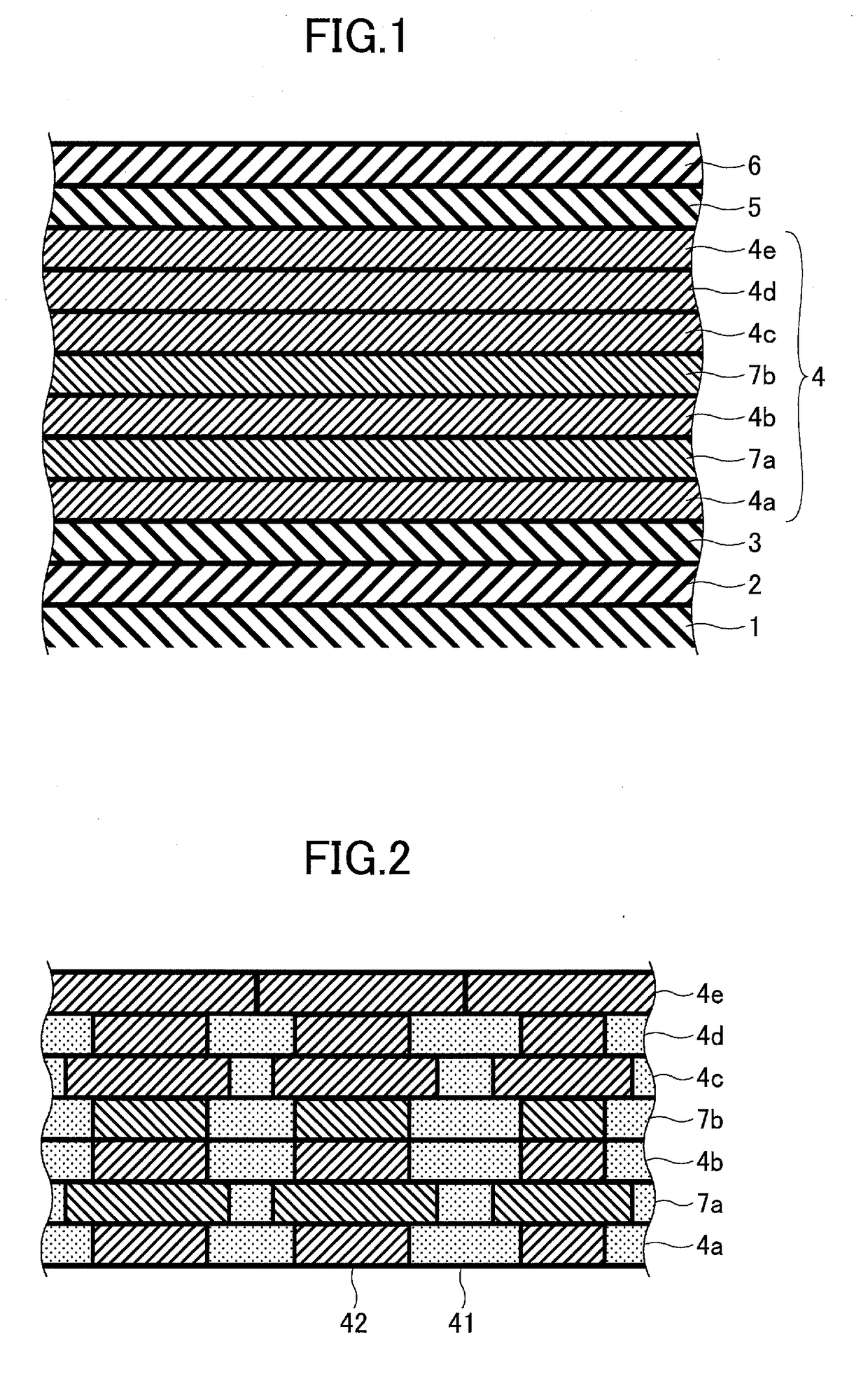
Perpendicular magnetic recording media and magnetic storage apparatus using the same
ActiveUS20050142388A1Excellent crystallographic texture and magnetic isolationExcellent write-abilityBase layers for recording layersRecord information storagePhysicsOxide
Embodiments of the invention provide a perpendicular magnetic recording medium that not only attains the magnetic isolation of crystal grains in a magnetic recording layer from one another in a region of the medium in which the thickness of an intermediate layer is equal to or smaller than about 20 nm but also exhibits excellent crystallographic texture and that exhibits small medium noise, excellent thermal stability, and high write-ability. In one embodiment, a perpendicular magnetic recording medium has at least a soft-magnetic underlayer, a first intermediate layer, a second intermediate layer, a third intermediate layer, and a magnetic recording layer successively formed on a substrate. The magnetic recording layer is composed of ferromagnetic crystal grains and oxides or nitrides, the third intermediate layer is composed of Ru or an Ru alloy, the second intermediate layer is composed of a metal or an alloy having the face-centered cubic lattice structure, and the first intermediate layer is composed of a metal or an alloy having the hexagonal close-packed structure.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Perpendicular magnetic recording media and magnetic storage apparatus using the same
ActiveUS7368185B2Hindering magnetic decouplingReduce manufacturing costBase layers for recording layersRecord information storageMagnetic storageAlloy
Embodiments of the invention provide a perpendicular magnetic recording medium that not only attains the magnetic isolation of crystal grains in a magnetic recording layer from one another in a region of the medium in which the thickness of an intermediate layer is equal to or smaller than about 20 nm but also exhibits excellent crystallographic texture and that exhibits small medium noise, excellent thermal stability, and high write-ability. In one embodiment, a perpendicular magnetic recording medium has at least a soft-magnetic underlayer, a first intermediate layer, a second intermediate layer, a third intermediate layer, and a magnetic recording layer successively formed on a substrate. The magnetic recording layer is composed of ferromagnetic crystal grains and oxides or nitrides, the third intermediate layer is composed of Ru or an Ru alloy, the second intermediate layer is composed of a metal or an alloy having the face-centered cubic lattice structure, and the first intermediate layer is composed of a metal or an alloy having the hexagonal close-packed structure.