Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34results about How to "Excellent Germplasm Resources" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for screening varieties with high utilization rate of nitrogen from multiple wheat varieties
InactiveCN106576728AEasy to operateImprove nitrogen use efficiencyFertilising methodsPlant cultivationBiological propertyRelative strain
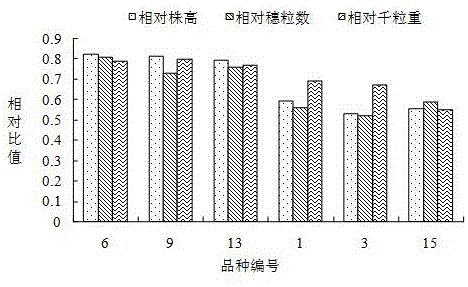
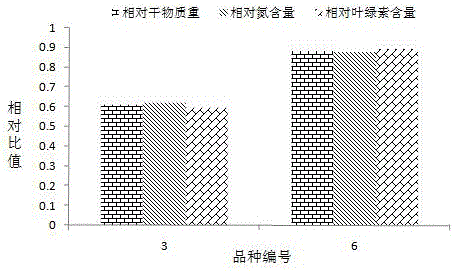
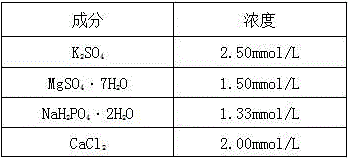
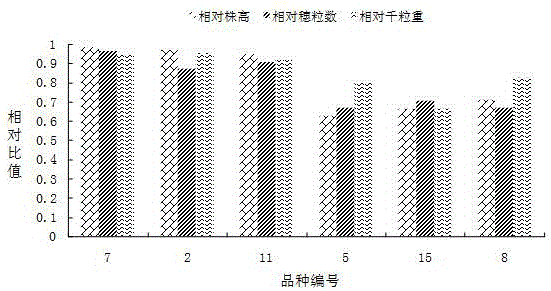
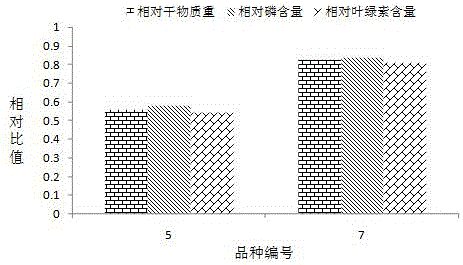
Provided is a method for screening varieties with the high utilization rate of nitrogen from multiple wheat varieties. The method comprises following steps: selecting wheat varieties with grains of the same size, placing the wheat varieties into a culture dish till the grains germinate to become rooted seedlings; selecting seedlings with growth uniformity from seedlings, dividing them into two groups and utilizing nutrition liquid with different nitrogen concentrations to pour till wheat become mature; testing and calculating relative strain height, relative grain number and relative thousand seed weight of each variety; making comprehensive comparisons and selecting several wheat varieties with three highest integrated indices as varieties with the high utilization rate of nitrogen; becoming re-screening seedlings through germination, taking re-screening seedlings with uniform growth, diving them into two groups, utilizing nutrition liquid with different nitrogen concentrations for water culture and testing and calculating relative dry matter weight, relative nitrogen content and relative chlorophyll content of each variety; and making comprehensive comparisons and selecting one wheat variety with three highest integrated indices as the variety with relatively higher utilization rate of nitrogen. The method for screening varieties with the high utilization rate of nitrogen from multiple wheat varieties has following beneficial effects: wheat varieties finally screened by the method provide material for further improvement of existing varieties and research of biological characteristics and physiochemical mechanisms.
Owner:GANSU AGRI UNIV
Cultivation substrate used for ex-situ transplantation of alpine rose old tree stumps
InactiveCN103636470AResolve recoverySolve problems such as new root regeneration difficultiesCultivating equipmentsForestryControlled releaseAlpine rose
The invention provides a special cultivation substrate and an application method for solving the problems that root system recovering and reestablishment are difficult after ex-situ transplantation of alpine rose old tree stumps. The method comprises the preparation steps of A, self preparing leaf mold, wherein wood bits are added in collected dead leaves, the ratio of the wood bits to the collected dead leaves is 1:5, the mixture of the collected dead leaves and the wood bits are smashed, water is added in the mixture of the collected dead leaves and the wood bits to drench the mixture of the collected dead leaves and the wood bits, the mixture of the collected dead leaves and the wood bits are buried in the soil for one year and are sufficiently decomposed, and the leaf mold is prepared; B, using turfy soil, the self-prepared leaf mold and pine needles according to the volume ratio of 7:2:1 for preparing substrate raw materials; C, preparing mixed base fertilizers, wherein three kinds of controlled-release fertilizers with the ratios of N to P to K being 10:11:18, 15:9:11, and 9:14:19 respectively are selected, and the three kinds of release fertilizers are evenly mixed in the proportion of 1.5: 1: 2; D, evenly mixing the substrate raw materials, and then adding the prepared 1 kg / m<3> of base fertilizers in the mixed substrate raw materials; E, conducting water purification process; F, using the water processed in the step E for wetting the substrate, and evenly stirring the substrate again, wherein the substrate materials are held into a spherical shape by hands and immediately loosen if the hands let the substrates go, the proper moisture content is 80-90 %, and the standards of loosening, ventilation and water retention are met.
Owner:SHIJIAZHUANG ACADEMY OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI +1
Method for breeding sexual triploids of colored zantedeschia by using 2n pollen
InactiveCN102217525AHigh induction rateExcellent Germplasm ResourcesPlant genotype modificationEvolutionary biology
The invention discloses a method for breeding sexual triploids of colored zantedeschia by using 2n pollen, and belongs to the technical field of plant ploidy breeding. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) determining a 2n pollen induced appropriate development stage; (2) preparing styles to be treated; (3) inducing the 2n pollen by colchicine treatment; (4) identifying the 2n pollen; (5) collecting the 2n pollen; (6) performing sexual polyploidy hybridization; and (7) identifying sexual triploid descendants. By the method, the sexual triploids of the colored zantedeschia can be successfully obtained in one step.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for screening variety with high phosphorus utilization efficiency from multiple wheat varieties
InactiveCN106577268AEasy to operateImproved germplasmCalcareous fertilisersMagnesium fertilisersNutrient solutionProviding material
The invention discloses a method for screening variety with high phosphorus utilization efficiency from multiple wheat varieties, comprising the following steps: selecting wheat varieties with same size seeds, putting the wheat varieties into a culture vessel to germinate seedlings with roots, selecting seedlings with consistent growth from the seedlings to divide into two groups, irrigating the seedlings with nutrient solvents with different phosphorus concentrations until the wheat is mature; detecting and calculating the relative plant height, the relative grain number and the relative thousand seed weight of each variety; comprehensively comparing to select several wheat varieties with the highest three indices in general to serve as varieties with the high phosphorus utilization efficiency; germinating the varieties with the high phosphorus utilization efficiency until secondary screened seedlings are rooted, selecting the secondary screened seedlings with consistent growth to divide into two groups, performing hydroponics with nutrient solvents with different phosphorus concentrations, detecting and calculating the relative weight of dry matter, the relative phosphorus content and the relative chlorophyll content of each variety; comprehensively comparing to select a wheat variety with the highest three indices in general to serve as the variety with the relatively highest phosphorus utilization efficiency. The wheat variety screened at the end by the method provided by the invention provides materials for further improving existing varieties and studying the biological property and the physiology and biochemistry mechanism of the existing varieties.
