Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
32results about How to "Ensure mutual insulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
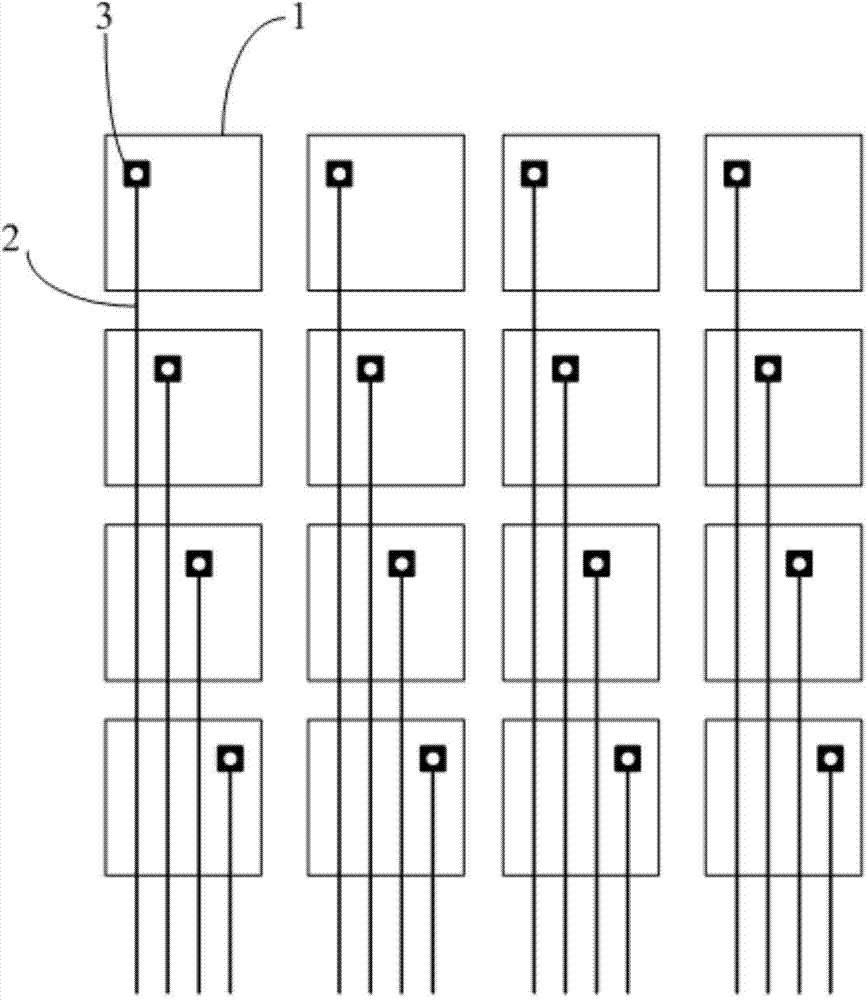
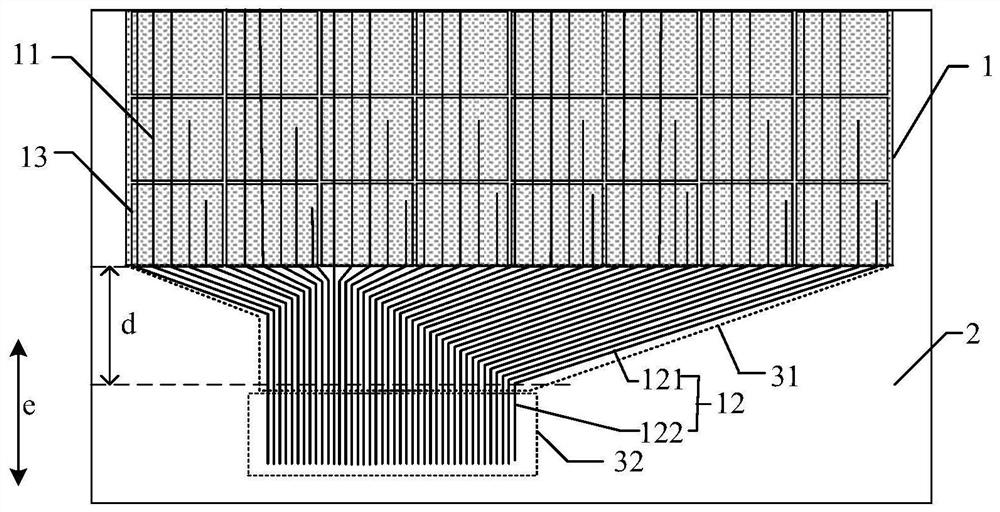
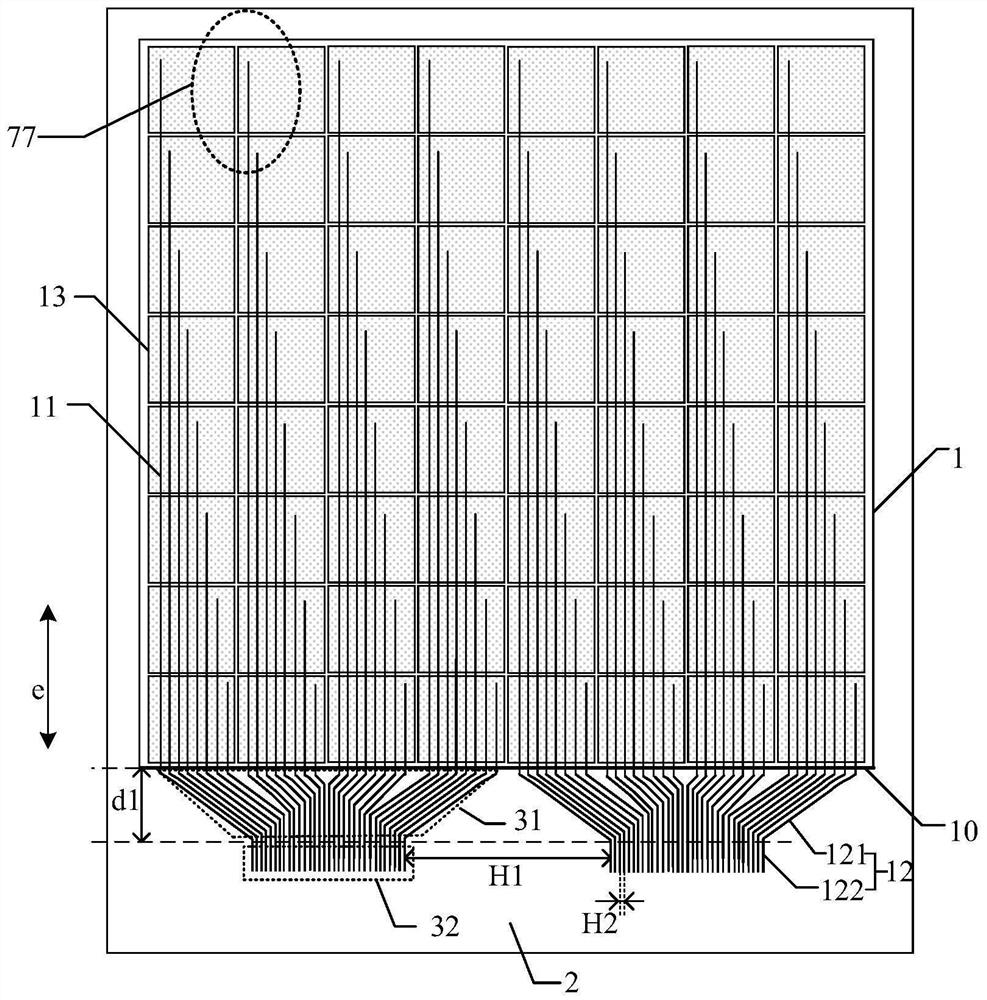
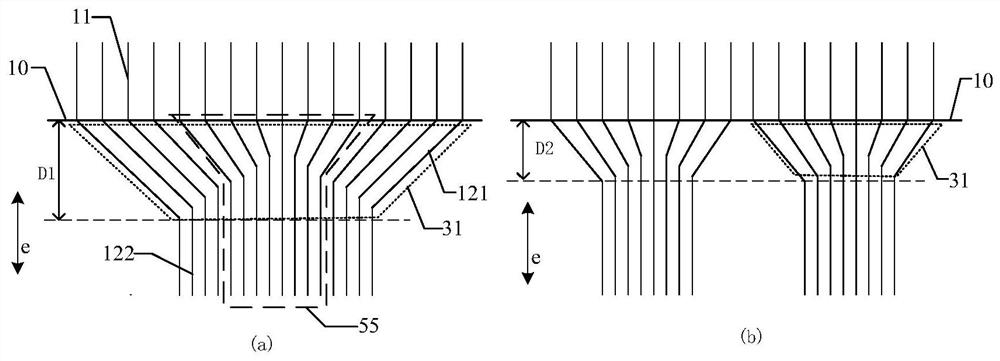
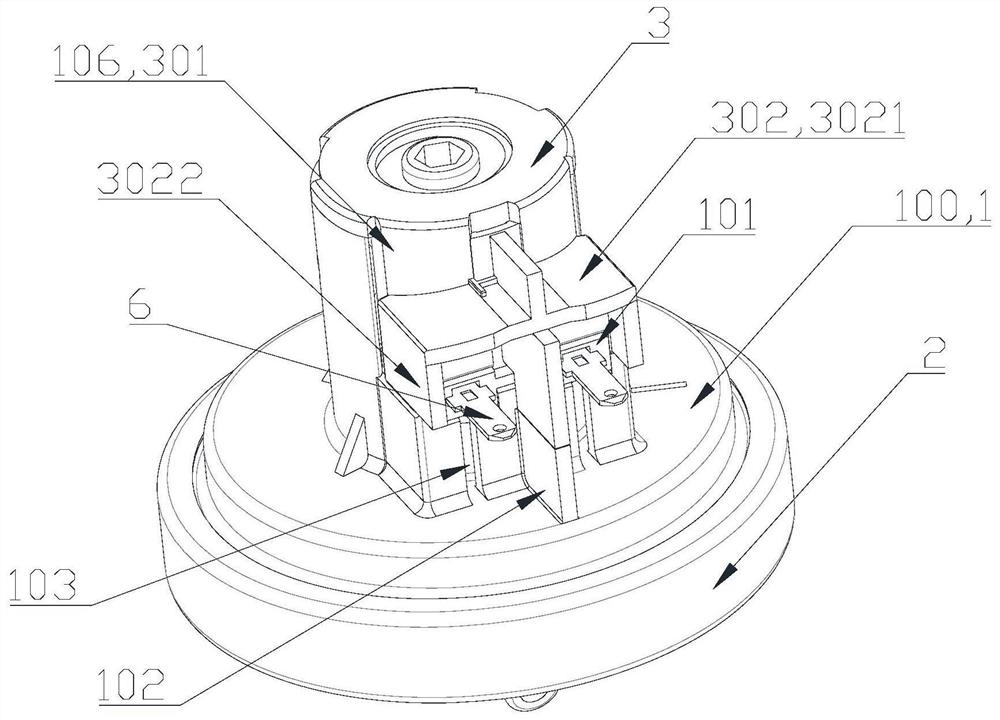
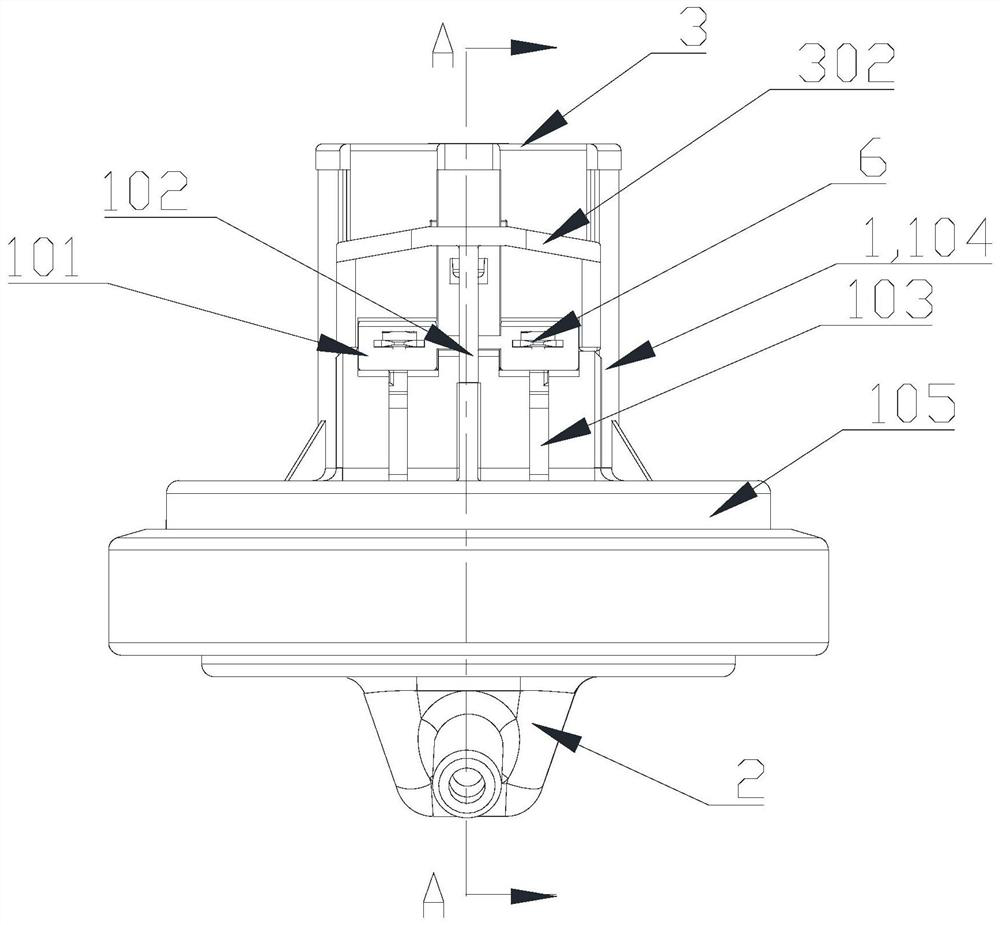
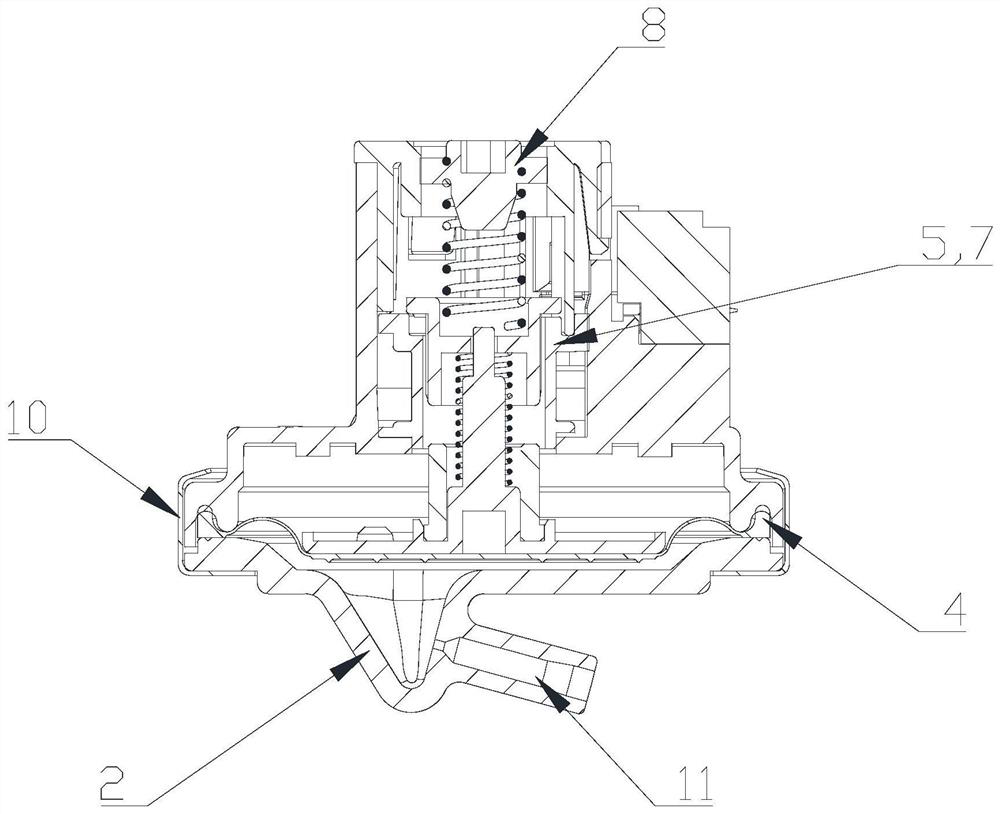
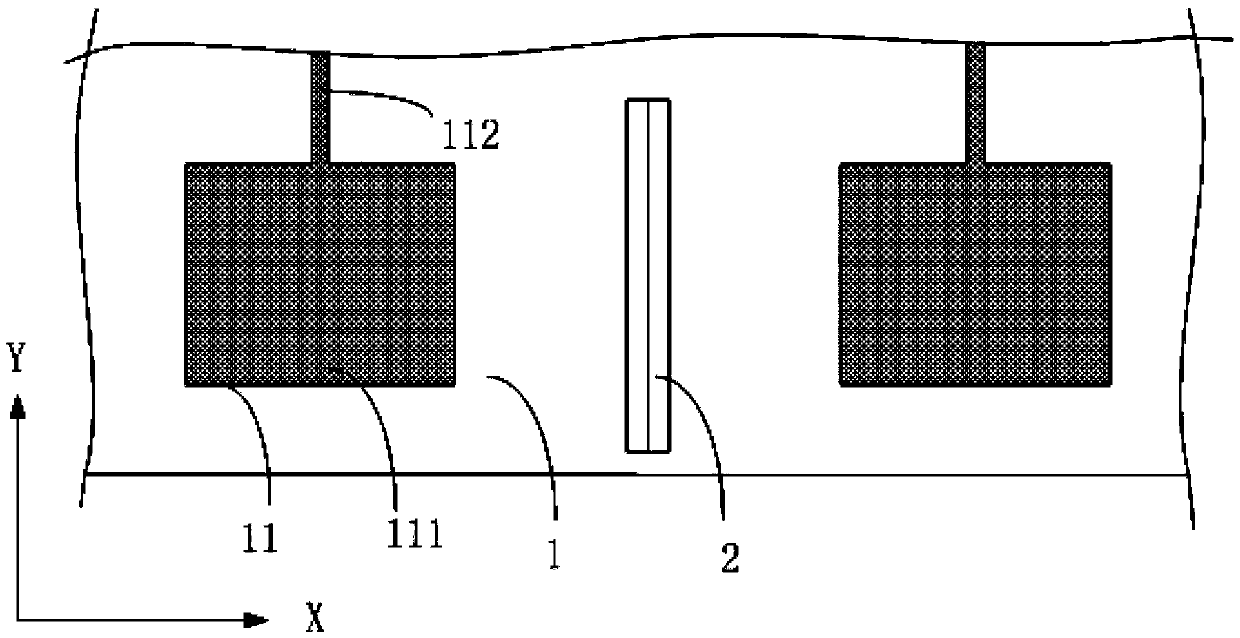
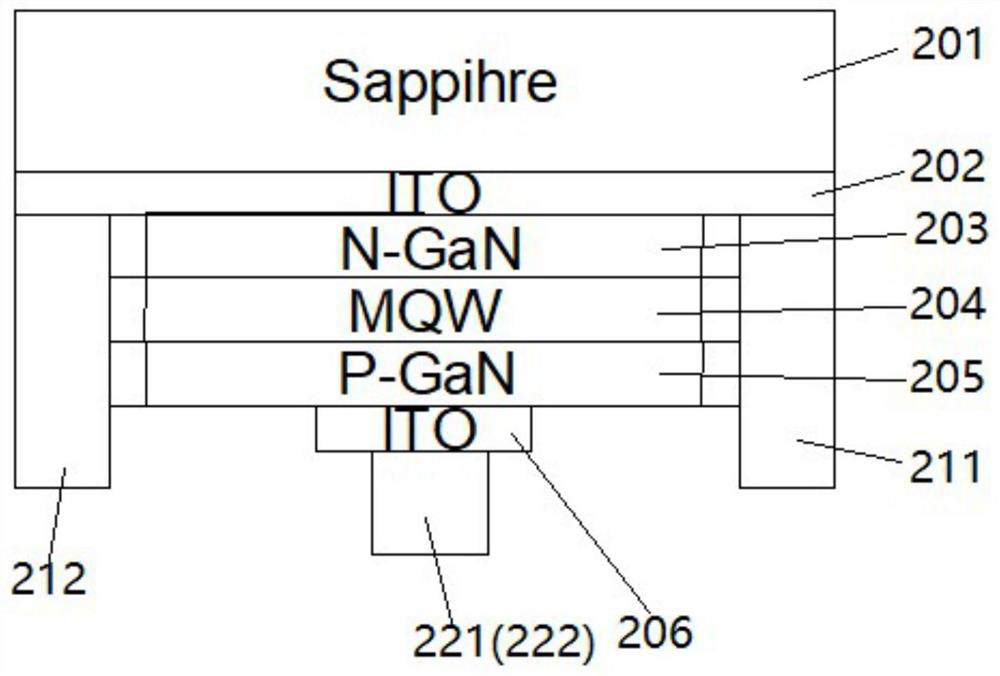
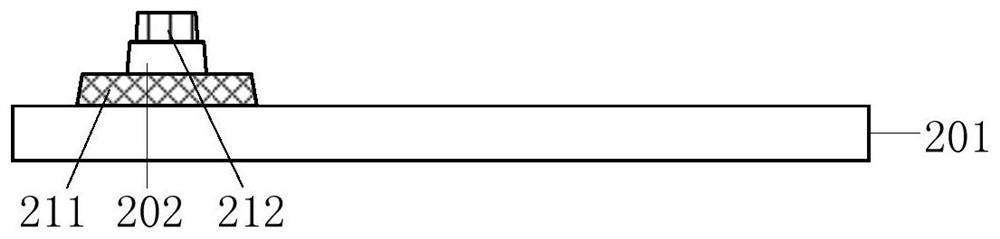
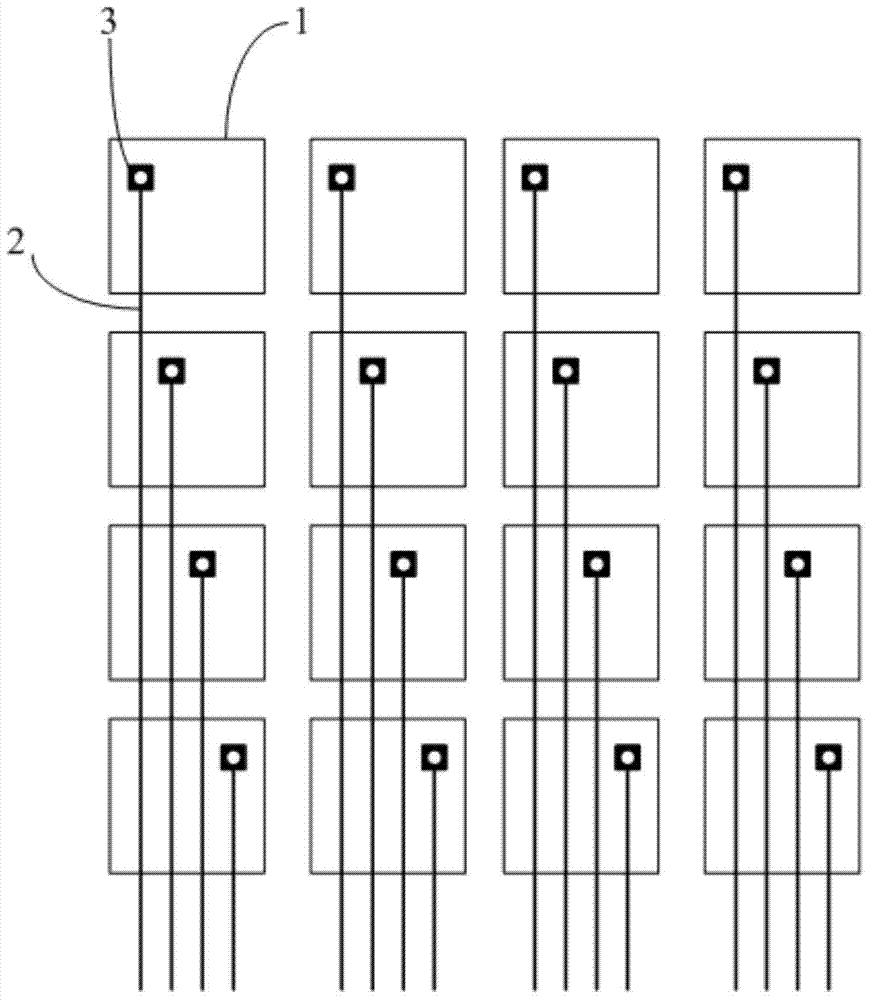
Embedded touch screen and display device
ActiveCN104503650AEnsure mutual insulationGuaranteed insulation performanceNon-linear opticsInput/output processes for data processingCapacitanceDisplay device
The invention discloses an embedded touch screen and a display device. The embedded touch screen comprises multiple connection wire groups arranged on a layer different from a layer where self capacitance electrodes are located besides guide wires and the self capacitance electrodes, wherein each connection wire group comprises multiple segments of sub connection wires arranged at intervals, each sub connection wire of each connection wire group is corresponding to each self capacitance electrode, each sub connection wire and each self capacitance electrode corresponding to each sub connection wire are connected through at least one via hole which runs through an insulating layer, no via hole is formed in an overlapped area of each guide wire and each self capacitance electrode, and each guide wire is connected with the corresponding self capacitance electrode through at least one sub connection wire connected with the corresponding self capacitance electrode of each guide wire. The