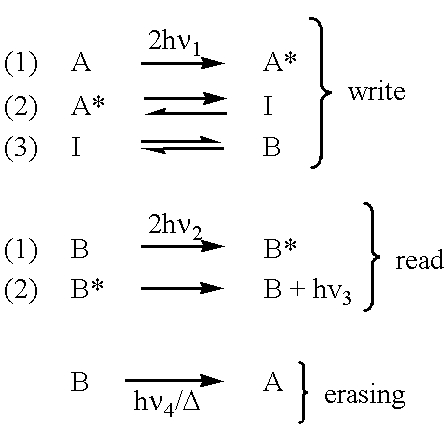Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
231results about "Recording involving reflectivity/absorption/color-change" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
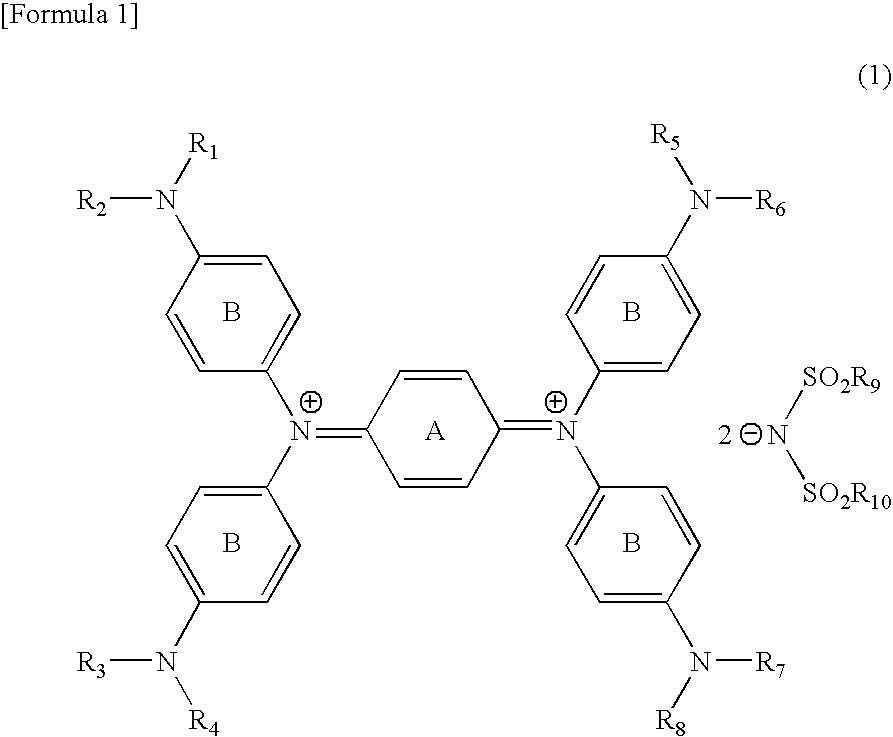
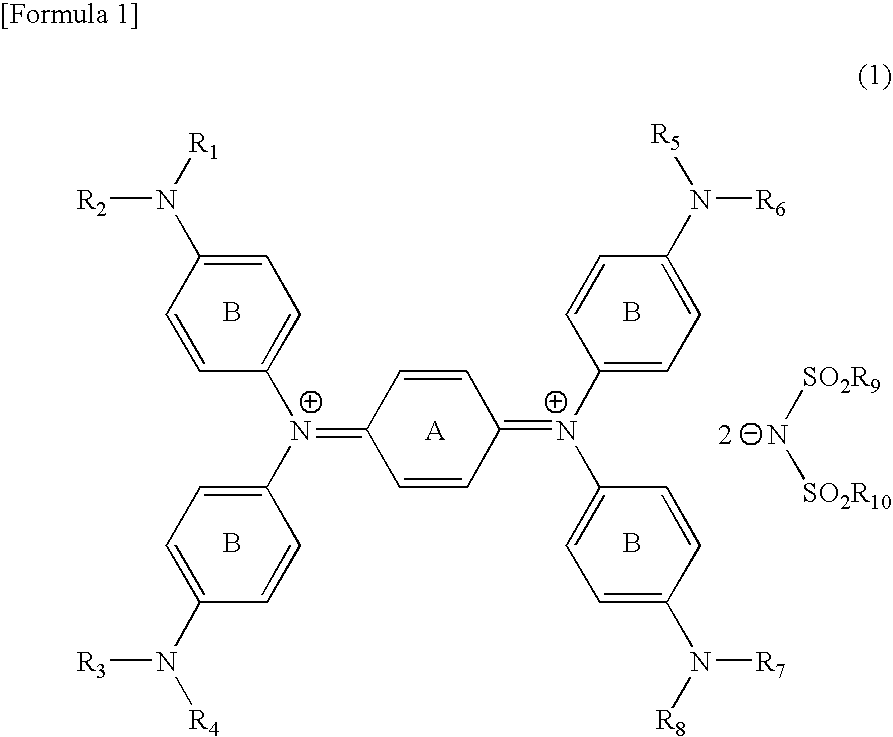
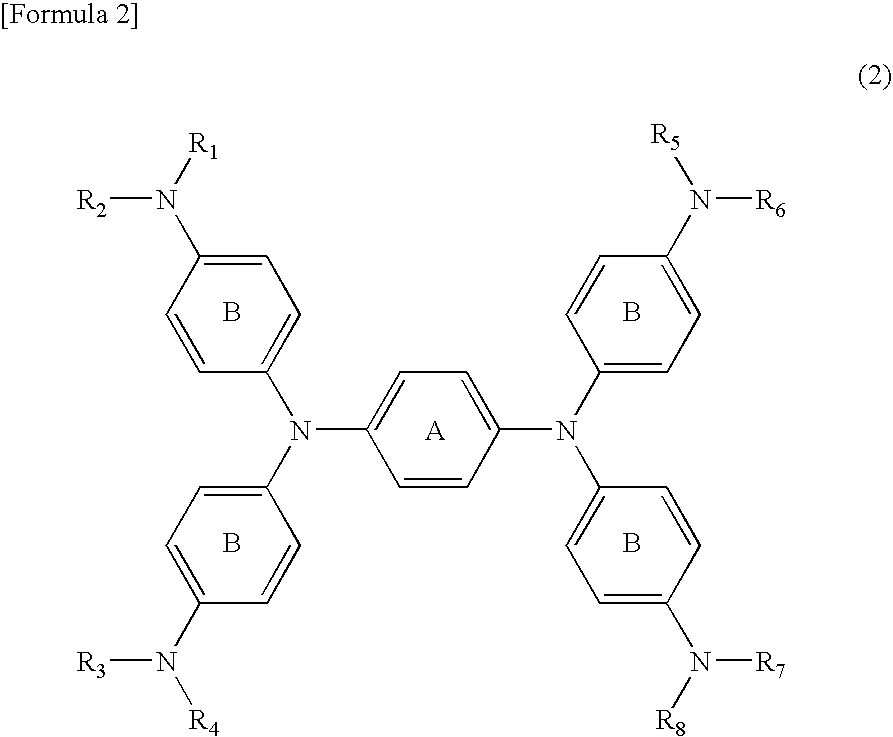
Diimmonium compound and use thereof
InactiveUS20050148786A1High visible light transmittanceHigh light transmittanceOrganic chemistryPhotomechanical apparatusInfraredAmmonium compounds
To provide a near-IR absorption compound free from antimony or arsenic and excellent in stability, especially, in heat resistance, light fastness, and moisture-and-heat resistance and also an IR absorption filter, an optical information recording medium, and a resin composition excellent in durability by using the near-IR absorption compound. The near-IR absorption compound is a diimmonium compound having the following structure and the resin composition contains the diimmonium compound: (wherein R1 to R8 independently denote hydrogen atom or an optionally substituted aliphatic hydrocarbon group; R9 and R10 independently denote an aliphatic hydrocarbon group optionally containing a halogen atom; and rings A and B may further have substituent groups.).
Owner:NIPPON KAYAKU CO LTD
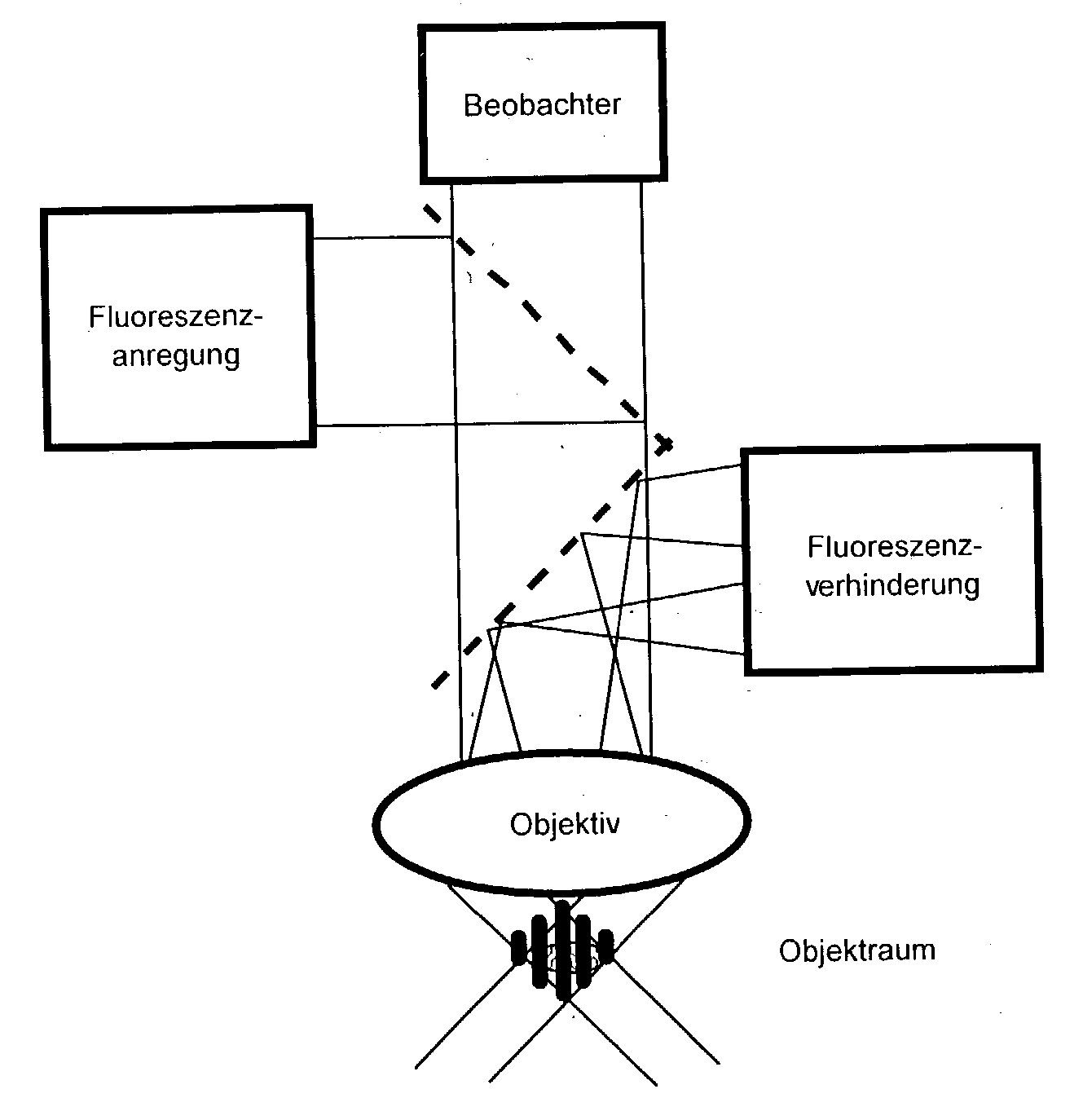
High spatial resoulution imaging and modification of structures
ActiveUS20040212799A1Small intensityLong lastingSpectrum investigationMaterial analysis by optical meansOptical propertyImage resolution
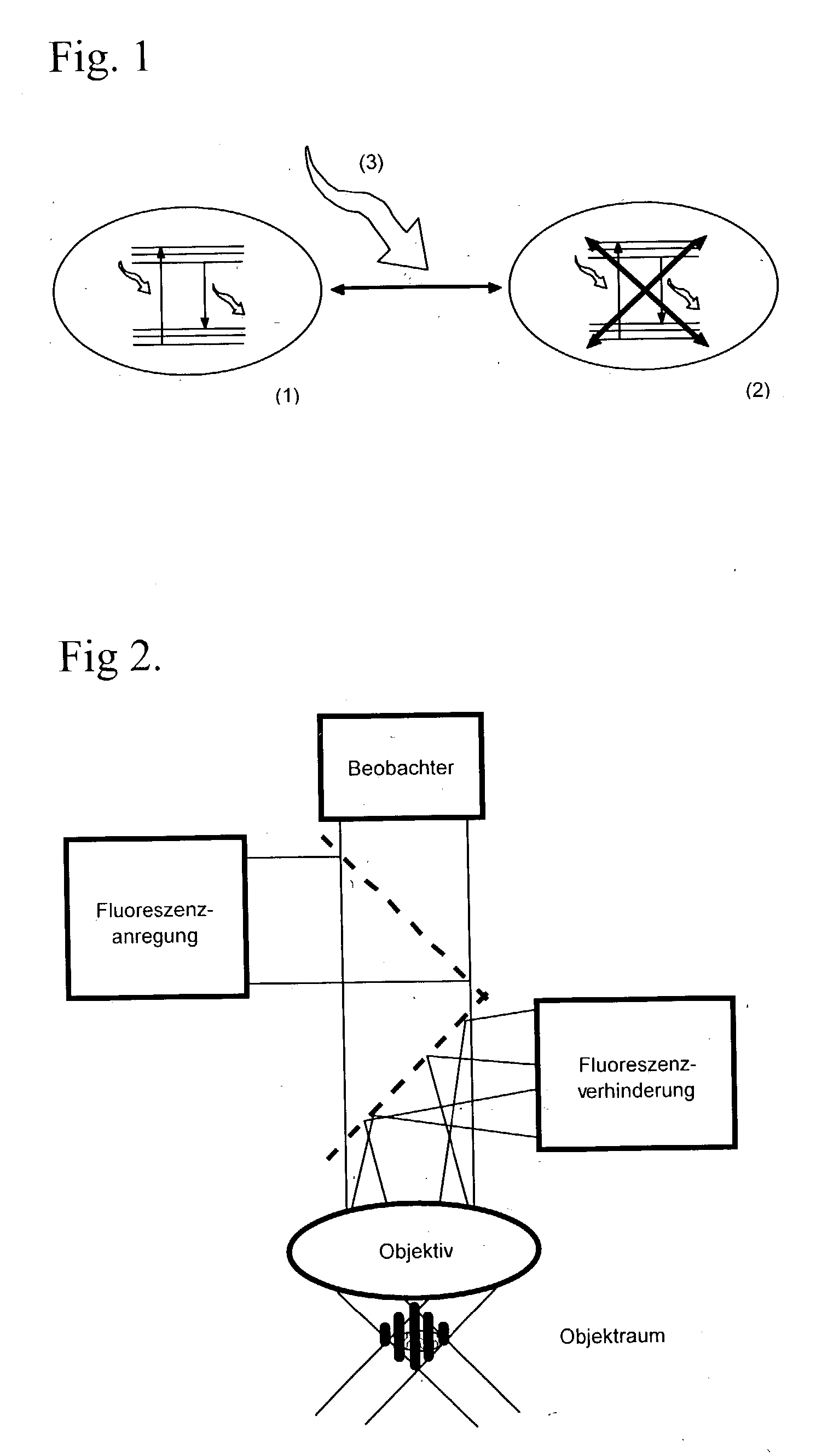
In a method of high spatial resolution imaging or modifying a structure, the structure is marked with a substance which is selected from the group of substances which can be transferred from a first state having first optical properties to a second state having second optical properties by means of an optical switch over signal. Then, the second state of the substance is adjusted with the switch over signal except for a spatially limited area. If the substance and the switch over signal are adapted to each other in such a way, that everywhere where the switch over signal exceeds a threshold value essentially the second state of the substance is adjusted, and if the spatial area purposefully omitted by the switch over signal is an intensity minimum of an interference pattern, the spatial area of the structure in which the substance is within the first state becomes smaller than the diffraction limit for the switch over signal.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
High spatial resoulution imaging and modification of structures
