Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
33results about How to "Enhance the performance of anti-total dose radiation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Manufacture method of VDMOS device with irradiation resistance
ActiveCN104576398ASimple processManufacturing process compatibleSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDielectricGate oxide
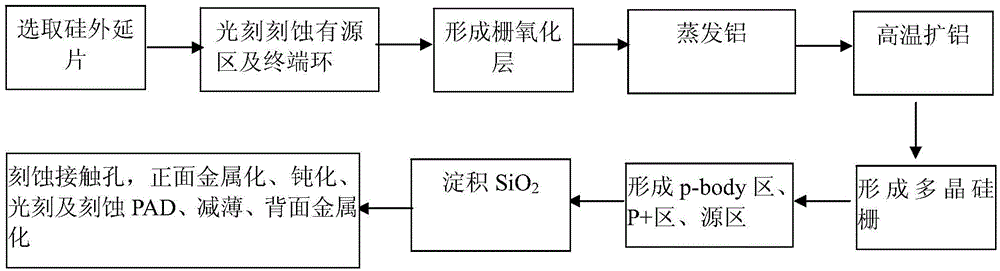
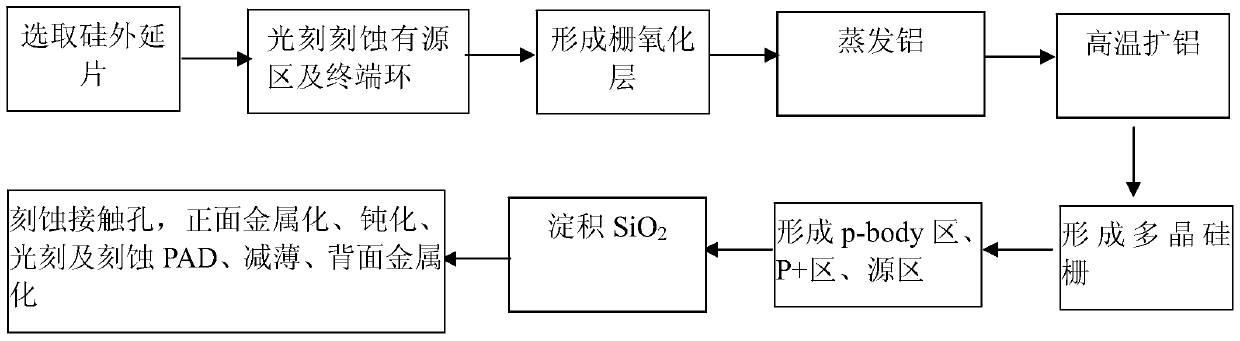
The invention discloses a manufacture method of a VDMOS device with irradiation resistance. The manufacture method of the VDMOS device is characterized by forming a gate oxide layer, evaporating aluminum on the gate oxide layer, and then diffusing aluminum at high temperature to form a gate medium of an Si-O-Al structure. Positive charges accumulated in the gate medium can be reduced when the VDMOS device is irradiated; the resistance to total dose irradiation of the device is improved; meanwhile, compared with the conventional silicon dioxide gate medium, the gate medium of the Si-O-Al structure is higher in dielectric constant; the resistance to single event gate rupture of the device can be improved. The manufacture method can be used for effectively overcoming the contradiction of requirements on the thickness of the resistance to total dose irradiation and the single event gate rupture and optimizing the resistance to total dose irradiation and the single event gate rupture at the same time; the process is simple; the resistance to the irradiation of the VDMOS device is improved.
Owner:BEIJING MXTRONICS CORP +1
Bulk-silicon MOSFET structure
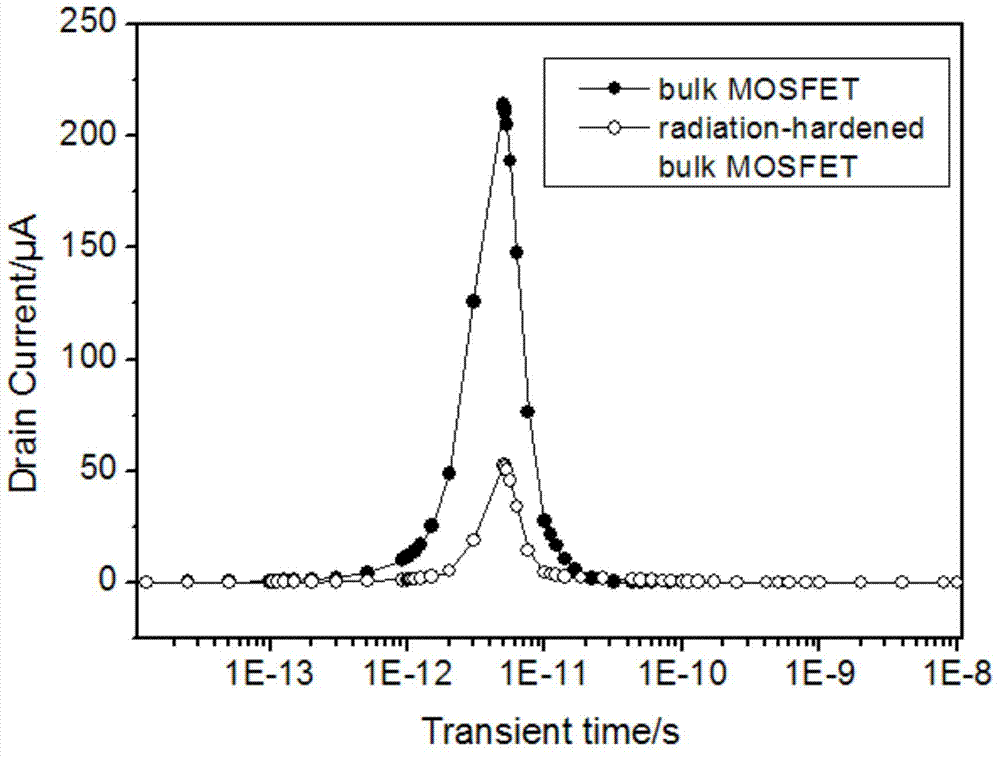
ActiveCN103500760AGood single event irradiation effectSuppression of single event radiation effectsSemiconductor devicesPhysicsMOSFET
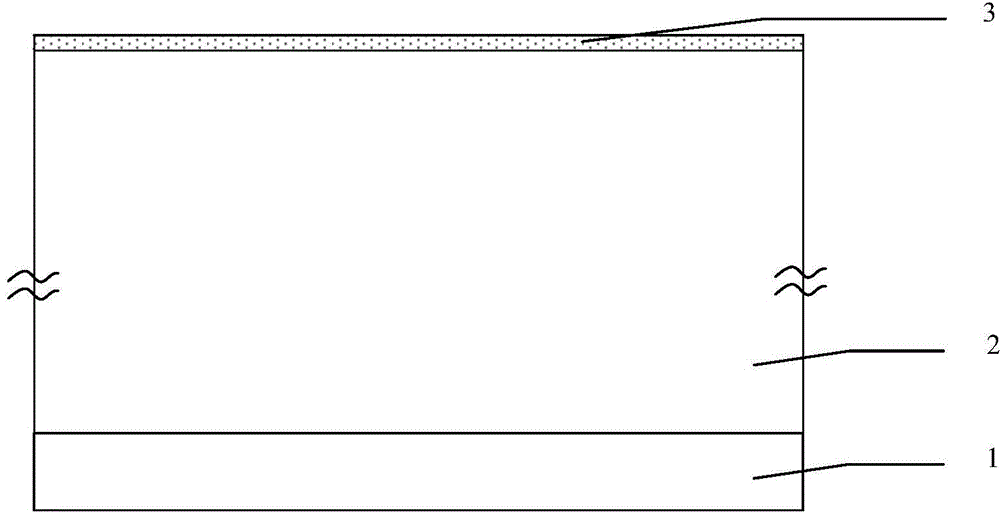
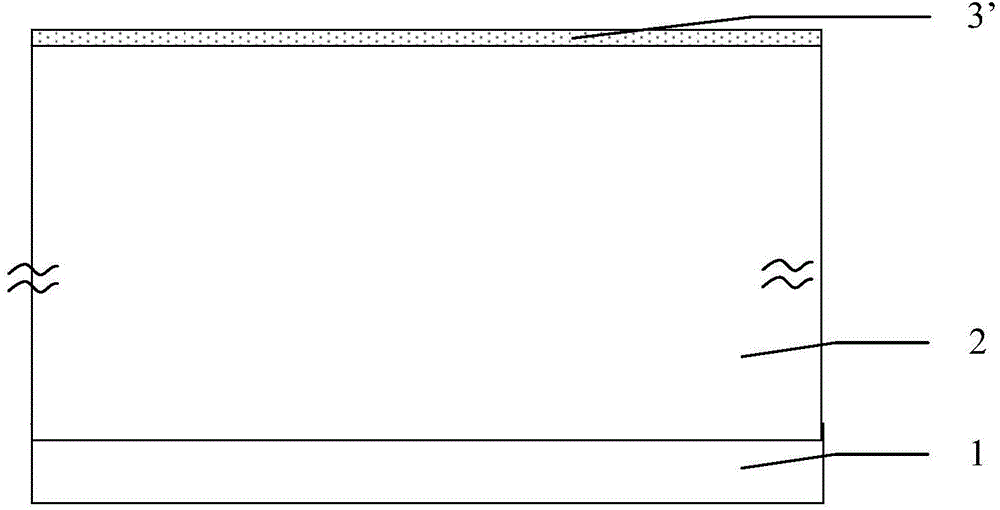
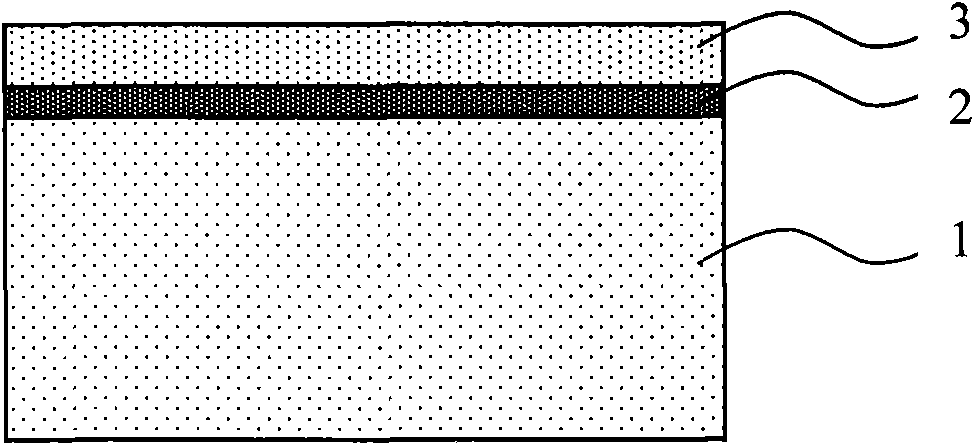
The invention discloses a bulk-silicon MOSFET (METAL-OXIDE-SEMICONDUCTOR FIELD-EFFECT TRANSISTOR) structure. The bulk-silicon MOSFET structure comprises a p+ layer (2) and an n- layer (3), wherein the p+ layer (2) and the n- layer (3) are directly contacted; the n- layer is made of wide-bandgap 6H-SiC material. The bulk-silicon MOSFET structure disclosed by the invention has the advantage that the radiation resistance of the bulk-silicon structure is improved. Compared with the SOI (Silicon On Insulator) technology, the bulk-silicon MOSFET structure disclosed by the invention has the beneficial effects that the self-heating effect is improved, the total dosage effect is eliminated, and the cost is reduced.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
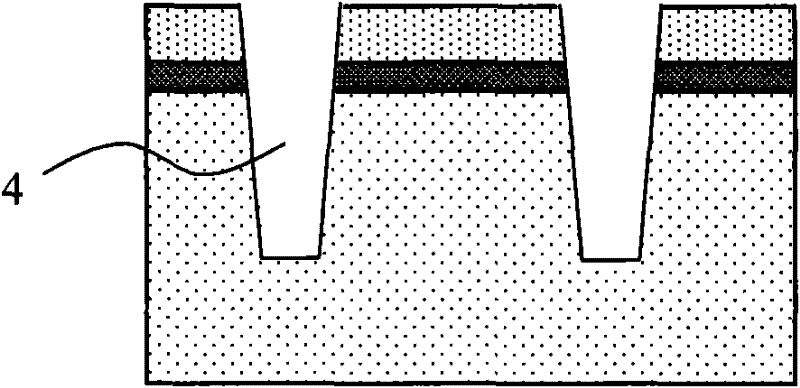
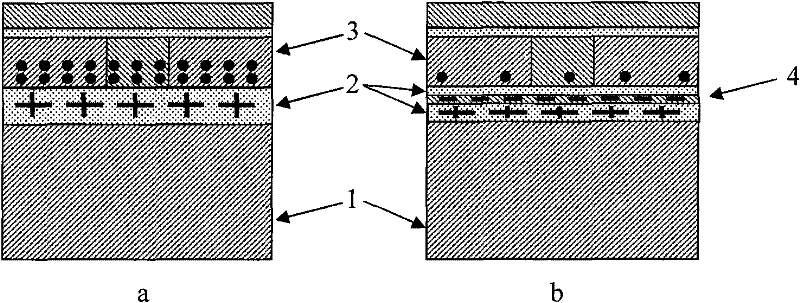
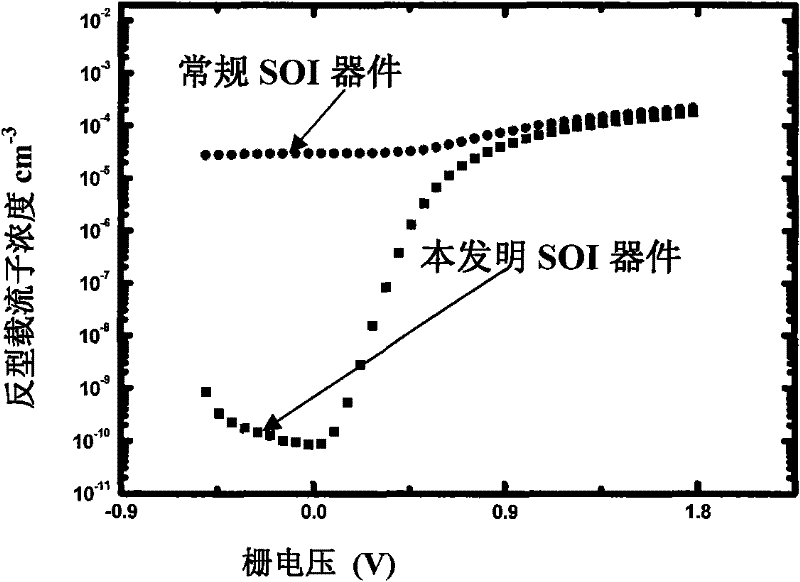
Novel anti-radiation device structure
InactiveCN106611778ANo need to add special process stepsEnhance the performance of anti-total dose radiationSemiconductor devicesBody contactEngineering
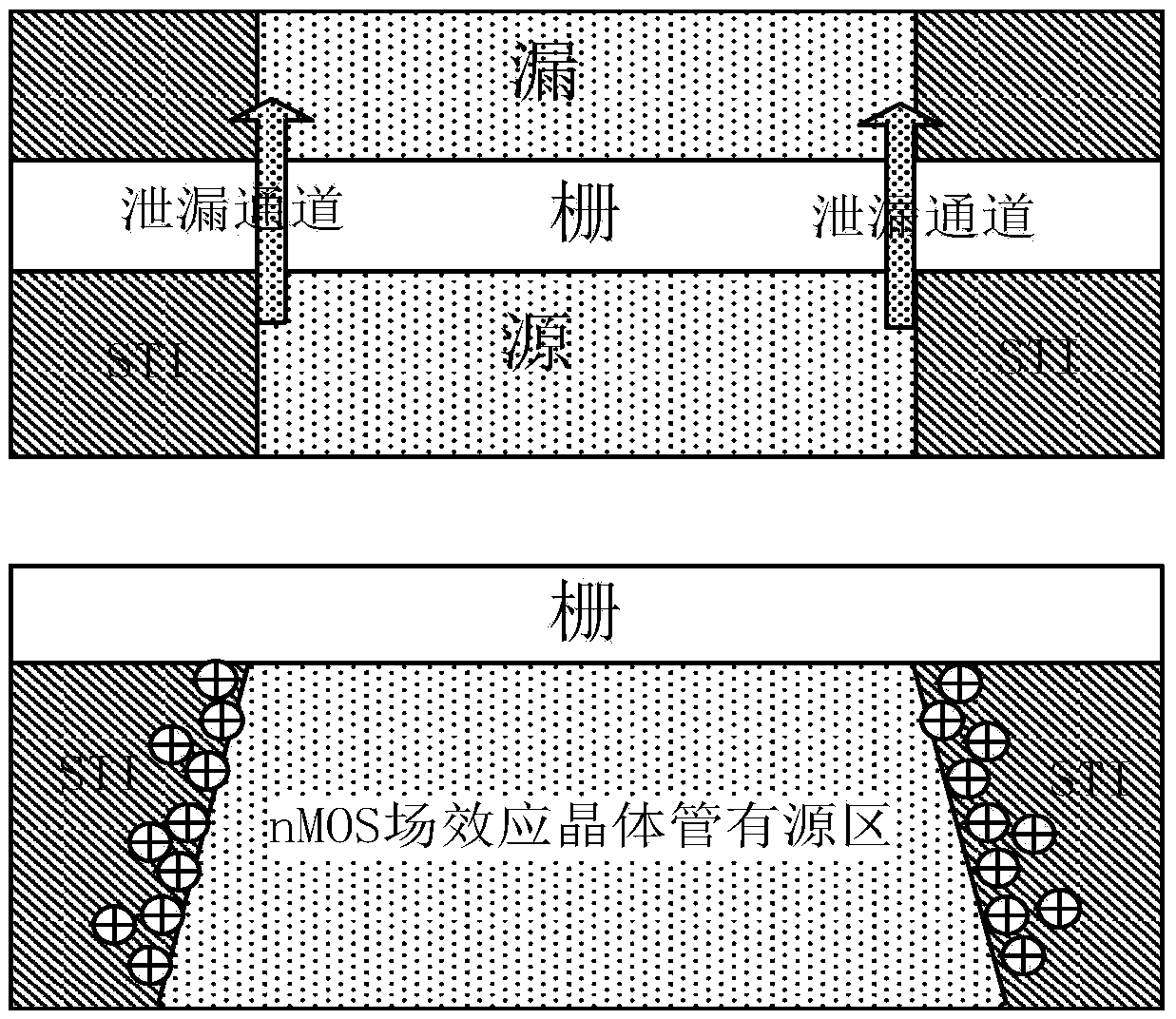
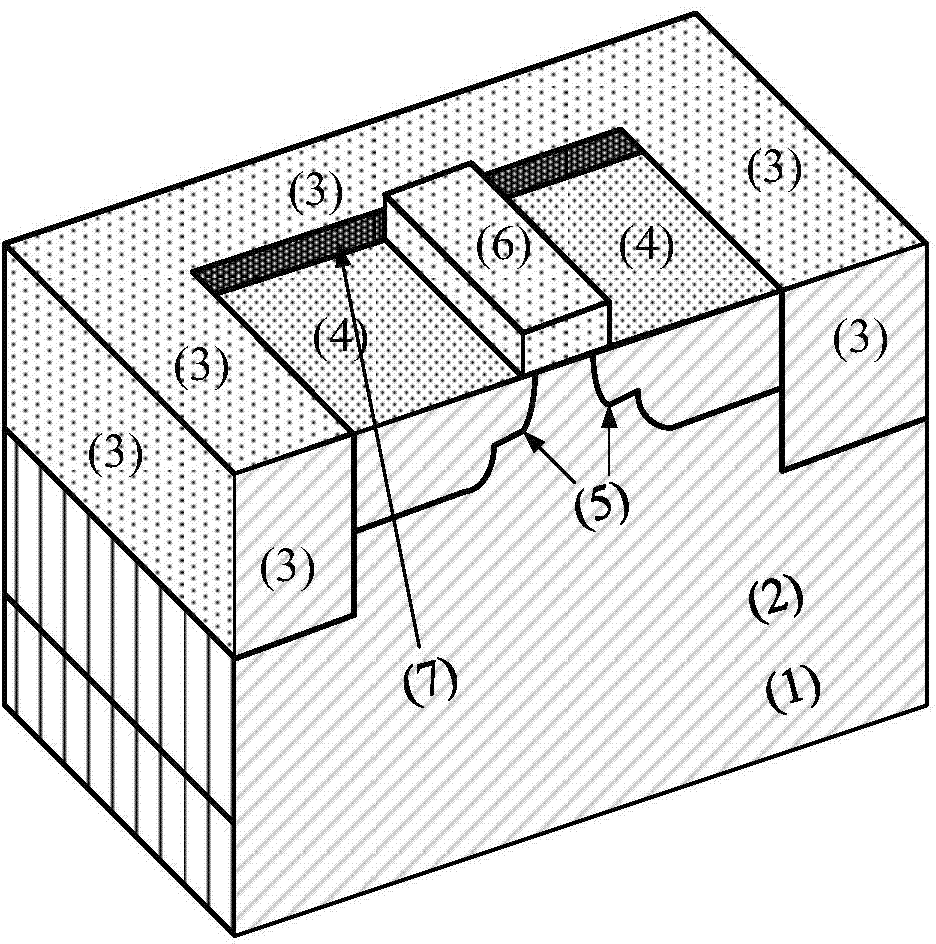
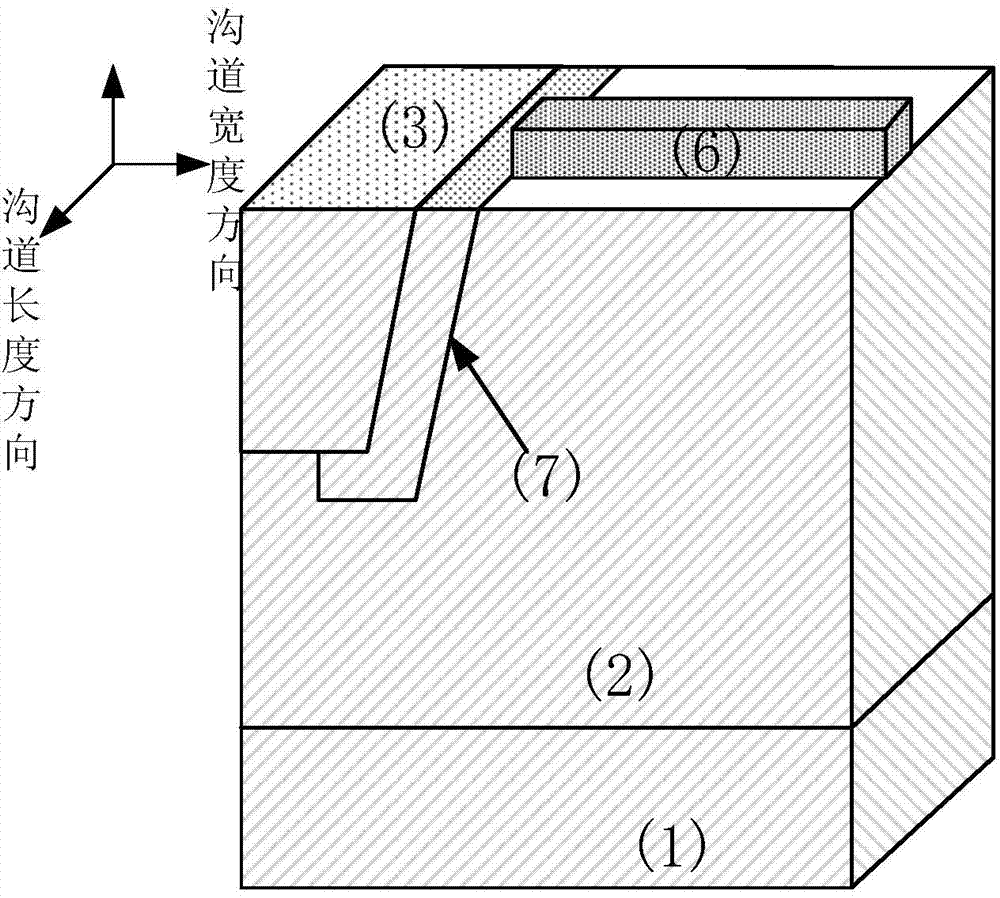
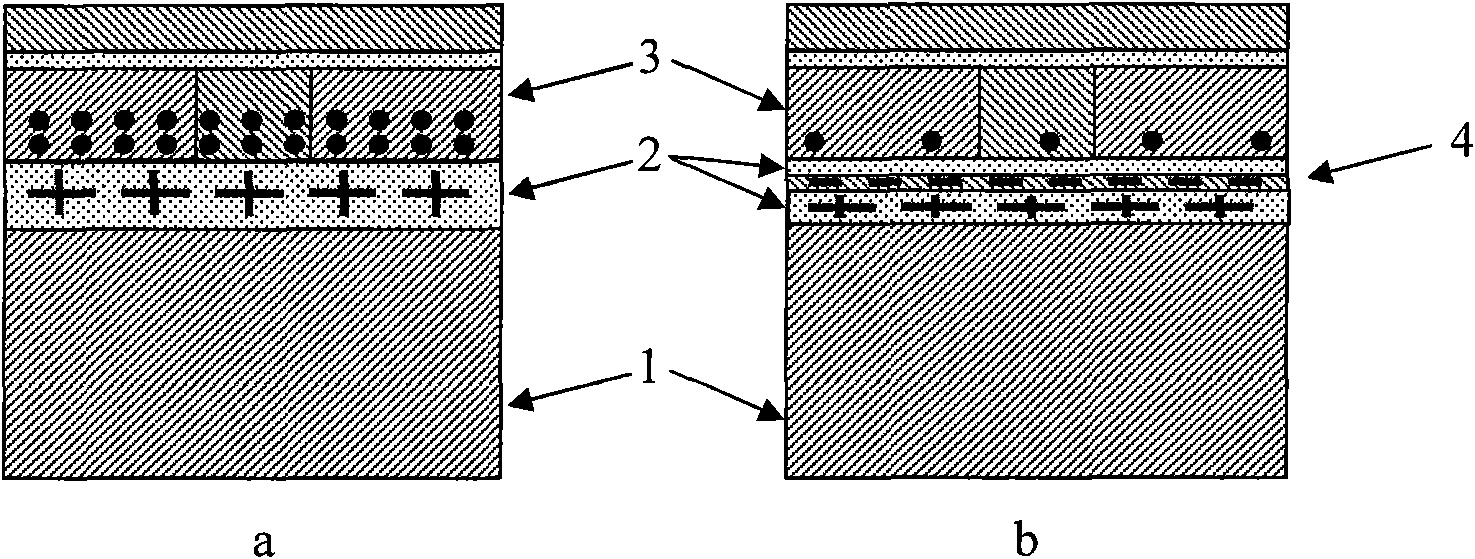
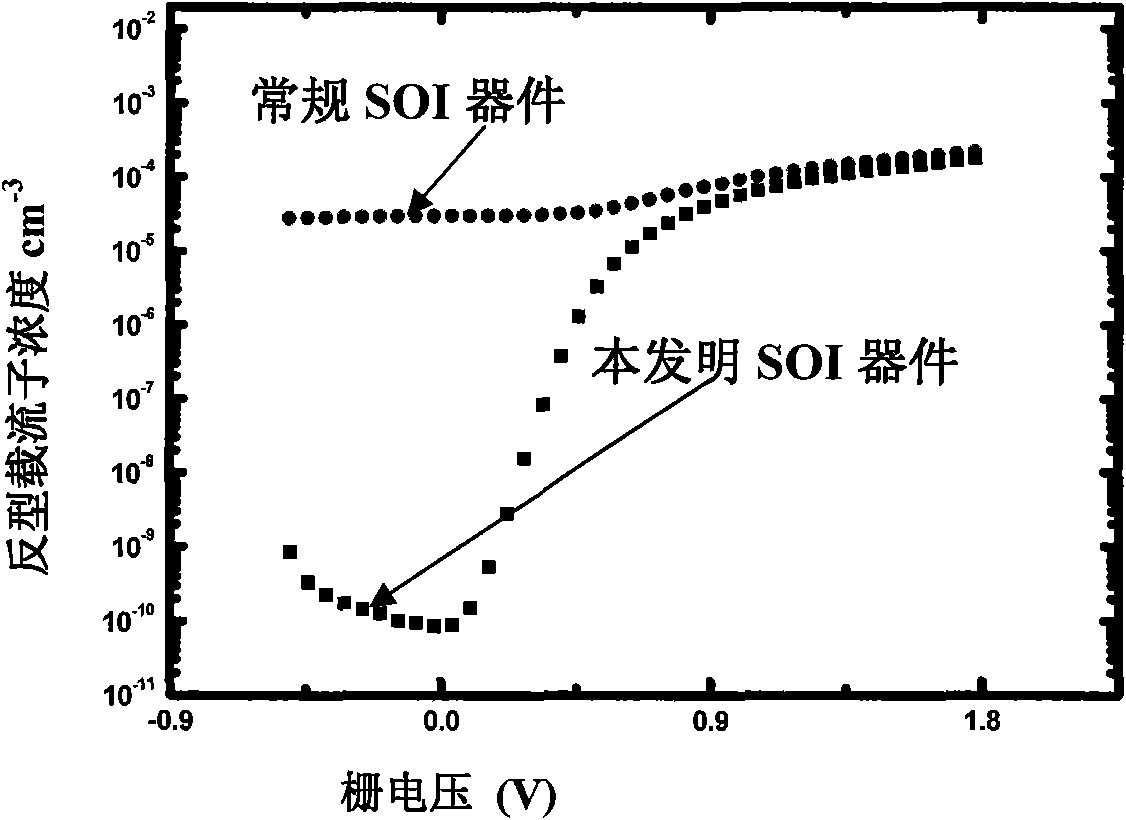
The invention belongs to the technical field of anti-radiation semiconductors, and relates to an SOI device capable of improving anti-radiation performance of the device based on a mainstream semiconductor process condition. The anti-radiation SOI device related by the invention is characterized in that through changing an insulating buried layer, the self-heating effect of the SOI device is reduced; and meanwhile, charges accumulated on a surface of a back gate can be reduced under a radiation condition; through changing a doped structure of an active area, a leakage current produced by a parasitic channel under the radiation condition is reduced, and simultaneously the body contact is realized better; and through changing a BTS structure, under the condition of keeping unchanged length-to-width ratio of the channel and the effective body contact, the layout area can be reduced. A novel anti-radiation device structure, under the condition of being compatible to a mainstream SOI process, can have the characteristics of relatively small self-heating effect, relatively small leakage current and relatively small layout area, etc.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Novel CMOS integrated circuit resisting total dose radiation