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Active matrix type display apparatus and driving method thereof
InactiveUS20090015571A1Improve writing abilityImproving current writing abilityCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingDriving currentCapacitance
During a first selection period, a second main conductive terminal of a drive transistor and a display element are isolated, and at the same time, a control terminal of the drive transistor and the second main conductive terminal and a signal line are connected, and the signal line is supplied with a constant current capable of conducting the drive transistor, and during a second selection period, a connection of the second main conductive terminal of the drive transistor and the signal line is broken, and the signal line is supplied with a signal current corresponding to a current injected to the display element, and during a non-selection period, the second main conductive terminal of the drive transistor and the display element are connected, and the drive current of the drive transistor corresponding to voltage between both terminals of a capacitive element is supplied to the display element.
Owner:CANON KK
Magnetic recording medium and magnetic recording apparatus
InactiveUS20050227120A1Improve writing abilityImprove abilitiesBase layers for recording layersRecord information storageMagnetic anisotropyThermal stability
Embodiments of the invention provide a perpendicular magnetic recording medium capable of reconciling a high recording density with high thermal stability, and having a high write-ability while maintaining high magnetic anisotropy energy. In one embodiment, a perpendicular magnetic recording medium has a soft-magnetic underlayer, and magnetic recording layers, and the magnetic recording layers comprises a first recording layer containing magnetic grains oriented in a direction normal to a medium plane, and a second recording layer containing magnetic grains tilted in a cross-track direction. There can be provided a perpendicular magnetic recording medium resistant to thermal fluctuation, small in medium noise, and excellent in write-ability.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