InactiveUS7064824B2Spectrum investigationMaterial analysis by optical meansOptical propertyImage resolution
In a method of high spatial resolution imaging or modifying a structure, the structure is marked with a substance which is selected from the group of substances which can be transferred from a first state having first optical properties to a second state having second optical properties by means of an optical switch over signal. Then, the second state of the substance is adjusted with the switch over signal except for a spatially limited area. If the substance and the switch over signal are adapted to each other in such a way, that everywhere where the switch over signal exceeds a threshold value essentially the second state of the substance is adjusted, and if the spatial area purposefully omitted by the switch over signal is an intensity minimum of an interference pattern, the spatial area of the structure in which the substance is within the first state becomes smaller than the diffraction limit for the switch over signal.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Multi-layer optical recording media and system for recording and reproducing information data
InactiveUS6498775B1Precise alignmentOptical beam sourcesRecord information storageEngineeringOptical recording
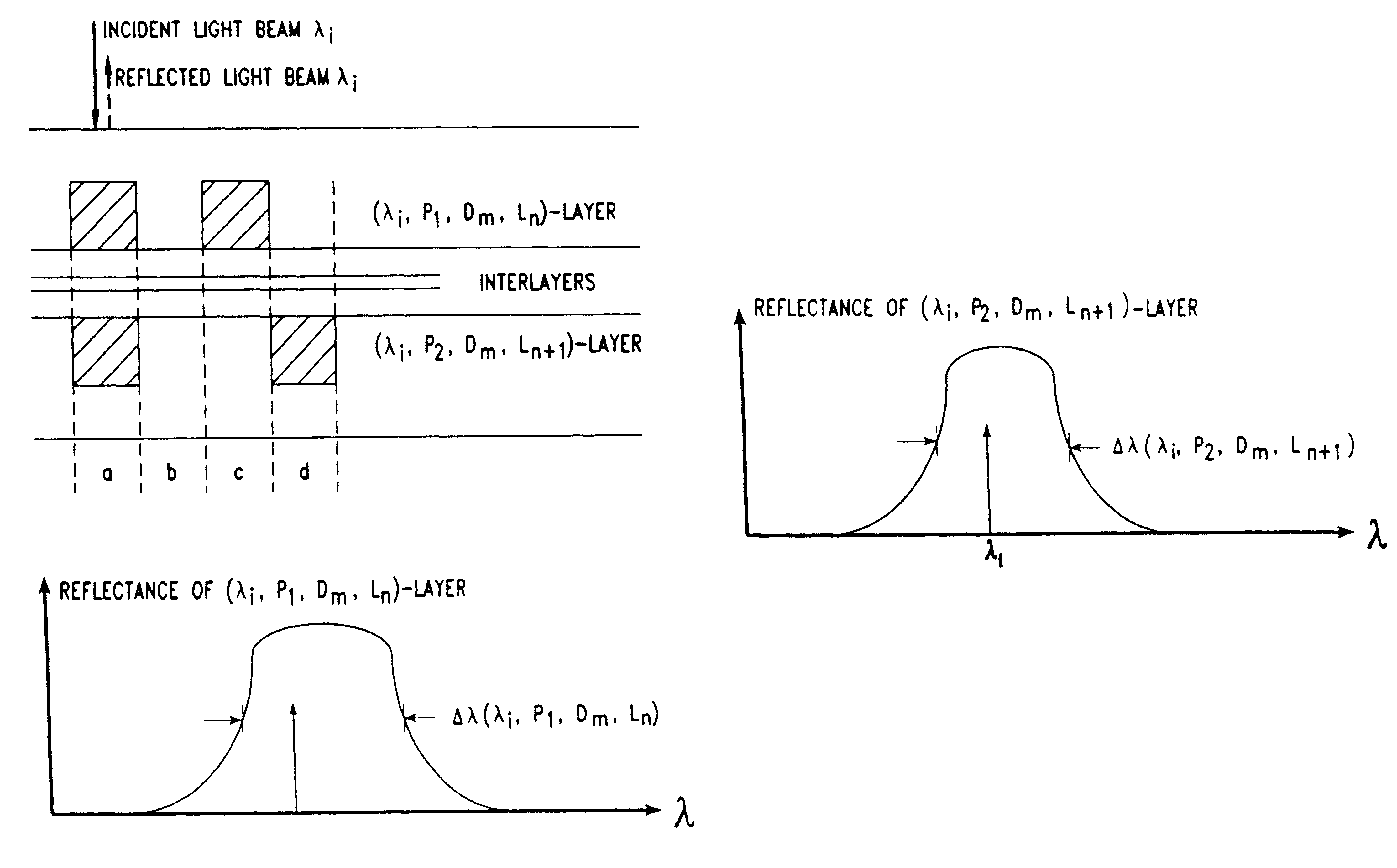
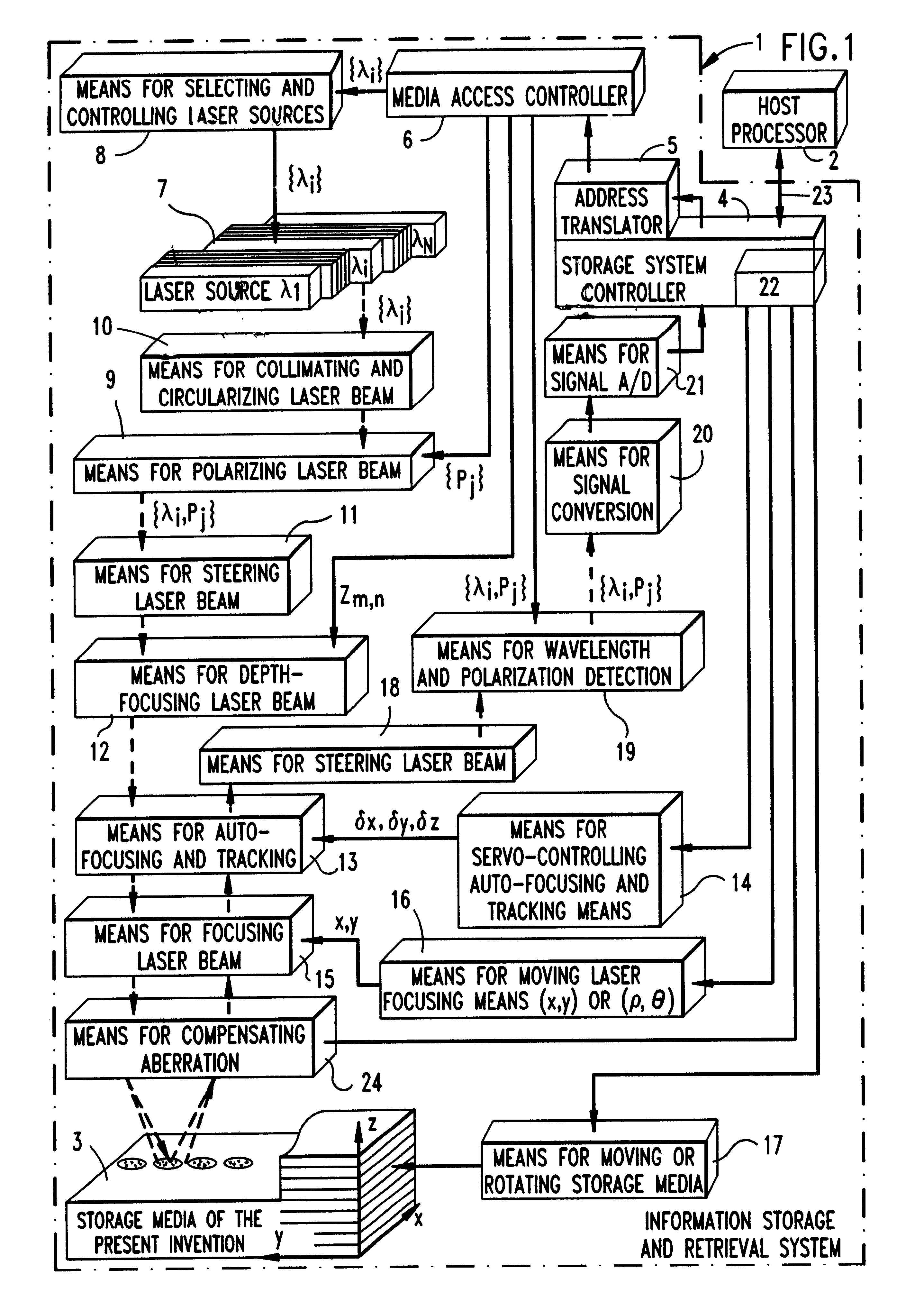
Disclosed is a novel multi-layered optical recording media and system for recording and reproducing information data. The multi-layered topical recording media has M information storage decks, and each information storage deck has N information storage layers, and each information storage layer has a pair of information storage structures. Each paired information storage structure has a characteristic wavelength and polarization state, and from which recorded information can be read by a laser beam having similar wavelength and polarization-state characteristics. In the illustrative embodiment, the multi-layered optical recording media of the present invention has MxNx2 information storage layers which can be read using only N laser lines (i.e. spectral components), thereby providing a 2M-fold increase in information storage capacity over prior art systems. The information storage and retrieval system of the present invention is completely backward compatible to allow for the reading of conventional CD-ROM devices.
Owner:REVEO
Storage medium, reproducing method, and recording method
InactiveUS20060210925A1High densityHigh speed recordingRecording strategiesRadiation applicationsSubstrate deformationComputer science