InactiveCN101661938AReduce power lossReduce application reliabilityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCMOSHigh energy
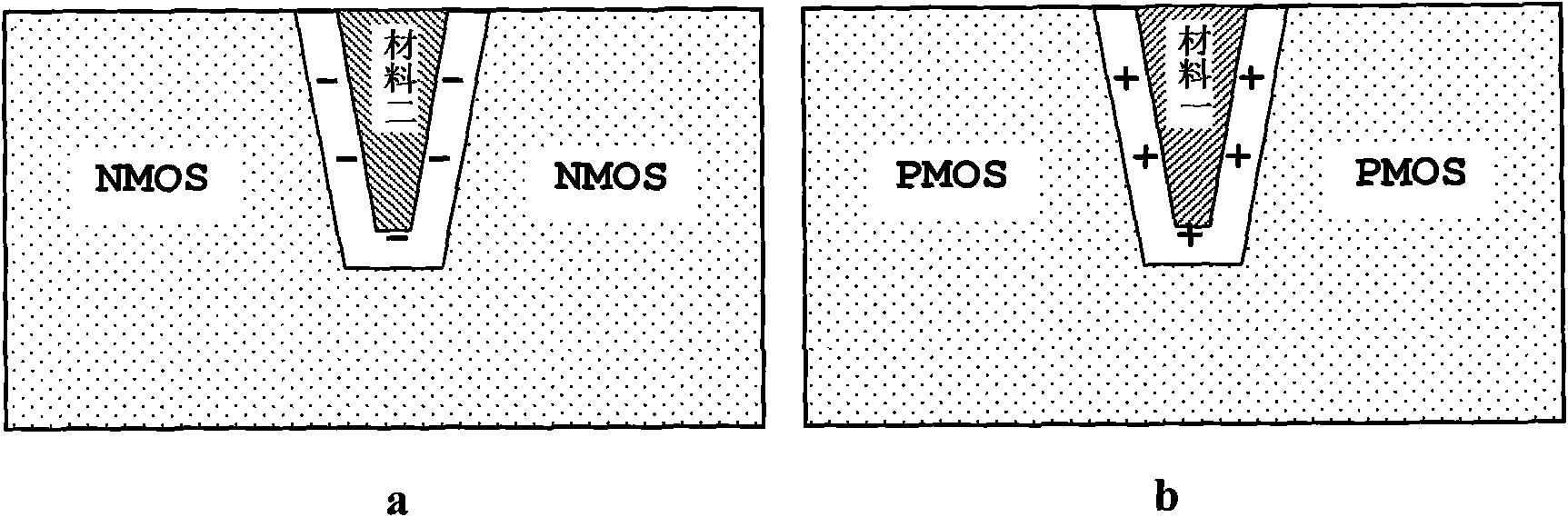
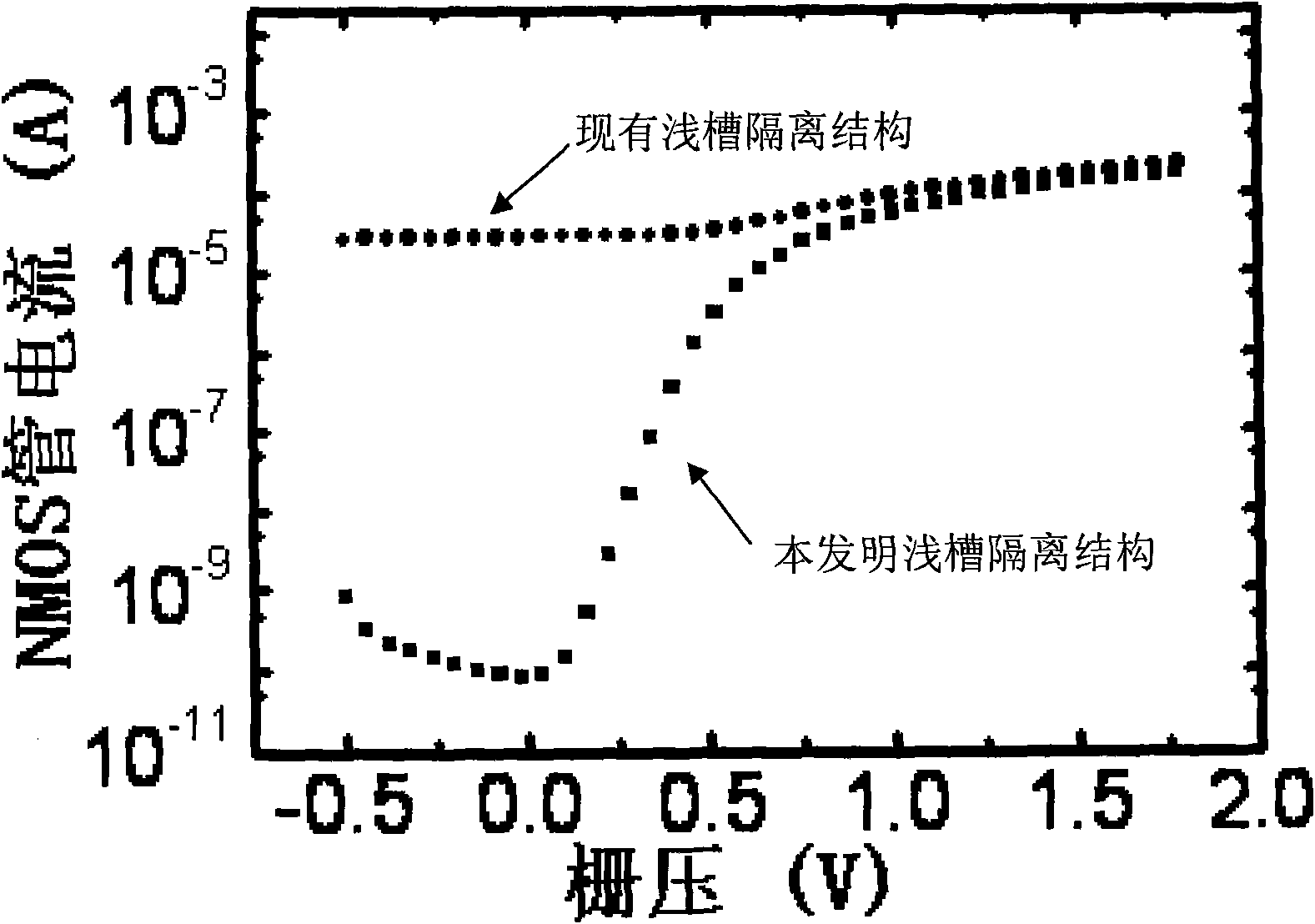
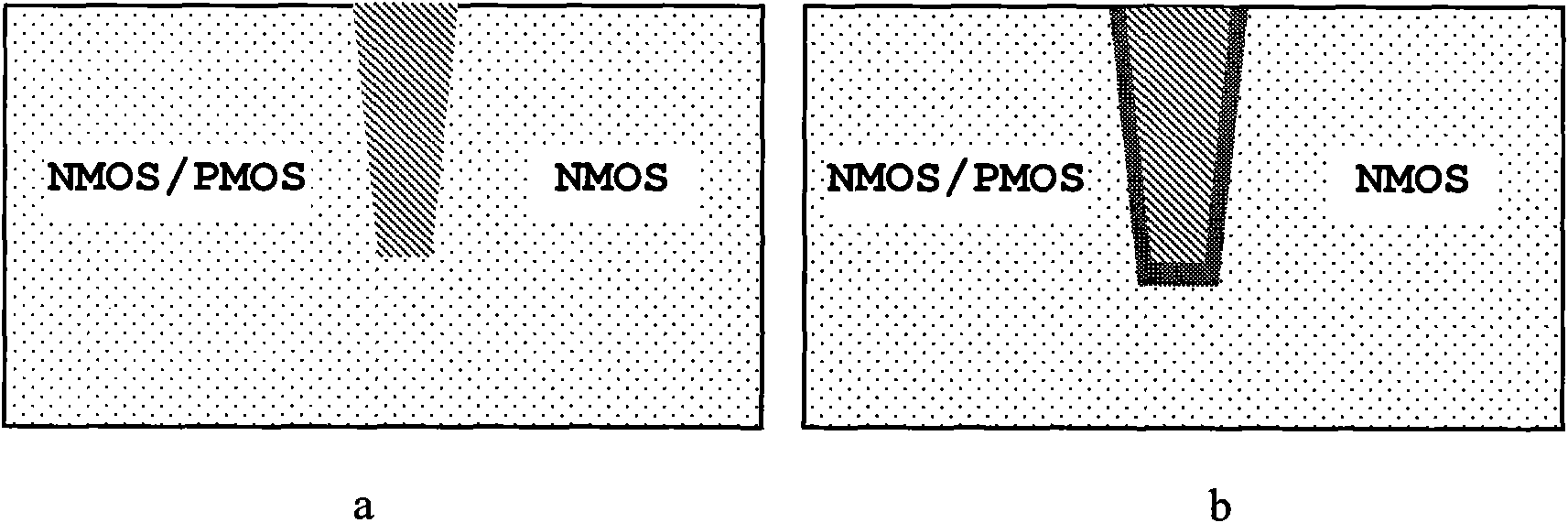
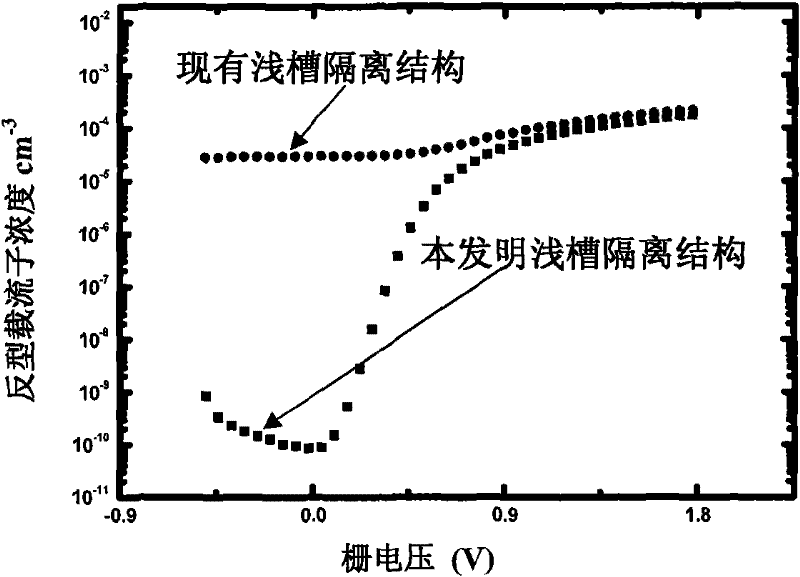
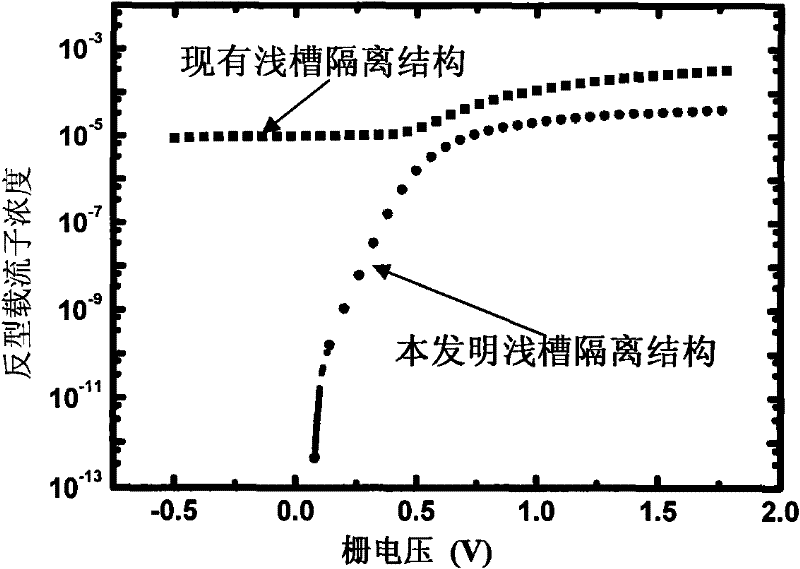
The invention discloses a novel CMOS integrated circuit resisting total dose radiation, belonging to the technetronic field. The CMOS integrated circuit comprises NMOS devices and PMOS devices; the devices are separated through grooves; grooves among the PMOS are filled with barrier materials I which generate fixed positive charge under total dose radiation; and grooves among the NMOS are filled with barrier materials II which generate fixed negative charge under the total dose radiation. In addition, grooves between NMOS and PMOS are filled with barrier materials I and II, wherein the barriermaterials I are close to PMOS and the barrier materials II are close to NMOS; or NMOS and PMOS are separated by two adjacent grooves, the groove adjacent to PMOS is filled with the barrier materialsI and the groove adjacent to NMOS is filled with the barrier materials II. The invention can be applied to the field related to total dose radiation such as aerospace, military, nuclear power, high energy physics and the like.
Owner:SEMICONDUCTOR MANUFACTURING INTERNATIONAL (BEIJING) CORP +1
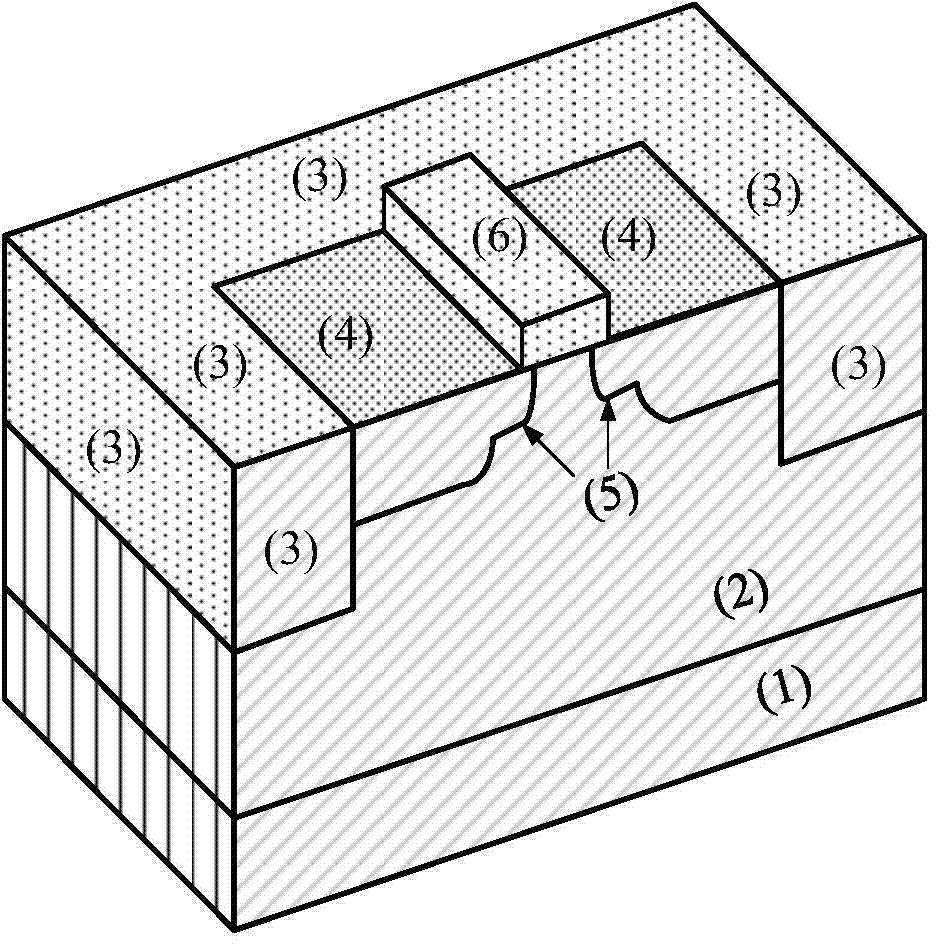
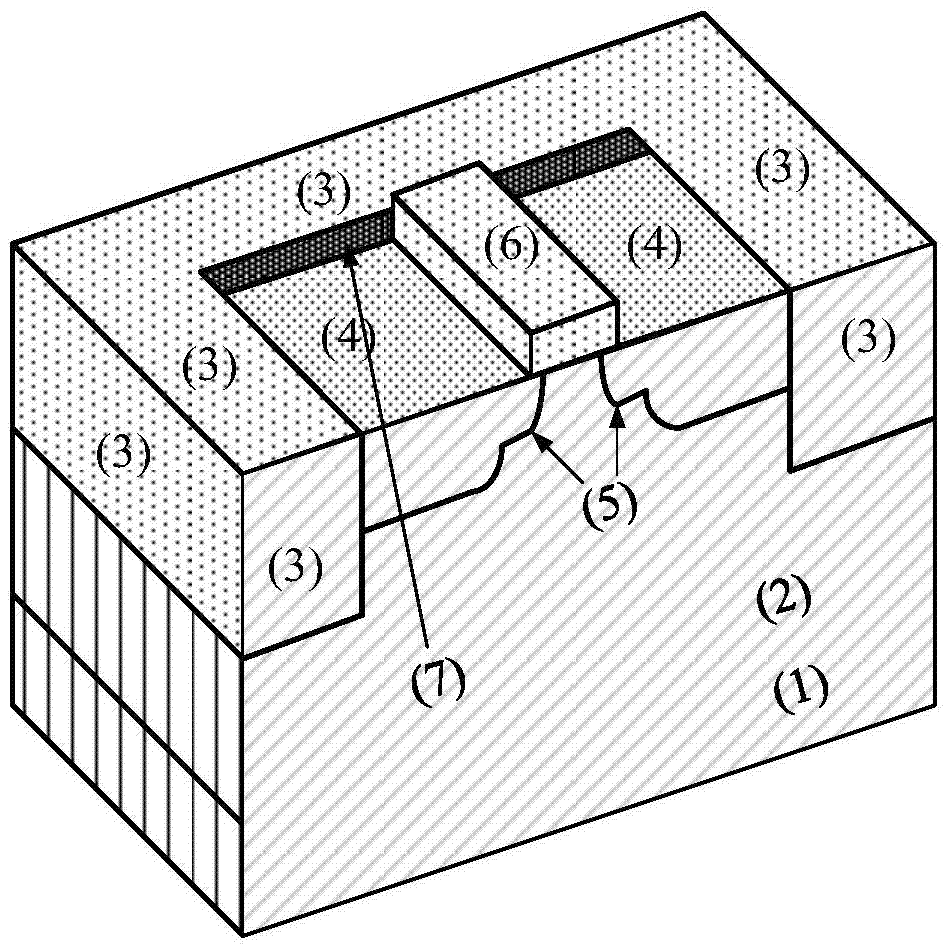
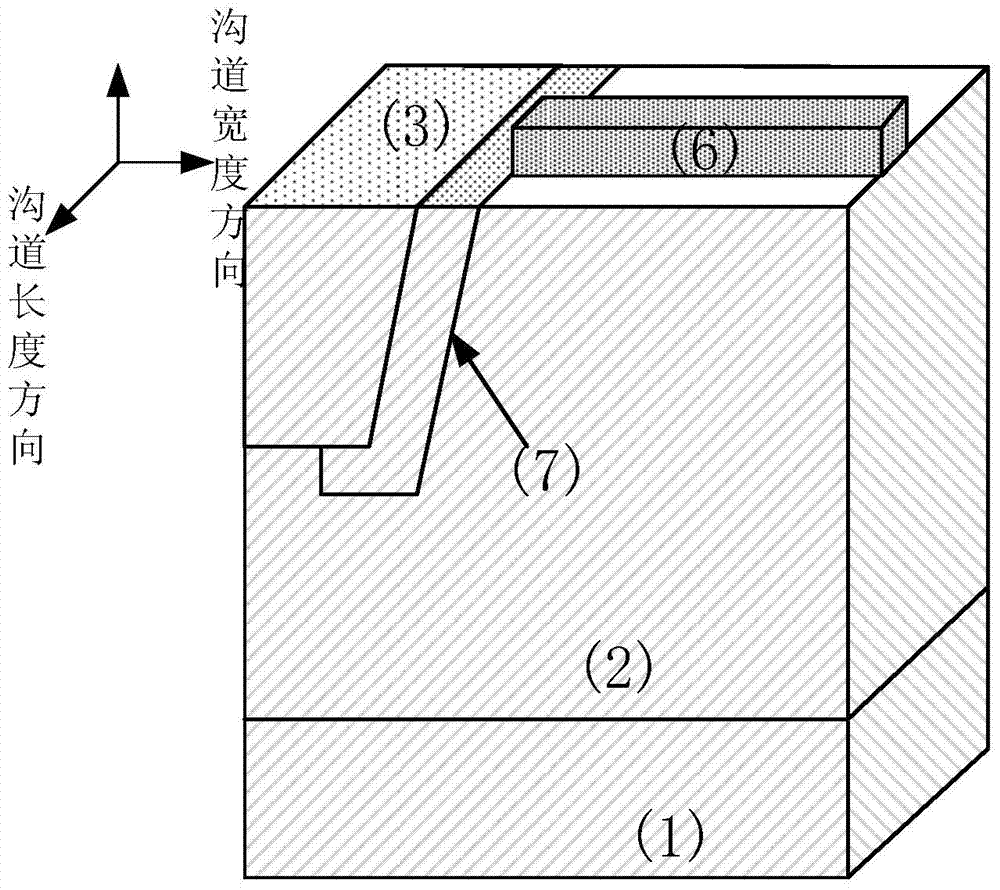
65nm technology-based super-steep reverse-doping radiation-proof MOS field-effect tube
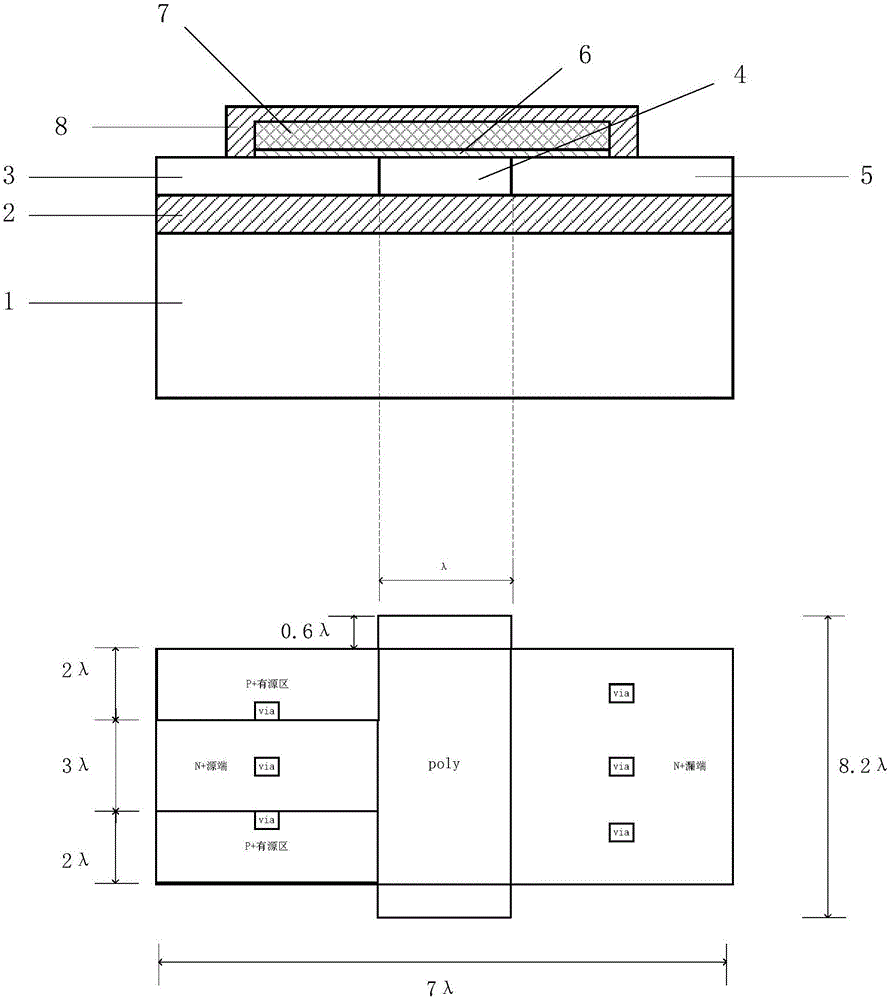
ActiveCN105514169AImprove radiation resistanceDoes not affect integrationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSubthreshold oscillationsThreshold voltage
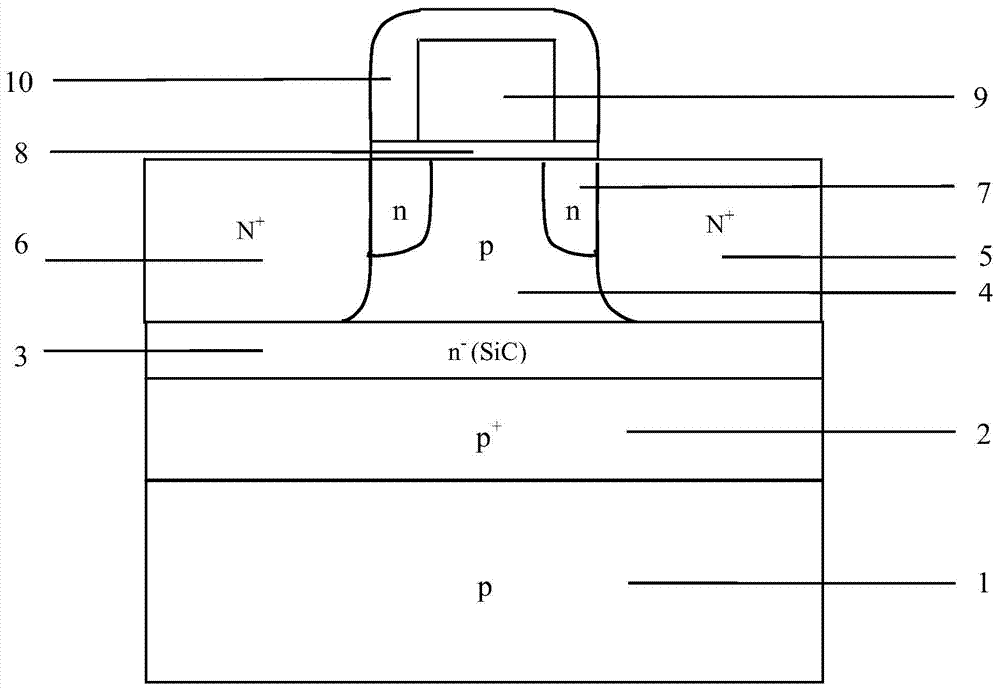
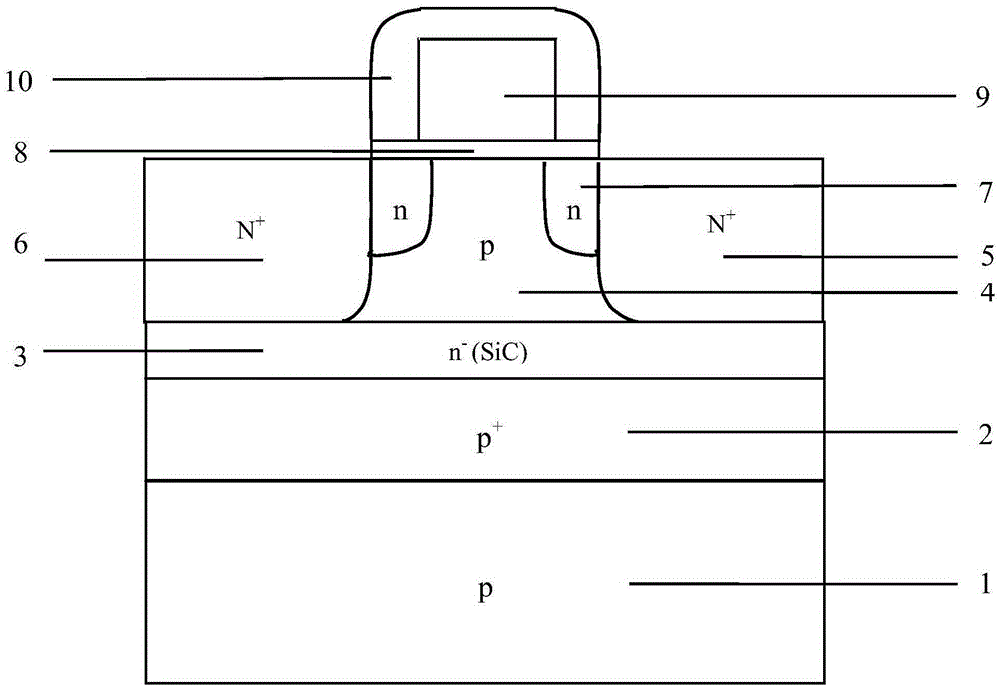
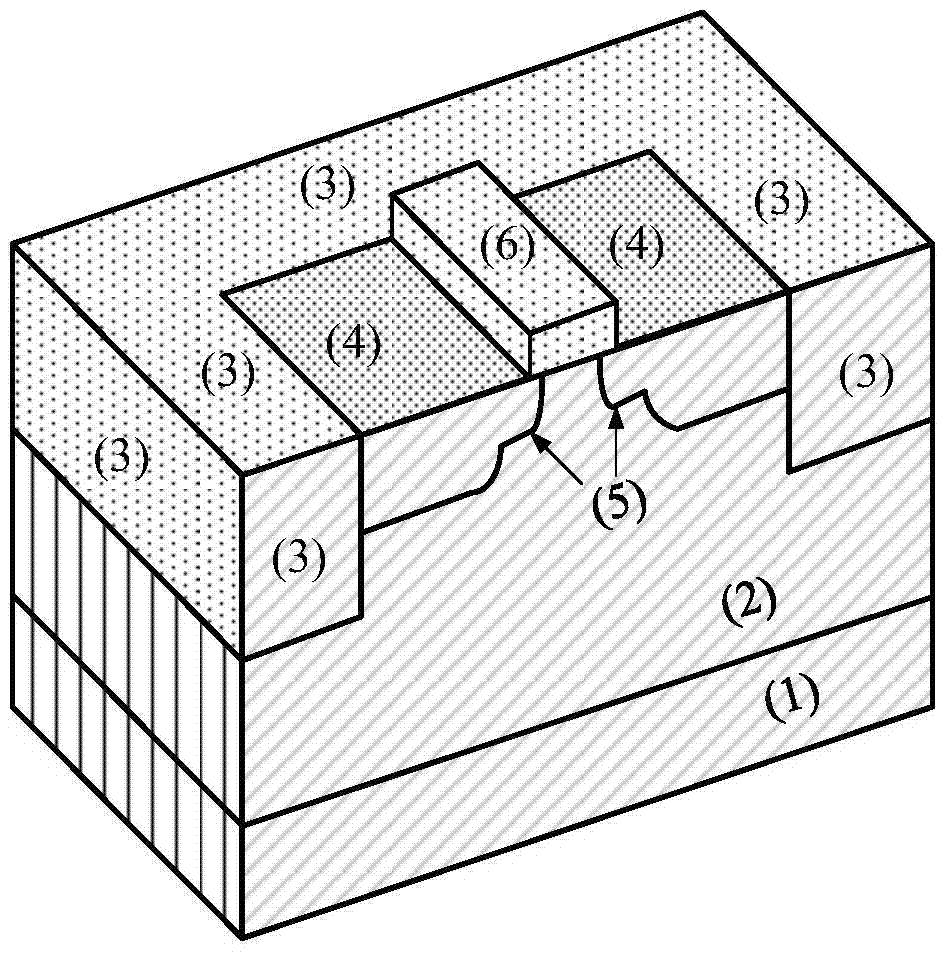
The invention discloses a 65nm technology-based super-steep reverse-doping radiation-proof MOS field-effect tube, mainly solving the problems of increased OFF leakage current, threshold voltage drift and subthreshold oscillation amplitude degradation of a conventional 65nm MOS field-effect tube under a total dose radiation environment. The MOS field-effect tube comprises a P-type substrate (1) and an epitaxial layer (2) located on the substrate, wherein an isolation groove (3) is formed around a place above the epitaxial layer, a grid electrode (4) is arranged at the middle above the epitaxial layer, a source region (5) and a drain region (6) are arranged in the epitaxial layer between two side boundaries of the grid electrode and the inner boundary of the isolation groove, light-doping source-drain regions (7) are arranged in the epitaxial layer below the two side boundaries of the grid electrode, a channel is formed in an area between the two light-doping source-drain regions and right below the grid electrode, and a heavy-doping super-steep reverse-doping region (8) is arranged below the channel between the two light-doping source-drain regions. The 65nm technology-based super-steep reverse-doping radiation-proof MOS field-effect tube improves the total dose irradiation resistance of a device, and can be used for the preparation of large scale integrated circuits.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
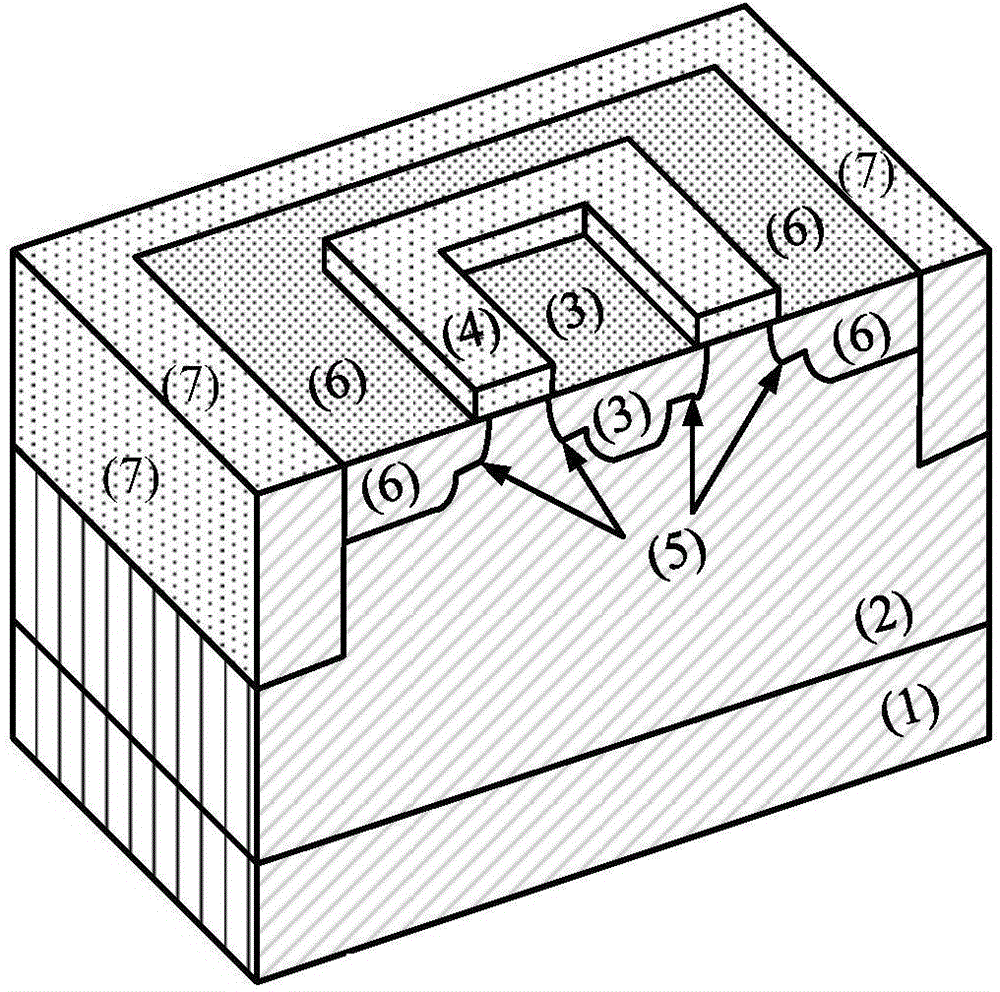
Gate-all-around anti-irradiation MOS field effect transistor based on 65 nm technology
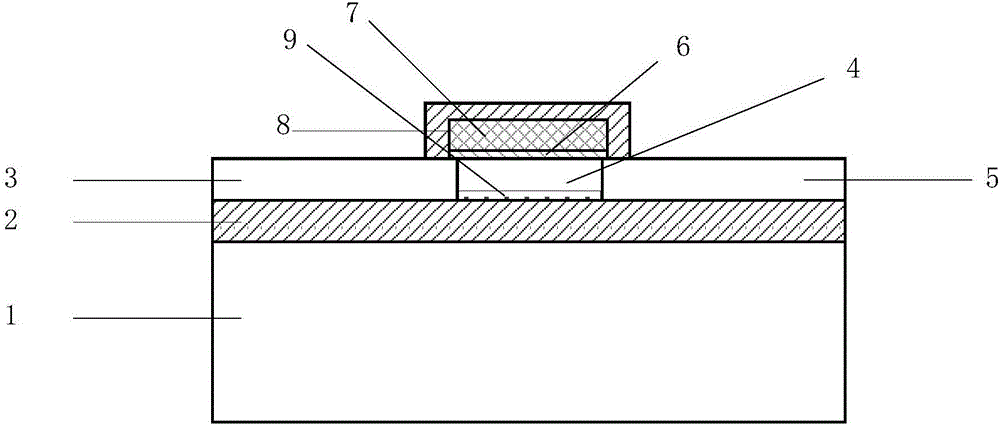
InactiveCN104934475AReduce leakage currentHigh working reliabilityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGratingSubthreshold swing