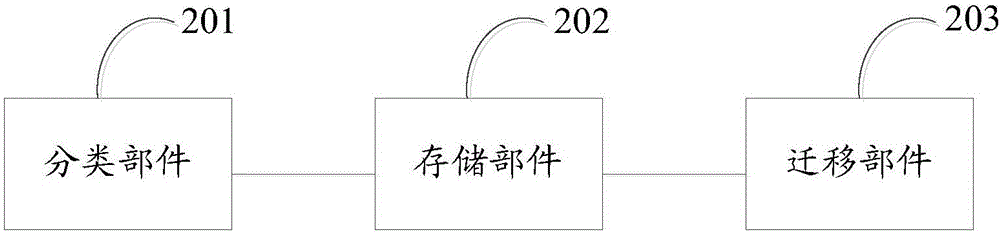
Hierarchical data optimization method and apparatus for hybrid disk
InactiveCN106484330AThe data distribution is validImprove writing abilityInput/output to record carriersDatabaseData optimization
The invention discloses a hierarchical data optimization method and apparatus for a hybrid disk. The method comprises the steps of classifying data according to data indexes; storing the classified data in corresponding storage devices of a hierarchical storage management system according to types; and when the data indexes are changed, performing upgrading migration or degrading migration on the data. According to the hierarchical data optimization method and apparatus for the hybrid disk, provided by the invention, the data distribution can be enabled to be more effective based on the hybrid disk; and the writing capability is ensured by utilizing the disk, and hotspot data is read by utilizing an SSD (Solid State Disk) to improve the reading capability, so that the read and write capabilities of the storage system are improved.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU YUNHAI INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
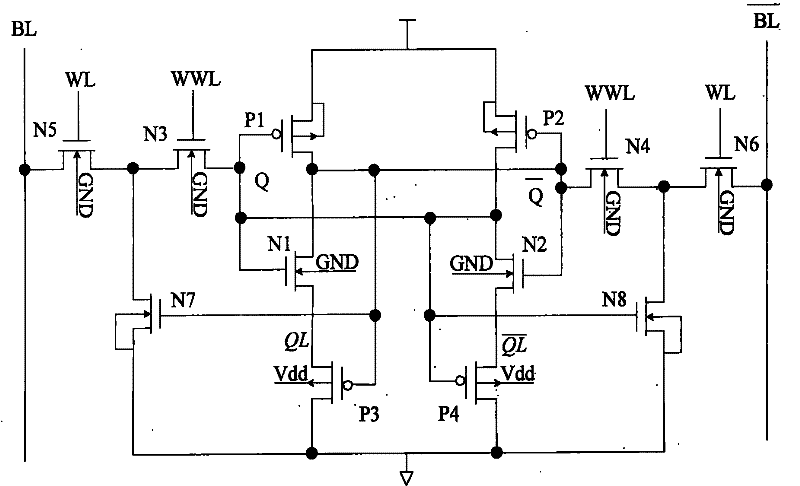
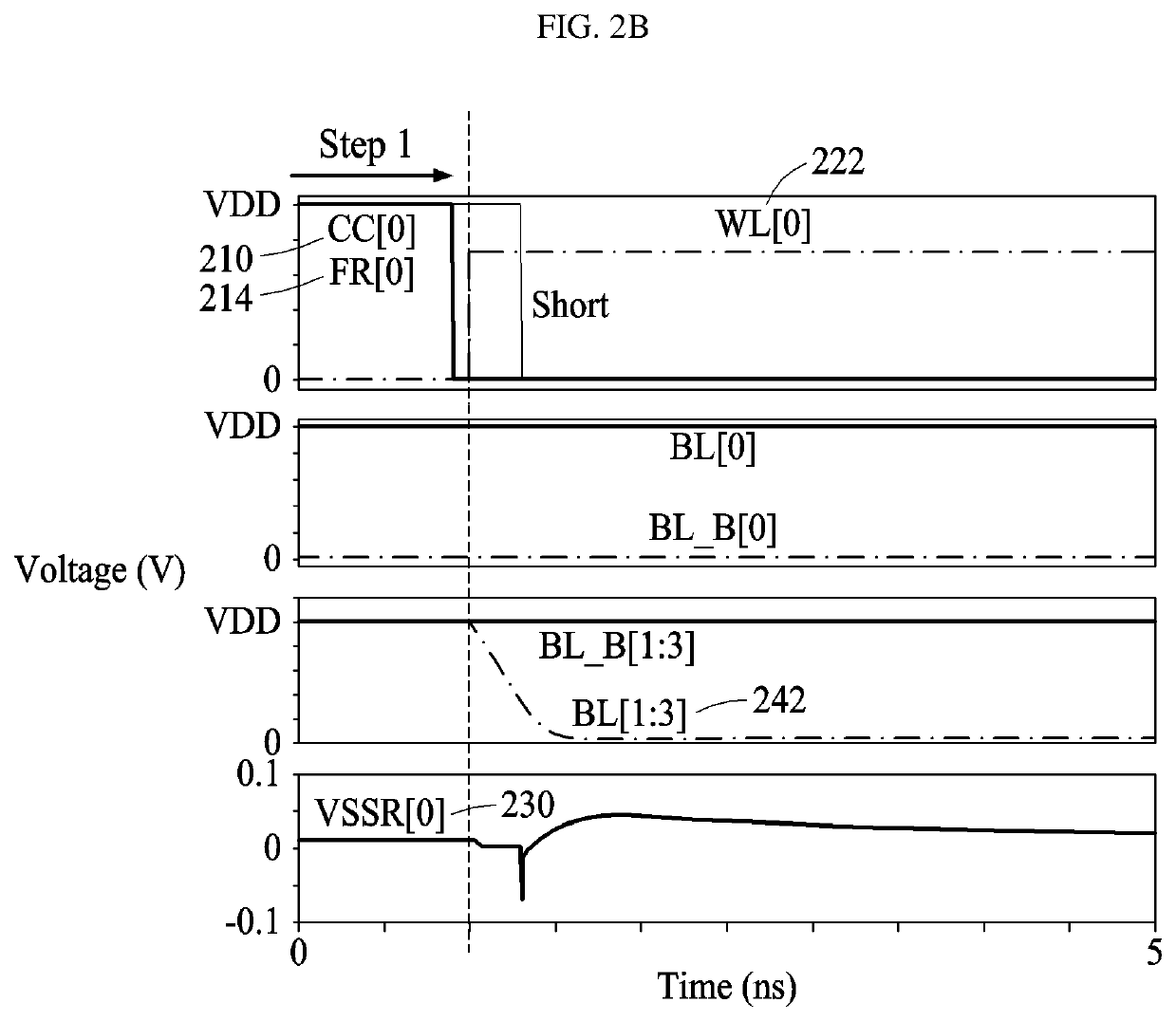
Storage unit circuit with adaptive leakage current cutoff mechanism
InactiveCN102176323AReduce dynamic power consumptionReduce leakage powerDigital storageBit lineSub threshold
The invention provides a storage unit circuit with an adaptive leakage current cutoff mechanism, which is a dual-port read-writing sub-threshold storage unit circuit. The circuit comprises a first inverter and a second inverter which are connected in a cross coupling way; the two inverters are connected between complementary bit lines through an equalizer pipe; and the grid end of the equalizer pipe is connected with an enhanced word line. The invention overcomes the defects of the prior art and provides the sub-threshold storage unit circuit with low power consumption and high robustness; and the sub-threshold storage unit circuit can reduce leakage power consumptions in dynamic operation and static operation while the leakage power at the same time on the premise of not increasing dynamic power consumption or reducing performance, and can balance each index of a storage unit so as to optimize system performance.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