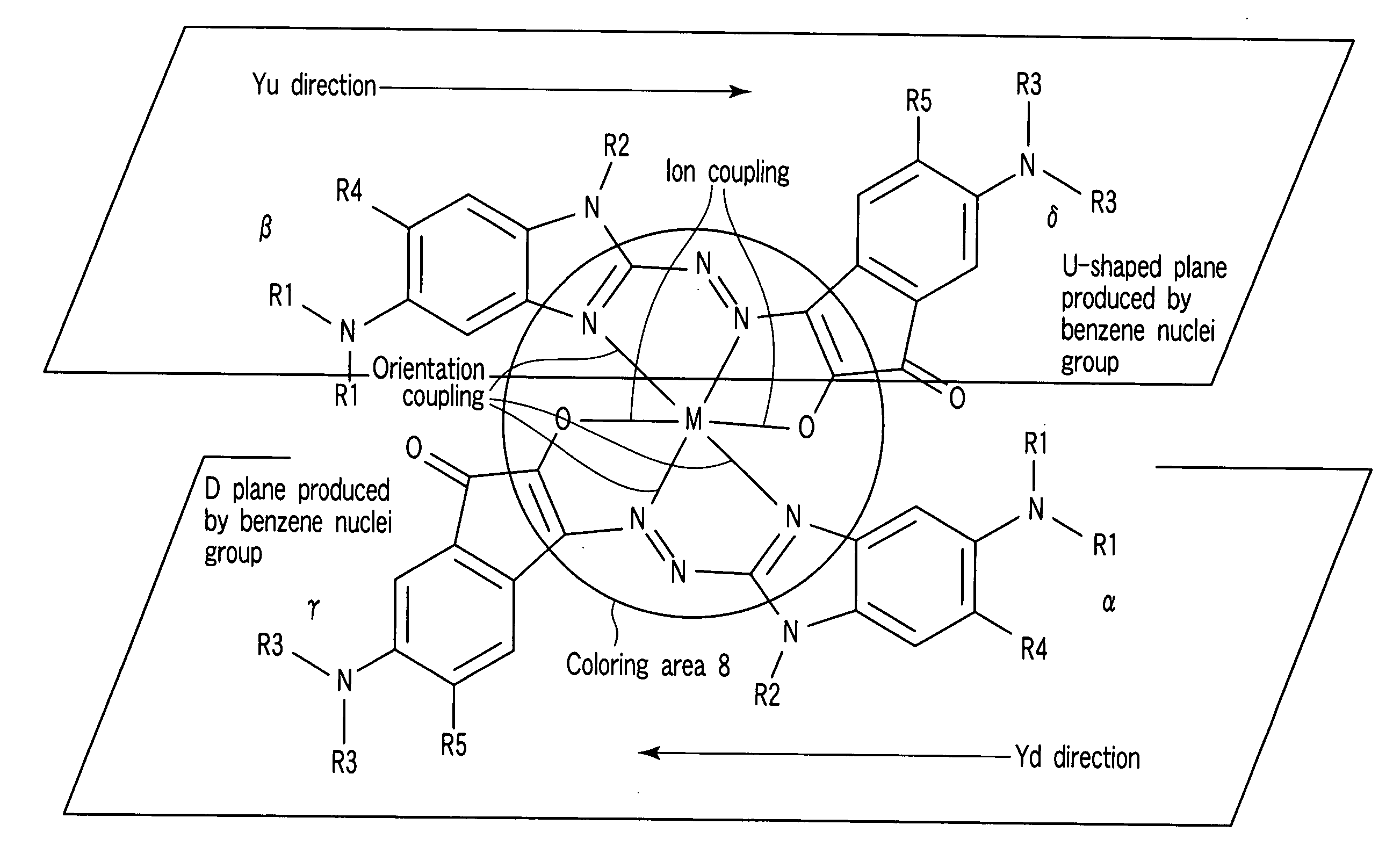
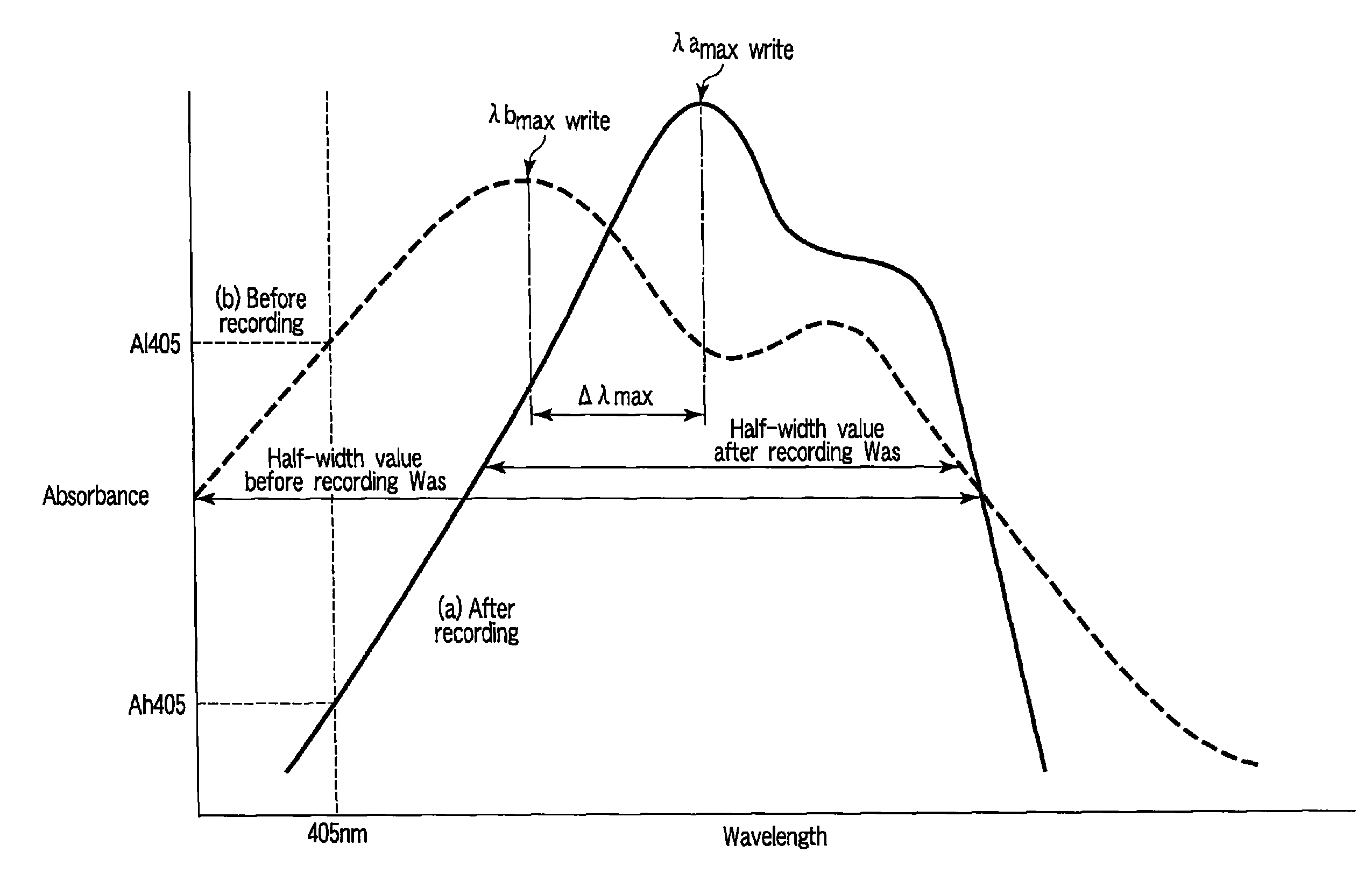
According to one embodiment, a write-once type information storage medium using a recording material which has a low to high characteristic that a light reflectivity in a recording mark increases with respect to a non-recording area and which has a recording characteristic in accordance with a principle of recording without substrate deformation, wherein the recording material includes at least an organic metal complex, and wherein the organic metal complex includes a center metal.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Optical recording medium and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20050073943A1Mechanical record carriersRecord information storageHeat conductingOptical recording
An optical recording medium is provided which can solve a problem of insufficient signal amplitude of one recording layer as compared with the other recording layer in a writable optical recording medium of a conventional double layer structure. An optical recording medium, in which a first substrate having a first groove formed thereon, a first recording layer formed on a first-groove forming surface of the first substrate, a semi-translucent first reflecting layer, an intermediate layer, a second recording layer, a second reflecting layer, and a second substrate having a second groove formed thereon are at least disposed in this order, wherein the optical recording medium further includes a heat conducting layer between the second recording layer and the intermediate layer and a heat insulating layer between the second recording layer and the second reflecting layer.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Two-photon, three-or four-dimensional, color radiation memory
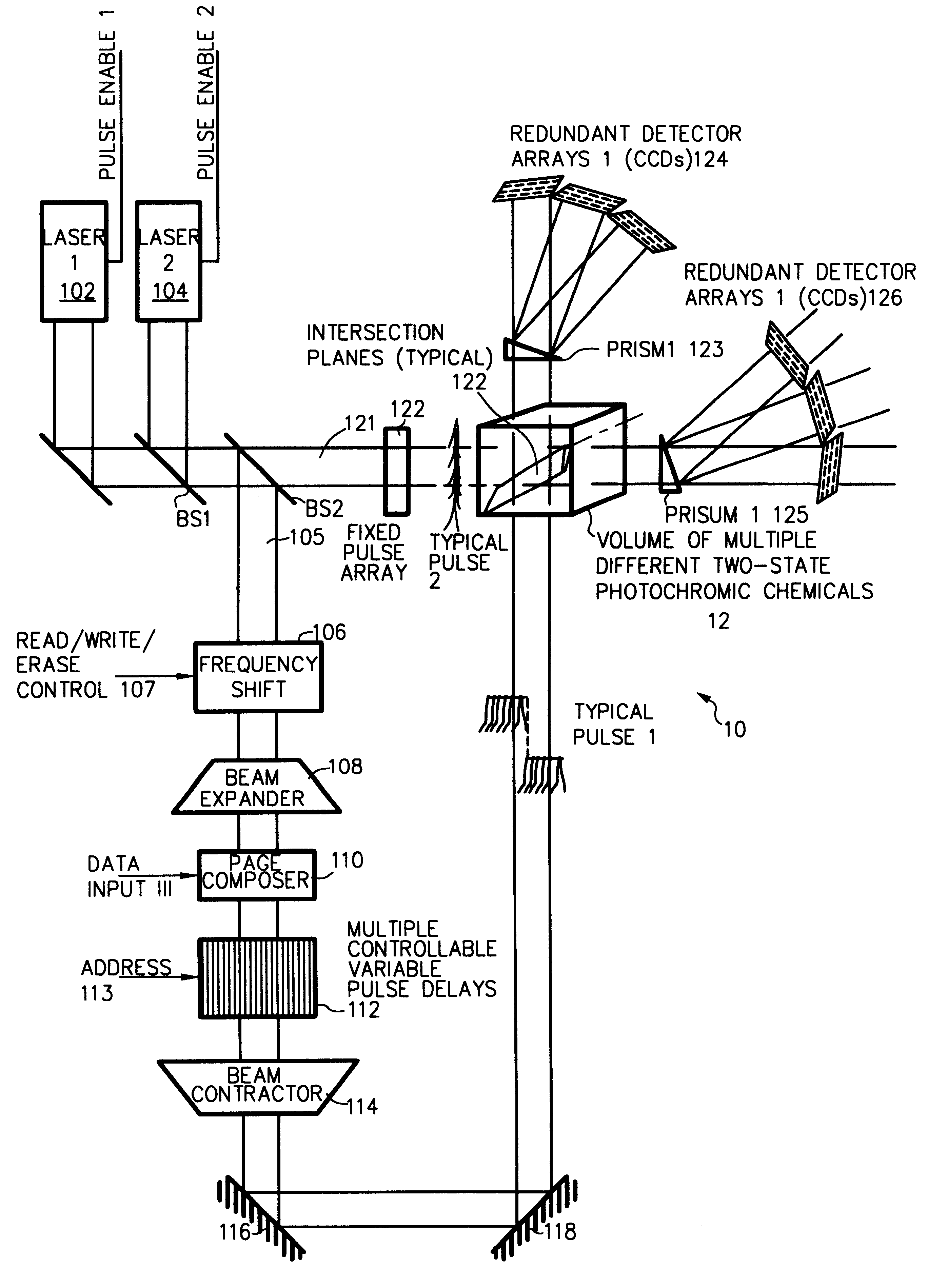
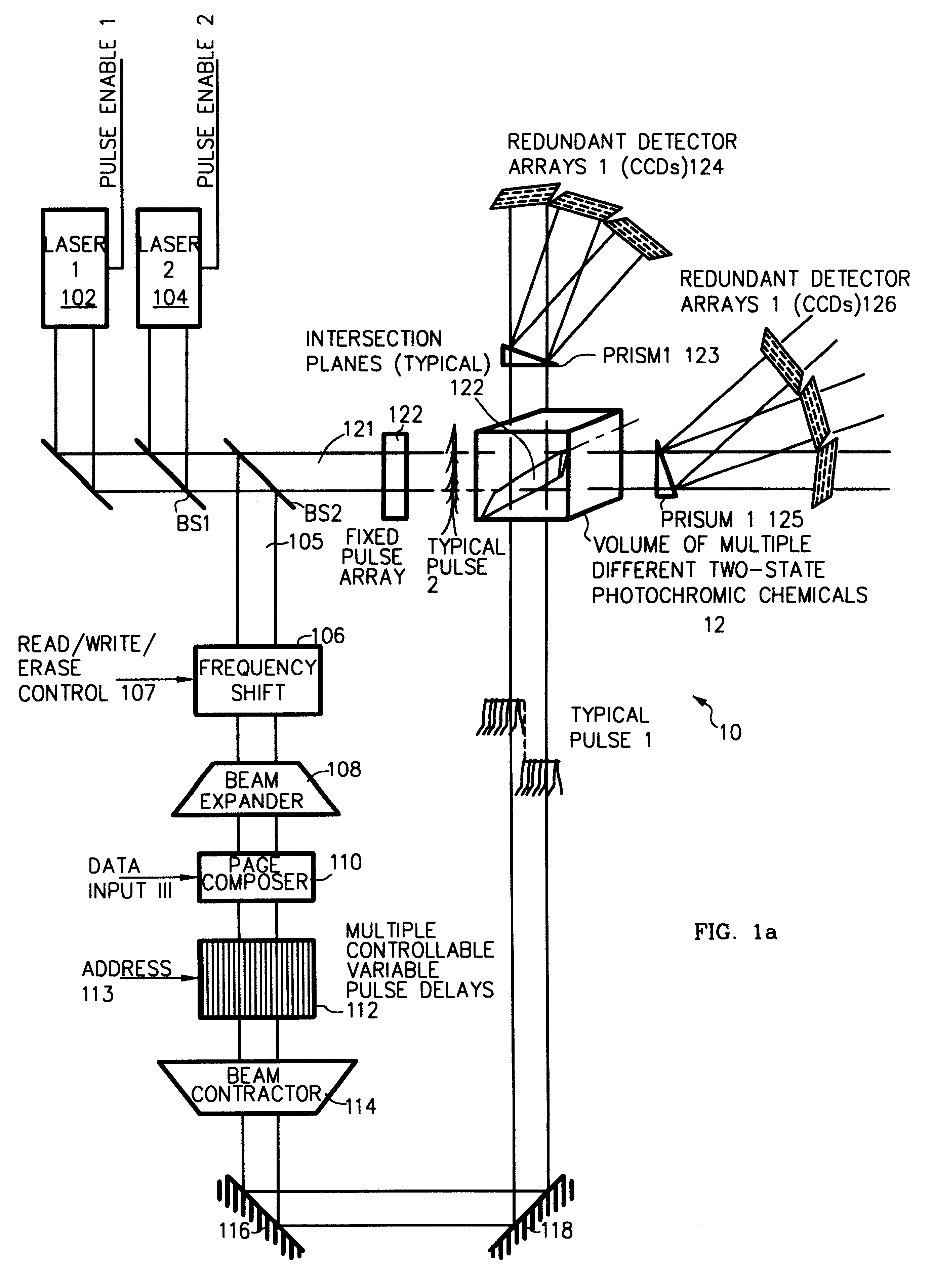
InactiveUS6483735B1Large storageEasy to getNanoinformaticsRecording involving hole burningDetector arrayPrism
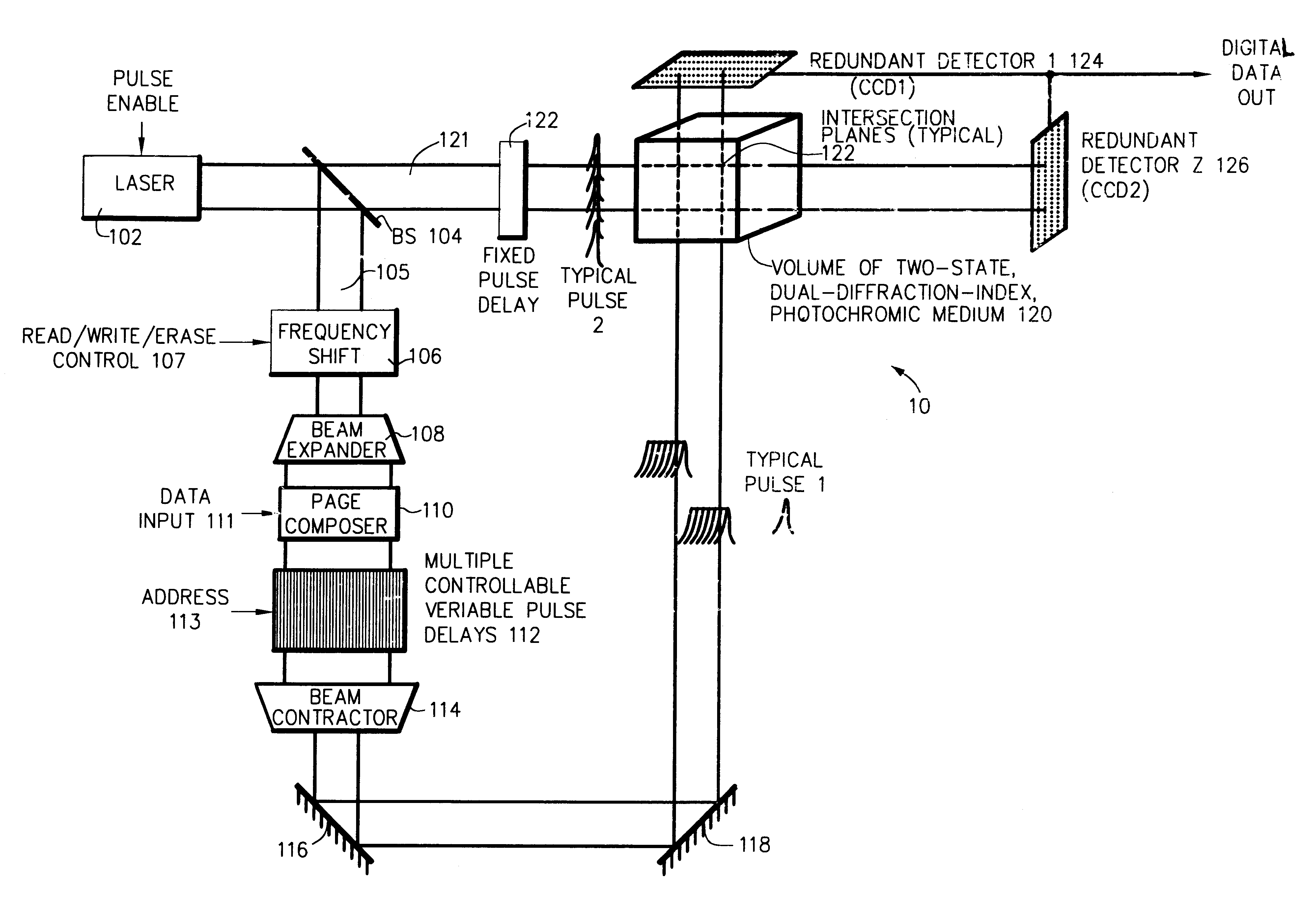
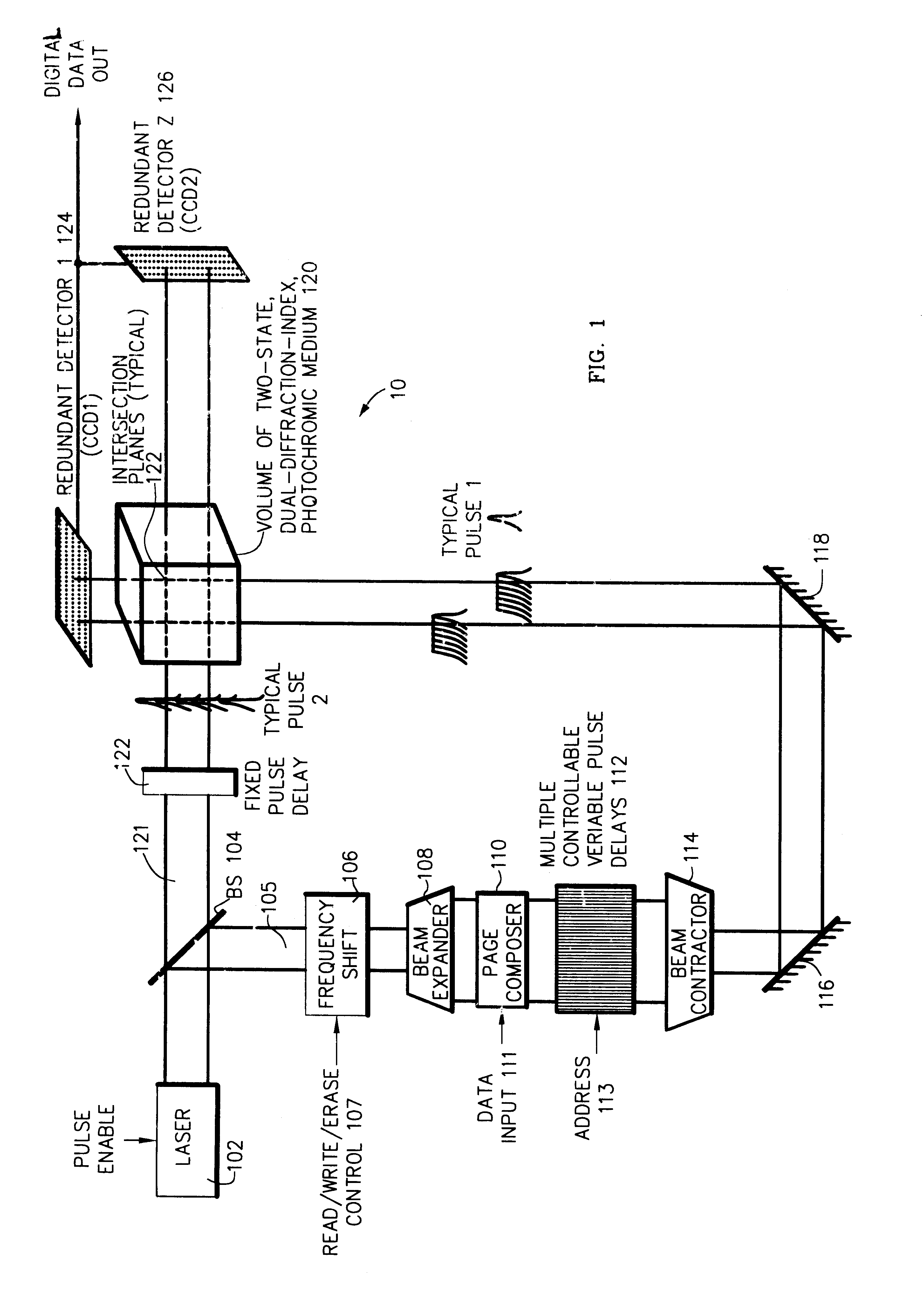
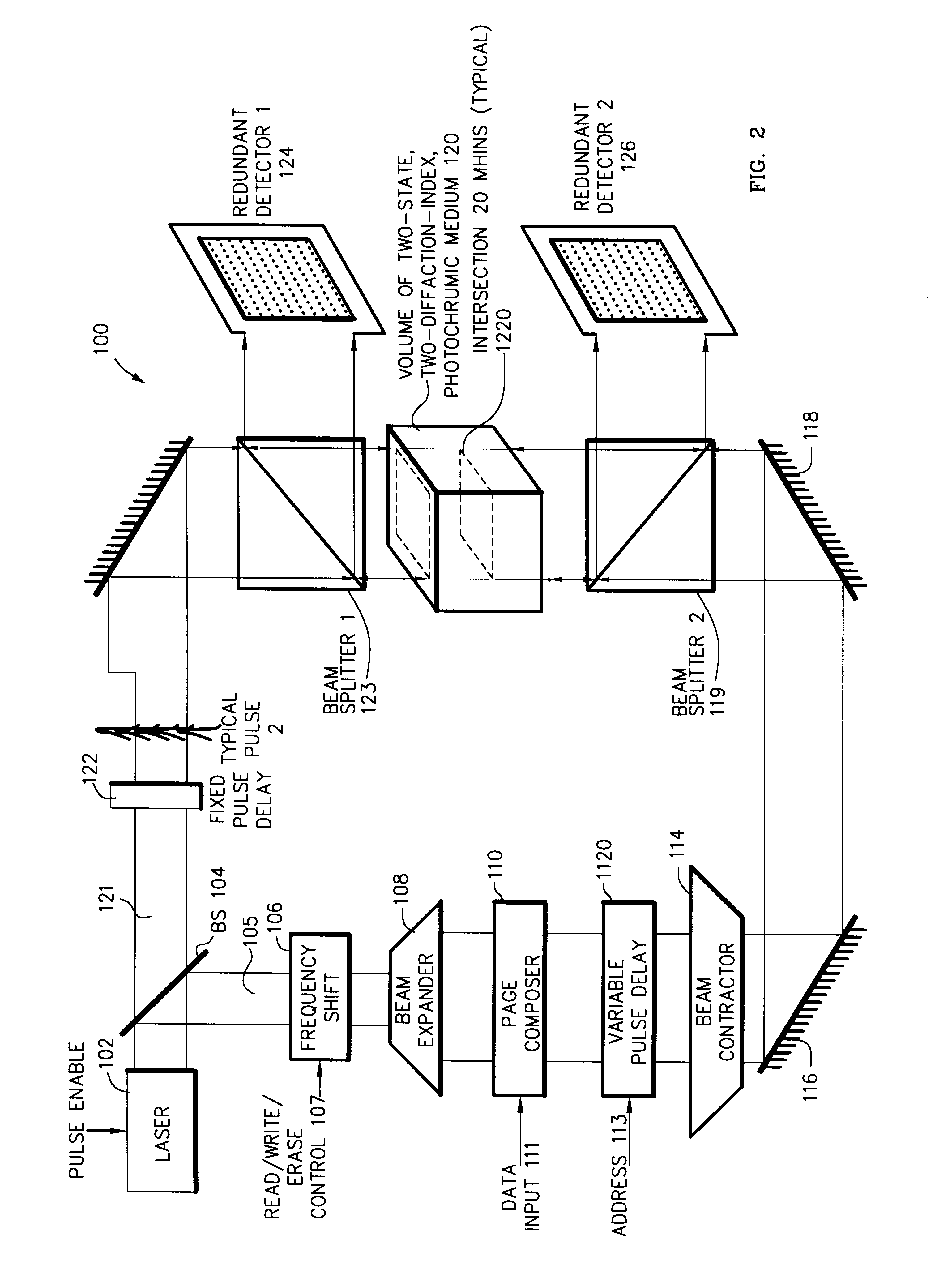
Three-, and four-dimensional ("3-D" and "4-D") volume radiation memories store multiple binary bits of information-typically about five to ten and more typically eight such bits-in the same physical volumes on several different photochromic chemicals co-located in the volume. Each of the multiple photochromic chemicals is individually selectively written with an individually associated pair of radiation beams of an appropriate combined frequency-i.e., a "color"-and energy by a process of two-photon ("2-P") absorption. All the multiple information bits that are stored within all the photochromic chemicals in each addressable domain are read in common, and induced to simultaneously fluoresce, again by process of 2-P absorption. The fluorescence of each of different photochromic chemical in each addressed domain-which fluorescence is selective in accordance with the written state of each such photochromic chemical-is separated from, and is separately detected from, the fluorescence of all other photochromic chemicals because it is of a unique color, and is spatially steered to an associated detector array, normally a Charge Coupled Device (CCD), by a monochromator, normally a prism. Exemplary fluorescent photochromic chemicals are spirobenzopyran, rhodamine, cumarin and anthracene. Suitable groups of photochromic chemicals are formed from individual photochromic chemicals exhibiting narrow, sharp, separate spectra of absorption and of emission suitably distinct from each other, and where no chemical's fluorescent emission energy overlaps the absorption energies of any other chemicals.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
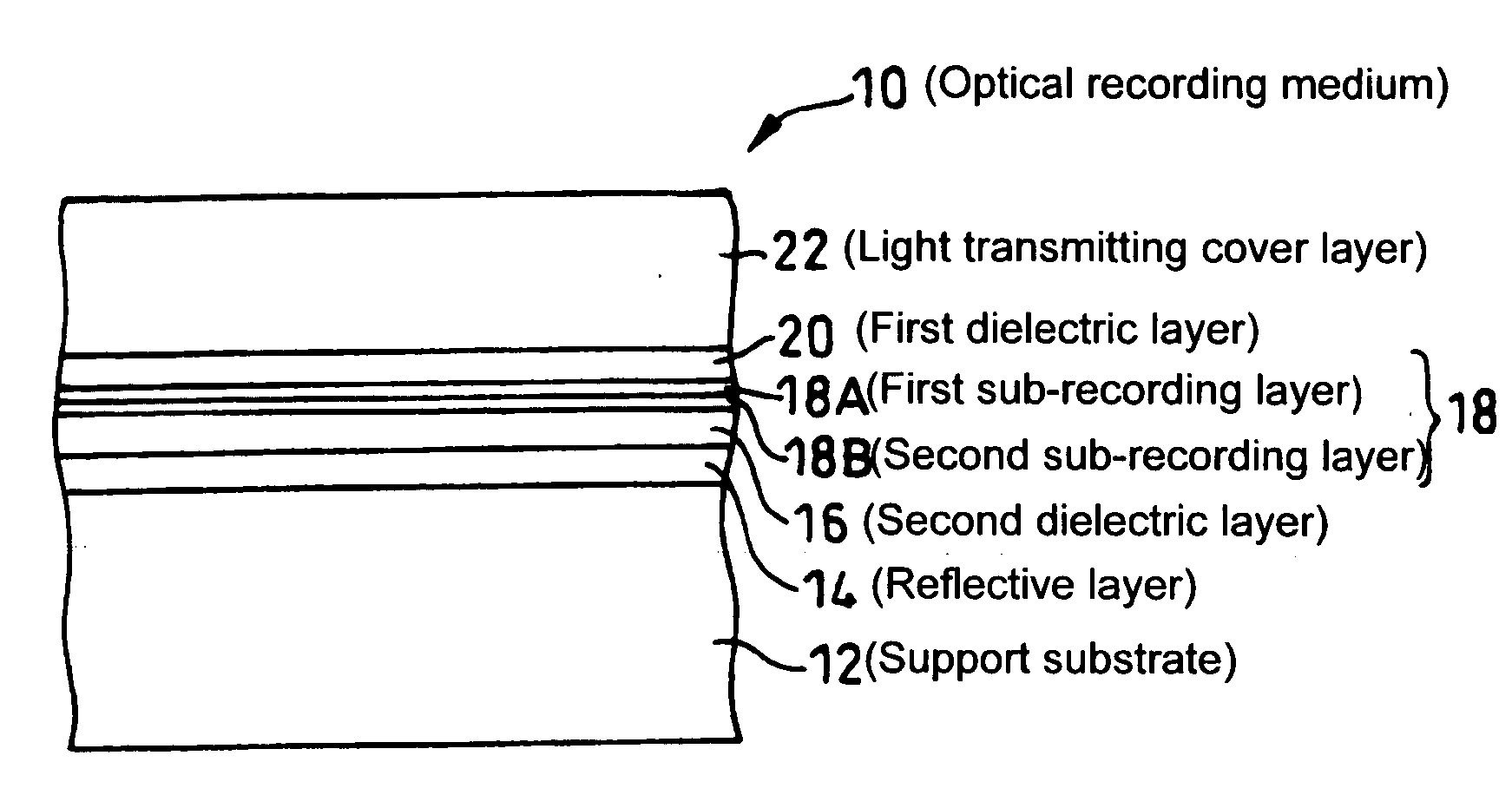
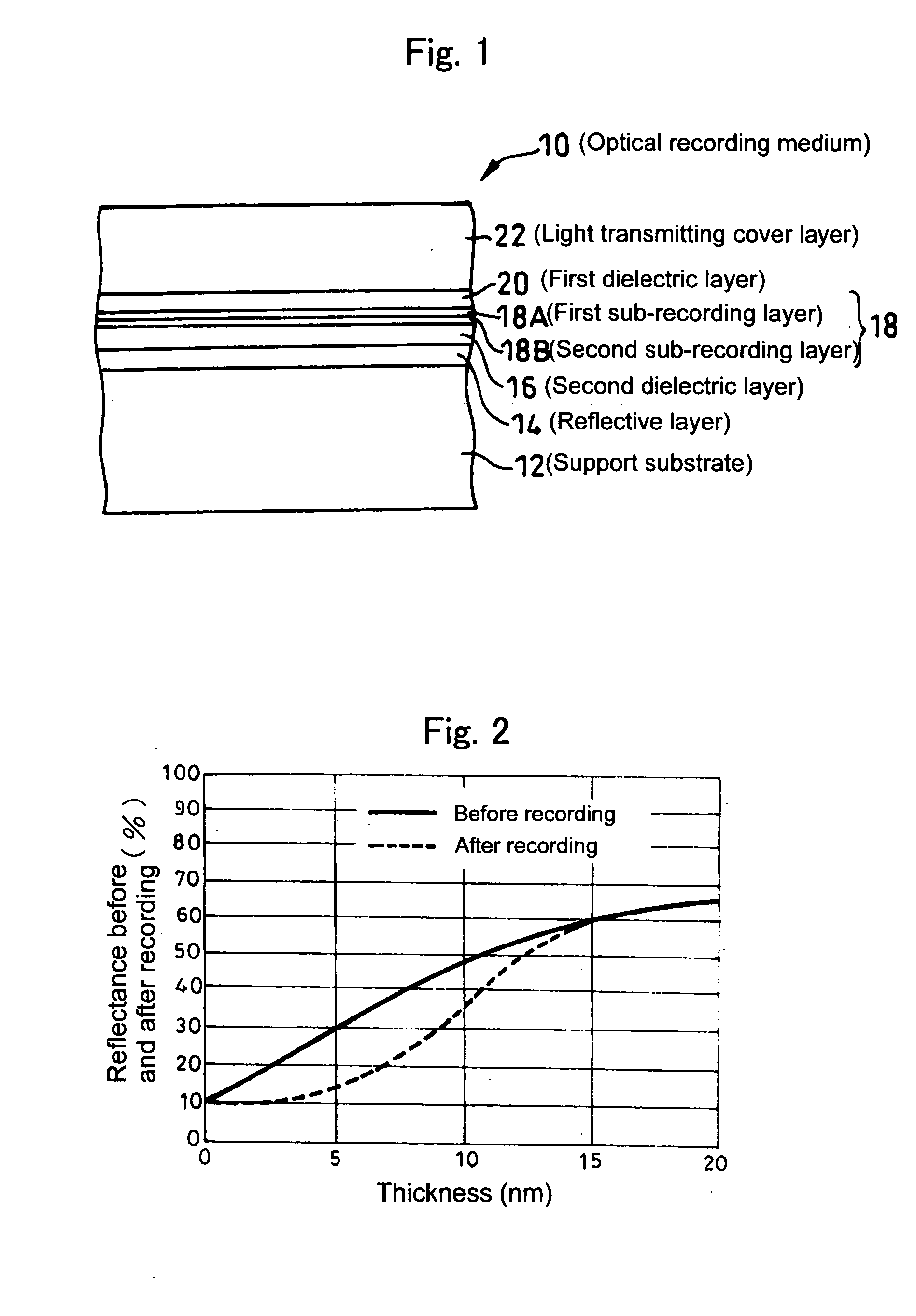
Method of regulating reflectance of worm type optical recording medium and worm type optical recording medium
InactiveUS20050081230A1Easily and reliably maintaining compatibilityHigh-speed, high density write-onceLayered productsRecord information storageOptical recordingLength wave
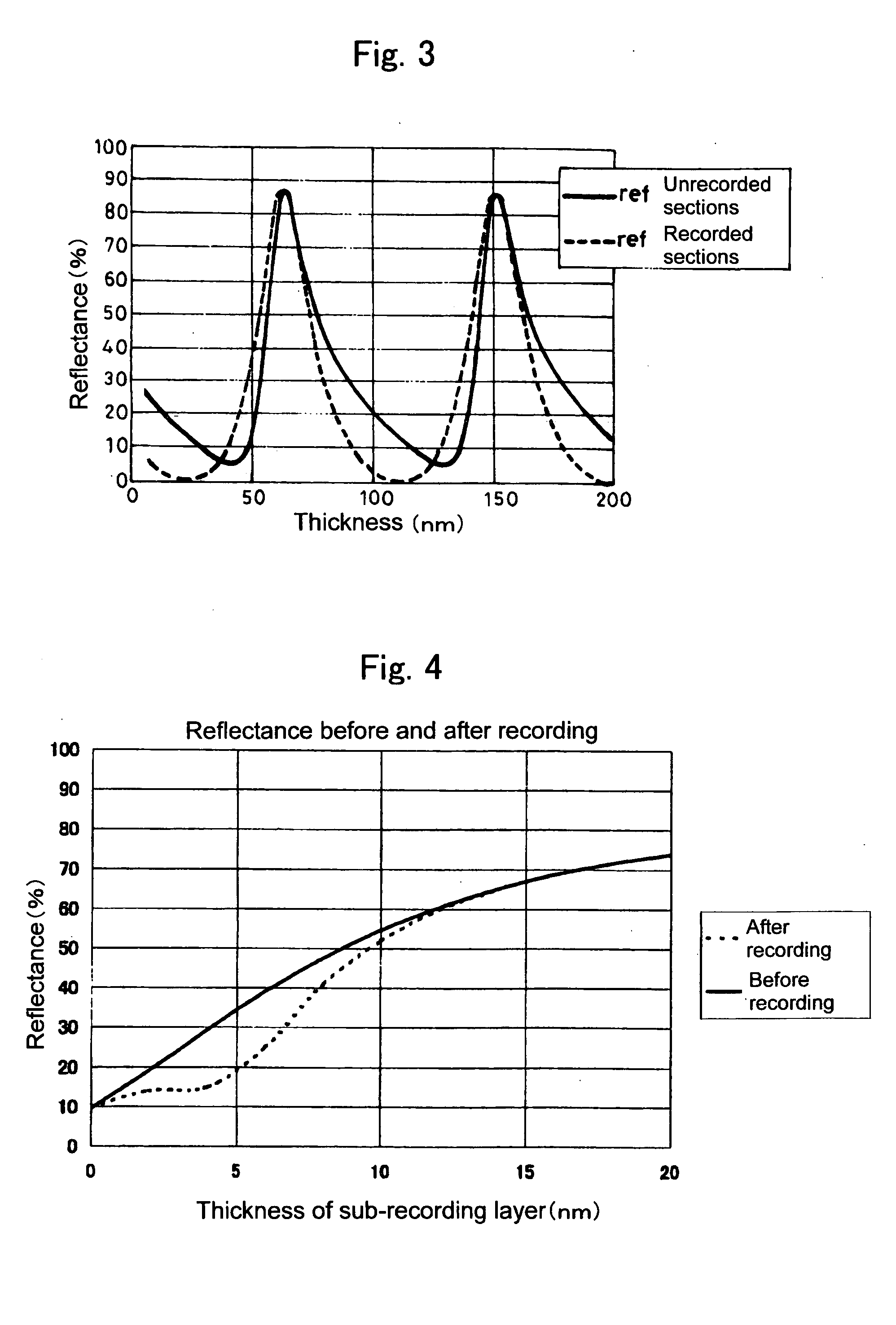
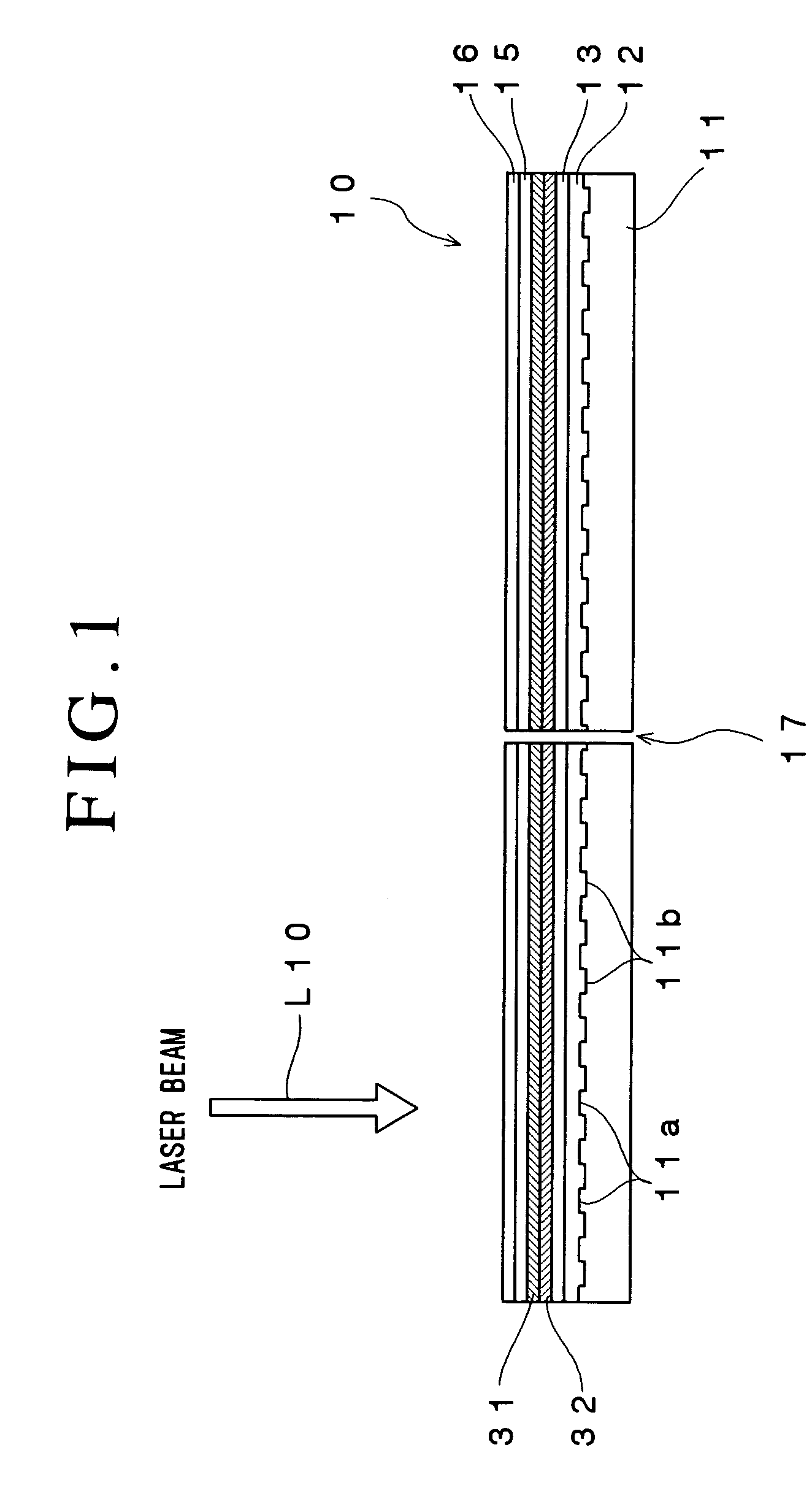
The reflectance of an optical recording medium for which high speed recording using a laser beam with blue wavelength or a shorter wavelength than blue light is possible is adjusted to a predetermined value of no more than 60%. A recording layer 18 of a high-speed write-once type optical recording medium 10 is formed by laminating first and second sub-recording layers 18A, 18B, each of which contains one type of different metal as a primary component. When laser beam of a blue wavelength is irradiated onto the recording layer 18, the irradiation causes the primary component metals contained within each of the first and second sub-recording layers 18A, 18B to diffuse and mix, and this mixing forms a recording mark with an irreversibly changed reflectance. The recording layer 18 is sandwiched between first and second dielectric layers 20, 16, and by adjusting the material and the thickness of the recording layer 18 and the first and second dielectric layers 20, 16, the reflectance of the unrecorded sections can be adjusted to a value within a range from 5% to 60%.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Optical recording apparatus with drawing capability of visible image on disk face