embedded touch screen guarantees that the via holes are evenly distributed by evenly forming the via holes in the areas of the embedded touch screen, corresponding to all the sub connection wires. Accordingly, the embedded touch screen can solve the problem that display frames are not even, caused by uneven distribution of via holes in an insulating layer in the prior art.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Wound battery cell and preparation method thereof, battery and electronic product
ActiveCN111554982AAvoid displacementReliable coverageFinal product manufactureLi-accumulatorsMetallic lithiumPhysical chemistry
The invention provides a wound battery cell and a preparation method thereof, a battery and an electronic product. The wound battery cell comprises a positive plate, a negative plate and an insulatingdiaphragm located between the positive plate and the negative plate, wherein the negative plate comprises a negative substrate layer, a negative coating and a negative tab arranged on the surface ofthe negative substrate layer, the negative coating covers the surface of the negative substrate layer, the negative coating is provided with a tab connecting area avoiding the negative tab, and the negative tab is located in the tab connecting area; the insulating diaphragm between the tab connecting area and the positive plate is provided with a barrier layer covering the tab connecting area, andthe barrier layer is used for preventing lithium ions from passing through, so that metal lithium can be prevented from being separated out and attached to a coating-free area near the negative tab in the quick charging process of the battery, and the safety risk caused by lithium separation of the lithium ion battery in the quick charging process is reduced.