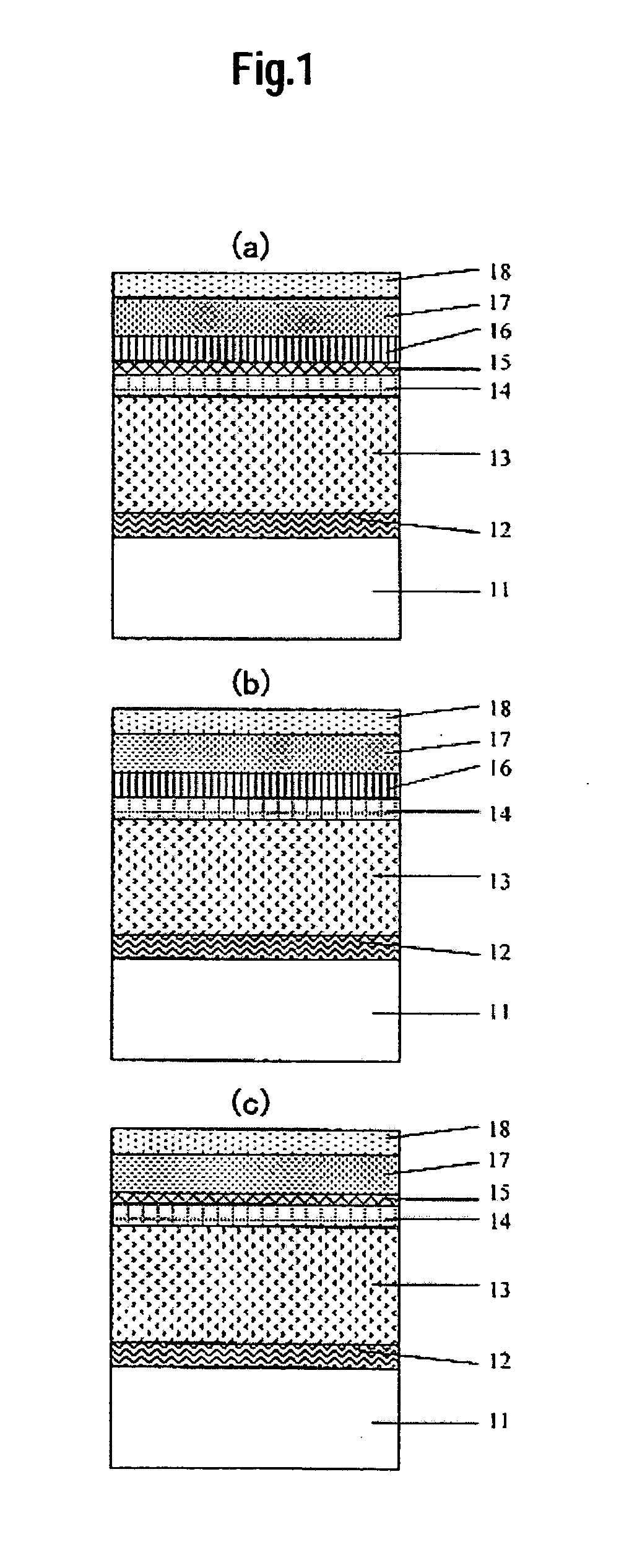
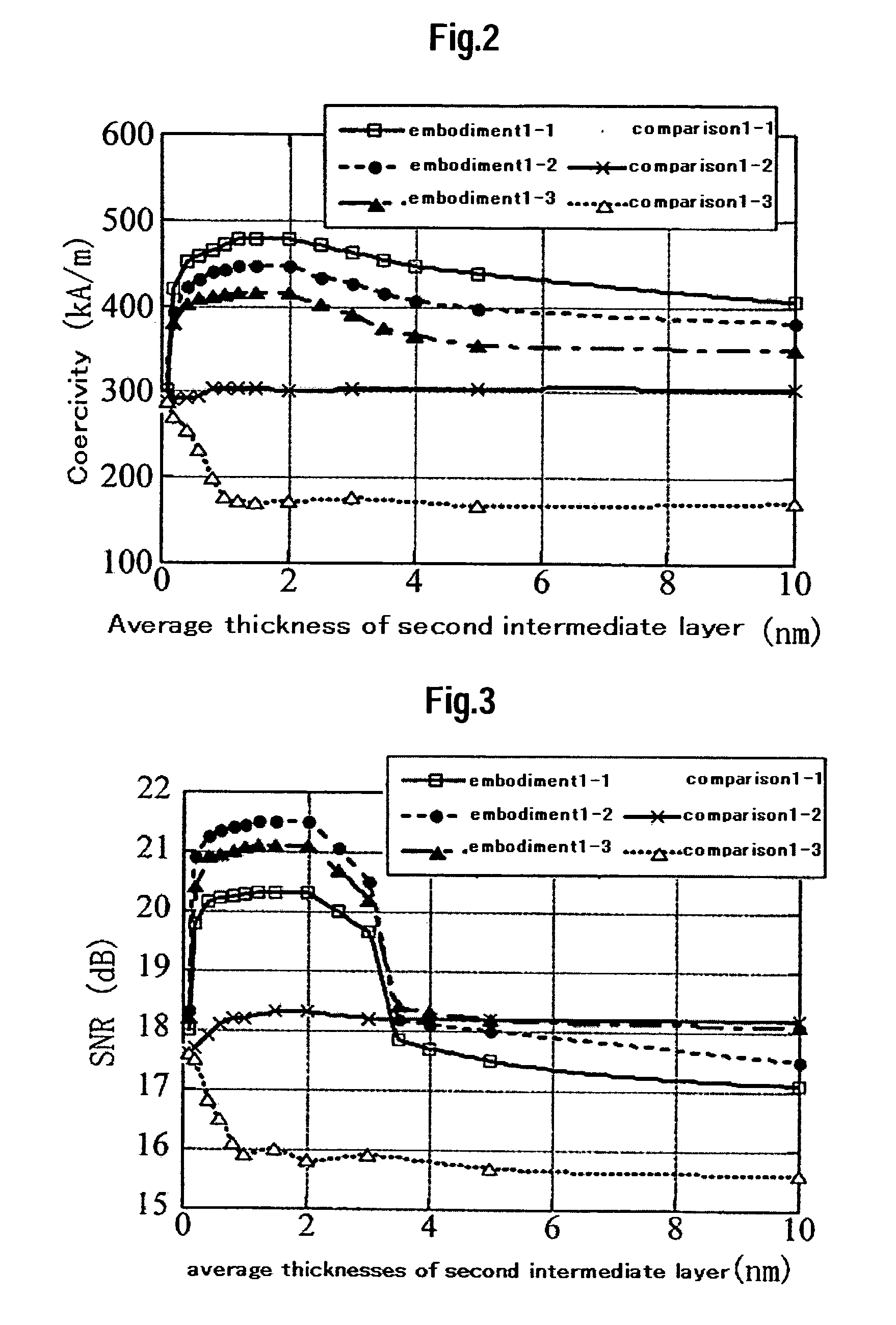
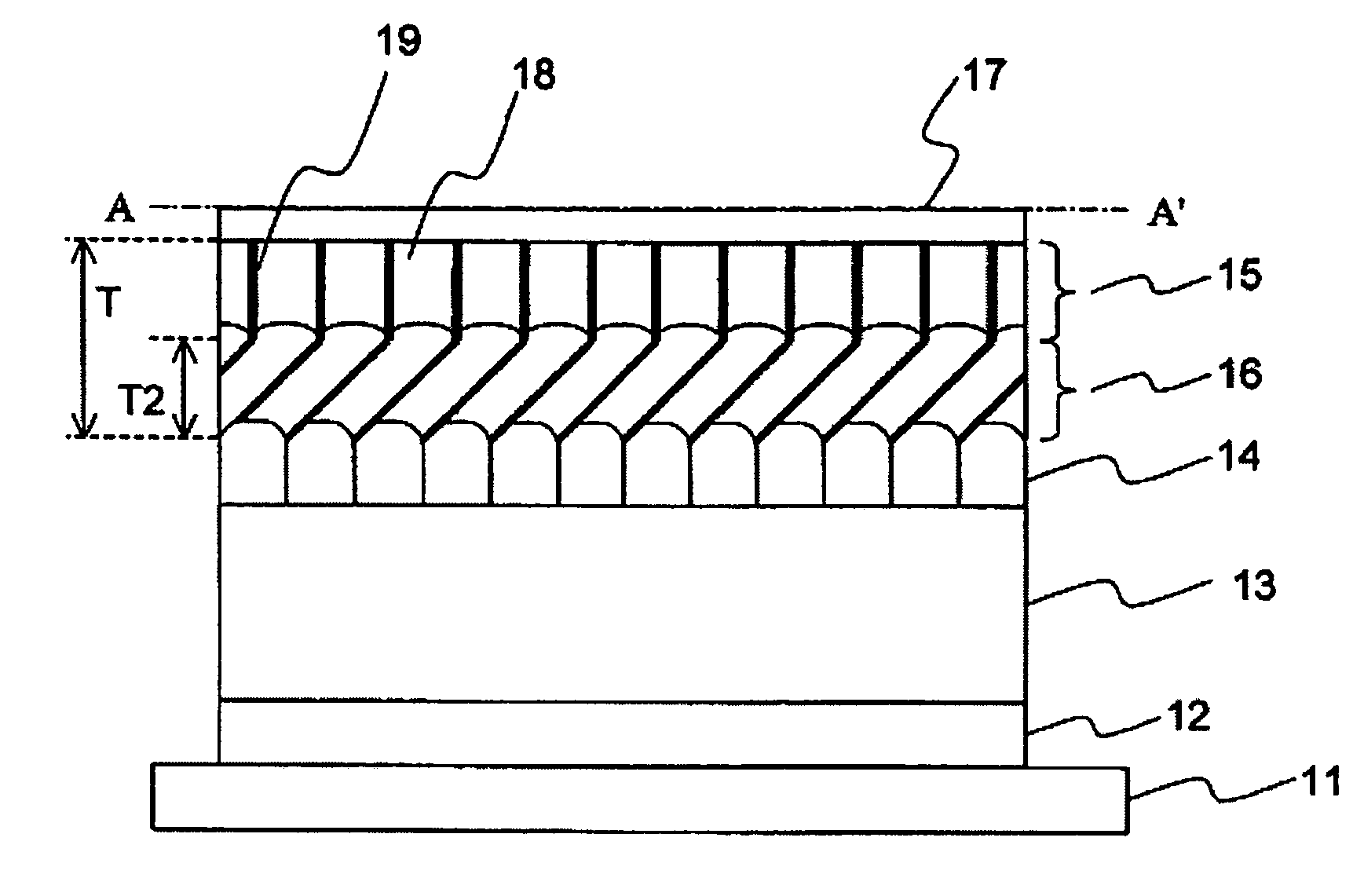
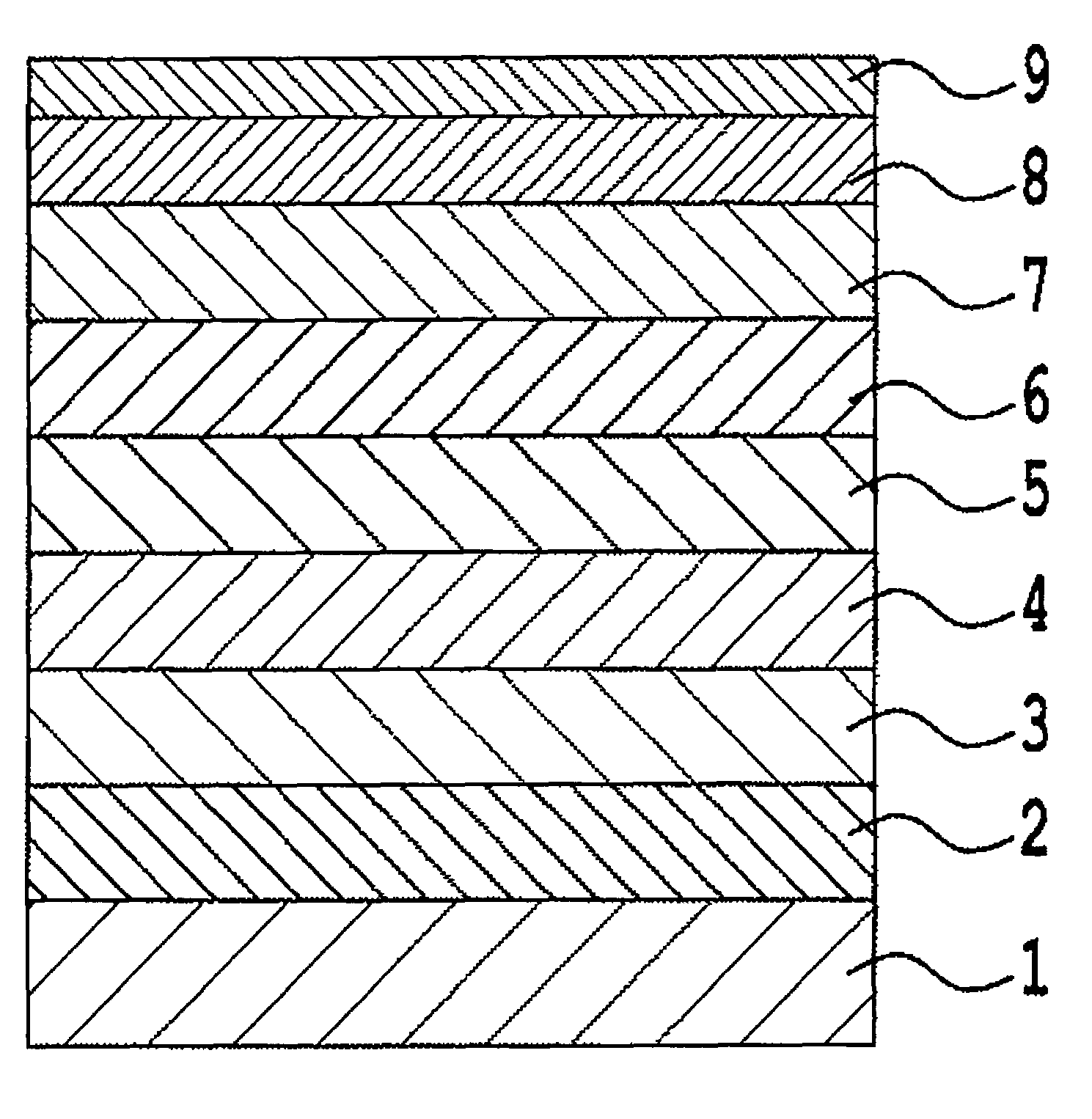
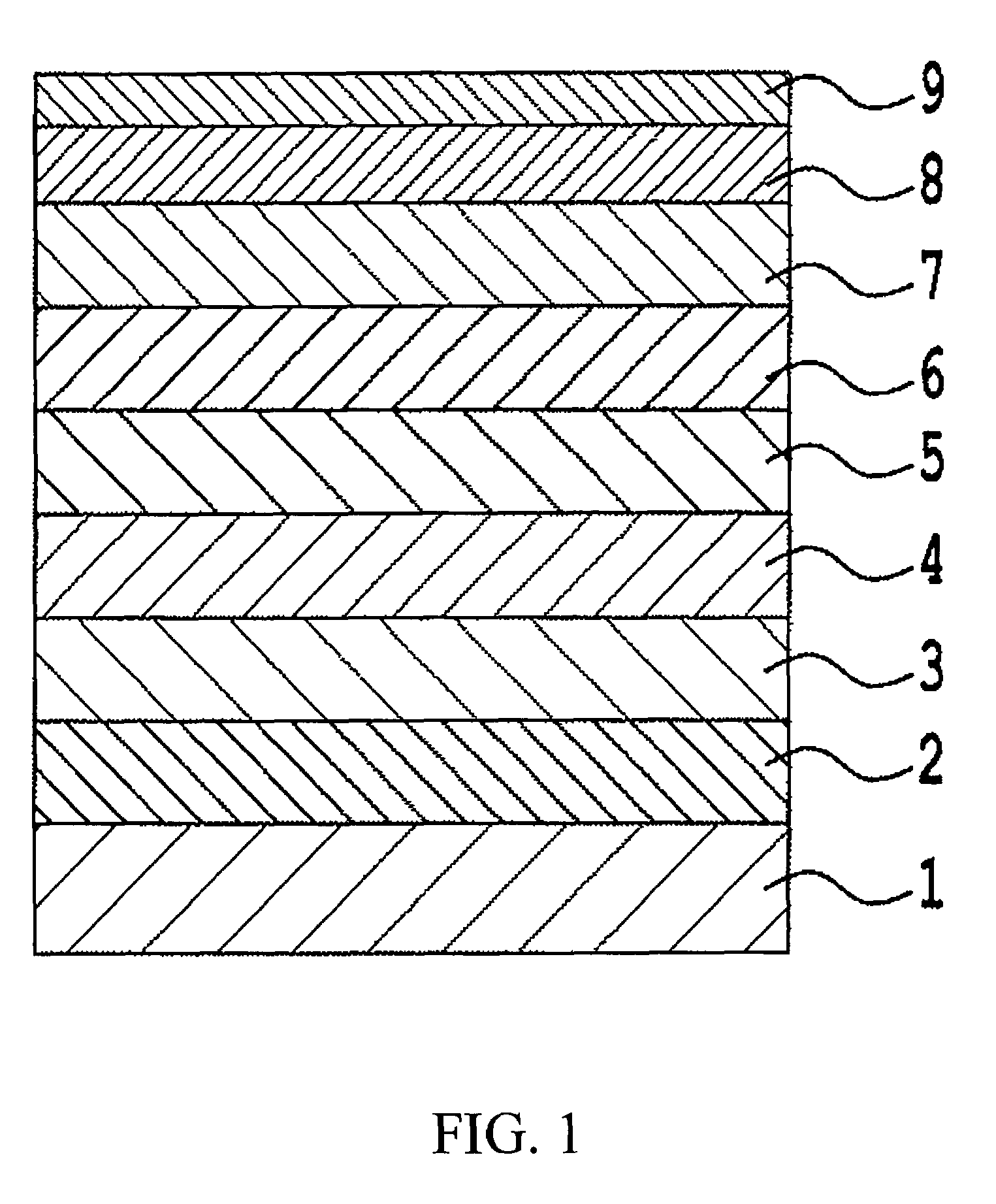
Perpendicular magnetic recording medium
ActiveUS20080096055A1Medium noise is reducedReduce distanceRecord information storageMagnetic recordingInter layerOptoelectronics
A perpendicular magnetic recording medium includes a nonmagnetic substrate; a first underlayer provided on the nonmagnetic substrate; a first nonmagnetic intermediate layer provided on the first underlayer; a second underlayer provided on the first nonmagnetic intermediate layer; a second nonmagnetic intermediate layer provided on the second underlayer; and a magnetic recording layer provided on the second nonmagnetic intermediate layer, wherein the first underlayer comprises a soft magnetic material which has a face-centered cubic structure and which includes at least Ni and Fe, and wherein the second underlayer comprises a soft magnetic material which has a face-centered cubic structure and which includes at least Co. The orientation dispersion is reduced and crystal grain diameters are smaller in the magnetic recording layer, and the film thickness of nonmagnetic intermediate layers can be decreased so that performance improvements such as reduced noise, increased S / N ratio, and improved write-ability are achieved.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
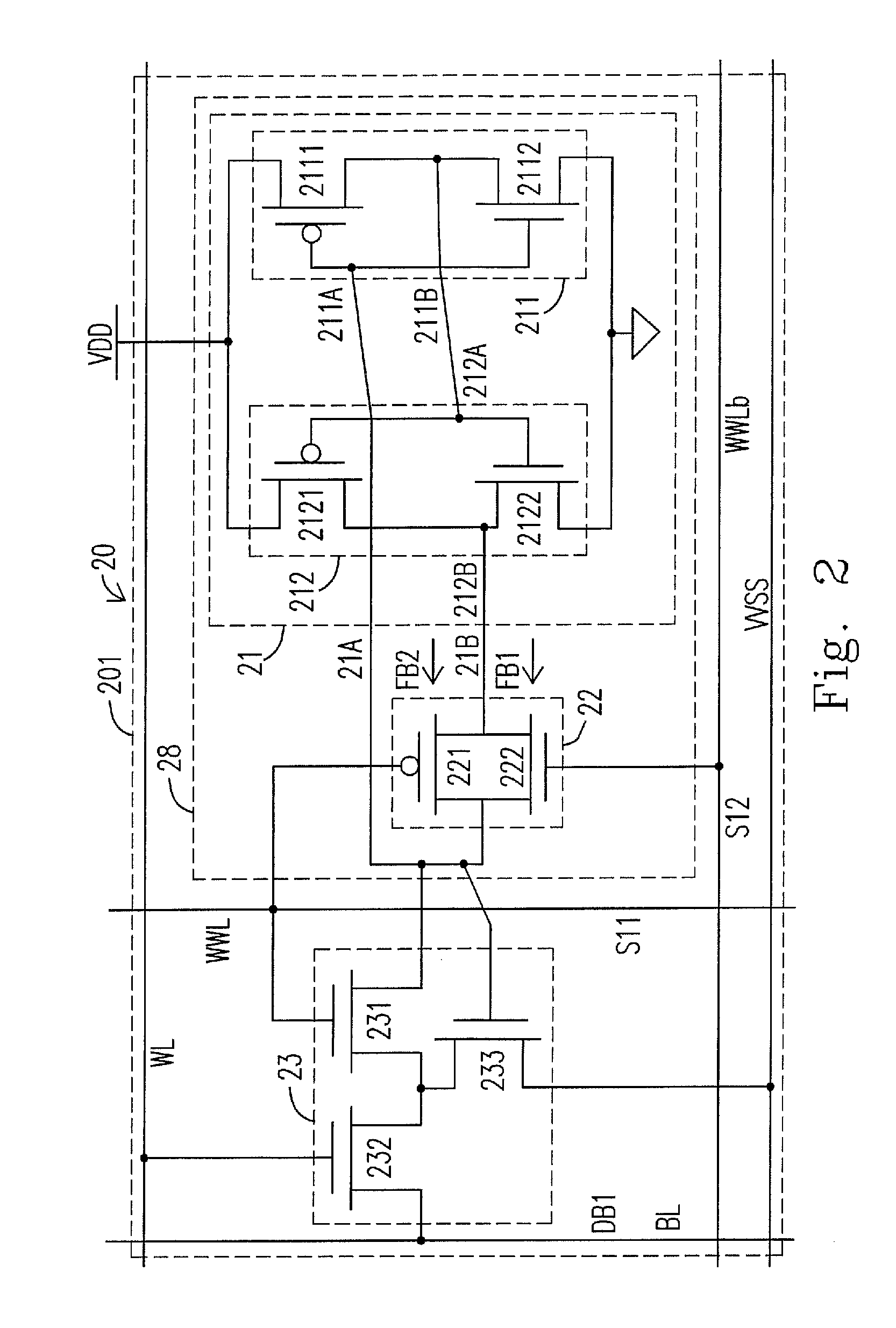
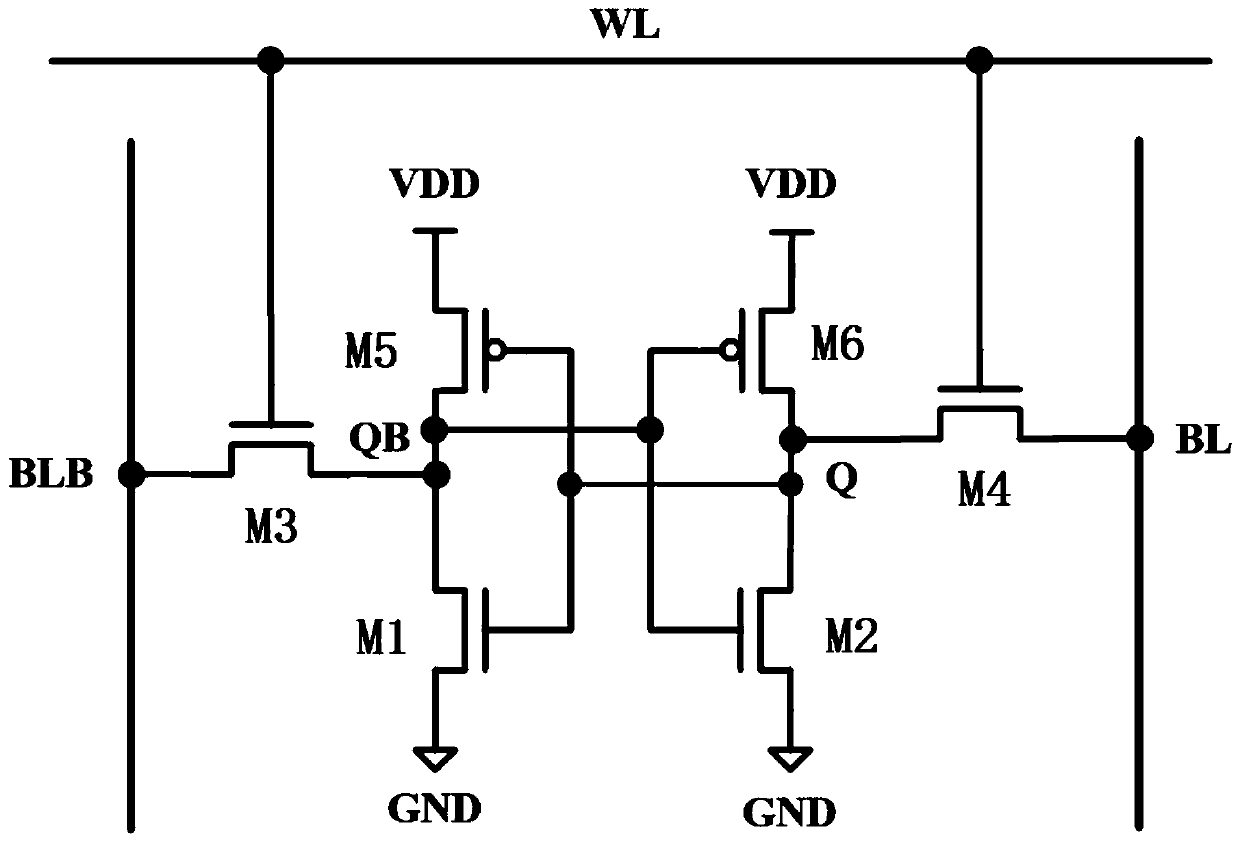
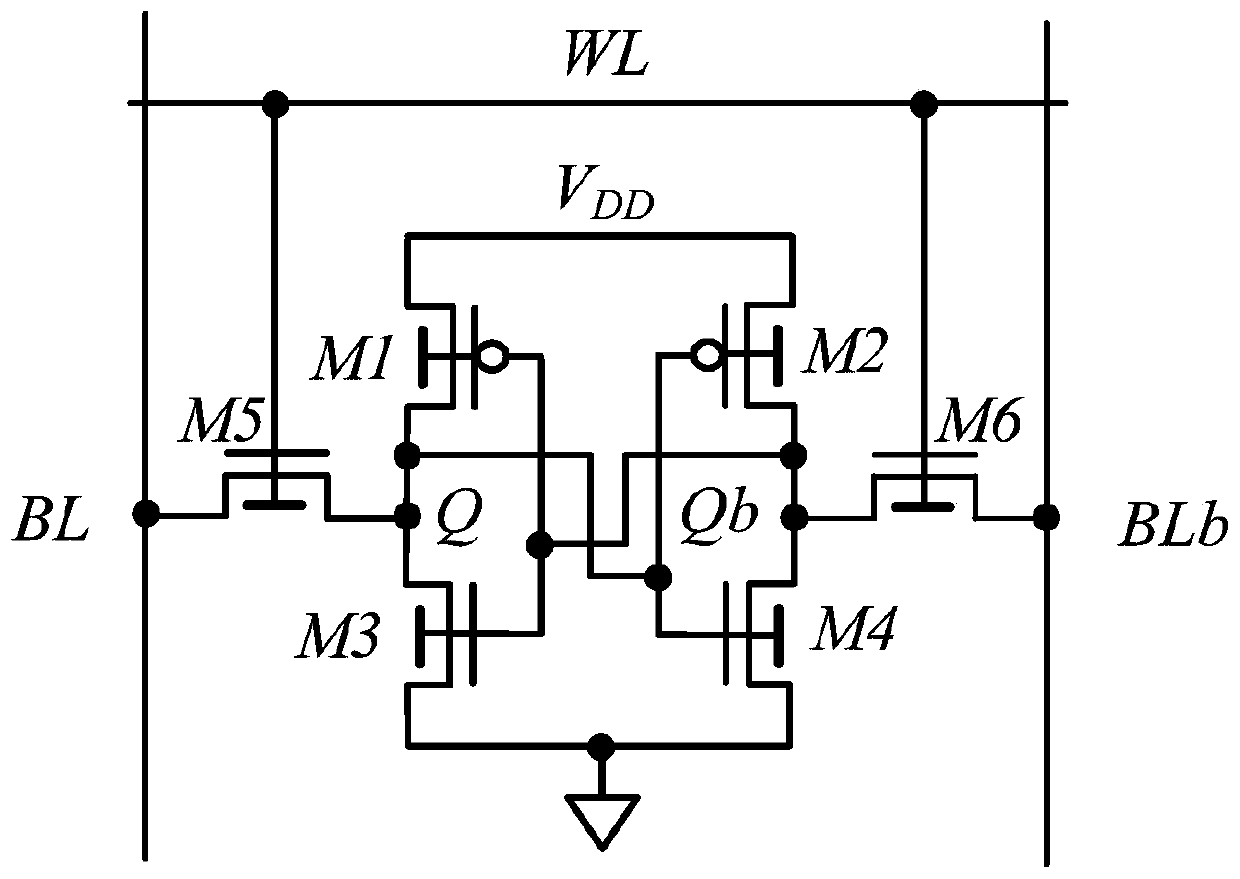
Static random access memory cell and method of operating the same
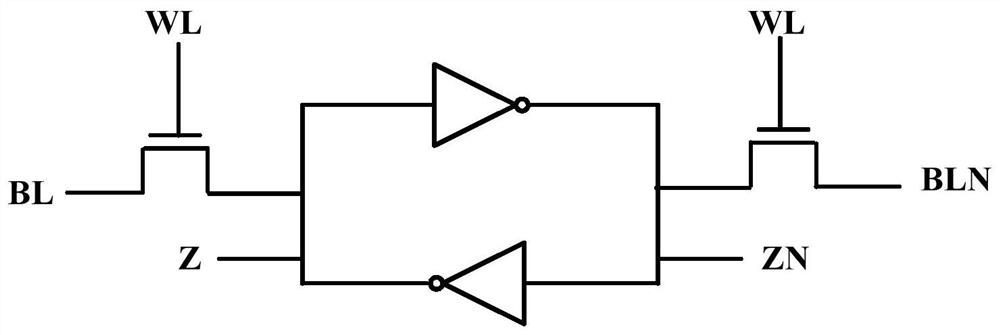
A static random access memory cell includes a latch unit. The latch unit includes a bi-inverting circuit and a switching circuit. The bi-inverting circuit has a first terminal and a second terminal. The switching circuit is electrically connected between the first terminal and the second terminal, wherein when the switching circuit is turned on, the switching circuit forms a feedback between the first terminal and the second terminal for latching the latch unit; and when the switching circuit is turned off, the feedback is removed to cause the SRAM cell to write a data bit to the latch unit.
Owner:NATIONAL CHIAO TUNG UNIVERSITY
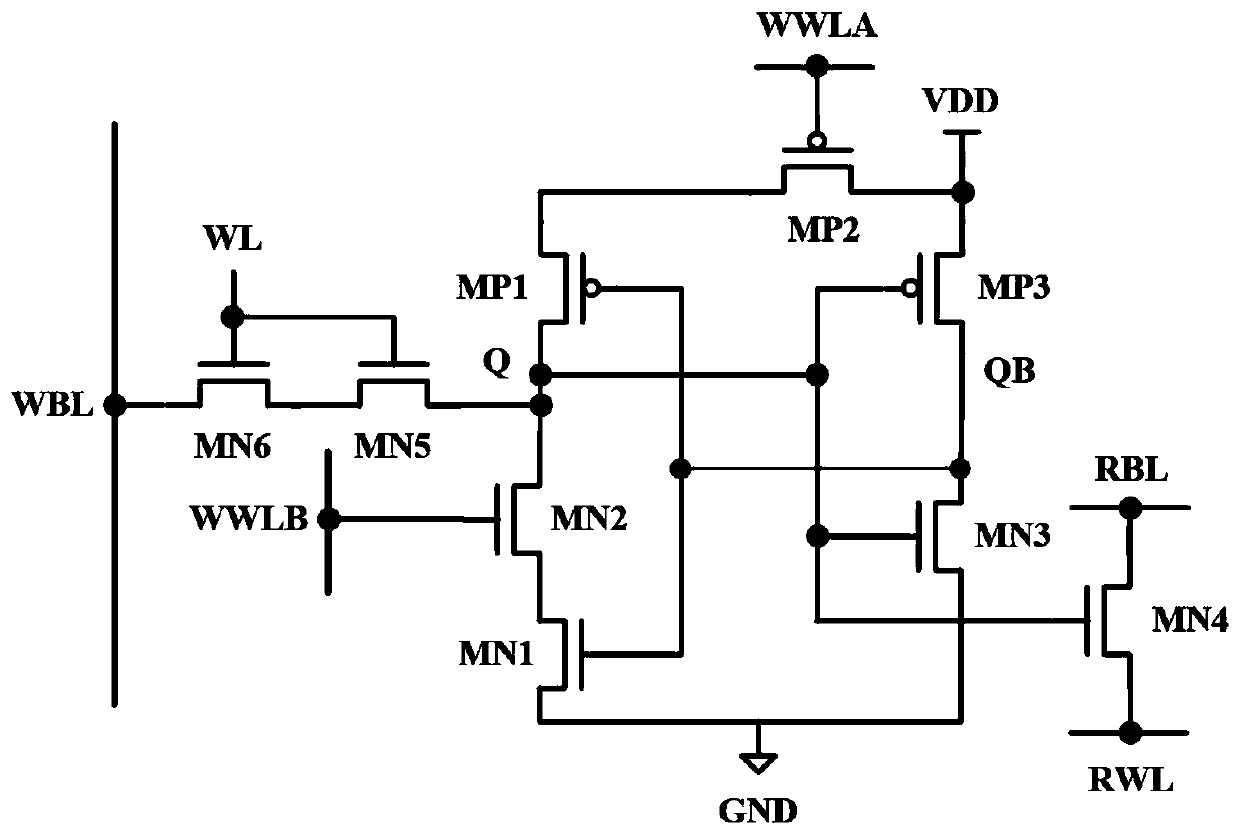