InactiveUS7082094B2Increase the diameterIncrease the areaRecording apparatusAccessories for auxillary signalsTime segmentOptical recording
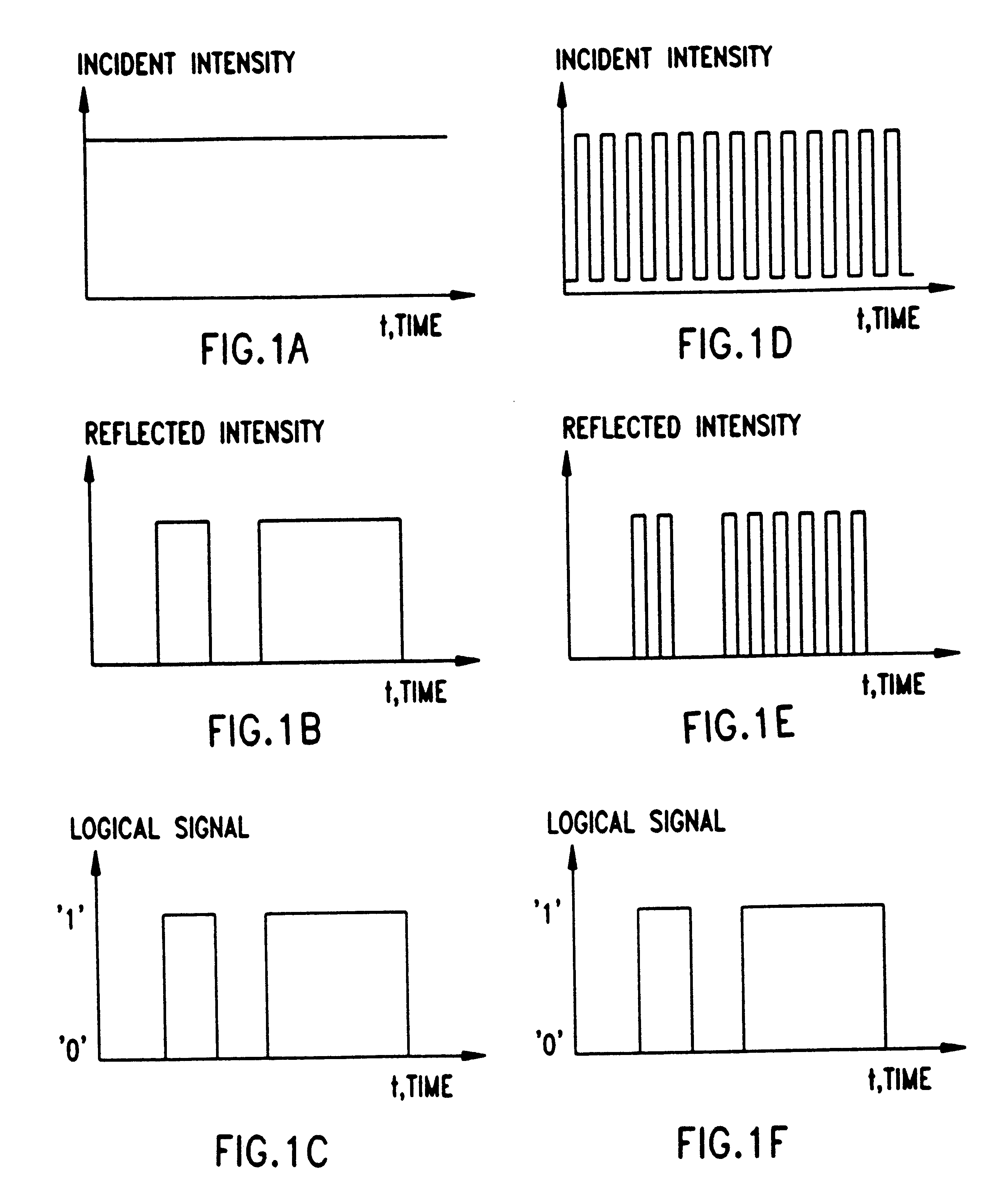
An optical disk apparatus records information by irradiating a laser beam from a pickup onto an optical disk. A scanning section scans the laser beam relative to the optical disk. A recording control section controls the scanning section to effect recording of information. A drawing control section is provided for controlling the pickup and the scanning section to effect drawing of a visible image on the optical disk according to image information, such that the laser beam is changed between a first intensity incapable of acting on the optical disk and a second intensity capable of acting on the optical disk. A servo section periodically detects the laser beam reflected back from the optical disk when the laser beam has the first intensity, and servo-controls the irradiating of the laser beam during the drawing of the visible image based on the detection of the laser beam. The drawing control section controls the pickup for forcibly changing the laser beam to the first intensity from the second intensity when the second intensity is maintained over a predetermined period pursuant to the image information, thereby enabling the servo section to detect the laser beam having the first intensity for continuing the servo-control.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
Optical recording medium and optical recording method of the same
InactiveUS20060204706A1Good recording/reading characteristicHigh-density opticalLayered productsMechanical record carriersPhase shiftedHigh density
By use of a substrate which can be stably formed and has a relatively small groove depth, a very high density optical recording medium having good recording / reading characteristics is provided. In an optical recording medium of a surface incidence type, in which a reflective layer, a recording layer containing a dye as a main component and a cover layer are sequentially formed on a substrate having guide grooves formed therein, a guide groove part on a far side from a plane of incidence of a recording / reading light beam on the cover layer is set as a recording groove part, and reflected light intensity in a recorded pit portion formed in the recording groove part is increased by a phase shift and is set higher than reflected light intensity in unrecorded.