Owner:GANSU AGRI UNIV
Strain YAB-3 for degrading PFOA (perfluorooctanoic acid) and application thereof
InactiveCN104974968AReduce concentrationSimple methodBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPerfluorooctanoic acidMicrobiology
The invention discloses a strain YAB-3 for degrading PFOA (perfluorooctanoic acid) and an application thereof. The strain for degrading PFOA is sphingomonas yanoikuyae, with the collection number of CCTCC (China Center for Type Culture Collection) NO:M2015281, the collection date of May 7, 2015 and the collection unit of CCTCC. A method for degrading PFOA-containing materials by utilizing the strain YAB-3 is characterized by comprising the following steps: firstly inoculating the single colony YAB-3 into an LB culture medium for 12-18 hours, then preparing bacterial suspension with certain OD600 with the culture medium, and finally treating the PFOA-containing materials with the bacterial suspension. The invention provides the strain YAB-3 for degrading PFOA and the method for treating the PFOA-containing materials by utilizing the strain. The strain has strong capability of degrading PFOA. The method for treating the PFOA-containing materials is simple and effective and can achieve the effect of obviously reducing the concentration of PFOA in the materials.
Owner:JISHOU UNIVERSITY
Molecular marker for corn tripsacum monosome addition line nucleic male sterility genes and application thereof
ActiveCN104946644ANo effect on growth and developmentRich genetic baseMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationAgricultural scienceNucleotide
The invention discloses a molecular marker which is used for corn tripsacum monosome addition line nucleic male sterility genes and belongs to the field of crop molecular markers. The molecular marker is composed of nucleotide sequences shown by SEQ ID No:1. The invention further discloses an SCAR primer pair used for amplifying the molecular marker and composed of SEQ ID No:2 and SEQ ID No:3. In addition, the invention further discloses a method of using the molecular marker for backcross and recurrent selection breeding. The molecular marker is not limited by time and environment conditions, can identify and screen the corn tripsacum monosome addition line nucleic male sterility genes at the seedling stage, selects and weeds out the nucleic male sterility genes easily, saves manpower and material resources in large quantities, improves the breeding efficiency, shortens the breeding process and time, and substantially reduces breeding cost. In addition, the molecular marker can serve as a tool for large-scale recurrent selection for corns and continuously extend the corn heredity basis and is beneficial for selecting out a breakthrough corn variety.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Method for screening phosphorus high efficiency utilizing variety from multiple barley varieties
InactiveCN106718718AEasy to operateImproved germplasmGrowth substratesCulture mediaBiological propertyHordeum vulgare
Provided is a method for screening a phosphorous high efficiency utilizing variety from multiple barley varieties. The method comprises the steps of selecting barley varieties with the same sizes of grains, putting the varieties into a culture dish, and germinating the varieties into seedlings with roots; selecting seedlings of which growth is consistent from the seedlings, dividing the seedling of which growth is consistent into two groups, and using a nutrient solution with different phosphorus concentration to pour on the seedlings until the barley is mature; measuring and calculating the relative plant height, the relative kernels per spike and the relative thousand seed weight of each variety, conducting comprehensive comparison, and selecting several barley varieties of which the three indexes are comprehensively the highest as phosphorus high efficiency utilizing varieties; germinating the barley varieties into after-screening seedlings with roots, selecting the after-screening seedlings of which the growth is consistent, dividing the after-screening seedlings into two groups, using the nutrient solution with different phosphorus concentration to conduct water planting, and measuring and calculating the relative dry matter weight, the relative phosphorus content and the relative chlorophyll content of each variety; comprehensively comparing, and selecting one barley variety of which the three indexes are comprehensively the highest as the variety of which the phosphorus utilizing efficiency is relatively the highest. According to the method for screening the phosphorous high efficiency utilizing variety from multiple barley varieties, the finally screened barley variety provides materials for further improving an existing variety and studying the biological characteristics of the existing variety and a physiology and biochemistry mechanism.
Owner:GANSU AGRI UNIV
Cyclocarya paliurus non-tube rapid propagation method
InactiveCN105010136AIncrease productionConsensus germplasm lineCultivating equipmentsHorticulture methodsPlant tissueGreenhouse
The invention discloses a cyclocarya paliurus non-tube rapid propagation method. According to the cyclocarya paliurus non-tube rapid propagation method, plant tissue culturing principles are adopted, pruning and sprouting promotion of seedlings of cyclocarya paliurus maternal plant plantations are carried out, light matrix non-woven fabric nutritional bags are used, rooting hormone is applied, bactericidal treatment is carried out, all sunlight intelligent breeding greenhouses are adopted, batch-type mist spray is controlled accurately, so that seedling period of cyclocarya paliurus is shortened, seedling surviving rate and yield of cyclocarya paliurus are increased, problems that formation of callus tissue is inhibited because cyclocarya paliurus is high in tannin content, and cottage processing ratio is low are solved, and a problem that cyclocarya paliurus genetic resources are scarce is solved effectively.