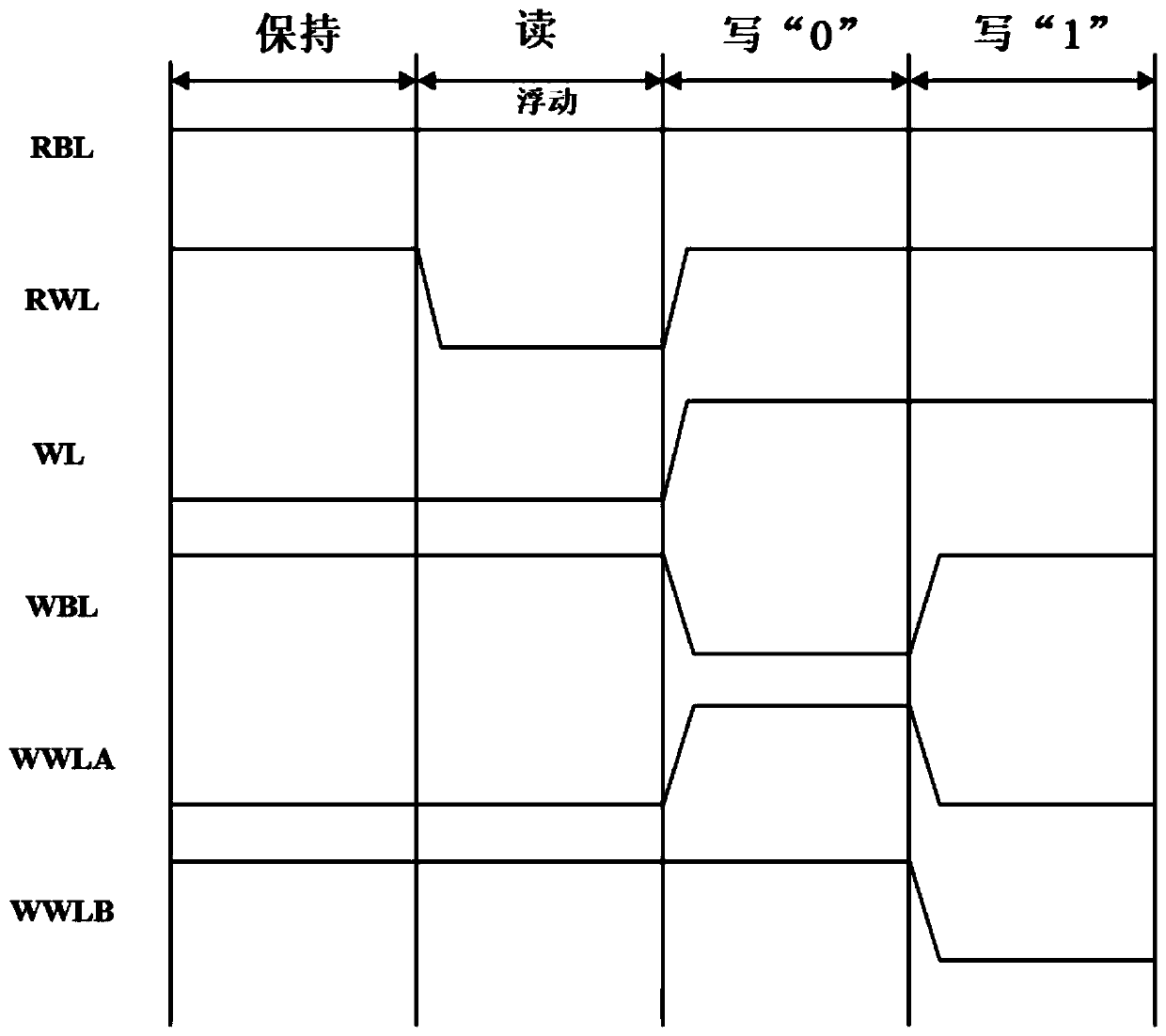
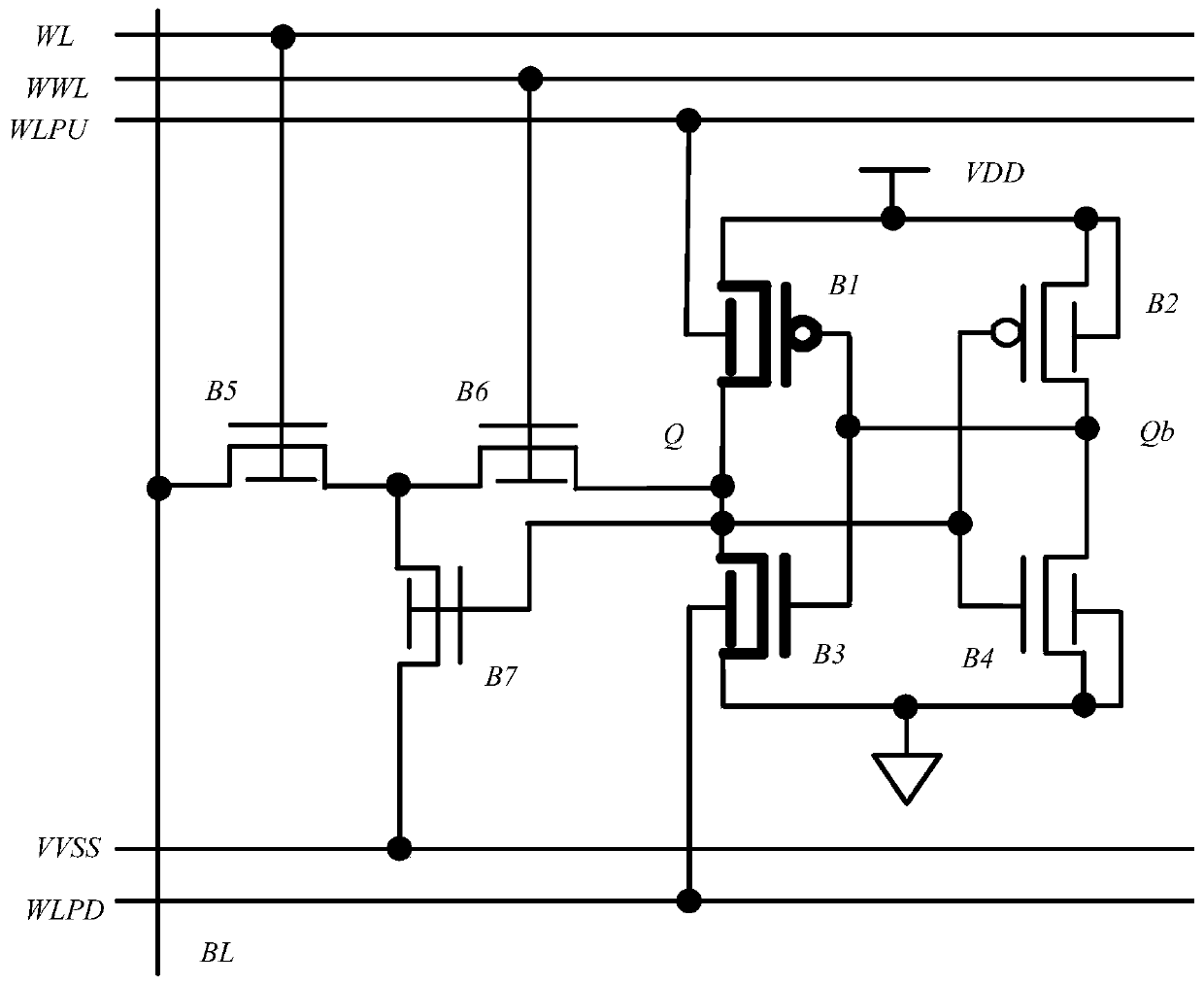
Single-end-operated subthreshold storage unit circuit
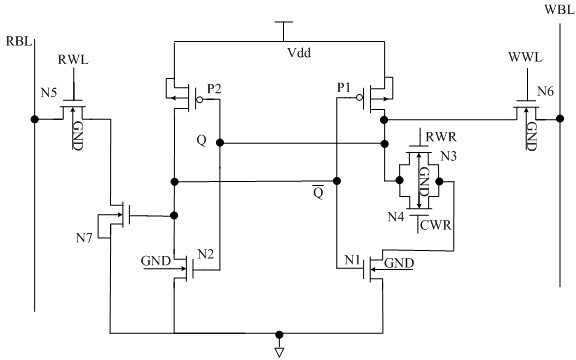
InactiveCN102592660AImprove noise immunityImprove robustnessDigital storageOxide semiconductorP channel
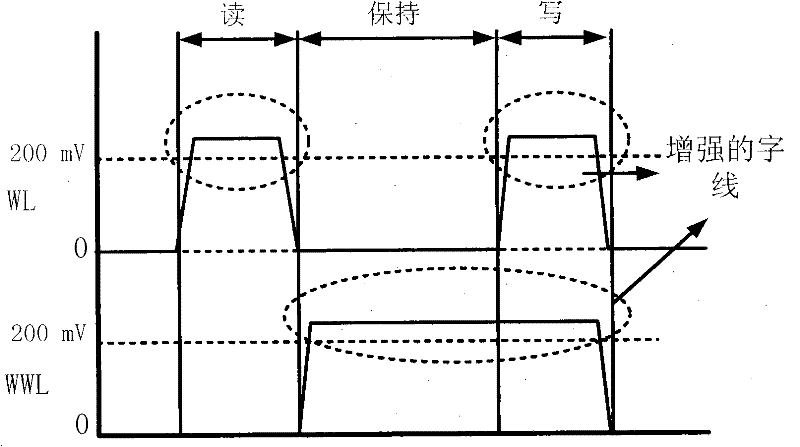
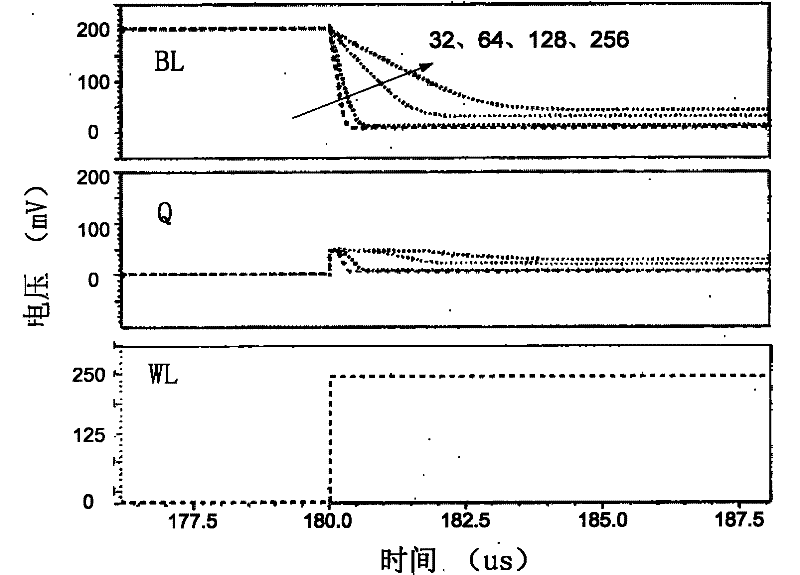
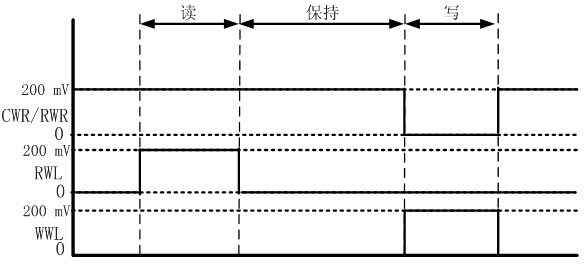
The invention discloses a single-end-operated subthreshold storage unit circuit, comprising two PMOS (P-channel Metal Oxide Semiconductor) transistors, namely P1 and P2, and seven NMOS (N-channel Metal Oxide Semiconductor) transistors, namely N1-N7, wherein the body ends of P1 and P2 are connected with a voltage drain-drain Vdd after being connected with the respective sources; the body ends of N1-N7 as well as the sources of N1, N2 and N7 are all grounded; the grid of N3 is connected with a row-writing control signal RWR; the grid of N4 is connected with a column-writing control signal CWR; an inverter is composed of N2 and P2; the output end of the inverter is connected with the grids of N2 and P2; the input end of the inverter is connected with the drain of P1; the grid of the N5 is connected with a reading word line RWL; the drain of N5 is connected with a reading bit line RBL; the source of N6 is connected with a writing bit line WBL; and the grid of N6 is connected with a word writing line WWL.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
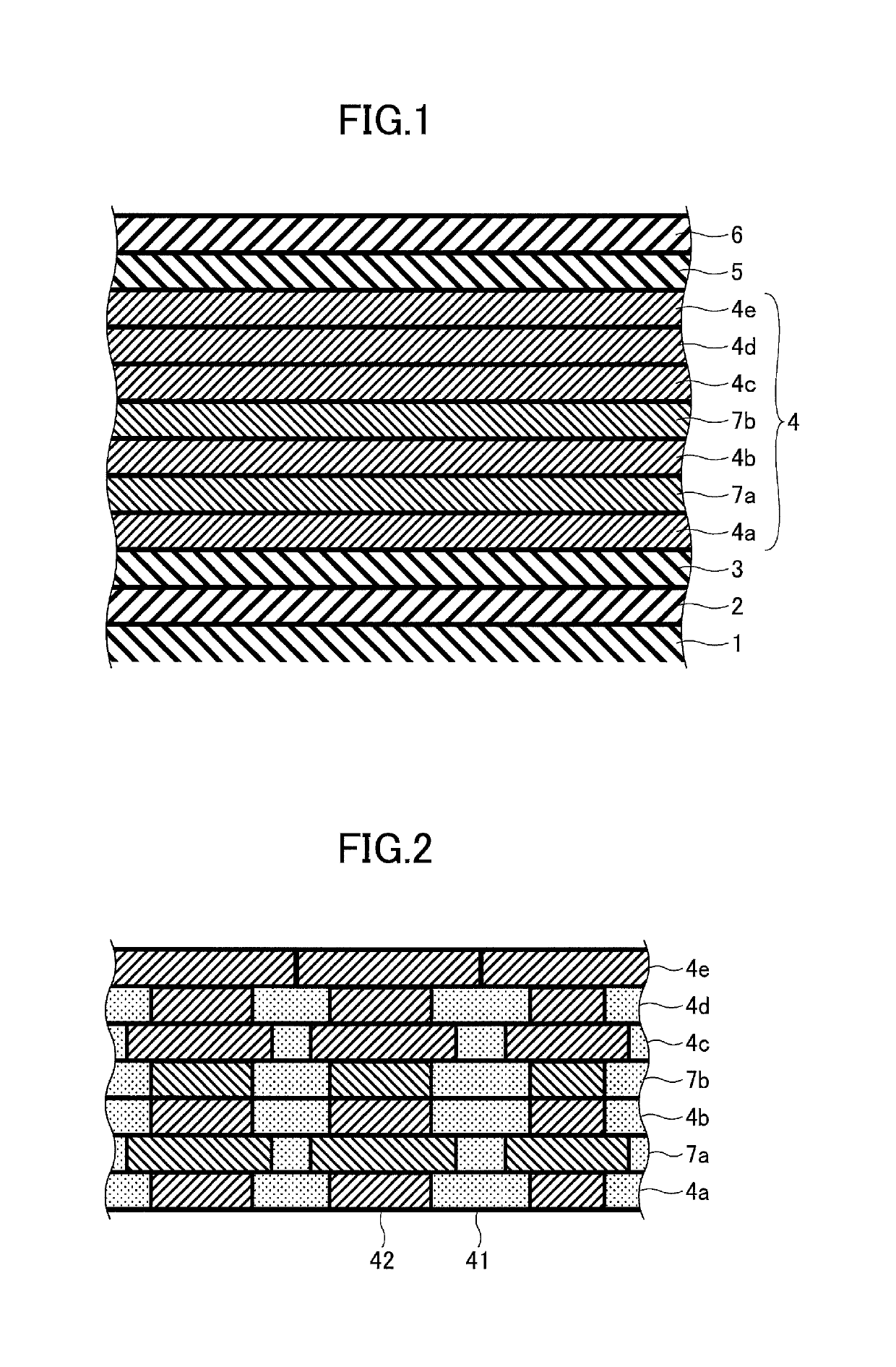
Magnetic recording medium, method of manufacturing magnetic recording medium and magnetic recording reproducing apparatus
InactiveUS20100033873A1Maintain abilityEnhance layeringRecord information storageDisk carriersInter layerEngineering
In a perpendicular magnetic recording medium in which at least a soft magnetic underlayer, an orientation control layer, a magnetic recording layer and a protective layer are formed on a non-magnetic substrate in order from the bottom, the orientation control layer has a laminated structure of two or more layers including an intermediate layer and a seed layer which is disposed closer to the non-magnetic substrate than the intermediate layer. The seed layer includes two or more kinds of elements having a face-centered cubic structure, has face-centered cubic (111) plane crystals oriented in a direction perpendicular to a substrate surface, and has a pseudo-hexagonal structure.