The present invention discloses a gate-all-around anti-irradiation MOS field effect transistor based on a 65 nm technology for mainly solving the problems of threshold voltage drift, subthreshold swing degeneration and off-state leakage current degeneration of a conventional 65 nm MOS field effect transistor under a total dose radiation environment. The gate-all-around anti-irradiation MOS field effect transistor based on the 65 nm technology comprises a P-type substrate (1) and an epitaxial layer (2) located on the substrate, a drain region (3) is arranged in the middle of the epitaxial layer, and a grid (4) is arranged above the epitaxial layer adjacent to the periphery of the drain region (3). Light doping source drain regions (5) are arranged in the epitaxial layer below the boundaries at the inner and outer sides of the grid, an area between the light doping source drain regions forms a channel, and a source region (6) is arranged in the epitaxial layer adjacent to the periphery of the grid. An isolating groove (7) is arranged in the epitaxial layer adjacent to the periphery of source region, and a grating ring, a source ring and an isolating groove ring sleeve structure surrounding the exterior of an active region orderly are formed. The gate-all-around anti-irradiation MOS field effect transistor based on the 65 nm technology of the present invention enables the device anti-total dose radiation capability to be improved, and can be used to manufacture a large-scale integrated circuit.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
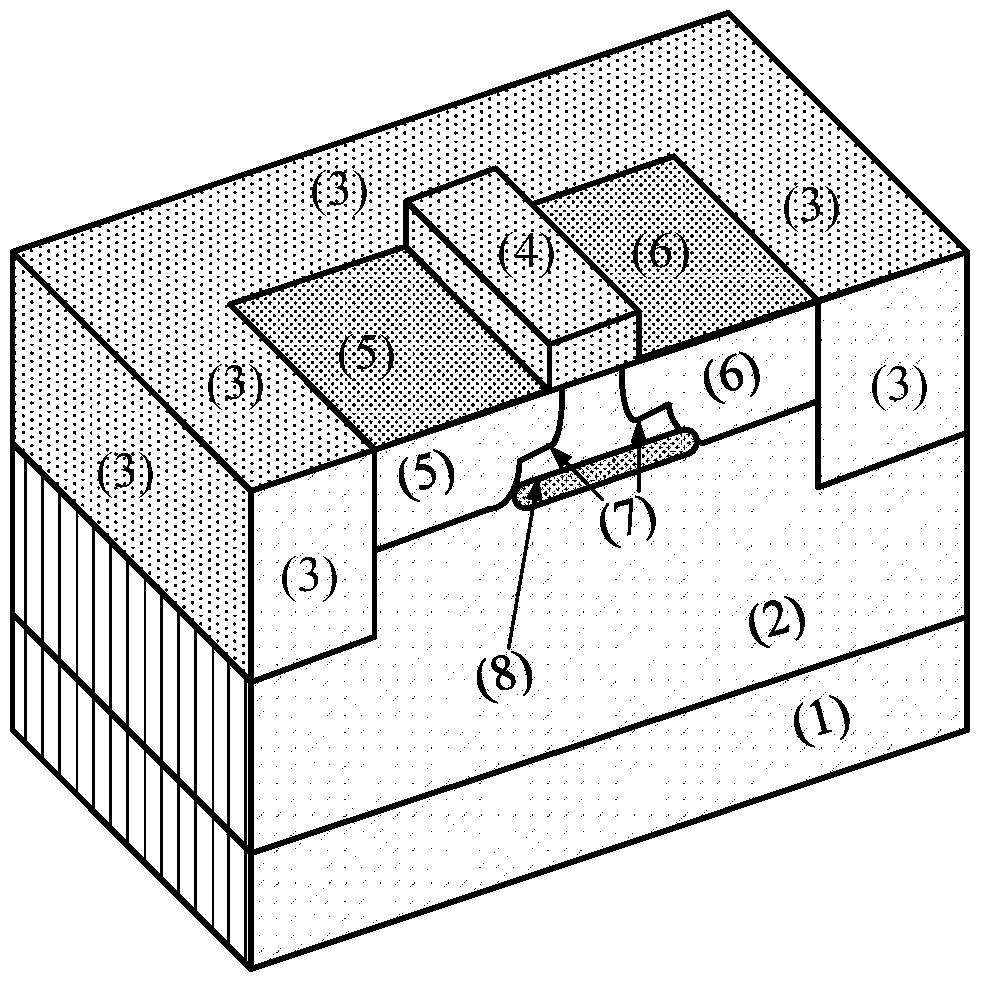
Redundant doping radiation-proof MOS (Metal Oxide Semiconductor) field-effect tube based on 65nm process
ActiveCN104752513AAvoid conductionReduce sensitivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEngineeringField-effect transistor
The invention discloses a redundant doping radiation-proof MOS (Metal Oxide Semiconductor) field-effect tube based on a 65nm process, and mainly solves that a traditional 65nm MOS field-effect tube has the problems of threshold voltage drifting, sub-threshold swing degeneration and the degeneration of OFF leakage current under a total dose irradiation environment. The field-effect tube comprises a P-type substrate (1) and epitaxial layers (2) located on a substrate, wherein isolation grooves (3) and grids (6) are respectively arranged all around the upper parts and middle parts of the epitaxial layers, the epitaxial layers between the two side boundaries of a grid and the boundaries in the isolation grooves are internally provided with source and drain active areas (4), and the epitaxial layers below the two side boundaries of the grid are internally provided with light dope source and drain areas (5); a channel is formed in an area between the two light dope source and drain areas (5) is located just below the grid, and a redundant doping areas (7) are inserted in the interfaces of the epitaxial layers at the bottom of the two side isolating grooves which are parallel to the length direction of the channel. According to the MOS field-effect tube provided by the invention, the total dose resistant radiation capacity of devices can be improved, and the field-effect tube can be used for preparing massive integrated circuits.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
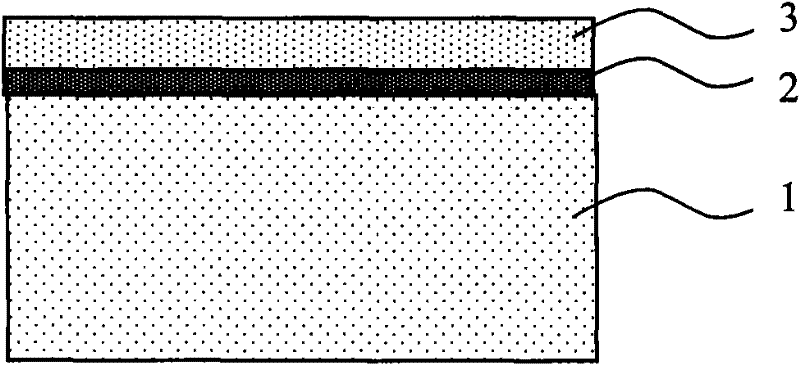
SOI device resistant to total dose radiation and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN101859782AThe preparation process steps are simpleEnhance the performance of anti-total dose radiationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh energyGas phase
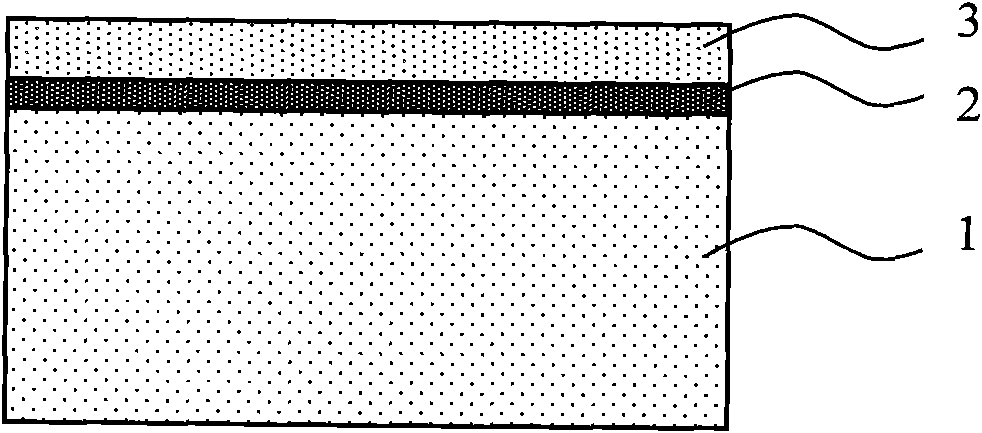
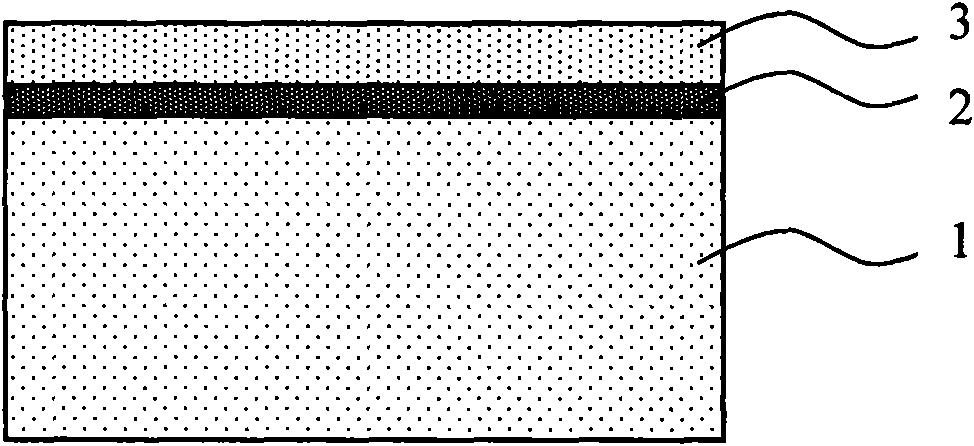
