Molecular marker for corn tripsacum monosome addition line nucleic male sterility genes and application thereof
A molecular marker, additional line technology, applied in application, plant genetic improvement, microbial assay/inspection, etc., can solve problems such as limited application, incomplete pollen abortion, and no discovery.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0076] Example 1 Screening Test of Molecular Markers of Monosomy Addition Line GMS Gene in Maize
[0077] Proceed as follows:
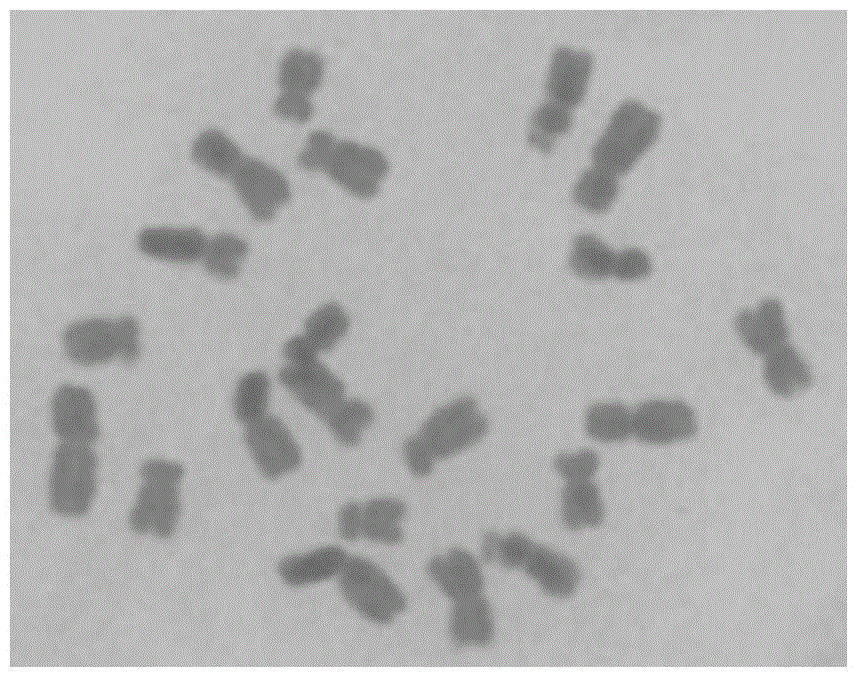
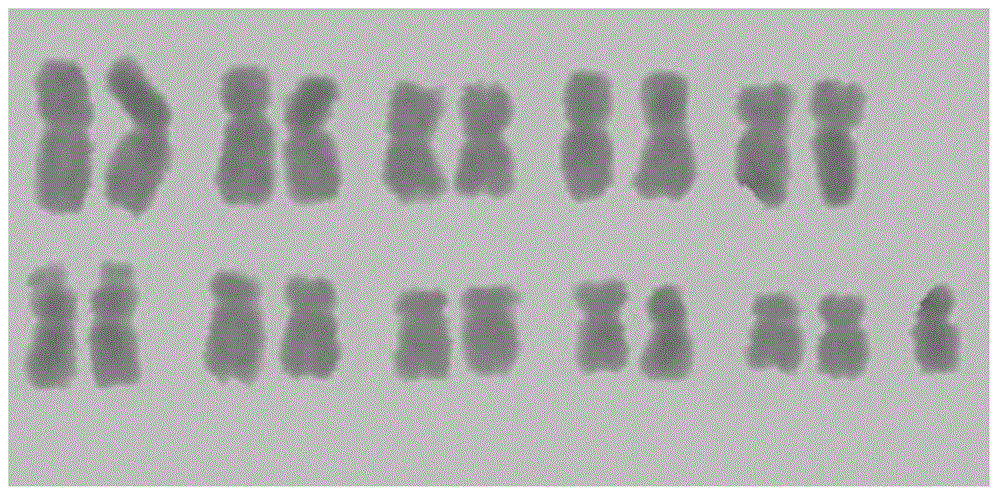
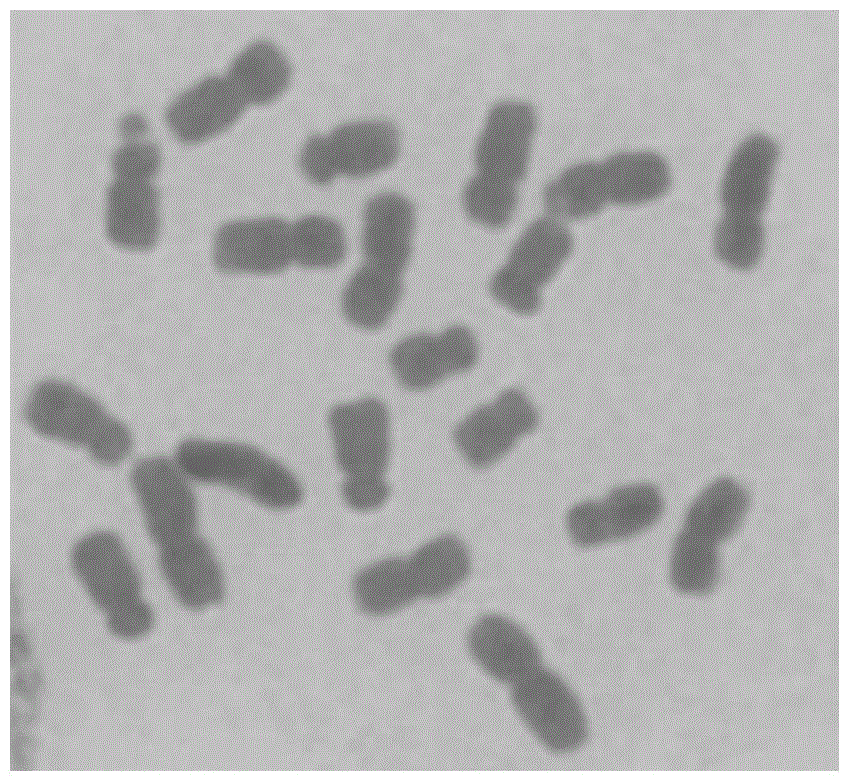
[0078] (1) In late March, 2012, at the Chengdu Campus of Sichuan Agricultural University, 10 seeds of Tripscaum and 50 seeds of Tripscaum monomer addition line 220B introduced from the US USDA were planted in germination boxes. The substrate is coarse river sand, placed in an artificial climate box with a temperature of 28°C and a humidity of 70% for germination. When the plants grow to three leaves and one heart, they are transplanted into plastic flower pots with a diameter of 30 cm and a height of 25 cm.
[0079] (2) When the corn friction grain additional line 220B plant is as high as 30cm, cut off the root tip of about 0.5cm at 10:00-14:00 at noon on a sunny day and when the temperature is higher than 25°C, and use saturated α-bromine Naphthalene aqueous solution was pretreated in the dark for 2 hours, and the pretreated root tips were hypotonic...
Embodiment 2
[0088]Example 2 Verification test of the molecular marker of the GMS gene in the monosomy addition line of maize friction grain
[0089] Proceed as follows:
[0090] In late March 2013, at the Chengdu Campus of Sichuan Agricultural University, the corn friction grain addition line (abbreviation: monomer addition line) MTchr2 (which was deposited in the China Microbiological Culture Collection Management Committee on July 18, 2014) was planted. Center, the preservation number is: CGMCC No.9552) 50 seeds (including monosomy addition seeds with 21 chromosomes and ordinary seeds with 20 chromosomes), when the plants grow to 5 to 6 leaves, single plants are listed. Genomic DNA of leaves was extracted, and PCR amplification was carried out using Mst1-F and Mst1-R as primers, and the specific method was the same as step (7) of Example 1. At the same time, the male fertility of the plants was identified during the flowering and pollination stage. Results The sterile strains (2n=20+1...
Embodiment 3
[0091] Example 3 Experiment of using the SCAR marker of the GMS gene of the monosomy addition line of maize to breed the male sterile line of maize
[0092] (1) Test materials:
[0093] (1), Maize Friction Grass monomer addition line (Zea mays) MTchr2 (preserved in the General Microbiology Center of China Microbiological Culture Collection Management Committee on July 18, 2014, and the preservation number is: CGMCC No.9552)
[0094] (2) Maize inbred lines: B73, Zheng 58, Chang 7-2 (all provided by the Maize Institute of Sichuan Agricultural University).
[0095] (2) Test site:
[0096] Chengdu Campus of Sichuan Agricultural University and Xishuangbanna Experimental Base of Corn Research Institute of Sichuan Agricultural University
[0097] (3) Test method
[0098] (1) In late March 2013, at the Chengdu Campus of Sichuan Agricultural University, the additional line MTchr2 of corn friction grain monomer was obtained (it was deposited in the General Microorganism Center of Chi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com