Owner:ZHUHAI COSMX BATTERY CO LTD
Device for tensile test of metal material under function of current
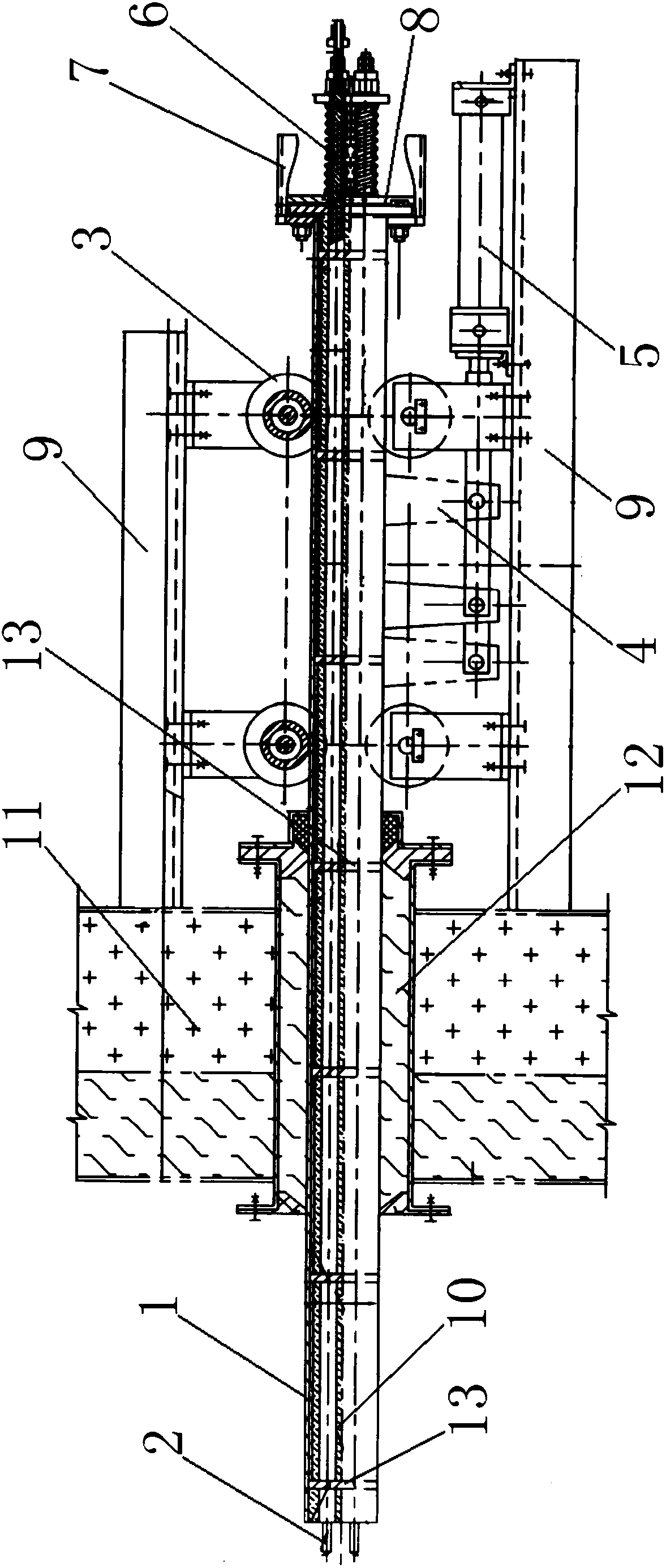
The invention relates to the technical field of mechanical property testing devices, and particularly relates to a device for a tensile test of a metal material under the function of current. The device comprises a fixture and a tensile sample, wherein the fixture comprises a clamping seat, an insulating ceramic bar, an insulating upper padding plate and an insulating lower padding plate, one end of the clamping seat is provided with a U-shaped groove, the insulating upper padding plate, the tensile sample and the insulating lower padding plate are sequentially arranged in the U-shaped groove from top to bottom, and the insulating ceramic bar penetrates through the clamping seat, the insulating upper padding plate, the tensile sample and the insulating lower padding plate. By adopting the structure, the fixture of a tensile testing machine is not needed to be modified, the mechanical property of the metal material under the function of current can be measured through the tensile test by only clamping the fixture onto the tensile testing machine and utilizing the tensile sample provided by the invention, and meanwhile, the fixture can ensure that the tensile sample is insulated from tensile equipment.
Owner:HAIAN GASOLINEEUM SCI RES INSTR
Device and method for constant-pressure electromagnetic forming of metal plate under action of heterodromous currents
The invention provides a device for constant-pressure electromagnetic forming of a metal plate under the action of heterodromous currents. The device comprises a u-shaped mold, and further comprises acapacitance power module, a magnet supply branch and two vertical side pressing plates. The capacitance power module comprises an energy storage capacitor. The magnet supply branch comprises a constant-pressure coil and is connected to the two ends of the capacitance power module. The upper ends of the side pressing plates are bent oppositely and extend to form closed plates, and therefore a containing cavity with an opening being downward is formed between the two side pressing plates and below the two closed plates. The constant-pressure coil is fixedly arranged in the containing cavity. During use, a power supply branch is formed by the two closed plates, the two side pressing plates and the to-be-formed metal plate; the power supply branch and the magnet supply branch are connected inparallel and are connected to the two ends of the capacitance power module by taking the free ends of the two closed plates as the electric access points. When the energy storage capacitor carries out discharge, discharge currents opposite in direction are formed in the constant-pressure coil and the power supply branch. According to the device, the magnitude of the currents on the formed plate is enhanced, the stress balance performance of the constant-pressure coil is improved, and processing capacity is improved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Y63-series special-type electric connector for high-speed rails
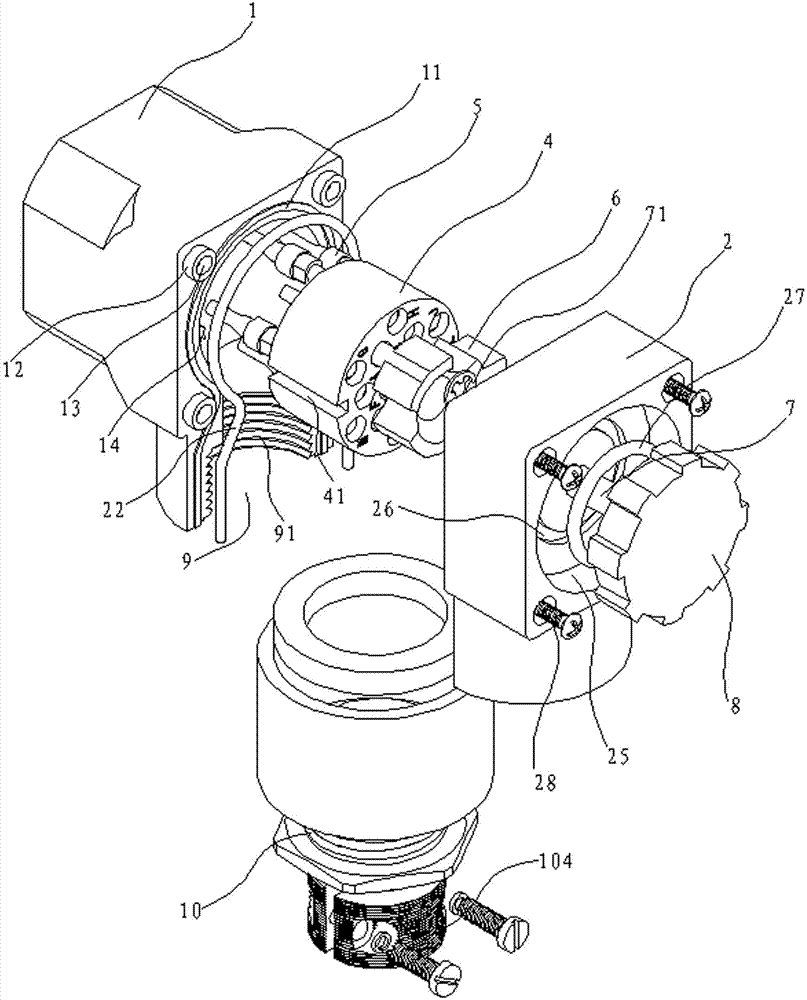
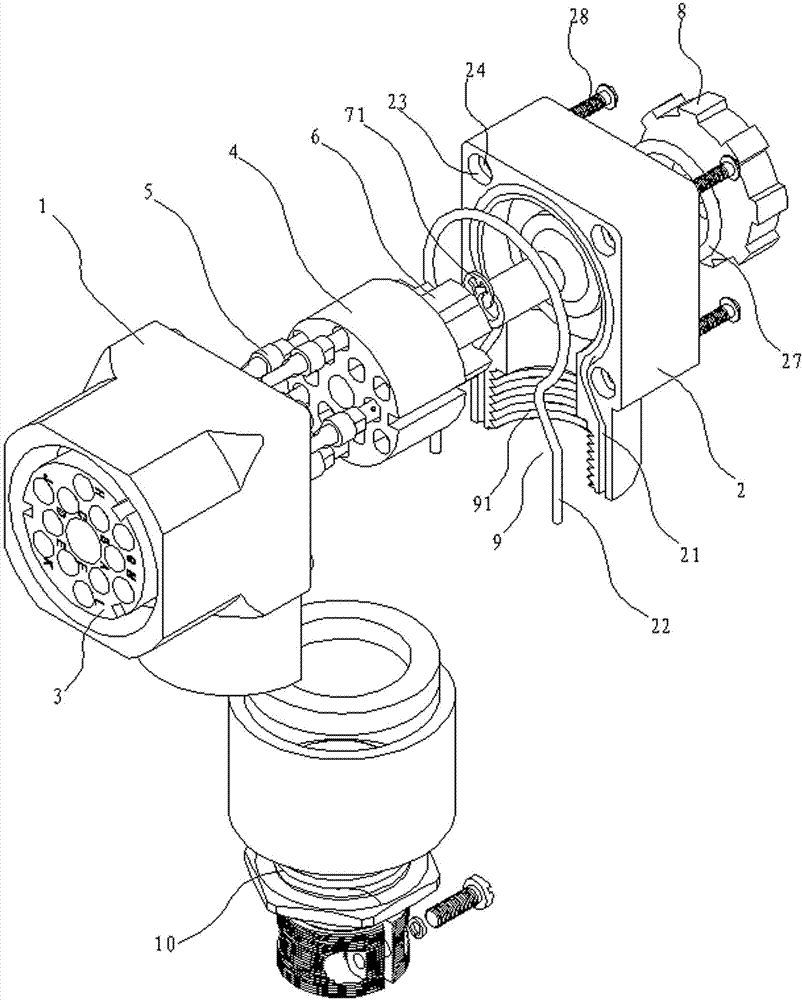
ActiveCN102231457AAvoid positional tolerancesImprove sealingRelieving strain on wire connectionSecuring/insulating coupling contact membersElectricityControl system
The invention relates to an Y63-series special-type electric connector for high-speed rails, comprising a shell, an insulator and circular contact elements. The shell comprises a front shell and a back shell, the insulator comprises a front insulator and a back insulator, the front insulator is arranged in the front shell, more than one circular contact element is connected to the back insulator,and the back shell presses out the back insulator between the front shell and the back shell so that the part of more than one circular contact element, which is over the back insulator, is arranged in the front insulator. The front shell and the back shell are connected in series with the front insulator and the back insulator by central screw assemblies to form an electric connecting line with a vertical outside-line opening, and the circular contact elements with hermaphroditic structures, which are inserted on the back insulator, are matched, thus the electric connector has the advantagesof simple and compact structure, stability and firmness in connection, good sealing performance, high switched-on power performance and high safety, and is suitable for train control system responderunits of high-speed rails, underground railways and the like.