The invention discloses a polysilicon-based SOI device resistant to total dose radiation and a manufacturing method thereof, belonging to the field of electric technology. The SOI device comprises a substrate layer, a buried oxide layer and a top layer, wherein the buried oxide layer comprises a polysilicon sacrificial layer and generates fixed negative charges in the polysilicon sacrificial layer; the substrate layer is made of P-type silicon; and the buried oxide layer is made of silicon dioxide. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps: a) forming a first SiO2 layer on the silicon wafer by thermal oxide growth; b) forming the polysilicon sacrificial layer on the first SiO2 layer by low pressure chemical vapor deposition; c) forming a second SiO2 layer on the polysilicon sacrificial layer by thermal oxide growth; and d) forming the P-type silicon layer on the second SiO2 layer by low pressure chemical vapor deposition. The invention can be applied to such industries related to total dose radiation as aerospace, military, nuclear power, high-energy physics and the like.
Owner:SEMICONDUCTOR MANUFACTURING INTERNATIONAL (BEIJING) CORP +1
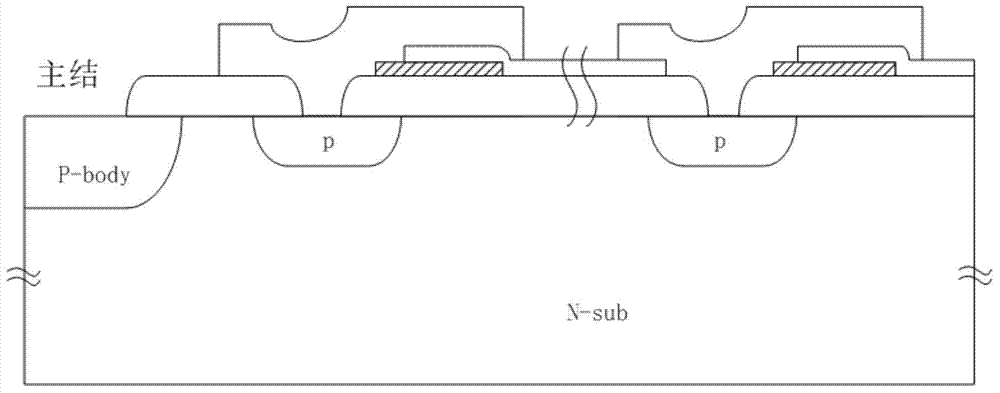
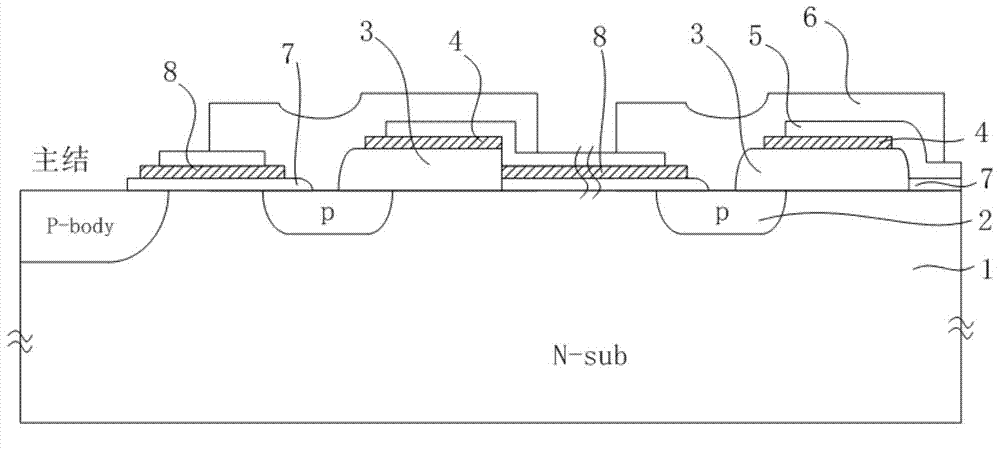
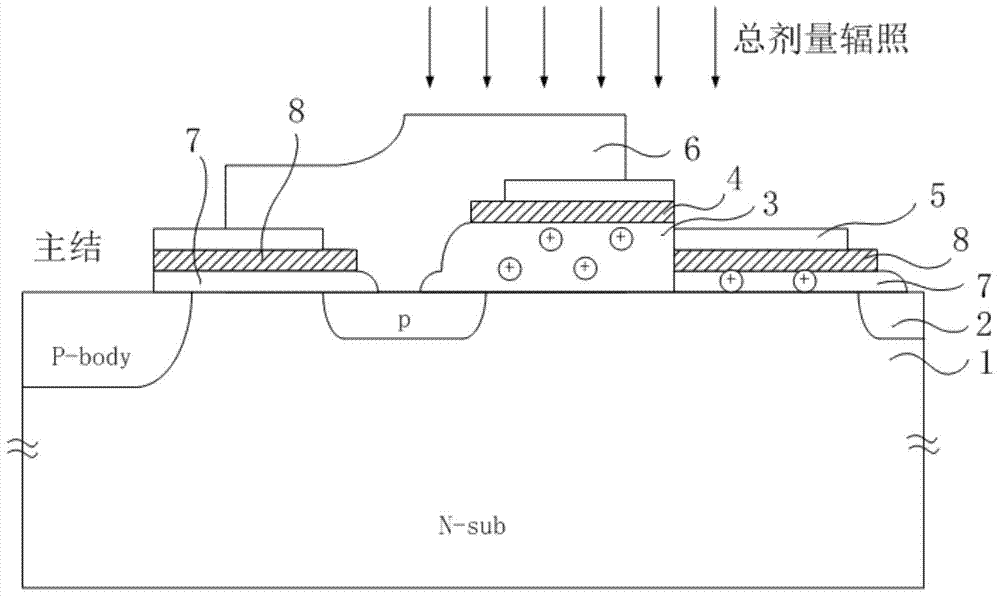
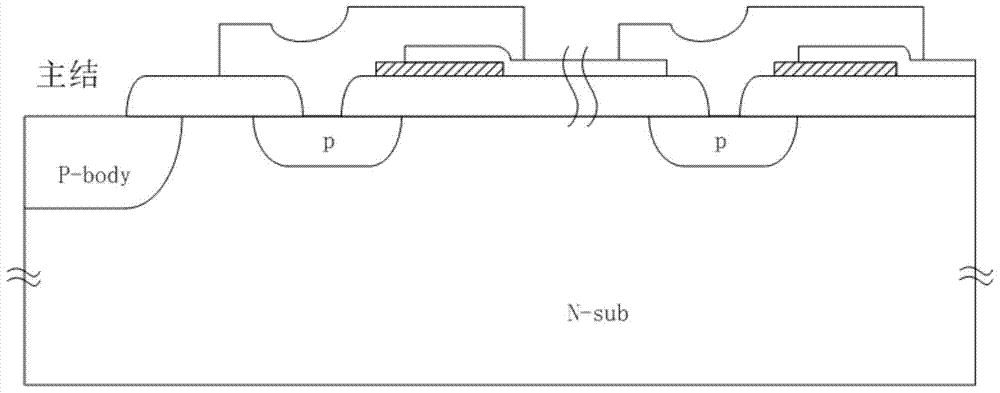
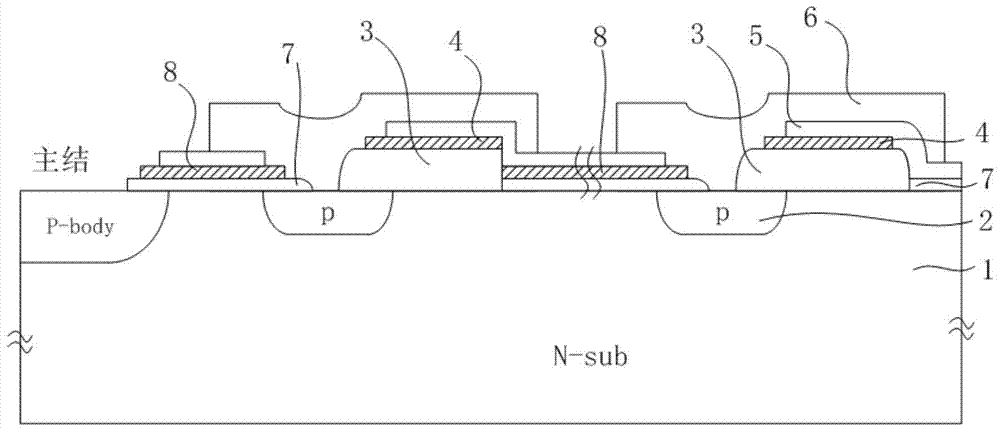
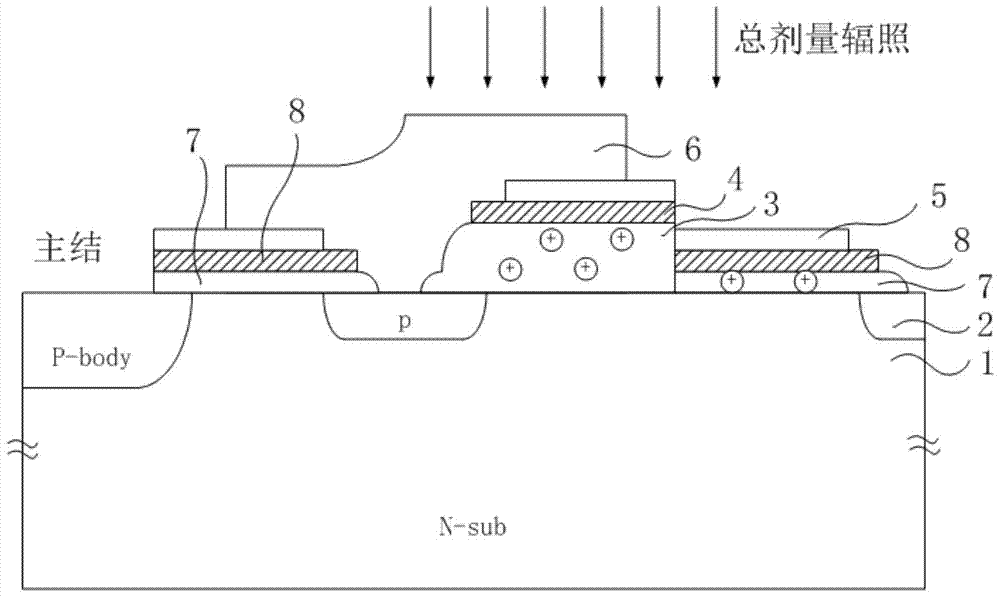
Junction terminal structure for power device
ActiveCN104505401AEnhance the performance of anti-total dose radiationReduced withstand voltage dropSemiconductor devicesCapacitancePower semiconductor device
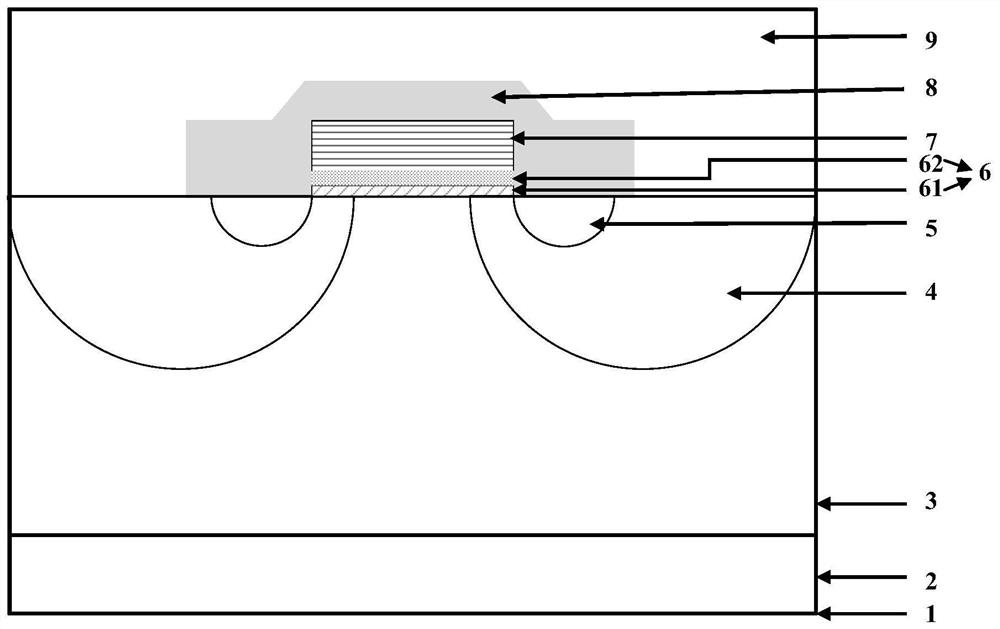
The invention relates to the technical field of power semiconductors, in particular to a junction terminal structure capable of improving the total dose radiation resistance. The junction terminal structure is mainly characterized in that different thicknesses of field oxide layers are arranged on both sides above a field limiting ring, and polycrystalline silicon field plates are arranged on both sides above the field limiting ring; since the thicknesses of the field oxide layers below the polycrystalline silicon field plates are different, a height difference exists in the longitudinal direction of the polycrystalline silicon filed plates on both sides; a structure with a capacitor function is formed by the polycrystalline silicon field plate structures which are formed in a staggered manner and the field oxide layer structure below the polycrystalline silicon field plates, an overlaying effect formed by total dose radiation to an electric field below the field plate on the right side is weakened by redistribution, and thus the voltage endurance capability of a junction terminal after total dose radiation is improved to a certain degree. According to the junction terminal structure disclosed by the invention, the total dose radiation resistance of the device is improved on the premise of not increasing the area of the junction terminal, so that the voltage endurance drop caused by radiation is reduced, and the demands under high-power and complex environment application are met. The junction terminal structure is especially applicable to power semiconductor devices.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
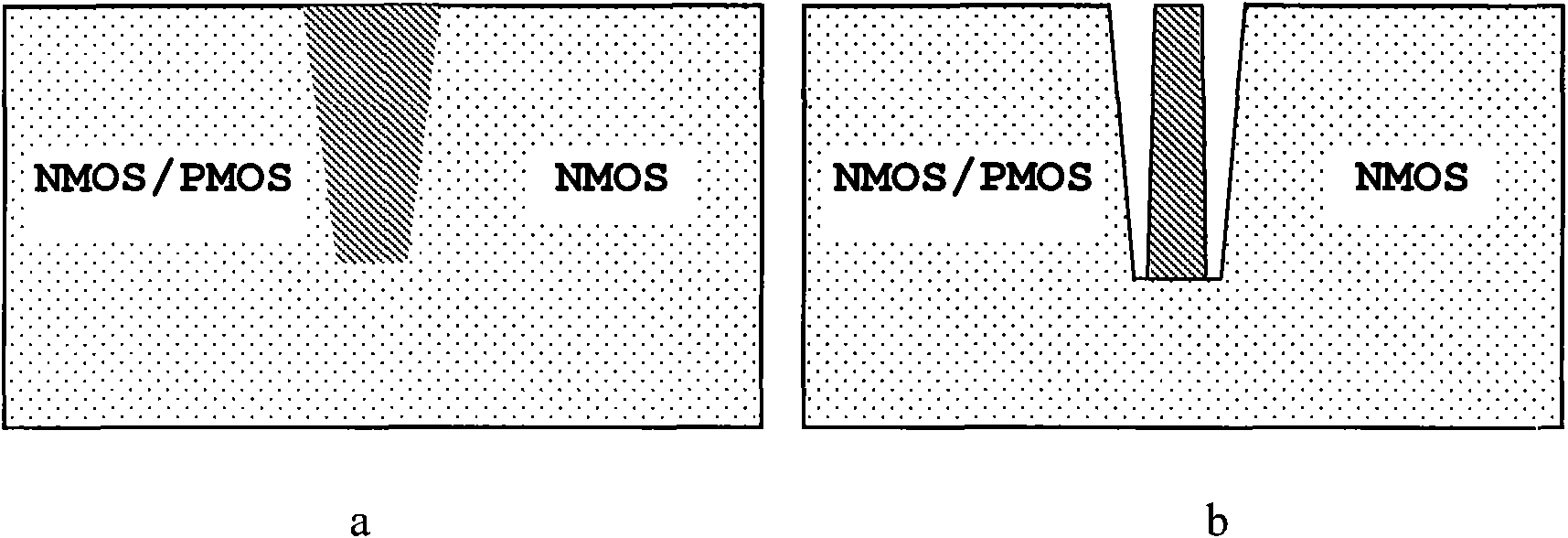
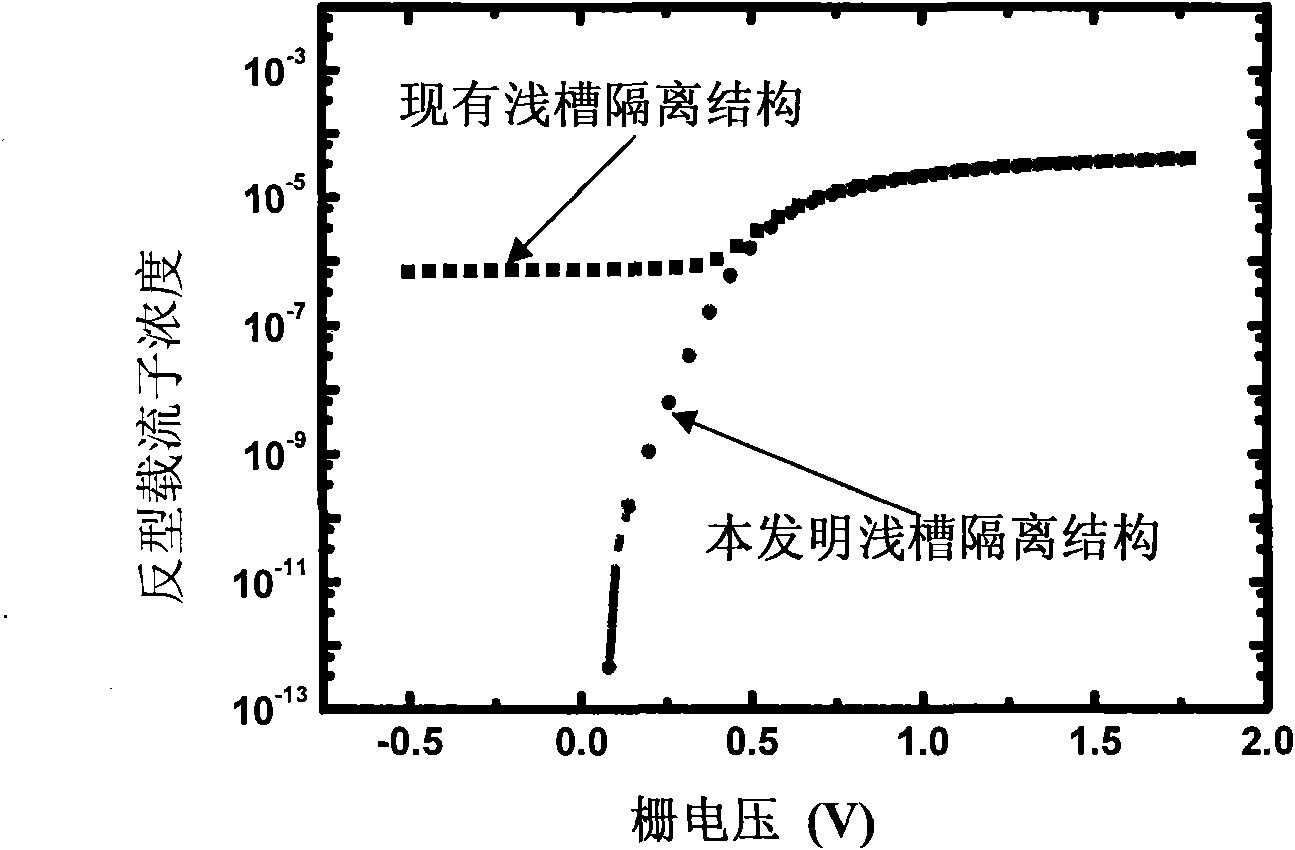
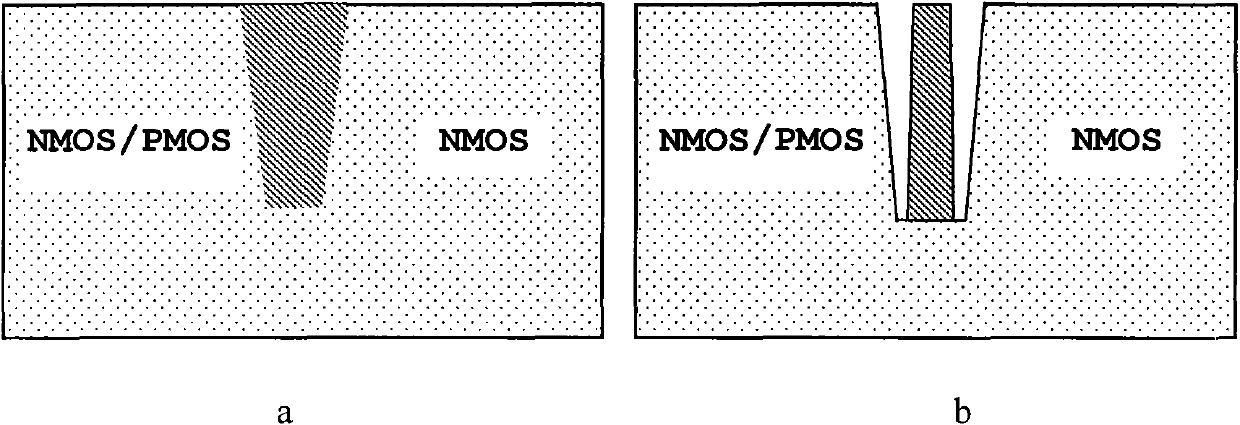
Integrated circuit resisting NMOS element total dose radiation based on materials with high dielectric constants
InactiveCN101667577AThe preparation process steps are simpleEnhance the performance of anti-total dose radiationTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh energyNuclear power
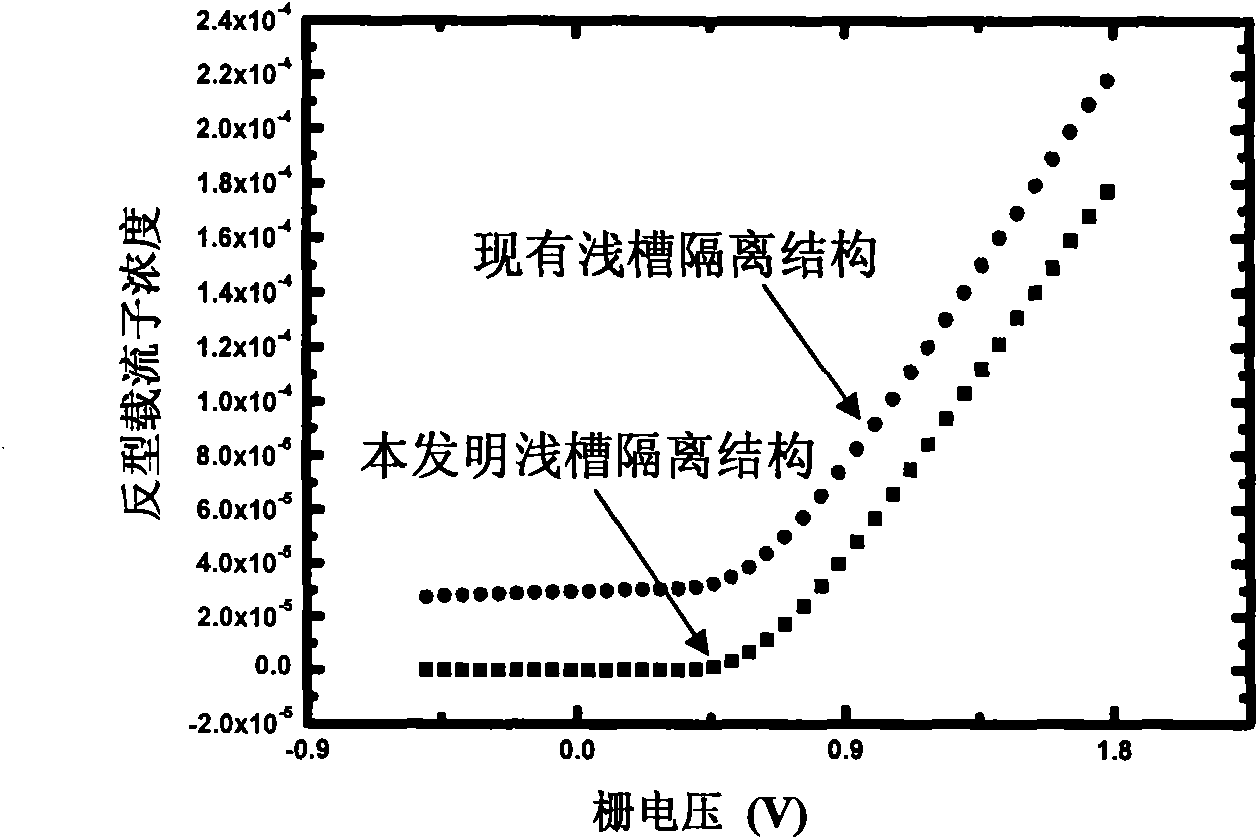
The invention discloses an integrated circuit resisting NMOS element total dose radiation based on materials with high dielectric constants, belonging to the technical field of electronics. The integrated circuit resisting NMOS element total dose radiation comprises an NMOS element and can also comprise a PMOS element, wherein the elements are insulated by a groove on a substrate. The integrated circuit resisting NMOS element total dose radiation is characterized in that an interface material with a high dielectric constant exists between a groove filling material and a substrate material in the groove adjacent to the NMOS element. The dielectric constant of the interface material is preferably larger than 3.9. The interface material can be one or more selected from nickel oxide, zirconiumoxide, lead oxide, aluminum oxide, nitrogen oxide, lanthanum oxide, hafnium oxide and tantalum oxide. The invention can be applied to spaceflight, military, nuclear power, high energy physics and other industries relevant to total dose radiation.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