Owner:TOSHIBA ELECTRONICS DEVICES & STORAGE CORPORARTION +2
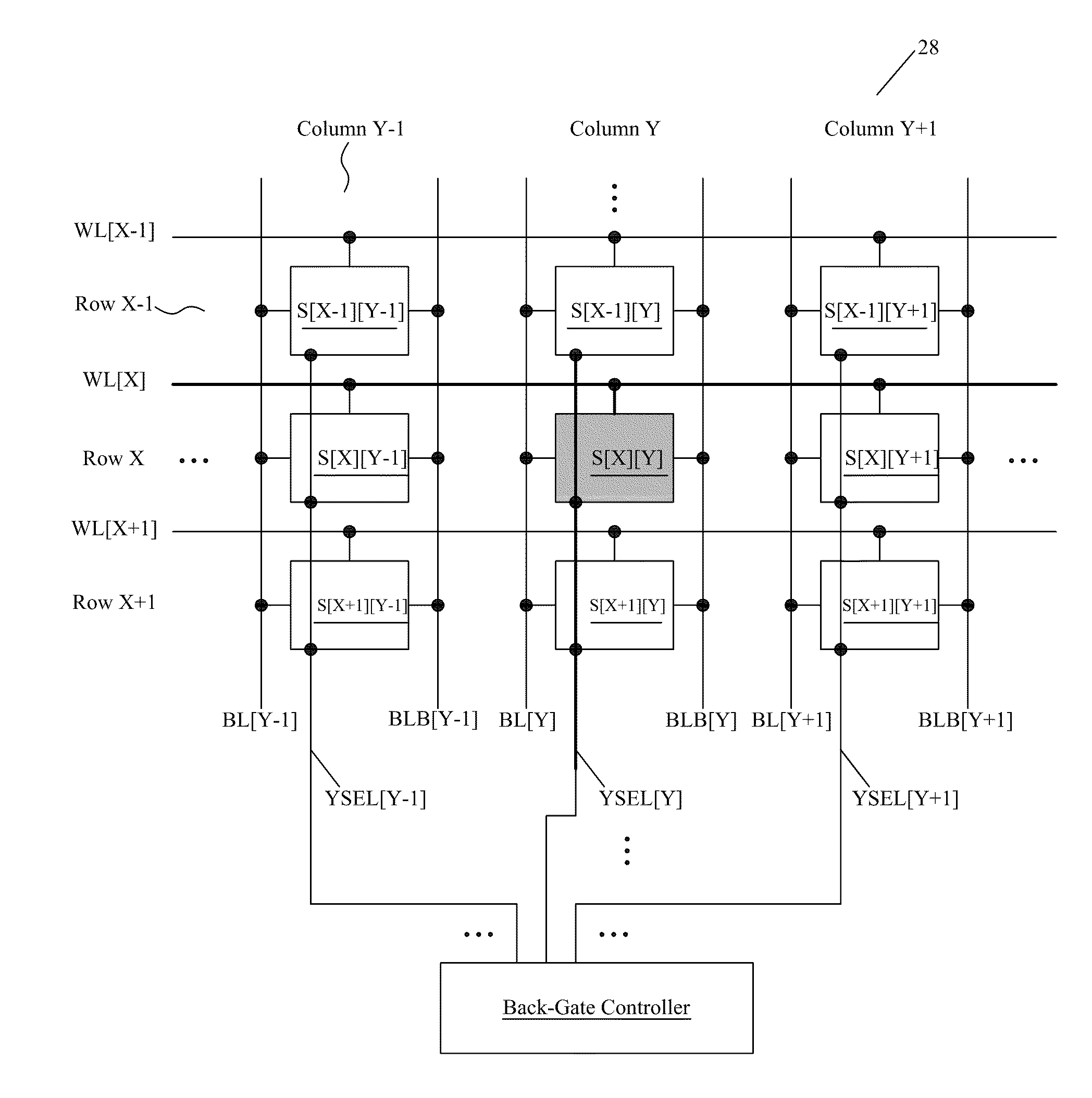
Read/Write Margin Improvement in SRAM Design Using Dual-Gate Transistors
InactiveUS20100165707A1Improve writing abilityReduce leakage currentTransistorSolid-state devicesStatic random-access memoryWrite margin
An integrated circuit structure includes a static random access memory (SRAM) cell. The SRAM cell includes a pull-up transistor and a pull-down transistor forming an inverter with the pull-up transistor. The pull-down transistor includes a front gate connected to a gate of the pull-up transistor, and a back-gate decoupled from the front gate.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Perpendicular magnetic recording medium
ActiveUS7592080B2Medium performanceReduce noiseRecord information storageMagnetic recordingInter layerOptoelectronics
A perpendicular magnetic recording medium includes a nonmagnetic substrate; a first underlayer provided on the nonmagnetic substrate; a first nonmagnetic intermediate layer provided on the first underlayer; a second underlayer provided on the first nonmagnetic intermediate layer; a second nonmagnetic intermediate layer provided on the second underlayer; and a magnetic recording layer provided on the second nonmagnetic intermediate layer, wherein the first underlayer comprises a soft magnetic material which has a face-centered cubic structure and which includes at least Ni and Fe, and wherein the second underlayer comprises a soft magnetic material which has a face-centered cubic structure and which includes at least Co. The orientation dispersion is reduced and crystal grain diameters are smaller in the magnetic recording layer, and the film thickness of nonmagnetic intermediate layers can be decreased so that performance improvements such as reduced noise, increased S / N ratio, and improved write-ability are achieved.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Static random access memory cell and method of operating the same
ActiveUS8437178B2Guaranteed uptimePositive feedbackDigital storageElectricityStatic random-access memory
A static random access memory cell includes a latch unit. The latch unit includes a bi-inverting circuit and a switching circuit. The bi-inverting circuit has a first terminal and a second terminal. The switching circuit is electrically connected between the first terminal and the second terminal, wherein when the switching circuit is turned on, the switching circuit forms a feedback between the first terminal and the second terminal for latching the latch unit; and when the switching circuit is turned off, the feedback is removed to cause the SRAM cell to write a data bit to the latch unit.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
Magnetic recording medium containing first and second recording layers, each layer containing a columnar structure
InactiveUS7556871B2Improve writing abilityImprove abilitiesDifferent record carrier formsBase layers for recording layersMagnetic anisotropyRecording layer
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Read/write margin improvement in SRAM design using dual-gate transistors
InactiveUS8144501B2Improve writing abilityReduce leakage currentTransistorSolid-state devicesStatic random-access memoryWrite margin
An integrated circuit structure includes a static random access memory (SRAM) cell. The SRAM cell includes a pull-up transistor and a pull-down transistor forming an inverter with the pull-up transistor. The pull-down transistor includes a front gate connected to a gate of the pull-up transistor, and a back-gate decoupled from the front gate.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Magnetic recording medium, method of manufacturing magnetic recording medium and magnetic recording reproducing apparatus
InactiveUS8034471B2Maintain abilityEnhance layeringRecord information storageDisk carriersInter layerEngineering
In a perpendicular magnetic recording medium in which at least a soft magnetic underlayer, an orientation control layer, a magnetic recording layer and a protective layer are formed on a non-magnetic substrate in order from the bottom, the orientation control layer has a laminated structure of two or more layers including an intermediate layer and a seed layer which is disposed closer to the non-magnetic substrate than the intermediate layer. The seed layer includes two or more kinds of elements having a face-centered cubic structure, has face-centered cubic (111) plane crystals oriented in a direction perpendicular to a substrate surface, and has a pseudo-hexagonal structure.
Owner:TOSHIBA ELECTRONICS DEVICES & STORAGE CORPORARTION +2
Near-threshold 8-tube static random memory unit
InactiveCN104882159AEliminate Data Retention CapabilitiesEasy to writeDigital storageBit lineEngineering
The invention relates to a near-threshold 8-tube static random memory unit, and belongs to the field of design of integrated circuits. The unit structurally comprises a first phase inverter consisting of a first NMOS transistor and a first PMOS transistor, and a second phase inverter consisting of a second NMOS transistor and a second PMOS transistor; the input ends and output ends of the two phase inverters in serial connection are respectively connected with a source electrode and a drain electrode of a third PMOS transistor so as to form a latch structure; the source electrode and drain electrode of the third PMOS transistor are respectively connected with a bit line BL and a data storage point L; a grid electrode of the second NMOS transistor and a grid electrode of the third PMOS transistor are both connected to a write line WWL; a drain electrode and a source electrode of a fourth NMOS transistor are respectively connected with a bit line BR and a source electrode of a fifth NMOS transistor; a grid electrode of the fourth NMOS transistor is connected to a read line RWL; a grid electrode of the fifth NMOS transistor is connected to a data storage point R; the drain electrode of the fifth NMOS transistor is connected to ground gnd. The structure can be used for reinforcing the stability and the read and write capabilities of a near-threshold working voltage, and further reducing the power consumption, has no size construction of pull-down ratio and the like, is capable of simplifying the design difficulty further, and has no cost of area sacrifice.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
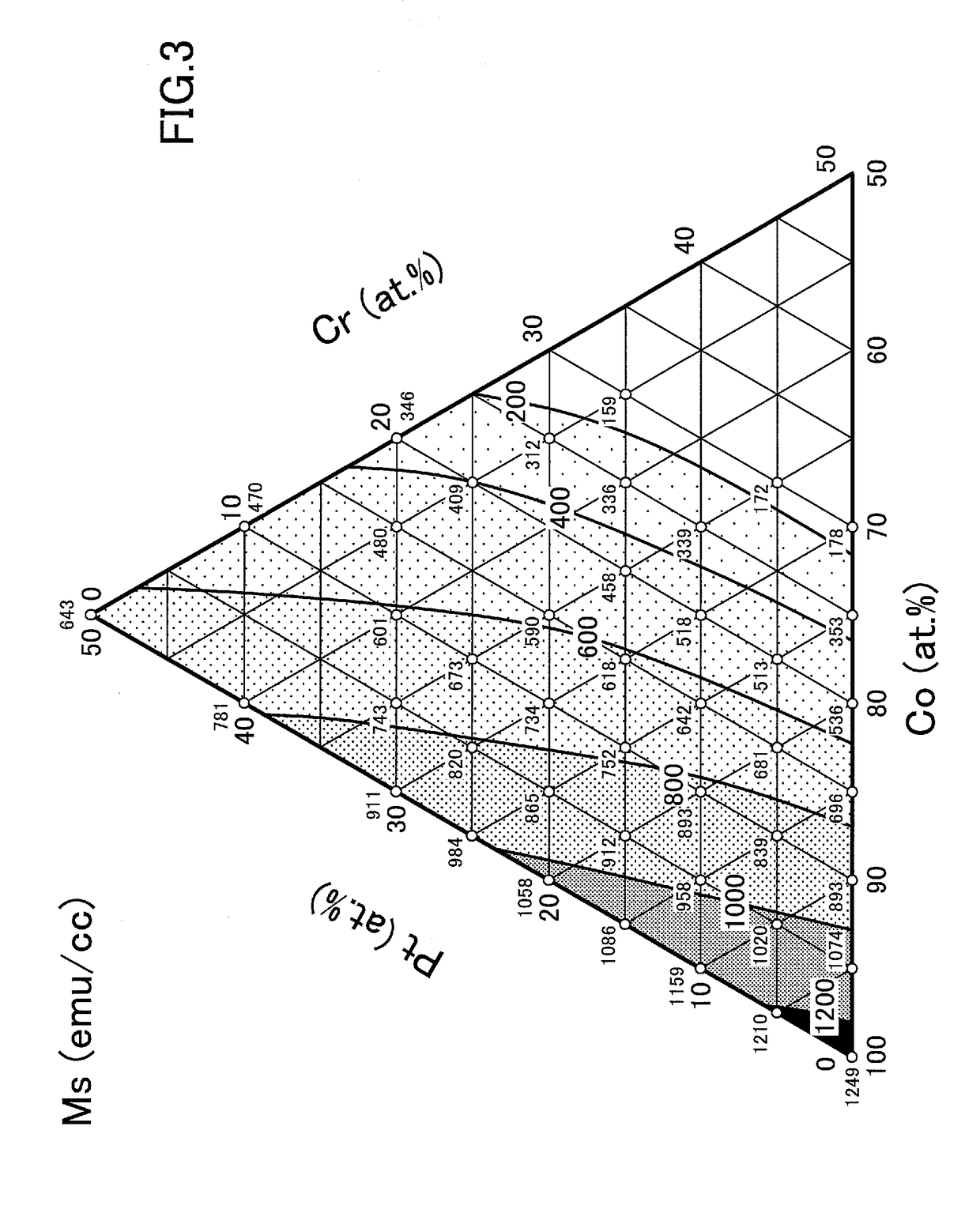