Owner:LUEYANG COUNTY JINXIU AGRI DEV CO LTD
Method for protecting and restoring germplasm of citrus-Hunglongbing-infected citrus according to two-step method
InactiveCN106034894ADoes not destroy agronomic traitsDelay drug resistanceBiocideGraftingGermplasmAntibiotic Y
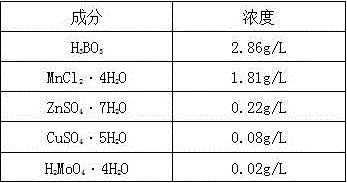
The invention provides a method for protecting and restoring germplasm of citrus-Hunglongbing-infected citrus according to a two-step method. The method comprises the steps of soaking seeds into alcohol with concentration of 70% for one minute, soaking the seeds into NaOH with concentration of 5% for eliminating pectin, then soaking the seeds into sodium hypochlorite solution with concentration of 3% for 20 minutes, cleaning with sterile water by 2-3 times, then immersing the seeds in normal-temperature water for 5-10 hours, then performing thermal treatment on the seeds by means of wet-and-hot air with temperature of 50-55 DEG C for 40-60 minutes, then removing seed shells, sowing the seeds into an MS medium in which enrofloxacin sodium and sulfadimethoxine sodium antibiotic are added, transplanting seedlings into disinfected nutrient soil after the seedlings are grown to a height of 5cm, and grafting the newly grown branch from a nursery stock as a scion on a stock seedling which is grown from a stock seedling which is processed in the same way. According to the method of the invention, the antibiotic composition which comprises the enrofloxacin sodium and the sulfadimethoxine sodium antibiotic is utilized for reasonable mixing; and a two-step method which comprises thermal treatment and adding the antibiotic is firstly utilized for performing sterilization on the citrus-Hunglongbing-infected citrus, thereby realizing higher sterilization effect.
Owner:PLANT PROTECTION RES INST OF GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Breeding method of high-temperature-resistant stichopus japonicus strain
ActiveCN106259067AMeet the characteristics of patienceImprove selection efficiencyClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaSexual maturityZoology
The invention discloses a breeding method of a high-temperature-resistant stichopus japonicus strain and belongs to the field of genetic breeding of aquatic products. Stichopus japonicus surviving after natural high temperature elimination in summer in different regions is selected as a parent, families are constructed through breeding after sexual maturity, heat shock at the temperature of 28 DEG C is performed at the auricularia stage of each family, 20% of families are reserved according to the survival rate and the malformation rate, the reserved families are mixed and bred until the average weight of individuals is larger than 50 g, high-temperature stress is performed at 32 DEG C to remove dead and damaged individuals, less than 25% of individuals are reserved and continuously bred until sexual maturity, heat shock selection and breeding of three generations are performed continuously in the same principle, and the new stichopus japonicus strain with the high-temperature-resistant character is obtained. The original parent of stichopus japonicus better conforms to the tolerance characteristic of the actual breeding environment; high-temperature domestication screening of the families in the larva period and high-temperature stress screening in the breeding period are performed, family breeding and group breeding are combined, and the selection efficiency is improved; breeding of three generations is performed continuously, the high-temperature-resistant character is stabilized, and the breeding method has good economic benefit and broad breeding prospect.
Owner:山东省海洋资源与环境研究院
Brassica napus L promoter pBnUnng0942890 and application thereof
ActiveCN109439663AImprove qualityGreat application potentialPlant peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionBrassicaGermplasm
The invention discloses brassica napus L promoter pBnUnng0942890 and application thereof. By cloning a promoter of a gene pBnUnng0942890 in the brassica napus L, a plant expression vector of a reporter gene GUS regulated by the promoter is constructed; by using an agrobacterium-mediated inflorescence impregnating method to transform arabidopsis, GUS histochemical staining is carried out on screened positive transgenic strains; the result shows that the pBnUnng0942890 has the functions of driving preferential expression of downstream genes in roots, flowers and seeds, and not expressing or realizing low expression in other tissues and organs. The promoter has good application potential in the aspects of improving crop quality by rapeseed transgene, artificially creating germplasm resourcesand the like.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Sorghum dwarfing mutation breeding method
PendingCN111328710AFast mutation frequencyBreeding process is fastPlant phenotype modificationPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyMutation breeding
The invention belongs to the field of sorghum breeding, and particularly relates to a sorghum dwarfing mutation breeding method. The method comprises the steps of conducting pretreatment after seed selection; conducting physical mutation, wherein sorghum seeds are put into a plastic bag for irradiation treatment; conducting chemical mutation, wherein the seeds subjected to irradiation treatment are soaked in a chemical mutation agent for treatment, and chemical mutation seeds are obtained; conducting mutation aftertreatment; screening dwarfing sorghum mutants; planting M1-generation seeds harvested from a single plant in the next year to form M2-generation strains, selecting untreated seeds as a contrast, comparing the flowering period with the contrast, observing the stability of the characters of the flowering period in the strains, conducting mixed harvesting and mixed threshing on the seeds which tend to be stable, harvesting M3-generation seeds, and obtaining a dwarf variant sorghum variety; and planting the strains with the characters continuously separated, continuing to plant and harvest the single plant, harvesting M3-generation seeds, and continuing to conduct identification and selection on the next system in the M4 generation till the dwarf variant sorghum variety is obtained.
Owner:SHANXI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI SORGHUM RES INST
Molecular marker AhyWptc closely linked with white seed coat of peanut and application of molecular marker AhyWptc
ActiveCN114525364AImprove breeding efficiencyIncrease credibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyForward primer
The invention discloses a molecular marker AhyWptc closely linked with white seed coats of peanuts and application of the molecular marker AhyWptc, and relates to the technical field of agricultural biology. A specific primer pair of the molecular marker AhyWptc comprises a forward primer as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 and a reverse primer as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2. By utilizing the molecular marker AhyWptc provided by the invention, the seed coat color of a next-generation harvested material can be determined in advance by detecting the DNA of a cotyledon, and the molecular marker AhyWptc is applied to molecular breeding and peanut variety improvement, so that the breeding time can be greatly shortened, the breeding efficiency can be improved, and more excellent peanut germplasm resources can be obtained within shorter time.