Owner:CHINA NORTH IND GRP HANGLIAN TECH CO LTD
Voltage-sharing shielding ring hyper-frequency signal lead-out device in basin-type insulator
ActiveCN103399179AAvoid low sensitivitySimple structureMeasurement instrument housingVIT signalsElectricity
The invention provides a voltage-sharing shielding ring hyper-frequency signal lead-out device in a basin-type insulator, which is used for leading out a hyper-frequency signal of a GIS (Gas Insulated Switchgear). The device comprises a conductive lead-out rod arranged inside a bolt mounting hole of the basin-type insulator to be electrically connected with a voltage-sharing shielding ring, insulated fixed sleeves sleeving on the outer side of the conductive lead-out rod to insulate the conductive lead-out rod from an outer casing and insulate the conductive lead-out rod from an outer conductor of a monitoring device, and metal conductive bands arranged on the outer surface of the insulated fixed sleeves and capable of being electrically connected with the outer casing. The invention is used in the fields of partial discharge monitoring and fault diagnosis, avoids the phenomena that the sensitivity of an external sensor of the GIS is poor and an internal sensor of the GIS affects the insulativity, and provides the signal lead-out device; the structures of all the components of the device are simpler, the assembly of the components and the operation of integrally mounting with the GIS are comparatively convenient and fast, and the purpose that the GIS is monitored more precisely, conveniently and quickly can be achieved.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
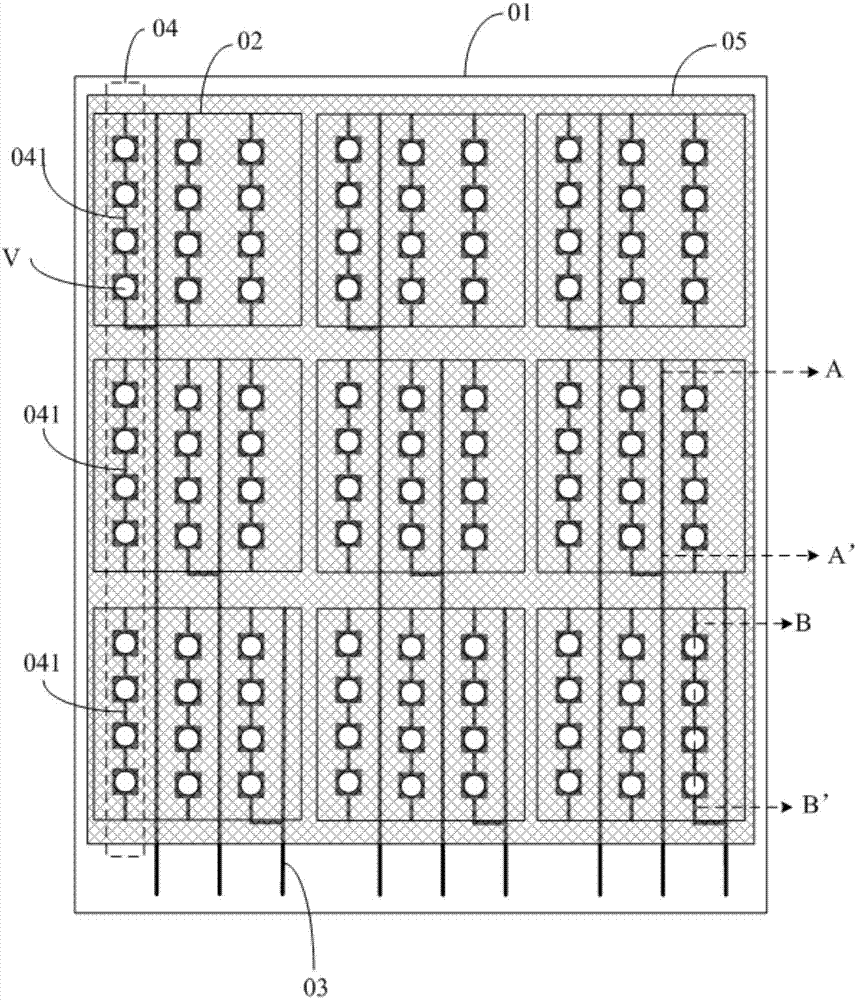
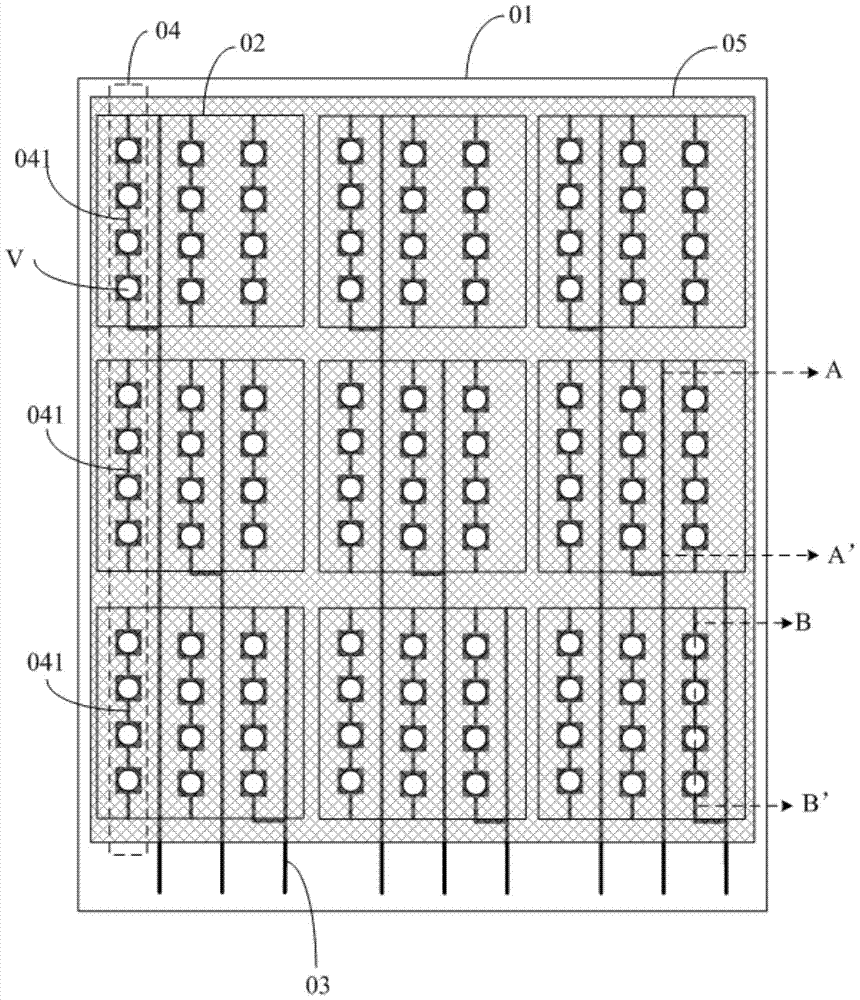
Pressure-sensitive sensor, touch feedback device and related device
ActiveCN105808009ASimple structureEnsure mutual insulationInput/output processes for data processingEngineeringPressure - action
The invention discloses a pressure-sensitive sensor, a touch feedback device and a related device. The pressure-sensitive sensor comprises a first base plate, a second base plate, frame sealing glue, a public electrode, pressure-sensitive detection electrodes and a pressure-sensitive detection circuit; the frame sealing glue seals and supports the first base plate and the second base plate, and it can be guaranteed that the pressure-sensitive detection electrodes are insulating with the public electrode when no pressure action exists; the pressure-sensitive detection electrodes are in contact with the public electrode only when the first base plate and / or the second base plate are / is under pressure, so that it is guaranteed that the pressure-sensitive detection electrodes generate voltage only when the base plates are under pressure, therefore it is guaranteed that the pressure-sensitive detection circuit judges the touch position by detecting voltage values on all the pressure-sensitive detection electrodes, and the pressure-sensitive sensor is simple in structure.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
Metal insulation chip test needle frame
InactiveCN102520216AEnsure mutual insulationGuaranteed reactanceElectrical measurement instrument detailsElectrical testingElectricityMetallic aluminum
A metal insulation chip test needle frame relates to chip test equipment in a semiconductor and electronic connector industry. The needle frame comprises: a probe / chip location plate which is made of a metal material, a needle frame body, a probe maintenance plate and spring probes inserted into the probe maintenance plate, wherein the probe / chip location plate which is made of a metal material, the needle frame body, the probe maintenance plate and the spring probes inserted into the probe maintenance plate are mutually connected. An inner wall and a side surface which are formed by the probe / chip location plate, the needle frame body and the probe maintenance plate are insulating coatings. The insulating coating comprises: an aluminum-oxide layer formed by using a metallic aluminum oxidation technology and a Teflon layer formed by using a Teflon coating technology. The insulating coating can be used in a controllable reactance chip test needle frame with a coaxial structure. By using the chip test needle frame which adopts the insulating coatings, intensity can be substantially increased. When a number of the spring probes exceed 1500, the chip test needle frame can still work normally. Simultaneously, the reactance of the test needle frame from a top to a bottom maintains a constant value so that an electrical property of the test needle frame can be increased. The needle frame can be used in occasions with a chip operation speed which is above 30 megahertz.