Magnetic recording medium and magnetic recording and reproducing apparatus
ActiveUS20170221515A1Eliminate the problemImprove featuresMagnetic materials for record carriersRecord information storageMagnetic anisotropyControl layer
A magnetic recording medium includes a non-magnetic substrate on which at least a soft magnetic underlayer, an orientation control layer, a perpendicular magnetic layer, and a protective layer are disposed. The perpendicular magnetic layer includes first to fourth magnetic layers. A first exchange coupling control layer is disposed between the first magnetic layer and the second magnetic layer. A second exchange coupling control layer is disposed between the second magnetic layer and the third magnetic layer. Following relations are satisfied where Kui is a magnetic anisotropic constant of an i-th magnetic layer, Msi is a saturation magnetization of the i-th magnetic layer, and t1 is a film thickness of the i-th magnetic layer, Ku1>Ku2, Ku2>Ku3, Ms1×t1>Ms2×t2, Ms2×t2>Ms3×t3 r Ku3<Ku4, and Ms3×t3<Ms4×t4.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Static random access memory including assist circuit
ActiveUS10522216B2Improve efficiencyReduce consumptionTransistorSolid-state devicesStatic random-access memoryRandom access memory
Disclosed is a static random access memory including an assist circuit. More particularly, a static random access memory according to an embodiment of the present disclosure may include a bit cell part including at least one bit cell connected between a first ground voltage node and a second ground voltage node; and a controller including a first transistor configured to control connection between the first ground voltage node and the second ground voltage node, a second transistor configured to float a first ground voltage of the first ground voltage node, and a third transistor configured to float a second ground voltage of the second ground voltage node, wherein the controller controls the first and second ground voltages supplied to the bit cell part using the first, second, and third transistors.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND YONSEI UNIV
SRAM (Static Random Access Memory) storage unit circuit capable of realizing high read-write stability under low voltage
ActiveCN110808076AEliminate the effects ofImprove writing abilityDigital storageEnergy efficient computingPhysicsOxide semiconductor
An SRAM (Static Random Access Memory) storage unit circuit capable of realizing high read-write stability under low voltage is of a nine-tube structure, a grid electrode of a sixth NMOS (N-channel Metal Oxide Semiconductor) tube is connected with a grid electrode of a fifth NMOS tube and a first writing line, a drain electrode of the sixth NMOS tube is connected with a writing bit line, and a source electrode of the sixth NMOS tube is connected with a drain electrode of the fifth NMOS tube; the grid electrode of the second NMOS tube is connected with a third writing line, the drain electrode of the second NMOS tube is connected with the source electrode of the fifth NMOS tube, the drain electrode of the first PMOS tube and the grid electrodes of the third PMOS tube, the third NMOS tube andthe fourth NMOS tube, and the source electrode of the second NMOS tube is connected with the drain electrode of the first NMOS tube; the grid electrode of the second PMOS tube is connected with the second writing line, the drain electrode of the second PMOS tube is connected with the source electrode of the first PMOS tube, and the source electrode of the second PMOS tube is connected with the source electrode of the third PMOS tube and the power supply voltage; the drain electrode of the third NMOS transistor is connected with the drain electrode of the third PMOS transistor and the grid electrodes of the first NMOS transistor and the first PMOS transistor, and the source electrode of the third NMOS transistor is connected with the source electrode of the first NMOS transistor and the ground; and the drain electrode of the fourth NMOS transistor is connected with a read bit line, and the source electrode is connected with a read word line. The method can improve the writing capability of the SRAM storage unit, reduces the static power consumption of the system, does not affect the reading stability, and is especially suitable for low-voltage application.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method for improving the stabillity, write-ability and manufacturability of magneto-resistive random access memory
InactiveUS20150063011A1Significant changeImprove manufacturabilityDigital storageProduction rateElectrical resistance and conductance
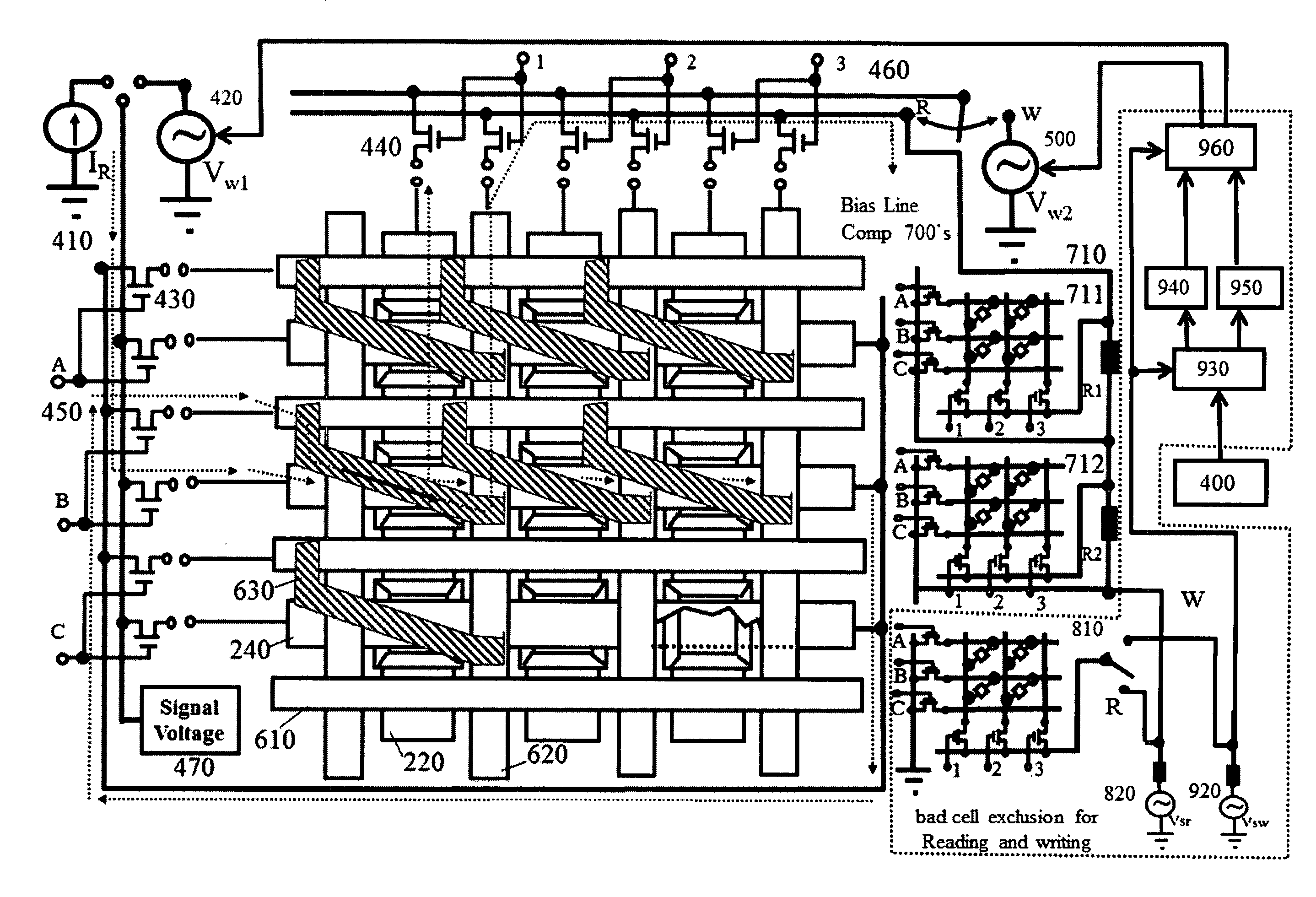
This invention provides the method to overcome 4 backwards which limit the manufacturability or production yield rate of Magneto-resistive random access memory (MRAM). The key points of this invention are: (1) providing method to improve the manufacturability through reducing bias variation, by using a compensation module to correct the bias point of extreme cells; (2) providing method to improve the manufacturability through removing outlier cells (called bad cells), by using “writing jump-over” and “reading exclusion” to exclude bad-cells; (3) providing method to reduce the bias point, amplitude and asymmetry variation, using shared fixed-magnetic-reference-layer and proper shape anisotropy; (4) providing method to improve the write-ability, using flipping-assistant-field to speed up STT flipping process by large current, and using heating resistance and heating cells by the same current (including global heating, row heating, column heating, or local cell heating, i.e. heating with conventional thermal nature or heating with thermagnonic spin-transfer torque).
Owner:CHEN LAURENCE LUJUN
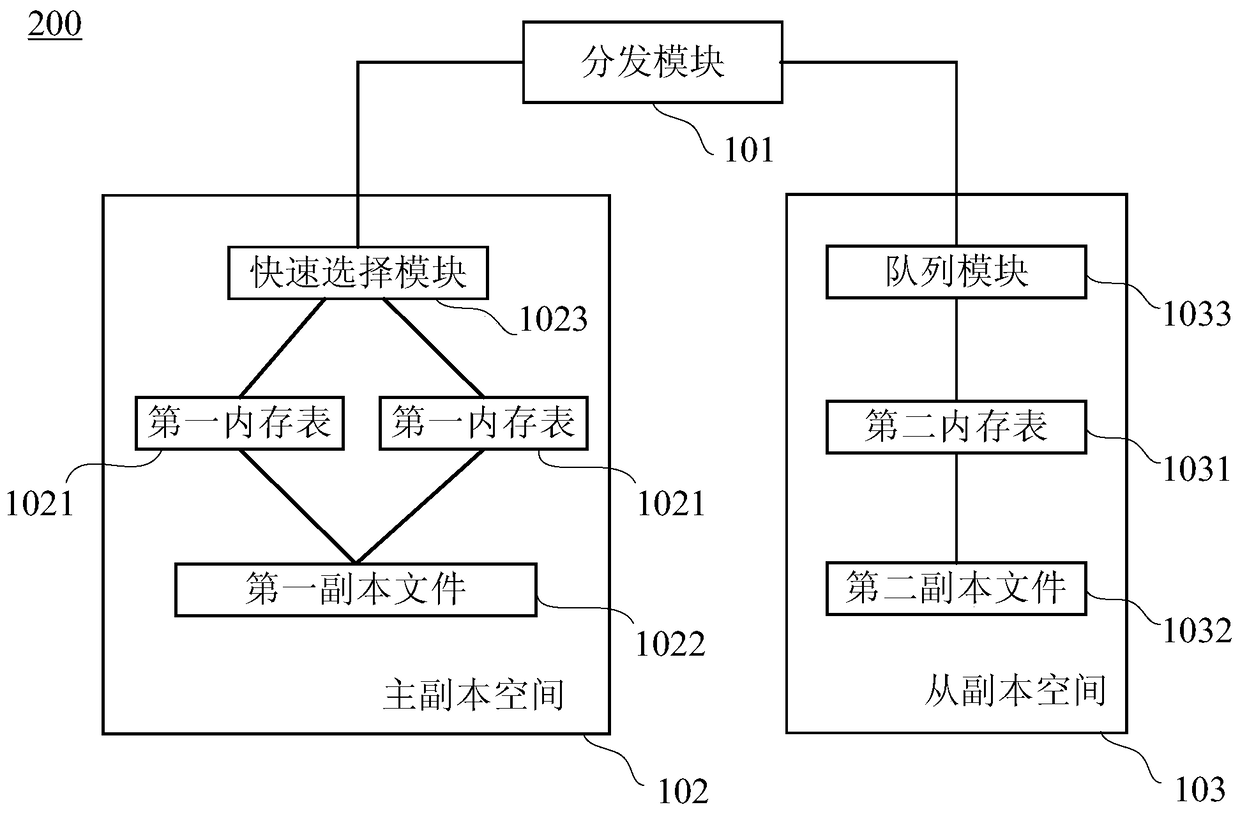
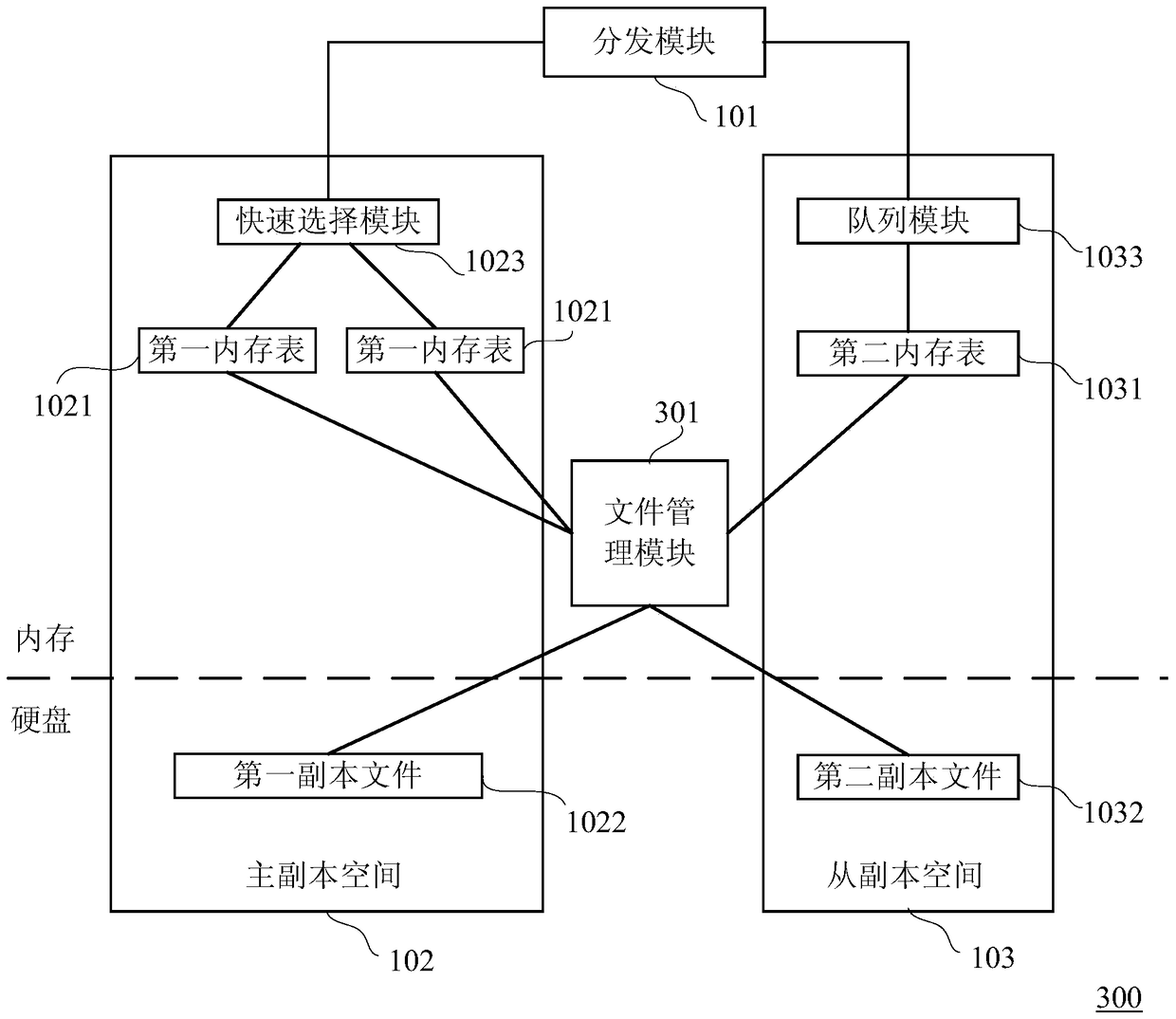
Copy storage device and copy storage method
ActiveCN104461768BReduce processing delayImprove writing abilityTransmissionRedundant operation error correctionResource consumptionData traffic
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Intelligent composition correction method and system
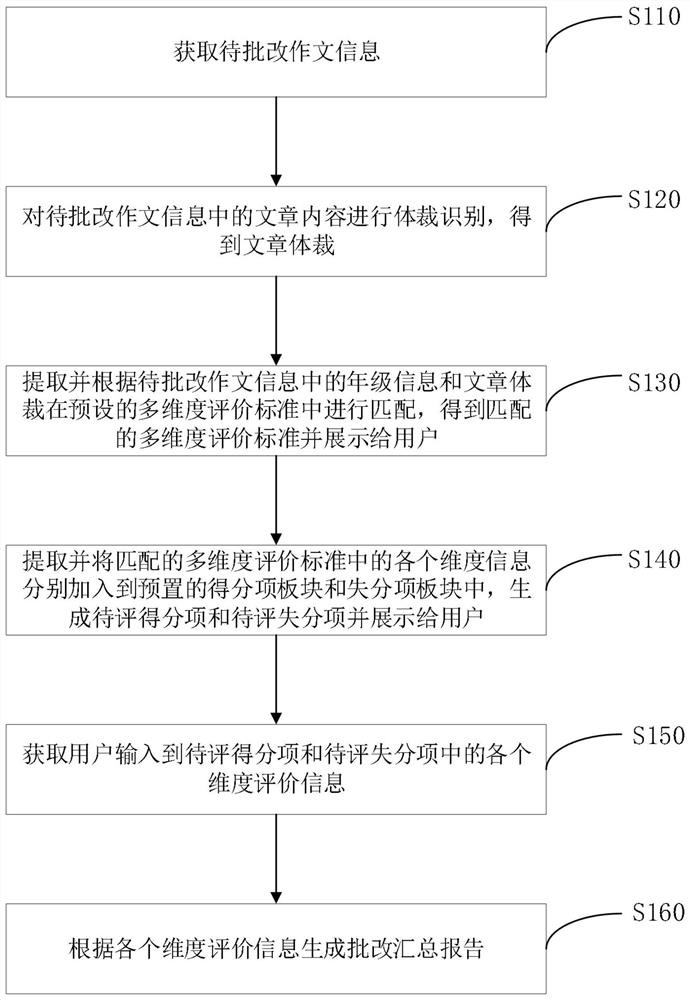
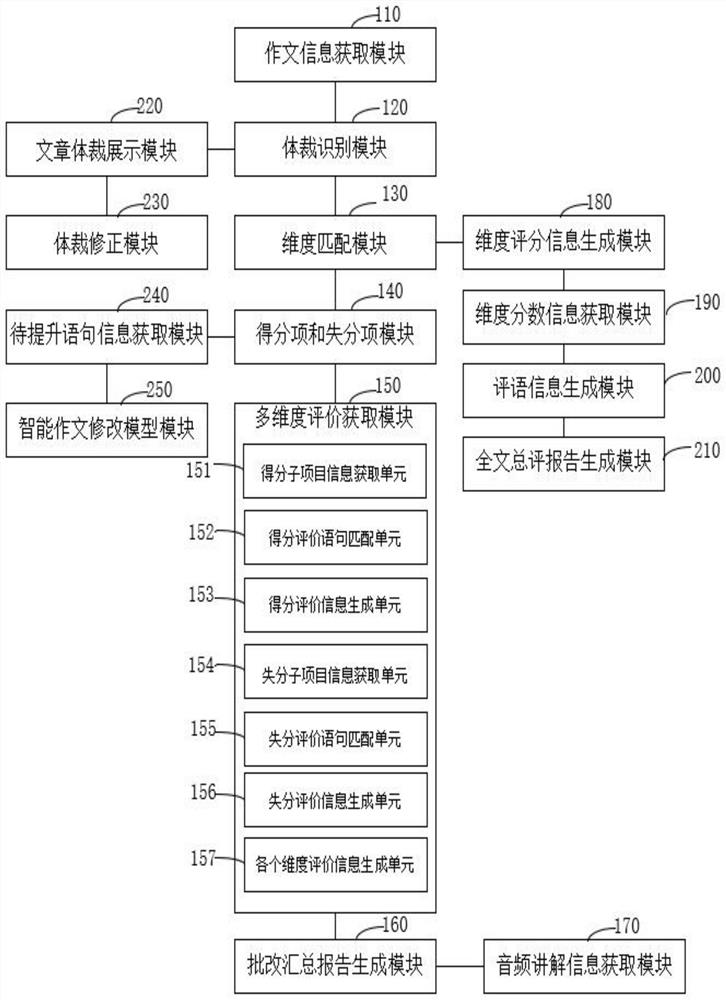
PendingCN114048739AAccurate correctionImprove objectivityCharacter and pattern recognitionNatural language data processingUser inputEngineering