Owner:VEGETABLE RES INST OF SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI +1
Construction method for anti-insect transgene corn with stable heredity
InactiveCN103667340AAchieve conversionStrong resistanceVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsAgricultural scienceGermplasm
The present invention discloses a construction method for anti-insect transgene corn with stable heredity, wherein embryonic corn callus is adopted as a transformation acceptor material. According to the present invention, a gene gun-mediated genetic transformation method is adopted, a transformation vector pCAMBIA3300 carrying exogenous gene is wrapped with gold powder, and then is adopted to bombard the corn embryonic callus to complete transformation, tissue culture, screening, differentiation, seedling exercising and transplantation are sequentially performed to obtain the new anti-insect transgene corn material with stable heredity, and excellent performances of the resistance gene in different genetic backgrounds are verified through the backcross and molecular marker-assisted selection method so as to provide excellent germplasm resources for subsequent breeding of new anti-stem borer corn varieties.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Method for acquiring asparagus homozygous diploid by culturing anther
InactiveCN107873519ADiameter stableUniform diameterHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureAsparagalesBiology
The invention provides a method for acquiring asparagus homozygous diploid by culturing anther. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring asparagus anther, pre-treating the asparagus anther,performing callus induction for the asparagus anther, performing sub-generation differentiation for the asparagus anther, rooting a test-tube seedling, and multiplying haploid chromosome. By adoptingthe method for acquiring the asparagus homozygous diploid by culturing anther, the induction rate of callus with hard and compact texture of the asparagus anther is 7.2 to 17 percent; and the callusinduction rate of the variety ''champion'' with hard and compact texture is 15.8 to 17 percent or higher. According to the method for acquiring asparagus homozygous diploid by culturing anther, the haploid differentiation rate is 2.2 to 7.2 percent, the success rate for obtaining the homozygous diploid and multiploid by inducing the haploid is 45.86 to 49.73 percent, and the ratio of the homozygous diploid is 1.6 to 2.9 percent.
Owner:SHANDONG WEIFANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Technique for processing plant under low temperature by polygonum cuspidatum callus
InactiveCN106342685AConservation of Germplasm ResourcesExcellent Germplasm ResourcesDead plant preservationPlant tissue cultureGermplasmPOLYGONUM CUSPIDATUM
The invention discloses a technique for processing plant under low temperature by polygonum cuspidatum callus. A callus obtained by induction of a polygonum cuspidatum seed is used as a material, an in-vitro ultra-low temperature storage technique system of polygonum cuspidatum is set up, thus high-quality germplasm resource of polygonum cuspidatum is effectively protected. Through callus induction, pre-cultivation, loading, dehydration, cooling, washing, re-cultivation and regeneration, and other processes, the ultra-low temperature storage of the polygonum cuspidatum callus is realized; the technique can be used as a method for stably storing germplasm resources for a long term, so as to reduce the economic cost for storage, and effectively protect rare germplasm resources.
Owner:李志勇
Resistance identification method of sweet potato scab for stem tip vegetables
PendingCN112522359AIncreased risk of contaminationIncrease labor costMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseInoculation methods
The invention discloses a resistance identification method of sweet potato scab for stem tip vegetables, relates to the technical field of resistance identification of sweet potato scab, and specifically relates to the resistance identification method of sweet potato scab for stem tip vegetables. The method comprises the following steps: S1, preparing a sweet potato material to be identified; S2,preparing and activating pathogenic bacteria; S3, preparing a disease inoculum; S4, disease nursery induction and artificial inoculation; and S5, disease resistance evaluation: after the susceptible control variety Guangdong sweet potato No.5 is completely attacked, starting to investigate the attack situation, calculating the disease index, and carrying out resistance evaluation according to thedisease index. The invention provides the resistance identification method of sweet potato scab for stem tip vegetables. The method is reliable, stable in result, and suitable for identifying and evaluating the resistance of sweet potato scab, by combining disease nursery induction with a spore suspension artificial inoculation method, and utilizing a control variety with stable anti-infection phenotype.
Owner:CROP RES INST GUANGDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Hybridization breeding method for fructus jujubae trees
A jujube tree hybridization method, that is, by effectively isolating the entire plant or a branch group of the female parent tree, collecting pollen from the male parent tree at the best time after flowering to artificially pollinate the female parent tree, and collecting seed cores after the fruit matures , store, sow in spring to cultivate progeny jujube seedlings, retain the progeny jujube seedlings with cultural traits, and collect spike seedlings on plants with obvious outstanding and excellent cultural traits, and scions enter the excellent-line high-grain identification nursery for determination until they are obtained. Excellent variety. The method can effectively overcome the disadvantages of jujube crossbreeding such as difficulties and low operability, and realizes directional hybridization, which is beneficial to the accurate directionality of hybrid offspring, improves breeding progress, shortens breeding time, and improves breeding efficiency.
Owner:CANGZHOU ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
A kind of artificial domestication and cultivation method of lip carp
InactiveCN105028273BMaintain ecological balanceMaintain diversityClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaOrganismDrainage basin
The invention relates to a method for artificial domestication and cultivation of semilabeo notabilis. The method comprises the steps of 1, building a semilabeo notabilis cultivation pond; 2, collecting and selecting parent fish fry; 3, conducting food habit conversion; 4, conducting artificial domestication of fry; 5, observing gonad development; 6, conducting domestication management. By the adoption of the method, massive cultivation and population continuation of semilabeo notabilis are facilitated, native commercial fish aquaculture and new species are added, ecological balance of a water area is maintained, local native fish resources are protected, population quantity is increased, biodiversity and ecological balance are maintained, and conditions are provided for semilabeo notabilis cultivation and considerable economic benefits are obtained by means of the natural resources in the Dabang river drainage basin.
Owner:安顺汇成特色农业科技发展有限责任公司
Brassica napus embryo-specific promoter pbnaa09g21960d and its application
ActiveCN107099532BSpatiotemporal expression specificityImprove qualityVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsBrassicaAgricultural science
The invention discloses a cabbage-type rape embryo specific promoter pBnaA09g21960D and an application thereof. According to the invention, the promoter of a gene BnaA09g21960D is cloned from the cabbage-type rape, a plant expression vector DX2181-pBnaA09g21960D of a report gene GUS regulated and controlled by the promoter is constructed, an agrobacterium-mediated inflorescence dipping method is employed for conveying arabidopis thaliana, GUS histochemical method staining is carried out by the screened positive transgene lines, the result shows that pBnaA09g21960D has function for driving a downstream gene for specific expression in the embryo, and does not expression in other tissue organs. The promoter has good application potential for enhancement of the crop quality by the rape transgene and artificial creation of germplasm resource.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
The method of breeding a variety of colorful double-tailed goldfish by distant hybridization
ActiveCN110915727BBeautiful weightFast growthClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaYolkAnimal science
The invention discloses a method for breeding a variety of colored two-tailed goldfish through distant hybridization. The Hunan Army crucian carp was obtained, and the male and female Hunan Army crucian carp were selected for cultivation in special ponds. Artificial induced labor, artificial dry insemination, and running water incubation were carried out until the self-bred offspring of the male and female Hunan Army crucian carp were pointing to the waist, and the yolk disappeared. Artificial intensive breeding, from which the homodiploid Hunan army goldfish with red pattern on white background, double tail forked, and high back was screened out. Strong reverse ability, strong fecundity and other advantages. Then hybridize Xiangjun goldfish with other goldfish in nature to breed a variety of beautiful double-tailed goldfish with different colors and colors. These double-tailed goldfish have obvious hybrid advantages and have very high sperm production and egg production It plays a very important role in the improvement of other goldfish.