Owner:ANTARES ADVANCED TEST TECH SUZHOU CO LTD
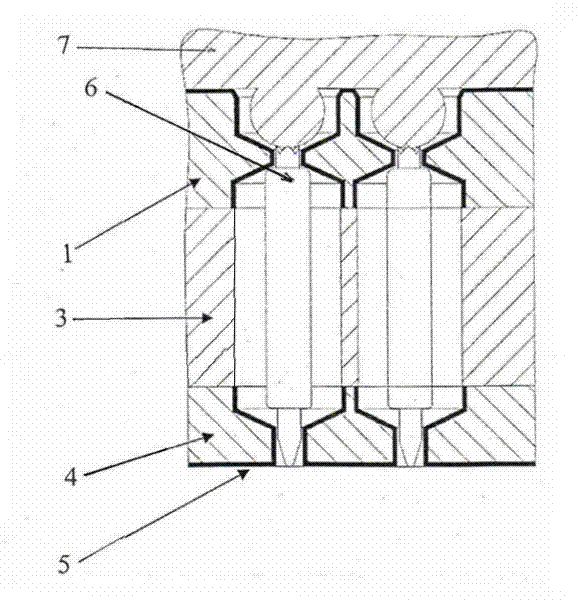
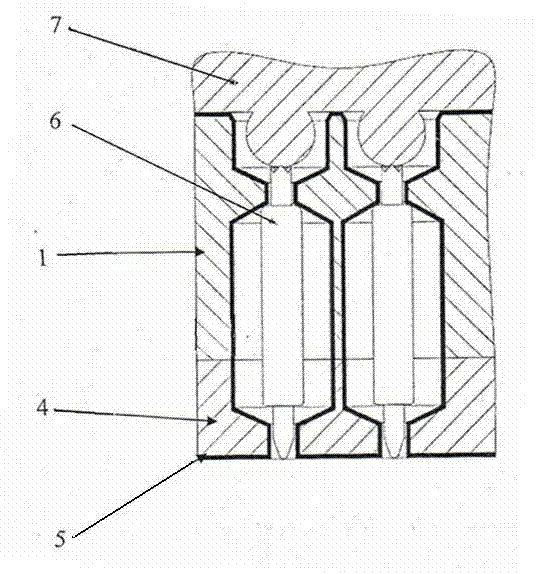
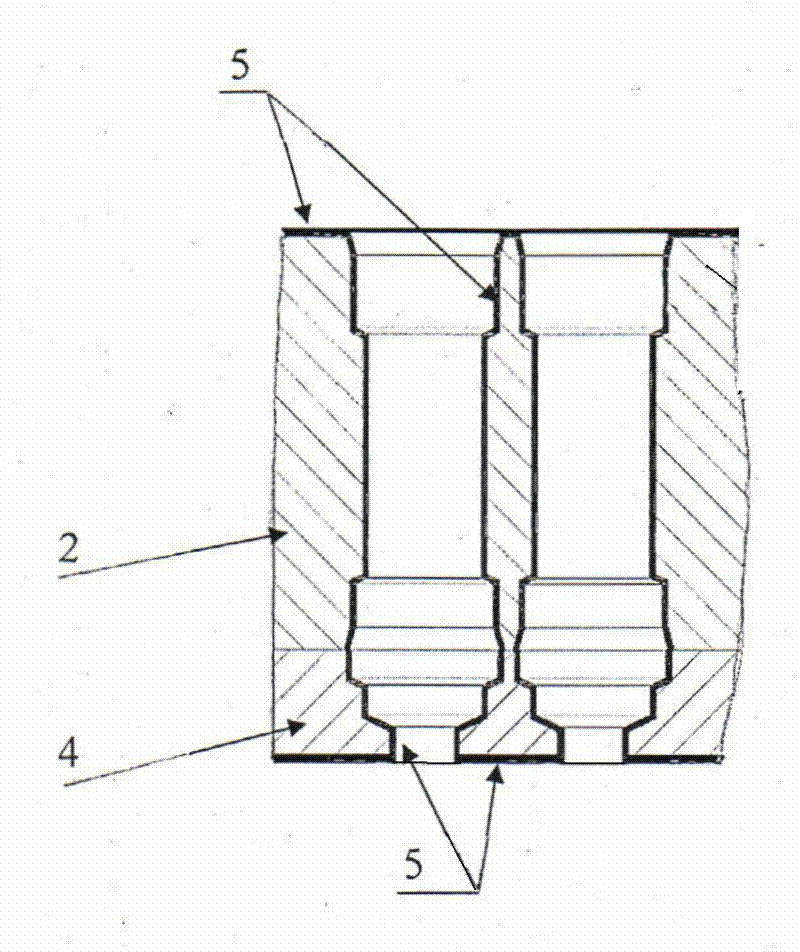
Micro light emitting diode display substrate and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111128942AImprove insulation performanceAvoid differencesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesAdhesiveLight-emitting diode
The invention discloses a micro light emitting diode display substrate and a preparation method thereof. According to the preparation method, each Micro LED structure is fixed with a receiving substrate through an organic adhesive, two sides of the Micro LED structure are provided with electrodes, the Micro LED structure is provided with an undercut structure, and the receiving substrate is also provided with an undercut structure, so that a top electrode and a self-aligned wire for connecting electrodes between the Micro LED structures and the receiving substrate can be obtained only by adopting an open mask plate to deposit an electrode material, and the electrodes have good insulativity therebetween; the connection of the corresponding electrodes between all Micro LED structures and thereceiving substrate can be completed at one time, difference in connection between each Micro LED structure and the receiving substrate can be avoided, and the manufacturing yield of the device is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS SEMICON DISPLAY TECH CO LTD
Super-high-enthalpy arc heater anode
InactiveCN105517312AEnsure mutual insulationReduce burning lossElectric discharge heatingPlasma techniqueElectrical resistance and conductanceElectricity
The invention discloses a super-high-enthalpy arc heater anode. With the super-high-enthalpy arc heater anode adopted, a situation that arc heaters in the prior art cannot be used for simulating environments with super-high-enthalpy values can be avoided. The arc heater anode includes a plurality of anode terminals, an insulating ring, a cavity and a plurality of resistors; the plurality of anode terminals are fixed onto the insulating ring in a manner that the plurality of anode terminals do not contact with each other, so that the plurality of anode terminals can be mutually insulated; the cavity is taper-shaped; one large-inner diameter end of the cavity is fixedly connected with the insulating ring; the direction of an electric arc changes when the electric arc passes through the cavity the inner diameter value of which is gradually increased, and therefore, a resulting magnetic force makes plasmas flow to and concentrate at a center region of the cavity, and accelerate; one end of each resistor is electrically connected with an anode terminal, and the other end of the corresponding resistor is electrically connected with the positive pole of a power source; the root of the electric arc can be uniformly divided into a plurality of root units through adjusting the resistance values of the resistors, and the plurality of root units are attached to the plurality of anode terminals, and therefore, a uniform flow field can be generated. The super-high-enthalpy arc heater anode of the invention can be applied to simulation high-altitude thermal environments in which aerospace crafts returning from deep space exploration.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF AEROSPACE AERODYNAMICS
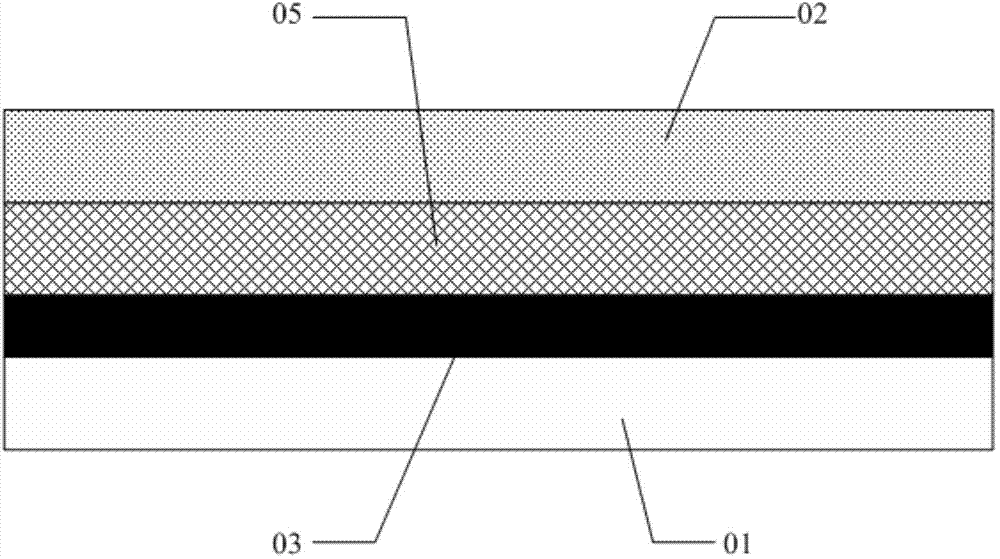
Light board, backlight module and curved display device
InactiveCN110297356AEasy accessSolve the problem of short circuitNon-linear opticsElectricityDisplay device
The embodiment of the invention discloses a light board, a backlight module and a curved display device. The light board comprises a substrate basal plate, multiple light sources and an insulation structure; multiple bonding pads are arranged on the substrate basal plate; each the bonding pad comprises a first part and a second part; the light sources are electrically connected with the substratebasal plate through the bonding pads; orthographic projection of the first part in the plane, where the substrate basal plate is, is positioned in corresponding orthographic projection of the light source in the plane, where the substrate basal plate is; and orthographic projection of the second part in the plane, where the substrate basal plate is, is positioned in orthographic projection of theinsulation structure in the plane, where the substrate basal plate is. According to the light board in the embodiment of the invention, the short-circuiting problem due to the fact that bonding pads of adjacent light sources are easily contacted when the light board is curved can be solved; mutual insulation among the bonding pads is ensured; simultaneously, the insulation structure can be used for relieving bending stress of the bonding pads; and breakage of the bonding pads when the light board is curved is prevented.
Owner:XIAMEN TIANMA MICRO ELECTRONICS
Display panel and electronic equipment
ActiveCN113296624AReduce the numberEnsure mutual insulationInput/output processes for data processingEngineeringElectrode array
The embodiment of the invention provides a display panel and electronic equipment. The display panel comprises a display area and a non-display area; the display area comprises a touch electrode array composed of a plurality of touch electrodes and a plurality of touch signal lines; the non-display area comprises at least two fan-out wiring areas; the at least two fan-out wiring areas are arranged along a first boundary between the non-display area and the display area, and each fan-out wiring area comprises a plurality of touch leads; each fan-out wiring area comprises a fan-shaped area and a linear area, and the fan-shaped areas are located between the first boundaries and the linear areas; each touch lead comprises a first sub-lead located in the fan-shaped area and a second sub-lead located in the linear area; the distance between every two adjacent second sub-leads located in different linear areas is a first distance, the distance between every two adjacent second sub-leads located in the same linear area is a second distance, and the first distance is larger than the second distance. According to the invention, the frame width occupied by the fan-shaped area formed by the touch leads can be reduced, and the narrowing of the frame is realized.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Figuring yarn guiding device of war knitting machine
A patterning finger tricot machine, the needle being integrated with the intermediate by dielectric made of electric materials, and then fixed onto the guide bar. The dielectric has piezoelectric coatings on both sides, which consist of interior electrode, piezoelectric coating covered by exterior electrode. The exterior electrode binds one control circuit which produces electron-positron pair to affect exterior electrode. The structure of this instrument is simple and the cost is low.
Owner:王占洪
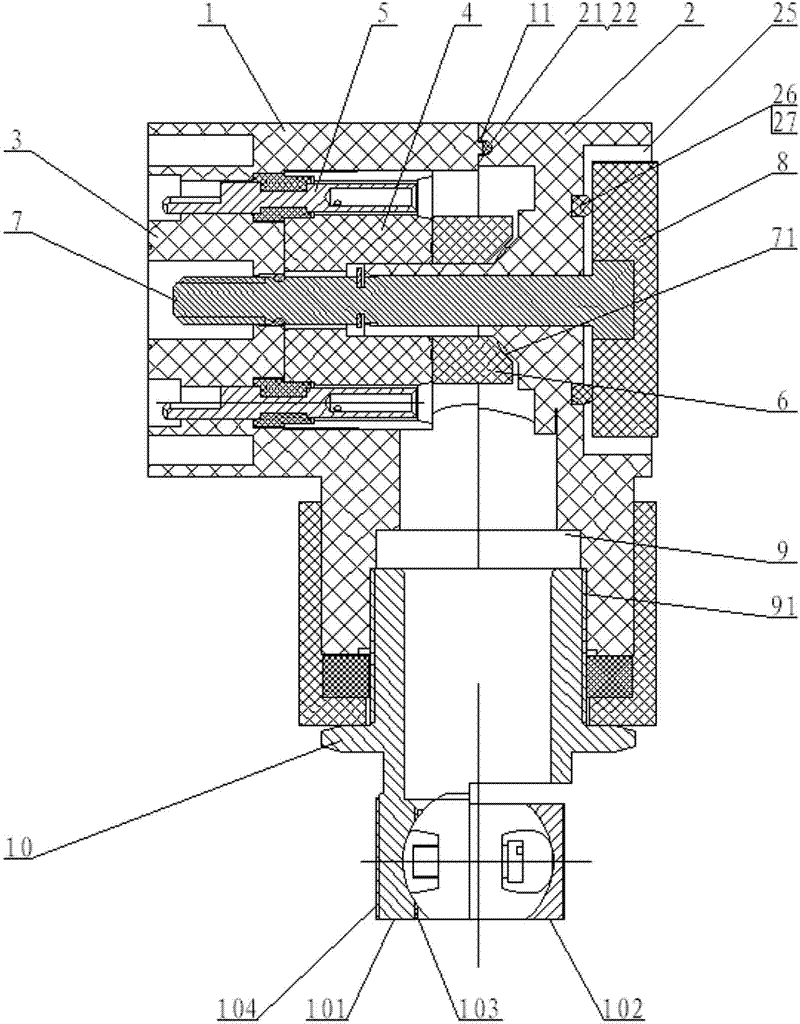
Circuit breaker
PendingCN114783816AAchieve compactnessGood elasticity and conductivityHigh-tension/heavy-dress switchesAir-break switchesPhysicsEngineering
The invention relates to a circuit breaker which comprises an arc extinguish chamber barrel fixedly provided with an arc extinguish chamber and an operating mechanism arranged on one side of the arc extinguish chamber barrel, and a supporting structure supported on a movable support is arranged in the arc extinguish chamber barrel. The supporting structure comprises two electric conductors, the upper ends of the two electric conductors are connected through a closing resistor, and the circuit breaker comprises a closing resistor containing cavity used for covering the closing resistor. The circuit breaker further comprises a closing resistor static contact and a closing resistor moving contact, the closing resistor static contact comprises static contact split bodies arranged on the two electric conductors respectively, and the closing resistor moving contact is used for stretching into and being clamped between the two static contact split bodies so as to short-circuit the closing resistor. According to the embodiment of the invention, the arc extinguish chamber cylinder only needs to be provided with the closing resistor accommodating chamber with the corresponding size at the position, corresponding to the closing resistor, of the upper side of the arc extinguish chamber cylinder, and the overall size of the arc extinguish chamber cylinder in the radial direction and the axial direction cannot be affected.