SOI device resistant to total dose radiation and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN101859781AAnti-type effect is weakenedIncrease distanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh energyP type silicon
The invention discloses an SOI device resistant to total dose radiation and a manufacturing method thereof, belonging to the field of electric technology. The SOI device comprises a substrate layer, a buried oxide layer and a top layer, wherein a sacrificial layer is arranged between the buried oxide layer and the substrate layer and generates negative charges after the SOI device is subjected to total dose radiation; the sacrificial layer is made of silicon nitride; the substrate layer is made of P-type silicon; and the buried oxide layer is made of silicon dioxide. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps: a) forming the SiO2 buried oxide layer on the silicon wafer; b) forming the silicon nitride sacrificial layer on the SiO2 buried oxide layer; and c) forming the P-type silicon substrate layer on the silicon nitride sacrificial layer. The invention can be applied to such industries related to total dose radiation as aerospace, military, nuclear power, high-energy physics and the like.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Novel integrated circuit resisting NMOS element total dose radiation
InactiveCN101667576AThe preparation process steps are simpleEnhance the performance of anti-total dose radiationTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsNuclear powerHigh energy
The invention discloses a novel integrated circuit resisting NMOS element total dose radiation, belonging to the technical field of electronics. The novel integrated circuit resisting NMOS element total dose radiation comprises an NMOS element and can also comprise a PMOS element, wherein the elements are insulated by a groove on a substrate. The novel integrated circuit resisting NMOS element total dose radiation is characterized in that a silicon dioxide material prepared through steam oxidation exists between a groove filling material and a substrate material in the groove adjacent to the NMOS element. The silicon dioxide prepared through steam oxidation is prepared by the following method: introducing mixed gases of high purity water and oxygen into an interface containing silicon to oxidize the silicon in the interface so as to obtain silicon dioxide. The invention can be applied to spaceflight, military, nuclear power, high energy physics and other industries relevant to total dose radiation.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Integrated circuit resisting NMOS element total dose radiation
InactiveCN101667573AThe preparation process steps are simpleEnhance the performance of anti-total dose radiationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesHigh energyNuclear power
The invention discloses an integrated circuit resisting NMOS total dose radiation, belonging to the technical field of electronics. The integrated circuit resisting NMOS total dose radiation comprisesan NMOS element and can also comprises a PMOS element, wherein the elements are insulated by a groove on a substrate. The integrated circuit resisting NMOS total dose radiation is characterized in that an insulation material exists between a groove filling material and a substrate material in the groove adjacent to NMOS element and generates fixed negative charges under total dose radiation. Theinsulation material is selected from silicon nitride, titanium nitride and tantalum nitride or a mixture thereof. The thickness of the insulation material ranges from 10 nm to 80 nm. The invention canbe applied to spaceflight, military, nuclear power, high energy physics and other industries relevant to total dose radiation.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