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Brassica napus promoter pbnunng0942890 and its application
ActiveCN109439663BImprove qualityGreat application potentialPlant peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyStaining
The invention discloses a brassica napus promoter pBnUnng0942890 and its application. The promoter of the gene BnUnng0942890 is cloned from Brassica napus, and a plant expression vector of the reporter gene GUS regulated by the promoter is constructed. The inflorescence dipping method was used to transform Arabidopsis thaliana, and GUS histochemical staining was performed on the screened positive transgenic lines. The results showed that pBnUnng0942890 had the dominant expression of downstream genes in roots, flowers and seeds, but no expression or low expression in other tissues and organs. expressive function. The promoter has good application potential in improving crop quality through transgenic rape and artificially creating germplasm resources.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Molecular Marker and Application of Genic Sterile Gene of Monosomy Addition Line in Maize
ActiveCN104946644BNo effect on growth and developmentRich genetic baseMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationAgricultural scienceNucleotide
The invention discloses a molecular marker of a maize trichomonad additional line nuclear sterility gene belonging to the field of crop molecular markers. The molecular marker consists of the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID No:1. The present invention also discloses a pair of SCAR primers composed of SEQ ID No: 2 and SEQ ID No: 3 for amplifying the above-mentioned molecular markers. In addition, the invention also discloses a method for backcrossing and recurrent selection breeding using the above-mentioned molecular markers. The molecular marker of the present invention is not limited by time and environmental conditions, and can identify and screen the genital sterility gene of the monosomy addition line of maize at the seedling stage, which is easy to select and eliminate, saves a lot of manpower and material resources, and improves the breeding efficiency , shorten the breeding process and time, and significantly reduce the breeding cost; in addition, the invention can also be used as a tool for large-scale recurrent selection of corn, continuously expanding the genetic basis of corn, and is conducive to the selection of breakthrough corn varieties.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
A method for creating a homozygous breeding material of head cabbage without wax powder and bright leaves
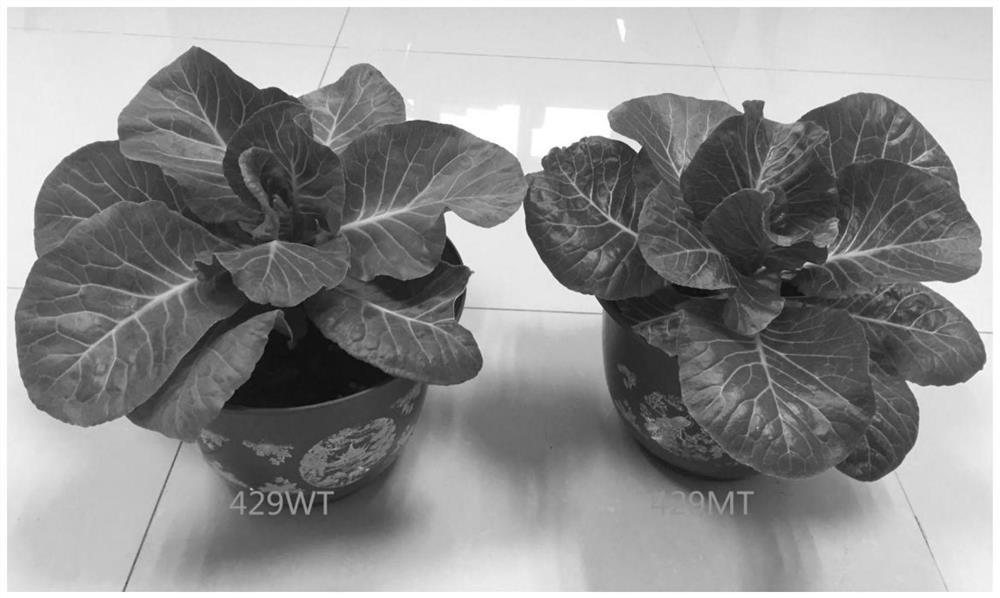
ActiveCN108401893BExcellent agronomic traitsResistant to boltingPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsBiotechnologySporeling
The invention discloses a production method of a homozygous material for the breeding of a common head cabbage with wax-free bright leaves. The method comprises following steps: taking a common head cabbage mutant material (429MT) having a wax-free bright leaf single gene (a recessive inheritance gene) as the female parent and a wax containing excellent homozygous common head cabbage material as the male parent to carry out hybridization to obtain first generation F1; making F1 carry out selfing to obtain F2; choosing excellent strains with a wax-free bright leaf character from F2 generation as seeds; and carrying out free spore cultivation in next spring during the blossoming period to obtain a homozygous double haploid wax-free bright leaf material. The application of the wax-free brightleft mutant material is promoted; the production of the novel wax-free bright leaf breeding material is accelerated, and the cultivation process of high quality common head cabbage is shortened.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