Owner:PINGGAO GRP +1
Novel water level sensor and washing machine
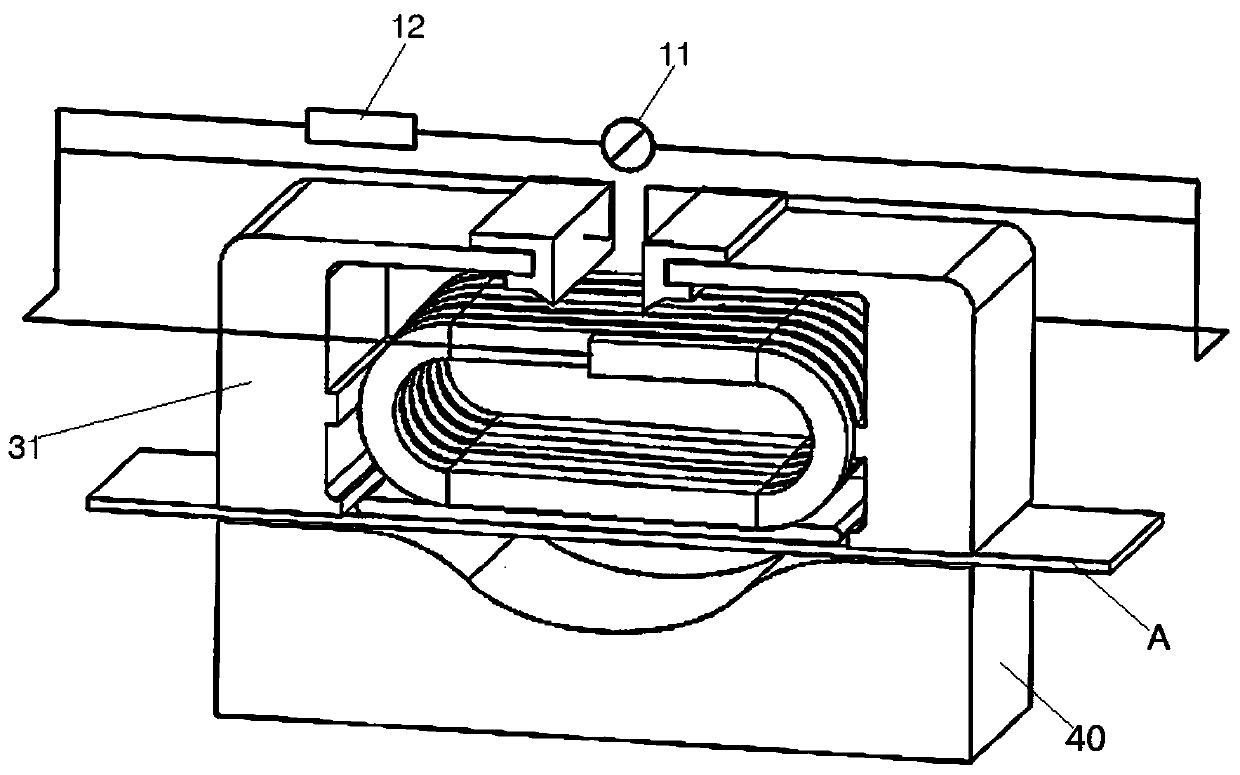
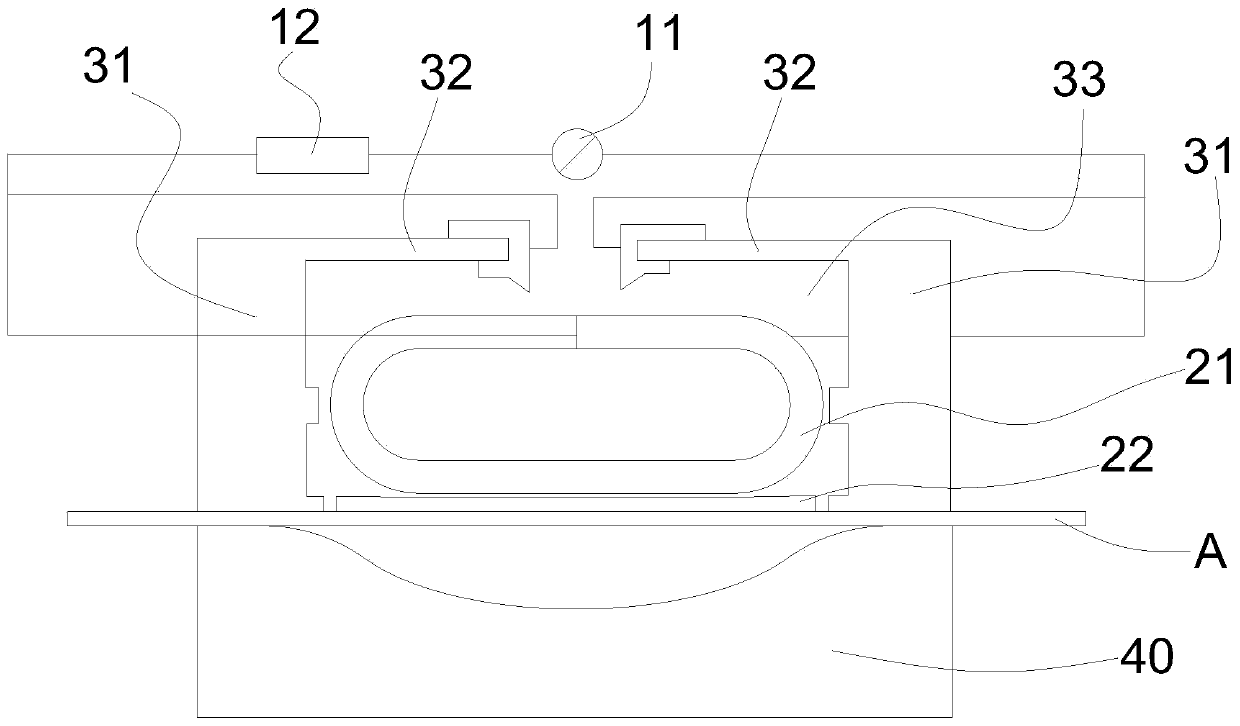
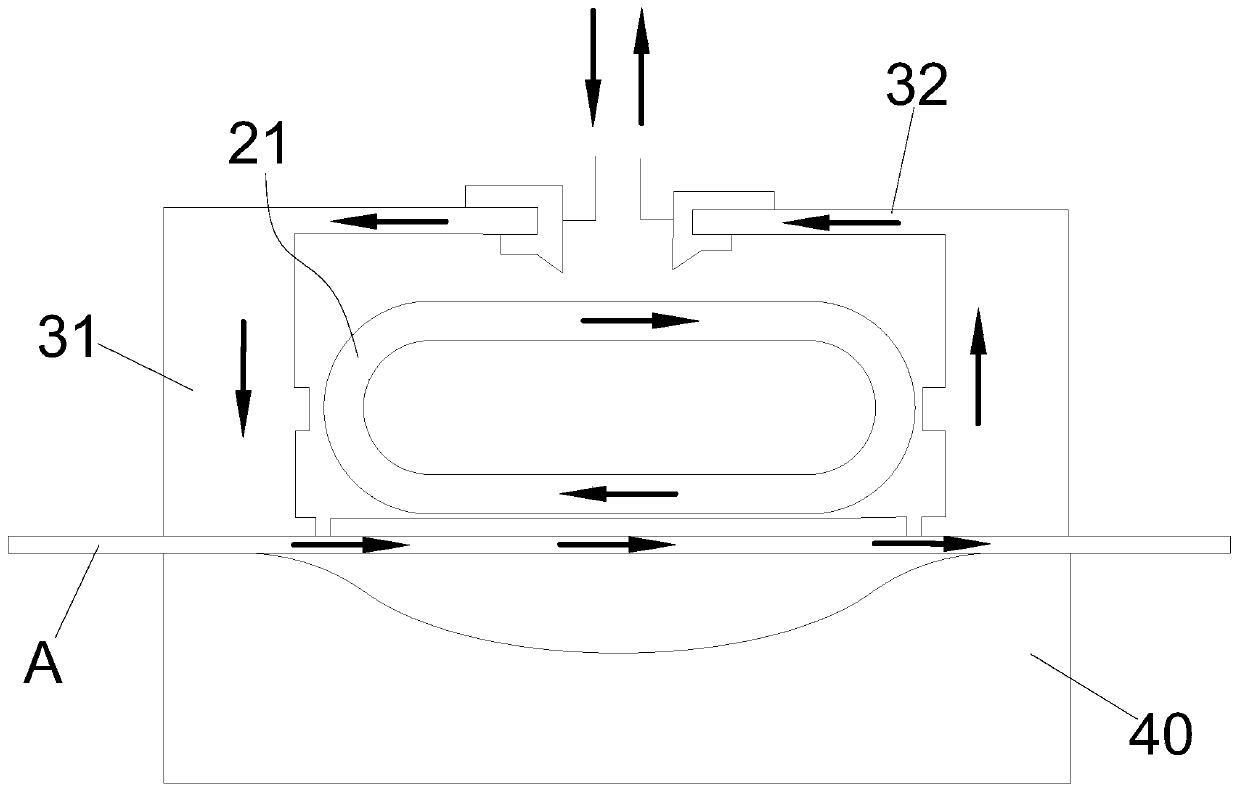
ActiveCN108642812AEnsure mutual insulationAvoid short circuitOther washing machinesControl devices for washing apparatusWater levelWaste management
The invention discloses a novel water level sensor which comprises a shell, an air cover and an adjusting screw bearing plate, a coil unit is arranged inside a cavity formed by the shell and the air cover, the coil unit comprises at least two terminals, the terminals stretch out from a socket of the shell, the terminals are all fixed to the same side of the shell, and a baffle located between theadjacent terminals is arranged on the outer wall of the shell so that the adjacent terminals can be separated. The invention further discloses a washing machine which is provided with any water levelsensor, the water level sensor is communicated with an air chamber of the washing machine, and the baffle located between the adjacent terminals is arranged on the shell, so that mutual insulation between the adjacent terminals is ensured, and short-circuits of the terminals caused by dew formation of the shell are avoided.
Owner:FOSHAN SHUNDE HAIER ELECTRIC APPLIANCES CO LTD +1
Material temperature measuring device for soaking furnace
InactiveCN108254095AEasy to replaceIsolated and lostThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsUsing electrical meansReciprocating motionSilicon alloy
The invention discloses a material temperature measuring device for a soaking furnace. The material temperature measuring device comprises a cylinder passing through a furnace wall, a guiding mechanism, and a driving mechanism. Four metal rods penetrate the cylinder; and two of the four metal rods are nickel-chromium alloy rods and the other two rods are nickel-silicon alloy rods. Guiding wheels are fixed on a rack and are in contact with the outer surface of the cylinder. The driving mechanism drives the cylinder to make axial reciprocating motion. A longitudinal insulating plate is arrangedinside the cylinder along the axial direction and separates the four metal rods mutually. A plurality of horizontal insulating plates are arranged inside the cylinder along the direction perpendicularto the axial direction and are distributed at intervals; and the horizontal insulating plates and the longitudinal insulating plate are fixed mutually. Lead screws are arranged at the tails of the metal rods. A limiting plate protruding radially is arranged at the shaft end of one side of the cylinder; and internal threads cooperating with the lead screws are formed in the limiting plates. Therefore, the temperature of the aluminum alloy ingot in the furnace can be measured accurately; the material temperature measuring device can be utilized repeatedly; and the temperature measuring is donequickly and efficiently.
Owner:SUZHOU BONENG FURNACE TECH CO LTD
UHF signal lead-out device for equalizing shielding ring in basin type insulator
ActiveCN103399179BEnsure mutual insulationEnsure electrical continuityMeasurement instrument housingElectricityElectrical conductor
The invention provides a voltage-sharing shielding ring hyper-frequency signal lead-out device in a basin-type insulator, which is used for leading out a hyper-frequency signal of a GIS (Gas Insulated Switchgear). The device comprises a conductive lead-out rod arranged inside a bolt mounting hole of the basin-type insulator to be electrically connected with a voltage-sharing shielding ring, insulated fixed sleeves sleeving on the outer side of the conductive lead-out rod to insulate the conductive lead-out rod from an outer casing and insulate the conductive lead-out rod from an outer conductor of a monitoring device, and metal conductive bands arranged on the outer surface of the insulated fixed sleeves and capable of being electrically connected with the outer casing. The invention is used in the fields of partial discharge monitoring and fault diagnosis, avoids the phenomena that the sensitivity of an external sensor of the GIS is poor and an internal sensor of the GIS affects the insulativity, and provides the signal lead-out device; the structures of all the components of the device are simpler, the assembly of the components and the operation of integrally mounting with the GIS are comparatively convenient and fast, and the purpose that the GIS is monitored more precisely, conveniently and quickly can be achieved.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
A New Water Level Sensor Applied in Washing Machine
ActiveCN108642812BEnsure mutual insulationAvoid short circuitOther washing machinesControl devices for washing apparatusLaundry washing machineWaste management
The invention discloses a new type of water level sensor, which comprises a housing, an air cover, and an adjusting screw receiving plate. A coil unit is installed in a chamber surrounded by the housing and the air cover. The coil unit includes at least two terminals, and the terminals are separated from the housing The sockets of the two terminals protrude and are fixed on the same side of the housing. The outer wall of the housing is provided with a baffle in the middle of the adjacent terminals to separate the adjacent terminals. The present invention also discloses a washing machine, on which the water level sensor described above is installed, and the water level sensor communicates with the air chamber of the washing machine. By arranging a baffle plate located in the middle of adjacent terminals on the housing, mutual insulation between adjacent terminals is ensured, and short circuit of the terminals caused by dew condensation on the housing is avoided.