Owner:CMC MAGNETICS CORPORATION
Optical recording medium and method for recording data in the same
InactiveUS20040038080A1Good signalImprove carrier-to-noise ratioRecording strategiesLayered productsRecording layerOptical recording
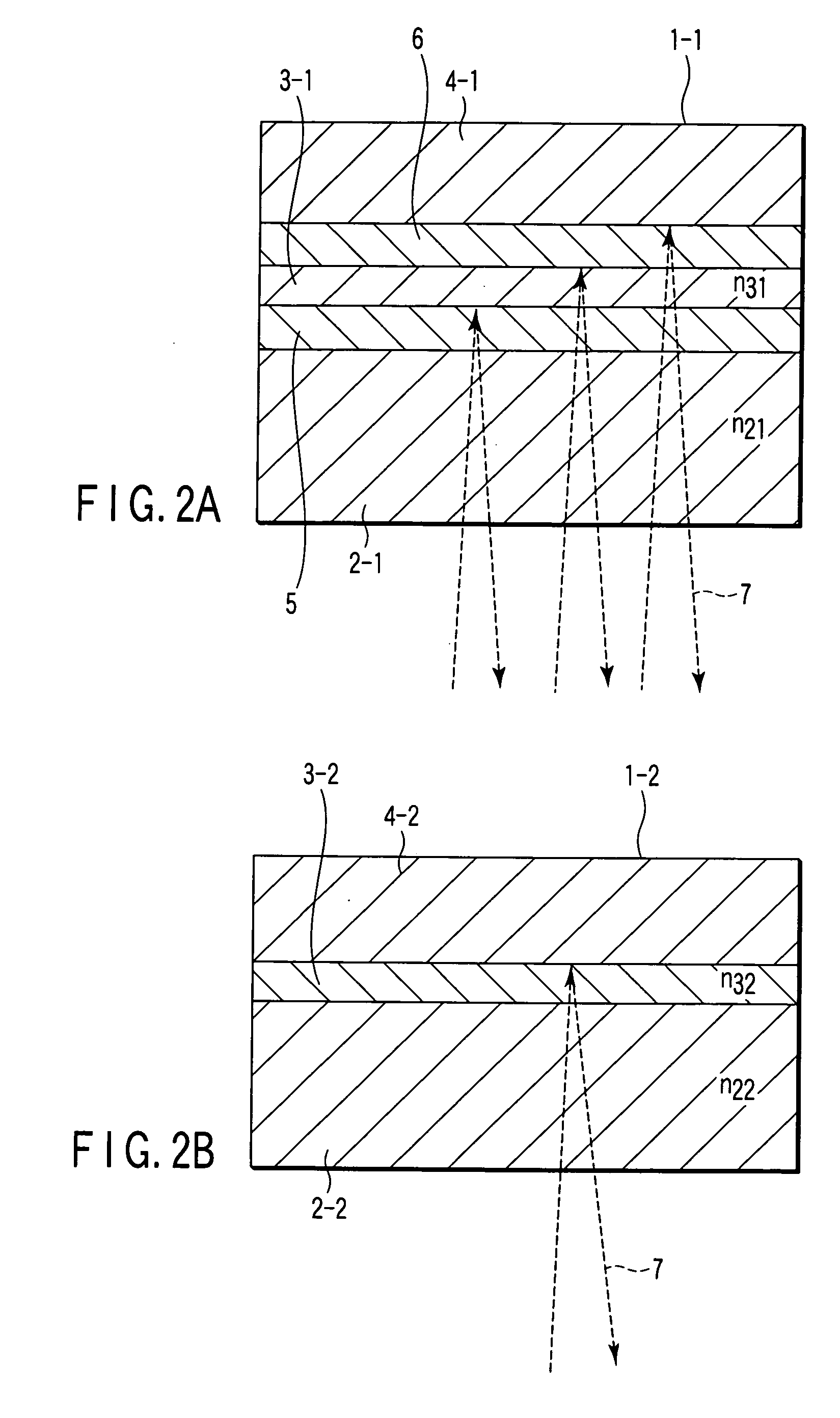
An optical recording medium includes a substrate, two recording layers provided on the substrate and two dielectric layers each provided adjacent to one of the recording layers, the optical recording medium being constituted so that when it is irradiated with a laser beam having a wavelength lambda via an objective lens having a numerical aperture NA satisfying lambda / NA<=640 nm from the side opposite from the substrate, a record mark whose reflection coefficient is different from those of other regions of the recording layers is formed in the recording layers and at least a part of a region(s) of the dielectric layers adjacent to the record mark is crystallized to form a crystallized region. According to the thus constituted optical recording medium, it is possible to reproduce a signal having excellent signal characteristics.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Information recording medium
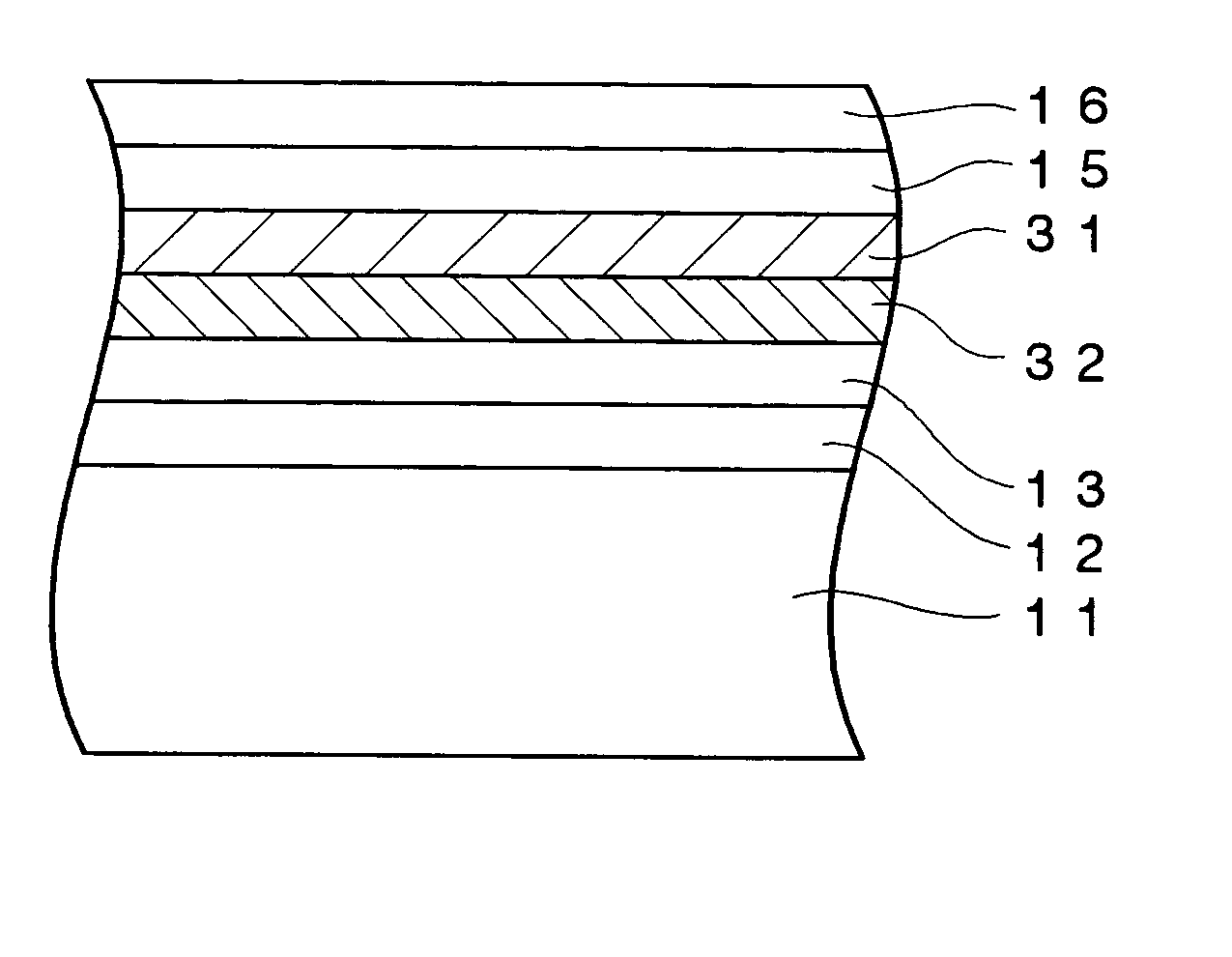
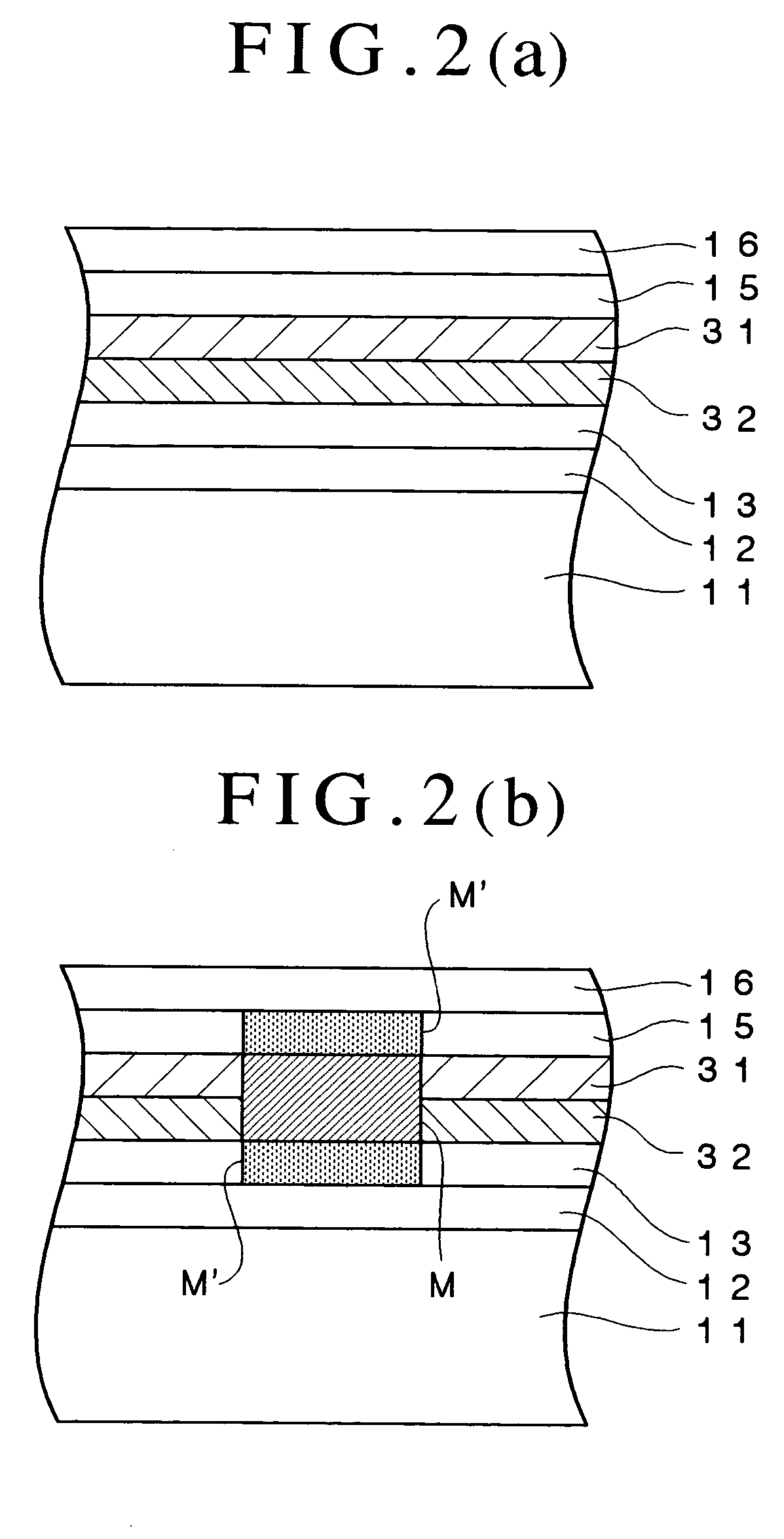
In an information recording medium comprising at least a substrate, a recording layer, and a resin layer, the substrate is formed with at least a pit corresponding to a read only area 31 and a groove corresponding to a recording / reproducing area 32 without overlapping with each other. A reflectivity of the recording layer is specified to be more than 10%. The recording layer and the resin layer are continuously adhered over both the read only and recording / reproducing areas 31 and 32. The information recording medium is characterized in that both push-pull signal outputs T1 and T2, which are reproduced from the read only area 31 and the recording / reproducing area 32 respectively, are more than 0.1 and satisfy an inequality 1.5≧T1 / T2≧0.5.
Owner:JVC KENWOOD CORP A CORP OF JAPAN
Optical recording medium
ActiveUS20040004932A1Improve featuresImprove conductivityMechanical record carriersPhotomechanical apparatusLight beamRecording layer
An optical recording medium includes a substrate, a light transmission layer and a plurality of recording layers between the substrate and the light transmission layer and capable of recording data in the plurality of recording layers and reproducing data recorded in the plurality of recording layers by projecting a laser beam via the light transmission layer onto the plurality of recording layers, at least one recording layer other than a farthest recording layer from the light transmission layer including a reflective film containing Ag as a primary component and C as an additive. In the thus constituted optical recording medium, recording characteristics and reproducing characteristic of the respective recording layers can be improved.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Optical recording medium for use at short wavelengths and its recording method
An optical recording medium adapted for high density recording with a light of short wavelength which exhibits excellent jitter properties, and its recording method are provided. The optical recording medium recorded and / or reproduced with a light at a wavelength of 600 to 680 nm comprises a substrate having grooves formed on its surface at a track pitch of up to 0.8 mu m, and a recording layer containing an organic die disposed on the substrate. Depth A and width B of the groove ( mu m) and leveling ratio C are in the relation:0.035< / =AxB< / =0.06, and2< / =C / A< / =3.5when the leveling ratio C is represented by the following formula (I): leveling ratio=[thickness of the recording layer on the groove ( mu m)-thickness of the recording layer on the land ( mu m)] / [depth of the groove ( mu m)]
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
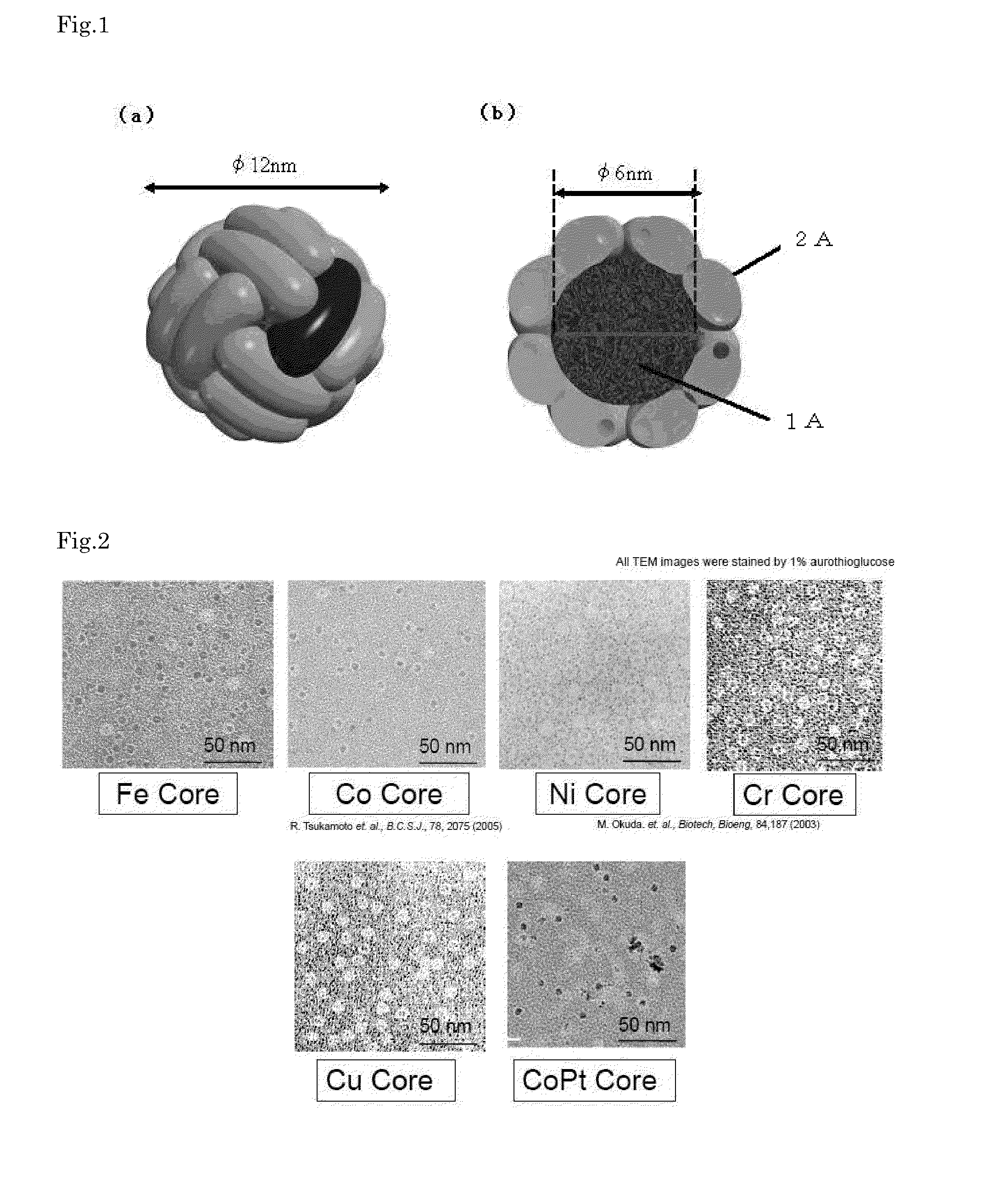
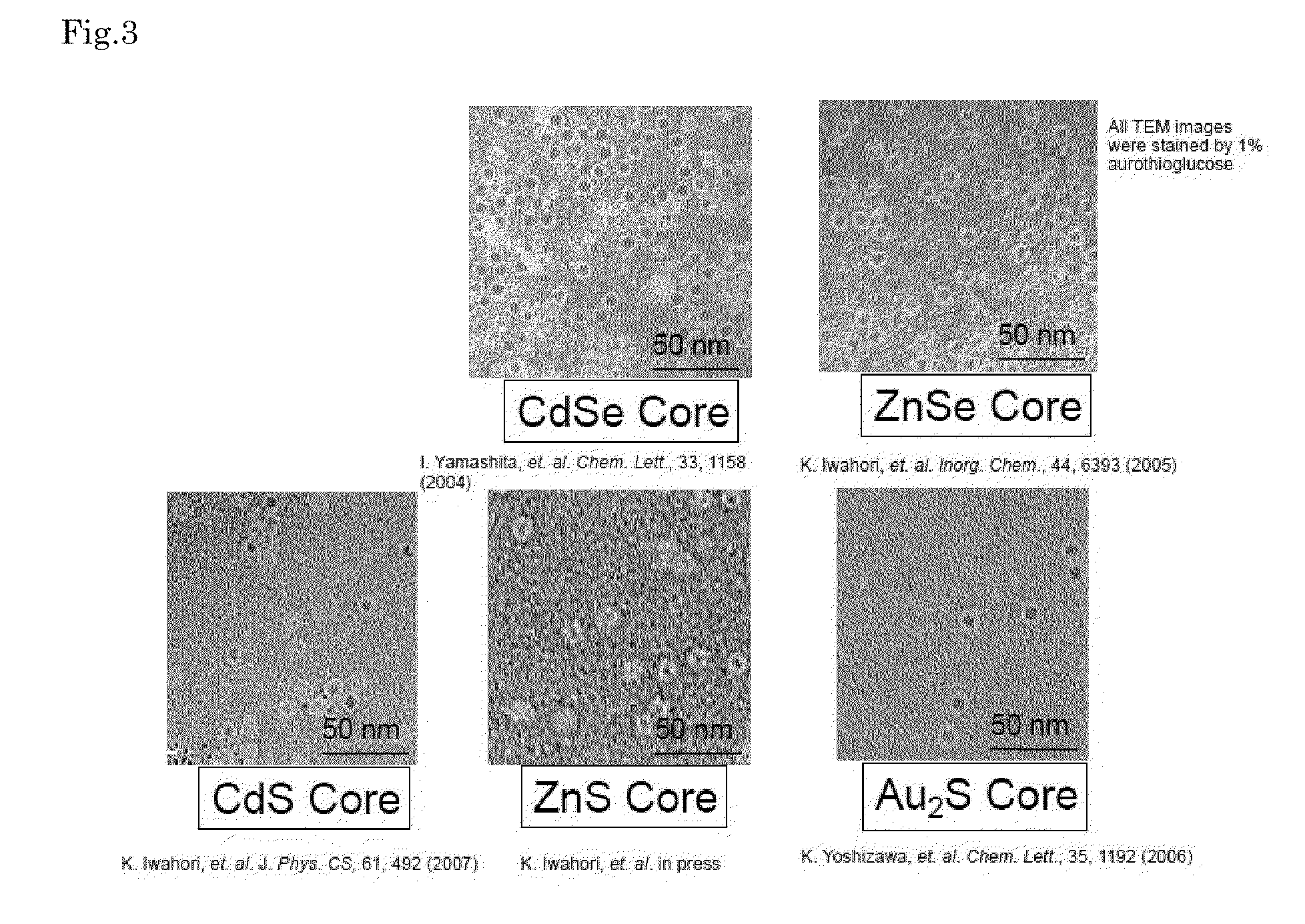
Circularly Polarized Light-Emitting Nanoparticle
Provided is a compound semiconductor nanoparticle that exhibits circularly polarized luminescence characteristics. CdS prepared inside a core of ferritin, which is a cage-like protein, exhibits a high circularly polarized luminescence (CPL). A wavelength of the circularly polarized luminescence (CPL) can be controlled by laser irradiation, thereby enabling utilization of the compound semiconductor nanoparticle in the field of bionanotechnology, for example, in creating a WORM (Write-Once Read-Many times) memory. As the cage-like protein, which is a protein with a cavity formed therein, a protein belonging to the ferritin protein family, such as apoferritin, or a recombinant thereof can be used.