A single-cell oil-producing cryptococcus and a method for producing oil by culturing crude glycerol
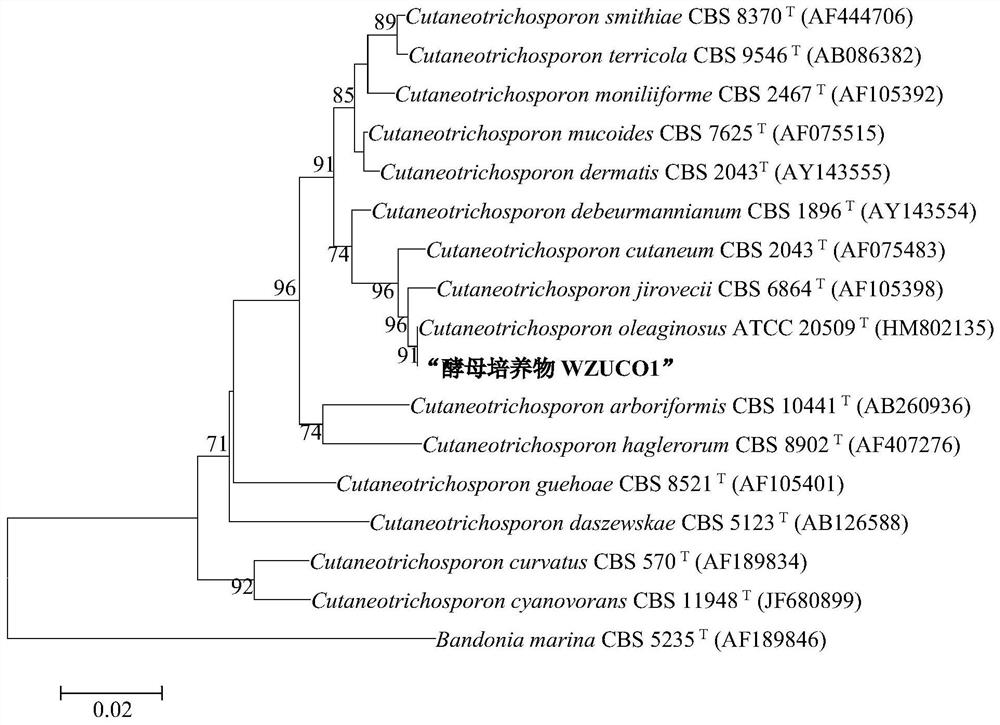
ActiveCN107988104BExcellent Germplasm ResourcesGreat application potentialBacteriaBiofuelsBiodieselGlycerol
The invention discloses a single-cell oil-producing cryptococcus and a method for cultivating the single-cell oil-producing cryptococcus with crude glycerol, a by-product of biodiesel. The bacterial strain is Cryptococcus curvatus (Cryptococcus curvatus) WZUC01, which is preserved in the General Microbiology Center of China Microbiological Culture Collection Management Committee, and the registration number of the preservation center is CGMCC NO.8096. The strain has high oil content and the main fatty acids are palmitic acid, stearic acid and oleic acid, and its fatty acid composition is suitable for biodiesel production. The fed-batch culture method was used to culture Cryptococcus curvatus WZUC01 with the pretreated biodiesel by-product crude glycerol. After 160 hours of culture, the biomass and oil production reached 81.37±2.01g / L and 66.89±3.15g / L, respectively, which has a great effect. potential for practical application.
Owner:WENZHOU UNIV
Non-test-tube rapid propagation method of Cyclocarya paliurus
InactiveCN105010136BIncrease productionConsensus germplasm lineCultivating equipmentsHorticulture methodsPlant tissueGreenhouse
The invention discloses a cyclocarya paliurus non-tube rapid propagation method. According to the cyclocarya paliurus non-tube rapid propagation method, plant tissue culturing principles are adopted, pruning and sprouting promotion of seedlings of cyclocarya paliurus maternal plant plantations are carried out, light matrix non-woven fabric nutritional bags are used, rooting hormone is applied, bactericidal treatment is carried out, all sunlight intelligent breeding greenhouses are adopted, batch-type mist spray is controlled accurately, so that seedling period of cyclocarya paliurus is shortened, seedling surviving rate and yield of cyclocarya paliurus are increased, problems that formation of callus tissue is inhibited because cyclocarya paliurus is high in tannin content, and cottage processing ratio is low are solved, and a problem that cyclocarya paliurus genetic resources are scarce is solved effectively.
Owner:LUEYANG COUNTY JINXIU AGRI DEV CO LTD
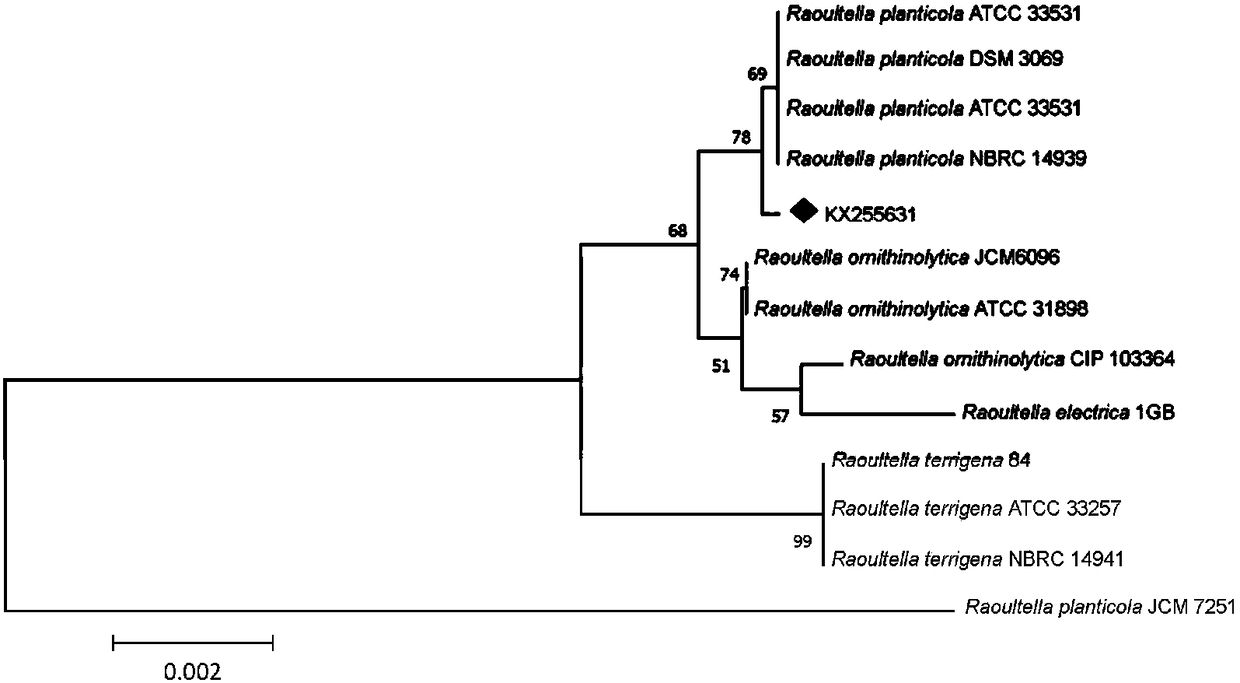
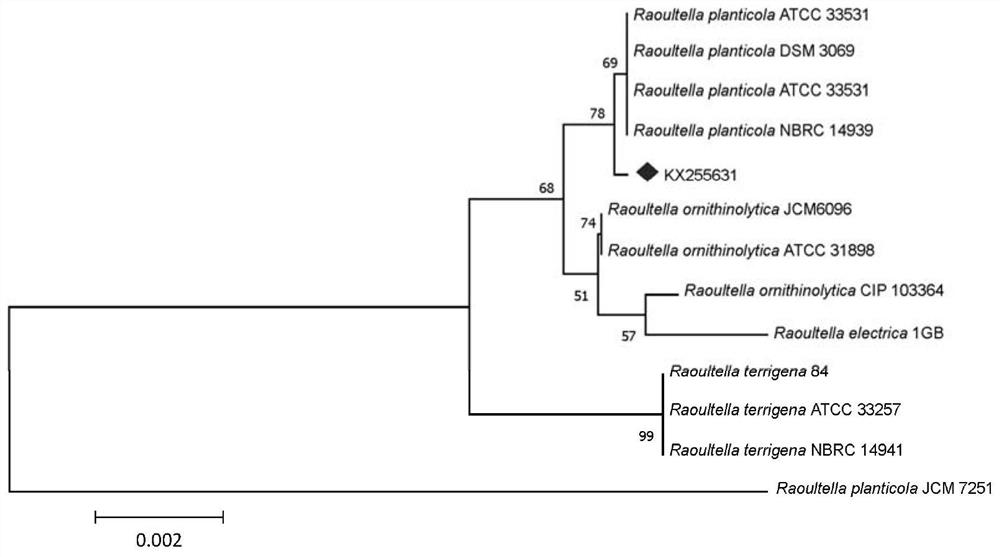
Raoultella sp. and application thereof in pyrene-Cr(VI) composite pollution co-detoxication
ActiveCN108546666AExcellent Germplasm ResourcesWide adaptability to the environmentBacteriaWater contaminantsBiologyPyrene
The invention provides Raoultella sp. and application thereof in pyrene-Cr(VI) composite pollution co-detoxication in a tolerant environment. Concretely, the Raoultella sp. has the effect of degradingpyrene and reducing Cr(VI) in the tolerant environment.