Owner:FOSHAN SHUNDE HAIER ELECTRIC APPLIANCES CO LTD +1
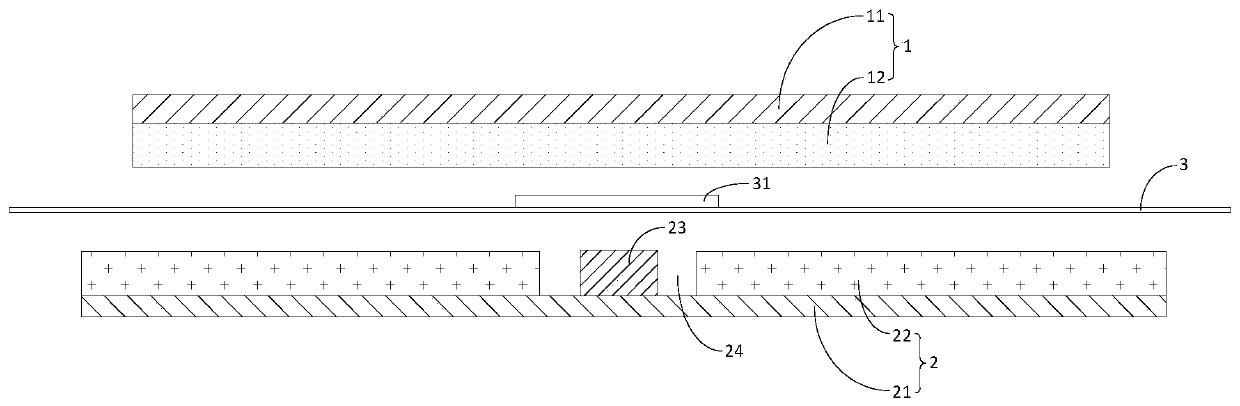
Electrical connection structure of touch liquid crystal display device
ActiveCN103294248BEnsure mutual insulationReduce areaElectrically conductive adhesive connectionsNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayHigh density
The present application discloses an electrical connection structure of a touch controlled liquid crystal display device, including: a first substrate; a plurality of first conductive pads on the first substrate, each of the first conductive pads being electrically connected with one first signal line; and at least one isolator between two adjacent first conductive pads. In the electrical connection structure of the touch controlled liquid crystal display device according to the present application, the isolator is arranged between two adjacent first conductive pads so that when the first conductive pads and the isolator are subsequently covered with conductive glue including conductive balls, the conductive balls in the conductive glue between two adjacent first conductive pads will not contact with each other to thereby ensure that the first conductive pads can be kept insulated from each other even if the conductive balls are distributed in the conductive glue at a high density.
Owner:SHANGHAI TIANMA MICRO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
A light-emitting chip and a light-emitting module
ActiveCN111640835BStructure Simplification and OptimizationThe overall thickness is thinSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesEngineeringMaterials science
The invention provides a light-emitting chip, comprising a chip body, a first electrode connection end and a second electrode connection end, the chip body includes a first electrode layer and a second electrode layer insulated from each other, and the first electrode connection end and the second electrode connection end are arranged at the bottom of the chip body, the first electrode connection end is electrically connected to the first electrode layer, and the second electrode connection end is electrically connected to the second electrode layer connection; the first electrode connection end includes a first row connection end and a second row connection end electrically connected to each other, and the second electrode connection end includes a first column connection end and a second column connection end electrically connected to each other end. The light-emitting chip can be applied on a circuit board with a specific single-layer structure to assemble a light-emitting module with a specific structure. In addition, the invention also provides a lighting module.
Owner:FOSHAN NATIONSTAR OPTOELECTRONICS CO LTD
A micro light emitting diode display substrate and its preparation method
ActiveCN111128942BImprove insulation performanceAvoid differencesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesAdhesiveEngineering
The present application discloses a micro light emitting diode display substrate and a preparation method thereof. In the preparation method, the Micro LED structure and the receiving substrate are fixed with an organic adhesive, and electrodes are arranged on both sides of the Micro LED structure, with an undercut structure on it, and an undercut structure on the receiving substrate, so that only open The electrode material is deposited on the mask to obtain the top electrode and the self-aligned wire connecting the electrode between the Micro LED structure and the receiving substrate. The electrodes have good insulation; all the corresponding electrodes between the Micro LED structure and the receiving substrate can be completed at one time The connection between each Micro LED structure and the receiving substrate can be avoided, and the yield rate of the device can be improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS SEMICON DISPLAY TECH CO LTD
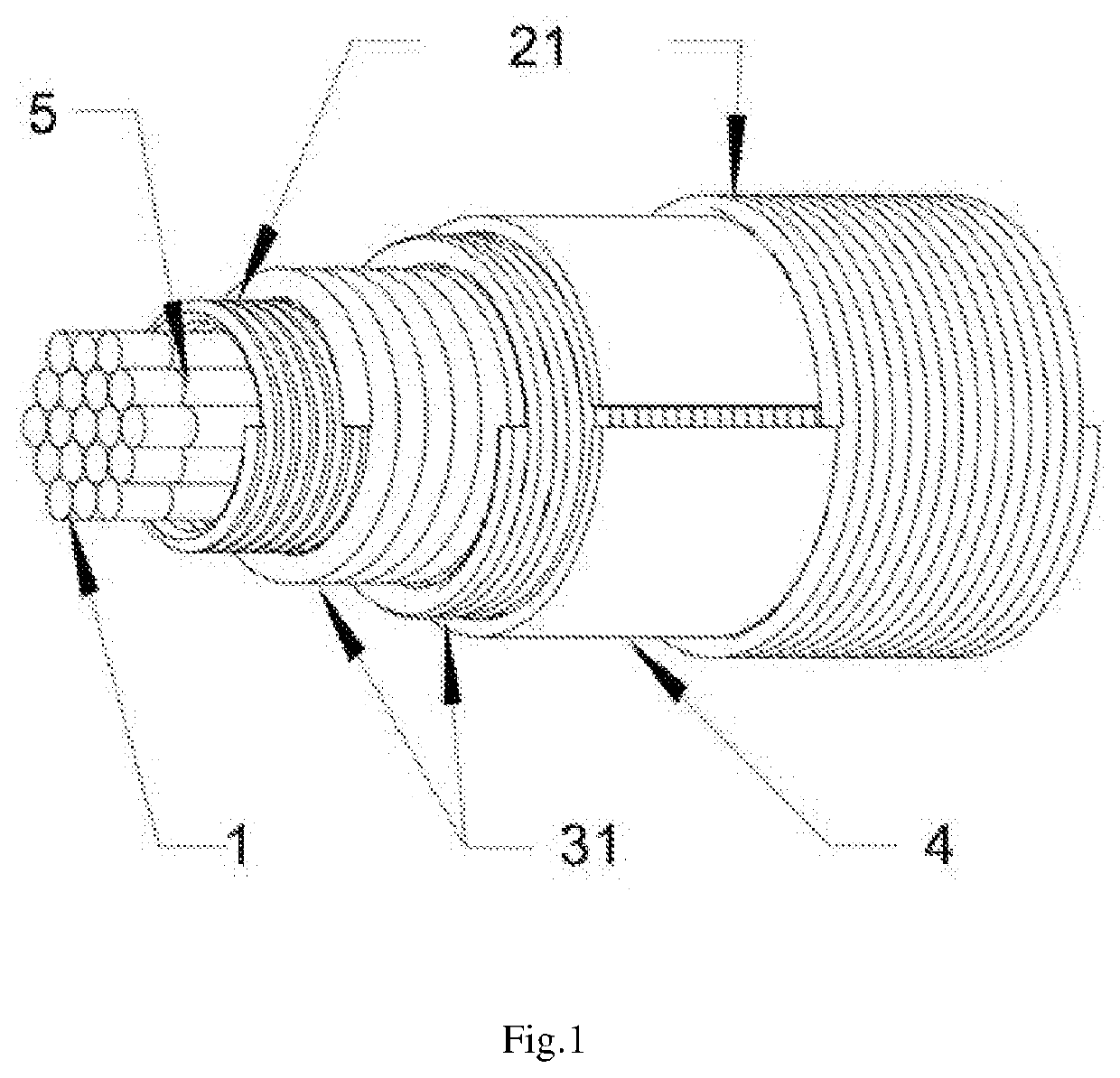
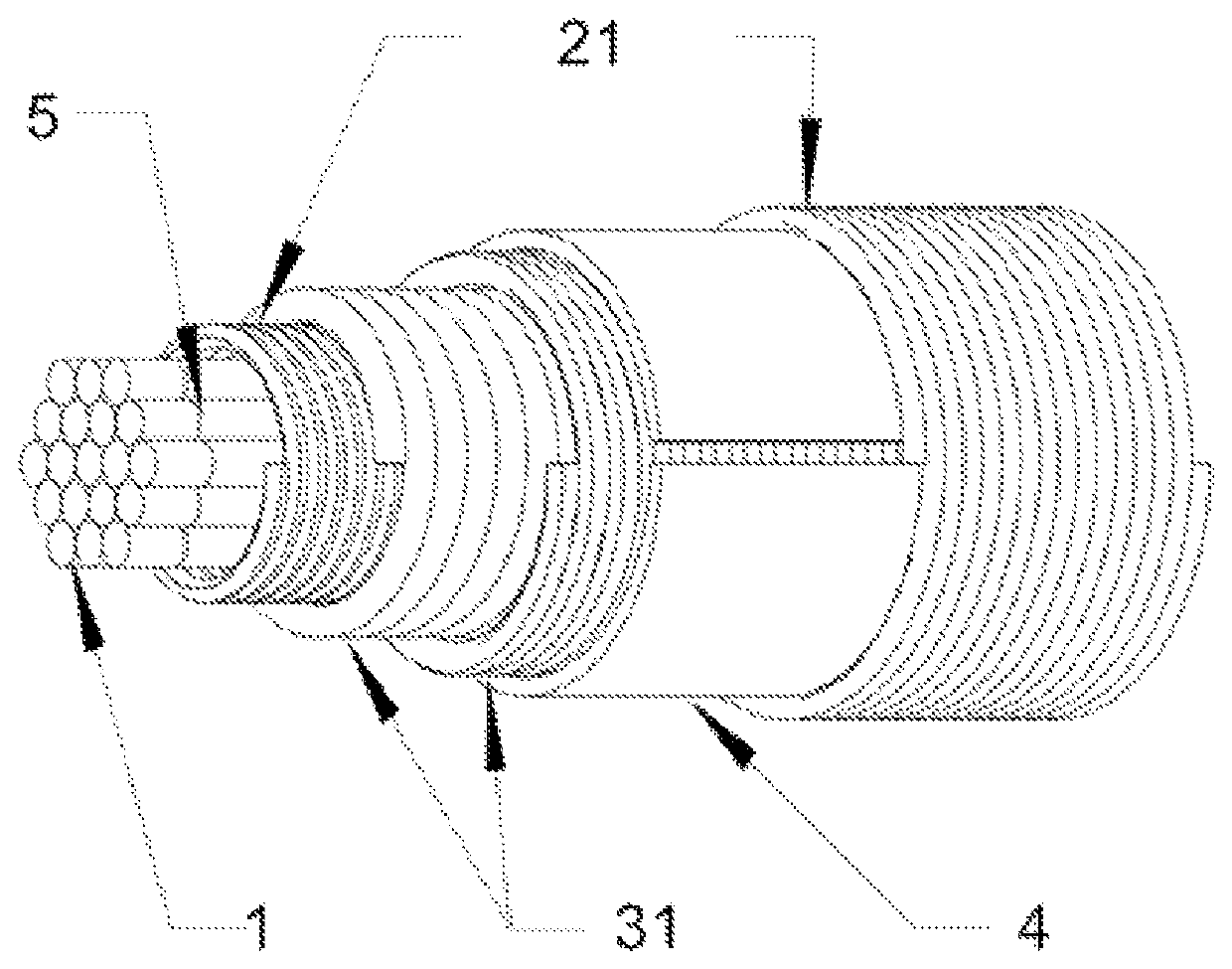
Flexible current sensor with stranded core
ActiveUS20200124644A1Improve accuracyEnsure long-term dimensional and thermal stabilityVoltage/current isolationCurrent transducerFiber
A flexible current sensor comprising a sensing coil wound on a cylindrical flexible core where the sensing coil comprises two in series connected overlapping windings wound along the cylindrical flexible core in mutually opposite direction. The cylindrical flexible core comprises a plurality of individual fibers from a nonmagnetic material arranged into the nearest approximation of a cylindrical shape and the sensing coil is equipped with a nonconductive separation layer located between its windings.