Owner:NARA INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Storage medium, reproducing method, and recording method
InactiveUS7960093B2High densityHigh sensitivityRecording strategiesRadiation applicationsSubstrate deformationComputer science
According to one embodiment, a write-once type information storage medium using a recording material which has a low to high characteristic that a light reflectivity in a recording mark increases with respect to a non-recording area and which has a recording characteristic in accordance with a principle of recording without substrate deformation, wherein the recording material includes at least an organic metal complex, and wherein the organic metal complex includes a center metal.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Optical recording medium and method for optically recording data in the same
InactiveUS20040027973A1Reduce noise levelImprove carrier-to-noise ratioMechanical record carriersPhotomechanical apparatusNoise levelRecording layer
An optical recording medium includes a substrate, a first recording layer formed on the substrate and containing an element selected from the group consisting of C, Si, Ge and Sn as a primary component, and a second recording layer located in the vicinity of the first recording layer and containing an element selected from the group consisting of C, Si, Ge and Sn and different from the element contained as a primary component in the first recording layer as a primary component. According to thus constituted optical recording medium, it is possible to optically record data therein and reproduce data therefrom by projecting a laser beam having a wavelength of 350 nm to 450 nm thereonto, which includes two or more recording layers and is capable of decreasing noise level and improving C / N ratio of a reproduced signal.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Multi-layer optical recording media and method for recording and reproducing information using the same
InactiveUS6094410AEasy and inexpensive way to upgrade the information storage and reading capabilitiesPrecise alignmentOptical beam sourcesRecord information storageOptical storageLength wave
Disclosed is a novel optical information storage media having M information storage decks. Each information storage deck has N information storage layers, and each information storage layer has a pair of information storage structures. Each paired information storage structure has a characteristic wavelength and polarization state, and from which recorded information can be read by a laser beam having similar wavelength and polarization-state characteristics. A novel system is provided for reading the optical information storage media of the present invention. In the illustrative embodiment, an optical storage device of the present invention having MxNx2 information storage layers can be read using only N laser lines (i.e. spectral components), thereby providing a 2M-fold increase in information storage capacity over prior art systems. The information storage and retrieval system of the present invention is completely backward compatible to allow for the reading of conventional CD-ROM devices. Various techniques are disclosed for manufacturing and reading the optical storage devices of the present invention.
Owner:REVEO
Information recording medium and information recording method
InactiveUS20050084660A1Shorten the overall cycleLarge-capacity super-high speed recordingSynthetic resin layered productsRecord information storageElectricityHigh density
The present invention relates to an information recording medium for recording and reproducing information using light and an information recording method to attain high-speed recording and high-density recording. An electrolyte layer 2 is sandwiched by the first conductive polymer layer (an electrochromic layer) 1 comprising a conductive polymer electrochromic material and the second electrolyte layer 7, and both sides of the first and the second conductive polymer layers are sandwiched by electrode layers 3 and 4. The heat generation area in recording is so narrow that some drift in auto-focusing and tracking is allowable, which enables high-speed rotation leading to high-speed recording and high-density recording.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Apparatus and method for recording an optical disc identification code
InactiveUS6414913B1Protect dataReduce adverse effectsAccessories for indicating/preventing prior/unwanted useRecord information storageComputer hardwareOptical pickup
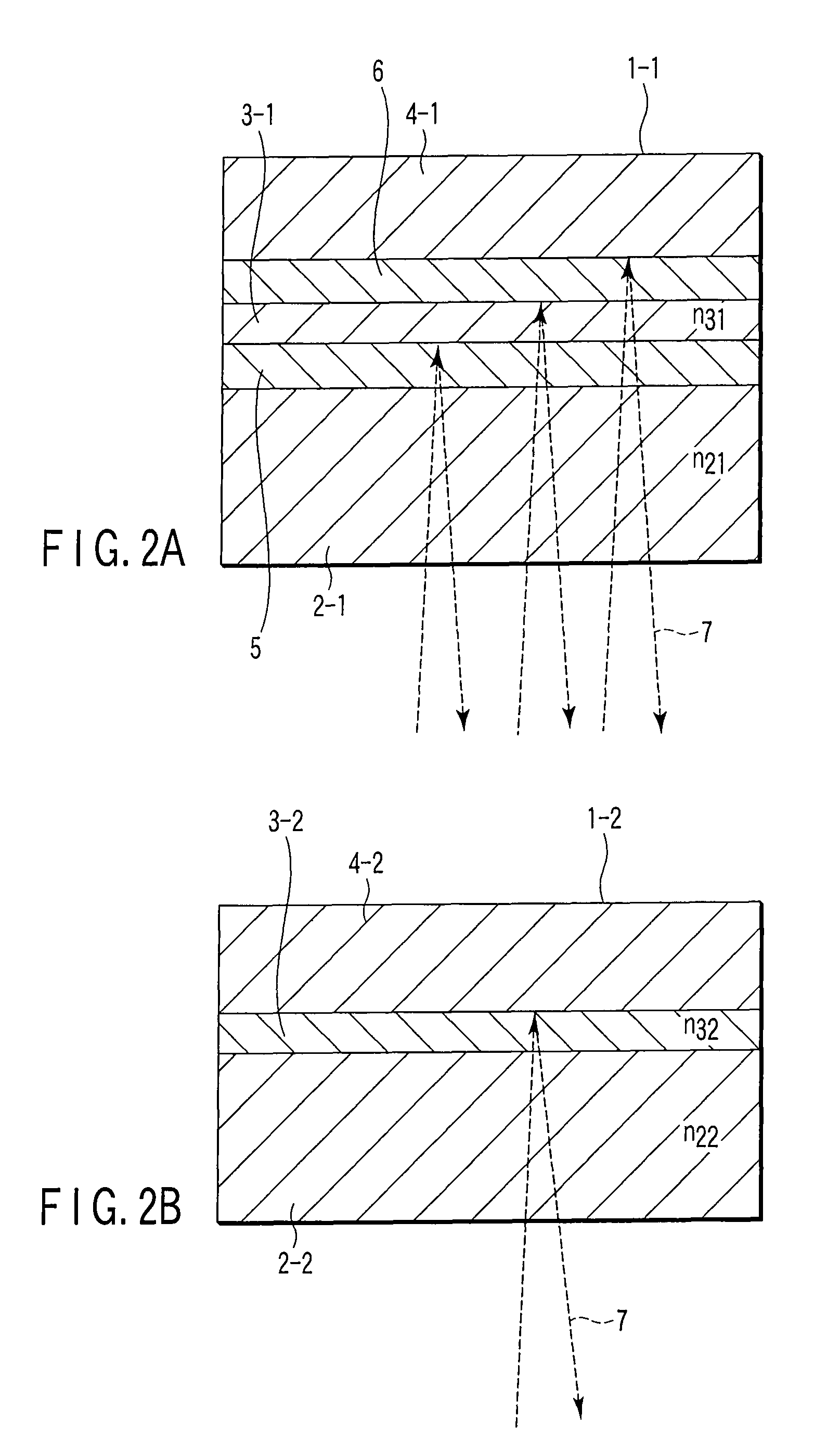
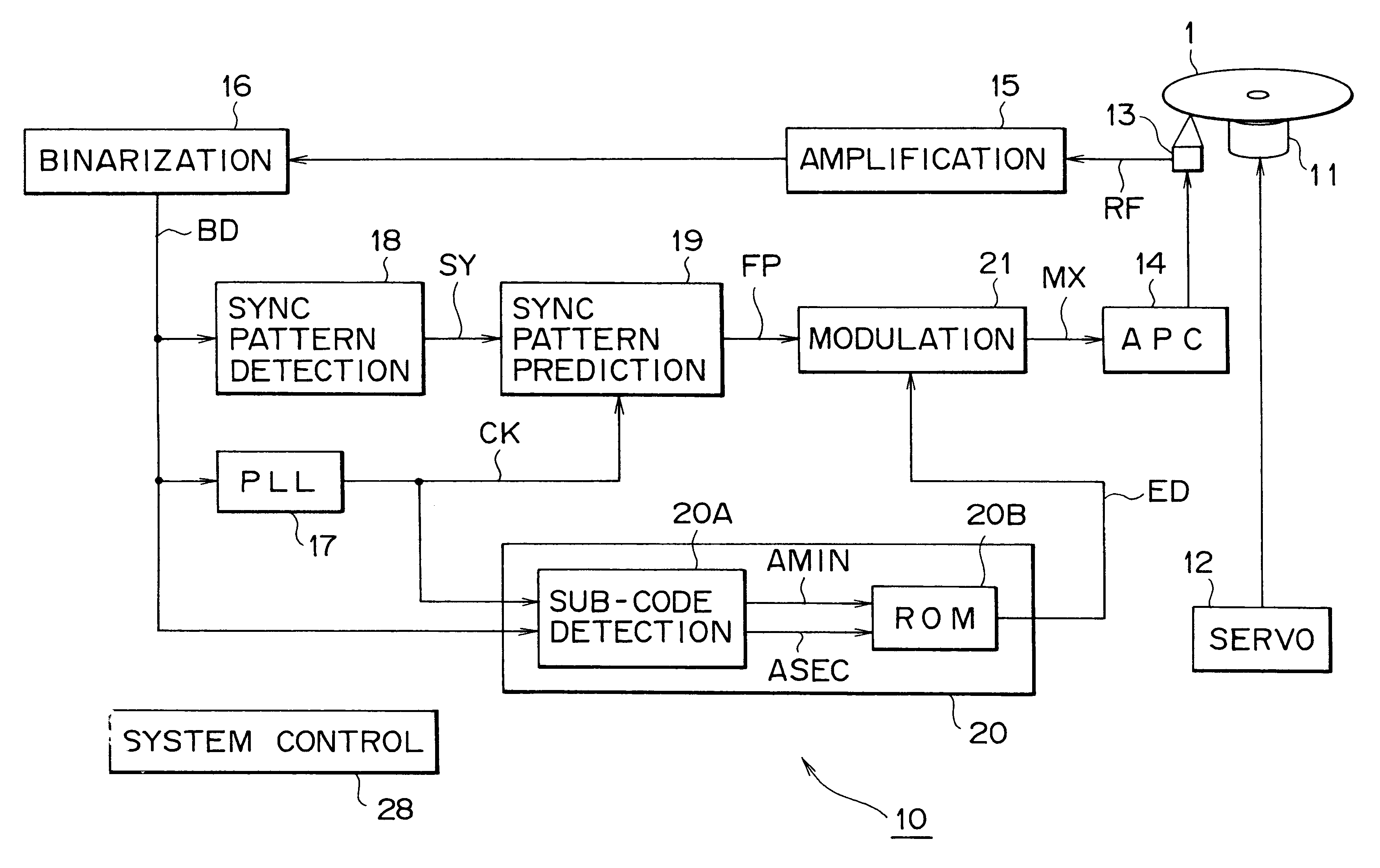
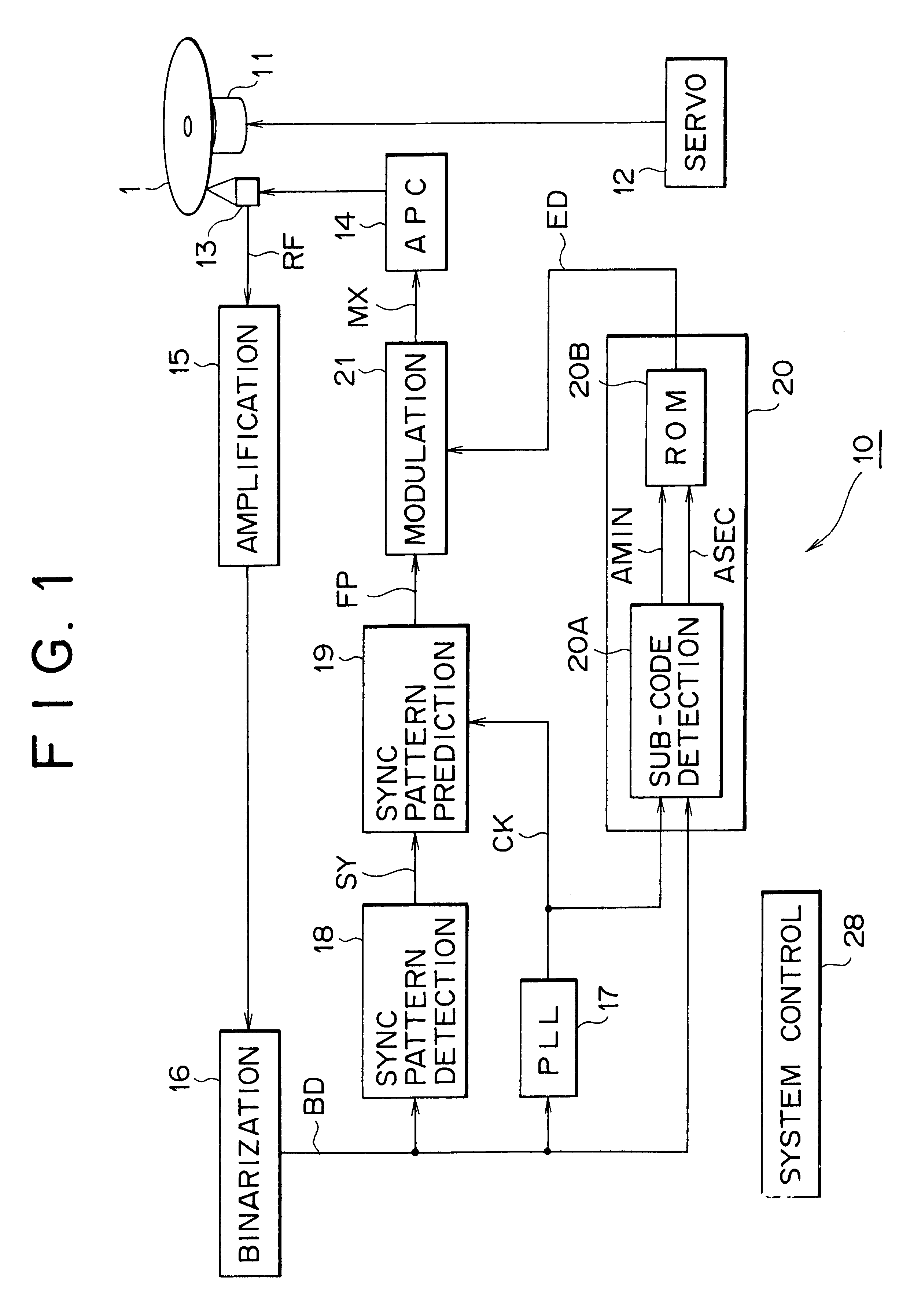
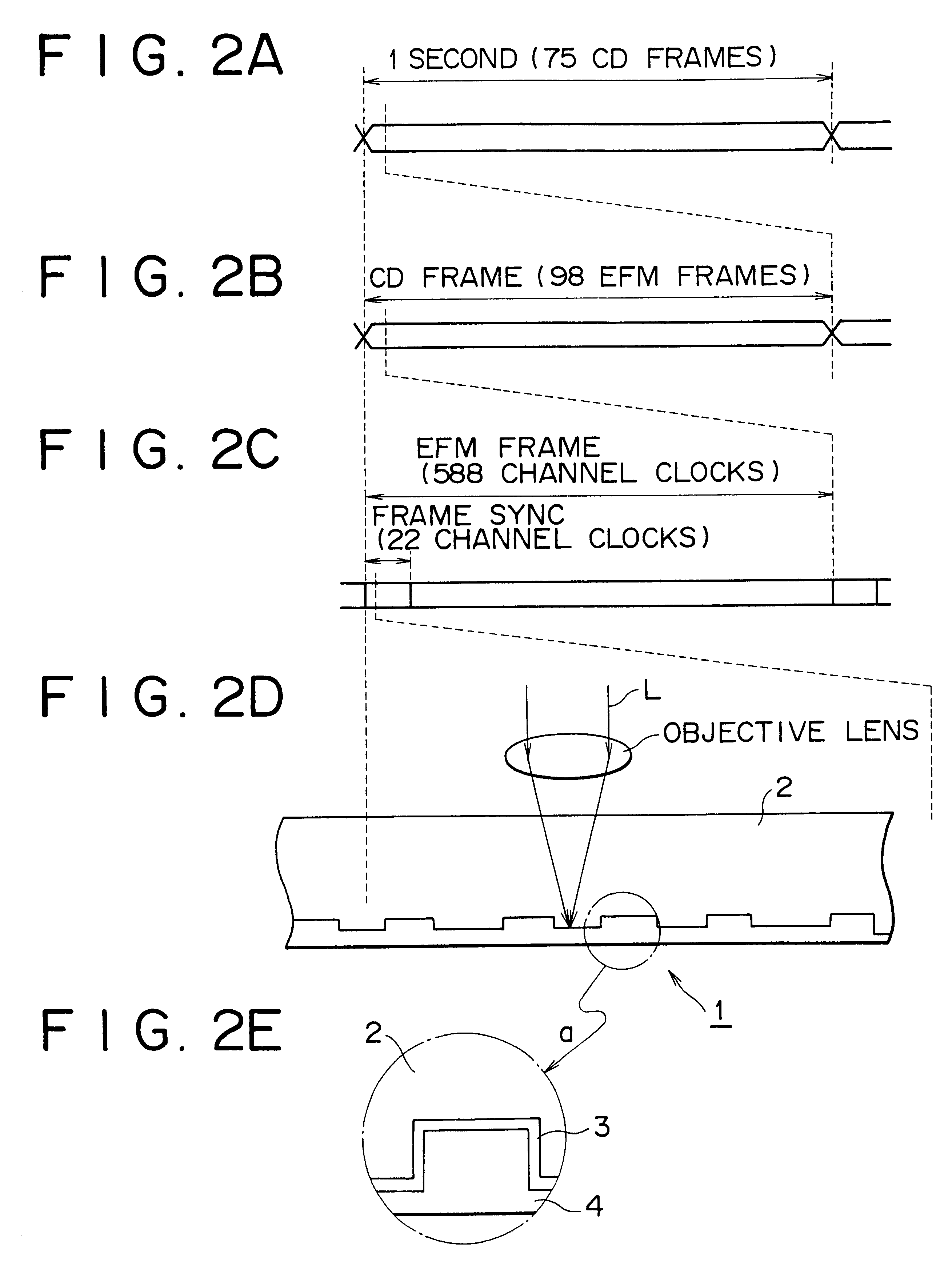
This invention related to an optical disc recording apparatus, an optical disc recording method, and an optical disc, and the present invention is applied to, for example, apparatus for recording on a compact disc, compact discs, and compact disc players, and sub-data strings are recorded so that the main data strings is reproducible by an optical pickup for reproducing the main data string and the main data strings are protected from being copied illegally without any adverse effect on reproduction of the pit-and-land main data strings. The sub-data string ED is recorded by locally changing the reflectance of the reflection film in the form of irregularity such as pit or mark at the timing which does not affect the position information of the edge.