A kind of anti-total dose radiation hardening method of flash storage circuit
ActiveCN109215715BEnhance the performance of anti-total dose radiationRead-only memoriesRadiation resistantHemt circuits
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Novel integrated circuit resisting NMOS element total dose radiation
InactiveCN101667578AEnhance the performance of anti-total dose radiationReduce power consumptionTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsNuclear powerAir interface
The invention discloses a novel integrated circuit resisting NMOS total dose radiation, belonging to the technical field of electronics. The novel integrated circuit resisting NMOS total dose radiation comprises an NMOS element and can also comprises a PMOS element, wherein the elements are insulated by a groove on a substrate. The novel integrated circuit resisting NMOS total dose radiation is characterized in that: in the groove a adjacent to the NMOS element, an air interface layer exists between a groove filling material and a substrate material arranged at one side of the groove filling material, and another air interface layer also exists between the groove filling material and a substrate material arranged at the other side of the groove filling material. The air interface layers are formed through etching contact parts among the groove filling material and the substrate materials. The invention can be applied to spaceflight, military, nuclear power, high energy physics and other industries relevant to total dose radiation.
Owner:SEMICONDUCTOR MANUFACTURING INTERNATIONAL (BEIJING) CORP +1
A bulk silicon mosfet structure
ActiveCN103500760BReduce heating effectReduce manufacturing costSemiconductor devicesMOSFETField-effect transistor
The invention discloses a bulk-silicon MOSFET (METAL-OXIDE-SEMICONDUCTOR FIELD-EFFECT TRANSISTOR) structure. The bulk-silicon MOSFET structure comprises a p+ layer (2) and an n- layer (3), wherein the p+ layer (2) and the n- layer (3) are directly contacted; the n- layer is made of wide-bandgap 6H-SiC material. The bulk-silicon MOSFET structure disclosed by the invention has the advantage that the radiation resistance of the bulk-silicon structure is improved. Compared with the SOI (Silicon On Insulator) technology, the bulk-silicon MOSFET structure disclosed by the invention has the beneficial effects that the self-heating effect is improved, the total dosage effect is eliminated, and the cost is reduced.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
A kind of vdmos device manufacturing method with anti-irradiation performance
ActiveCN104576398BSimple processManufacturing process compatibleSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDielectricGate oxide
The invention discloses a manufacture method of a VDMOS device with irradiation resistance. The manufacture method of the VDMOS device is characterized by forming a gate oxide layer, evaporating aluminum on the gate oxide layer, and then diffusing aluminum at high temperature to form a gate medium of an Si-O-Al structure. Positive charges accumulated in the gate medium can be reduced when the VDMOS device is irradiated; the resistance to total dose irradiation of the device is improved; meanwhile, compared with the conventional silicon dioxide gate medium, the gate medium of the Si-O-Al structure is higher in dielectric constant; the resistance to single event gate rupture of the device can be improved. The manufacture method can be used for effectively overcoming the contradiction of requirements on the thickness of the resistance to total dose irradiation and the single event gate rupture and optimizing the resistance to total dose irradiation and the single event gate rupture at the same time; the process is simple; the resistance to the irradiation of the VDMOS device is improved.