Owner:GRHACEK OVER NO LADISLAV
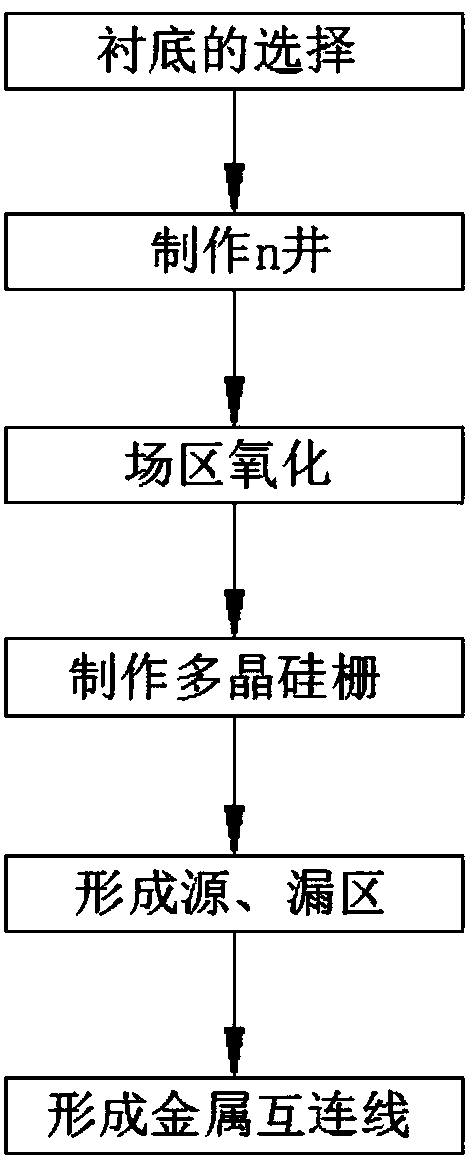
CMOS digital integration circuit board manufacturing process
InactiveCN108493158AReach deep distributionReduce stressSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSEngineering
The present invention discloses a CMOS digital integration circuit board manufacturing process. The manufacturing process comprises the following steps of: S1, selection of a substrate; S2, manufacturing of an n well; S3, oxidation of court areas; S4, manufacturing of a polysilicon gate; S5, formation of a source region and a drain region; S6, formation of a metal interaction wire; and S7, coverage of a layer of phosphorosilicate glass passive film on a silicon wafer after formation of the metal interaction wire to perform once photoetching to expose a leading-out terminal and pressure pointsof a silicon wafer of the integration circuit and connect the pressure points of the silicon wafer and corresponding pins of a tube.
Owner:南浔双林荣丰磁材厂
Device and method for uniform pressure electromagnetic forming of sheet metal under the action of different directions of current
The invention provides a device for constant-pressure electromagnetic forming of a metal plate under the action of heterodromous currents. The device comprises a u-shaped mold, and further comprises acapacitance power module, a magnet supply branch and two vertical side pressing plates. The capacitance power module comprises an energy storage capacitor. The magnet supply branch comprises a constant-pressure coil and is connected to the two ends of the capacitance power module. The upper ends of the side pressing plates are bent oppositely and extend to form closed plates, and therefore a containing cavity with an opening being downward is formed between the two side pressing plates and below the two closed plates. The constant-pressure coil is fixedly arranged in the containing cavity. During use, a power supply branch is formed by the two closed plates, the two side pressing plates and the to-be-formed metal plate; the power supply branch and the magnet supply branch are connected inparallel and are connected to the two ends of the capacitance power module by taking the free ends of the two closed plates as the electric access points. When the energy storage capacitor carries out discharge, discharge currents opposite in direction are formed in the constant-pressure coil and the power supply branch. According to the device, the magnitude of the currents on the formed plate is enhanced, the stress balance performance of the constant-pressure coil is improved, and processing capacity is improved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
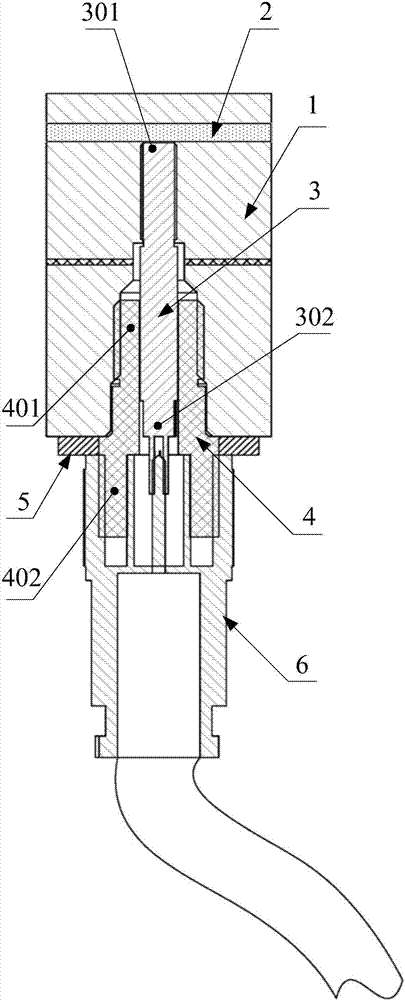
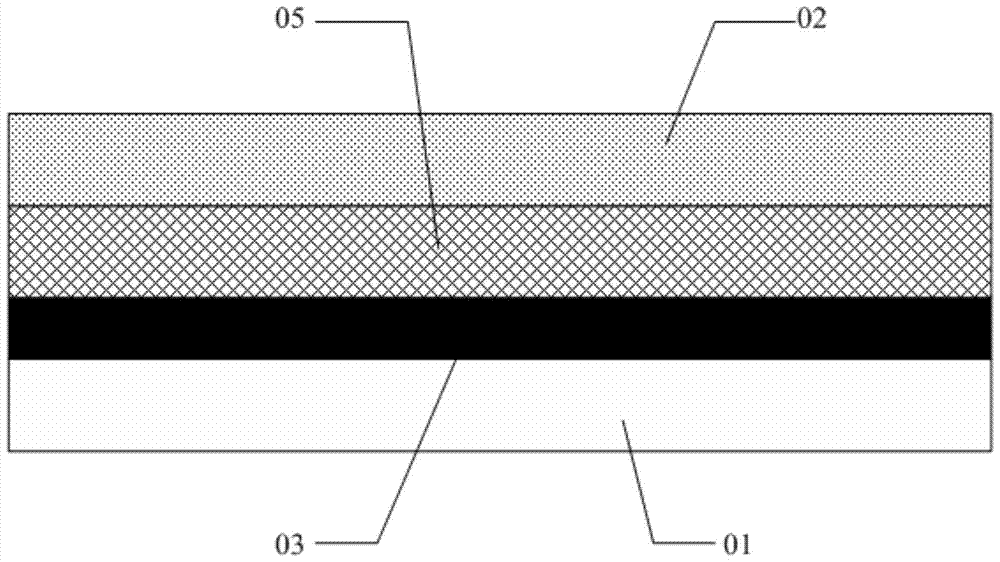
Power device and substrate thereof
PendingCN112635429AImprove cooling effectImprove safety and reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesThermodynamicsElectrical and Electronics engineering
The invention relates to the technical field of electronic appliances, in particular to a power device and a substrate thereof. The substrate comprises an insulating part, a heat conduction part, a first conductive part and a second conductive part, one of two opposite sides of the insulating part in the thickness direction is connected with the heat conduction part, the other side of the insulating part is connected with the first conductive part and the second conductive part, and an insulating interval is formed between the first conductive part and the second conductive part; a sinking groove is formed in the portion, located at the insulation interval, of the insulating part and extends from the surface of the insulating part to the direction where the heat conduction part is located. Even if the size of the substrate provided by the invention is relatively small, the insulation reliability of the substrate is relatively high, and the potential safety hazard is relatively small.
Owner:GREE ELECTRIC APPLIANCES INC
Winding electric core and its preparation method, battery and electronic product
ActiveCN111554982BEnsure mutual insulationKeep out of the wayFinal product manufactureNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodesMetallic lithiumPhysical chemistry
The invention provides a wound electric core and a preparation method thereof, a battery and an electronic product. The wound electric core includes a positive electrode sheet, a negative electrode sheet, and an insulating diaphragm between the positive electrode sheet and the negative electrode sheet; the negative electrode sheet includes a negative electrode base layer, Negative electrode coating and the negative electrode tab that is arranged on the surface of the negative electrode base layer, the negative electrode coating covers the surface of the negative electrode base layer, and the negative electrode coating has a tab connection area that avoids the negative tab, and the negative tab is located in the tab connection area; the tab connection The insulating diaphragm between the positive electrode area and the positive electrode sheet is provided with a barrier layer covering the tab connection area. The barrier layer is used to prevent lithium ions from passing through, thereby preventing metal lithium from being precipitated and attached to the area near the negative tab during the fast charging process of the battery. The uncoated area is beneficial to reduce the safety risk caused by lithium precipitation during the fast charging process of lithium-ion batteries.
Owner:ZHUHAI COSMX BATTERY CO LTD
An embedded touch screen and display device
ActiveCN104503650BEnsure mutual insulationGuaranteed insulation performanceNon-linear opticsInput/output processes for data processingCapacitanceDisplay device
The invention discloses a built-in touch screen and a display device. In addition to including wires and self-capacitance electrodes, it also includes several sets of connecting wire groups arranged in different layers with the self-capacitating electrodes; each connecting wire group includes multiple sub-connections arranged at intervals Each segment of the connecting line belonging to the same connecting line group corresponds to a different self-capacitance electrode, and each segment of the connecting line is connected to the corresponding self-capacitance electrode through at least one via hole penetrating the insulating layer; when the wire and the self-capacitance electrode intersect No via hole is provided in the stacked area, and the wire is connected to the corresponding self-capacitance electrode through at least a section of sub-connection line connected to the corresponding self-capacitance electrode. The aforementioned in-cell touch screen ensures uniform distribution of the via holes in the in-cell touch screen by uniformly arranging the via holes in the areas corresponding to the sub-connecting lines. Therefore, the in-cell touch screen can solve the problem of uneven display images caused by uneven distribution of via holes in the insulating layer in the prior art.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Flexible current sensor with stranded core
ActiveUS10732208B2Improve accuracyEnsure long-term dimensional and thermal stabilityMagnetic field measurement using flux-gate principleVoltage/current isolationCurrent transducerFiber
A flexible current sensor comprising a sensing coil wound on a cylindrical flexible core where the sensing coil comprises two in series connected overlapping windings wound along the cylindrical flexible core in mutually opposite direction. The cylindrical flexible core comprises a plurality of individual fibers from a nonmagnetic material arranged into the nearest approximation of a cylindrical shape and the sensing coil is equipped with a nonconductive separation layer located between its windings.
Owner:GRHACEK OVER NO LADISLAV
Liquid crystal display screen wire with filtering and shielding function
InactiveCN101800364AUndisturbedGuaranteed normal transmissionElectrically conductive connectionsCoupling for high frequencyState of artLiquid-crystal display
The invention discloses a liquid crystal display screen wire with filtering and shielding function, belonging to a screen wire, the structure thereof includes a screen wire and a screen wire plug, the terminal of the screen wire is connected with the screen wire plug, each screen wire is in three-layer structure, a wire core, a shielding layer and an insulating layer respectively, the outside of the wire core is wrapped with the shielding layer, and the outside of the shielding layer is wrapped with the insulating layer; the screen wire plug comprises a case and a signal pin; the wire core of the screen wire is connected with the signal pin of the screen wire plug, the shielding layer of the screen wire is connected with the case of the screen wire plug; and the screen wire is connected into a three-terminal filter. Compared with the prior art, the liquid crystal display screen wire with filtering and shielding function of the invention has good filtering function and shielding function.
Owner:SHANDONG CHAOYUE DATA CONTROL ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Y63-series special-type electric connector for high-speed rails
ActiveCN102231457BAvoid positional tolerancesImprove sealingRelieving strain on wire connectionSecuring/insulating coupling contact membersControl systemEngineering
The invention relates to an Y63-series special-type electric connector for high-speed rails, comprising a shell, an insulator and circular contact elements. The shell comprises a front shell and a back shell, the insulator comprises a front insulator and a back insulator, the front insulator is arranged in the front shell, more than one circular contact element is connected to the back insulator,and the back shell presses out the back insulator between the front shell and the back shell so that the part of more than one circular contact element, which is over the back insulator, is arranged in the front insulator. The front shell and the back shell are connected in series with the front insulator and the back insulator by central screw assemblies to form an electric connecting line with a vertical outside-line opening, and the circular contact elements with hermaphroditic structures, which are inserted on the back insulator, are matched, thus the electric connector has the advantagesof simple and compact structure, stability and firmness in connection, good sealing performance, high switched-on power performance and high safety, and is suitable for train control system responderunits of high-speed rails, underground railways and the like.
Owner:CHINA NORTH IND GRP HANGLIAN TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com