The invention provides an intelligent composition correction method and system, and relates to the technical field of data processing. The intelligent composition correction method comprises the following steps: acquiring to-be-corrected composition information; enabling article content in the composition information to be corrected to be subjected to physical identification; extracting grade information in the to-be-corrected composition information and matching in a preset multi-dimensional evaluation standard according to the grade information and the article style in the to-be-corrected composition information; then, extracting and respectively adding each piece of dimension information in the matched multi-dimension evaluation standard into a preset score item plate and a lost score item plate; obtaining evaluation information of each dimension in the to-be-evaluated score item and the to-be-evaluated score item input by the user; and finally, generating a diagnosis and treatment type correction summary report according to the evaluation information of each dimension. Therefore, accurate detailed batch is realized, the correction result is more accurate, and the objectivity of composition correction is improved. The writing ability of students can be improved; teachers can conveniently master scientific and accurate correction compositions, and the service quality is improved.
Owner:王月珠
Static random access memory including assist circuit
ActiveUS20190027213A1Improve efficiencyRaise the possibilityTransistorSolid-state devicesStatic random-access memoryRandom access memory
Disclosed is a static random access memory including an assist circuit. More particularly, a static random access memory according to an embodiment of the present disclosure may include a bit cell part including at least one bit cell connected between a first ground voltage node and a second ground voltage node; and a controller including a first transistor configured to control connection between the first ground voltage node and the second ground voltage node, a second transistor configured to float a first ground voltage of the first ground voltage node, and a third transistor configured to float a second ground voltage of the second ground voltage node, wherein the controller controls the first and second ground voltages supplied to the bit cell part using the first, second, and third transistors.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC CORP FOUND YONSEI UNIV
A finfet-based single-ended read-write storage unit
ActiveCN108461104BWith power control functionStable functionDigital storageControl theoryStorage cell
The invention discloses a single side reading and writingstorage unit based on FinFET. The single side writing and reading storage unit comprises a first FinFET pipe, a second FinFET pipe, a third FinFET pipe, a fourth FinFET pipe, a fifth FinFET pipe, a sixth FinFET pipe, a seventh FinFET pipe, a position line, a character line, a character writing line, an upper-character writing line, a lower-character writing line and a dotted line, the first FinFET pipe and the second FinFET pipe are both P-type FinFET pipes, and the third FinFET pipe, the fourth FinFET pipe, the fifth FinFET pipe, the sixth FinFET pipe and the seventh FinFET pipe are all N-type FinFET pipes. The single side writing and reading storage unit has the advantages that on the basis of guaranteeing the reading operation stability, a high writing noise limit can be obtained, the storage value result is stable, the circuit function is stable, the leaked power consumption is small, the delay is also small, and data is quickly and stably accessed.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Magnetic recording medium and magnetic recording and reproducing apparatus
ActiveUS10283155B2Improve featuresImprove writing abilityRecord information storageMagnetic recordingControl layerMagnetic anisotropy
A magnetic recording medium includes a non-magnetic substrate on which at least a soft magnetic underlayer, an orientation control layer, a perpendicular magnetic layer, and a protective layer are disposed. The perpendicular magnetic layer includes first to fourth magnetic layers. A first exchange coupling control layer is disposed between the first magnetic layer and the second magnetic layer. A second exchange coupling control layer is disposed between the second magnetic layer and the third magnetic layer. Following relations are satisfied where Kui is a magnetic anisotropic constant of an i-th magnetic layer, Msi is a saturation magnetization of the i-th magnetic layer, and ti is a film thickness of the i-th magnetic layer, Ku1>Ku2, Ku2>Ku3, Ms1×t1>Ms2×t2, Ms2×t2>Ms3×t3, Ku3<Ku4, and Ms3×t3<Ms4×t4.
Owner:RESONAC CORPORATION
Method for improving the stability, write-ability and manufacturability of magneto-resistive random access memory
InactiveUS9177627B2Significant changeImprove manufacturabilityDigital storageStatic random-access memorySpin-transfer torque
Owner:CHEN LAURENCE LUJUN
MOSFET-TFET hybrid 11T SRAM unit circuit
PendingCN112509621AReduce static power consumptionImprove stabilityDigital storageMOSFETHemt circuits
The invention discloses a MOSFE-TFET hybrid 11T SRAM unit circuit, which comprises five NTFET transistors, four PTFET transistors and two NMOSFETs, and is characterized in that a power supply VDD is electrically connected with a source electrode of a PTFET transistor P3; the drain electrode of the PTFET transistor P3 is electrically connected with the source electrode of the PFET transistor P1; the drain electrode of the PTFET P2 is electrically connected with the drain electrode of the NTFET N2, the drain electrode of the NMOSFET N4, the grid electrode of the PTFET P1, the grid electrode of the NTFET N1 and the grid electrode of the NTFET N6; and the source electrode of the NTFET transistor N5 and the source electrode of the NTFET transistor N6 are both electrically connected with the GND. According to the circuit, the writing capability of the SRAM unit is enhanced, the static power consumption of the circuit is reduced, and the stability of the SRAM unit in a maintaining state is improved.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
A New Testable Structure of Lookup Table
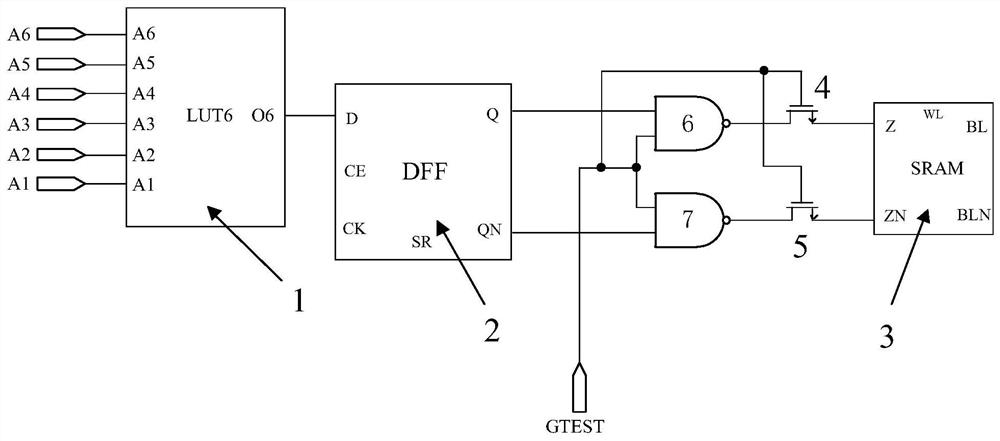
ActiveCN112147492BImprove reading speedImprove reading efficiencyDigital circuit testingTransmission gateProgrammable logic device
Owner:WUXI ESIONTECH CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com