Owner:SONY CORP
Optical recording/reproducing method and optical recording medium
ActiveUS7136343B2Simple structureImprove featuresMechanical record carriersRecord information storageDielectricState variation
An optical recording / reproducing method and an optical recording medium capable of performing excellent optical recording with a simple structure in a recording layer made of environmentally friendly materials. The optical recording medium has a recording layer formed on a substrate and made of a mixture of a recording assist material and a dielectric material. A laser beam of which intensity is modulated in accordance with information to be recorded is irradiated onto this recording layer to cause a state change in the recording assist material and / or the dielectric material. The information can be recorded by changing optical characteristics thereof such as reflectivity. The recording assist material includes an element selected from Sn, Ti, Si, Bi, Ge, and C as a principle component, while the dielectric material as a base material for the dielectric layers is at least one of ZnS, SiO2, AlN, and Ta2O5.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Metal alloys for the reflective or the semi-reflective layer of an optical storage medium
InactiveUS20050042406A1Improve reflectivityHigh sputtering characteristicCombination recordingLayered productsIridiumHigh reflectivity
Metal alloy thin films are provided for use in the highly reflective and semi-reflective layers of optical discs. Alloys include silver alloyed with gold, palladium, copper, rhodium, ruthenium, osmium, iridium, and platinum. Other alloys include copper alloys with silver, magnesium, cadmium, aluminum, nickel, beryllium, zirconium and zinc. These alloys have moderate to high reflectivity and reasonable corrosion resistance in the ambient environment.
Owner:TARGET TECH
Two-photon four-dimensional optical memory
InactiveUS6608774B1Accurate resolutionRecording involving hole burningNanoinformaticsSpatial light modulatorFluorescence
Selected domains, normally 2x103x2x103 such domains arrayed in a plane, within a three-dimensional (3-D) volume of radiation-sensitive medium, typically 1 cm3 of spirobenzopyran containing 2x103 such planes, are temporally and spatially simultaneously illuminated by two radiation pulses, normally laser light pulses in various combinations of wavelengths 532 nm and 1024 nm, in order, dependent upon the particular combination of illuminating light, to either write binary data to, or read binary data from, the selected domains by process of two-photon (2-P) interaction / absorption. One laser light pulse is preferably directed to illuminate all domains during its propagation along one directional axis of the volume. The other laser light pulse is first spatially encoded with binary information by 2-D spatial light modulator, and is then (i) directed and (ii) time sequenced to intersection with the other light pulse in a locus of intersection domains. During writing the selected, simultaneously illuminated, intersection domains change their index of refraction, attendant upon a change in isomeric molecular form, by process of 2-P absorption. During reading selected intersection domains selectively refract each of two read light pulses identically-as well as fluoresce-dependent upon their individually pre-established, written, states. The selective refraction of each read pulse in its passage straight through the volume is sensed in a detector array. I / O bandwidth to each cm3 of radiation-sensitive medium is on the order of 1 Gbit / sec to 1 Tbit / sec.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Optical recording medium and optical recording method
InactiveUS20010022769A1High sensitivityExcellent in information keeping qualityMaterial nanotechnologyMechanical recordingChemical compoundRecording layer
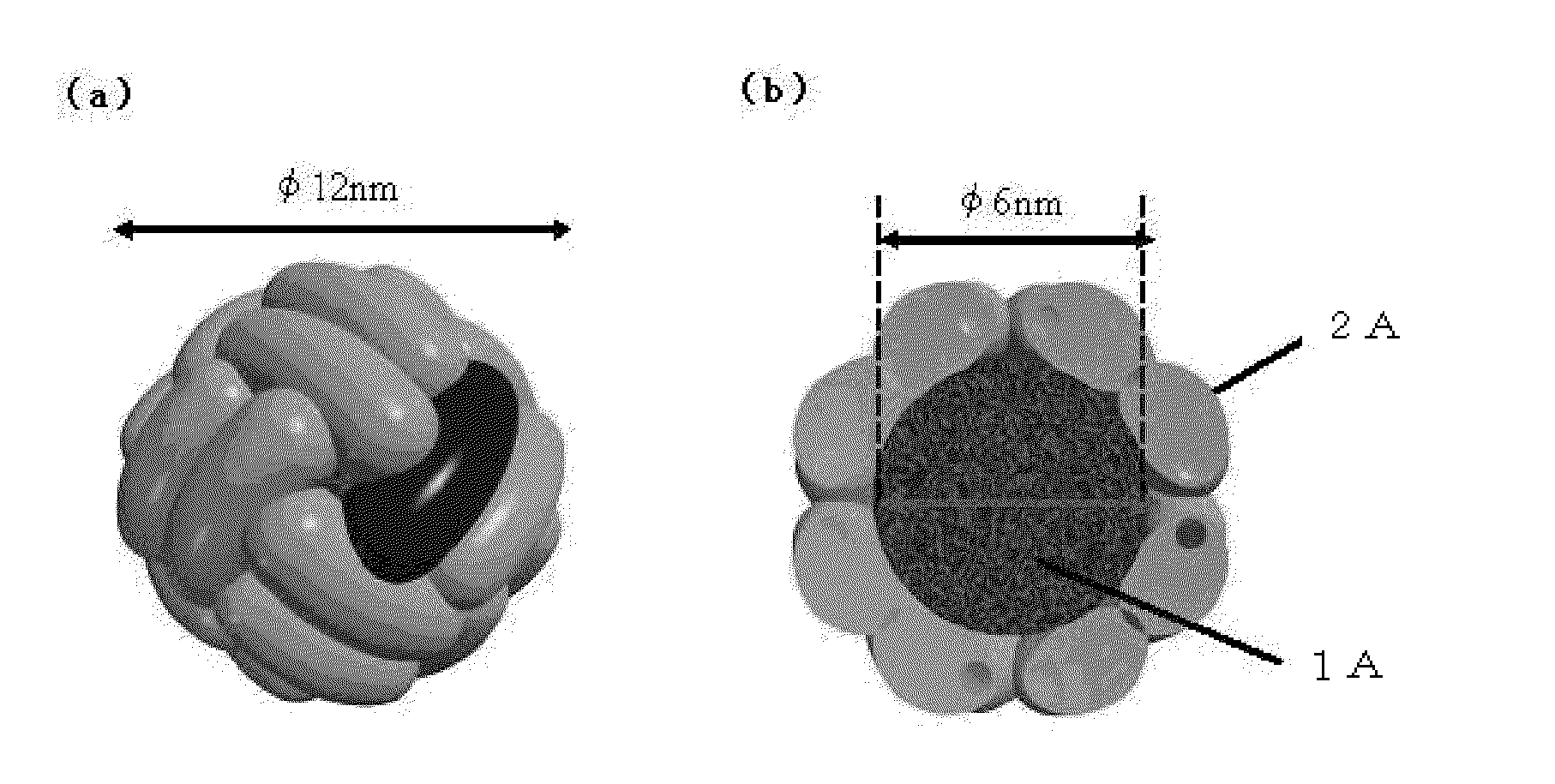
An optical recording medium comprising a recording layer containing ultrafine particles of a metal selected from the Group 8 and Group 1B elements, said particles having an average particle size of 1 nm to 50 nm, and surfaces thereof being modified with an adsorptive compound.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Optical information reproduction device
InactiveUS20060140070A1Increase the areaNanoinformaticsOptical beam sourcesPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
An information recording medium (21) of the optical information reproduction device of the present invention includes a recording unit (3) capable of recording information three-dimensionally and provided with a track, and information is recorded by forming a plurality of recording marks along the track of the recording unit by a mark length recording method. When the track direction of the recording marks is assumed to be their longitudinal direction and the direction perpendicular to the track direction is assumed to be their lateral direction, with the present invention, for recording marks located substantially in the same plane, the total area of elongated recording marks, whose longitudinal length is greater than their lateral length, is greater than the total area of recording marks having other than elongated shapes. The optical information reproduction device of the present invention includes a first light source (20a) for emitting a reproduction light (22b) having a wavelength λ1, an objective lens (6) for focusing the reproduction light on the recording unit, and a first photodetector (19a) for detecting a reproduction signal from the reflected light from the recording unit. The focused reproduction light includes as its main component a polarized light component that is polarized perpendicular to the track direction. Also, the recording unit has a track pitch of no more than 1.3 times the wavelength λ1 of the reproduction light.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Information recording medium and its manufacturing method,recording/preproducing method, and optical information recording/reproducing device
An information recording medium is provided that includes a recording portion (3), which is irradiated with a recording light or a reproducing light so that information is recorded or reproduced thereto or therefrom. The recording portion (3) contains a first phosphor and a photon-mode photosensitive material. The first phosphor has a property of absorbing a first light having a wavelength of λ1 / n and then emitting a second light having a wavelength longer than that of the first light, where λ1 is a wavelength of the recording light. The photosensitive material absorbs the second light and then exhibits a change in an optical constant thereof. A n-photon absorption sensitivity of the first phosphor with respect to the recording light is greater than a n-photon absorption sensitivity of the photosensitive material with respect to the recording light, where n is an integer not less than 2.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Write-once-read-many optical disk having low-to-high recording property accommodating short wavelength recording
InactiveUS20070037095A1Eliminate the problemRecording strategiesLayered productsOptical recordingLength wave
A write-only-read-many type optical recording medium includes a substrate, an organic material layer having a light absorption function that is sufficient for recording in the recording / reproduction wavelength range, the organic material layer being situated on the substrate, and a reflection layer being situated on the organic material layer. The recording medium is configured to have a Low-to-High recording property and record with a laser having a wavelength that is no greater than 500 nm.
Owner:RICOH KK
Device and method for optical data storage having multiple optical states
InactiveUS6115344APhotography auxillary processesMechanical record carriersPolymer substrateOptical storage
PCT No. PCT / NO96 / 00125 Sec. 371 Date Nov. 20, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Nov. 20, 1997 PCT Filed May 22, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 37888 PCT Pub. Date Nov. 28, 1996The optical storage device and method includes a fluorescent layer arranged on a substrate and having a surface. The fluorescent layer is composed of fluorescent dye molecules embedded in a transparent polymeric base material. A group of data-carrying structures are arranged in the fluorescent layer. Each of the data-carrying structures has more than two optical states represented by a specific degree of quenching of fluorescence emitted from the data-carrying structure when irradiated with a fluorescence exciting radiation.
Owner:THIN FILM ELECTRONICS ASA +1
Information recording medium having pair of electrodes
InactiveUS6977883B2Easy to identifyHigh densityRecording by physical/electrical perturbationsRecord information storageHigh densityOptoelectronics
Disclosed herewith is a method for enabling fast and high density recording of information. A voltage is applied to a recording layer formed between a pair of electrodes. The distance between the pair of electrodes is set wider at one of land and groove areas of a subject optical disk and narrower at the other, or the disk has multi-recording layer structure and light absorption occurs only in the layer on which coloring voltage is applied. The optical disk is provided with a layer of which light absorption spectrum changes according to the application of voltage, thereby absorbing the light. The layer may be the recording layer itself or a layer adjacent to the recording layer. Because a heat generates only in a selected area of the optical disk at the time of recording, the disk can also avoid cross-talks between layers during reading and can be turned rapidly and permissively to the auto focusing and tracking offsets, thereby enabling fast and high density recording. The disk can thus be formed with easily selectable multiple layers.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Metal alloys for the reflective or the semi-reflective layer of an optical storage medium
InactiveUS7045187B2Moderate to high reflectivityImprove corrosion resistanceCombination recordingLayered productsIridiumHigh reflectivity
Metal alloy thin films are provided for use in the highly reflective and semi-reflective layers of optical discs. Alloys include silver alloyed with gold, palladium, copper, rhodium, ruthenium, osmium, iridium, and platinum. Other alloys include copper alloys with silver, magnesium, cadmium, aluminum, nickel, beryllium, zirconium and zinc. These alloys have moderate to high reflectivity and reasonable corrosion resistance in the ambient environment.
Owner:TARGET TECH
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com