Owner:WENZHOU UNIVERSITY
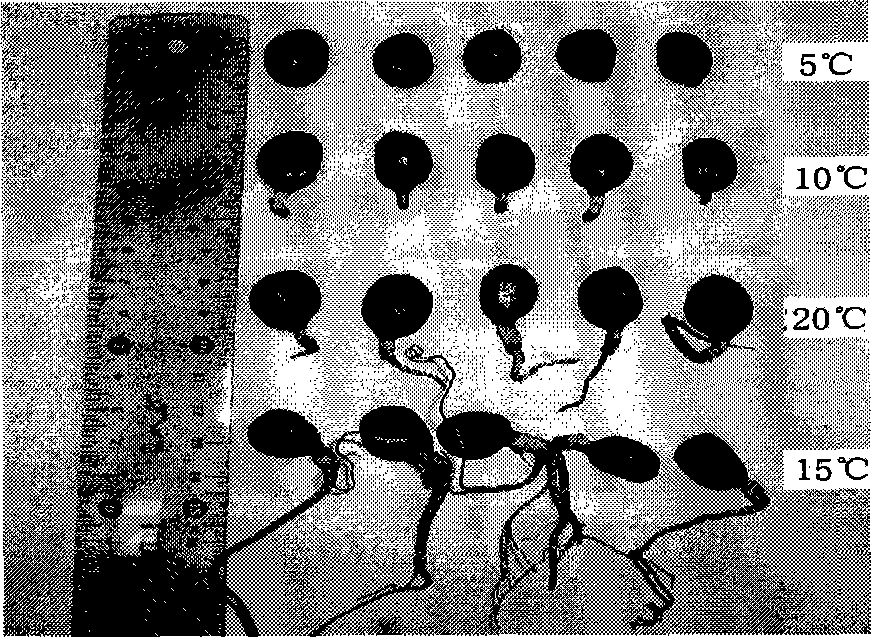
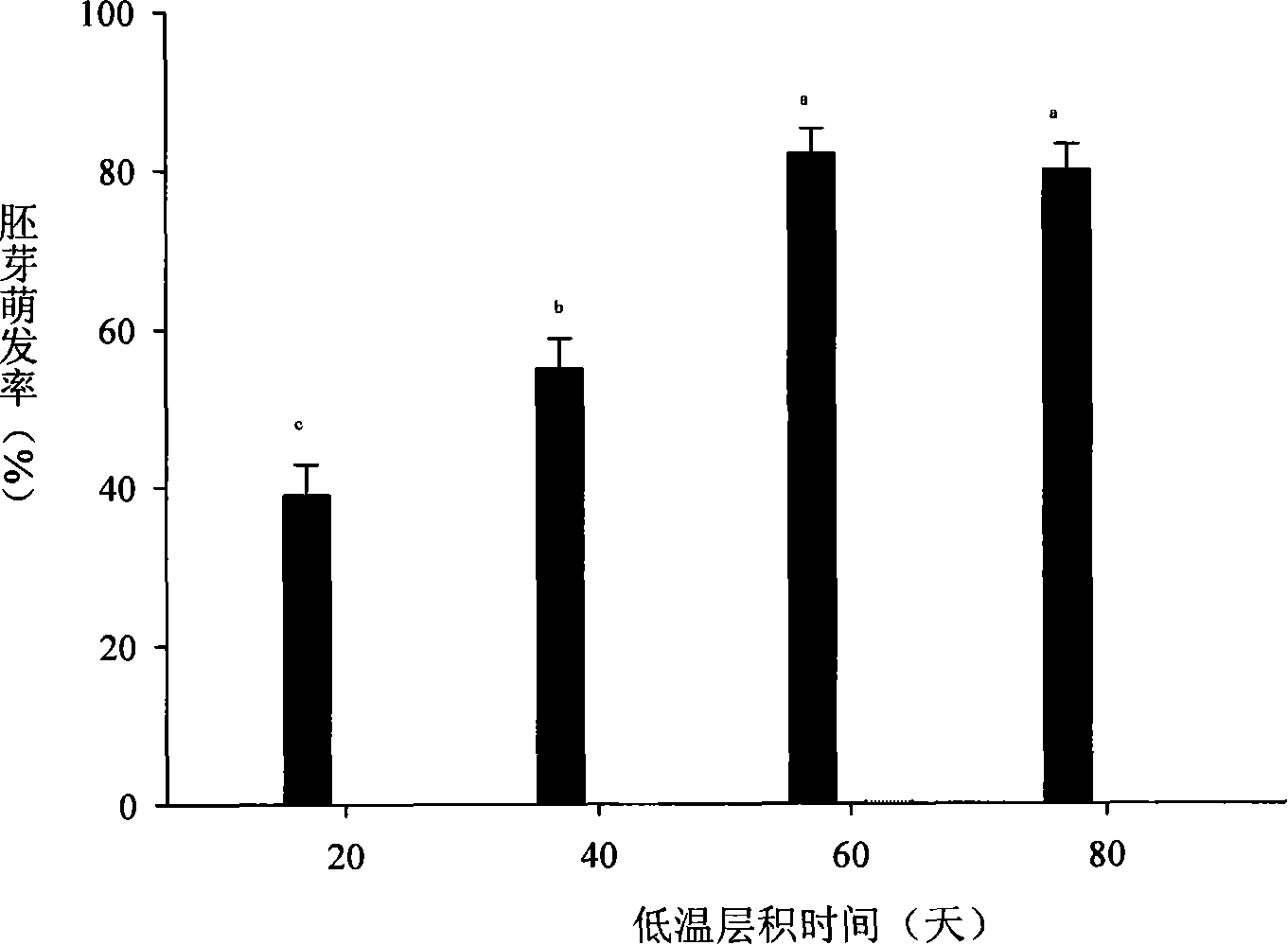
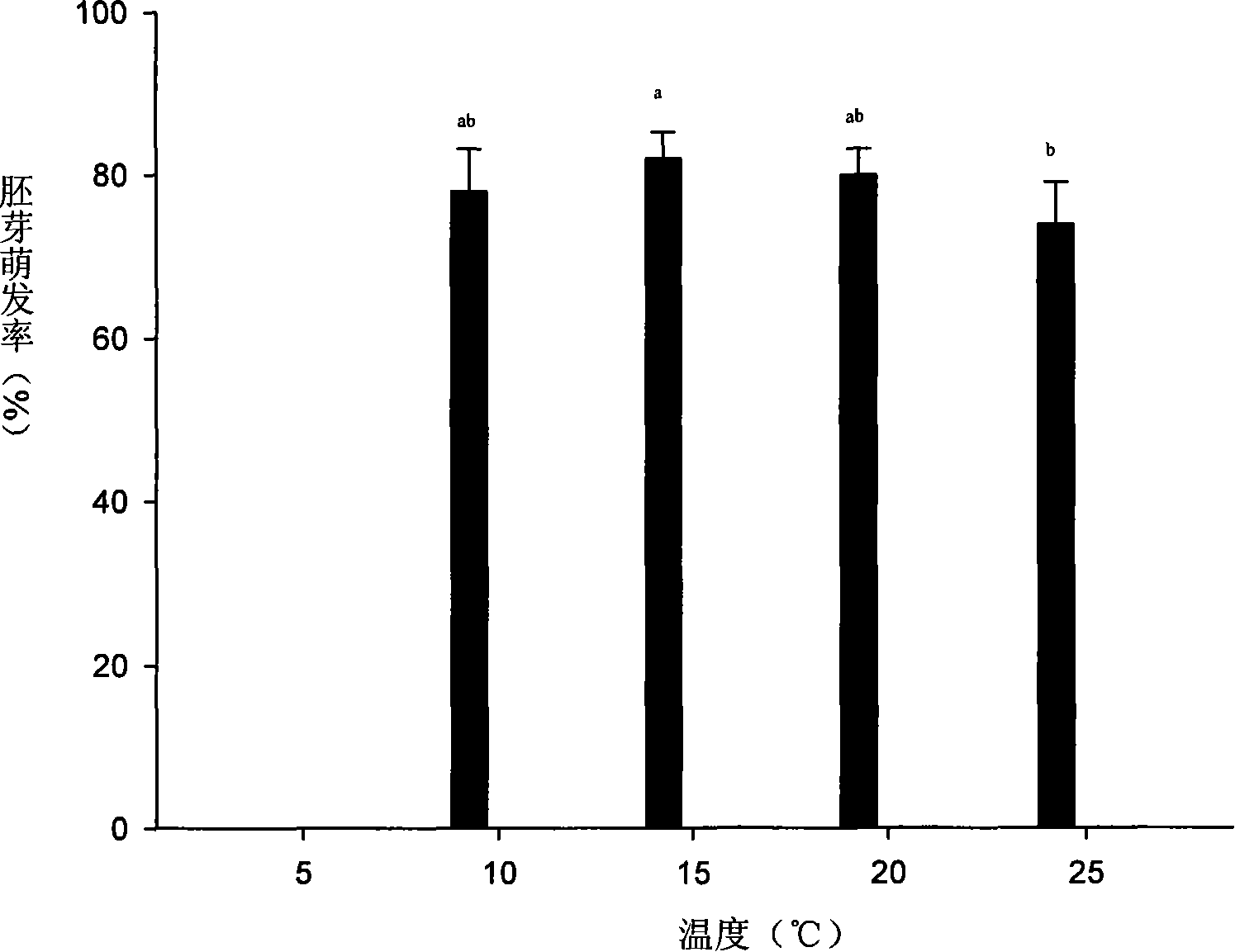
Method for promoting germination of Paeonia ludlowii seed
InactiveCN101288360BGuaranteed MaturityQuality assuranceSeed immunisationGerminating apparatusPaeonia ludlowiiSeedling
The invention discloses a method for promoting germination of seeds of Paeonia ludlowii. The method for promoting germination of seeds of Paeonia ludlowii provided in the invention includes the following steps: the seeds of Paeonia ludlowii are laminated under the condition of 15 DEG C, after the length of the radicel thereof is longer than 6cm, the seeds are laminated under the condition of 5 DEG C for 60-80 days, then the germinated seeds are obtained. The method overcomes the defects that the germination time is long, the germination rate is low and the emergence of seedlings is irregular.The method of the invention can allow the emergency rate to rise to more than 70% and the germination time to be shortened by one year. The method has the advantages of fast propagation rate, short cycle and high emergency rate.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A strain of Raoultia and its application in co-detoxification of pyrene-cr(vi) compound pollution
ActiveCN108546666BExcellent Germplasm ResourcesWide adaptability to the environmentBacteriaWater contaminantsEnvironmental engineeringRaoultella electrica
Owner:WENZHOU UNIVERSITY
A kind of breeding method of high temperature resistant sea cucumber strain
ActiveCN106259067BMeet the characteristics of patienceImprove selection efficiencyClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaSexual maturityZoology
Owner:山东省海洋资源与环境研究院
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com