Owner:BEIJING MXTRONICS CORP +1
A vdmos device with anti-total dose radiation and its manufacturing method
ActiveCN109950306BIncreasing the thicknessGuaranteed thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMedicinePolysilicon gate
The invention provides a VDMOS device with total dose irradiation resistance and a manufacturing method thereof. The device comprises a composite gate oxide layer, a polysilicon gate electrode and anN-epitaxial layer. The composite gate oxide layer comprises a silicon dioxide layer and a silicon nitride layer, and the composite gate oxide layer is between the N-epitaxial layer and the polysilicongate. The present invention provides the VDMOS device with a two-layer composite gate oxide structure and total dose irradiation resistance and the manufacturing method thereof.
Owner:浙江航芯源集成电路科技有限公司
Total dose radiation resistant strengthening method of a flash memory
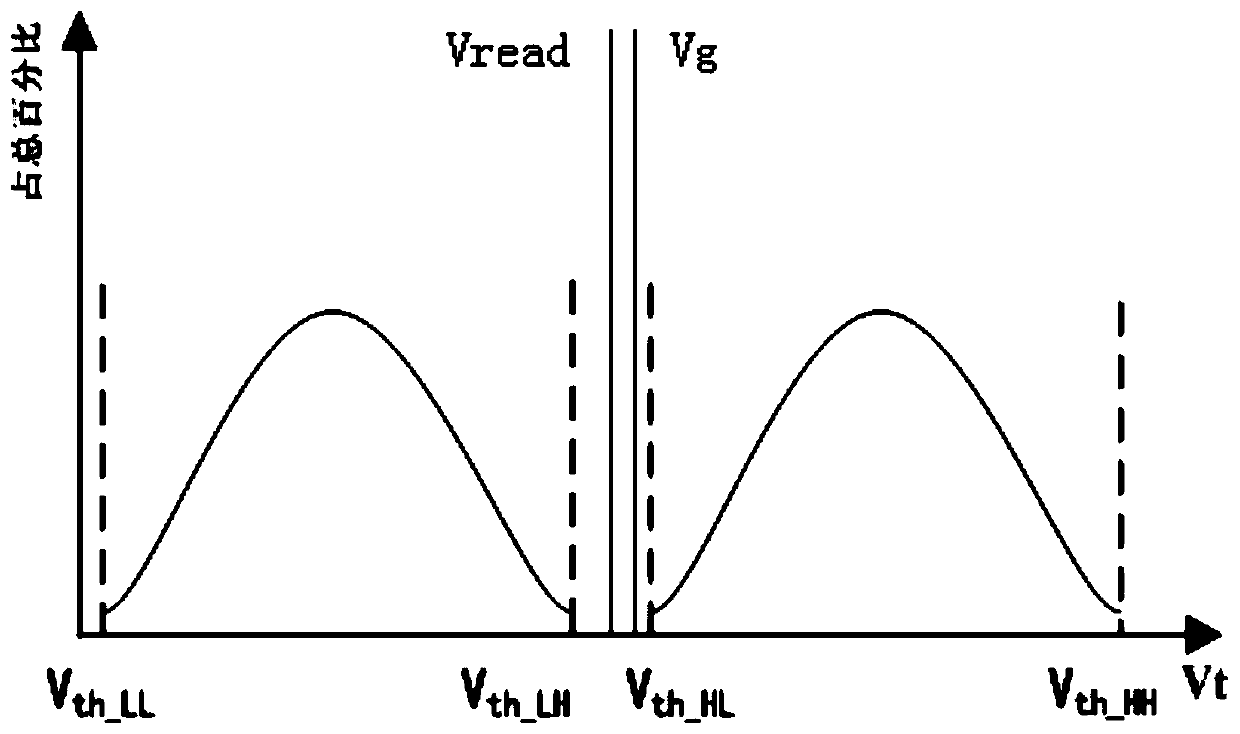
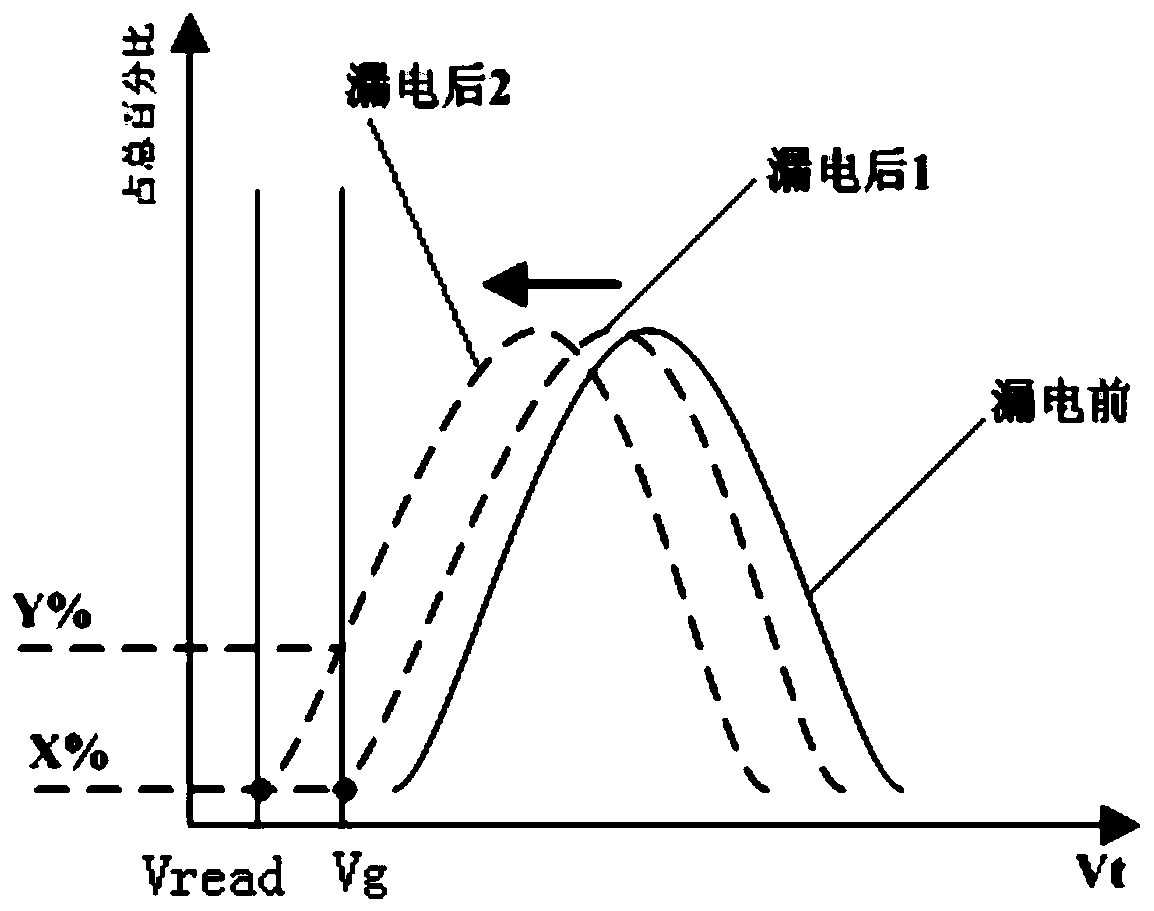
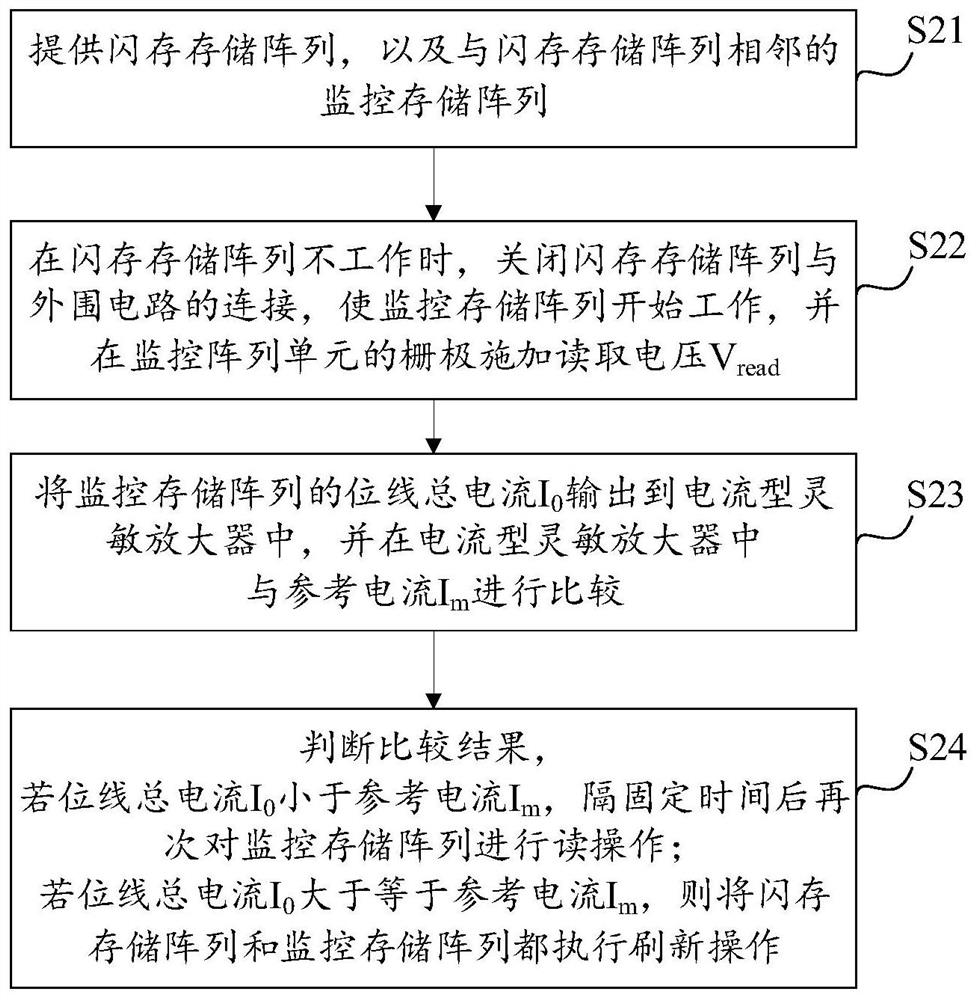
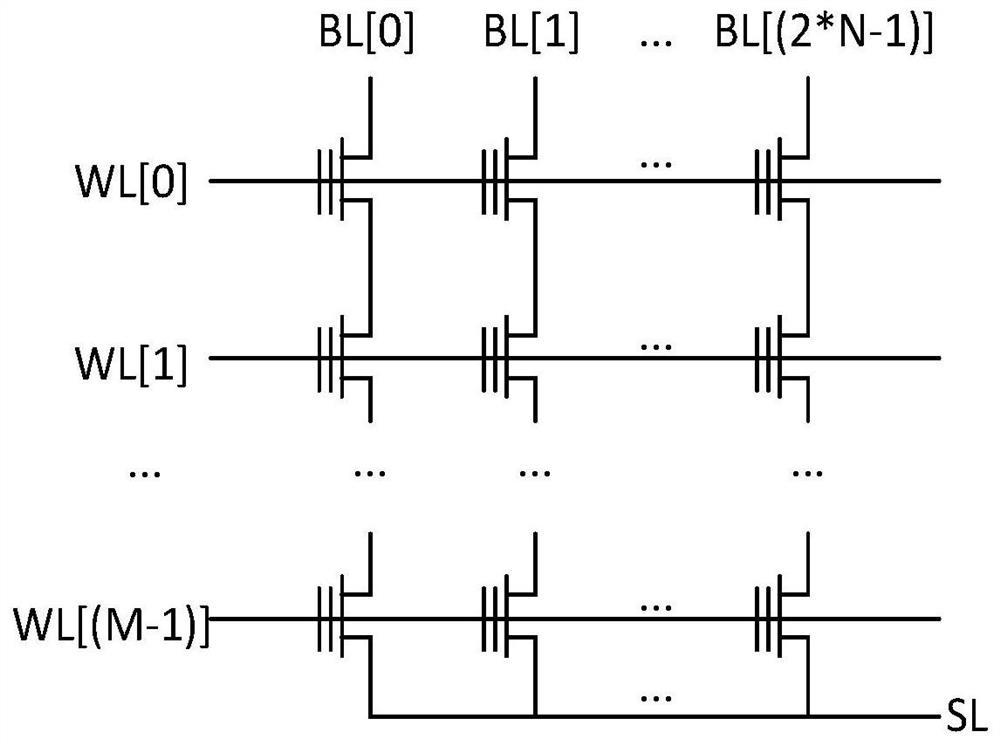
ActiveCN109213620AEnhance the performance of anti-total dose radiationDigital storageRedundant data error correctionBit lineRadiation resistant
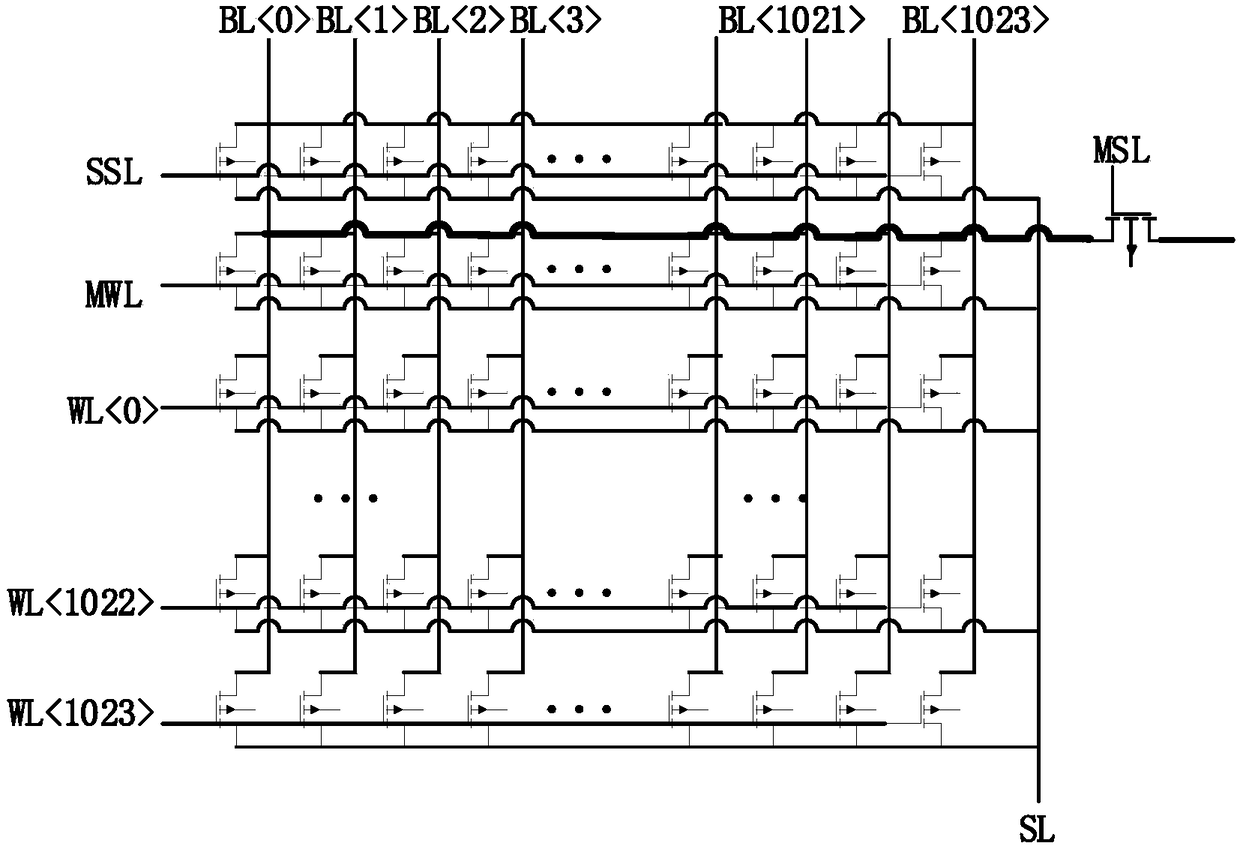
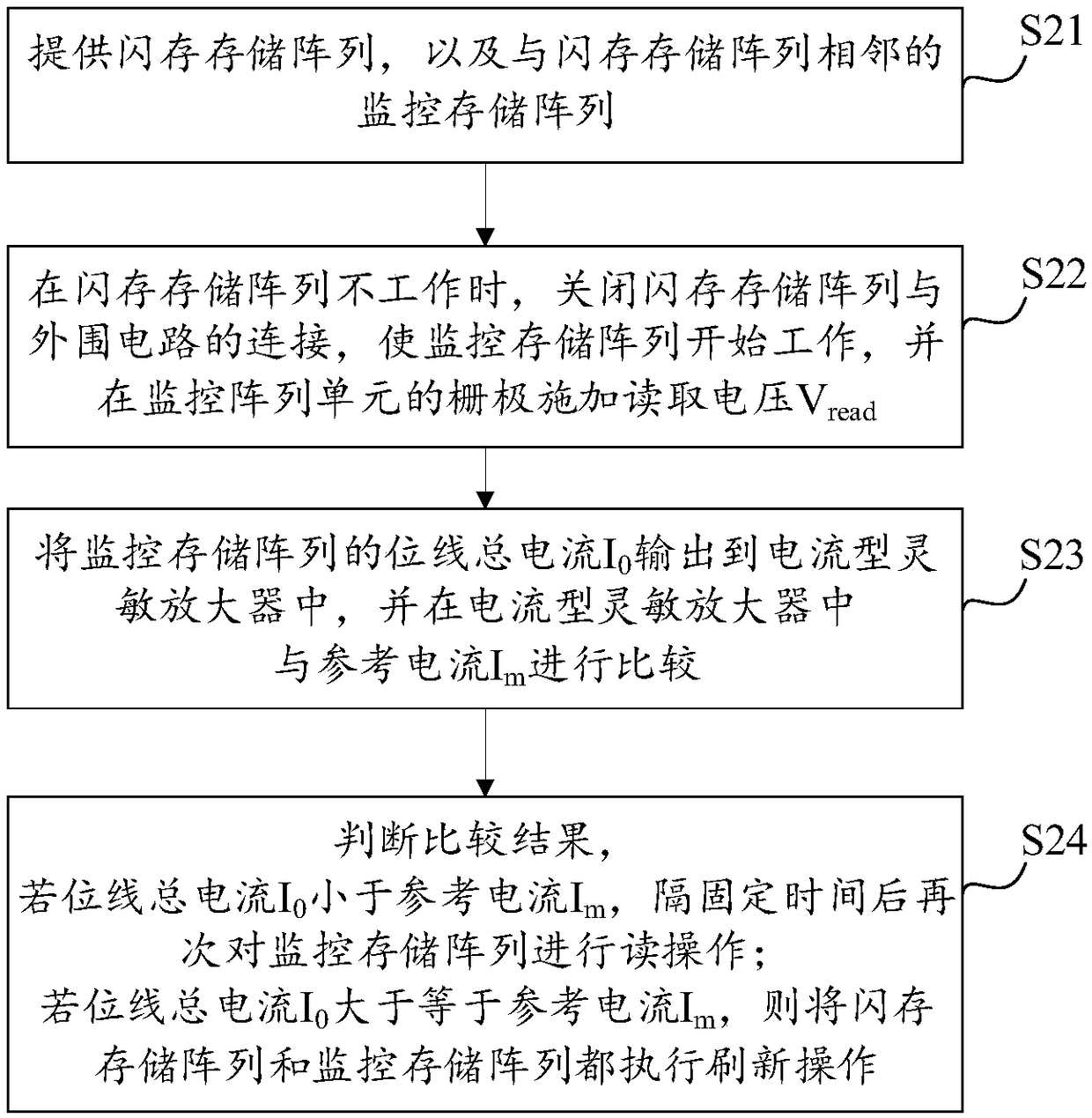
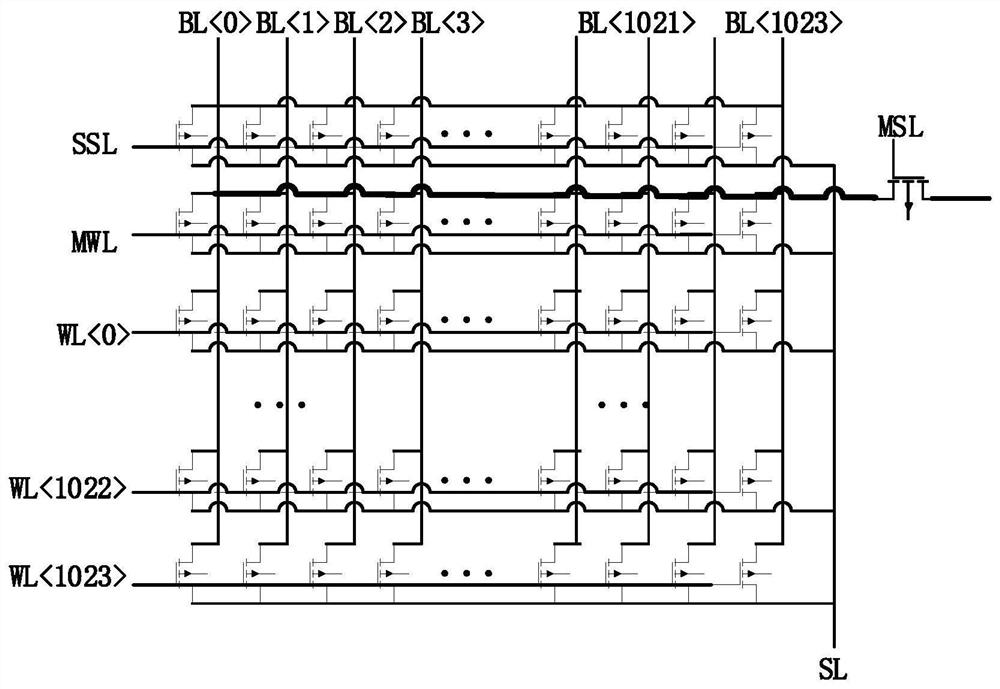
The invention provides a total dose radiation resistant strengthening method of a flash memory, which comprises the following steps of: 1, providing a flash memory array and a monitoring memory arrayadjacent to the flash memory array; 2, when that flash memory array does not work, closing the connection between the flash memory array and the peripheral circuit, so that the monitor memory array starts to work, and applying a read voltage to the grid of the monitoring array unit; 3, comparing the total current output of the bit line of the monitoring memory array with a reference current threshold; 4, judging the comparison result, and if the total current of the bit line is less than the reference current, reading the monitor memory array again after a fixed time interval; if the total bitline current is greater than or equal to the reference current, performing a refresh operation on the flash memory array and the monitor memory array. The invention can detect leakage current by monitoring the magnitude of the bit line current of the memory array, and improve the total dose radiation resistance ability of the memory array.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A kind of anti-total dose radiation hardening method of flash memory
ActiveCN109213620BEnhance the performance of anti-total dose radiationDigital storageRedundant data error correctionBit lineReference current
The present invention provides a method for hardening anti-total dose radiation of flash memory, which includes: step 1, providing a flash memory storage array, and a monitoring storage array adjacent to the flash memory storage array; step 2, when the flash memory storage array is not working, Close the connection between the flash memory storage array and the peripheral circuit, make the monitoring storage array start to work, and apply a read voltage to the gate of the monitoring array unit; step 3, output the total current of the bit line of the monitoring storage array, and compare it with the reference current threshold Compare; step 4, judge the comparison result, if the total current of the bit line is less than the reference current, read the monitoring storage array again after a fixed time interval; if the total current of the bit line is greater than or equal to the reference current, then read the flash memory storage array and the monitoring storage array Perform a refresh operation. The invention can find electric leakage by monitoring the magnitude of the bit line current of the storage array, and improve the ability of the storage array to resist total dose radiation.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A dielectric isolation structure and method for SOI process
ActiveCN106328651BHighly integratedEnhance the performance of anti-total dose radiationTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInsulation layerProcess conditions
Owner:58TH RES INST OF CETC
New type integrated circuit for resisting full-scale irradiation of NMOS component
InactiveCN101719497BThe preparation process steps are simpleEnhance the performance of anti-total dose radiationTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMain group elementHigh energy
Owner:SEMICONDUCTOR MANUFACTURING INTERNATIONAL (BEIJING) CORP +1
CMOS integrated circuit resisting total dose radiation
InactiveCN101667580BEnhance the performance of anti-total dose radiationEliminates parasitic leakageTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCMOSNuclear power
The invention discloses a CMOS integrated circuit resisting total dose radiation, belonging to the technical field of electronics. The CMOS integrated circuit resisting total dose radiation comprises an NMOS element and a PMOS element which are insulated by a groove. The CMOS integrated circuit resisting total dose radiation is characterized in that the groove is filled with a mixture of a first insulation material and a second insulation material, wherein the first insulation material generates fixed positive charges under the total dose radiation, the second insulation material generates fixed negative charges under the total dose radiation, and the mixture is in weak charges or electric neutrality. The invention can be applied to spaceflight, military, nuclear power, high energy physics and the other industries relevant to total dose radiation.
Owner:SEMICONDUCTOR MANUFACTURING INTERNATIONAL (BEIJING) CORP +1
SOI device resistant to total dose radiation and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN101859782BThe preparation process steps are simpleEnhance the performance of anti-total dose radiationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh energyNuclear power
The invention discloses a polysilicon-based SOI device resistant to total dose radiation and a manufacturing method thereof, belonging to the field of electric technology. The SOI device comprises a substrate layer, a buried oxide layer and a top layer, wherein the buried oxide layer comprises a polysilicon sacrificial layer and generates fixed negative charges in the polysilicon sacrificial layer; the substrate layer is made of P-type silicon; and the buried oxide layer is made of silicon dioxide. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps: a) forming a first SiO2 layer on the silicon wafer by thermal oxide growth; b) forming the polysilicon sacrificial layer on the first SiO2 layer by low pressure chemical vapor deposition; c) forming a second SiO2 layer on the polysilicon sacrificial layer by thermal oxide growth; and d) forming the P-type silicon layer on the second SiO2 layer by low pressure chemical vapor deposition. The invention can be applied to such industries related to total dose radiation as aerospace, military, nuclear power, high-energy physics and the like.
Owner:SEMICONDUCTOR MANUFACTURING INTERNATIONAL (BEIJING) CORP +1
Total dose radiation resistant strengthening method of a flash memory circuit
ActiveCN109215715AImprove the ability to resist total dose radiationEnhance the performance of anti-total dose radiationRead-only memoriesVoltageRadiation resistant
The invention provides a total dose radiation resistant strengthening method of a flash memory circuit, which comprises the following steps of: 1, providing a flash memory array and adding a monitoring memory array with a pre-stored logic value of 0 connected to the flash memory array; 2, determining the read voltage of the monitoring memory array; 3, determining a threshold value of a number of monitor memory array cells whose logical value changes to 1; 4, sequentially reading the read data of the monitoring memory array unit and adding the read data under the working state of the flash memory array; 5, comparing the addition result with the quantity threshold value of the monitoring memory array cell, and clearing the addition result when the addition result is less than the quantity threshold value; when the addition result is greater than or equal to the number threshold, refreshing the flash memory array and the monitor memory array. The invention can detect the leakage of the memory array in advance and refresh the memory array in time, thereby improving the total dose radiation resistance of the memory array and ensuring the stability of the device.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A power device junction terminal structure
ActiveCN104505401BEnhance the performance of anti-total dose radiationReduced withstand voltage dropSemiconductor devicesCapacitancePower semiconductor device
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Novel integrated circuit resisting NMOS element total dose radiation
InactiveCN101667578BEnhance the performance of anti-total dose radiationReduce power consumptionTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsNuclear powerAir interface
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (BEIJING) CORP +1
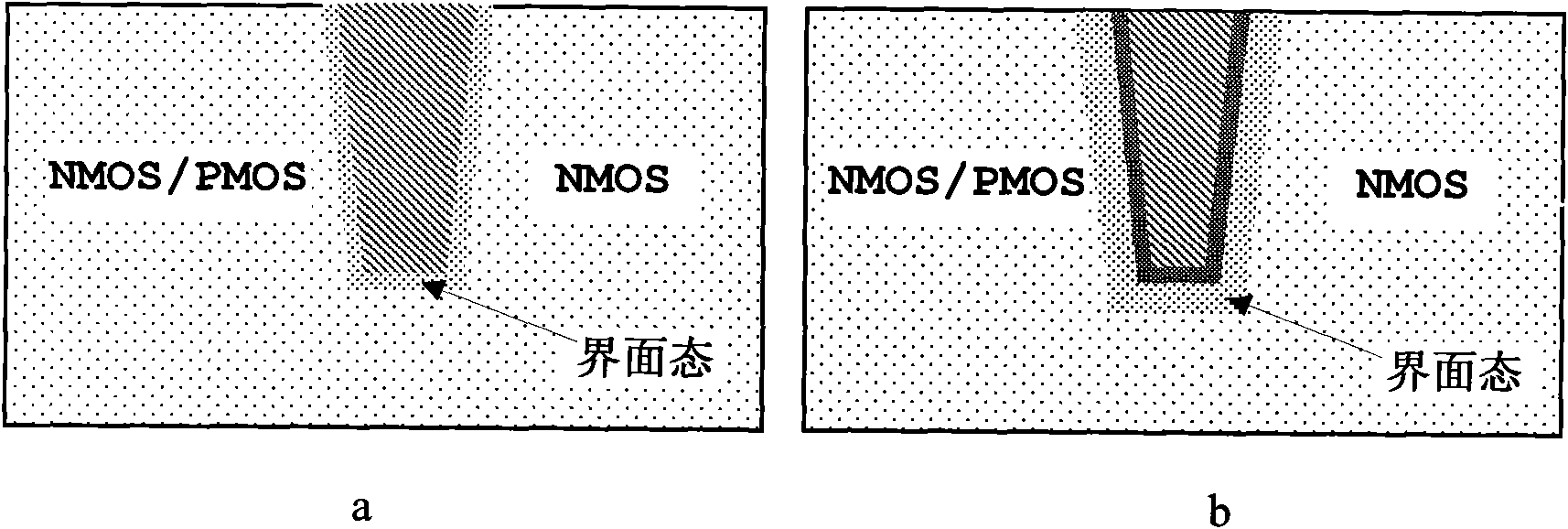
Method for improving total dose irradiation resistance of FinFET device
InactiveCN111697048ALow densityEnhance the performance of anti-total dose radiationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCrystal orientationTotal dose
The invention discloses a method for improving the total dose irradiation resistance of a FinFET device. According to the method, the trap charge density of an oxide layer and the crystal orientationdependence of an interface state are utilized; during layout design, the placement direction of the device is properly adjusted; the channel crystal orientation of the FinFET device is ensured to be (100), so the oxide layer trapped charge density and the interface state density generated in the prepared FinFET device by the total dose irradiation are lower, the influence of the total dose irradiation on the FinFET device is reduced, and the total dose irradiation resistance of the FinFET device is improved.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Anti-Total Dose Effect Reinforcement Method for Flash Storage Circuit
ActiveCN109119110BEnhance the performance of anti-total dose radiationDigital storageParallel computingTotal dose
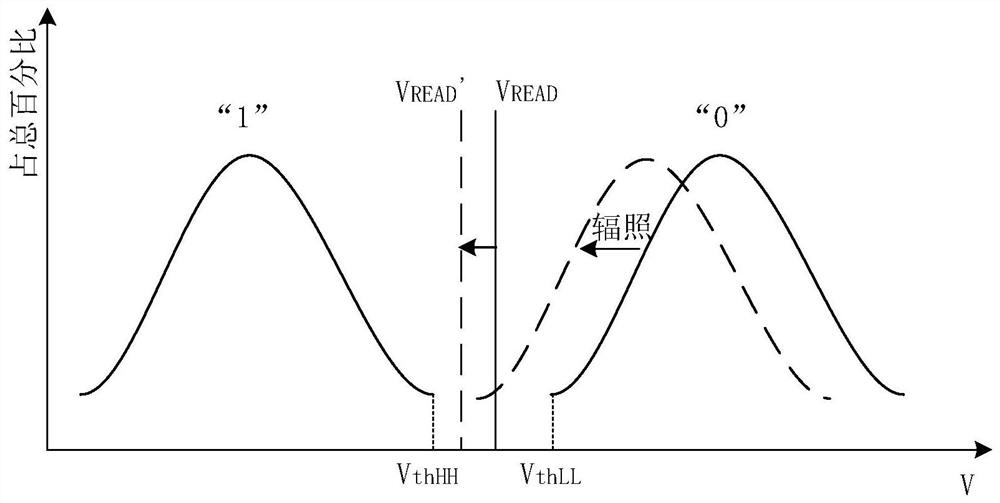
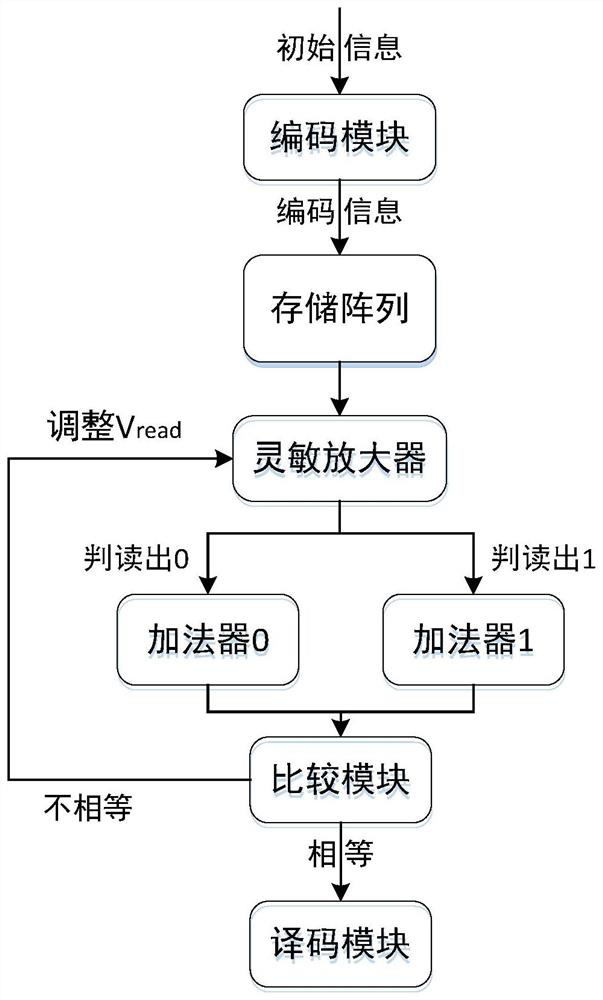
The present invention provides a flash memory storage circuit anti-total dose effect reinforcement method, comprising: step 1, providing a flash memory storage array; step 2, compiling initial information into coded information, and inputting the flash memory storage array, the binary code in the coded information " The number of "0" and "1" is equal; Step 3, interpret the coding information in the flash memory storage array, and count the number of binary codes "0" and "1" obtained from the interpretation; Step 4, compare the statistical results, When the numbers of the interpreted binary codes "0" and "1" are equal, the coded information is decoded and read; when the interpreted numbers are not equal, the read voltage of the flash storage array is adjusted until the interpreted binary code "" The number of 0" and "1" is equal. The invention can effectively maintain the performance stability of the flash storage circuit by adjusting the reading voltage.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com